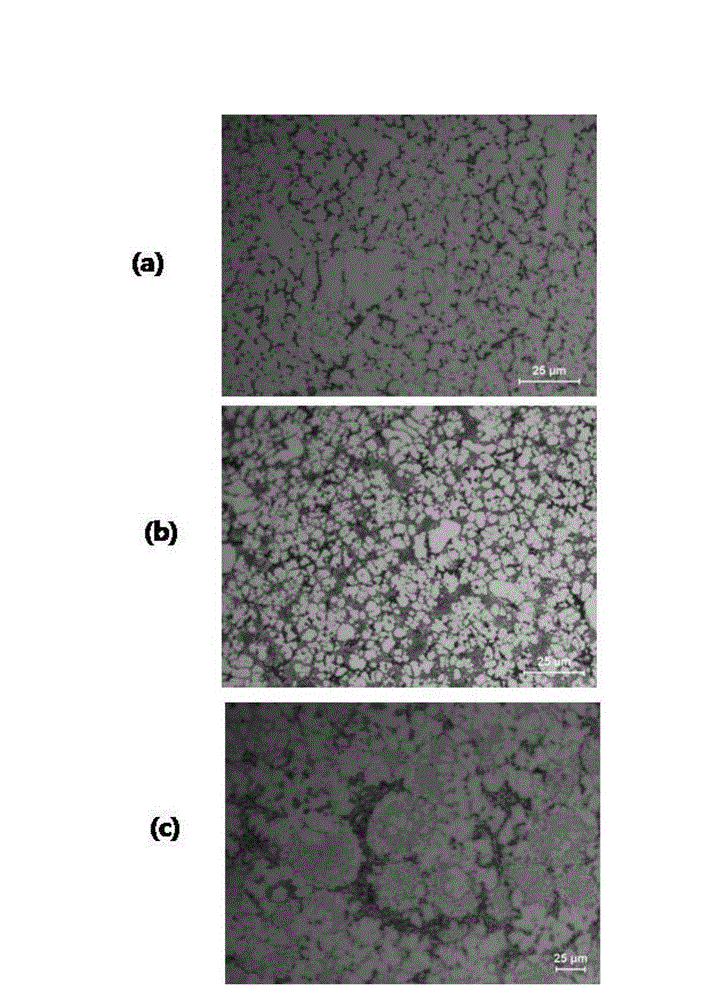
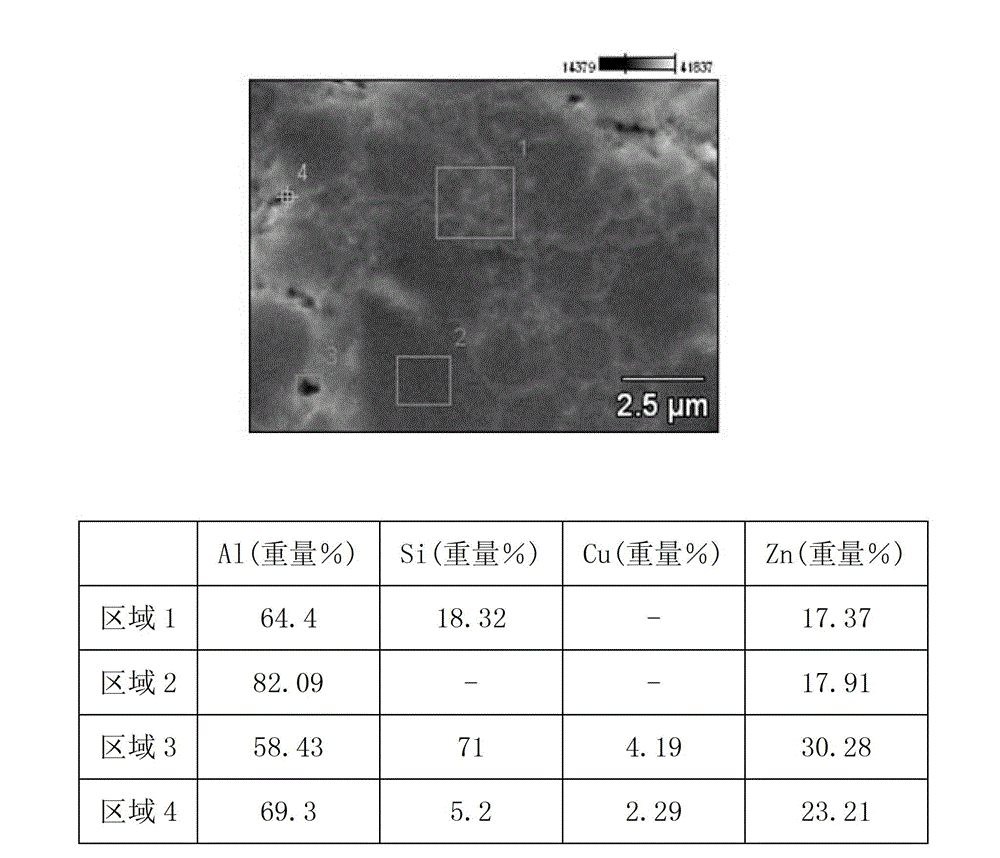
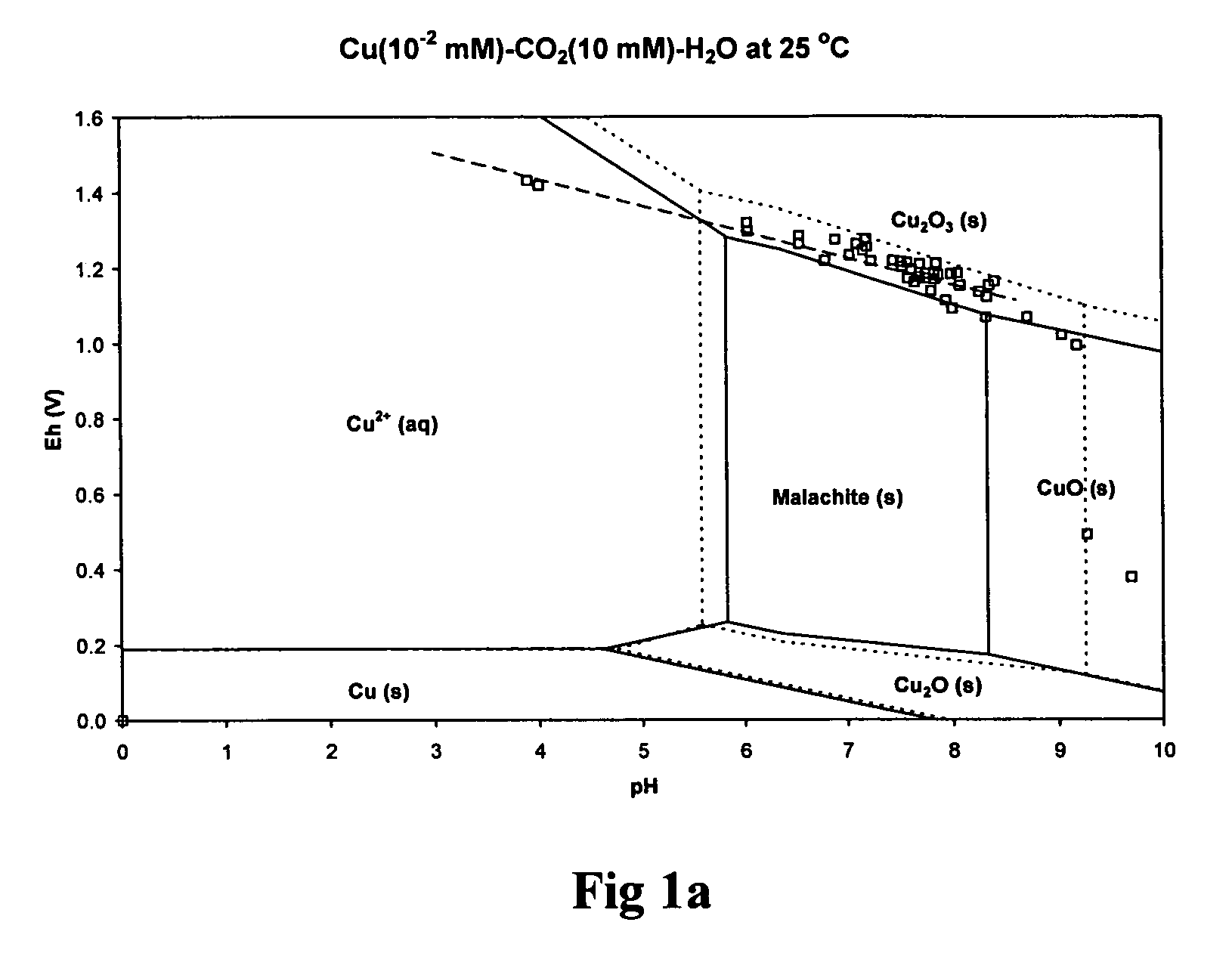
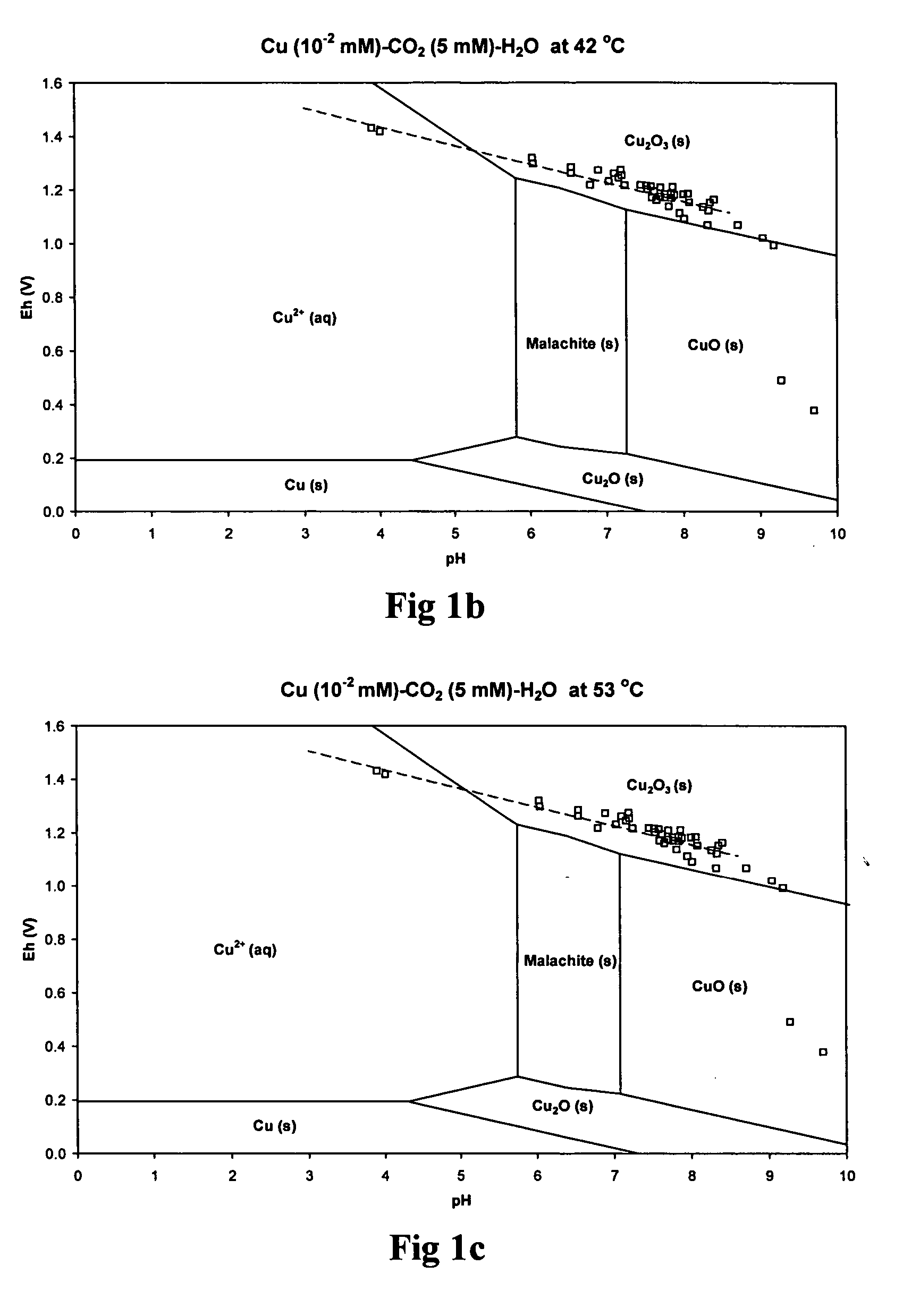
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Base metal alloy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of base metal. 1 : a metal or alloy (such as zinc, lead, or brass) of comparatively low value and relatively inferior in certain properties (such as resistance to corrosion) —opposed to noble metal.
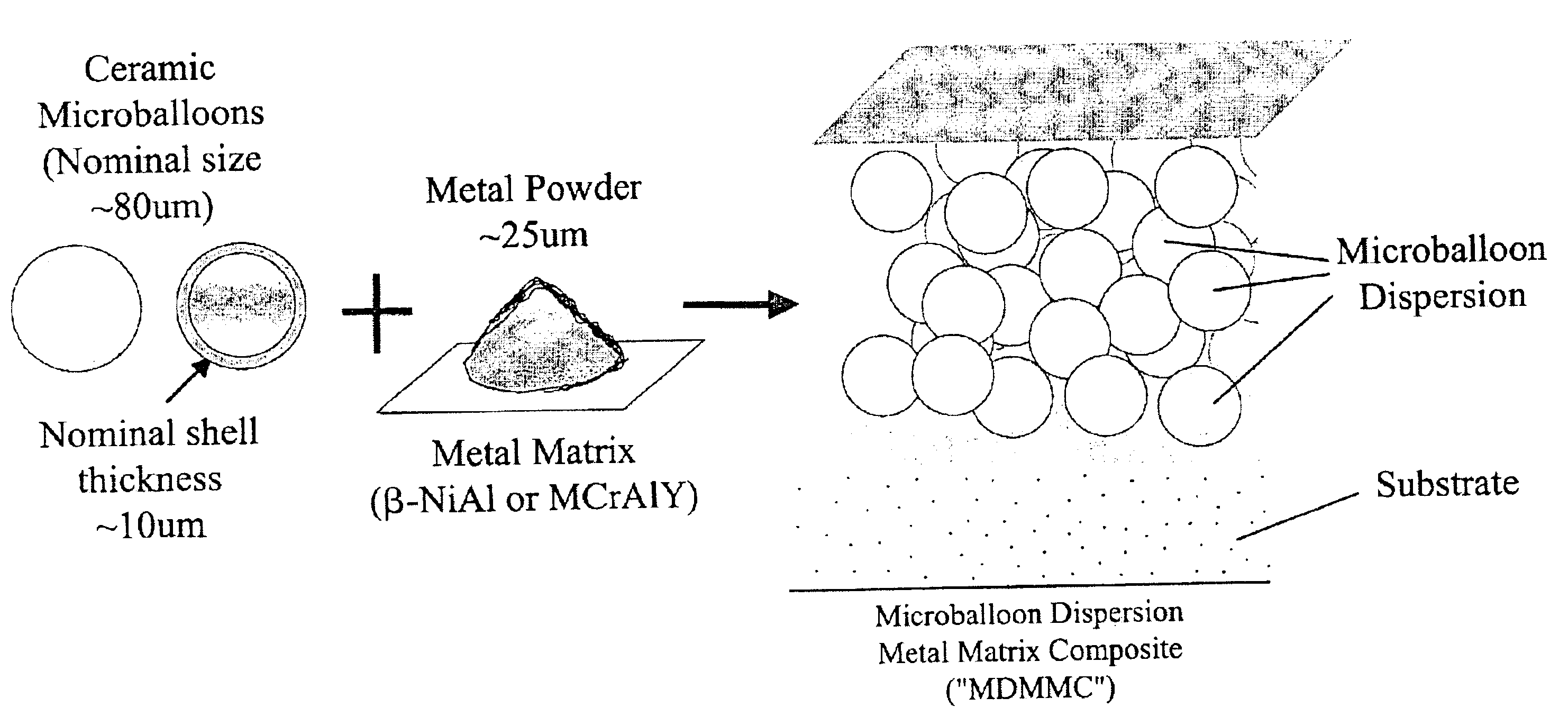
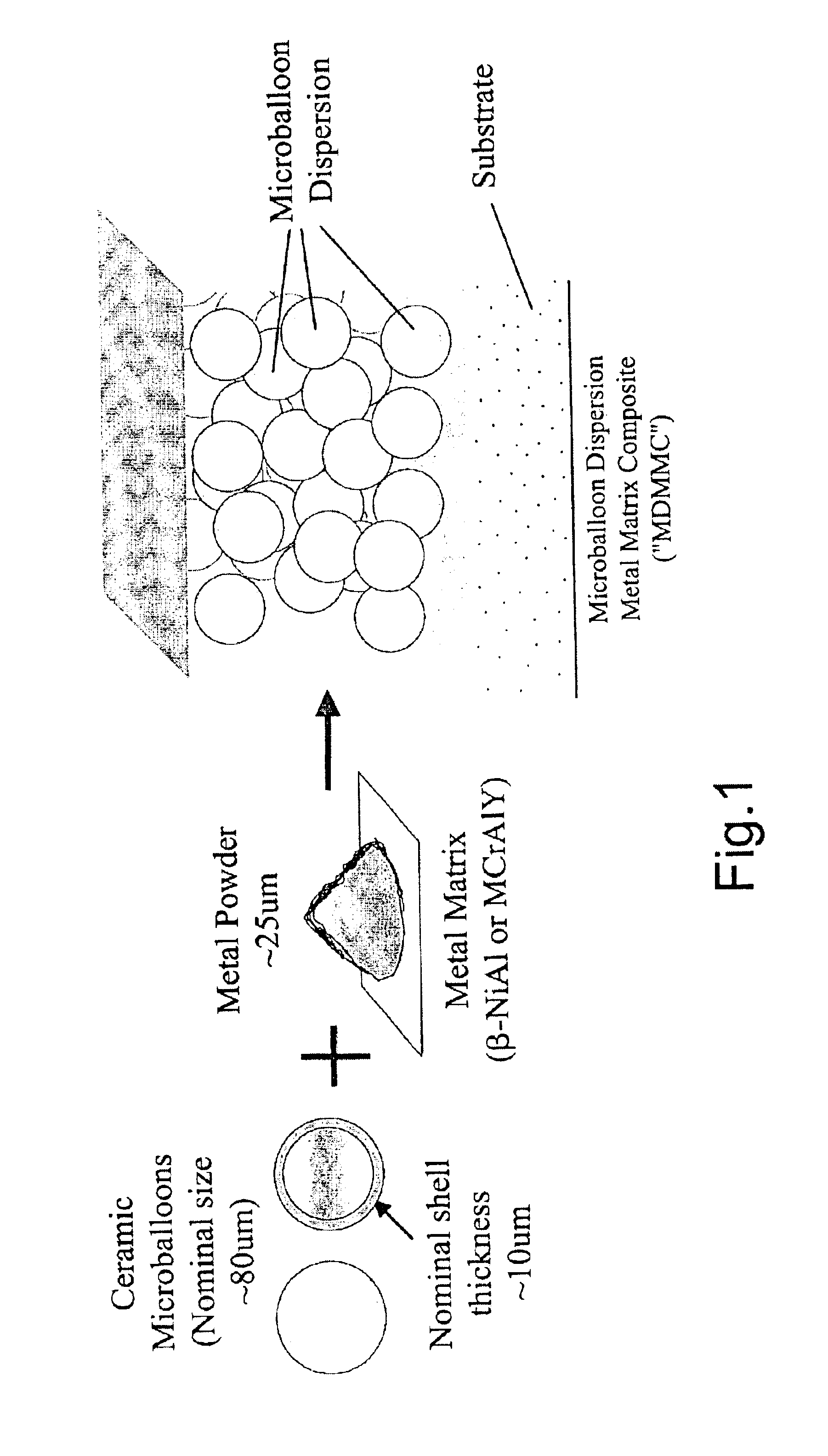
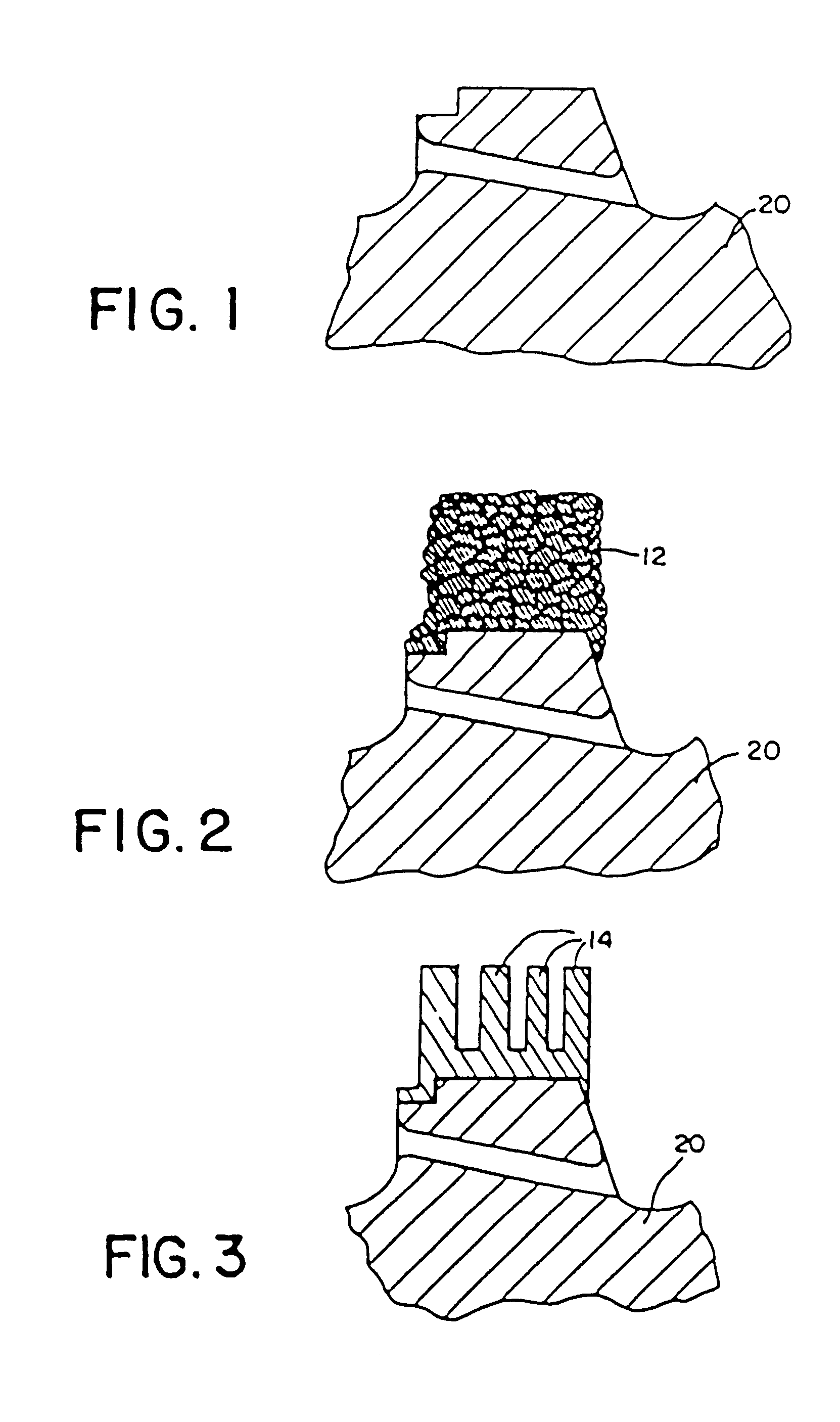
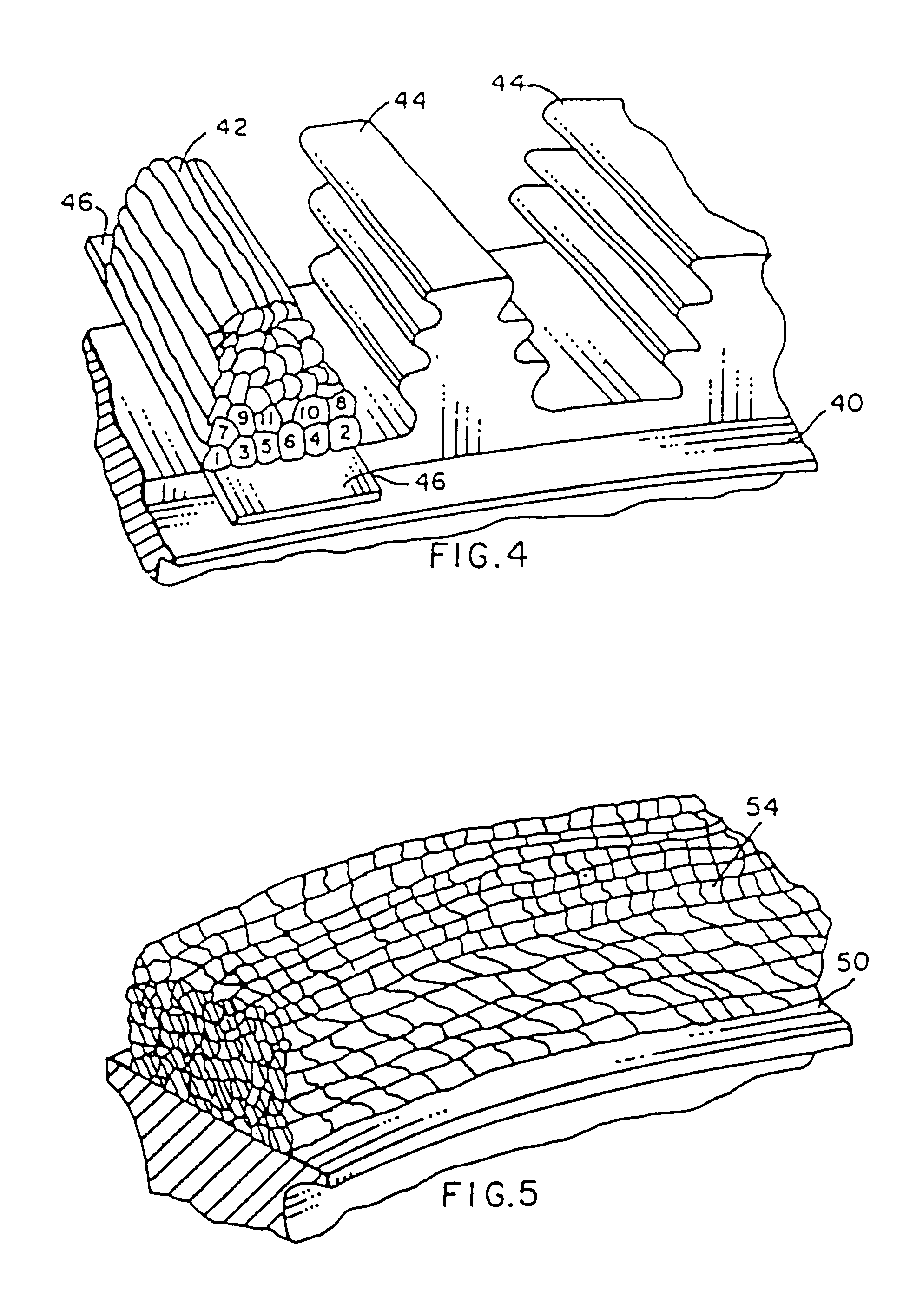
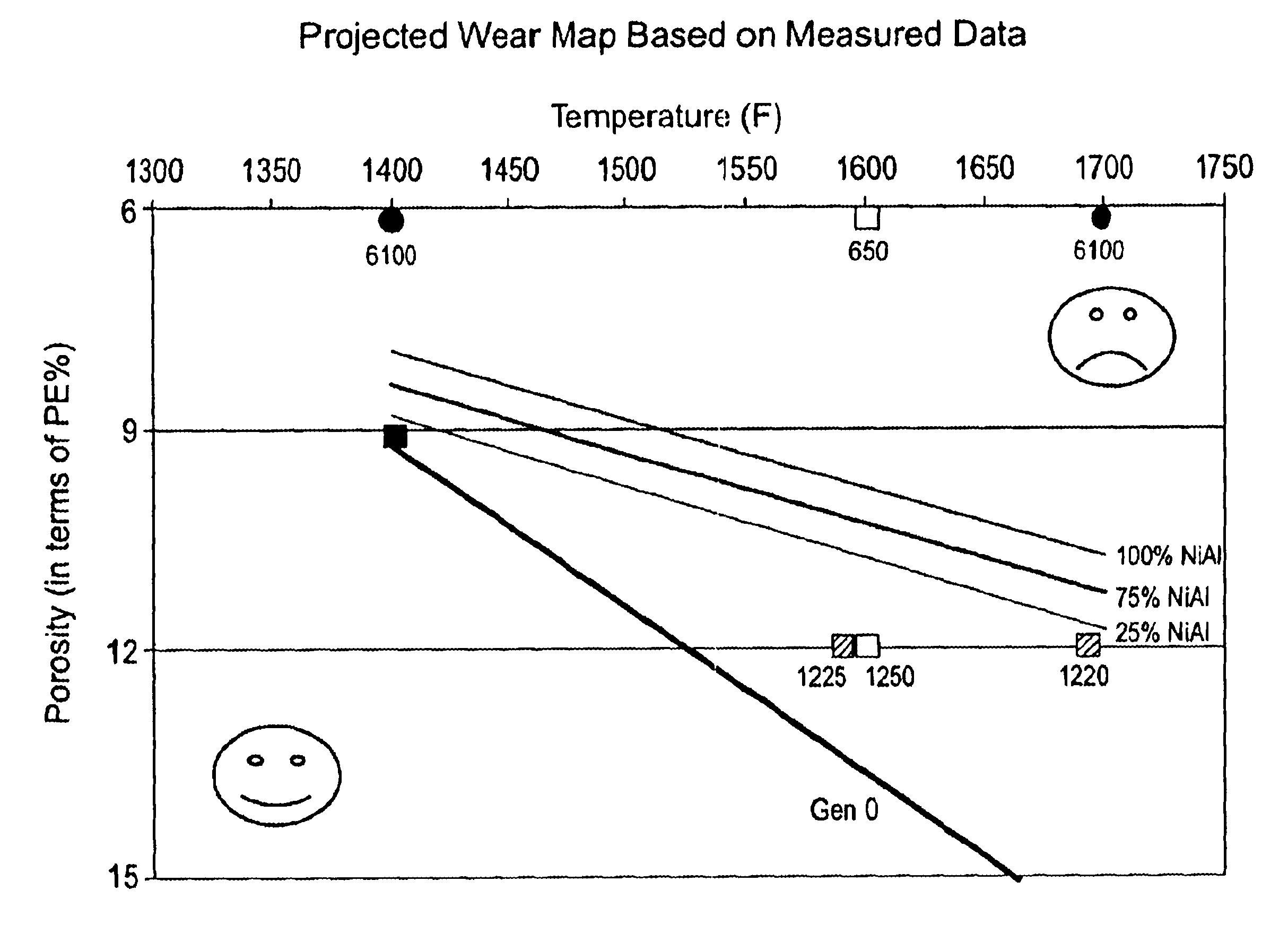
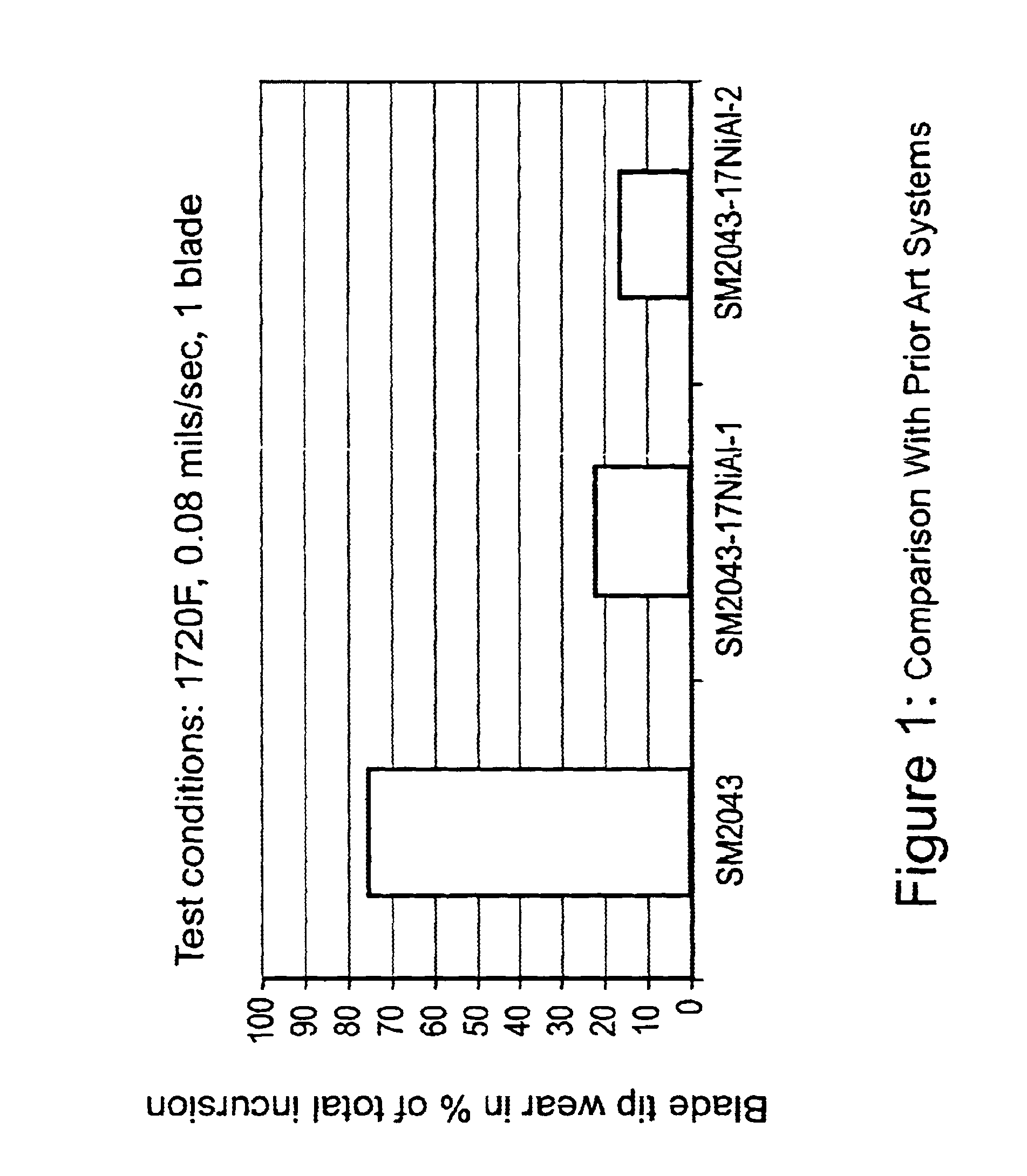
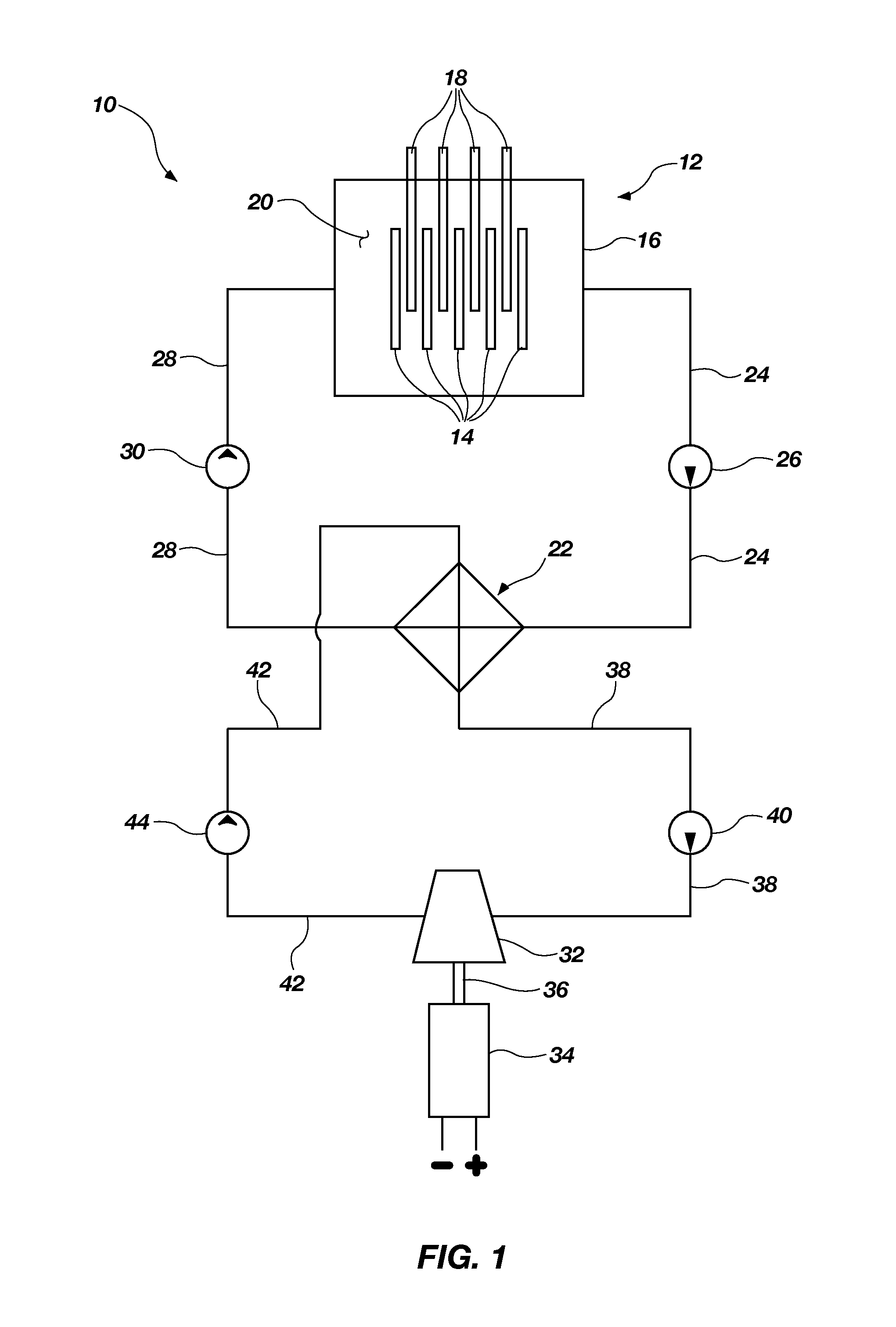
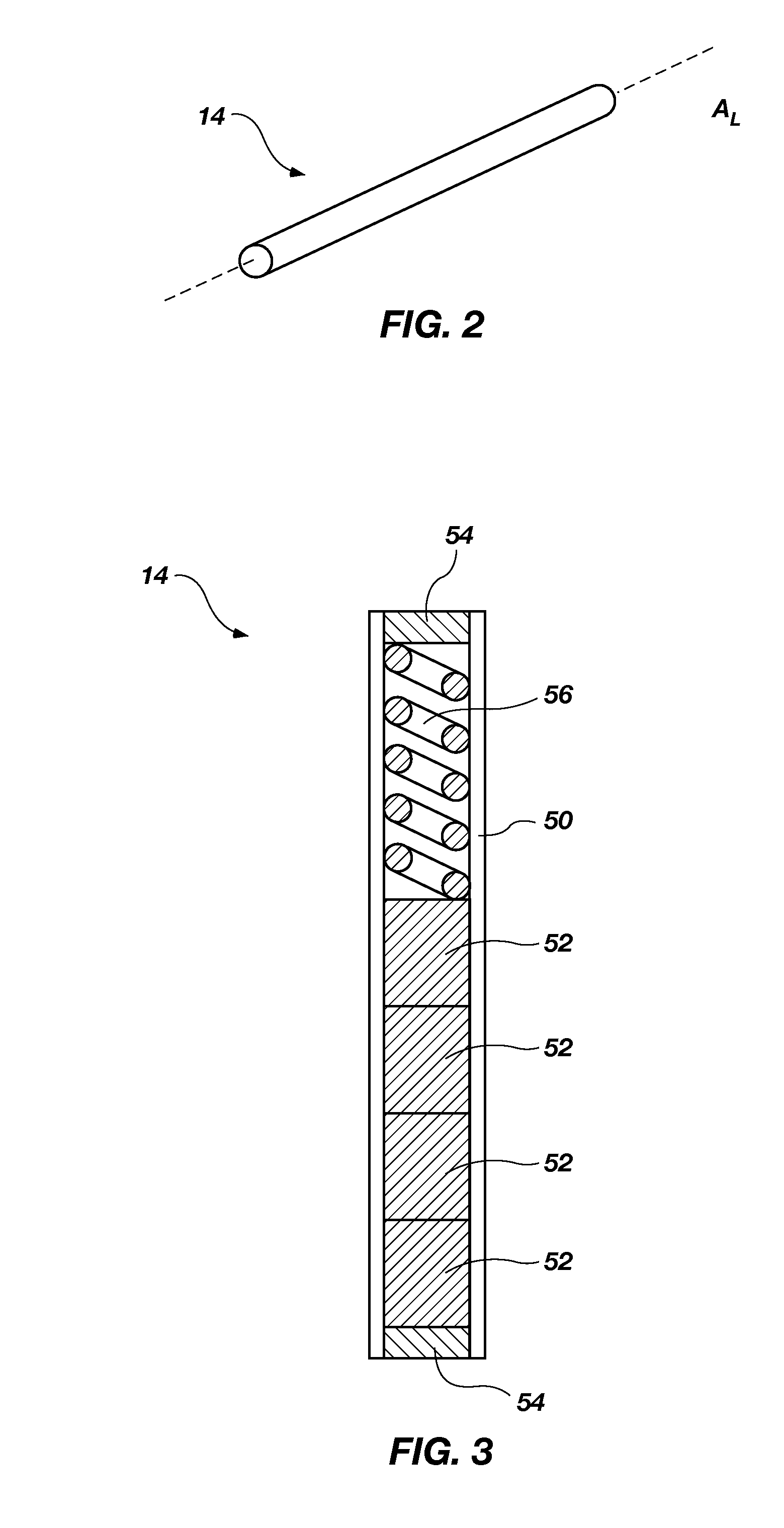
High temperature, oxidation-resistant abradable coatings containing microballoons and method for applying same
InactiveUS6916529B2Effective timeReducing hot gas leakageMolten spray coatingPropellersThermal sprayingMicrosphere
An abradable coating composition for use on shrouds in gas turbine engines or other hot gas path metal components exposed to high temperatures containing an initial porous coating phase created by adding an amount of inorganic microspheres, preferably alumina-ceramic microballoons, to a base metal alloy containing high Al, Cr or Ti such as β-NiAl or, alternatively, MCrAlY that serves to increase the brittle nature of the metal matrix, thereby increasing the abradability and oxidation resistance of the coating at elevated temperatures. Coatings having a total open and closed porosity of between 20% and 55% by volume due to the presence of ceramic microballoons ranging in size from about 10 microns to about 200 microns have been found to exhibit excellent abradability for applications involving turbine shroud coatings. An abradable coating thickness in the range of between 40 and 60 ml provides improved performance for turbine shrouds exposed to gas temperatures between 1380° F. and 1800° F. Abradable coatings in accordance with the invention can be used for new metal components or to repair existing equipment. The coatings can be applied to the metal shroud using thermal spray, processes that integrate sintering and brazing, or direct write techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Amorphous fe and co based metallic foams and methods of producing the same
Amorphous Fe- and Co-based metal foams and methods of preparing the same are provided. The Fe- and Co-based foams are prepared from Fe- and Co-based metal alloys of low hydrogen solubility having an atomic fraction of Fe or Co greater than or equal to the atomic fraction of each other alloying element. A method for producing the Fe- and Co-based foams includes the in situ decomposition of a hydride in a molten Fe- or Co-based alloy.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Manufacture of Controlled Rate Dissolving Materials
ActiveUS20150240337A1Improve ductilityImprove propertiesTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusAlloyBase metal alloy
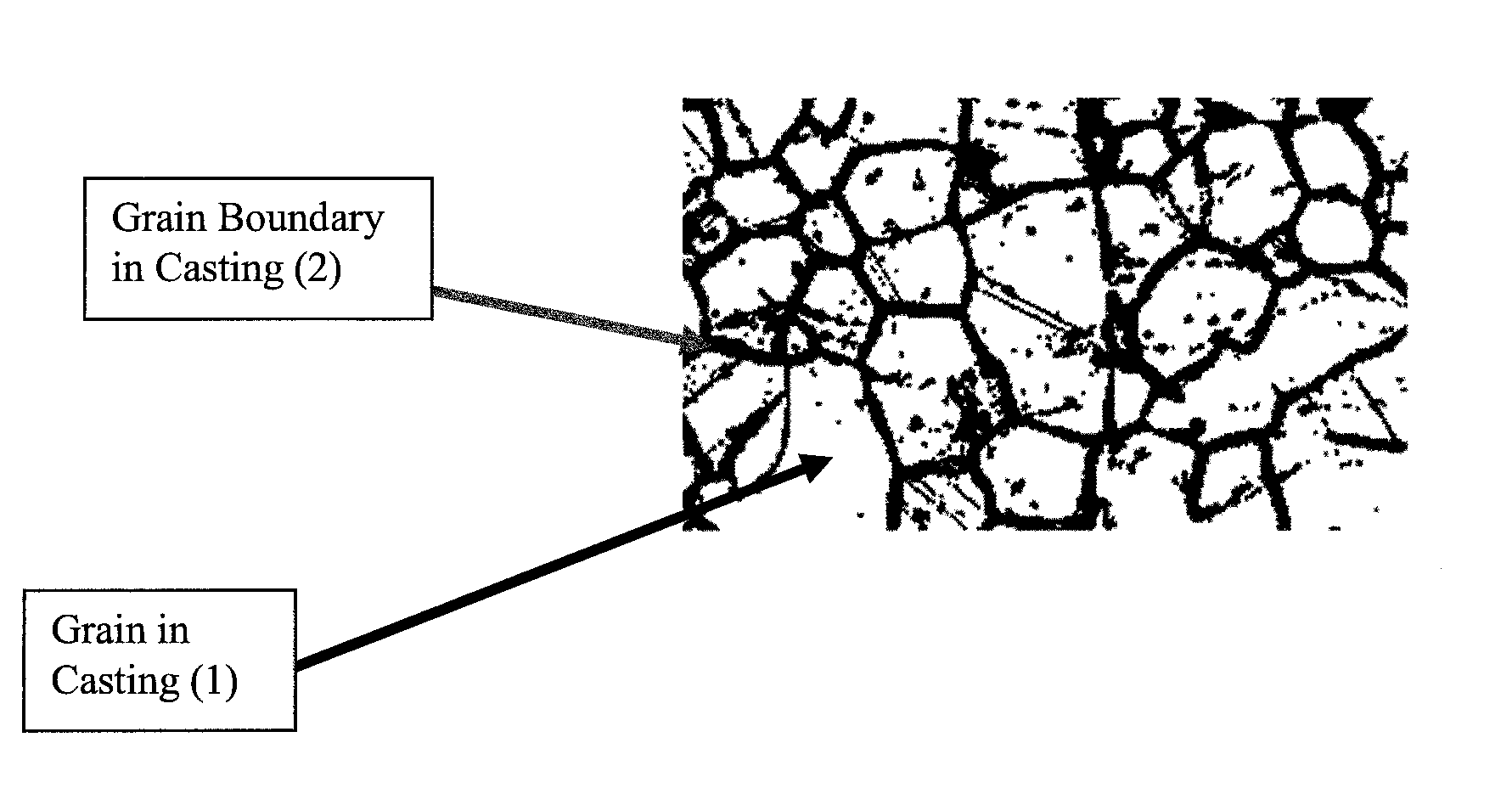
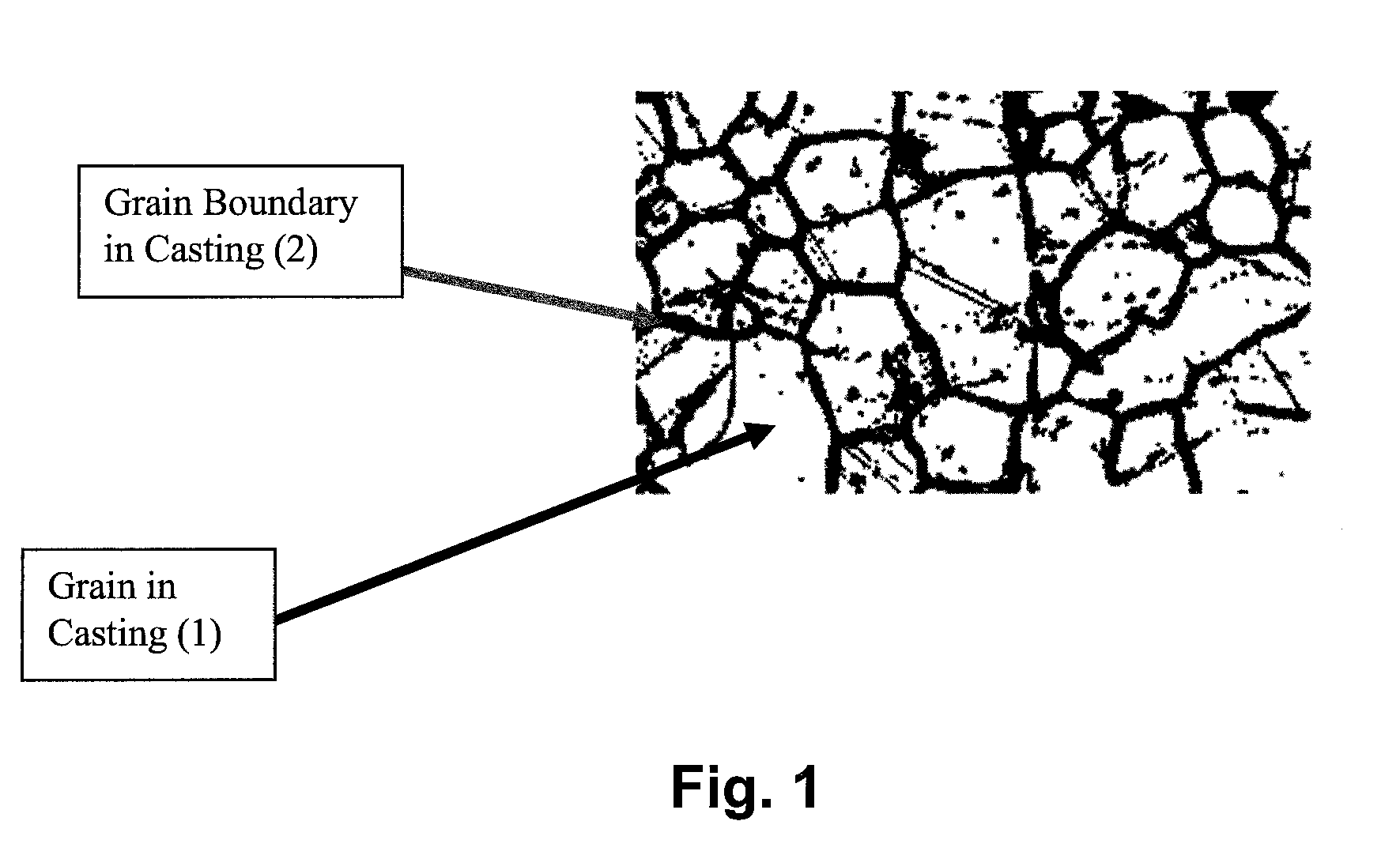
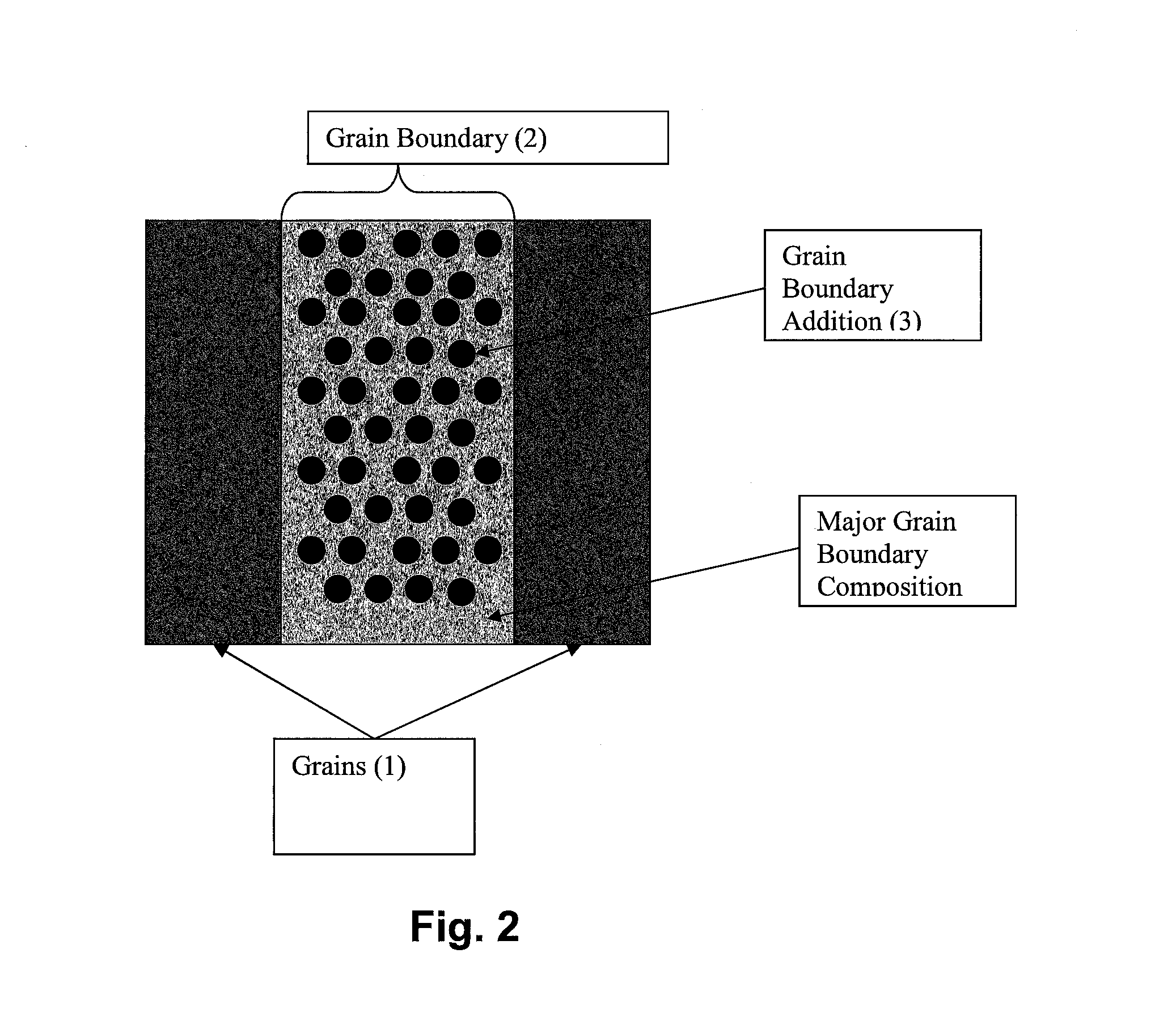
A castable, moldable, or extrudable structure using a metallic base metal or base metal alloy. One or more insoluble additives are added to the metallic base metal or base metal alloy so that the grain boundaries of the castable, moldable, or extrudable structure includes a composition and morphology to achieve a specific galvanic corrosion rates partially or throughout the structure or along the grain boundaries of the structure. The insoluble additives can be used to enhance the mechanical properties of the structure, such as ductility and / or tensile strength. The insoluble particles generally have a submicron particle size. The final structure can be enhanced by heat treatment, as well as deformation processing such as extrusion, forging, or rolling, to further improve the strength of the final structure as compared to the non-enhanced structure.
Owner:TERVES
Electrode catalyst for fuel cell and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6911278B2High catalytic activityImprove performanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsActive material electrodesPlatinumFuel cells
An electrode catalyst for a fuel cell includes a conductive support, and catalytic particles loaded on the conductive support. The catalytic particles include platinum and a base metal being on the lower end of the electrochemical series with respect to platinum. The number of the atoms of the base metal, forming metallic oxides without alloying with the platinum, is less than 5 atomic % of the number of the atoms of the platinum on a surface of the catalytic particles. The electrode catalyst is produced by loading the platinum and base metal on the conductive support, alloying the platinum and base metal thereon by a heat treatment, thereby making the catalytic particles, and removing metallic oxides from a surface of the catalytic particles. The electrode catalyst is less expensive comparatively, exhibits high catalytic activities, and hardly lowers the battery performance of fuel cells.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Variable melting point solders
The present invention relates to variable melting point solder formulations. The solder is comprised of at least one base metal or base metal alloy, preferably alloyed with at least one melting point depressant metal, such that the solidus point of the solder composition is reduced to an initial solidus temperature. Said base metal or base metal alloy, alloyed with at least one melting point depressant metal is mixed with at least one additive metal or additive metal alloy. When heated to a process temperature above said initial solidus temperature, a reaction occurs between the melting point depressant metal, and the additive metal, such that solidification occurs at the process temperature via the formation of intermetallic phases, effectively increasing the solidus of the base metal, and of the overall solder.
Owner:DYNAJOIN CORP
Turbine system having more failure resistant rotors and repair welding of low alloy ferrous turbine components by controlled weld build-up
InactiveUSRE37562E1Minimize weld stressMinimize cracksPropellersArc welding apparatusHeat-affected zoneAlloy
System for repairing worn surfaces of steam turbine components and especially high pressure turbine rotors, are disclosed. These systems include depositing a first layer of weld metal on a worn surface of the component, whereby a heat-affected zone is created. A second layer of weld metal is then deposited over the first layer using a greater amount of heat to temper at least a portion of the heat-affected zone produced by the first layer. The preferred embodiments include the use of gas tungsten arc welding for providing fine-grain size and more creep resistance, especially in the weld and heat-affected zone. The resulting build-up can be machined, for example into a blade fastening to produce a component having properties equal to or better than the base-metal alloy. The invention also provides a longer lasting turbine system, including rotors which have serrated steeples that are more resistant to failure.
Owner:SIEMENS POWER GENERATION
High temperature abradable coating for turbine shrouds without bucket tipping
InactiveUS6660405B2Reduce gas leakageImprove turbine efficiencyLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPolyesterPorous coating
An abradable coating composition for use on shrouds in gas turbine engines (or other hot gas path metal components exposed to high temperatures) containing an initial porous coating phase created by adding a "fugitive polymer" (such as polyester or polyimide) to the base metal alloy, together with a brittle intermetallic phase such as .beta.-NiAl that serves to increase the brittle nature of the metal matrix, thereby increasing the abradability of the coating at elevated temperatures, and to improve the oxidation resistance of the coating at elevated temperatures. Coatings having about 12 wt % polyester has been found to exhibit excellent abradability for applications involving turbine shroud coatings. An abradable coating thickness in the range of between 40 and 60 ml provides the best performance for turbine shrouds exposed to gas temperatures between 1380.degree. F. and 1850.degree. F. Abradable coatings in accordance with the invention can be used for new metal components or to repair existing equipment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrothermal organic power resistance slurry for heater
InactiveCN101735561ALow temperature curingWith high temperature useHeating element materialsLow temperature curingUltra fine
The invention relates to an electrothermal organic power resistance slurry for a heater. The main formula of the slurry comprises the following components by weight percent: 28%-60% of resin I, 5%-13% of flame-retardant heat-resistant polymer containing boron element, 3%-6% of latent curing agent, 1%-2% of latent curing accelerator, 0-30% of resin II, 10%-15% of nano-carbon series conductive filler, 4%-5% of temperature coefficient adjustment additive, 0-5% of ultra-fine base metal alloy powder conductive filler, 0-3% of silicon series far infrared radiating material and 0-4% of ultra-fine mica powder, in addition to the main formula, the slurry further contains a small amount of function auxiliary phase. The slurry can solve the problems that the ordinary slurry is difficult to realize thinness, light weight or special shape; furthermore, the slurry has the properties of low temperature curing and high temperature use and can be directly used for printing or spraying and meet the technical development requirements of an electric heater on the trends of miniature, thinness, light weight and (shape and purpose) special shape.
Owner:西安宏星电子浆料科技股份有限公司
Aluminum alloy, and aluminum alloy casting
The present invention relates to a metal alloy, and more specifically, to an aluminum alloy used in electrical, electronic, mechanical parts and the like, and an aluminum alloy casting prepared by using the same. An aluminum alloy according the one embodiment comprises 4-13 wt% of silicon (Si), 1-5 wt% of copper (Cu); zinc (Zn) in an amount equal to or more than 26 wt% and less than 40 wt%; and the remaining aluminum (Al) and inevitable impurities.
Owner:INTERPLEX QUANTUM
Copper processing using an ozone-solvent solution
InactiveUS20060084260A1Avoid corrosionAccurate removalPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialAlloy
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for treating materials such as copper or copper based metal alloys, used in fabricating semiconductor devices with an ozone solvent solution and avoiding damage to metals by corrosion. The invention is also applicable to treating of materials such as copper and copper based alloys for the purpose of forming a protective layer on the exposed metal surface for protection of those copper surfaces from damage or corrosion caused by subsequent exposure to other liquid, gas, or plasma environments. This can be achieved by properly selecting the composition of the ozone solvent solution and controlling the pH and ORP of the ozone-solvent solution while avoiding the use of certain chemical constituents in the ozone solvent solution.
Owner:BOYERS DAVID G +1
Electrode catalyst for fuel cell and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20030054227A1High oxygen reducing activityHigh catalytic activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsActive material electrodesPlatinumFuel cells
An electrode catalyst for a fuel cell includes a conductive support, and catalytic particles loaded on the conductive support. The catalytic particles include platinum and a base metal being on the lower end of the electrochemical series with respect to platinum. The number of the atoms of the base metal, forming metallic oxides without alloying with the platinum, is less than 5 atomic % of the number of the atoms of the platinum on a surface of the catalytic particles. The electrode catalyst is produced by loading the platinum and base metal on the conductive support, alloying the platinum and base metal thereon by a heat treatment, thereby making the catalytic particles, and removing metallic oxides from a surface of the catalytic particles. The electrode catalyst is less expensive comparatively, exhibits high catalytic activities, and hardly lowers the battery performance of fuel cells.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
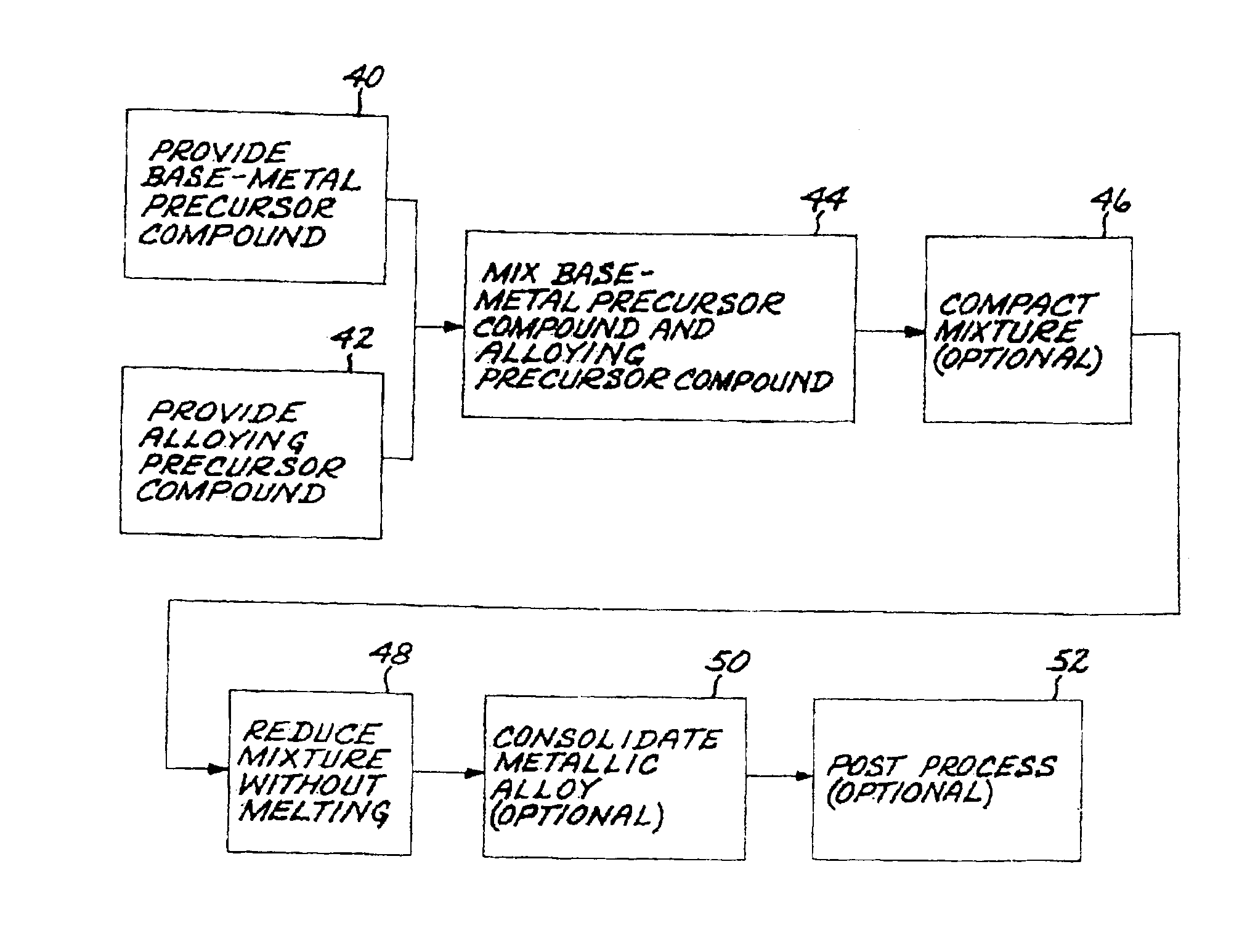
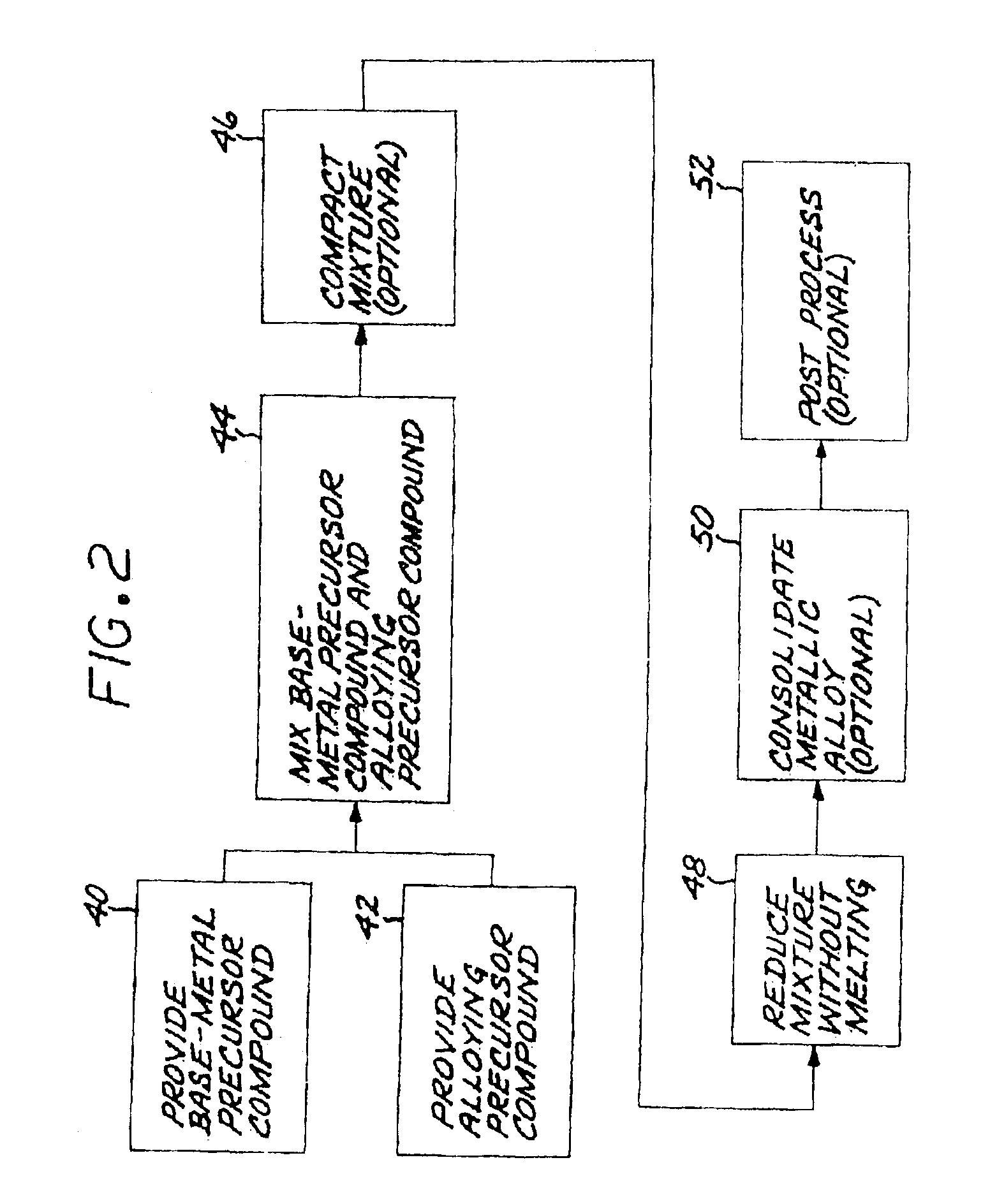
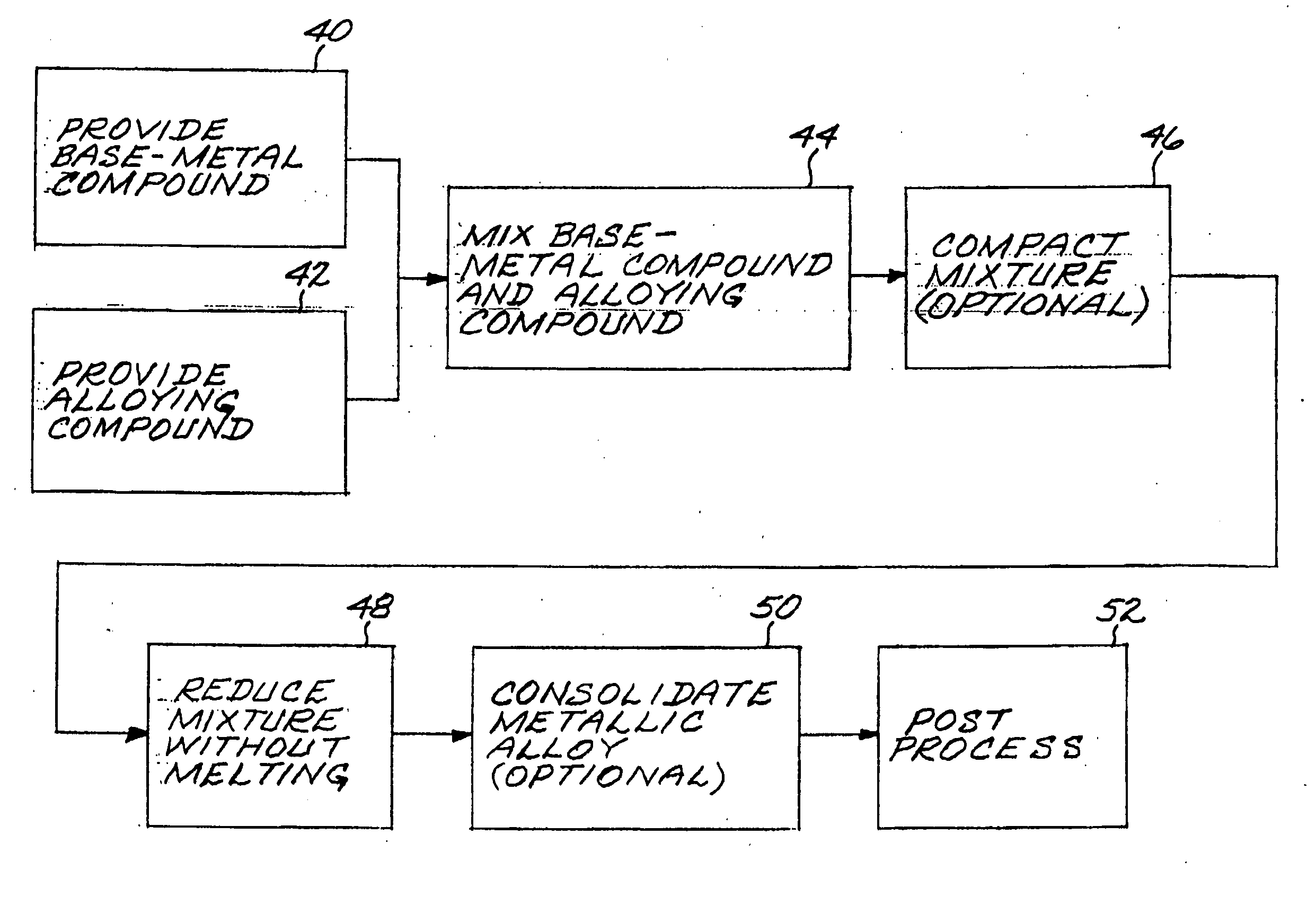
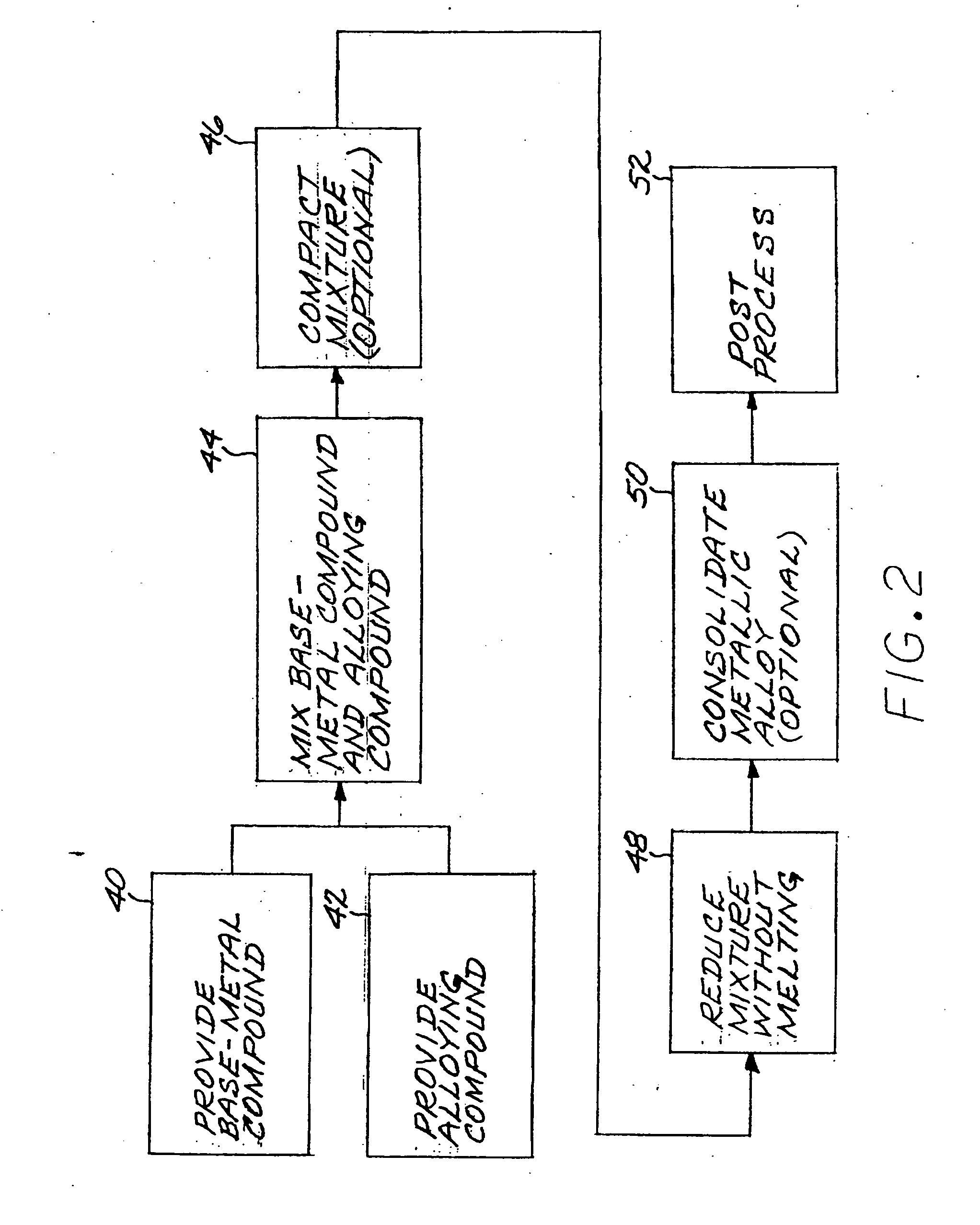
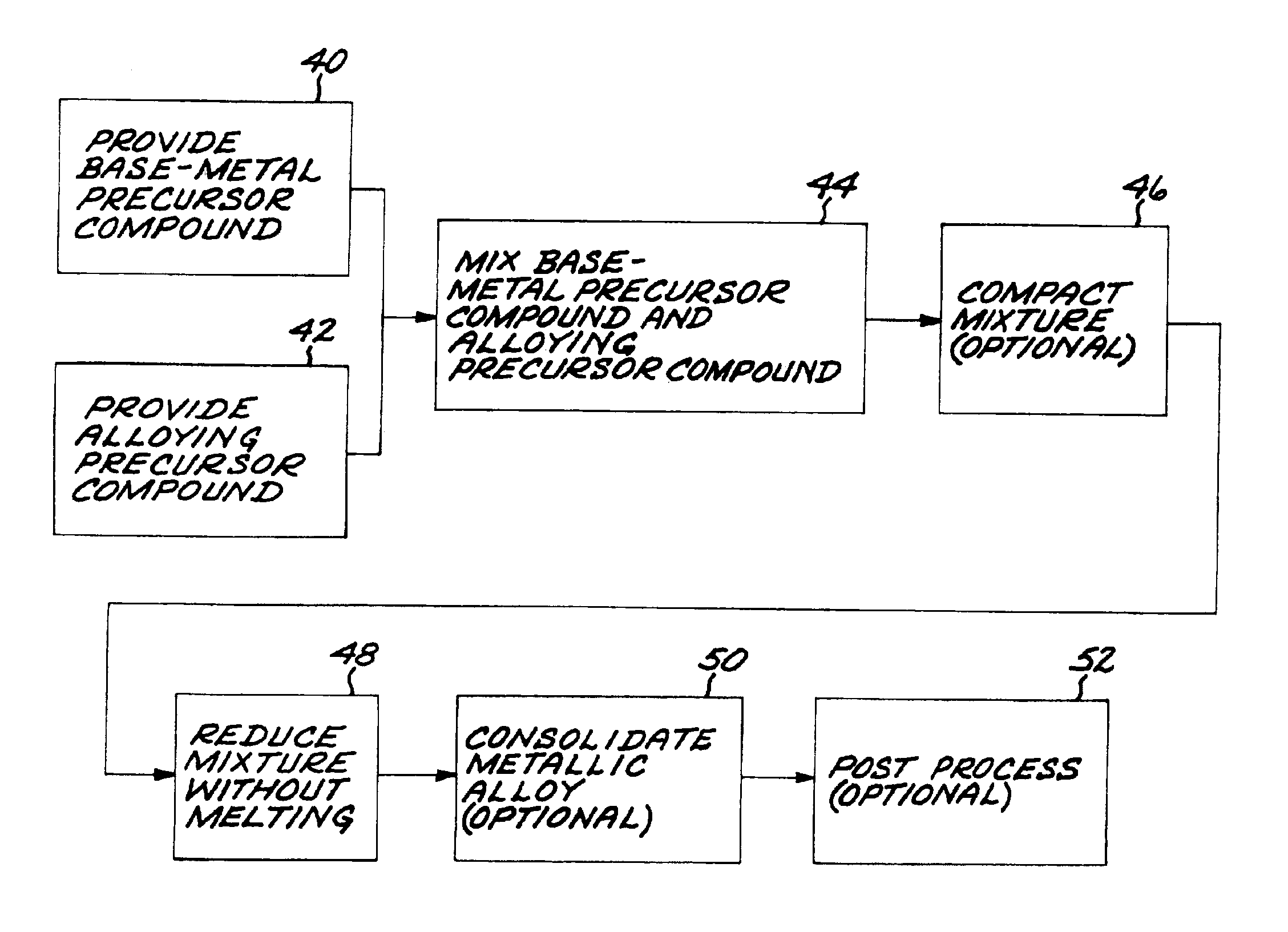
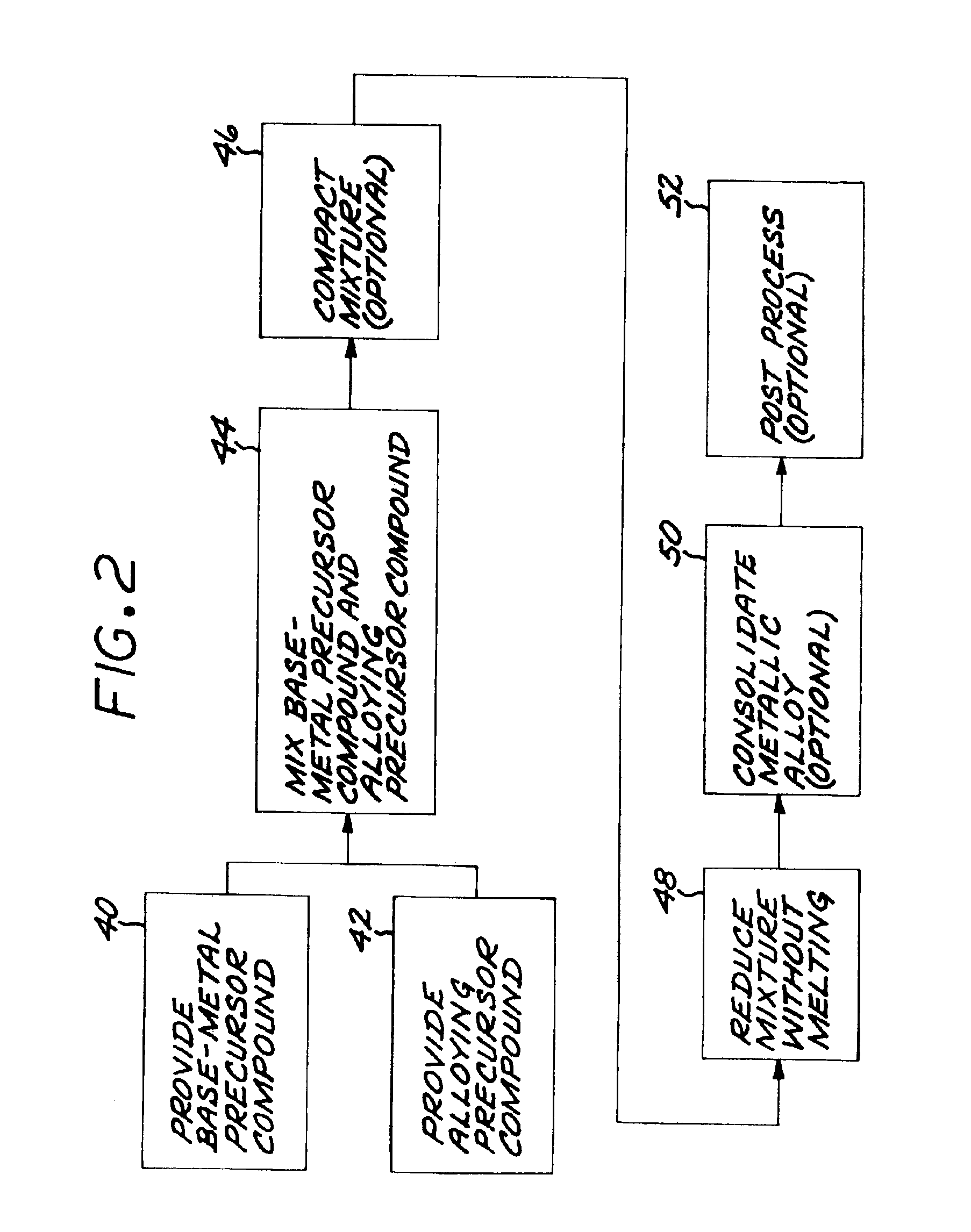
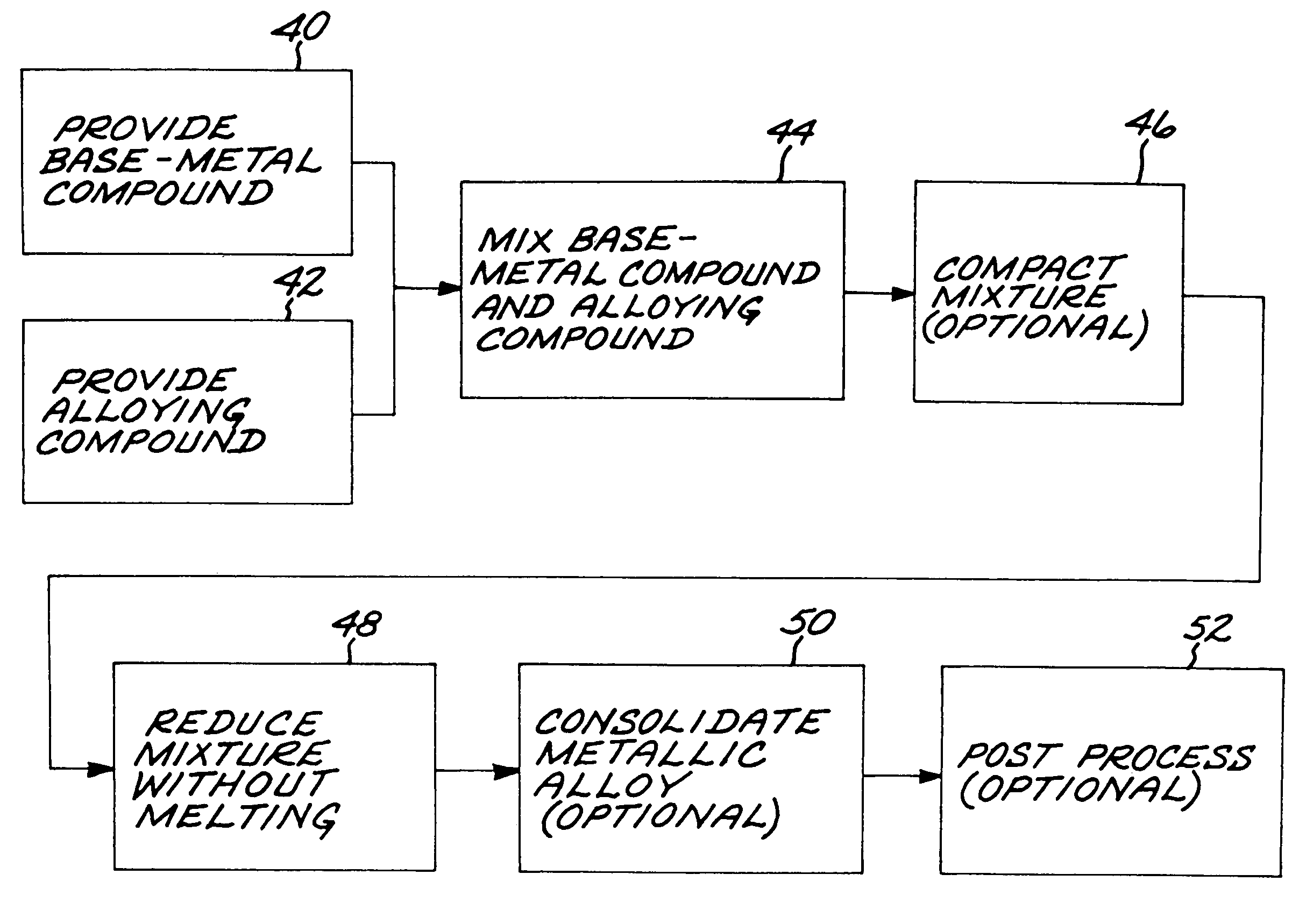
Method for preparing metallic superalloy articles having thermophysically melt incompatible alloying elements, without melting
An article of a base metal alloyed with an alloying element is prepared by mixing a chemically reducible nonmetallic base-metal precursor compound of a base metal and a chemically reducible nonmetallic alloying-element precursor compound of an alloying element to form a compound mixture. The base metal is nickel, cobalt, iron, iron-nickel, or iron-nickel-cobalt. One or more of the alloying elements are thermophysically melt incompatible with the base metal. The method further includes chemically reducing the compound mixture to a metallic superalloy, without melting the metallic superalloy, and thereafter consolidating the metallic superalloy to produce a consolidated metallic article, without melting the metallic superalloy and without melting the consolidated metallic article.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
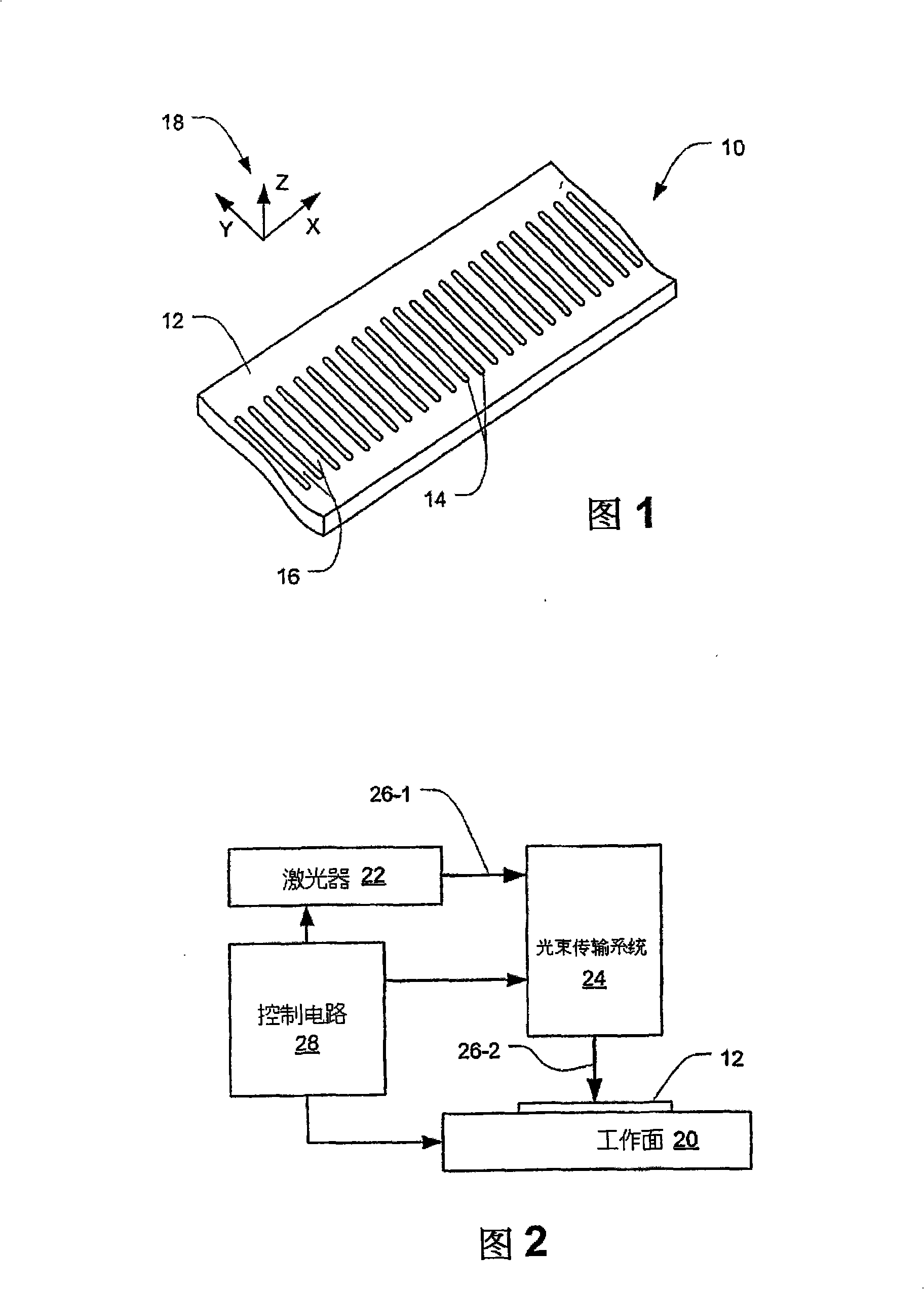
Optical metrological scale and laser-based manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN101356304AAblative recordingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOptical reflectionMetal alloy
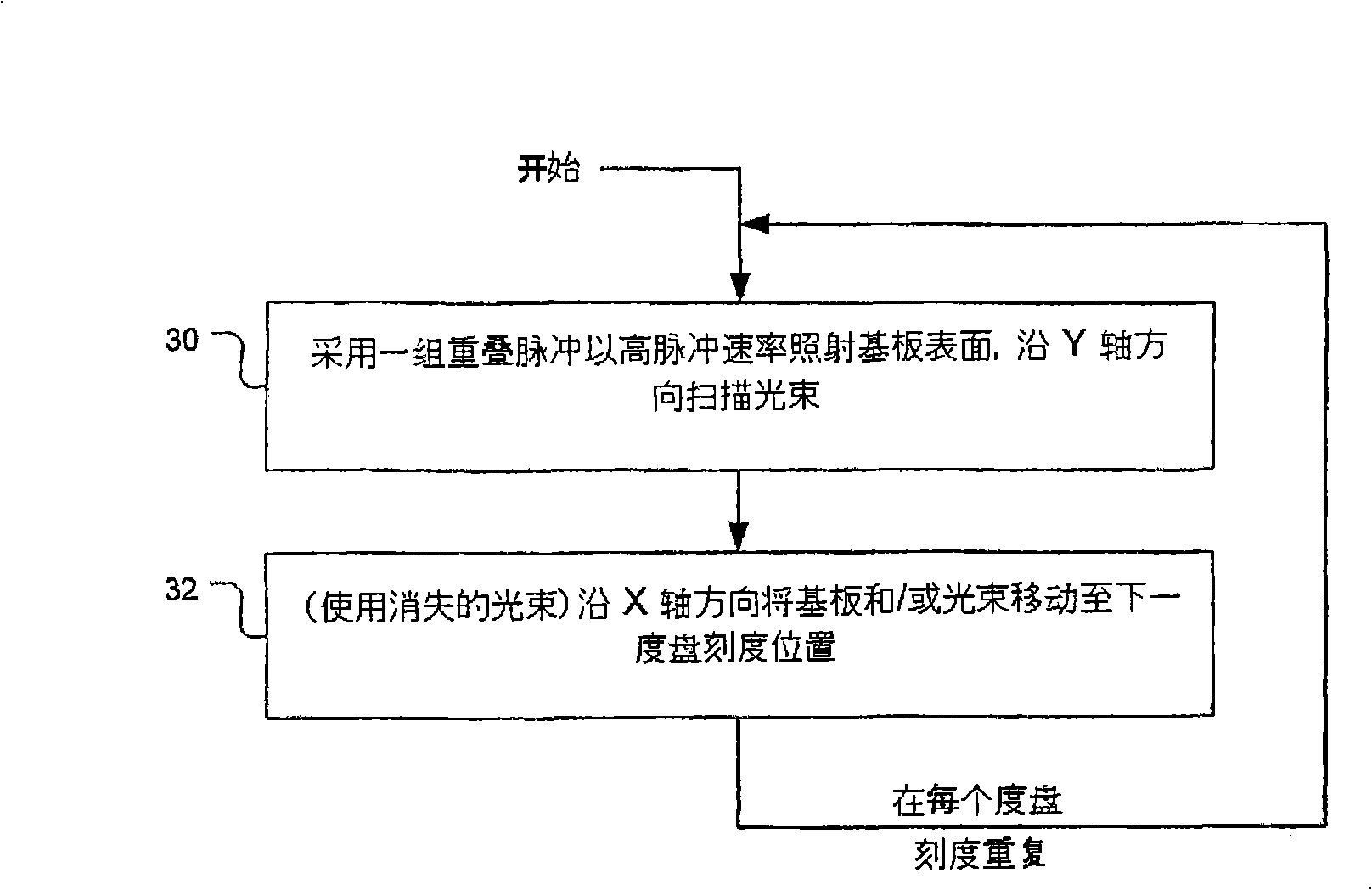
A reflective metrological scale has a scale pattern of elongated side-by-side marks surrounded by reflective surface areas of a substrate, which may be a nickel-based metal alloy such as Invar TM or Inconel TM and may be a thin and elongated flexible tape. Each mark has a furrowed cross section and may have a depth in the range of 0.5 to 2 microns. The central region of each mark may be rippled or ridged and may be darkened to provide an enhanced optical reflection ratio with respect to surrounding reflective surface areas. A manufacturing method includes the repeated steps of (1) creating a scale mark by irradiating a surface of the substrate at a mark location with a series of overlapped pulses from a laser, each pulse having an energy density of less than about 1 joule per cm<2>, and (2) changing the relative position of the laser and the substrate by a displacement amount defining a next mark location on the substrate at which a next mark of the scale is to be created.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC
Aluminium production cells with iron-based metal alloy anodes
InactiveUS20050000823A1Reduce pollutionMachining electrodesElectrical-based machining electrodesElectrolysisRare earth
An iron-based metal anode for the electrowinning of aluminium by the electrolysis of alumina in a molten fluoride electrolyte has an electrochemically active integral outside oxide layer on an iron-based alloy that consists of 75 to 90 weight % iron; 0.5 to 5 weight % in total of at least one rare earth metal, in particular yttrium; 1 to 10 weight % aluminium; 0 to 10 weight % copper; 0 to 10 weight % nickel; and 0.5 to 5 weight % of other elements. The total amount of aluminium, copper and nickel is in the range from 5 to 20 weight %; and the total amount of rare earth metal(s), aluminium and copper is also in the range from 5 to 20 weight %. The electrochemically active surface layer is predominantly of iron oxide that slowly dissolves into the electrolyte during operation and is maintained by progressive slow oxidation of iron at the interface of the bulk metal of the alloy with the oxide layer. This progressive slow oxidation of iron corresponds to the dissolution of iron into the electrolyte which remains at or below saturation level at the operating temperature, the operating temperature being maintained sufficiently low to limit the contamination of the product aluminium to an acceptable level, and the electrolyte being circulated to maintain a sufficient concentration of alumina in the anode cathode gap.
Owner:NGUYEN THINH T +2
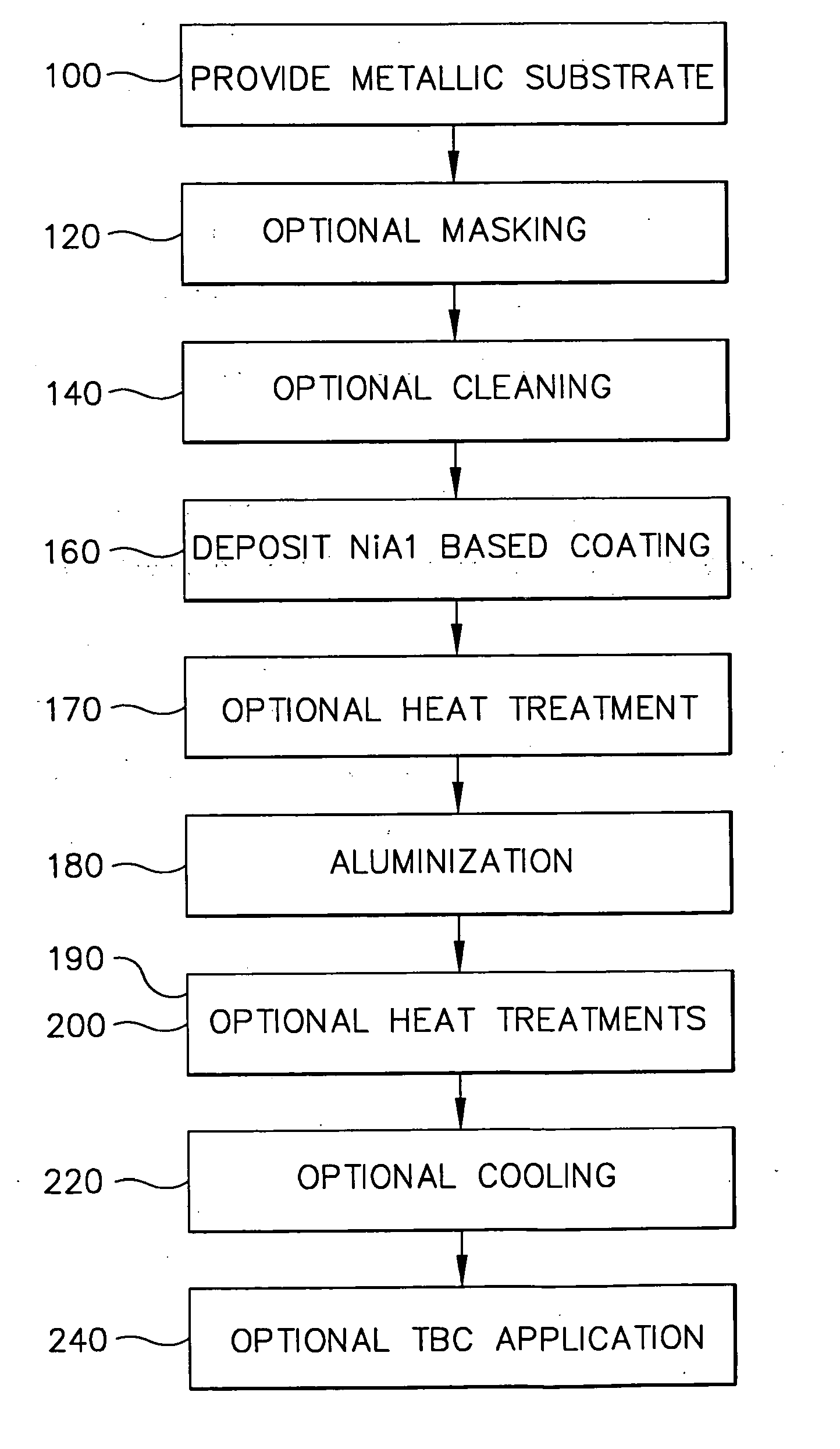
Bond coat with low deposited aluminum level and method therefore
A method for applying a NiAl based bond coat and a diffusion aluminide coating to a metal substrate comprises, in part, coating a portion of the external surface of the superalloy substrate, by physical vapor deposition with a layer of a NiAl based metal alloy, wherein the deposited NiAl based metal alloy includes a controlled amount of about 6 to 25 weight percent aluminum, wherein the deposited aluminum level of the NiAl based metal alloy is controlled to be about 50-100% of its final level after aluminizing to form a coated external portion; and subsequently, simultaneously aluminizing the coated external portion and a different surface of the superalloy substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Meltless preparation of martensitic steel articles having thermophysically melt incompatible alloying elements
An article of iron base metal base metal alloyed with an alloying element is prepared by mixing a chemically reducible nonmetallic base-metal precursor compound of the iron base metal and a chemically reducible nonmetallic alloying-element precursor compound of an alloying element to form a compound mixture. The alloying element is preferably thermophysically melt incompatible with the iron base metal. The method further includes chemically reducing the compound mixture to a metallic alloy, without melting the metallic alloy, and thereafter consolidating the metallic alloy to produce a martensitic-composition consolidated metallic article, without melting the metallic alloy and without melting the consolidated metallic article.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrothermal organic electrode slurry for heater
ActiveCN101938859AMeet miniaturizationMeet thinnessHeating element materialsEpoxyLow temperature curing
The invention relates to an electrothermal organic electrode slurry for a heater. The slurry comprises the following main components in percentage by weight: 5-30% of epoxy modified high polymer, 2-6% of flame-retardant temperature-resistant high polymer, 3-6% of latent curing agent, 1-2% of latent curing promoter, 5-10% of silicon modified high polymer, 50-70% of superfine metal powder conductive filler, 1-3% of antioxidant assistant, 0-5% of base metal alloy powder conductive filler and a small amount of functional auxiliary phase. The invention solves the problem that the ordinary slurry is difficult to realize thin type, light type or special type, has the characteristics of low-temperature curing and high-temperature use, ensures direct printing or spraying and satisfies the technical development requirements of small type, thin type, light type (shape and application) and special type of the electric heater.
Owner:西安宏星电子浆料科技股份有限公司
Metallurgical slag coatings for refractory substrates
InactiveUS20160186290A1Good treatment effectImprove filtration efficiencyBlast furnace detailsCharge manipulationParticulatesMetallurgical slag
Coatings comprising metallurgical slag are applied to refractory substrates having molten metal-contacting surfaces to create a chemically active and viscous surface that dramatically increases the ability of the treated substrate to remove slag, dross and other inclusions from a base metal alloy as it passes through or contacts the substrate. The refractory substrates include molten metal filters used by foundries and metal casters such as reticulated ceramic foam, cellular / honeycomb, silica mesh, and others that rely on their physical or sieving ability to remove particulate impurities from the base alloy being cast. The chemically active surfaces significantly increase filtration efficiency through a treatment process tailored to the specific chemistry of the alloy being filtered, such as ferrous metals that include iron, steel and more. Other refractory substrates such as aluminum oxide, magnesium oxide, zirconium oxide, aluminum silicate, silicon carbide (as common with reticulated ceramic foam filters) and the like may also include the coatings.
Owner:COMANCHE TECH
Method for preparing aluminum-base metallic alloy articles without melting
InactiveUS6926755B2Inhibition formationImprove propertiesMachines/enginesWind motorsBase metal alloyMetal
An article of aluminum base-metal alloyed with an alloying element is prepared by mixing a chemically reducible nonmetallic base-metal precursor compound of the aluminum base-metal and a chemically reducible nonmetallic alloying-element precursor compound of an alloying element to form a precursor compound mixture. The alloying element may be, but is not necessarily, thermophysically melt incompatible with the aluminum base metal. The method further includes chemically reducing the precursor compound mixture to a metallic alloy, without melting the metallic alloy, and thereafter consolidating the metallic alloy to produce a consolidated metallic article, without melting the metallic alloy and without melting the consolidated metallic article.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Orthopaedic implants fabricated from amorphous or partially amorphous calcium-based metal alloys
InactiveUS20070166349A1Additive manufacturing apparatusBone implantArticular surfacesBase metal alloy
Orthopaedic implants are formed using processes whereby a metal alloy is cooled at a rate rapid enough that an amorphous or partially amorphous structure is retained. In the preferred embodiment, the metal alloy is a calcium-based metal alloy. The fabrication process may include die-casting or additive manufacturing process of the type wherein material increments are consolidated in accordance with the description without melting the material in bulk. Such processes include ultrasonic consolidation, electrical resistance consolidation, and frictional consolidation. The material increments are provided in the form of sheets, elongated tapes, filaments, dots or droplets. A preferred method includes a casting process to produce an initial form having an outer surface followed by an additive manufacturing process used to build up at least a portion of the outer surface. For example, the portion may include an intramedullary stem, bone-ingrowth surface, or articulating surface.
Owner:SOLLDICA
Coatings for Refractory Substrates
ActiveUS20110283836A1Good treatment effectImprove filtration efficiencyFurnace componentsBlast furnace detailsParticulatesFoundry
A temperature-specific compound applied to refractory substrates having molten metal-contacting surfaces creates a chemically active and viscous surface that dramatically increases the ability of the treated substrate to remove slag, dross and other inclusions from a base metal alloy as it passes through or contacts the substrate. The refractory substrates include molten metal filters used by foundries and metal casters such as reticulated ceramic foam, cellular / honeycomb, silica mesh, and others that rely on their physical or sieving ability to remove particulate impurities from the base alloy being cast. The chemically active surfaces significantly increase filtration efficiency through a treatment process tailored to the specific chemistry of the alloy being filtered, such as ferrous metals that include iron, steel and more. Other refractory substrates such as aluminum oxide, magnesium oxide, zirconium oxide, aluminum silicate, silicon carbide (as common with reticulated ceramic foam filters) and the like may also include the coatings.
Owner:COMANCHE TECH
Energy-saving intermittent pulse-feeding technology of closed submerged arc furnace
The invention relates to an energy-saving intermittent pulse-feeding technology of a closed submerged arc furnace. The feeding method of the closed submerged arc furnace is a smelting intermittent pulse-feeding mode of the closed (semi-closed) submerged arc furnace, which is proposed after various smelting principles and a plurality of special factors are deeply researched and can be applied to the smelting of calcium carbide, yellow phosphorus, silicon-based metal alloys (ferrosilicon, calcium silicon, barium ferrosilicon, metallic silicon, and the like), manganese-based metal alloys (ferromanganese, silicon manganese, metallic manganese, and the like), nickel-based metal alloys, chrome-based metal alloys, tammite, ferrotitanium, and the like or other smelting. The technology enables a domestic closed furnace using general raw materials to lower the power ton consumption by 3-10 percent and increase the yield by 2-20 percent and benefit the safe and stable operation of subsequent environment-friendly dedusting equipment and the implementation of an unmanned control technology of submerged arc furnaces, thereby having a profound popularization meaning and development potential on various large-scale closed submerged arc furnaces over 25*10<6> VA.
Owner:巴涌
Noble metal-base metal alloy catalyst, evaluation of such catalyst, and method of producing such catalyst
InactiveUS7060385B2Simple and accurate of performanceFinal product manufactureFuel cell auxillariesComposite numberCatalytic function
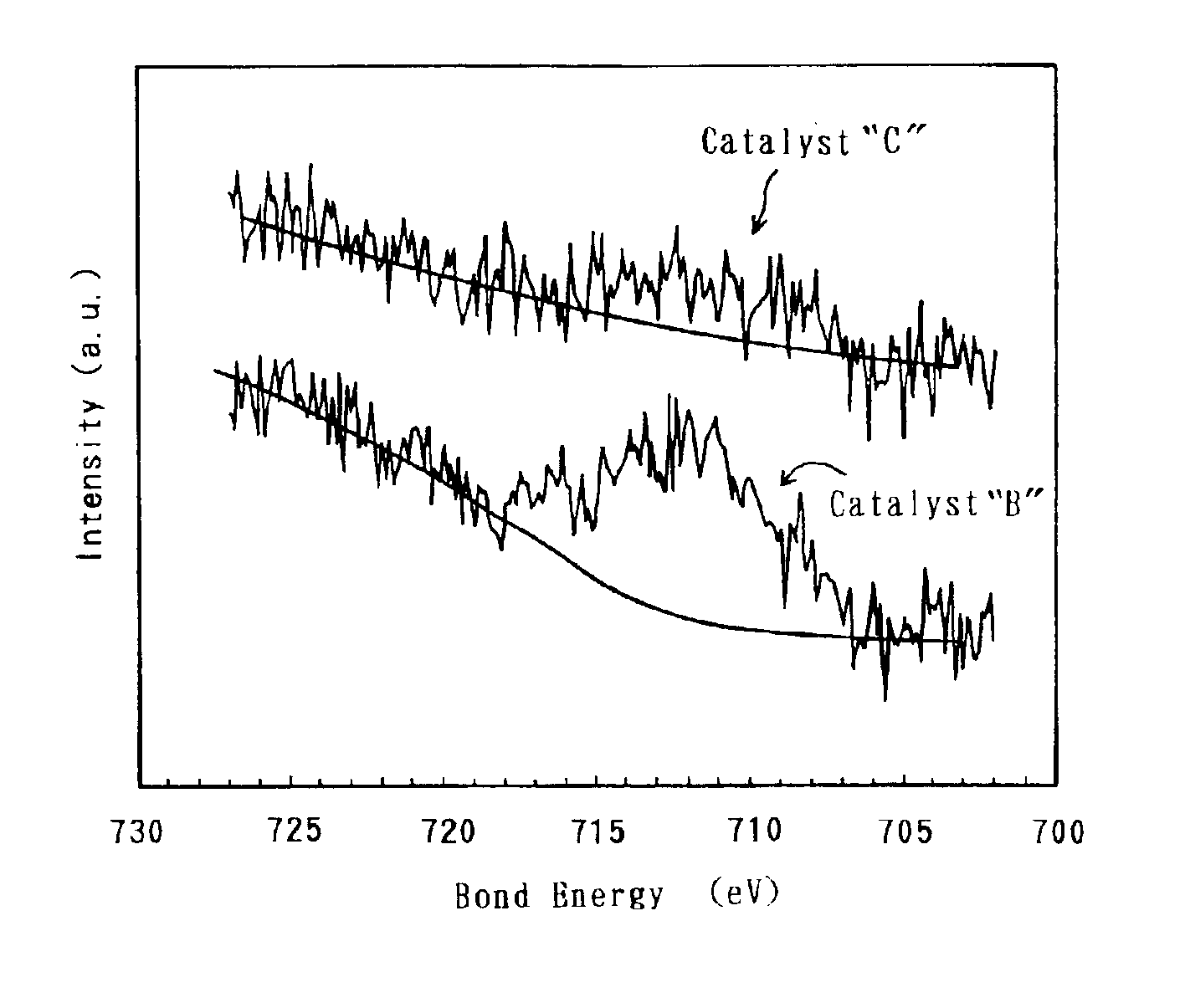
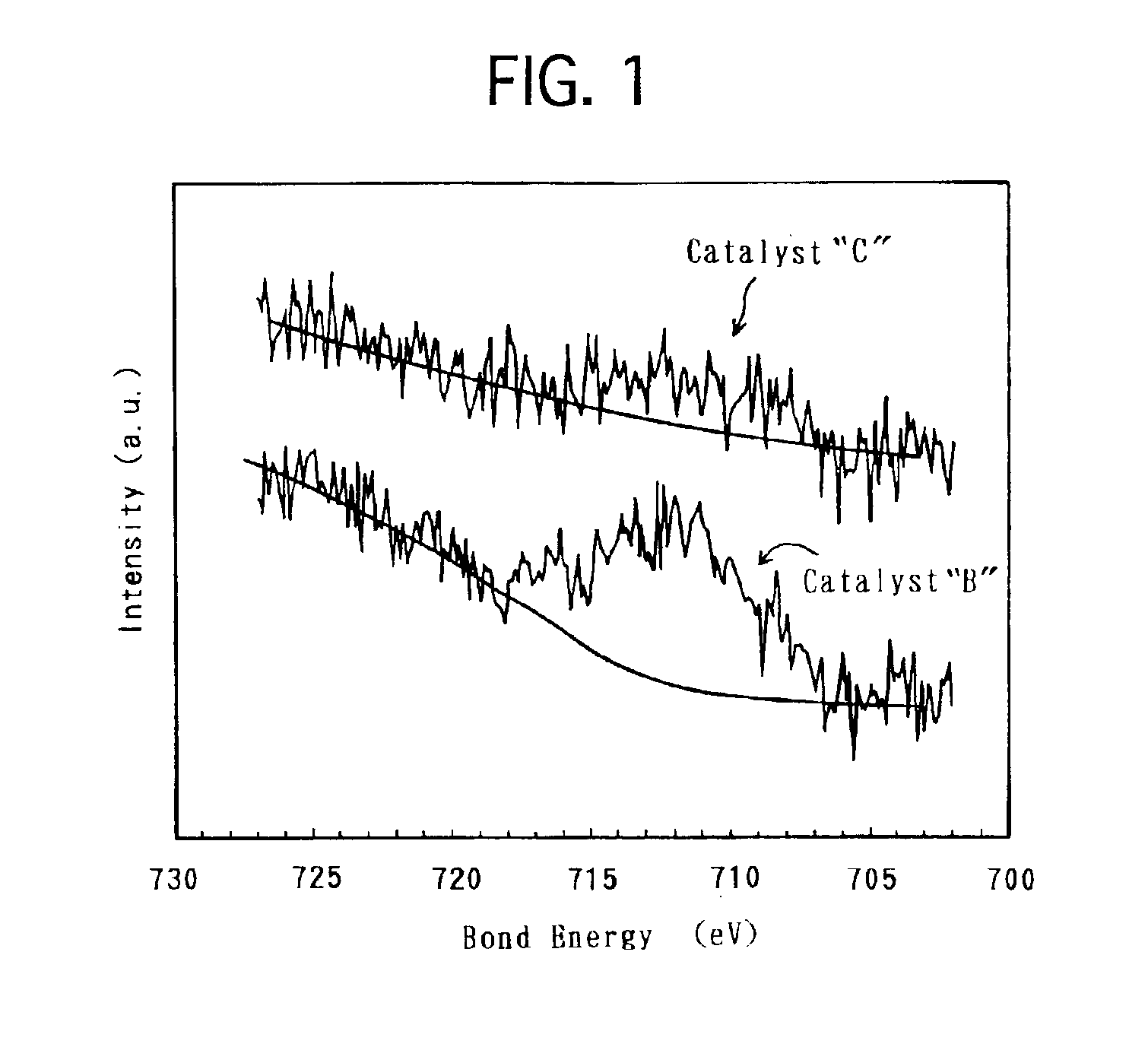
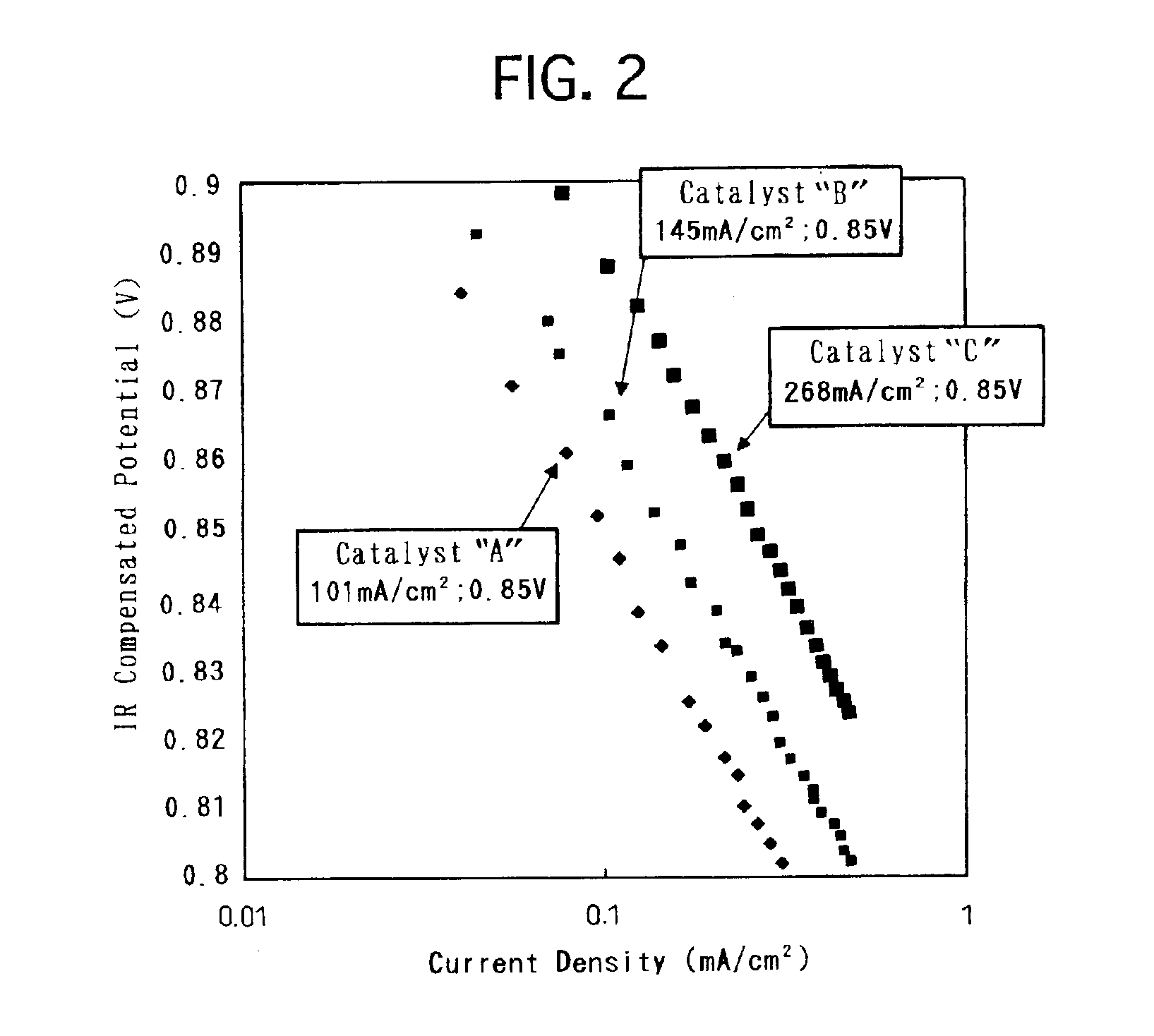
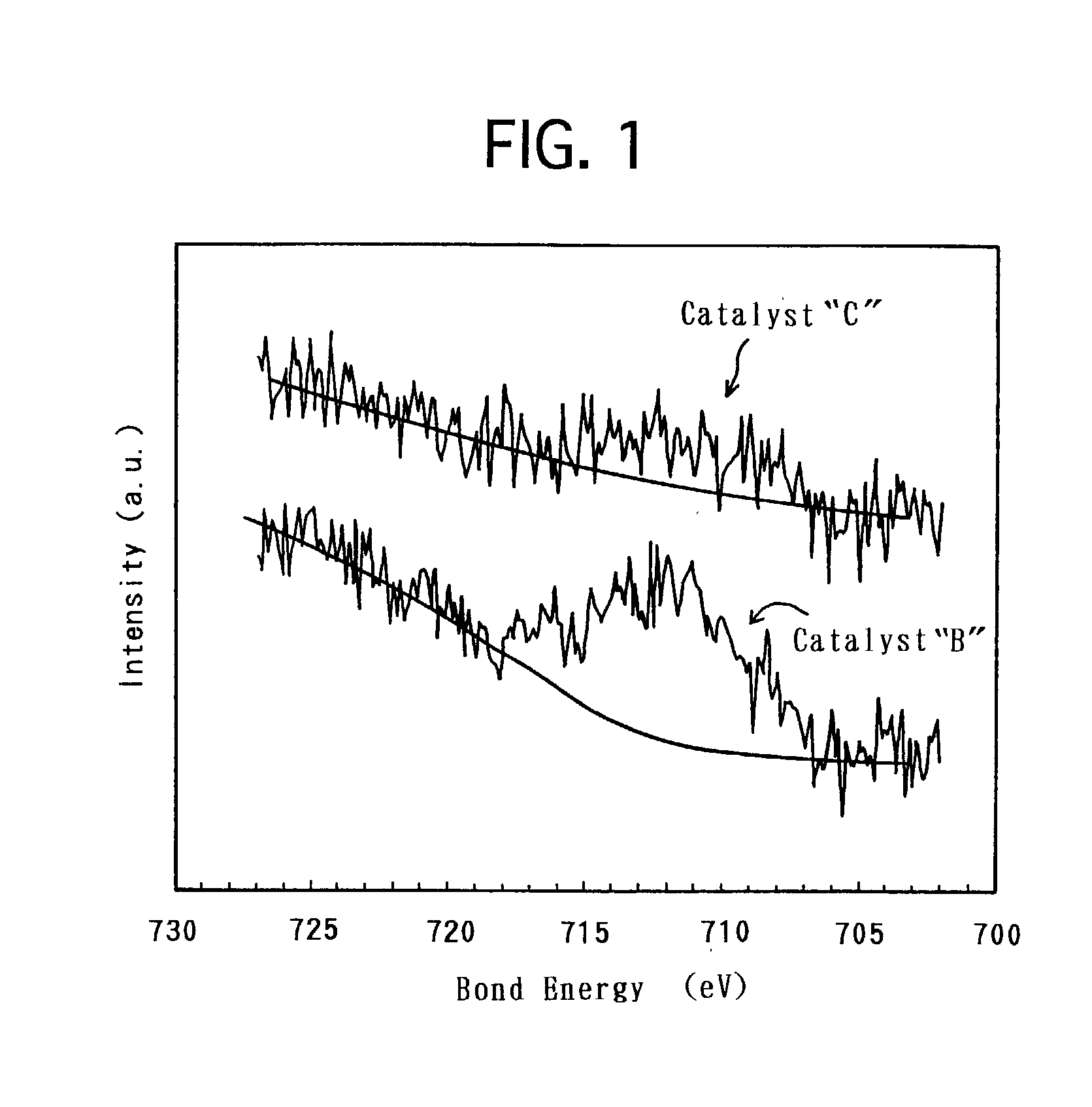
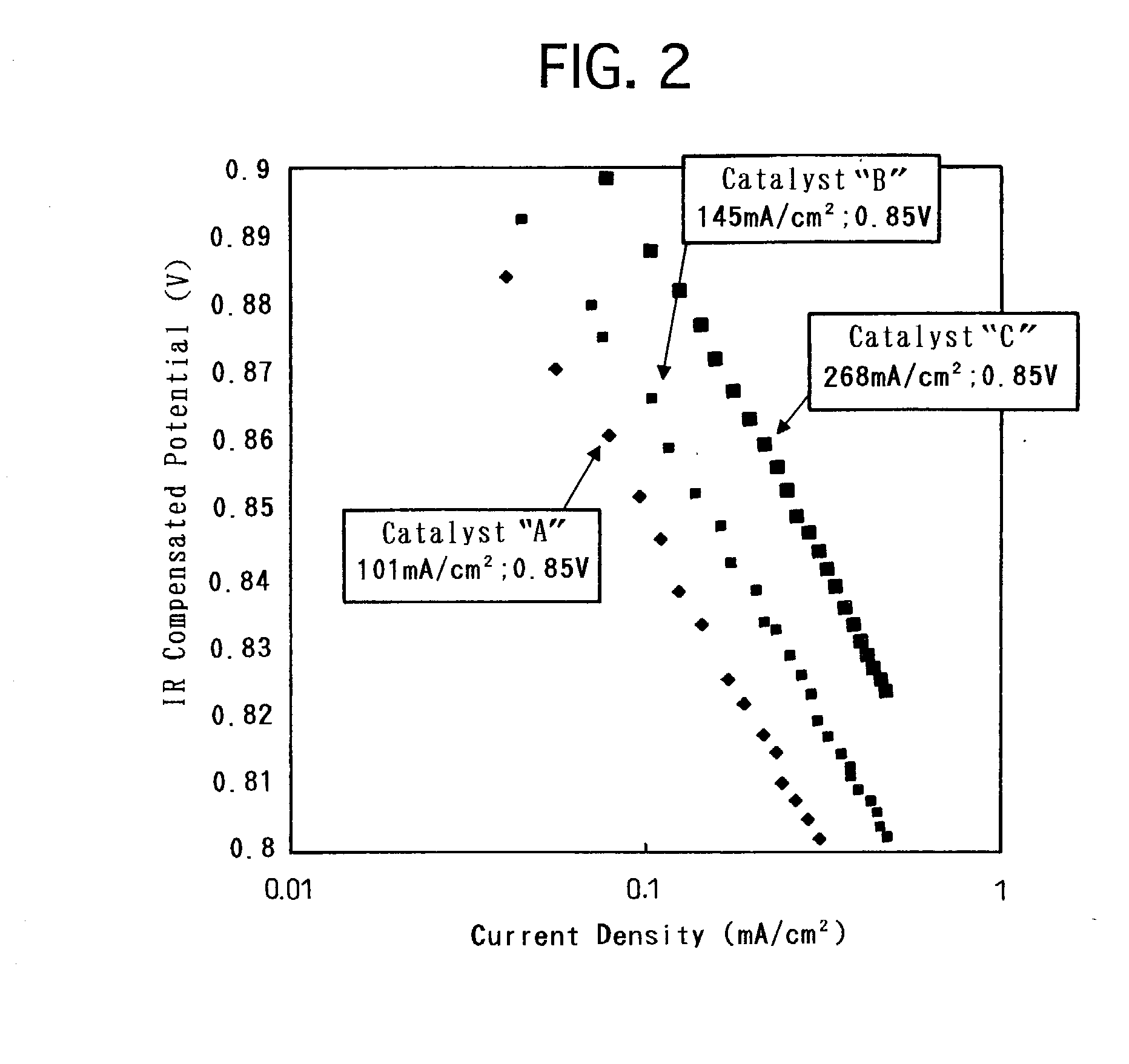
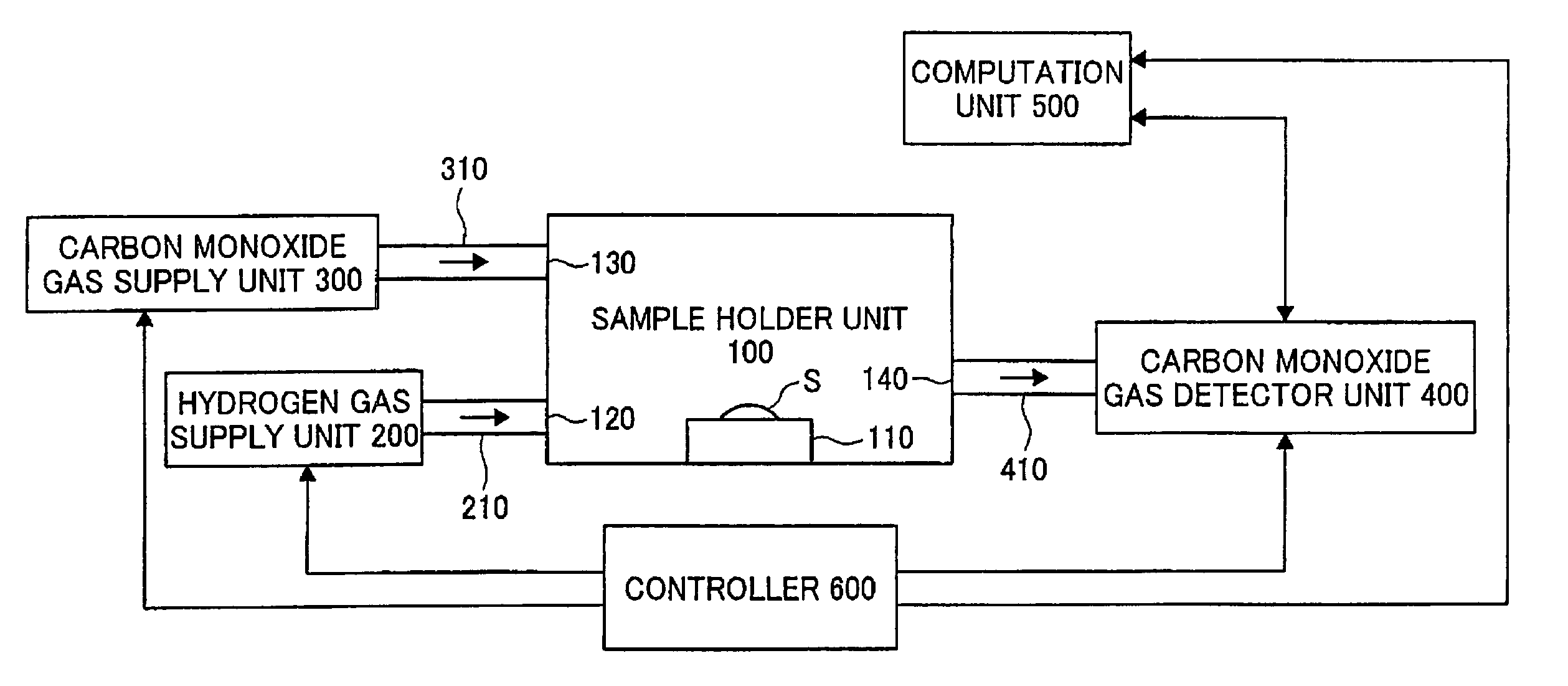
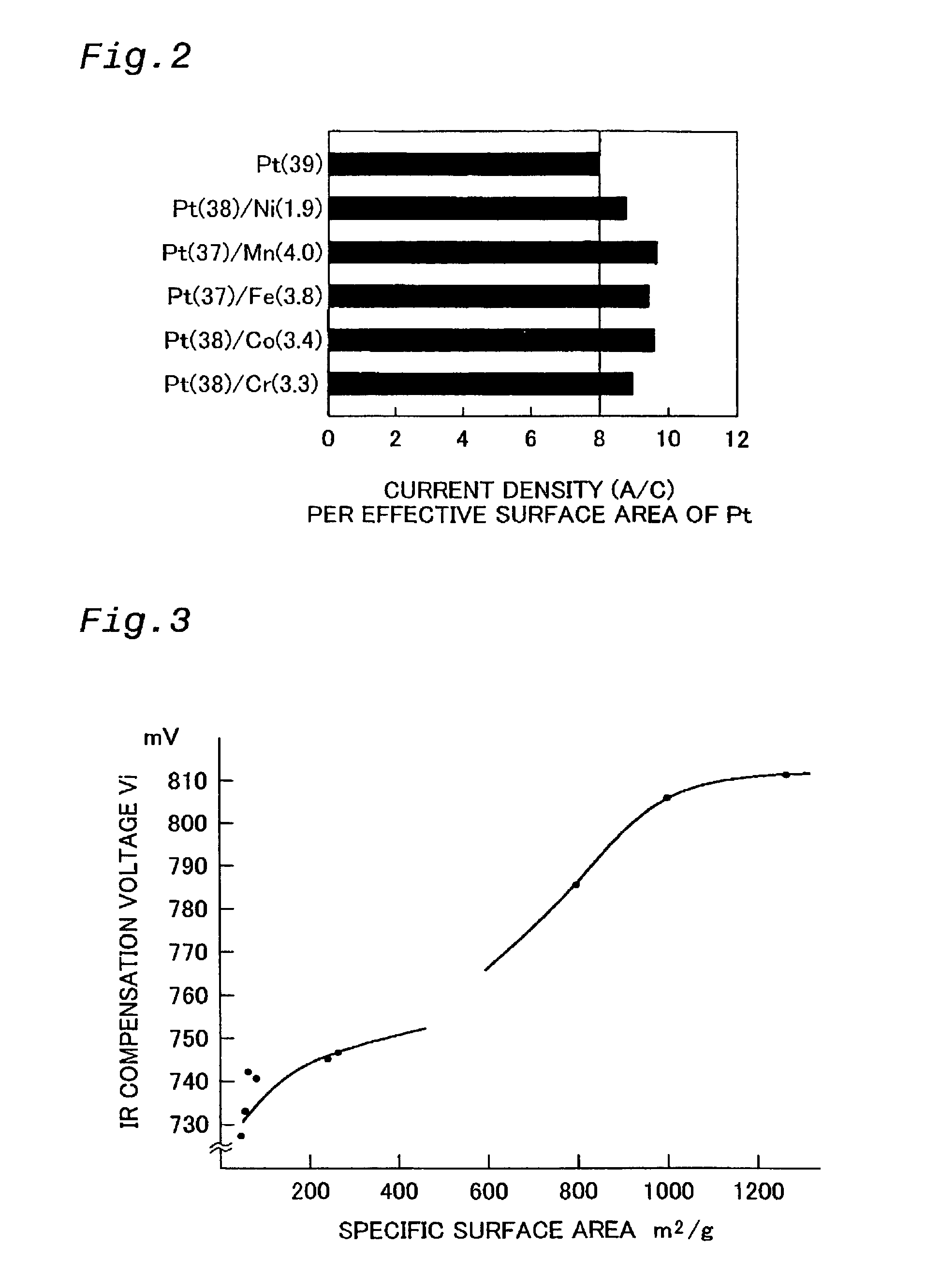
The technique of the present invention attains simple and accurate evaluation of the performance of a fuel cell and enables produce of a high-performance electrode catalyst and a high-performance fuel cell. The procedure makes platinum, a noble metal, and iron, a base metal, carried on carbon having a large specific surface area, and heats up the carbon with platinum and iron to a specific temperature to reduce iron. A resulting platinum-iron alloy electrode catalyst exerts excellent catalytic functions. A fuel cell using this electrode catalyst has a high IR compensation voltage. The quantity of carbon monoxide adsorbed by this novel electrode catalyst is not less than 14 Ncc per one gram of platinum. The atomic number ratio of iron (Fe) to platinum (Pt) in the catalyst is not lower than 0.14 by EDX analysis, and the ratio of the binding number of Pt atom with Fe atom to the total binding number relating to Pt atom is not lower than 0.10 by EXAFS analysis. Each electrode catalyst produced is evaluated by measurement of these data. The fuel cell including the electrode catalyst having the favorable result of evaluation ensures the desired performances.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Zirconium-based alloys, nuclear fuel rods and nuclear reactors including such alloys, and related methods
InactiveUS20120201341A1Reduce penetrationOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreSolubility
Zirconium-based metal alloy compositions comprise zirconium, a first additive in which the permeability of hydrogen decreases with increasing temperatures at least over a temperature range extending from 350° C. to 750° C., and a second additive having a solubility in zirconium over the temperature range extending from 350° C. to 750° C. At least one of a solubility of the first additive in the second additive over the temperature range extending from 350° C. to 750° C. and a solubility of the second additive in the first additive over the temperature range extending from 350° C. to 750° C. is higher than the solubility of the second additive in zirconium over the temperature range extending from 350° C. to 750° C. Nuclear fuel rods include a cladding material comprising such metal alloy compositions, and nuclear reactors include such fuel rods. Methods are used to fabricate such zirconium-based metal alloy compositions.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
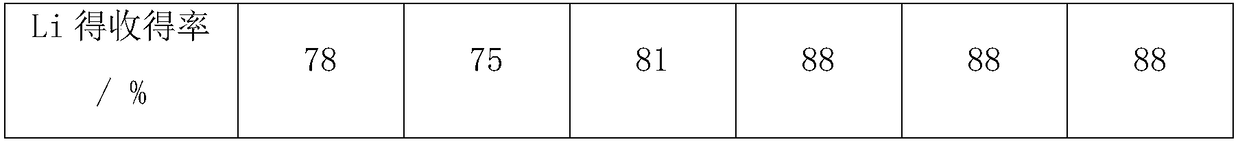
Ultra-light high-modulus high-strength casting aluminum-lithium matrix composite and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an ultra-light high-modulus high-strength casting aluminum-lithium matrix composite and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum-lithium matrix composite comprises a matrix alloy and a strengthening phase, the matrix alloy comprises the following elements of, by mass, 2.5%-3.5% of Li, 1%-2.5 % of Cu, 0.4%-0.5% Mg, 0.15%-0.2% of Sc, 0.15%-0.2% Zr, 0-0.2% of Cd, less than 0.2% of the total content of impurity elements and the balance Al; and the strengthening phase is TiB2. The preparation method comprises the steps that Ti B2 / Al base metal alloy is prepared by using in-situ synthesized reaction; and then the TiB2 / Al base metal alloy, pure aluminum and Al-Cu, Al-Li and other intermediate alloys are smelted to obtain a composite, and after specific solid solution andaging treatment are carried out, the ultra-light high-modulus high-strength casting aluminum-lithium matrix composite is obtained. The ultra-light high-modulus high-strength casting aluminum-lithium matrix composite has higher strength and elastic modulus and lower density, and has lower cost meanwhile.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing a metallic article having an other additive constituent, without any melting
InactiveUS7416697B2Quality improvementAvoid problemsTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusAdditive ingredientBase metal alloy
A method for preparing an article of a base metal alloyed with an alloying element includes the steps of preparing a compound mixture by the steps of providing a chemically reducible nonmetallic base-metal precursor compound of a base metal, providing a chemically reducible nonmetallic alloying-element precursor compound of an alloying element, and thereafter mixing the base-metal precursor compound and the alloying-element precursor compound to form a compound mixture. The compound mixture is thereafter reduced to a metallic alloy, without melting the metallic alloy. The step of preparing or the step of chemically reducing includes the step of adding an other additive constituent. The metallic alloy is thereafter consolidated to produce a consolidated metallic article, without melting the metallic alloy and without melting the consolidated metallic article.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Garbage truck body
InactiveCN103496538AIsolate Corrosion DamageExtend the life of noodlesRefuse vehiclesTruckBase metal alloy
The invention discloses a garbage truck body which comprises a garbage truck body itself. An anti-corrosion layer is arranged on the inner surface of the garbage truck body. An insulating layer is arranged on the outer surface of the anti-corrosion layer and is smaller than the garbage truck body itself in thickness. The anti-corrosion layer is made of aluminum-base metal alloy. The insulating layer is made of phenolic resin materials. According to the garbage truck body, the anti-corrosion layer is arranged on the inner surface of the garbage truck body, and the insulating layer is arrange outside the anti-corrosion layer so as to effectively insulate corrosion damage of collected garbage to the truck body itself, prolong the service life of a garbage truck, and reduce maintenance cost.
Owner:陈玉婷
Silica-based metal alloy film, case provided with same, electronic device and manufacture method
InactiveCN101619437AThe amorphous continuous structure hasGuaranteed normal transmissionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingColor changesBase metal alloy
The silicon content of the silica-based metal alloy film of the invention is 62-85% in terms of weight percent, the remaining weight percent is metals selected from clusters of aluminum, nickel, titanium, zinc or the combination of the metals. Furthermore, the silica-based metal alloy film is arranged on the case, e.g. case surface of the electronic device can be manufactured into an electronic device provided with the silica-based metal alloy film. The silica-based metal alloy film of the invention can not generate dampening to any electromagnetic signals, has metal glossiness and texture so as to add product values, and has the efficacies of unlikely color change, high defect-free yield, tiny difference in color among batches, good weather-proofing, strong adhesiveness, long storage time for semi-finished products and the like. In addition, the silica-based metal alloy film can be directly applied to inner die emitting technique of high yield to increase output, and can be manufactured by using direct current sprinkle plating method with low cost, thus reducing production cost.
Owner:CHINA STEEL
Process for forming side electrode of chip concave type electrode network resistor
ActiveCN101916636AIncrease dosageReduce manufacturing costResistors adapted for applying terminalsResistive material coatingSputteringAlloy
The invention discloses a process for forming a side electrode of a chip concave type electrode network resistor. The process comprises the following steps of: forming a side electrode conduction layer which is the upper part of the side electrode in the prior art in a hole filling way after printing a front electrode; forming a back electrode and a through hole wall sputtering layer in the way of film-shaped sputtering by mask sputtering; and completely covering the side electrode conduction layer with the through hole wall sputtering layer to form an effective side electrode. The process overcomes the defect of the prior art that the front electrode and the back electrode of an resistor can not be completely connected to form a conductive side electrode since the buckling of an insulation substrate is not consistent with a hole filling path, thereby greatly reducing hidden quality dangers; in addition, since a base metal alloy material is used for sputtering the sputtering layers and cost and consumption are both lower, the production cost is effectively lowered and the market competitiveness of the products is enhanced.
Owner:UNIROYAL ELECTRONICS IND
Variable melting point solders
The present invention relates to variable melting point solder formulations. The solder is comprised of at least one base metal or base metal alloy, preferably alloyed with at least one melting point depressant metal, such that the solidus point of the solder composition is reduced to an initial solidus temperature. Said base metal or base metal alloy, alloyed with at least one melting point depressant metal is mixed with at least one additive metal or additive metal alloy. When heated to a process temperature above said initial solidus temperature, a reaction occurs between the melting point depressant metal, and the additive metal, such that solidification occurs at the process temperature via the formation of intermetallic phases, effectively increasing the solidus of the base metal, and of the overall solder.
Owner:DYNAJOIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com