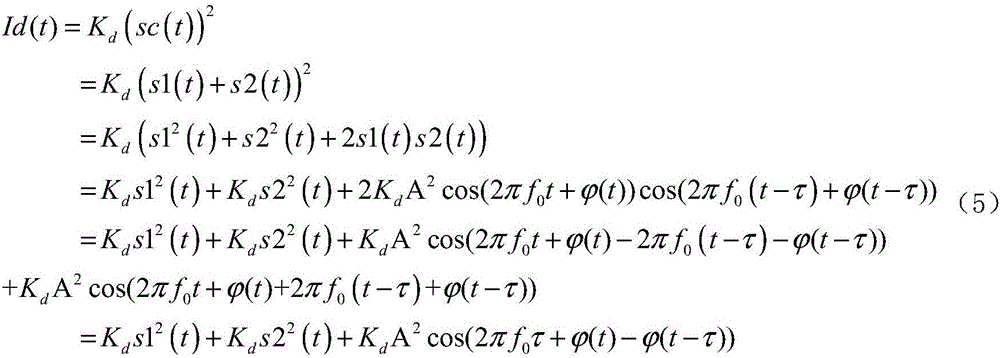Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
160 results about "Laser linewidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laser linewidth is the spectral linewidth of a laser beam. Two of the most distinctive characteristics of laser emission are spatial coherence and spectral coherence. While spatial coherence is related to the beam divergence of the laser, spectral coherence is evaluated by measuring the laser linewidth of the radiation. Although the concept of laser linewidth can have varied theoretical descriptions, this article provides a simple experimental perspective. One of the first methods used to measure the coherence of a laser was interferometry. An alternative approach is the use of spectrometry.
Method and apparatus for phase shift keyed optical communications
ActiveUS20110274429A1High data rateConstructionsModulated-carrier systemsTransceiverOptical communication
A burst-mode differential phase shift keying (DPSK) communications system according to an embodiment of the present invention enables practical, power-efficient, multi-rate communications between an optical transmitter and receiver. An embodiment of the system utilizes a single interferometer in the receiver with a relative path delay that is matched to the DPSK symbol rate of the link. DPSK symbols are transmitted in bursts, and the data rate may be varied by changing the ratio of the burst-on time to the burst-off time. This approach offers a number of advantages over conventional DPSK implementations, including near-optimum photon efficiency over a wide range of data rates, simplified multi-rate transceiver implementation, and relaxed transmit laser line-width requirements at low data rates.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
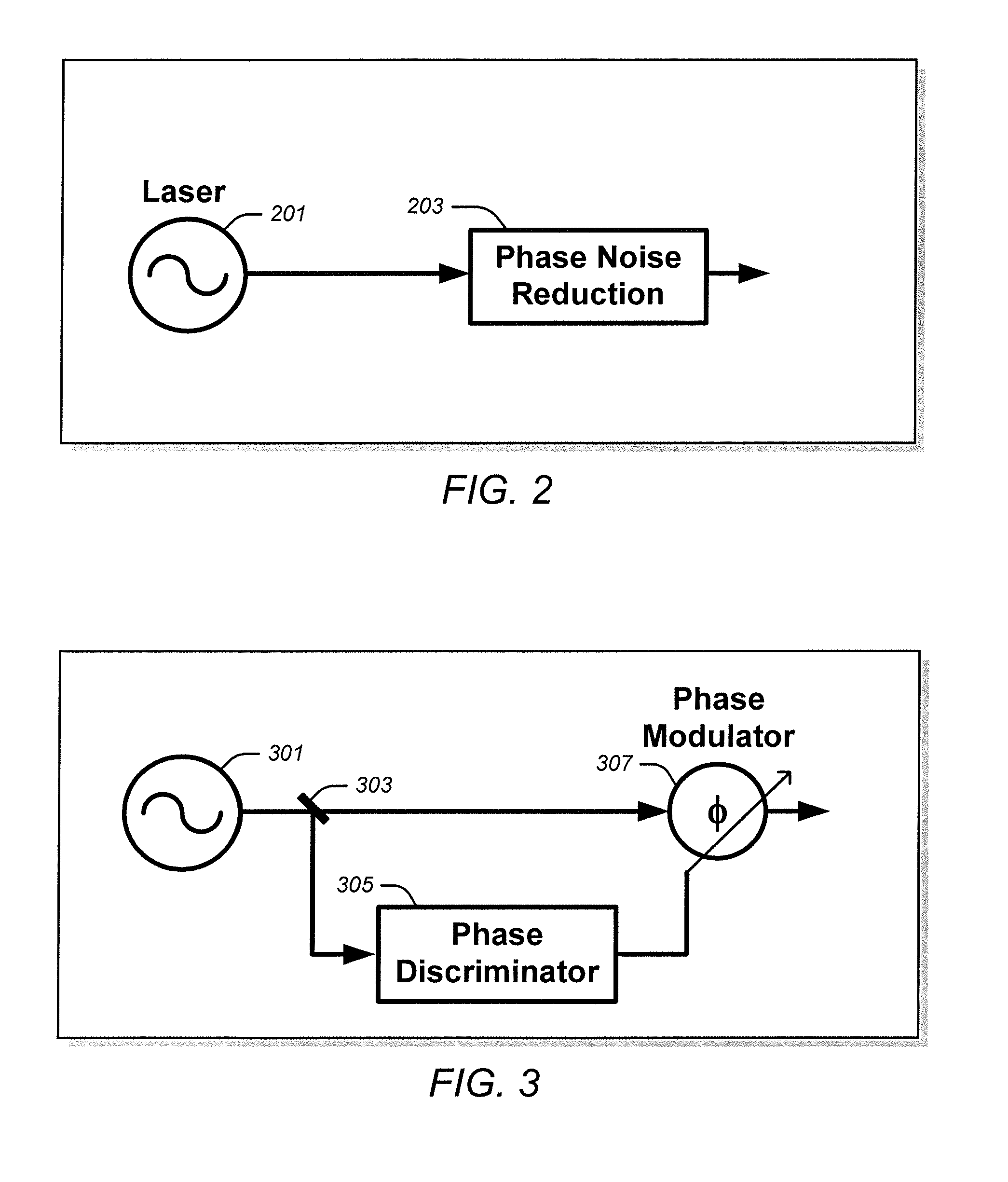
Wideband tunable laser line-width reduction
InactiveUS20130215919A1Reduce phase noiseLaser detailsWave based measurement systemsDiscriminatorPhase noise
Various examples of feed-forward systems that reduce phase noise in a laser field generated by a laser. These include feed-forward systems that utilize phase and / or frequency discriminators, filters, integrators, voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs), current controlled oscillators (CCOs), phase modulators, and / or amplitude modulators. It also includes systems that use both feed-forward and feedback phase noise reduction systems, tunable semiconductor lasers, and multiple, sequential feed-forward systems.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method for locking DDS acousto-optic modulation wavelength
InactiveCN101442179ANarrow output laser linewidthSufficient error signal amplitudeLaser detailsFrequency stabilizationLine width
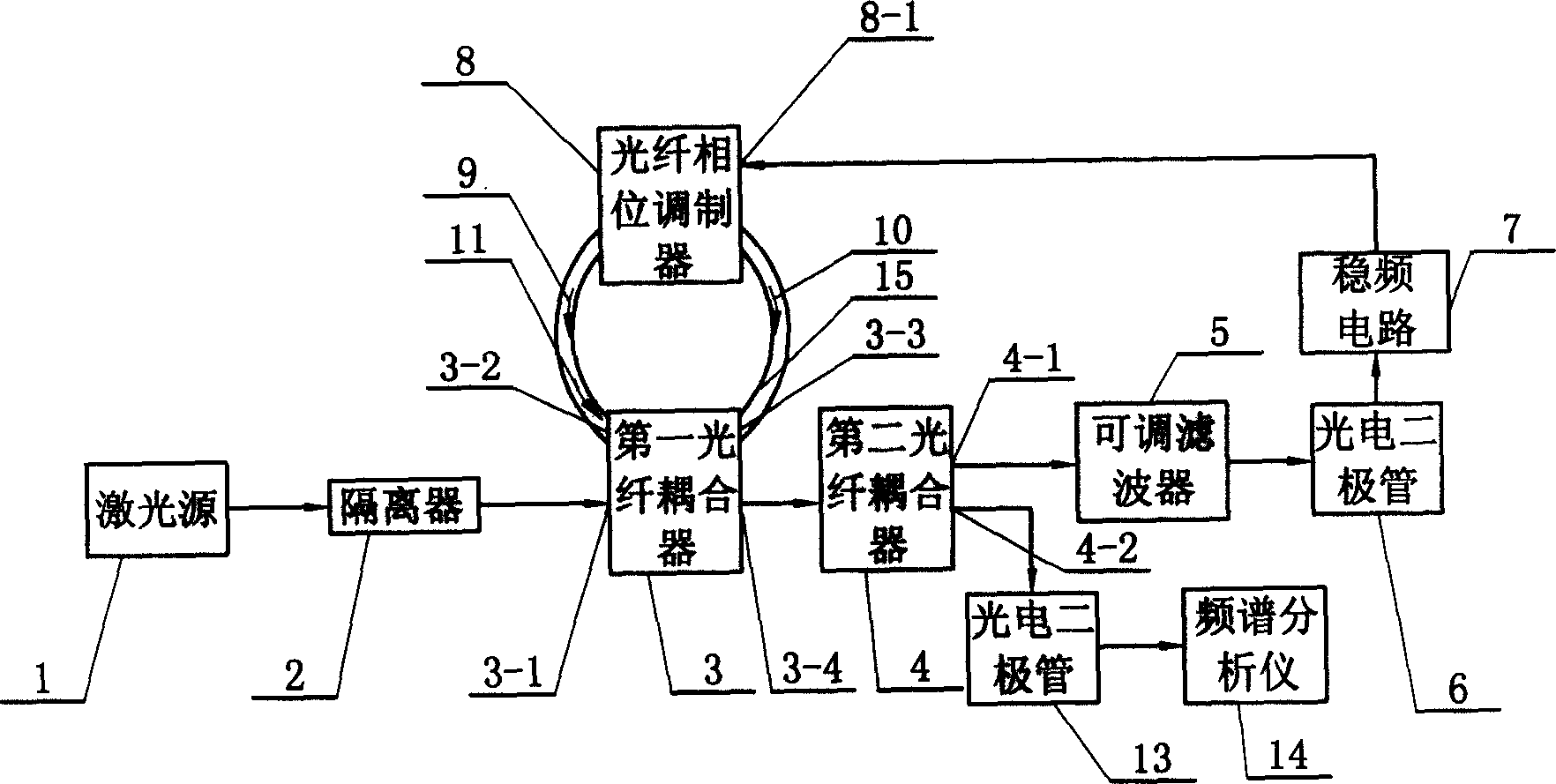
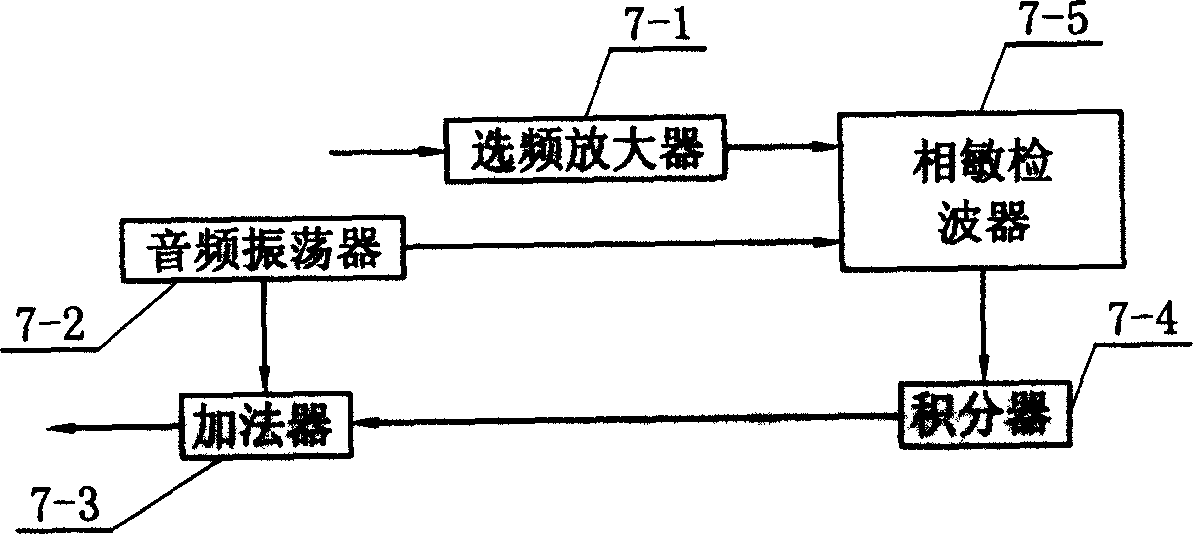
The invention relates to a DDS acoustooptic modulation wavelength locking device and a wavelength locking method. The wavelength locking method can be realized by arranging an acoustooptic modulator and a convex lens on the basis of modulating a laser cavity in the prior art. The DDS acoustooptic modulation wavelength locking device has a concise light path, is easy to adjust, and can obviously narrow the laser linewidth and acquire enough error signal amplitude to realize stable frequency locking; due to adoption of the acoustooptic modulator, the stability of locked frequency is good and superior to that of a general voltage controlled oscillator; and due to adoption of digital frequency modulation, the DDS acoustooptic modulation wavelength locking device is flexible and convenient, and is convenient to cooperate with a digital industrial control device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
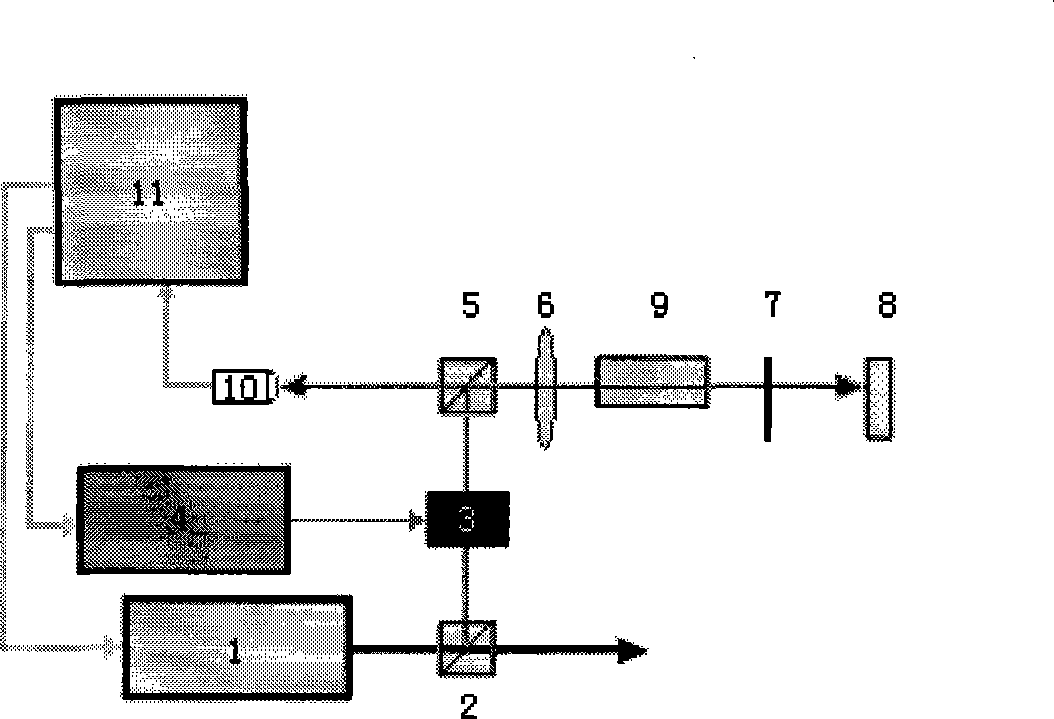
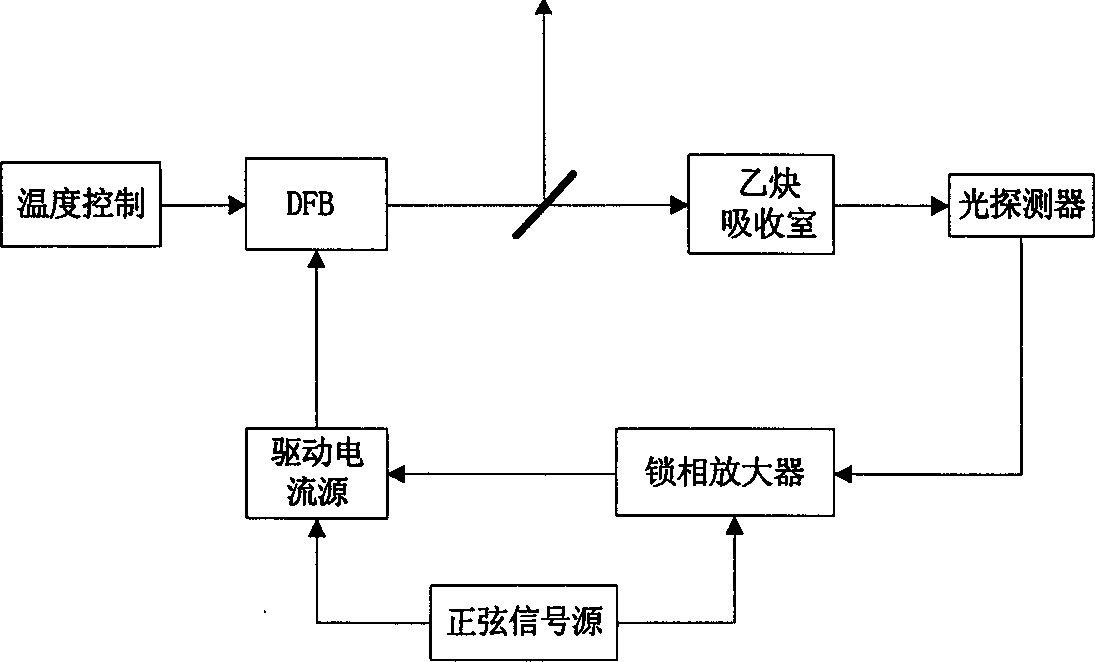
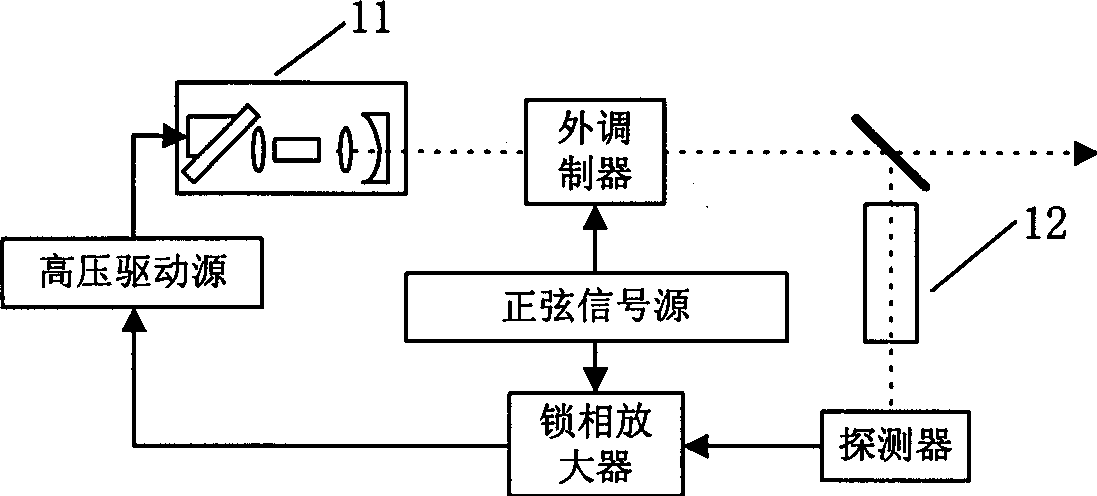
Frequency-stabilizing device of fiber-optical grating external cavity semiconductor laser and its frequency-stabilizing method
InactiveCN1341986ASolving wavelength tuningAddressing AC ModulationLaser detailsOptical multiplexFrequency stabilizationPartial reflection
The invention relates to a technique field of frequency stabilization of laser light source. It consists of laser source, acetylene gas absorption chamber, and servo-feedback controller. The laser source as a semiconductor laser with optical fiber grating outer cavity is composed of semiconductor laser tube core in quanta trap F-P type and an optical fiber grating. A reflection reducing coating is coated on the coupling end surface of the tube core and optical fiber grating. The other end of the optical fiber grating is linked to a collimator. There are two pieces of piezoelectric ceramics end to end on the two ends of the optical fiber grating. The two input ends of phase locking amplifier in the servo-feedback controller are connected to the output end of light sensor and sine signal source respectively. The one end of the signal source and the high voltage drive are connected to a phase locking amplifier; with the other end connected to said two pieces of piezoelectric ceramics. There is an isolator and a partial reflector located on the optical path between the collimator and the acetylene gas absorption chamber. The invention possesses the advantages of higher stability in frequency, very narrow laser line-width as well as simple structure and higher stability in mechanics.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Laser line width measuring system and method based on electro-optic modulator and adjustable radio source
InactiveCN105651492ALow insertion lossHigh measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesSpectrum analyzerLine width
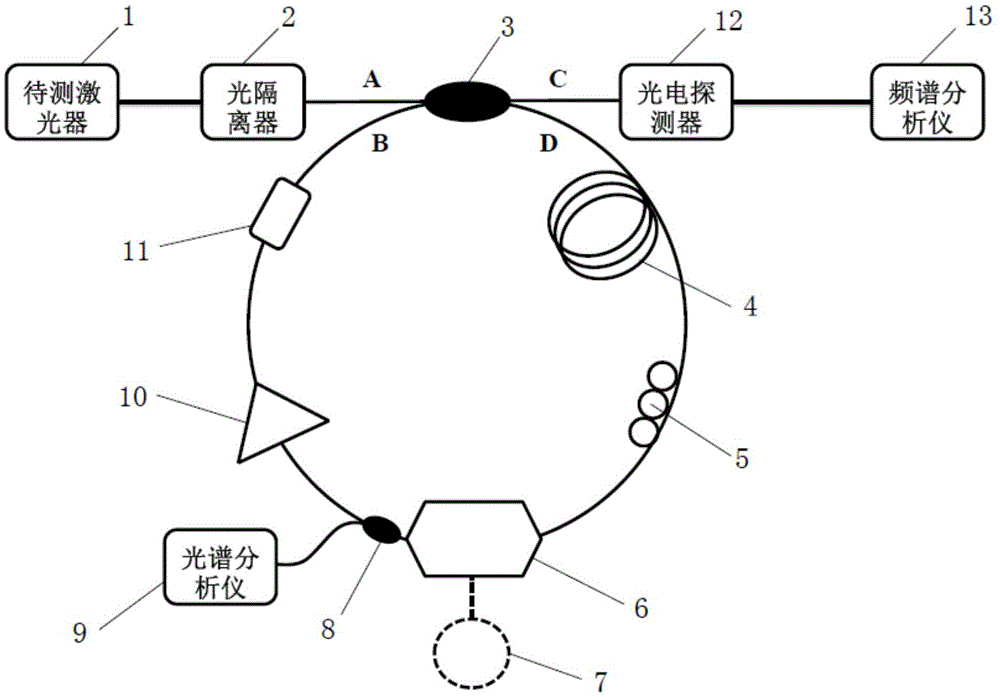
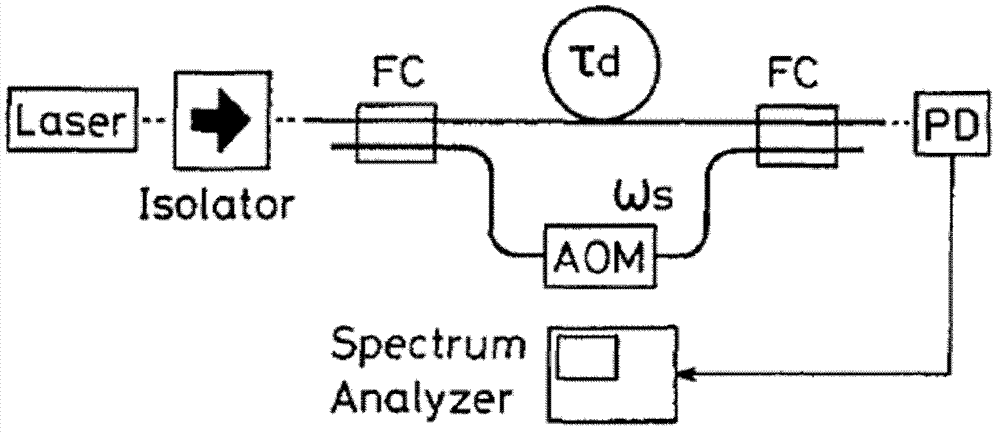
The invention discloses a laser line width measuring system and method based on an electro-optic modulator and an adjustable radio source. The system comprises a to-be-measured laser, an opto-isolator, a 2*2 optical fiber coupler, an integrated photoelectric detector, a spectrum analyzer and a frequency shift fiber ring. The frequency shift fiber ring is connected between an output port D and an input port C of the 2*2 optical fiber coupler and at least comprises a frequency shifting device and an optical fiber delay line, wherein the frequency shifting device is composed of the electro-optic modulator and the adjustable radio source. The adjustable radio source is used for providing radio driving signals with the adjustable frequency shifting amount for the electro-optic modulator, and the frequency shifting amount can be adjusted in real time by controlling the modulation frequency injected into the electro-optic modulator by the adjustable radio source. The frequency shifting amount can be increased, the adjustable band width range is enlarged to 10 GHz, and the line width measurement limit reaches 1 Hz.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and equipment for measuring laser line width
InactiveCN102901616AAccurate informationSolutions for Measuring Narrow LinewidthsTesting optical propertiesLine widthOptoelectronics
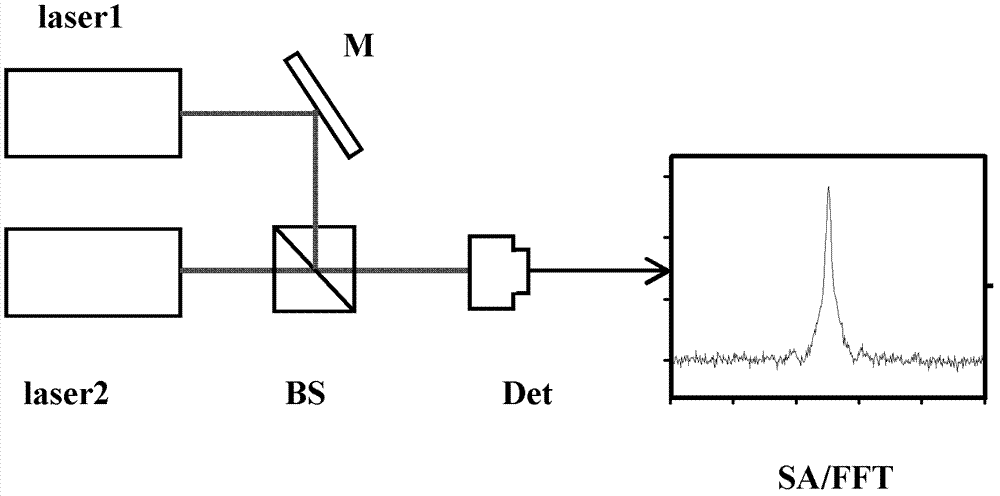
The invention discloses a method and equipment for measuring laser line width. The method comprises the following steps of: combining a first laser output by a first laser device with a second laser output by a second laser device; dividing a combined beat note signal fb into a first beat note signal and a second beat note signal; mixing the first beat note signal fb and an ideal signal of which the frequency is f0 to obtain a difference frequency signal, namely the absolute value of fb-f0; due to a controllable bandwidth follow-up oscillator, generating a follow-up signal ft equal to the absolute value of fb-f0 under the follow-up bandwidth set by the follow-up oscillator; mixing the second beat note signal with the follow-up signal ft to output a difference frequency signal f0; and analyzing the difference frequency signal f0 to obtain the laser line width of the first laser device and / or the second laser device. Due to a circuit which is relatively simple, and by changing the servo bandwidth of the bandwidth-variable follow-up oscillator, the laser line width under a certain bandwidth of a narrow line width laser device and an ultra-narrow line width laser device can be measured.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Optical communication method and system
InactiveCN102427387AIncrease line widthEnhanced ability to resist inter-carrier interferenceBaseband system detailsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumStream data
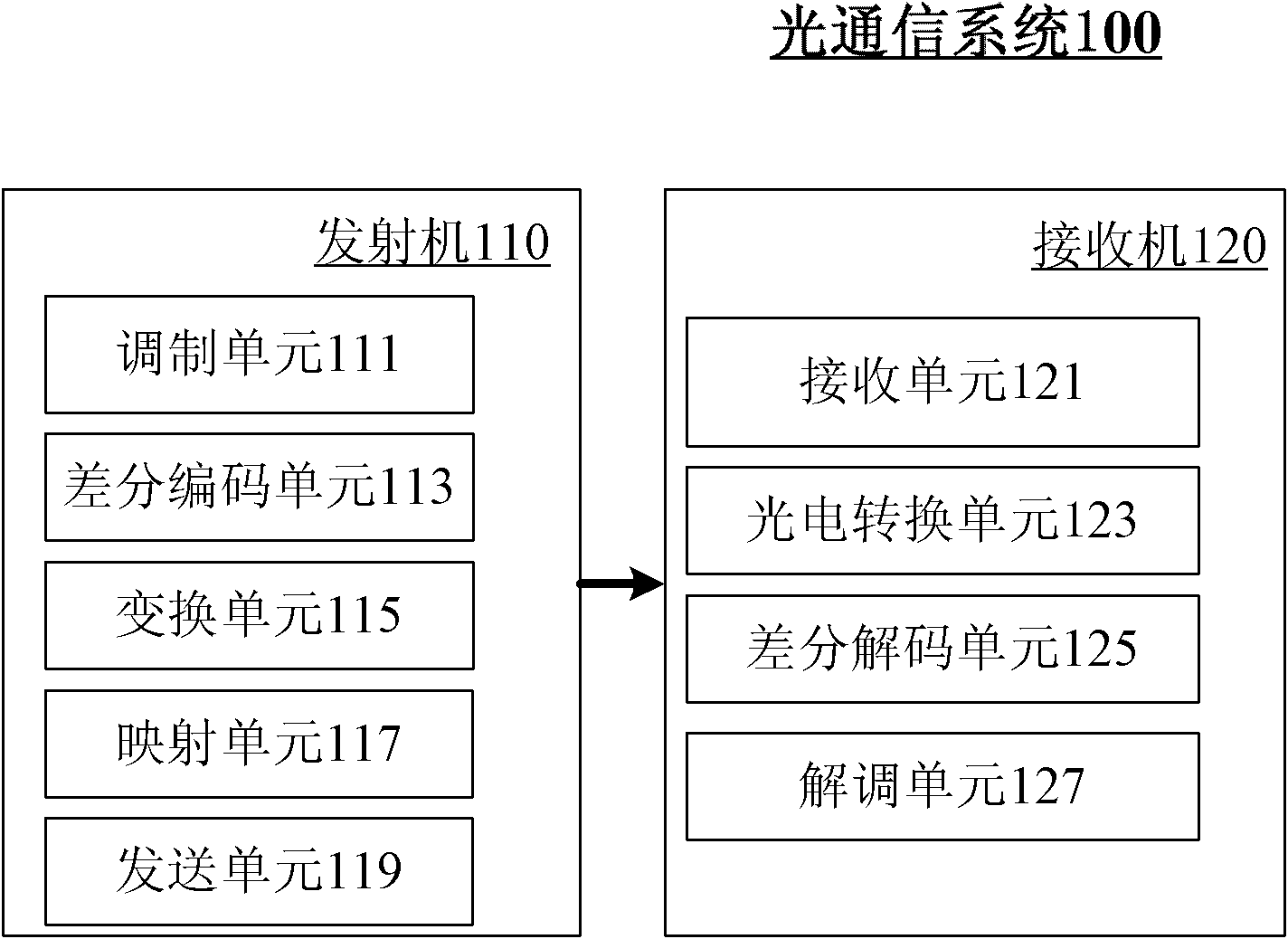
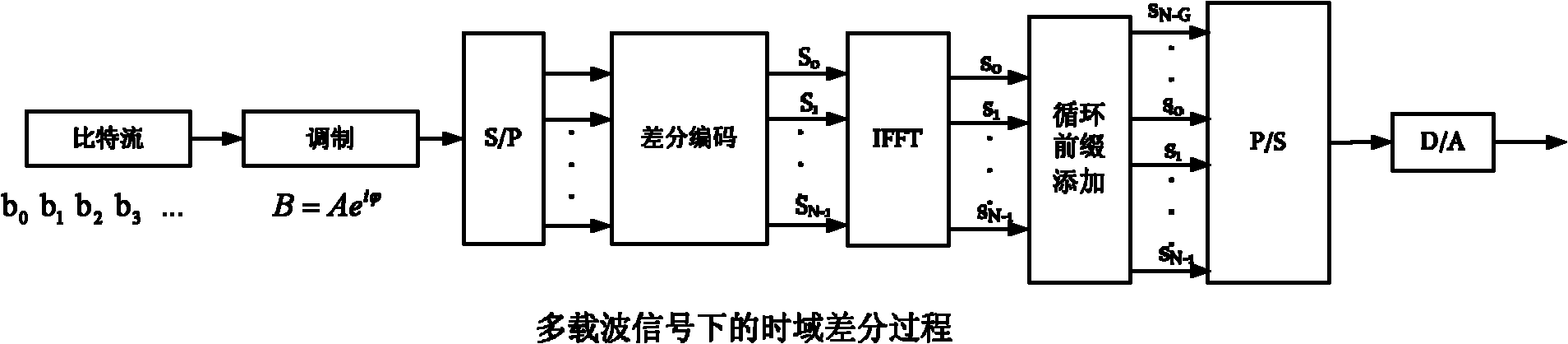
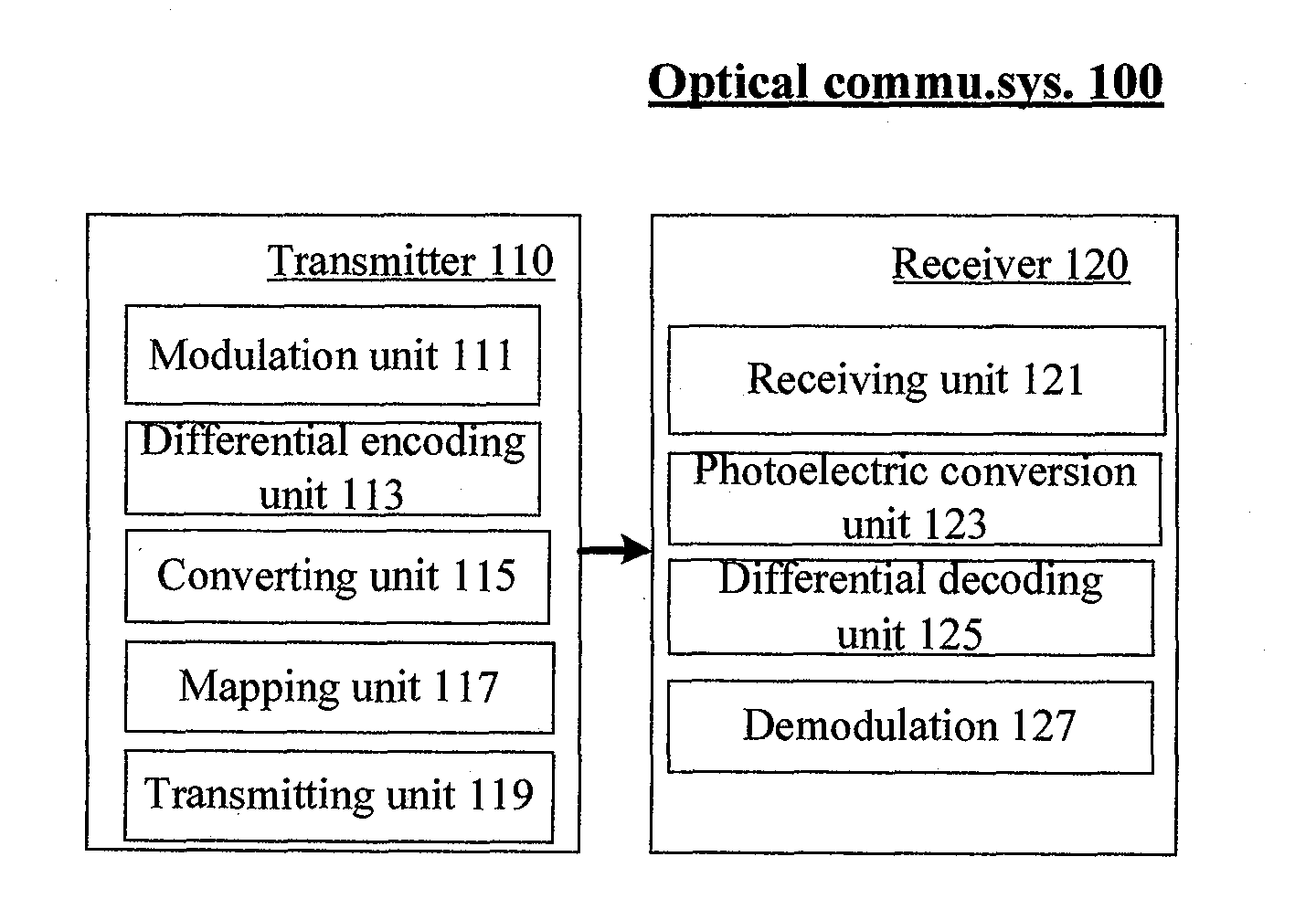
The invention provides an optical communication method which comprises the steps of: modulating obtained bit stream data to obtain a modulating signal; carrying out differential coding on the modulating signal to obtain a differential coding signal; converting the differential coding signal into an electrical signal; mapping the electrical signal on an optical carrier to form an optical signal; and then transmitting the optical signal. By using the method, on the premise that a frequency spectrum utilization rate is not reduced, the system capability of resisting disturbance among carriers is enhanced; thus, the tolerance of the existing optical communication sysem for resisting laser linewidth, quick change PMD (Physical Media Dependent), nonlinear fiber, disturbance among channels and other damage is enhanced; and system performance is greatly enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
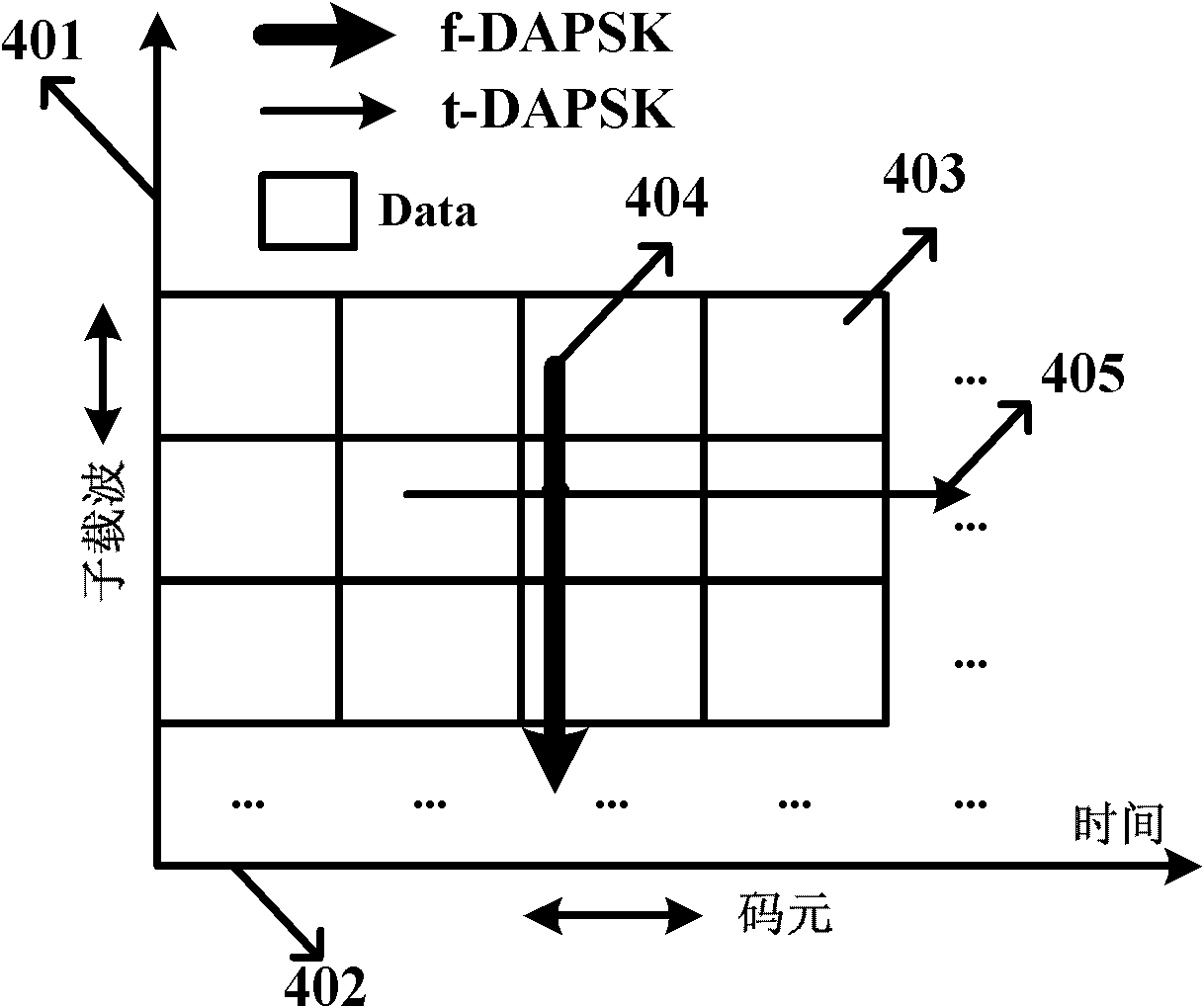
Multi-carrier Optical Communication Method and System Based on DAPSK
ActiveUS20130070866A1Improve toleranceSpectrum efficiency of spectrum is reducedError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumStream data
The present invention provides an optical communication method, comprising: performing modulation on the obtained bit stream data to generate modulated signals; performing differential encoding on the modulated signals to generate differentially encoded signals; converting the differentially encoded signals into electrical signals; and mapping the electrical signals onto optical carriers to generate optical signals for transmission. With the present invention, it is possible to enhance the system's capability of resisting inter-carrier interference without decreasing spectrum efficiency, hence improving the tolerance of existing optical communication systems towards laser linewidth, fast-changing PMD, optical fiber nonlinearity, inter-channel interference and other damages, greatly enhancing system performances.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus for measuring ultra narrow laser line width by Brillouin optical fibre ring laser and measuring method
InactiveCN1598480AOvercoming complexityOvercome precisionUsing optical meansFiber couplerMeasurement device
The invention is a device and measuring method for using Brillouin optical fiber circle laser to measure linewidth of ultra-narrow laser, which relates to a measuring device and method for laser linewidth. The output of the laser source is connected to the input of the isolator, the output of the isolator is connected to the input of the fiber coupler, the output of the coupler is connected to the inlet of the fiber coupler, the output of the fiber coupler is connected to the input of the photoelectric diode, the output of the photoelectric diode is connected to the input of the frequency spectrum analyzer, the fiber circular cavity is formed by connection one end of the aperture circle made up of unimodular fiber and the port of the fiber coupler, another end of the aperture circle is connected to the port three of the coupler. The method is: the laser needed to be measured is sent into the fiber circle cavity, when the power of the laser needed to be measured reach the threshold of SBS, it generates a first order Stokes light in the coupler, when the power of the first order stokes light reach the SBS threshold, it generates the second order stokes light in the coupler, then the second order stokes light and the laser needed to be measured frequency are analyzed by the frequency spectrum analyzer, and the linewidth can be acquired.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Miniaturized external cavity laser (ECL) implemented with acoustic optical tunable filter
InactiveUS6930819B2Good optical performanceIncrease output powerLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserLine width
An optical tunable laser design for the optical telecommunication industry is disclosed in this invention. This new design is economical, reliable, robust and with superior optical performances. The design offers broadband tunability, high output power, narrow laser line-width and high SMSR. And in addition, the tunable laser is distinguishable from conventional designs by the mere facts that there are no moving parts, therefore, making it very reliable, and the tuning method of this invention is non-thermal and non-mechanical making its tuning very fast in the sub-millisecond range. In the manufacturing front, it is low cost and easy to produce. It can be achieved with automation equipment like those used in the IC placement and PC assembly industry, therefore, the products as that disclosed in this invention can be provided with significantly reduced production costs and marketed with very competitive price.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
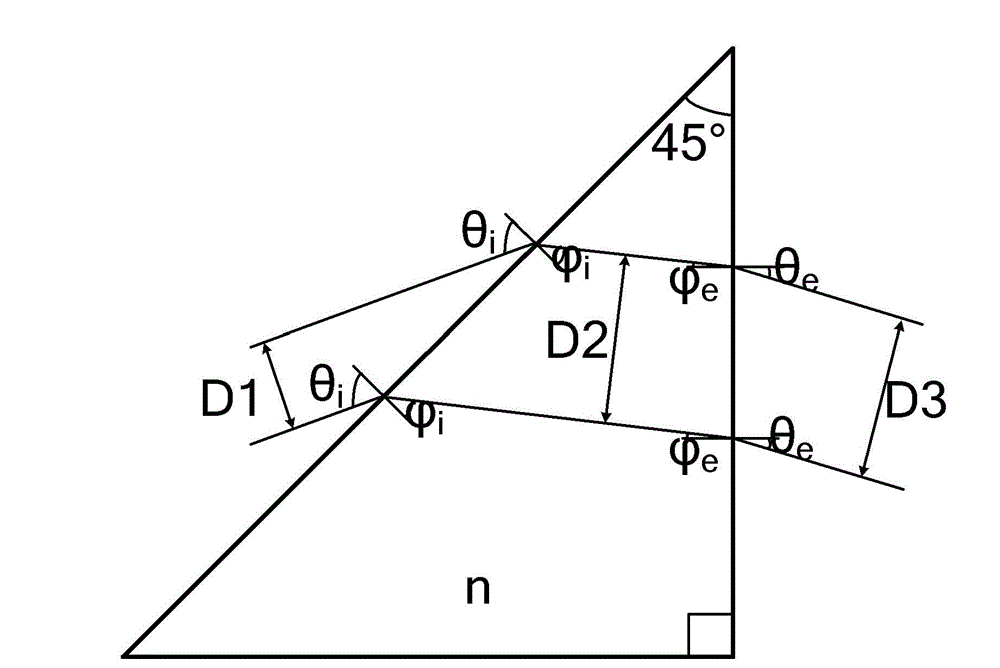
Laser line-width reduction and beam expanding method and system based on isosceles right angle triangular prism
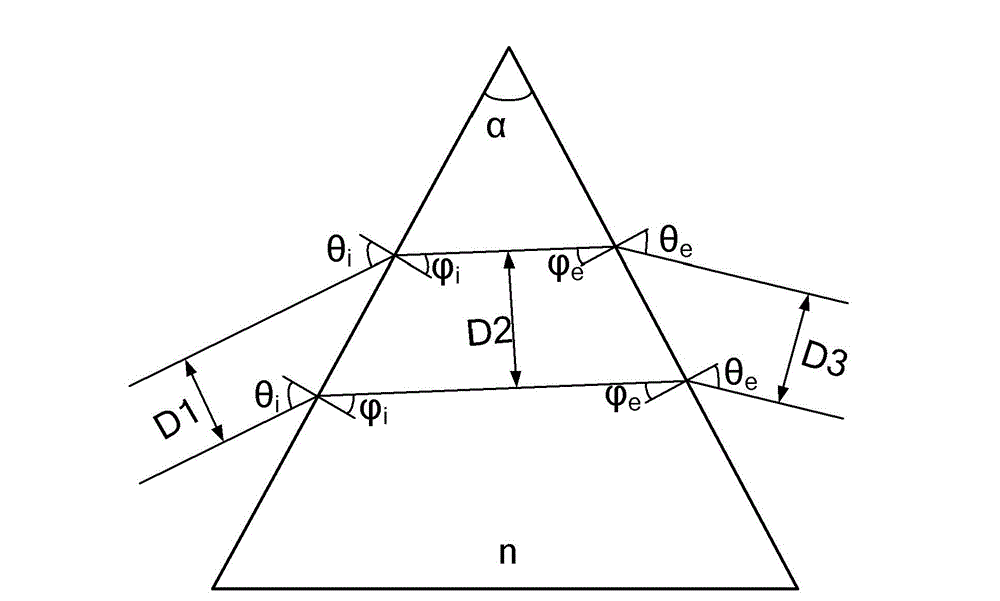
The invention discloses a laser line-width reduction and beam expanding method and a system. The system comprises a beam expanding device and a grating, wherein the beam expanding device is used for conducting one-dimensional beam expanding on laser light; the grating is used for conducting central wavelength selection on the laser light, so that line-width reduction is realized. The beam expanding device consists of a single prism or a prism combination, wherein the single prism and the prisms constituting the prism combination are isosceles right angle triangular prisms. The laser line-width reduction and beam expanding method and the system have the advantages that the structure simple, the processing precision is high, and a small effect is caused on beam transmission wavefront; different laser beam expanding multiplying factors are realized by selecting an angle of incidence and the number of elements of the prism combination; and a required narrow-band laser line-width is obtained.
Owner:RAINBOW SOURCE LASER RSLASER
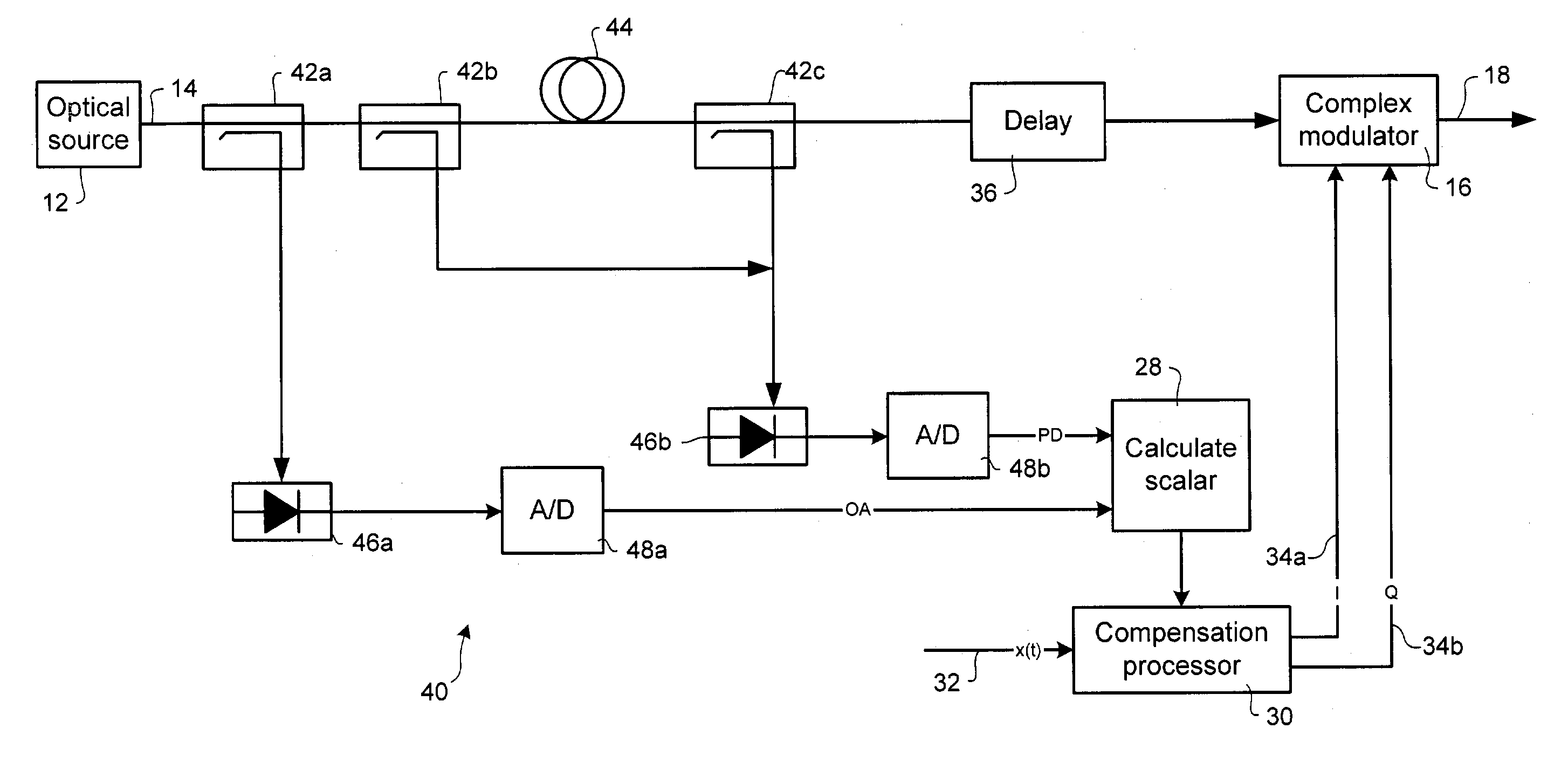
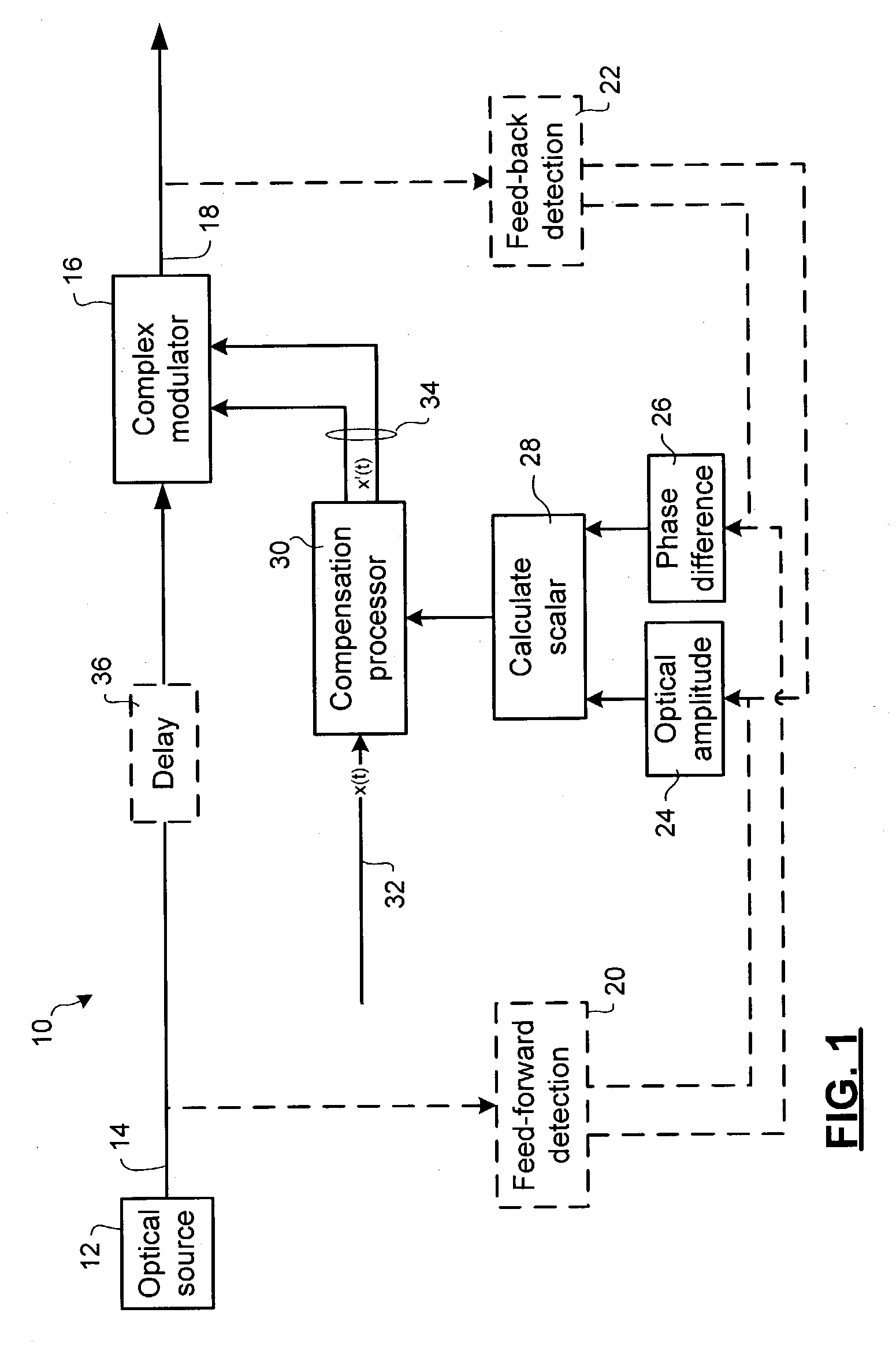
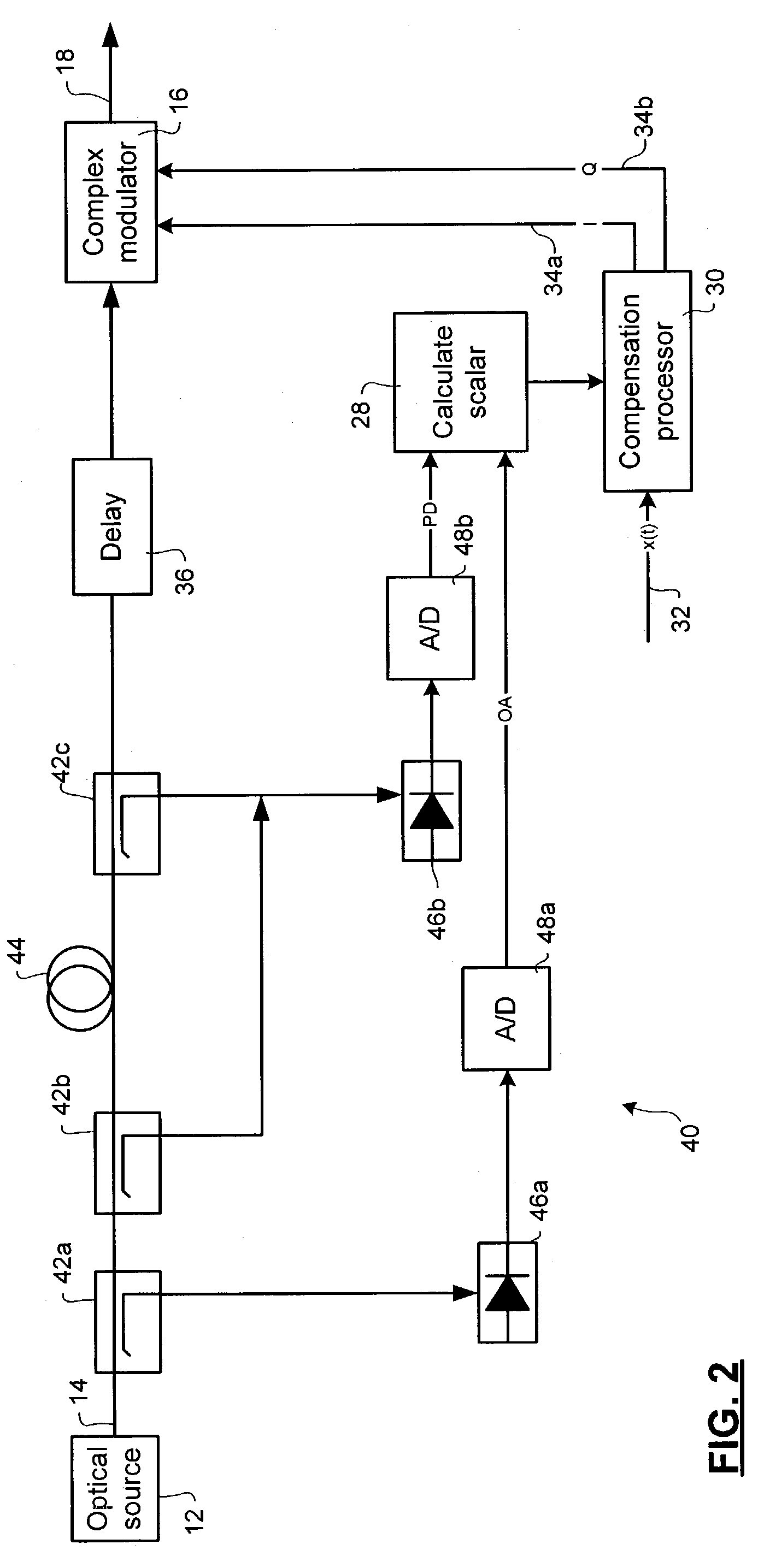
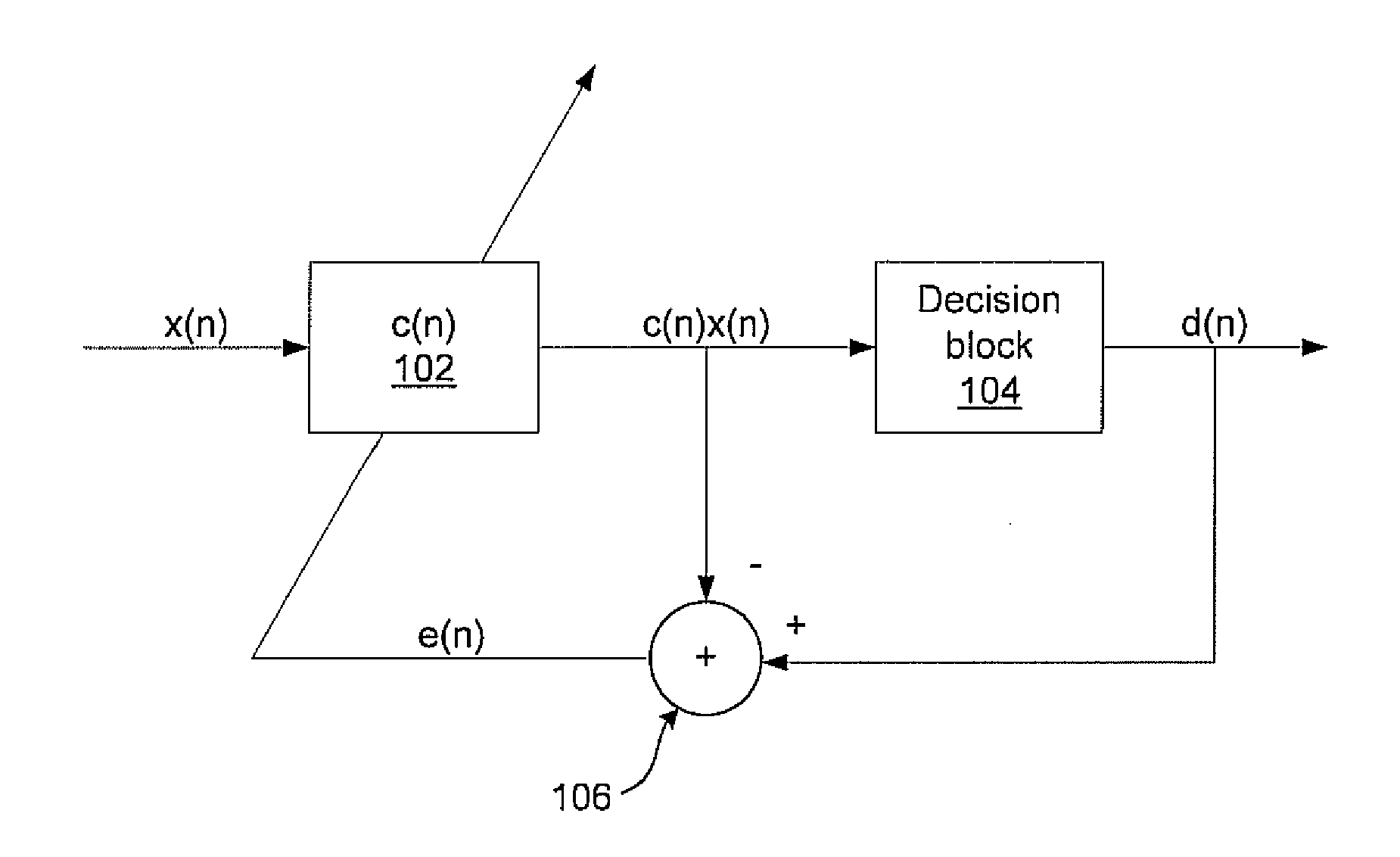
Method and apparatus for laser line-width compensation
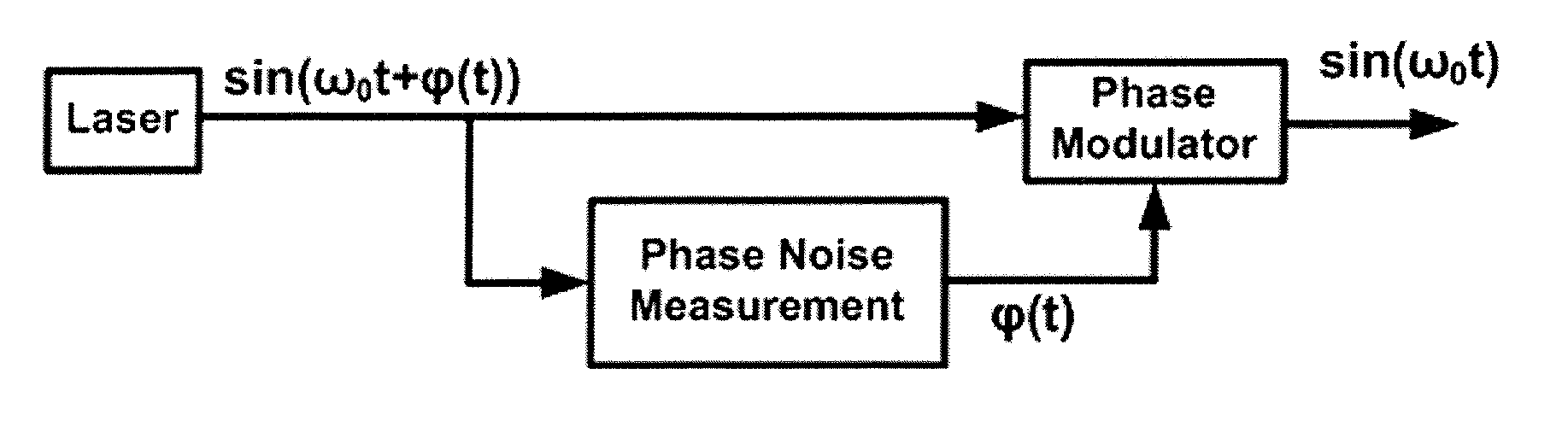
Laser line-width compensation is performed by detecting noise in an optical signal output by a laser of an optical communications system and controlling a complex modulator to cancel the detected noise. Line-width compensation can be performed for both amplitude and phase noise in the optical signal. Noise measurements are used to compute a complex scalar. The complex scalar is used by a compensation processor to modify an input signal that is to be transmitted by the optical communications system. The modified input signal controls the complex modulator, which modulates the output signal to cancel the noise.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Laser linewidth measuring device
ActiveCN102628736ARealize onlineReal-time measurementUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesLine widthOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a laser linewidth measuring device comprising a plurality of optical fiber couplers. The optical fiber couplers are connected with a multichannel optical switch through an optical fiber, a laser beam passing through the optical switch irradiates vertically on ground glass, the laser beam passing through the ground glass enters an F-P etalon, the laser beam passing through the F-P etalon irradiates directly on a CCD after passing through a lens and a vertical slit successively, the CCD transforms an optical signal into an electric signal and communicates the electric signal with a PC machine. The measuring device of the invention has compact structure and convenient operation, realizes the online, instant, precise and automatic measurement of laser linewidth parameters, is capable of measuring a linewidth of continuous laser and a linewidth of pulse laser, and measureing linewidths of multi-path different lasers quickly.
Owner:RES INST OF PHYSICAL & CHEM ENG OF NUCLEAR IND
Asymmetric phase shift grating-based narrow linewidth DFB (Described Feedback) semiconductor laser
ActiveCN103078250AImprove frequency stabilityIncrease output powerLaser optical resonator constructionLaser active region structureFrequency stabilizationGrating
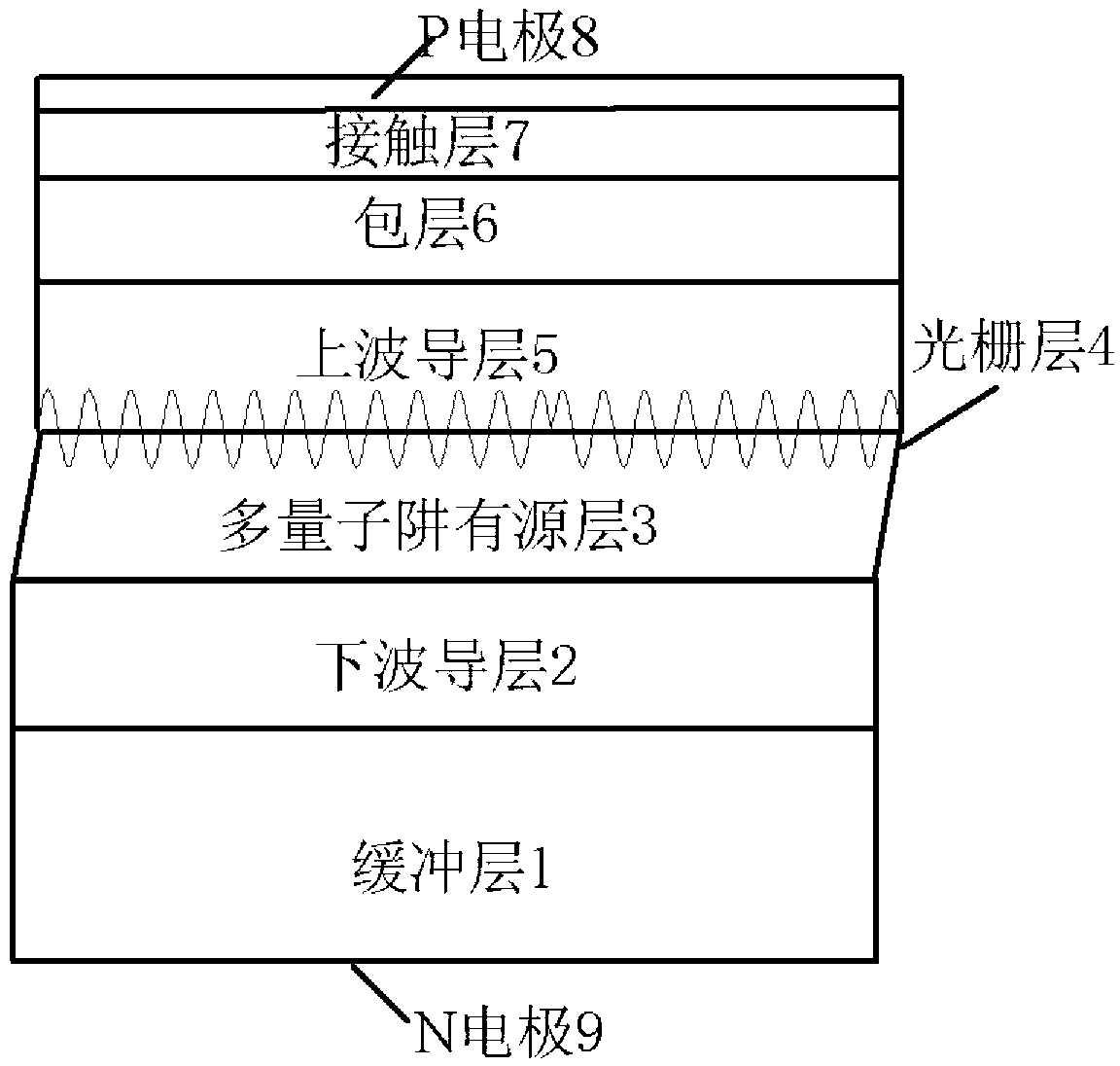
The invention relates to an asymmetric phase shift grating-based narrow linewidth DFB (Described Feedback) semiconductor laser which comprises a buffer layer, a lower waveguide layer, a multiple-quantum well active layer, a grating layer, an upper waveguide layer, a package layer, a contact layer, a P electrode and an N electrode, wherein the lower waveguide layer is manufactured on the buffer layer, the multiple-quantum well active layer is manufactured on a lower package layer, the grating layer is manufactured on the multiple-quantum well active layer, the upper waveguide layer is manufactured on the grating layer, the package layer is manufactured on the upper waveguide layer, the contact layer is manufactured on the package layer, the P electrode is manufactured on the contact layer, and the N electrode is manufactured on the back surface of the buffer layer. The asymmetric phase shift grating-based narrow linewidth DFB semiconductor laser is capable of overcoming the influence of the outer reflected light to the inside of a laser device; and the laser linewidth is reduced, the frequency stability of the laser is increased and the effect of output power is improved.
Owner:山东中科际联光电集成技术研究院有限公司
Spectrally pure short pulse laser
InactiveUS20170365974A1Reduce laser linewidthReduce usageActive medium materialColor/spectral properties measurementsWavelength filterLine width
A short-pulse, narrowband, line-selectable and tunable solid-state laser is described. The device requires a pump source, an active solid-state laser medium, an enclosing cavity, mirrors to contain the light, a method of removing the pulse from the cavity, a wavelength selection system, and a laser linewidth narrowing system. One implementation of this is an Er:YAG laser, side pumped by semiconductor lasers in the erbium absorption band near 1475 nm, with an intracavity etalon and a switchable spectral filter. To remove the pulse from the cavity, cavity dumping issues, which assures constant pulse energy and pulse length over a range of repetition rates, in this case from 100 Hz to 20 kHz. Line selection is obtained by use of wavelength filters and fine tuning with an etalon, which also acts as the linewidth narrowing system.
Owner:LUMINIT
Narrow bandwidth laser device with wavelength stabilizer
ActiveUS20150200730A1High speed communicationReduce transmittanceLaser detailsSolid-state devicesLaser lightPhotodiode
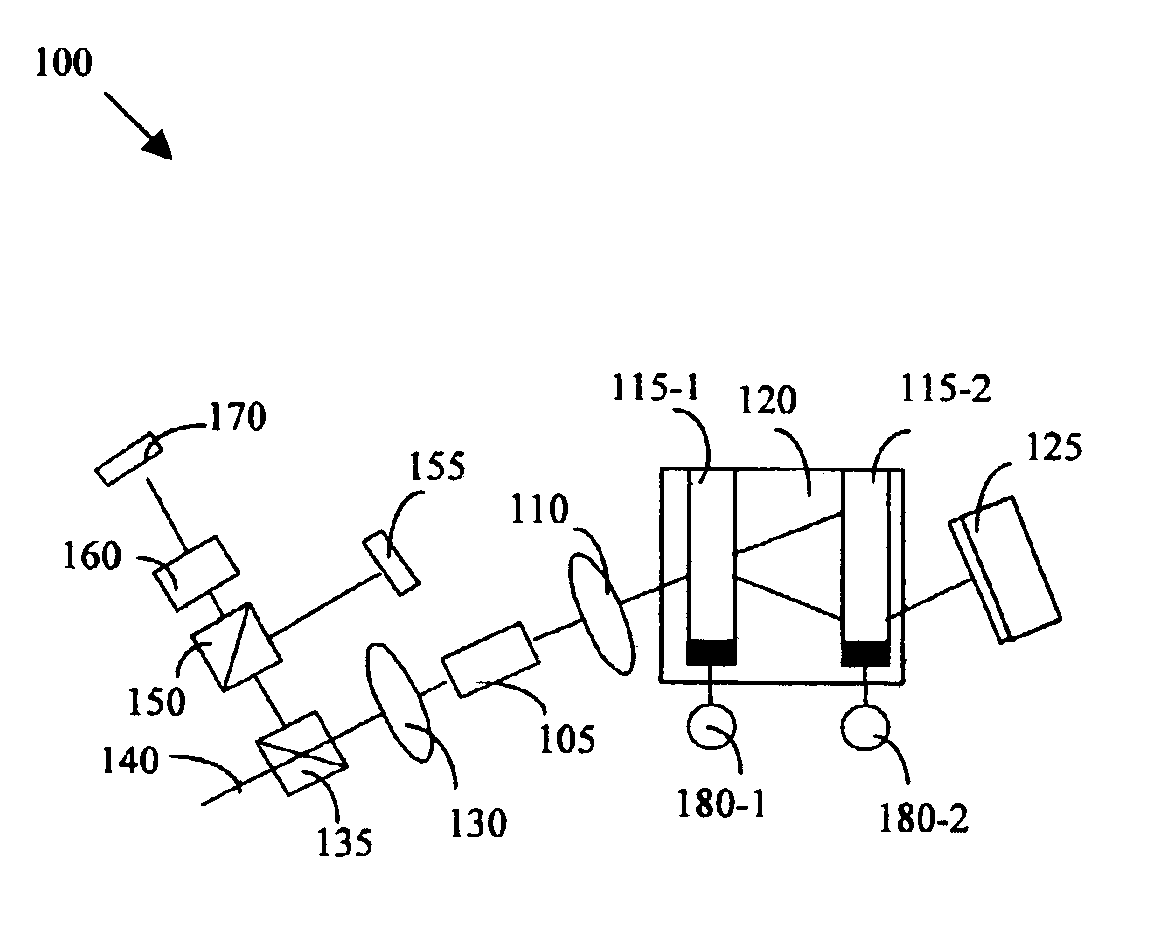
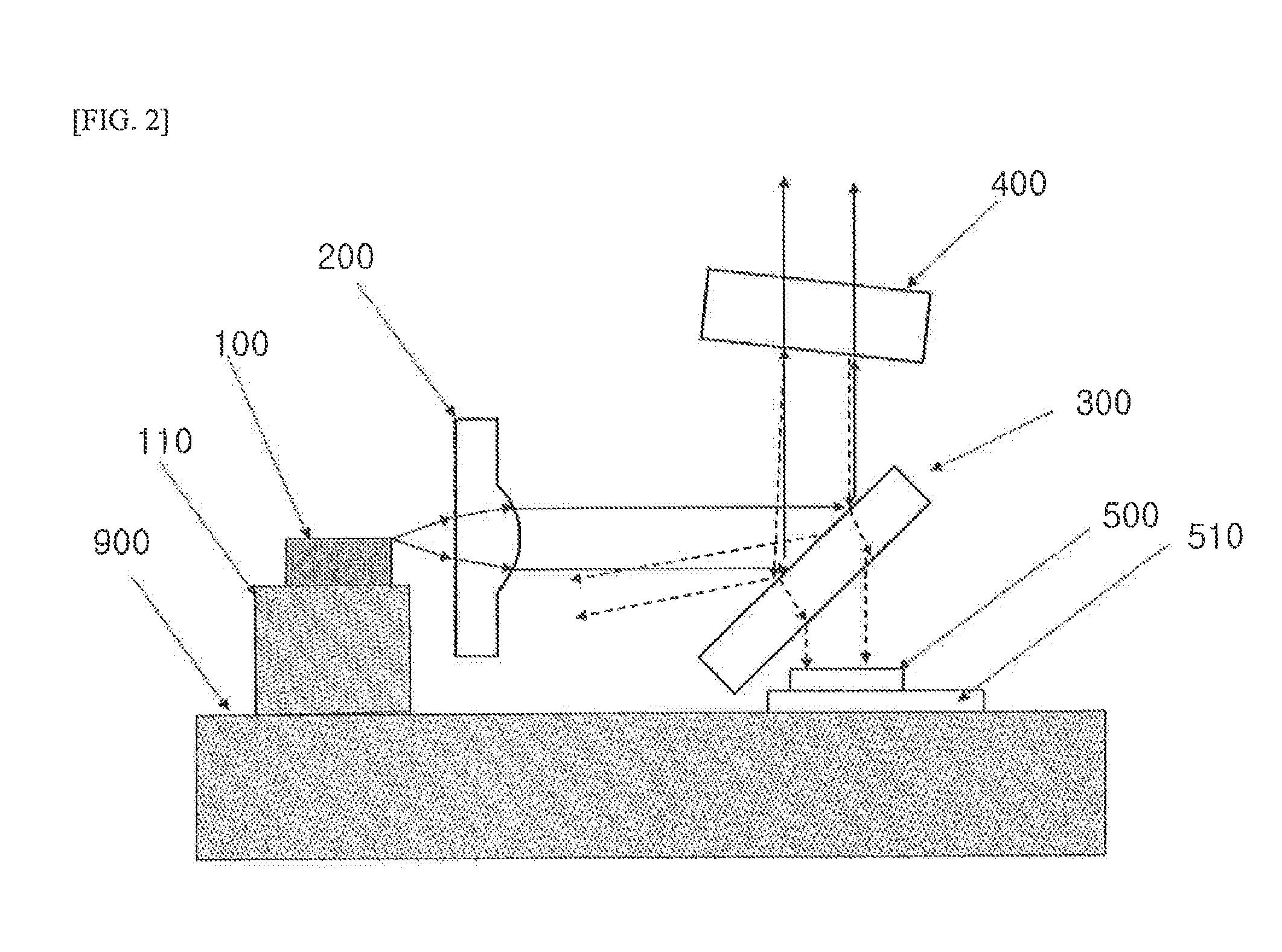
A TO type laser device that can perform long-distance transmission due to a reduced line breadth of laser light. A semiconductor laser device which comprises a laser diode chip (100) that emits laser light; a wavelength-selective filter; a collimating lens (200) disposed in a light path between the laser diode chip (100) and the wavelength-selective filter and to collimate light emitted from the laser diode chip (100); a 45°-partial reflective mirror (300) disposed in a light path between the laser diode chip (100) and the wavelength-selective filter for changing laser light traveling parallel to the bottom of a package into laser light traveling perpendicularly to the bottom of the package; and an optical wavelength supervisory photodiode (500) disposed in a light path along which laser light reflecting from the wavelength-selective filter, after being emitted from the laser diode chip (100), passes through the 45°-partial reflective mirror (300).
Owner:PHOVEL
Common-aperture lath amplification laser incoherent synthesis device
ActiveCN109713555APrevent degradationHighly integratedLaser arrangementsOptical elementsLine widthLight beam
A common-aperture lath amplification laser incoherent synthesis device comprises a seed laser source (1), a light beam coupling alignment module (2), a lath laser gain module (3), a light beam opticalconversion module (4) and a diffraction optical element (5), which are sequentially arranged along a light path. According to the device, seed laser beams with various wavelengths emitted by the seedlaser source (1) are inputted into the lath laser gain module (3) through the light beam coupling alignment module (2) for laser amplification; and the amplified laser beams with various wavelengthsenter the diffraction optical element (5) through the light beam optical conversion module (4) for combination, so that the common-aperture and collinear output of the amplified incoherent synthetic laser is realized. The lath laser gain module (3) is adopted, and the gain narrowing effect of the lath laser gain module (3) can compress the laser line width in the laser amplification process to compress light beam quality degradation after beam combination. Moreover, the laser amplification process is basically not affected by the nonlinear effect, and the laser power is greatly improved.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Guided mode resonance grating narrow line width vertical-cavity surface emitting laser (VESEL) and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107257084AHigh anti-bandwidthHigh inverse bandwidthLaser detailsLaser active region structureMicro nanoVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
The present invention provides a guided mode resonance grating narrow line width vertical-cavity surface emitting laser and a preparation method thereof. According to the present invention, a guided-mode resonant effect of a micro-nano grating is utilized, and a sub-wavelength guided-mode resonant microcavity structure of high reflection and narrow resonance line width is used as a part of the vertical-cavity surface emitting laser, thereby achieving the purposes of narrower laser line width, wider high reflection bandwidth, smaller size and stable polarization control. According to the present invention, by utilizing the guided-mode resonant effect of the micro-nano grating, and by the equivalent medium theoretical calculation, a weak modulated sub-wavelength grating guided-mode resonant microcavity structure of which the resonant wavelength is 852 nm is designed, and a wall used for controlling the mode line width is added between a grating layer and a waveguide layer, so that the mode line width can reach 1 nm or less. Relative to a conventional VCSEL, the narrow line width vertical-cavity surface emitting laser has the narrower laser line width, the wider high reflection bandwidth, the smaller size and the stable polarization control.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Optimized normalized least mean square phase estimation
ActiveUS20120106983A1Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsMean squareSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Methods and systems for normalized least mean square phase estimation are shown that include receiving optical transmissions that include a modulated signal, determining a step size based on a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and a laser linewidth that provides a balance between convergence speed and precision, estimating phase error using the determined step size, derotating the modulated signal to remove the estimated phase error, and demodulating the derotated signal to produce a bitstream.
Owner:NEC CORP
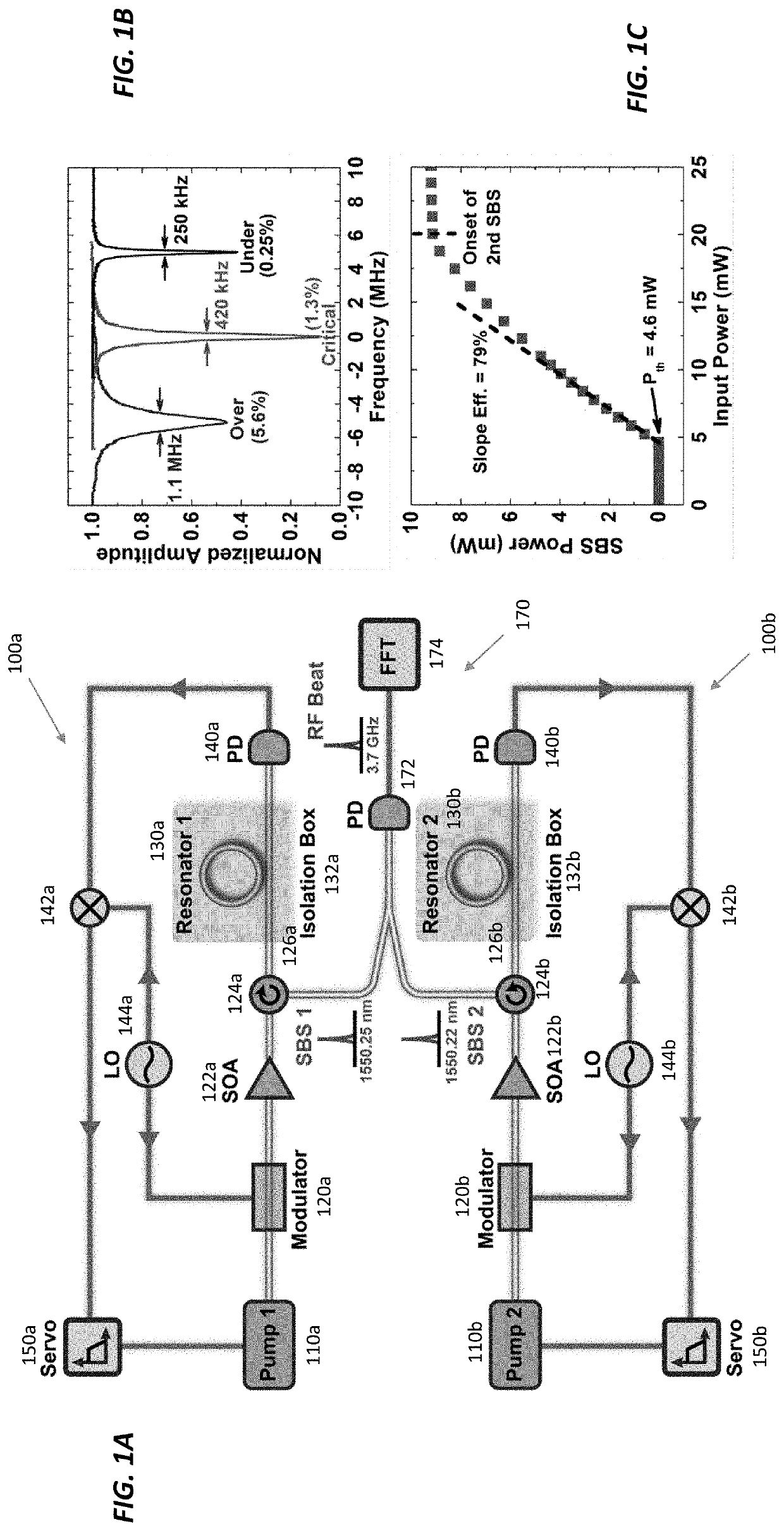
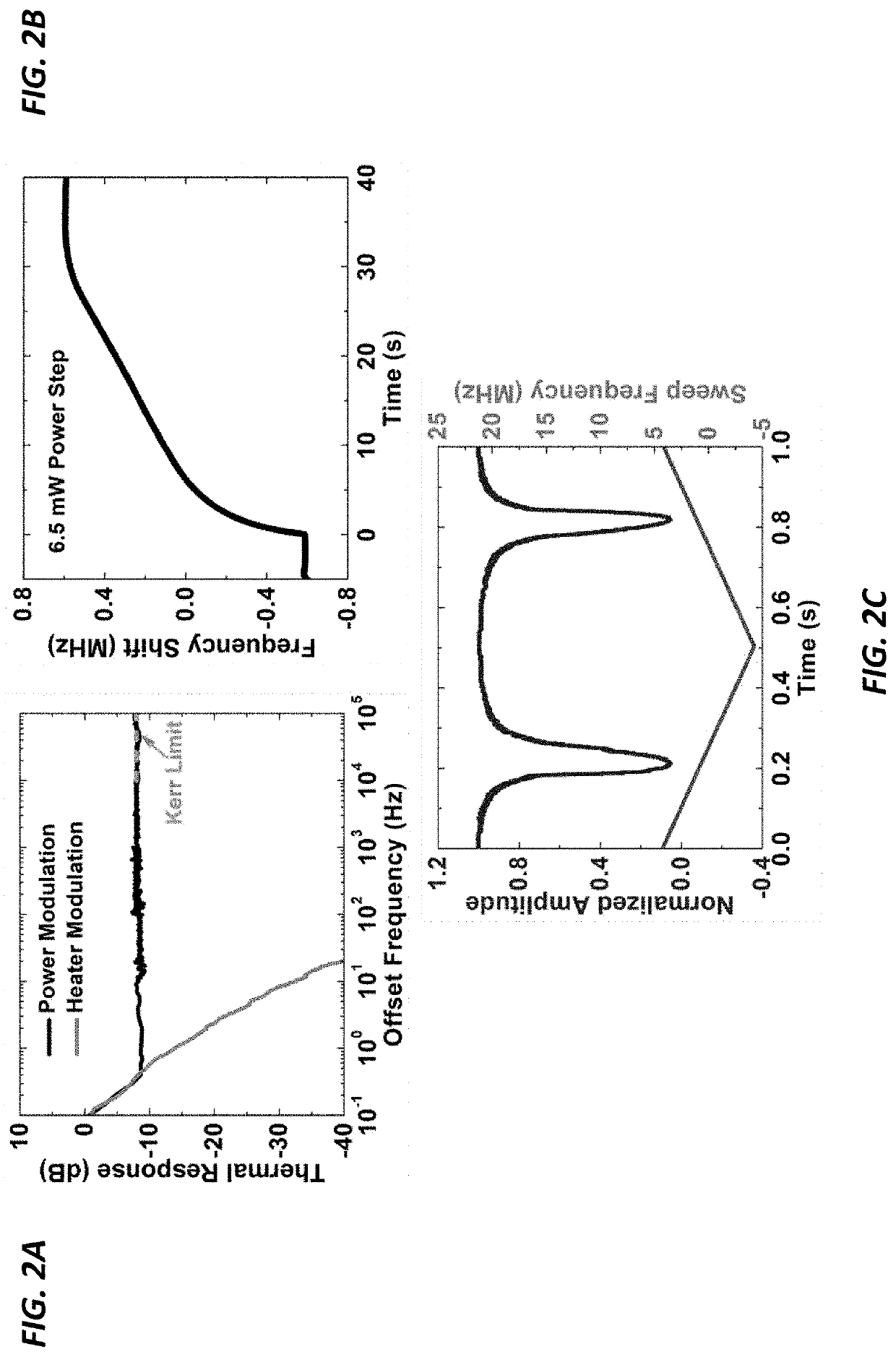
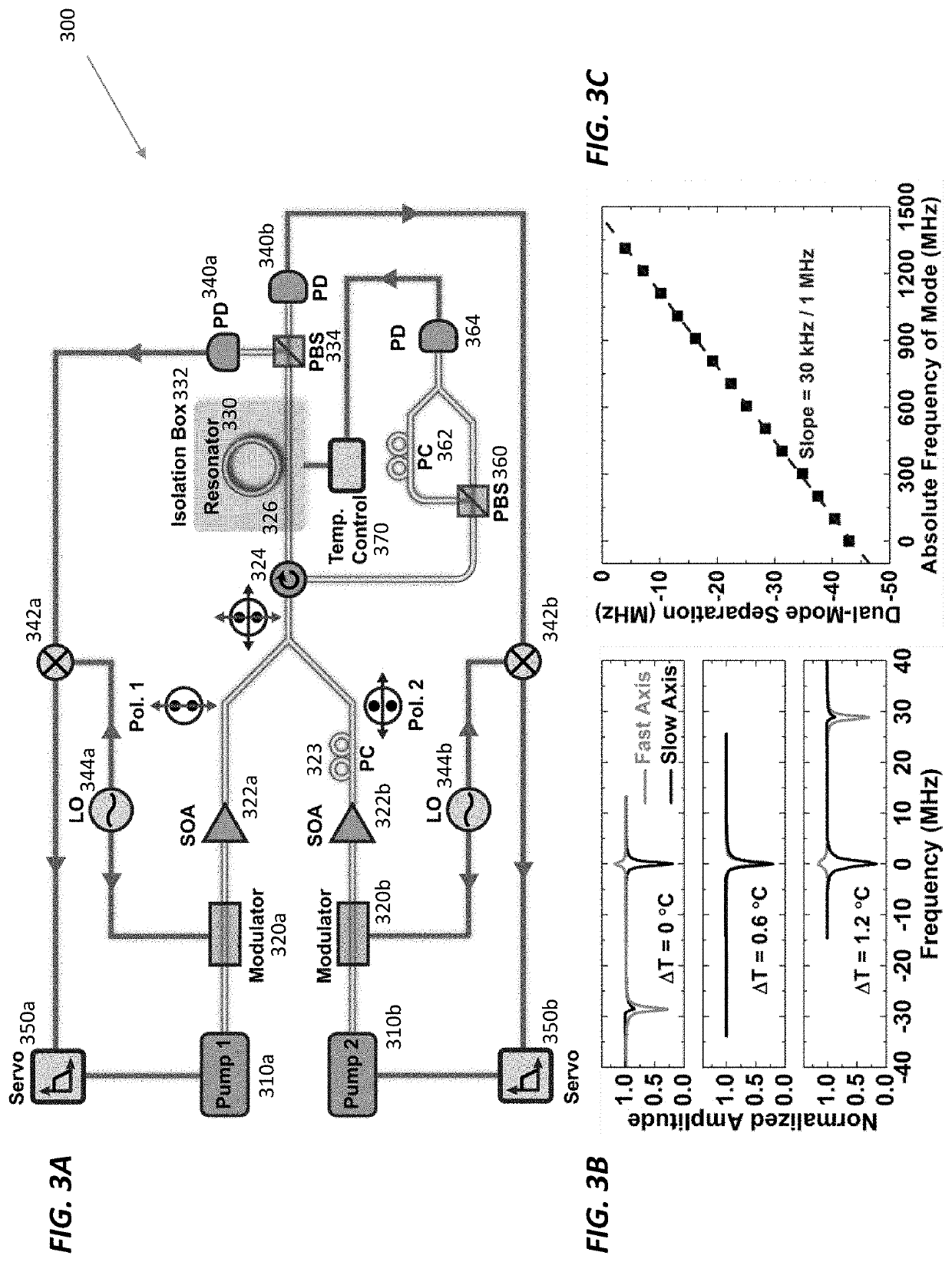
Narrow-linewidth microcavity brillouin laser with suppressed temperature fluctuations
ActiveUS20190341739A1Suppress noiseAddress limitationsLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLine widthCenter frequency
Ultrastable lasers serve as the backbone for advanced scientific experiments and enable atomic spectroscopy and laser interferometry at high levels of precision. But is not clear how to realize an ultrastable laser that is compact and portable for field use. An ultrastable laser source should be insensitive to both short- and long-term fluctuations in temperature, which ultimately broaden the laser linewidth and cause drift in the laser's center frequency. Fortunately, using a large mode-volume optical resonator, which suppresses the resonator's fast thermal fluctuations, together with the stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) optical nonlinearity presents a powerful combination that enables the ability to lase with an ultra-narrow linewidth of 20 Hz. The laser's long-term temperature drift is compensated by using the narrow Brillouin line to sense minute changes in the resonator's temperature (e.g., changes of 85 nK). The precision of this temperature measurement enables the stabilization of resonators against environmental perturbations.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensing system based on coherent detection
InactiveCN103323041AStable jobShorten the lengthConverting sensor output opticallyLine widthSignal light
A distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensing system based on coherent detection comprises a pump laser and couplers. Lasers emitted by the pump laser are divided into two routes of detecting light through the first coupler. The first route of detecting light enters a Brillouin optical fiber annular laser device of a lower arm light path, and output Brillouin lasers serve as local oscillation light. The second route of detecting light enters a distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensor of an upper arm light path, and obtained backward Brillouin signal light with temperature and strain information serves as scattered light. After frequency mixing is conducted on the Brillouin signal light and the Brillouin lasers through the second coupler, the Brillouin signal light and the Brillouin lasers are connected to a photo-electric detector to undergo photo-electric conversion. The distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensing system based on coherent detection has the advantages that high nonlinearity optical fibers are adopted in the Brillouin optical fiber annular laser device, the output Brillouin lasers are small in line width and stable in frequency, and sensing precision is increased; the distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensor can measure temperature and strain signals at the same time, and therefore high-frequency detection is converted to low-frequency detection, cost is greatly saved, and system complexity is lowered.
Owner:武汉华之洋科技有限公司
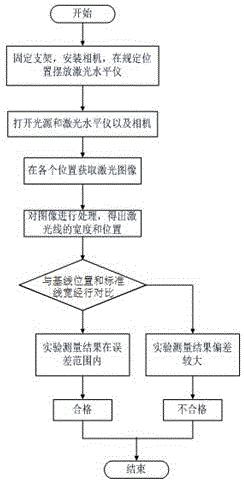
Method for detecting emergent laser rays of laser level based on machine vision
ActiveCN106546263AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressMeasurement devicesHuman–machine interfaceMachine vision
The invention discloses a method for detecting the emergent laser rays of a laser level based on machine vision. The method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring the data of a plurality of images of a plurality of horizontal or vertical laser rays in real time; 2) transmitting the image data to a PC; 3) preprocessing images; 4) detecting the positions of laser rays in every image and determining the information like the width of the laser rays; 5) fusing the related image information of the laser rays and determining whether the positional information of straight laser rays undergo emergent offset along top-to-bottom and left-to-right directions; 6) fusing the width information of the plurality of images of the laser rays and determining whether each laser ray is less than or equal to a prescribed diffraction angle so as to guarantee that width meets production requirements; and 7) displaying information indicating whether the laser level is qualified on a human-computer interface, presenting determination results and bases, and storing the number of the detected laser level and the widths, positions and other information of the detected laser level in every direction into a database. The method can realize precision identification of the positions of the laser rays and accurate measurement of the widths of the laser rays.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Resonant cavity device, and system and device using resonant cavity device
InactiveCN102769251ARealize line width narrowingStable deliveryLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency stabilizationResonant cavity
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Semiconductor laser MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) system for pumping alkali metal vapor
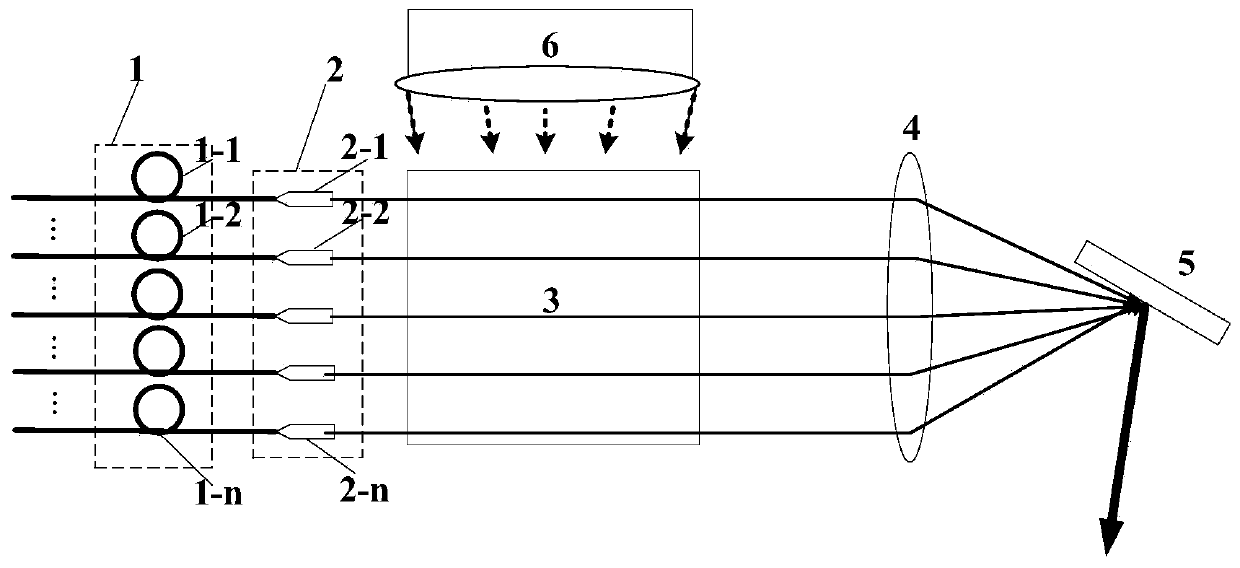
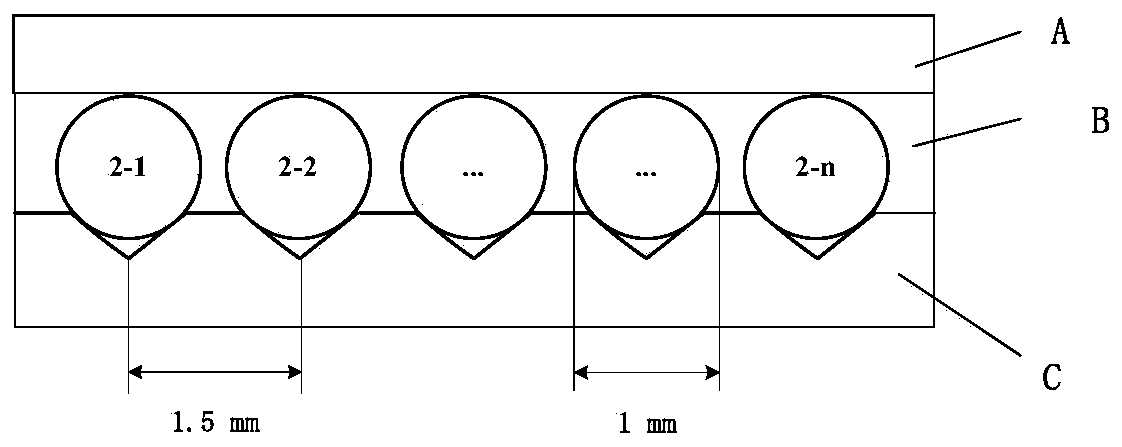
The invention discloses a semiconductor laser MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) system for pumping alkali metal vapor, wherein a linewidth compression system, a beam shaping and coupling system, a seed optical system and a power amplification system are sequentially connected; a semiconductor laser linewidth compression system which consists of a fast-axis collimation lens, two plano-convex lenses and a holographic grating is used, meanwhile a buffer gas with a determinate optimized pressure value is charged into a master oscillation pool in the seed optical system and an amplification pool in the power amplification system so as to broaden an alkali metal atomic absorption line; and the linewidth of an LDA (Laser Diode Array) can be effectively compressed to the magnitude of that of the broadened alkali metal atomic absorption line so as to realize the matching of the linewidth of the LDA and the alkali metal atomic absorption line. Pump lights are allocated to two gain medium pools, i.e. the master oscillation pool and the amplification pool, according to the proportion of 1: 4, and as the structures of the two oscillation pools are completely identical, the quality of beams is ensured and meanwhile the heat quantity is dispersed, and the power can be amplified over multiple times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multi-section-type FP (FabryPerot) cavity single wavelength laser based on deeply etched grooves
ActiveCN102545045AReduce lossSimple and cheap production processLaser detailsLaser active region structureLine widthQuantum well
The invention discloses a multi-section-type (FabryPerot) cavity single wavelength laser based on deeply etched grooves. The laser disclosed by the invention is structurally characterized by at least comprising a laser waveguide, a first deeply etched reflecting surface and a second deeply etched reflecting surface which are respectively positioned at two ends of the laser waveguide, and a deeplyetched groove array arranged between the first deeply etched reflecting surface and the second deeply etched reflecting surface, wherein the deeply etched groove array is composed of 2-6 deeply etched grooves; the laser is manufactured on a semiconductor epitaxial wafer, and respectively comprises a lower cladding layer, a quantum well layer, an upper cladding layer and certain auxiliary layers among the lower cladding layer, the quantum well layer, the upper cladding layer layers from bottom to top; and the laser waveguide is divided into a plurality of sections of independent waveguides by the deeply etched groove array, the first deeply etched reflecting surface and the second deeply etched reflecting surface, each section of waveguide is covered with an electrode, and each electrode is respectively injected with a current so as to control the laser wavelength and power. Compared with the background technology, the laser disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the production process is simpler and cheaper due to only once epitaxial growth, the manufacturing error is smaller, the energy consumption for the apparatus operation is less, and the laser line width is narrower.
Owner:深圳市迅特通信技术股份有限公司 +1
Ultra-narrow-linewidth nonlinear gain amplification multi-wavelength fiber laser
InactiveCN103296567AReduce complexityReduce use costActive medium shape and constructionLine widthOptical communication
The invention provides an ultra-narrow-linewidth nonlinear gain amplification multi-wavelength fiber laser, belongs to the technical field of photoelectric information and aims at solving the problem that an existing multi-wavelength fiber laser is large in output laser linewidth, complicated in system and poor in stability. The technical scheme is that light emitted by a high-power narrow-linewidthBrillouin pump is irradiated into a port a of an input / output circulator, and a port b of the input / output circulator is connected with a port j of a second coupler. A port m of the second coupler is connected with a polarization controller, and a port k and a port n are respectively connected with a port I and a port o of a single mode fiber. The polarization controller is connected with a reflection circulator. The other two ports of the reflection circulator are connected. A port c of the input / output circulator is connected with an Er-doped fiber, the Er-doped fiber is further connected with a first coupler, and the other two ports of the first coupler are connected. A port d of the input / output circulator is an output port. The ultra-narrow-linewidth nonlinear gain amplification multi-wavelength fiber laser has wide application prospect in the fields of dense wavelength division multiplexing optical communication systems, distributed optical fiber sensing and microwave photonics.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Speed measurement method and system based on double etalons
InactiveCN105974396ASimple structureLow costTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesFluid speed measurementFrequency stabilizationLine width
The invention discloses a speed measurement method and system based on double etalons. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the inversion of the speed of a to-be-measured target object through measuring the Doppler frequency shift of an echo signal, returned by the to-be-measured target object, of a laser beam; enabling the laser beam to form a plurality of narrow band laser beams with the split frequencies through a receiving etalon, and irradiating the to-be-measured target object; enabling the echo signal to be divided into two ways, wherein one way passes through the receiving etalon and a Doppler frequency shift detection signal is obtained, and the other way serves as a reference light signal; and obtaining the speed of the to-be-measured target object through the comparison of the Doppler frequency shift detection signal and the reference light signal. The system is simple in structure, and exerts low requirements on the laser line width and the frequency stability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Method for measuring laser linewidth of ultra-narrow linewidth laser
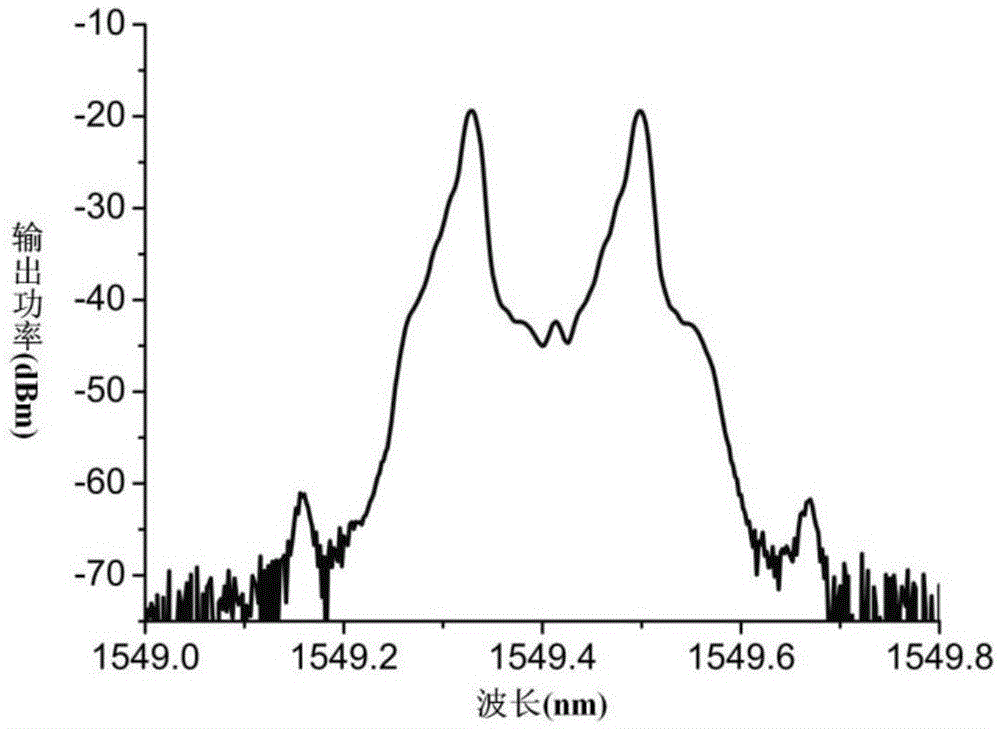
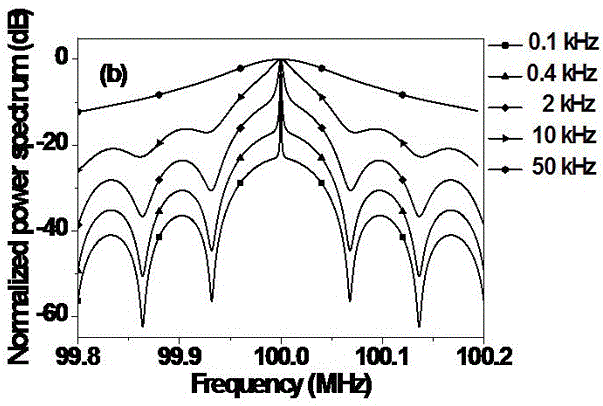
ActiveCN105571830ARealize measurementSolve the noise problemTesting optical propertiesFiberLine width
The invention discloses a method for measuring laser linewidth of an ultra-narrow linewidth laser. The method is creatively characterized in that by use of an automatic heterodyne detection system, a power spectrum of the ultra-narrow linewidth laser under an automatic heterodyne conduction is obtained; and a peak and a valley which are adjacent to each other in terms of positions are selected from an area beyond high-peak pulses on the power spectrum, a difference delta S between the contrast of the peak and the valley on the power spectrum are respectively calculated, and the laser linewidth delta f is calculated according to the delta S. The method for measuring the laser linewidth of the ultra-narrow linewidth laser, brought forward by the invention, has the following technical advantages that the method can realize measurement of ultra-narrow linewidth under the condition of quite short delay fibers, greatly reduces hardware demands, can effectively prevent the problem of noise brought by large-length delay fibers and is quite good in measurement precision.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Optoelectronic feedback-based short-time delay laser linewidth measurement system and measurement method thereof
ActiveCN106092519AFast Linewidth MeasurementAutomatically adjust drive currentTesting optical propertiesPhase noiseBeam splitter
The invention discloses an optoelectronic feedback-based short-time delay laser linewidth measurement system. According to the thought of the system, the laser is used for acquiring laser signals s(t), an optical power beam splitter converts the laser signals s(t) into two paths of laser signals, reference light signals 0.5 s(t) and measurement light signals 0.5 s(t) are obtained, a time delay optical fiber carries out phase shift on the measurement light signals 0.5 s(t), measurement light signals s1(t) after phase shift are obtained, an optical coupler carries out coupling on the s1(t) and the reference light signals 0.5 s(t) to obtain combined laser signals sc(t), an optoelectronic detector carries out optoelectronic conversion on the sc(t) to obtain combined electric signals Id(t), an amplifier amplifies the Id(t), combined electric signals Vd(t) after amplification are obtained, a low-pass filter carries out low-pass filtering on the Vd(t), combined electric signals Vf(t) after low-pass filtering are obtained, a voltage-current converter contains set preset electric signals Vpre(t), the Vf(t) and the Vpre(t) are added for conversion from voltage to current, current signals are obtained, the current signals serve as working current of the laser to be sent to the laser, phase noise of the laser signals s(t) is acquired, and thus, a 3dB linewidth of a phase noise power spectrum for the laser signals s(t) is further calculated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
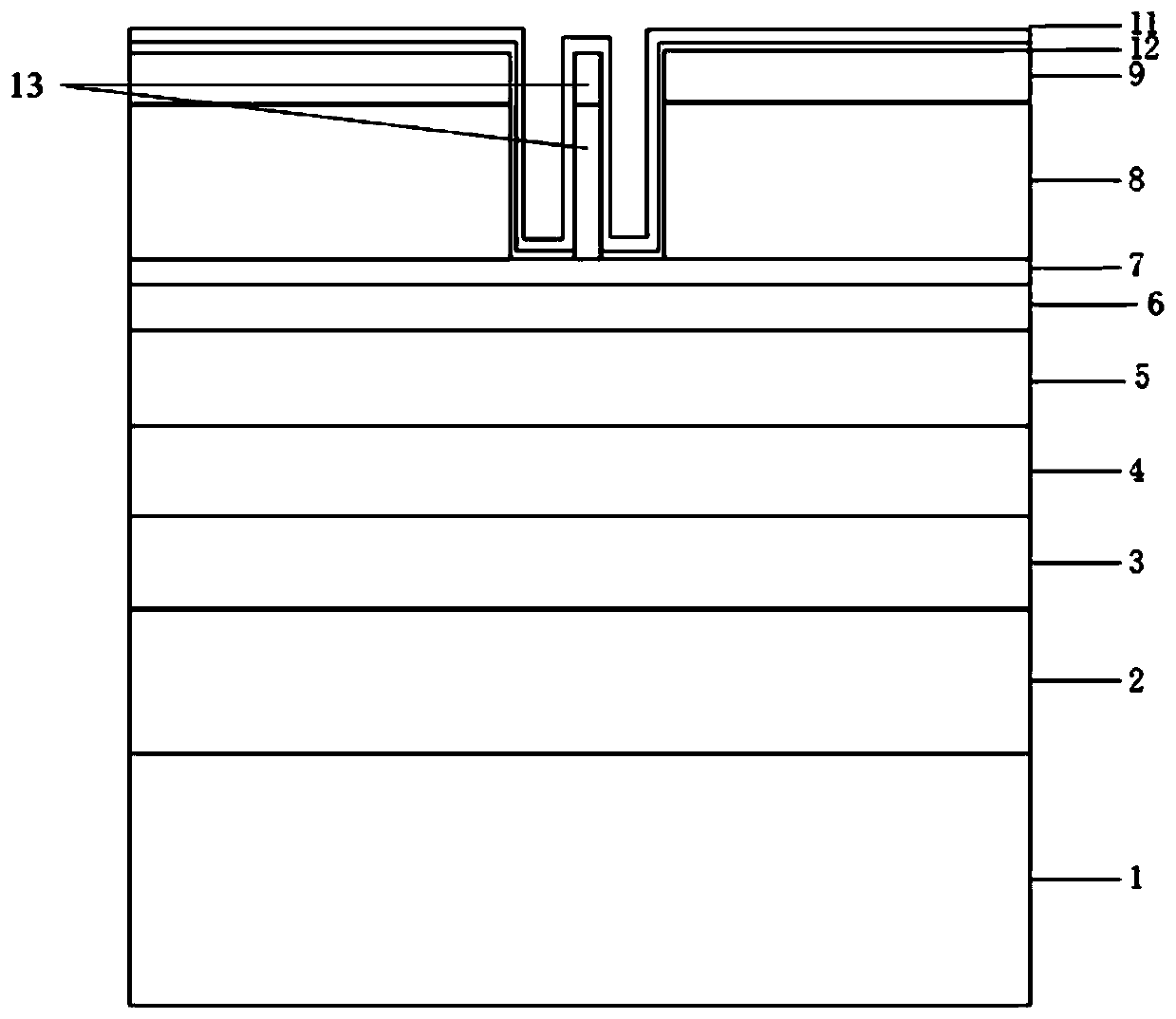
Narrow-linewidth distributed feedback semiconductor laser and preparation method thereof
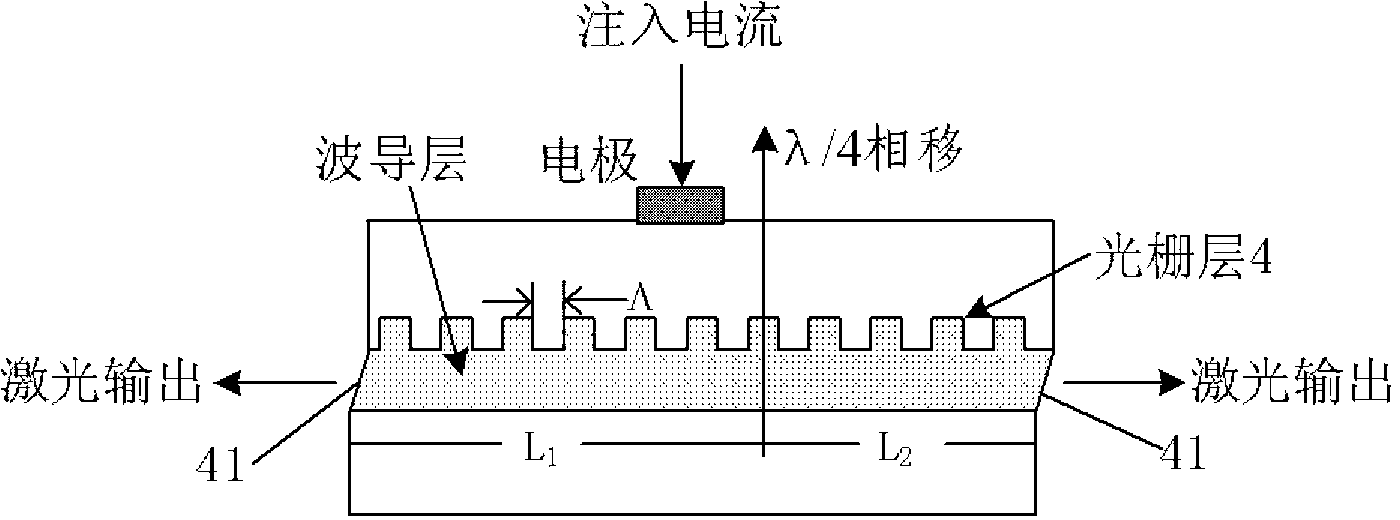
ActiveCN111313229AStable working wavelengthHigh side mode suppression ratioOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionGratingLine width
The invention provides a distributed feedback semiconductor laser which sequentially comprises an N-surface electrode layer, a substrate layer, a buffer layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active layer, an upper waveguide layer, a secondary epitaxial grating layer, an etching self-stop layer, a cladding layer, an ohmic contact layer, a passivation layer and a P-surface electrode layer from bottom to top. The cladding layer and the ohmic contact layer form a waveguide structure, and the waveguide structure is a ridge waveguide structure. An upper grating structure and a lower grating structure in the vertical direction are used for jointly feeding back mode selection. Secondary epitaxial gratings distributed near the active region are efficiently coupled with a light field so that frequencyselection and line width reduction are realized. The single reflection peak line width of the electrode sampling grating is narrow, the electrode sampling grating is fully coupled with a light field in the waveguide for feedback, the working wavelength can be further stabilized, the side-mode rejection ratio is improved, the line width factor is reduced and the laser line width is effectively narrowed.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com