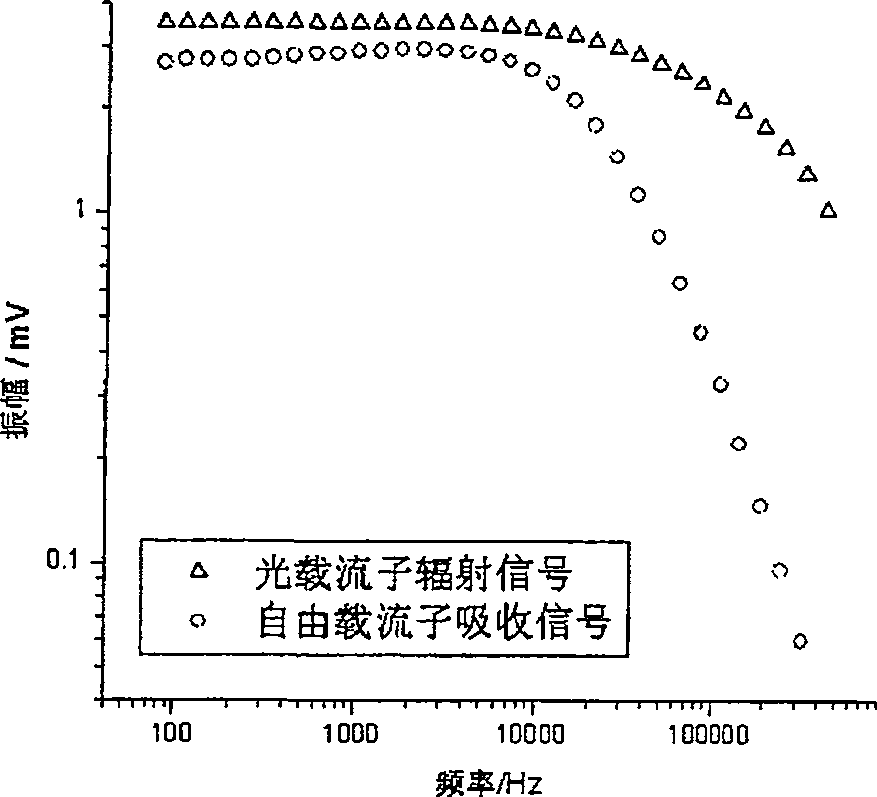
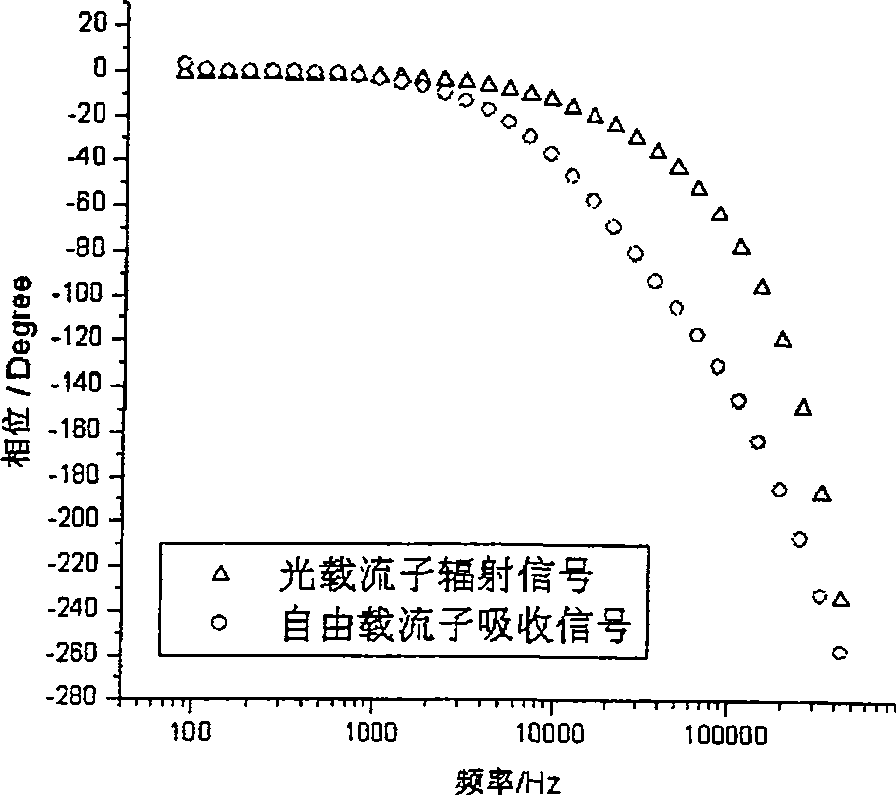
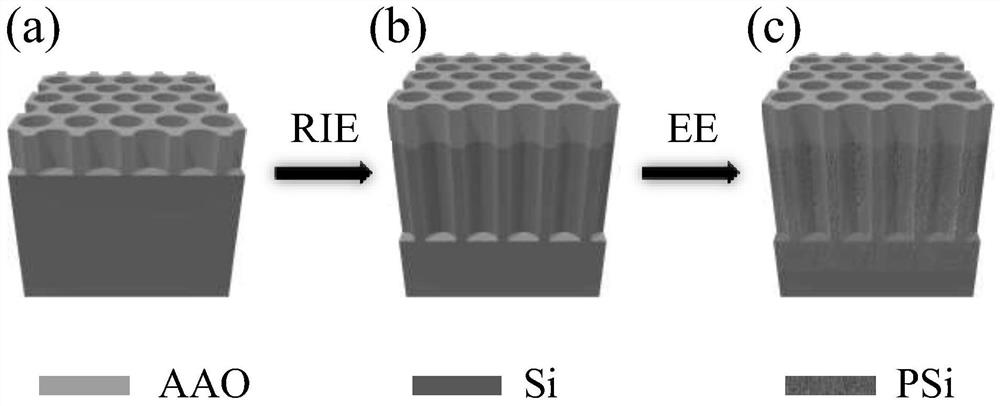
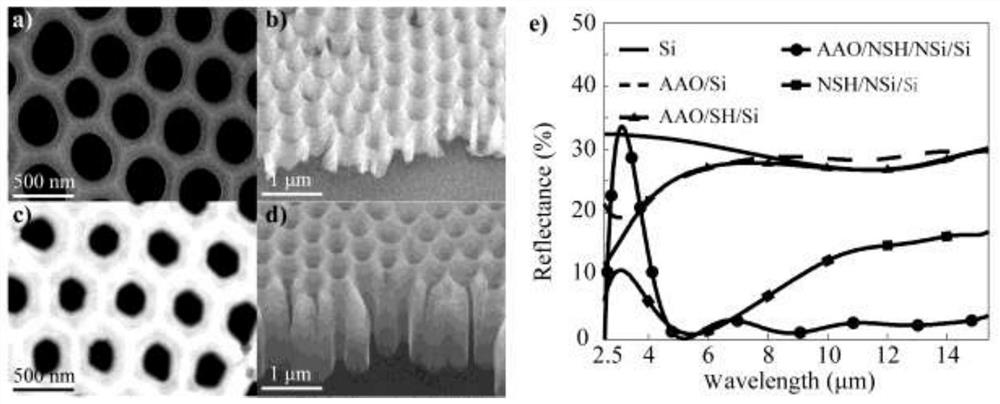
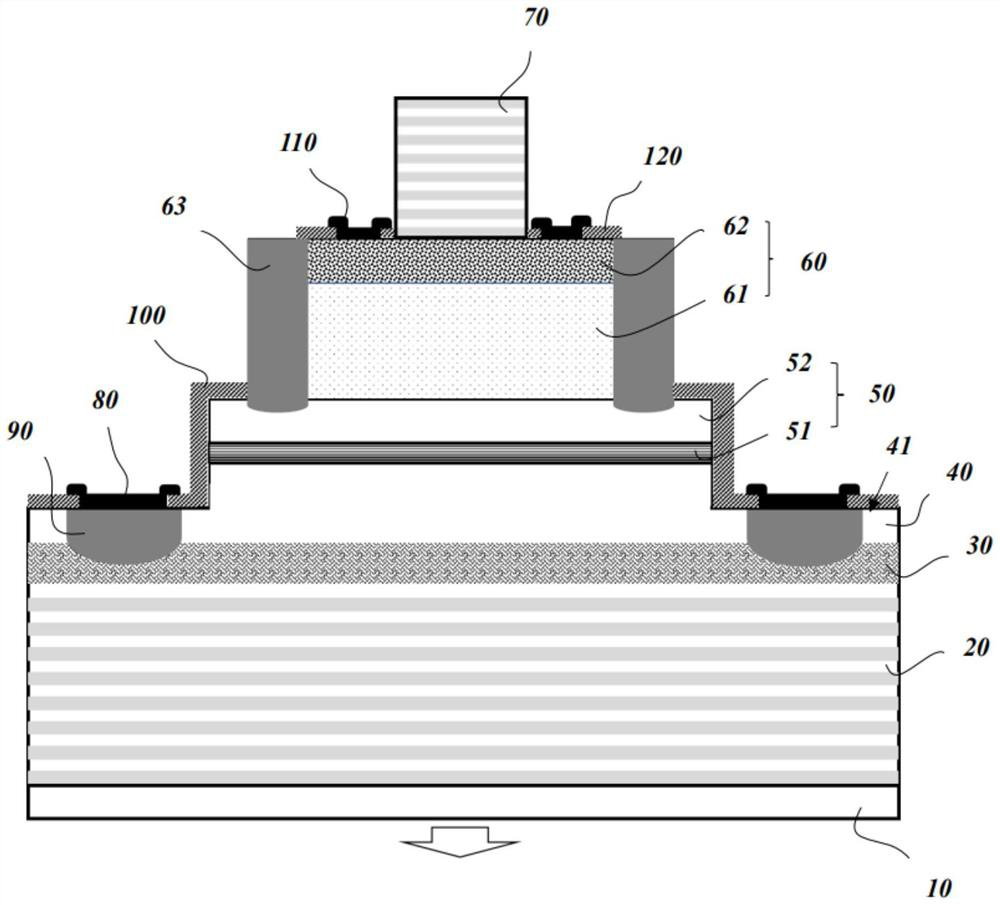
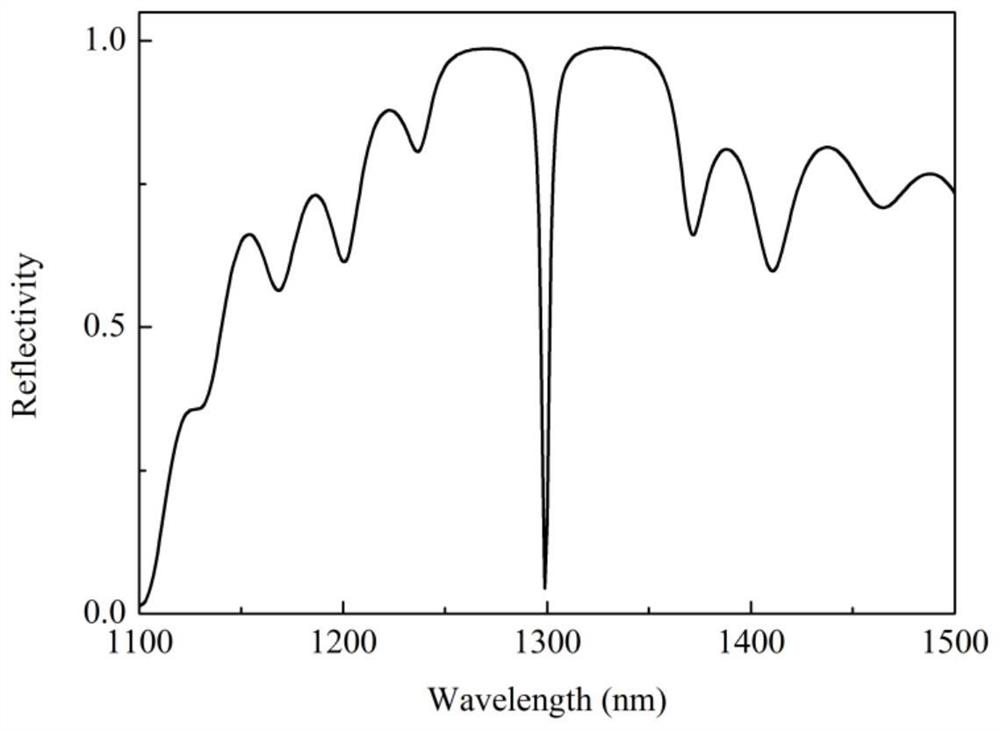
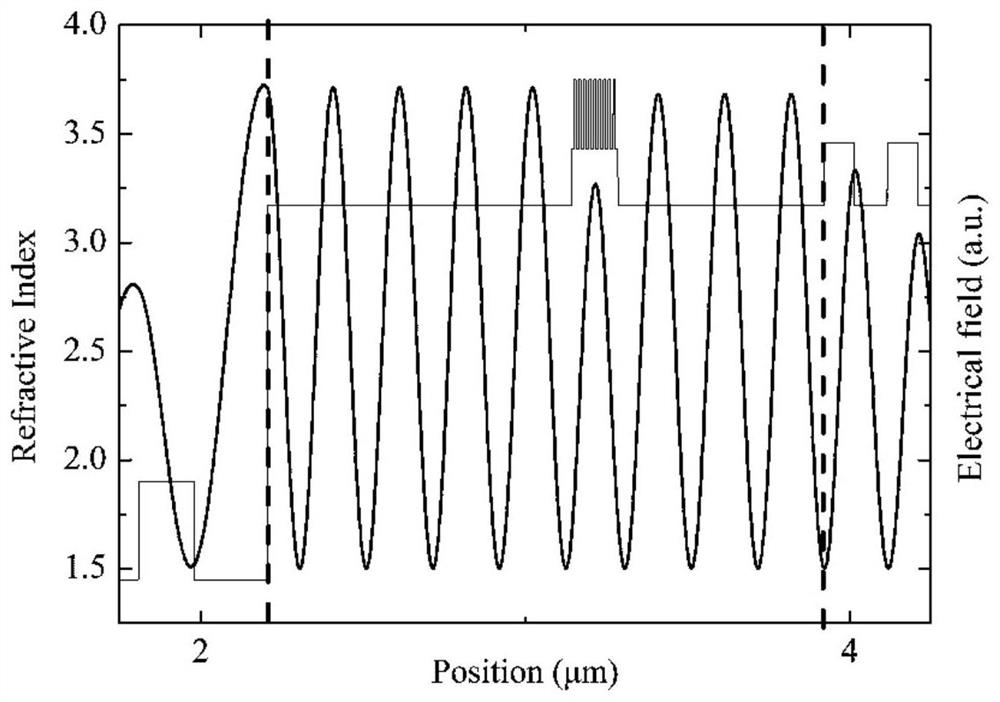
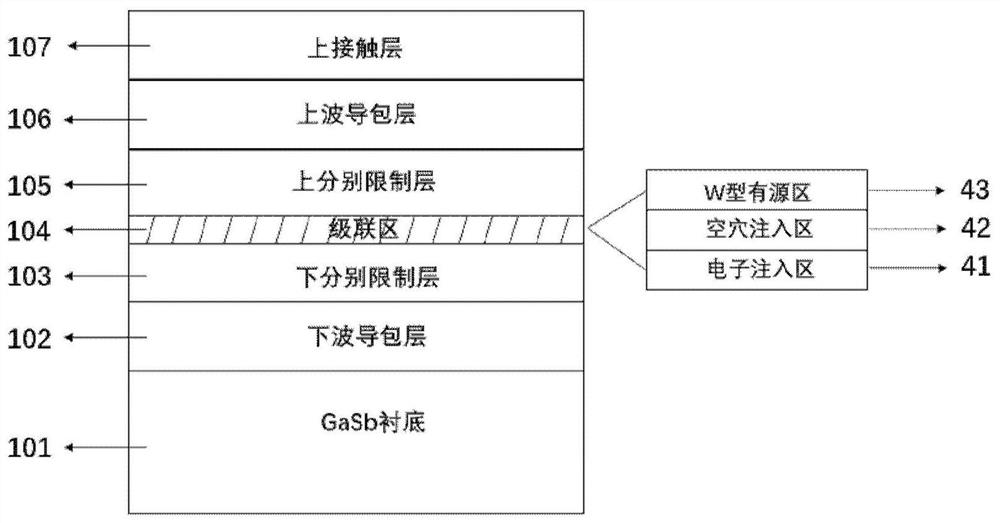
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Free carrier absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
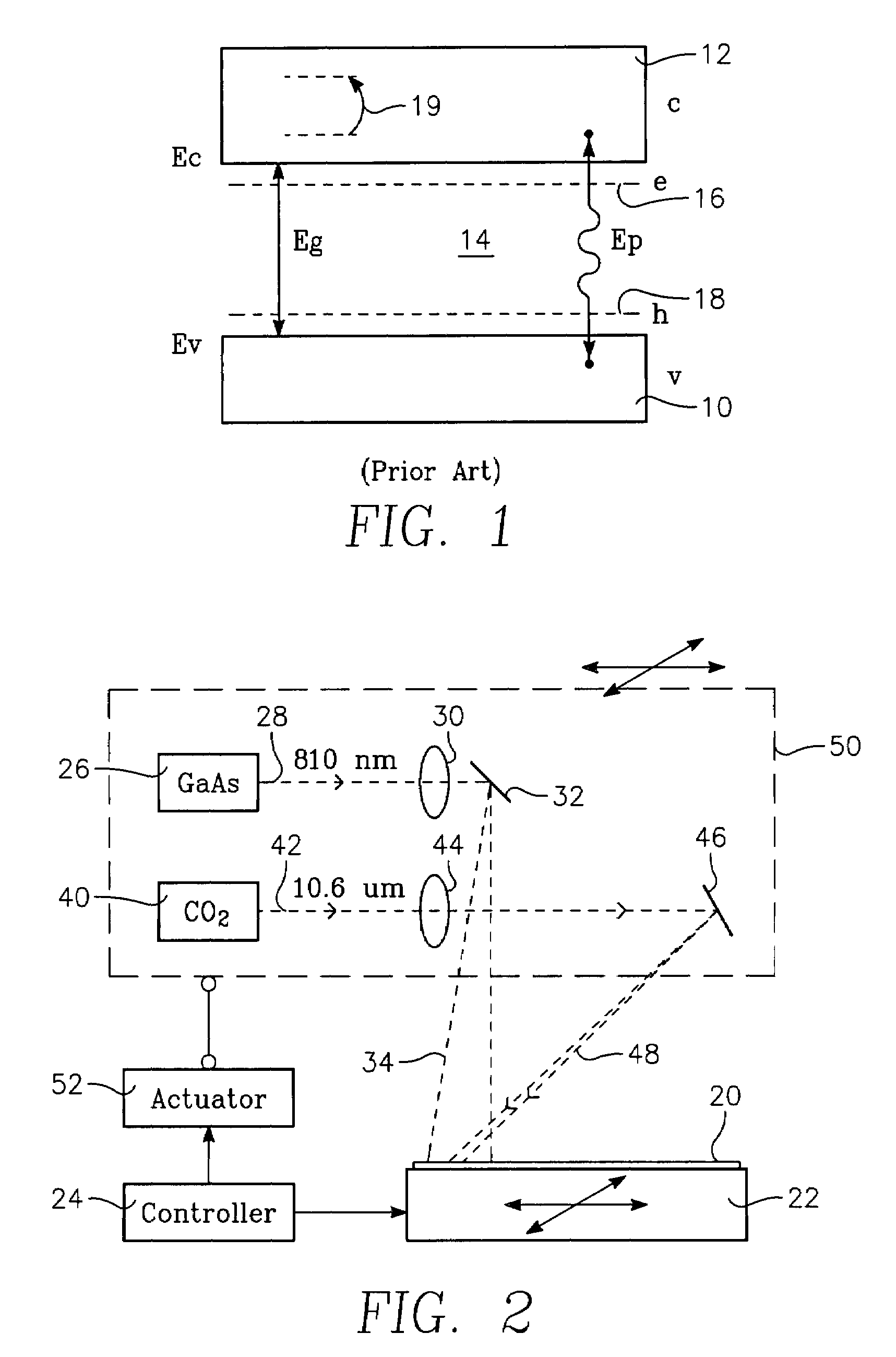
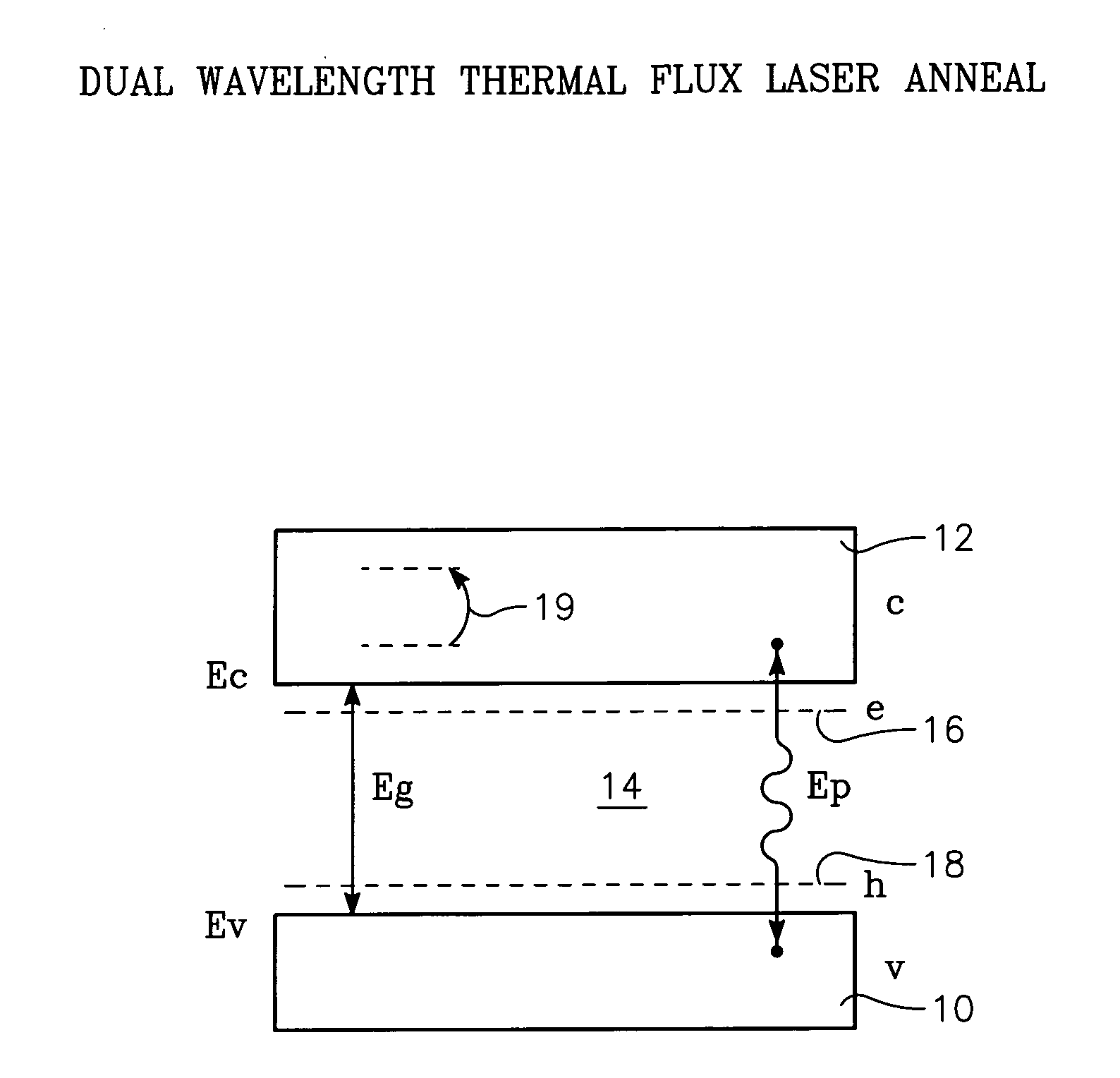
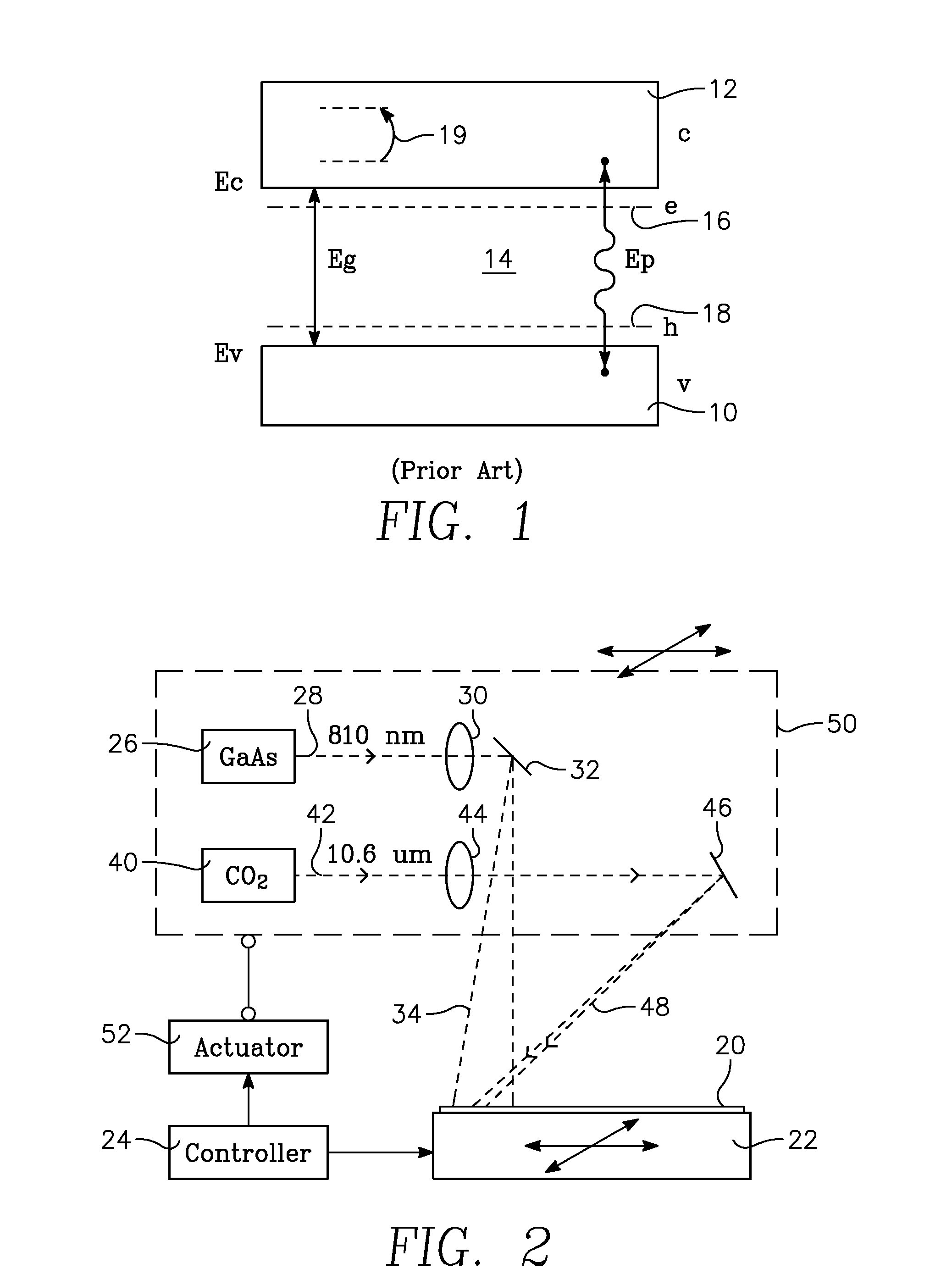
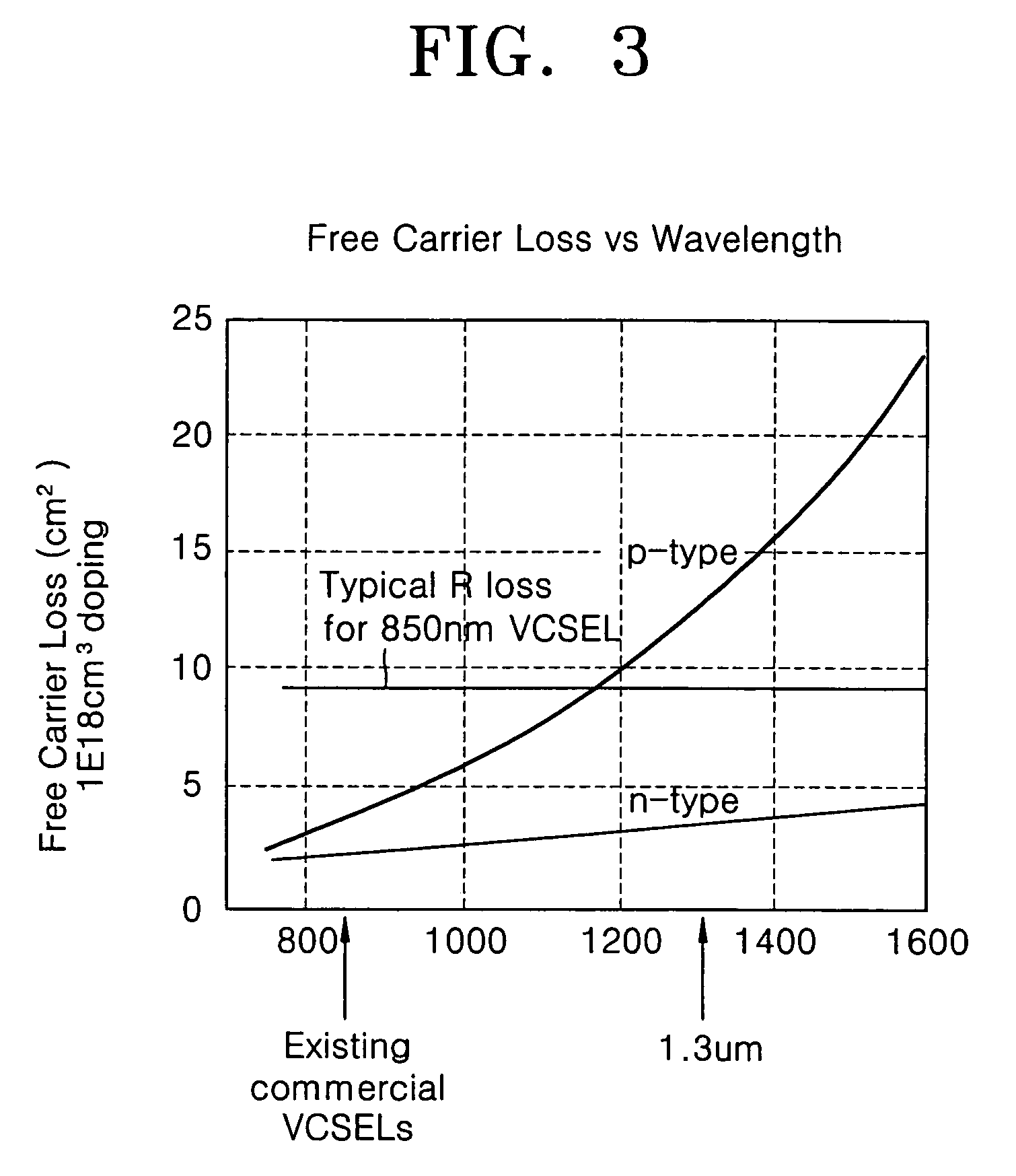
Free carrier absorption occurs when a material absorbs a photon, and a carrier (electron or hole) is excited from an already-excited state to another, unoccupied state in the same band (but possibly a different subband). This intraband absorption is different from interband absorption because the excited carrier is already in an excited band, such as an electron in the conduction band or a hole in the valence band, where it is free to move. In interband absorption, the carrier starts in a fixed, nonconducting band and is excited to a conducting one.
Dual wavelength thermal flux laser anneal
ActiveUS7279721B2Effective radiationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingLight beam
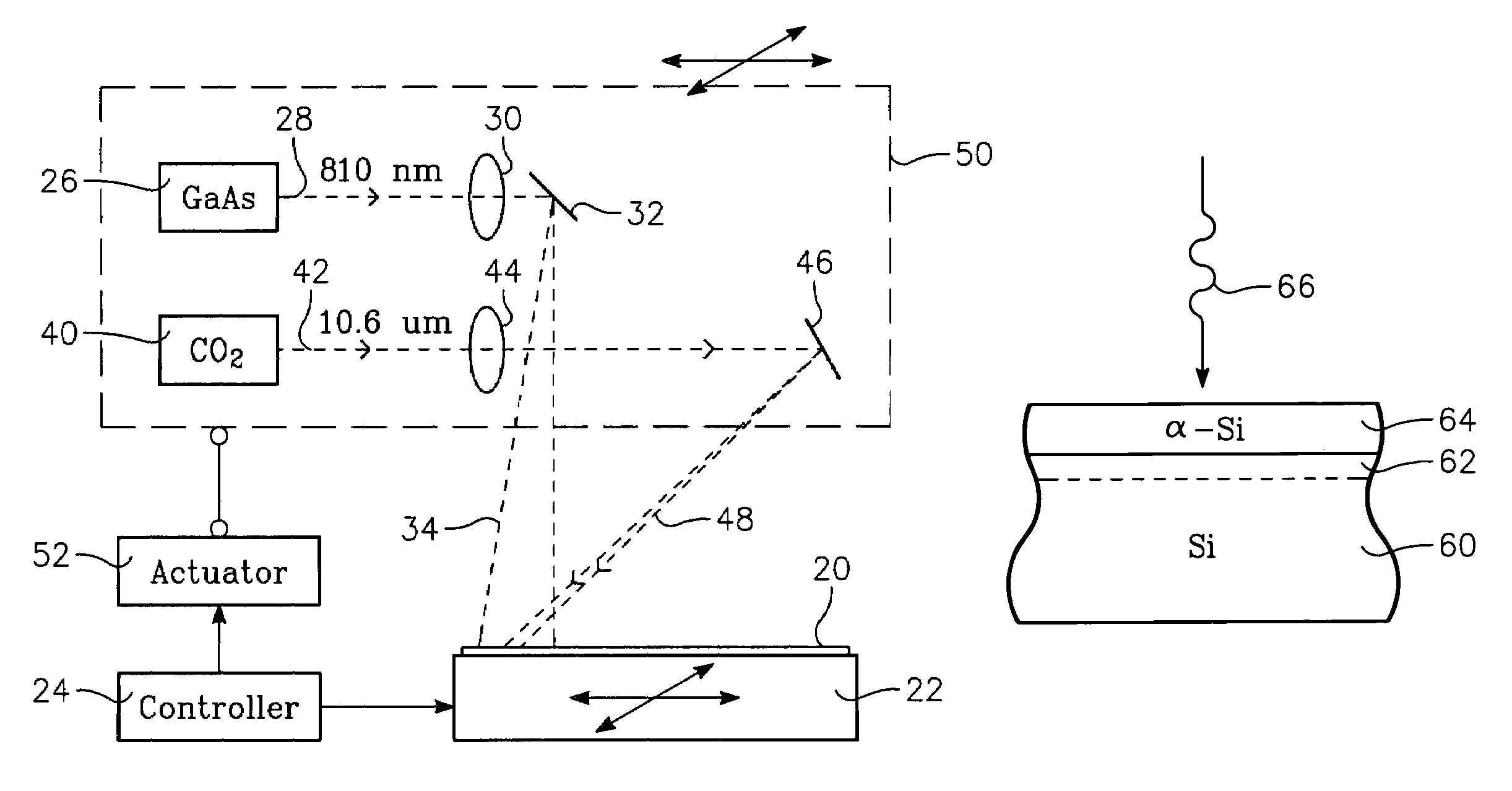
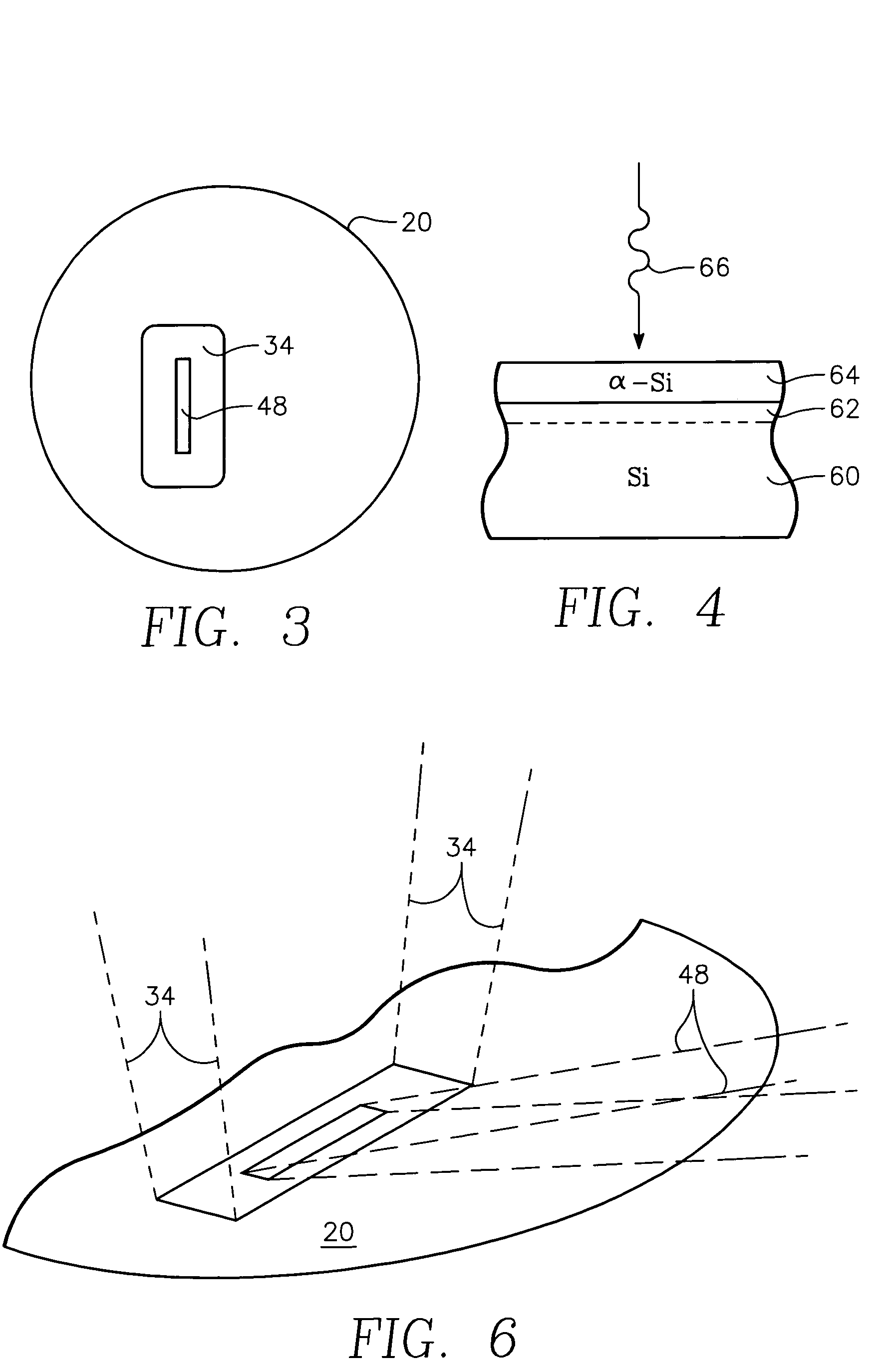
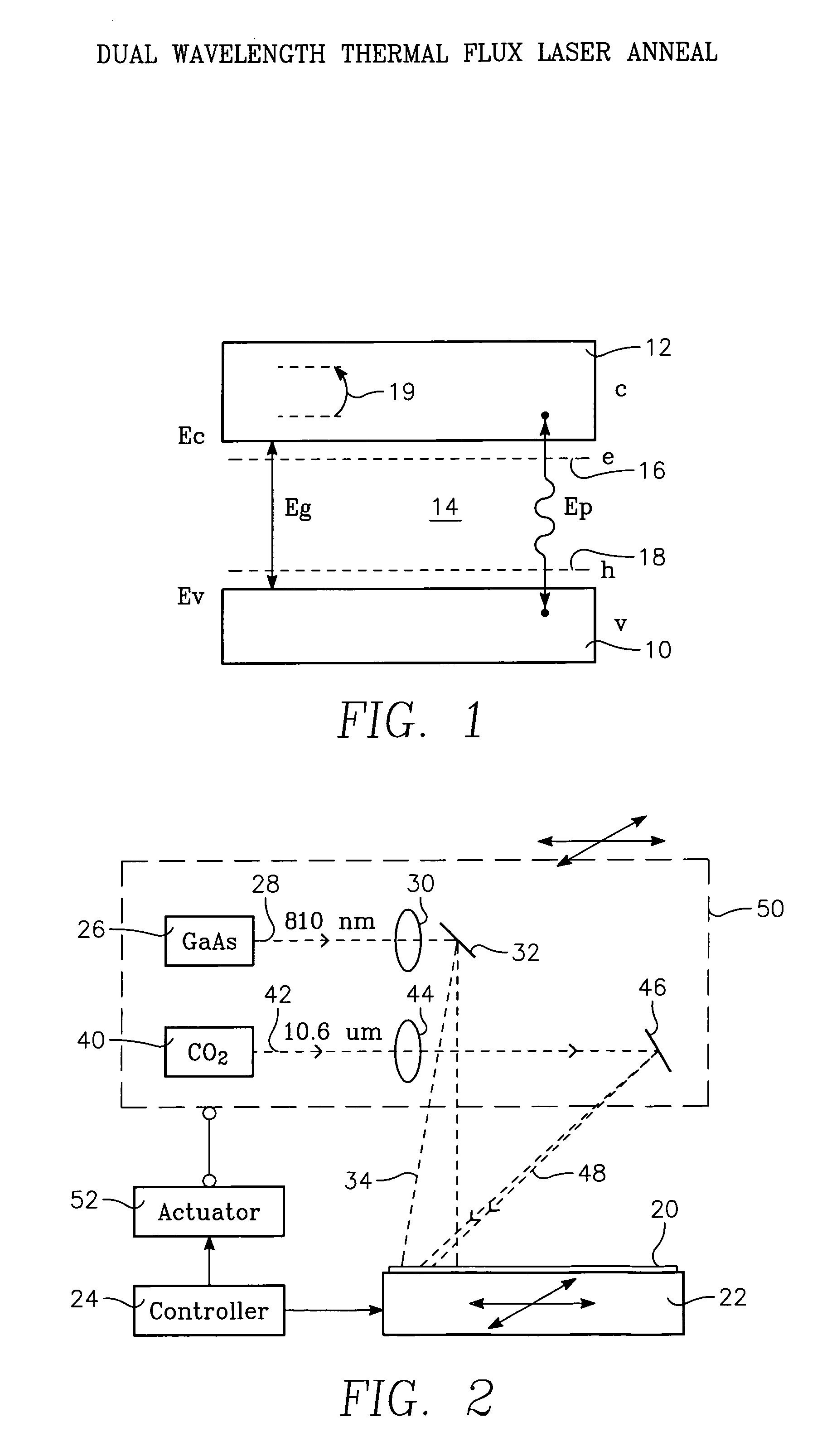
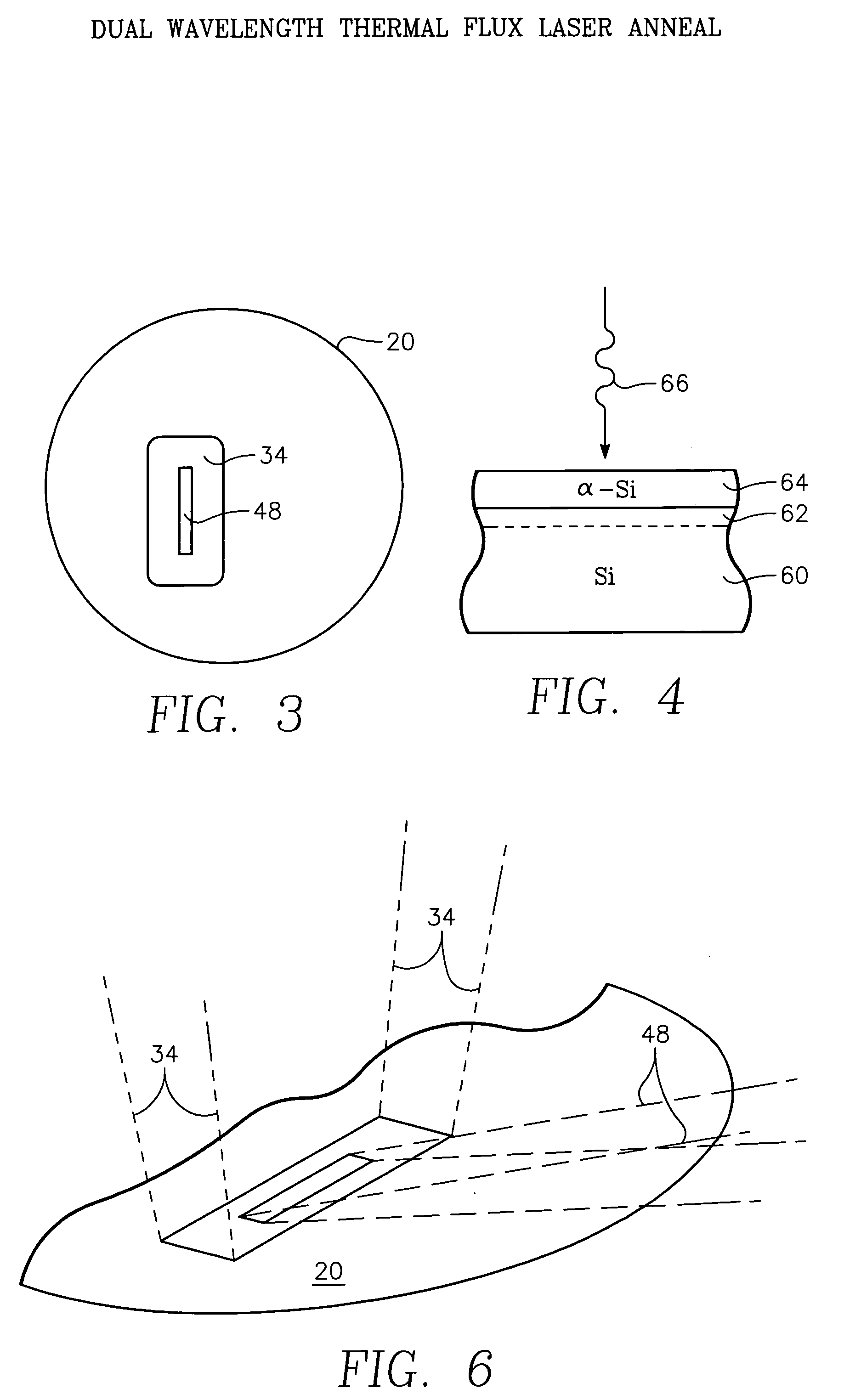
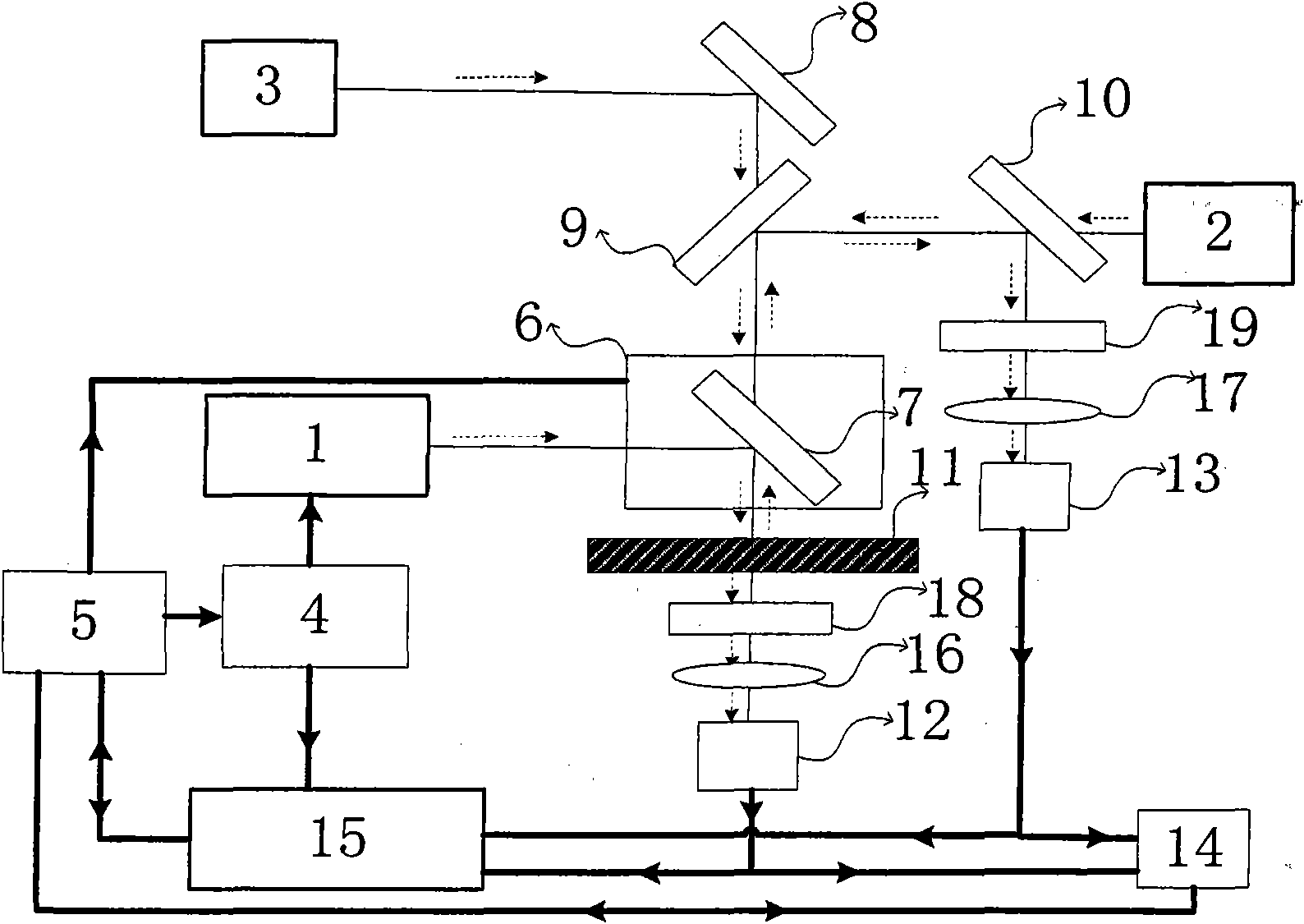
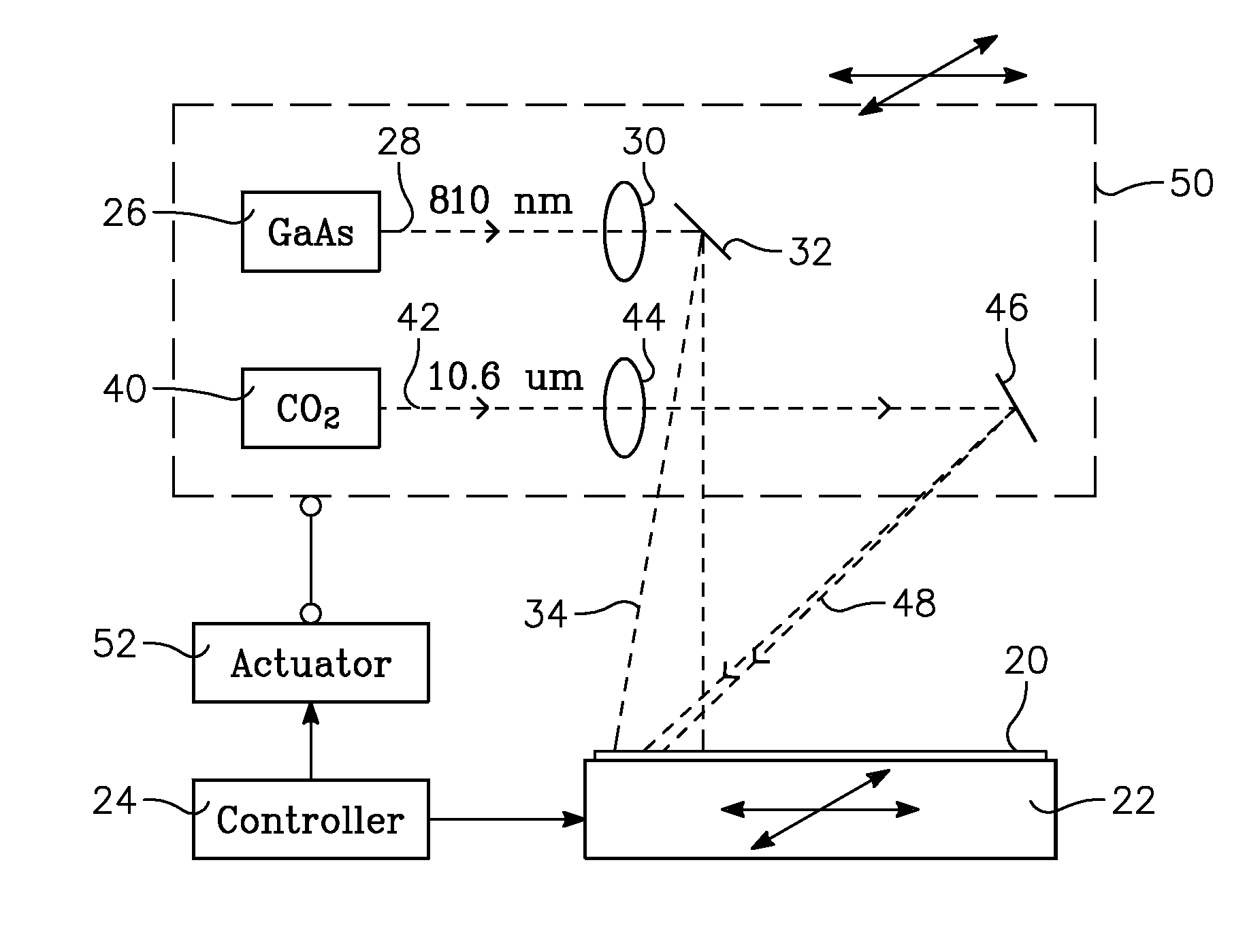
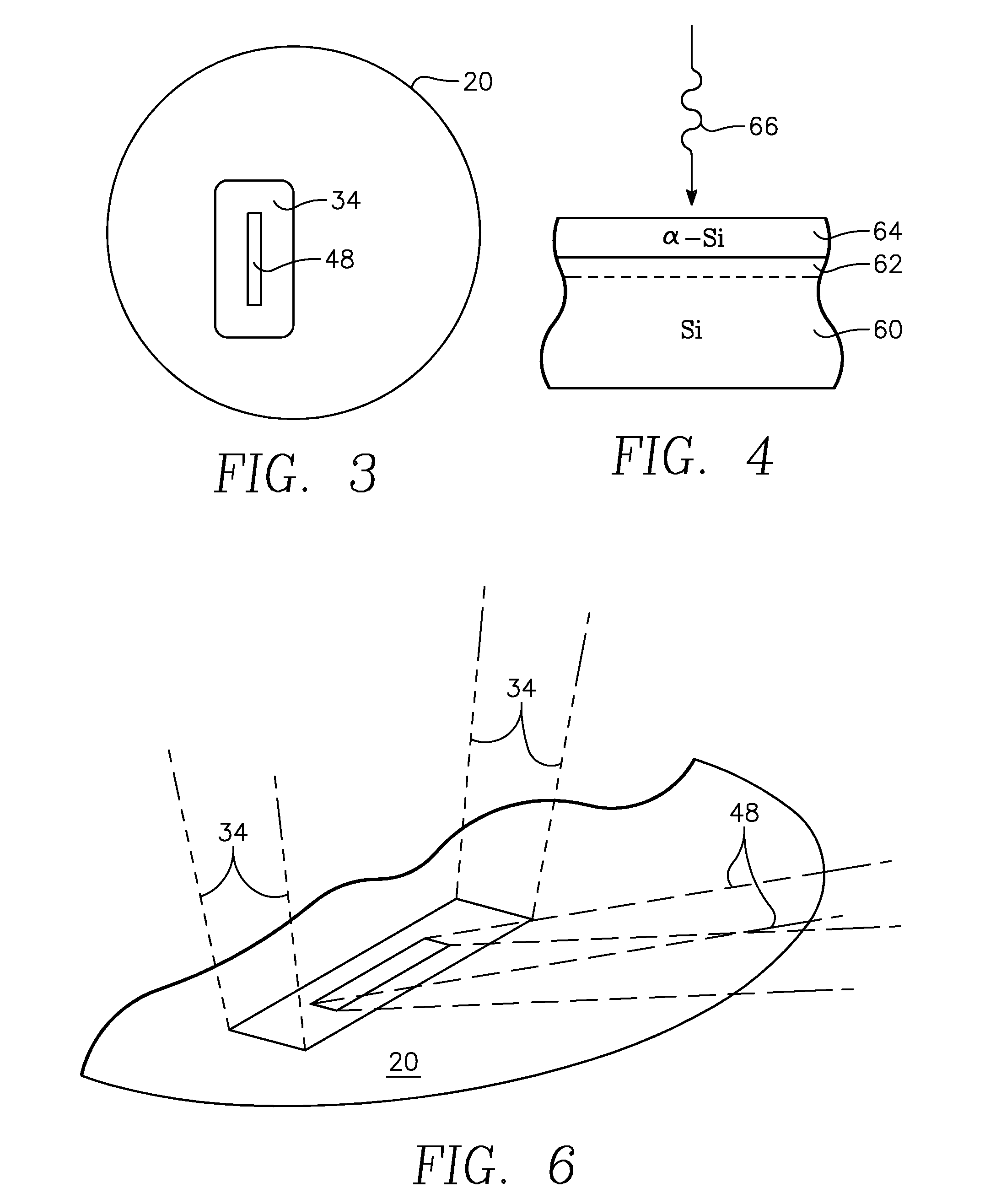
A thermal processing apparatus and method in which a first laser source, for example, a CO2 emitting at 10.6 μm is focused onto a silicon wafer as a line beam and a second laser source, for example, a GaAs laser bar emitting at 808 nm is focused onto the wafer as a larger beam surrounding the line beam. The two beams are scanned in synchronism in the direction of the narrow dimension of the line beam to create a narrow heating pulse from the line beam when activated by the larger beam. The energy of GaAs radiation is greater than the silicon bandgap energy and creates free carriers. The energy of the CO2 radiation is less than the silicon bandgap energy so silicon is otherwise transparent to it, but the long wavelength radiation is absorbed by the free carriers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dual wavelength thermal flux laser anneal
ActiveUS20060234458A1Effective radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusHeat fluxLaser source
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for measuring semiconductor doping concentration
InactiveCN101159243AHigh measurement accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCharge carrierMeasurement precision
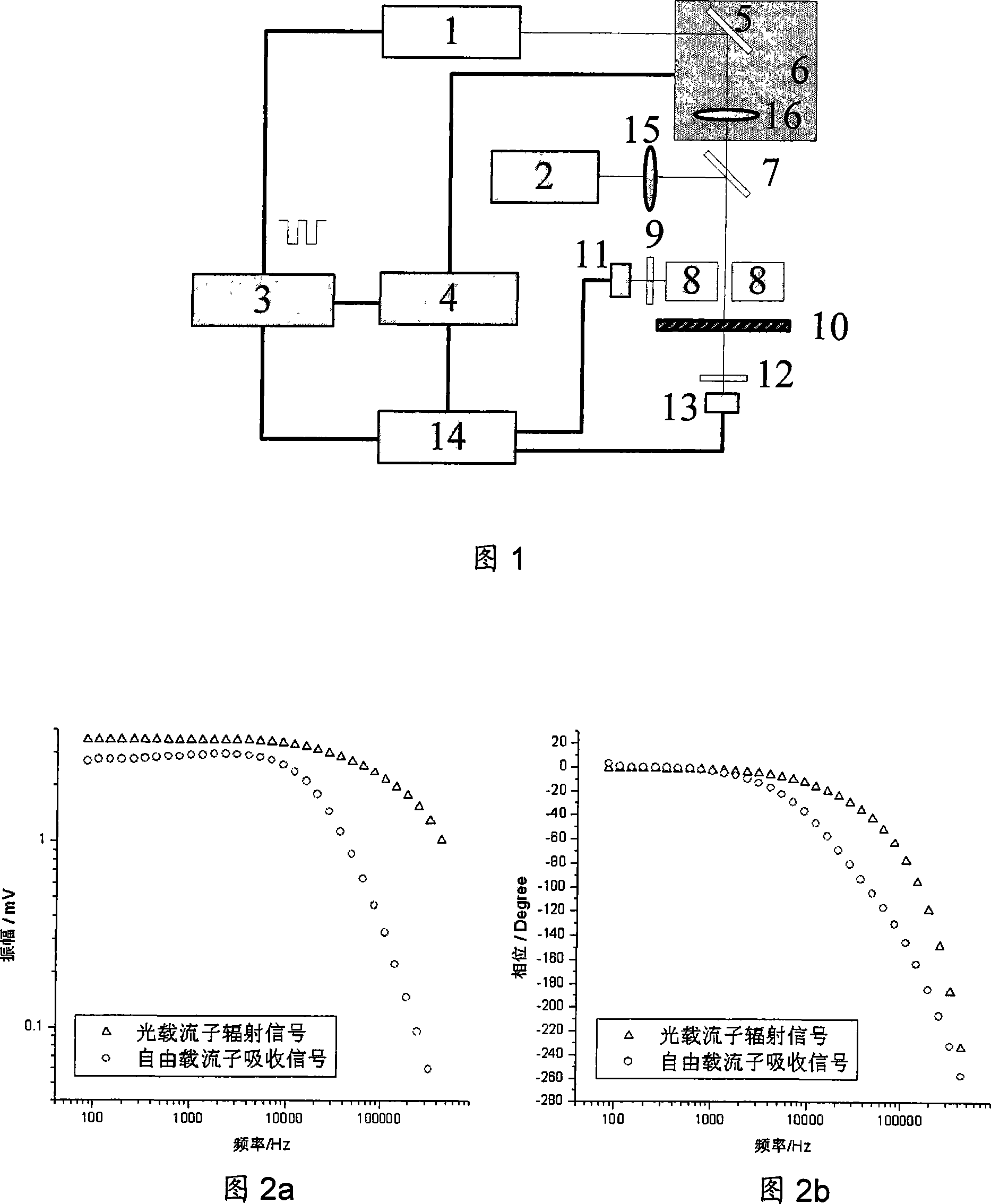
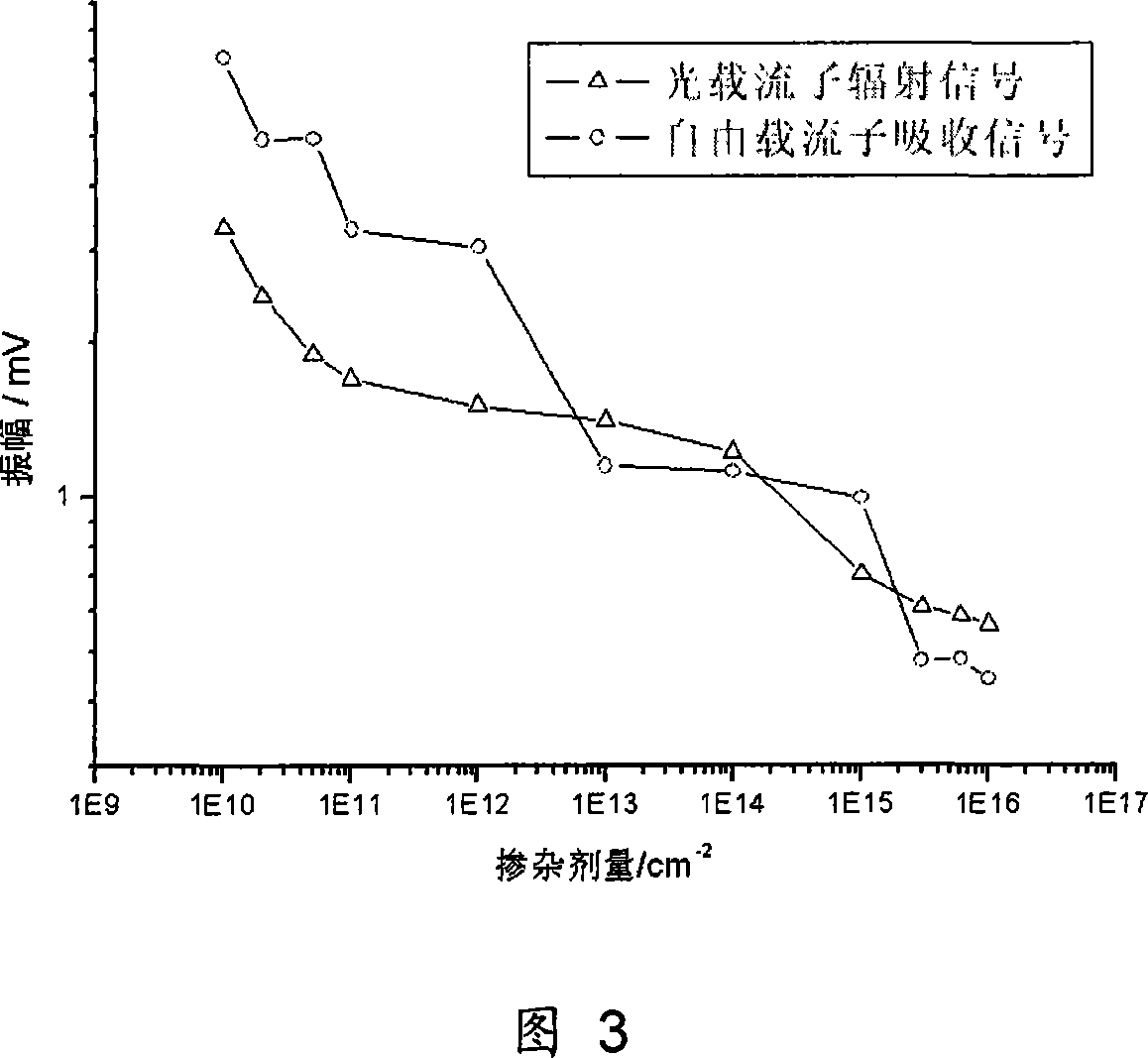
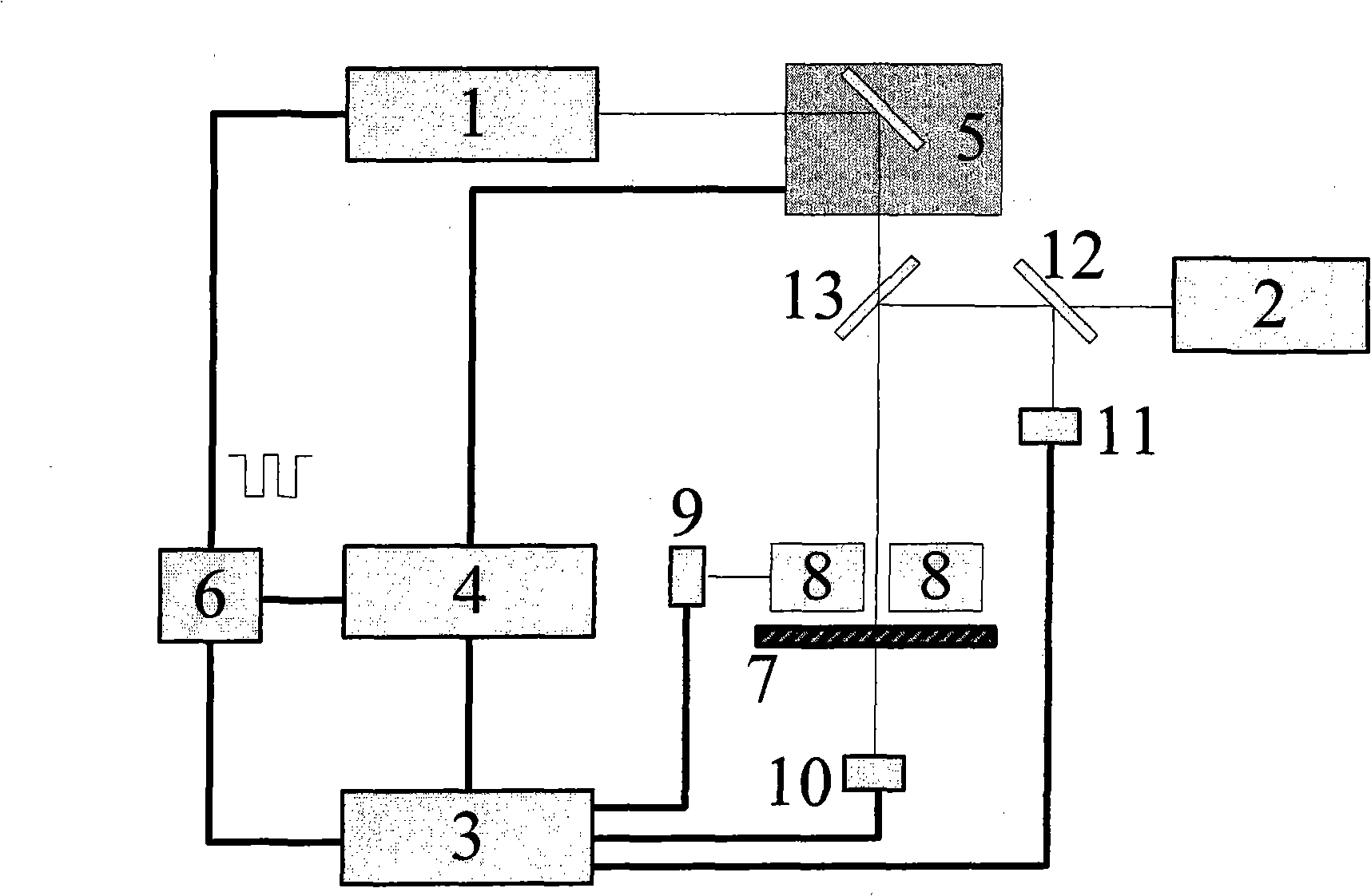
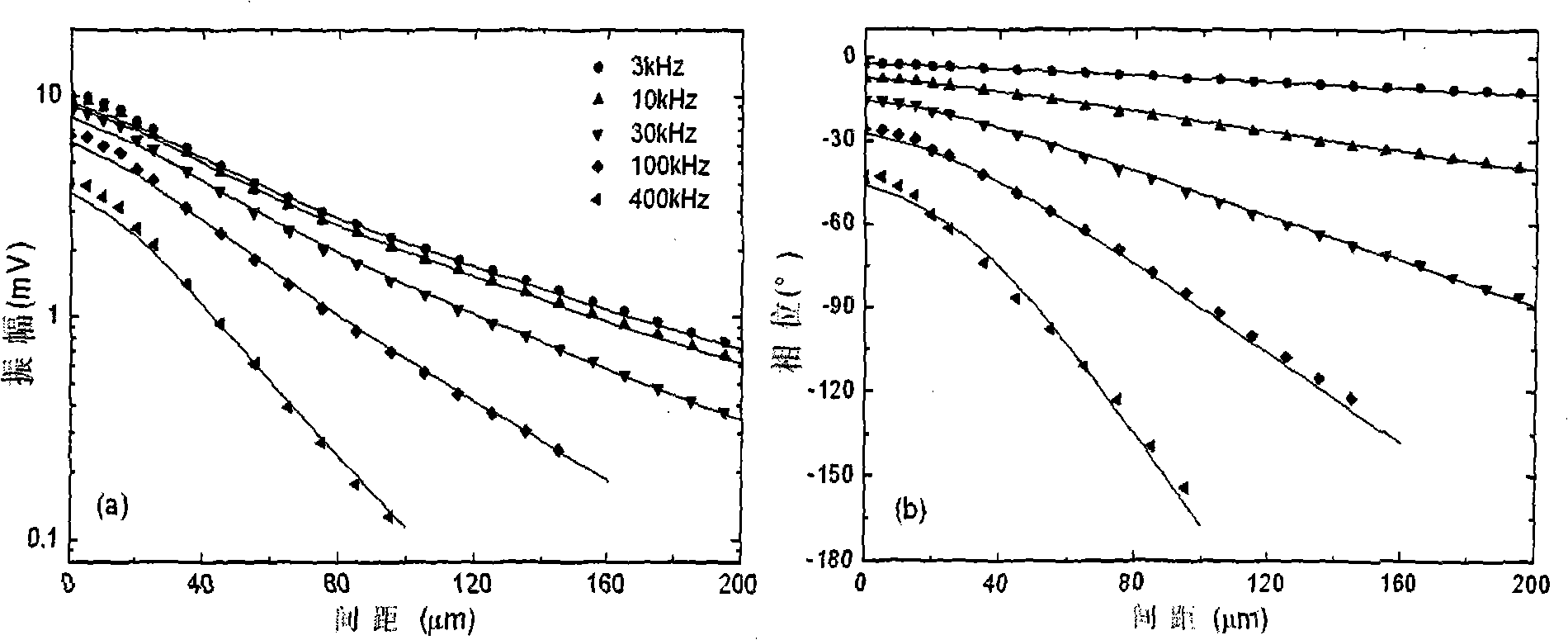
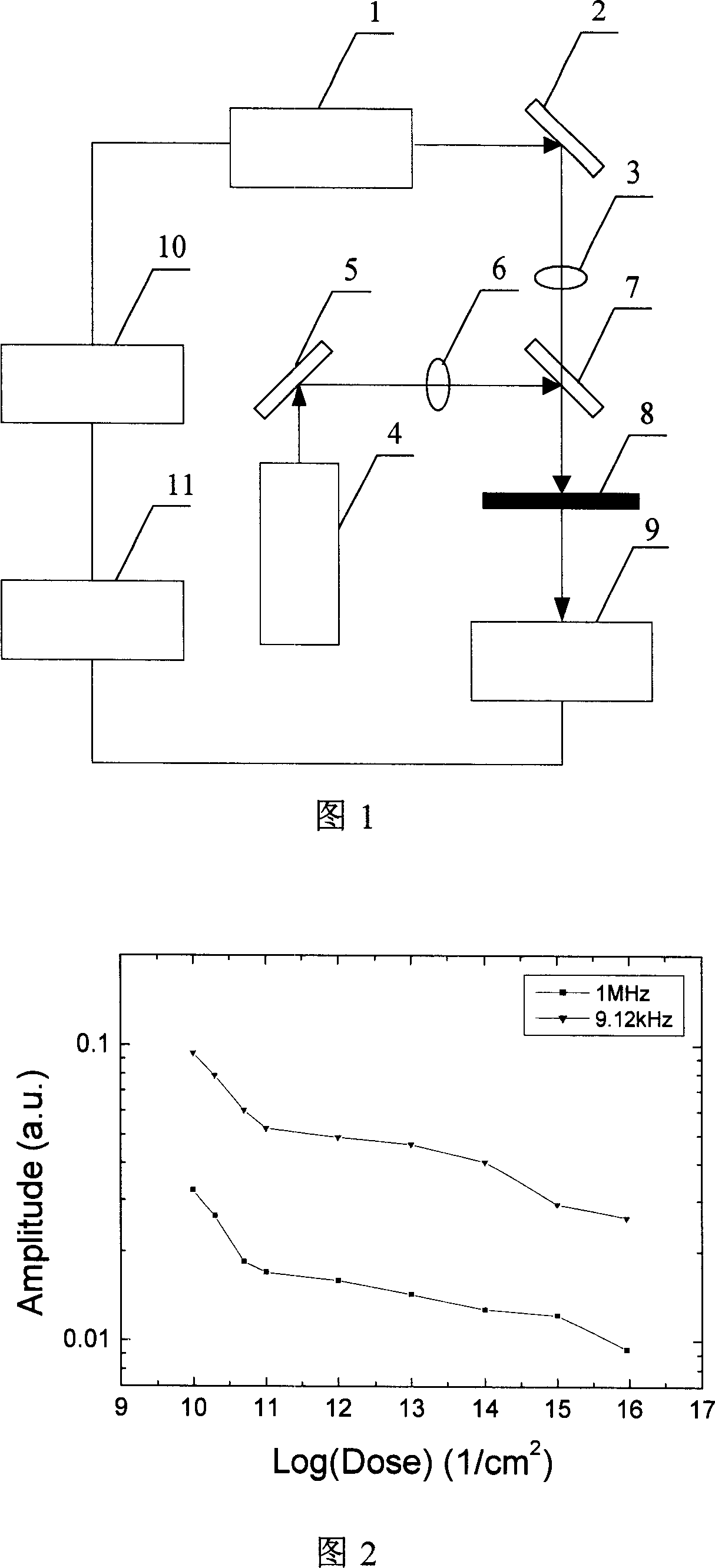
A method for measuring semi-conductor doping density is characterized in that photocarrier radiometric technique and free carrier absorption measurement technique are integrated in a measurement system for simultaneously obtaining the complex radiation signal and absorption signal of the free carrier; the carrier radiation signal and absorption signal of a frequency domain are obtained through varying the modulating frequency of exciting light; the carrier radiation signal and absorption signal of a space domain are obtained through varying the distance between the exciting light and detecting light; and the doping density of the sample to be measured is obtained through comparing with the carrier radiation signal and absorption signal of a standard sample. The invention is based on photocarrier radiometric technique and free carrier absorption measurement technique, and integrates the information of two independent paths in respect frequency domain and space domain, so as to remarkably improve the measurement accuracy of doping density.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor material characteristic measuring device and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN101527273AGuarantee confidenceGuaranteed accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsMeasurement deviceSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a semiconductor material characteristic measuring device and a method thereof which are used for measuring characteristic parameters of the semiconductor material and evaluating the processing quality of the material. In a test system, a light carrier radiation measuring signal, a free carrier absorption measuring signal and a light modulation reflection measuring signal of a sample can be simultaneously or respectively obtained just by an exciting light and a probe light. Light carrier radiation, free carrier absorption and light modulation reflection signal data are simultaneously or respectively analyzed and processed to obtain the characteristic parameters of the semiconductor material; when the data are compared with signal data of a standard or calibration sample, parameters of impurity concentration, defect concentration, and the like which are introduced during the processing of the semiconductor material can be measured.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring doping content of semiconductor based on free carrier absorption technique
InactiveCN1971868ALarge measuring rangeReduce monotonySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMeasurement precisionBand width
This invention relates to one semiconductor mixture contraction measurement method based on freedom load flow absorption technique, which is characterized by the following: using one beam of photon with energy larger than the continuous laser with light intensity modulation of forbidden band as pump light source; using another beam of light smaller than semiconductor forbidden band width as detector light source; two beams of light are lighting onto same or adjacent positions on semiconductors; the semiconductor absorbs pump light to generate modulation free load flow; due to modulation free load flow absorbing through semiconductor or reflection detector light intensity by lock phase type or reflection detecting light signals for once resonance vibration and phase to get the mixture concentration.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A semiconductor material property measurement device and method based on double probe beam
InactiveCN101551324ACompensate for the shortcomings of low measurement accuracyIncrease credibilityResistance/reactance/impedenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMeasurement deviceSemiconductor materials
The invention is a semiconductor material property measurement device and method based on double probe beam for measuring the characteristic parameters of semiconductor materials and monitoring the doping process. It obtains the free carrier absorption signal and the light-modulated reflecting signal simultaneously in the same set of test system based on the absorption of the exciting light of the periodic intensity modulation by the semiconductor materials; it obtains the free carrier absorption signal and light-modulated reflecting signal of the frequency domain by changing the modulation frequency of the exciting light; it obtains the free carrier absorption signal and light-modulated reflecting signal of the spatial domain by changing the spacing between the exciting light and the probe light; it may obtain the characteristic parameters of semiconductor materials and the process parameters as the doping concentration through the analysis and processing of the signals obtained or the comparison with the signal data of the calibration sample. The invention makes up for the shortcomings of the single technology and improves the measurement accuracy; it obtains two kinds of signals simultaneously in one device and more important parameters of the semiconductor materials comparing with the single technology.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of Laser Annealing Using Two Wavelengths of Radiation
ActiveUS20070293058A1Effective radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamLength wave
A thermal processing apparatus and method in which a first laser source, for example, a CO2 emitting at 10.6 μm is focused onto a silicon wafer as a line beam and a second laser source, for example, a GaAs laser bar emitting at 808 nm is focused onto the wafer as a larger beam surrounding the line beam. The two beams are scanned in synchronism in the direction of the narrow dimension of the line beam to create a narrow heating pulse from the line beam when activated by the larger beam. The energy of GaAs radiation is greater than the silicon bandgap energy and creates free carriers. The energy of the CO2 radiation is less than the silicon bandgap energy so silicon is otherwise transparent to it, but the long wavelength radiation is absorbed by the free carriers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN110429473AReduce difficultyPromote growthLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserMaterial growth
The present invention provides a vertical cavity surface emitting laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The vertical cavity surface emitting laser comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, a lower DBR, an active layer, a current limiting aperture, a current diffusion layer, an undoped suspension type HCG layer, an n side electrode and a p-side electrode. The material extension difficulty of the vertical cavity surface emitting laser is reduced, the universality of material growth is improved, the free carrier absorption is reduced, and the output efficiency of the device is improved; and thevertical cavity surface emitting laser has polarization selection and single mode output characteristics, and can be expanded to a tunable vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The vertical cavity surface emitting laser can be applied to the fields such as optical communication, optical interconnection, optical sensing, medical imaging and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
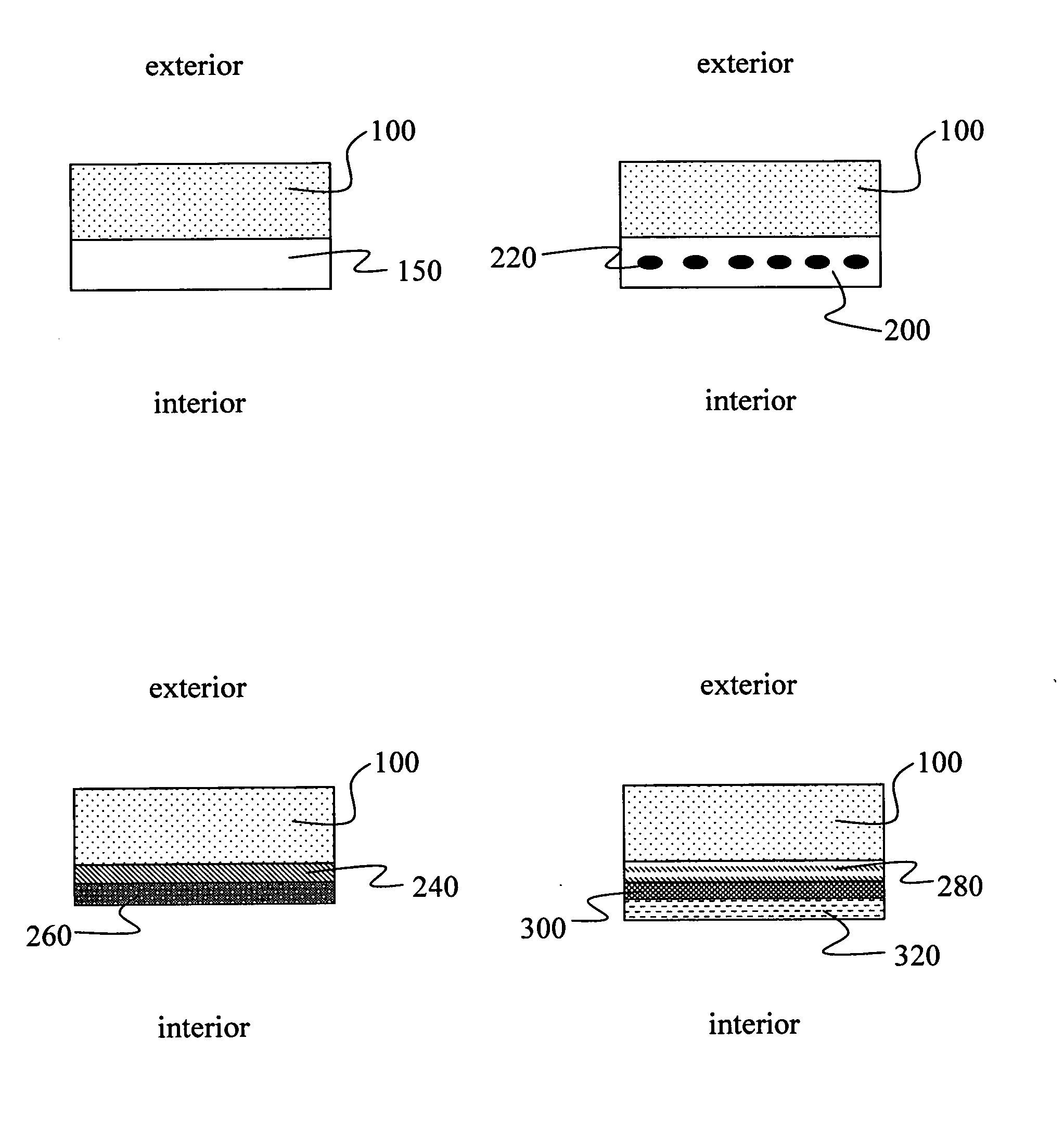
Thermal barrier
InactiveUS20080311392A1Improve insulation performanceEnhanced couplingClimate change adaptationRecord information storageElectrical conductorThermodynamics
A composite thermal barrier material. The material includes a support layer coated on one or both sides with an infrared active material to improve thermal retention characteristics. The support layer is typically a flexible organic or polymer material. The infrared active material increases reflectance of thermal infrared radiation and reduces the flow of heat from the interior side of the barrier to the external surroundings. The infrared active material operates through vibrational absorption in the infrared and / or free carrier absorption. Representative infrared active materials include oxides, transparent conductors, and nanoscale metals.
Owner:MING SCI
High-speed electro-absorption modulator with low drive voltage
InactiveUS7102807B2Increase confinement factorReduced insertion lossNanoopticsNon-linear opticsElectricityElectro-absorption modulator
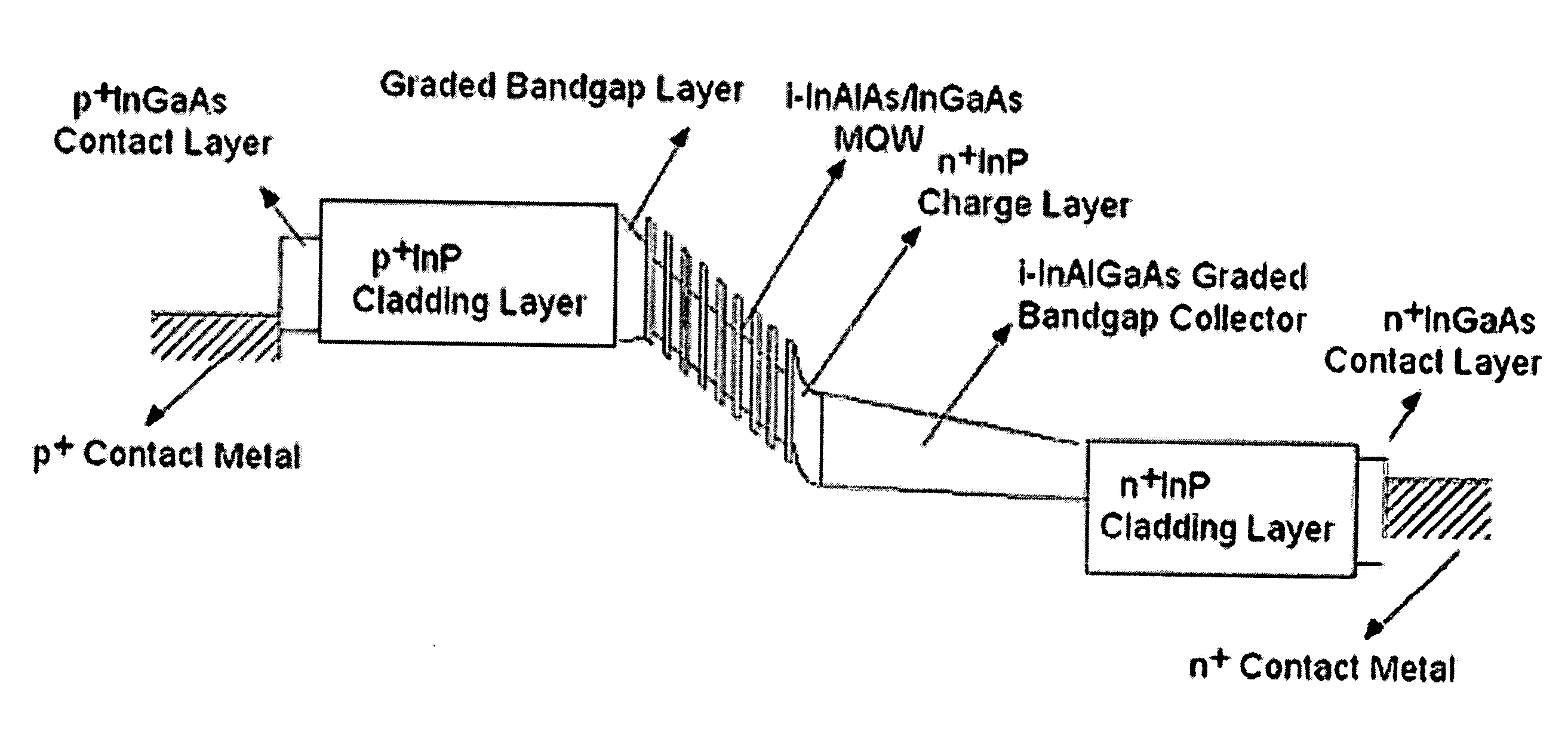
The present invention is an electro-absorption modulator with a p-i-n-i-n epitaxy layer whose structure is p-i(MQW)-n+-i(collector)-n to release the trade-off between the operation voltage and the speed, to increase the confinement factor of the light in the un-doped layers, and to reduce the insertion loss caused by the free-carrier absorption in the doped layers, wherein MQW stands for Multiple-Quantum Well.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity strained quantum well laser with low linewidth
InactiveCN102332681AReduce spectral widthQuality improvementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSpectroscopyOptical measurements
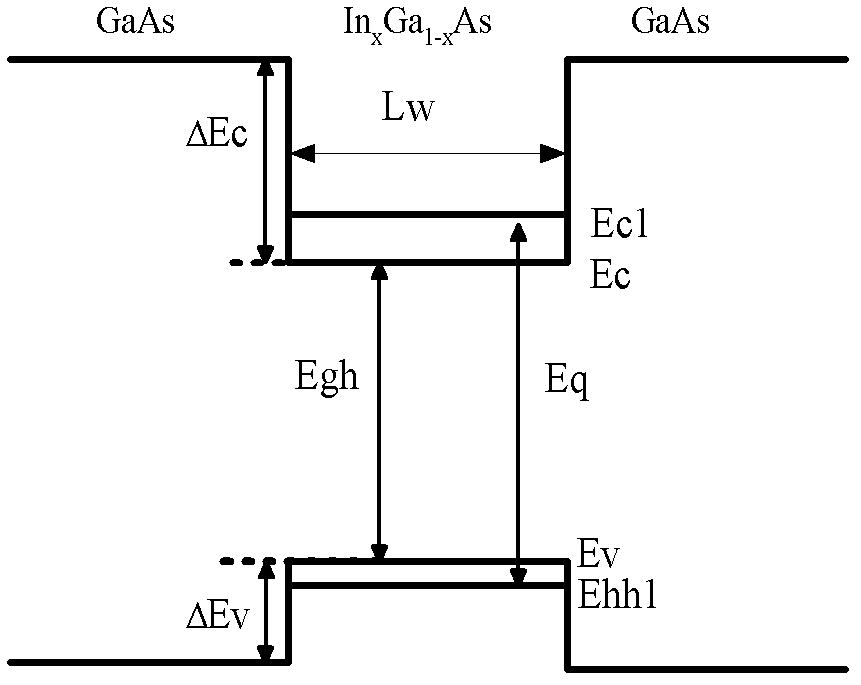
The invention provides an F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity strained quantum well laser with low linewidth. The F-P cavity strained quantum well laser comprises a substrate (1), a buffer layer (2), an n type lower limiting layer (3), a lower waveguide layer (4), a lower barrier layer (5), an active layer (6), an upper barrier layer (7), an upper waveguide layer (8), a p type upper limiting layer (9) and an ohmic contact layer (10) which are sequentially connected. Through the optimal design of the active layer (6), a linewidth enhancement factor generated by interband transition of a quantum well and a linewidth enhancement factor generated by free carrier absorption and band-gap shrinkage can offset mutually, thereby realizing the low linewidth and improving the quality of a light beam of the quantum well laser. The active layer of the laser provided by the invention is made of InxGa1-xAs materials, wherein x is equal to 0.33, the width thickness of the well is 3-5nm, the center wavelength lambda is equal to 980nm-1036nm, and the linewidth of the F-P cavity strained quantum well laser can be reduced by three orders of magnitude in comparison with a quantum well laser. The F-P cavity strained quantum well laser can be used for optical measurement, solid-state laser pumping, laser spectroscopy research and other fields.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
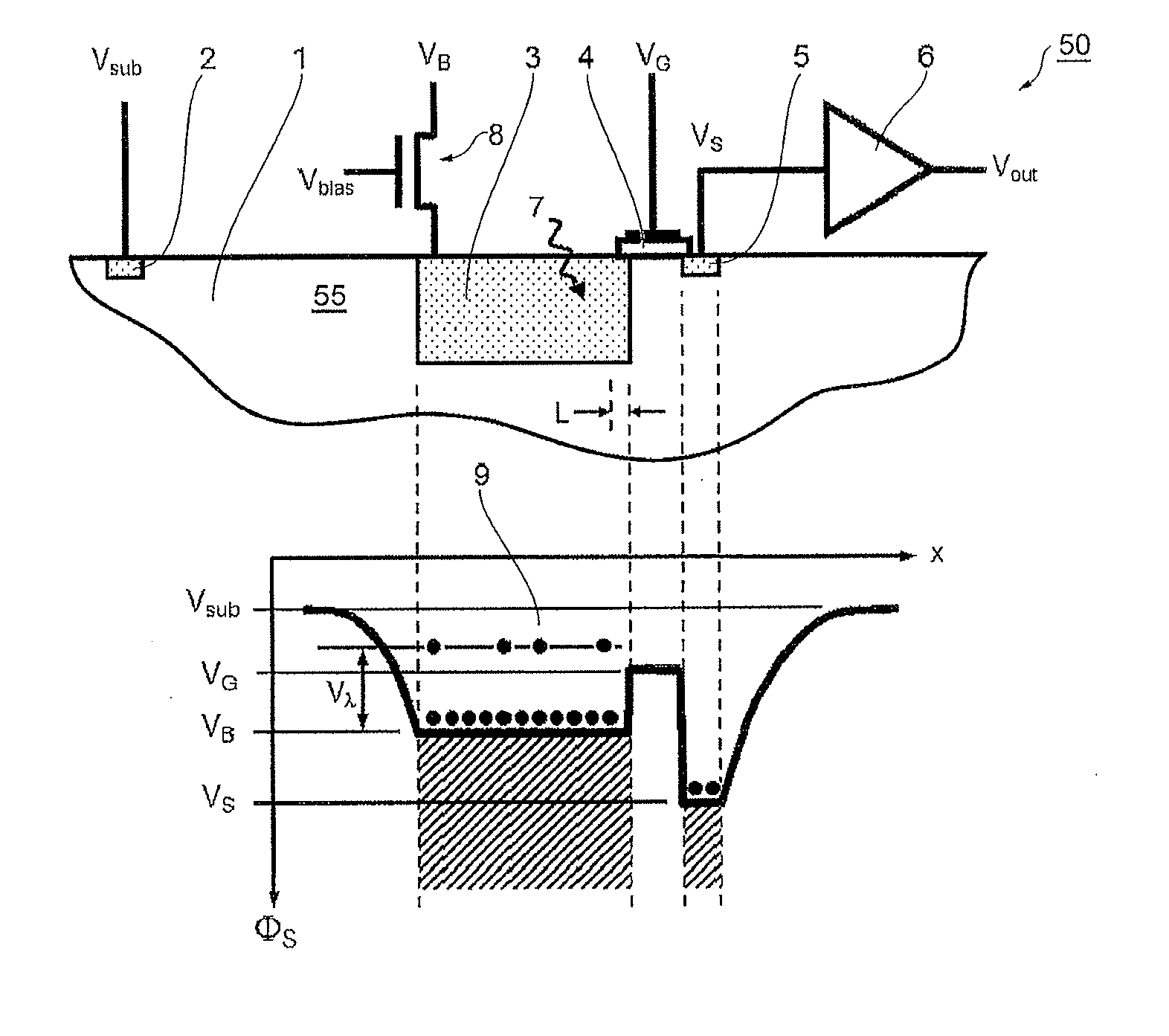
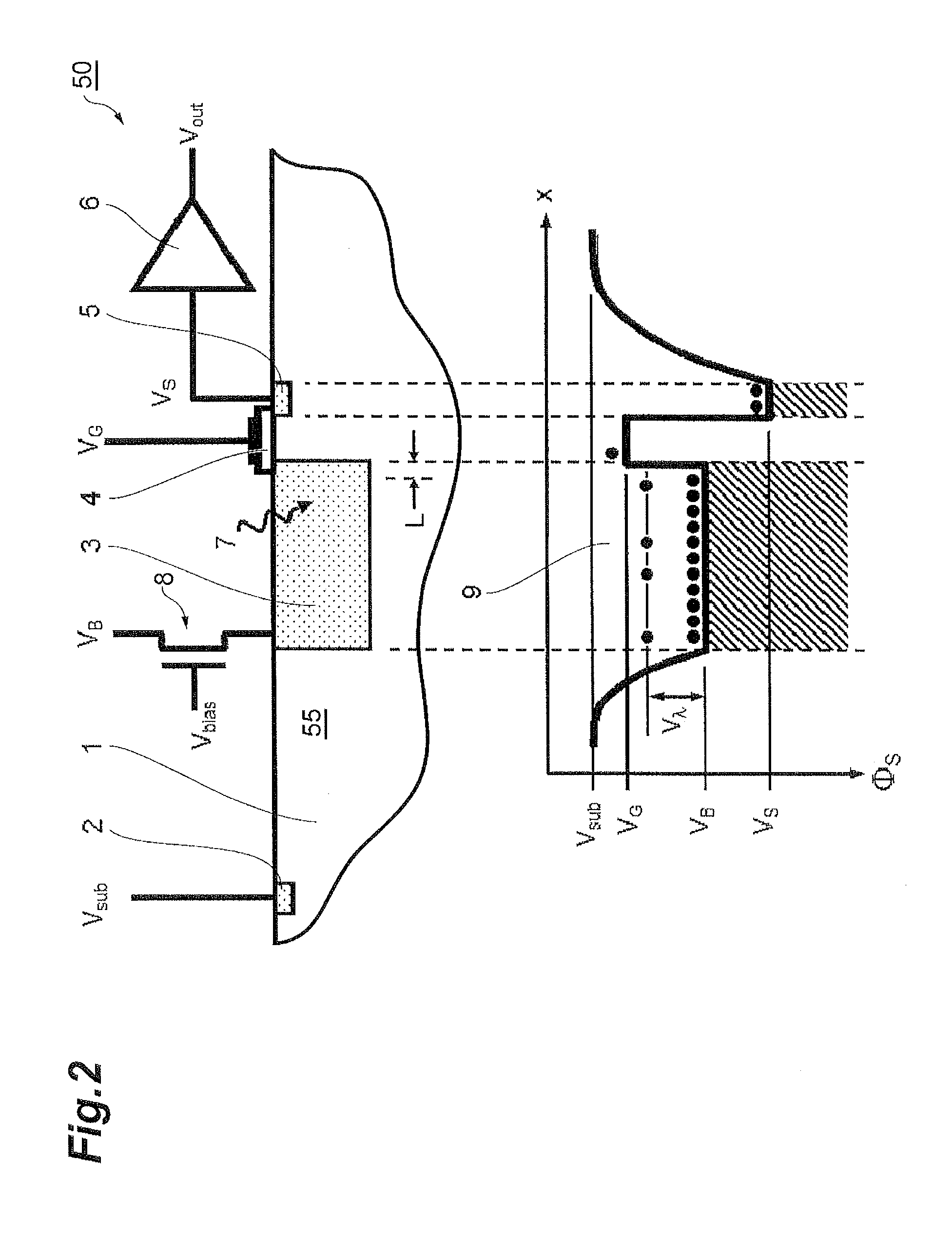
Semiconductor photosensor for infrared radiation
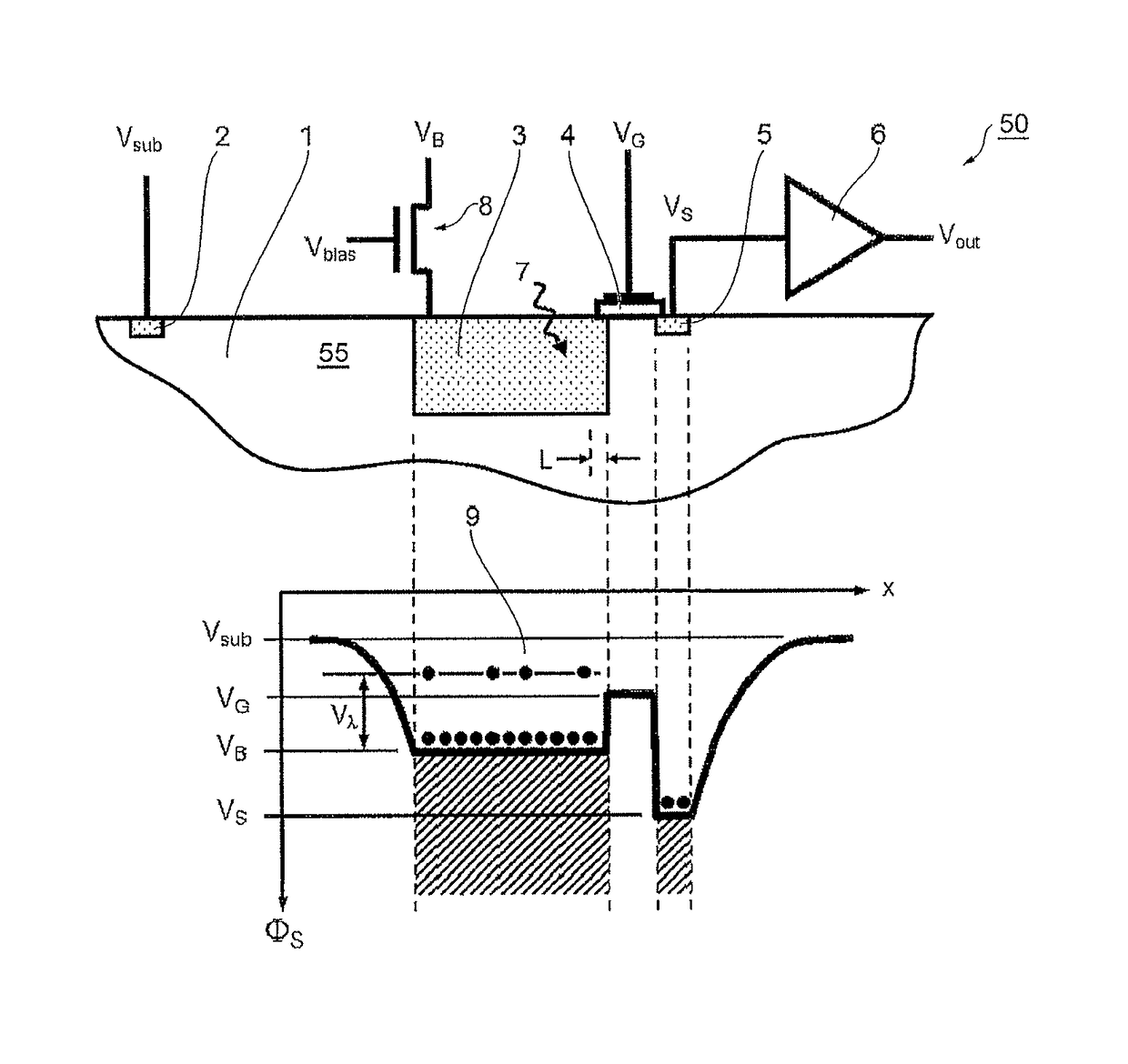
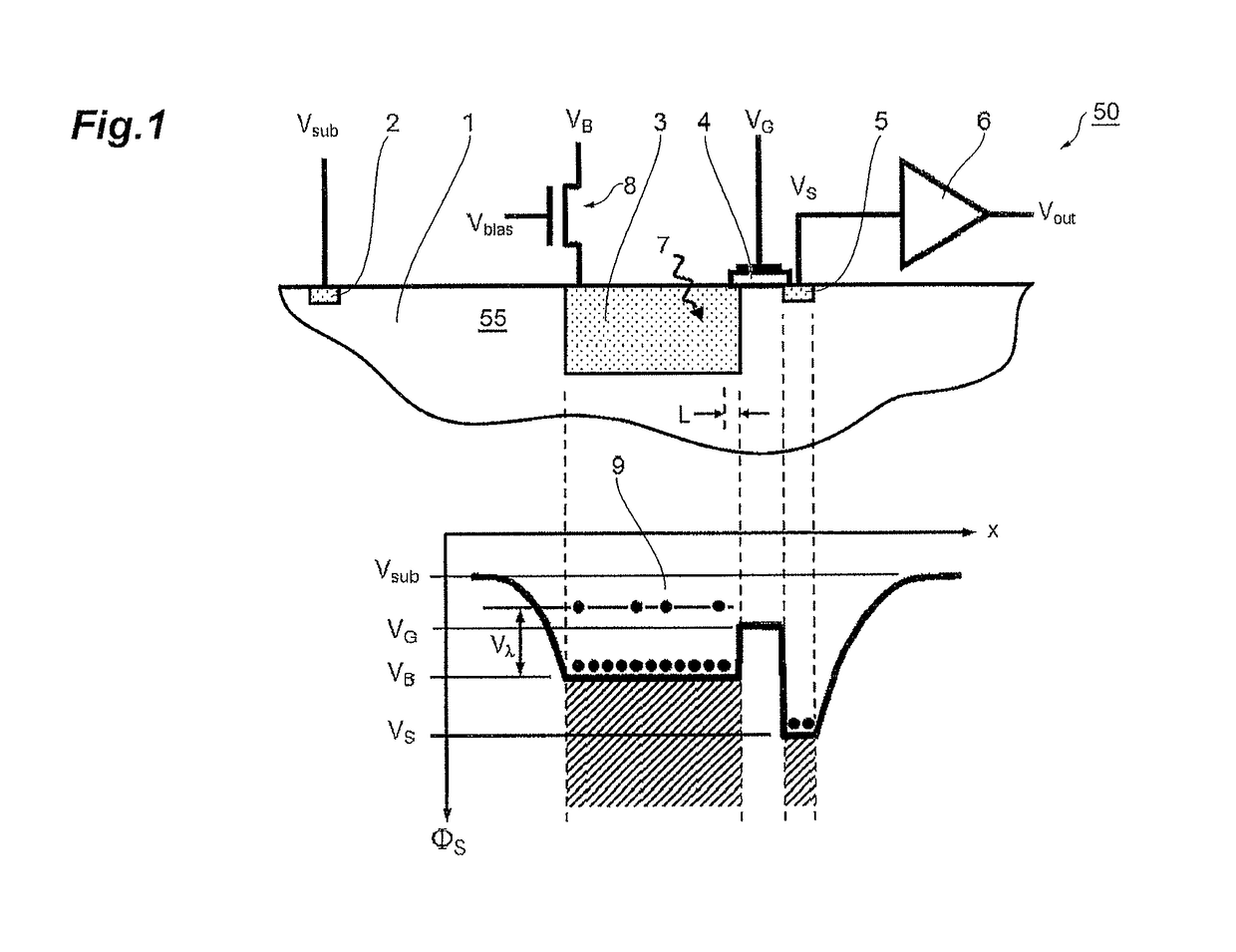
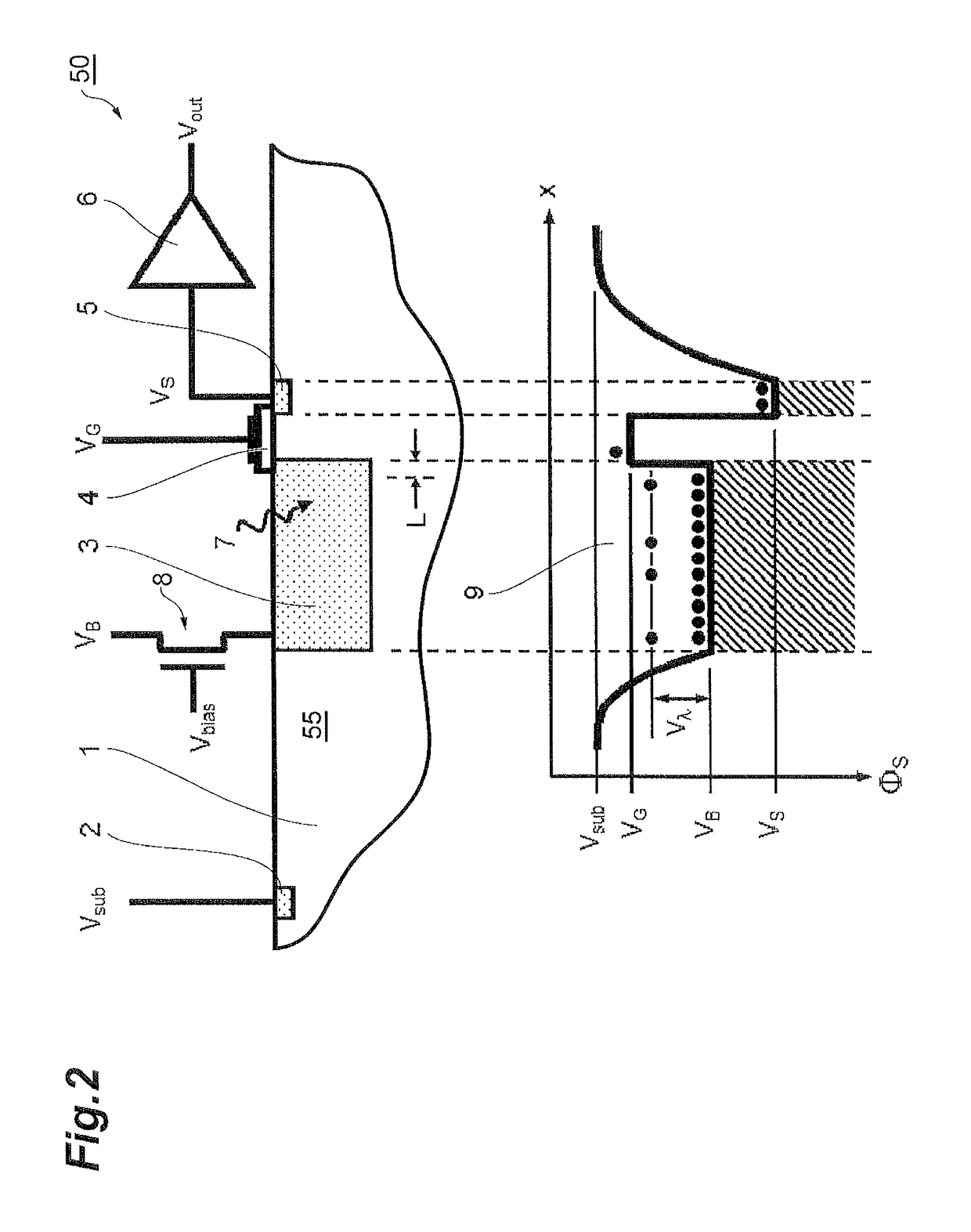
ActiveUS20150280047A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMobile chargeParticle physics
A photosensor for the detection of infrared radiation in the wavelength range of 1 to 1000 micrometers consists of a semiconductor substrate with a highly doped interaction volume for the incoming radiation. At the edge of this highly doped region, an extended gate electrode is placed consisting of a conducting material on top of an insulating layer. On the other side of the gate electrode, another highly doped semiconductor region is placed, acting as a charge collector. Through free carrier absorption in the interaction volume, incoming photons impart their energy on mobile charge carriers. In the case of free electrons, the gate electrode is biased slightly below the reset voltage of the interaction volume, so that the electrons carrying the additional energy of the absorbed photons can predominantly make the transition from the interaction volume across the gate electrode area to the charge collector volume.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
High-wavelength antimonide semiconductor laser structure
InactiveCN102208757AImprove performanceImprove structural efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCharge carrierWavelength
The invention discloses a high-wavelength antimonide semiconductor laser structure, which belongs to the field of epitaxial structures made from novel materials for semiconductor lasers and aims at the problems and shortcomings that the power, efficiency and the like of an antimonide laser are lowered along with the increasing of wavelengths. The laser structure can alleviate the problem that the power and efficiency of the laser are lowered due to free charge carrier absorption and the like, has the characteristics of low optical mode loss, strong cavity restrictions, low internal loss, high quantum well laser structure efficiency and the like, and can improve the performance of the antimonide laser such as the power, the efficiency and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
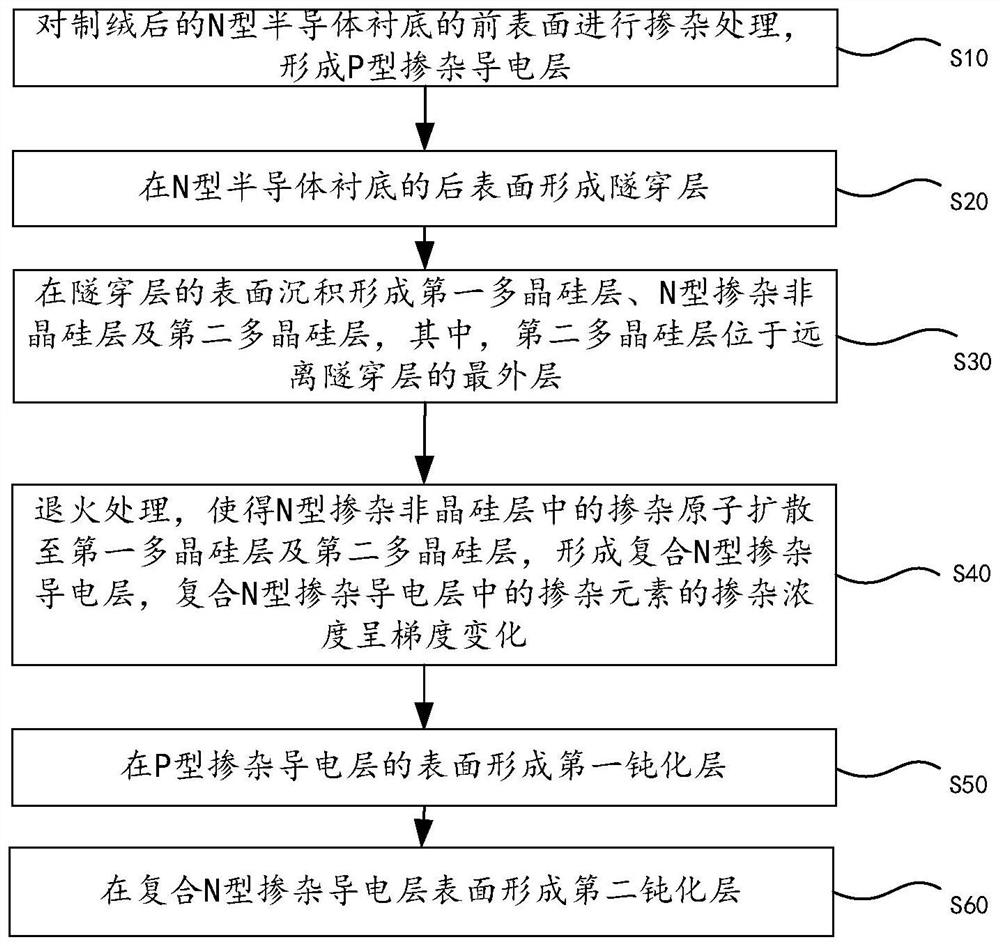
Solar cell, preparation method thereof and photovoltaic module
ActiveCN114038928AIncrease short circuit currentReduce absorptionPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesAmorphous siliconEngineering
The invention provides a solar cell and a preparation method thereof, and a photovoltaic module, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the doping of the front surface of a textured N-type semiconductor substrate, so as to form a P-type emitter; forming a tunneling layer on the rear surface of the semiconductor substrate; depositing and forming a first polycrystalline silicon layer, an N-type doped amorphous silicon layer and a second polycrystalline silicon layer on the surface of the tunneling layer; carrying out annealing treatment , so that doping elements in the N-type doped amorphous silicon layer are diffused to the first polycrystalline silicon layer and the second polycrystalline silicon layer, and a composite N-type doped polycrystalline silicon layer is formed; forming a first passivation layer on the surface of the P-type emitter; and forming a second passivation layer on the surface of the composite N-type doped polycrystalline silicon layer. According to the solar cell provided by the invention, the loss of parasitic optical absorption and free carrier absorption on the rear surface of the solar cell can be reduced, and the passivation performance is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINKO SOLAR CO LTD +1
Metal nanoparticle-insulator composite material grating coupler
InactiveCN106501898AImprove coupling efficiencyRealize filteringCoupling light guidesGrating couplingElectron-beam lithography
The invention discloses a metal nanoparticle-insulator composite material grating coupler and a preparation method and an application thereof. The grating coupler is composed of a metal nanoparticle-insulator composite material coupling grating and an insulator optical planar waveguide. The metal nanoparticle-insulator composite material coupling grating is a two-dimensional orthogonal rectangular diffraction grating which is prepared on the surface of the insulator optical planar waveguide implanted with metal ions by use of electron beam lithography and reactive ion beam etching technologies based on a formed metal nanoparticle-insulator composite material modified layer. Compared with an insulator grating coupler of the same structure, the grating coupler of the invention has higher coupling efficiency, and there is no loss caused by free carrier absorption. In addition, the grating coupler is insensitive to the polarization direction of light. In the realization process of light coupling, light can be filtered, split and deflected with the aid of the formation of guided wave and diffraction distortion. The metal nanoparticle-insulator composite material grating coupler can be used in the field of preparation of large-scale integrated optical circuits.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Optical measurement method for resistivity of semiconductor material
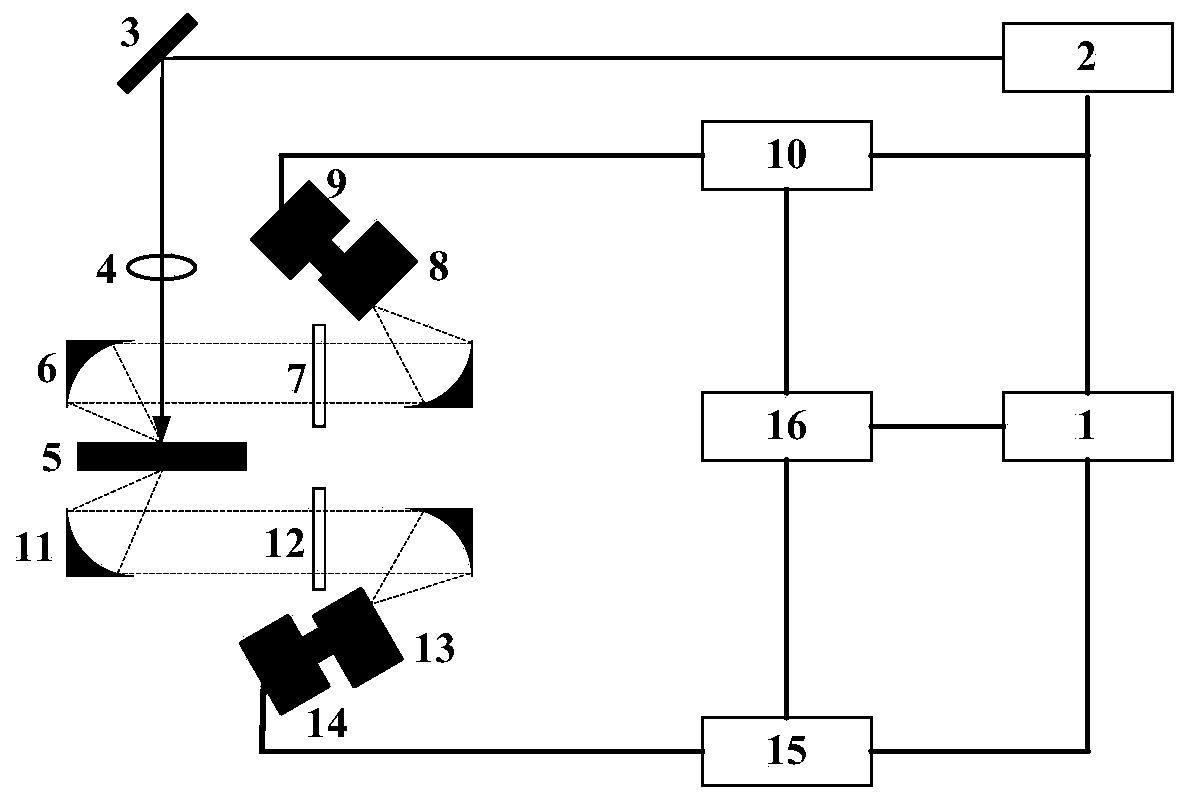
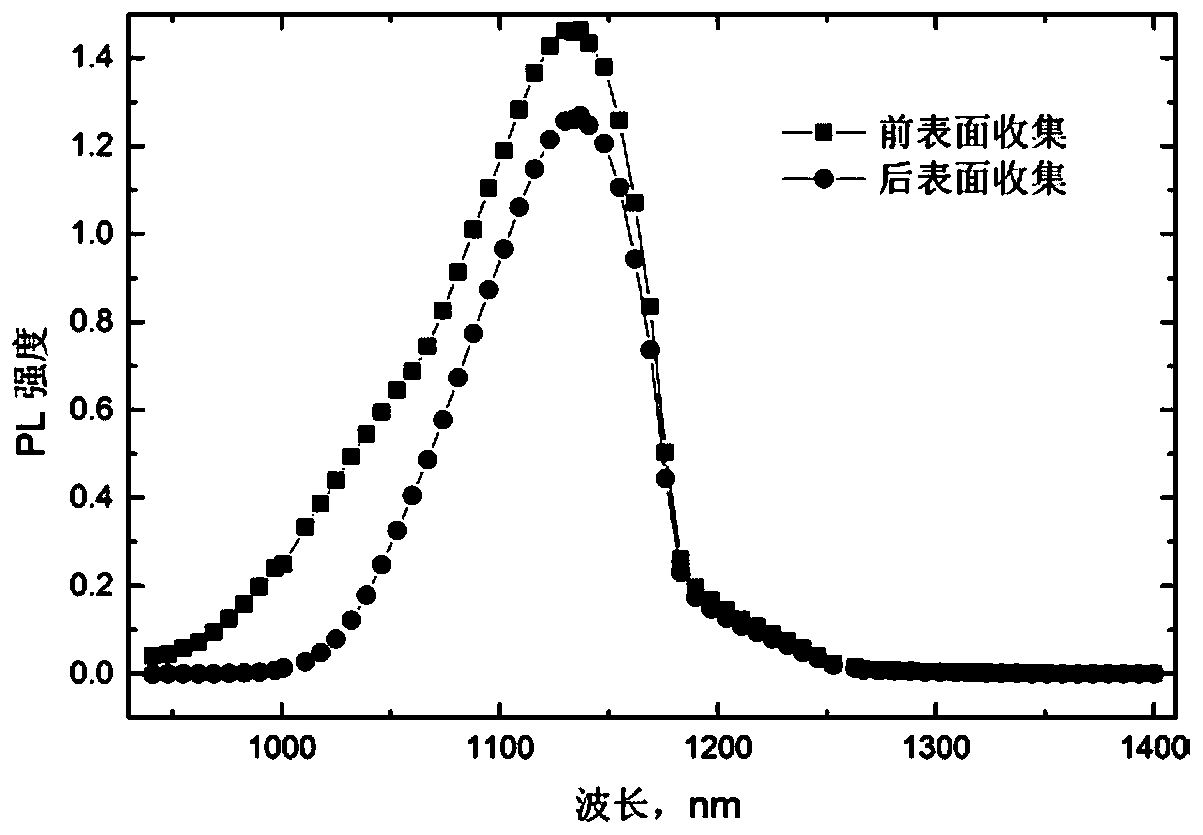
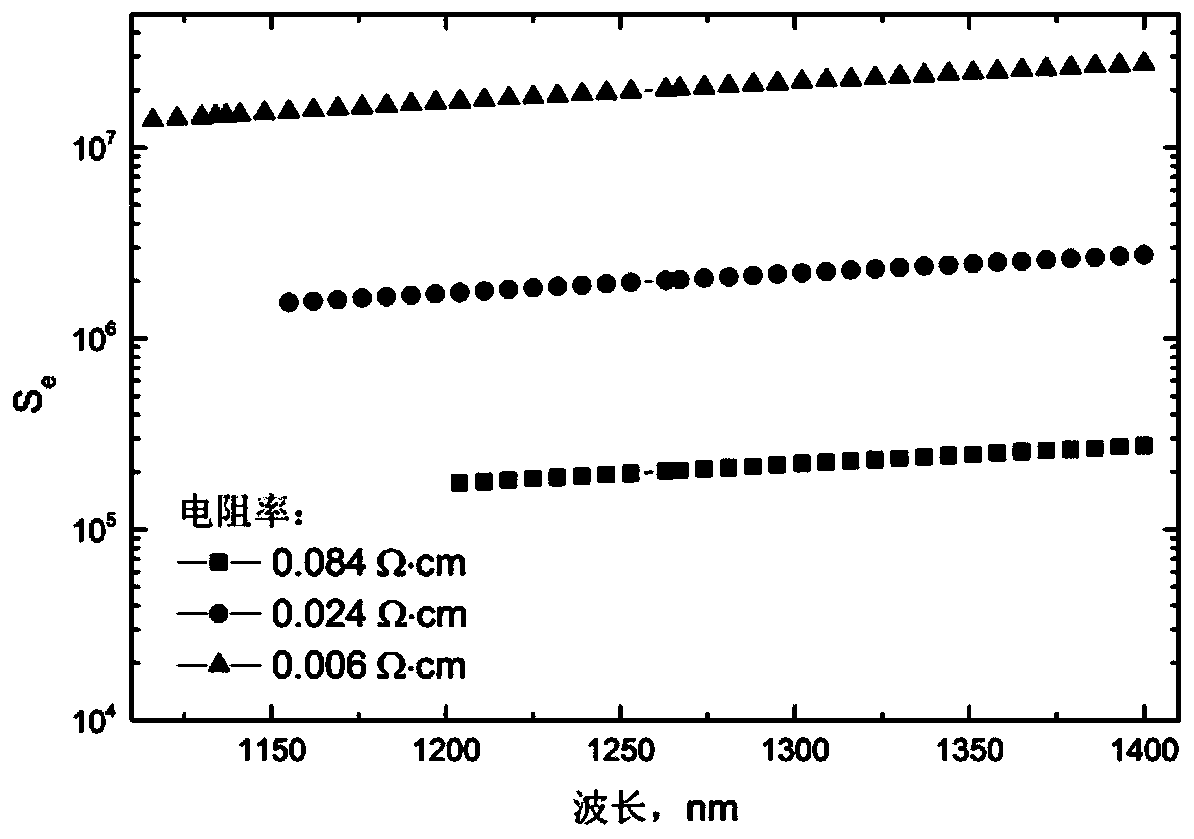
ActiveCN110646384ANo damageNo increase in measurement errorResistance/reactance/impedenceAnalysis by material excitationPhoton transmissionSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to an optical measurement method for resistivity of a semiconductor material. The principle of the optical measurement method is as follows: a semiconductor material generates excess carriers after absorption of a pump beam with the photon energy greater than the forbidden bandwidth; the excess carriers are subjected to radiative recombination to generate photons, and the photons are reabsorbed by the material during the process of transmitting the photons to the front and back surfaces; since the magnitude of a re-absorption coefficient is related to the photon energy, in addition to the difference in photon transmission paths, the photoluminescence spectra collected and measured by the front and back surfaces are different. The re-absorption of the photons mainly comprises intrinsic absorption and free carrier absorption; the magnitude of the free carrier absorption is related to the doping concentration of the semiconductor material, therefore, the doping concentration of the semiconductor material can be obtained by analyzing and calculating the photoluminescence spectra collected by the front and back surfaces, and the resistivity can be further calculated by a formula. According to the method of the invention, the defect that a traditional four point probe technology needs to be in contact with a sample is overcome, and the measurement precision of the resistivity of the semiconductor material is improved.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Method for measuring semiconductor doping concentration
InactiveCN100511623CHigh measurement accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTest sampleCharge carrier
A method for measuring semiconductor doping concentration, characterized in that: photocarrier radiation measurement technology and free carrier absorption measurement technology are integrated in the same test system, and the composite radiation signal and absorption signal of free carriers are obtained at the same time ; By changing the modulation frequency of the excitation light, the carrier radiation signal and absorption signal in the frequency domain are obtained; by changing the distance between the excitation light and the probe light, the carrier radiation signal and absorption signal in the space domain are obtained; The carrier radiation signal and absorption signal data of the standard sample are compared to obtain the doping concentration of the tested sample. The invention is based on the optical carrier radiation measurement technology and the free carrier absorption technology, and greatly improves the measurement accuracy of the doping concentration because the information of the two independent signals in the frequency domain and the space domain is integrated.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
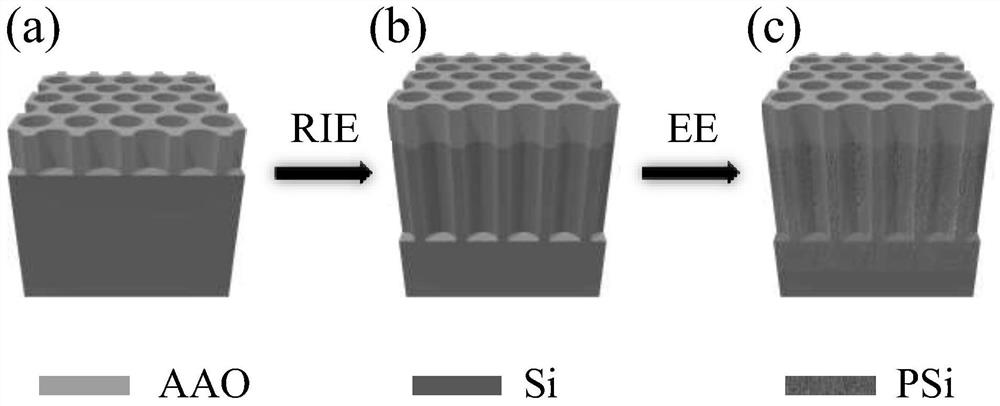
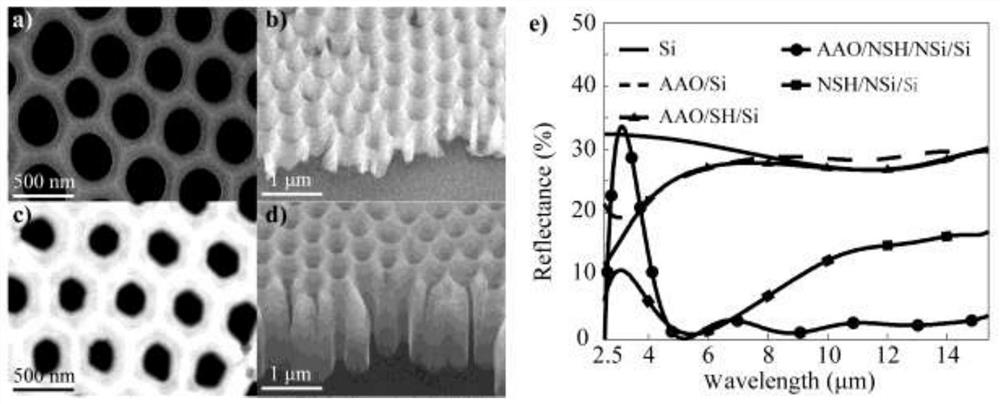
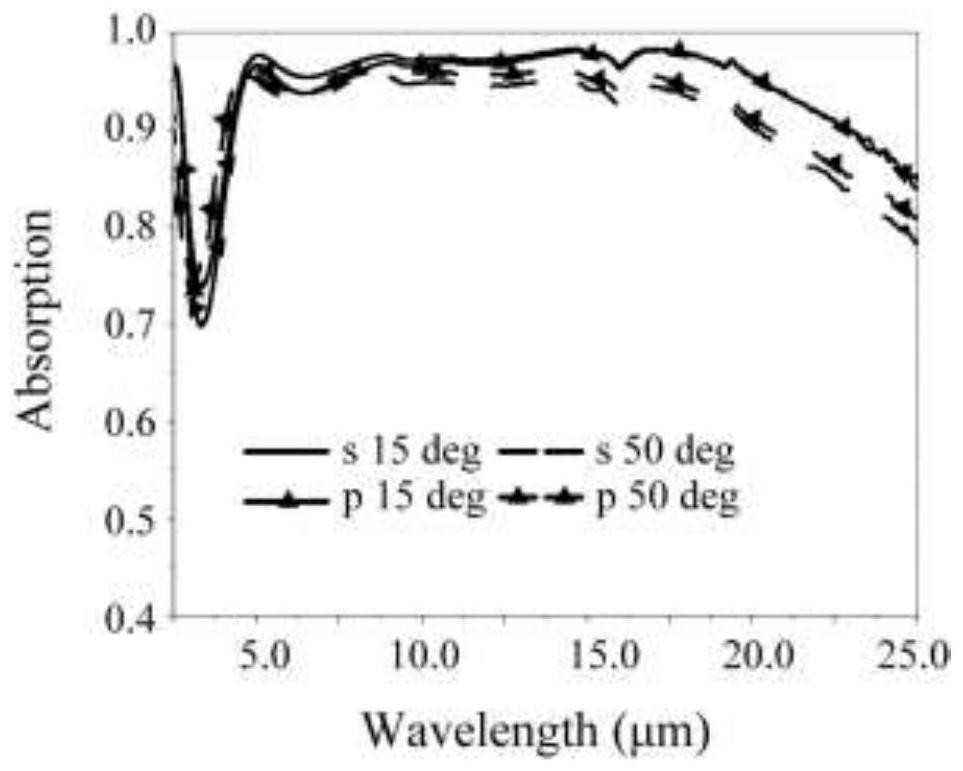
Medium-long wave infrared wide-spectrum light absorption material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111880247AReduce Impedance MismatchImprove light absorption efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyOptical elementsNanoholeRefractive index
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of inorganic functional materials, and particularly relates to a medium-long-wave infrared wide-spectrum light absorption material and a preparation method thereof, the medium-long-wave infrared wide-spectrum light absorption material is formed by sequentially stacking an alumina pore structure, a silicon pore structure, a silicon nano-pore structure and a silicon substrate; and the silicon nanopore structures are distributed in the silicon hole structures and the silicon substrate. The medium-long-wave infrared wide-spectrum light absorption material is formed by stacking four layers of materials in sequence, a refractive index gradient material is formed, and high-temperature-resistant wide-spectrum light absorption of medium-far infraredbands is achieved through free carrier absorption of a silicon material with the adjustable doping concentration in the medium-long-wave infrared bands. The medium-long wave infrared wide-spectrum light absorption material is large in absorption wavelength range, high in absorption efficiency, small in absorption layer thickness, free of polarization dependence, large in incident angle range andresistant to high temperature.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
High-speed electro-absorption modulator with low drive voltage
InactiveUS20060082855A1Increase confinement factorReduced insertion lossNanoopticsNon-linear opticsElectricityElectro-absorption modulator
The present invention is an electro-absorption modulator with a p-i-n-i-n epitaxy layer whose structure is p-i(MQW)-n+-i(collector)-n to release the trade-off between the operation voltage and the speed, to increase the confinement factor of the light in the un-doped layers, and to reduce the insertion loss caused by the free-carrier absorption in the doped layers, wherein MQW stands for Multiple-Quantum Well.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN114006265AReduce absorptionPrevent oxidationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a vertical cavity surface emitting laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The laser comprises a substrate, a non-doped first Bragg reflector, a first contact layer, a non-doped lower coating layer and a non-doped first table top, and the first table top comprises an active layer and an upper coating layer which are sequentially formed on the lower coating layer; N n-type doped second table top, formed on the first table top, the second table top comprising a current expansion layer and a second contact layer which are sequentially formed on the first table top, and the side face of the second table top being subjected to p-type diffusion to form an annular diffusion region; and a non-doped second Bragg reflector formed on the second mesa. According to the invention, current limitation is carried out by using a p++ n junction depletion region through a micro-mesa side selection region p-type diffusion method, so that oxidation and multiple epitaxial processes with high difficulty and low yield are avoided. In addition, the non-doped DBR structure is adopted, so that the free carrier absorption can be reduced while the epitaxial growth difficulty is reduced.
Owner:苏州镓港半导体有限公司
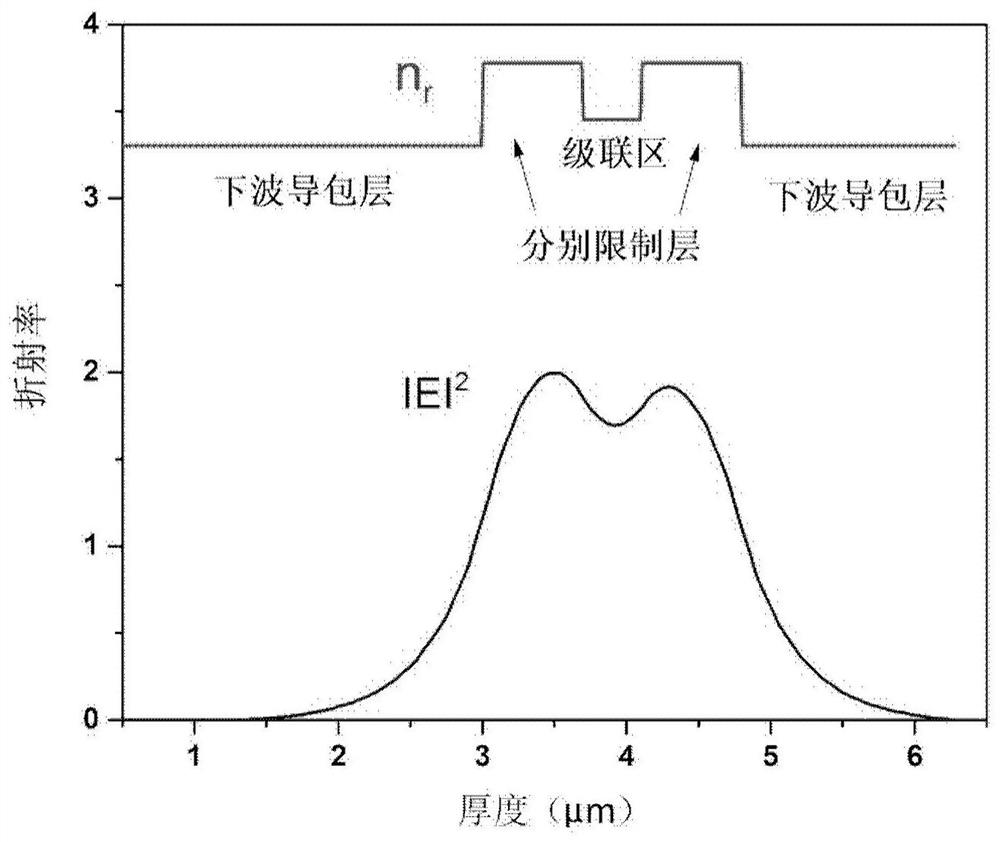
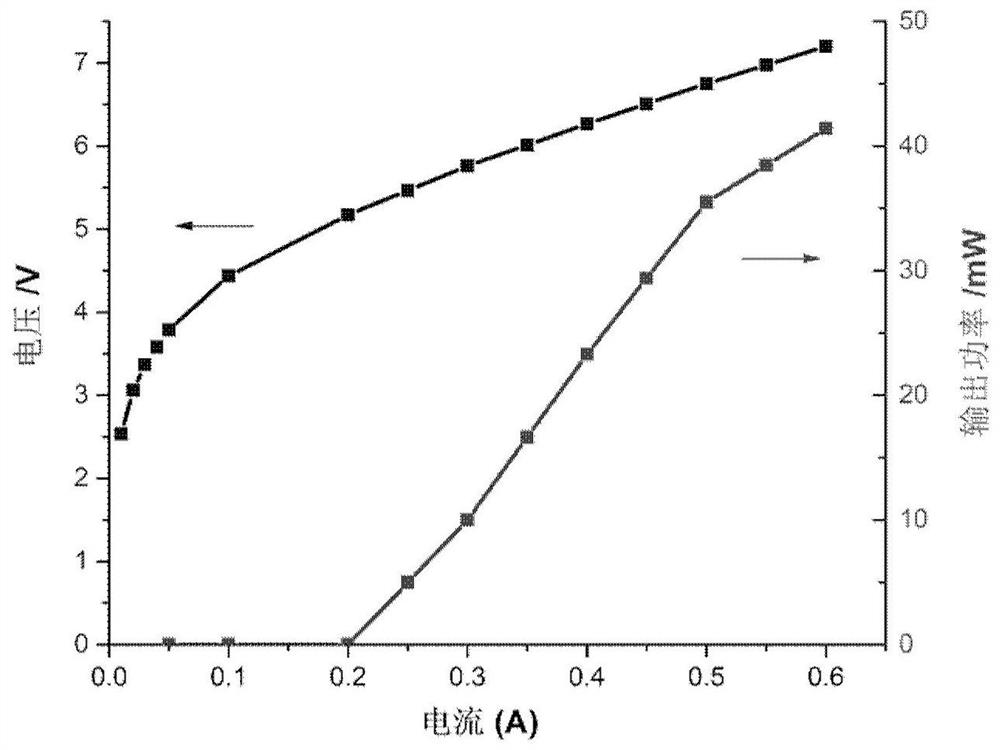
Gradually doped wide waveguide interband cascaded laser and its preparation method
ActiveCN109149368BIncrease the doping concentrationReduce doping concentrationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersHeterojunctionGain
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
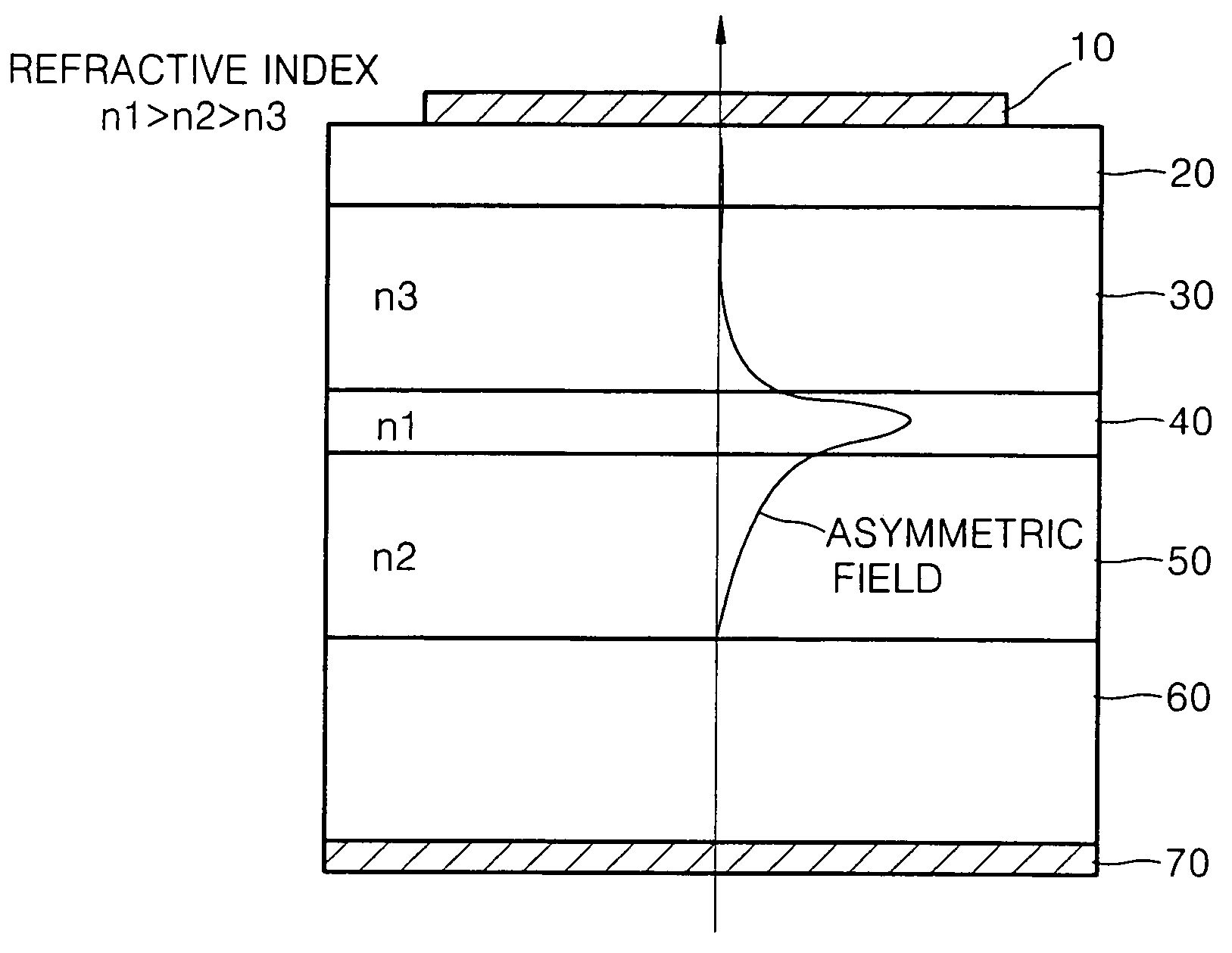
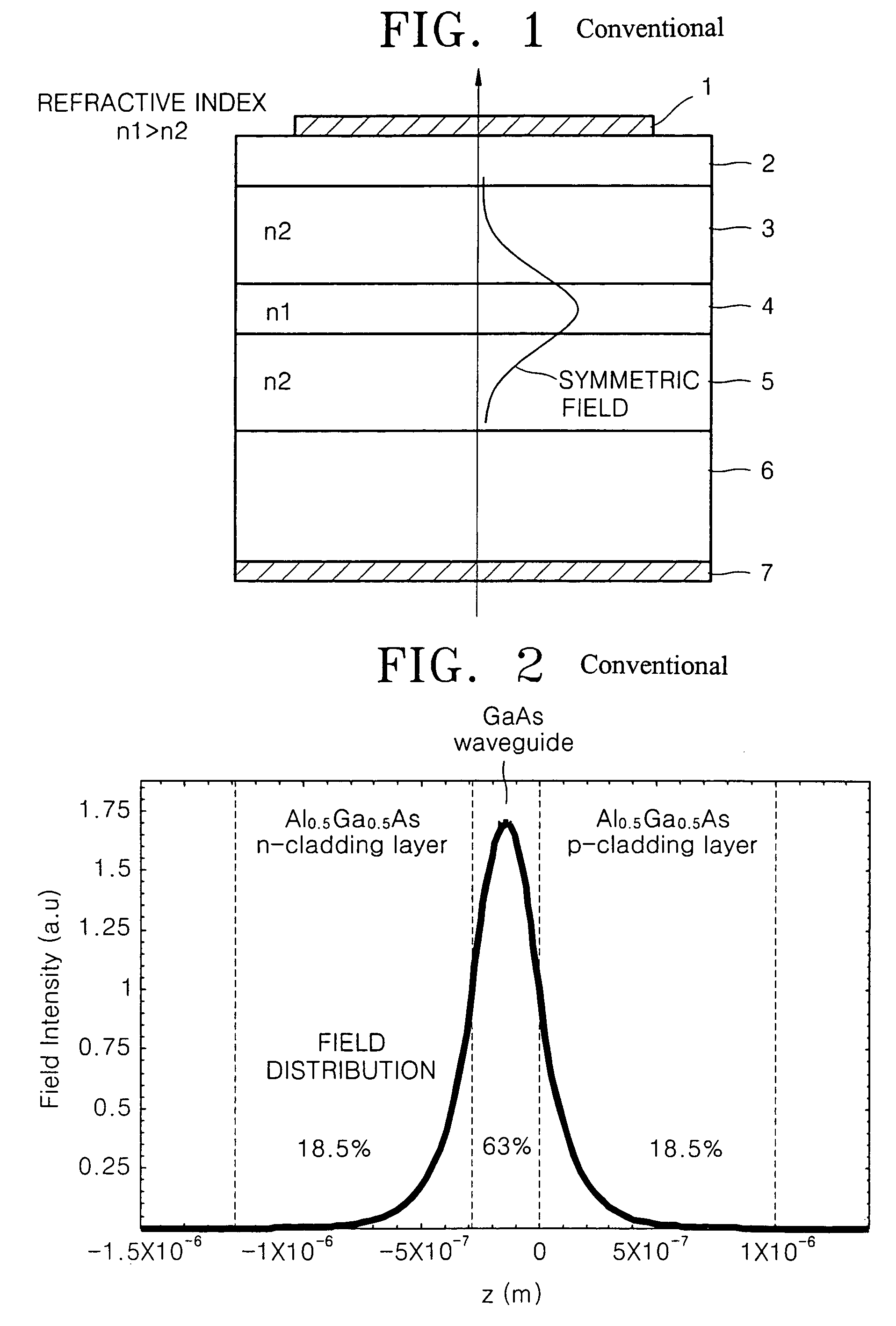
Asymmetric waveguide GaInAs laser diode
InactiveUS7113531B2Improve luminous efficiencyTotal current dropOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureWaveguideActive layer
A laser diode is provided. The laser diode has a structure in which reflective index of an n-cladding layer formed on a first face of the active layer is higher than that of a p-cladding layer formed on a second face. This asymmetric waveguide structure suppresses extension of field into the p-cladding layer thus reducing free carrier absorption in the p-cladding layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A kind of mid-long wave infrared broad-spectrum light-absorbing material and its preparation method
ActiveCN111880247BWide absorption wavelength rangeImprove absorption efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyOptical elementsNanoholeFar-red
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of inorganic functional materials, and particularly relates to a medium-long-wave infrared wide-spectrum light-absorbing material and a preparation method thereof. The silicon substrates are stacked sequentially, and the silicon nanoporous structure is distributed in the silicon hole structure and the silicon substrate. The medium and long-wave infrared wide-spectrum light-absorbing material of the present invention is composed of four layers of materials stacked in sequence to form a material with a gradient gradient of refractive index. The COSCO High-temperature resistant broad-spectrum light absorption in the infrared band. The medium and long-wave infrared wide-spectrum light-absorbing material of the invention has a large absorption wavelength range and high absorption efficiency, a thin absorption layer, no polarization dependence, a large incident angle range, and high temperature resistance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114825030AImprove cooling effectOverall small sizeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
The vertical cavity surface emitting laser comprises a substrate, a lower grating layer, an active layer, a contact layer and an upper grating layer which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top, the upper grating layer is arranged in the middle of the contact layer in a protruding mode, and a first step part is formed between the side wall of the upper grating layer and the contact layer; the contact layer and the active layer are arranged in the middle of the lower grating layer in a protruding mode, a second step portion is formed between the side wall of the contact layer and the side wall of the active layer and the lower grating layer, a p-type electrode is further arranged on the contact layer, a heat dissipation electrode is further arranged on the p-type electrode, and the heat dissipation electrode extends to the second step portion from the first step portion. According to the invention, the p-type electrode is arranged on the contact layer, so that the p-type electrode is close to the active layer, and free carrier absorption and spontaneous heating phenomena can be effectively reduced; in addition, the p-type electrode is also provided with the heat dissipation electrode, so that the contact surface between the heat dissipation electrode and the outside is further increased, and the heat dissipation performance of the vertical cavity surface emitting laser is improved.
Owner:LITUREX GUANGZHOU CO LTD
High-wavelength antimonide semiconductor laser structure
InactiveCN102208757BImprove performanceImprove structural efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCharge carrierLength wave
The invention discloses a high-wavelength antimonide semiconductor laser structure, which belongs to the field of epitaxial structures made from novel materials for semiconductor lasers and aims at the problems and shortcomings that the power, efficiency and the like of an antimonide laser are lowered along with the increasing of wavelengths. The laser structure can alleviate the problem that thepower and efficiency of the laser are lowered due to free charge carrier absorption and the like, has the characteristics of low optical mode loss, strong cavity restrictions, low internal loss, highquantum well laser structure efficiency and the like, and can improve the performance of the antimonide laser such as the power, the efficiency and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for mfg. semiconductor device
InactiveCN1476061AImprove temperature control effectSmall temperature deviationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlLight irradiation
Provided is a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device which can reduce variations of temperature in a wafer surface at a low cost, by improving the temperature controllability of an RTP. In a step for performing thermal treatment by subjecting the semiconductor substrate with a lamp light irradiation, a free carrier absorption layer for absorbing the irradiated lamp light is provided, in advance, in the semiconductor substrate. Thus, it is possible to increase the temperature controllability in a low temperature range during RTP process, and to reduce, at a low cost, variations in the substrate temperature, not only in a low temperature range but also in a processing temperature range. As a result, semiconductor devices that require precise thermal treatment can be manufactured, without deteriorating the characteristics of the resulting semiconductor devices.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
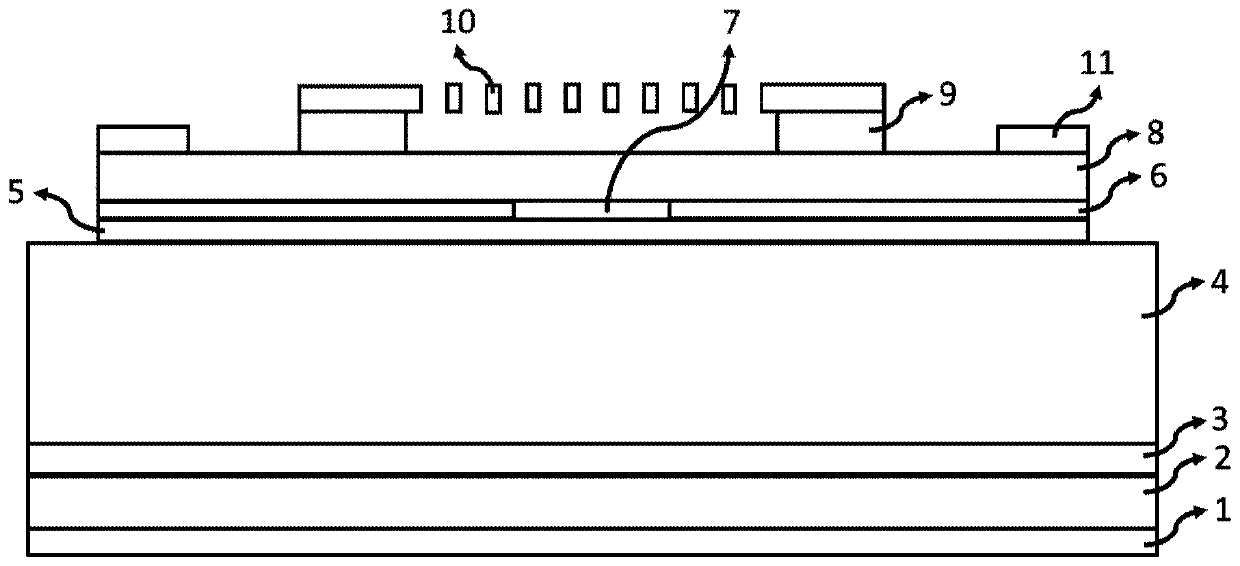
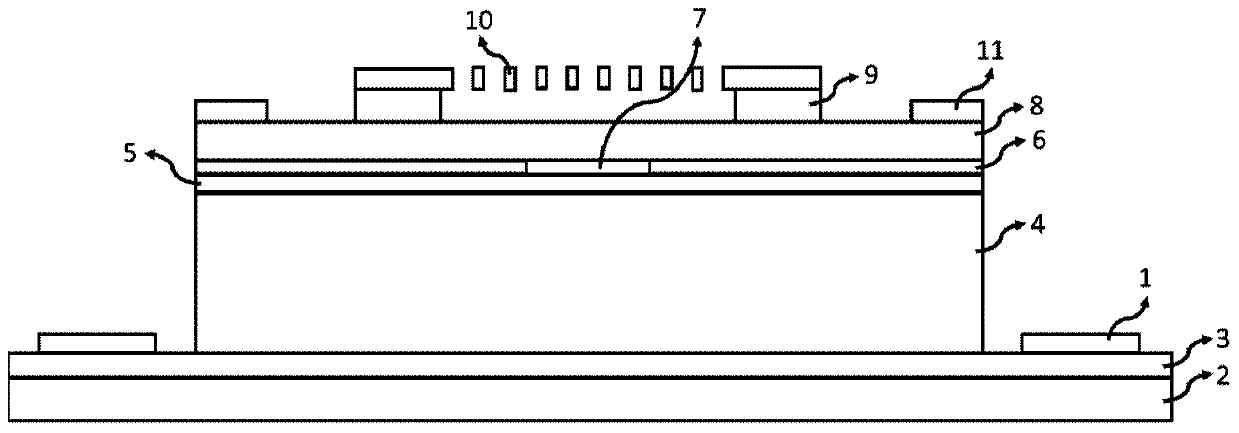
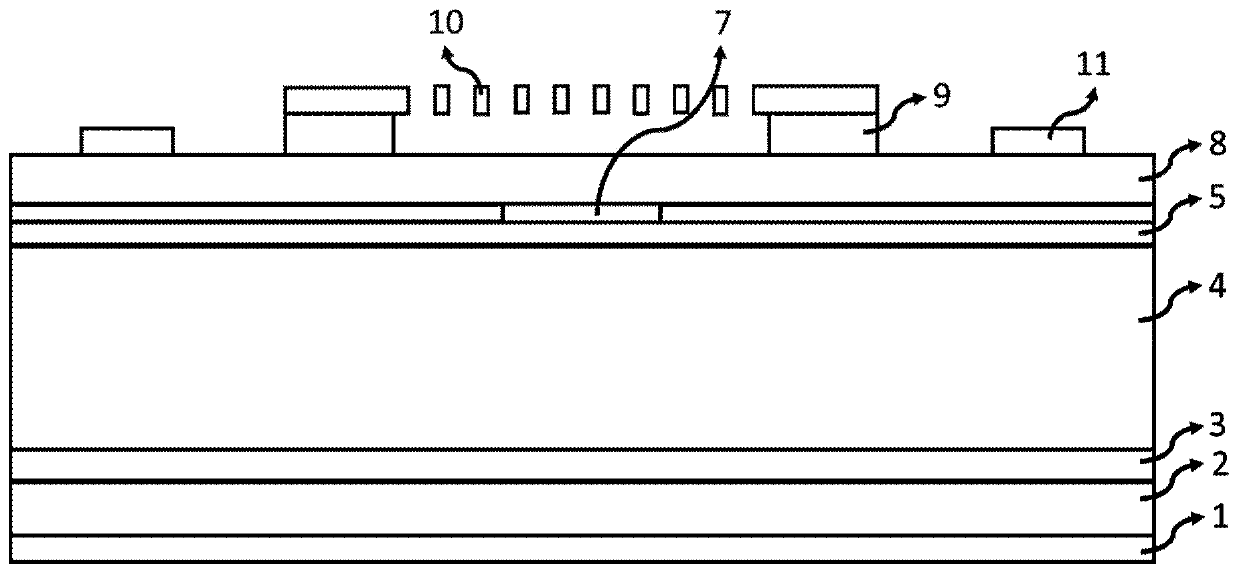
Method for testing free carrier absorption loss and battery sample
PendingCN114675199AAdapt to the requirements of mass rapid testingOmit the preparation processMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic energy generationQuantum efficiencyParticle physics
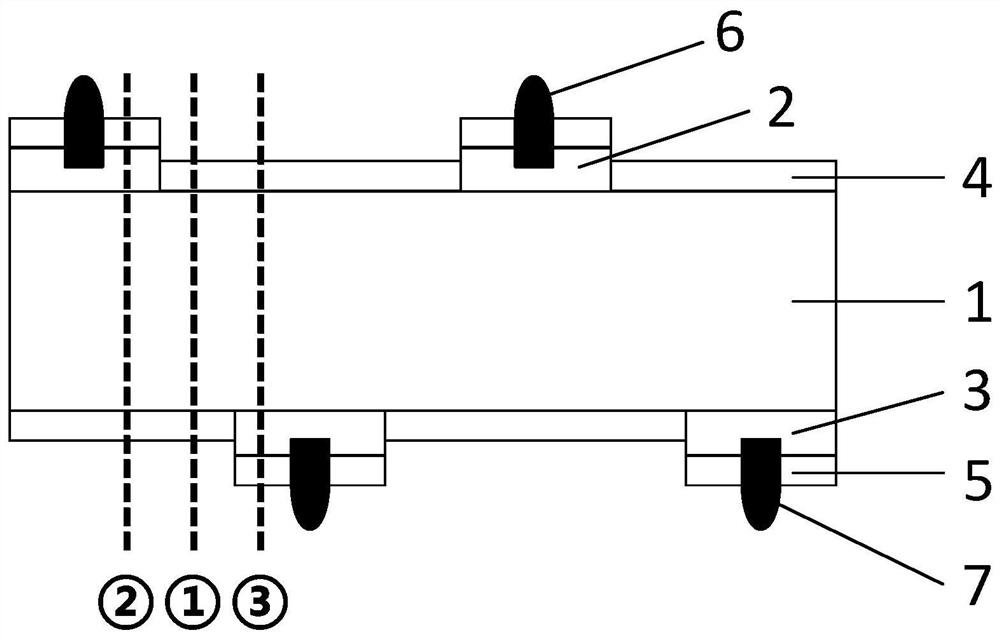
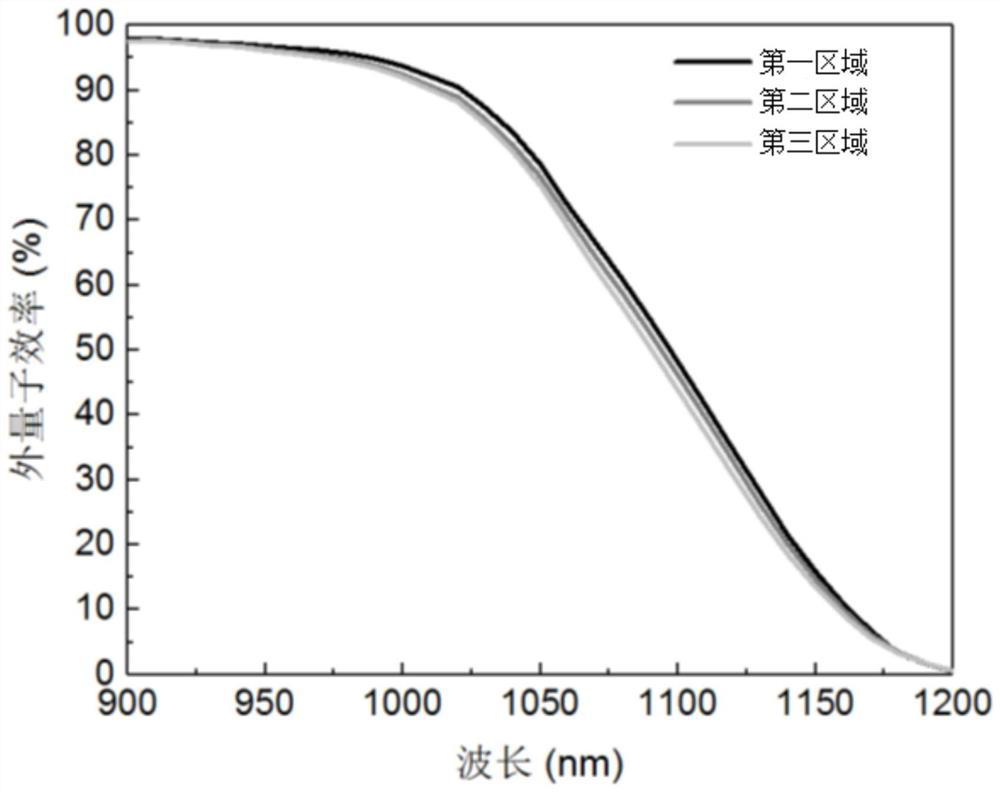
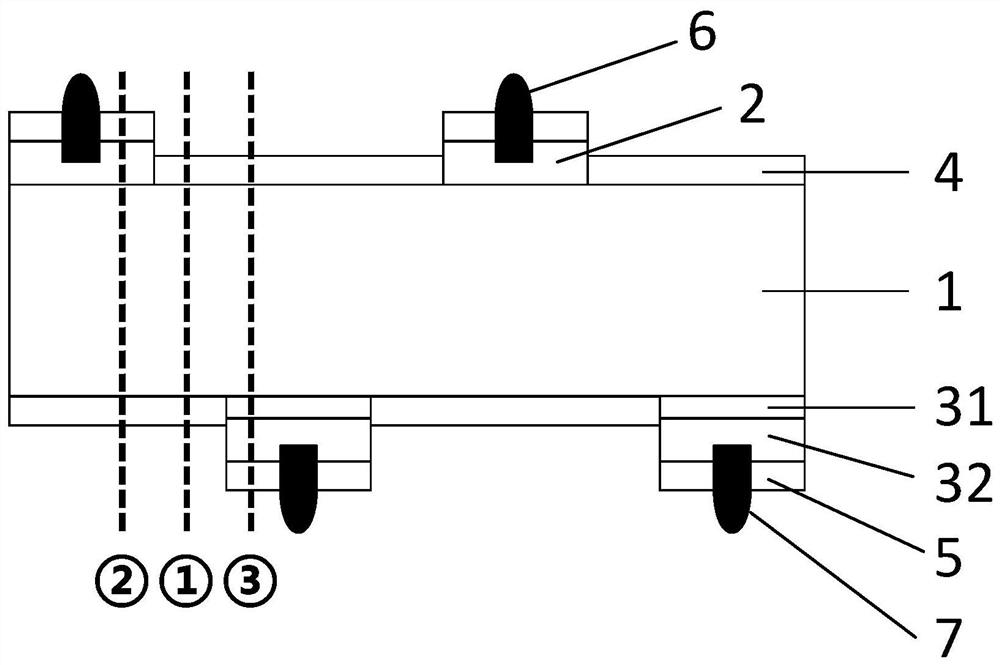
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cells, and provides a method for testing free carrier absorption loss and a cell sample, and the method comprises the steps: preparing a cell sample with a specific structure, the battery sample comprises a first region, a second region and a third region; the first region is provided with a first heavily-doped layer on the front surface and then a second heavily-doped layer on the rear surface; the third region is provided with a second heavily-doped layer on the front surface and then a second heavily-doped layer on the rear surface; testing the external quantum efficiency of the first area, the second area and the third area in the near-infrared band; obtaining integral current density values of the first region, the second region and the third region according to the external quantum efficiency and the AM1.5 G spectrum of the first region, the second region and the third region; and obtaining the free carrier absorption loss according to the integral current density values of the first region, the second region and the third region. The method is simpler in test, short in time consumption and low in cost, and can quickly and accurately realize quantitative detection of free carrier absorption loss.
Owner:TAIZHOU ZHONGLAI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
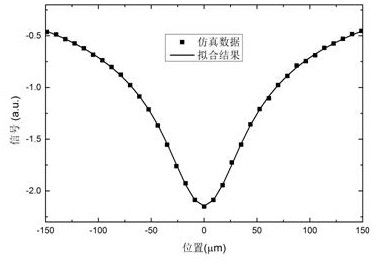
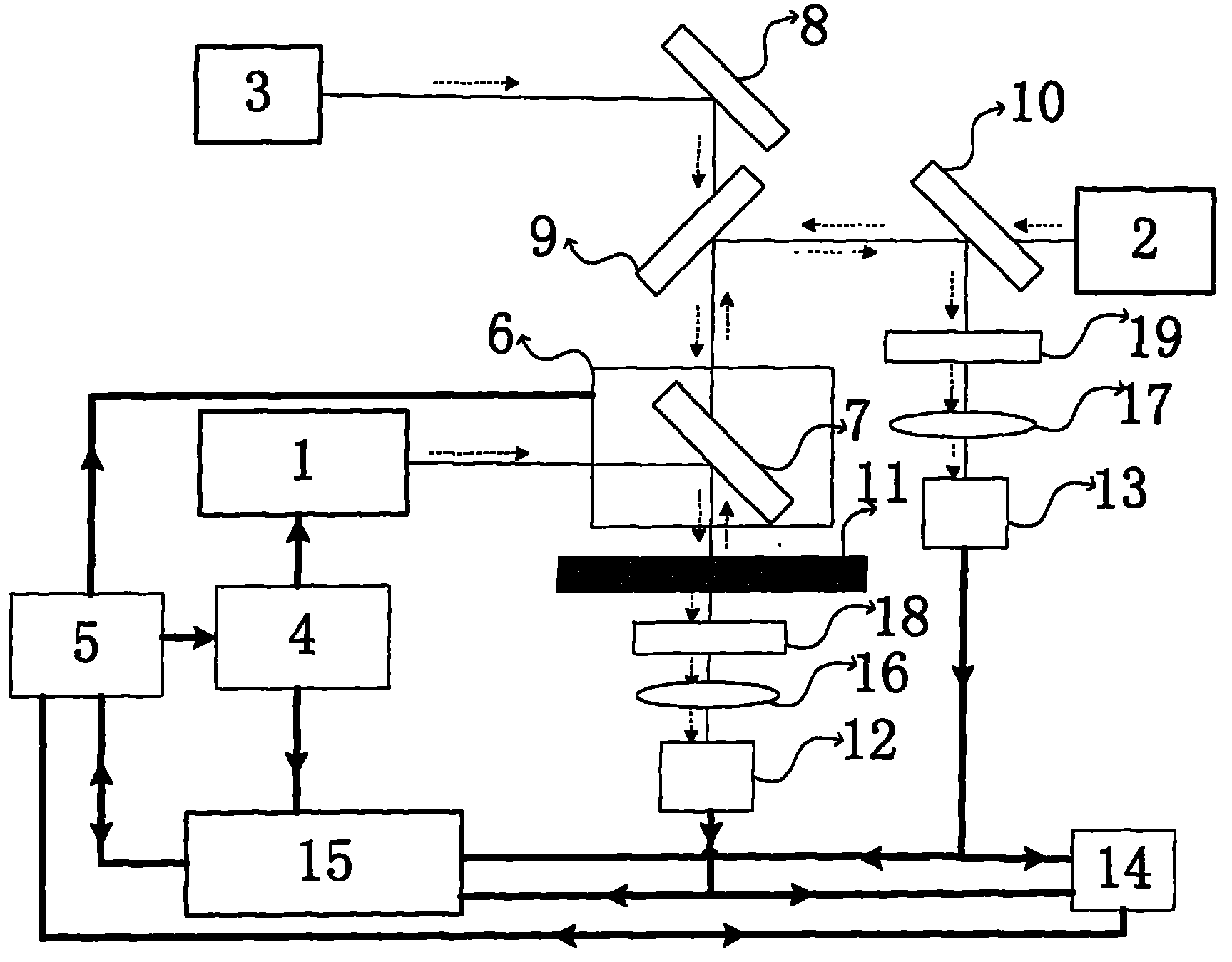
A Method for Measurement of Semiconductor Material Properties Based on Free Carrier Absorption Imaging
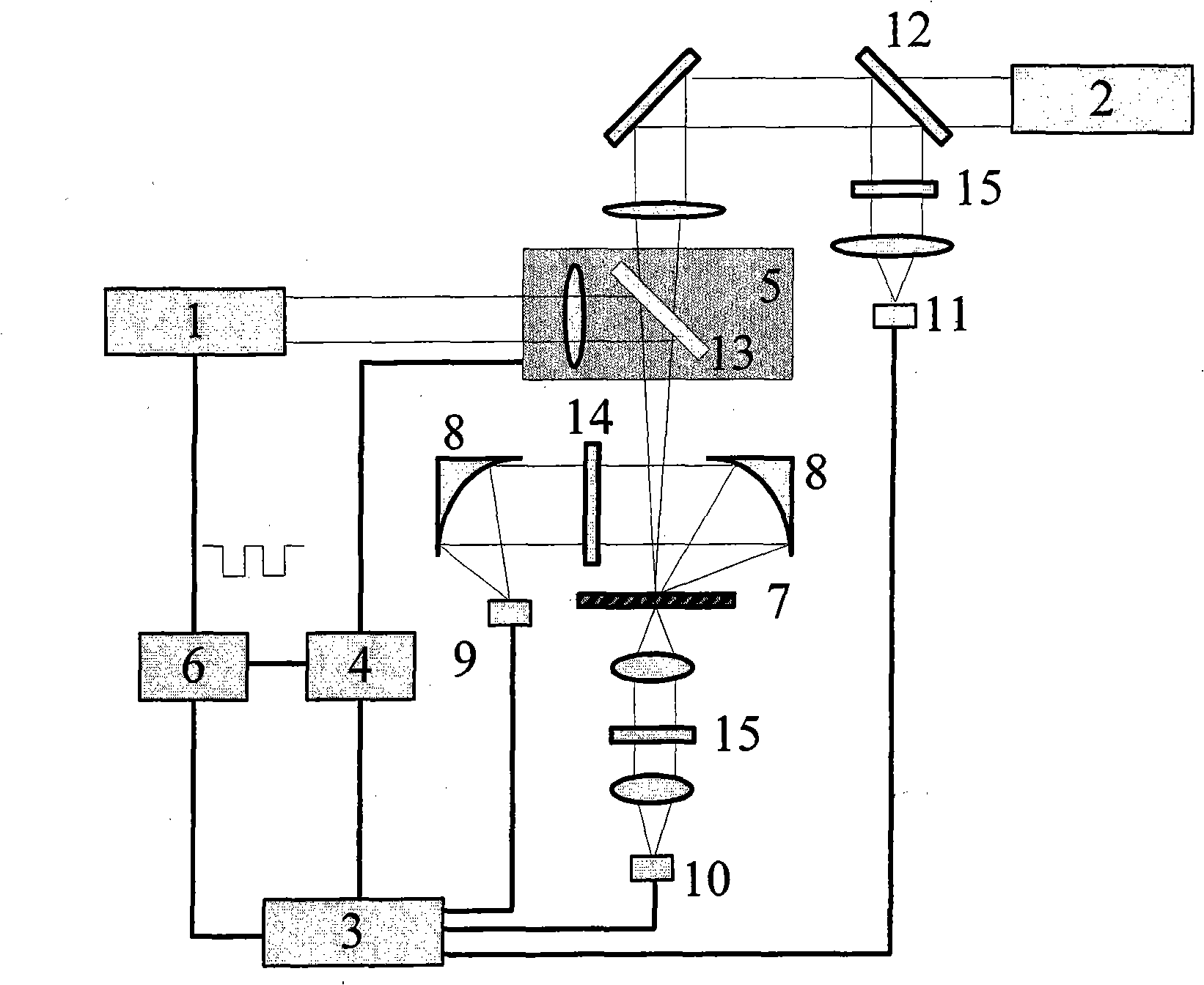
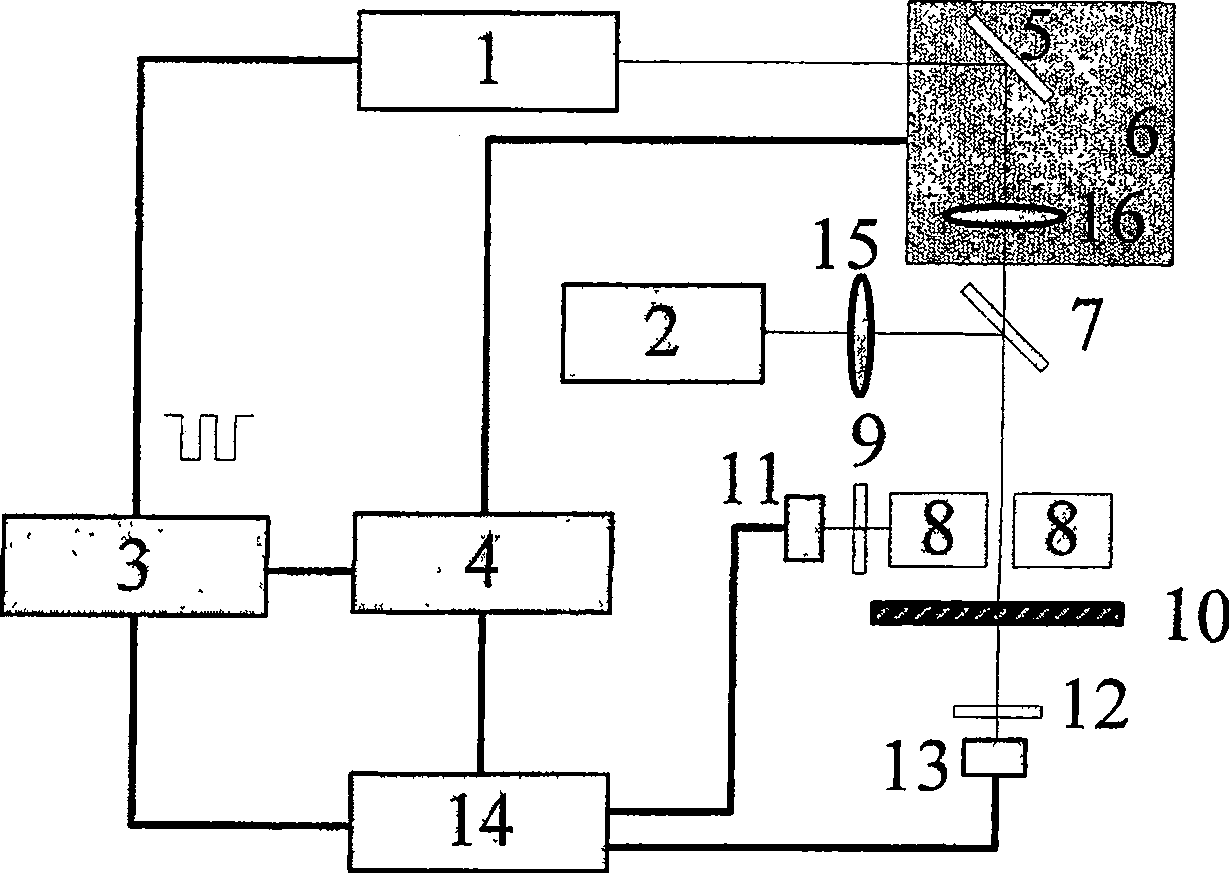
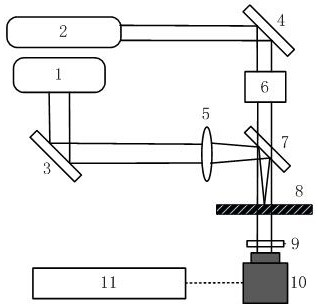
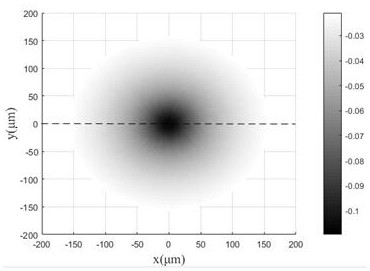
ActiveCN109239023BFast measurementAvoid errorsAnalysis by material excitationSemiconductor materialsPhoto irradiation
The invention relates to a measurement method for semiconductor material characteristics based on free carrier absorption imaging and solves the problems of defect of an existing semiconductor material characteristic measurement technology. The method adopted by the invention comprises the steps of (1) vertically irradiating continuous detection laser light to a surface of a measured semiconductorsample, measuring by a near-infrared camera and recording the transmitted detection light intensity spatial distribution S0 at this time by a computer; (2) vertically irradiating the focused continuous pumping laser light to a center position of a sample detection light radiation region, measuring by the near-infrared camera and recording the transmitted detection light intensity spatial distribution S1 at this time by the computer, wherein the size of a detection laser light beam incident to the surface of the sample is greater than the size of a pumping laser light beam focusing on the surface of the sample; (3) processing the transmitted detection light intensity spatial distribution imaging results S0 and S1 obtained in steps (1) and (2), that is S=(S1-S0) / S0; and (4) intercepting measurement data having different distances to a peak value along the peak position of the free carrier absorption imaging result to obtain multiple characteristic parameters of the to-be-measured sample.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
A semiconductor material property measurement device and method based on double probe beam
InactiveCN101551324BCompensate for the shortcomings of low measurement accuracyIncrease credibilityResistance/reactance/impedenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMeasurement deviceSemiconductor materials
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor photosensor for infrared radiation
A photosensor for the detection of infrared radiation in the wavelength range of 1 to 1000 micrometers consists of a semiconductor substrate with a highly doped interaction volume for the incoming radiation. At the edge of this highly doped region, an extended gate electrode is placed consisting of a conducting material on top of an insulating layer. On the other side of the gate electrode, another highly doped semiconductor region is placed, acting as a charge collector. Through free carrier absorption in the interaction volume, incoming photons impart their energy on mobile charge carriers. In the case of free electrons, the gate electrode is biased slightly below the reset voltage of the interaction volume, so that the electrons carrying the additional energy of the absorbed photons can predominantly make the transition from the interaction volume across the gate electrode area to the charge collector volume.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com