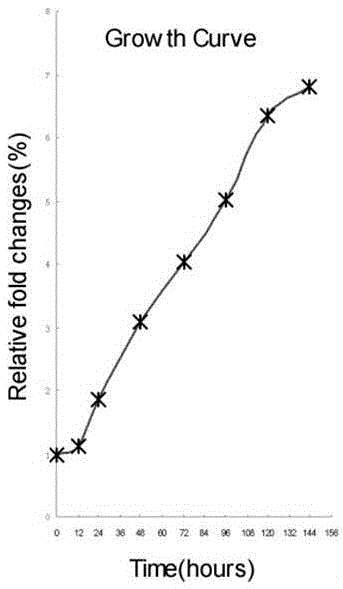
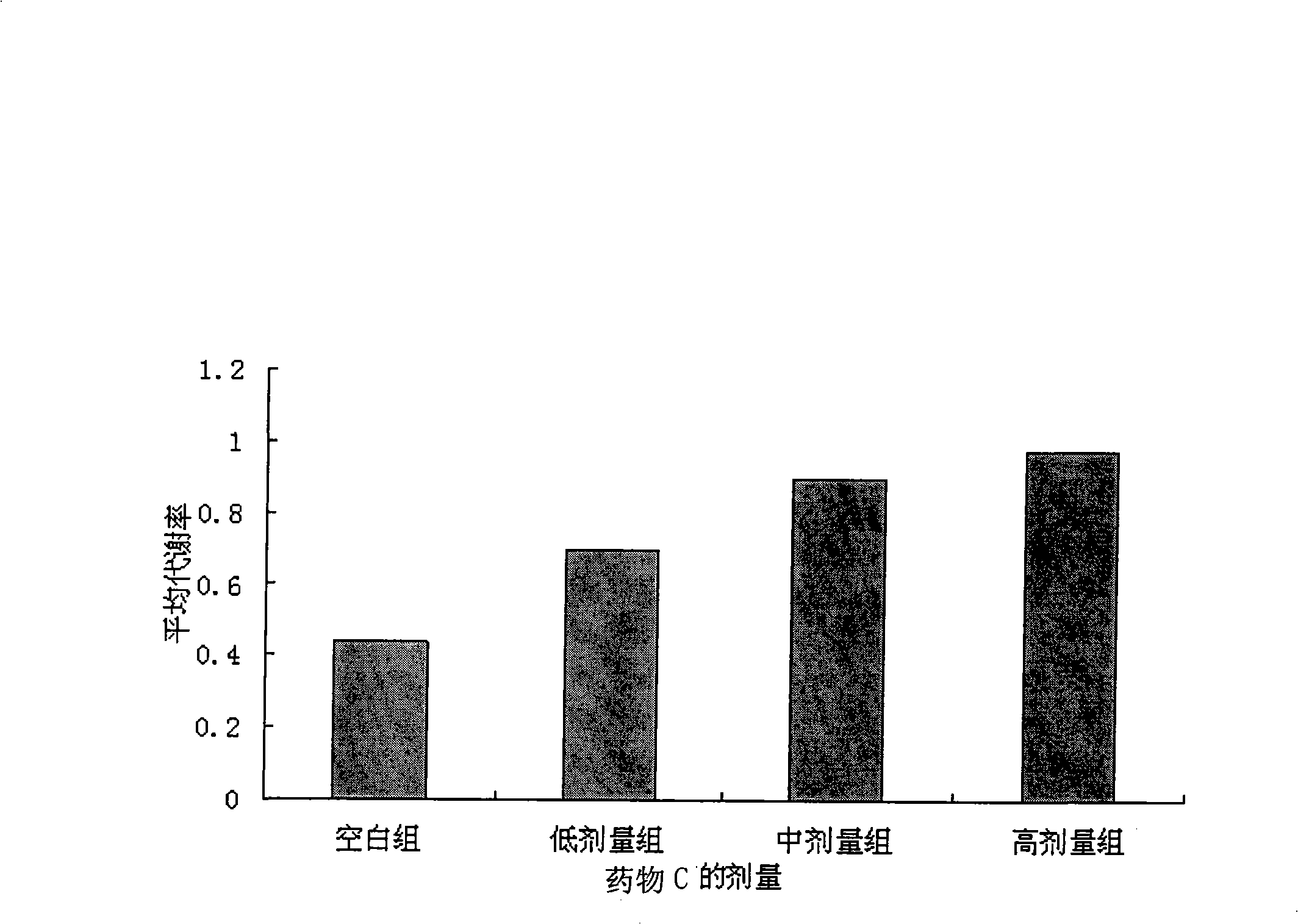
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
503 results about "In vitro incubation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
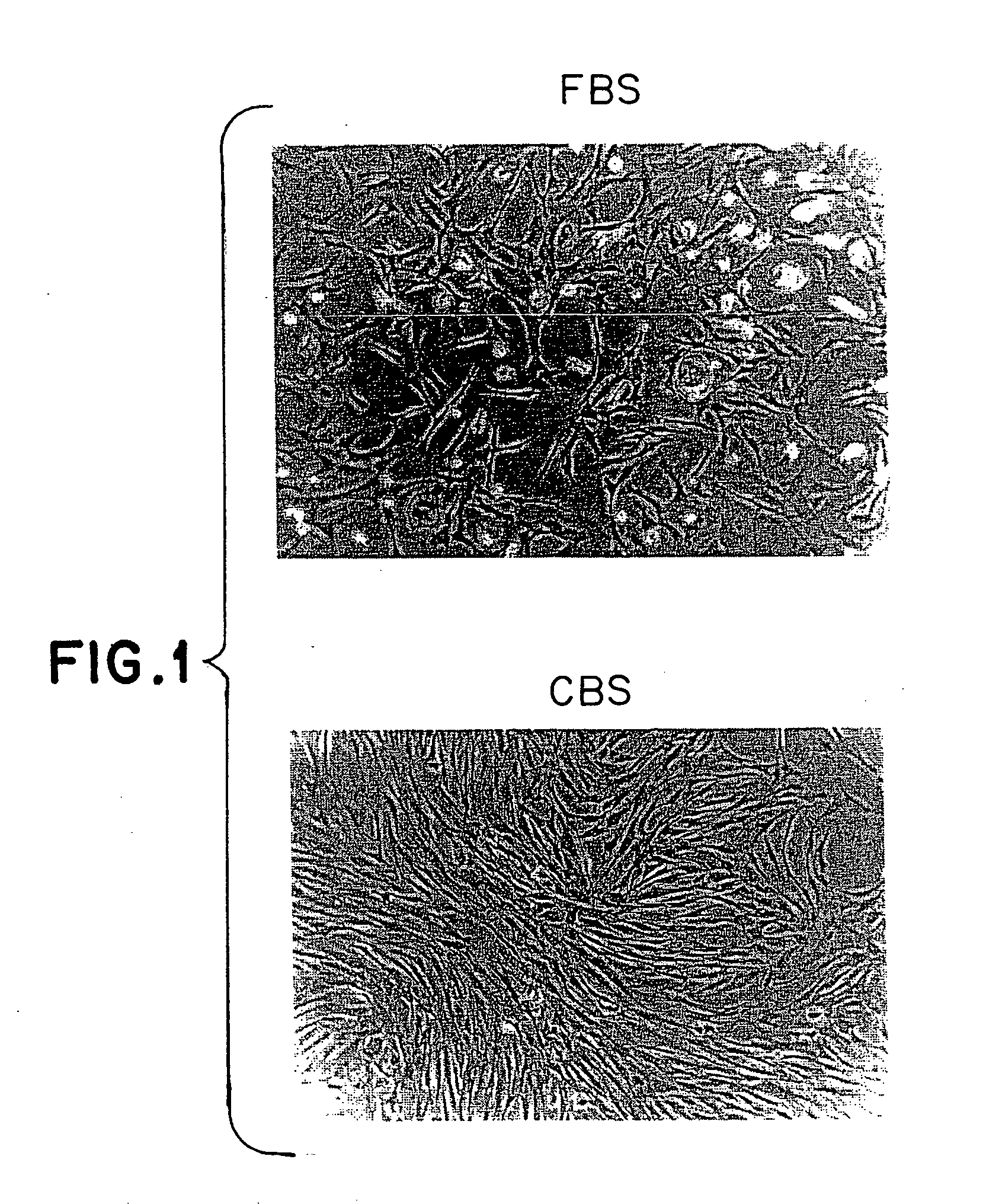
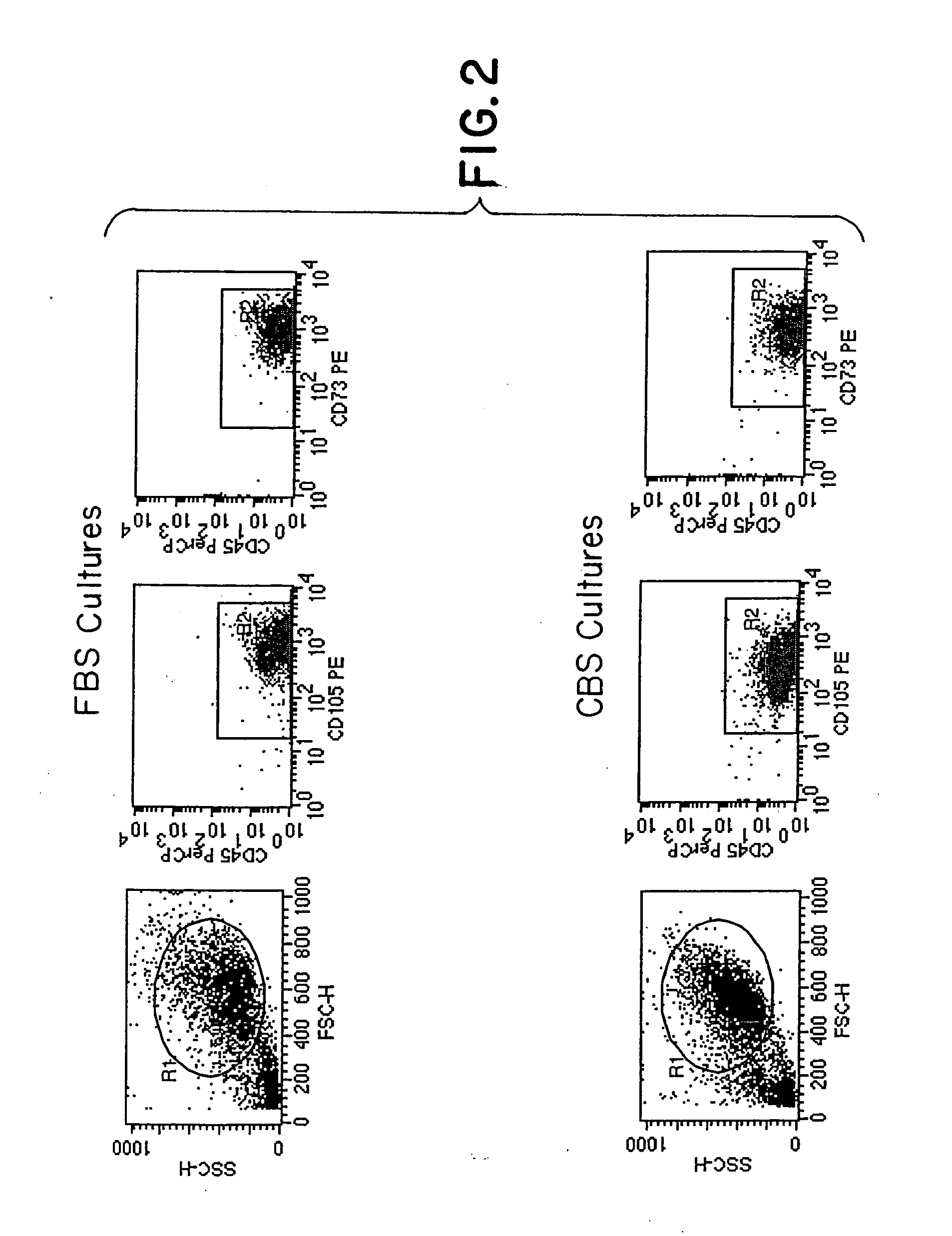
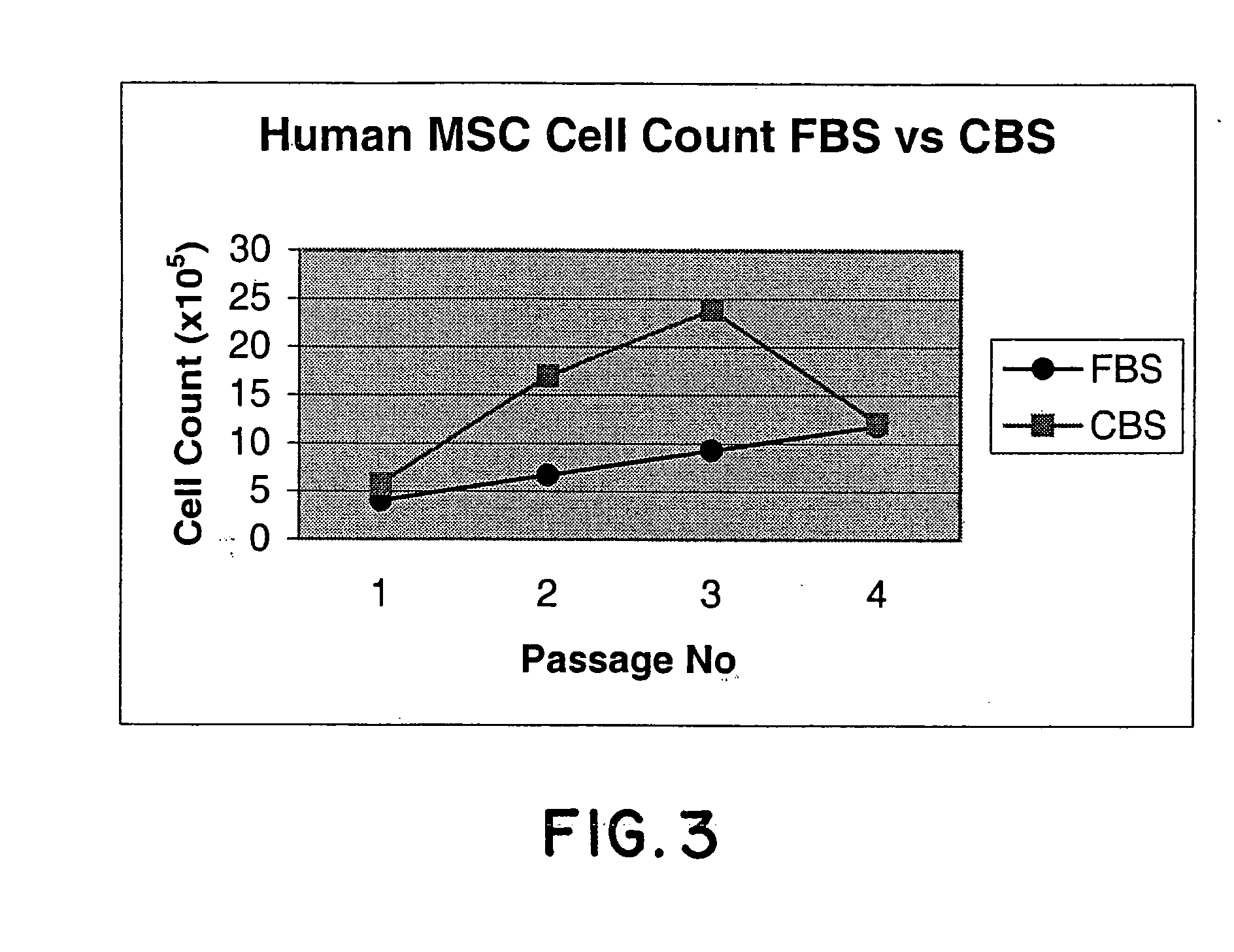
In vitro culture of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and a process for the preparation thereof for therapeutic use
InactiveUS20050059152A1Promote growthEliminate riskCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsCord blood stem cellMesenchymal stem cell
Method of culturing mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) by culturing the stem cells in a culture medium containing Cord Blood Serum, and a process for preparation thereof for therapeutic use.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
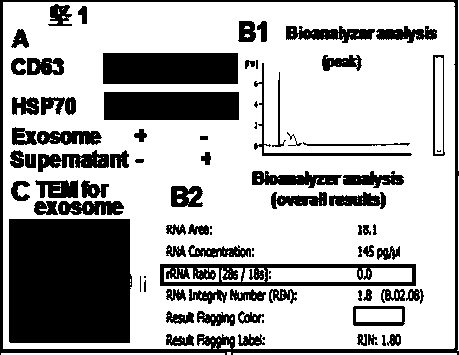
Preparation and application of exosome secreted by human derived blood or mesenchymal stem cell
InactiveCN103767985AAvoid blocking, not easily absorbed by cellsProtection stabilityCosmetic preparationsSenses disorderStem cell cultureSomatic cell
The invention discloses preparation and application of exosome secreted by human derived blood or mesenchymal stem cell. The preparation process of exosome comprises: extracting mesenchymal stem cells from health-human body blood or a stem cell culture supernatant, performing in-vitro culture and amplification, and utilizing means such as low-temperature separation, purification and the like to prepare high-purity high-bioactivity exosome. The blood or mesenchymal stem cell secreted exosome is added into medicines, health-care products and cosmetics according to ratios for developing of products with bioactivity, is capable of effectively regulating and controlling body cell signal transduction, activating cell regeneration, enhancing health cell proliferation and differentiation capacity, further regulating physiologic restoration or removing damaged, pathologic and aged cells of a body, fundamentally changing body physiologic functions, and helping to generate anti-tumor treatment effect by adjusting cellular immunity. The blood or mesenchymal stem cell secreted exosome is applicable to fields of medical science, health care and beauty treatment, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:珠海霍普金斯医药研究院股份有限公司
Method for regenerating human intact skin tissue by use of in vitro cultured cells
ActiveCN103785064APromote wound healingTreat aging skinIn-vivo testing preparationsProsthesisDiseaseCuticle
The invention discloses a skin model and application. The method comprises separately culturing epidermal cells and dermal cells derived from fetus scalp, newborn prepuce or adult scalp, and subculturing, wherein the used culture medium and culture method can maintain multiple functions of skin cells; separately digesting the cultured and proliferated multifunctional epidermal cells and dermal cells into single cells, and mixing to obtain suspension; transferring onto a semipermeable polymer or silica gel membrane substrate for incubation; transplanting cells on adhesive film to a receptor. The method can regenerate human intact functional skin and hair, the regenerated skin contains an epidermal layer, a dermal layer and a subcutaneous tissue as well as skin appendant organs. The skin model regenerated by the method disclosed by the invention can be used for study of human skin diseases, screening of skin drugs, and development of cell products for treating wound and other skin diseases.
Owner:JINAN PANSHENG BIOTECH
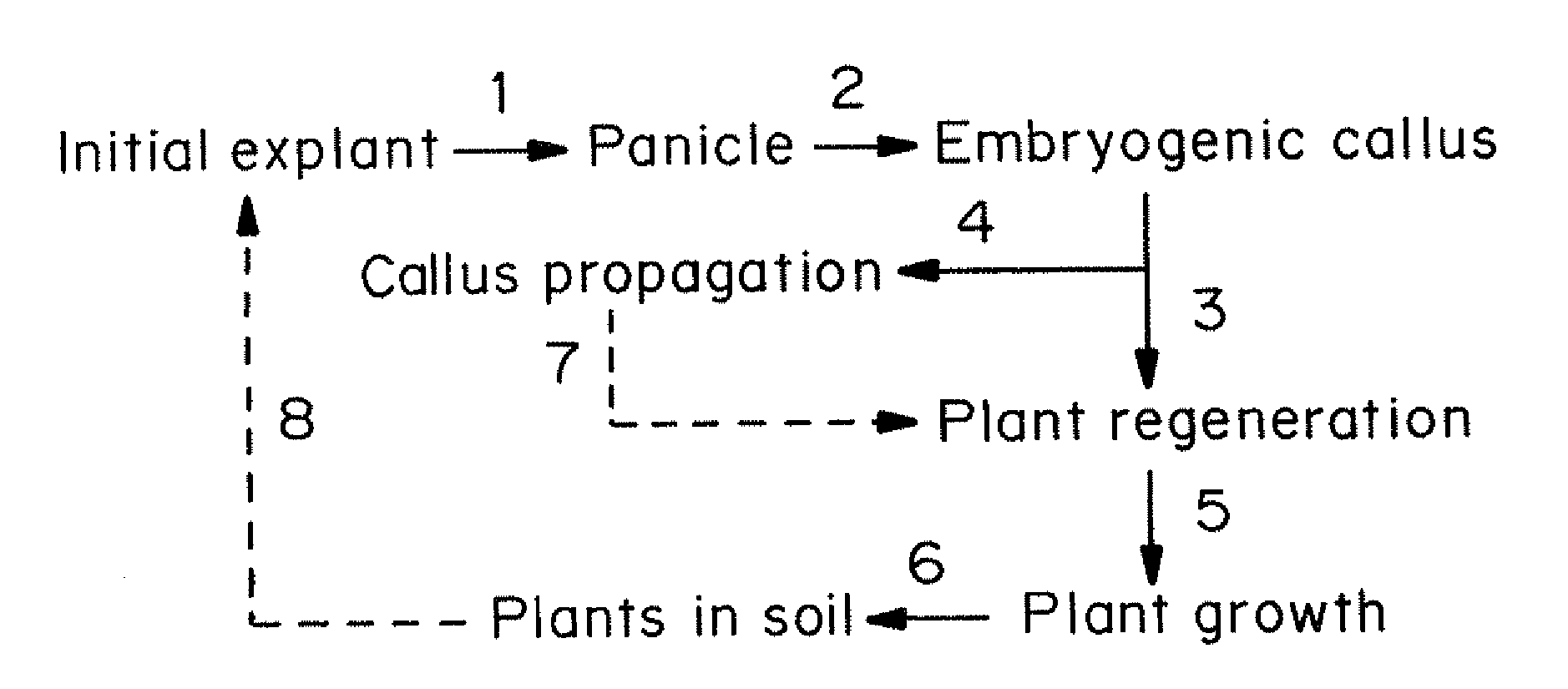
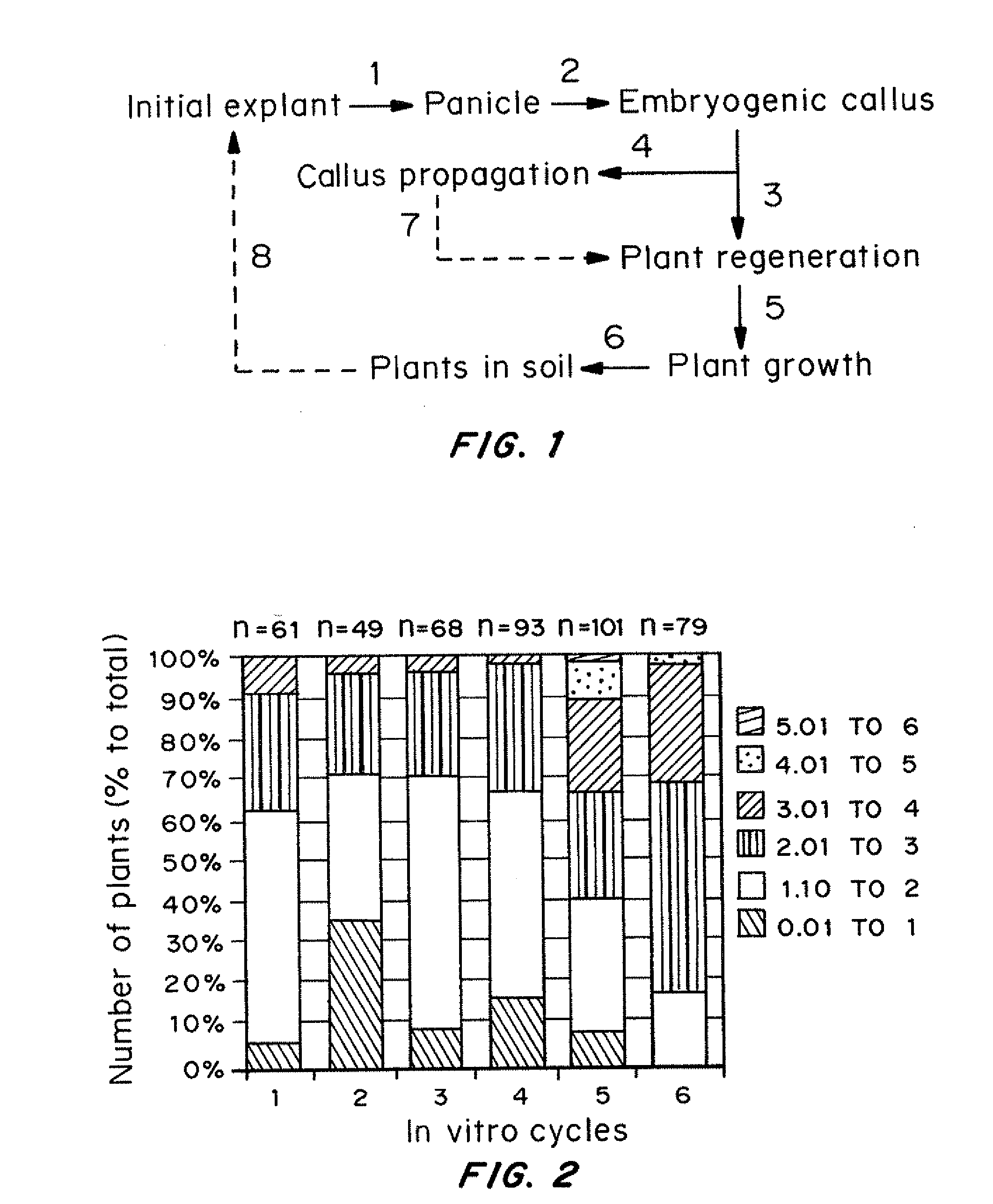
Propagation of transgenic plants
InactiveUS20100229256A1Improve featuresIncrease biomassGenetic engineeringPlant tissue cultureEngineered geneticTransgene
Methods for increasing the product yield from plants, preferably transgenic plants, are provided. It has been discovered that in vitro cultures from donor plants produce plants that have two or three fold increase in product yield. One embodiment provides a method for increasing product yield from a transgenic plant by initiating an in vitro culture from a donor transgenic plant, wherein the donor transgenic plant is genetically engineered to produce a product and regenerating a second transgenic plant from the in vitro culture, wherein the yield of the product from the second transgenic plant is greater than the yield of the product from the donor transgenic plant. In a preferred embodiment, the transgenic plant is a graminaceous plant such as switchgrass.
Owner:METABOLIX
Rapid preparation of stem cell matrices for use in tissue and organ treatment and repair
InactiveUS7906110B2Cost effectiveImprove propertiesBiocideGenetic material ingredientsMedicineEngineering
The invention is directed to preparation of stem cell and physiologically acceptable matrix compositions. Compared with previous tissue engineering materials, the stem cell-matrix compositions of the present invention do not require long-term incubation or cultivation in vitro prior to use in vivo applications. The stem cells can be from numerous sources and may be homogeneous, heterogeneous, autologous, and / or allogeneic in the matrix material. The stem cell-matrix compositions provide point of service utility for the practitioner, wherein the stem cells and matrix can be combined not long before use, thereby alleviating costly and lengthy manufacturing procedures. In addition, the stem cells offer unique structural properties to the matrix composition which improves outcome and healing after use. Use of stem cells obtained from muscle affords contractility to the matrix composition.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
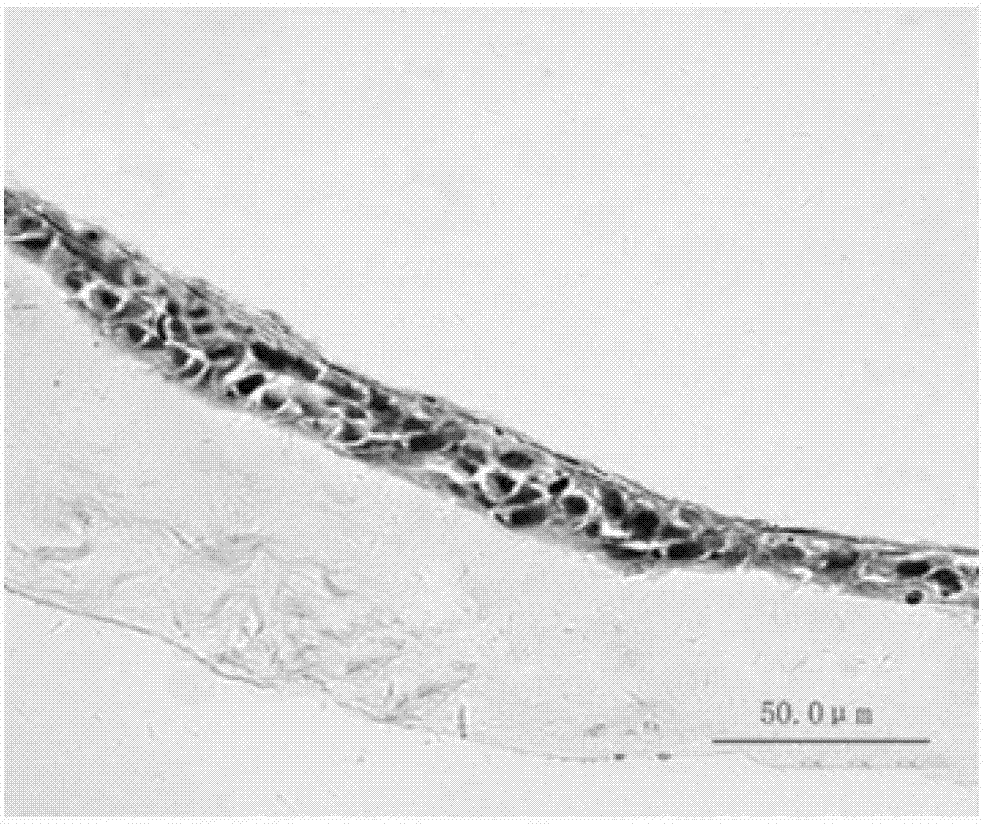
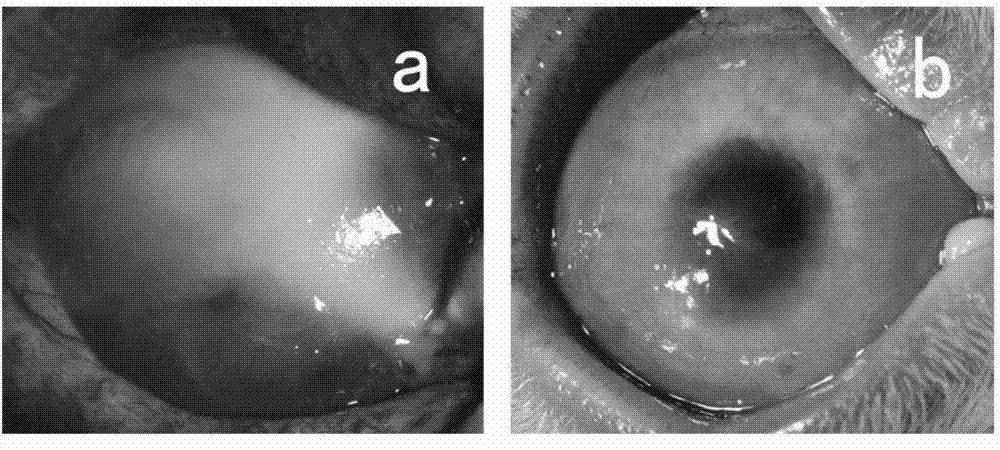
Whole layer biological cornea as well as construction method and use thereof
The invention aims at providing a novel full-thickness biological cornea used for transplantation. The full-thickness biological cornea takes an animal cornea acellular matrix as a carrier, and the acellular matrix comprises animal cornea matrix cells, epithelial cells and endothelial cells which are cultured and augmented in vitro. The cornea is characterized in that the xenogenic corneal acellular matrix prepared by a biochemical method can be used as a good carrier for in vitro constructing the biological cornea in the aspects of shape, structure and biological compatibility, the matrix cells, epithelial cells and endothelial cells of the cornea are planted respectively, and dynamically cultured in the simulated in vivo environment of a biological reactor, so that the full-thickness biological cornea with nearly normal tissue structure and characteristics can be constructed in vitro, and the biological cornea can be used to simulate the physiological cornea for fundamental research on physiology, pathology and pharmacology; moreover, the biological cornea can also be directly used as the donator for corneal transplantation.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
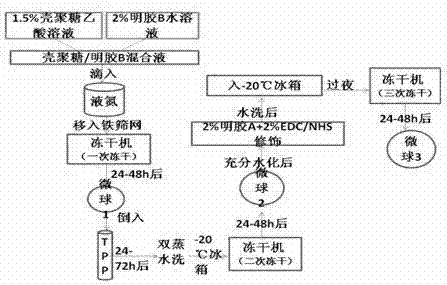
Three-dimensional porous chitosan/gelatine microsphere, preparation method thereof and application in liver cell culture
InactiveCN102172498AThe size is easy to controlControllable ApertureArtificial cell constructsTumor/cancer cellsCross-linkGelatin microspheres
The invention discloses a three-dimensional porous chitosan / gelatine microsphere, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof in liver cell culture. The preparation method thereof comprises the following steps of: rapidly freezing mixture into spheres by dropping liquid nitrogen by virtue of a high-pressure pulse microcapsule moulding instrument after chitosan and gelatine B are mixed, carrying out secondary freeze-drying after microspheres subjected to primary freeze-drying are crosslinked and cured with saturated tripolyphosphate-85% ethanol solution, fully hydrating the microspheres obtained by the secondary freeze-drying, adding cross linking agent carbodiimide / N-hydroxy succinyl, modifying the microspheres with gelatine A, removing unreacted carbodiimide / N-hydroxy succinyl and gelatine A by washing after water bath and reaction in dark place are carried out, and carrying out tertiary freeze-drying, thus the three-dimensional porous chitosan / gelatine microspheres with the diameter of 300-800Mum and the surface aperture of 50-200mu m are obtained, and the surface of each microsphere is connected with the aperture of the interior of the microsphere. The three-dimensional porous chitosan / gelatine microspheres obtained by the invention can be used for in vitro culture of high-density and high-activity liver cells.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
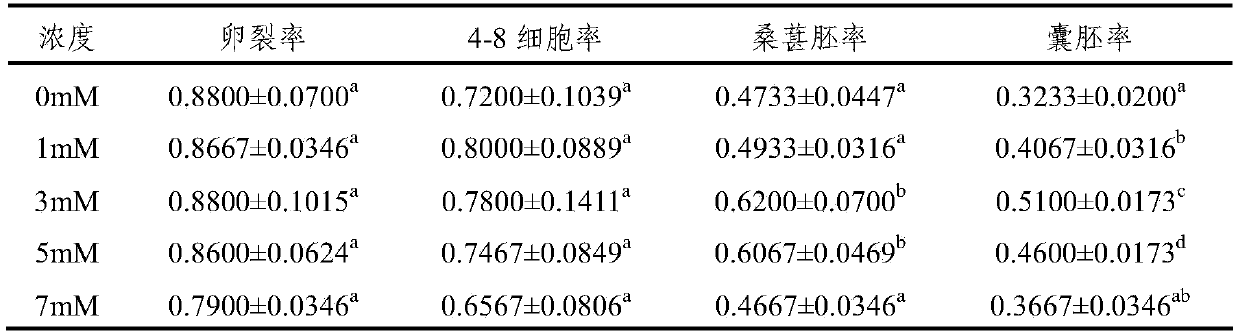
Bovine in vitro fertilization embryo culture medium and culture method
InactiveCN103898046BImprove developmental abilityIncrease development rateEmbryonic cellsCulture fluidEmbryo
The invention provides a culture fluid exclusively used in cow in-vitro fertilization embryos. The culture fluid contains 109.0mM-110mM of NaCl, 2.9mM-3.1mM of KCl, 26.0mM-26.5mM of NaHCO3, 0.5mM-1.0mM of MgCl2.6H2O, 1.0mM-1.3mM of KH2PO3, 0.4mM of sodium pyruvate, 1.5 mM of glucose, 5mM of galacturonic calcium, 10v / v% fetal bovine serum, 1mM of L- glutamine, 2v / v% essential amino-acid, 1v / v% nonessential amino acid and 1mM-10mM of glutathione. The cow in-vitro fertilization embryos are placed into the culture fluid to carry out in-vitro cultivation, and results are shown to be obviously superior to those of a control group which is not added with GSH (glutathione), and therefore, developmental rate of blastula and embryo quality are improved, cost for producing embryos in vitro is lowered, experimental basis is provided for applying a cow IVF (in vitro fertilization) technology to practice, and a genetic breeding process can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Assembling type cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane compound bone repairing material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108310467AEnhance bone regeneration abilityGood osteoinductivityTissue regenerationProsthesisHuman bodyCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides an assembling type cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane (ECM) compound bone repairing material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The bone repairingmaterial is prepared by the following steps: completely covering a three-dimensional degradable biological scaffold with a sheet-shaped acellular matrix membrane under sterile conditions and then freezing the three-dimensional degradable biological scaffold for 24 to 48h under the condition of -20 to -80 DEG C; then carrying out freeze drying treatment to obtain the ECM membrane compound bone repairing material, wherein the sheet-shaped acellular matrix membrane is a cell-derived extracellular matrix which is generated by in-vitro culture of cells, is subjected to decellularization treatment and has certain bone induction activity, and the three-dimensional degradable biological scaffold is a biological scaffold which is prepared from natural polymers, has a three-dimensional porous microscopic structure and can be completely degraded and absorbed in human bodies. The assembling type cell-derived extracellular matrix membrane compound bone repairing material has a good bone induction capability; furthermore, the bone regeneration capability of the compound material is strengthened; a construction method is simple and feasible and the material can be stored for a long time and has awide clinical application potential.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
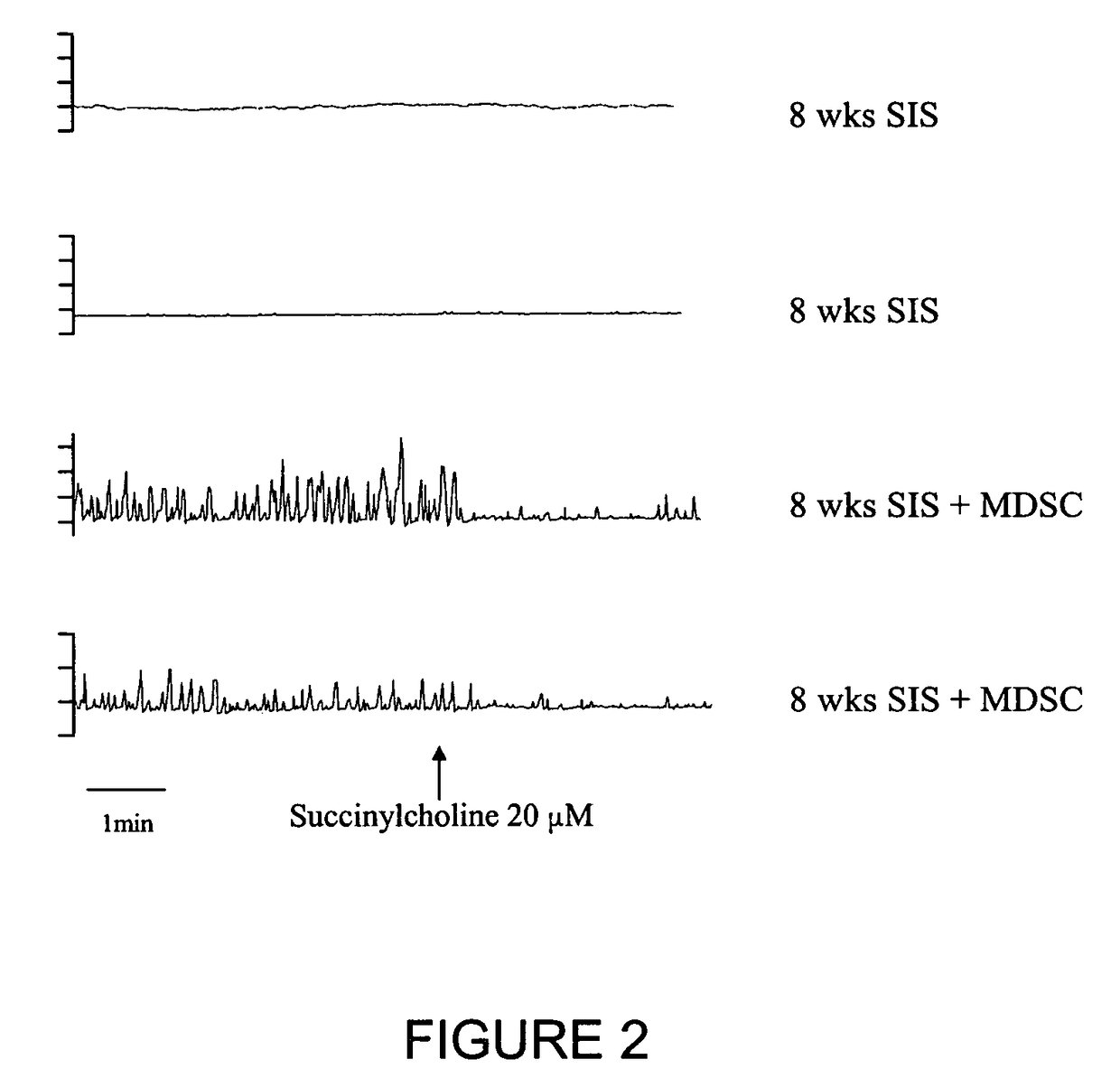
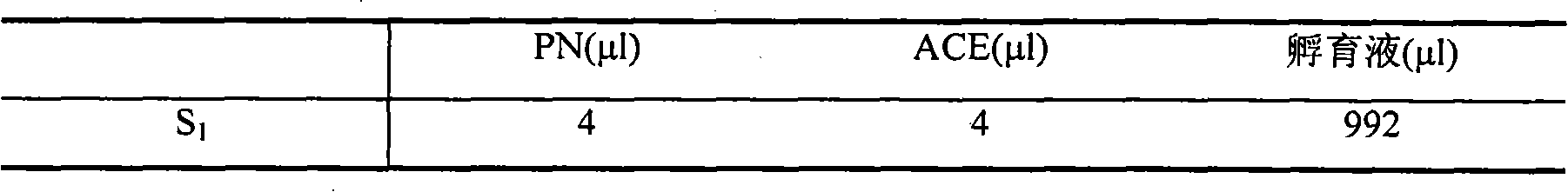
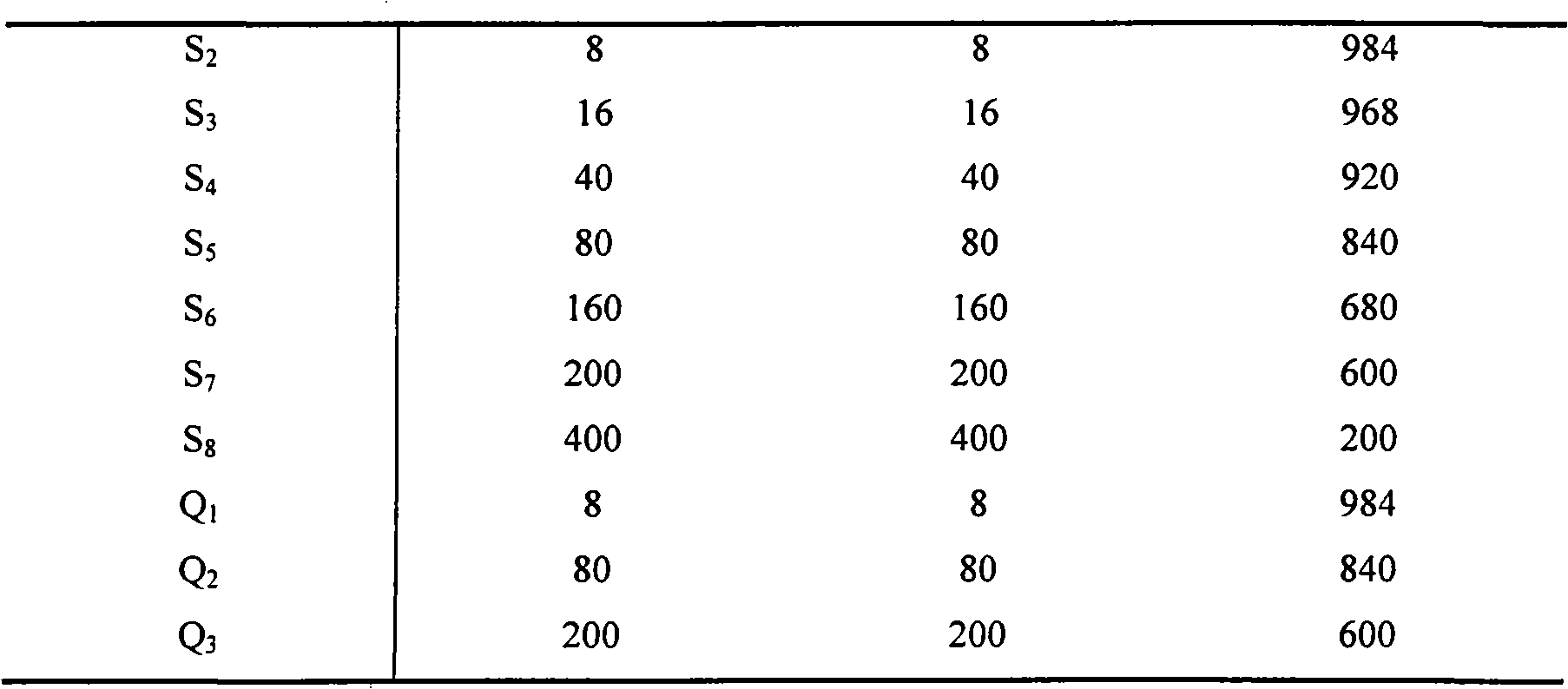
Method for in vitro incubation of macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN101720684AOvercoming Biological DifficultiesFill in research gapsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiological propertyShrimp
The invention relates to a method for in vitro incubation of fertilized eggs of macrobrachium nipponense, which is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of selection of parent shrimps, mating and oviposition, treatment of incubation water, egg stripping, egg washing, incubation, daily management and the like. The method for the in vitro incubation of the fertilized eggs of the macrobrachium nipponense solves the problem of biological characteristics that the fertilized eggs depend on parent bodies to be incubated, lays a foundation for genetic operations of the macrobrachium nipponense such as gene transfer, nuclear transplantation and the like, fills the research gap of the field, and has important practical application value.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Cell lines with latent immunodeficiency virus and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20030157693A1Reduce in quantityVirus peptidesDrug screeningImmunodeficiency virusActivation cells
The present invention provides isolated cells that comprise, integrated into the genome of the cell, a transcription-competent immunodeficiency virus or a transcription-competent immunodeficiency virus-based retroviral vector. Under basal in vitro culture conditions, the immunodeficiency virus is latent, and the expression of the latent immunodeficiency virus can be reactivated. The invention further provides methods of making a subject cell. The invention further provides screening methods for identifying agents that activate a latent immunodeficiency virus; and screening method for identifying agents that block reactivation of latent immunodeficiency virus expression in response to T cell activation signals. The invention further provides agents identified in the subject screening assays. The invention further provides methods of treating an immunodeficiency virus infection.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
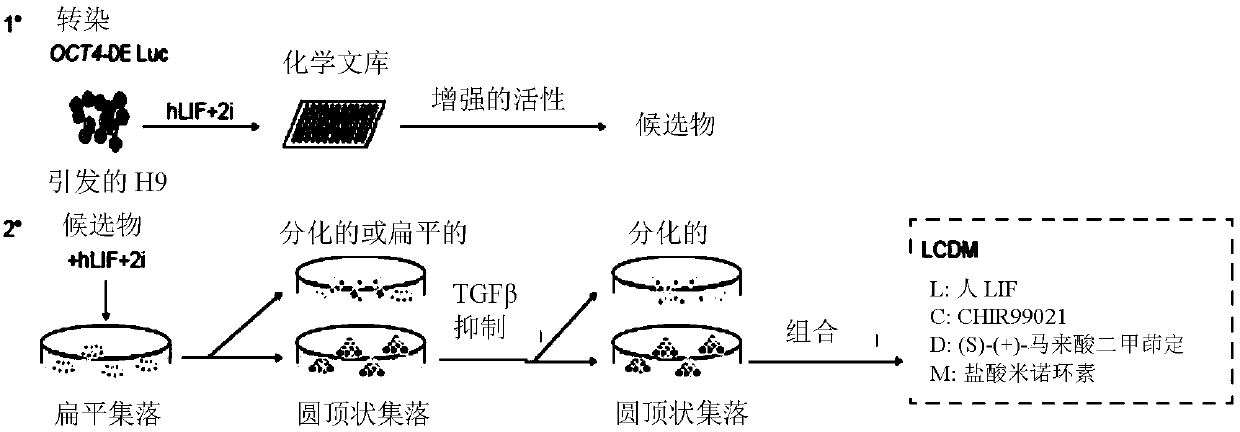
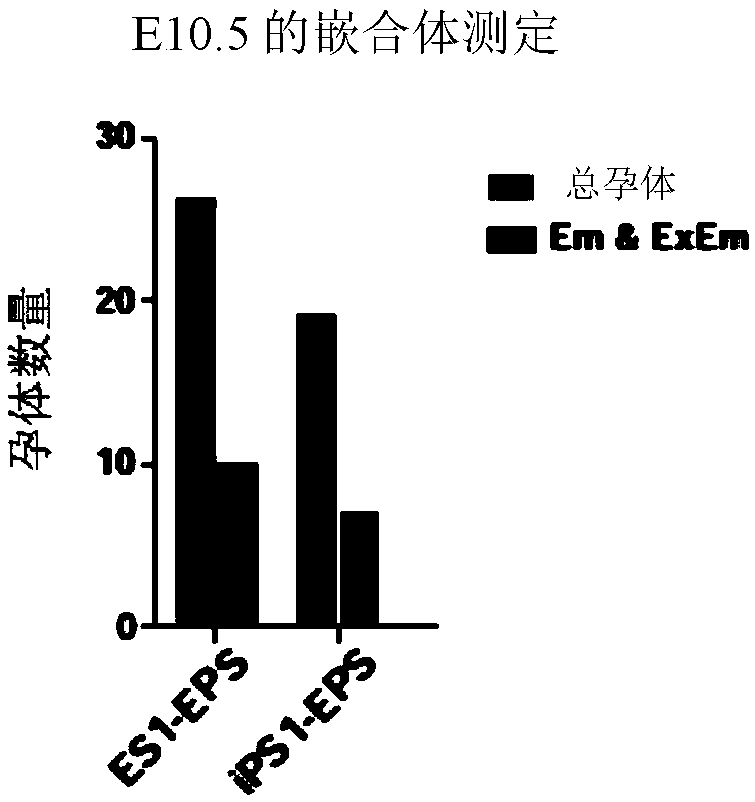
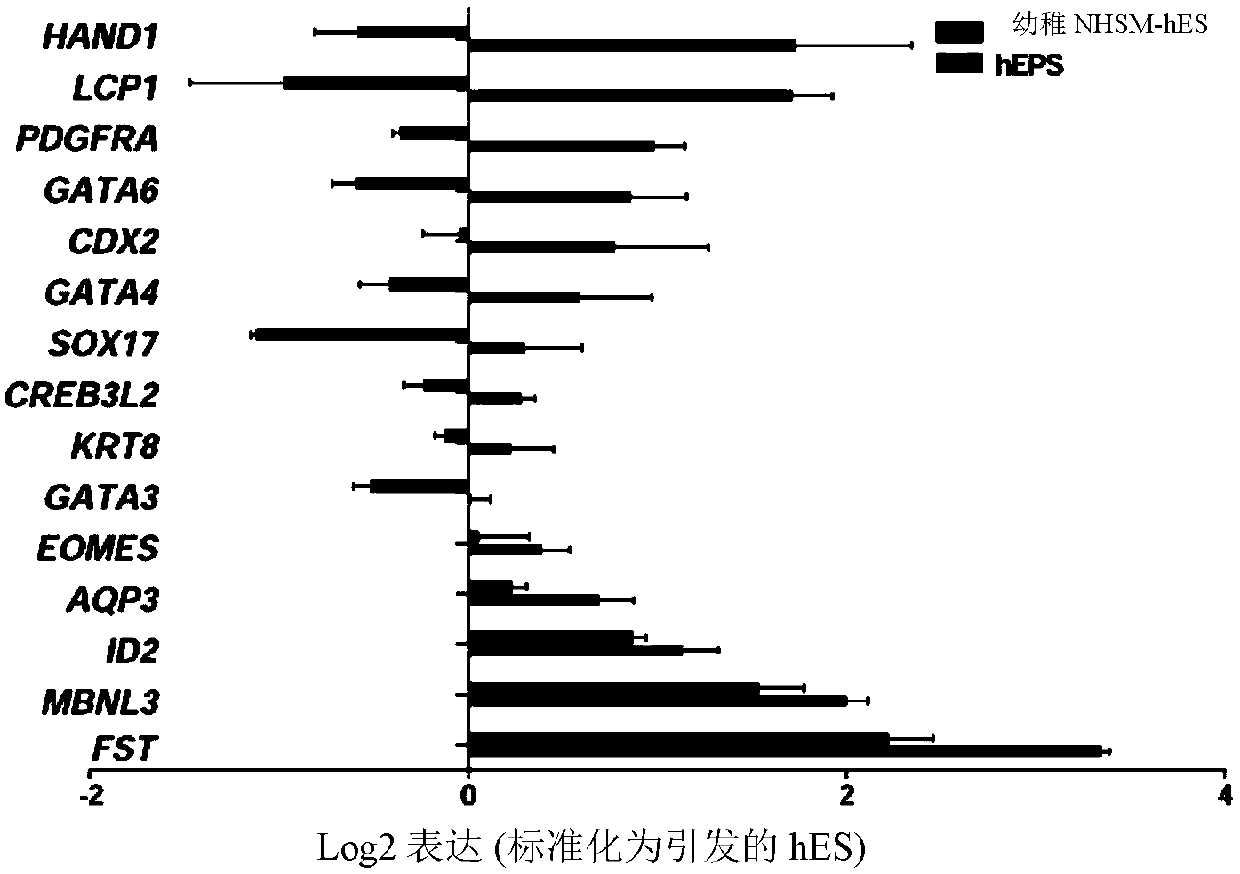
Induced extended pluripotent stem cells, methods of making and using
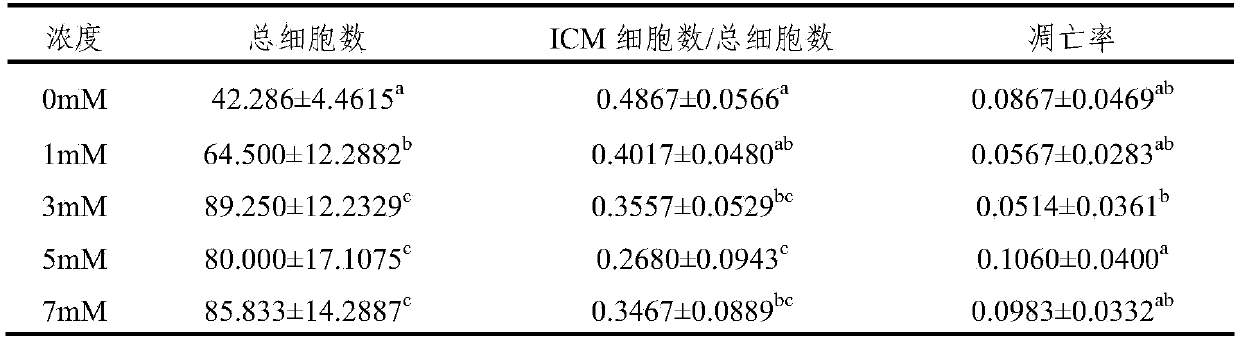
Factors for extending the ability of isolated pluripotent stem cells to generate extraembryonic lineages in vivo, following in vitro culture, herein, chemical extenders of pluripotency (CEP). Methodsof extending the ability of a pluripotent cell to generate embryonic and extraembryonic lineages. The cell to be reprogrammed is contacted with effective amounts of the CEPs for a sufficient period oftime to reprogram the cell into a chemically induced extended pluripotent cell (ciEPSC). ciEPSC are identified as an extended pluripotent cell based on properties including: (i) morphologically and (ii) functionally for example, based on their ability contribute to both TE and ICM, in vivo. The ciEPSCs can be cultured or induced to differentiate into cells of a desired type, and used in a numberof applications, including but not limited to cell therapy and tissue engineering.
Owner:BEIHAO STEM CELL & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST CO LTD +2
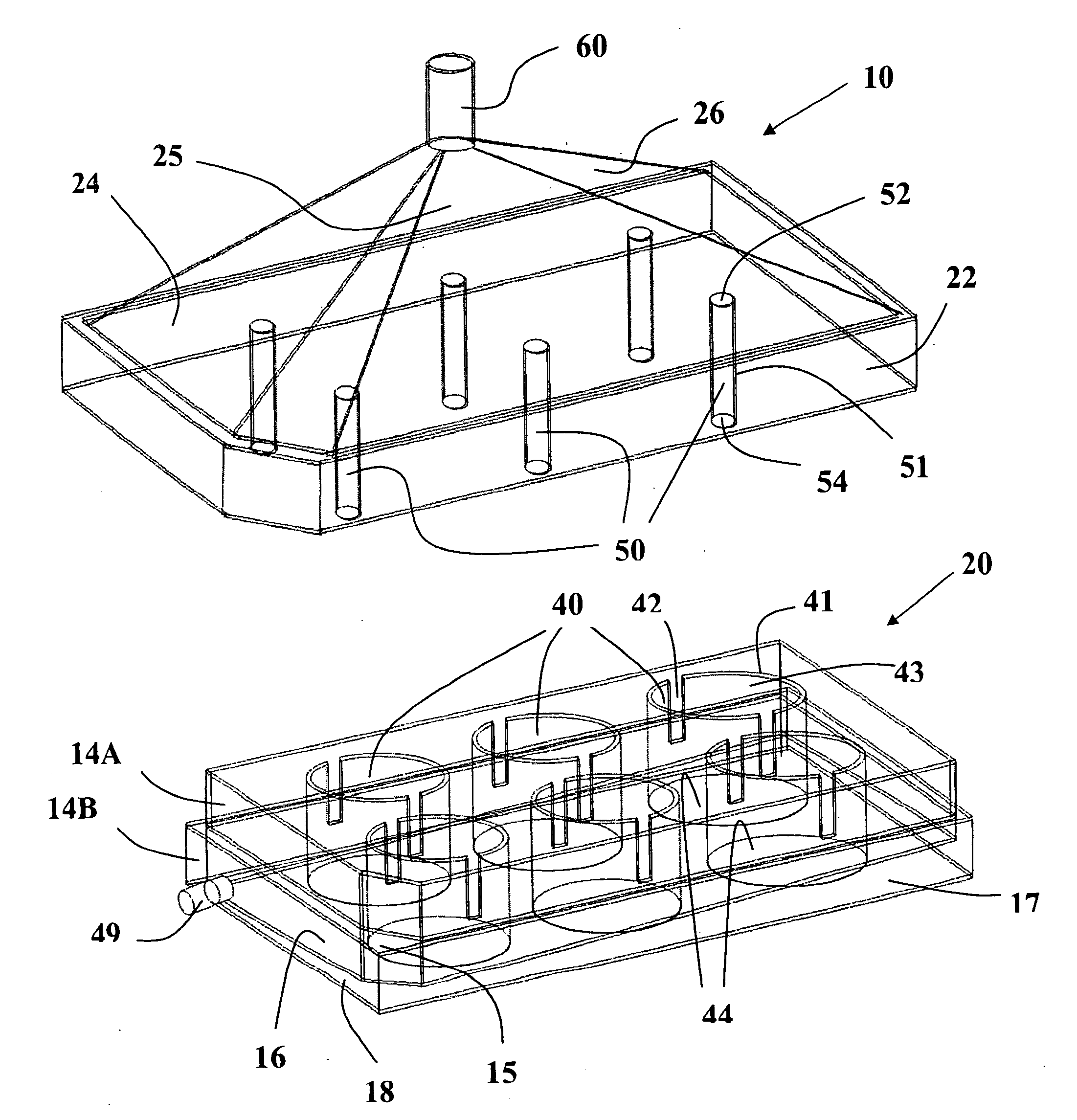
Assembly and methods for cell or tissue culture and treatment
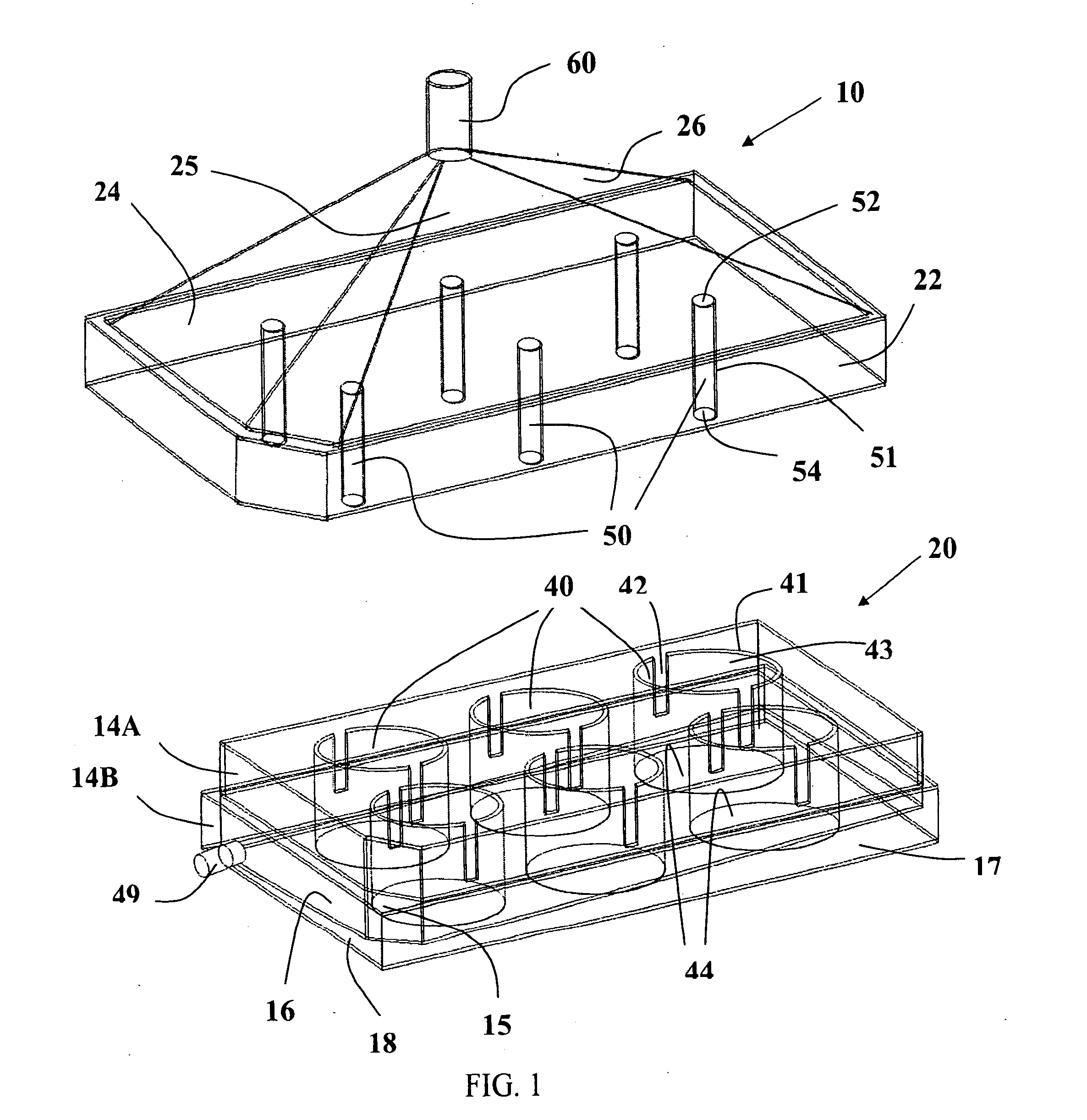
InactiveUS20100029000A1Reduce cross contaminationEasy to watchBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCulture cellMicrobiology
The invention provides an assembly designed under the multiwell plate make and methods of using the same for dynamic-based cell culture and pharmacokinetic-based cell treatment. The assembly comprises a multiwell plate and a lid which permits continuously adding and removing culture medium for culturing cells or tissues in vitro. The dynamic medium makes it possible to culture cells or tissues exposing to changing concentration of a drug candidate over time.
Owner:ZHONG SHILONG +1
METHOD FOR PREPARATION OF PLATELET FROM iPS CELL
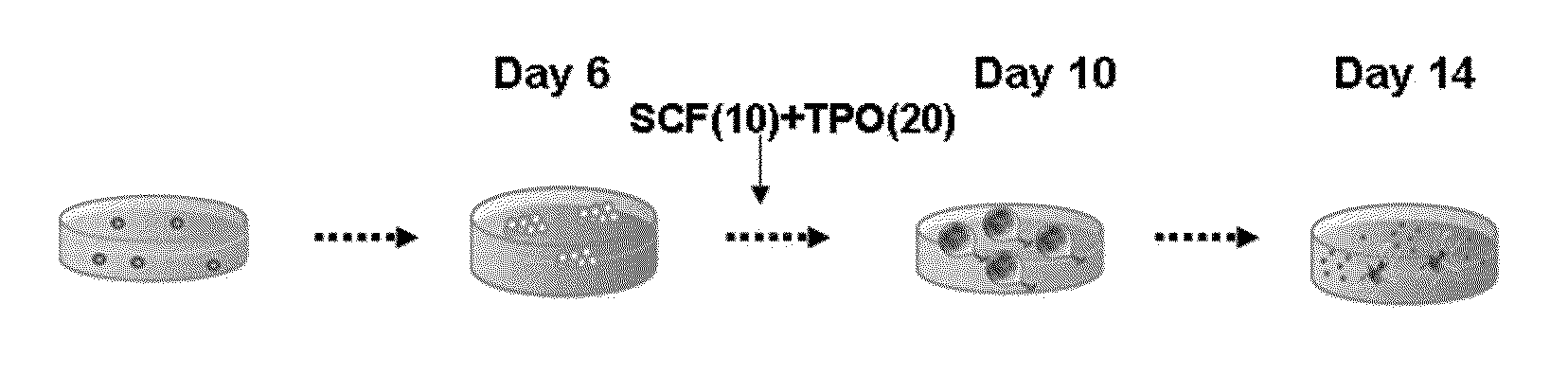
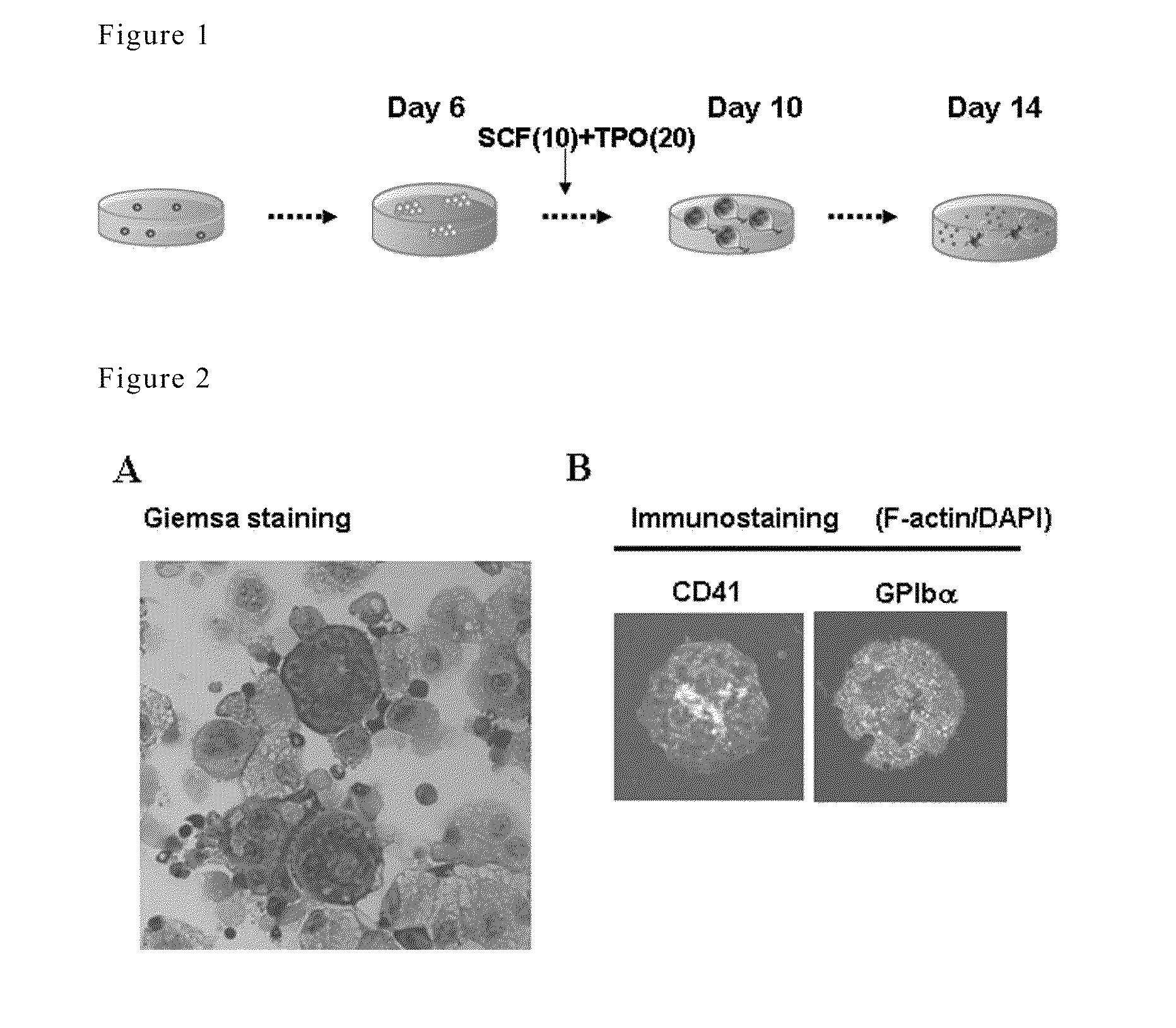
ActiveUS20110053267A1Avoid generationEfficiently obtainMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHematopoietic progenitor cell differentiationMolecular biology
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for efficiently preparing blood cells, such as mature megakaryocytes and platelets, from iPS cells in an in vitro culture system.The present invention provides a sac-like structure enclosing hematopoietic progenitor cells, which is obtained by inoculating iPS cells onto feeder cells and then culturing the iPS cells under conditions suitable for inducing the differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Moreover, the present invention also provides a method for producing various types of blood cells, which comprises culturing hematopoietic progenitor cells enclosed in the sac-like structure under conditions suitable for inducing the differentiation of blood cells. Furthermore, the present invention also provides a method for producing various types of blood cells, particularly megakaryocytes and platelets, without involving the sac-like structure.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Stem cell culture medium and method for culturing endometrium stem cells
InactiveCN105586308ALess prone to agingLess prone to degradationCulture processDead animal preservationSimple componentTrypsinization
The invention provides a stem cell culture medium and a method for culturing endometrium stem cells by using the stem cell culture medium. The method comprises the following steps: separately collecting menstrual blood and endometrium tissues, respectively culturing the menstrual blood and endometrium tissues in the stem cell culture medium provided by the invention to respectively obtain menstrual blood adherent cells and endometrium adherent cells, culturing the menstrual blood adherent cells and endometrium adherent cells in a cell culture bottle, collecting the adherent cells by trypsinization, inoculating the adherent cells in a cell coculture dish, and culturing the adherent cells in the stem cell culture medium provided by the invention. The stem cell culture medium has the advantages of simple components, fewer added components and lower cost. After more than 20 generations of in-vitro culture, the cells can not easily have the phenomenon of aging or degeneration, and can maintain the activity and stem property of the stem cells for a long time. The stem cell culture method is simple and effective, the cell proliferation efficiency is high, and the in-vitro culture doubling time is only 20 hours or so. The cells can be stably amplified by 50 generations.
Owner:HANGZHOU S EVANS BIOSCI LTD
Mass-production method for seedling of seed potato
InactiveUS20070094754A1Maximizing numberPreventing soft rot and rotSeed and root treatmentPlant phenotype modificationNutrient solutionSolanum tuberosum
Disclosed is a method of mass producing potato seedlings, comprising collecting growing points of seed potatoes and culturing the growing points in a liquid or solid medium; introducing in vitro plantlets obtained from the culture of the growing points to solid culture; and removing the in vitro plantlets from the solid culture, and planting through stem cutting and acclimatizing the in vitro plantlets in deep flow culture, in which a nutrient solution is circulating. When in vitro-cultured plantlets are planted in DSCAC through stem cutting, and sprouts from the terminal and lateral buds of the plantlets are hardened by gradually increasing light levels from the dark condition, the plantlets have healthy dark-green leaves and a high accumulation of carbohydrates, thereby obtaining potato seedlings having long stems that appear robust but not overgrown, and elastic and short nodes. Upon planting in hydroponic facilities, such potato seedlings have high adaptability to the external environment and thus rapidly, uniformly generate roots in a short time. The rapid root anchoring prevents planted seedlings from withering, leading to death, growing poorly, and the like. The direct planting of in vitro plantlets through stem cutting without a separate acclimatization process shortens the overall production period of potato seedlings by omitting the acclimatization process.
Owner:KOE SAN COUNTY
Method for minim hepatic tissue in vitro incubation and detecting CYP450 enzymatic activity
InactiveCN101308119AHigh simulationSave costsComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteCytochrome p450 enzyme
Disclosed is a method for detecting CYP450 enzymatic activity by means of micro-liver tissue incubation in vitro, which is characterized in that: a liver trace puncturing method used in clinic takes micro-liver tissues of 0.1 to 0.2g, or kills a mouse to take out the liver in an animal experiment, and builds a micro-liver tissue in vitro incubation system, then uses a one-probe medicine to perform the liquid phase chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for detecting probe substrates and concentration of corresponding metabolites, and obtains the activity of P450 enzyme according to metabolite ratios thereof. The method has the advantages of: 1. micro scale: only micro-liver tissues of 0.1 to 0.2g are needed for detecting cytochrome P450enzyme activity, and can be used for animal experiment and checking clinic micro-liver tissue liver drug enzyme activity; 2. time saving and convenience: costly ultracentrifugation equipment used in the conventional method is saved, costs and time for detection are greatly saved, and liver enzyme metabolic condition simulation is better; and 3. establishing indexes for evaluating the enzyme metabolic activity: metabolite ratios.
Owner:CENT HOSPITAL XUHUI DISTRICT SHANGHAI CITY
Cultural method for inducing human embryonic stem cell to directionally differentiate into corneal limbal stem cell
ActiveCN102952779AGood in vitro differentiation and proliferation abilitySuppress generationArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsImmunofluorescenceMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a cultural method for inducing a human embryonic stem cell to directionally differentiate into a corneal limbal stem cell, which comprises the following steps that firstly, a DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium) / F12 conditioned medium is adopted to culture a human primary corneal limbal stem cell to prepare a corneal limbal stem cell conditioned medium, and then the corneal limbal stem cell conditioned medium is utilized and combined with IV type collagen culture in vitro to induce the human embryonic stem cell to directionally differentiate into the corneal limbal stem cell. According to the corneal limbal stem cell obtained by utilizing the cultural method, through light microscope observation in vitro, electron microscope observation, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, cloning efficiency determination and the like, the induced cell has a similar shape and phenotype with a normal corneal limbal stem cell, has good differentiation and proliferation capacity in vitro, can be transferred in vitro for more than four generations and can be used as a seed cell for preparing a corneal graft.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Human-derived stem cell bioactive substance, its preparation and application
InactiveCN102465148AOvercome purityOvercome yieldArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsOrganismBiology
The invention discloses a human-derived stem cell bioactive substance, its preparation and application. The method comprises: first extracting healthy human-derived stem cells, which are then subjected to in vitro culture and amplification, collecting stem cells of specific phases, and utilizing modern ultralow temperature as well as other biological technologies to prepare a stem cell bioactive substance group composition. Mainly coming from mesenchymal stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells, the stem cell substance group can be developed into products with a cytobiological activity function. When applied on human bodies, the products can activate body stem cells, repair or substitute damaged, pathological and aging cells, adjust the metabolic function of body cells, enhance body immunity, and delay aging, etc. The human-derived stem cell bioactive substance group composition in the invention boasts substantial application prospects in medicine, healthcare and beauty maintaining fields.
Owner:张正前
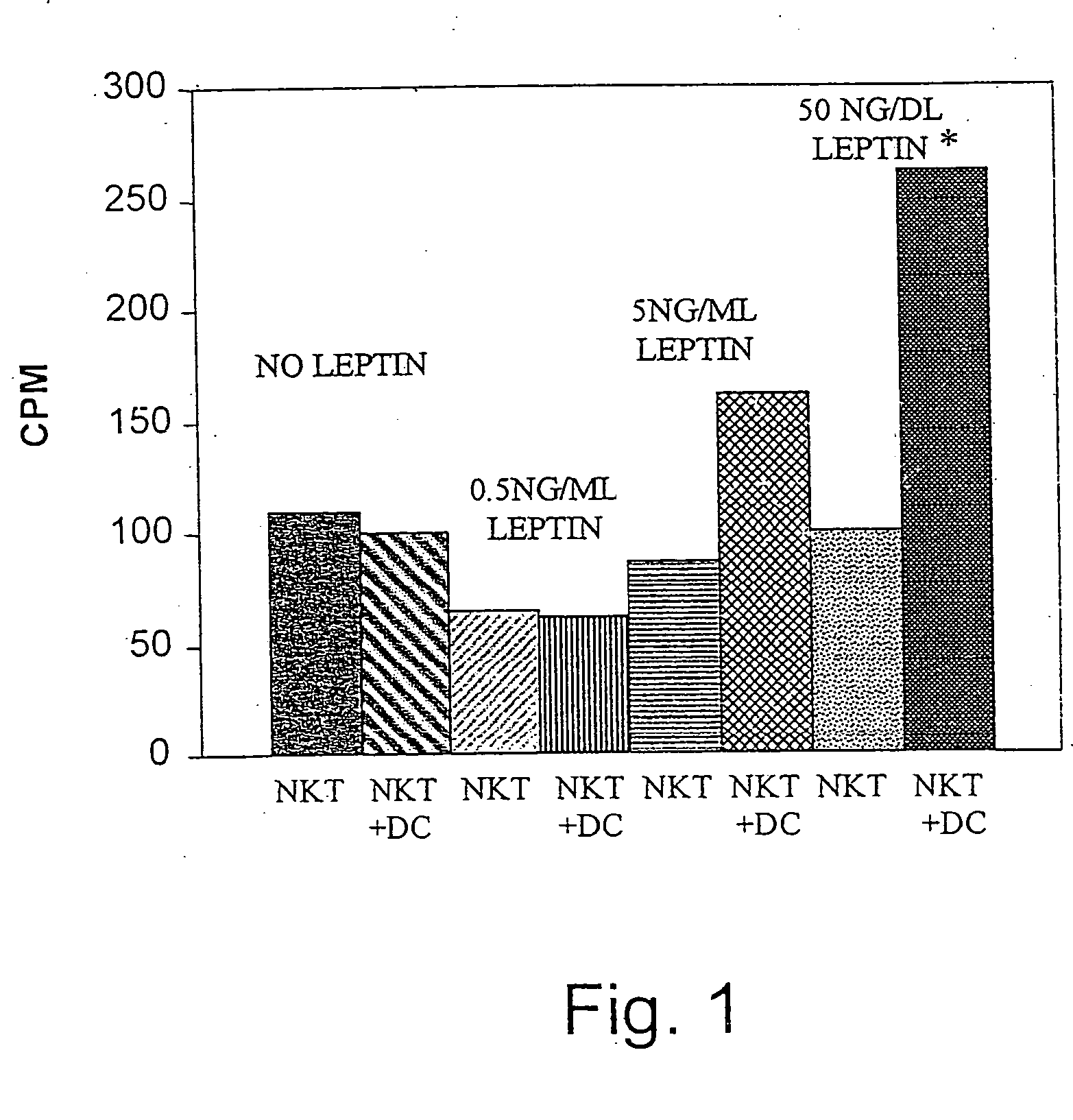
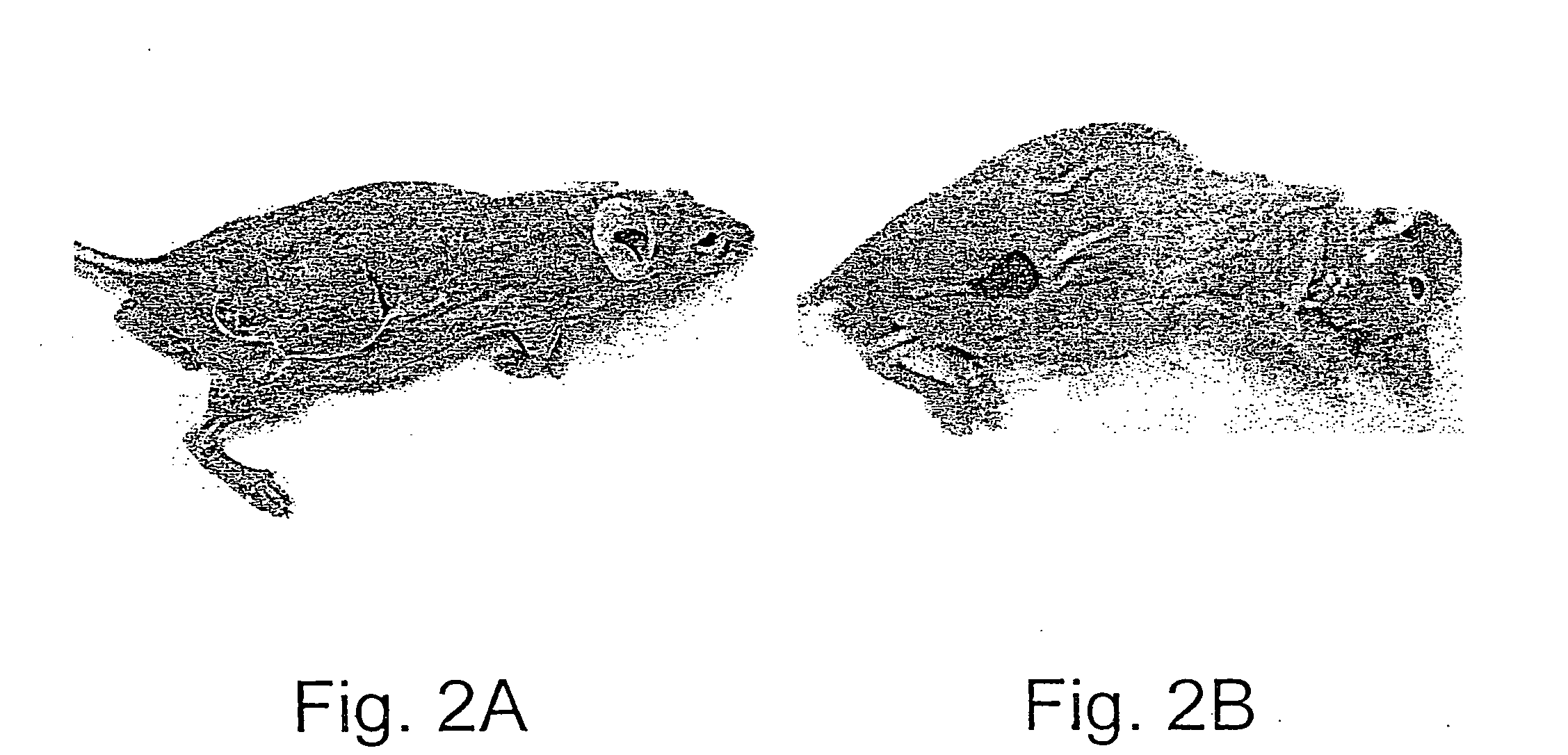
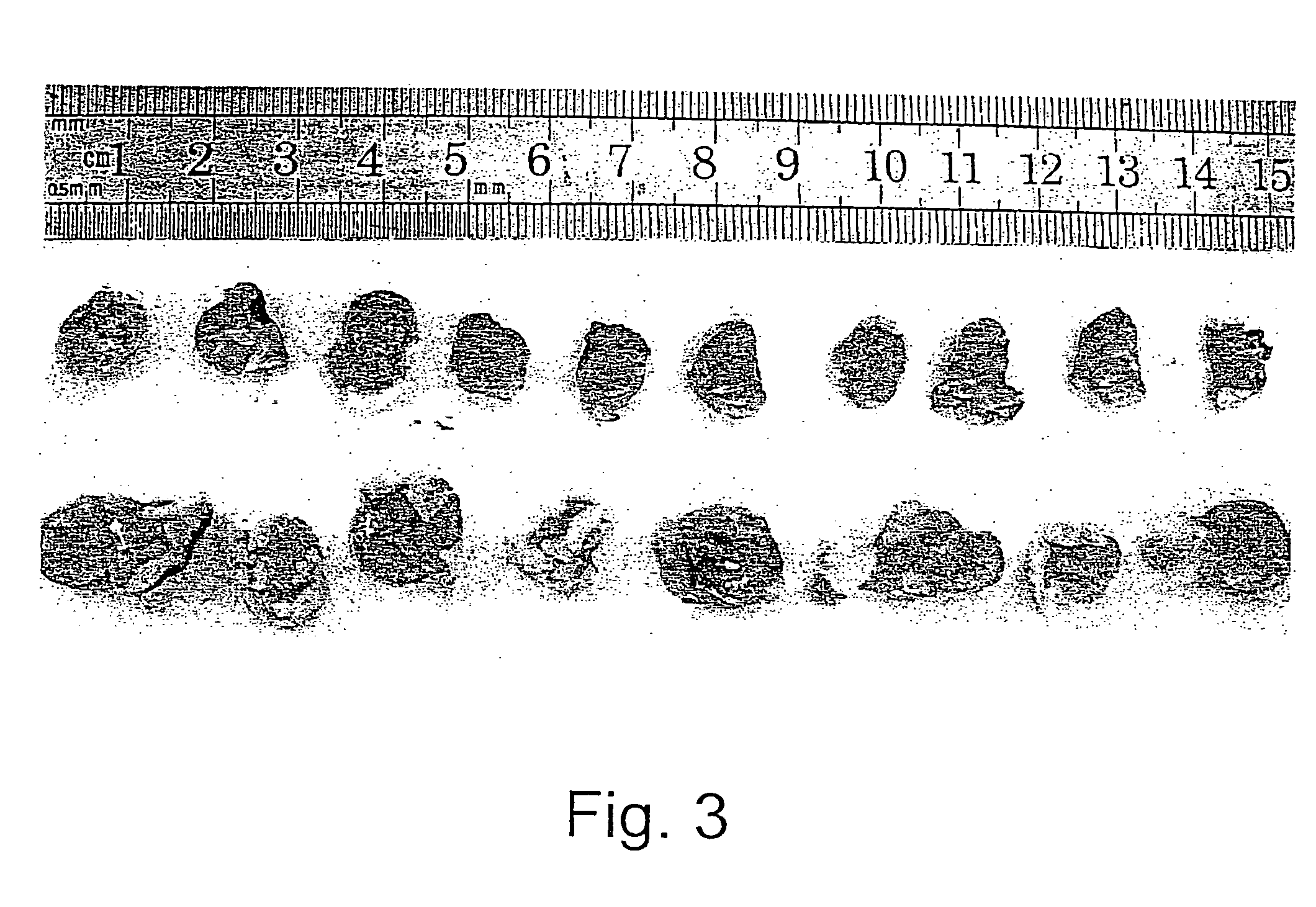
Methods and uses of leptin in immune modulation and hepatocellular carcinoma
Leptin was previously demonstrated to exert potent immune modulatory properties in several immune mediated disorders. The aim of the study was to determine leptin's anti-tumor effect in a murine model of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In vivo, Athymic T cell deficient (nude) mice transplanted with 1×106 human Hep3B cells, followed by administration of two daily intraperitoneal doses of 0.5 mg / gram leptin for 6 weeks. Leptin administration induced a significant reduction in tumor size and improved survival in nude mice. Histologically, tumors of leptin-administered mice featured increased inflammatory exudate in interphase areas. Leptin-induced tumor suppression was associated with a significant increase in peripheral natural killer (NK) cell number. Splenocytes from leptin-treated mice featured decreased expression of CIS mRNA. To determine which lymphocyte subset is a prerequisite for the anti tumor effect of leptin, T&B cell deficient (Scid) mice and T,B& NK deficient (Scid-Beige) mice were subcutaneously implanted with Hep3B tumor cells, with and without the daily intraperitoneal administration of 0.5 mg / gram leptin for 6 weeks. SCID mice featured leptin-associated tumor suppression similar to those of nude mice. In contrast, NK-deficient SCID-Beige mice developed larger tumors. To further establish natural killer cell's central role in mediation of leptin's anti-tumor effect, NK cells were incubated in vitro with increasing doses of leptin, demonstrating a dose-dependent increase in cytotoxic activity. Incubation of leptin with hepatoma cell line was found to induce a dose-dependent reduction in hepatoma cell proliferation, suggesting an additive direct anti-tumor effect. Further synergism in inhibition of hepatoma cell proliferation in vitro was achieved following addition of natural killer cells. HCC cells expressed leptin receptor mRNA, while addition of leptin induced increased mRMA expression of STAT2 and SOCS1 on tumor cell lines. Leptin administration induces a significant suppression of human HCC. This effect is mediated by induction of natural killer cell proliferation and activation, and by direct inhibition of tumor growth. Decreased natural killer cell expression of inhibitory CIS protein and over expression of the anti-proliferative STAT2 and SOCS1 proteins in HCC lines may underline both anti cancerous effects of leptin.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS
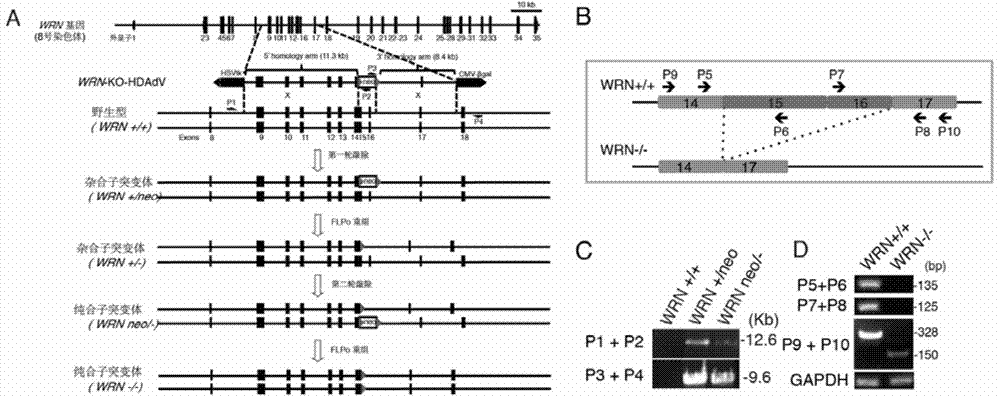
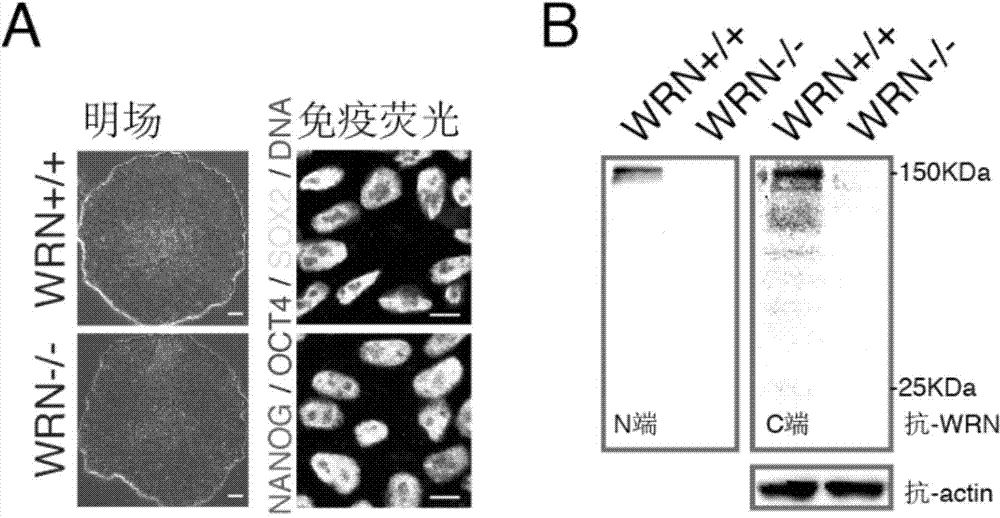
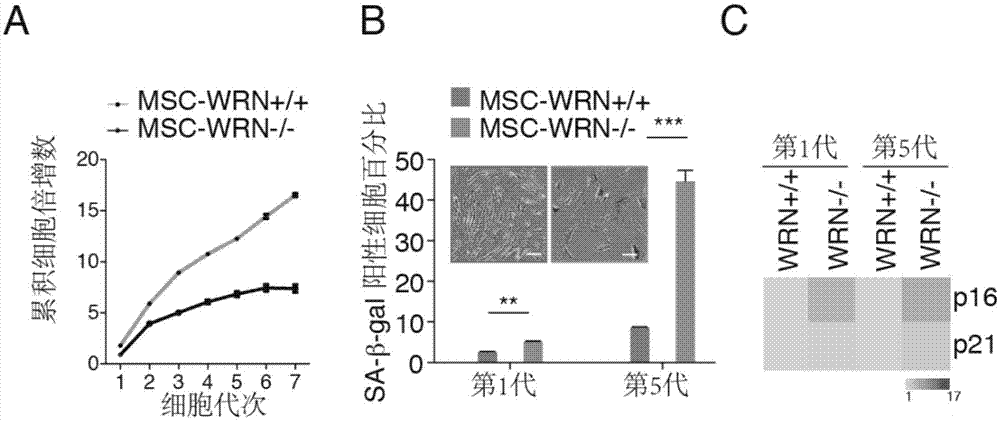
Multipotent stem cells carrying human adult premature senility syndrome gene mutations and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104726496ASlow down natural agingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringPremature senility syndromeMesenchymal stem cell
The invention discloses multipotent stem cells carrying human adult premature senility syndrome gene mutations, mesenchymal stem cells and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking human multipotent stem cells cultured in vitro, and mutating human adult premature senility syndrome genes WRN in the human multipotent stem cells to enable the WRN to lose functions, so as to obtain the human multipotent stem cells with the function-lost WRN; and (2) carrying out induced directional differentiation on the human multipotent stem cells with the function-lost WRN to obtain the mesenchymal stem cells with the function-lost WRN. The mesenchymal stem cells derived from the multipotent stem cells provided by the invention can be used for establishing a medicine screening platform for screening a WS treatment medicine, and providing more clues for delaying a natural senility process.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Method for in vitro culture of lymphocytes and composition for use in immune therapy
InactiveUS20040161433A1Reduce expressionEasily damagedBiocideGenetically modified cellsAntigenCancer cell
The method for in vitro culture of lymphocytes involves incubating lymphocytes and cells with a particular gene expressed in a particular cancer cell line or cells, which are deficient or lowered in expression of a class 1 antigen and the particular gene has already been expressed, to amplify mainly NK cells or non-MHC-bound or MHC-bound killer T cells and then to amplify killer T cells specific to an antigen to a cancer. The in vitro culture of the lymphocytes can produce a group of lymphocytes composed mainly of killer cells. The group of the lymphocytes so produced can be used for immune therapy effective even for patients with cancer in the terminal stage to whom conventional cancer treatment and cancer curing agents.
Owner:TESHIGAWARA KEISUKE +1
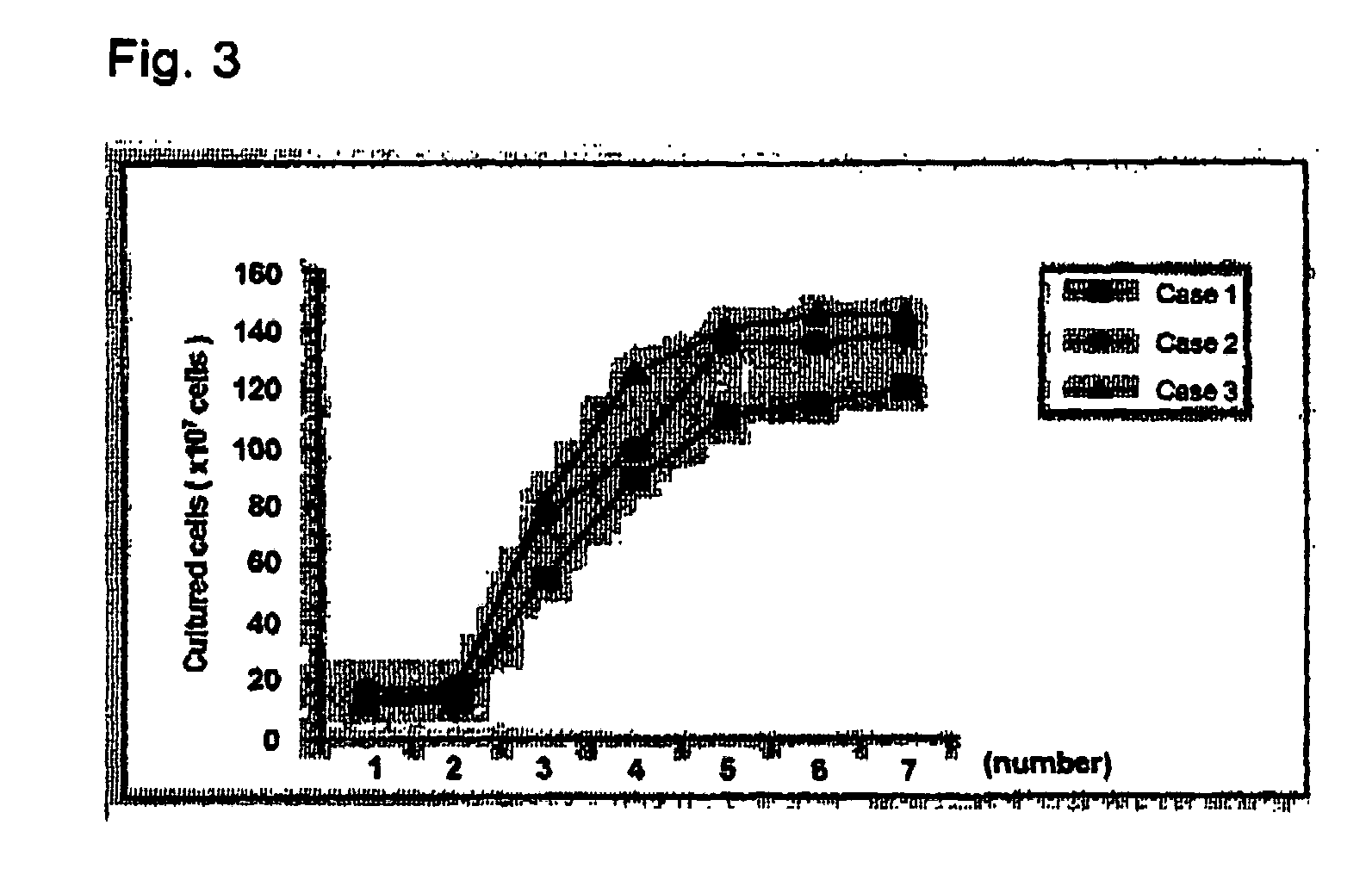
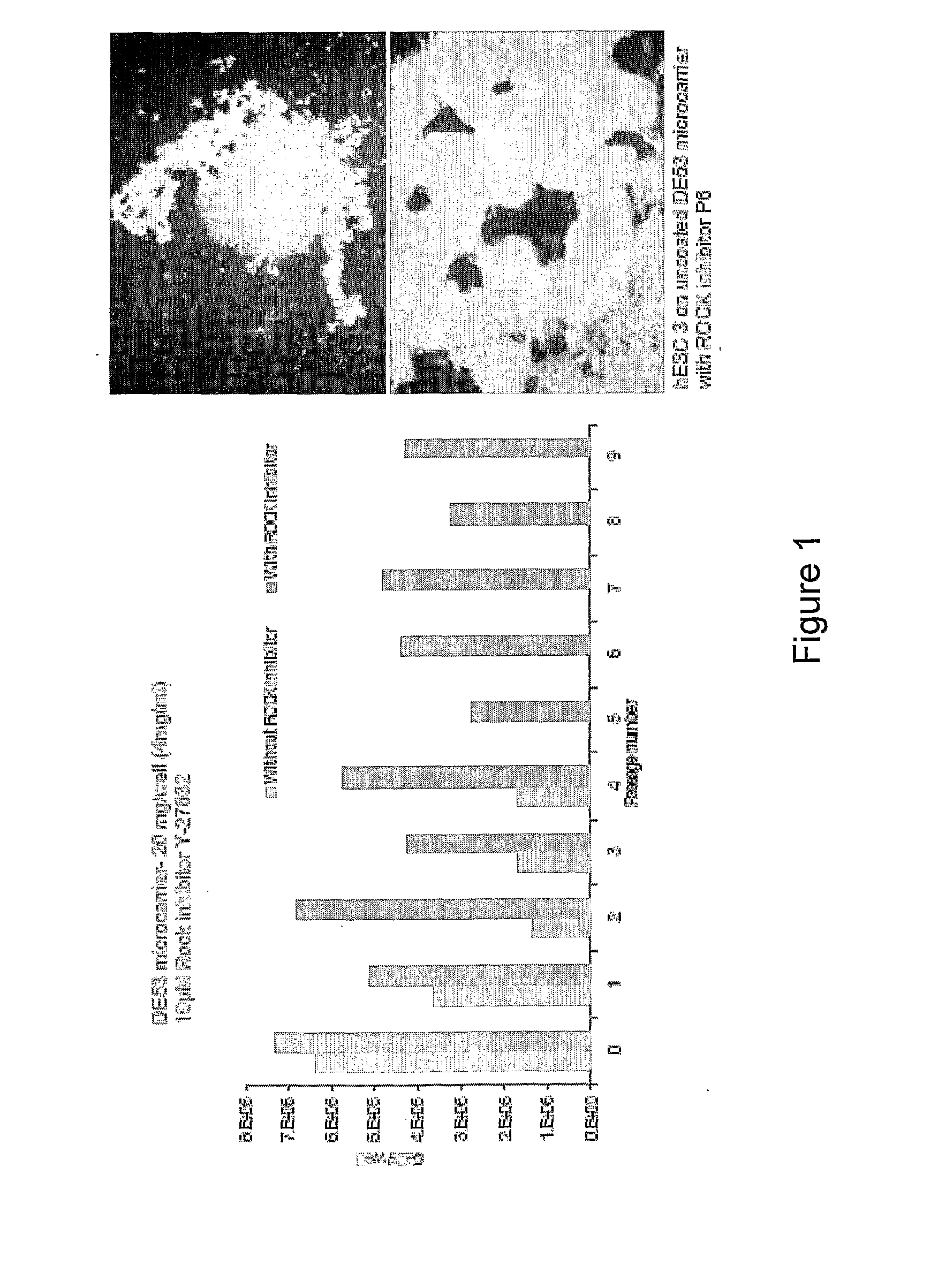
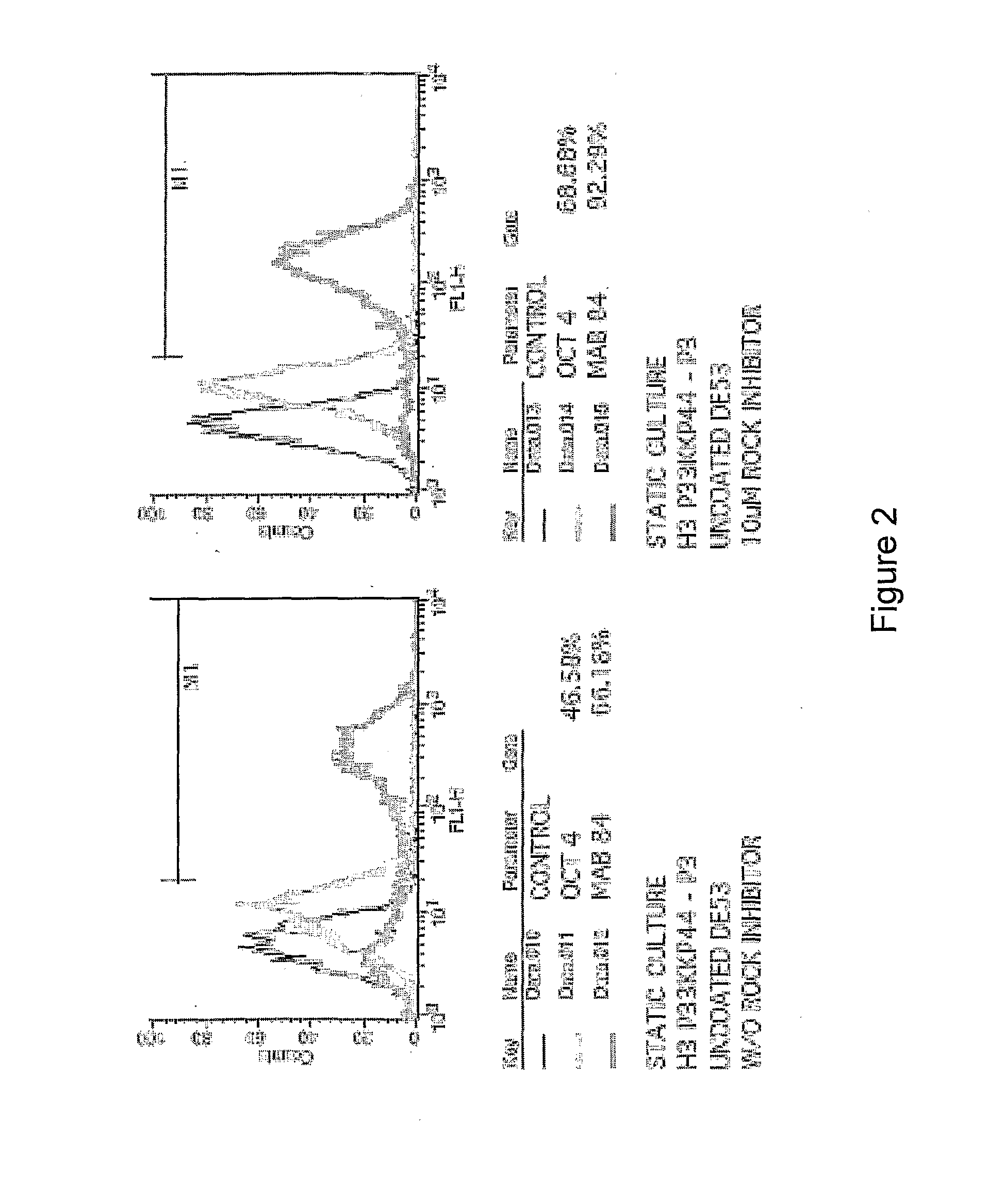
Culture of pluripotent and multipotent cells on microcarriers
ActiveUS20120009645A1Maintaining pluripotent statusProcess stabilityArtificial cell constructsMicrocarriersMicrocarrierMultipotent cell
A method is disclosed for culturing pluripotent or multipotent cells in vitro, the method comprising attaching pluripotent or multipotent cells to a plurality of microcarriers to form microcarrier-cell complexes, and culturing the microcarrier-cell complexes in suspension culture in the presence of a ROCK inhibitor.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
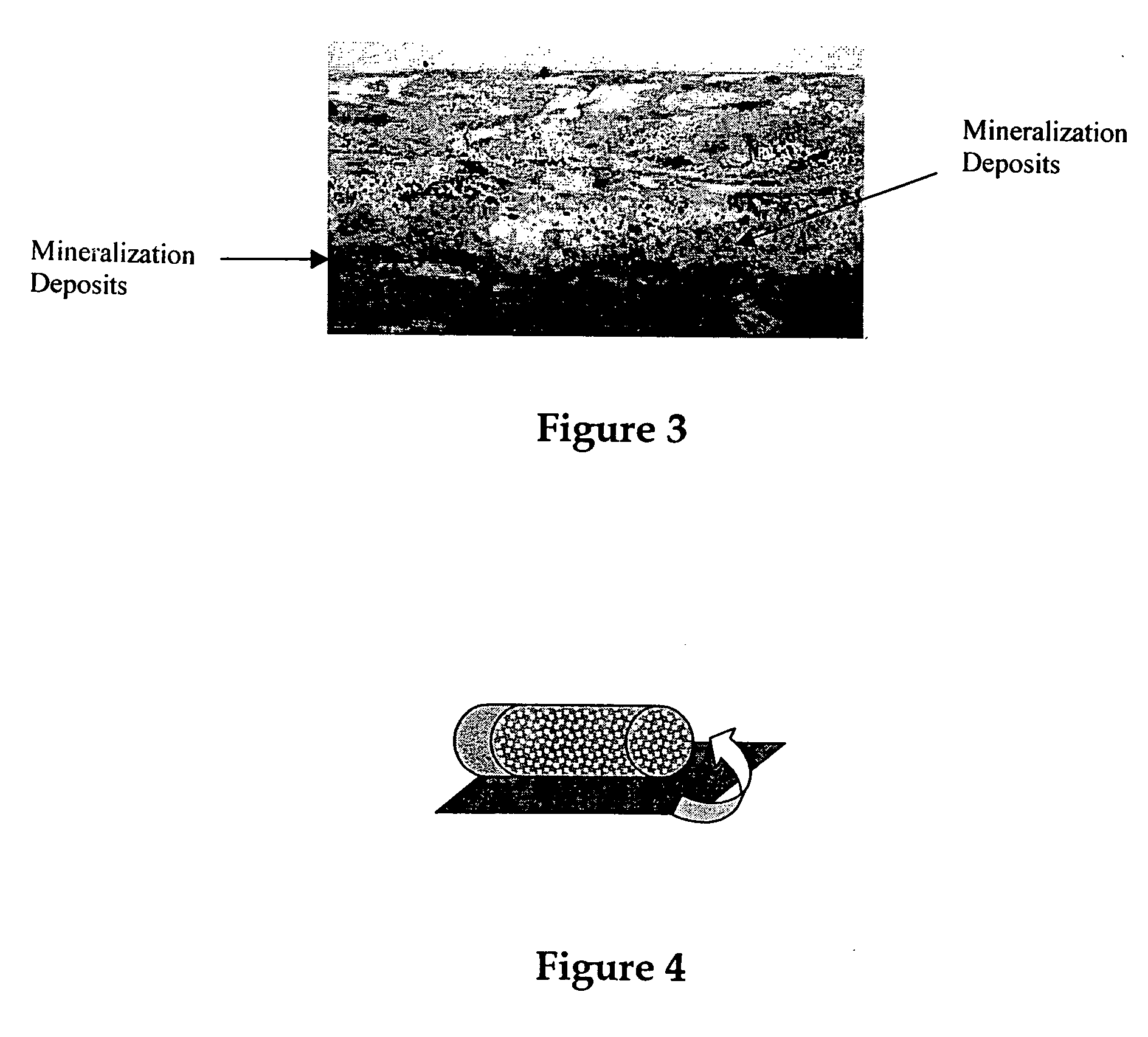
Cell constructs cultured in vitro, preparation and uses
InactiveUS20050053585A1Improve propertiesFacilitates merging and remodelingBiocideCulture processTissue architectureCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present invention relates to a cell construct cultured in vitro characterized in that it comprises (i) animal cells cultured in vitro in conditions ensuring formation of a three-dimensional tissue structure and (ii) an endogenous extracellular matrix in which said cells are imprisoned, and in that it comprises, among said cells, cells having a mineralization and / or ossification capacity. The invention is particularly useful in the fields of grafts and implantology (tissue reconstruction or repair), as well as in the pharmaceutical industry, for research on tissue and analysis of the toxic or beneficial profile of molecules capable of being used in pharmaceutics development and / or pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:NATURAL IMPLANT
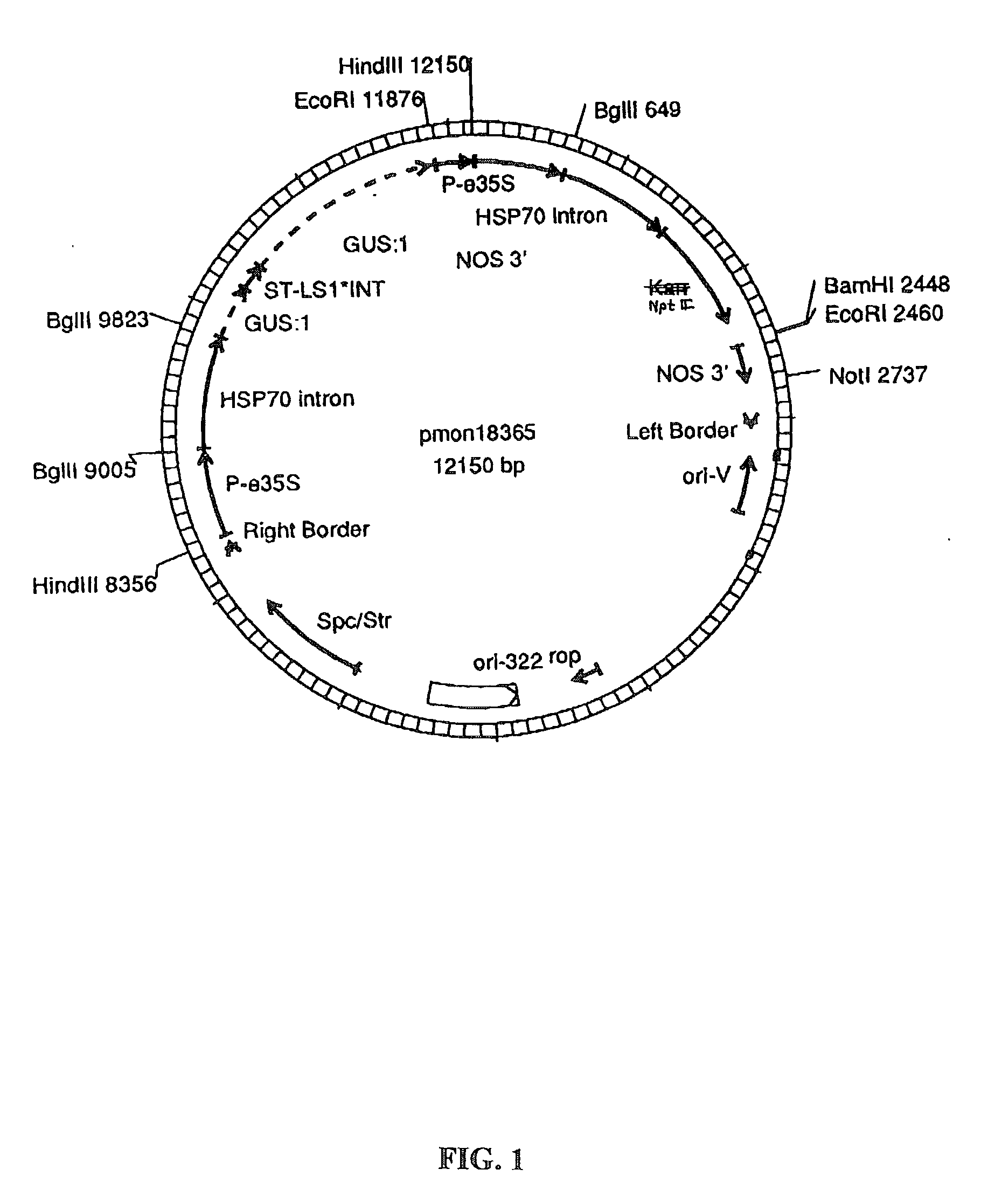
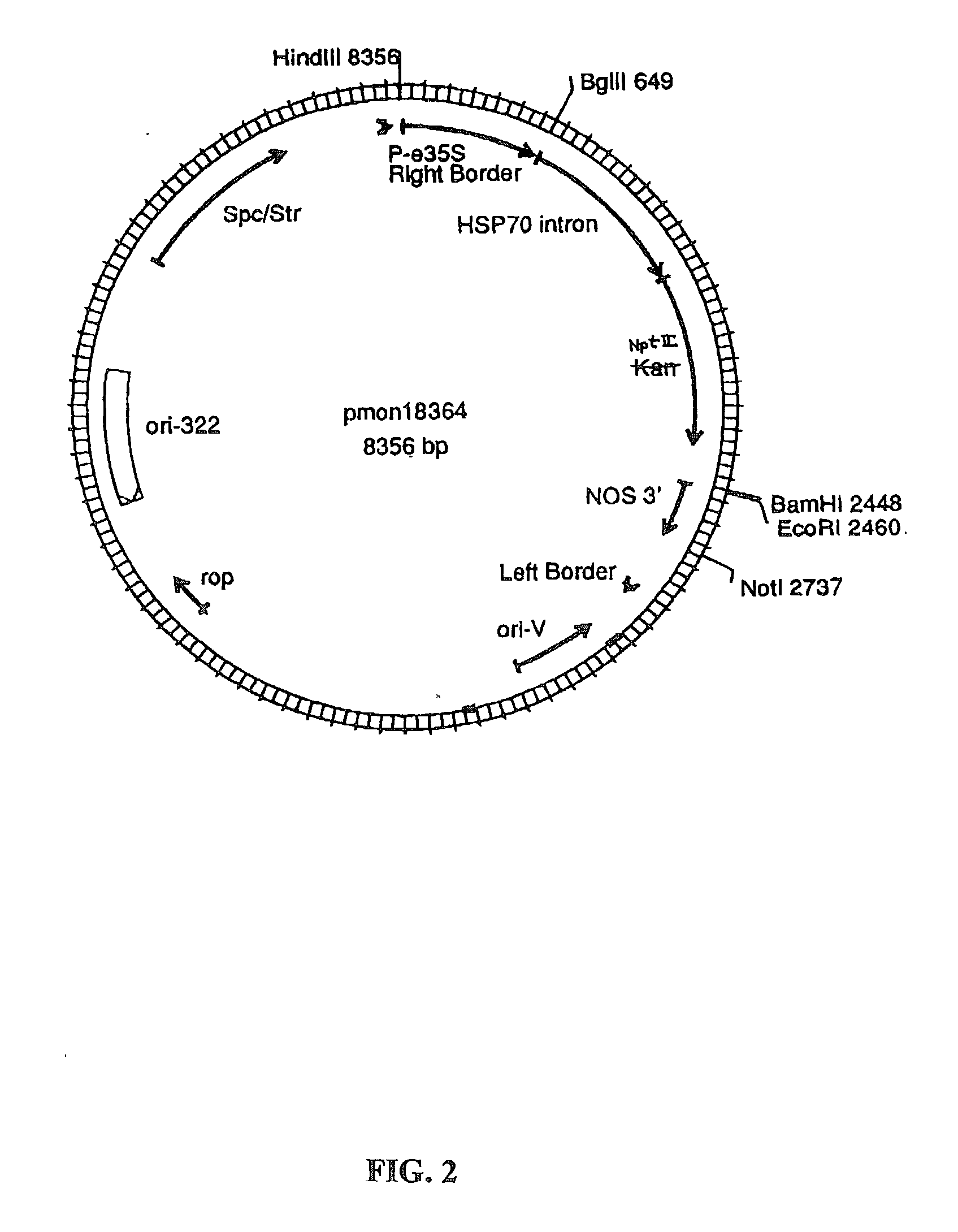
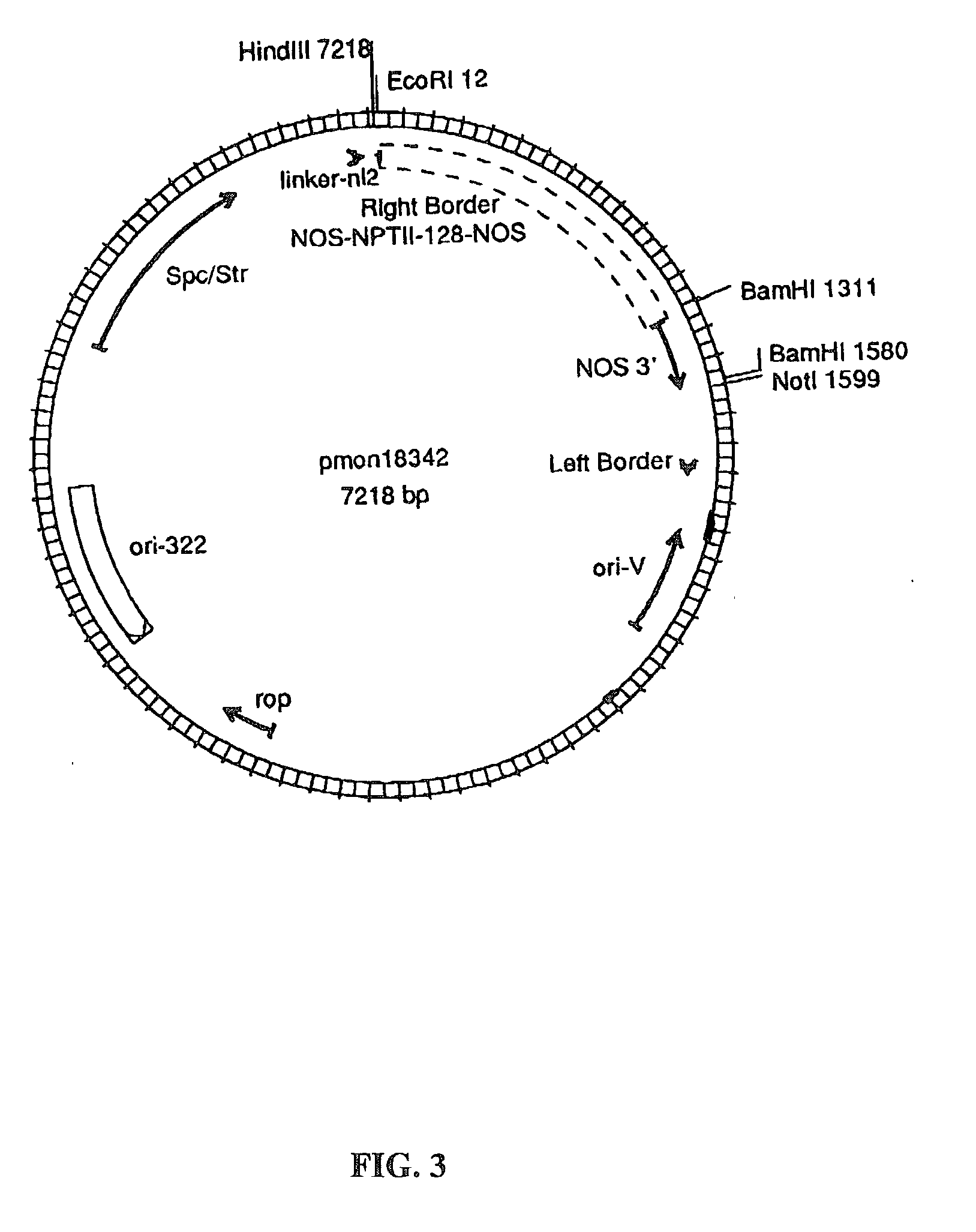
Methods for the production of stably-transformed, fertile wheat employing agrobacterium-mediated transformation and compositions derived therefrom
InactiveUS20030024014A1Efficient conversionOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureSomaclonal variationEmbryogenesis
Disclosed are processes for producing stably transformed fertile wheat a system of transforming wheat via Agrobacterium. This invention provides methods transforming a variety of explants, such as freshly isolated or pre-cultured immature embryos, embryogenic callus and suspension cells. Also disclosed are methods for recovering transgenic plants after transformation within a short period of time, if the explants are regenerable at the time of transformation. Thus the frequency of somaclonal variation associated with prolonged in vitro culture period is significantly reduced. The transformation frequency using this system is comparable to or better than published methods using other systems, such as microprojectile bombardment.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for the in vitro culture of Sporozoea sp. and uses thereof
The invention relates to a method of excysting and growing protozoal oocysts by in vitro tissue culture resulting in production of a continuous culture of merozoites. The invention also provides an economical and reliable supply of cultured Eimeria sp. for vaccine production, assays and research. Domesticated avians that have been vaccinated using the provied Eimeria sp. are also provided.
Owner:PATHOGENES +2
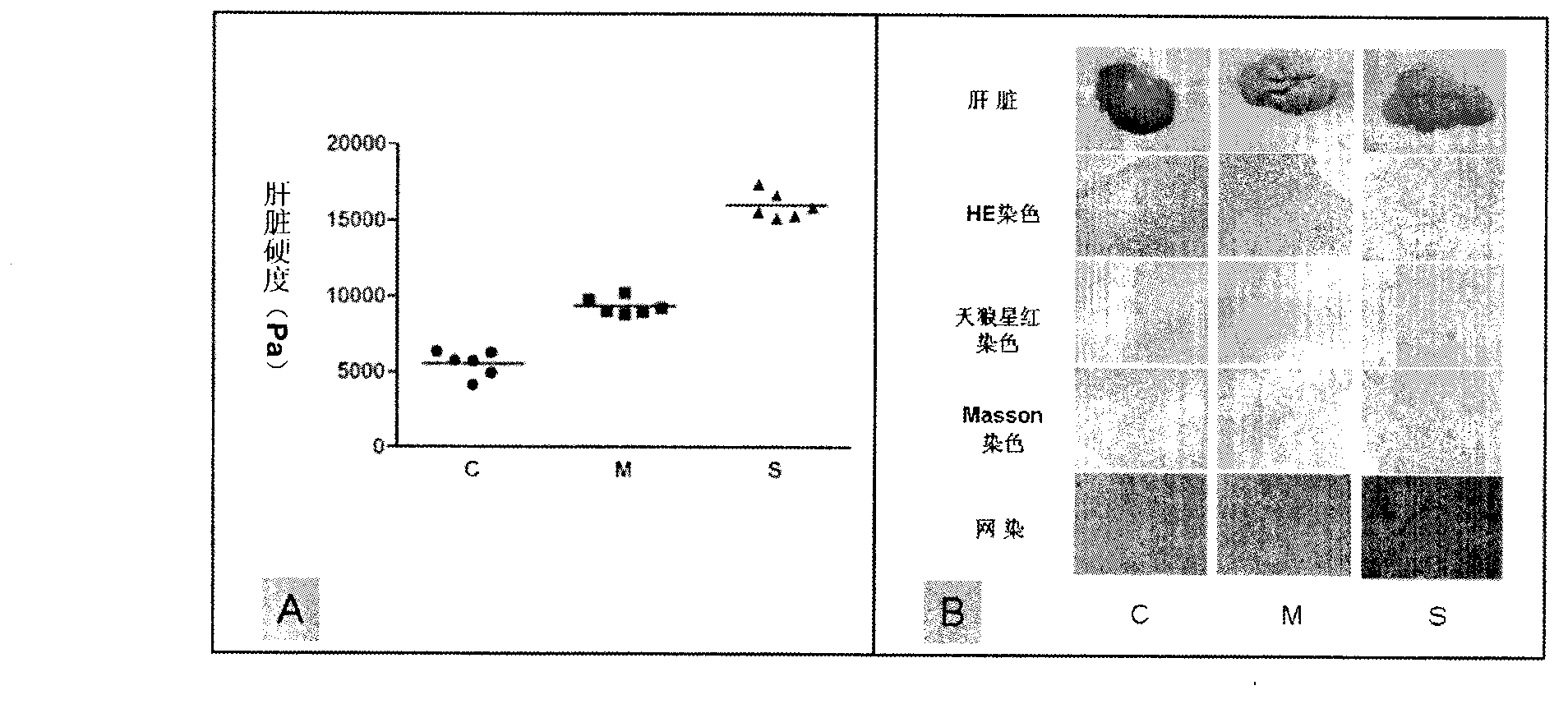
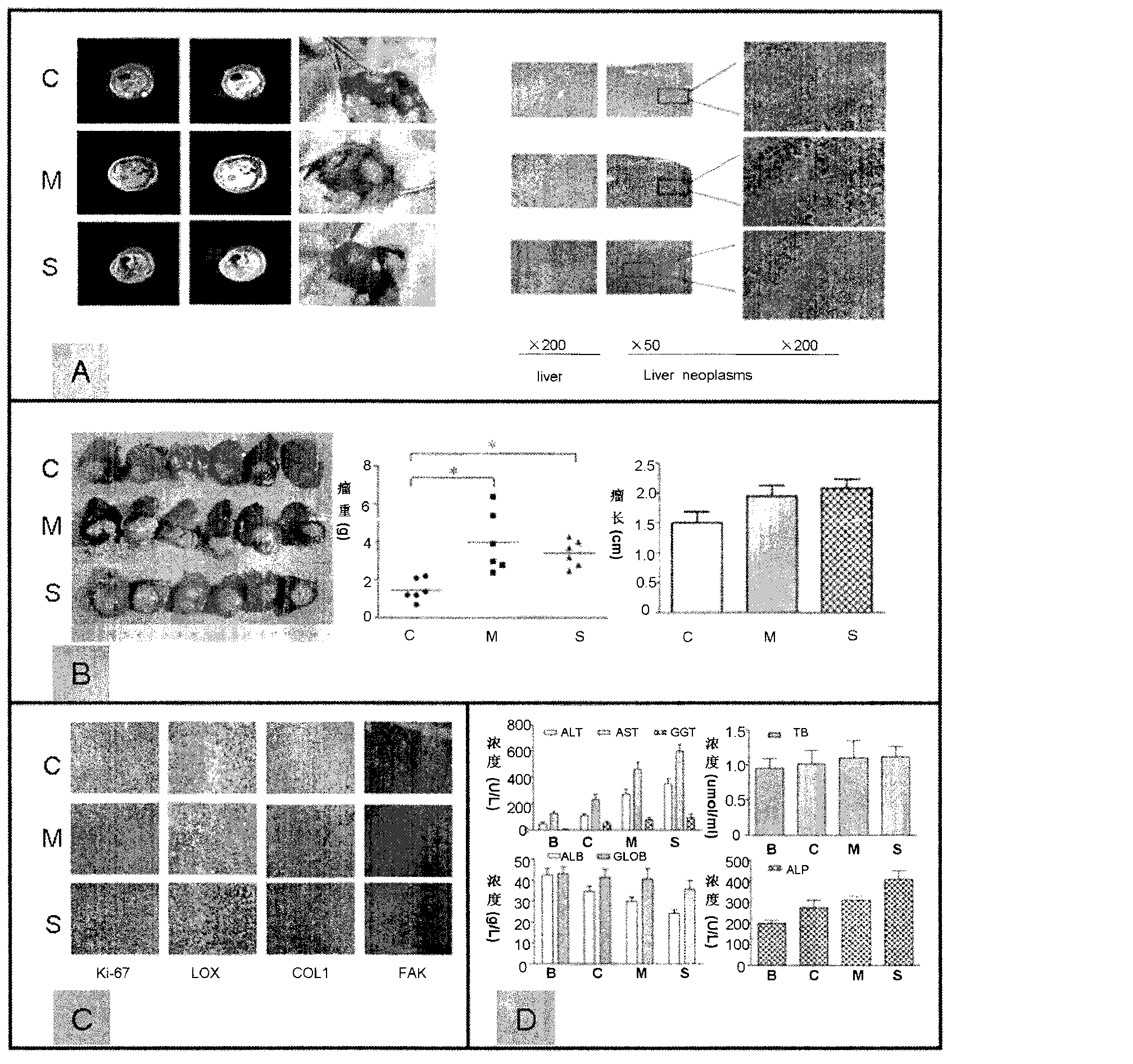
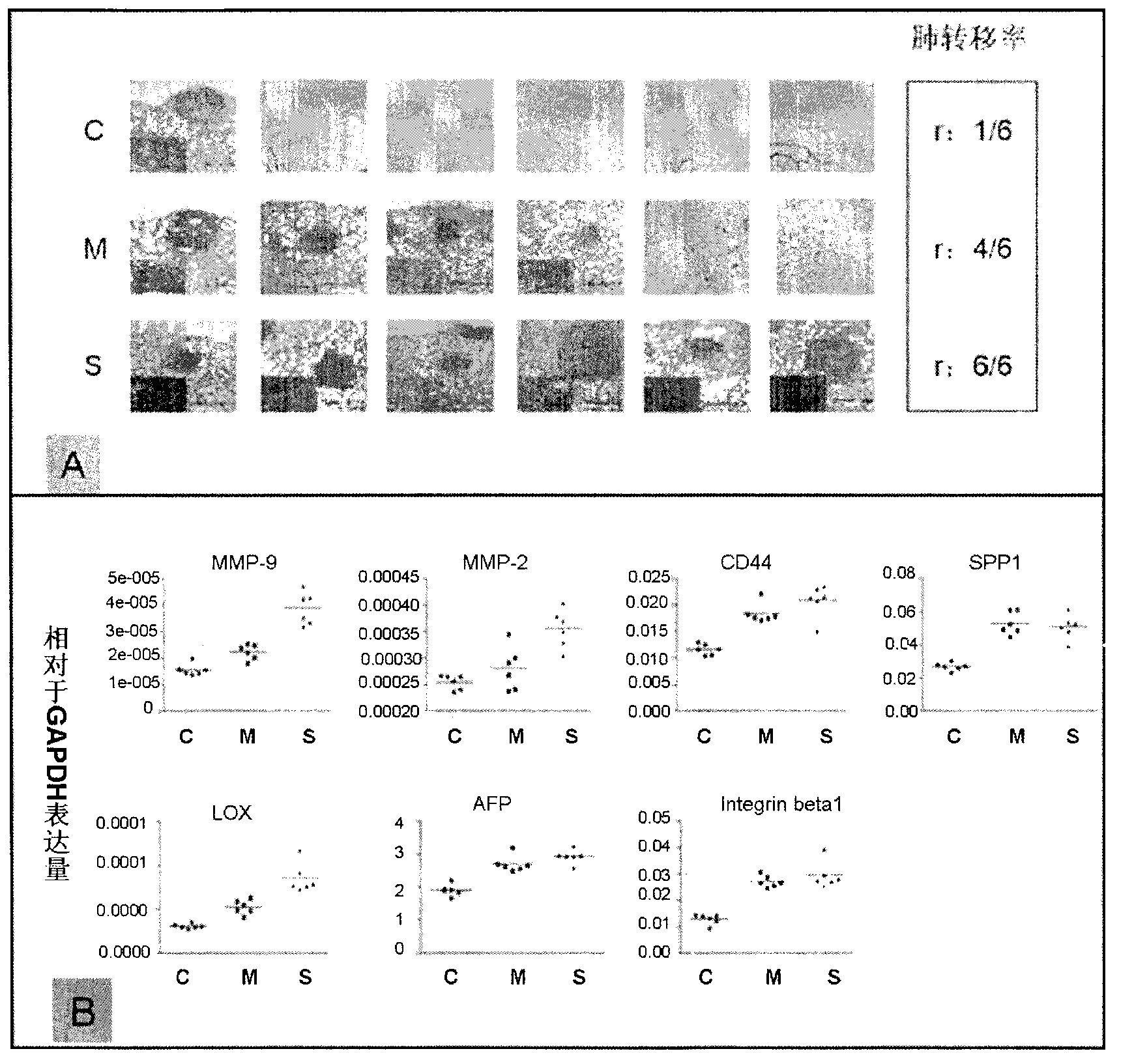
Rat liver cancer model with different liver matrix hardness backgrounds and preparation method of rat liver cancer model
InactiveCN103191148AReduce mortalityAvoid source complex featuresInorganic active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRat liver
The invention relates to a rat liver cancer model with different liver matrix hardness backgrounds and a preparation method of the rat liver cancer model. The method for preparing the rat liver cancer model with different liver matrix backgrounds is characterized by specifically comprising the following steps of: after grouping the rats, injecting pure carbon tetrachloride to an abdominal region in a hypodermic manner; injecting a carbon tetrachloride-olive oil solution to the abdominal region in the hypodermic manner; detecting through a texture analyzer to form the rat model with different liver matrix hardness; taking liver cancer cells which are in-vitro cultured and grown well and injecting the liver cancer cells to the rat to form hypodermic liver cancer cells; in-situ planting the formed liver cancer tumor source to the rat model with different liver matrix hardness to obtain the rat liver cancer model with different liver matrix hardness backgrounds. The rat liver cancer model with different liver matrix hardness backgrounds can be used for well displaying liver cancer malignant pathological characteristics under the liver matrix hardness interference, simulating and reproducing pathological characteristics of clinical liver matrix hardening background liver cancer and solving the problems that an ideal experiment system, an animal model and the like are lacked in reaching the development of the liver cancer due to the liver matrix hardness changes.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Construction method of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell bank
ActiveCN103422176AWide variety of sourcesUnrestricted by ethicsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLibrary creationSingle cell suspensionPancreatic hormone
The invention relates to a construction method of a human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell bank. The construction method comprises the following steps: taking a human amnion for detection, flushing and washing the human amnion with a phosphate buffered solution, then smashing the human amnion, diluting with the phosphate buffered solution, digesting with trypsin, digesting with collagenase IV and deoxyribonuclease I, and filtering to obtain a single-cell suspension; by adding human serum albumin, transferring, insulin and sodium selenite into a DMEM / F12 basal culture medium with the ratio of VDMEM to VF12 being 1 to 1, placing human amnion mesenchymal stem cells in an incubator under the serum-free condition, and then performing liquid exchange and culture transfer; subjecting the mesenchymal stem cells obtained through in vitro culture and proliferation to liquid nitrogen refrigeration, and preserving the cells according to the gender of newborn infants, the ABO / Rh type and the HLA type; establishing cell information files, so that the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell bank is constructed. The method has the characteristics of no other animal derivation, wide source range and no ethic limitation. With adoption of the method, the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells can be provided for cell therapy and other application.
Owner:沈阳艾米奥生物工程技术研发中心有限公司
Obtaining method of stem cell conditioned medium, and application of stem cell conditioned medium in skin ageing resistance
Owner:河南中科干细胞基因工程有限公司
Composite microcapsule model for use in in-vitro cell coculture
ActiveCN102286422AGood biocompatibilityReduce physical damageTissue cultureOn/in organic carrierCell-Extracellular MatrixEngineering
The invention discloses a composite microcapsule model for use in in-vitro cell coculture. The model is a sphere-in-sphere composite microcapsule model consisting of an inner sodium alginate gel microsphere and an outer sodium alginate gel microsphere, which is formed by using natural polysaccharide sodium alginate as a substrate material, dripping the polysaccharide sodium alginate into multivalent cation solution and performing gelatinization treatment twice, wherein the two gel microspheres may contain two different kinds of cells. The model can be used for the study on in-vitro coculture of various cells and overcomes the drawback that the interaction between cells of the same kinds and the interaction between cells of different kinds cannot be controlled, the drawback that different kinds of cells are difficult to separate in late-stage study and the drawback that cell dependency exists of the conventional coculture model; and the model can simulate cell-cell interaction, cell-extracellular matrix interaction and cell-soluble factor interaction and provide theoretical and technical support for in-vitro construction of a tumor model, optimization of in-vitro culture mode of cells and tissue engineering construction of various tissue and organ analogues or equivalents.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com