Asymmetric phase shift grating-based narrow linewidth DFB (Described Feedback) semiconductor laser
An asymmetric phase shift, semiconductor technology, applied in the structure of the optical resonator, the structure of the active area, etc., can solve the problems of low output power, unstable laser emission wavelength, and inability to meet the requirements of laser performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
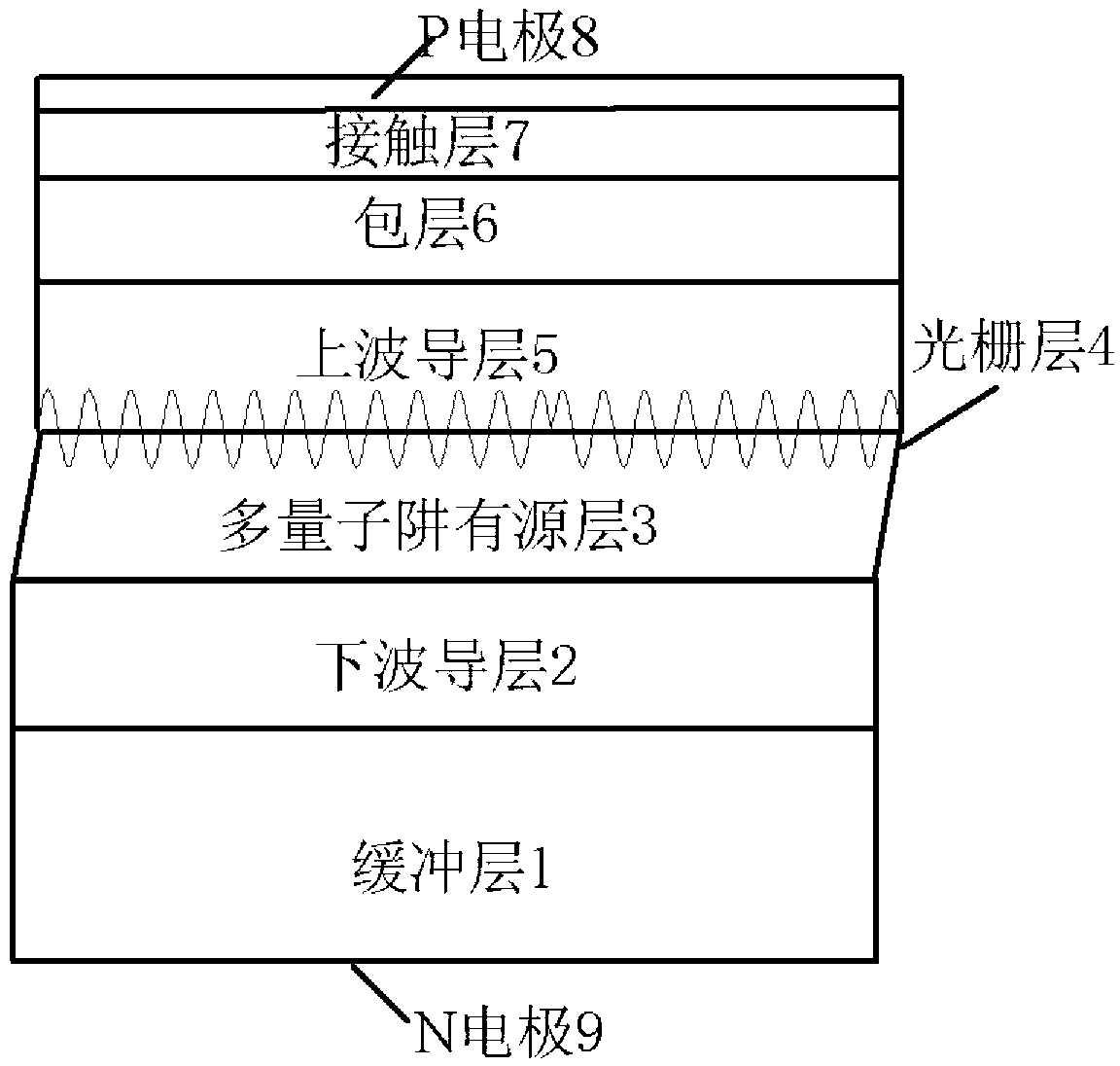
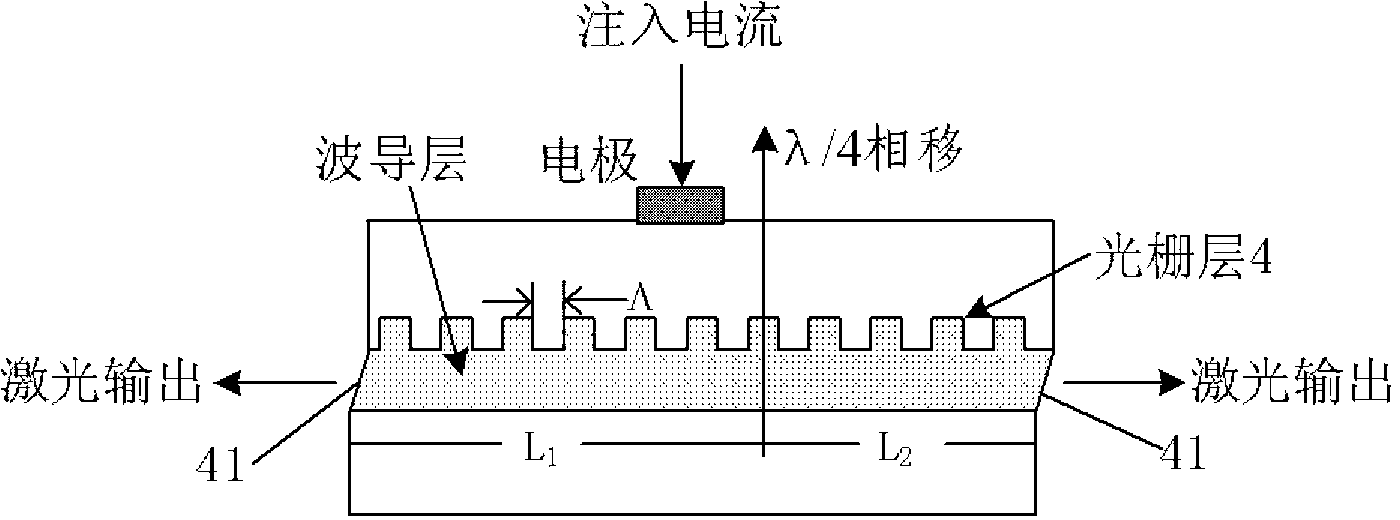
[0021] see Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, the present invention provides a kind of narrow-linewidth DFB semiconductor laser based on asymmetric phase-shift grating, comprising: a buffer layer 1, a lower waveguide layer 2, a multi-quantum well active layer 3, a grating layer 4, an upper A waveguide layer 5 , a cladding layer 6 , a contact layer 7 , a P electrode 8 and an N electrode 9 . in:
[0022] A buffer layer 1, the material of the buffer layer 1 is to select III-V group compound semiconductor material, II-VI group compound semiconductor material, IV-VI group compound semiconductor material or quaternary compound semiconductor material; for the InP buffer layer, the thickness is 200nm, doping concentration about 1×10 18 cm -2 .
[0023] The lower waveguide layer 2 is made on the buffer layer 1, and the thickness of the lower waveguide layer 2 is 100 nm of non-doped lattice-matched InGaAsP material.
[0024] A multi-quantum well active layer 3, the multi-quantum well ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com