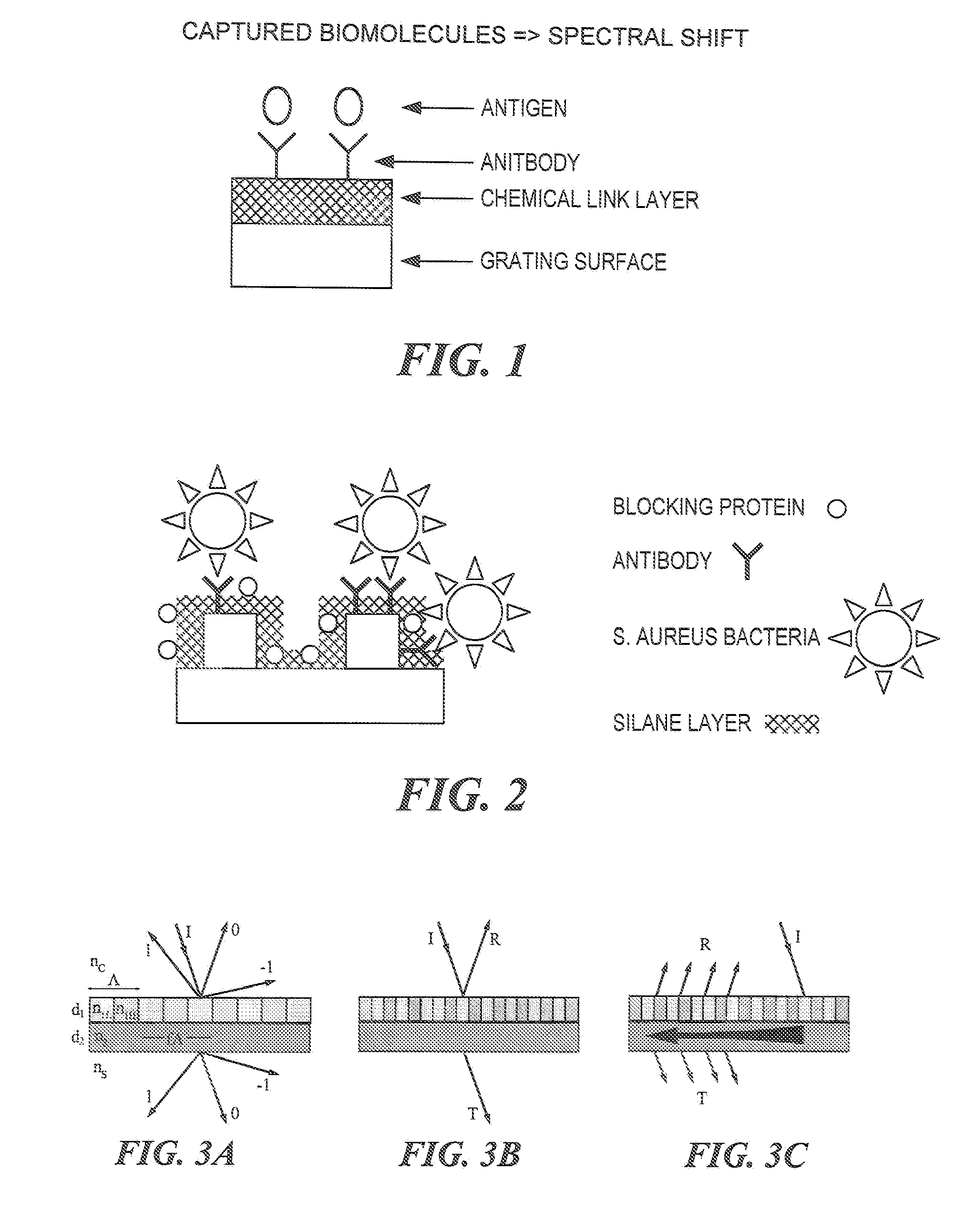
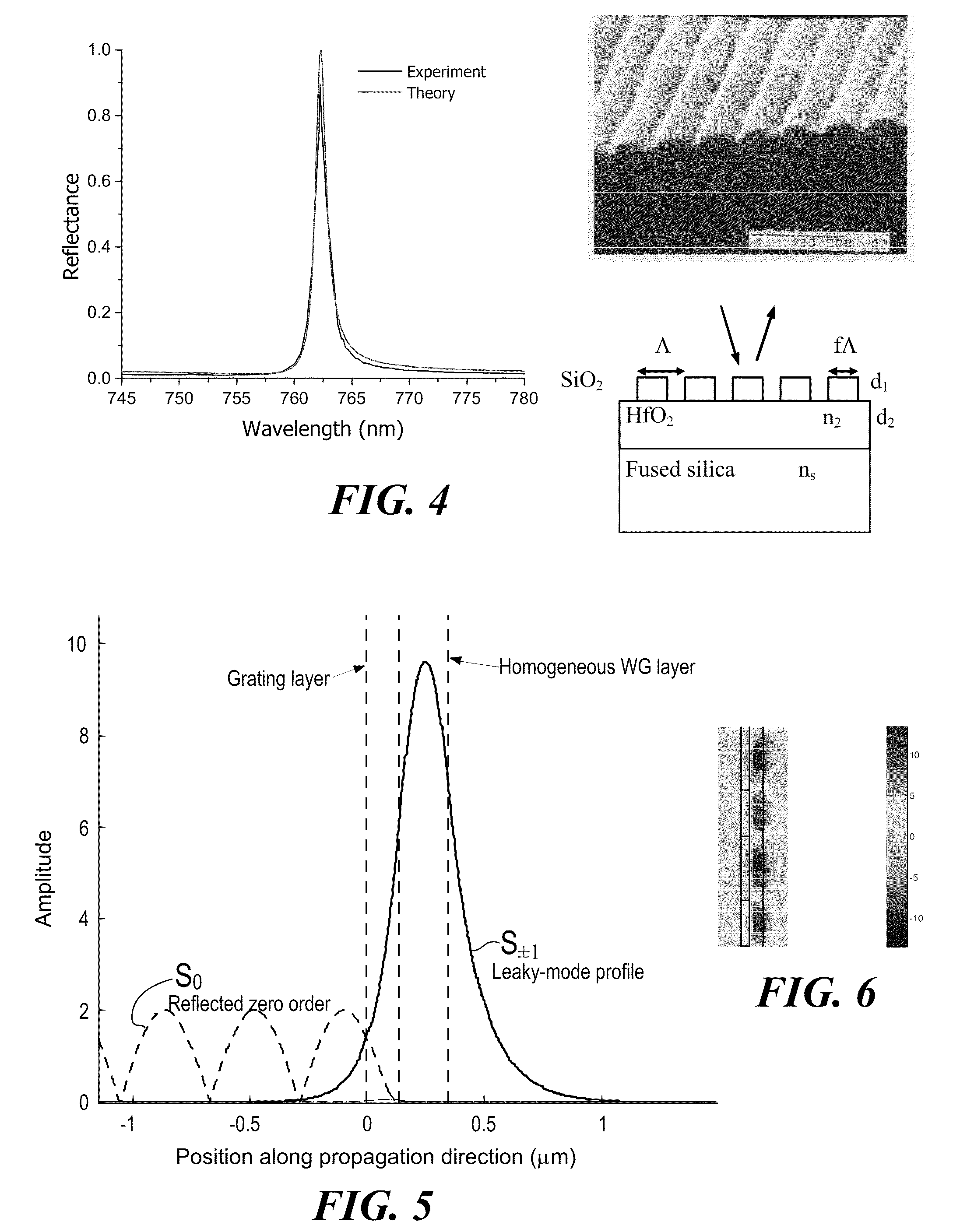
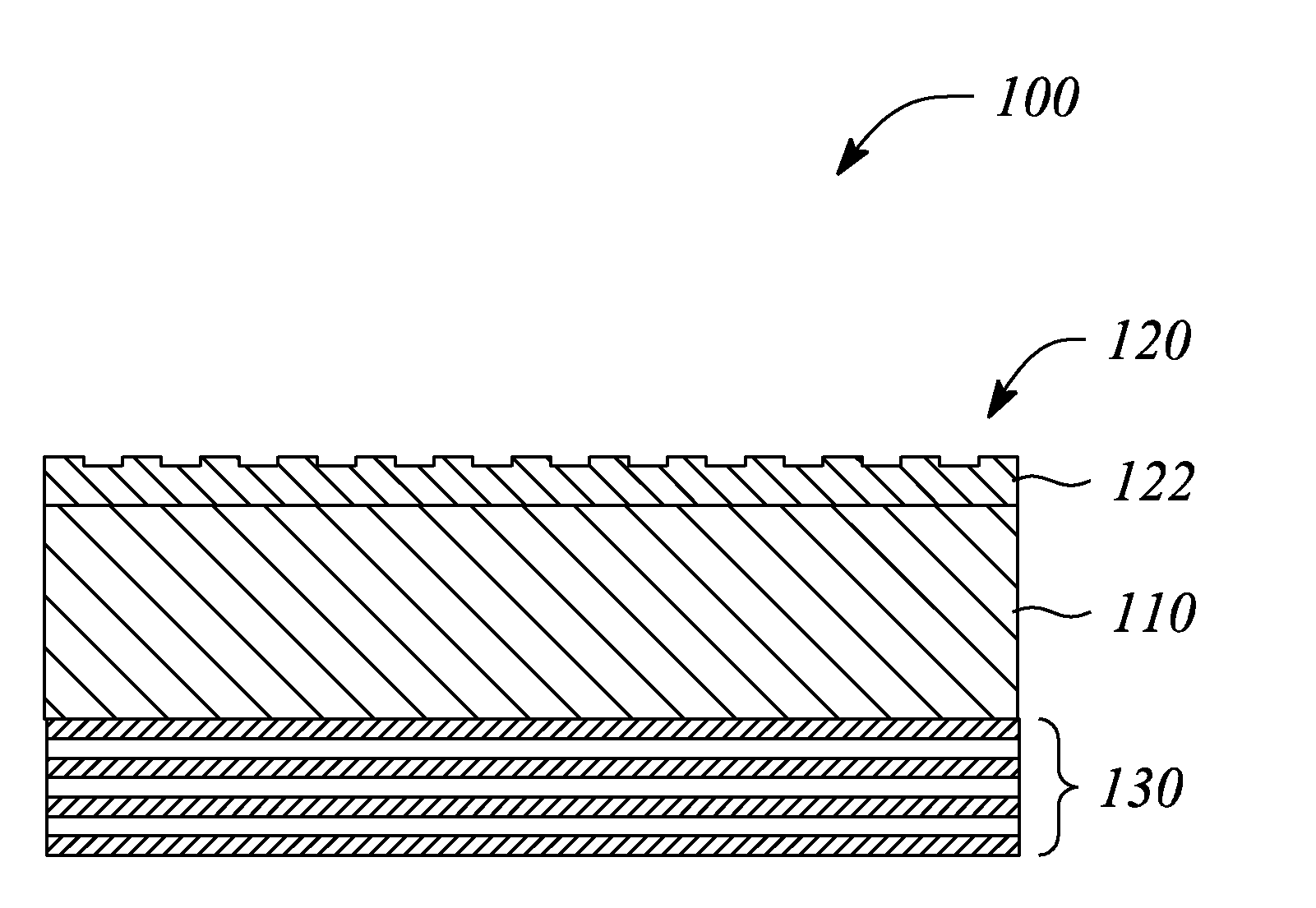
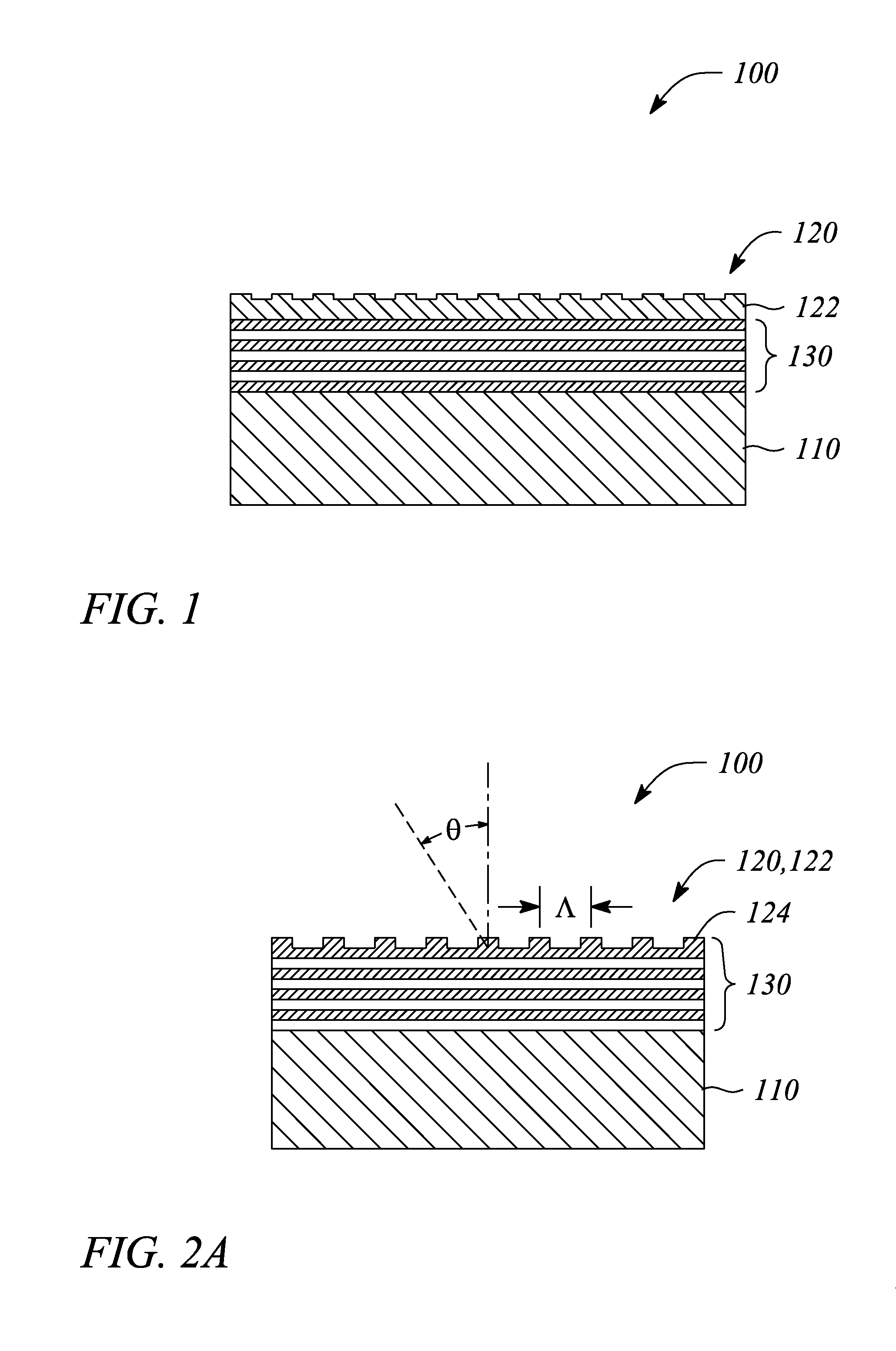
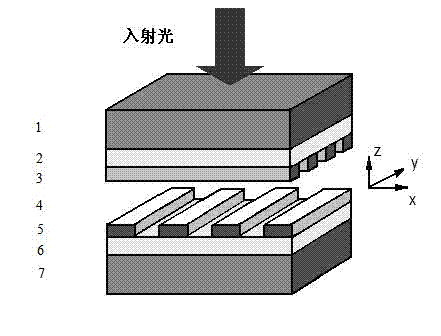
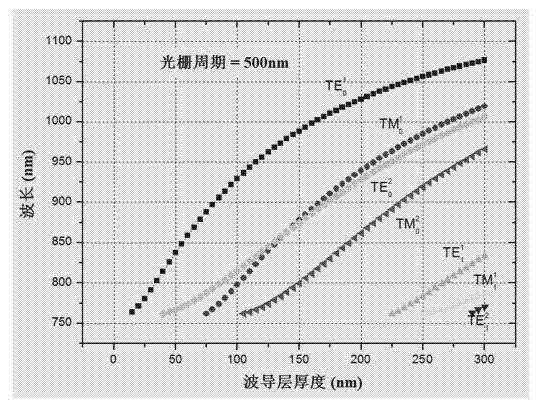
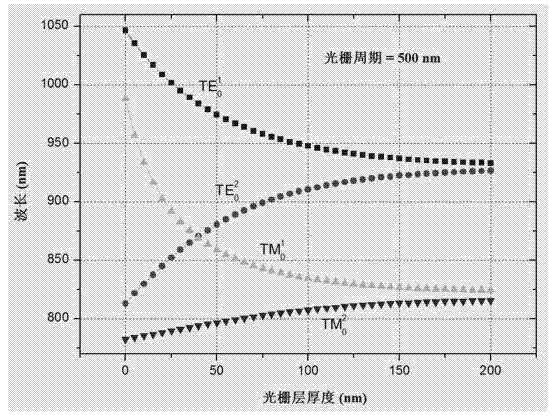
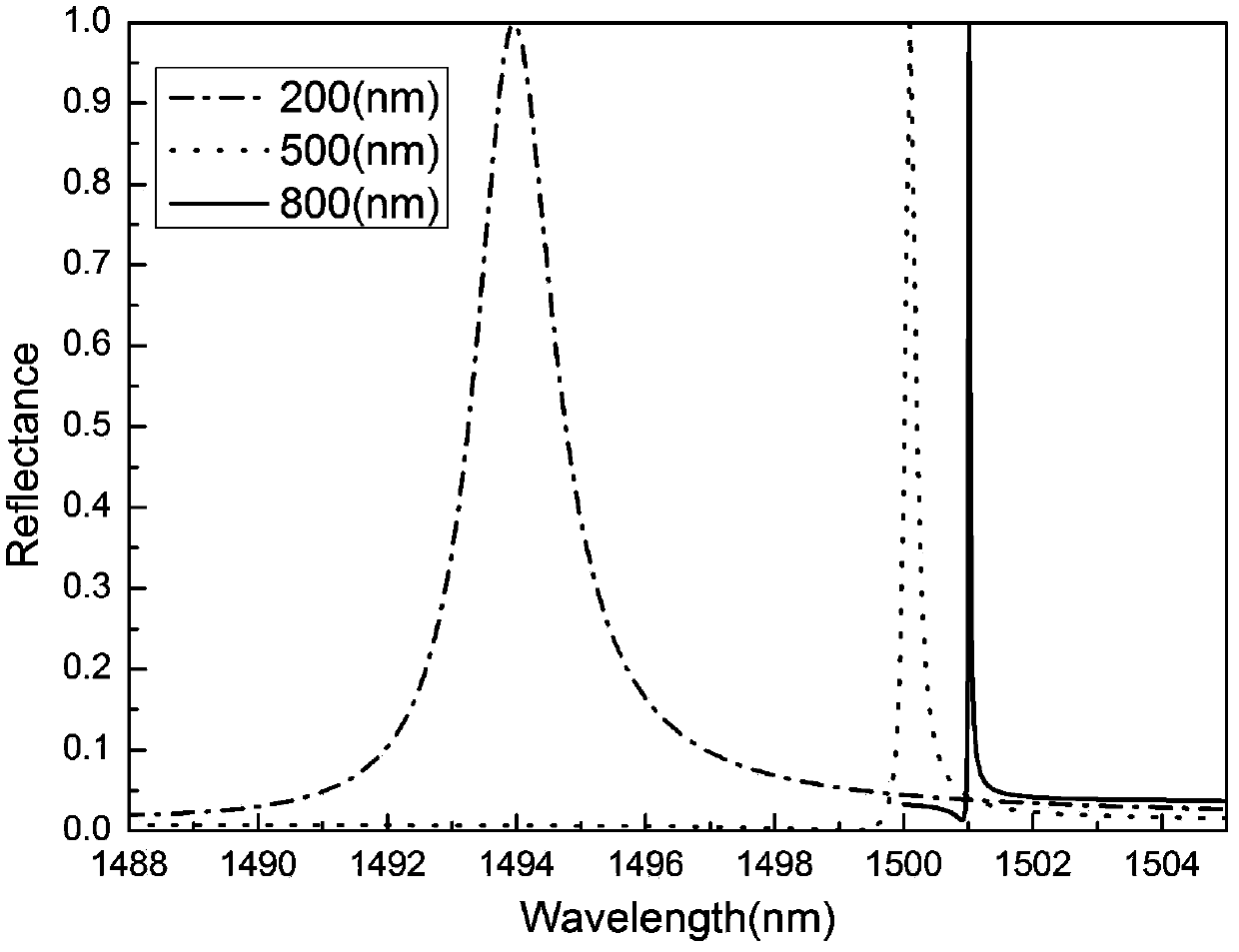
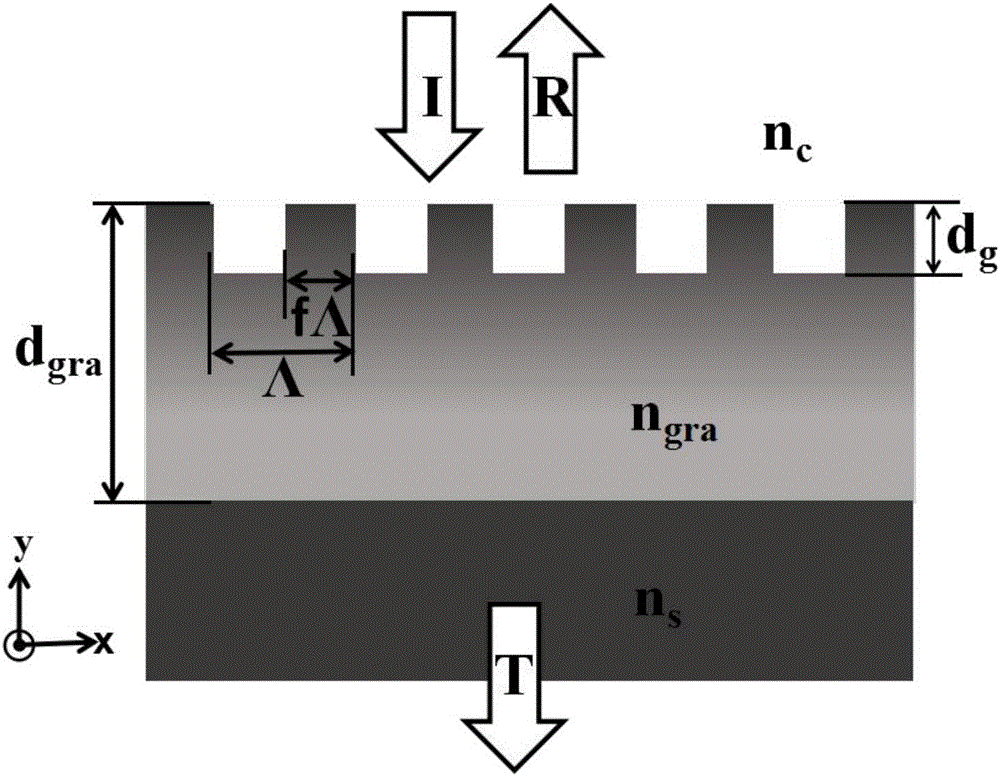
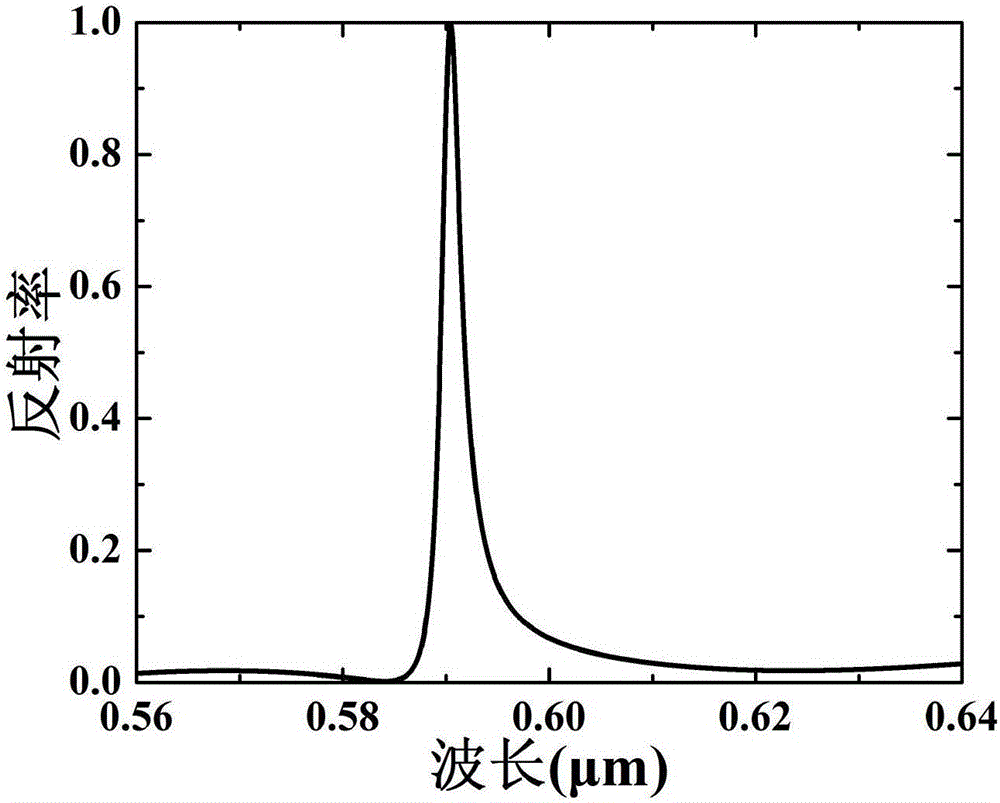
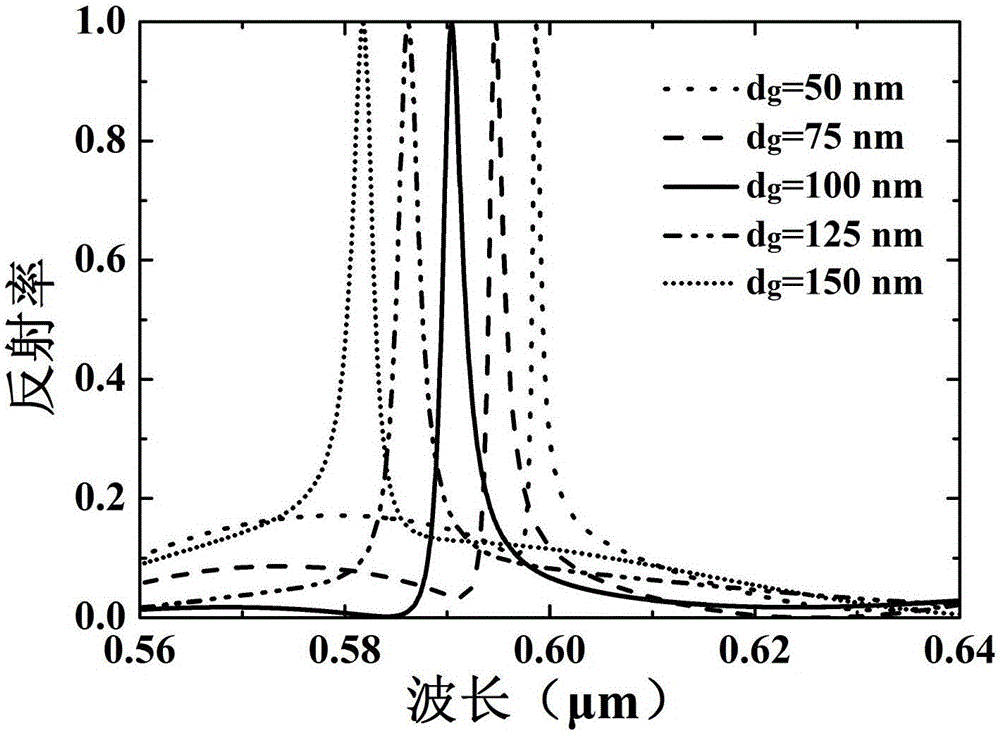
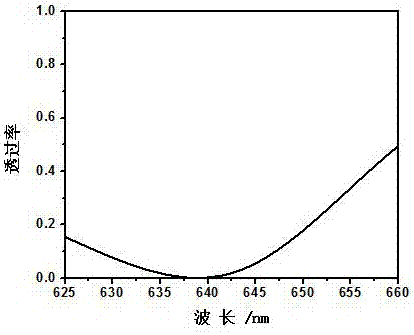
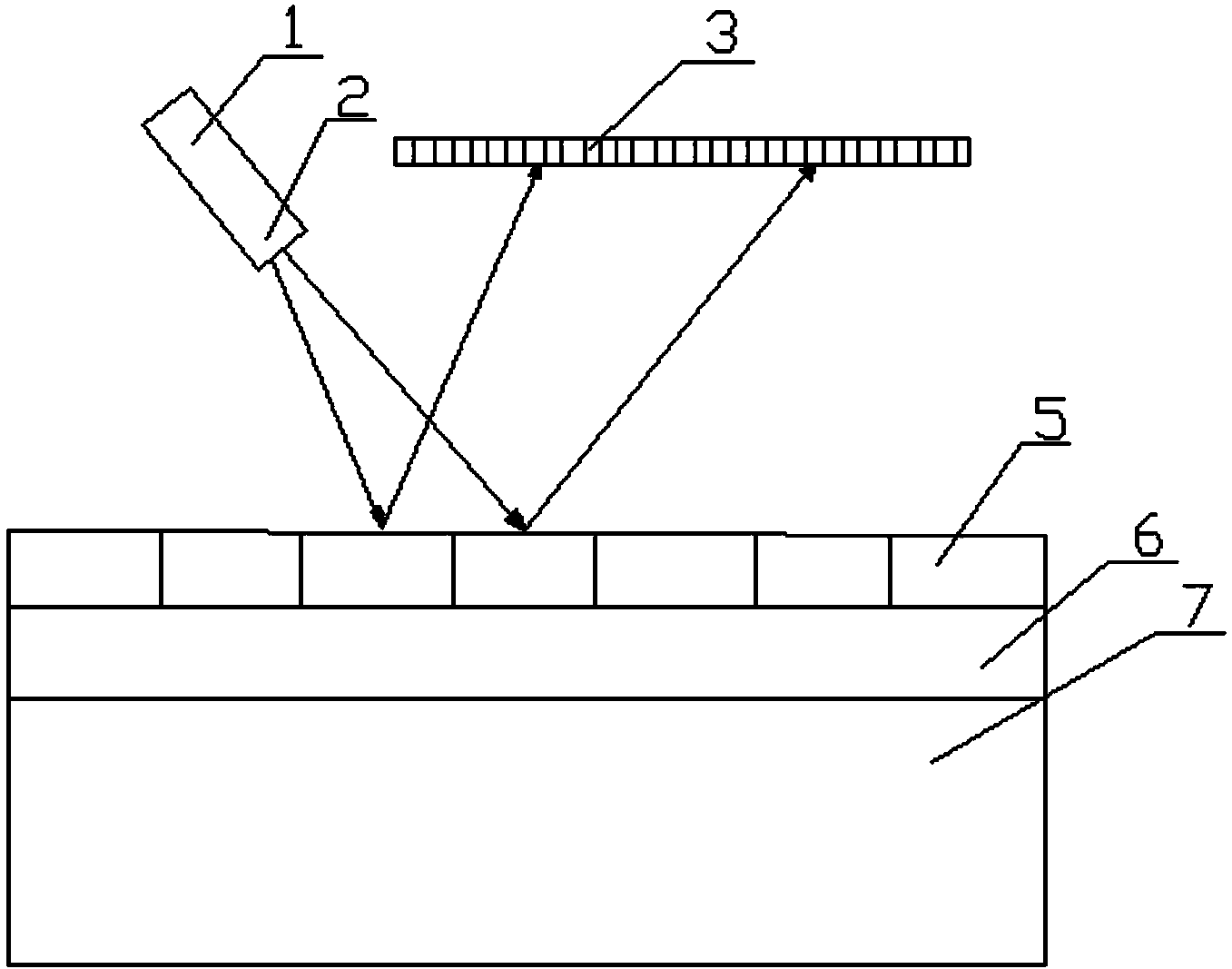
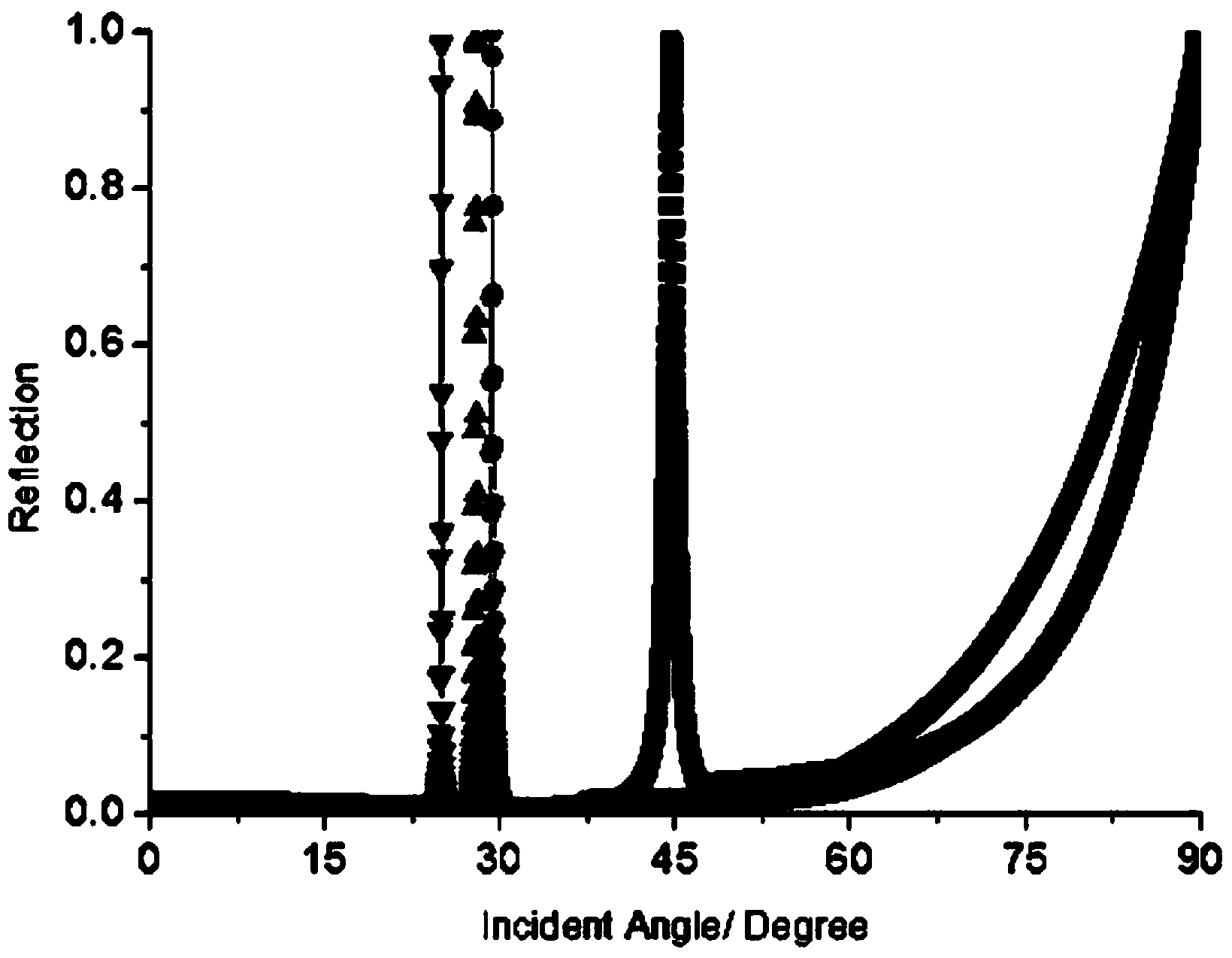
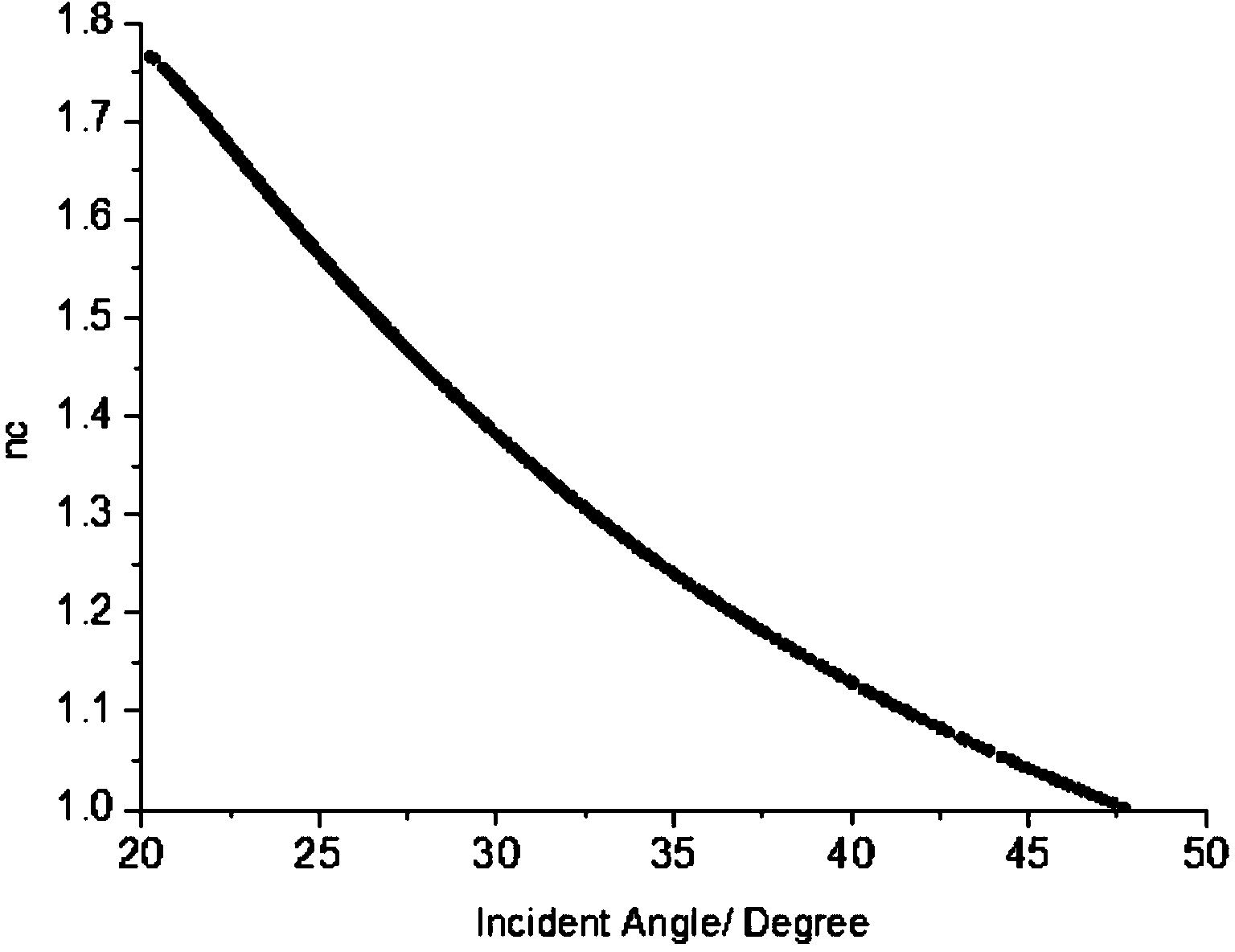
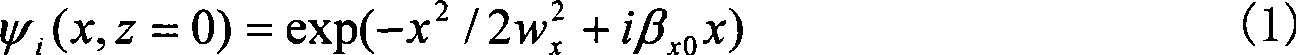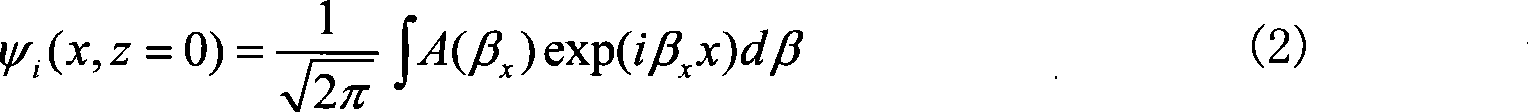Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127 results about "Guided-mode resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
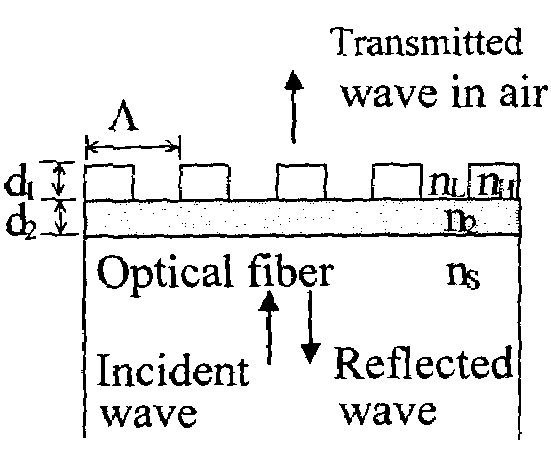
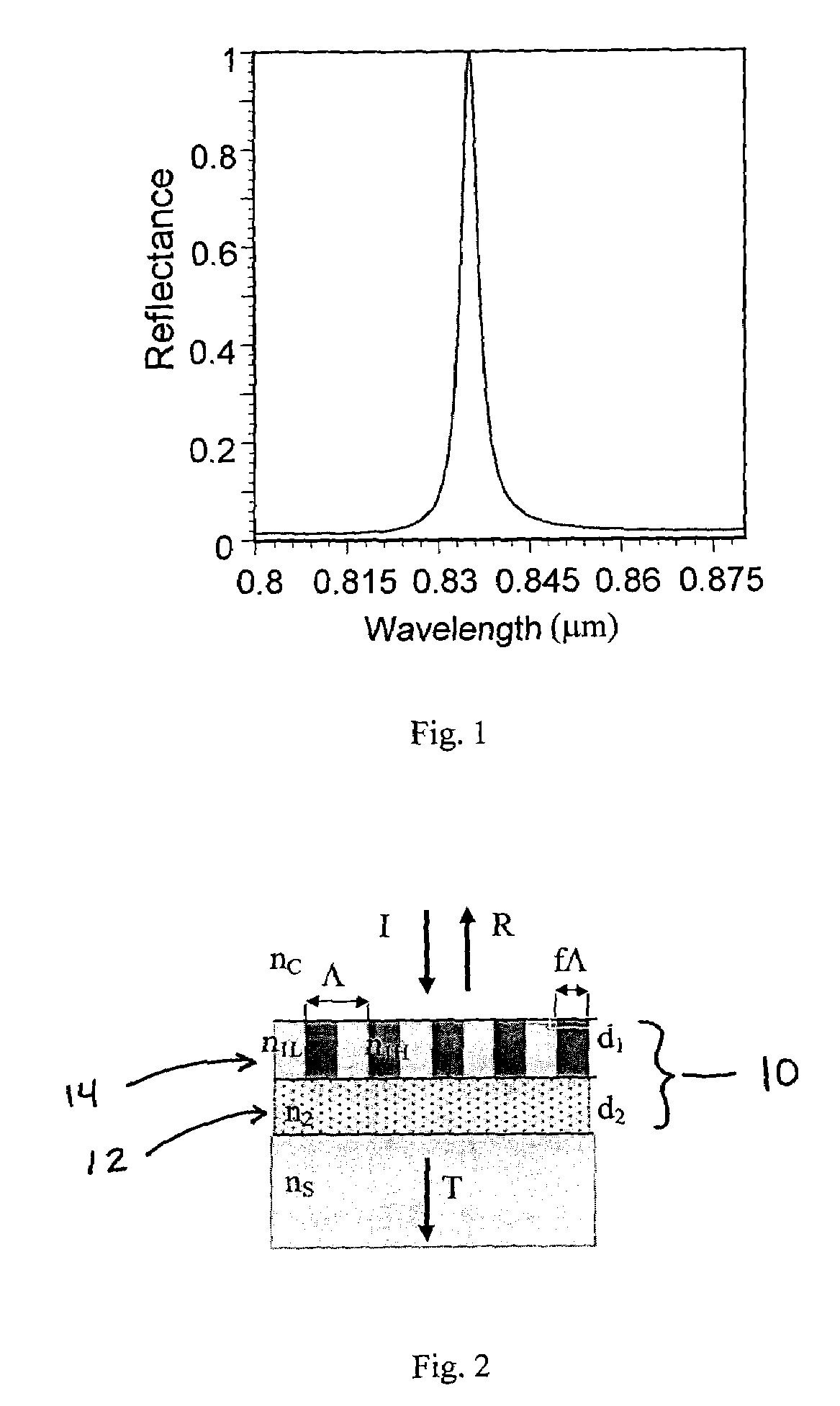
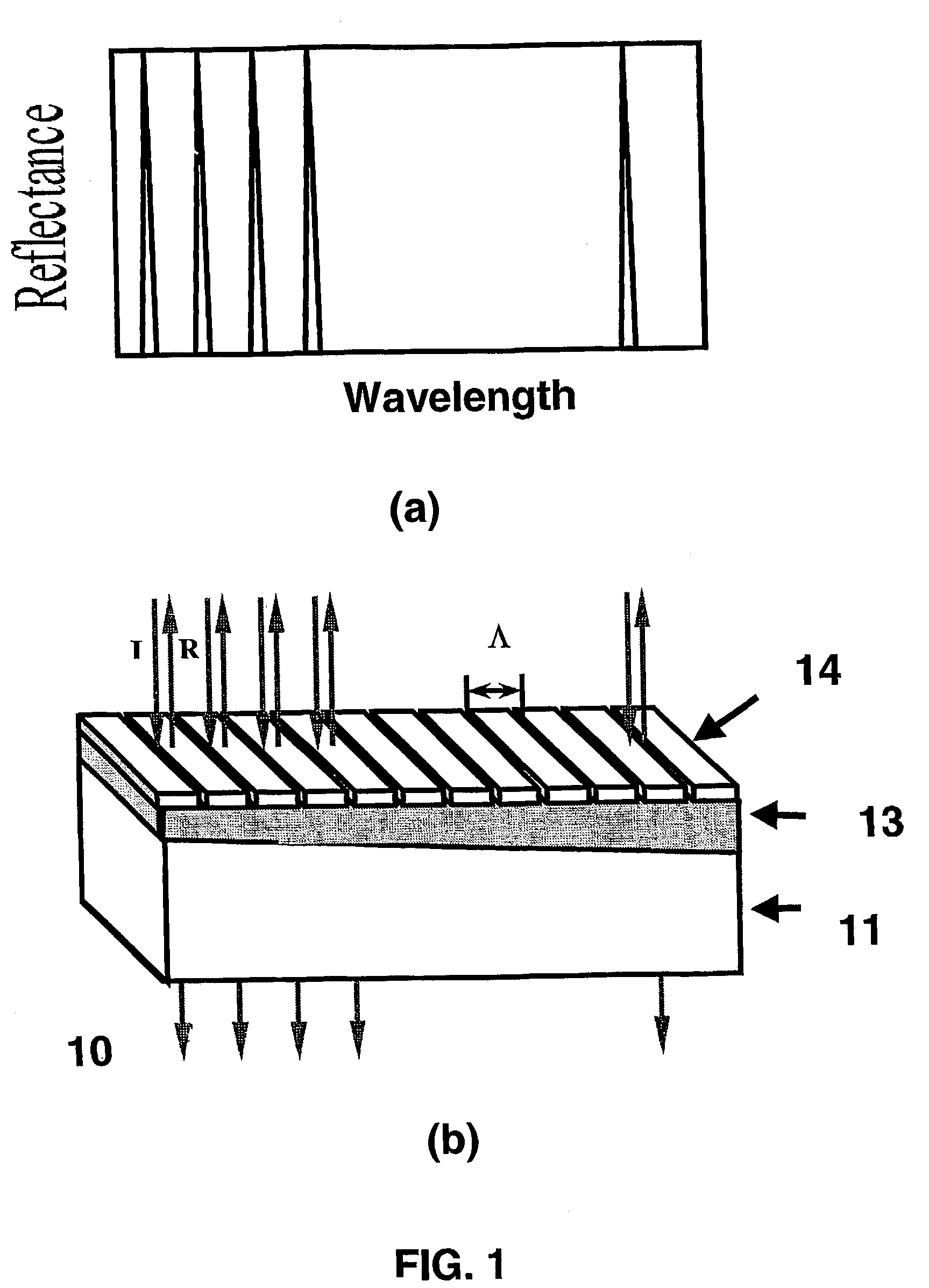
Guided-mode resonance or waveguide-mode resonance is a phenomenon wherein the guided modes of an optical waveguide can be excited and simultaneously extracted by the introduction of a phase-matching element, such as a diffraction grating or prism. Such guided modes are also called "leaky modes", as they do not remain guided, and have been observed in one and two-dimensional photonic crystal slabs.
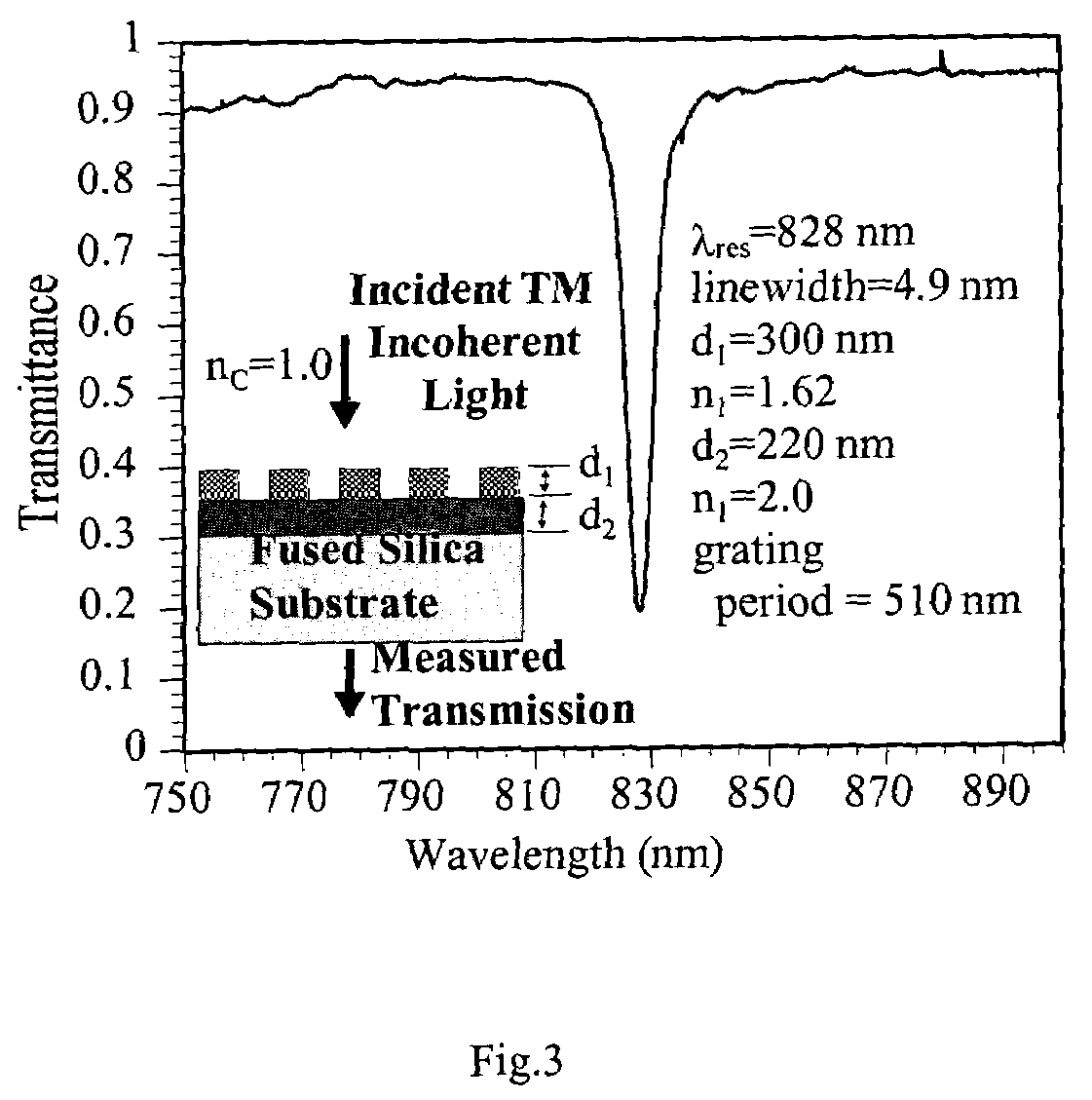
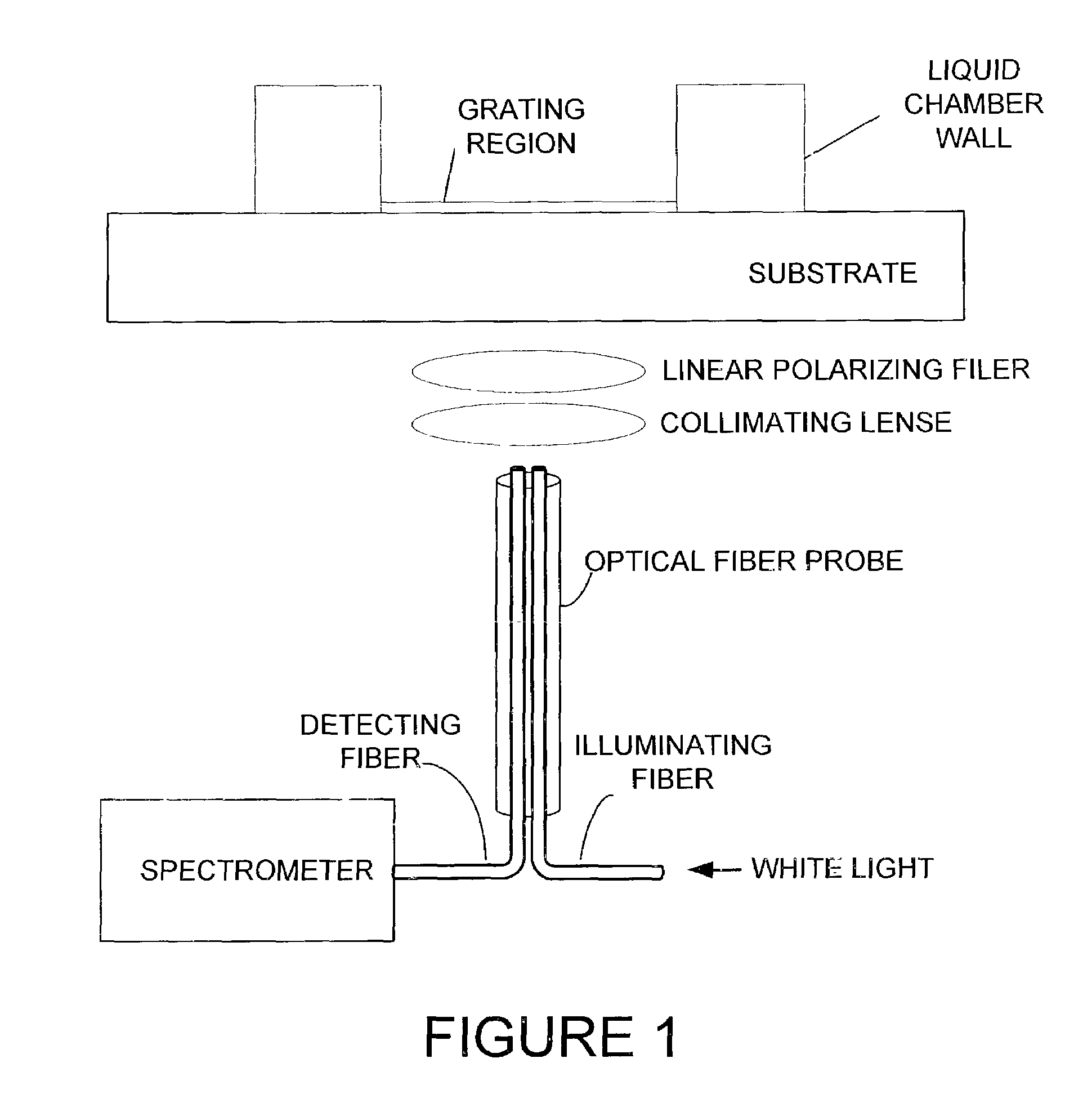
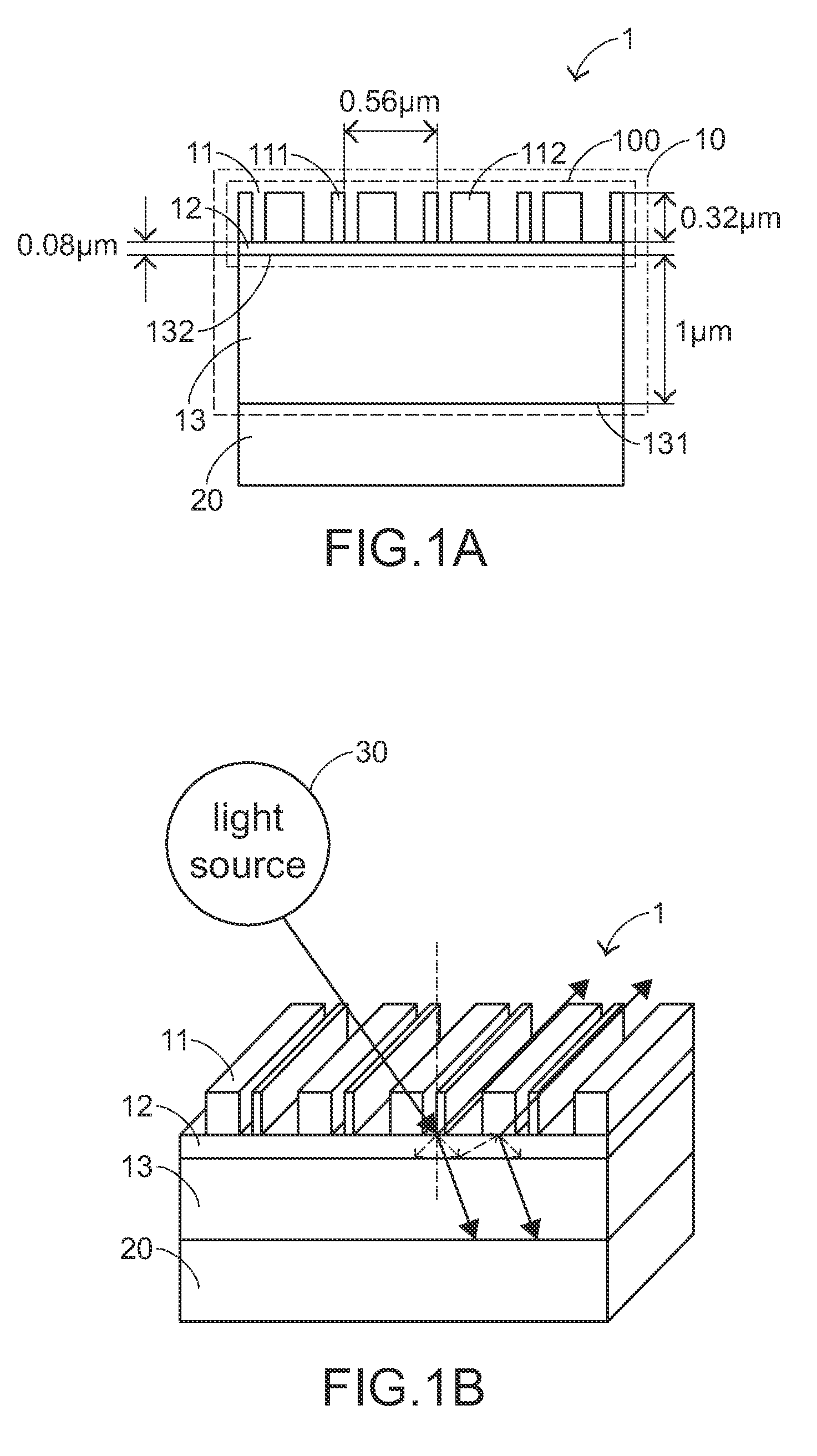
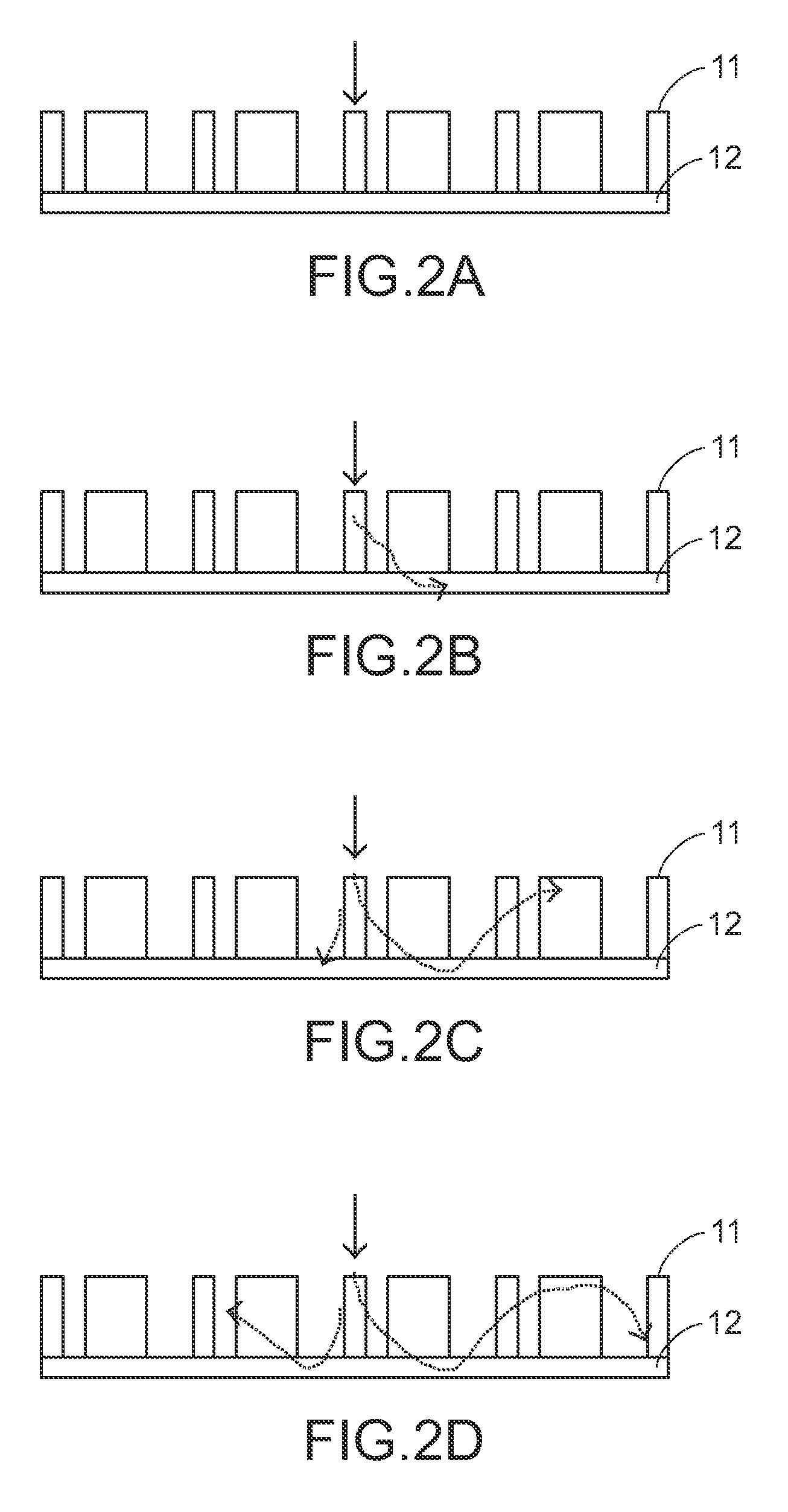
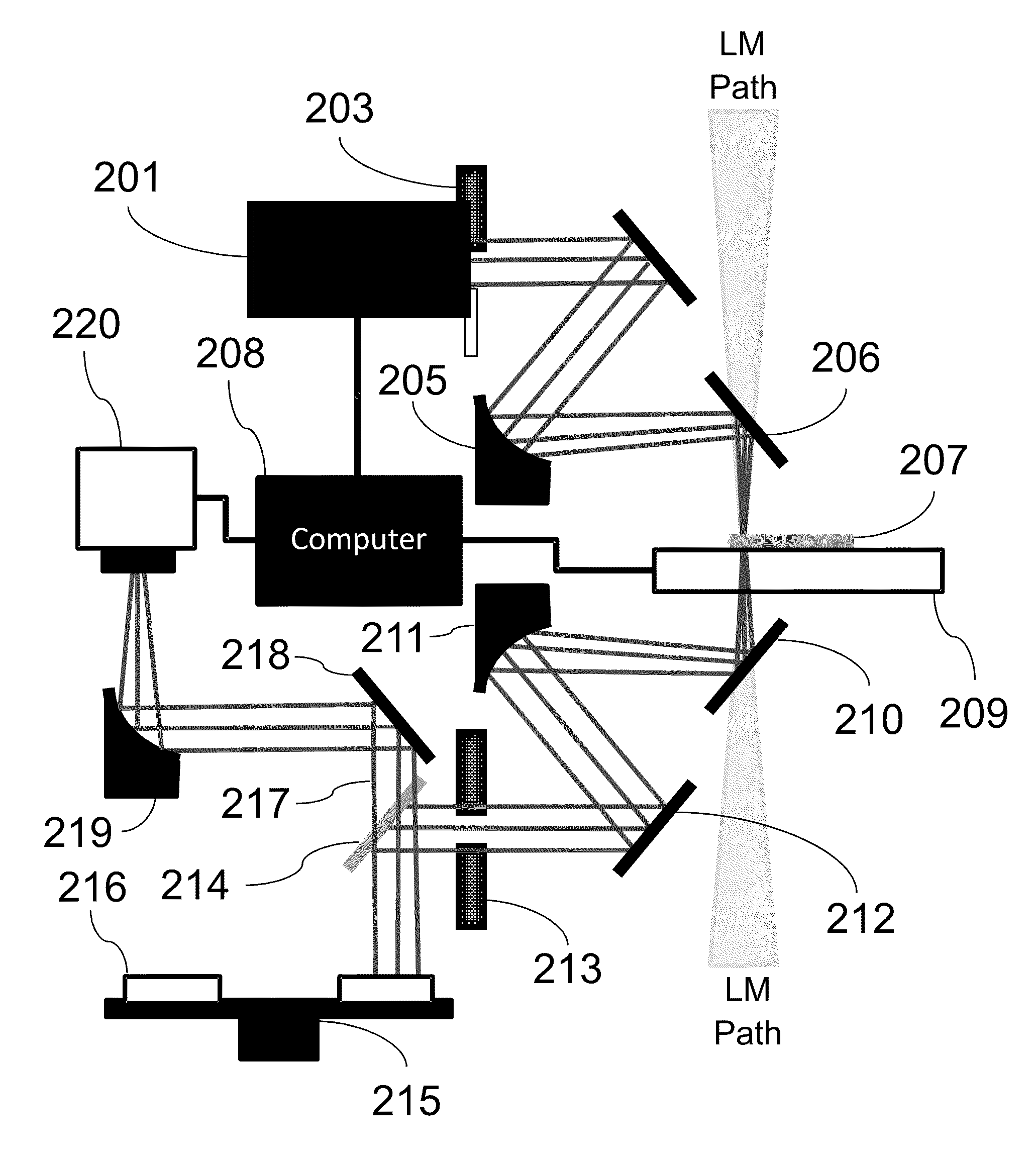
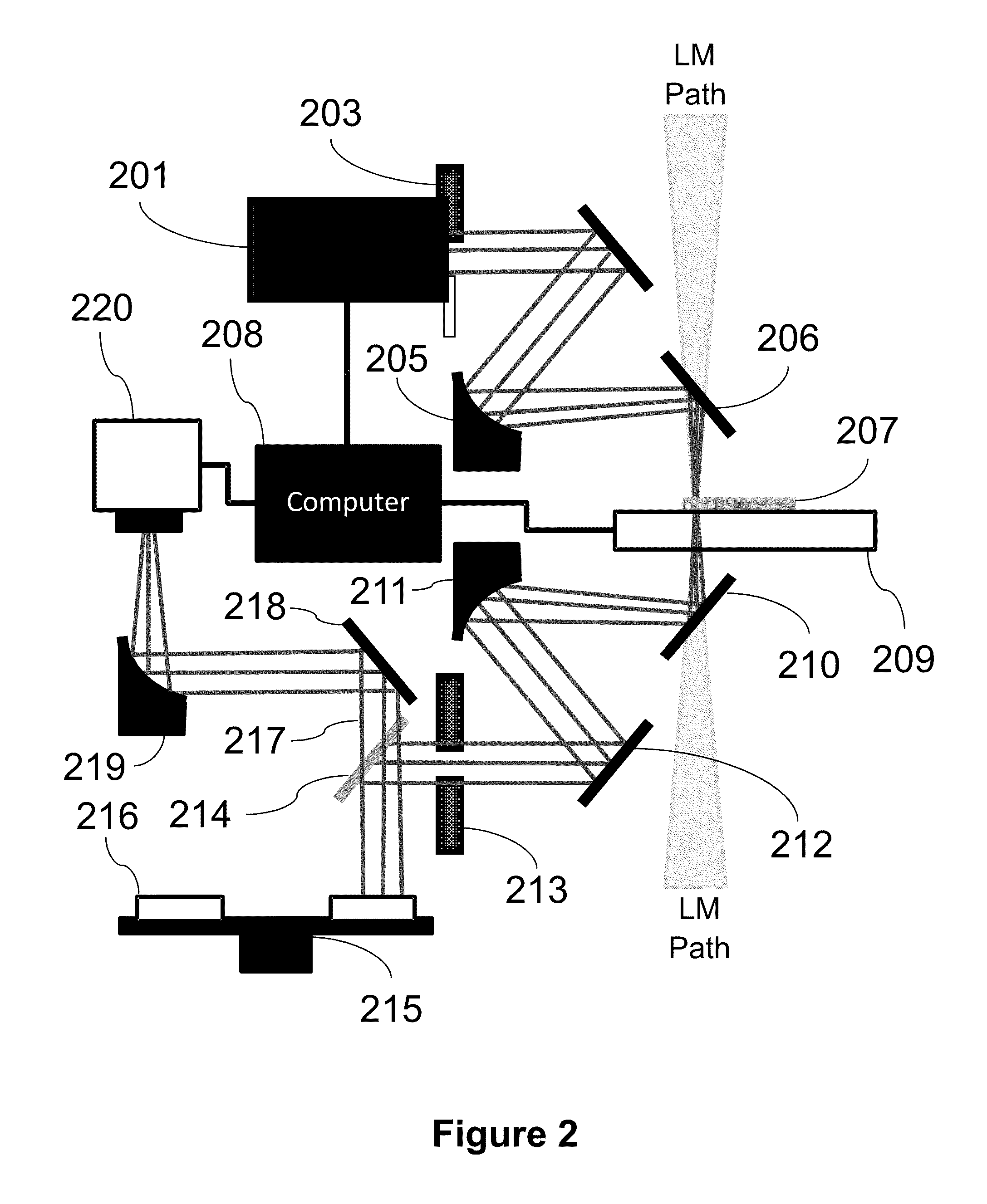
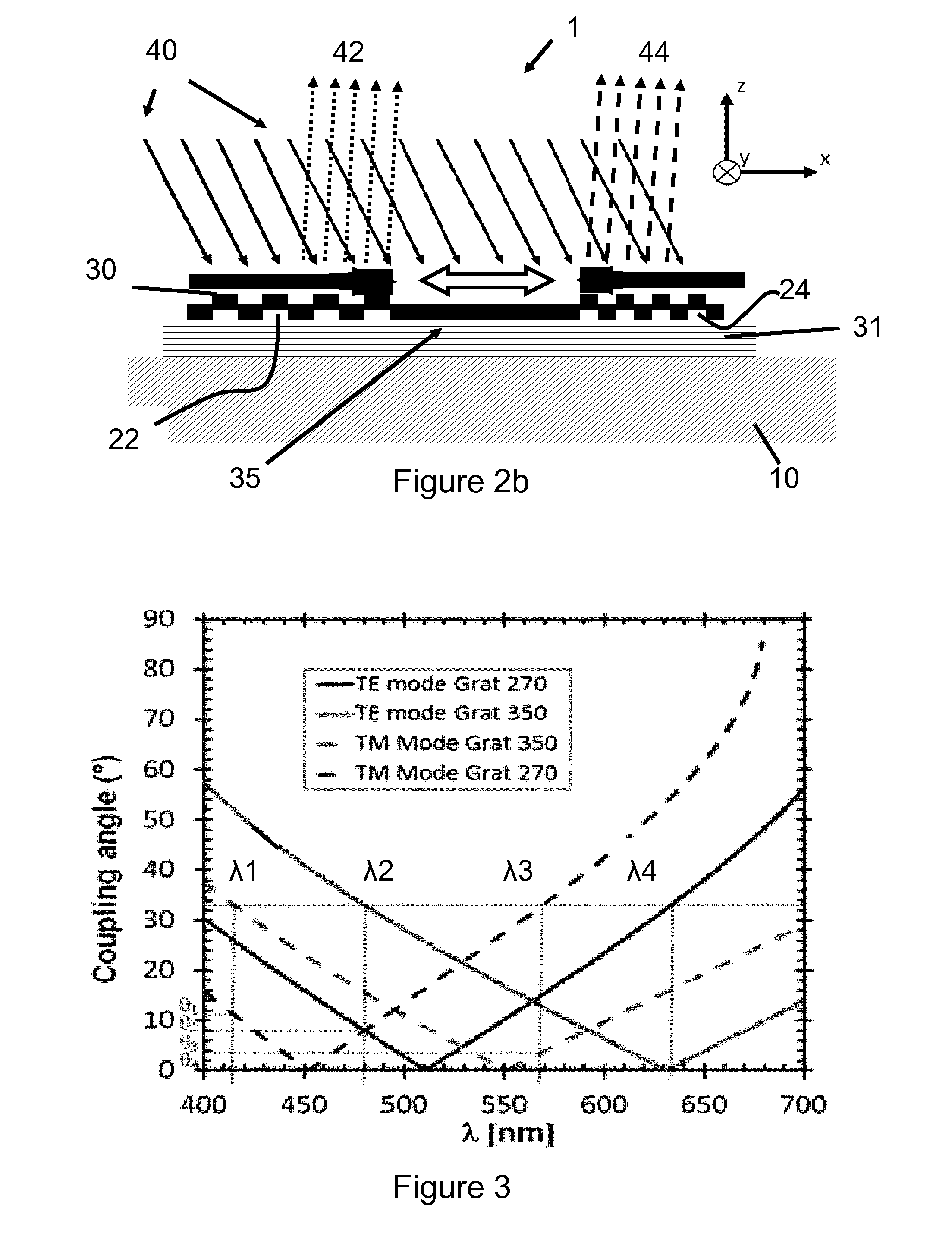
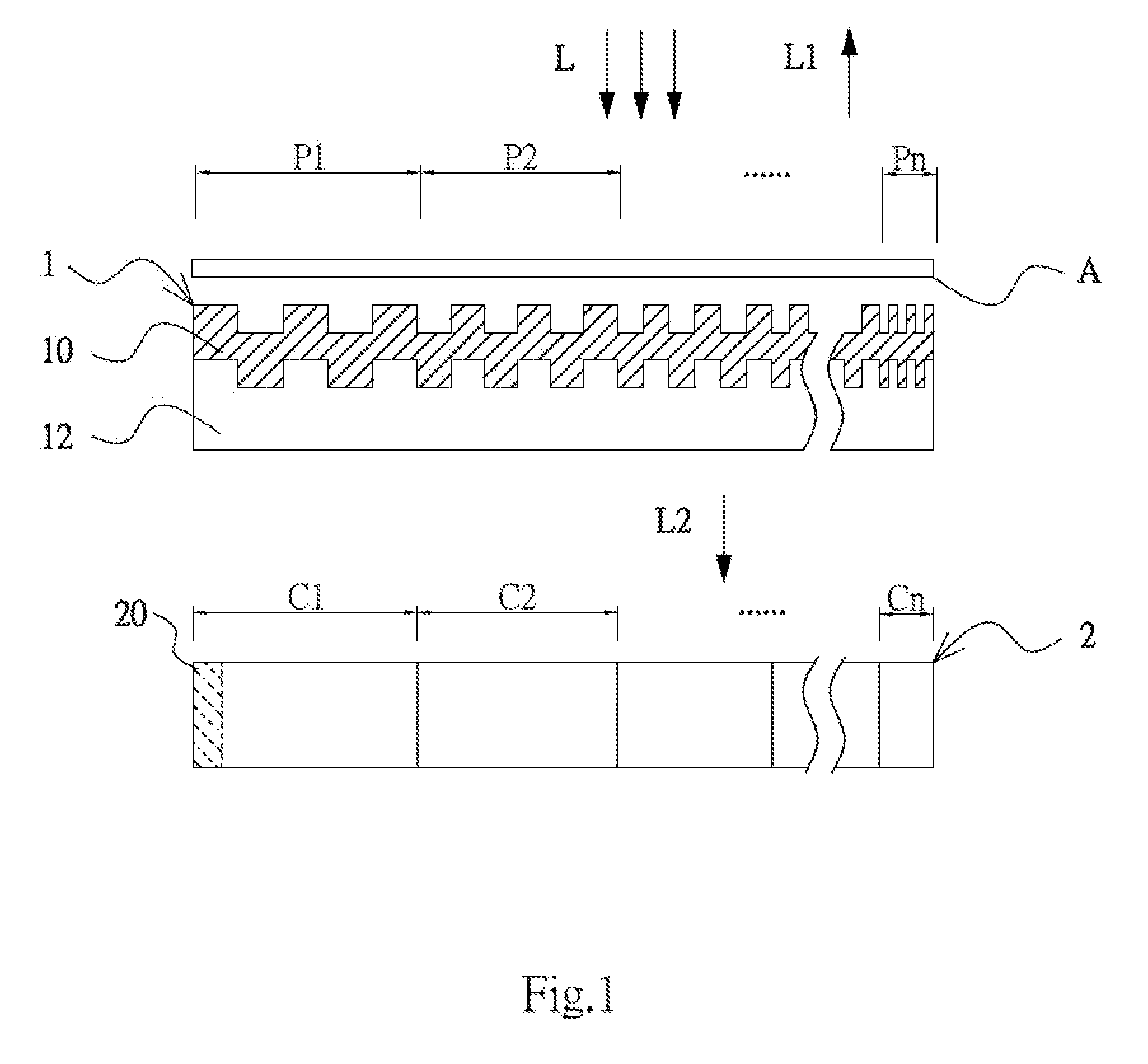
Resonant waveguide-grating filters and sensors and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS7167615B1Material analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesPermittivitySpectral filtering
Waveguide grating devices. One includes at least one waveguide having an end, the end having an endface; and a waveguide grating fabricated on the endface, the waveguide grating having at least one waveguide layer and at least one grating layer. The waveguide layer is a separate waveguide from the waveguide on which the waveguide grating is fabricated. Systems for spectral filtering. One, which utilizes a guided-mode resonance effect in a waveguide, includes at least one waveguide having a proximal end and a distal end having an endface; and a waveguide grating fabricated on the end of the waveguide and having a plurality of variable parameters such as permittivity of the grating layer(s) and permittivity of the waveguide layer(s). Methods of forming waveguide grating devices, and methods of detecting one or more parameters of a medium using a waveguide grating device are also disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
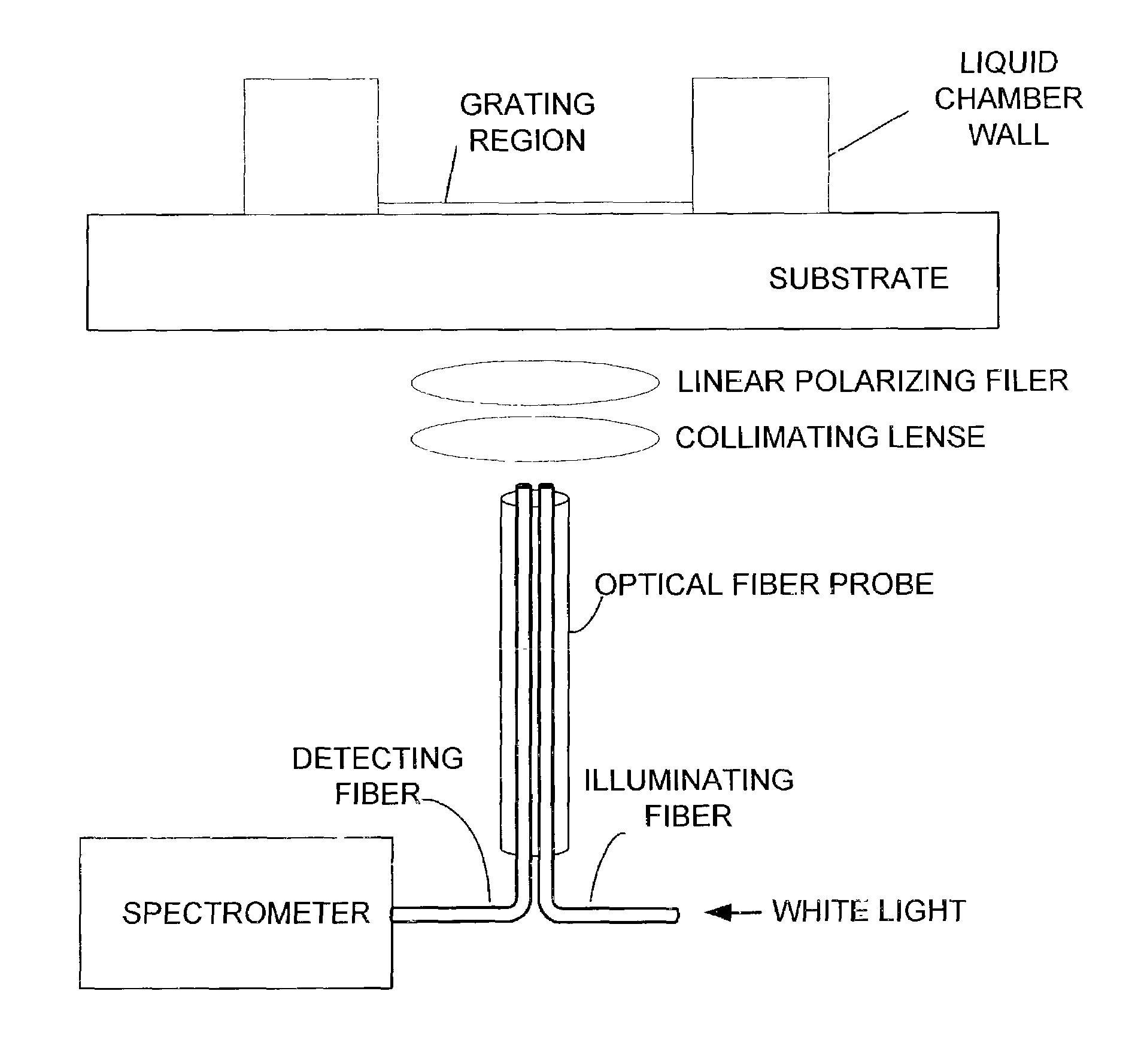
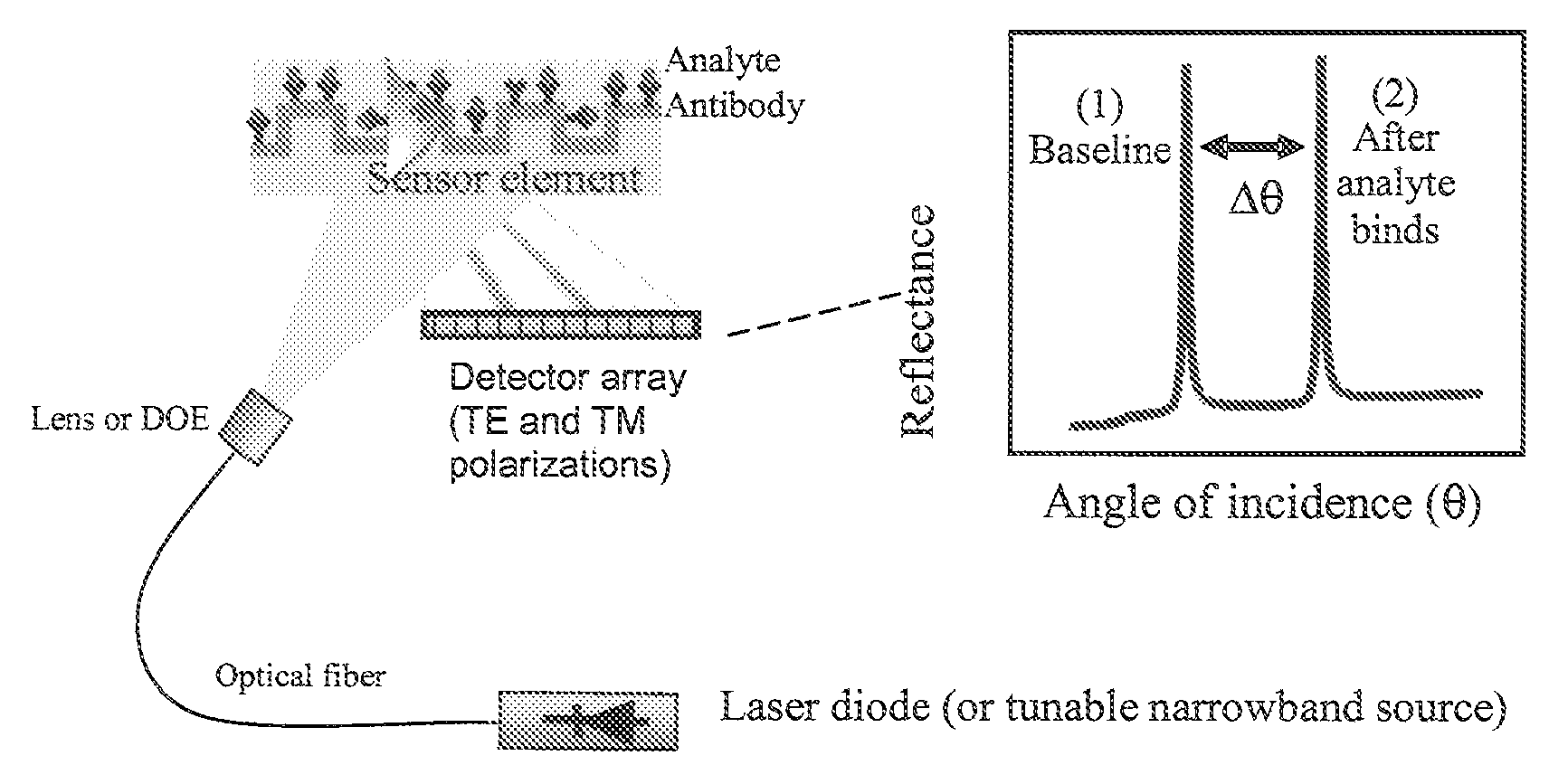
Method and apparatus for biosensor spectral shift detection
InactiveUS7217574B2Scattering properties measurementsLaboratory glasswaresFrequency spectrumResonance
Performing high-resolution determination of the relative shift of the spectral properties of a biosensor. The shift in the resonance peak of the biosensor is indicative of the amount of material bound to the surface of the biosensor. A preferred biosensor is a Guided Mode Resonant Filter Biosensor (GMRFB). In one aspect of the invention, curve fitting is used to determine the relative location of the spectrum of the unexposed biosensor with respect to those spectra that are altered (e.g., shifted) by the presence of materials bound to the surface of the biosensor. In an alternative embodiment, the cross correlation function is used to detect spectral peak offsets between a reference spectrum and a spectrum measured from an exposed biosensor. In yet another alternative, maximal likelihood estimation techniques are used to determine the spectral shift or offs.
Owner:X BODY
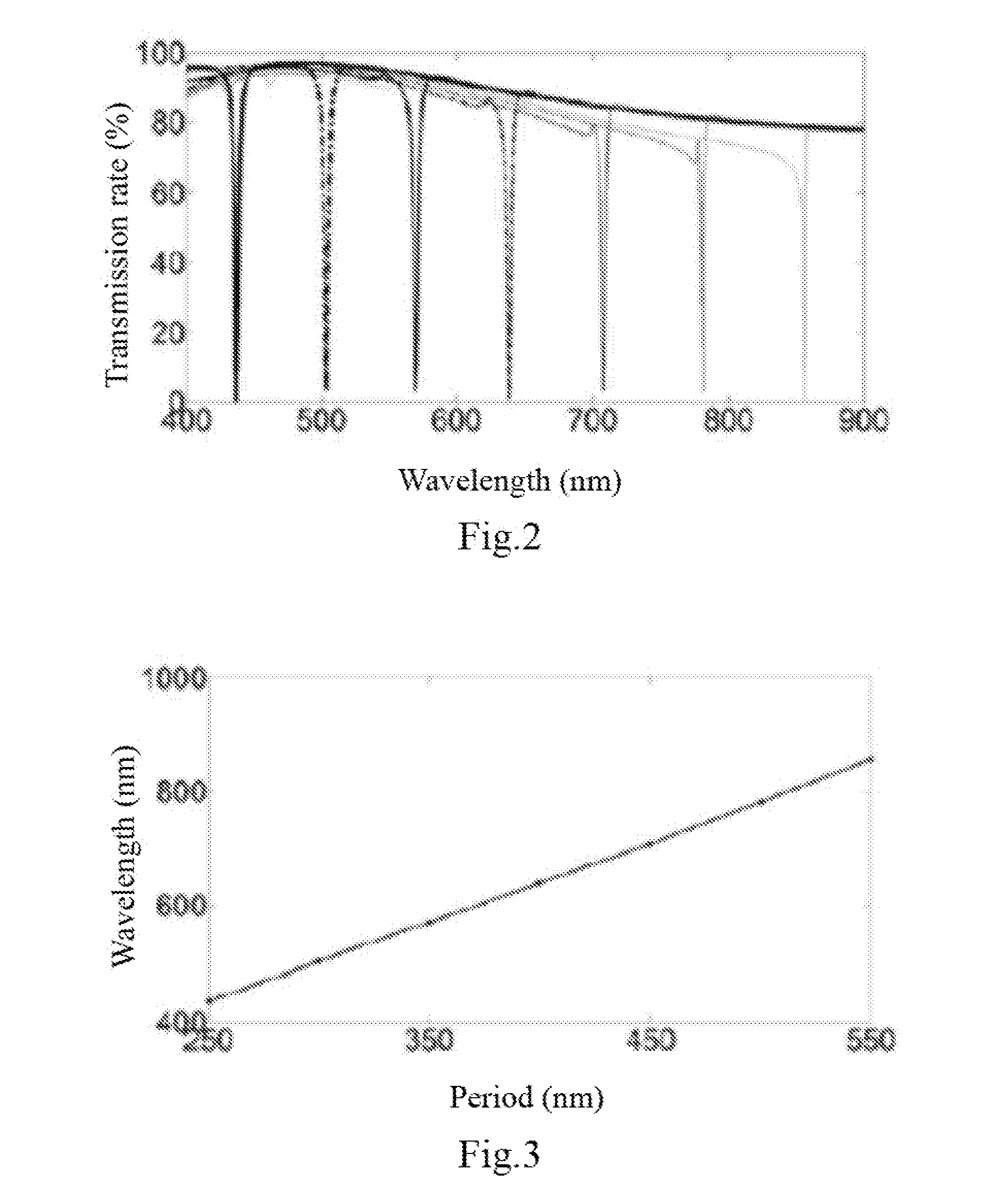
Array multispectral optical filter and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to an array multispectral optical filter and a manufacturing method thereof, belongs to the field of a micro-nano optical filter and solves the problem of integration of multichannel array detection in an existing nanofluidic chip. The optical filter only comprises the following four layers of structures: a two-dimensional metal grating layer, a buffer layer, a waveguide layer and a substrate. The invention also provides the manufacturing method of the optical filter, which utilizes a guided mode resonance principle of a two-dimensional metal grating and implements selection of different wavelengths by regulating the period of the grating. By the thickness of the buffer layer, the half-wave bandwidth of the cut-off wavelength also can be regulated. By regulating a suitable duty cycle of the two-dimensional metal grating layer, side lobes can be reduced. Therefore, relative to other turnable optical filters, the array multispectral optical filter manufactured by the method disclosed by the invention has the outstanding advantages of simple structure, low side lobes, adjustability of the half-wave bandwidth, high transmittance, no relation with polarization and the like. After the optical fiber disclosed by the invention is adopted, the integration of the nanofluidic chip can be implemented.
Owner:广东长光中科生物科技有限公司
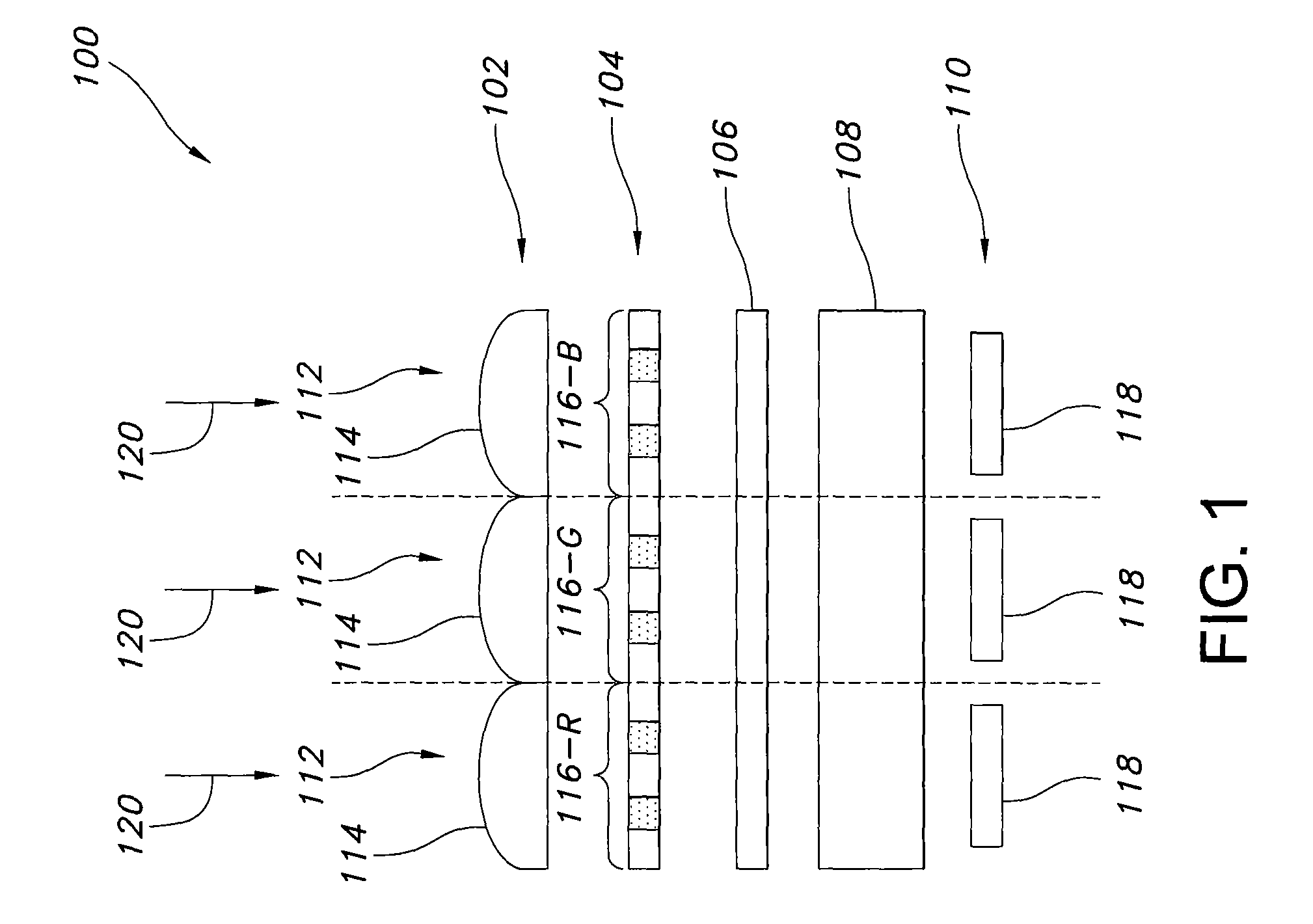
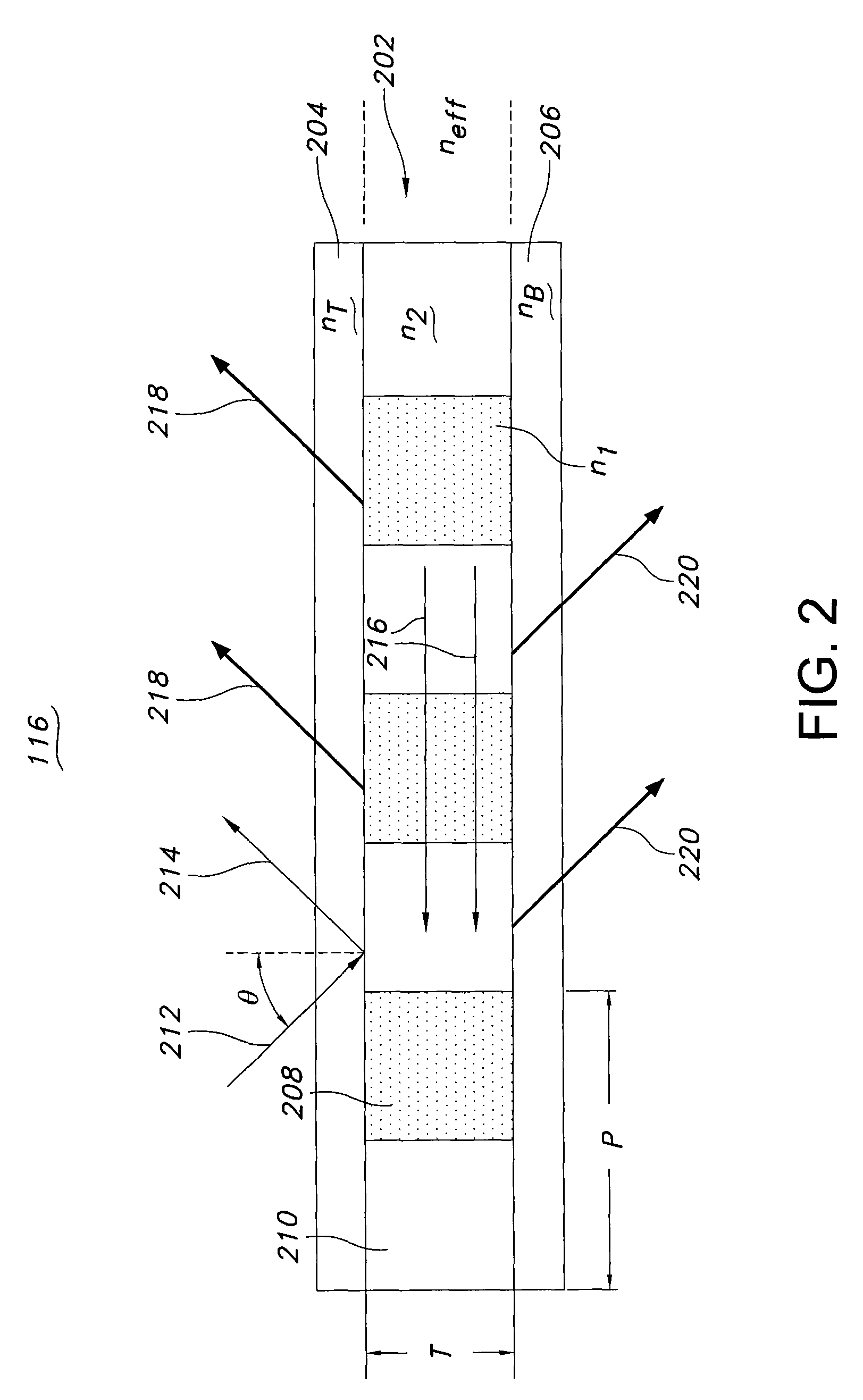
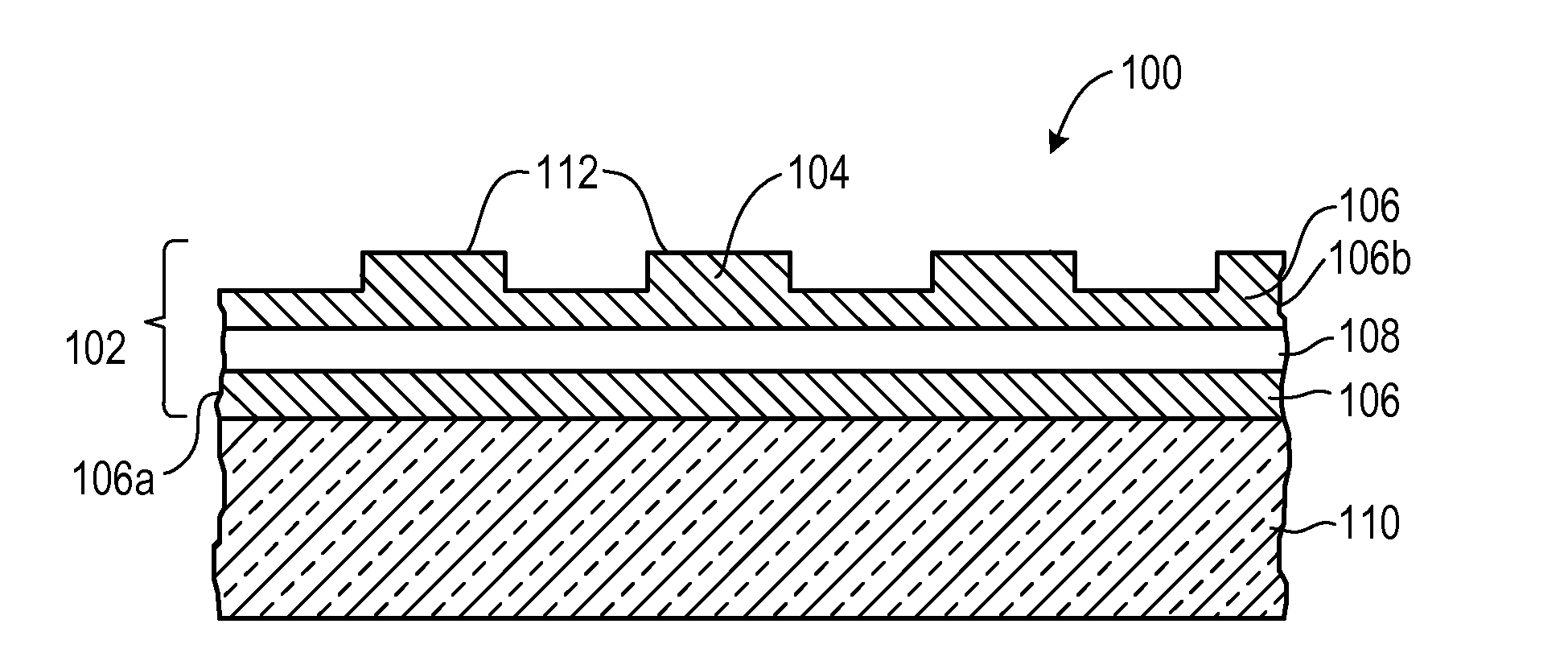
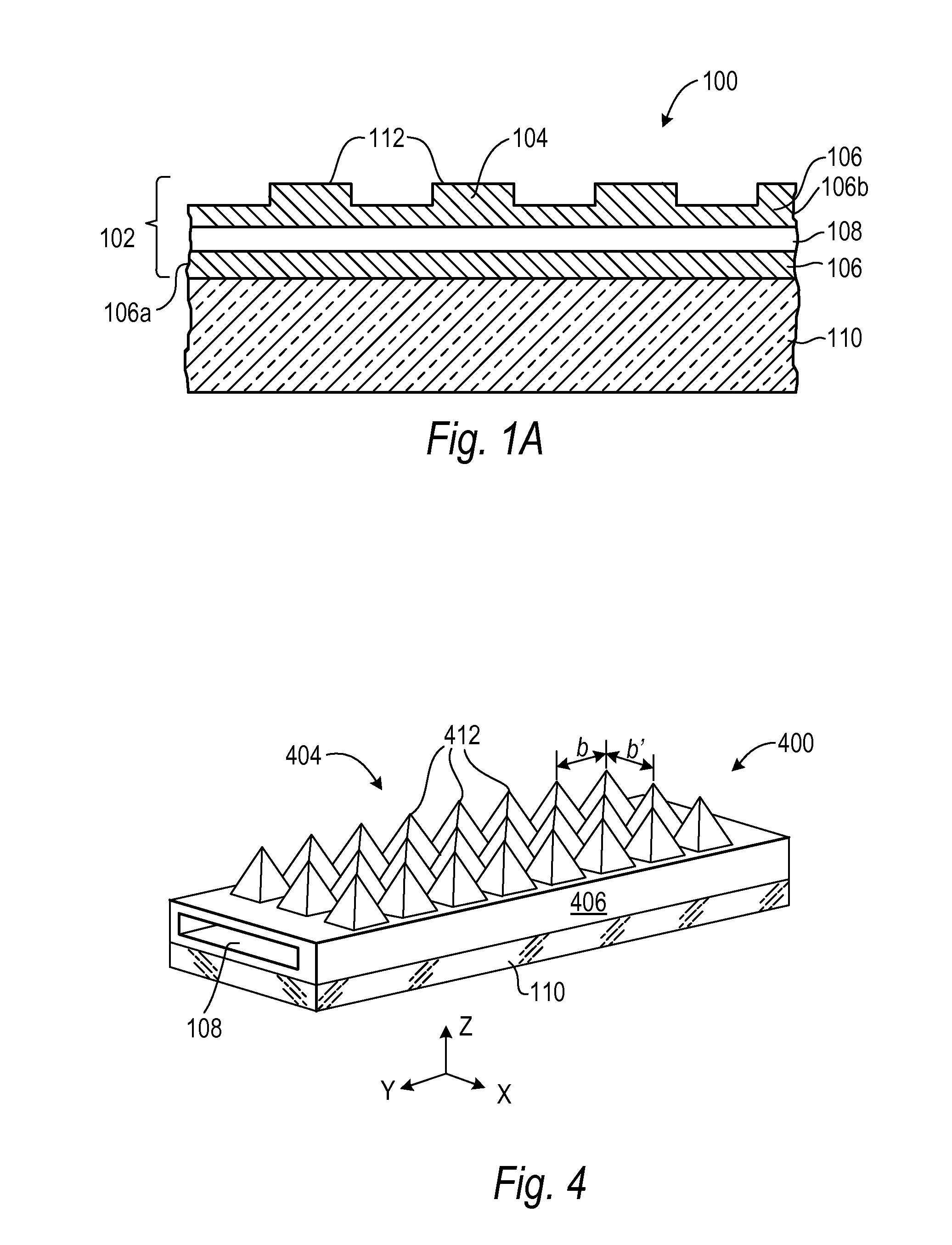
Guided-mode-resonance transmission color filters for color generation in CMOS image sensors
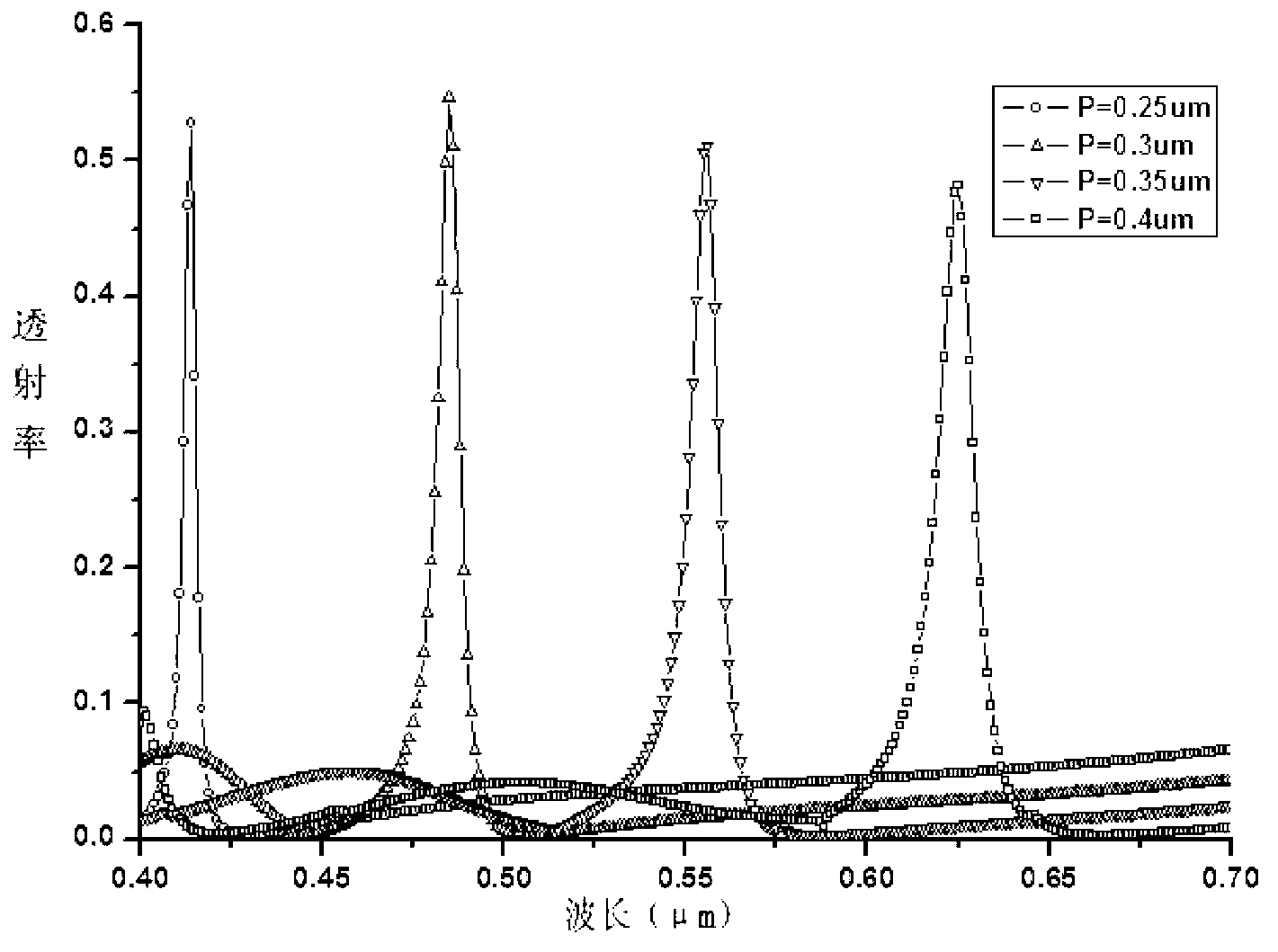
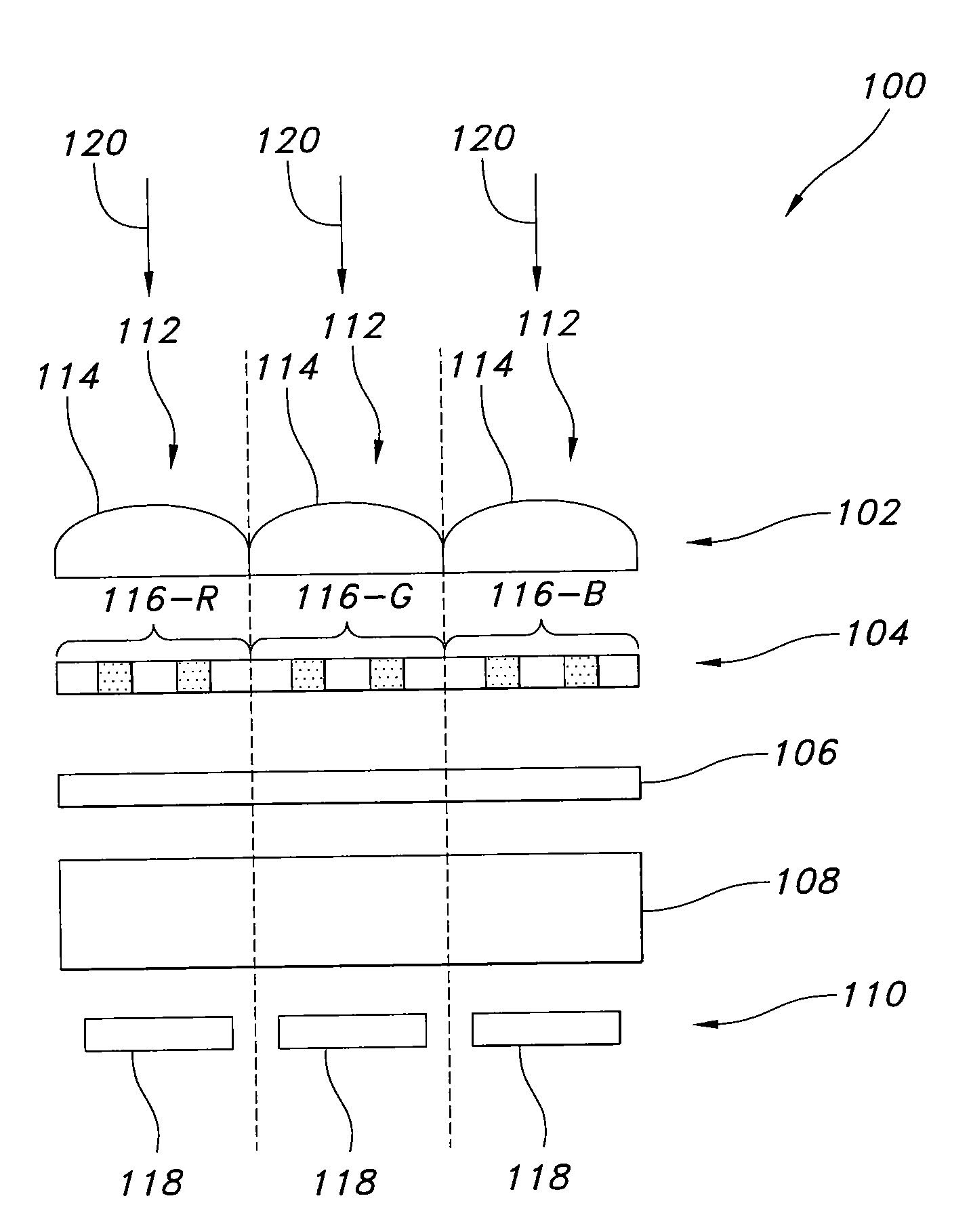
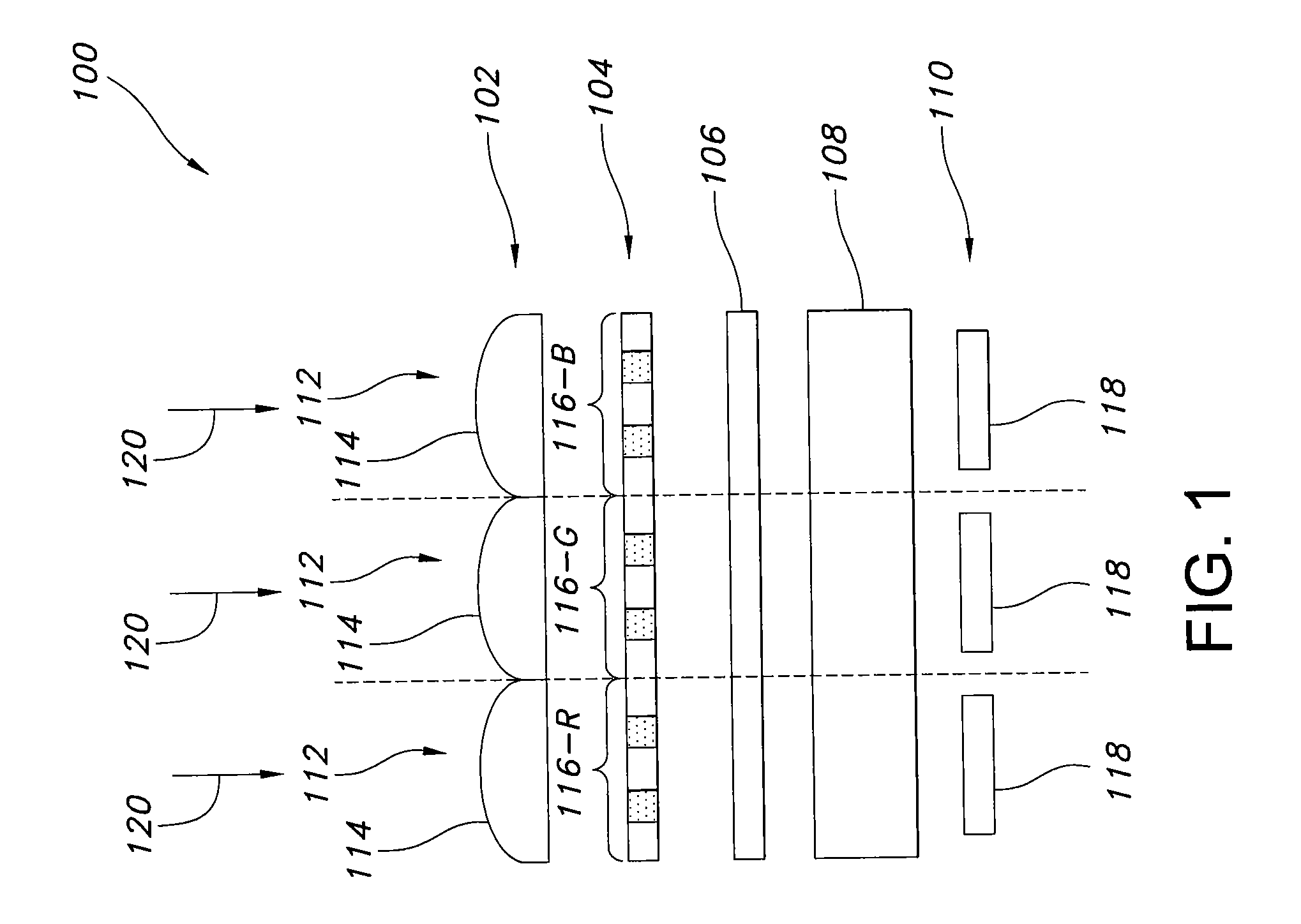
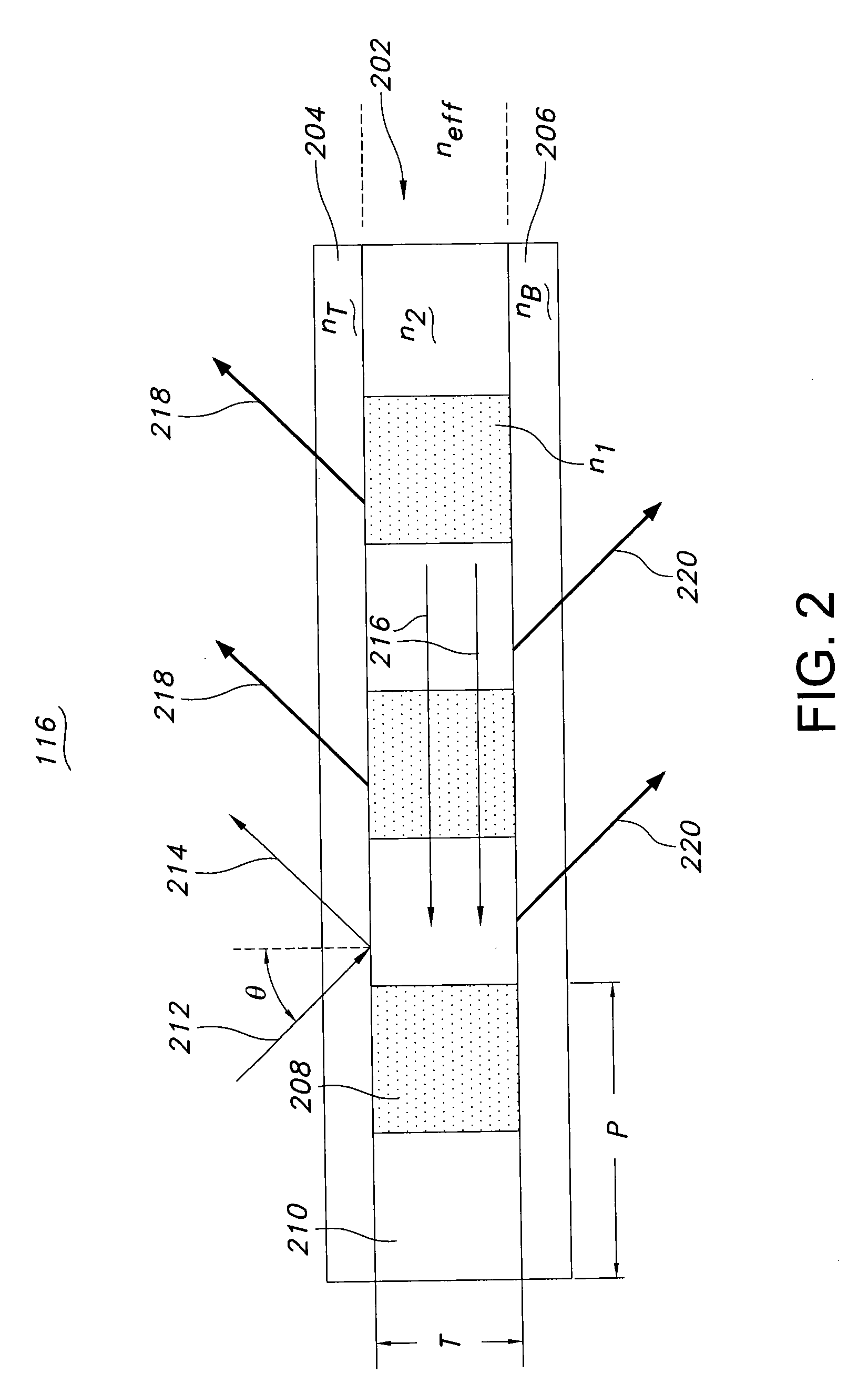
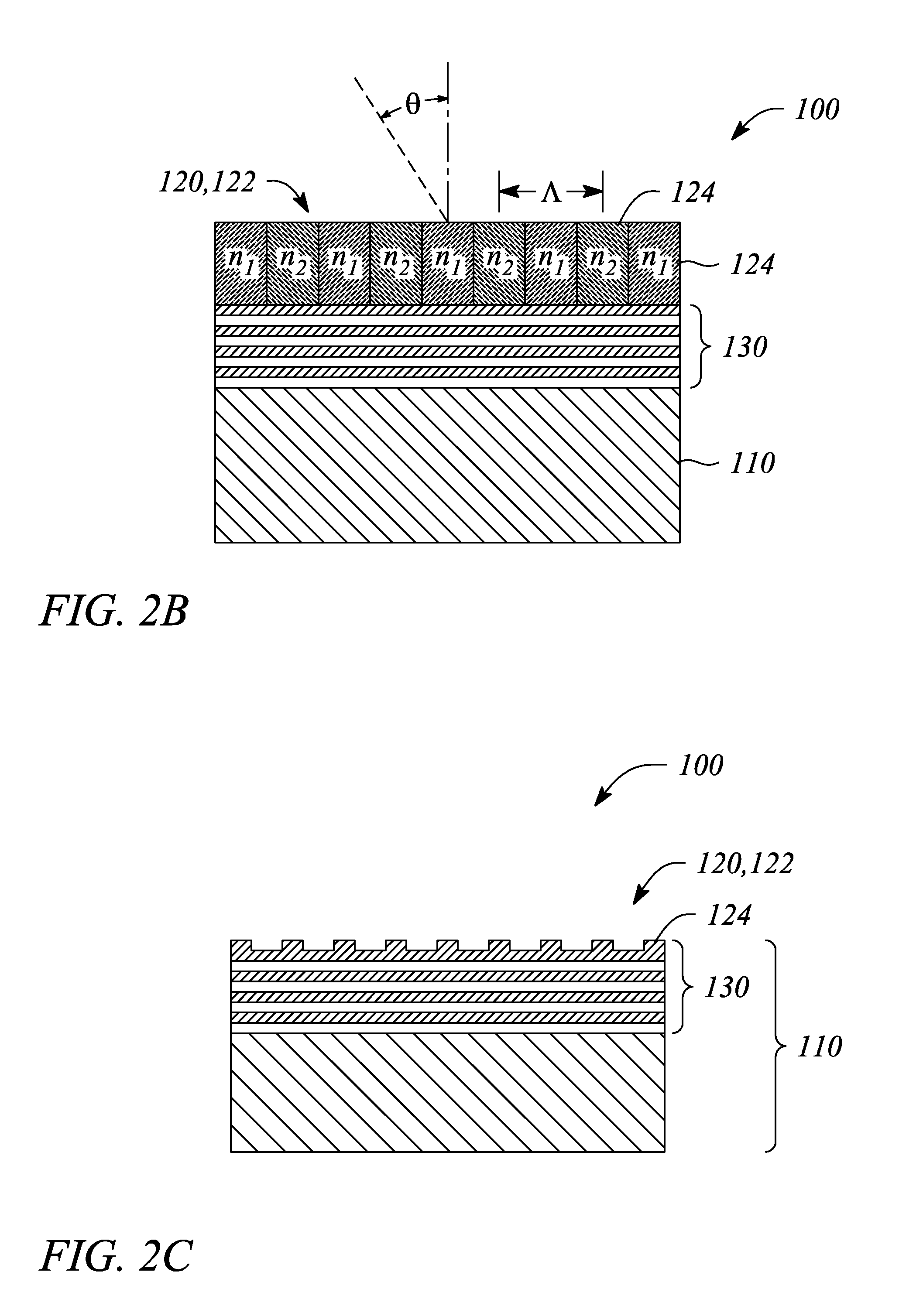
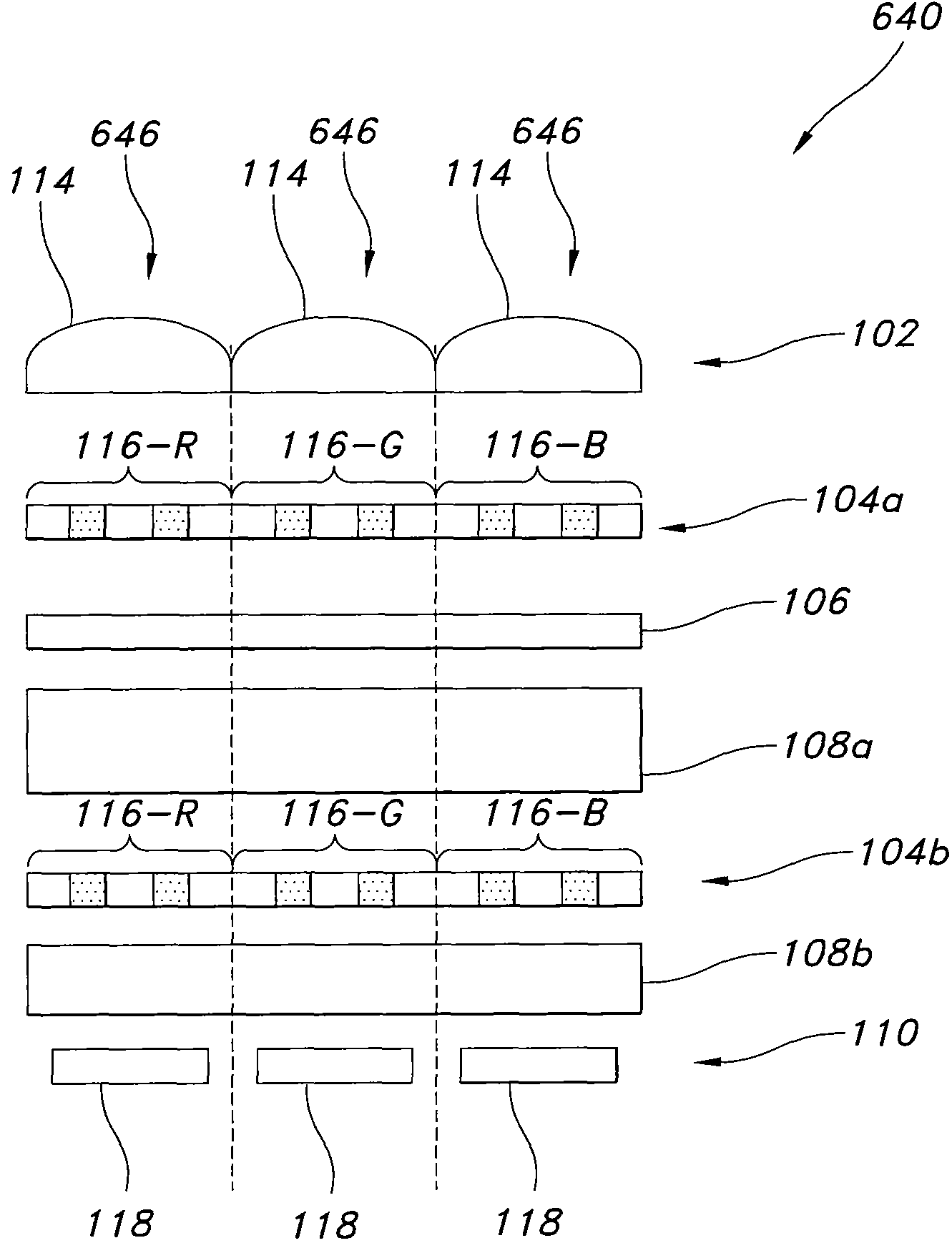
Imager pixel arrays and methods for forming imager pixel arrays. An image sensor pixel includes a photosensor and a waveguide grating resonance filter formed over the photosensor. The waveguide grating resonance filter is configured to pass light to the photosensor in a wavelength band and to block light outside of the wavelength band. The waveguide grating resonance filter includes a grating material having a first refractive index and arranged in a grating pattern with a grating pitch, and has an effective refractive index that is a function of the first refractive index. A combination of the grating pitch and the effective refractive index is selected to correspond to the wavelength band.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Nonlinear optical guided mode resonance filter
InactiveUS20050025422A1Easy and quick and relatively inexpensive to fabricateMaterial nanotechnologyCoupling light guidesNonlinear filterGrating
Nonlinear optical filters and associated methods. In a representative embodiment, a nonlinear optical filter includes a grating and a dye-doped polymer layer coupled to the grating. The dye-doped polymer layer may include ionic self-assembled layers. An associated method includes: providing a nonlinear filter comprising a grating and a dye-doped polymer layer coupled to the grating, directing an input broadband optical wave upon the filter, and backward diffracting the broadband optical wave from the grating as an output narrowband optical wave. The output narrowband optical wave may include a second harmonic beam.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Guided mode resonance solar cell
InactiveUS20100126577A1Easy to trapOptical path lengthCoupling light guidesPhotovoltaic energy generationGratingLight pillar
A guided mode resonance solar cell includes a solar cell body and a guided mode resonance unit. The solar cell body is used for converting optical energy into electrical energy. The guided mode resonance unit is formed on the solar cell body, and includes a grating structure and a waveguide structure. The grating structure includes multiple sub-wavelength light pillars. When a light emitted from a light source is incident onto the grating structure, a resonant of the light occurs in the grating structure to facilitate trapping the light in the waveguide structure and elongating an optical path length.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Nonlinear optical guided mode resonance filter
InactiveUS7218817B2Easy and quick and relatively inexpensive to fabricateMaterial nanotechnologyCoupling light guidesNonlinear filterGrating
Nonlinear optical filters and associated methods. In a representative embodiment, a nonlinear optical filter includes a grating and a dye-doped polymer layer coupled to the grating. The dye-doped polymer layer may include ionic self-assembled layers. An associated method includes: providing a nonlinear filter comprising a grating and a dye-doped polymer layer coupled to the grating, directing an input broadband optical wave upon the filter, and backward diffracting the broadband optical wave from the grating as an output narrowband optical wave. The output narrowband optical wave may include a second harmonic beam.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Guided-mode resonance sensors employing angular, spectral, modal, and polarization diversity for high-precision sensing in compact formats
InactiveUS20080062418A1Quality improvementHigh precisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPolarization diversityLeaky mode
A guided mode resonance (GMR) sensor assembly and system are provided. The GMR sensor includes a waveguide structure configured for operation at or near one or more leaky modes, a receiver for input light from a source of light onto the waveguide structure to cause one or more leaky TE and TM resonant modes and a detector for changes in one or more of the phase, waveshape and / or magnitude of each of a TE resonance and a TM resonance to permit distinguishing between first and second physical states of said waveguide structure or its immediate environment.
Owner:MAGNUSSON ROBERT +1
Discrete Frequency Spectroscopy and Instrumentation
ActiveUS20110080581A1Operation and useRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFrequency spectrumSpectroscopy
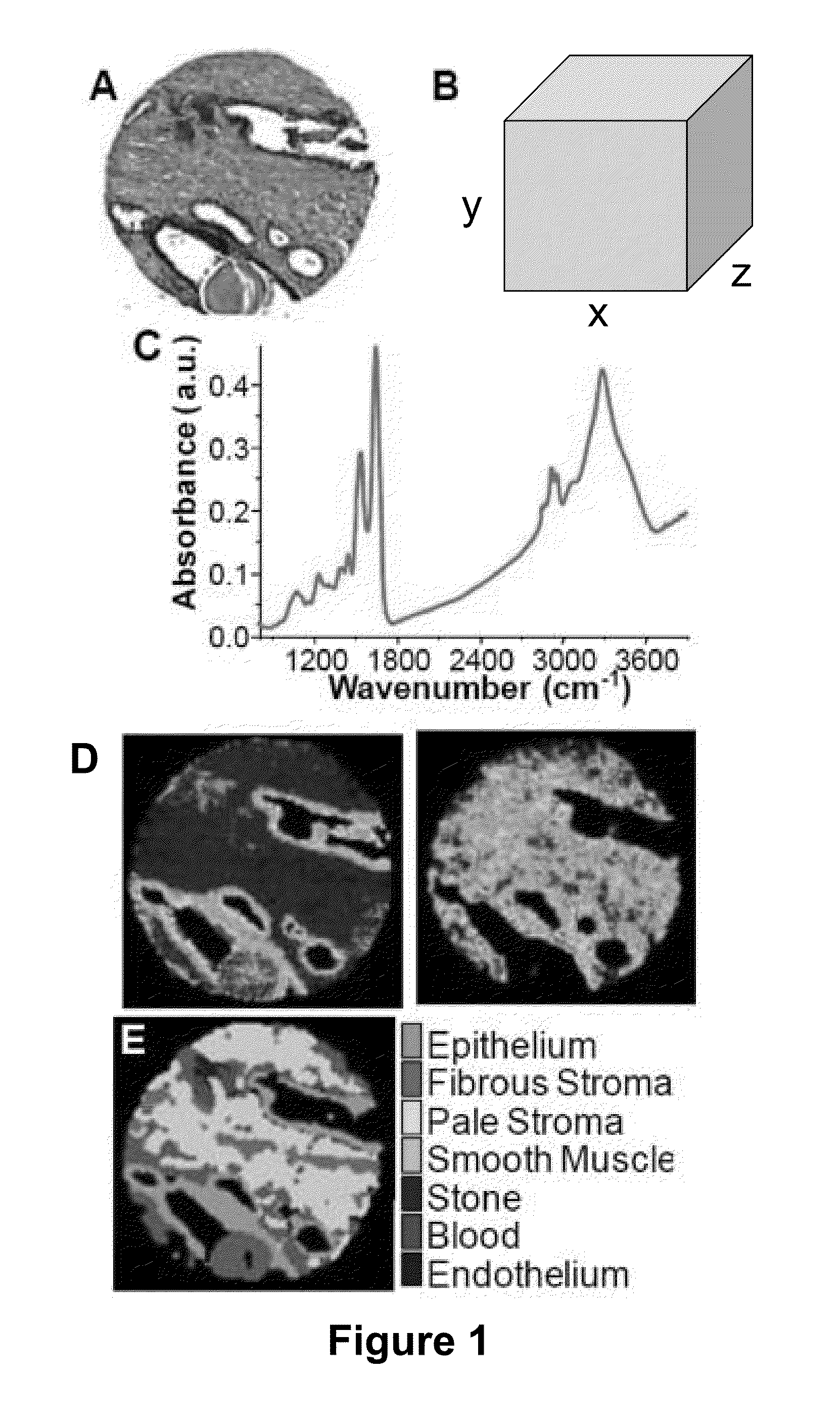
Described herein are spectrometers comprising one or more wavelength-selective filters, such as guided mode resonance filters. Some of the spectrometers described herein are configured for obtaining absorbance spectra in a discrete fashion by measuring absorbances of a sample at multiple discrete wavelengths or wavelength bands. In another aspect, methods are also provided for obtaining spectra, images and chemical maps of samples in a discrete fashion.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Guided-mode resonance sensors employing angular, spectral, modal, and polarization diversity for high-precision sensing in compact formats
InactiveUS8111401B2Quality improvementHigh precisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPolarization diversityLeaky mode
A guided mode resonance (GMR) sensor assembly and system are provided. The GMR sensor includes a waveguide structure configured for operation at or near one or more leaky modes, a receiver for input light from a source of light onto the waveguide structure to cause one or more leaky TE and TM resonant modes and a detector for changes in one or more of the phase, waveshape and / or magnitude of each of a TE resonance and a TM resonance to permit distinguishing between first and second physical states of said waveguide structure or its immediate environment.
Owner:MAGNUSSON ROBERT +1
Hybrid Guided-Mode Resonance Filter And Method Employing Distributed Bragg Reflection
InactiveUS20110188807A1Impedence networksDiffraction gratingsDistributed Bragg reflectorGuided-mode resonance
A hybrid guided-mode resonance (GMR) grating, an optical filter and a method of optical filtering employ distributed Bragg reflection. The hybrid GMR grating includes a waveguide layer that supports a GMR having a GMR resonant frequency. The hybrid GMR grating further includes a diffraction grating that couples a portion of a signal incident on the hybrid GMR grating into the waveguide layer; and a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) that reflects another portion of the incident signal. The coupled portion of the incident signal has a frequency corresponding to the GMR resonant frequency. The reflected portion has a frequency away from the GMR resonant frequency. The optical filter includes the hybrid GMR grating and a coupler. The method includes coupling an optical signal into the hybrid GMR grating and further coupling a reflected signal out of the hybrid GMR grating.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) device and manufacturing method therefor, and display apparatus
ActiveCN105633115AImplement tunable filteringClear image displaySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingFiltration
The invention provides an OLED (organic light-emitting diode) device and a manufacturing method therefor, and a display apparatus. A guided-mode resonance optical filter is formed by the OLED device between a positive electrode and an organic material layer of each sub pixel unit separately; each guided-mode resonance optical filter comprises a lower electrode, a raster layer, a PDLC layer and an upper electrode; and the refractive index of the PDLC layer is controlled by controlling the voltages of the lower electrode and the lower electrode. Therefore, the raster layer is matched with the PDLC layer to form regions with different refractive indexes, so that the guided-mode resonance optical filters can realize adjustable filtration for external light only through the optical waves having wavelengths corresponding to each sub pixel unit; even if under strong light, an OLED display screen can display clear images, and the luminance of the product is not affected.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Guided-mode-resonance transmission color filters for color generation in CMOS image sensors
Imager pixel arrays and methods for forming imager pixel arrays. An image sensor pixel includes a photosensor and a waveguide grating resonance filter formed over the photosensor. The waveguide grating resonance filter is configured to pass light to the photosensor in a wavelength band and to block light outside of the wavelength band. The waveguide grating resonance filter includes a grating material having a first refractive index and arranged in a grating pattern with a grating pitch, and has an effective refractive index that is a function of the first refractive index. A combination of the grating pitch and the effective refractive index is selected to correspond to the wavelength band.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Guided mode resonance device
ActiveUS20160356956A1Simple and cheap and quick wayGood colorMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiffraction gratingsGratingLight beam
A guided mode resonance device, comprising—a substrate,—a waveguide,—a grating structure associated with said waveguide, said grating structure being arranged to an incident surface of said substrate, said incident surface being intended to receive an incident light beam provided by at least one light source, said incident light beam having an incident angle, defined relative to the normal of said waveguide, said grating structure comprising at least one elementary structure comprising at least a first-type grating structure and at least a second-type grating structure,—wherein:—said waveguide is arranged to transfer light from_the first-type grating structures to the second-type grating structure and also to transfer light from the second-type grating structures to the first-type grating structure,—said first-type grating structure is arranged to couple out a first light beam,—said second-type grating structure is arranged to couple out a second light beam,—said first light beam having a different spectral distribution than said second light beam.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
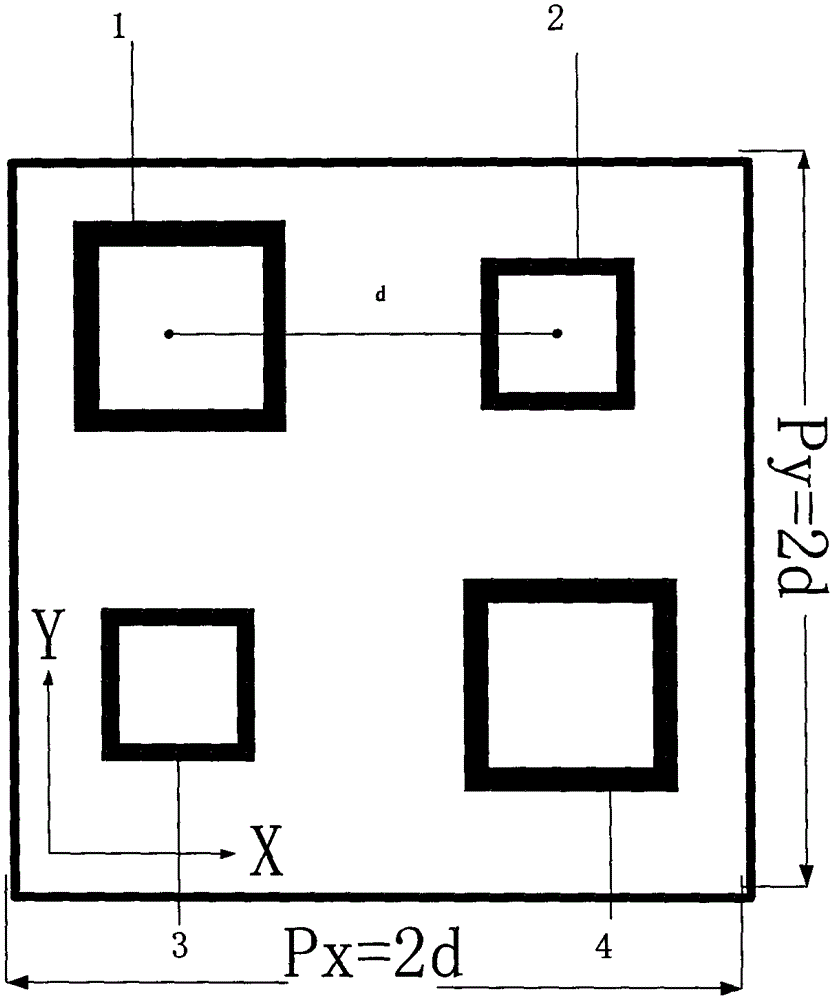
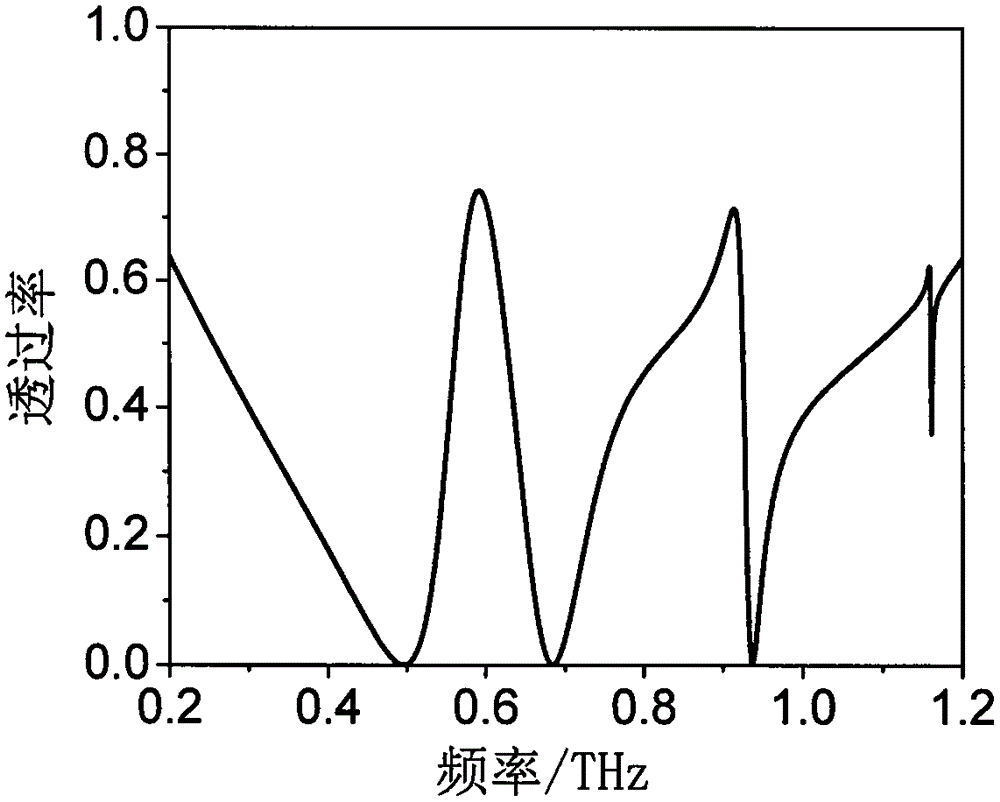
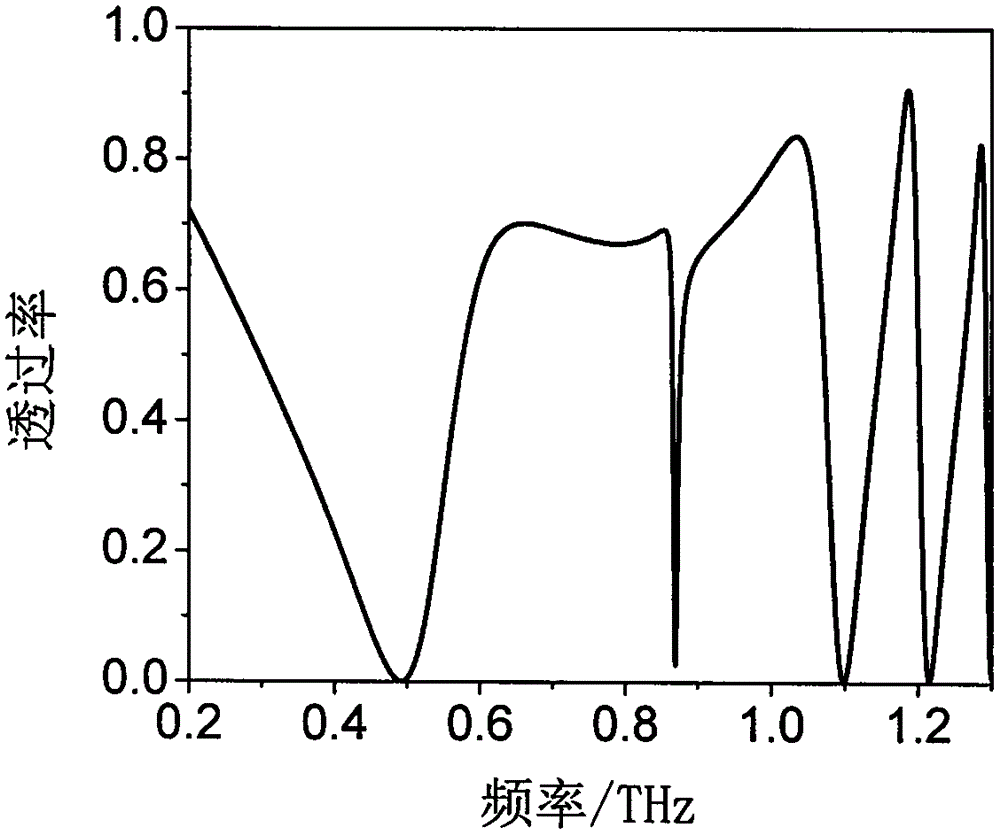
Polarization-insensitive meta-material resonance apparatus with adjustable guided-mode resonance quality factor
InactiveCN105633588AAchieving Electromagnetic Induction TransparencyAntennasDiffraction effectGrating
The invention discloses a polarization-insensitive meta-material resonance apparatus with an adjustable guided-mode resonance quality factor. The polarization-insensitive meta-material resonance apparatus comprises a planar waveguide and a meta-material unit that is arranged on the planar waveguide and is formed by a metal resonance unit. The meta-material resonance unit having a complex structure includes four metal resonance rings, wherein the four metal resonance rings is symmetric about the center of the resonance unit; and side lengths of the first metal resonance ring and the second metal resonance ring are not equal. Therefore, the resonance apparatus is not sensitive to the polarization. Besides, with the similar raster diffraction effect of the meta-material cladding layer, guided-mode resonance can be realized; and when the sizes of the metal resonance rings are changed, the quality factor of the guided-mode resonance can be adjusted and the mutual effect of the guided mode and the surface mode can be controlled, thereby realizing electromagnetic induction transparency.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Unpolarized tunable guided-mode resonance filter system and method for measuring nanometer gap
InactiveCN102364360ASimple structureEasy to buildOptical filtersUsing optical meansGratingFilter system
The invention relates to an unpolarized tunable guided-mode resonance filter system and a method for measuring a nanometer gap. The system is formed by parallelly placing two same guided-mode resonance filters in an opposite direction. The each guided-mode resonance filter is formed by a substrate layer, a waveguide layer and a grating layer. The guided-mode resonance filter system is an orthogonal double grating system. The grating layers of the two guided-mode resonance filters are parallel and opposite to each other. And stripes are mutually orthogonal. An air gap layer is arranged between the two grating layers. Through measuring the spacing of two split reflection peaks of a TE0 mode or a TM0 mode in a spectral region after incident light passes through the system, a size of the nanometer gap (<100nm) between the two gratings can be obtained. In the invention, an orthogonal double grating structure is adapted to any polarized incident light; separation of the two split reflection peaks of the TE0 mode and the two split reflection peaks of the TM0 mode can be realized; possible interference between the TE0 mode and the TM0 mode during measuring can be avoided.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Guided-mode resonance filter and fabrication method of same
ActiveUS7352932B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesGratingBulk micromachining
A silicon bulk-micromachining technology is used to fabricate a GMR filter by exploiting the structure of a suspended silicon nitride (SiNx) membrane on the silicon substrate. A first silicon nitride (SiNx) thin film and a second silicon nitride (SiNx) thin film are formed on opposite sides of the silicon substrate. A first opening is defined in the first silicon nitride (SiNx) thin film, and a grating structure is defined in the second silicon nitride (SiNx) thin film. By etching off a portion of the silicon substrate exposed from the first opening until a portion of the second silicon nitride (SiNx) thin film is exposed from the first opening, a light path space is defined.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Optimization method for photoresist layer of guide mode resonance optical filter
InactiveCN103424995AEasy to operateOptical filtersPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDirect effectsPeak value
The invention mainly provides the influence of thickness of photoresist on an optical filter and an optimization method for the photoresist. The method is characterized in that diffraction grating manufacturing is performed above a waveguide layer; in exposure and development process of the photoresist, the groove depth of the grating manufactured by a final holographic method is not the practical thickness of uniform glue as being affected by the exposure time and development time, so that a layer of non-sensitive photoresist layer is also arranged on a guide mode layer and a diffraction grating layer, which directly affects the width and peak value position of the practically manufactured optical filter. The method realizes the modulating function of unsuccessfully exposed and developed photoresist on the reflection of the optical filter, not only has guiding function for the thickness maximum of the uniform glue in the practical preparation process, but also can optimize the thickness of the undeveloped photoresist to adjust the process parameters of other later period optical filter according to the results. The method is convenient to implement and can be used for the field of optical filter manufacturing and biological sensing.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Guided mode resonance wave shifting device for scintillation detection
InactiveCN105204191AStrong absorption capacityImprove time resolutionNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystalFluorescence
The invention relates to a guided mode resonance wave shifting device for scintillation detection. The guided mode resonance wave shifting device comprises a substrate layer and a luminous film layer arranged on the substrate layer, and also comprises a photonic crystal layer arranged on the luminous film layer, wherein the photonic crystal layer consists of dielectric cylinders arranged into a period array in a triangular structure; the dielectric cylinders are vertically arranged on the upper surface of the luminous film layer; the materials of the dielectric cylinders are transparent for the light emitted by the luminous film layer. Compared with the prior art, the guided mode resonance wave shifting device has the advantages that the conversion efficiency and the time distinguishing capability are high; high light emission direction regulation and control capability is also realized; the detection efficiency on scintillation fluorescence such as ultraviolet rays can be improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Guided mode resonance grating narrow line width vertical-cavity surface emitting laser (VESEL) and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107257084AHigh anti-bandwidthHigh inverse bandwidthLaser detailsLaser active region structureMicro nanoVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
The present invention provides a guided mode resonance grating narrow line width vertical-cavity surface emitting laser and a preparation method thereof. According to the present invention, a guided-mode resonant effect of a micro-nano grating is utilized, and a sub-wavelength guided-mode resonant microcavity structure of high reflection and narrow resonance line width is used as a part of the vertical-cavity surface emitting laser, thereby achieving the purposes of narrower laser line width, wider high reflection bandwidth, smaller size and stable polarization control. According to the present invention, by utilizing the guided-mode resonant effect of the micro-nano grating, and by the equivalent medium theoretical calculation, a weak modulated sub-wavelength grating guided-mode resonant microcavity structure of which the resonant wavelength is 852 nm is designed, and a wall used for controlling the mode line width is added between a grating layer and a waveguide layer, so that the mode line width can reach 1 nm or less. Relative to a conventional VCSEL, the narrow line width vertical-cavity surface emitting laser has the narrower laser line width, the wider high reflection bandwidth, the smaller size and the stable polarization control.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Laser array for generating stable multi-wavelength laser outputs
InactiveUS7106920B2Improve line shapeImprove thermal stabilitySemiconductor laser arrangementsOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayLength wave
A multi-wavelength laser array is achieved by using a wavelength selectable optical device as a feedback mirror for a plurality of lasers. The wavelength of reflected light from the optical device depends upon the parameters in the local reflection positions of the optical device along the direction as determined by guided-mode resonance. Thus, the multi-wavelength laser array is able to emit a plurality of laser beams with desired wavelengths, each within the gain curve of its active element.
Owner:LIU ZHONGSHAN
Dispersive Element and Spectrometer Using the Same
ActiveUS20170059405A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using multiple reflectionSpectrometerPhysics
A dispersive element is incorporated with an optical sensor as a spectrometer. The dispersive element includes a guided-mode resonance filter having a plurality of resonance regions. The resonance regions respectively have different filter characteristics, each reflecting a first light beam of a tested light source or transmitting a second light beam of the tested light source light source to the optical sensor, wherein the wavelength of the first light beam is different from that of the second light beam. In one embodiment, the dispersive element is incorporated with an optical sensor to form a miniature, high-resolution and low-cost spectrometer. The spectrometer makes use of the transmission efficiencies of the resonance regions of the guided-mode resonance filter and the light intensity distribution detected by the photosensitive regions of the optical sensor to acquire the spectral data of the tested light source.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Guided mode resonator based raman enhancement apparatus
A system for performing Raman spectroscopy comprises a waveguide layer configured with at least one array of features, the at least one array of features being configured to provide guided-mode resonance for at least one wavelength of electromagnetic radiation; and at least one fluid channel disposed in the waveguide layer. An analyte sensor comprises an electromagnetic radiation source configured to emit a range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, the system for performing Raman spectroscopy, and at least one photodetector configured to detect Raman scattered light.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method for realizing guided-mode resonance filtering through single gradient-material grating
ActiveCN106772741AImproved resonance filter performanceGood anti-reflection propertiesOptical filtersGratingGradient material
The invention discloses a method for realizing guided-mode resonance filtering through a single gradient-material grating structure, and belongs to the field of an optical communication and MOEM (micro optical electro mechanical) system. The method is characterized in that an optical thin film, the refractive index of which increases progressively with the thickness, is prepared on a substrate, and by etching the refractive-index-gradient thin film, a guided-mode resonant grating structure is obtained, and furthermore, guided-mode resonance filtering can be realized; on the basis of the above, by selecting different etching depths, channel position of a filter can be adjusted; and with the etching depth being kept unchanged, by reducing gradient coefficient, multichannel filtering can be realized. The filtering performance of the guided-mode resonant grating structure is highly insensitive to change of substrate refractive index, so that even if the substrate refractive index is higher than the maximum value of the refractive index of the gradient thin film, the guided-mode resonance filtering performance keeps excellent; and the method breaks away from the limit that refractive index of a waveguide layer in a conventional guided-mode resonance filter needs to be higher than the substrate refractive index, and is more advantageous in practical application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Light beam translation electric control device and method based on Goos-Hanchen displacement effect
InactiveCN101419344AEnhanced lateral displacementEasy to controlNon-linear opticsPrismElectric control
The invention relates to a electric control device for beam translation based on Goos-Hanchen shift effect and a method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of laser control. A bottom surface of a prism and a lower surface of a lithium niobate wafer of an electro optic material are respectively plated with metal films, and the bottom surface of the prism and the surface of the lithium niobate wafer are adjusted to parallel and fixed by a metal bracket so as to form a wave guide double surfaces of which are clad by metal; and the wave guide is composed of an upper metal film, an air gap, the lithium niobate wafer and a lower metal film. When laser is emitted on the surface of the wave guide, the laser is coupled into a wave guiding layer to excite lateral shift of guided-mode resonance enhanced reflected light when a phase matching condition is satisfied. The upper metal film and the lower metal film are plated with electrodes and connected with an external DC voltage source, and the voltage is adjusted; parameters of the wave guiding layer are changed by electro optic effect and piezoelectric effect of the lithium niobate, which causes Goos-Hanchen shift change of the reflected light and further realizes control on the beam translation. The electric control device and the method thereof can achieve high stability and high precision of the beam translation control, and can be applied to general environments.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Thin film amorphous silicon solar cell based on antireflective structure and guided-mode resonance
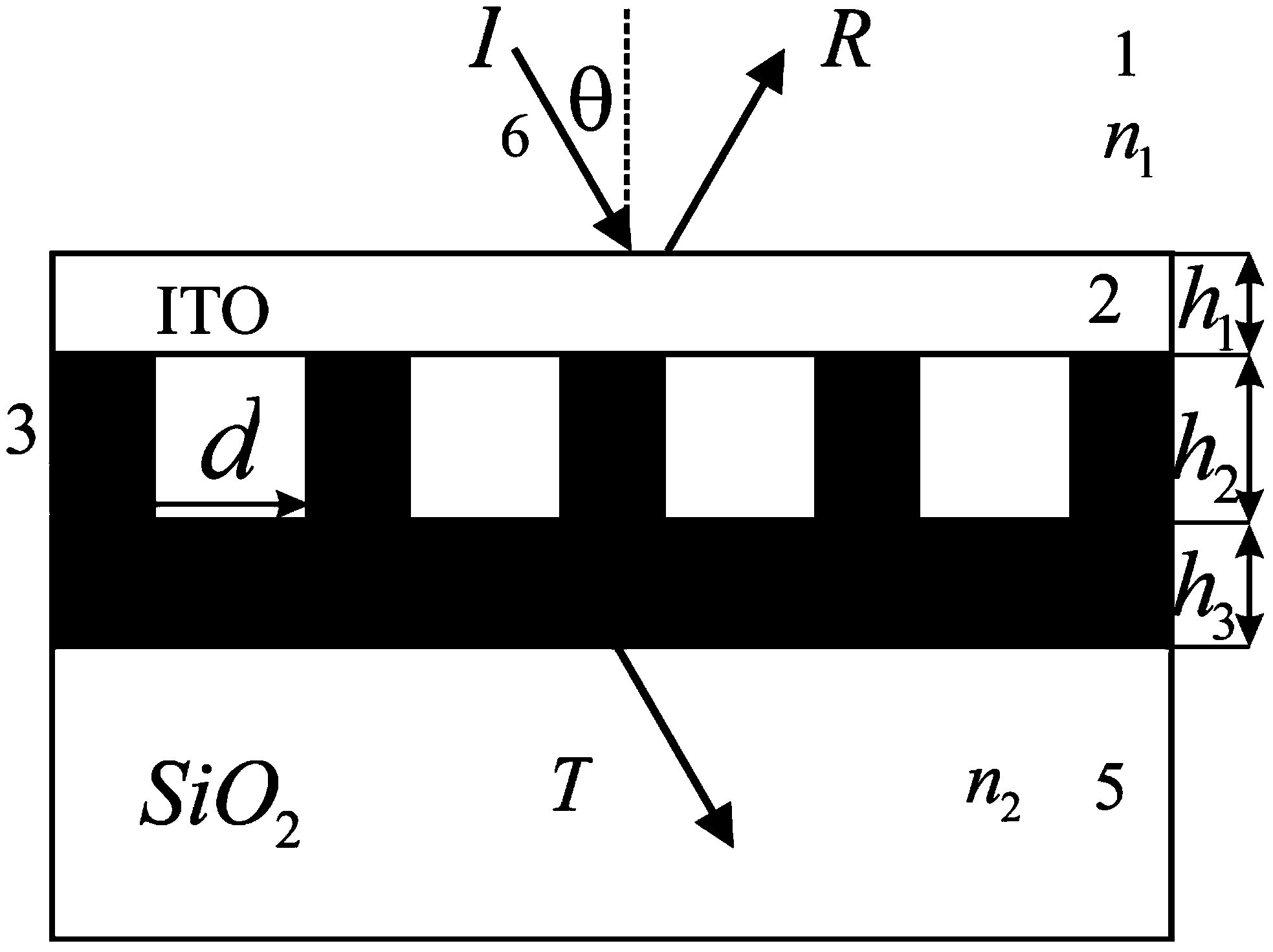
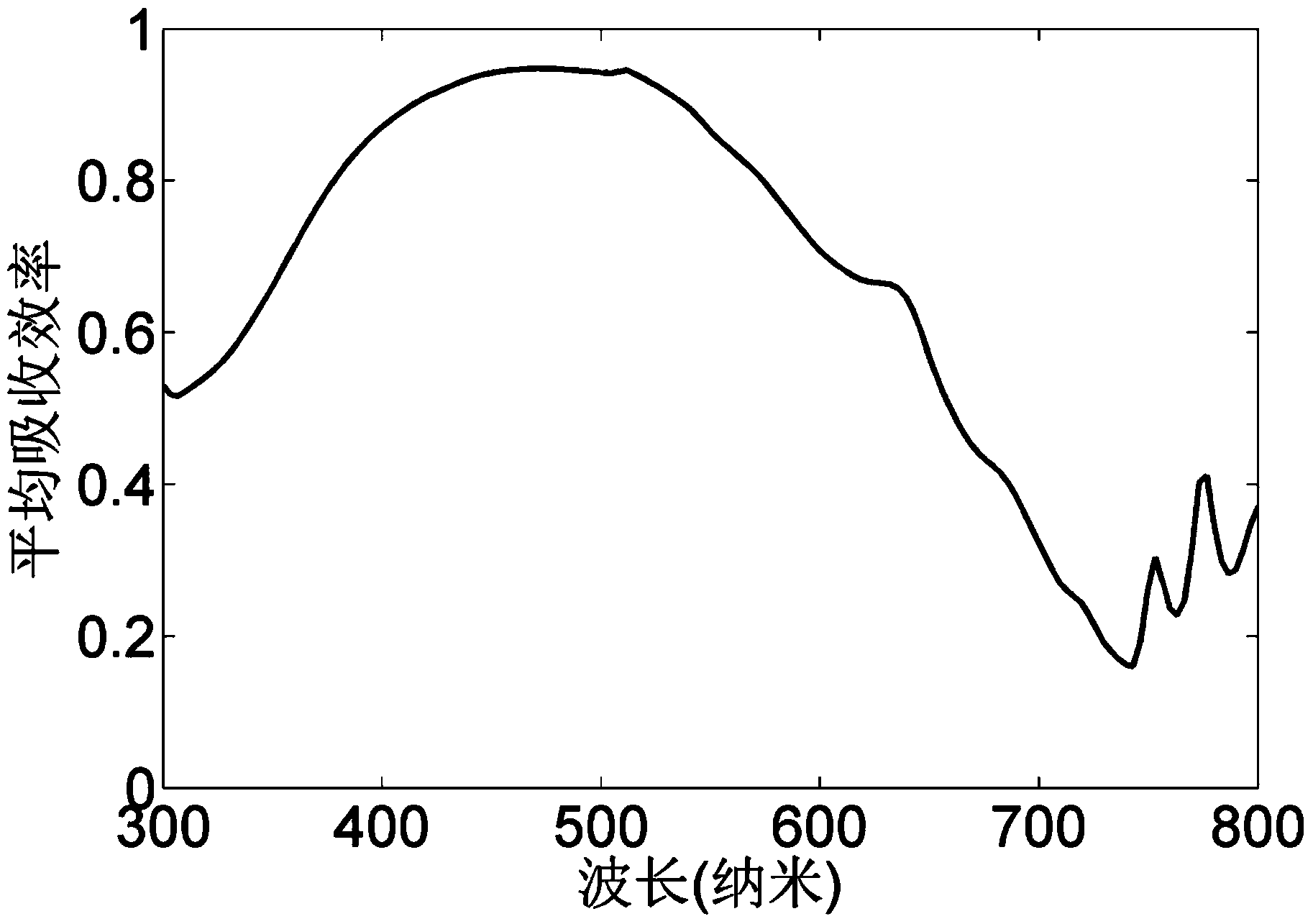
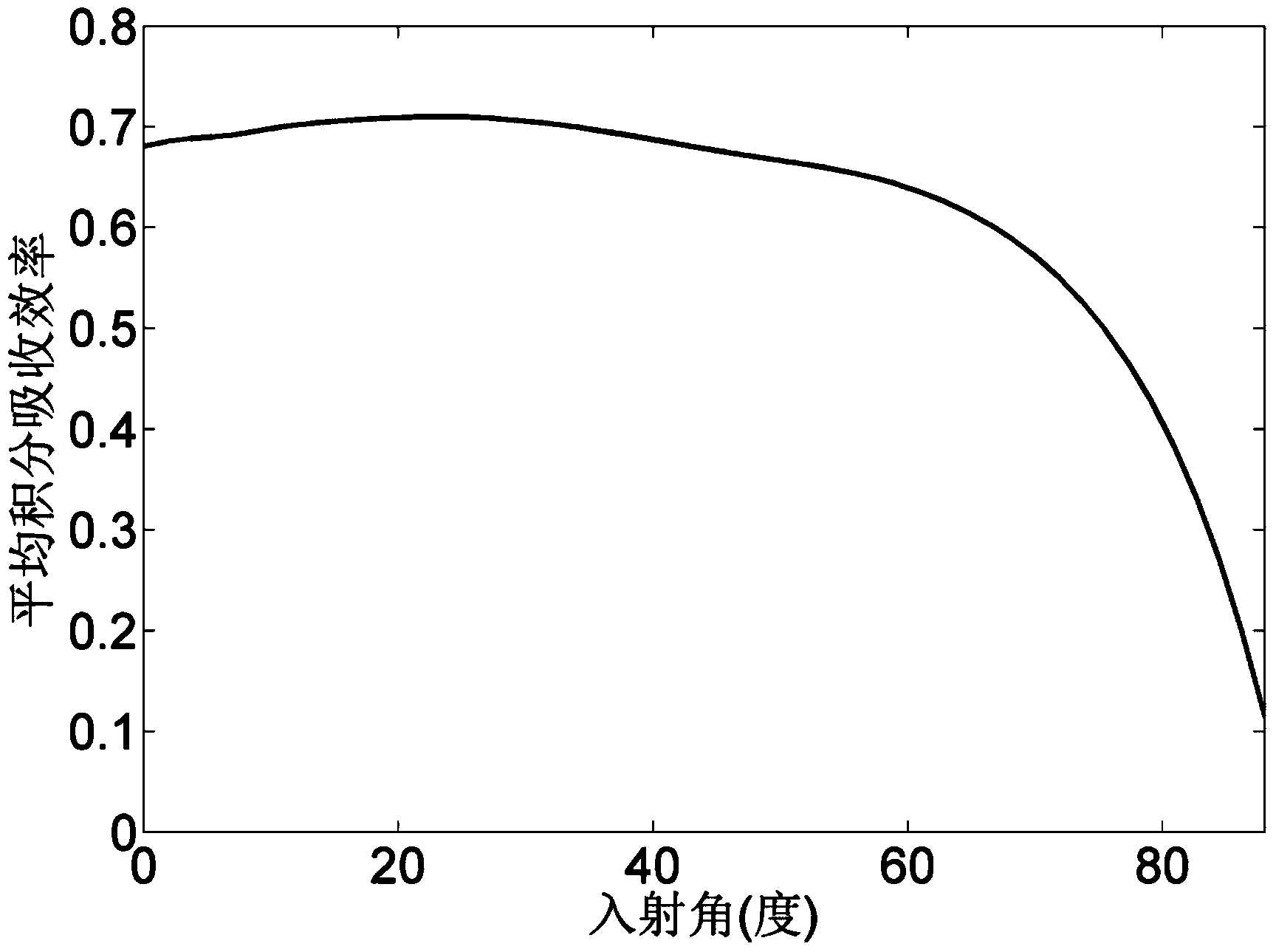
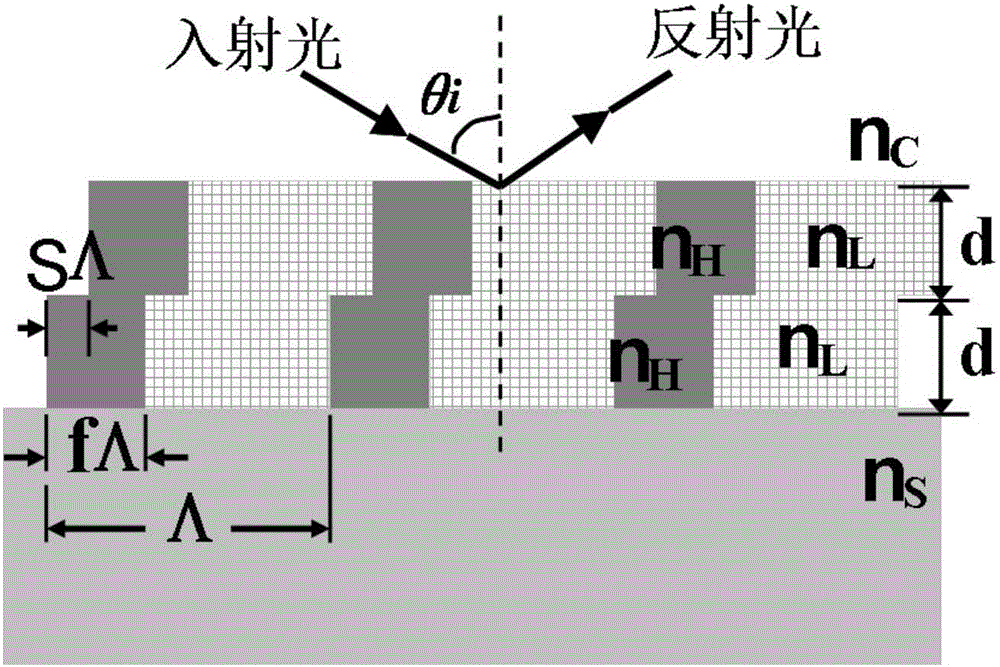
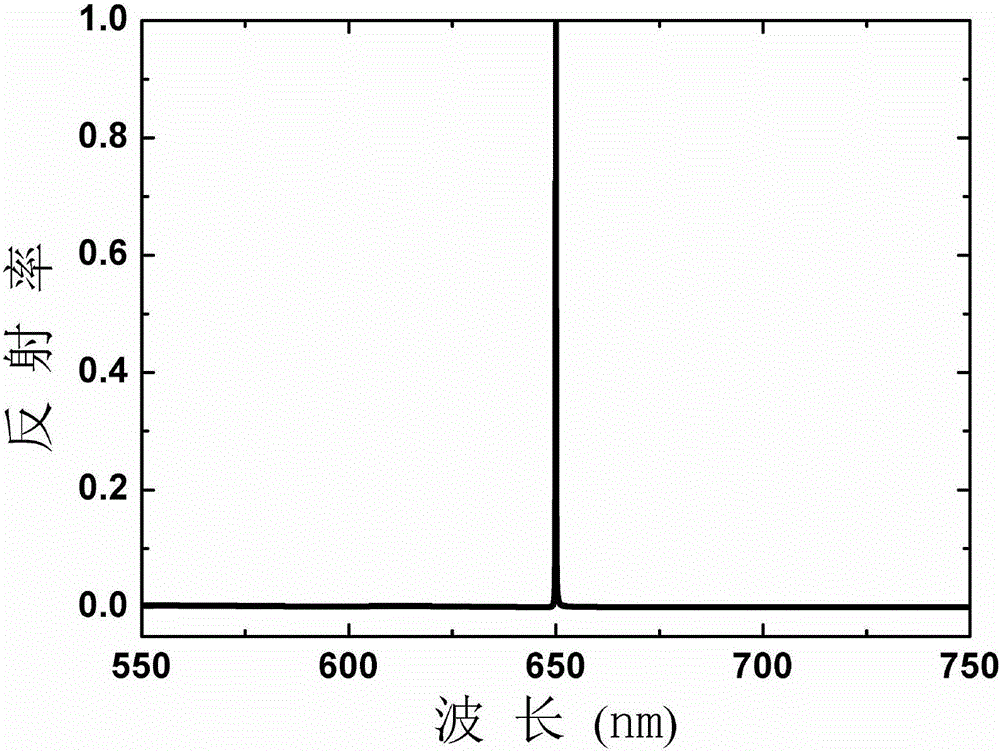
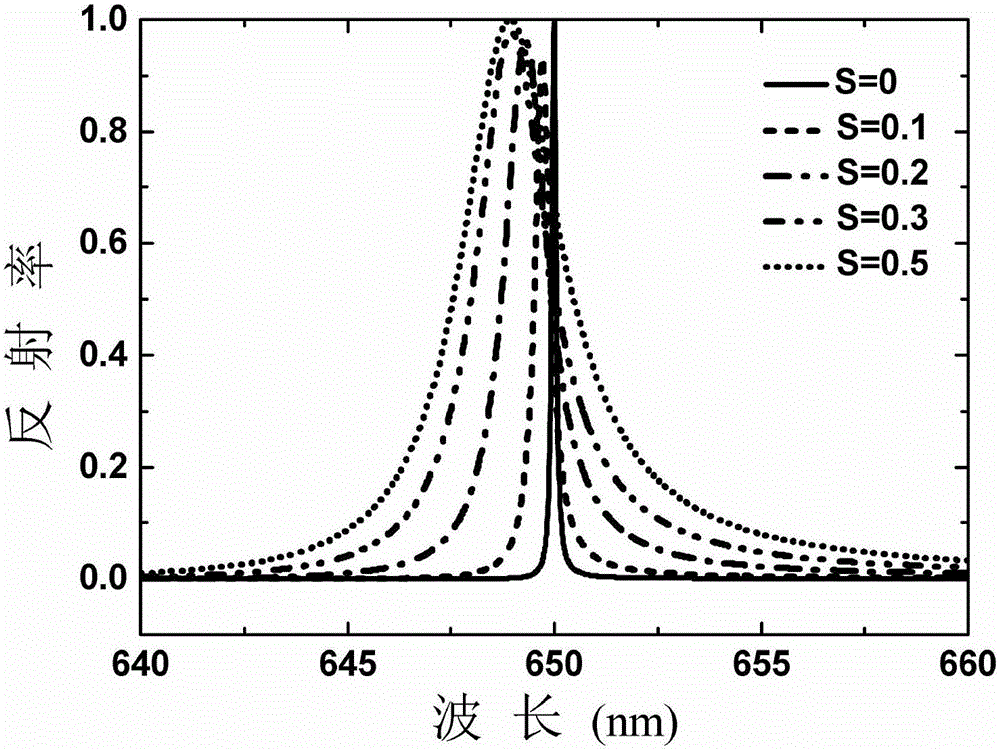
ActiveCN104362184AImprove performanceEasy to use and flexibleDiffraction gratingsPhotovoltaic energy generationEtchingGrating
The invention relates to a thin film amorphous silicon solar cell based on an antireflective structure and guided-mode resonance. The thin film amorphous silicon solar cell used for visible wavelengths ranging from 300 nanometers to 800 nanometers is characterized in that the top antireflective film of the solar cell is 55-60 nanometers in thickness, the period of the middle grating absorption layer is 505-515 nanometers, the middle grating absorption layer is 95-105 nanometers in thickness and 0.7-0.75 in duty ratio, and a waveguide absorption layer is 45-55 nanometers in thickness; when light comes in vertically, the average integral absorption efficiency of the light in the wavelengths of 300-800 nanometers is higher than 66%, the average integral absorption efficiency is large in angle independence, and the average integral absorption efficiency is higher than 60% in the incidence angle of 0-66 degrees. The thin film amorphous silicon solar cell based on the antireflective structure and guided-mode resonance has the advantages that the solar cell is machined by an electronic beam direct writing device combining with micro-electronics deep etching, and the solar cell is convenient in material taking, low in manufacturing cost, capable of achieving large-batch production, and promising in application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
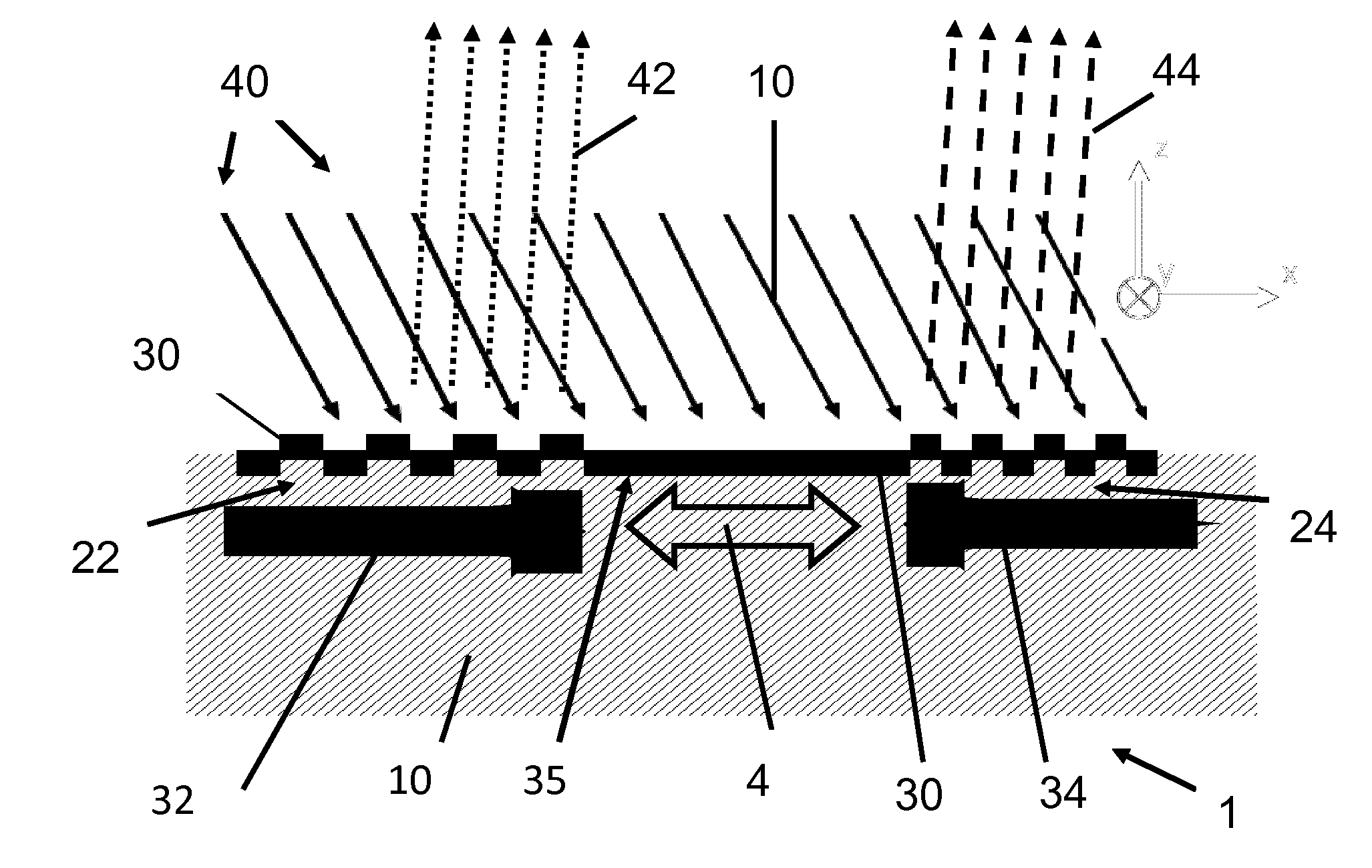
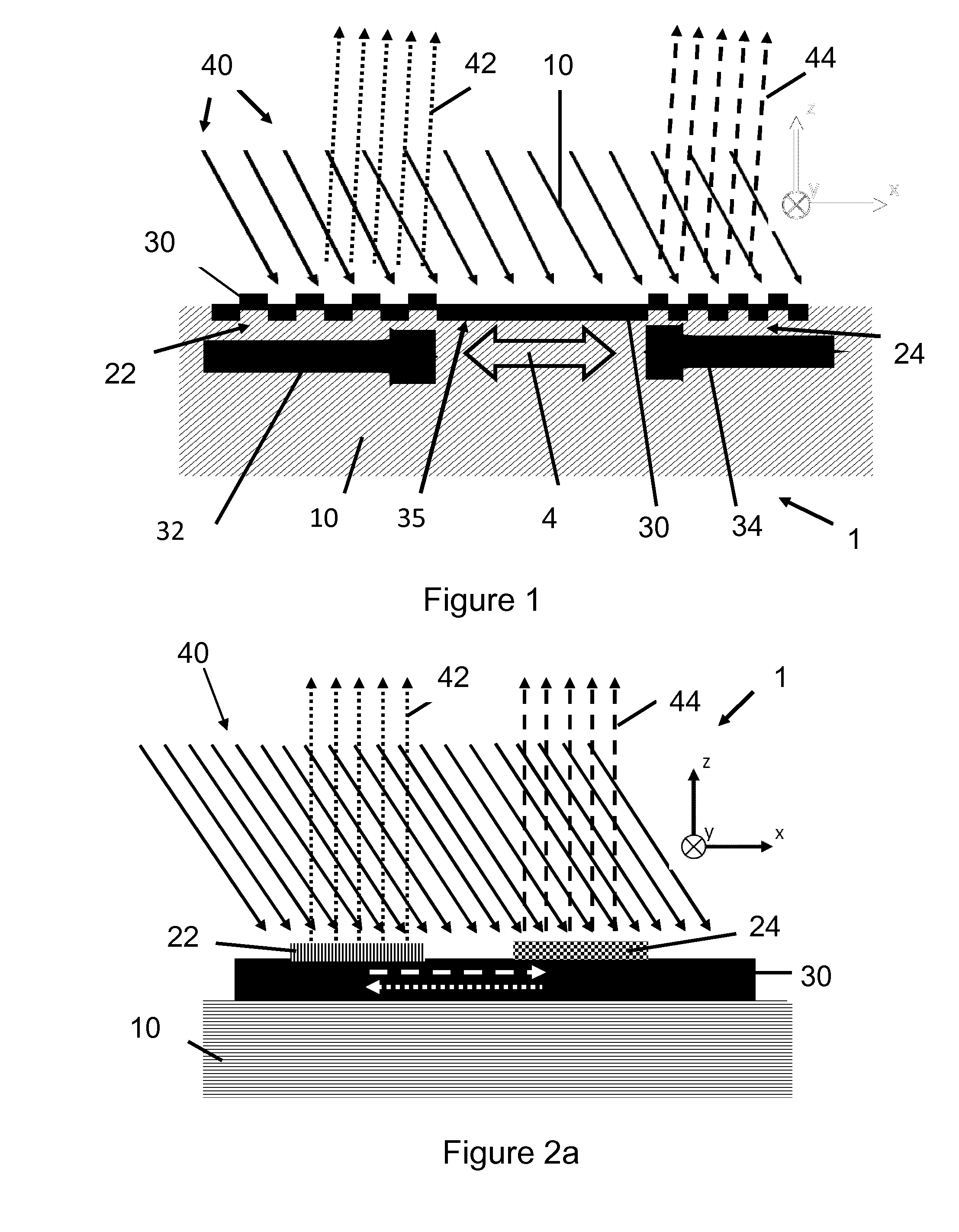
Method for dynamically controlling reflection spectrum bandwidth of guided-mode resonance filter
ActiveCN105759332AGood anti-reflection filter effectOptical filtersGratingMicroelectromechanical systems
The invention discloses a method for dynamically controlling the reflection spectrum bandwidth of a guided-mode resonance filter and belongs to the fields of optical communication and micro electro mechanical systems. A coupling grating provided by the invention is composed of double equivalent grating bodies with the thickness one half of the thickness of an absentee layer and stacked vertically, for TM polarized incident light, structural magnetic field distribution is changed nearby a Brewster angle by controlling micro / nanoscale relative lateral movement between the two grating bodies, and continuous control of the reflection spectrum bandwidth of the guided-mode resonance filter is achieved. In the lateral movement process of the grating bodies, a peak wavelength shift phenomenon caused by the relative lateral movement between the grating bodies is not obvious, but the reflection spectrum bandwidth changes remarkably, and excellent anti-reflection filtering characteristics of the filter are kept when the two grating bodies produce the relative lateral movement. By finely adjusting an incidence angle, reflection peak shift caused by the relative lateral movement of the two grating bodies can be compensated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
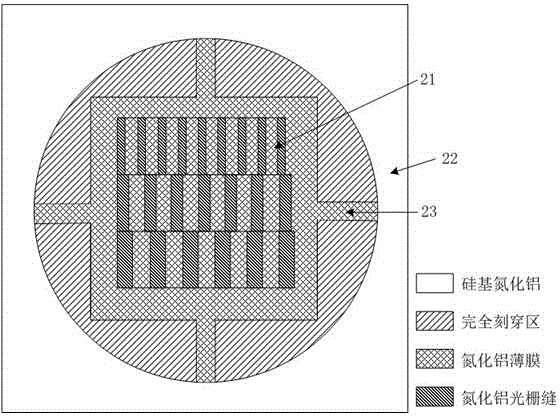
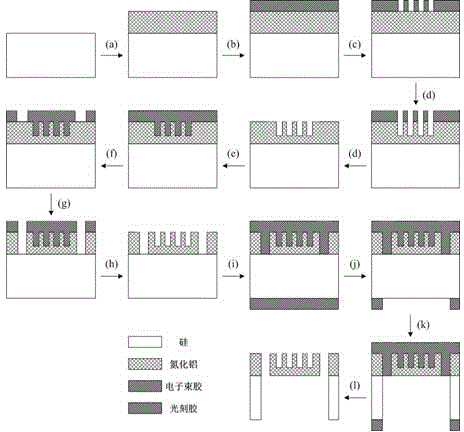
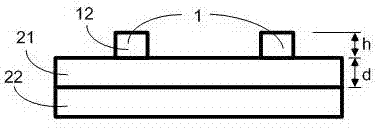
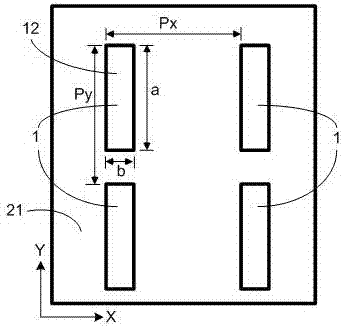
Aluminum nitride-based guided-mode resonant multichannel light filter and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104698537AControllable formantThe principle is simpleOptical waveguide light guideGratingElectron-beam lithography
Discloses an aluminum nitride-based guided-mode resonant multichannel light filter and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum nitride-based guided-mode resonant multichannel light filter comprises a silicon substrate layer, an aluminum nitride waveguide layer and an aluminum nitride optical grating; the aluminum nitride optical grating is composed of a plurality of rows of linear optical grating arrays different in cycles. The aluminum nitride-based guided-mode resonant multichannel light filter of a visible light waveband is realized on a silicon substrate aluminum nitride chip; techniques such as electron beam lithography, ion beam etching, photoetching and deep reactive ion etching are adopted to define and etch the device, and a back registration process and a deep silicon etching technique are adopted to remove the silicon substrate under the aluminum nitride optical grating, so that the aluminum nitride layer is completely suspended. The light filter realizes multichannel light filtration within the visible light waveband by use of the guided-mode resonance characteristic of the optical gratings different in cycle.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
All-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device
The present invention discloses an all-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device. The all-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device comprises a planar waveguide and a two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator; the planar waveguide comprises a first dielectric layer; the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator is composed of cuboid dielectric bars which are arranged at the upper surface of the first dielectric layer and are in two-dimensional periodic distribution; the refractive index of the cuboid dielectric bars is greater than the refractive index of the first dielectric layer; the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator has a resonant characteristic, so that the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator can generate a series of Mie resonance according to the Mie resonant principle; the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator has a grating-like effect, so that the two-dimensional periodic dielectric resonator can make incident waves diffracted and coupled with the guided mode of the planar waveguide; and an EIT-like effect can be generated through controlling the interaction of Mie resonance and guided mode resonance. With the all-dielectric metamaterial EIT (electromagnetically induced transparency)-like resonance device of the invention adopted, high-quality factor resonance and high resonance intensity can be achieved, and a high group refractive index can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Unmarked guided-mode resonance Brewster sensor detection device
InactiveCN104165864AHighly integratedImprove optical detection sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsBeam expanderGrating
The invention discloses an unmarked guided-mode resonance Brewster sensor detection device. The unmarked guided-mode resonance Brewster sensor detection device comprises an incident light source assembly, a guided-mode resonance grating sensor and a detection optical assembly, wherein the incident light source assembly comprises a laser light source and a beam expander group; the guided-mode resonance grating sensor comprises a grating layer, a waveguide layer and a substrate; the detection optical assembly comprises a CCD linear array and a drive circuit thereof; the beam expander group is installed in front of the laser light source, the waveguide layer is installed above the substrate, the grating layer is installed above the waveguide layer, and the CCD linear array is installed right above the grating layer. The unmarked guided-mode resonance Brewster sensor detection device is high in integration degree and suitable for detecting high-flux samples; the design for entering a guided-mode resonance optical device at a Brewster angle is favorable for actually establishing a biochemical detection device and improving the unmarked optical detection sensitivity.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF TSINGHUA UNIV ZHEJIANG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com