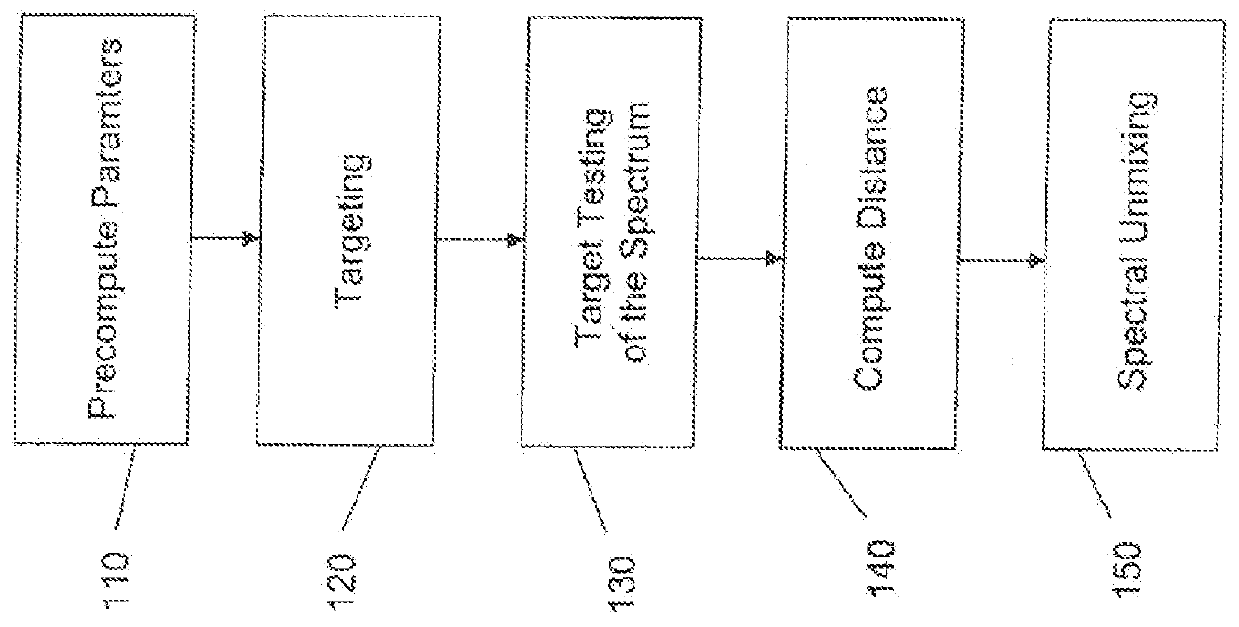
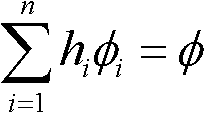Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
620 results about "Long wave infrared" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Very-long wave infrared (VLWIR) (12 to about 30 µm, covered by doped silicon). Near-infrared is the region closest in wavelength to the radiation detectable by the human eye. mid- and far-infrared are progressively further from the visible spectrum.
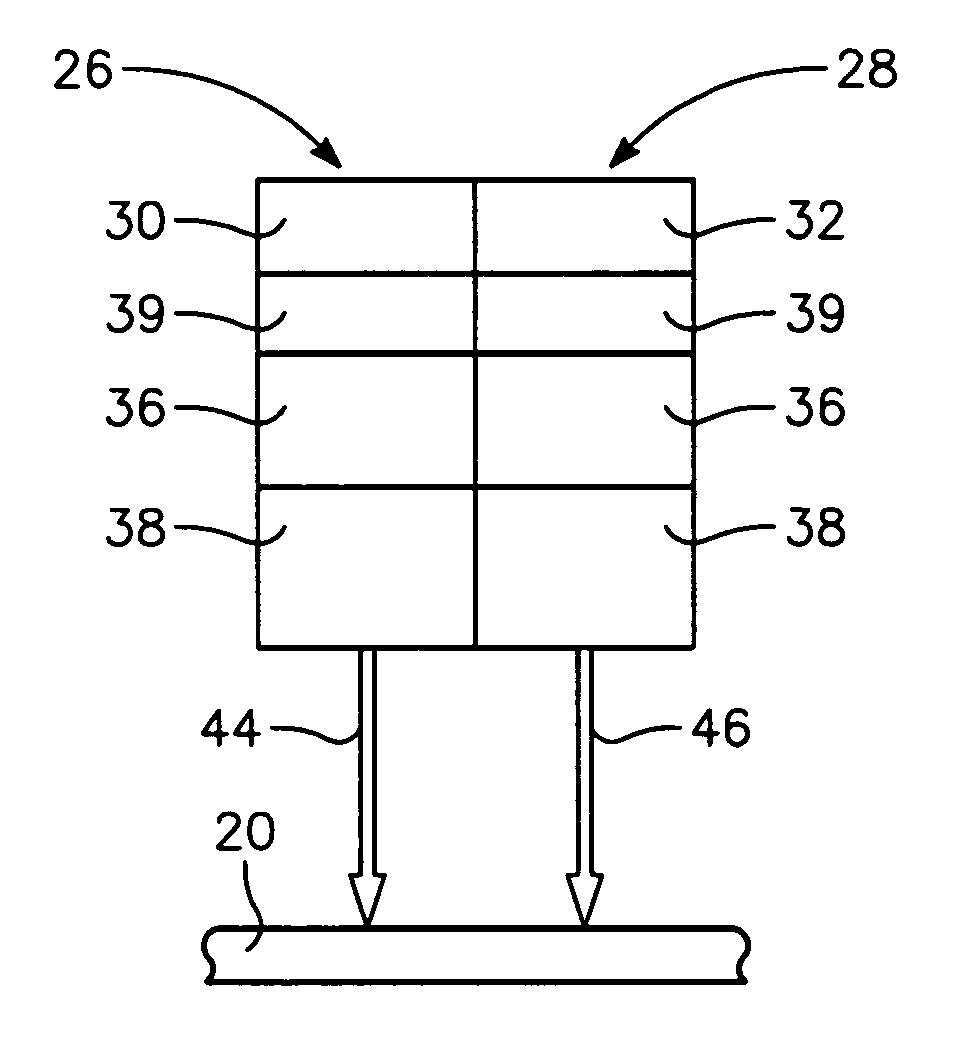
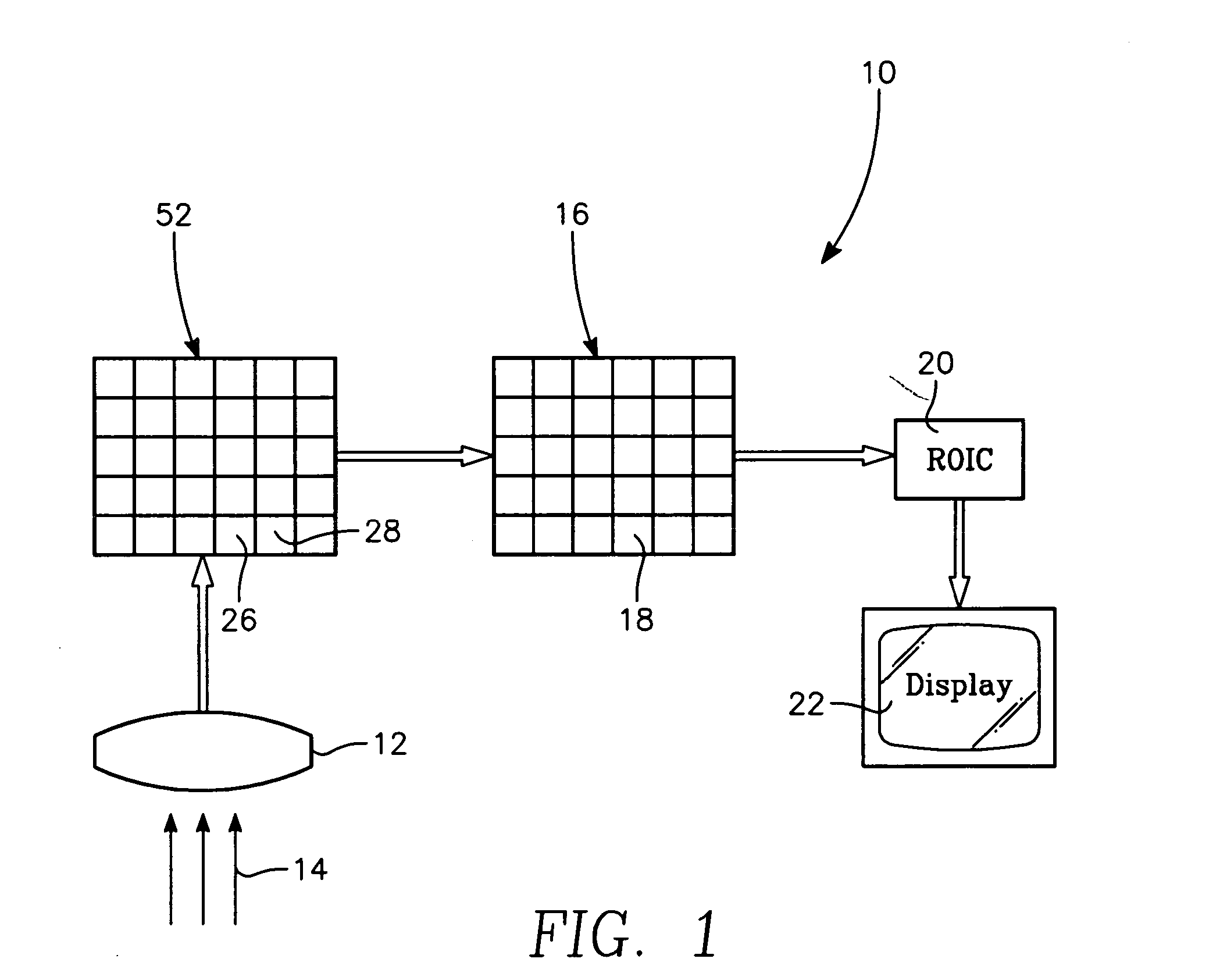
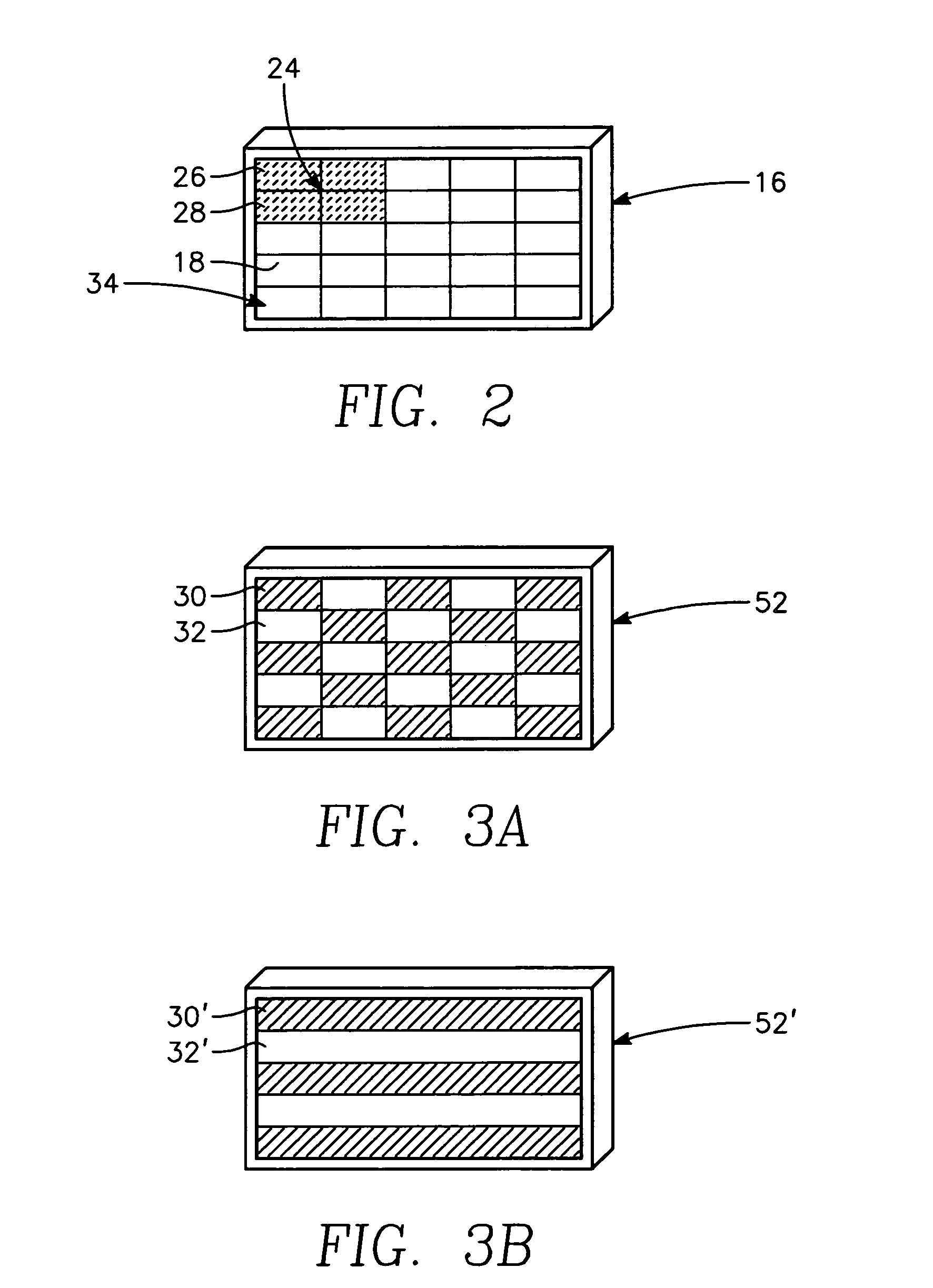
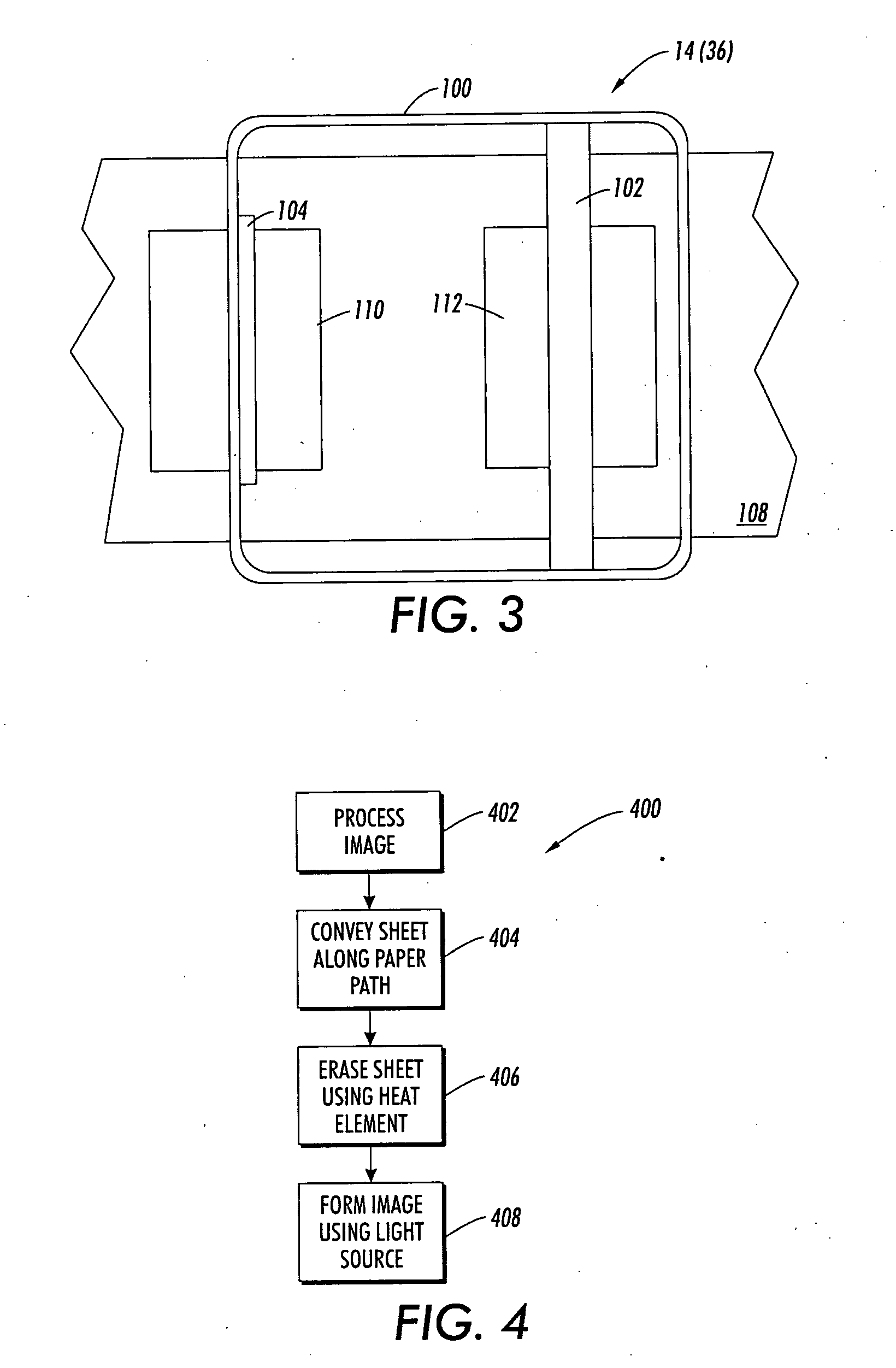
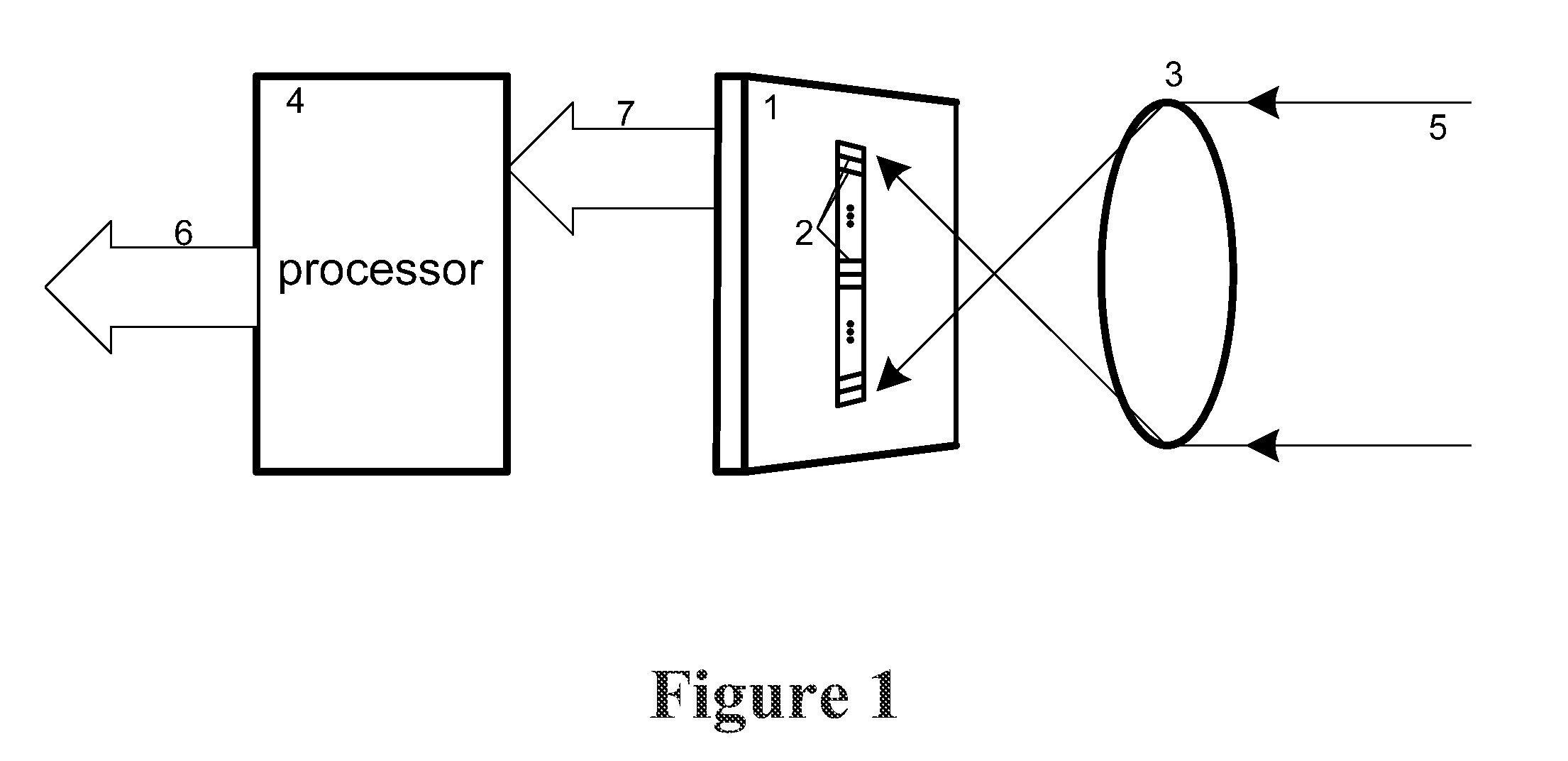
Multi-color infrared imaging device
InactiveUS7109488B2Television system detailsSolid-state devicesCheckerboard patternLong wave infrared
A multi-color IR imaging device includes optics that direct mid-wave infrared (MWIR) and long-wave infrared (LWIR) radiation onto a focal plane array having LWIR and MWIR detection layers. Pixel groups that include at least one first pixel and one second pixel are defined on the focal plane array, and a first filter and a second filter which form part of an inhomogeneous filter is placed over the respective first and second pixels in a checkerboard pattern, in close proximity to the detection layers. This allows MWIR radiation in M band, and LWIR radiation in an L1 band to pass therethrough and illuminate the first pixels, and M, L1, and a separate LWIR band designated L2 to pass therethrough and illuminate the second pixels. To simultaneously image both MWIR and LWIR, the focal plane array is placed at a predetermined distance from the optics so that the MWIR spot size covers a single pixel and the LWIR spot size is about the same area as the area of a group of two first pixels and two second pixels. Since all pixels receive the M band, half of the pixels in the group receive the L1 band, and the other half receives the L2 band, three bands can be generated. This allows simultaneous imaging of MWIR and two sub-bands of the LWIR from the same point in space.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
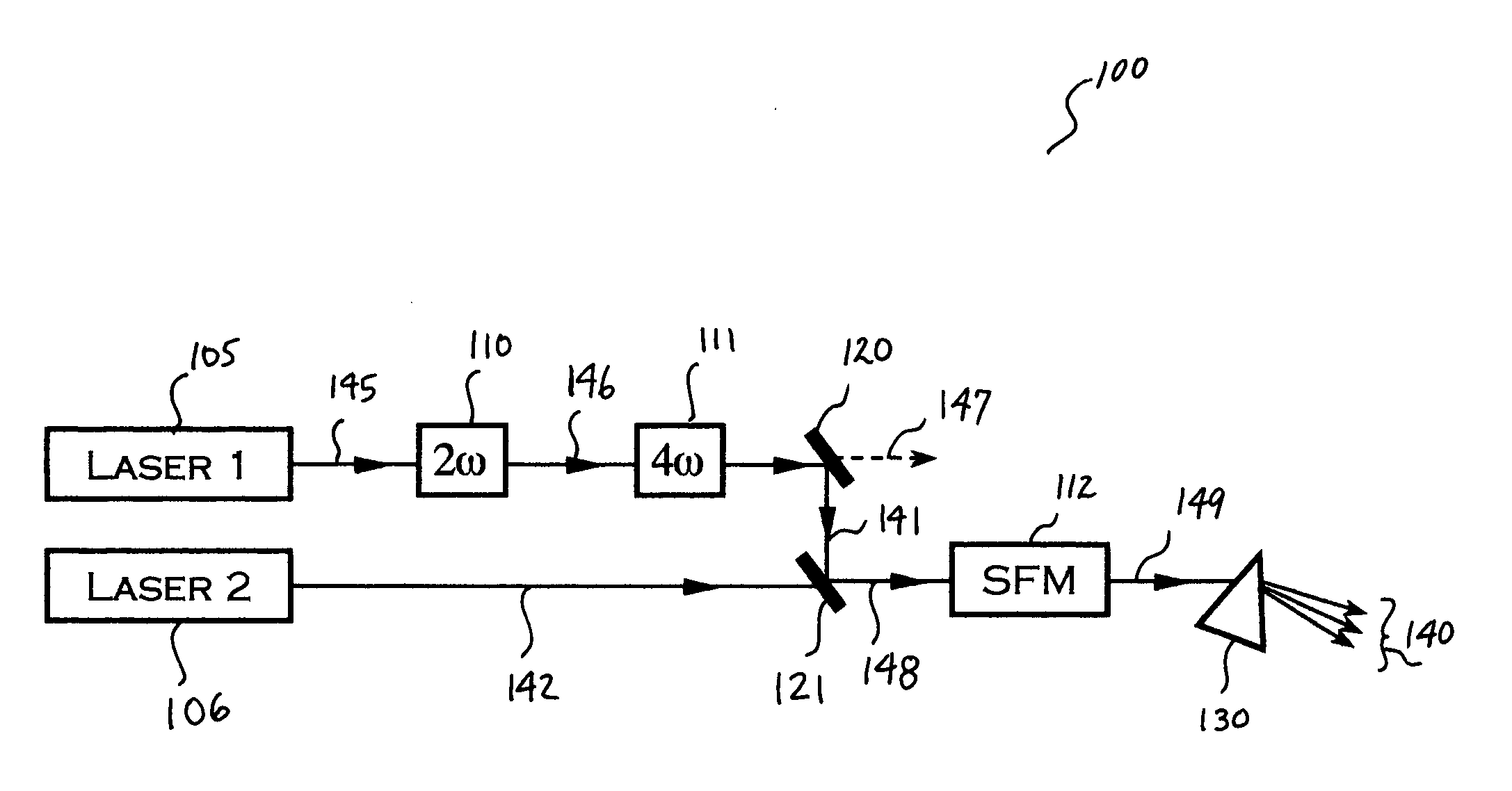
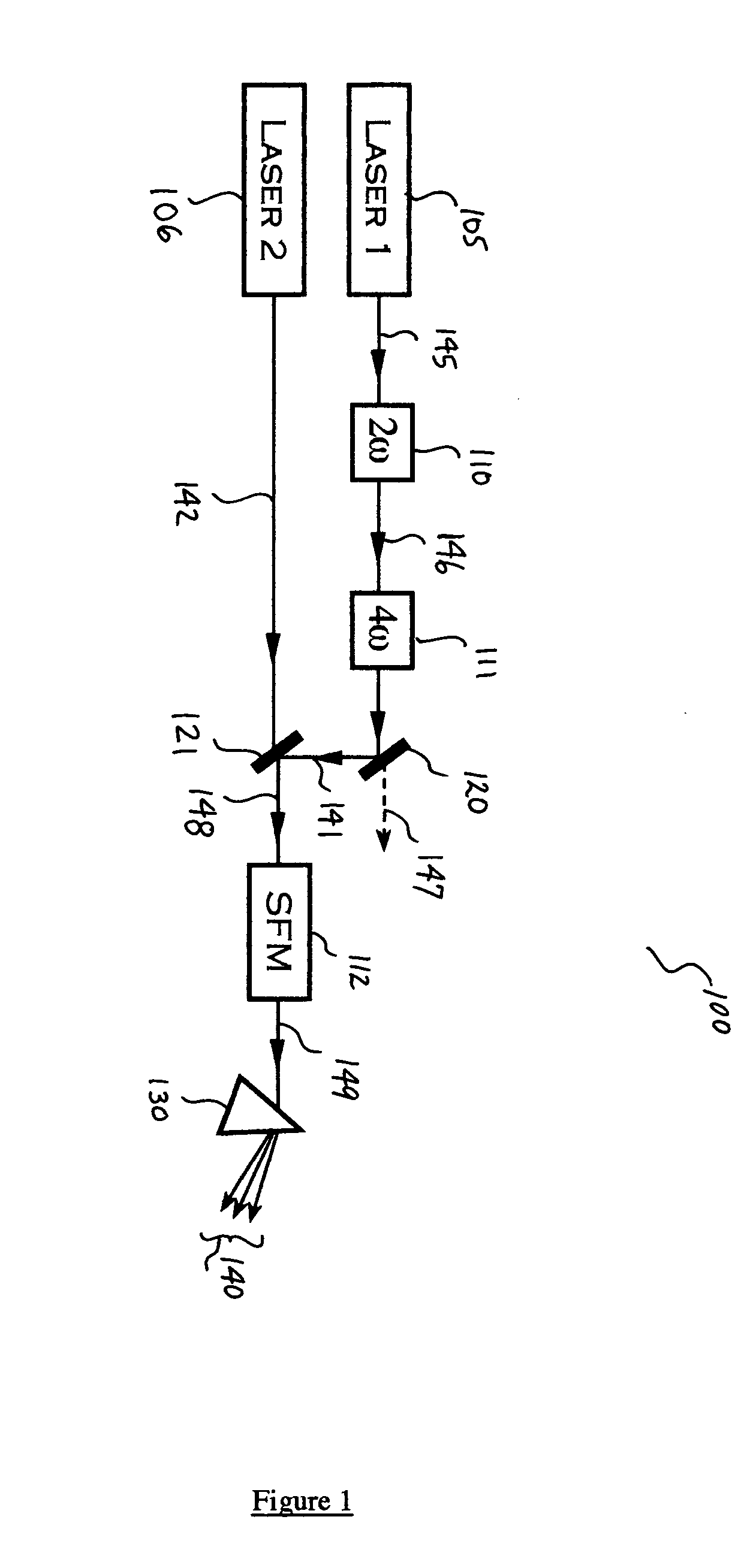
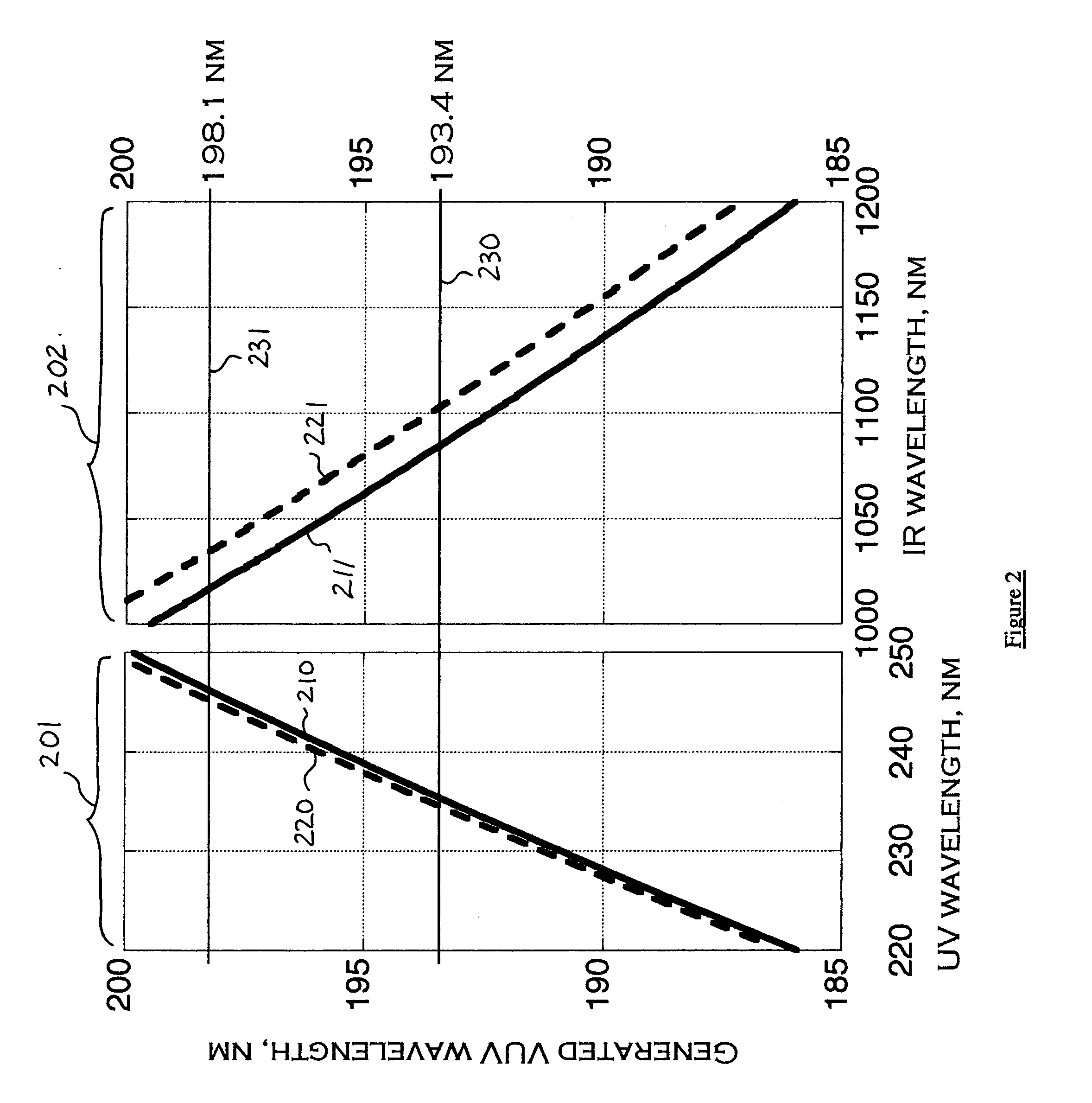
Laser architectures for coherent short-wavelength light generation
InactiveUS20050169326A1Increase power levelMaximize efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsPoynting vectorRare earth
Several methods are disclosed for the generation of coherent short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation through optical nonlinear frequency mixing means. The invention involves several stages of efficient nonlinear frequency conversion to shift the output of high-power infra-red fiber-lasers into the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV). The described laser source architecture is designed around non-critically phase-matched (NCPM) sum-frequency mixing (SFM) interactions in the nonlinear crystal CLBO. The NCPM interaction is an optimum condition for bulk frequency conversion of cw radiation because it allows tight focusing of the input laser radiation without Poynting vector walk-off, thereby increasing the non-linear drive significantly. The sub-200-nm output wave is generated from SFM of a long-wave IR laser field and a short-wave UV laser field. The long-wave laser beam may be derived directly from a rare-earth-doped fiber laser, whereas the short-wavelength UV beam is provided as the fourth frequency harmonic of a second rare-earth-doped fiber laser system.
Owner:JACOB JAMES JEFFREY +1
Method and system for forming temporary images
InactiveUS20080191136A1Television system detailsMangetographic processUltraviolet lightsColor changes
The presently described embodiments comprise a system that includes a color changing medium, an erasing device using heat or long wavelength infrared light as the erasing source, a writing device that can imagewise apply a UV light to write the image on the media, and a transport to transport the media along a paper path to be seen by the erasing device and the writing device. The system could also function in an alternative way. The image could be “erased” to the all dark state using light (e.g. ultraviolet light) and then heated or illuminated using, for example, infrared light in imagewise fashion to produce the image.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC +1
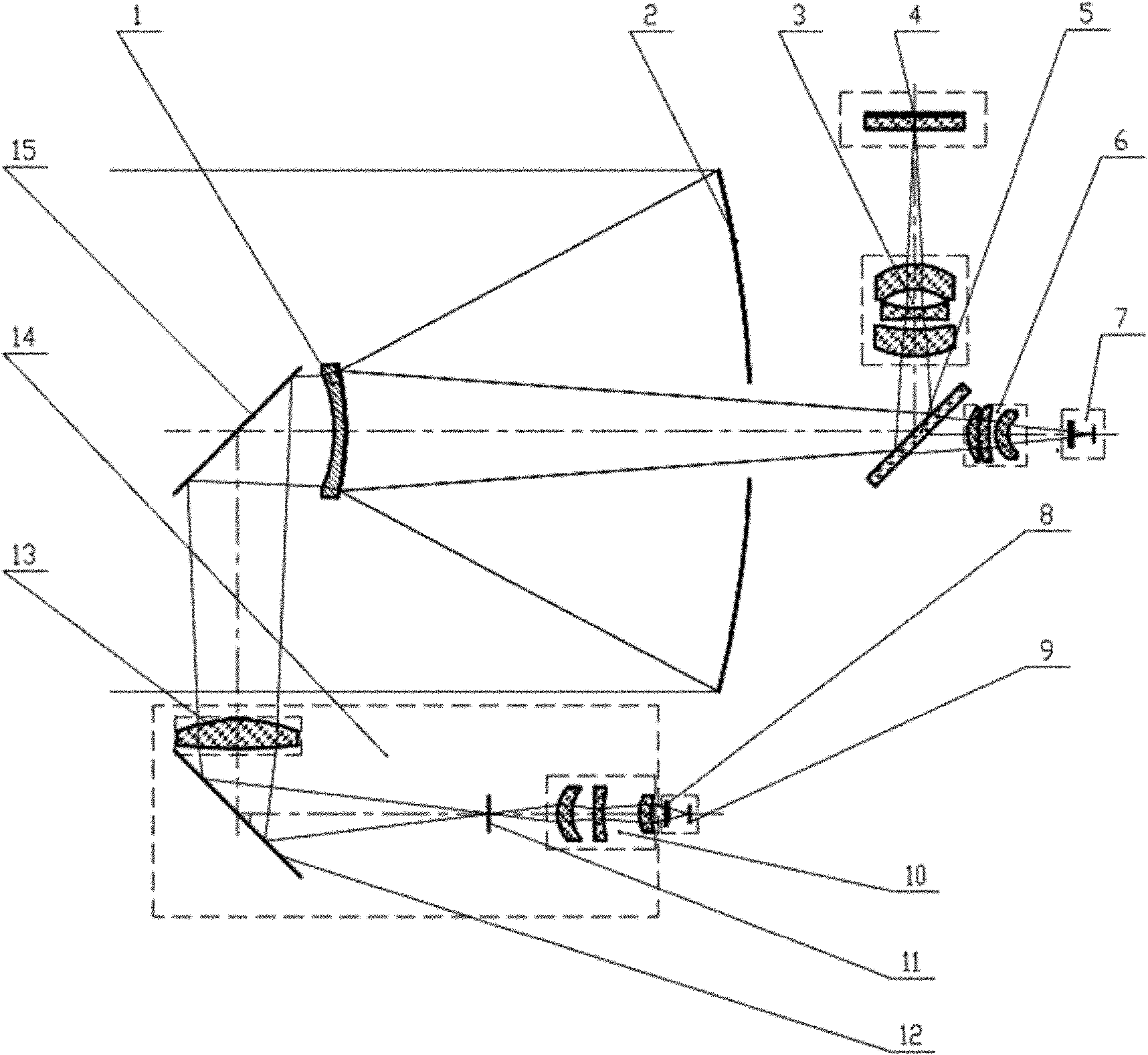
Laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system
ActiveCN103278916AReduce volumeExcellent aberration correctionOptical elementsBeam splitterImaging quality
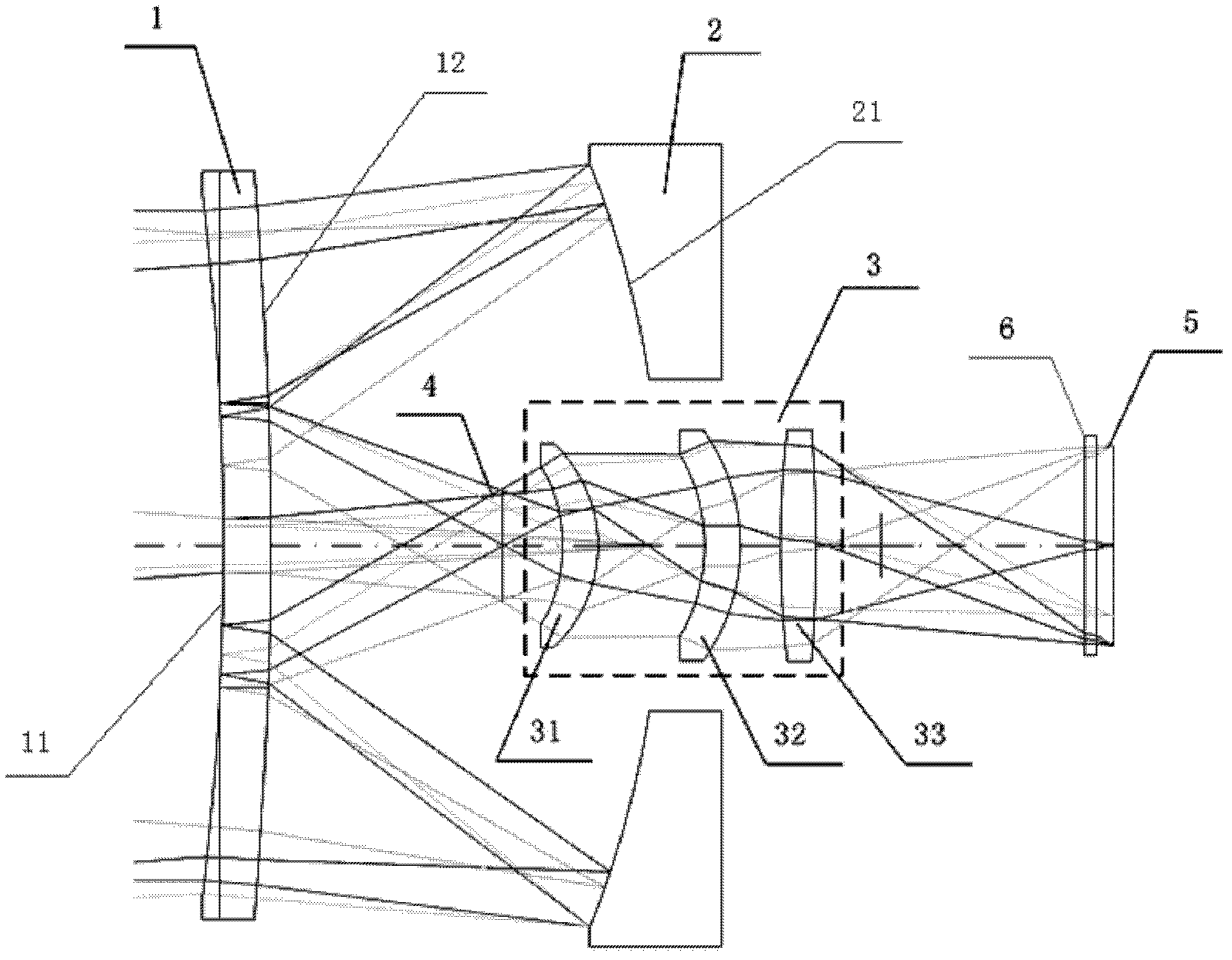
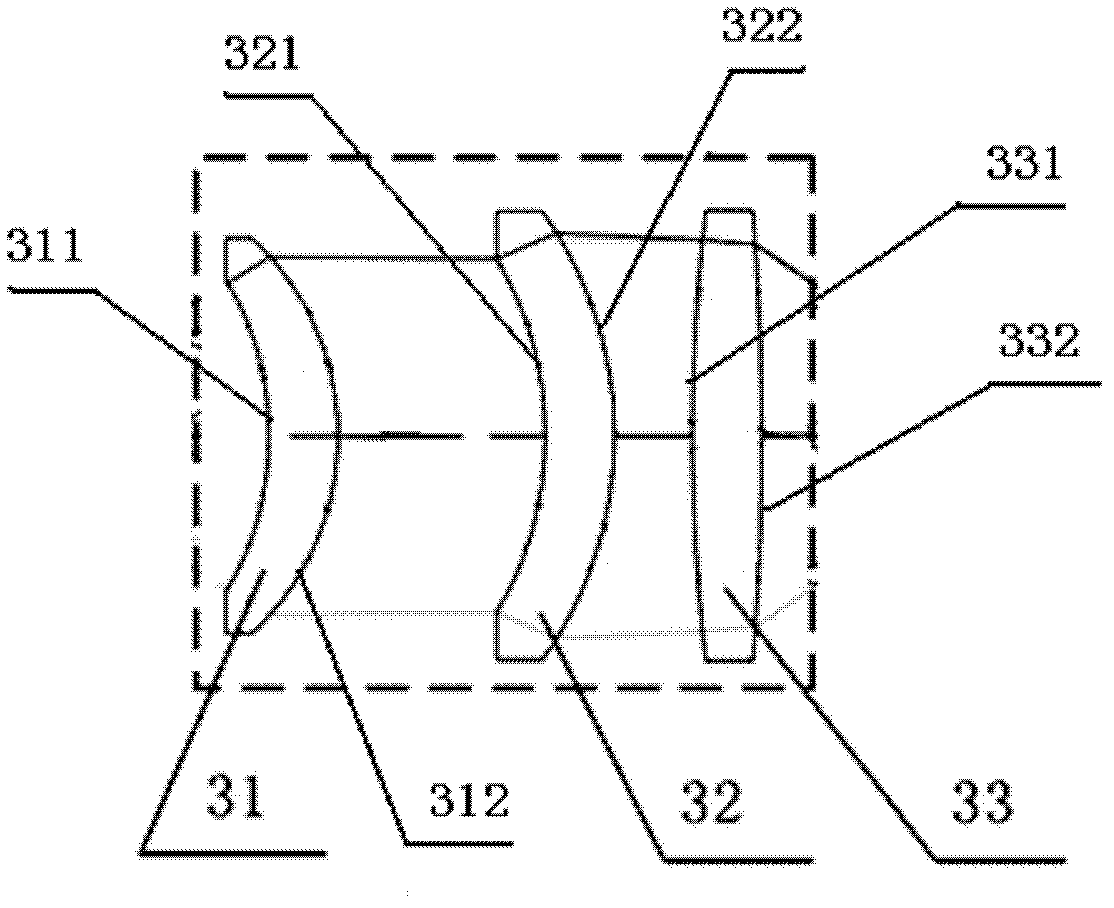
The invention relates to a laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system, which comprises an entrance pupil shared by each band, a primary mirror, a secondary convex mirror, a middle / long-wavelength infrared optical path imaging lens group, a laser converging light spot receiving unit, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared band beam splitter, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared dual-band imaging lens group and a detection image surface, wherein the reflection surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface, and a hole is formed in the center of the primary mirror. The system can be used for realizing the common-aperture collection of scene infrared radiation energy of the same object and laser echo energy reflected by the object; and the entrance pupil is positioned in front of the primary mirror, the secondary mirror is used for the beam splitting of laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands, and a dichroic mirror is inclined to split middle-wavelength infrared light and long-wavelength infrared light, so that the system is compact in structure, the utilization rates of optical energy and space of the system are increased, the aberration correction and beam focusing of middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands are facilitated respectively, and the imaging quality is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
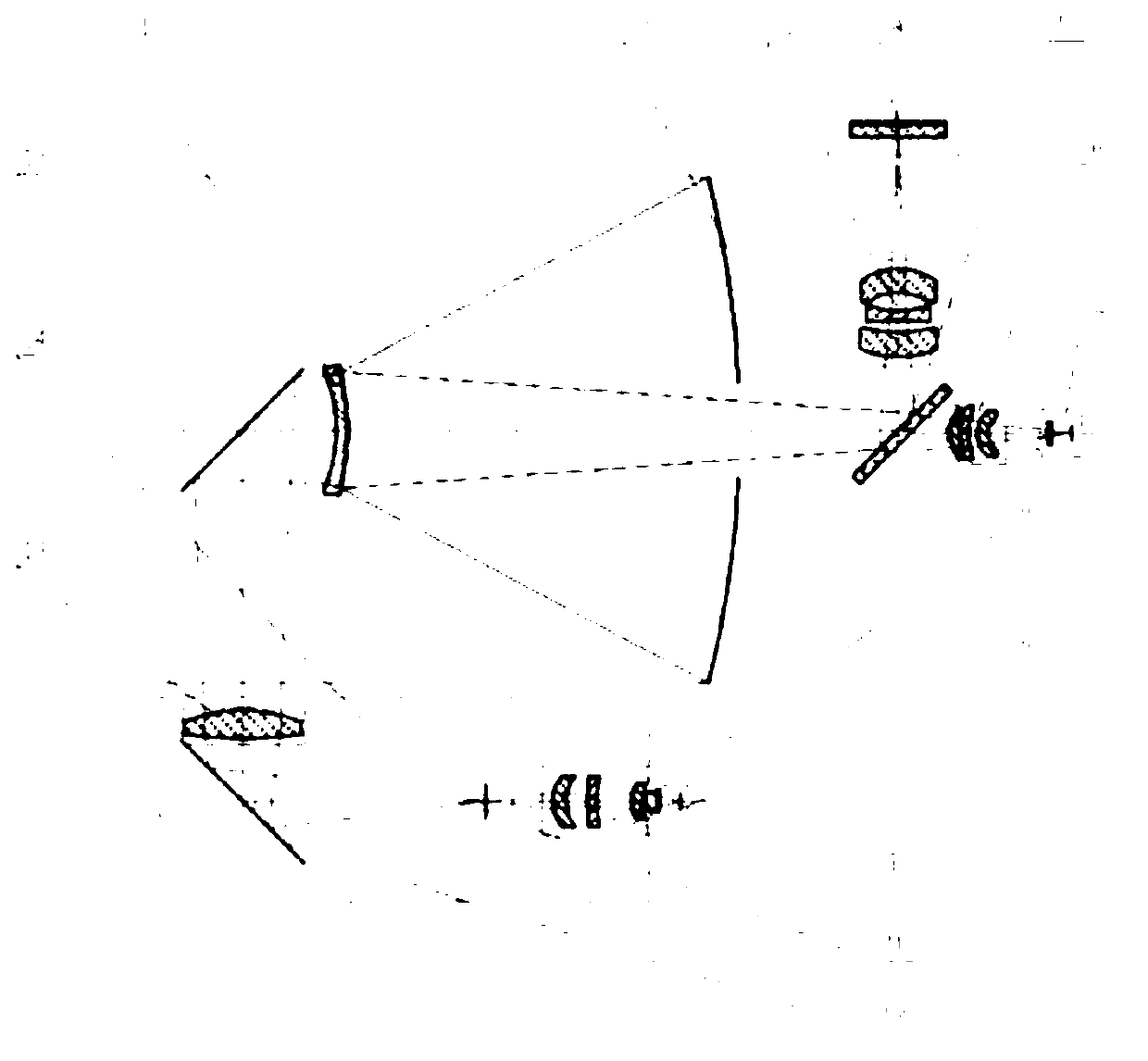
Spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system
InactiveCN102508361AReduce in quantityNo color differenceRadiation pyrometryCoatingsSpectral bandsLarge range
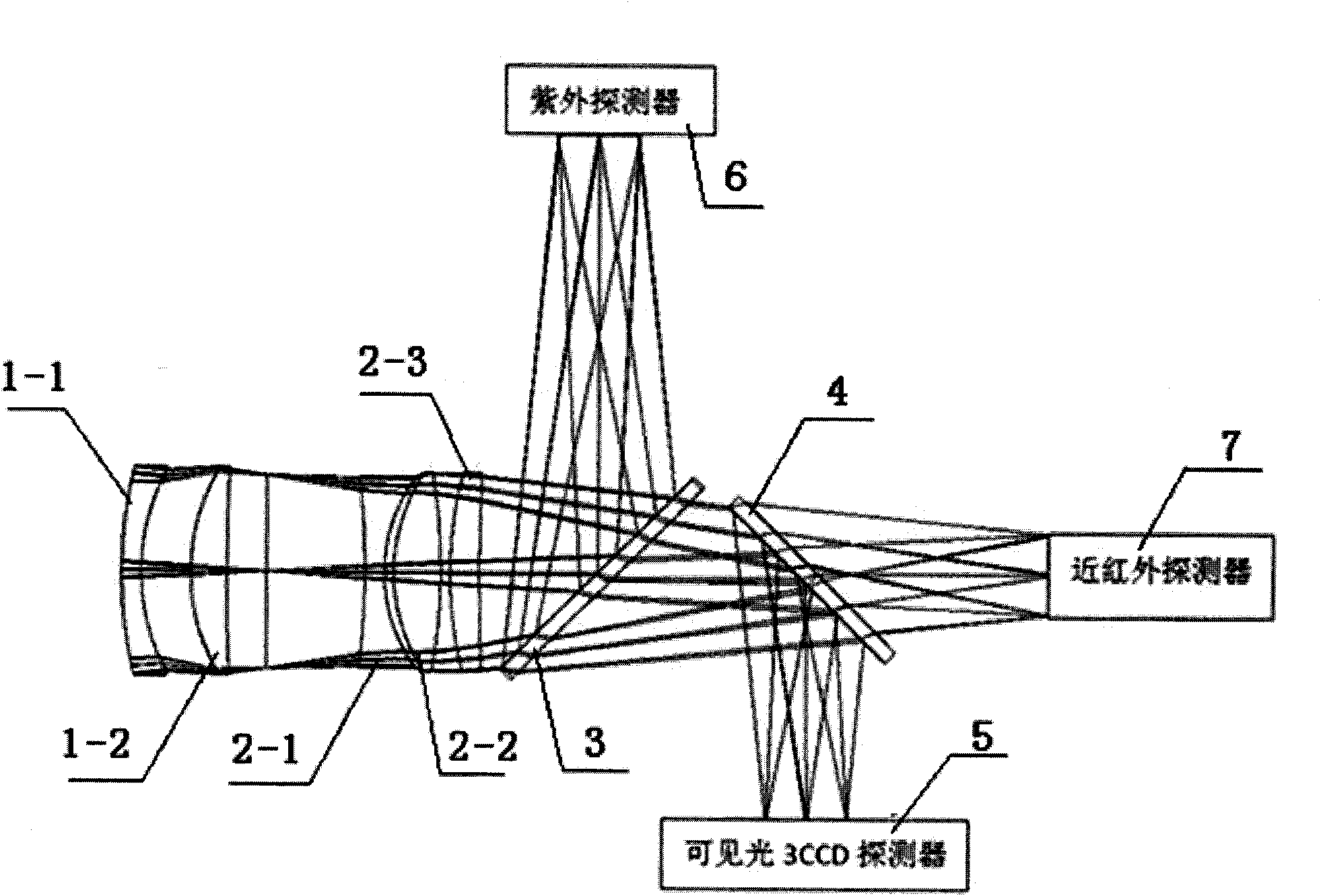
The invention discloses a spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system, which comprises a switching reflector, a main optical off-axis three-reflector system, a medium- and short-wave focus-free relaying optical system and a long-wave focus-free relaying optical system, wherein a radiation light beam of an imaging target enters from the switching reflector, and is divided into light rays in three channels, namely a visible multispectral channel, a short-wave / medium-wave channel and a long-wave infrared channel, by color division sheets after passing through the main optical off-axis three-reflector system; the light ray in the visible multispectral channel is reflected by the first color division sheet, and then full-color multispectral imaging is realized through a five-color device; the light rays in the short-wave / medium-wave channel and the long-wave infrared channel are transmitted / reflected by the second color division sheet, respectively pass through the own focus-free relaying optical systems, and then are focused on a focal surface for imaging after being subdivided by filters. The spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system has the advantages of large view field, large relative aperture, wide spectral range, high subdivision degree, compact structure, small volume, light weight and the like; and large-range, all-day and high-resolution dynamic and stable detection can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Metallized heat resistant material with thermal barrier
InactiveUS20050058790A1Reduce heat transferQuality improvementSynthetic resin layered productsDomestic containersAdhesiveUltraviolet
A laminated metallized film apparatus being fabricated through the use of roll-to-roll lamination machinery (e.g. using a gravure cylinder) which through the use of various combinations of adhesive, pressure, and temperature bonds various materials and substrates together, producing a thermal radiative and insulative barrier to impinging multiple heat sources in the range of ultra-violet longwave-infrared wavelengths. In applications the laminated metallized film apparatus may be constructed so as to create an insulating bag, pouch, tote, insulative wrap, or radiant reflector sheeting, through use of single or multiple layer films or foams of varying thickness and texture.
Owner:SIMON ROBERT +3
Infrared/ glimmer image fusion night vision system
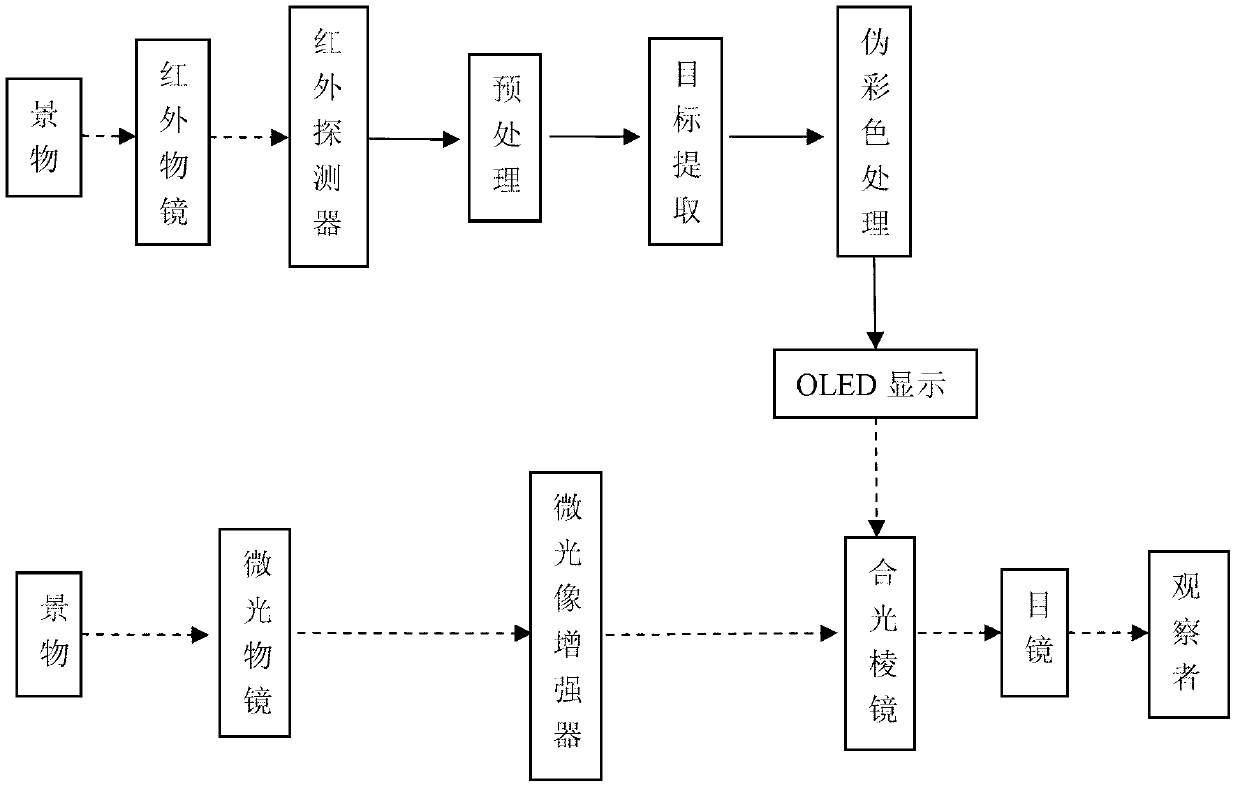
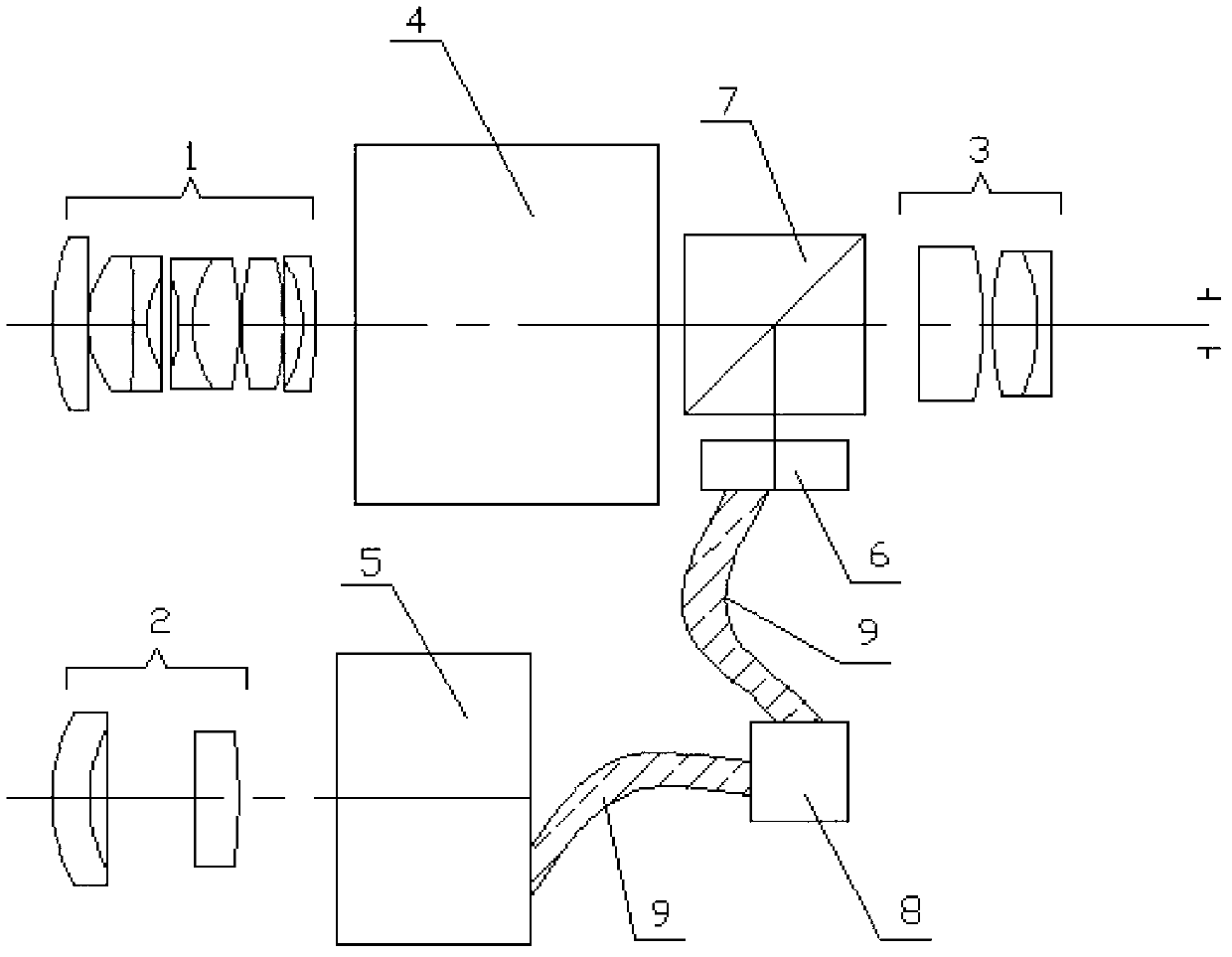
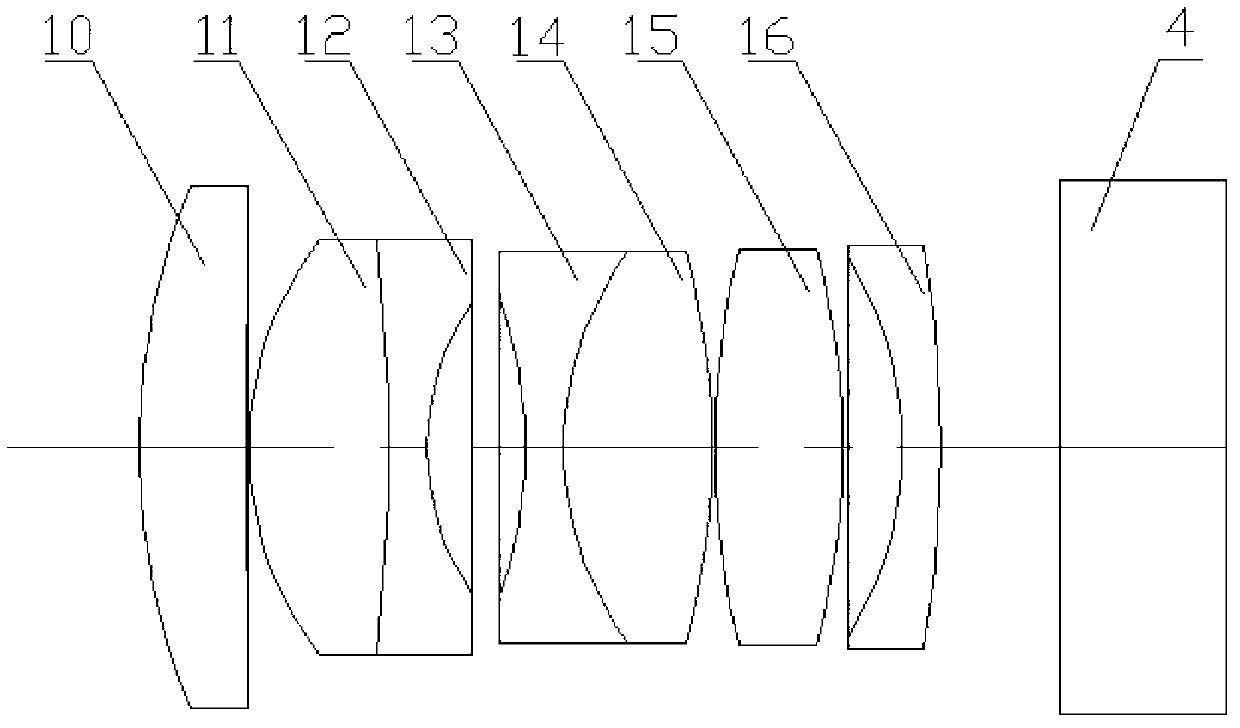
The invention discloses an infrared / glimmer image fusion night vision system, which consists of a glimmer object glass group, a glimmer image intensifier, an infrared object glass group, an uncooling long-wave infrared detector, an image processing circuit module, an electric signal transmission line, an OLED (organic light emitting diode) minitype display, an integrated optical prism and an eye lense system. The night vision system takes a glimmer image as the background, and the image fusion of a glimmer channel and an infrared channel is realized in a mode that a pseudo-color infrared target is optically projected. In order to obtain the good image fusion effect, the glimmer object glass group and the infrared object glass group both satisfy one time of magnifying power; an infrared image is subjected to denoising and enhancing pretreatments, target extraction and the electronic registration of the image; and then, a gray level image is subjected to pseudo-color treatment and is then output to the OLED minitype display for color display. The fused image has a clear glimmer background and an outstanding infrared target. The night vision system has the advantages of small size and light weight, can work for a long time and is especially suitable for night vehicle driving and for a single person to carry, observe and use.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Device and method for cooperatively detecting moving target by using all-optical-waveband map
ActiveCN105182436ASimple structureReduce dampingRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationVisible near infraredNarrow-band imaging
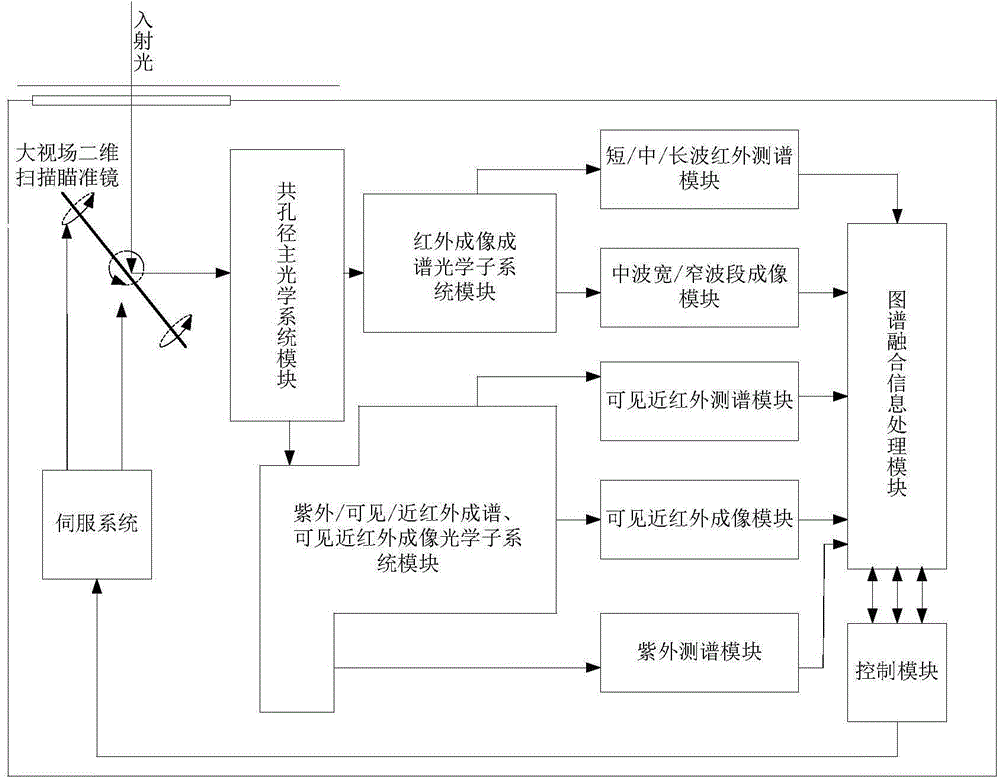
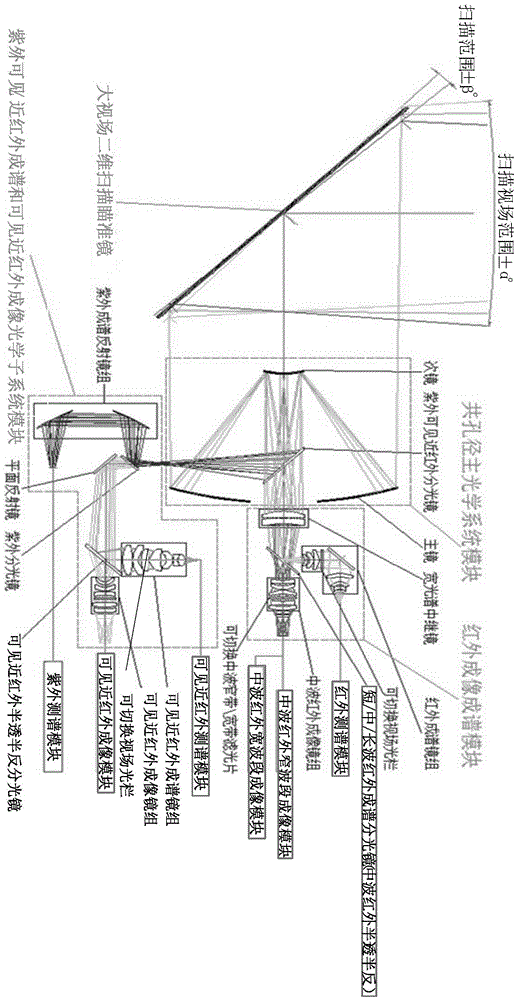
The invention discloses a device and a method for cooperatively detecting a moving target by using all-optical-waveband (including ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, medium-wave infrared and long-wave infrared) maps. The device comprises a large field-of-view two-dimensional scanning sighting telescope, a common aperture primary optical system module, an infrared imaging and spectrum forming optical subsystem module, an ultraviolet / visible / near-infrared spectrum forming and visible near-infrared imaging optical subsystem module, a short / medium / long-wave infrared spectrum measuring module, a medium-wave wide / narrow band imaging module, a visible near-infrared spectrum measuring module, a visible near-infrared imaging module, an ultraviolet measuring module, a map fusion signal processing module, a control module and a servo system. The device and the method utilizes medium-wave infrared imaging and visible near-infrared imaging for recognizing a suspected moving target and guides spectrum measurement, completes the final recognition of the suspected target with cooperation of spectrum measurement data, and solves the difficulties of the existing detection device such as incomplete detection bands, limited optical path layout, large equipment size, few types of detected moving targets and dynamic changing objects, and poor detection capability.
Owner:NANJING HUATU INFORMATION TECH
Short wave/medium wave/long wave infrared detector based on InAs/GaSb class II-type superlattice materials
ActiveCN104576805AImprove performanceSuppress crosstalkSemiconductor devicesContact layerMetal electrodes
The invention discloses a short wave / medium wave / long wave infrared detector based on InAs / GaSb class II-type superlattice materials. The detector comprises a GaSb substrate, an epitaxial structure deposited on the GaSb substrate, a passivation layer and a metal electrode, wherein the epitaxial structure sequentially comprises a GaSb buffering layer, an n-type InAs / GaSb superlattice contact layer, a first M-type InAs / GaSb / AlSb / GaSb / InAs superlattice hole blocking layer, a p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice long wave infrared absorbing layer, a first p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice contact layer, a p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice medium wave infrared absorbing layer, a second M-type InAs / GaSb / AlSb / GaSb / InAs superlattice hole blocking layer, a p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice short wave infrared absorbing layer, a second p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice contact layer and a cover layer. The detector is of a pMp-p-pi-M-n heterostructure and has the advantages of being low in crosstalk, low in dark current and high in detection rate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
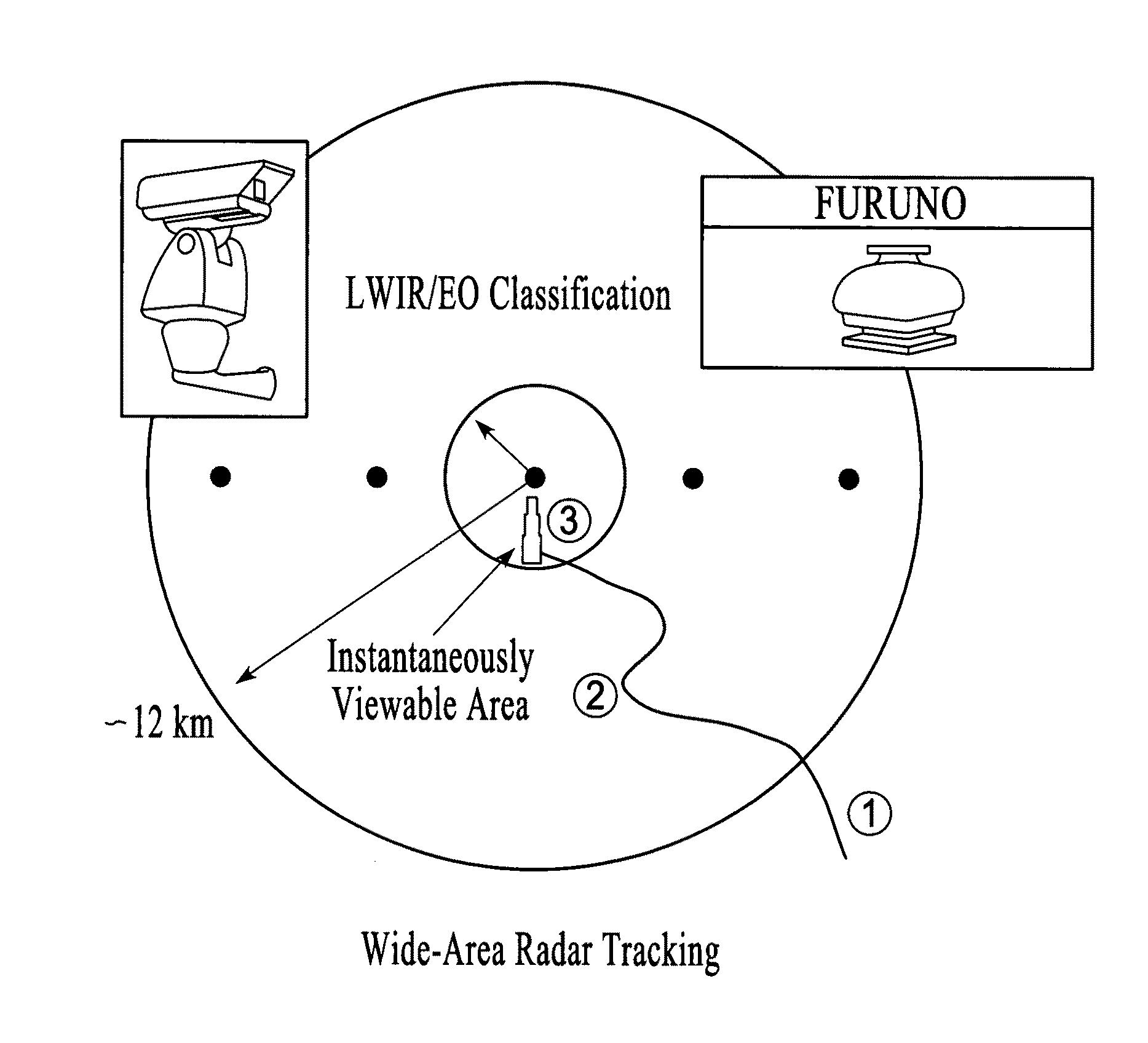
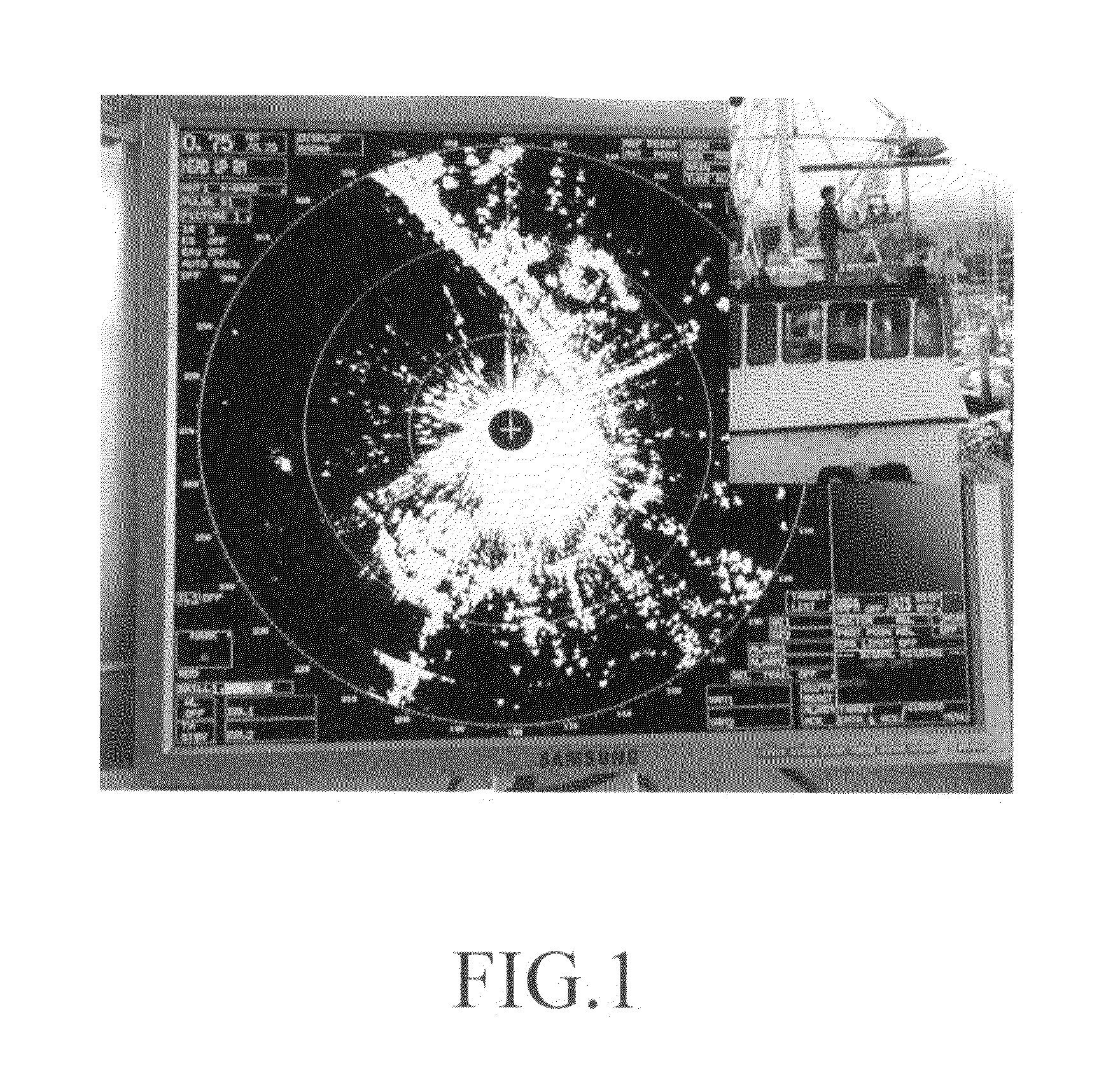
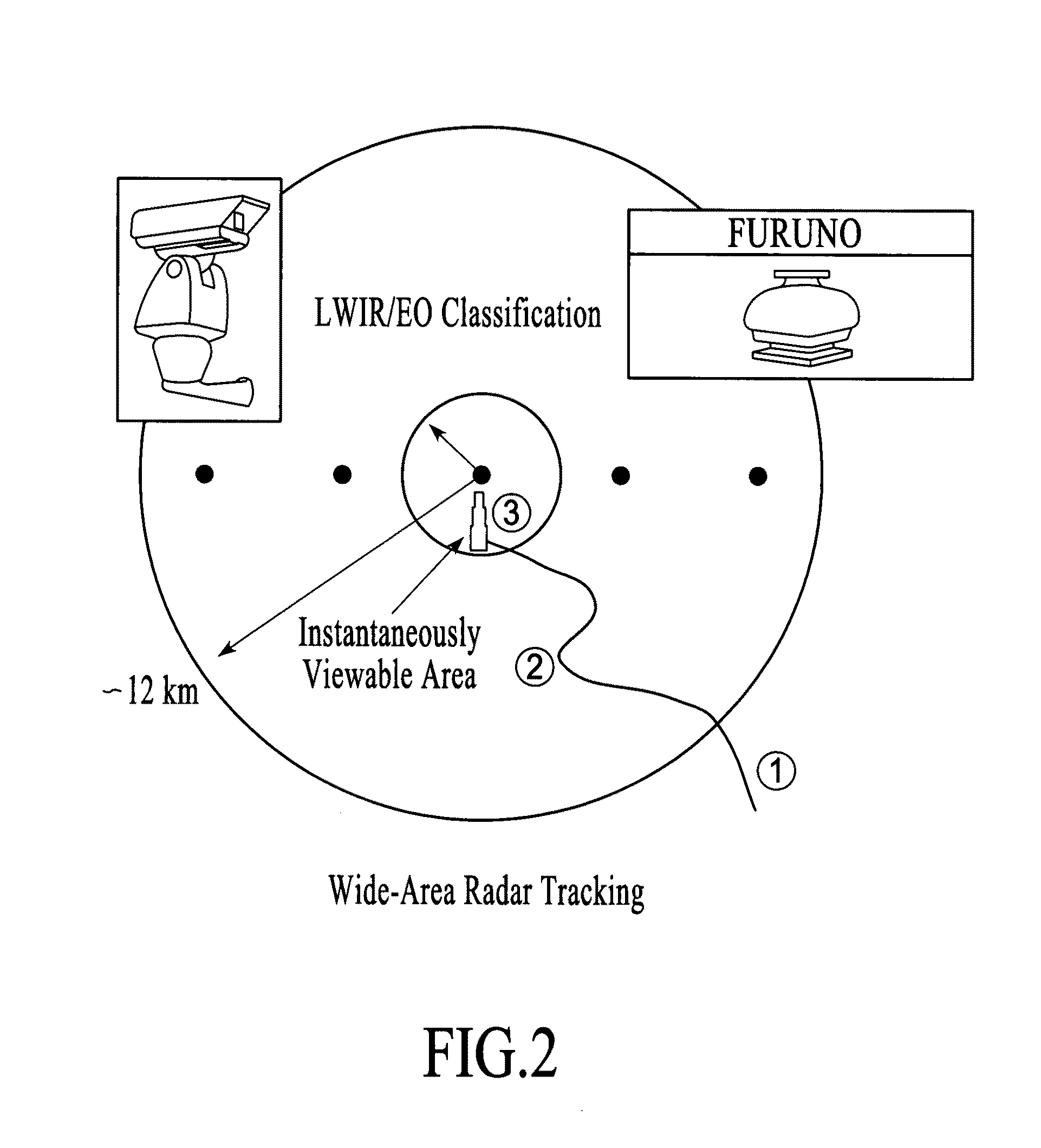
Method for surveillance to detect a land target
A land-based Smart-Sensor System and several system architectures for detection, tracking, and classification of people and vehicles automatically and in real time for border, property, and facility security surveillance is described. The preferred embodiment of the proposed Smart-Sensor System is comprised of (1) a low-cost, non-coherent radar, whose function is to detect and track people, singly or in groups, and various means of transportation, which may include vehicles, animals, or aircraft, singly or in groups, and cue (2) an optical sensor such as a long-wave infrared (LWIR) sensor, whose function is to classify the identified targets and produce movie clips for operator validation and use, and (3) an IBM CELL supercomputer to process the collected data in real-time. The Smart Sensor System can be implemented in a tower-based or a mobile-based, or combination system architecture. The radar can also be operated as a stand-alone system.
Owner:VISTA RES INC
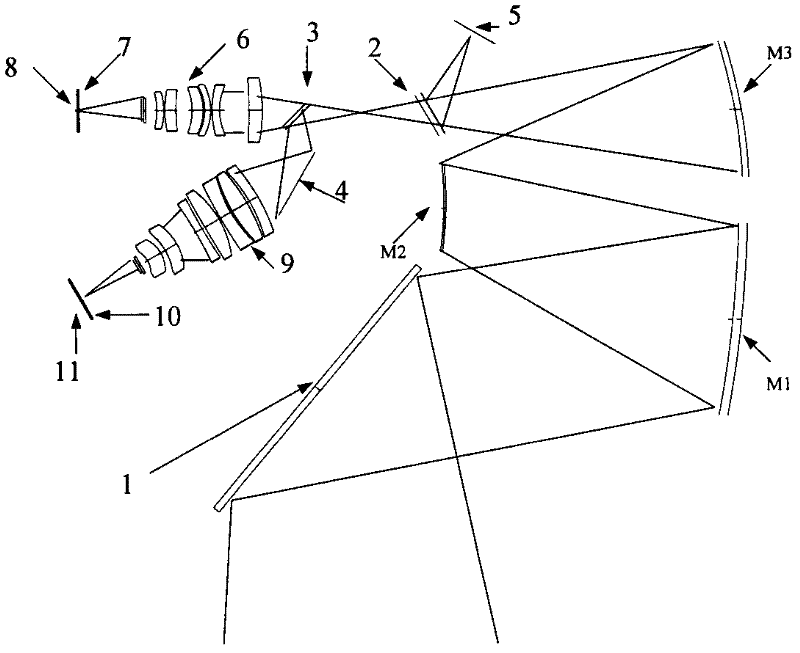
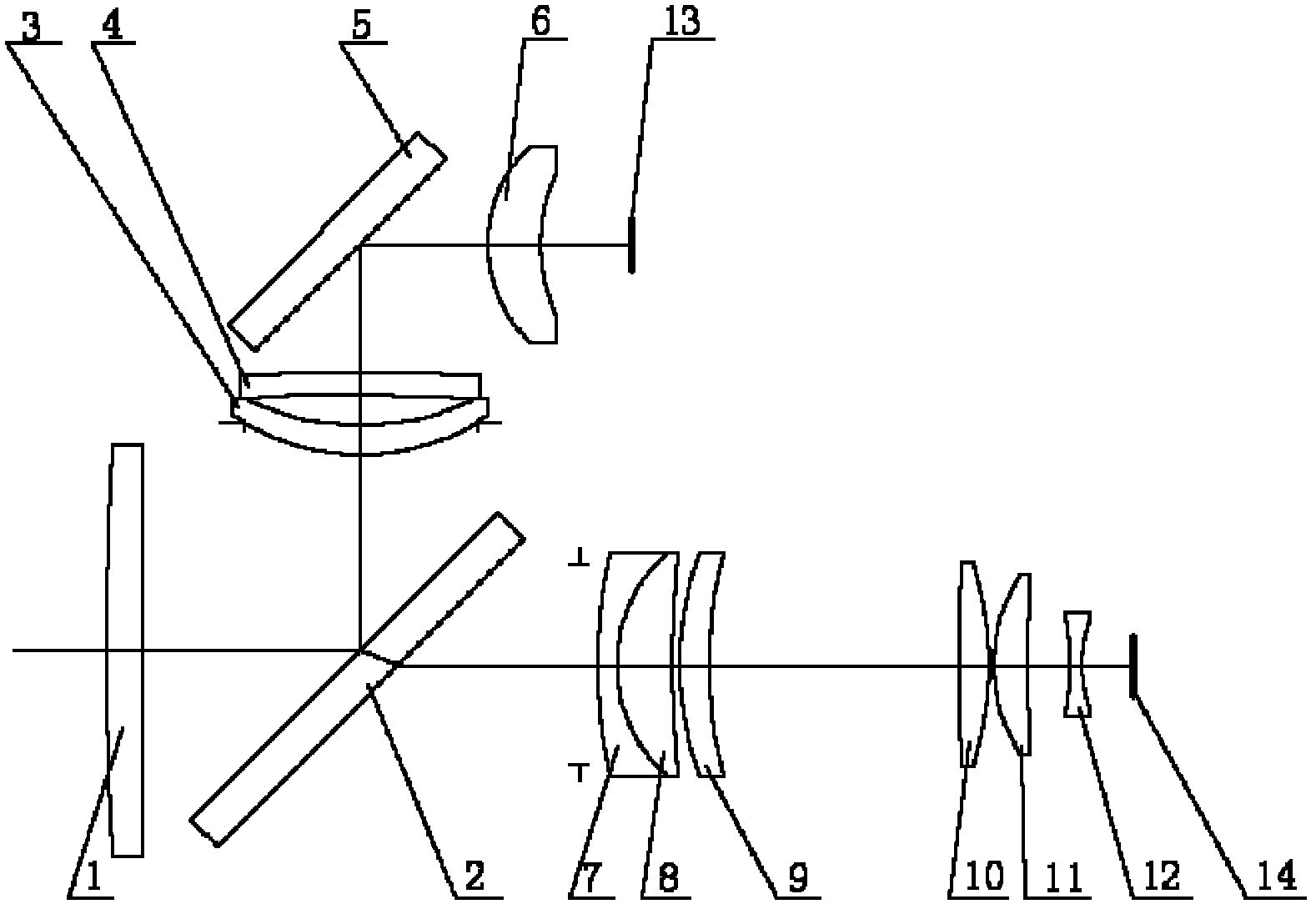
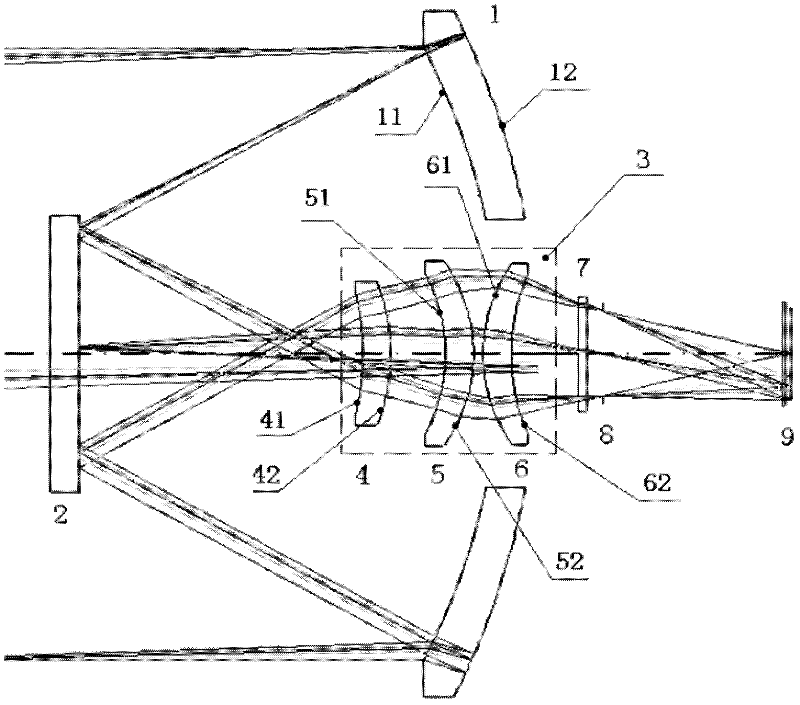
Compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system
InactiveCN102520506AAchieve long focal length imagingCompact structureOptical elementsMangin mirrorLight beam
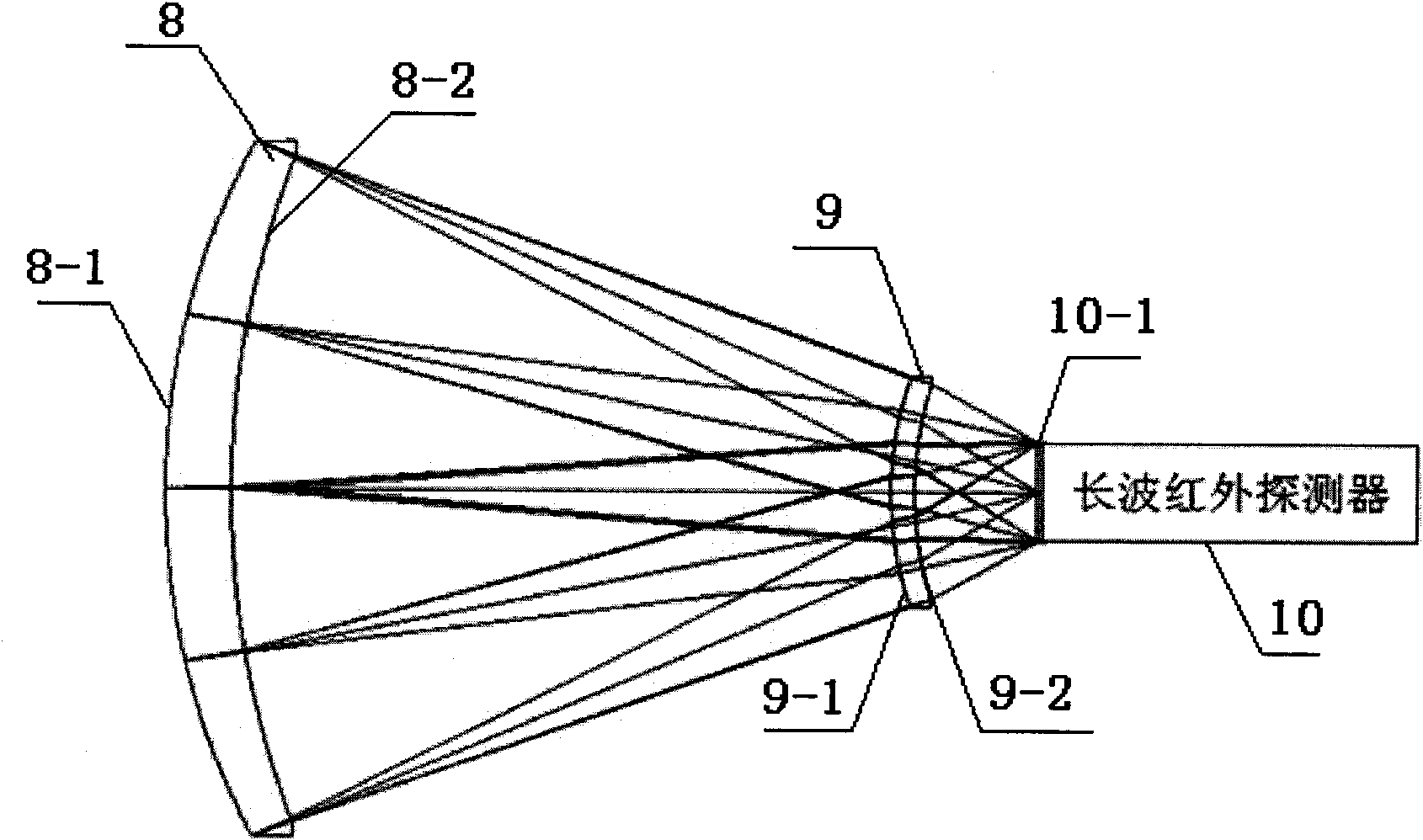
The invention relates to a compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system, which comprises a secondary lens, a primary reflective lens and a relay lens. The secondary lens is a catadioptric optical component with negative focal power and comprises an annular light transmission part and a central Mangin mirror; a light beam from an object is transmitted into the primary reflective lens through the annular light transmission part of the secondary lens and is then transmitted into the Mangin mirror of the secondary lens after reflection by the primary reflective lens, and catadioptric focusing is carried out by the Mangin mirror so that the target is imaged on a first image plane; the target on the first image plane is then transferred by the relay lens and focuses again on a second image plane; and the second image plane is overlapped with the focal plane of an image receiver. Image of long focal length can be realized, and the system has a compact structure and a large view field and can be applied in the optical imaging field of aviation and aerospace.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical system of multispectral area array CCD (Charge Coupled Device) imager
InactiveCN101866054AImprove performanceHighly integratedSpectrum investigationOptical elementsAviationOptic system
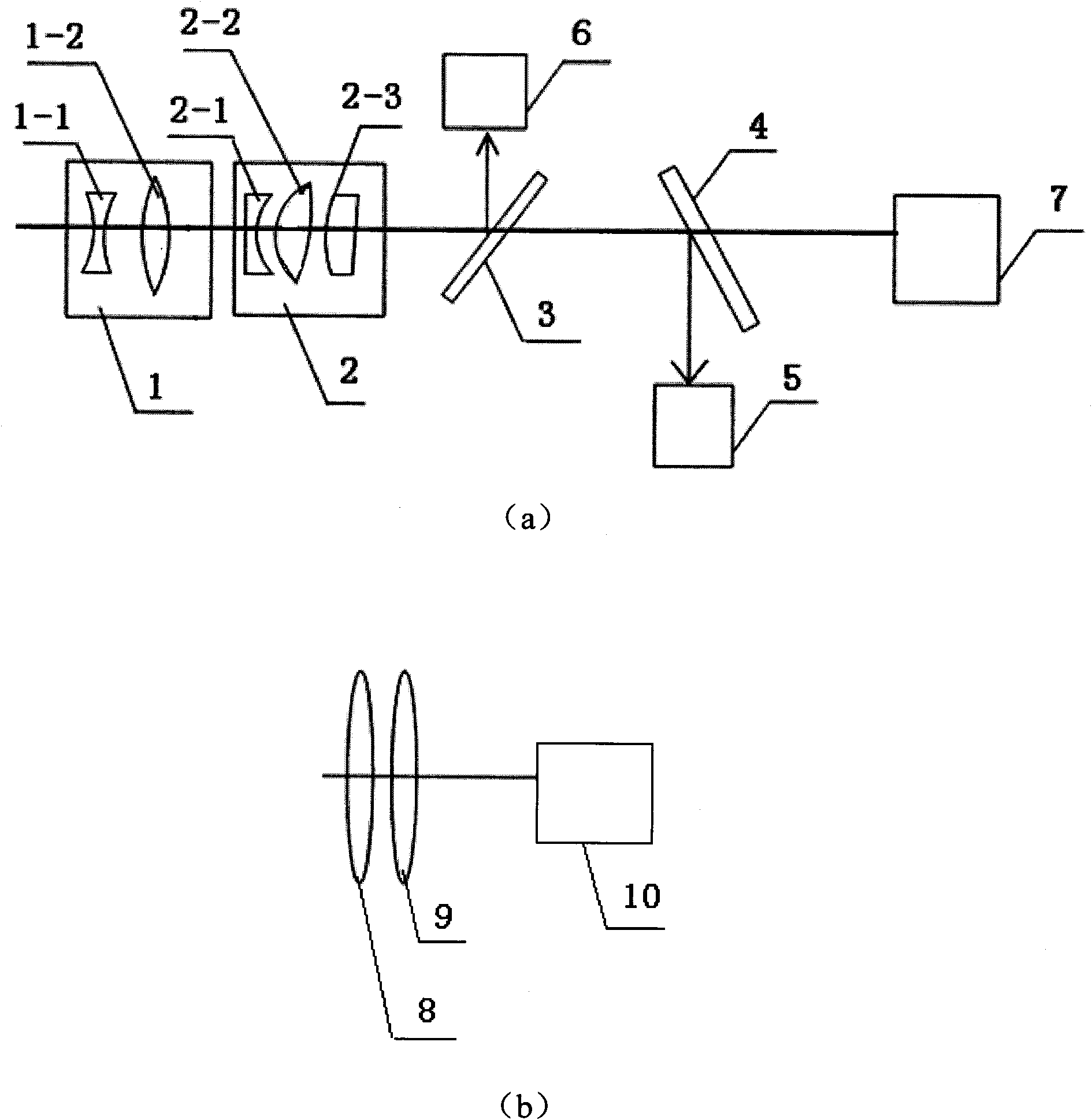
The invention discloses an optical system of a multispectral area array CCD (Charge Coupled Device) imager, relating to the field of design and manufacture of the optical system of the multispectral area array CCD imager and solving the problems that the traditional multispectral imager can only obtain spectrum information of a certain wave band of a target at the same time and can not realize the design requirements of a multispectral optical system with wide wave band range and temperature range and a long back working distance. The system consists of two sets of subsystems, a first set of subsystem realizes spectrum information of untraviolet, blue, green, red and infrared wave bands, and the system obtains information of different wave bands through two lens sets and a corresponding detector and carries out imaging; and a second set of subsystem image the obtained information by adopting two germanium lenses and a long wave infrared detector to realize spectrum information of a long wave infrared wave band. The invention realizes simultaneously imaging of a target at six wave bands by adopting two sets of optical systems and is suitable for multispectral imaging places with strict requirements on the volume and the weight, such as aviation shooting.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
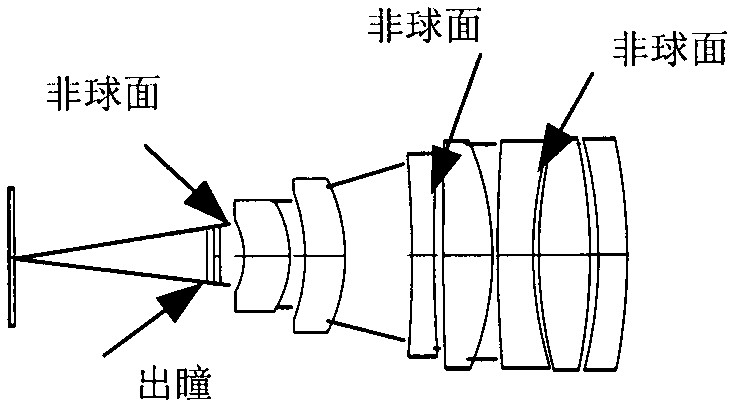
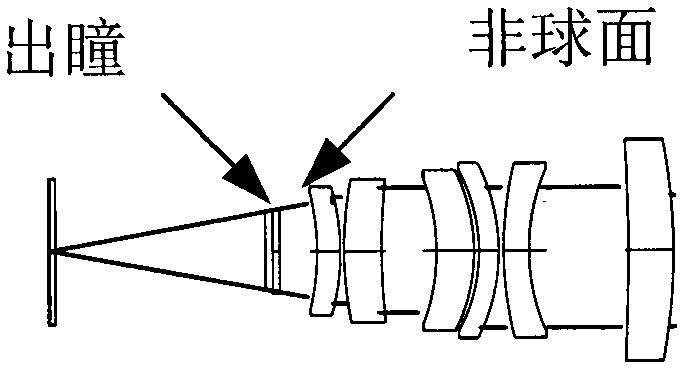
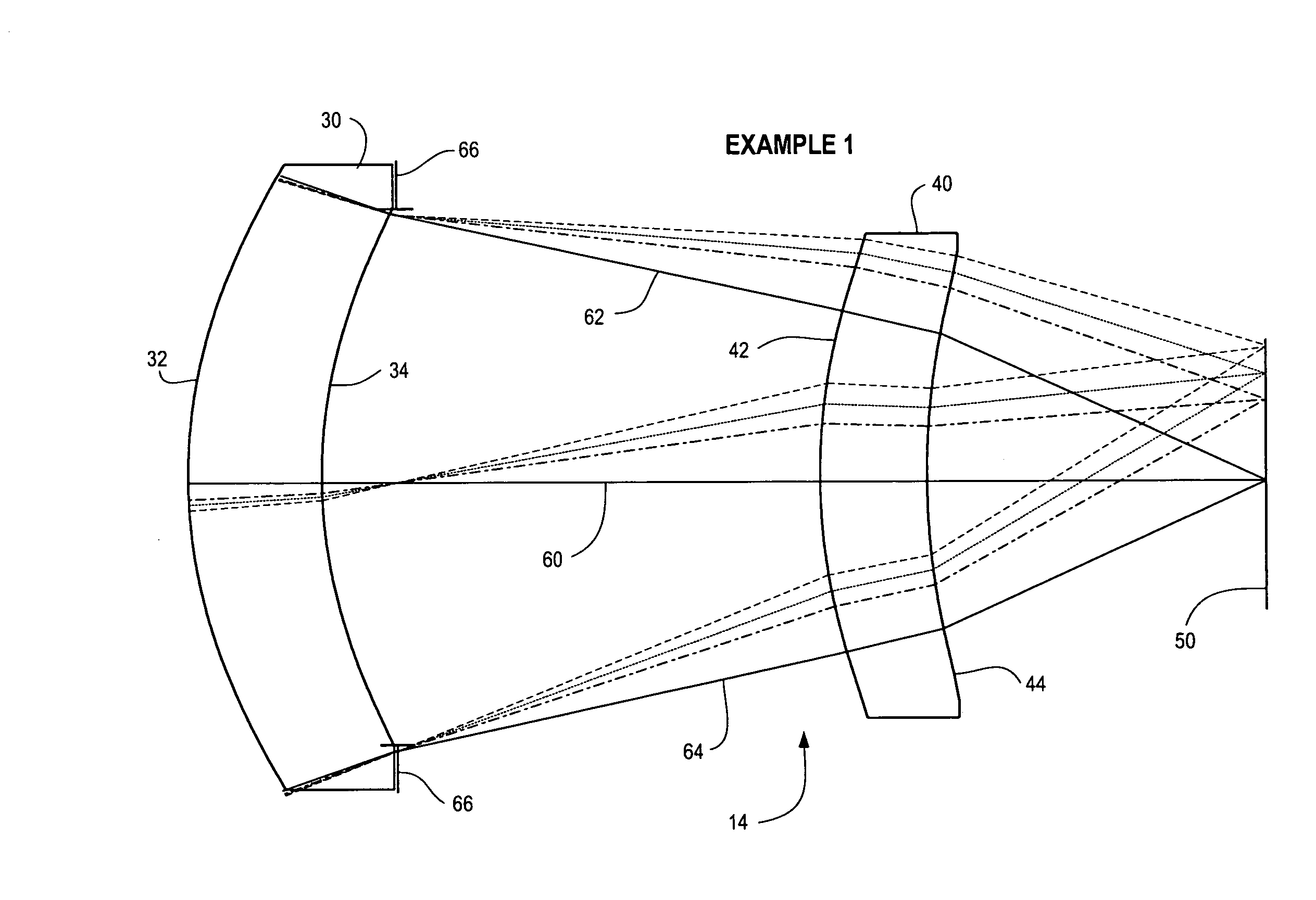
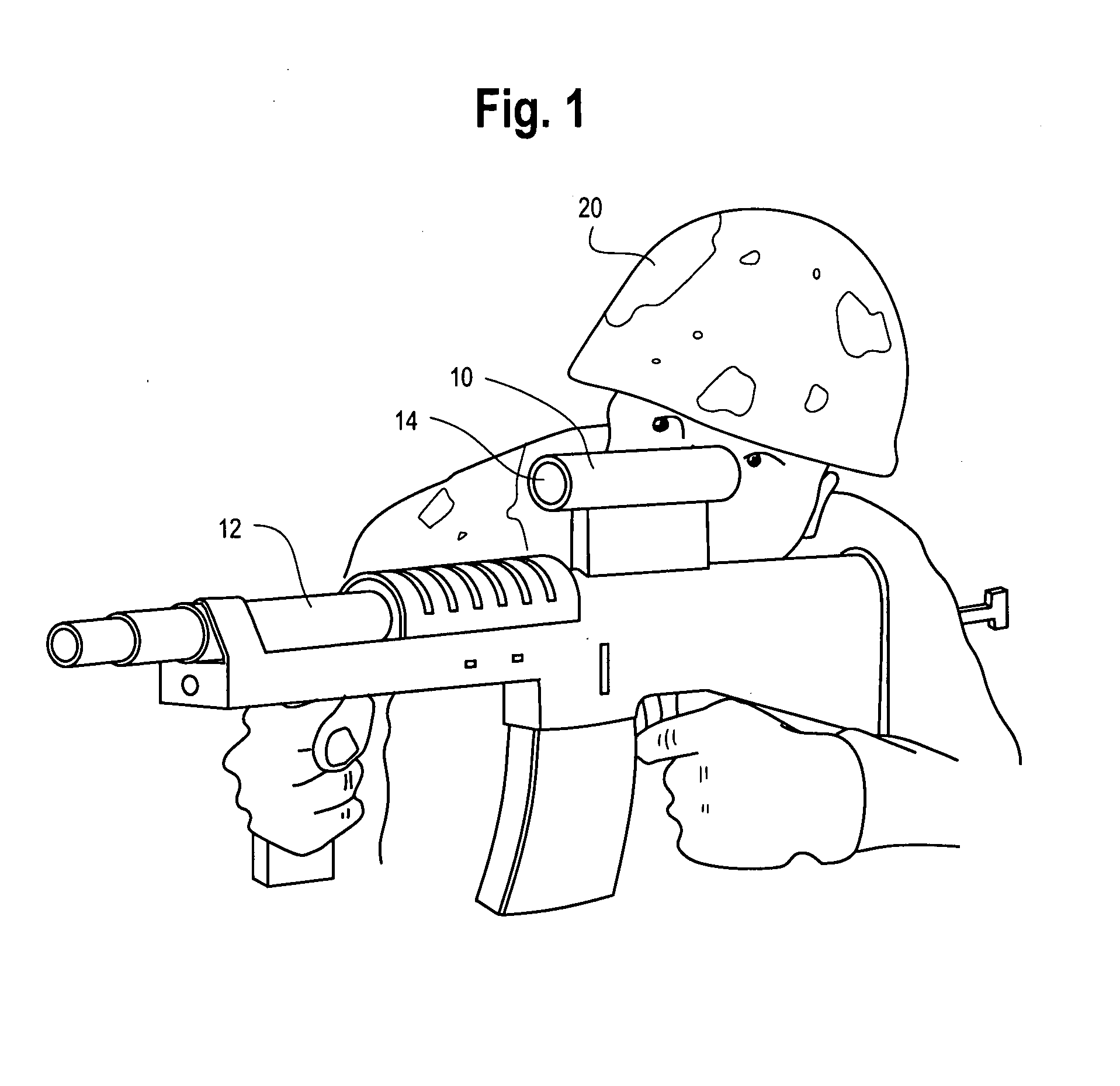
Compact two-element infrared objective lens and IR or thermal sight for weapon having viewing optics
A compact objective lens is disclosed which is particularly suitable for infrared optical systems. The lens features a simple design with only two lens elements, namely a first lens element receiving incident radiation and having front and rear surfaces, and a second lens element receiving incident radiation from the first element and having front and rear surfaces. The lens forms an image of a scene on a focal plane. At least three of the four surfaces of the elements are aspheric surfaces. The lens has an f-number less than about 2, a field-of-view less than about 30 degrees, and an effective focal length less than about 6 inches. The elements are made from a material selected to pass radiation in the infrared band of the electromagnetic spectrum, e.g., germanium. The lens is suitable for use as an objective lens for a long-wave infrared sight for small arms, e.g., rifle or shoulder-launched surface to air missile launching system, i.e., a lens optimized for operating in the electromagnetic spectrum between about 7.5 and about 15 micrometers.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Infrared-based vehicle component imaging and analysis
ActiveUS9134185B2High sensitivitySimple systemTemperature measurement of moving solidsSensing radiation from moving bodiesThermoelectric coolingElectrical conductor
An improved system for evaluating one or more components of a vehicle is provided. The system includes a set of imaging devices configured to acquire image data based on infrared emissions of at least one vehicle component of the vehicle as it moves through a field of view of at least one of the set of imaging devices. An imaging device in the set of imaging devices can include a linear array of photoconductor infrared detectors and a thermoelectric cooler for maintaining an operating temperature of the linear array of detectors at a target operating temperature. The infrared emissions can be within at least one of: the mid-wavelength infrared (MWIR) radiation spectrum or the long wavelength infrared (LWIR) radiation spectrum.
Owner:INT ELECTRONICS MACHINES
Catadioptric hybrid multispectral imaging system
InactiveCN102116673AImprove transmittanceSave spaceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention discloses a catadioptric hybrid multispectral imaging system, which comprises a primary mirror, a catadioptric dual-purpose secondary mirror, a wedge-shaped dichroic beam splitter, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dual-waveband imaging mirror assembly, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dichroic detector unit, a visible to near infrared waveband imaging mirror assembly, a visible to near infrared waveband beam splitting device and a detection unit thereof, a short wave infrared waveband imaging mirror assembly, and a short wave infrared waveband beam splitting device and a detection unit thereof, wherein a hole is formed at the center of the primary mirror, and the reflecting surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface; and the incident surface of the catadioptric dual-purpose secondary mirror is a convex surface. The system can realize imaging with common field of view and common aperture of a same object, improve the utilization rate of light energy, save space for the beam splitter and the system, prevent parasitic light from directly leaking into the imaging mirror assembly from the hole formed on the primary mirror, correct asymmetric aberration, be more conductive to realizing large aperture and the larger field of view and significantly improve the imaging quality. The imaging with the same optical axis and the common field of view can enable an image to be easy to register.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH +1
Sensor suite and signal processing for border surveillance
A land-based Smart-Sensor System and several system architectures for detection, tracking, and classification of people and vehicles automatically and in real time for border, property, and facility security surveillance is described. The preferred embodiment of the proposed Smart-Sensor System is comprised of (1) a low-cost, non-coherent radar, whose function is to detect and track people, singly or in groups, and various means of transportation, which may include vehicles, animals, or aircraft, singly or in groups, and cue (2) an optical sensor such as a long-wave infrared (LWIR) sensor, whose function is to classify the identified targets and produce movie clips for operator validation and use, and (3) an IBM CELL supercomputer to process the collected data in real-time. The Smart Sensor System can be implemented in a tower-based or a mobile-based, or combination system architecture. The radar can also be operated as a stand-alone system.
Owner:VISTA RES INC
Visible light/long-wave infrared broad band spectrum joint focusing optical imaging system
InactiveCN102495474AImprove image processing capabilitiesReduce usageMountingsCoatingsParallaxOptical axis
The invention discloses a visible light / long-wave infrared broad band spectrum joint focusing optical imaging system comprises a broad spectrum focusing window, a color separation film, a long wave infrared lens group and a visible light lens group. The color separation film and a horizontal optical axis form an angle of 45 degrees, and light incoming from the broad spectrum focusing window passes through the color separation film and the visible light lens group to image on a visible light sensor. The long wave infrared lens group is composed of a first lens, a second lens, a reflector and athird lens from an object space to an image space in sequence, the reflector is parallel to the color separation film, and infrared light in broad spectrum light passes through the color separation film and the long wave infrared lens group to image on a non-refrigeration detector. A first face of the second lens is a binary surface, a second face of the third lens is an aspheric surface, and systematic heat difference and optical aberration are removed through the design of the binary surface and the aspheric surface. The visible light / long-wave infrared broad band spectrum joint focusing optical imaging system can solve the problem that a single wave band is not high in detection accuracy, two wavebands and two lenses have optical parallax on imaging, two wavebands are big in imaging aberration, an infrared system has heat difference, and two wavebands need focusing mutually.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Share-aperture broad-band infrared optical system
InactiveCN104516110AImprove transmittanceSmall structureMountingsCoatingsBeam splitterLong wave infrared
The invention discloses a share-aperture broad-band infrared optical system, and belongs to an infrared optical system. The share-aperture broad-band infrared optical system realizes long wave infrared imaging and broad-band infrared spectral measurement, and solves the problems of the optical system that the optical road layout is restricted, the size is large and the cost is high. The share-aperture broad-band infrared optical system comprises a card type lens, a beam splitter mirror, a reflecting mirror, a plurality of lens groups, an FPA interface and an optical fiber interface. Light (2-12 [mu]m) enters the card type lens to be focused, and is split through the beam splitter mirror, 50% of long wave infrared light (8-10 [mu]m) transmits through the lens groups for aberration correction, an image surface is focused at an imaging interface again, the other 50% of long wave infrared light (8-10 [mu]m) and infrared light (2-10 [mu]m as well as 10-12 [mu]m) is subjected to infrared reflection through the lens groups and are reflected again by the reflecting mirror to be focused at the optical fiber interface. The share-aperture broad-band infrared optical system is compact in integral structure, convenient and flexible to use and relatively low in cost, can be integrated for spectrum correlated detection equipment, realizes automatic detection and tracking, and can be widely applied to the civil and military fields of environmental monitoring, infrared guidance and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mutually-visual-field common-aperture multi-spectral imaging system with Cassegrain front end
InactiveCN102175318AConvenient registrationImprove light energy utilizationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationImaging qualityImaging lens
The invention discloses a mutually-visual-field common-aperture multi-spectral imaging system with a Cassegrain front end. The system comprises a main lens, a refracting-reflecting dual-purpose secondary lens, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dual-waveband imaging lens group, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long infrared double-color detector unit, a visible to near infrared band imaging lens group, a visible to near infrared band color analyzer and a detection unit, wherein the main lens is provided with a central opening; the reflecting surface of the main lens is a concave surface; and the incident surface of the refracting-reflecting dual-purpose secondary lens is a convex surface. In the system, the main lens is taken as a public entrance pupil of each waveband and primary light splitting is realized by using the secondary lens, so that the luminous energy utilization ratio is increased, the spaces of a spectroscope and the system are saved, the realization of a long aperture and a large visual field is facilitated, and the imaging quality is improved remarkably. Due to the adoption of co-optical-axis mutually-visual-field imaging, images are easy to register.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Single lens multispectral imaging optical system
InactiveCN102103265AImprove imaging effectLarge spectral coverageRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsCamera lensBeam splitter
The invention discloses a single lens multispectral imaging optical system and belongs to the technical field of remote sensing. The system specifically comprises a multispectral apochromatic lens, a first beam splitter, a second beam splitter, a doublet lens, a visible light flat-panel detector, an infrared flat-panel detector and a laser flat-panel detector. The first beam splitter reflects visible light, and transmits infrared and laser; the second beam splitter reflects laser and transmits infrared; and the multispectral apochromatic lens, the first beam splitter and the second beam splitter are made of materials of high transmittance from the visible light to a long-wave infrared band, preferably chemical vapor deposition zinc sulfide. The function of performing multispectral imaging by using a single lens is realized, an image from the visible light to the long-wave infrared band can be obtained, and imaging performance is high; the spectrum coverage range is wide; and the system can be widely applied to the remote sensing of the fields of aerophotography, agriculture and forestry, geology and geography, hydrology and marine, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Integrated multi-waveband common-path synchronous continuous variable-focus optical system
The invention discloses an integrated multi-waveband common-path synchronous continuous variable-focus optical system. The optical system comprises a public front fixed group, a public zooming group and a public compensation group which are arranged in sequence along an optical axis, as well as a first group of beam splitter prisms for reflecting visible light and transmitting medium-wave infrared light and long-wave infrared light, and a second group of beam splitter prisms for reflecting long-wave infrared light and transmitting medium-wave infrared light. A common-caliber, common-path and common-variable-focus form is adopted, a visible waveband, a medium-wave waveband and a long-wave infrared waveband are zoomed synchronously and continuously along with the movement of the public zooming group in a zooming process, and the three wavebands are of the same focal lengths, zooming ratios and visual fields, thereby realizing synchronous observation, synchronous tracking and synchronous measurement of a target in the visible waveband, the medium-wave waveband and the long-wave infrared waveband. When different wavebands are needed for observing, path switching and new search of the target are unnecessary, thereby increasing the reaction speed of the optical system and preventing loss of a target moving at a high speed during path switching.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
Control method and system for forest fire exploration through unmanned plane
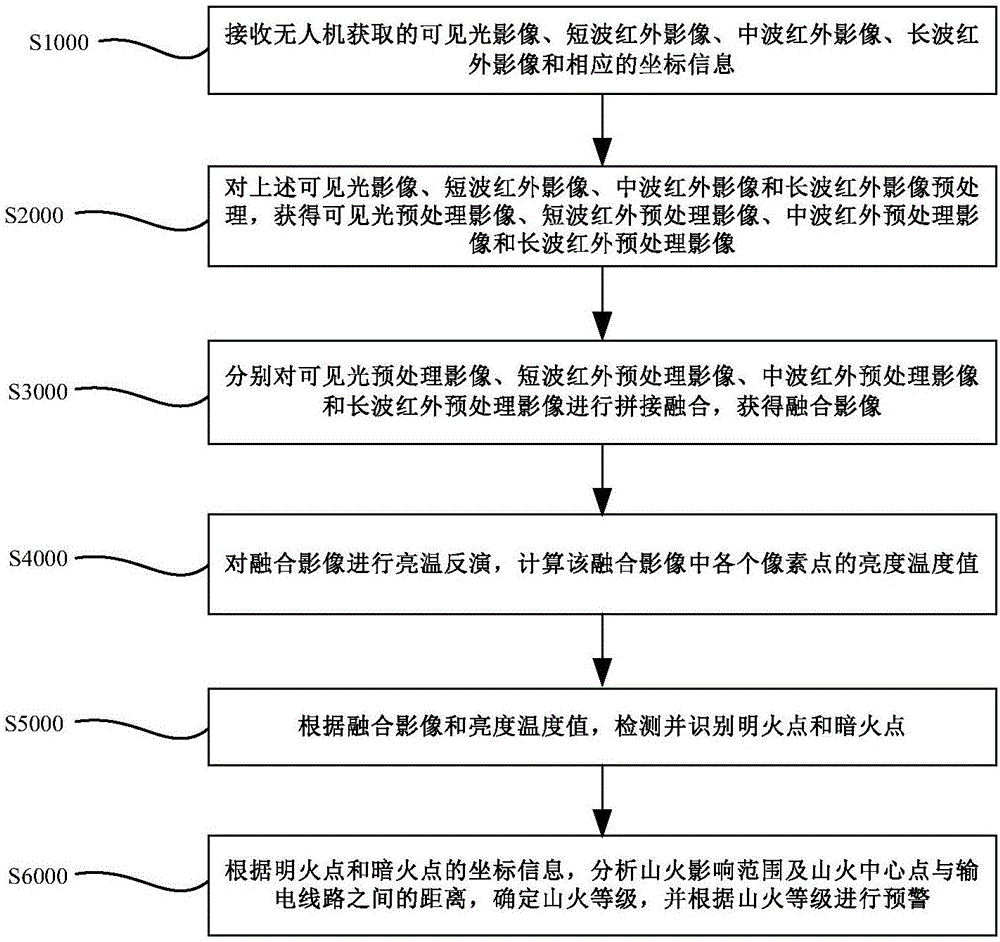
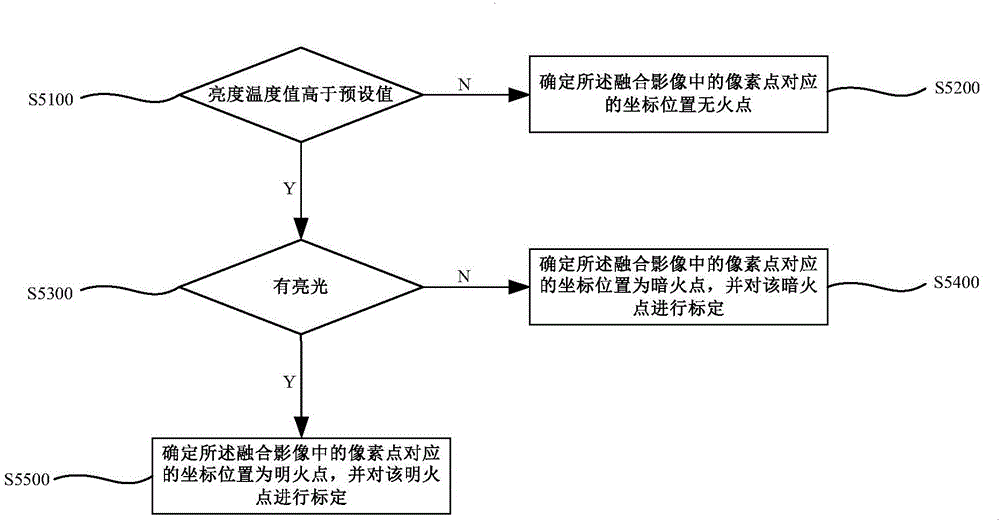
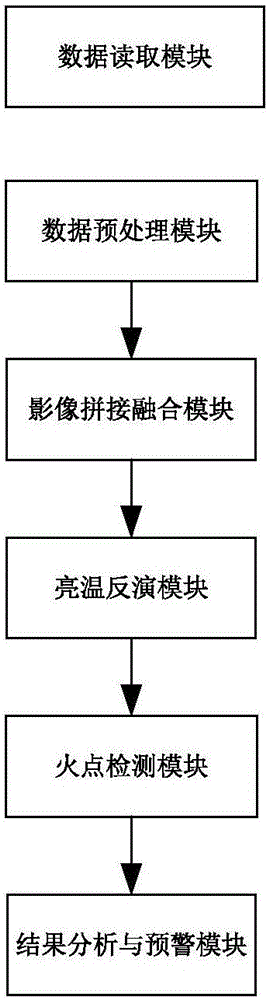
ActiveCN106297142AGuaranteed uptimeReduce security risksClimate change adaptationCharacter and pattern recognitionLightnessDetection rate
The embodiment of the invention discloses a control method and system for the forest fire exploration through an unmanned plane. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a fusion image and the brightness temperature values of all pixels in the fusion image through the preprocessing, splicing and fusion and brightness temperature inversion of a visible image, a short-wave infrared image, a mid-wave infrared image and a long-wave infrared image; recognizing the position of an open fire point and the position of a blind fire point according to the fusion image and the brightness temperature values of all pixels in the fusion image; finally analyzing the influence scope of forest fire and the distance between the center of the forest fire and a power transmission line according to the positions of the fire points, determining the level of forest fire, and carrying out the early warning according to the level of forest fire. Compared with the prior art, the method can effectively distinguish the open fire point and the blind fire point, can carry out the early warning timely according to the level of forest fire, can effectively improve the detection rate of the forest fire and the put-out success rate of the forest fire, reduces the safety risk of fire fighters, and guarantees the safe and reliable operation of power transmission lines.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Detection method for remote sensing day and night sea fog by stationary weather satellite
InactiveCN101464521AReal-timeRealize dynamic trackingElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationSplit windowData file
The invention relates to a detection method of sea fog remotely sensed by stationary meteorological satellites in the daytime and at night. The detection method comprises the following steps: firstly receiving and processing a data file S-VISSR by utilizing the number of the stationary meteorological satellites and obtaining a GPF document containing 5 channel data after being projected through calibration and location, data amendment, latitude and longitude projection and other pretreatments; then extracting sea fog information by utilizing 4 channel data in the GPF document, 2 split window channels in a long wave infrared window region, 1 intermediate infrared channel of 3.7 Mu m and 1 visible light channel of 0.67 Mu m according to the kinematic characteristics and the spectral characteristics of the sea fog; and firstly filtering a movable cloud boundary and a medium-high cloud boundary and then filtering water body in clear sky and partial low clouds by adopting the tertiary judging method, and finally determining a sea fog region by utilizing the region growing method. The invention not only achieves the real-time monitoring of the sea fog in a wide ocean plane and the dynamic track of the sea fog region, but also provides an important basis for the shot forecast of the sea fog, thereby obtaining sea fog real-time monitoring images per hour at least.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
Long-wave infrared polarization feature extraction and fusion image enhancement method
ActiveCN108492274AIncrease the amount of informationImprove effectivenessImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionDecomposition
The invention belongs to the field of infrared image processing, and relates to an image enhancement method based on long-wave infrared polarization feature extraction and fusion method. The method comprises the steps of (S1) collecting an infrared polarization image, and preprocessing the collected infrared polarization image; (S2) performing Stokes polarization state calculation on the preprocessed image in the step (S1), and calculating a polarization degree and a polarization angle according to a Stokes polarization state calculation result; (S3) carrying out completely polarized light decomposition calculation by using the polarization degree and the polarization angle; (S4) defining a polarization orthogonal difference value, setting a weighting coefficient, and extracting a polarization feature image, wherein the polarization feature image comprises a polarization parallel component image and a polarization vertical component image; and (S5) fusing the polarization feature imageand an infrared intensity image by using a non-downsampling shear wave algorithm. The method can effectively extract the polarization information of a target scene, has a good polarization feature extraction effect, performs fusion on the extracted polarization feature image and the infrared intensity image and significantly enhances the information content of the target scene.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
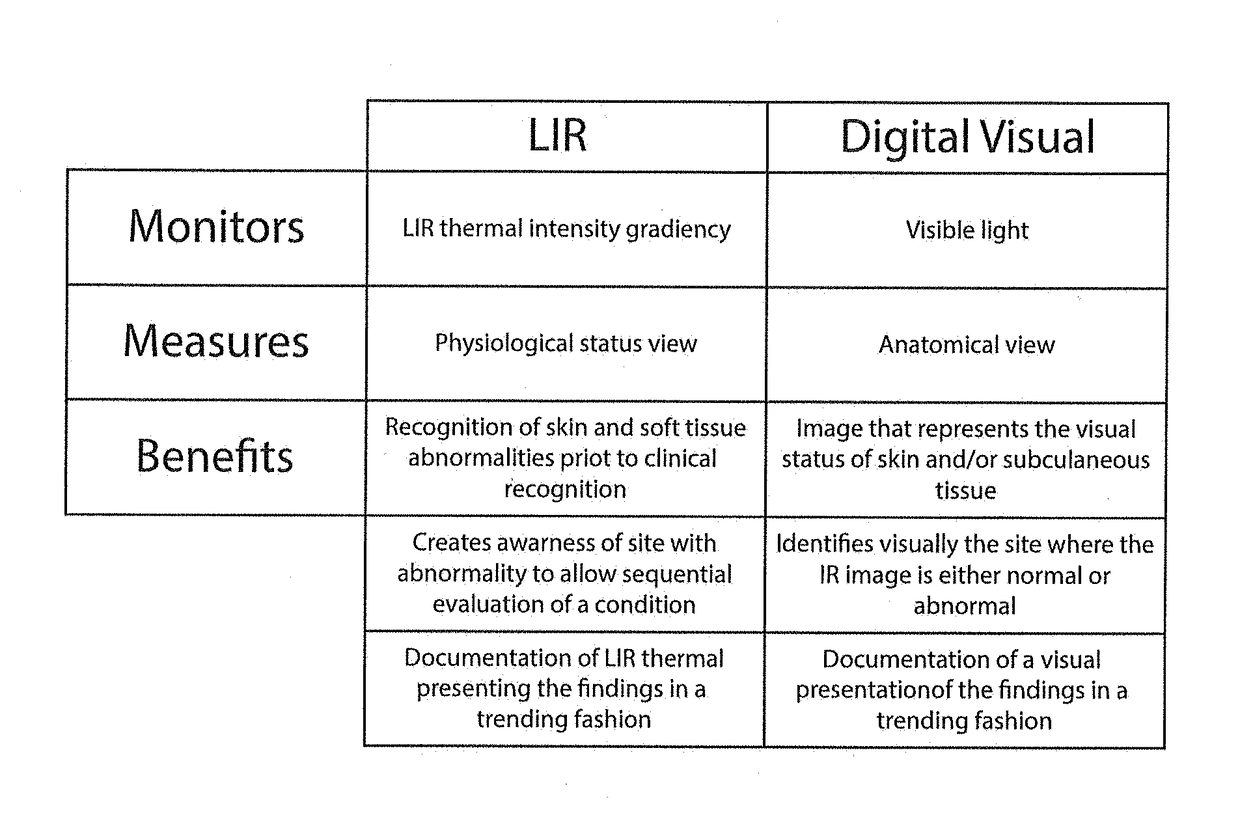
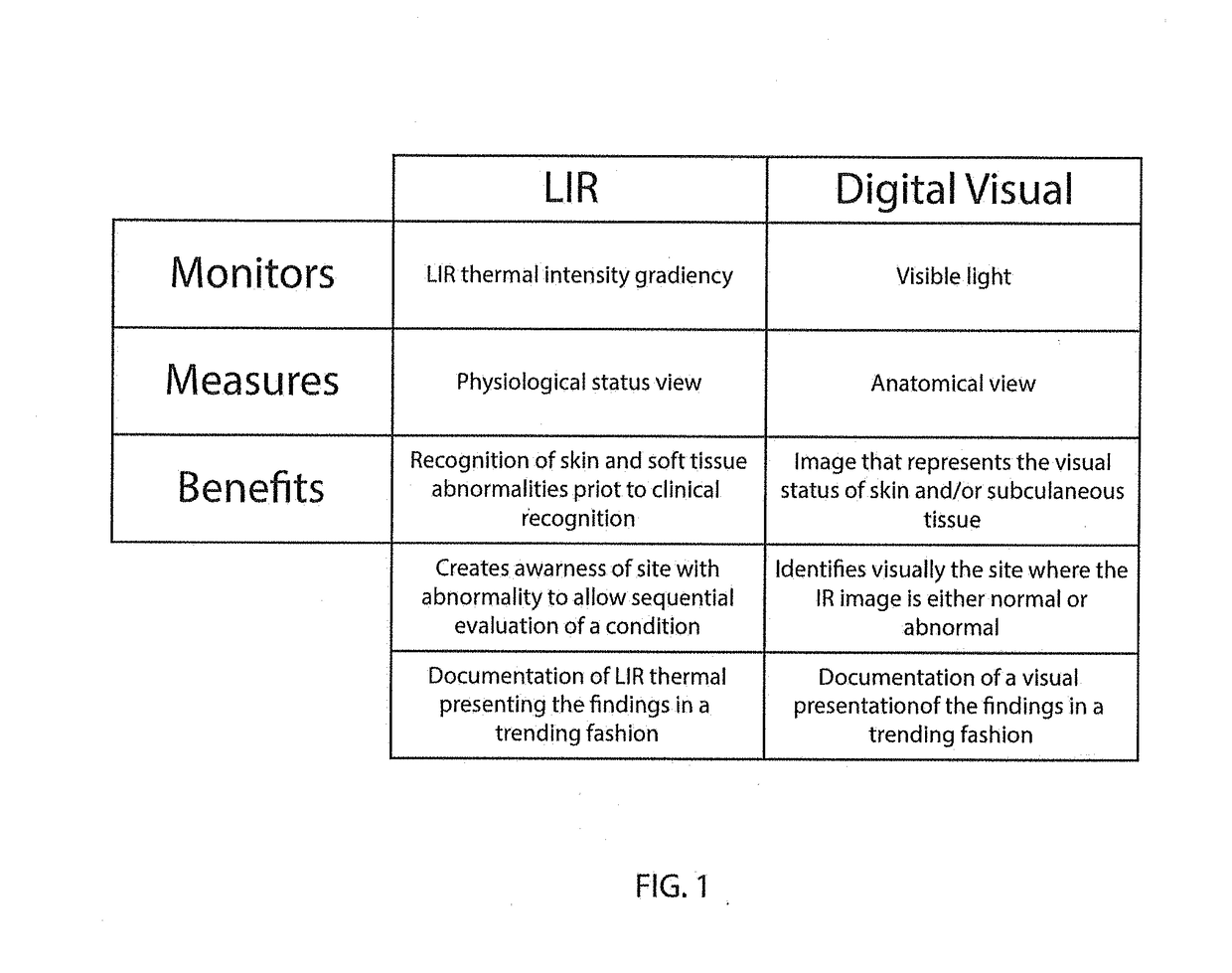
System, apparatus and method for assessing wound and tissue conditions
A combination thermal and visual image capturing device used to capture real time thermal and visual images of surface and subsurface biological tissue, said device comprising: a power source, said power source functionally connected to said device; a housing, a long wave infrared microbolometer, said microbolometer functionally connected to said power source a digital camera; a short wave infrared microbolometer, said microbolometer functionally connected to said power source; a digital camera, said digital camera functionally connected to said power source; and a digital camera, said digital camera functionally connected to said power source, wherein said digital camera and 3D camera are contained within a USB peripheral device; said imaging apparatus further comprising means to electronically provide combined thermal image information from the microbolometers and visual image information from said digital camera and said 3D camera to another electronic device.
Owner:SPAHN JAMES G +2
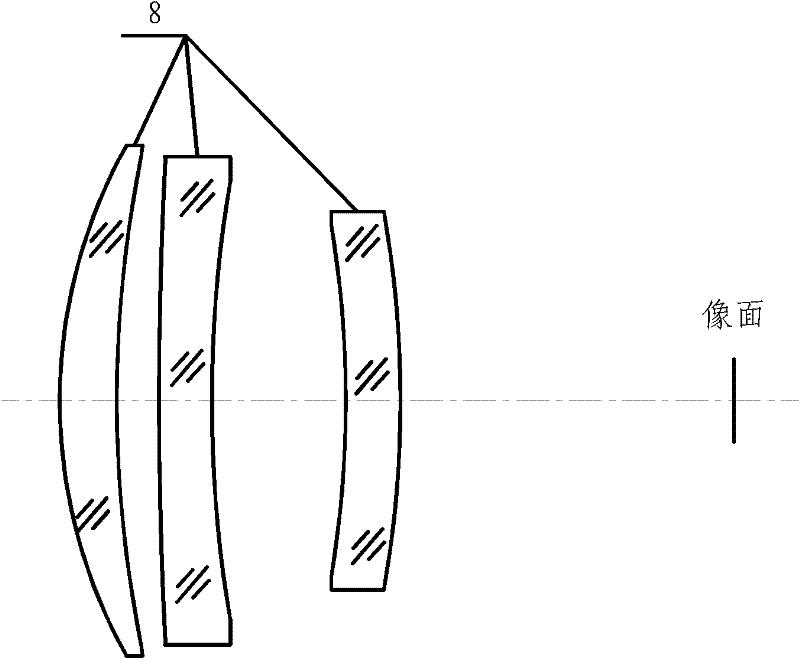
Two-color two-field infrared imaging optical system
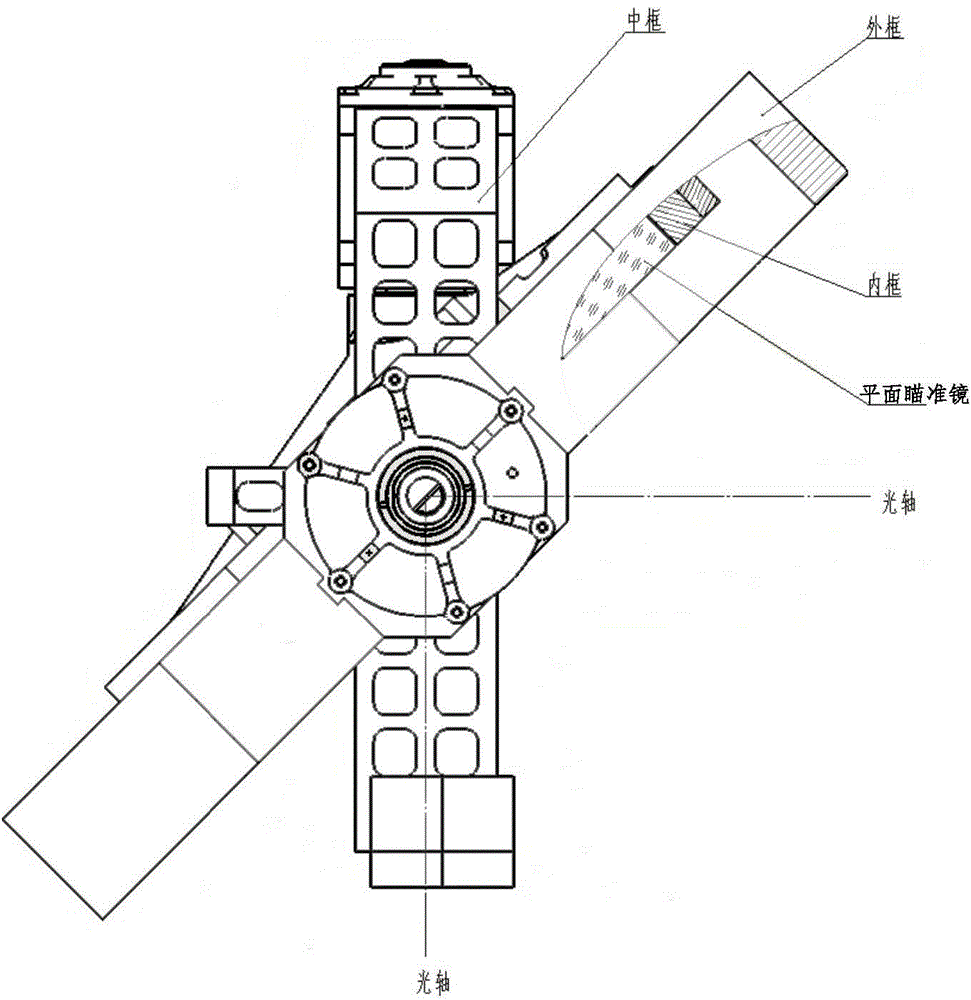
ActiveCN102269871AMiniaturizationTake into account the requirementsRadiation pyrometryOptical elementsSystems designMiniaturization
The invention discloses a bicolor dual-view field infrared imaging optical system. The bicolor dual-view field infrared imaging optical system is characterized by consisting of five lenses including a front fixing lens set (9), a multifocal lens set (10) and a rear fixing lens set (11), wherein the front fixing lens set consists of two lenses, the multifocal lens set consists of one lens, and therear fixing lens set consists of two lenses. The multifocal lens set can axially move in front of or behind a primary image surface to realize switching between a wide view field and a narrow view field; in the five lenses, lenses with a binary diffraction surface is used as a second surface of a second lens and a second surface of a fourth lens. The bicolor dual-view field infrared imaging optical system has the advantages of simple and compact structure, small system size and less lenses, can simultaneously performing imaging at a medium wave infrared wave band with wavelength of 4-5 microns and a long wave infrared wave band with wavelength of 8-9 microns while implementing functions of searching (a wide view field of 9 degrees* 6.75 degrees) and aiming (a narrow view field of 3 degrees*2.25 degrees). The system design takes account of miniaturization and lightweight requirement of the infrared system and meets the use technology requirement of the infrared system.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
System and Method for Multimodal Detection of Unknown Substances Including Explosives
InactiveUS20120134582A1Spectrum investigationCharacter and pattern recognitionReference databaseFluorescence
A system and method for identifying an unknown substance in a sample comprising multiple entities. A method may comprise generating a RGB image representative of a sample and assessing said RGB image to identify at least one region of interest. This region of interest may he assessed to generate a spatially accurate wavelength resolved image, which may be a hyperspectral image. This spatially accurate wavelength resolved image may comprise a fluorescence, Raman, near infrared, short wave infrared, mid wave infrared and / or long wave infrared image. This spatially accurate wavelength resolved image may be assessed to identify said unknown substance. A system may comprise: a reference database, a first detector for generating an RGB image, a second detector for generating a spatially accurate wavelength resolved image, and a means for assessing said RGB image and said spatially accurate wavelength resolved image.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
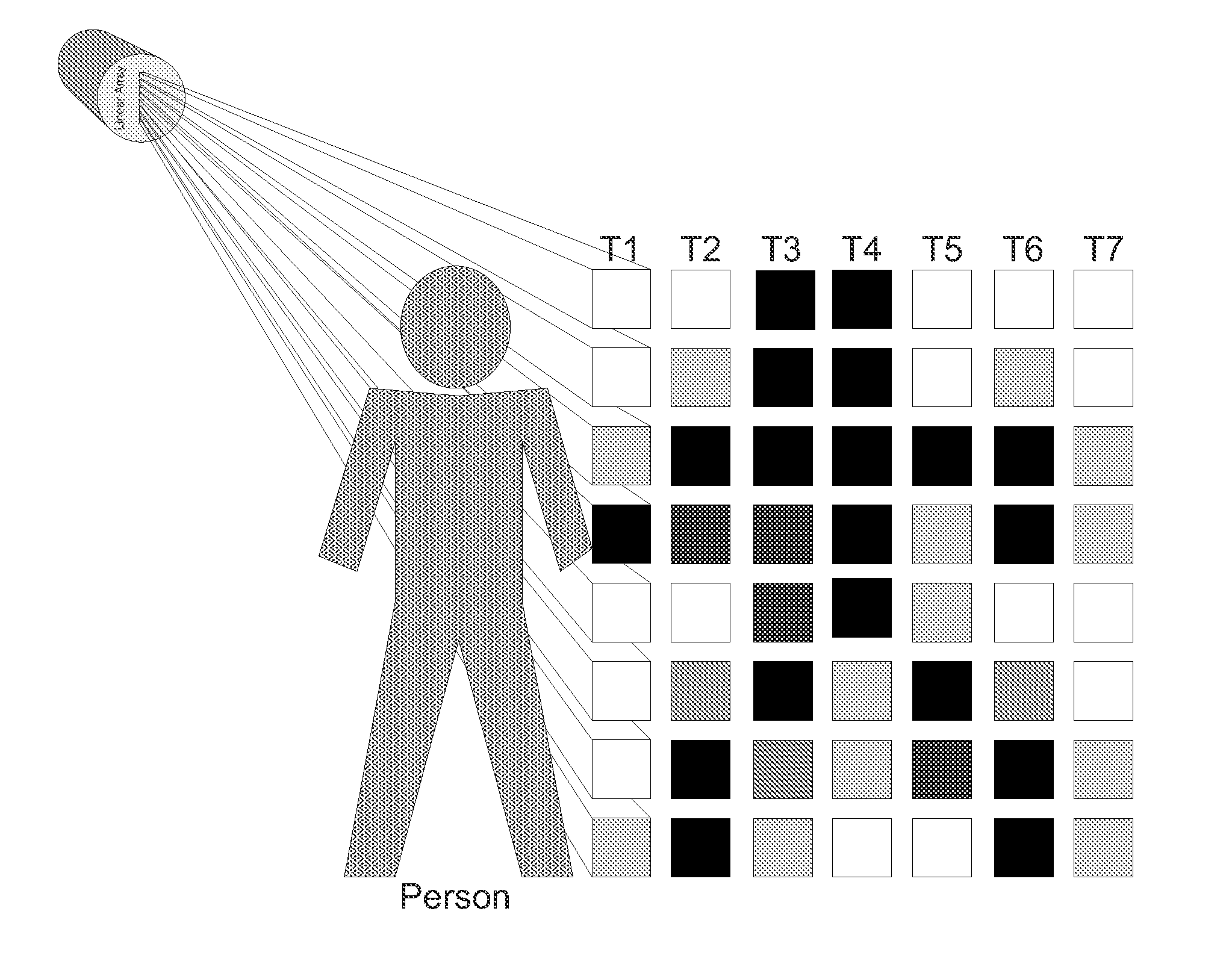
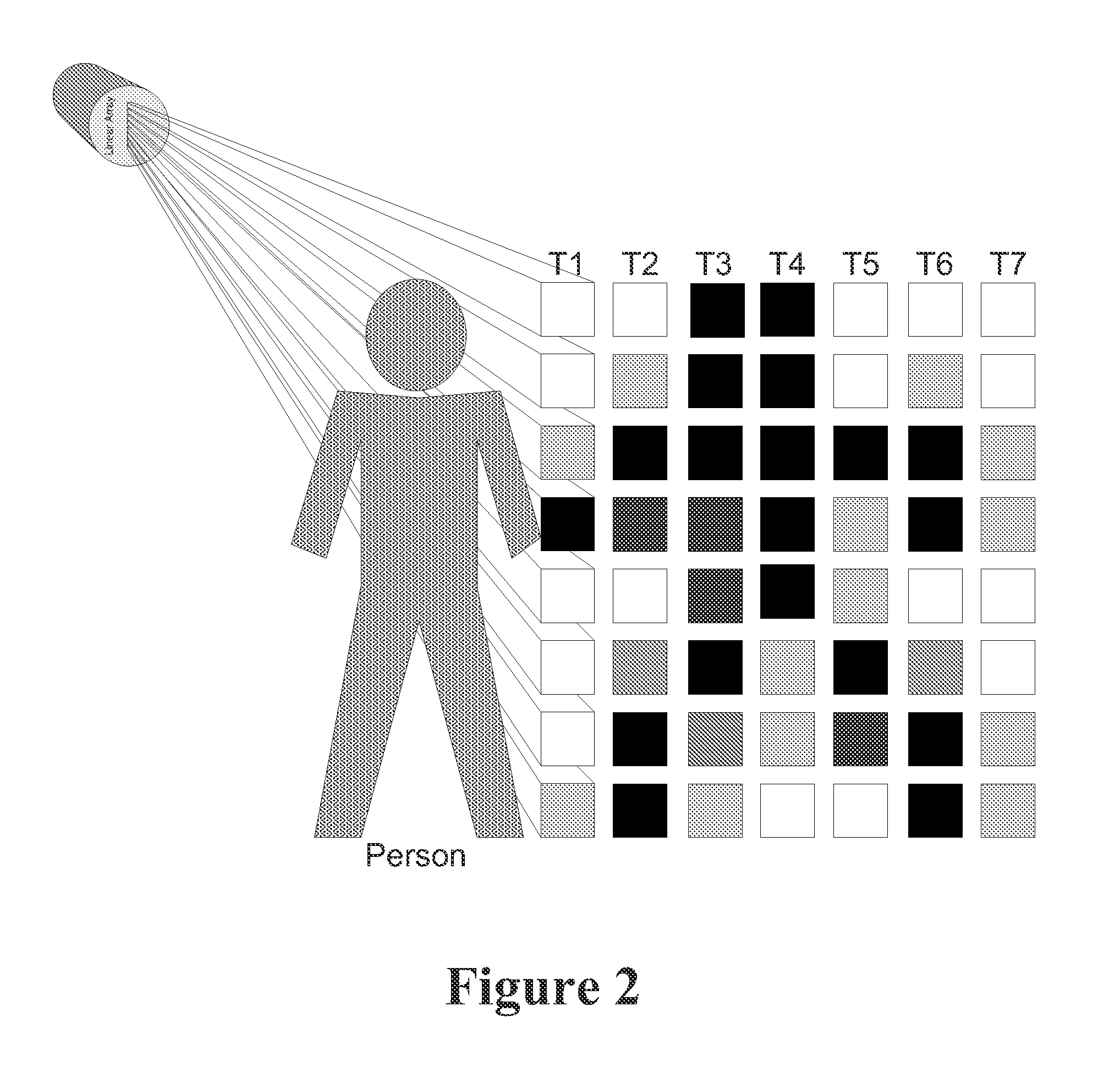
Self-Scanning Passive Infrared Personnel Detection Sensor
InactiveUS20120038778A1Reduce power consumptionLighting conditionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicrobolometerLong wave infrared
A system capable of low power personnel detection is based on a focused linear array of passive infrared detectors sampled and processed over time. For example, an exemplary system can have a sensor that captures infrared line images for personnel detection by scanning through a sensing plane of a linear array's field of view. In such a system, a processor controls the array sensor and stores the resulting images. Velocity characteristics of moving objects are incorporated into the images over time resulting in horizontal velocity profile images. Long wave infrared (LWIR) radiation can be sensed, which works in day and night conditions without illumination. LWIR sensors, such as microbolometers, as well as pyroelectrics, can be used.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Optical-compensation athermalizing long-wave infrared optical system
InactiveCN102540436AQuality improvementRealize thermal difference eliminationOptical elementsMangin mirrorPlane mirror
The invention relates to an optical-compensation athermalizing long-wave infrared optical system which comprises a primary mirror, a secondary mirror and a relay mirror; wherein the primary mirror is a Mangin mirror, the refracting surface of the Mangin mirror has a negative focal power, and the reflecting surface of the Mangin mirror is a concave surface, and the secondary mirror is a planar mirror; and an object target is refracted from the refracting surface of the primary mirror to the reflecting surface of the primary mirror, refracted by the refracting surface of the primary mirror for the second time and turned and reflected by the secondary mirror to irradiate on an image surface of a refrigeration type infrared detector sequentially through the relay mirror and a detector window.According to the optical-compensation athermalizing long-wave infrared optical system, as the Mangin mirror is adopted by the primary mirror, the optical system has a wide viewing field and compact structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrated infrared dual-band 20X zoom optical system
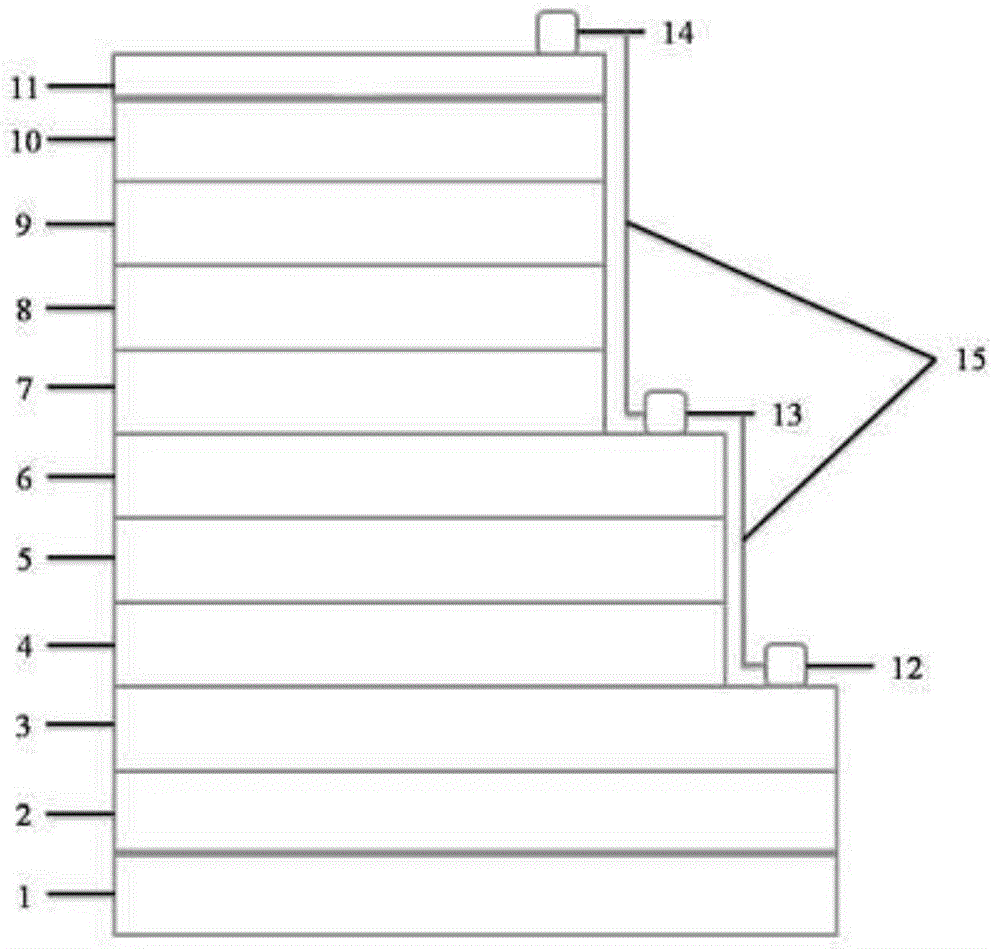
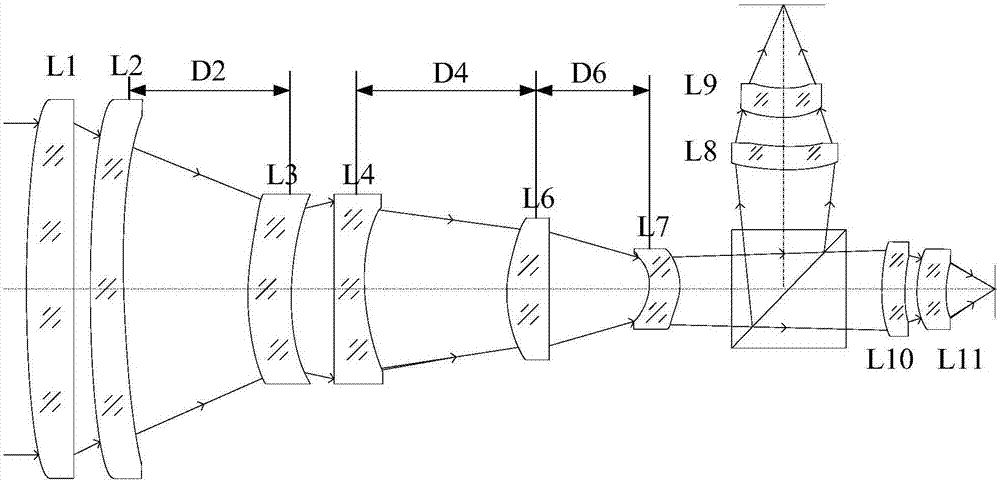
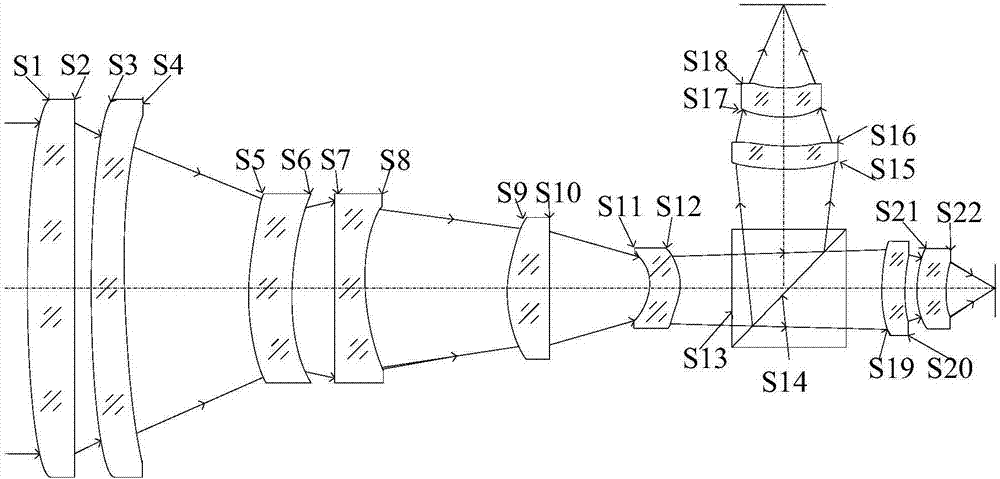
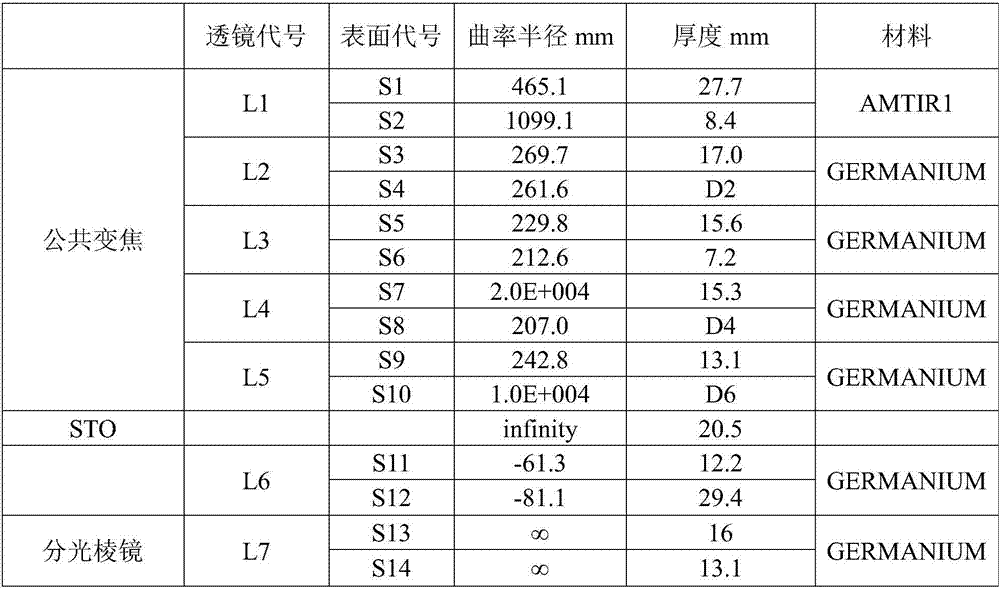
ActiveCN106950684AConsistent response timeShort reaction timeOptical elementsBeam splitterOptical axis
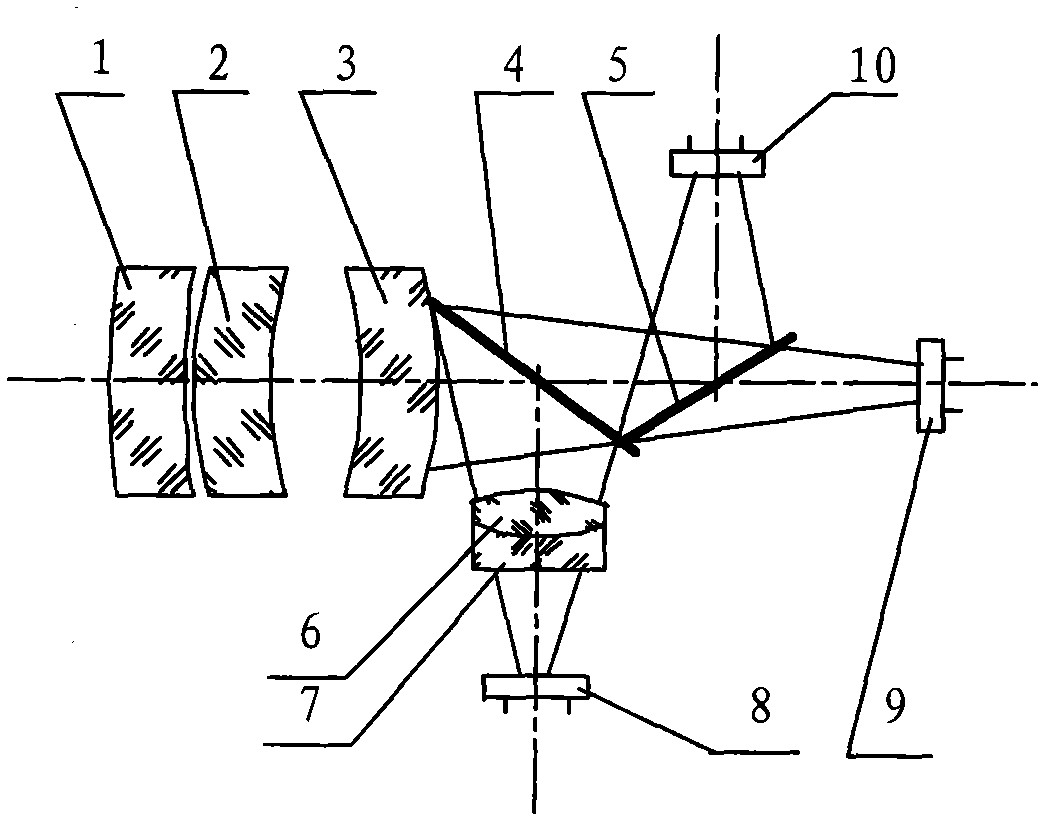
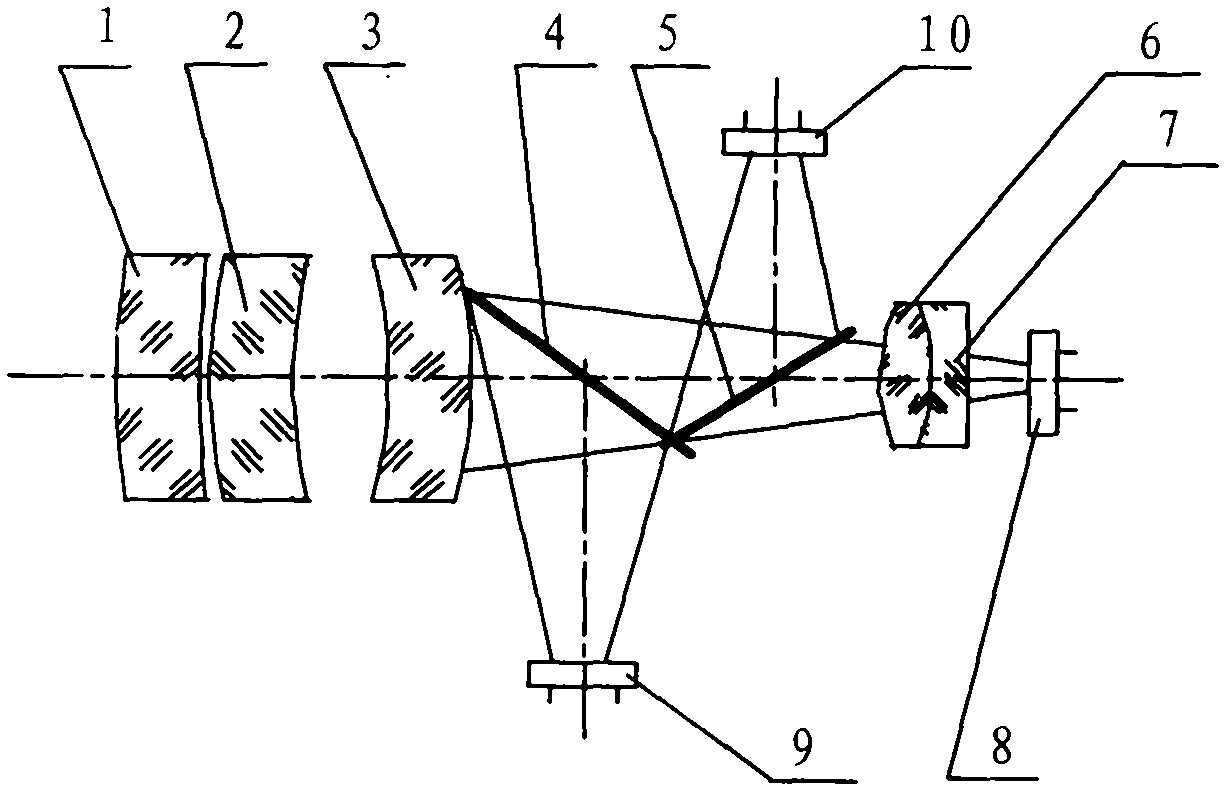
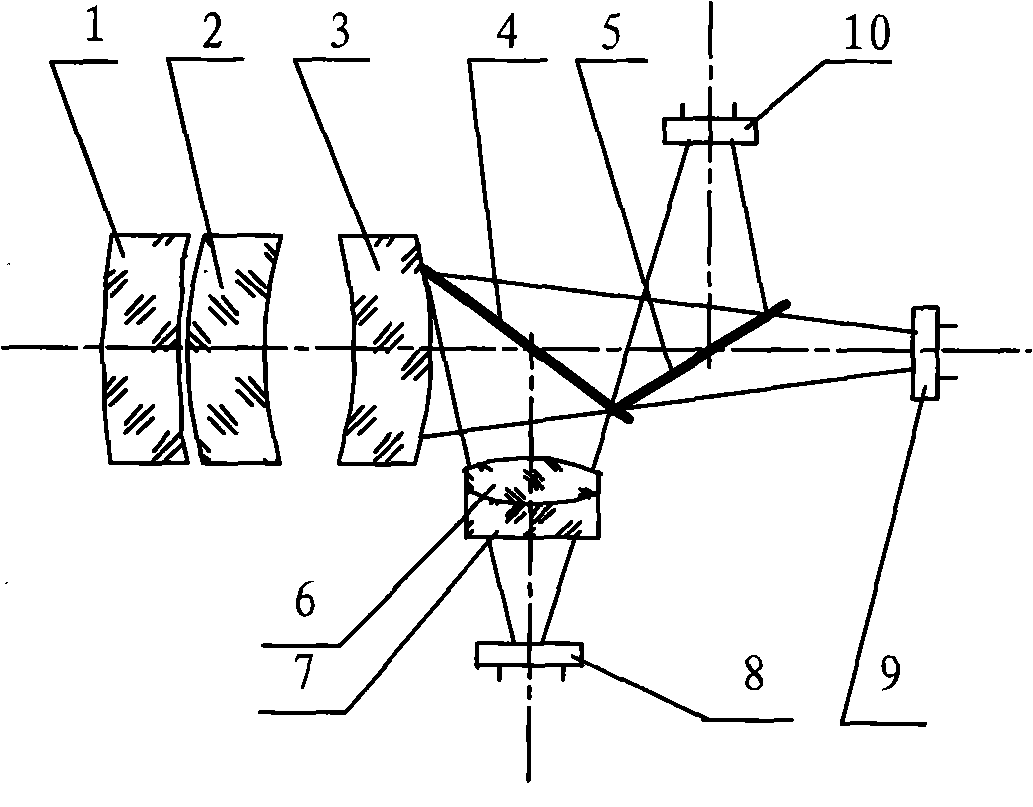
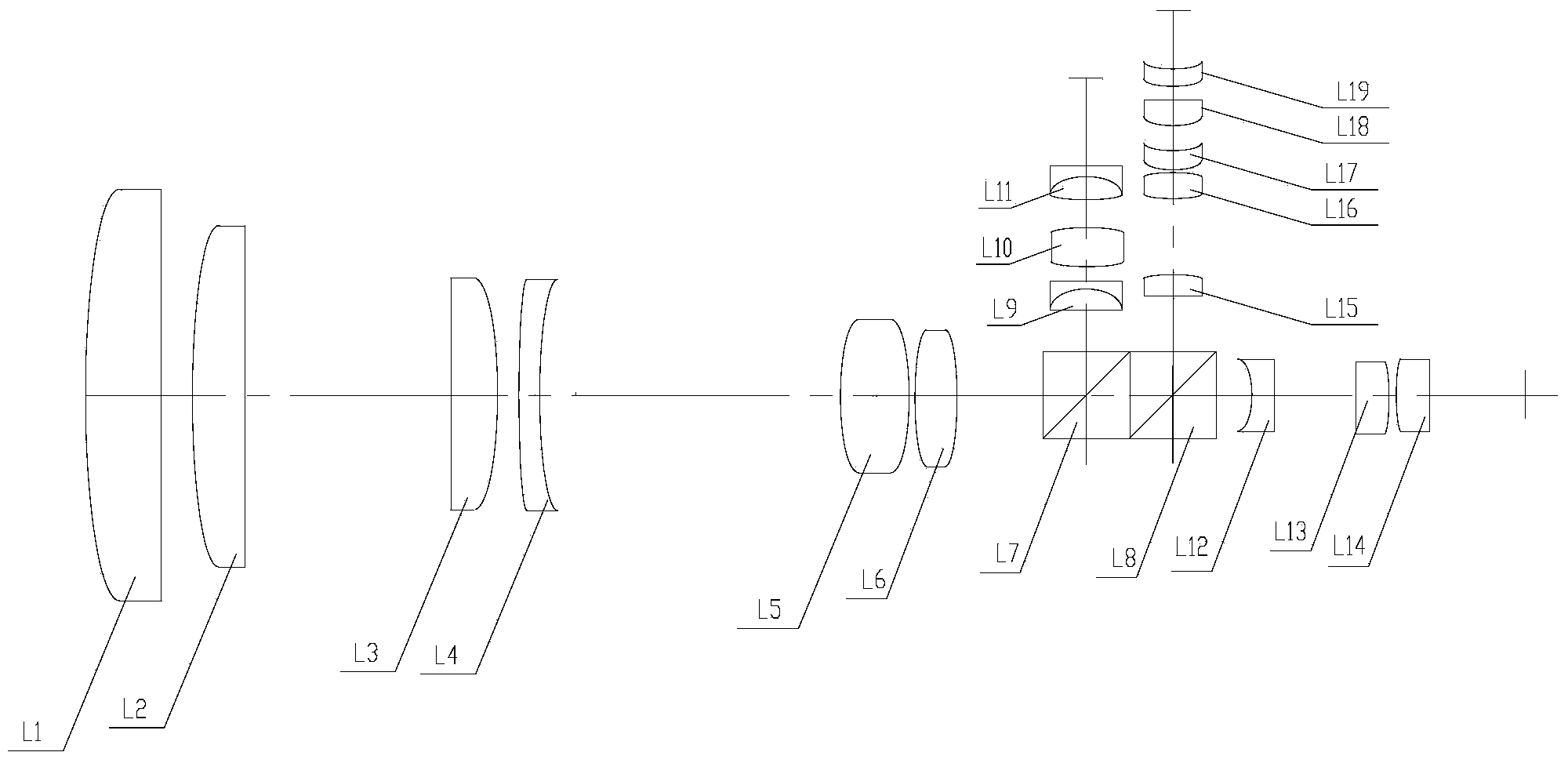
The invention discloses an integrated infrared dual-band 20X zoom optical system. The integrated infrared dual-band 20X zoom optical system is composed of a common front fixing set, a common zooming set, a common compensation set, a common rear fixing set, a beam splitter prism, a long-wave infrared light rear fixing set, a medium-wave infrared focal length compensation set and a medium-wave infrared light rear fixing set which are sequentially arranged from left to right along an optical axis, wherein the beam splitter prism is used for reflecting medium-wave infrared light and transmitting long-wave infrared light, the long-wave infrared light rear fixing set is arranged on a transmission optical path of the beam splitter prism, the medium-wave infrared focal length compensation set is arranged on a reflection optical path of the beam splitter prism. In the continuous zooming process, a difference value between corresponding focal lengths of dual bands is less than a difference value between corresponding focal depths of the dual bands, target information of the dual bands can be received by the same system without switching the optical paths, and problems existing in an existing dual-band system at present are solved.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com