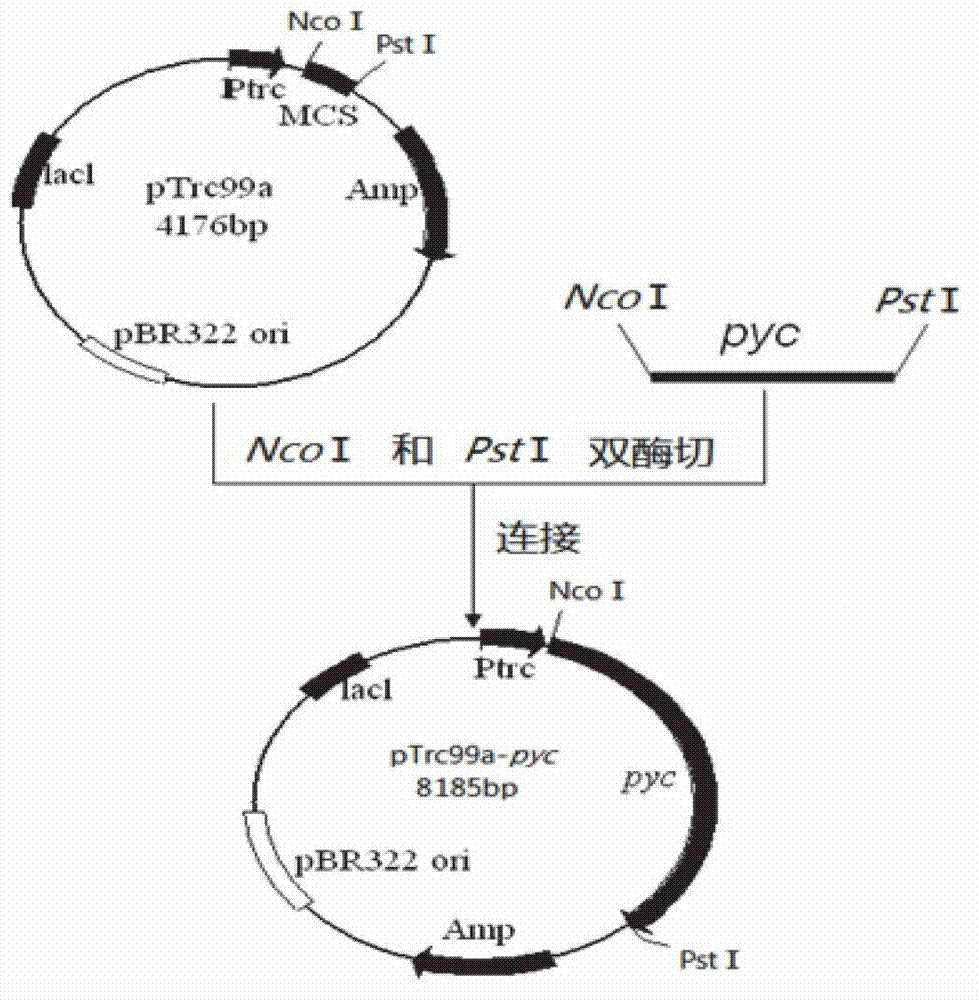
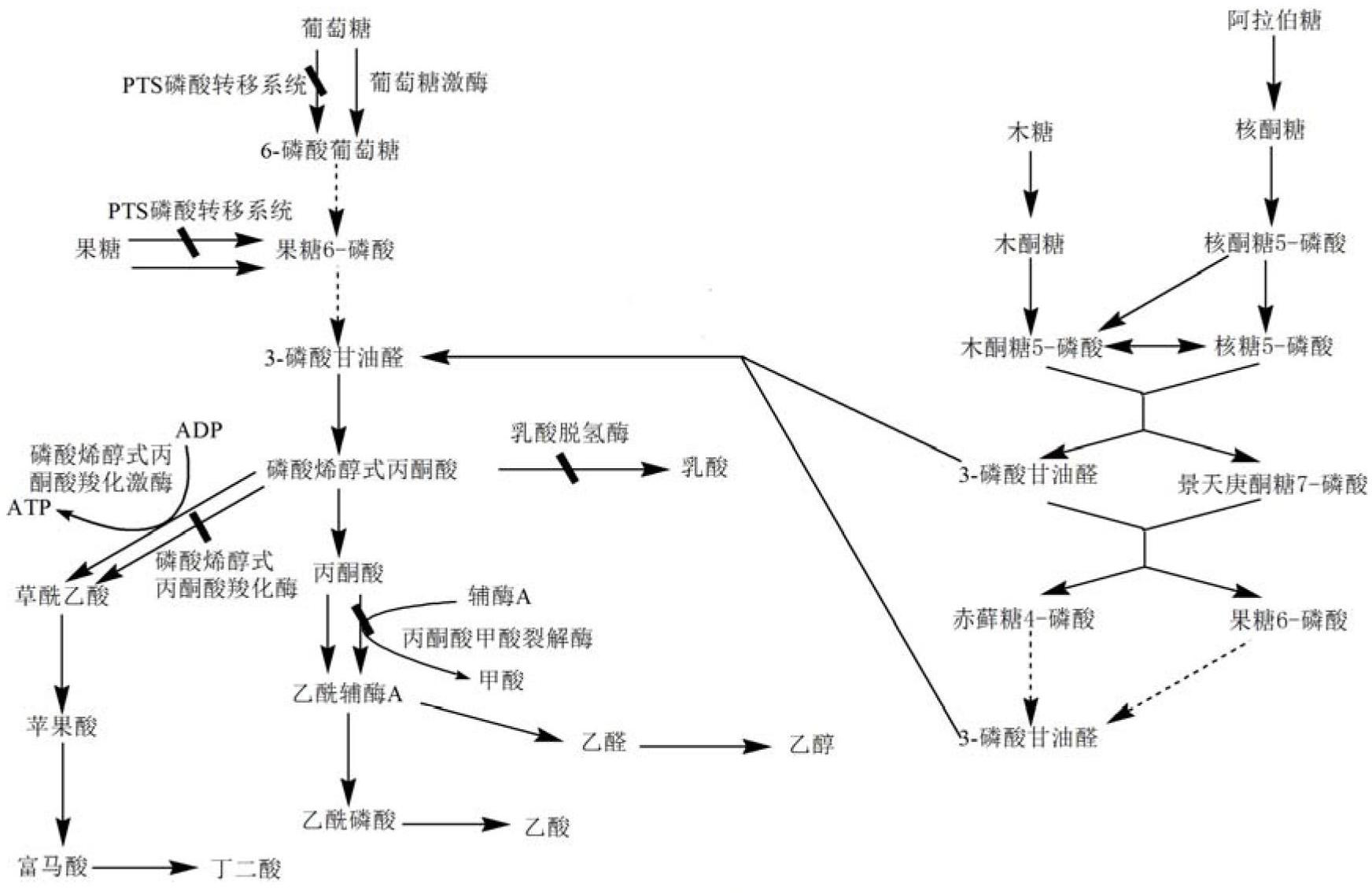
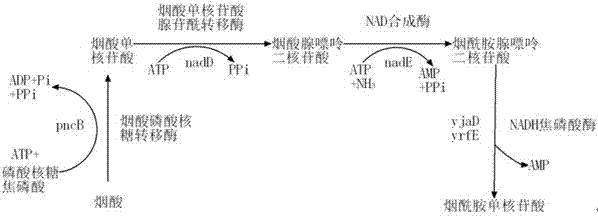
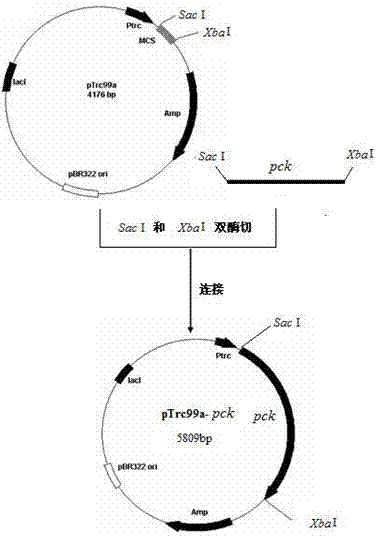
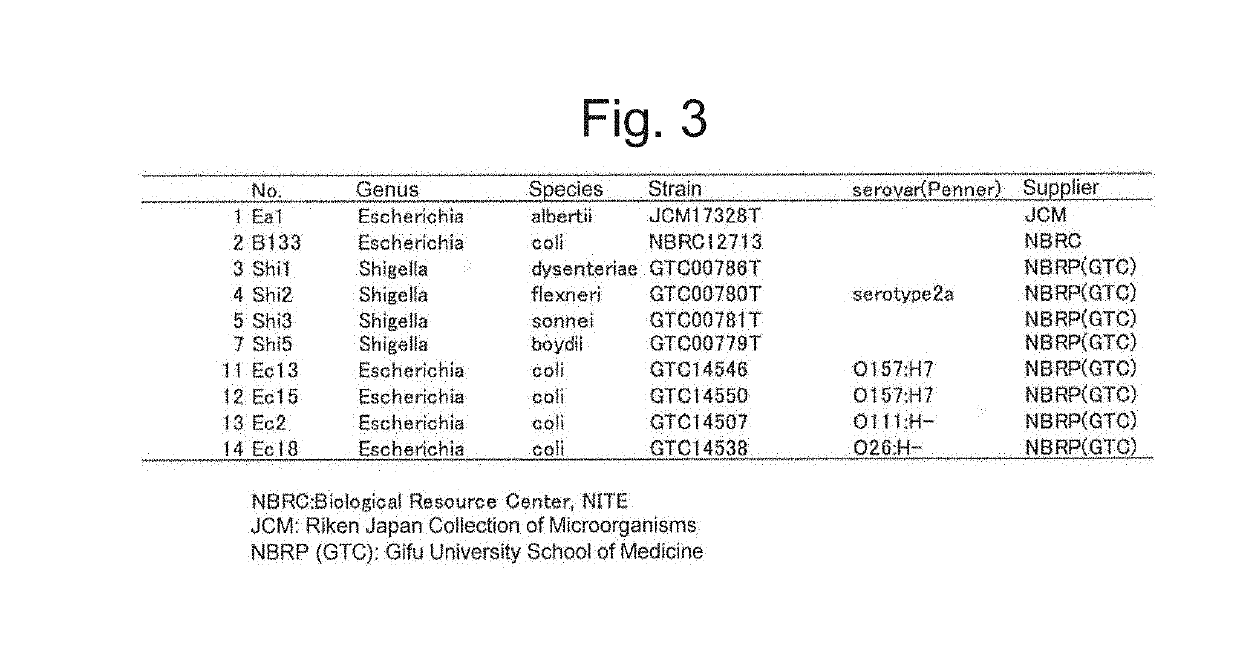
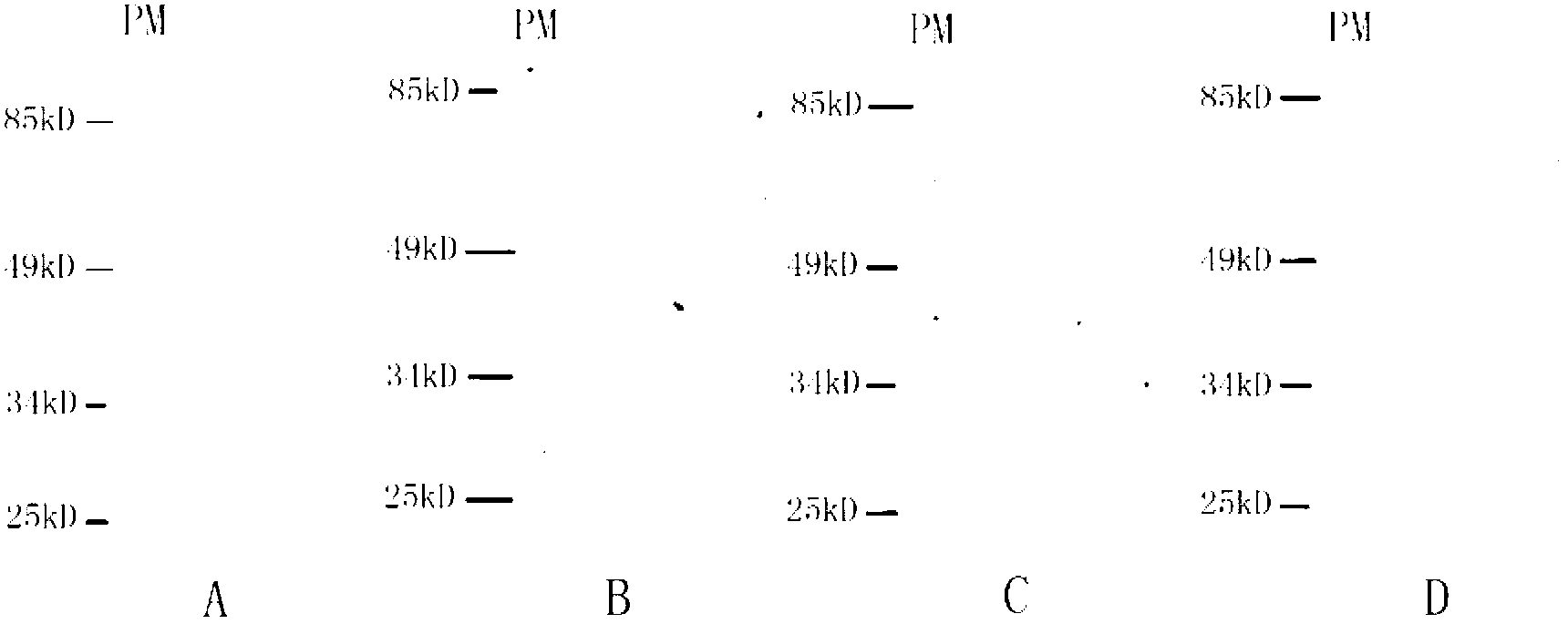Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Escherichia albertii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Escherichia albertii is a species of bacteria in the same genus as E. coli. It was described in 2003 after being isolated from the diarrhea of Bangladeshi children. Five different strains are known. The importance of the species in disease is unclear.
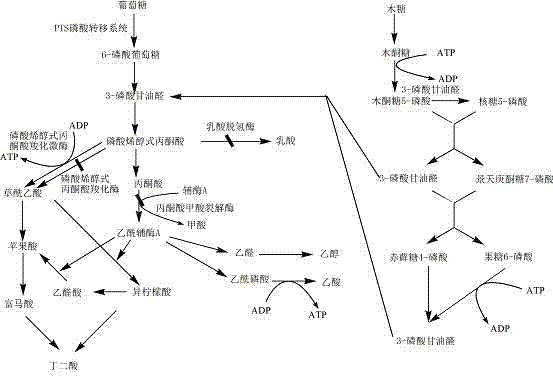
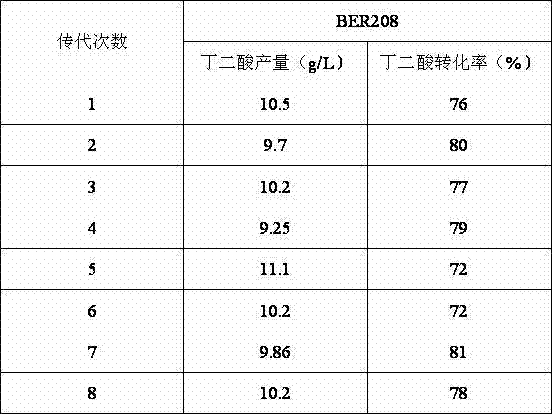
Strain capable of producing succinic acid, method for producing succinic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN102864113AIncrease productionPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesButanedioic acidMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain capable of producing succinic acid, a method for producing the succinic acid and an application thereof. The strain is named as Escherichichia coil BER208 with the collection number of CCTCCNO: M2012351. The strain grows quickly with glucose serving as the single carbon source in a fermentation medium under the anaerobic condition and is capable of highly producing the succinic acid. The optical density (OD) 6000 reaches 6.87 and the yield of the succinic acid reaches 10.5g / L after fermentation for 48 hours, and compared with an original strain, the yield of the succinic acid is improved by more than two times.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
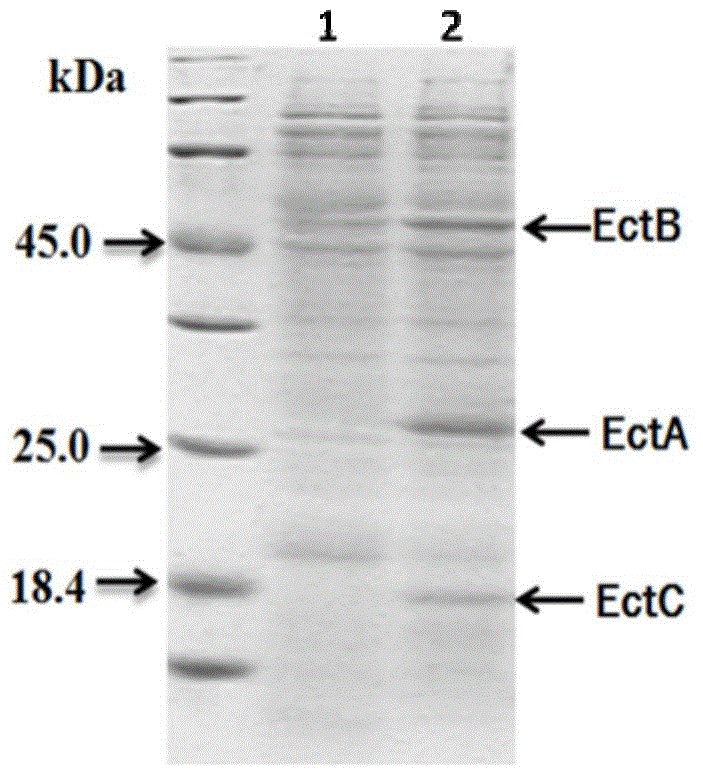
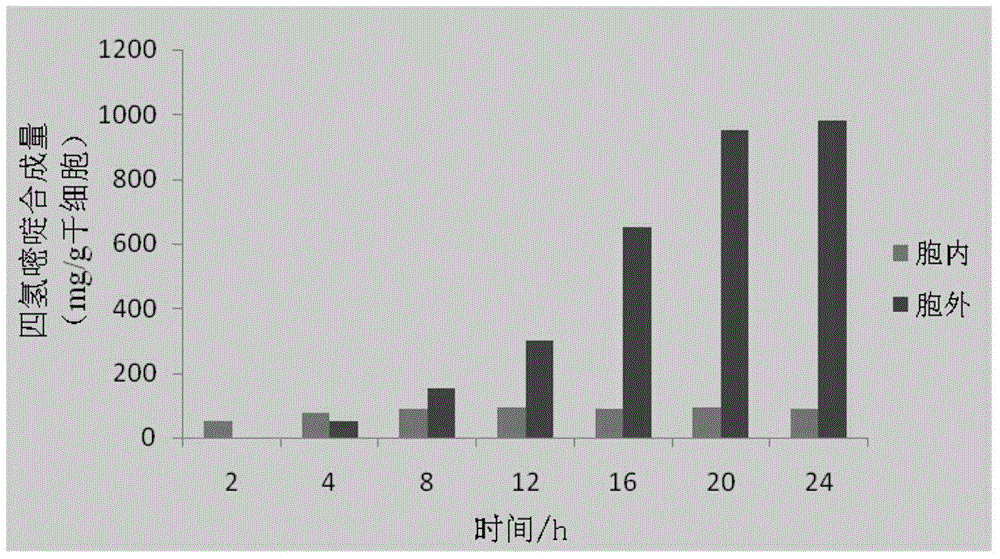
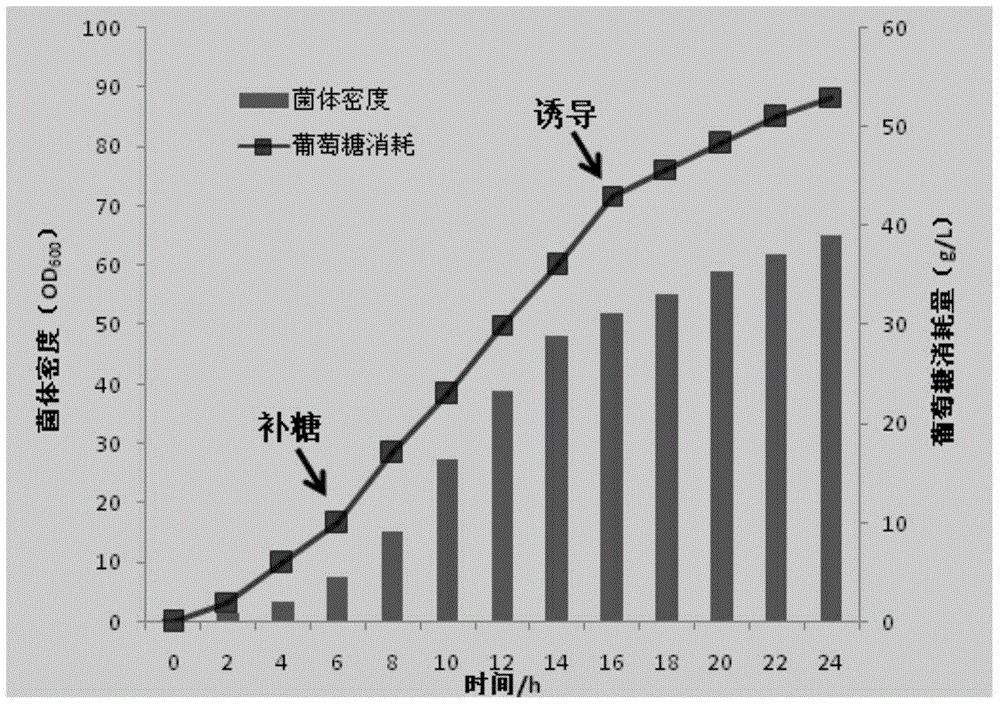
A method of producing ectoine by high-density culture of recombinant escherichia coli
A method of producing ectoine by high-density culture of recombinant escherichia coli is provided. The method includes subjecting sodium L-aspartate to a biotransformation reaction by utilizing escherichia coli BW-p-BAD-ectABC having an accession number of CGMCC NO.8334. According to the method, 87.5 g of extracellular ectoine can be synthesized in each liter of fermenting bacteria after the fermenting bacteria are used repeatedly for five times, the synthetic efficiency is 11.67 g / L.d, and both the synthetic yield and the synthetic efficiency are higher than the reported synthesis levels. The method has great significance for industrial production and large-scale application of the ectoine.
Owner:南京众惠生物材料科技有限公司
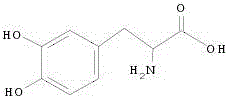
Trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as construction method thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria as well as a construction method thereof and application thereof. A tyrosine phenol lyase gene is constructed to express plasmids; chaperonin is introduced to express the plasmids to obtain the trosine phenol lyase engineering bacteria which are identified as escherichia coli FPLF8 (Escherichia coli HPLF8) preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on February 19, 2016, with a preservation number being CCTCCNO:M 2016065. The engineering bacteria can be synthesized into levodopa by fermentation and conversion, and are efficiently expressed; the expressed product is stable and high in activity, and can be synthesized into levodopa by conversion in the presence of related substrates; and the process is simple, the cost is low, the yield is high, emission of three wastes is a little, and the application value for industrial production is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Colibacillus capable of generating succinic acid by utilizing synthetic medium pure anaerobic growth and application thereof
InactiveCN102643770AGreat social significanceSignificant economyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
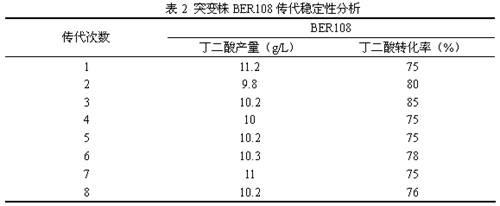
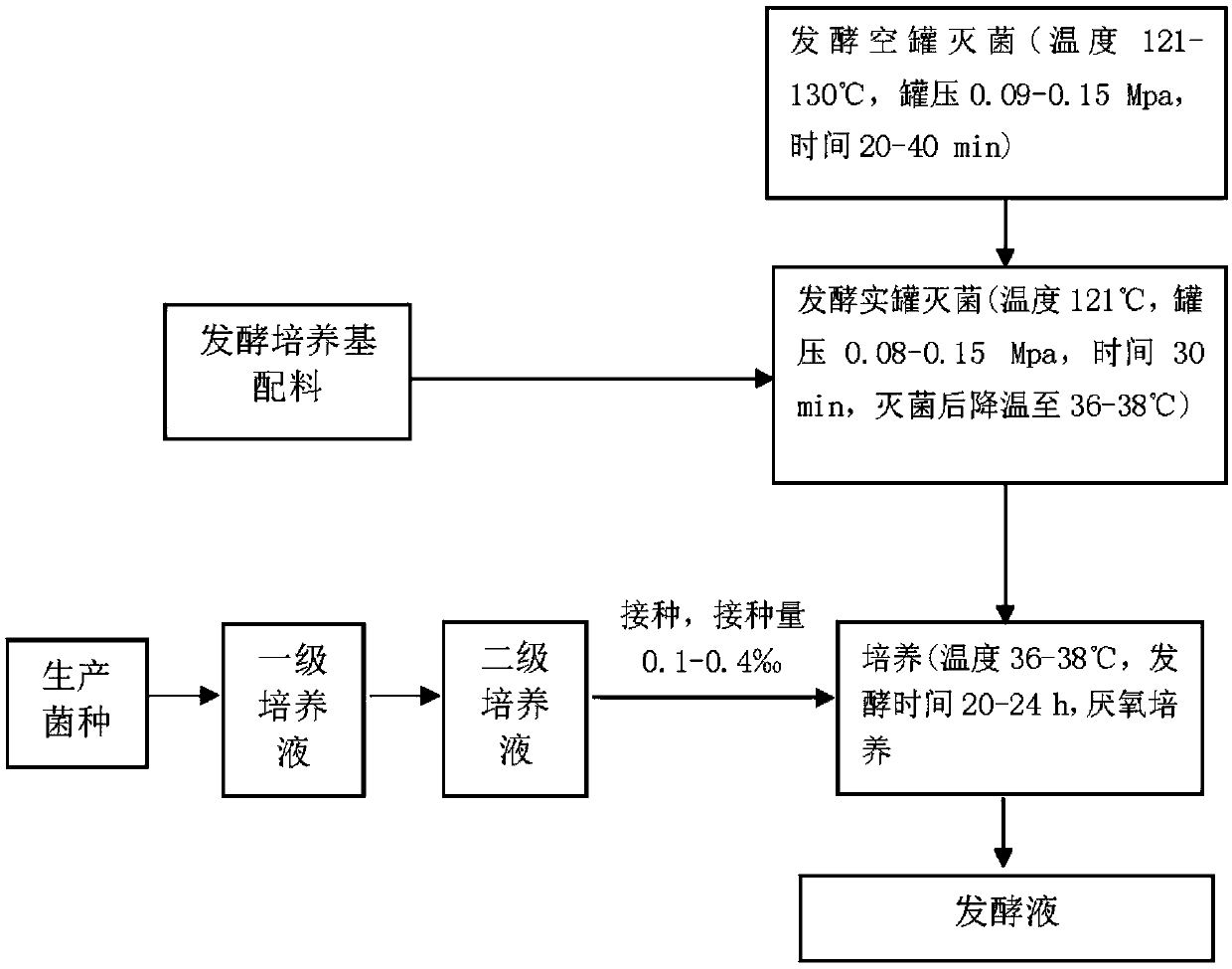
The invention relates to a colibacillus capable of generating succinic acid by utilizing synthetic medium pure anaerobic growth. The colibacillus is classified and named as EscherichiacoliBER108 and has the preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO.M2012068. The invention further discloses an application of the colibacillus to fermentation production of succinic acid. According to the invention, plasma is utilized to induce colibacillus, a synthetic medium flat screen is utilized to screen out a strain capable of growing rapidly under an anaerobic condition, and under the anaerobic condition, the strain grows by utilizing an inorganic nitrogen source and glucose and accumulates succinic acid; the strain is fermented in a shake flask for 72 hours by utilizing basic magnesium carbonate as a pH regulator; the OD600 of the strain reaches 7.6, the succinic acid yield reaches 11.2g / L, the yield of the succinic acid is increased by nearly three times compared with that of an original strain; and the original strain grows slowly and is low in acid yield under the pure anaerobic synthetic medium condition, so that the mutant strain BER108 has great social significance and economic value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
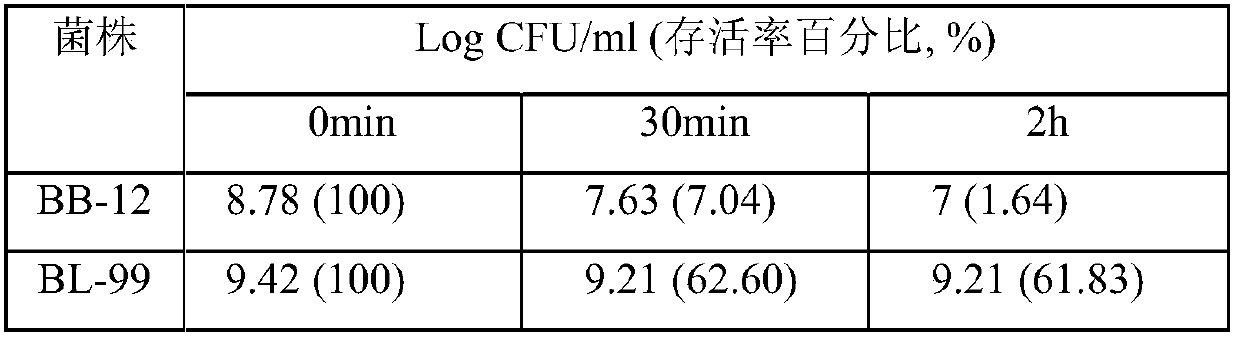
Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99 capable of regulating gastrointestinal florae and application of Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99
The present invention provides a Bifidobacterium lactis capable of regulating gastrointestinal florae and application of the Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The Bifidobacterium lactis has gastric acid resistance, the survival rate of viable bacteria is 62% or above after the Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99 is treated for 30 min in a pH 2.5 gastric acid solution, and the survival rate of viable bacteria is 61% or above after the Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99 is treated for 2 h. The bacterium can significantly promote the growth of bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria, and can inhibit desulphovibrio / enterobacter in intestinal tracts, especially curatively inhibit helicobacter pylori and / or Escherichia-Shigella, can be used to prepare food, medicines and feed with gastrointestinal tract flora regulation effects, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
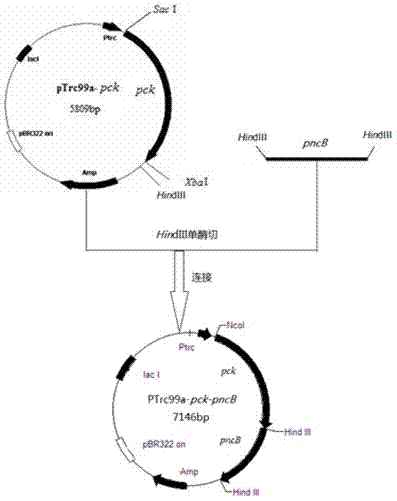
Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli
InactiveCN104212757AEfficient use ofEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesTheanine
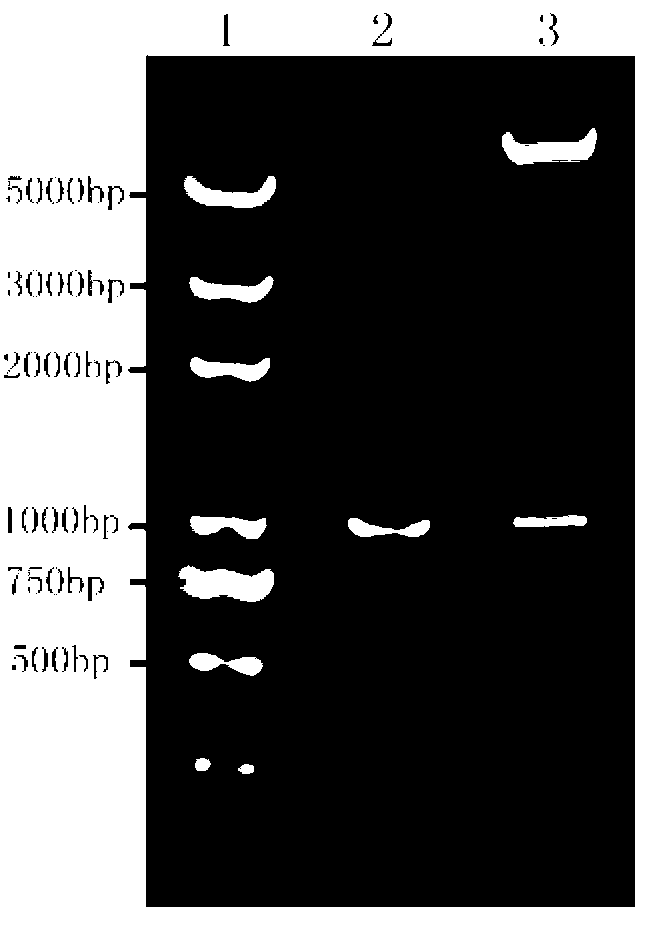
The invention relates to a genetic engineered bacterium which contains a recombinant plasmid pET28a-GMAS, is 6585 bp in a plasmid size, is 1308 bp in a fragment size of a GMAS, is named as Escherichia coli and has a kanapenecilin resistance. Genes of the [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase are inducibly expressed by isopropylsulpho-[beta]-D-galactoside. The genetic engineered bacterium has a capability of biologically synthesizing theanine. By means of glutamic acid and ethylamine as substrates, a method in the invention is simple in operation method, is convenient to control in production, is high in conversion and production efficiency of the theanine and has an excellent industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH
Alkaline pectinase PelN, as well as encoded gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103215244AImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPentagalacturonic acid
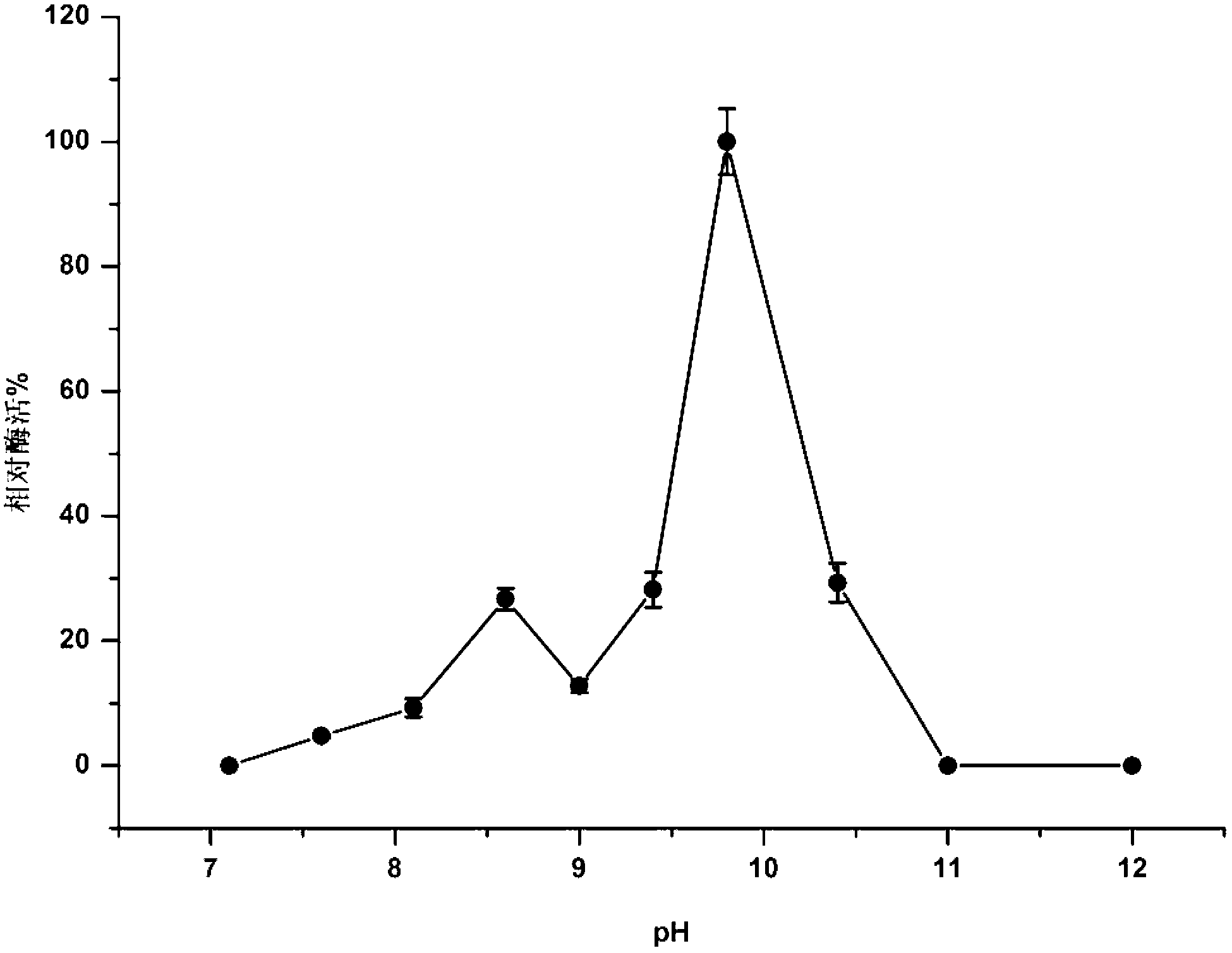
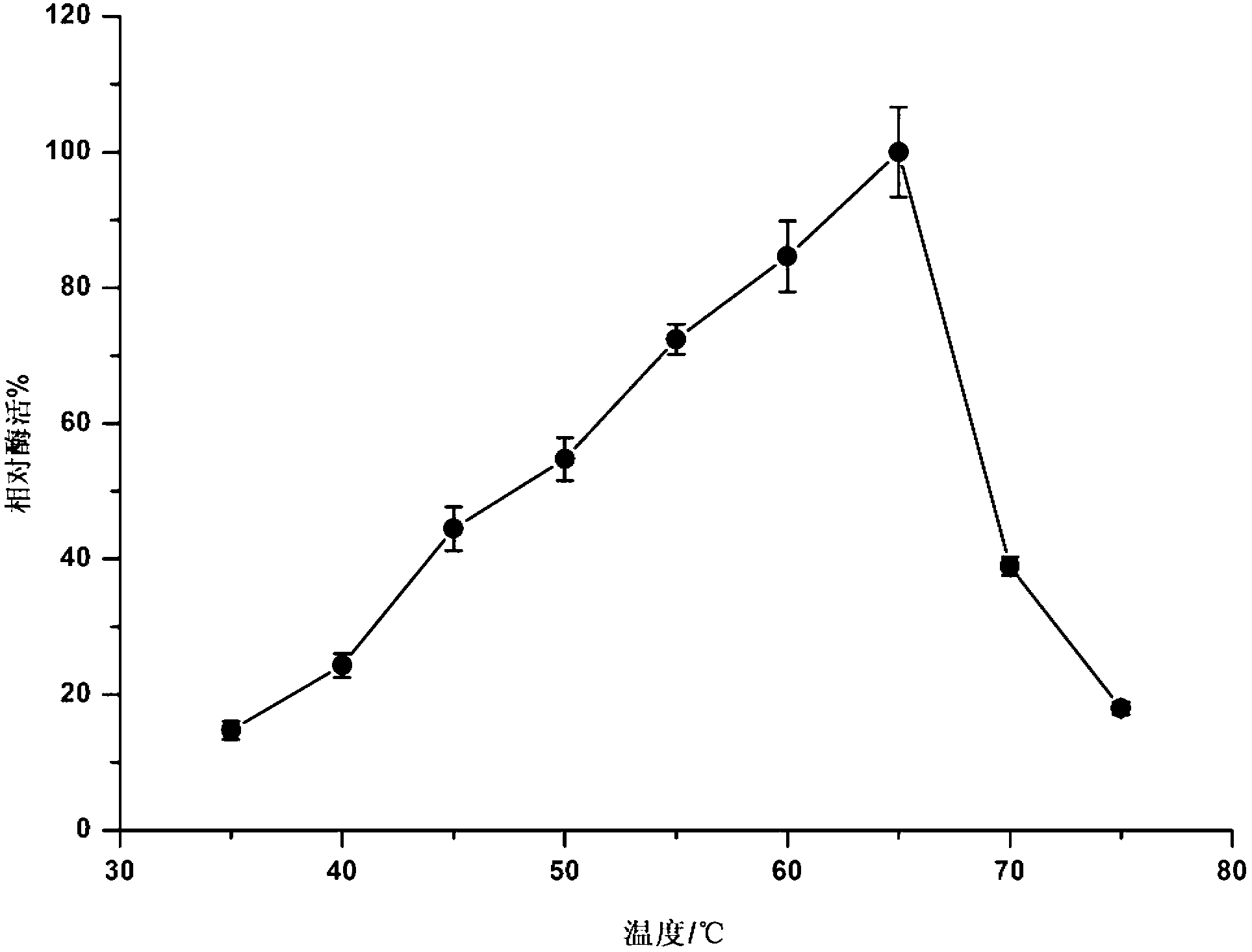
The invention discloses alkaline pectinase PelN, as well as encoded gene and an application of the alkaline pectinase PelN. The PelN is protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown as sequence 1 in a sequence table, and has alkaline pectinase activity, and the preservation number of a recombinant bacterium (escherichia coli) BL21 (DE3) PelN containing the encoded gene of the protein in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) is CGMCC No. 7166. Experiments prove that the enzyme activity of the protein PelN for degrading polygalacturonic acid is 4590-4950U / mg; the heat stability is better; the relative enzyme activity is above 90% through heat preservation for 120 minutes at 45 DEG C; the optimum pH value of the alkaline pectinase is 9.8; the optimum temperature is 65 DEG C; and production methods of the protein PelN, the recombinant bacterium and the alkaline pectinase provide efficient paths for industrial large-scale production of the alkaline pectinase.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Escherichia coli for producing adipic acid precursor namely cis,cis-muconic acid and application of escherichia coli
Cis,cis-muconic acid is an important chemical organic acid, has a wide range of application and can be used as a precursor of adipic acid. The cis,cis-muconic acid can be used for producing polymers including nylon 66 and the like after being converted into adipic acid through hydrogenation. The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli TIB-LEc340 CGMCC No 6435 for producing cis,cis-muconic acid, wherein the recombinant escherichia coli is established by the steps of combining 3-dehydrogenated shikimic acid dehydrase which comes from different microbes and is optimized by codons, protocatechuic acid decarboxylase, catechol 1,2-dioxidase and artificially designed constitutive promoters and terminators into a heterologous expression module, and then introducing the heterologous expression module into shikimic acid dehydrogenase mutated escherichia coli. The escherichia coli TIB-LEc340 CGMCC No 6435 is fermented for 16-120 hours at 30-40 DEG C to obtain fermentation liquor, and the maximum content of cis,cis-muconic acid in the fermentation liquor can reach 52g / L, so that the escherichia coli has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plant bacteriostatic composition and application thereof in liquid detergent
ActiveCN104255823AAdd lessGood antibacterial effectBiocideNon-ionic surface-active compoundsEscherichia coliStaphylococcus aureus
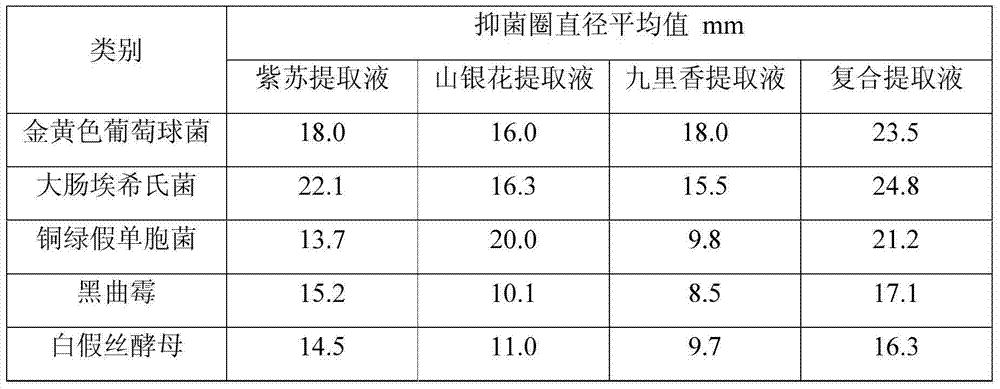
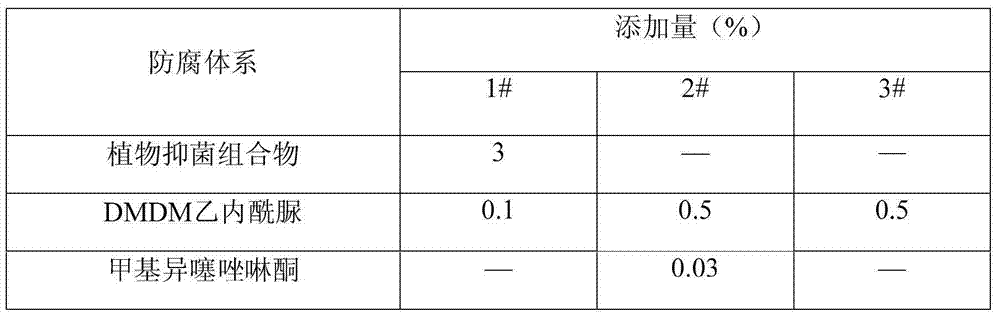
The invention provides a plant bacteriostatic composition and application thereof in a liquid detergent. The composition is compounded by perillae extracts, flos lonicerae extracts and murraya paniculata extracts. The composition has a good bacteriostatic effect, in particular, has a synergistic effect in the aspect of suppressing staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, aspergillus niger and candida albicans. The bacteriostatic composition can be applied to the liquid detergent to realize a bacteriostatic effect, so that the additive amount of chemosynthetic preservatives is reduced, and the expiration date of products is ensured to be unchanged.
Owner:TIANJIN YU MEI JING GRP
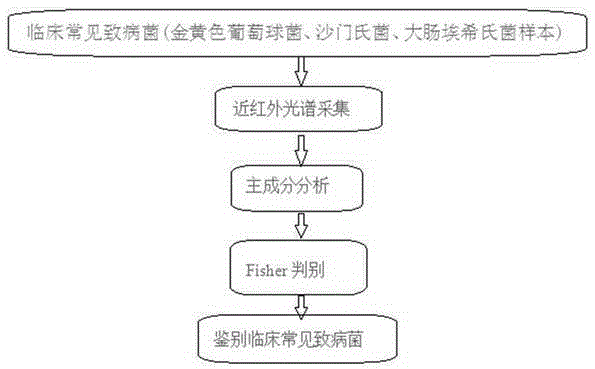
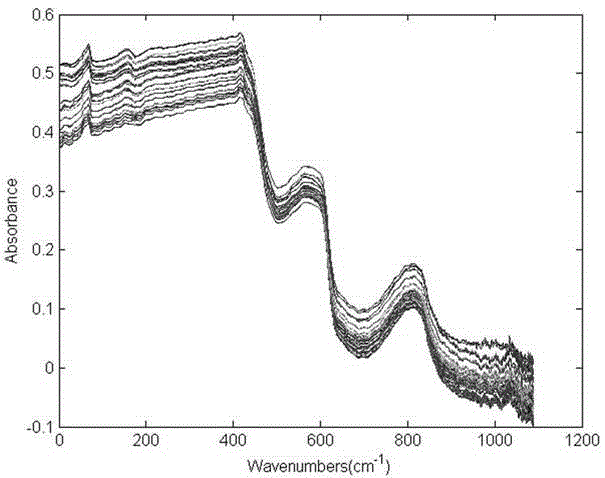
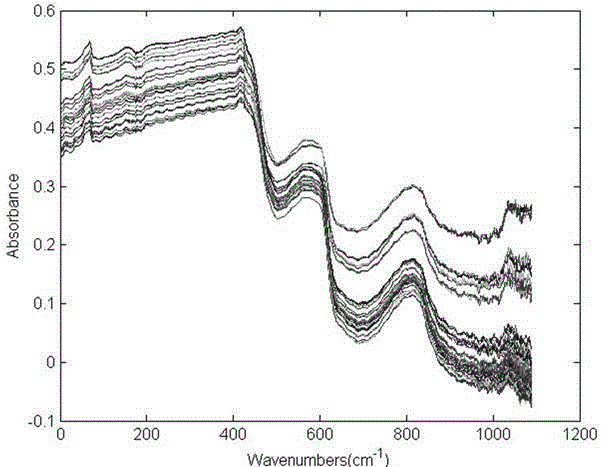
Method for fast identifying clinical pathogens based on principal component analysis and Fisher discriminance
InactiveCN105424645ARapid identificationHigh precisionMaterial analysis by optical meansEscherichia coliPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a method for fast identifying clinical pathogens (such as staphylococcus aureus, salmonellae and escherichia coli). The method includes the following steps that near infrared spectrograms of staphylococcus aureus, salmonellae and escherichia coli samples are collected; PCA dimension reduction processing is carried out on the near infrared spectrograms of the staphylococcus aureus, salmonellae and escherichia coli samples; a Fisher discrimination function is set up for classification. The adopted principal component analysis method in combination with Fisher discriminance is introduced to identify the common pathogens, the types of the pathogens can be fast identified, and the method has the advantages of being high in accuracy and easy to operate, making a great contribution to follow-up clinical strain identification and having good application prospects.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
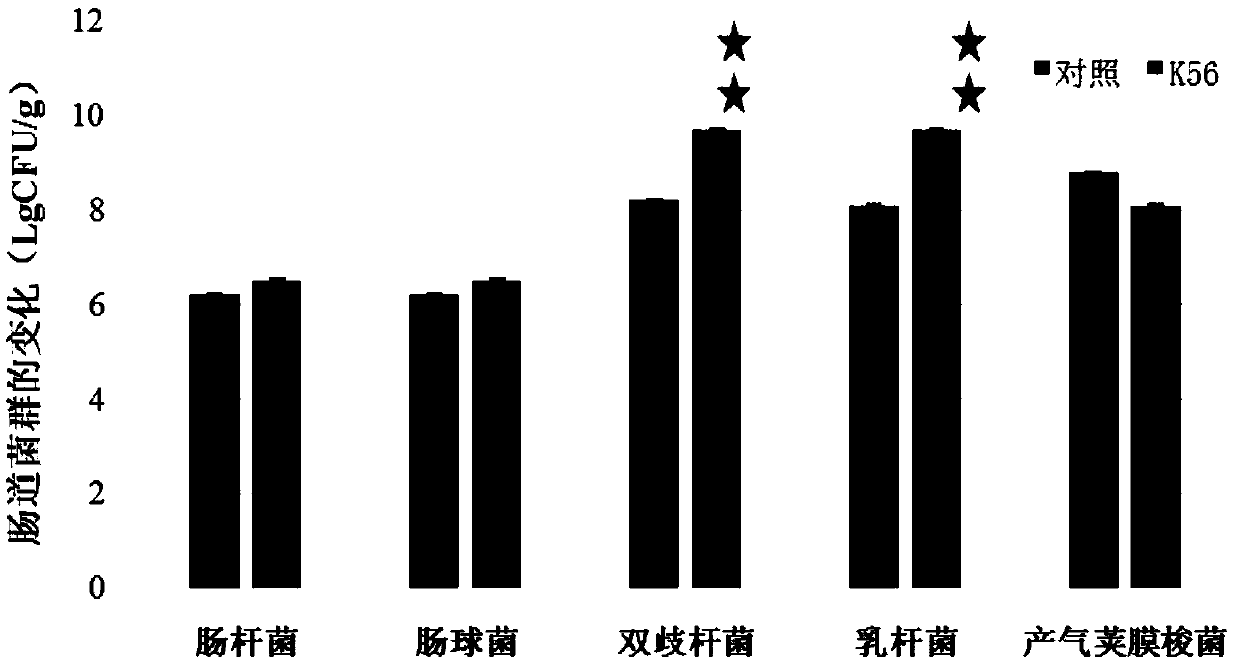
New application of lactobacillus paracausei K56 capable of adjusting gastrointestinal flora balance
The present invention provides a new application of lactobacillus paracausei K56 capable of adjusting gastrointestinal flora balance. The lactobacillus paracasei (lactobacillus paracausei subsp.paracasei) has a preservation number of DSM27447. The strain of the single bacteria has ability to significantly promote growth of intestinal bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria, can inhibit desulphovibrio and / or enterobacter, can inhibit helicobacter pylori and / or escherichia-shigella genera, and can tolerate stress environment of simulated gastrointestinal fluid in vitro. Mouse experiments show that the strain has no oral acute toxicity and no antibiotic resistance, is safe and can be used for food processing.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation of genetic engineering bacteria
InactiveCN102399738AImprove biosynthetic abilityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
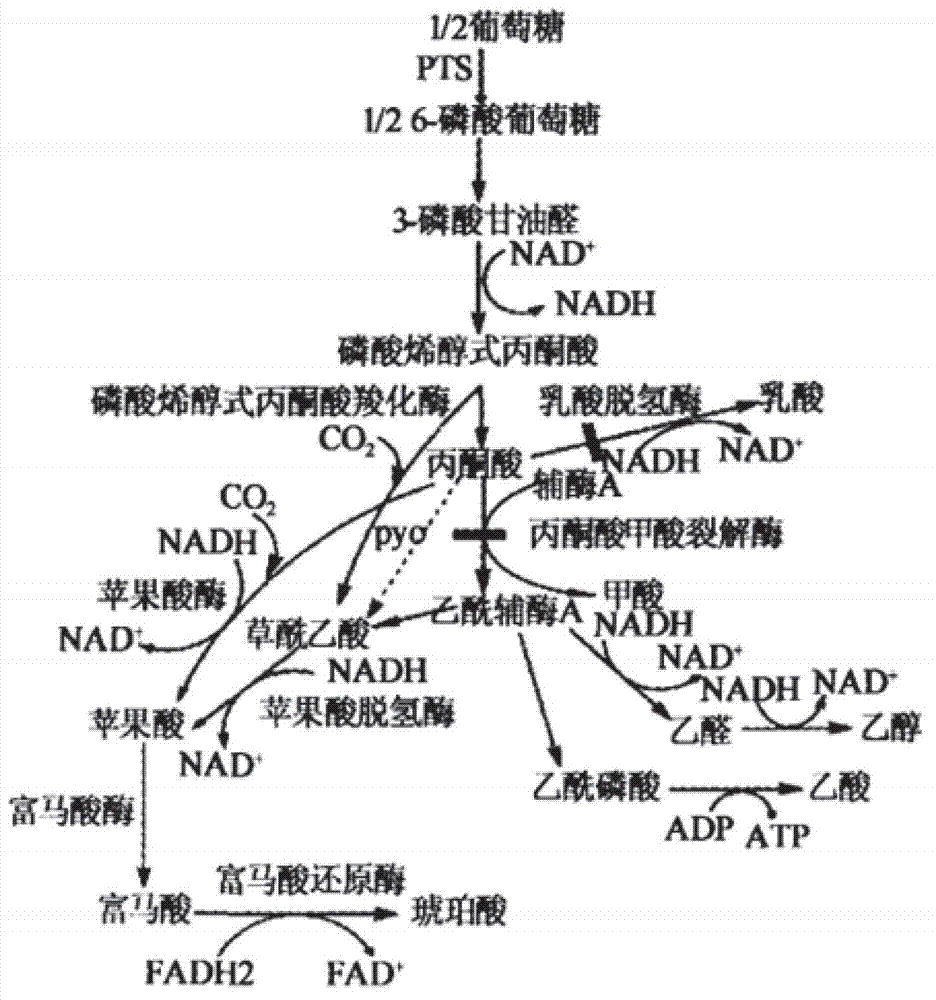
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid and a method for producing the succinic acid by fermentation, in particular to a recombinant strain which is grown by utilizing xylose efficiently and is used for producing the succinic acid and a method for producing the succinic acid by utilizing the fermentation of the strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing the succinic acid belongs to the class of Escherichia coli BA204, and the conservation register number is CCTCC No:M2011207. A construction process comprises the steps of: inactivating or removing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, and over-expressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylation kinase, so that the recombinant Escherichia coli can be grown by utilizing xylose metabolism to improve the synthetic efficiency of the succinic acid is improved substantially. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation mode is adopted, wherein in an aerobic stage, biomass is improved; and in an anaerobic stage, acid is produced by the fermentation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
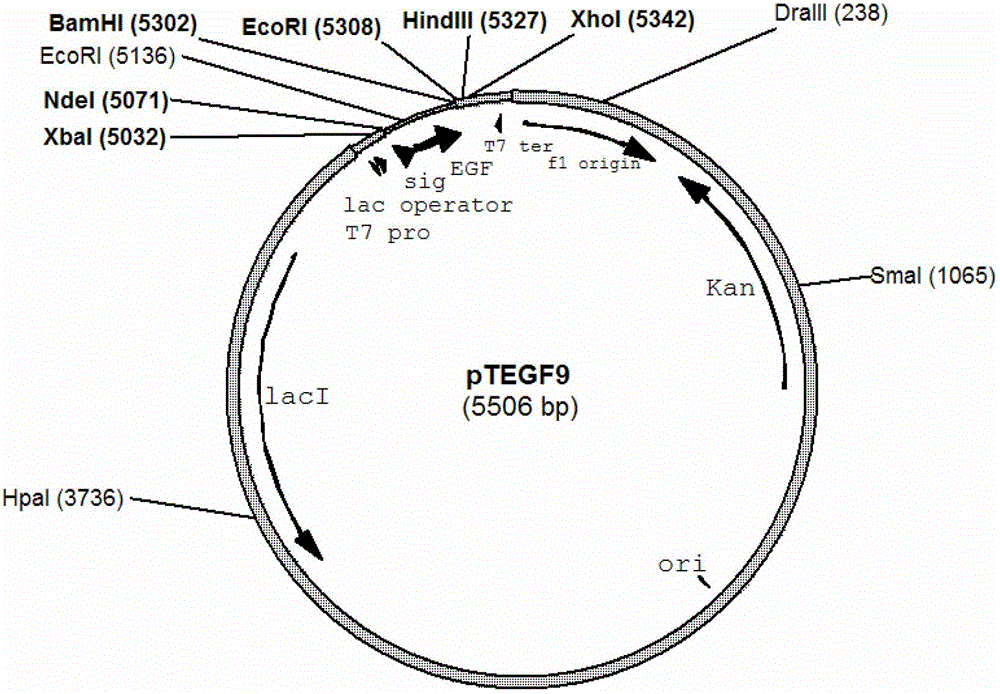
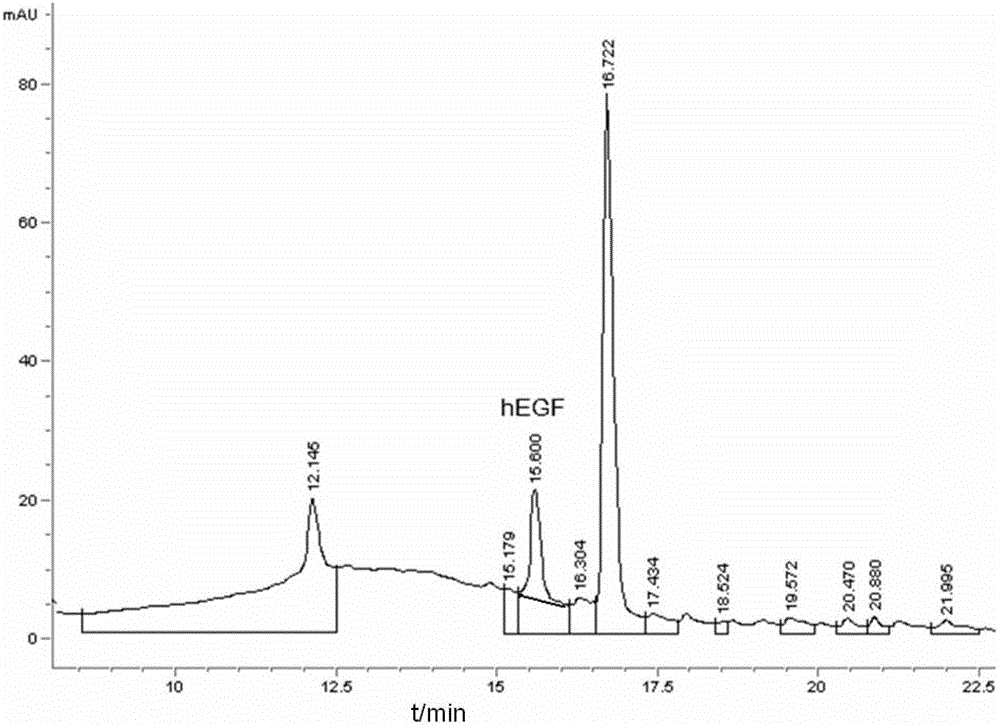
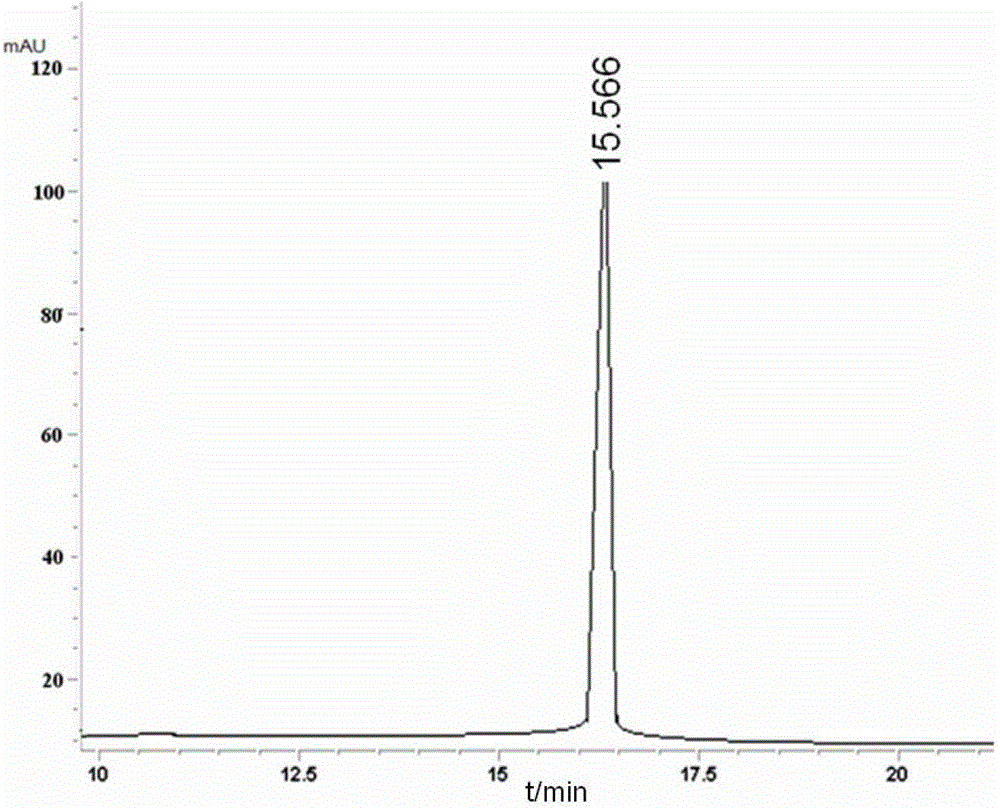
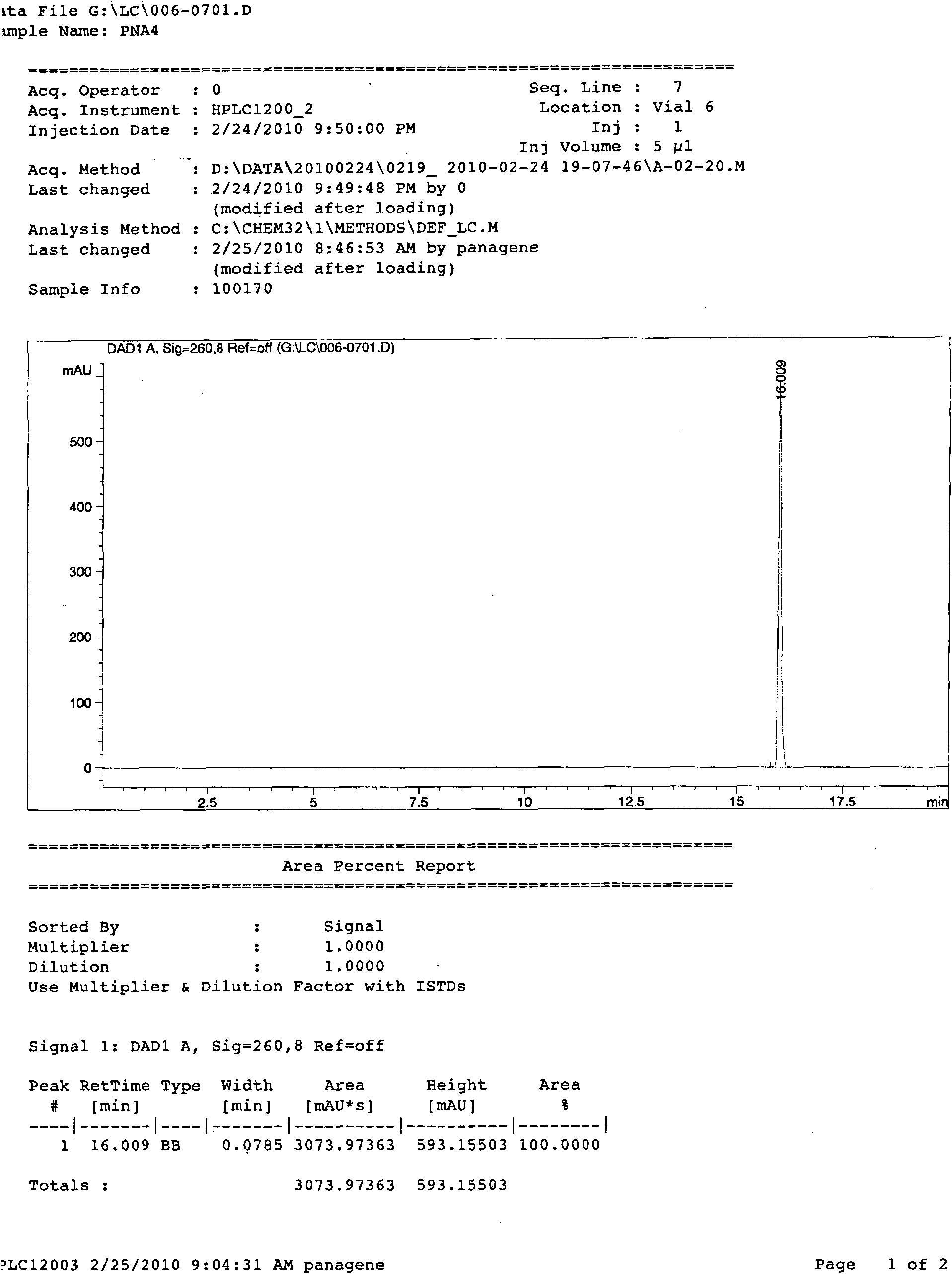
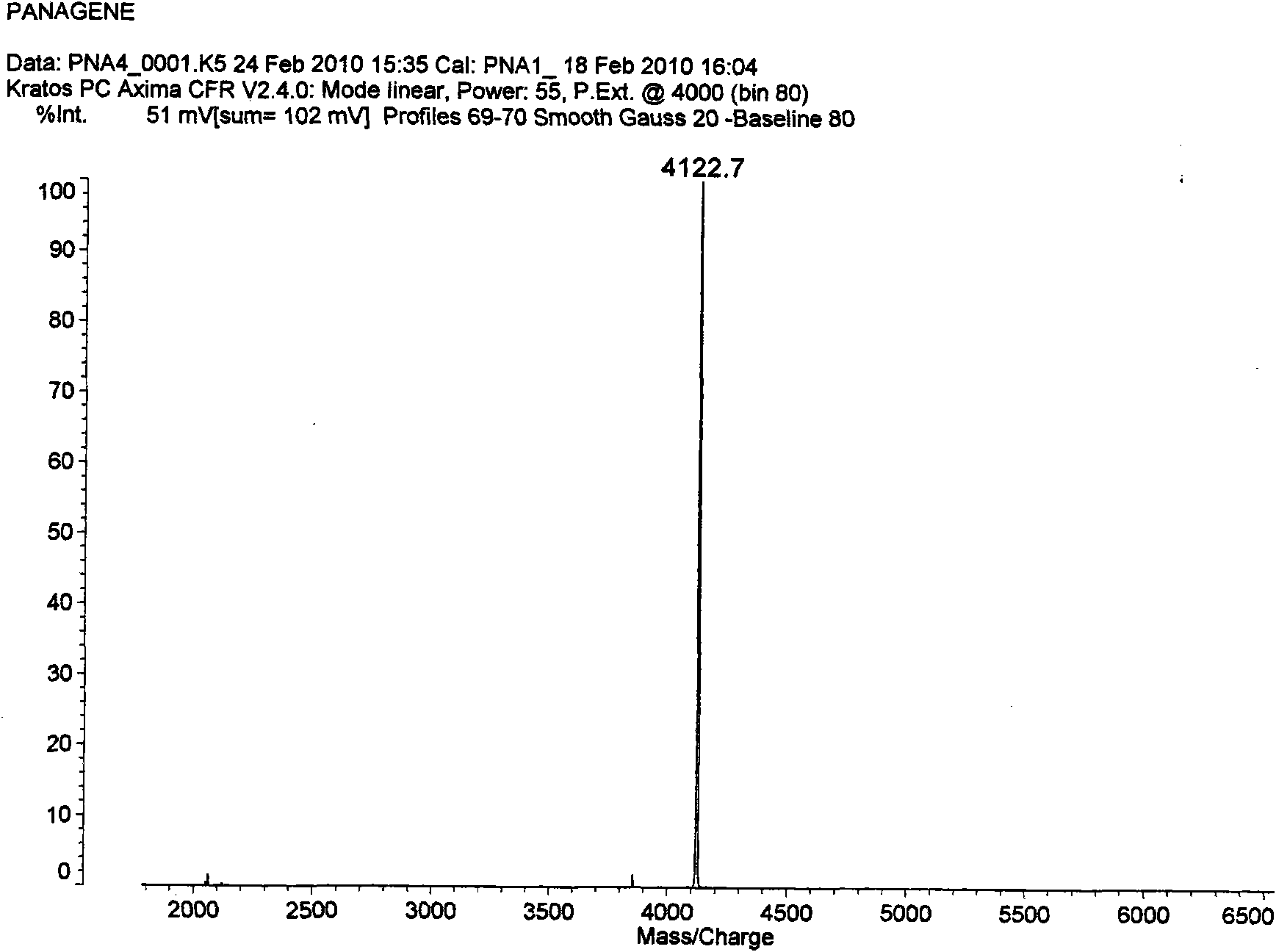
Escherichia coli and method for efficiently secreting and expressing human epidermal growth factor by using same
ActiveCN103060249AAvoid pollutionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEscherichia albertii
The invention relates to the construction and expression of a strain by virtue of a genetic engineering method, discloses (escherichia coli) BTE-9 which was collected in the CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on April 16, 2012 with the collection number of CGMCC NO. 6014 and provides a method for efficiently secreting and expressing the human epidermal growth factor by using the (escherichia coli) BTE-9. During fermenting and expressing, no inducer is used, so that the change of the physiological state and the loss of plasmids due to an adopted inducer are avoided, the production cost is reduced, and the pollution of the toxic inducer to a target product is avoided, and high expression quantity is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA KANGYU PHARMA +2
Antisense peptide nucleic acid of cell penetrating peptide-mediated antibacterial RNA polymerase sigma 70 factor gene rpoD
InactiveCN101891804AGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesDisease
The invention provides a group of peptide nucleic acid-cell penetrating peptide antisense antibacterial sequences taking bacterial gene rpoD as a target. The cell penetrating peptide-mediated antibacterial RNA polymerase sigma 70 factor gene rpoD which is antisense nucleic acid of a specificity target can selectively inhibit the expression of in-vivo ropD genes of Gram-negative bacterium (containing sensitive and multidrug resisting clinical pathogenicity Escherichia coli, salmonellatyphimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae and pseudomonas aeruginosa) or gram-positive bacterium (containing sensitiveand multidrug resisting staphylococcus aureus) and further inhibit bacteria growth and reproduction, thus having the advantages of good antibacterial effect, low toxicity, good stability and better tolerance. The invention also discloses a chemical preparation method of a peptide nucleic acid-cell penetrating peptide solid phase. The antibacterial peptide synthesized in the invention can be used for preparing multidrug-resistant bacteria infection proofing antisense drugs and has the potency of being developed into a broad-spectrum antisense antibacterial agent which is expressed by efficiently transferred and peculiarly blocked bacterium disease-causing genes.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant escherichia coli for expression of adenomethionine synthetase
ActiveCN101392230AHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliS-Adenosylmethionine Synthetase
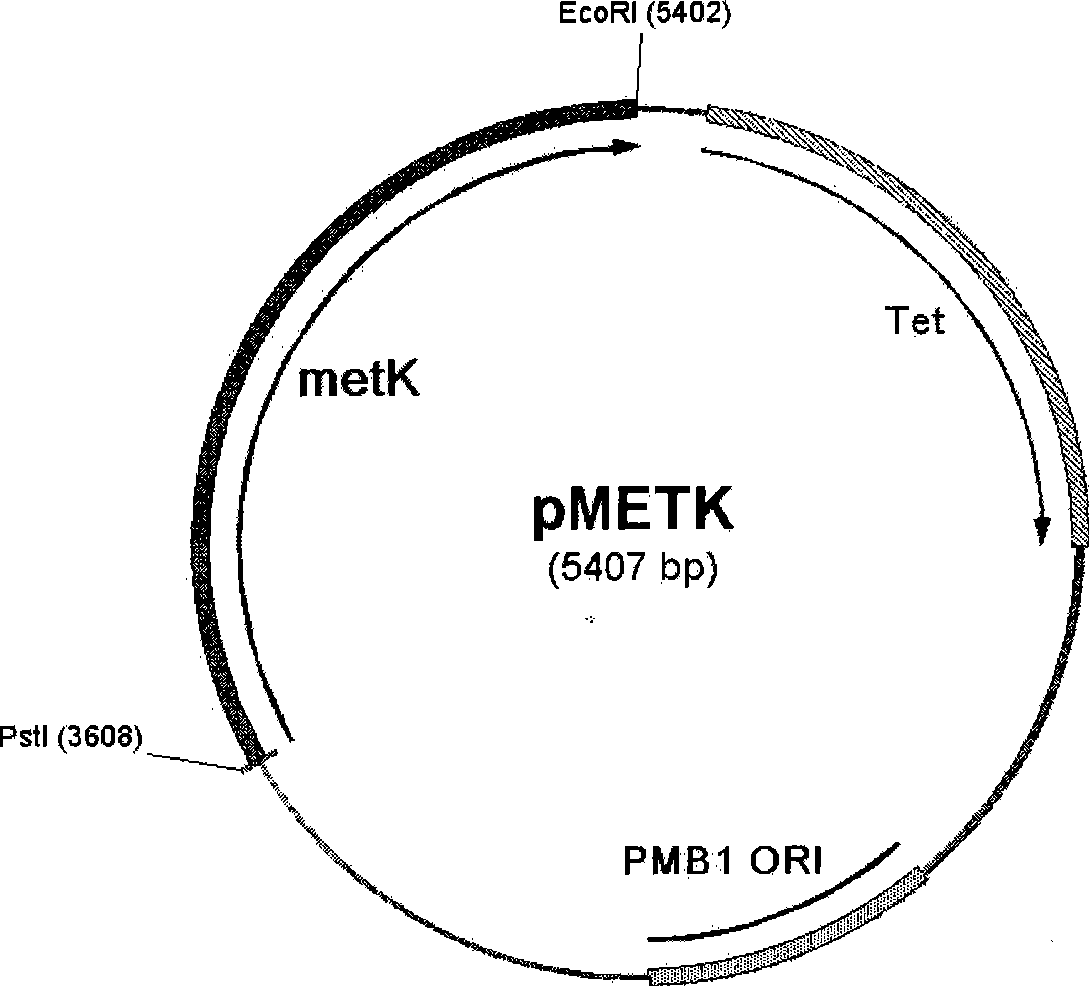
The invention provides a recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli expressing adenosine methionine synthetase with CGMCC No. 2299 and the composition method of the recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli. The invention further provides a recomposed expression carrier pMETK of adenosine methionine synthetase. In the recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli expressing adenosine methionine synthetase with CGMCC No. 2299, the expression quantity of the adenosine methionine synthetase accounts for 31.36 percent of soluble albumen of the strain, the activity of the adenosine methionine synthetase expressed is as high as 7.38U / ml, far higher than that of wild type strains.
Owner:BEIJING KAWIN TECH SHARE HLDG
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN102864116AEasy to buildThe fermentation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid. The genetic engineering bacterium strain is named as Escherichia coli BA016, the preserving number registration number CCTCC NO is M 2012350. The invention further provides a construction method of the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation, recombinant escherichia coli can grow by glucose metabolism through joint excessive expression of exogenous pyruvic carboxylase and nicotinic acid ribose phosphate transferase, generation of by-product pyruvic acid is reduced, and accordingly the yield and production intensity of succinic acid are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Gene engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation by using same
InactiveCN102643775AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and relates to a gene engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid, and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation by using the same. The classification designation of the gene engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid is Escherichia coli BA305, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2012102. The construction process mainly comprises the following steps: inactivating or knocking out phosphoenolpyruvic acid carboxylase gene and ptsG gene in a phosphate translocation system; and overexpressing the phosphoenolpyruvic acid carboxylase so that the recombinant colibacillus can efficiently utilize glucose, xylose, arabinose, levulose and other monosaccharides and efficiently utilize mixed saccharides in various proportions and cellulose hydrolysate, thereby greatly enhancing the synthesis efficiency of the succinic acid. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation mode: the aerobic stage can enhance the biomass, and the anaerobic stage is used for fermentation to produce the acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and acidogenic fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102533626AOvercomes the inability to utilize glucoseBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biology engineering technology, and relates to a genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and an acidogenic fermentation method of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose is named as Escherichia coli BA205 and the preservation number is registered as CCTCC No.M2011447. In the construction process, Escherichia coli which is short of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) gene and Pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) gene activity is mainly used as an original strain; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) gene is removed by utilizing a homologous recombination technology; and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase are excessively co-expressed; therefore the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly increased. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation manner is adopted, the biomass is improved in an aerobic stage and the acidogenic fermentation is carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
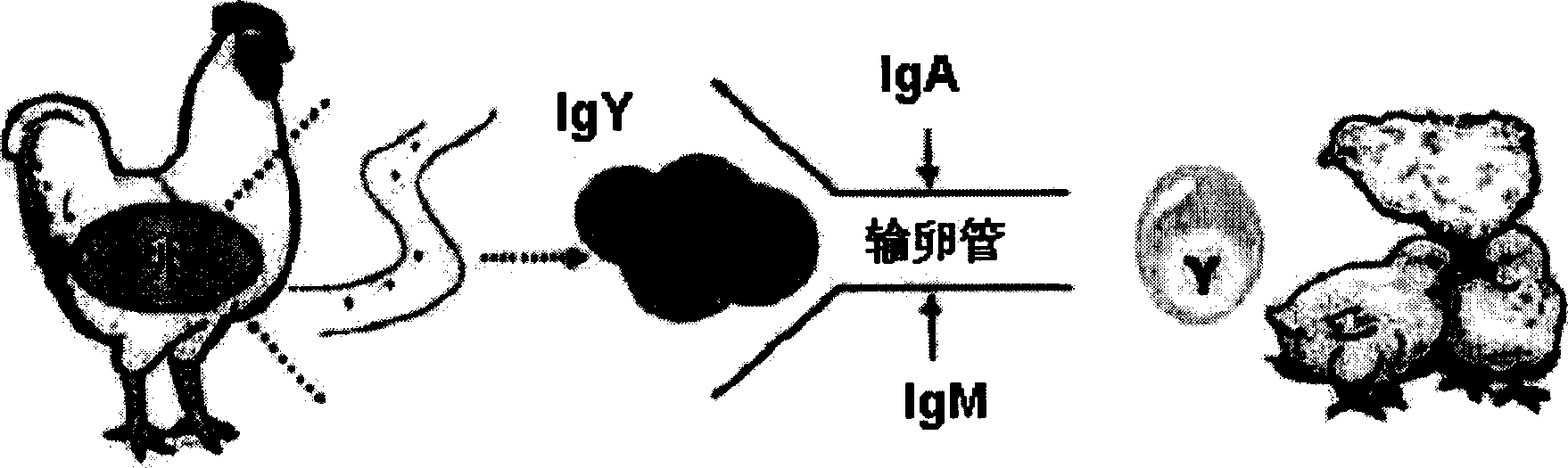
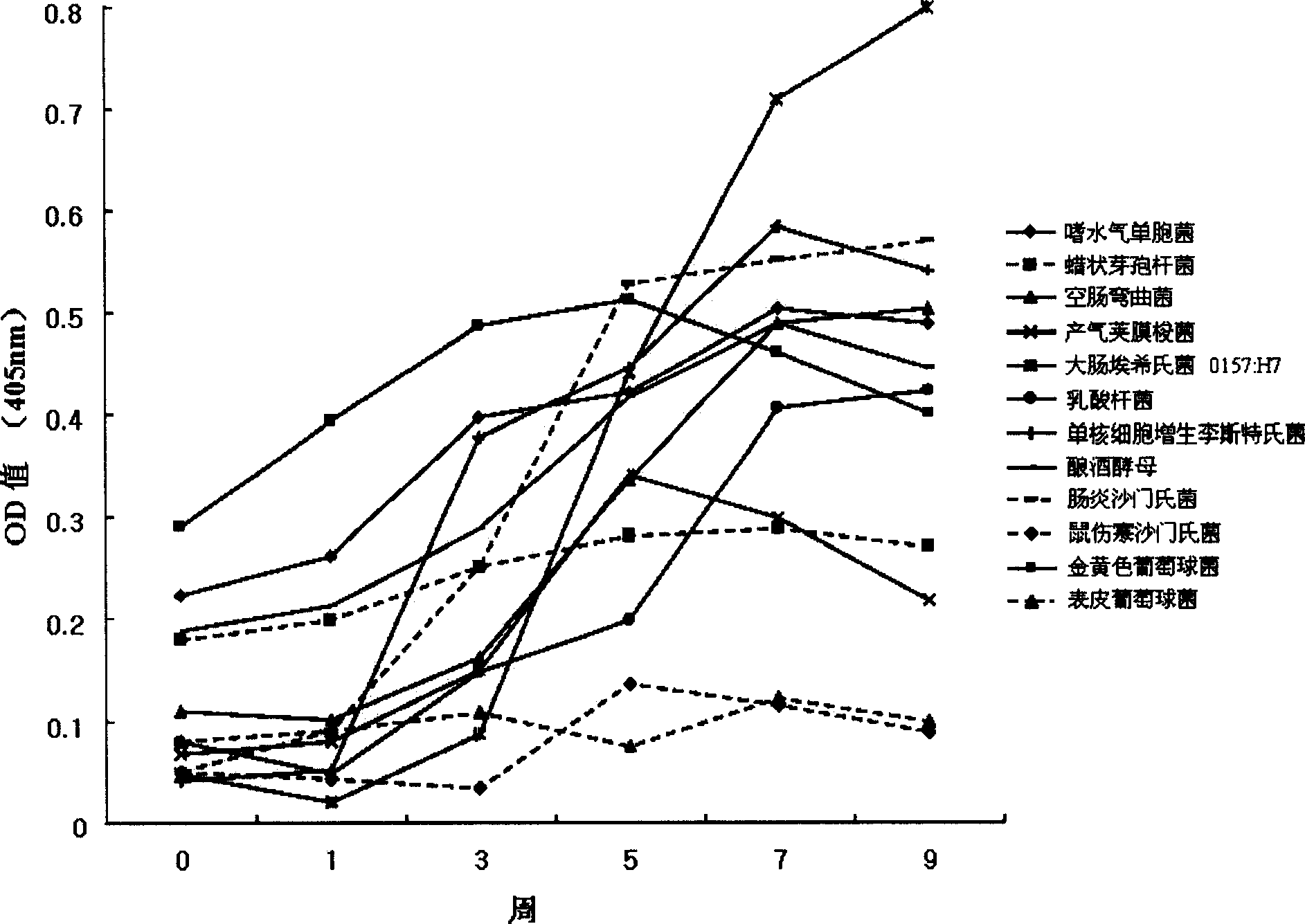
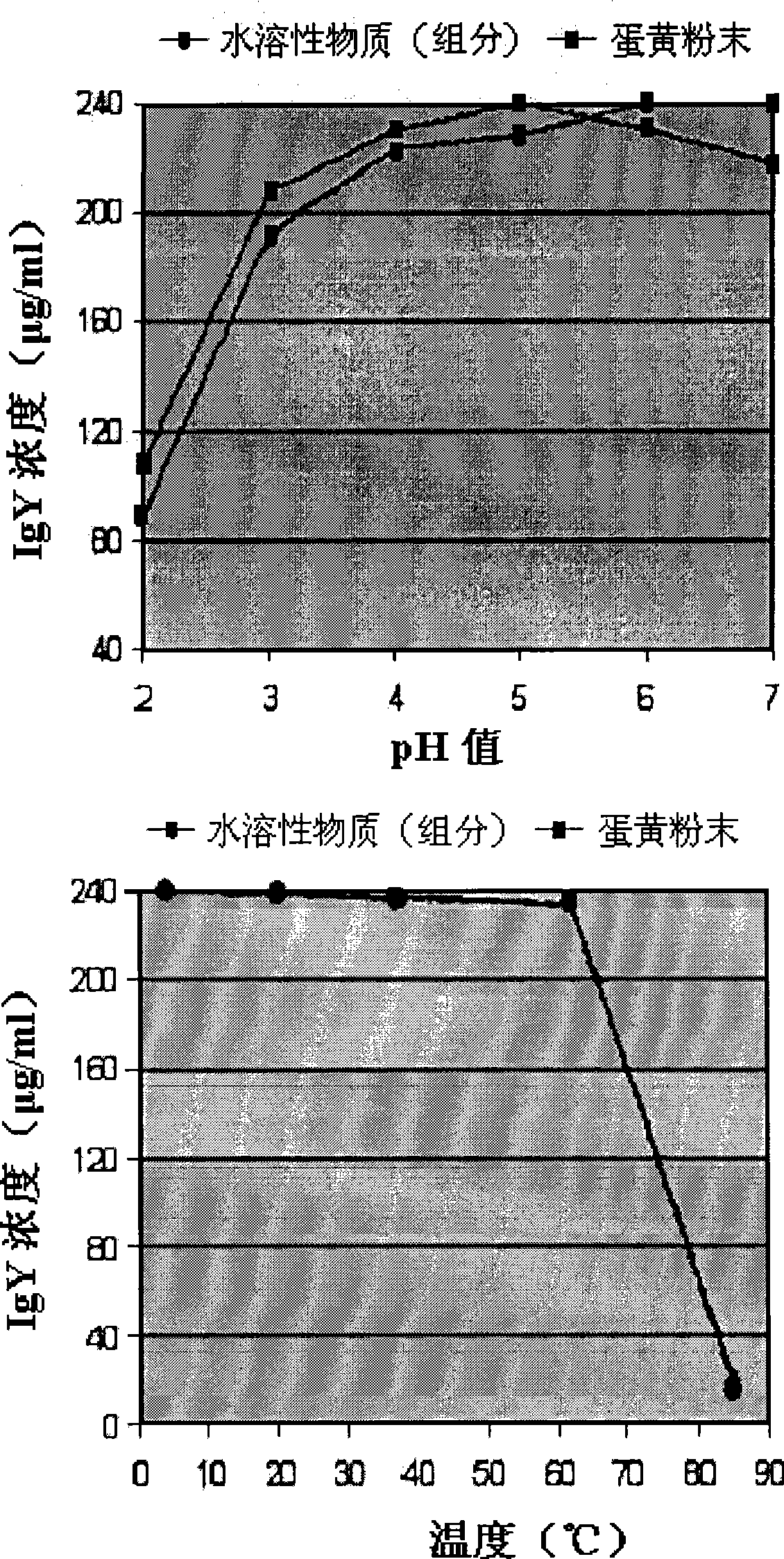
Growth inhibitory composition against pathogenic bacteria of meat based food stuff comprising igy
InactiveCN101400701AFunctionalProgramme-controlled sewing machinesEgg immunoglobulinsBiotechnologyYolk
The invention relates to growth-inhibitory composition against pathogenic bacteria of meat based food stuff comprising IgY. The IgY is a specific immunoglobulin derived from yolk of egg. 12 representative bacteria and other microbes deteriorating quality of process meat products that the IgY of the invention targets include Aeromonas hydrophila, Bacillus cereus, which comprises Aeromonas hydrophil, Bacillus cereus, Camphlobacter jejuni, Clotridium perfringens, 0157:H7 (Escherichia col, 0157:H7), Lactobacillus, Listeria monocytogens, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis. The 12 representative bacteria antigen forms are respectively injected the interior of chicks to obtain the IgY of the 12 antigens.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP +1
Inert carrier Escherichia coli and its potential application
ActiveCN110257276AImprove and refine specificity bottlenecksBacteriaBiological material analysisEscherichia coliAgglutination assay
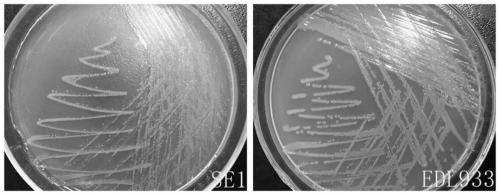
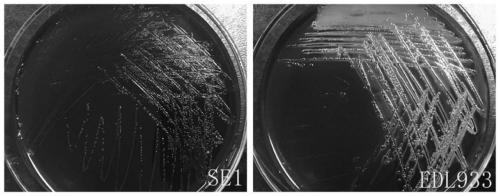
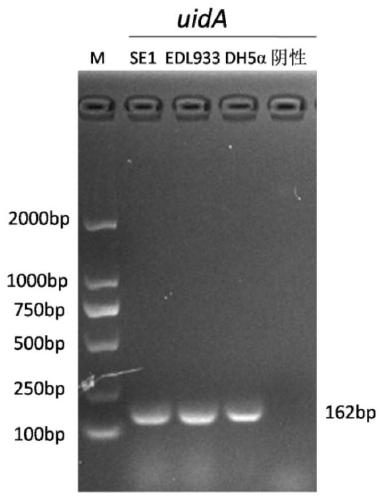
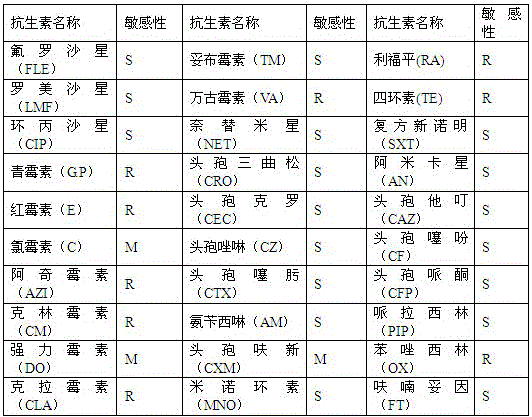
The present invention relates to an inert carrier Escherichia coli and its potential application, the Escherichia coli isolated strain has the inert carrier property, and is expected to be developed into a carrier strain for an indirect agglutination test. The inert carrier Escherichia coli is preserved in the China General Microorganisms Collection and Management Center (CGMCC), and a preservation address is Beijing, China, a preservation number is CGMCC No. 17339, a preservation date is March 18, 2019, a classification name is Escherichia coli, and a strain code is SE1. The Escherichia coli isolated strain is from a healthy flock, the bacteria number at a higher working concentration does not cause any macroscopic agglutination reaction with various chicken serums of different genetic backgrounds, and does not generate non-specific agglutination reaction with chicken source serum, so that the Escherichia coli is called as an inert carrier Escherichia coli. The application provides an inert carrier strain and its potential application for developing a simple and rapid indirect agglutination assay.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Escherichia coli JLTrp and application thereof to fermentation production of L-tryptophan
ActiveCN105861380AImprove stabilityReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to Escherichia coli JLTrp and application thereof to the fermentation production of L-tryptophan. The Escherichia coli JLTrp has a culture collection number of CGMCC NO. 7.217. The application of the Escherichia coli JLTrp to the fermentation production of the L-tryptophan comprises the following steps: performing inoculation with mature cultures in a fermentation tank, at a temperature of 34-36 DEG C, controlling pH (potential of Hydrogen) in a staged manner by adopting liquid ammonia replenishment, controlling dissolved oxygen in the staged manner, controlling the pressure to be 0.03-0.08MPa and the air volume to be 0.3-2.0VVM, controlling residual sugar to be 0.01-0.5% in a process, and cultivating and preparing L-tryptophan. A bacterial strain of the Escherichia coli JLTrp greatly improves the stability of the cultures, and reduces the generation, which is caused by insufficient conditions, of an organic acid, so that the vitality of the cultures is improved, cultivation conditions are gradually lowered, and energy consumption is greatly reduced. Escherichia coli JLTrp provided by the invention can be used for the fermentation production of L-tryptophan, is relatively greatly improved in both yield and percent conversion, and has obvious progress.
Owner:HENAN JULONG BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium and method for fermenting and producing succinic acid
InactiveCN102643774AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium and a method for fermenting and producing succinic acid. Bacterial strains of the succinic acid genetic engineering bacterium are classified and named as Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) BA306 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2012103. A construction process mainly comprises inactivating or knocking phosphoric acid enol pyruvic carboxylase genes and ptsG genes in a phosphoric acid movement system, conducting excessive coexpression on phosphoric acid enol pyruvic carboxylase and niacin ribose phosphate transferring enzyme, enabling recombination of colon bacillus to be capable of efficiently using monosaccharide of glucose, xylose, arabinose, fructose and the like, simultaneously efficiently using mixed sugar and cellulose hydrolysate in various proportions for growth, and substantially improving combined efficiency of the succinic acid. A fermentation process adopts a two-stage fermentation mode, biomass liveweight is improved in an aerobic stage, and fermentation and acid production are carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Triad inactivated vaccine for newcastle disease and bird flu (H9 subtype) and escherichia coli disease and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to triad inactivated vaccine for newcastle disease, bird flu (H9 subtype) and escherichia coli disease and a preparation method thereof. The vaccine is an effective coping strategy aiming at a prevalence situation of mixed infection of the newcastle disease, the H9 subtype bird flu and the escherichia coli, and two kinds of disease can be controlled at the same by means of immunization at one time. According to the vaccine, a La Sota strain of a newcastle disease virus, a LG1 strain of an H9 subtype bird flu virus, a QL1 strain (O1) of bird source escherichia coli, QL2 strain (O2) of the bird source escherichia coli, QL78 strain (O78) of the bird source escherichia coli, and QL36 strain (O36) of the bird source escherichia coli serve as vaccine reserve virus strains, and the vaccine is formed through antigen liquid preparation, inactivation, concentration and mixing according to a certain proportion. The vaccine and the preparation method are related with the La Sota strain of the newcastle disease virus, the H9 subtype bird flu virus and the bird source escherichia coli which are all domestic prevalence virus strains, and current prevalence disease can be effectively prevented.
Owner:QILU ANIMAL HEALTH PROD
Escherichia coli JL-GlcN and application thereof
ActiveCN107384827AGrow fastThe fermentation process is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliN-Acetylglucosamine
The invention relates to an escherichia coli JL-GlcN and application thereof. The culture preservation number of the escherichia coli JL-GlcN is CGMCC NO.13924; the escherichia coli JL-GlcN is activated through a slope, is cultivated in a biochemical incubator at 37 DEG C for 20h, and coats an LB culture medium through gradient dilution; single colonies are inoculated into an LB slant culture-medium separately and cultivated in the biochemical incubator at 30-36 DEG C for 12h; a seed solution is inoculated into a fermentation tank containing a fermentation medium for cultivation; when thallus OD is 10-15, IPTG is added for induction and cultivation is performed for 10-20h to obtain a fermentation liquid containing N-acetylglucosamine; and the N-acetylglucosamine in the fermentation liquid containing the N-acetylglucosamine is extracted. The escherichia coli JL-GlcN strain fermentation is aerobic fermentation and the bacteria growth is fast; and the fermentation process is simple and easy to control, and the escherichia coli JL-GlcN is easy to amplify for industrial production.
Owner:HENAN JULONG BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Indirect ELISA (enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) detection method for escherichia coli OmpT (Outer-membrane protease T) antibody
InactiveCN102707054AStrong specificitySuitable for testingMaterial analysisEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention provides an indirect ELISA (enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) detection method for an escherichia coli OmpT (Outer-membrane protease T) antibody, and a detection antigen on an ELISA plate in the ELISA is OmpT recombinant protein. The detection method comprises the following steps that after being diluted according to the ratio of 1:640, the serum to be detected is incubated with the OmpT recombinant protein on the ELISA plate at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 1.5 h, and the plate is washed three times; rabbit anti-bovine IgG marked by horse radish peroxidase is added to be incubated with the serum to be detected at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 1.5 h; a TMB (tetramethylbenzidine) substrate is added for developing for 10 min; and OD450 is detected after the reaction is ended, the antibody is positive if the OD450 is larger than or equal to 0.335, and the antibody is negative if the OD450 is smaller than 0.335. The recombinant protein prepared from the symbolic gene OmpT of the escherichia coli is used as the detection antigen for ELISA, the recombinant antigen can be produced on a large scale in a standardizing mode, has strong specificity, and is suitable for the antibody detection after the infection of all serotype bacteria of the escherichia coli.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
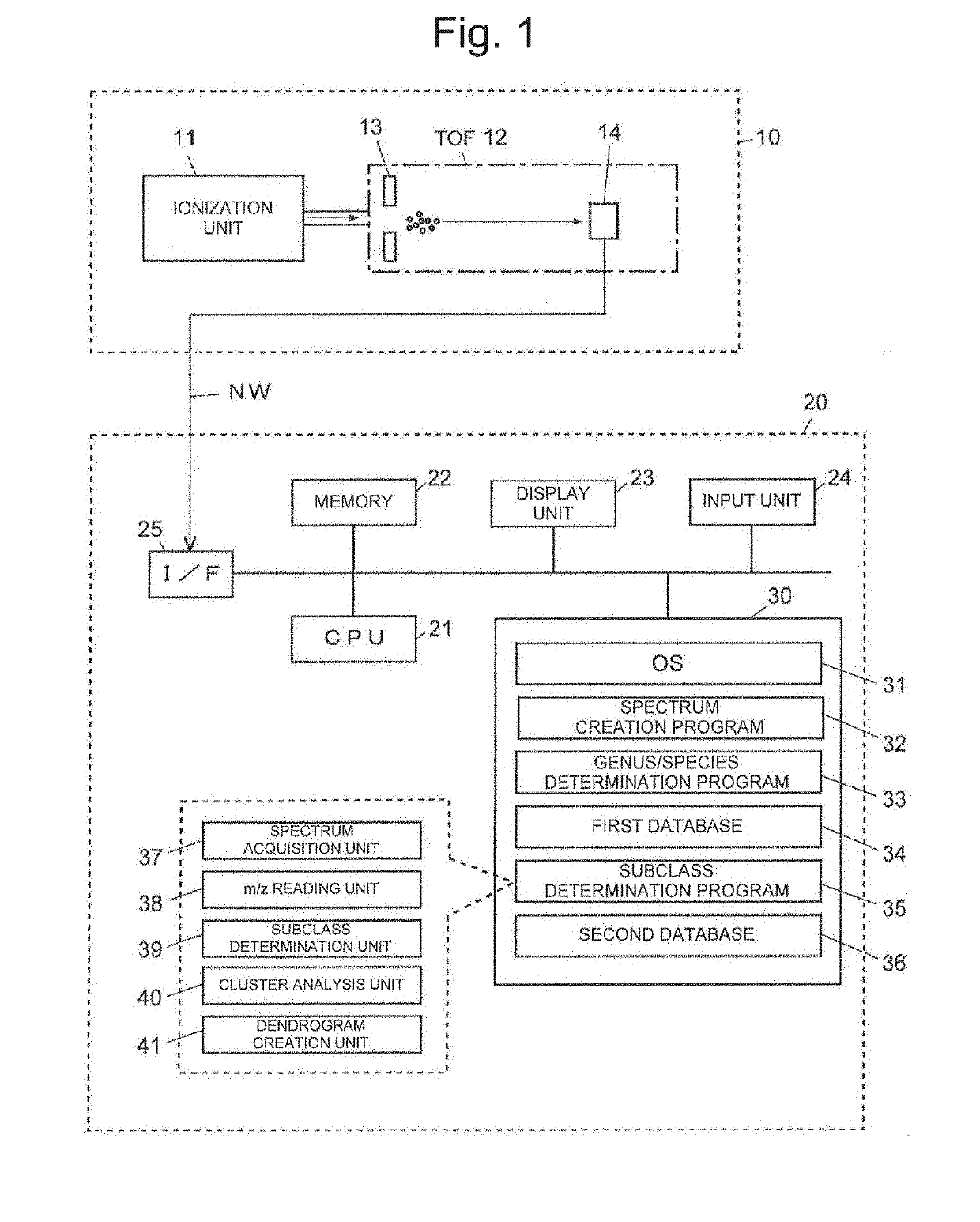
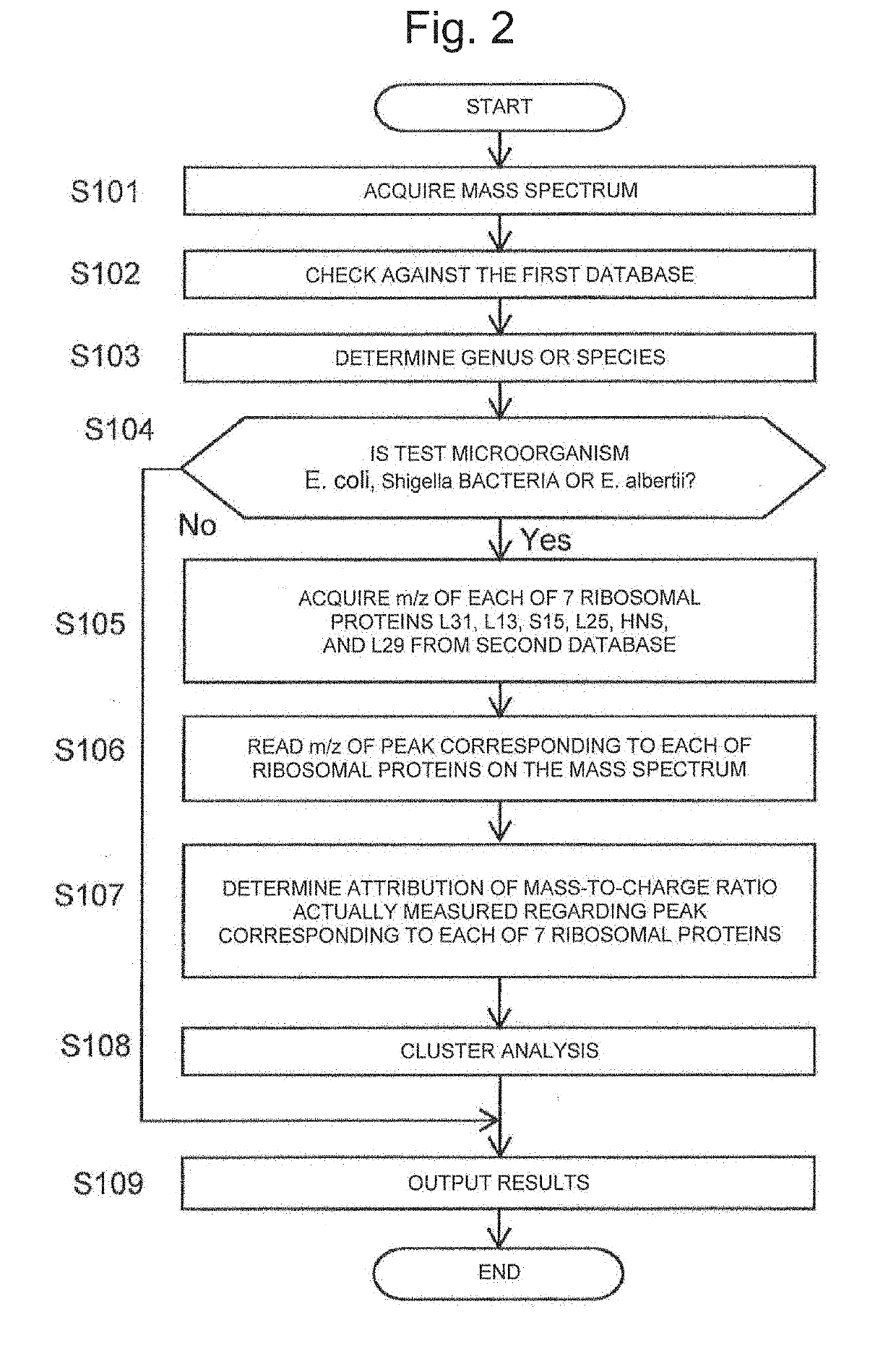
Method for discriminating microorganism
ActiveUS20190242903A1Rapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliMicroorganism
To provide a method for discriminating a microorganism including: a step of subjecting a sample containing a microorganism to mass spectrometry to obtain a mass spectrum; a reading step of reading a mass-to-charge ratio m / z of a peak derived from a marker protein from the mass spectrum; and a discrimination step of discriminating which bacterial species of Escherichia coli, Shigella bacteria, and Escherichia albertii the microorganism contained in the sample contains based on the mass-to-charge ratio m / z, in which at least one of 13 ribosomal proteins S5, L15, S13, L31, L22, L19, L20, L13, S15, L25, HNS, HdeB, and L29 is used as the marker protein.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
Escherichia coli engineering bacteria and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103275919AHas adsorption capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to an escherichia coli expression vector PcPcS1-pET-22b (+) of callery pear phytochelatin synthase genes PcPCS1 and an escherichia coli strain PcPCS1-Pet-22b (+) / Rosetta (DE3), and the preservation No. is CGMCCNo. 7569. The phytochelatin synthase genes PcPCS1 are derived from callery pear. On the basis, the invention relates to a method for quantitatively determining callery pear phytochelatin synthase genes absorbing cadmium, copper and sodium based on escherichia coli heterologous-expression and an atomic absorption spectrometry. The endurance capacity and the accumulation capacity of recombined escherichia coli strain PcPCS1-Pet-22b (+) / Rosetta (DE3) to Cd2+, Cu2+ and Na+ are increased, and the recombined escherichia coli strain PcPCS1-Pet-22b (+) / Rosetta (DE3) can be used for microbial remediation for liquid-phase carriers polluted by Cd2+, Cu2+ or Na+ metal ions.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection primers for three bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN102747162AHigh detection sensitivityAvoid False Positive ResultsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliAlicyclobacillus
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
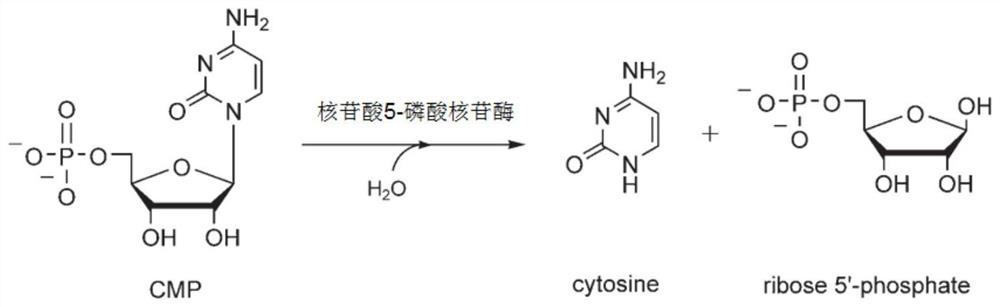
Recombinant microorganism for producing cytosine and method for producing cytosine
ActiveCN112359006AProduction environmental protectionGreen productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCytosine
Owner:SUZHOU BIOSYNTHETICA CO LTD
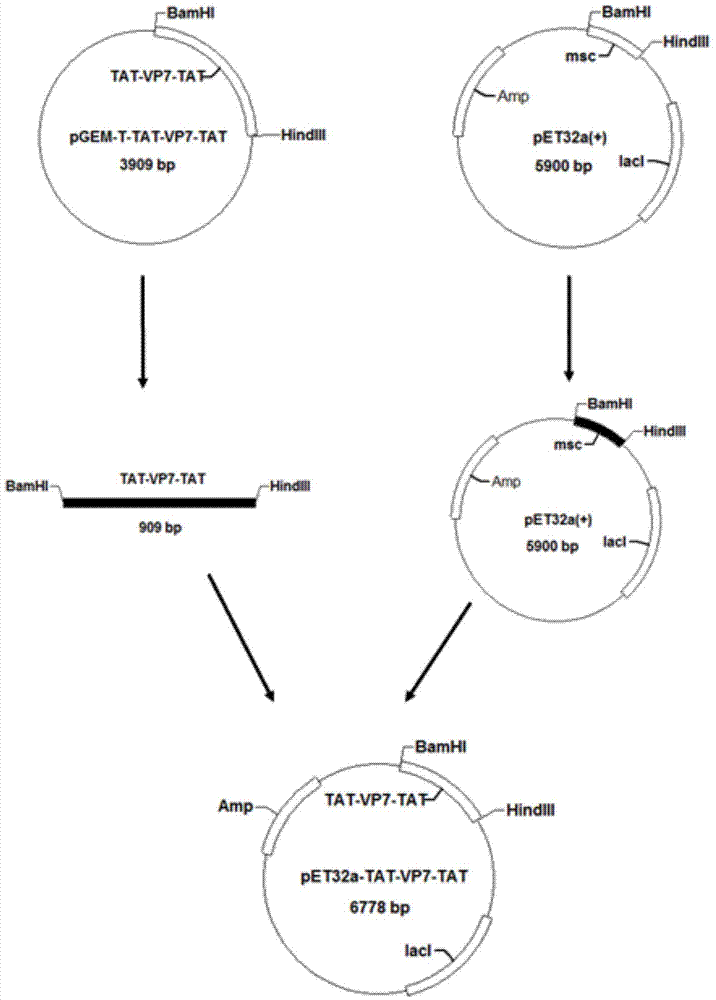
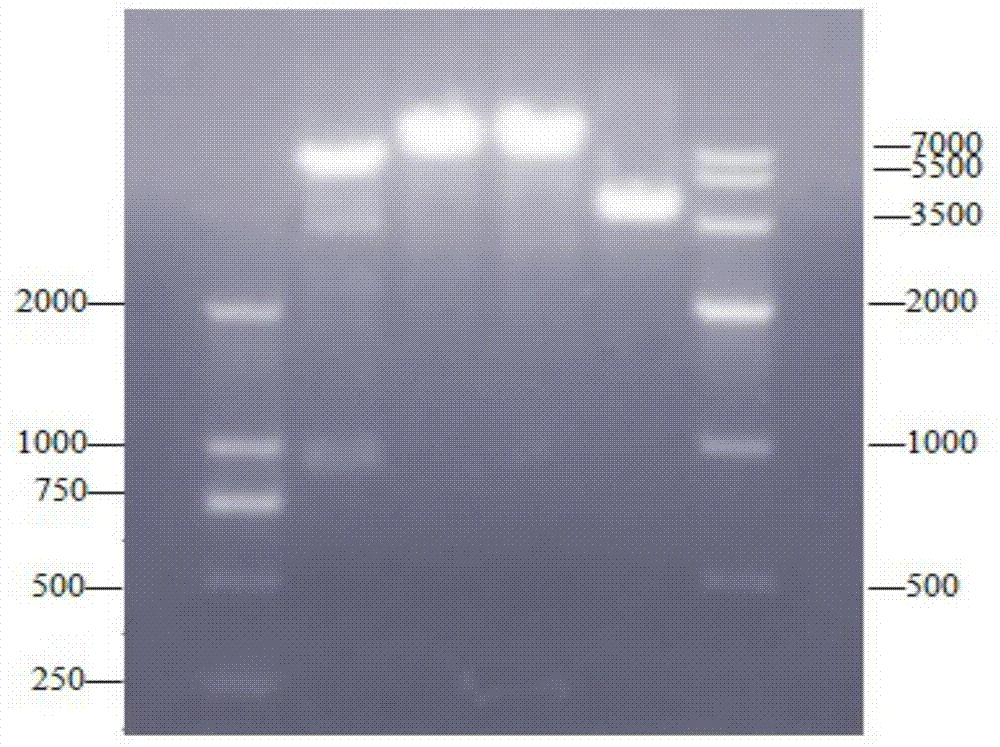
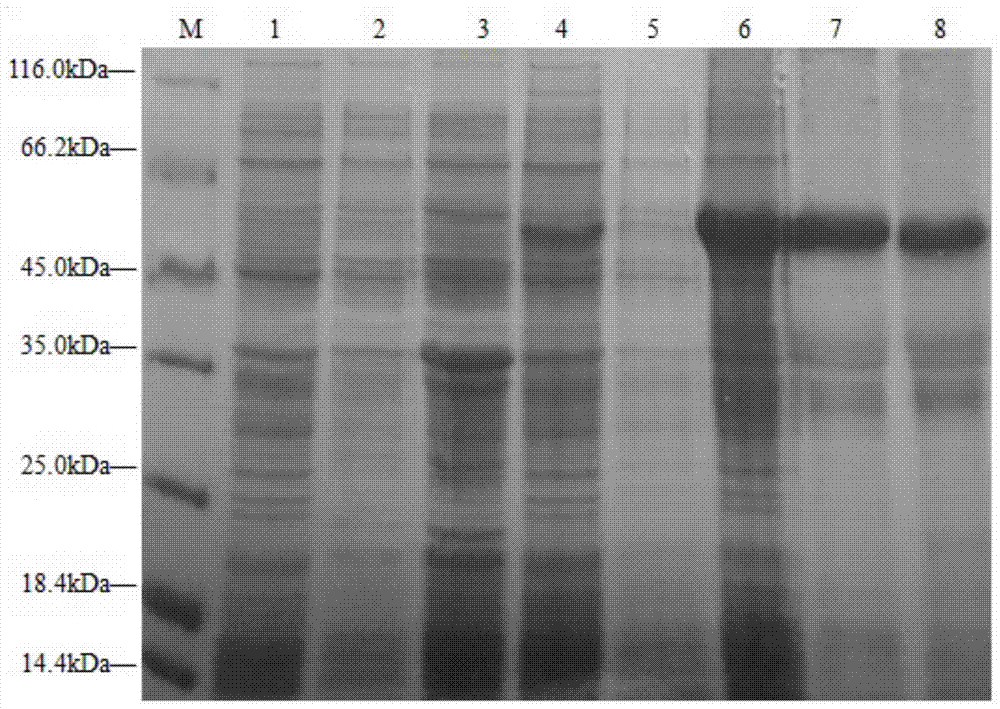
Grass carp haemorrhagic virus resisting engineered protein TAT (Trans-activating Transcriptional Activator)-VP7-TAT as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104744595AEnhanced transmembrane activityReduce dosageBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a grass carp haemorrhagic virus resisting engineered protein TAT (Trans-activating Transcriptional Activator)-VP7-TAT as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the TAT-VP7-TAT protein is shown as SEQ ID NO:2, and a corresponding nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. By using Eschierichia coli BL21(DE3) / pET-32a-TAT-VP7-TAT to perform inducible expression for 4 to 5 hours, a TAT-VP7-TAT fusion protein can be efficiently expressed; the N end and the C end of the protein are respectively provided with protein transduction domain polypeptide TAT. The genetic engineering fusion protein provided by the invention can be used for preventing grass carp haemorrhagic virus diseases. The fusion protein has the advantages of high expression, easiness for industrial production, low cost and good safety; grass carp orally takes the fusion protein, so that better immune protection is realized.
Owner:HUBEI TAIYANGHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d07e9897-9b5a-4b04-af13-722aec5a2368/140704155216.PNG)
![Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d07e9897-9b5a-4b04-af13-722aec5a2368/140704155227.PNG)
![Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d07e9897-9b5a-4b04-af13-722aec5a2368/93258DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.PNG)