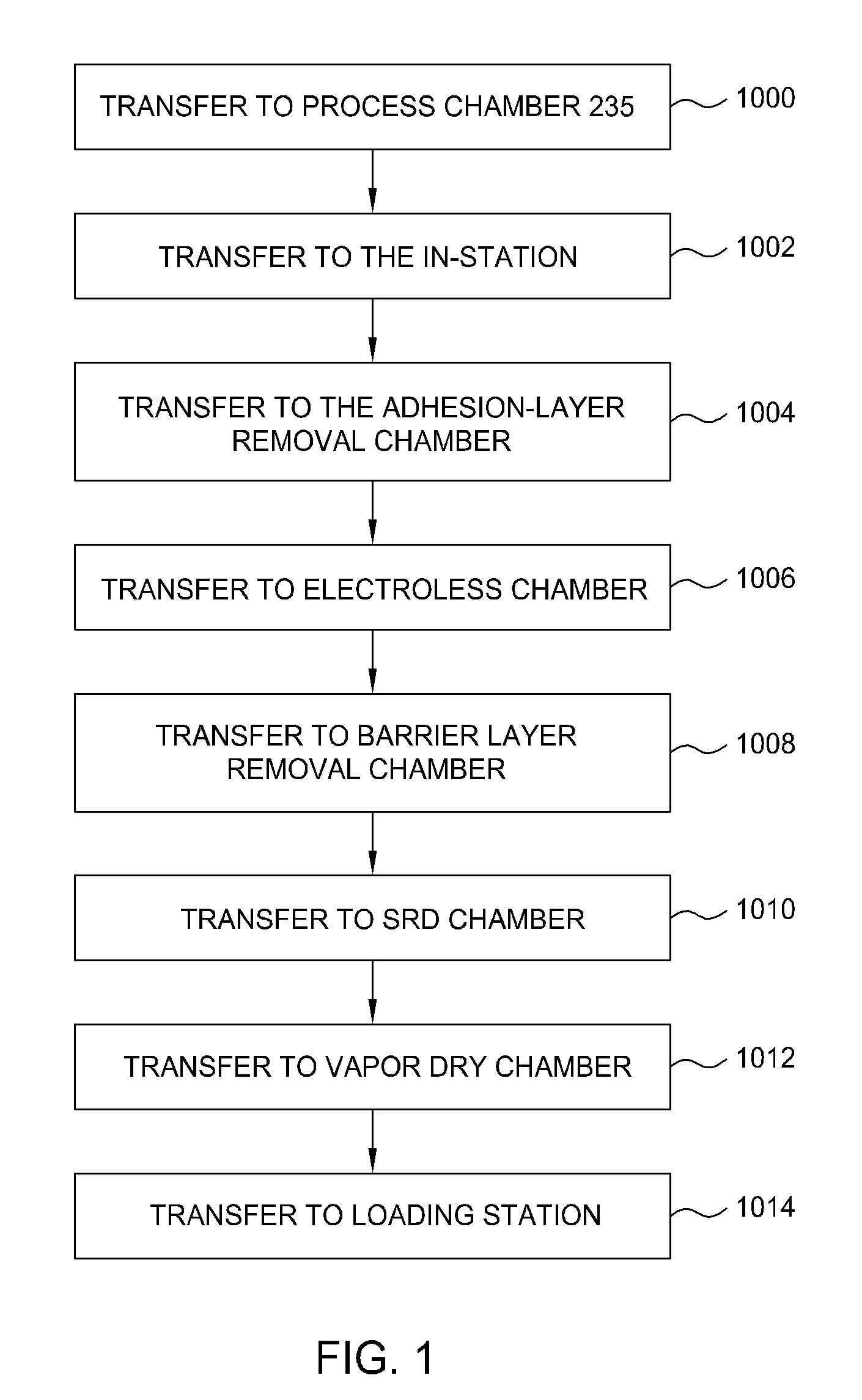
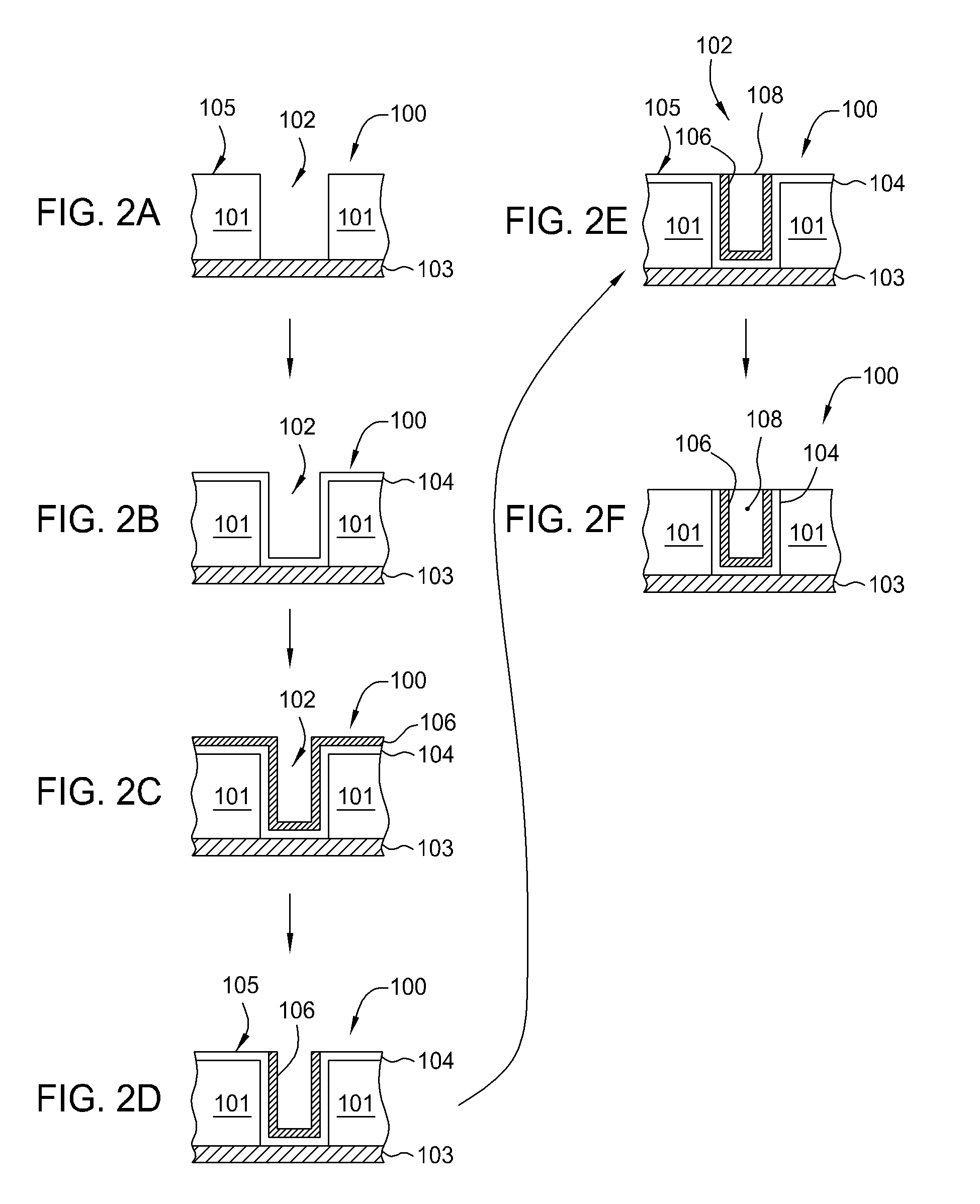
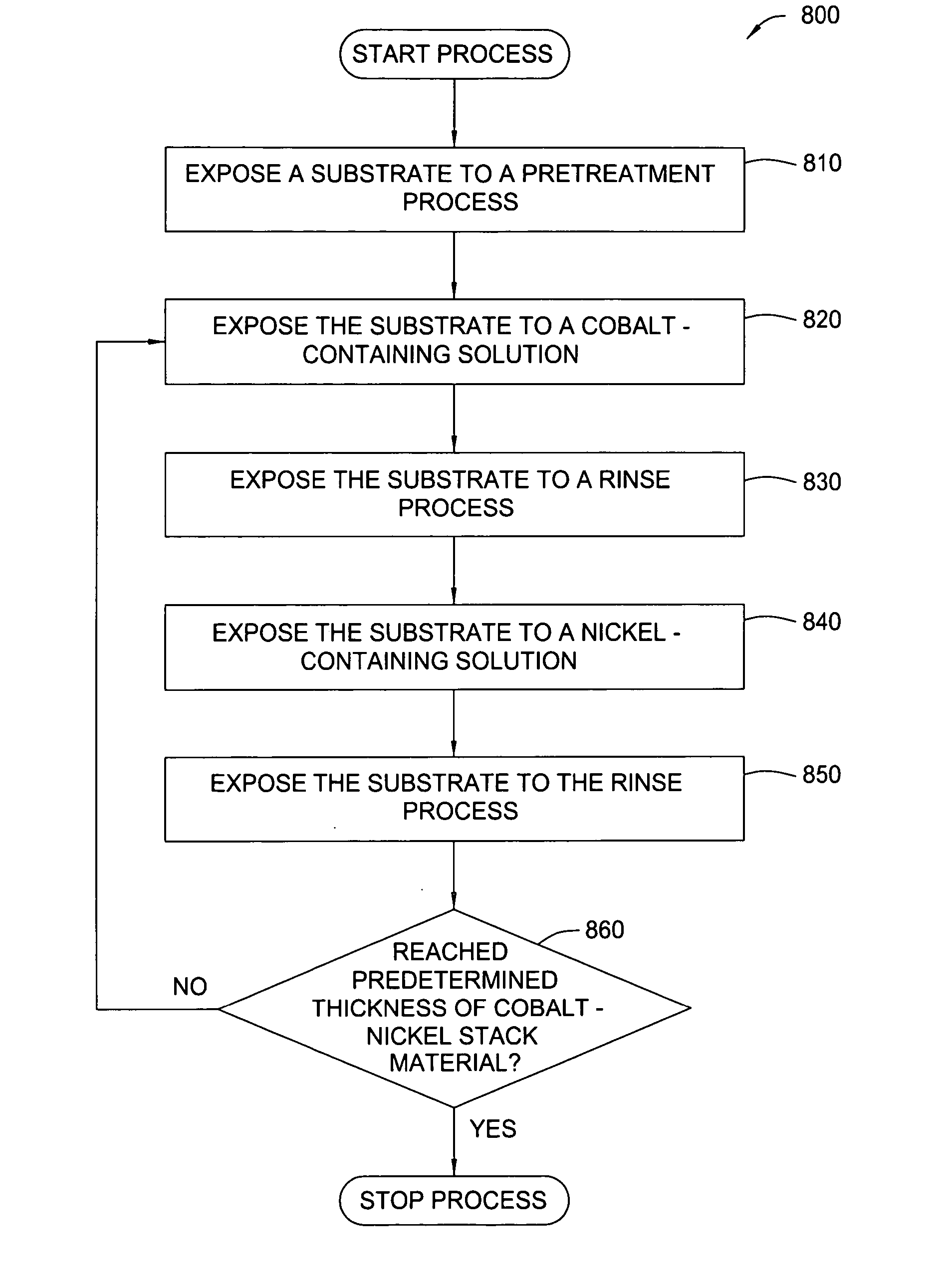
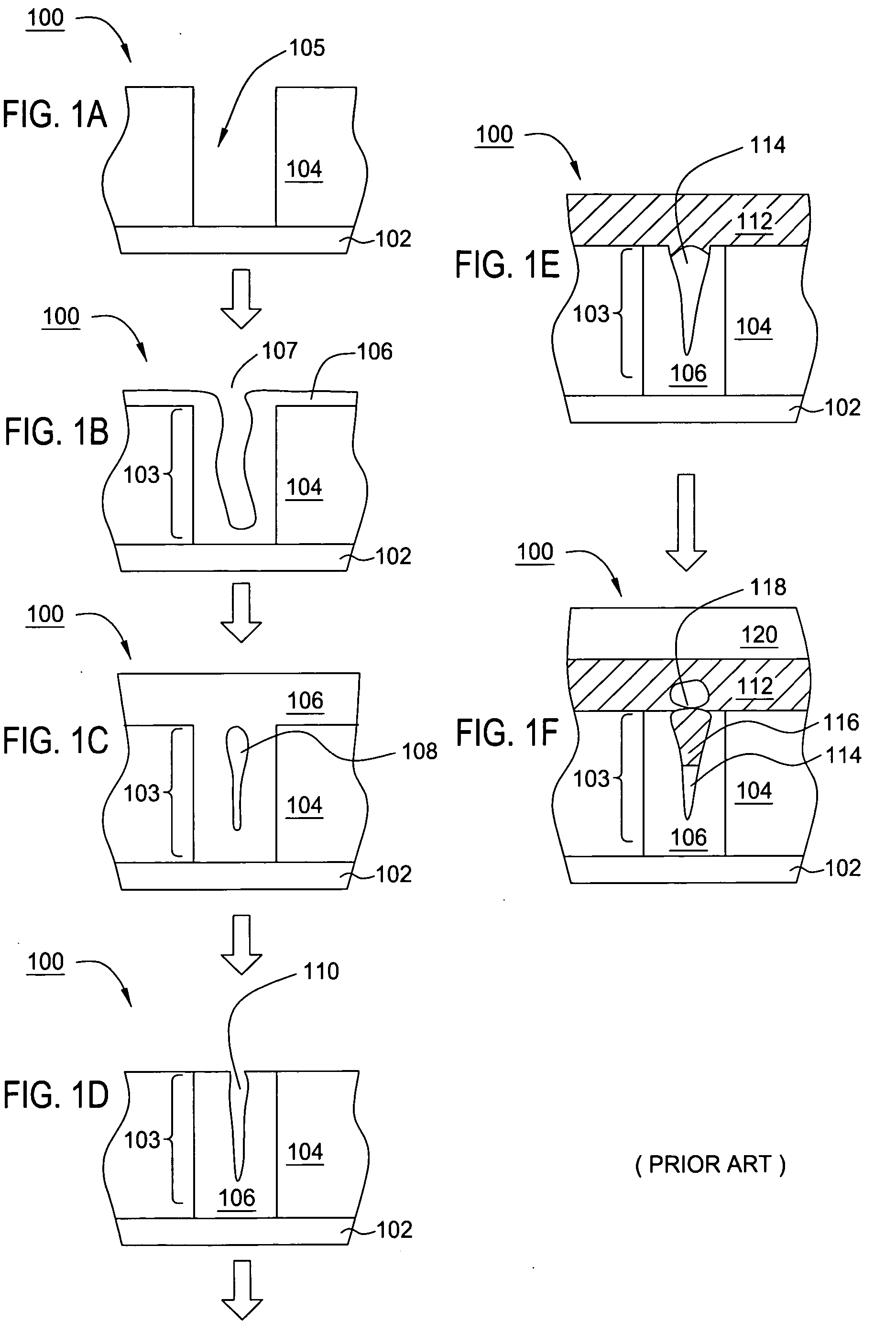
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2602results about "Resistive material coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
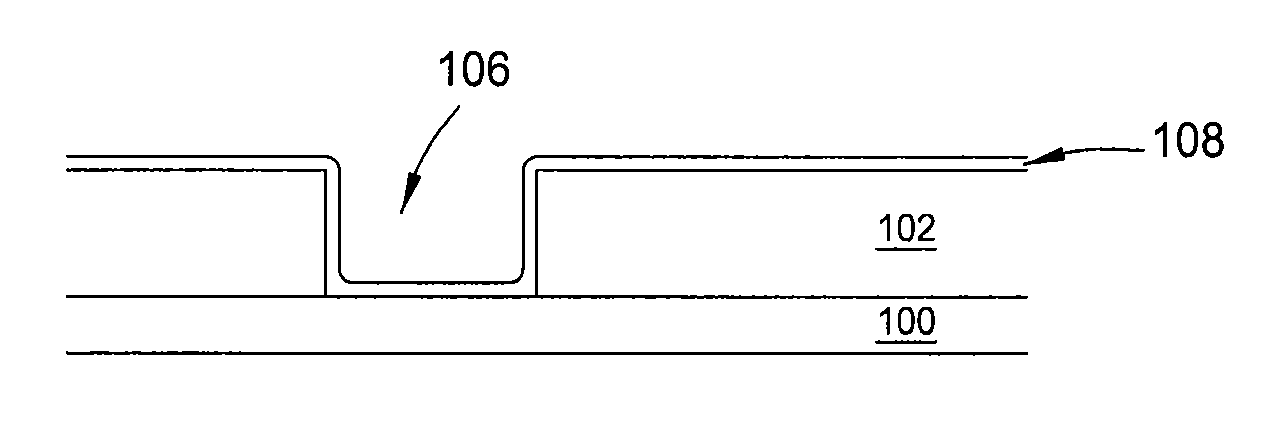
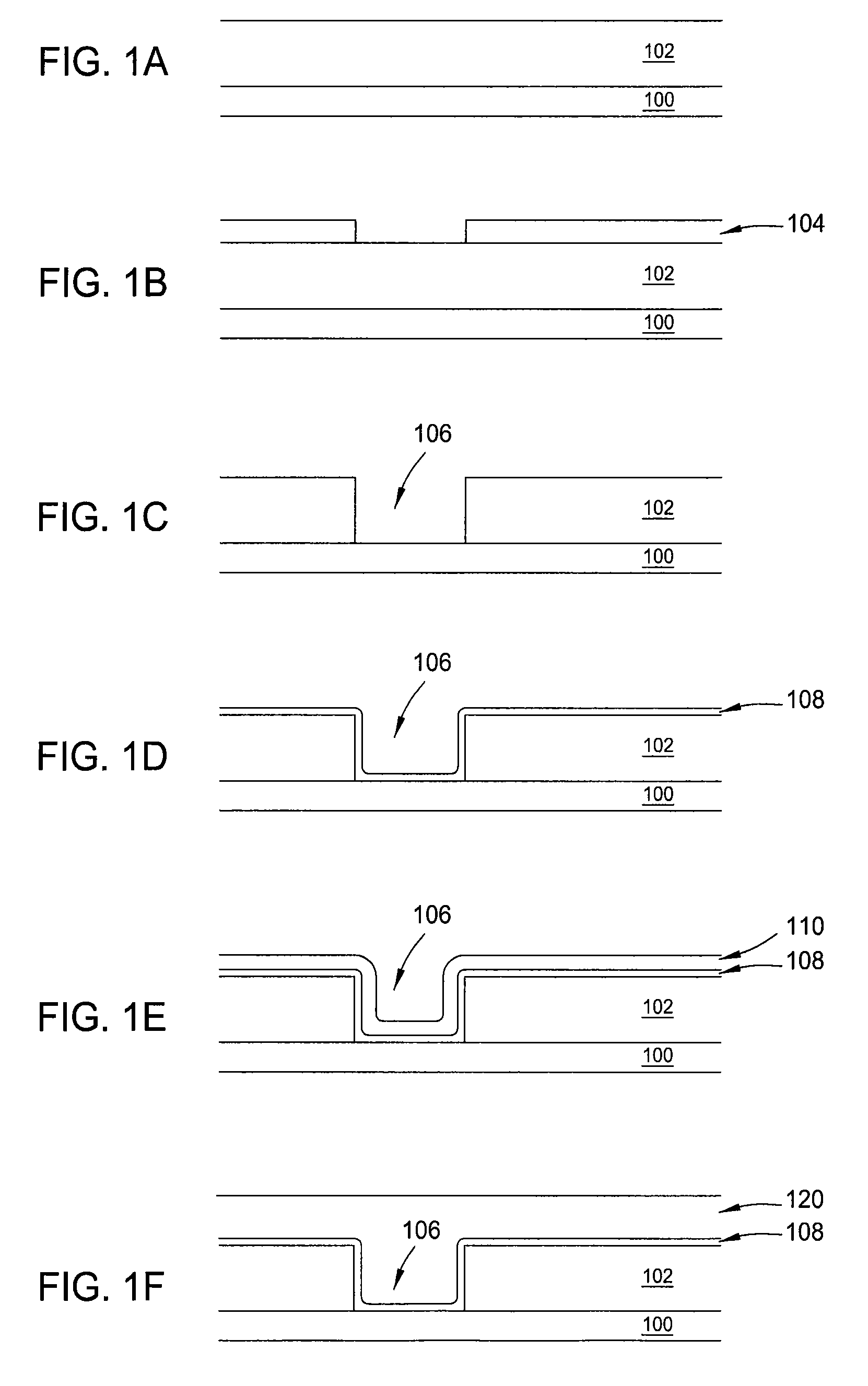
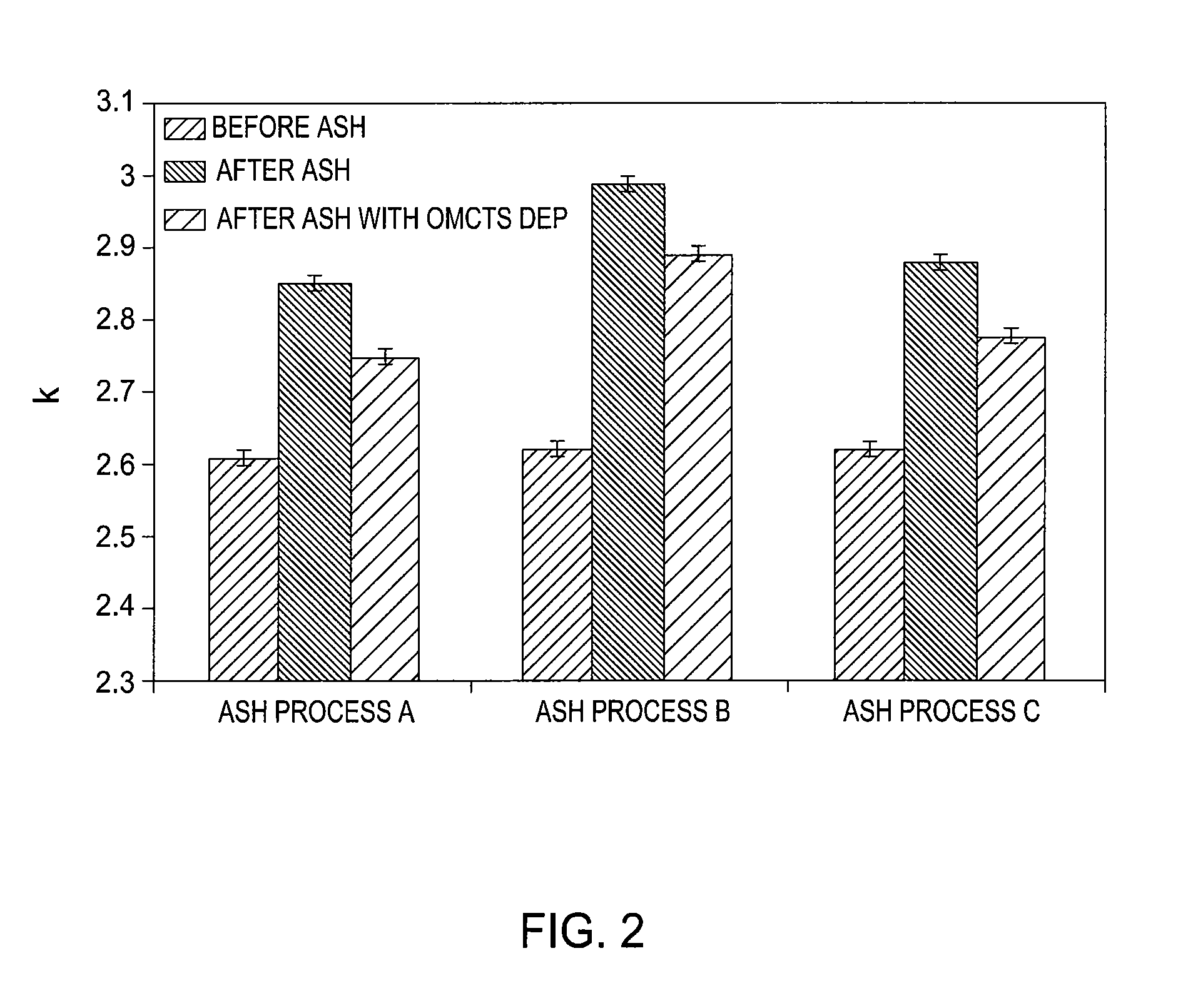
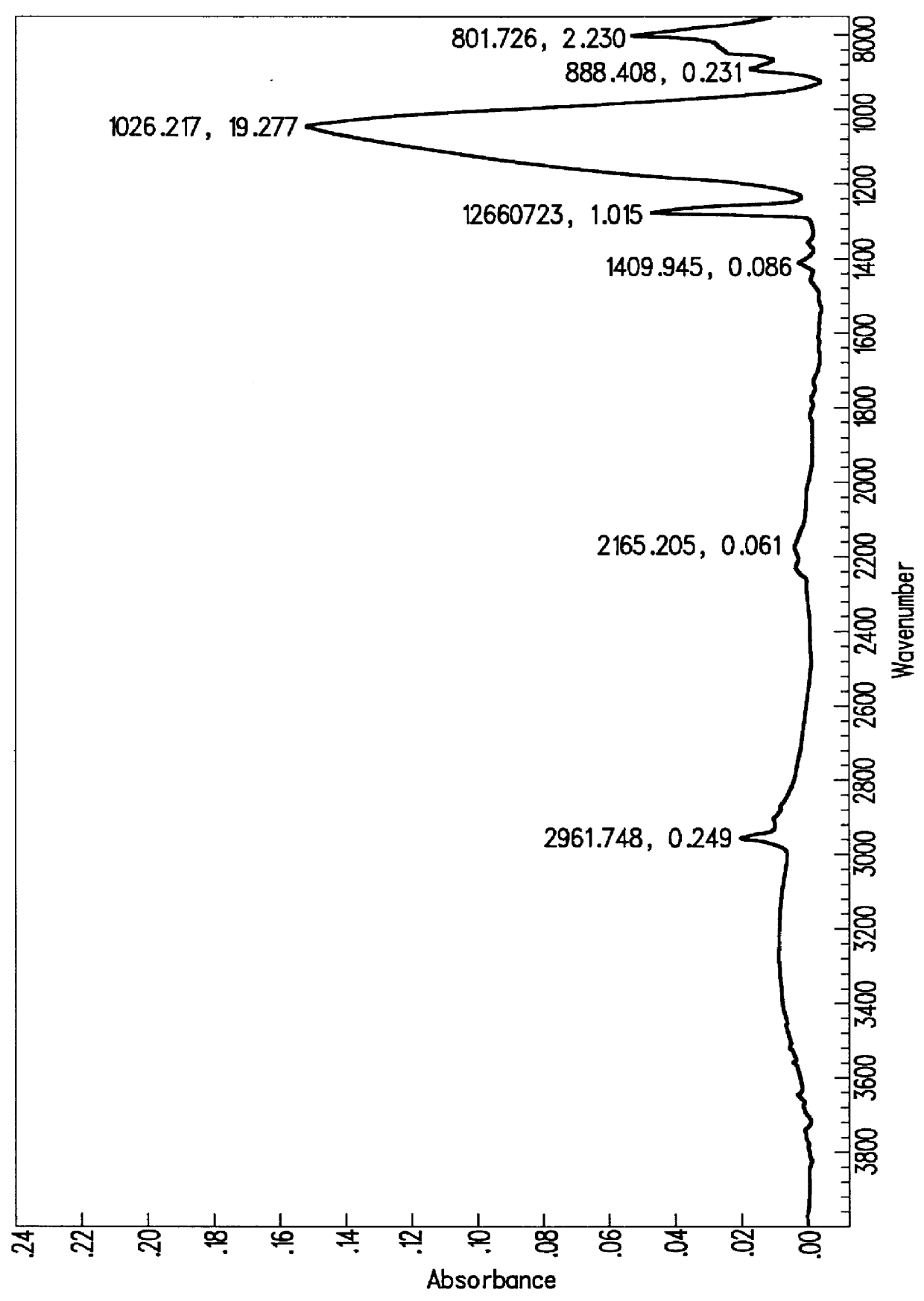
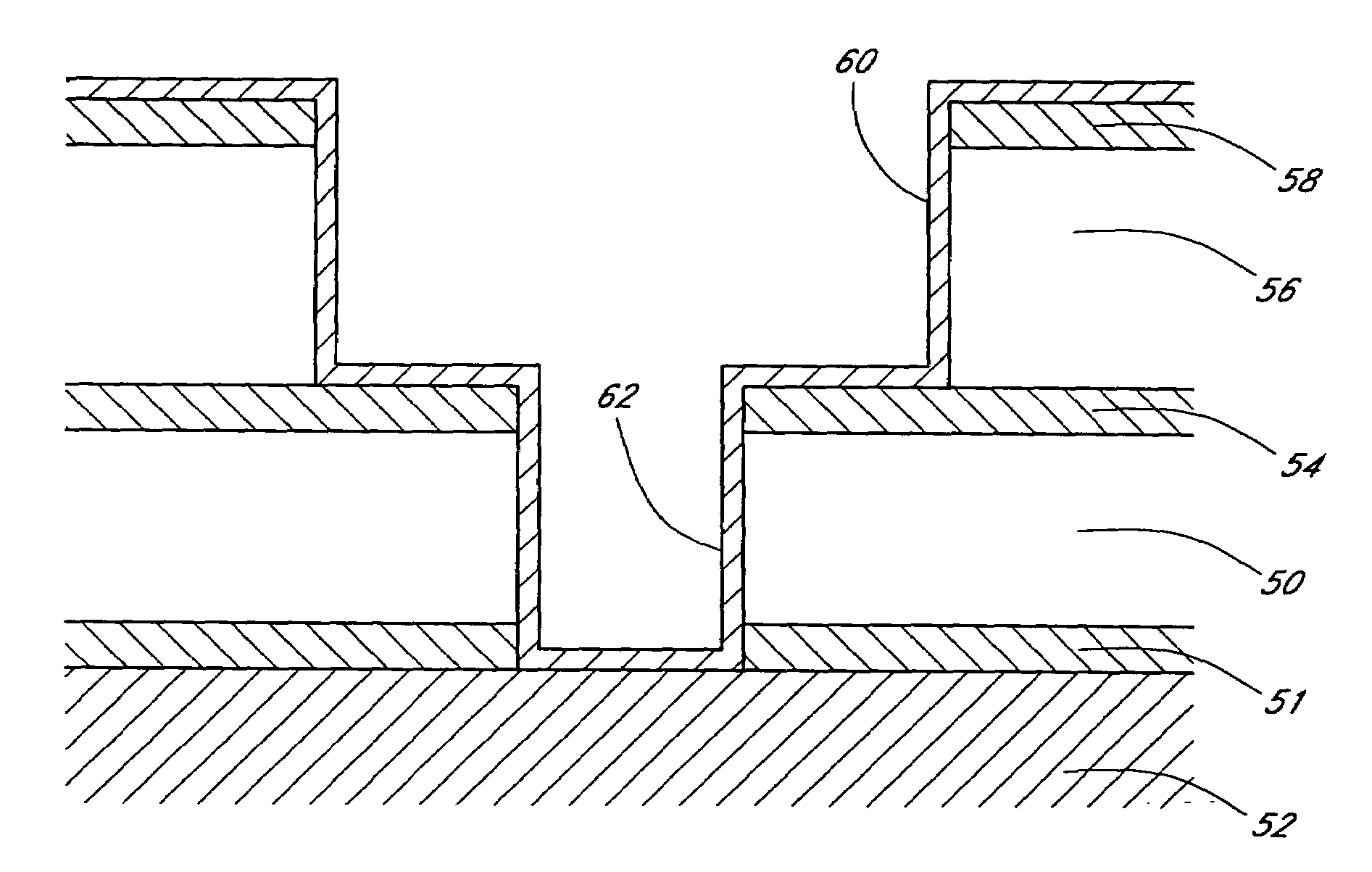
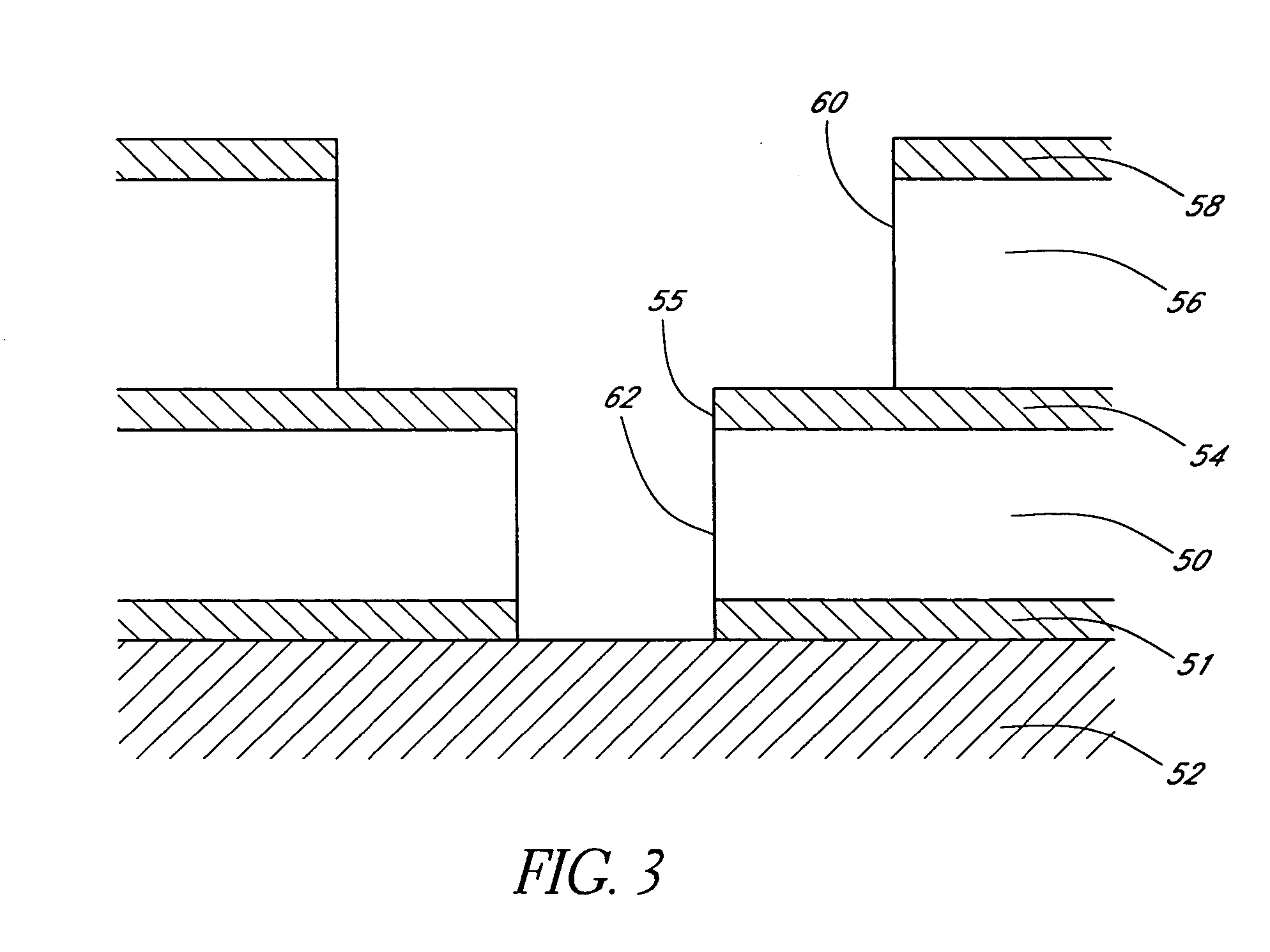
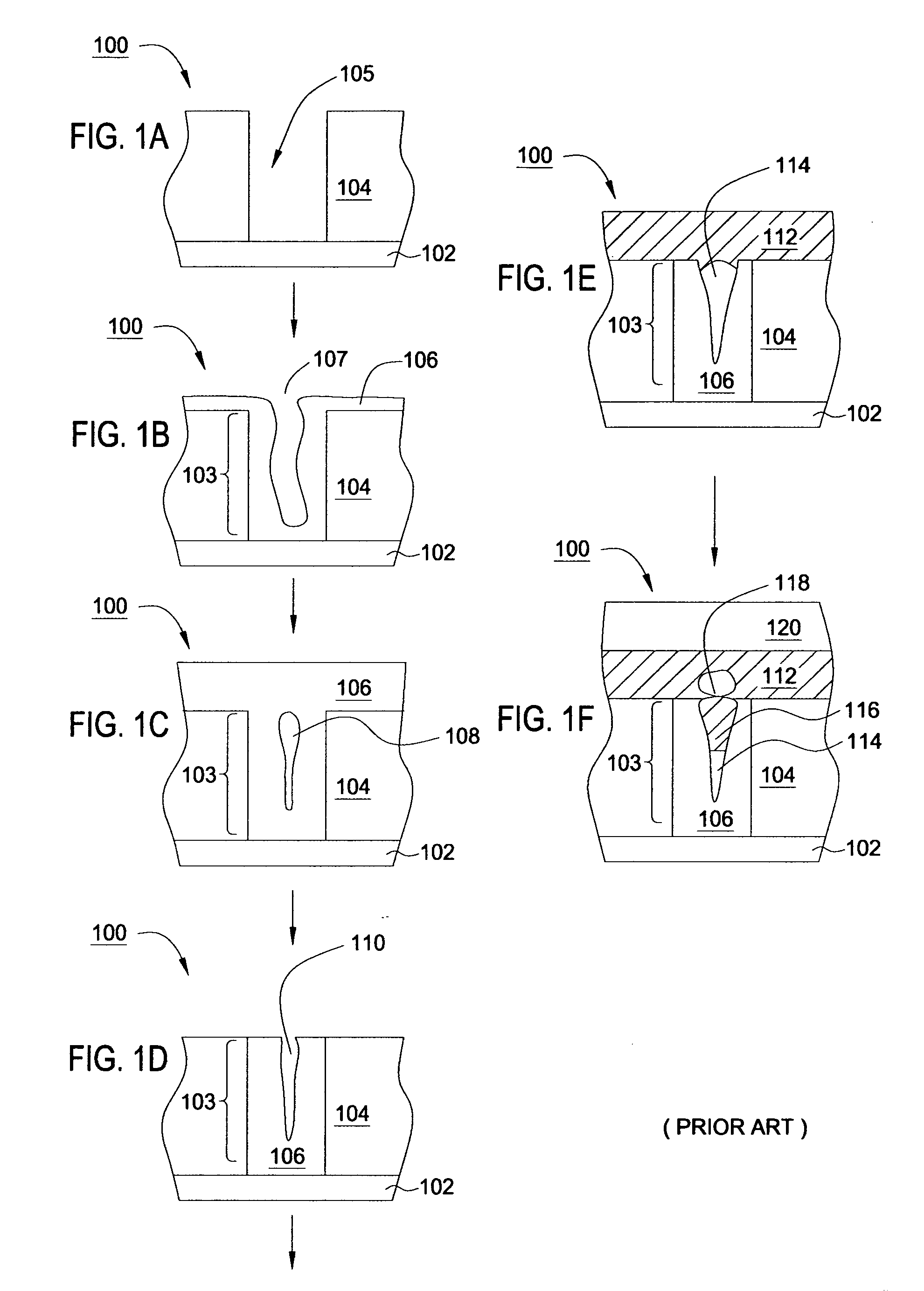
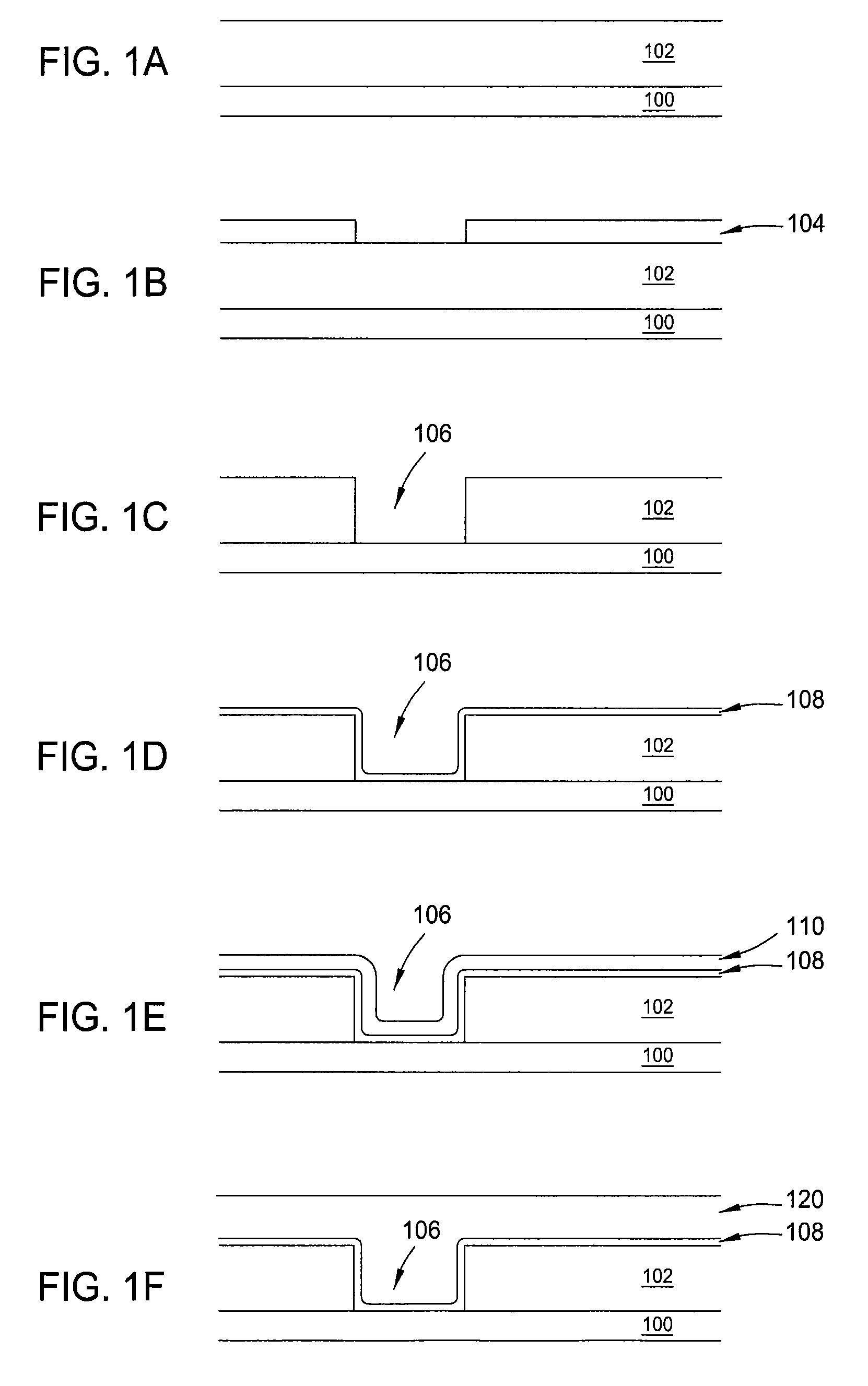
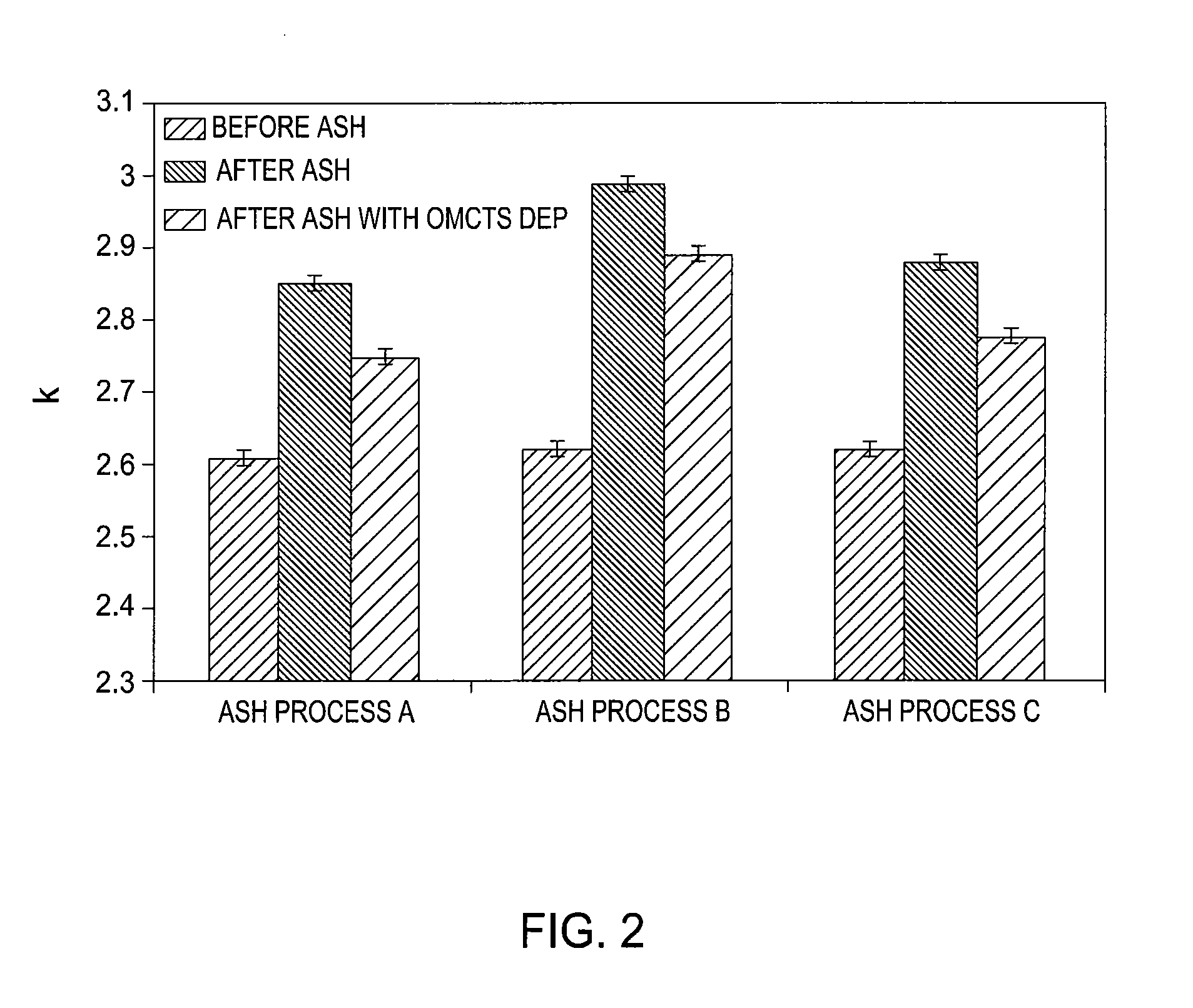
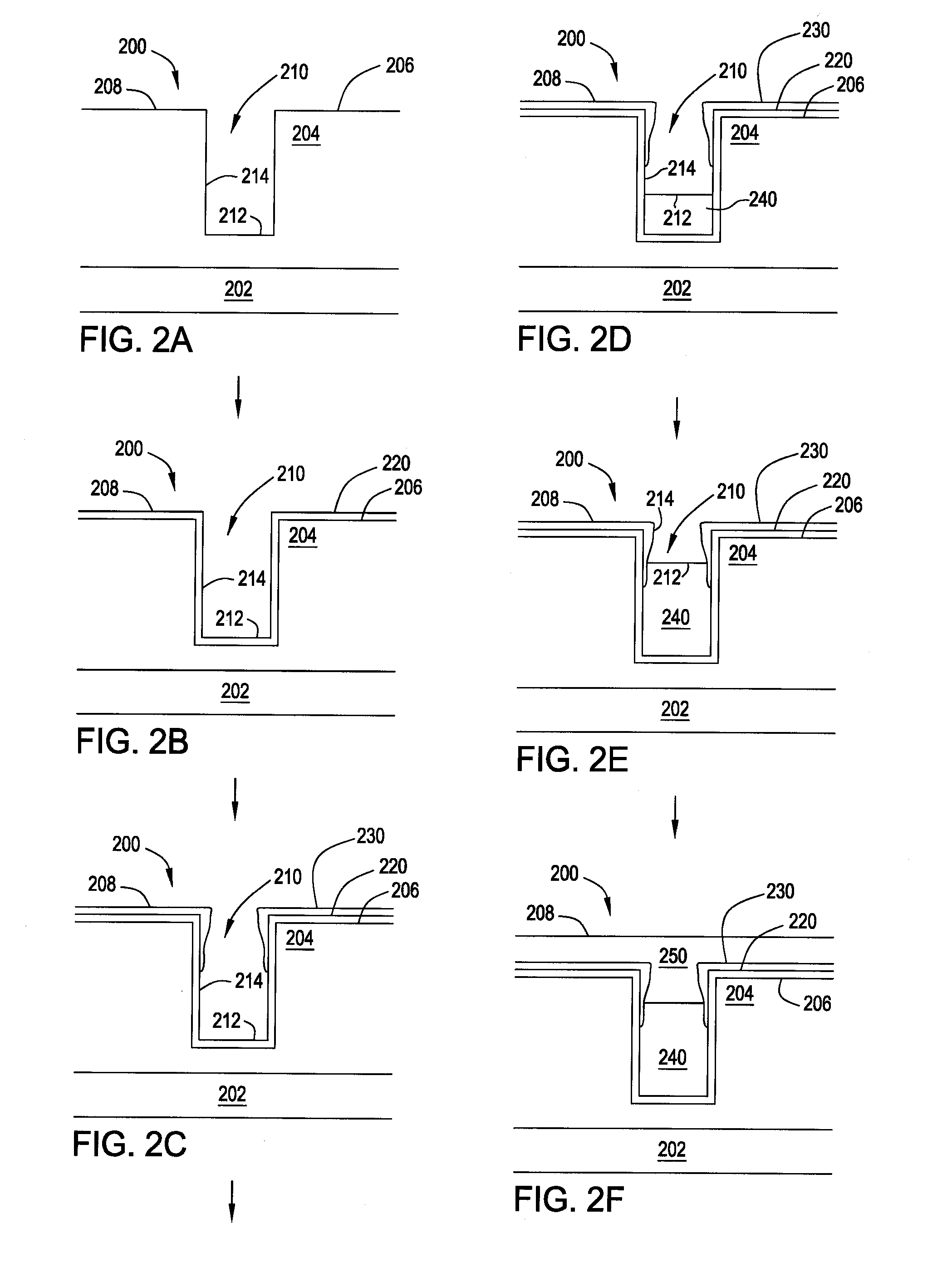
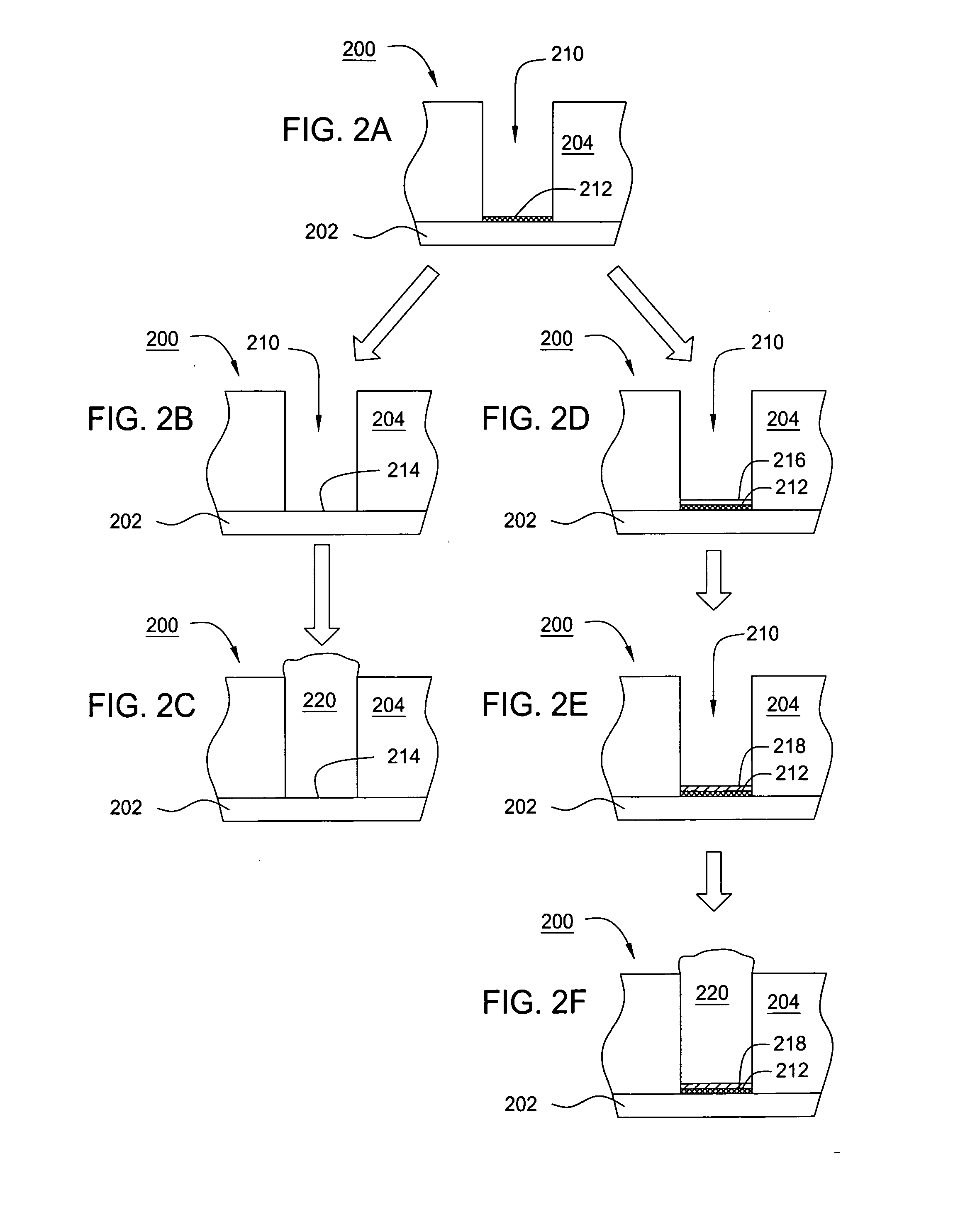
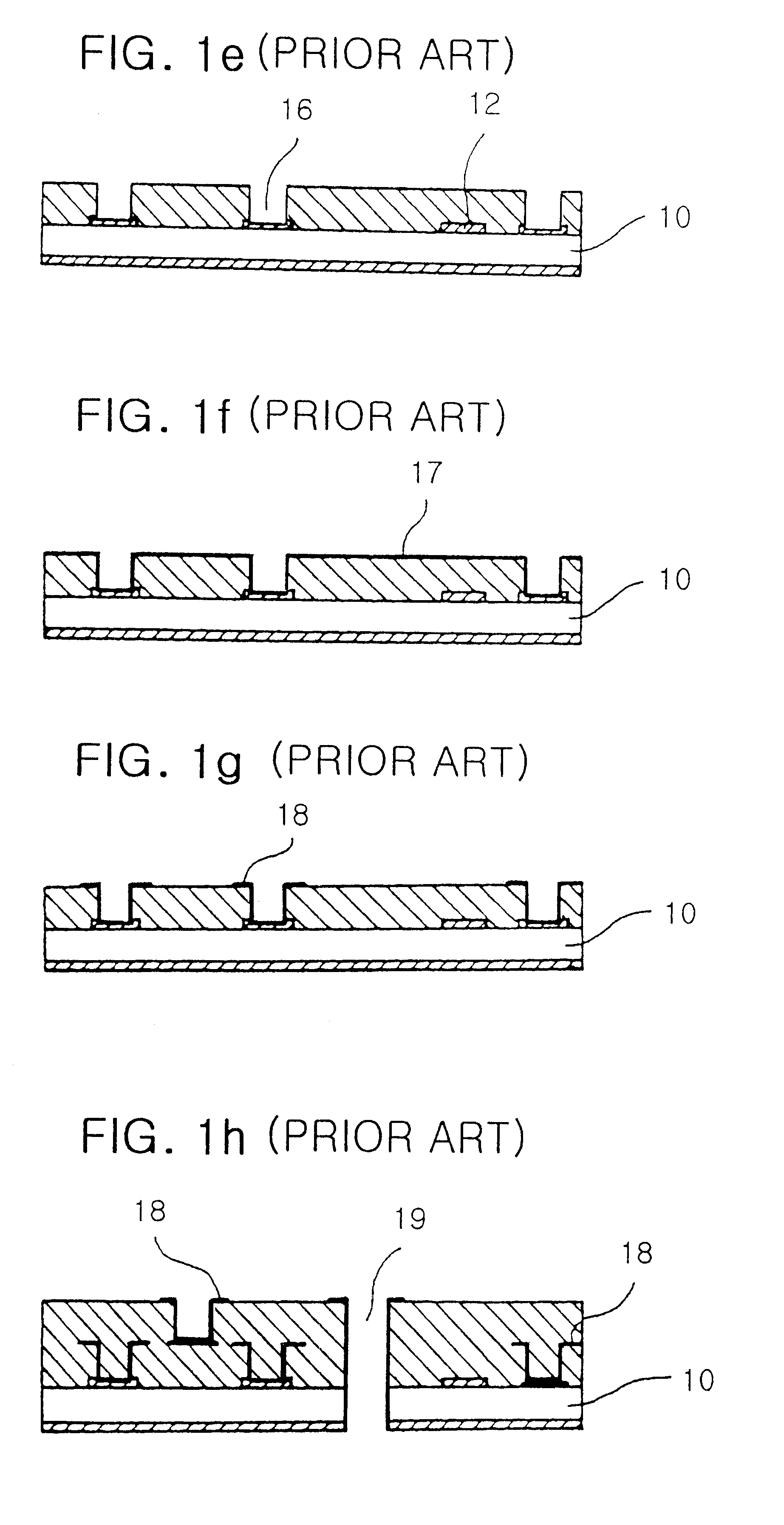
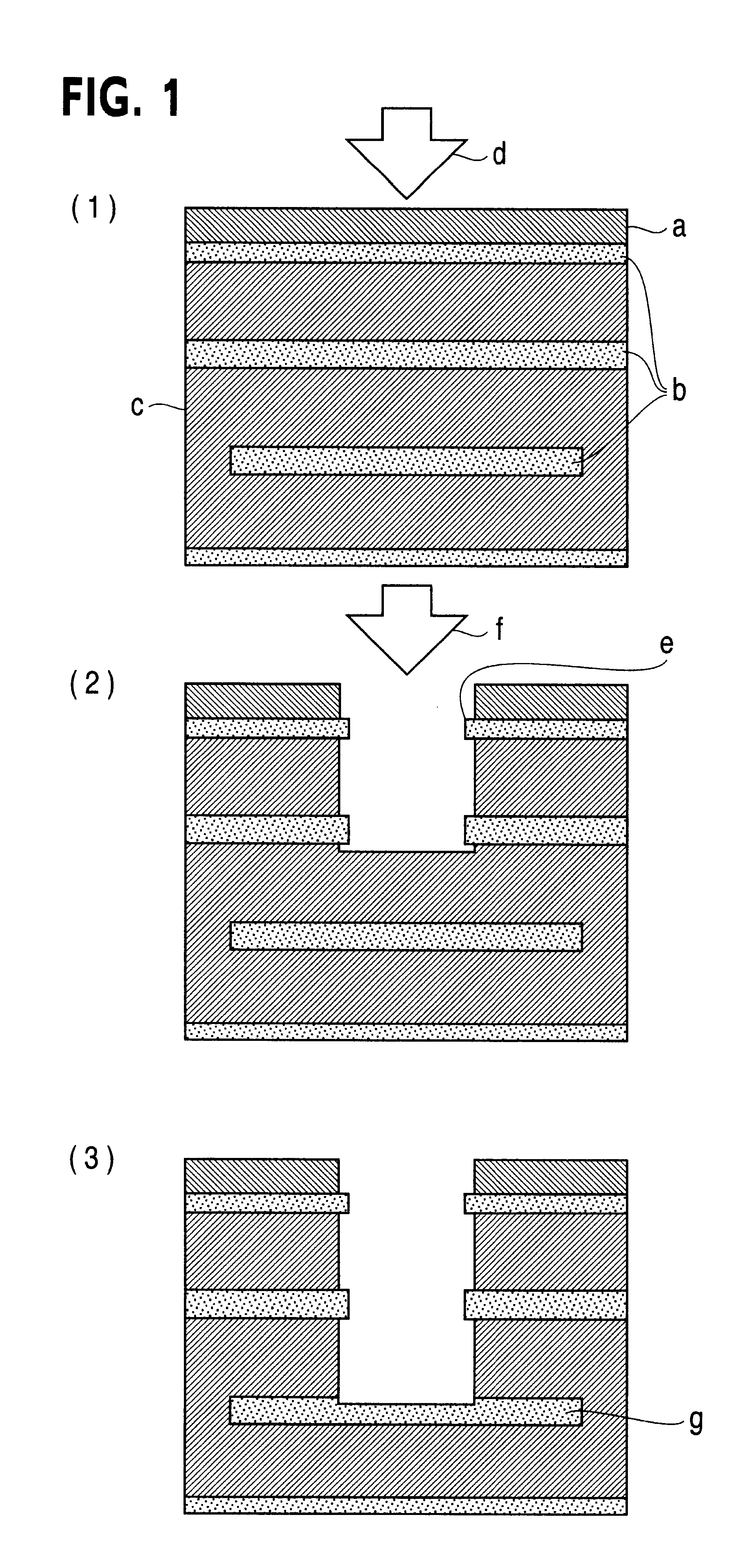
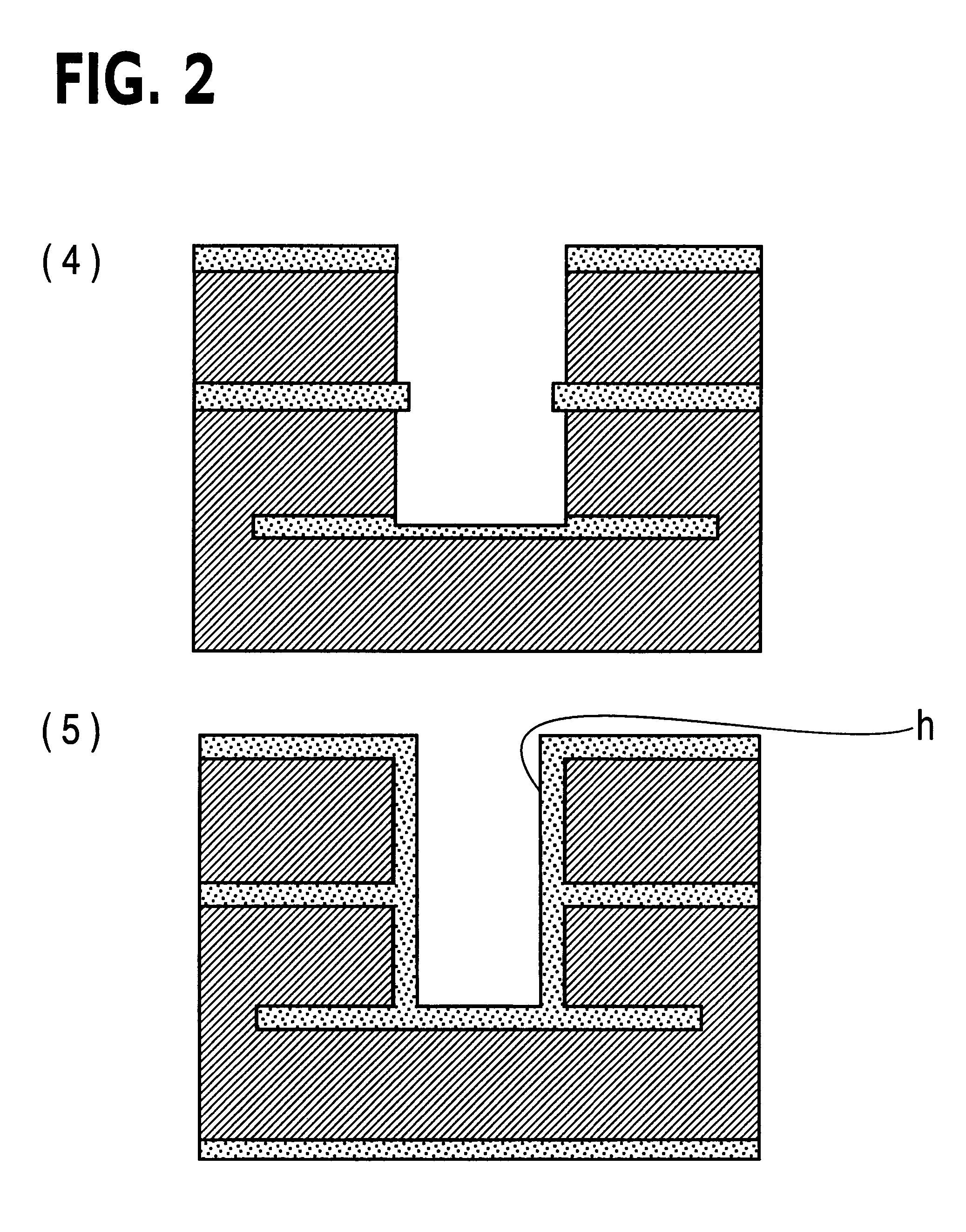
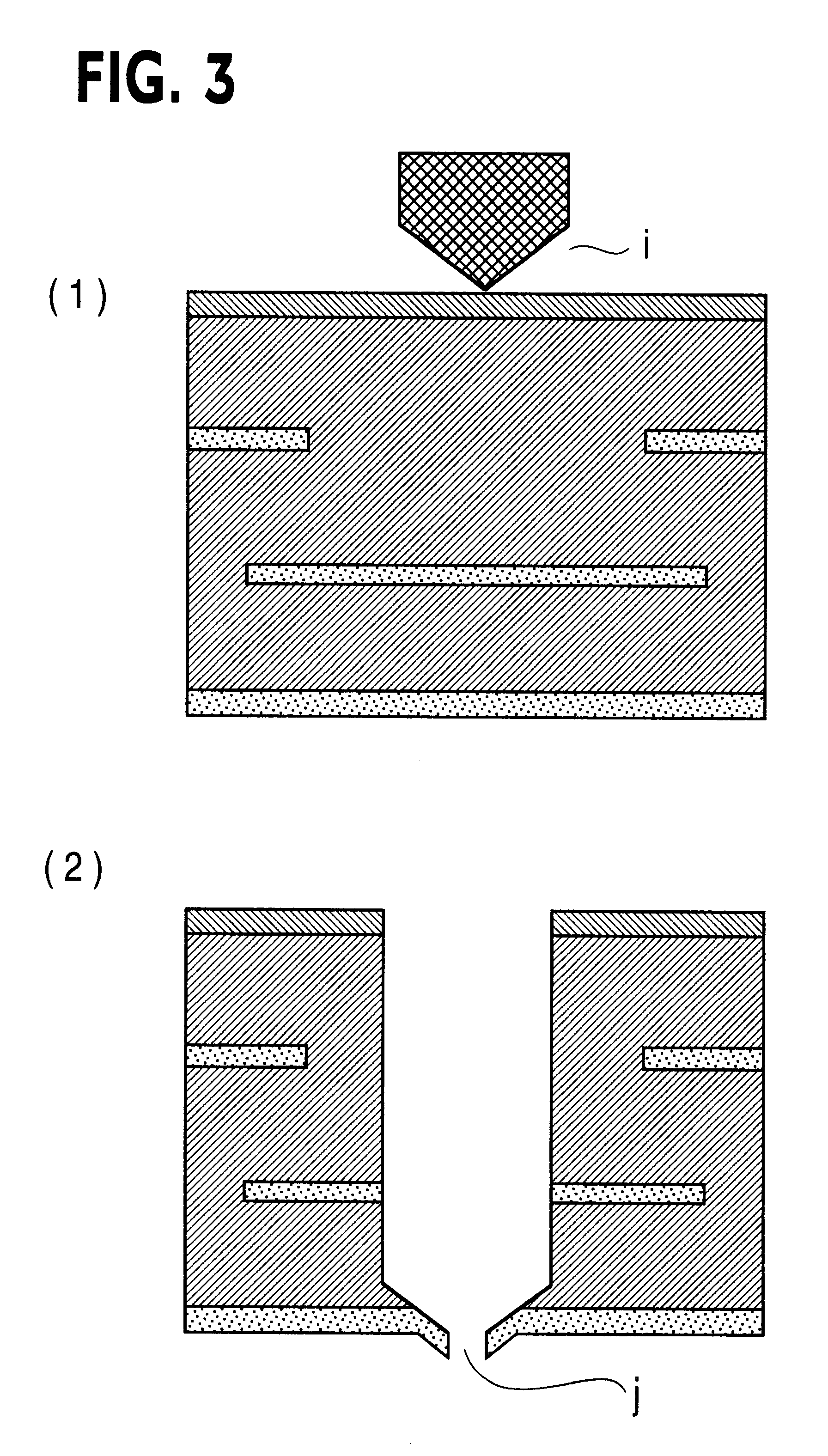
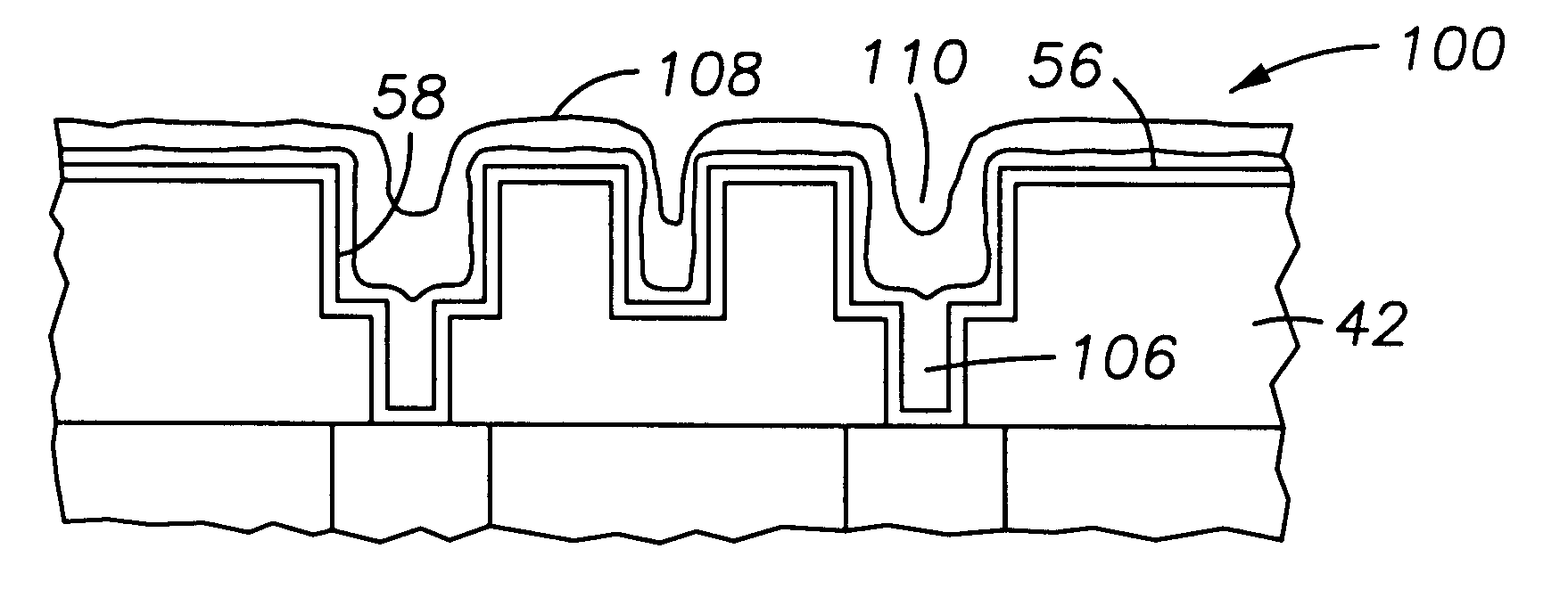
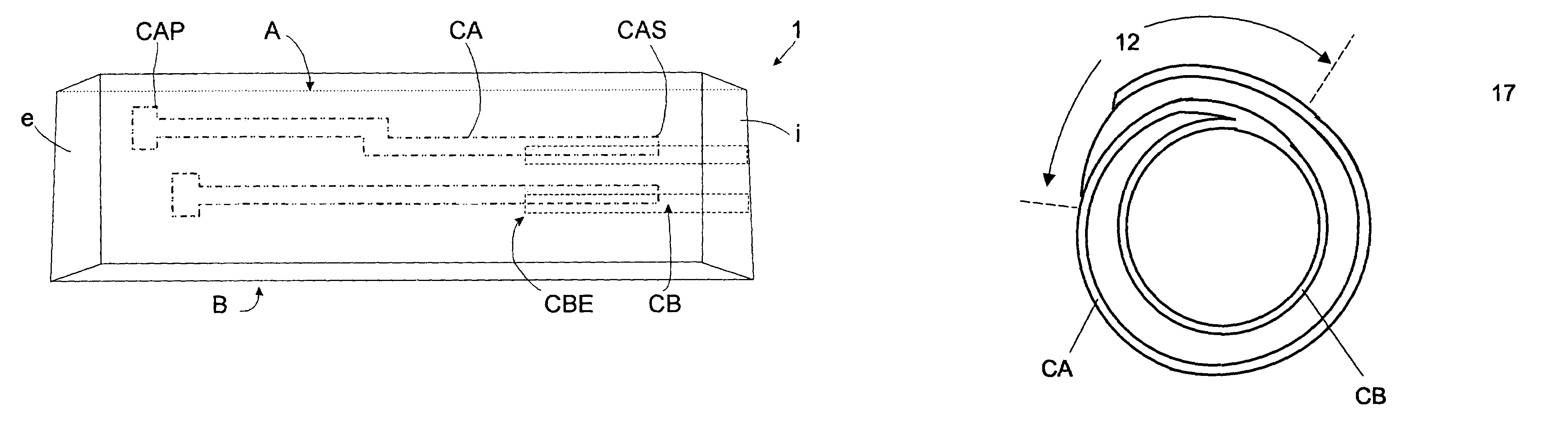
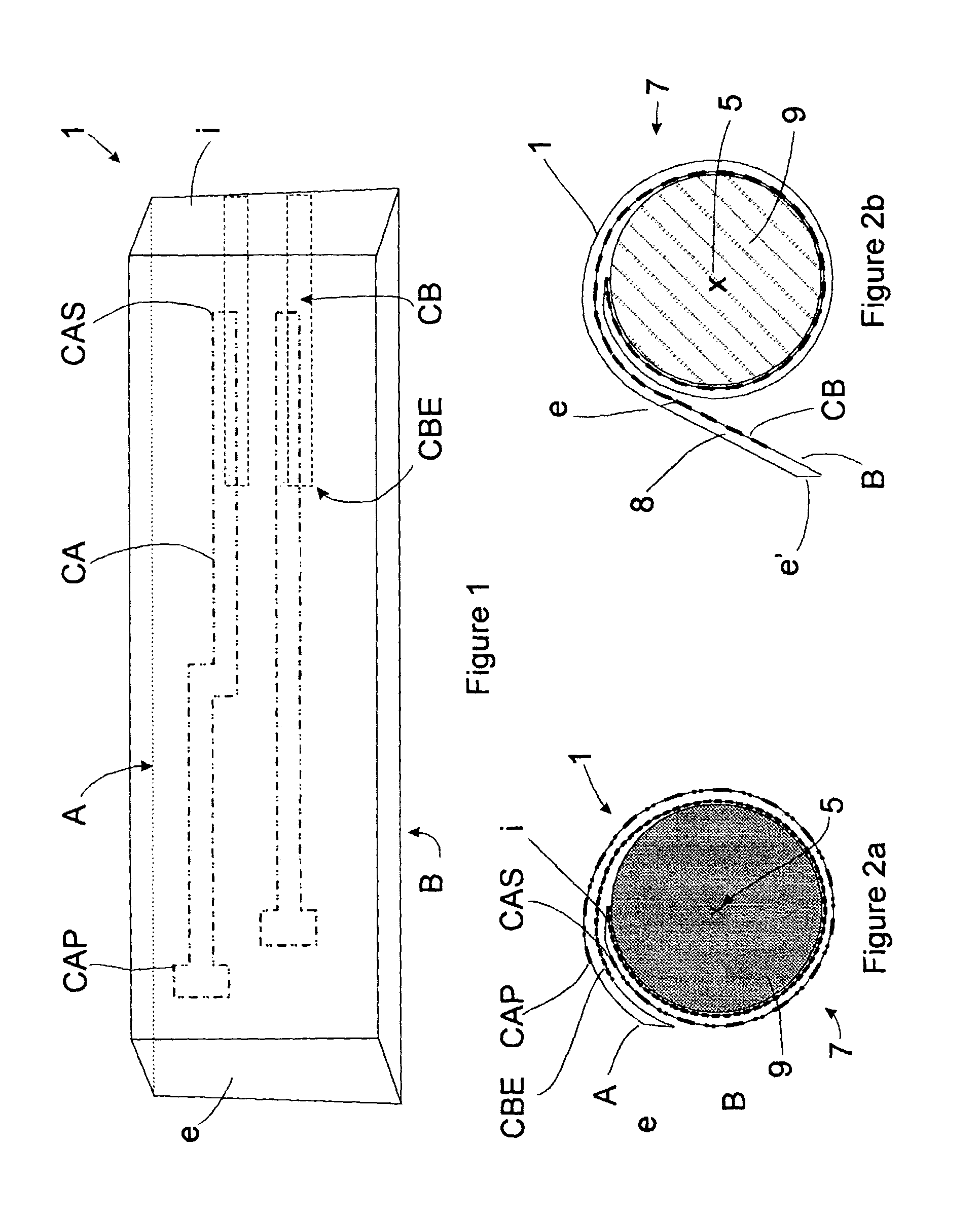
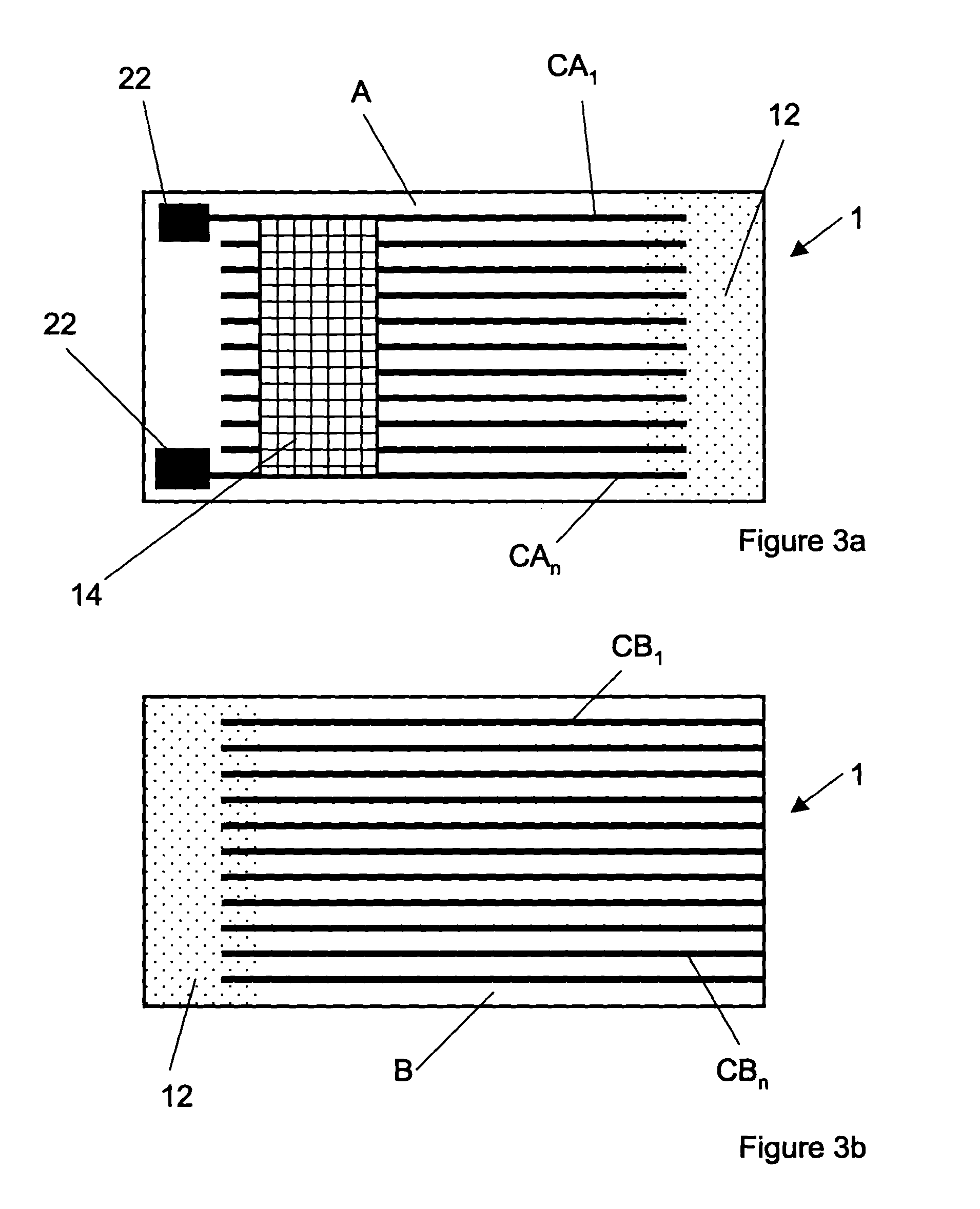
Method to minimize wet etch undercuts and provide pore sealing of extreme low k (k<2.5) dielectrics
ActiveUS8445075B2Constant ratePrevents undercuts and CD lossVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesNitrogenThin layer
Methods of processing films on substrates are provided. In one aspect, the methods comprise treating a patterned low dielectric constant film after a photoresist is removed from the film by depositing a thin layer comprising silicon, carbon, and optionally oxygen and / or nitrogen on the film. The thin layer provides a carbon-rich, hydrophobic surface for the patterned low dielectric constant film. The thin layer also protects the low dielectric constant film from subsequent wet cleaning processes and penetration by precursors for layers that are subsequently deposited on the low dielectric constant film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
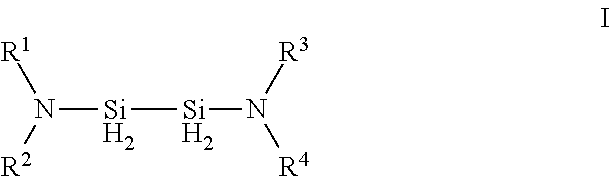
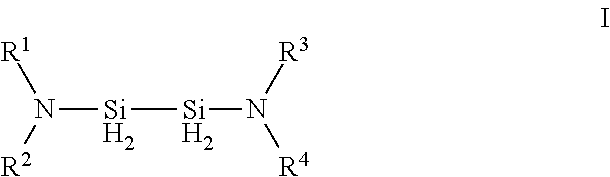
Organoaminodisilane precursors and methods for depositing films comprising same
Described herein are precursors and methods for forming silicon-containing films. In one aspect, there is a precursor of following Formula I:wherein R1 and R3 are independently selected from linear or branched C3 to C10 alkyl group, a linear or branched C3 to C10 alkenyl group, a linear or branched C3 to C10 alkynyl group, a C1 to C6 dialkylamino group, an electron withdrawing and a C6 to C10 aryl group; R2 and R4 are independently selected from hydrogen, a linear or branched C3 to C10 alkyl group, a linear or branched C3 to C10 alkenyl group, a linear or branched C3 to C10 alkynyl group, a C1 to C6 dialkylamino group, an electron withdrawing, and a C6 to C10 aryl group; and wherein any one, all, or none of R1 and R2, R3 and R4, R1 and R3, or R2 and R4 are linked to form a ring.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method of making low kappa dielectric inorganic/organic hybrid films
InactiveUS6068884AImprove thermal stabilityLow dielectric constantLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor
A method of depositing a dielectric film exhibiting a low dielectric constant in a semiconductor and / or integrated circuit by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is provided. The film is deposited using an organosilicon precursor in a manner such that the film is comprised of a backbone made substantially of Si-O-Si or Si-N-Si groups with organic side groups attached to the backbone.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Metal nitride carbide deposition by ALD
InactiveUS7410666B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
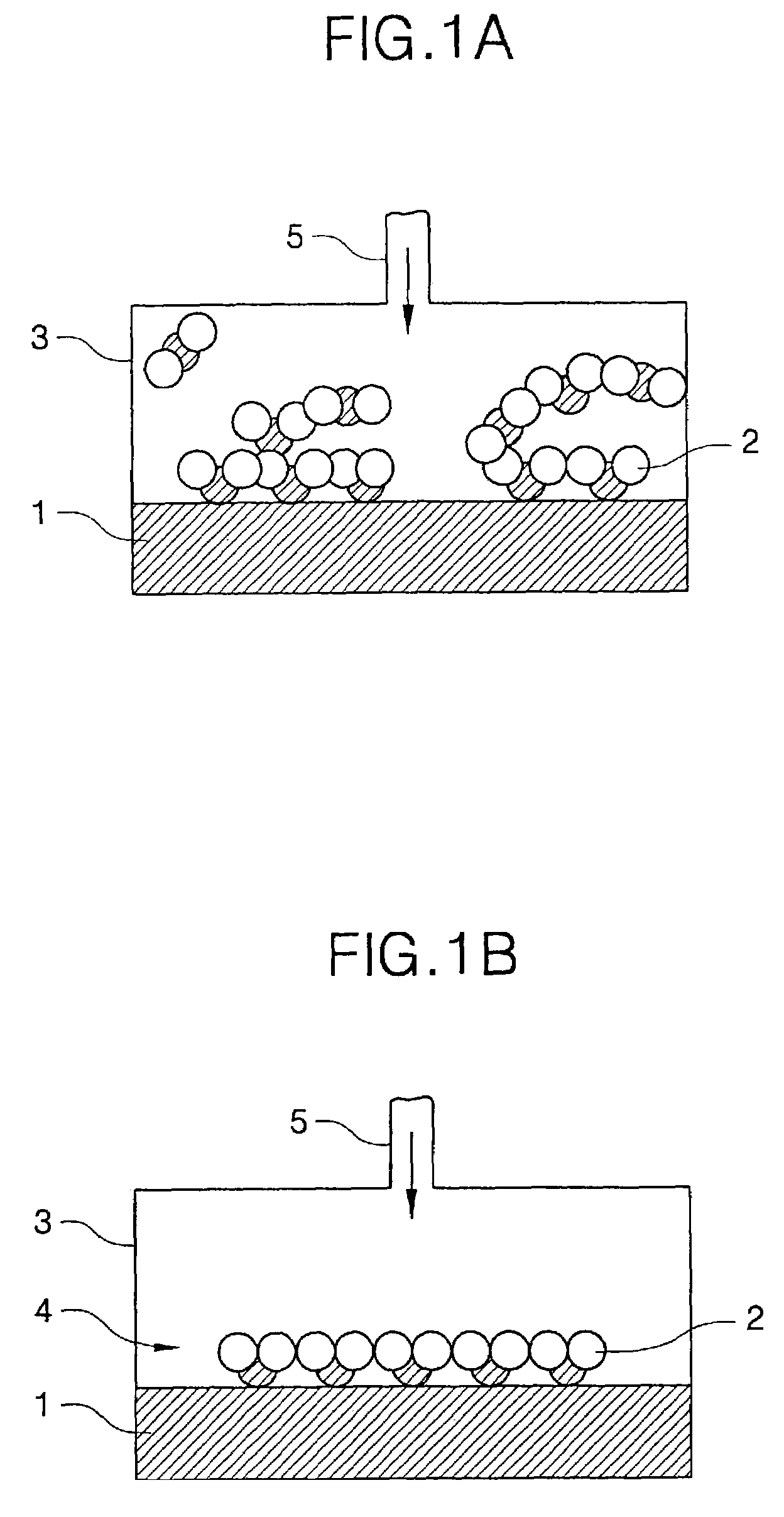
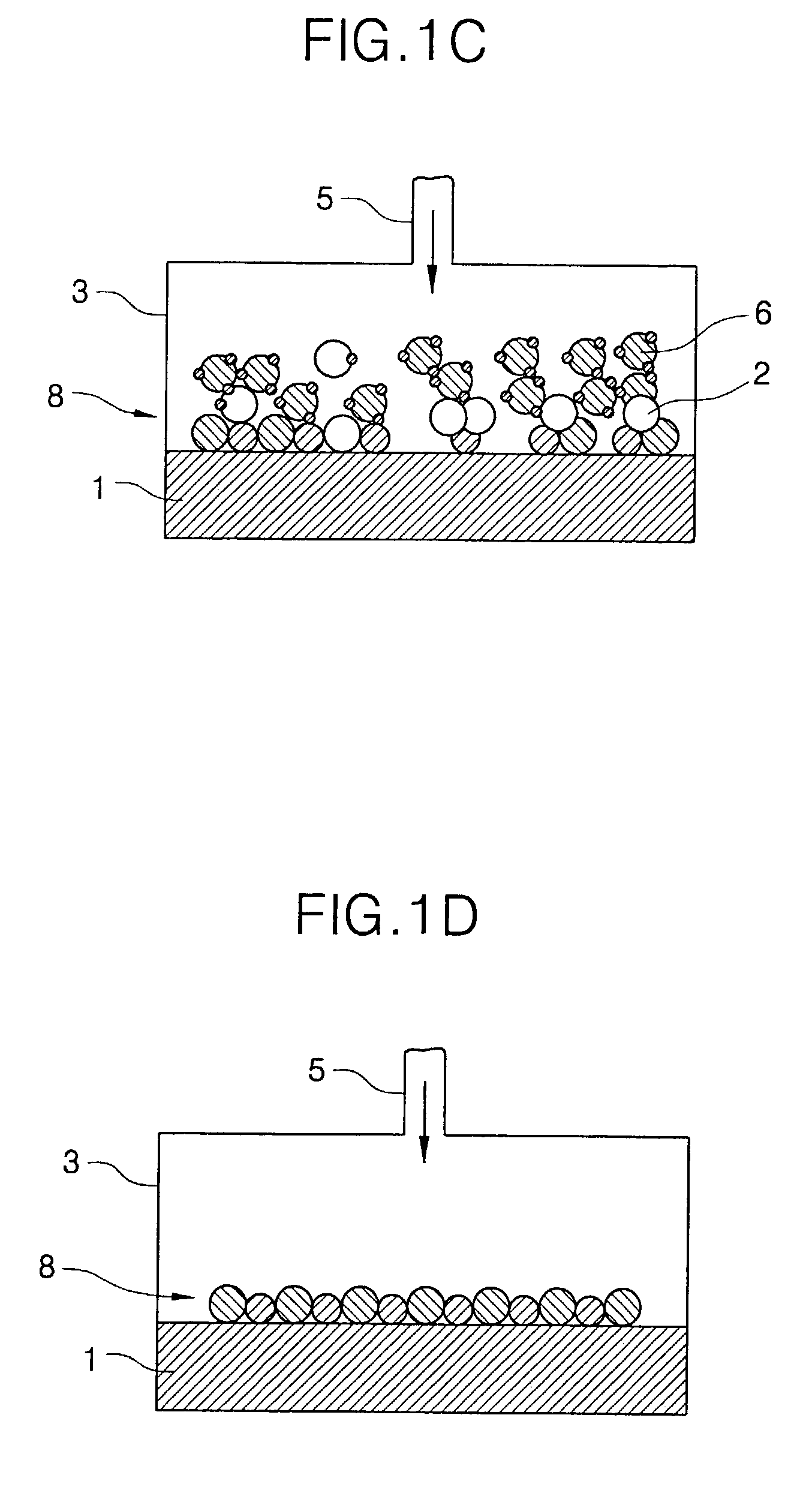
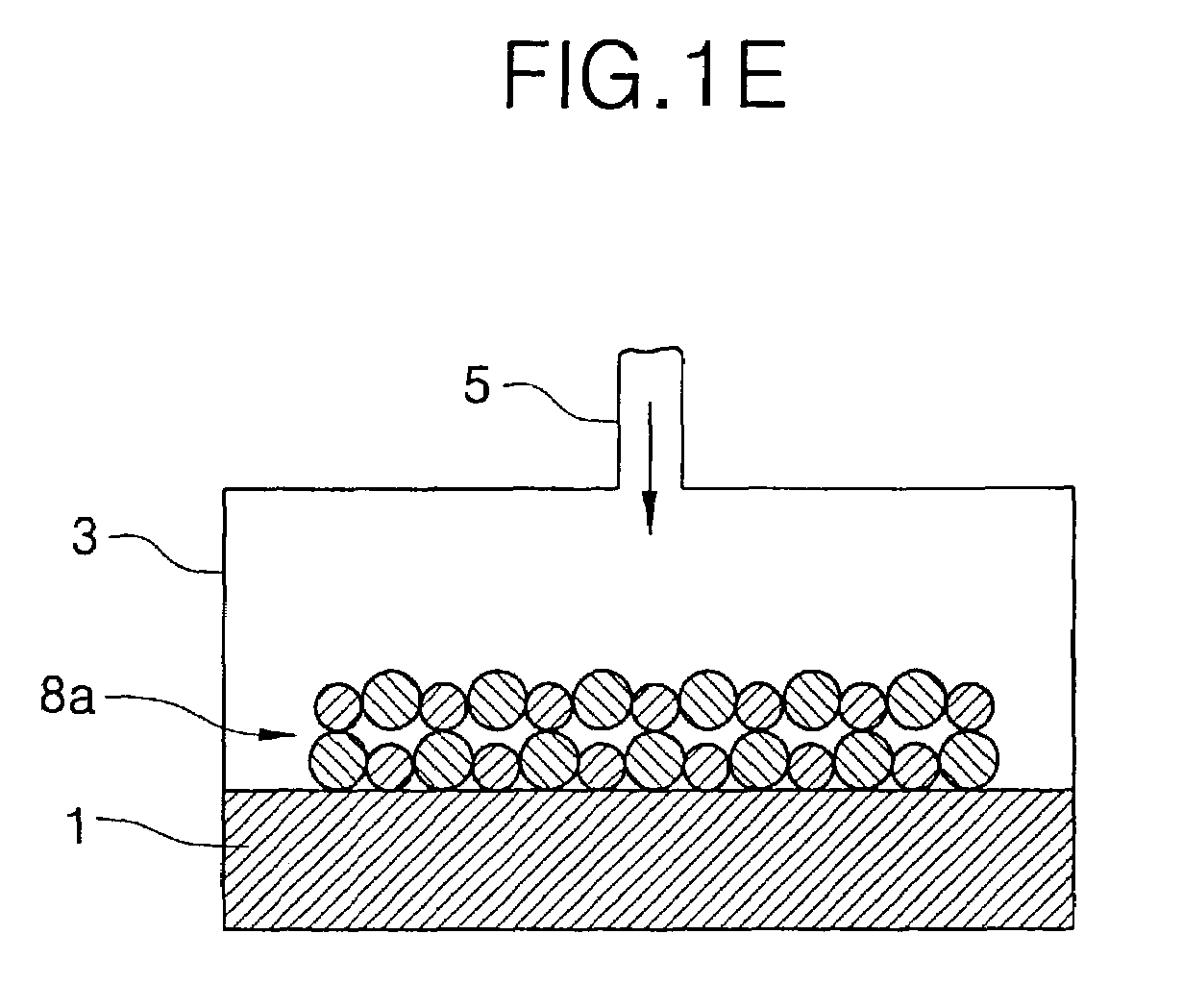
Methods of forming atomic layers of a material on a substrate by sequentially introducing precursors of the material
InactiveUS7201943B2Easy to integrateHigh dielectric constantVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricTitanium
A thin film is formed using an atomic layer deposition process, by introducing a first reacting material including tantalum precursors and titanium precursors onto a substrate. A portion of the first reacting material is chemisorbed onto the substrate. Then, a second reacting material including oxygen is introduced onto the substrate. A portion of the second reacting material is also chemisorbed onto the substrate, to form an atomic layer of a solid material on the substrate. The solid material may be used as a dielectric layer of the capacitor and / or a gate dielectric layer of the transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
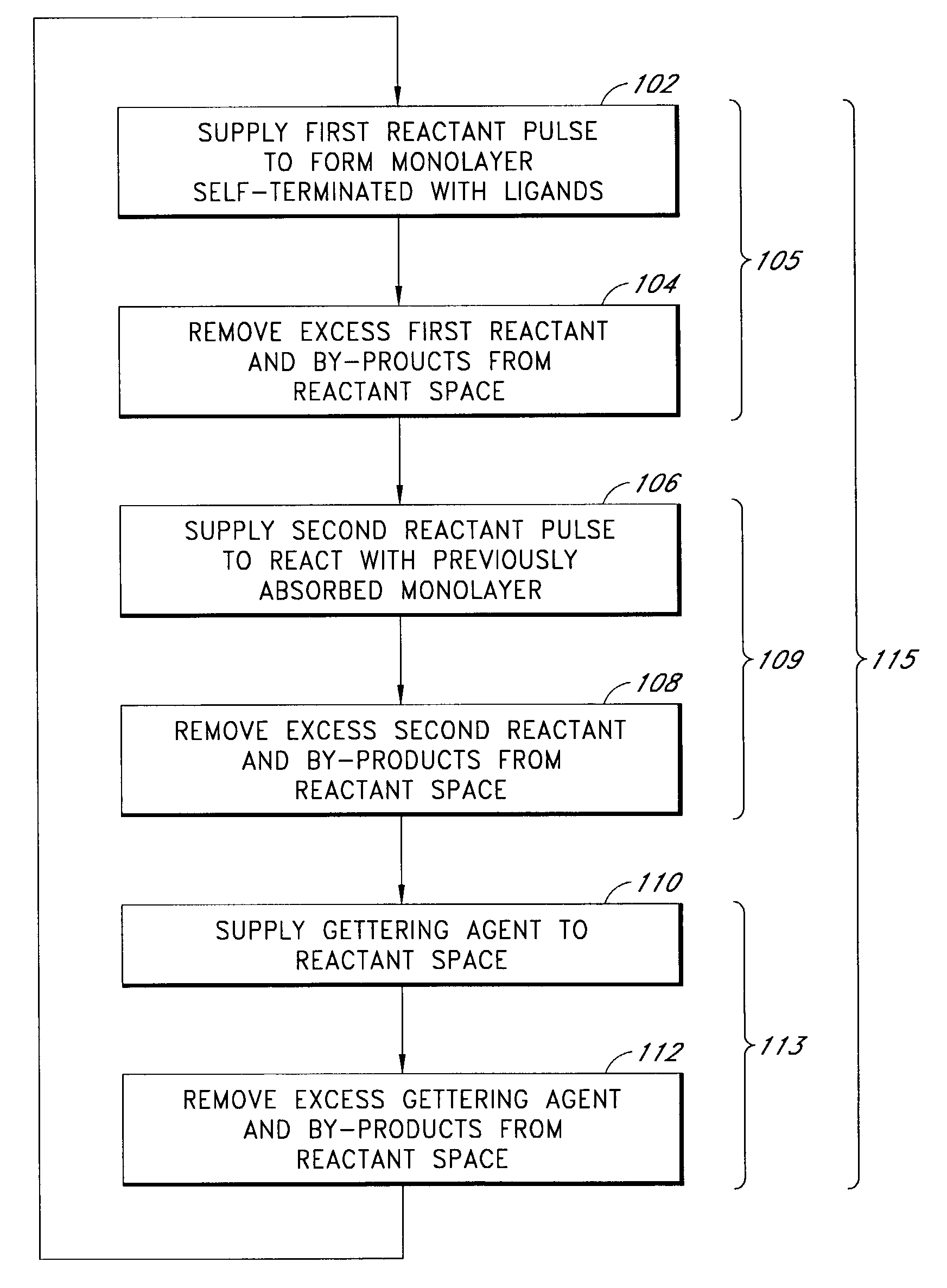
Metal nitride deposition by ALD with reduction pulse
The present methods provide tools for growing conformal metal thin films, including metal nitride, metal carbide and metal nitride carbide thin films. In particular, methods are provided for growing such films from aggressive chemicals. The amount of corrosive chemical compounds, such as hydrogen halides, is reduced during the deposition of transition metal, transition metal carbide, transition metal nitride and transition metal nitride carbide thin films on various surfaces, such as metals and oxides. Getter compounds protect surfaces sensitive to hydrogen halides and ammonium halides, such as aluminum, copper, silicon oxide and the layers being deposited, against corrosion. Nanolaminate structures incorporating metallic thin films, and methods for forming the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
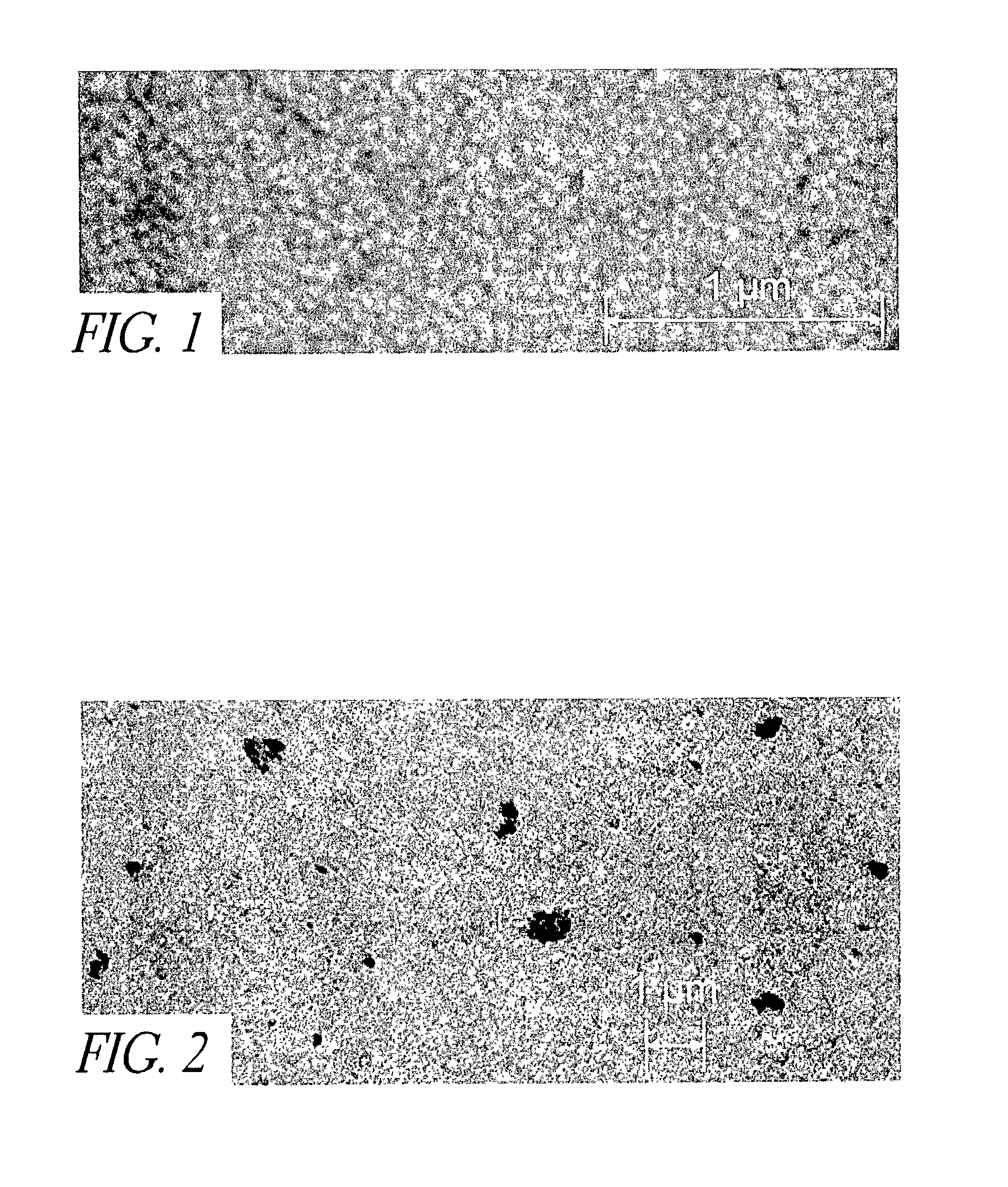
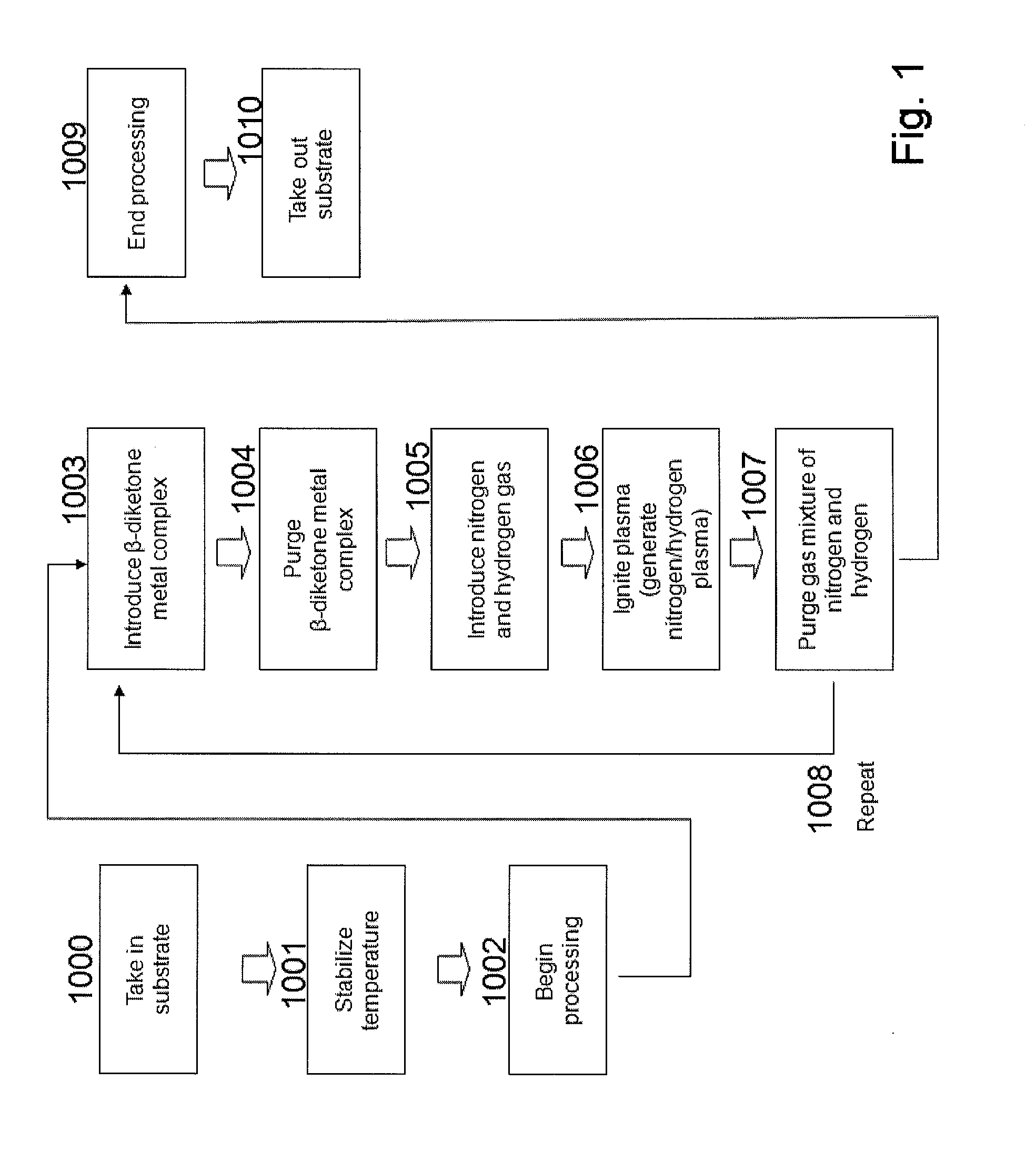
Method for forming metal film by ald using beta-diketone metal complex
ActiveUS20100092696A1Improve shielding effectRapid and reliable mannerVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesDiketoneHydrogen
A method of forming a single-metal film on a substrate by plasma ALD includes: contacting a surface of a substrate with a β-diketone metal complex in a gas phase; exposing molecule-attached surface to a nitrogen-hydrogen mixed plasma; and repeating the above steps, thereby accumulating atomic layers to form a single-metal film on the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
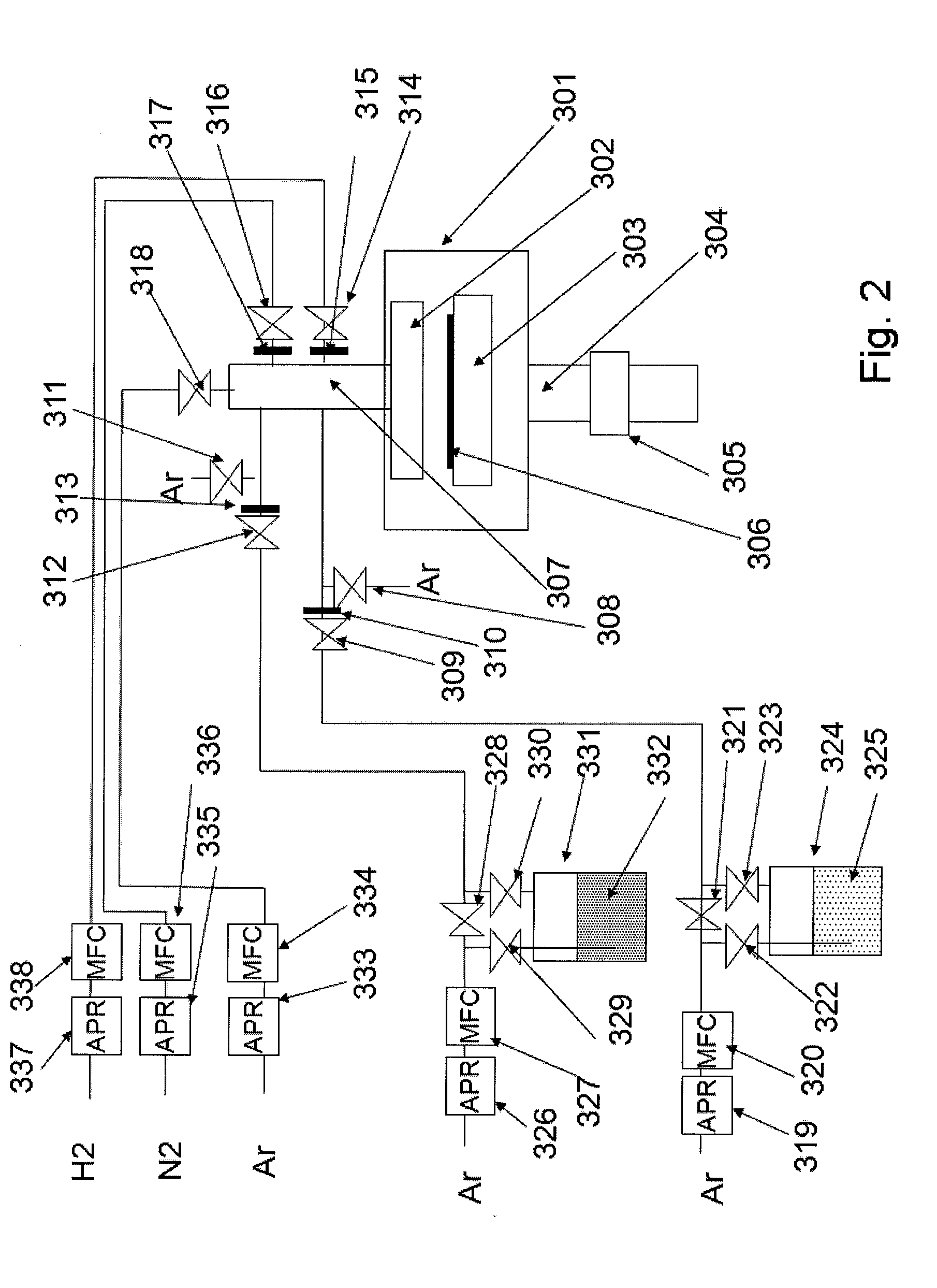
Contact metallization scheme using a barrier layer over a silicide layer
ActiveUS20060251800A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialElectroless deposition
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods of filling contact level features formed in a semiconductor device by depositing a barrier layer over the contact feature and then filing the layer using an PVD, CVD, ALD, electrochemical plating process (ECP) and / or electroless deposition processes. In one embodiment, the barrier layer has a catalytically active surface that will allow the electroless deposition of a metal on the barrier layer. In one aspect, the electrolessly deposited metal is copper or a copper alloy. In one aspect, the contact level feature is filled with a copper alloy by use of an electroless deposition process. In another aspect, a copper alloy is used to from a thin conductive copper layer that is used to subsequently fill features with a copper containing material by use of an ECP, PVD, CVD, and / or ALD deposition process. In one embodiment, a portion of the barrier layer is purposely allowed to react with traces of residual oxide at the silicon junction of the contact level feature to form a low resistance connection.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
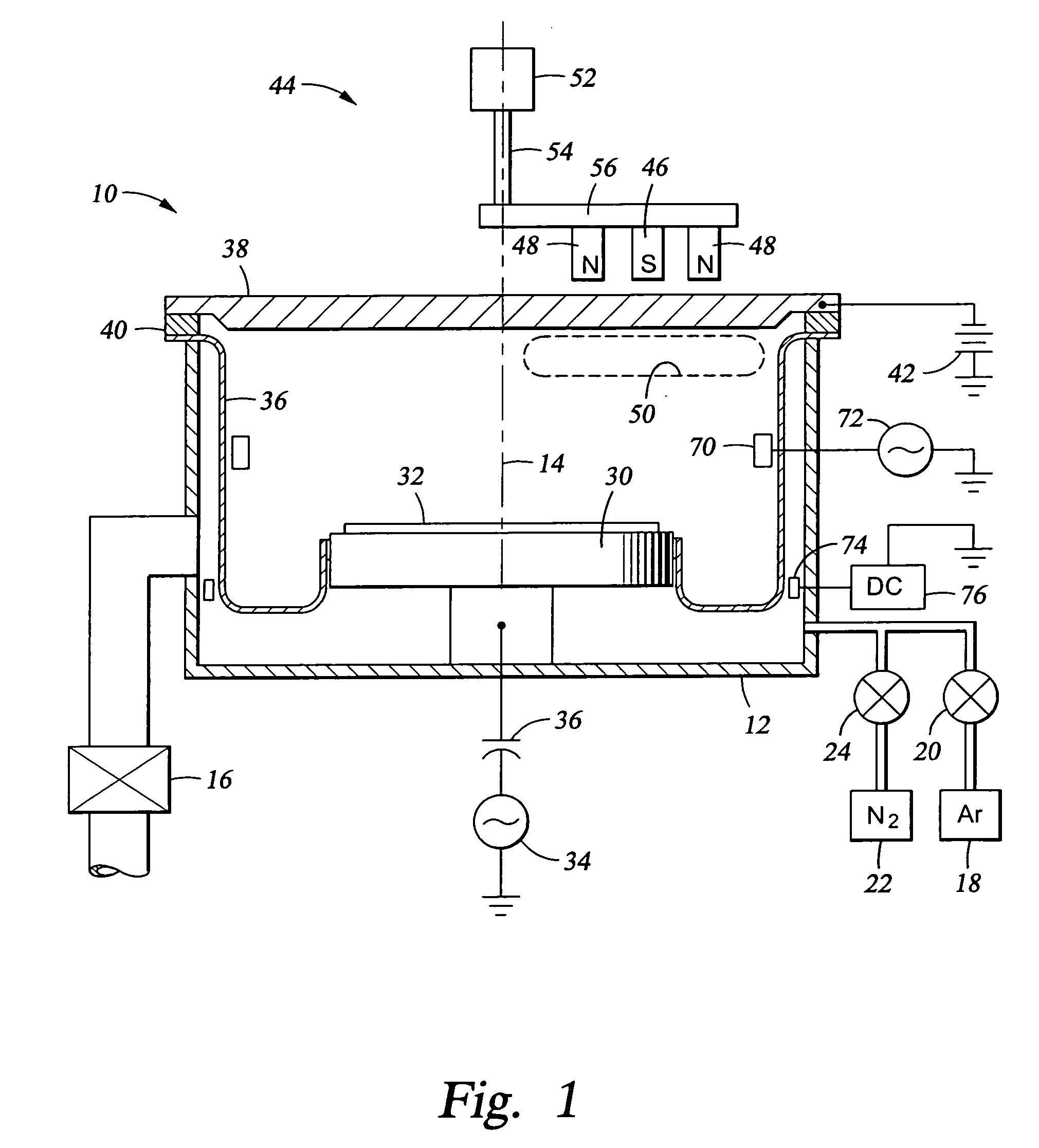
Thermal Processing System and Configurable Vertical Chamber
InactiveUS20070243317A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingEngineeringIsothermal process
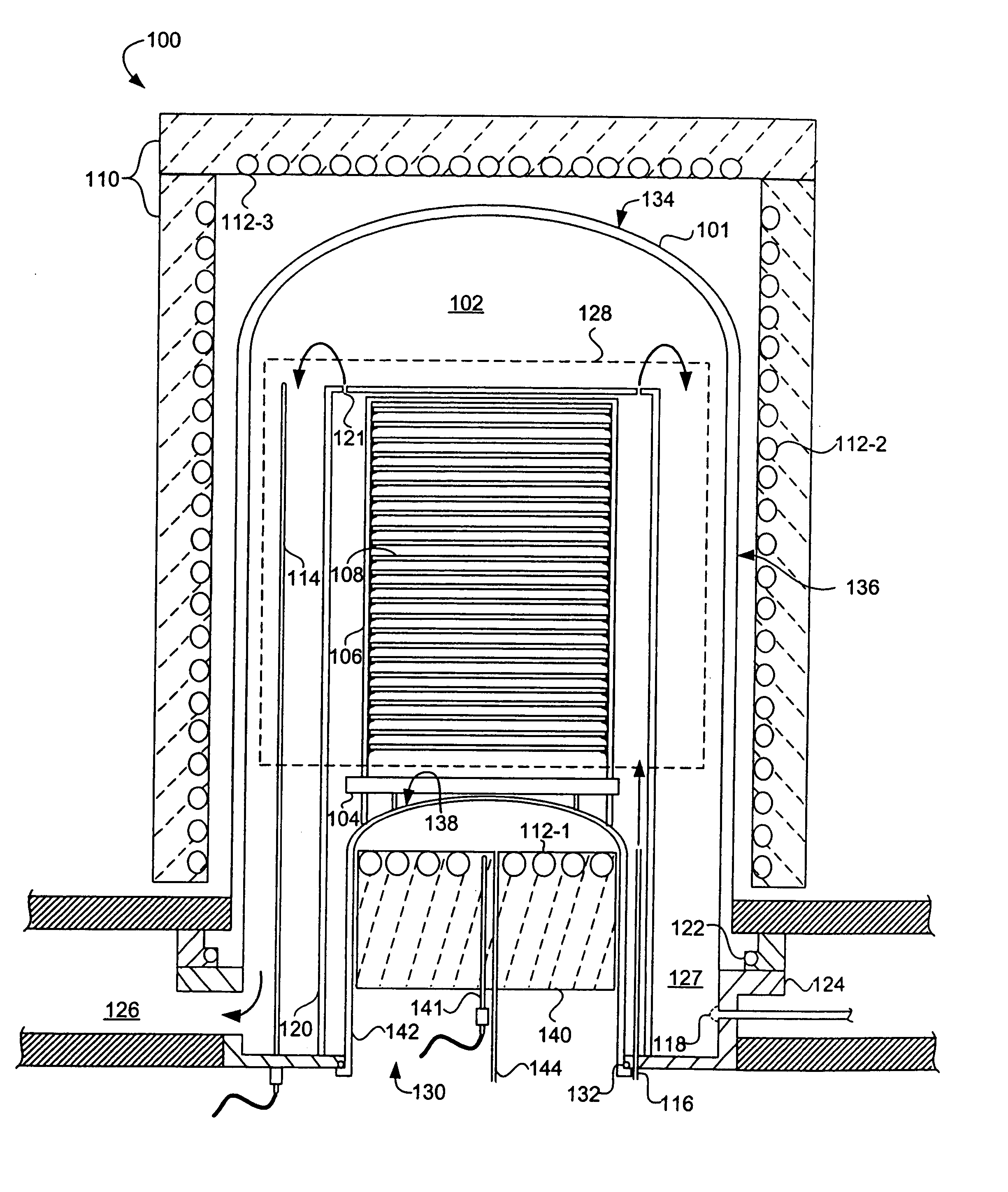
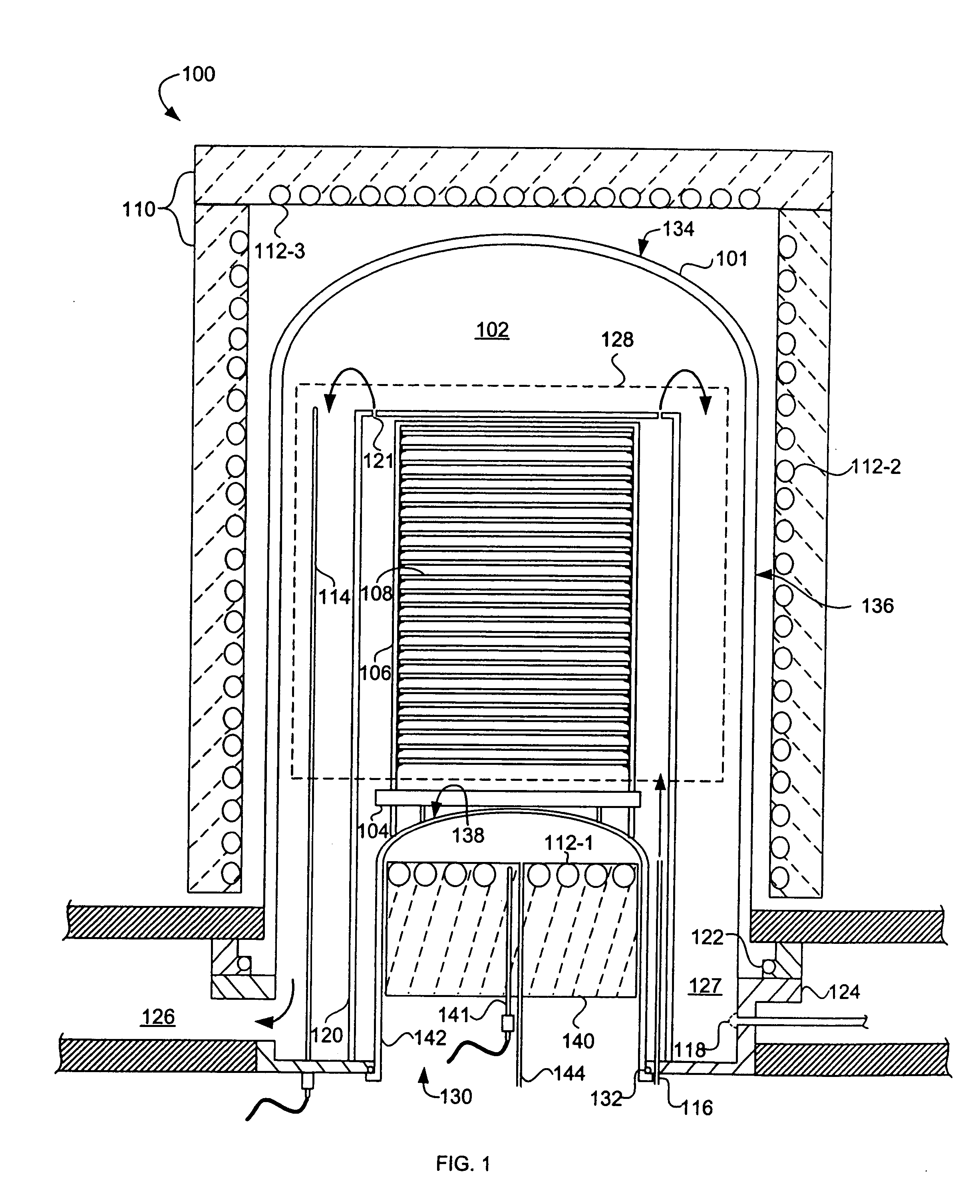
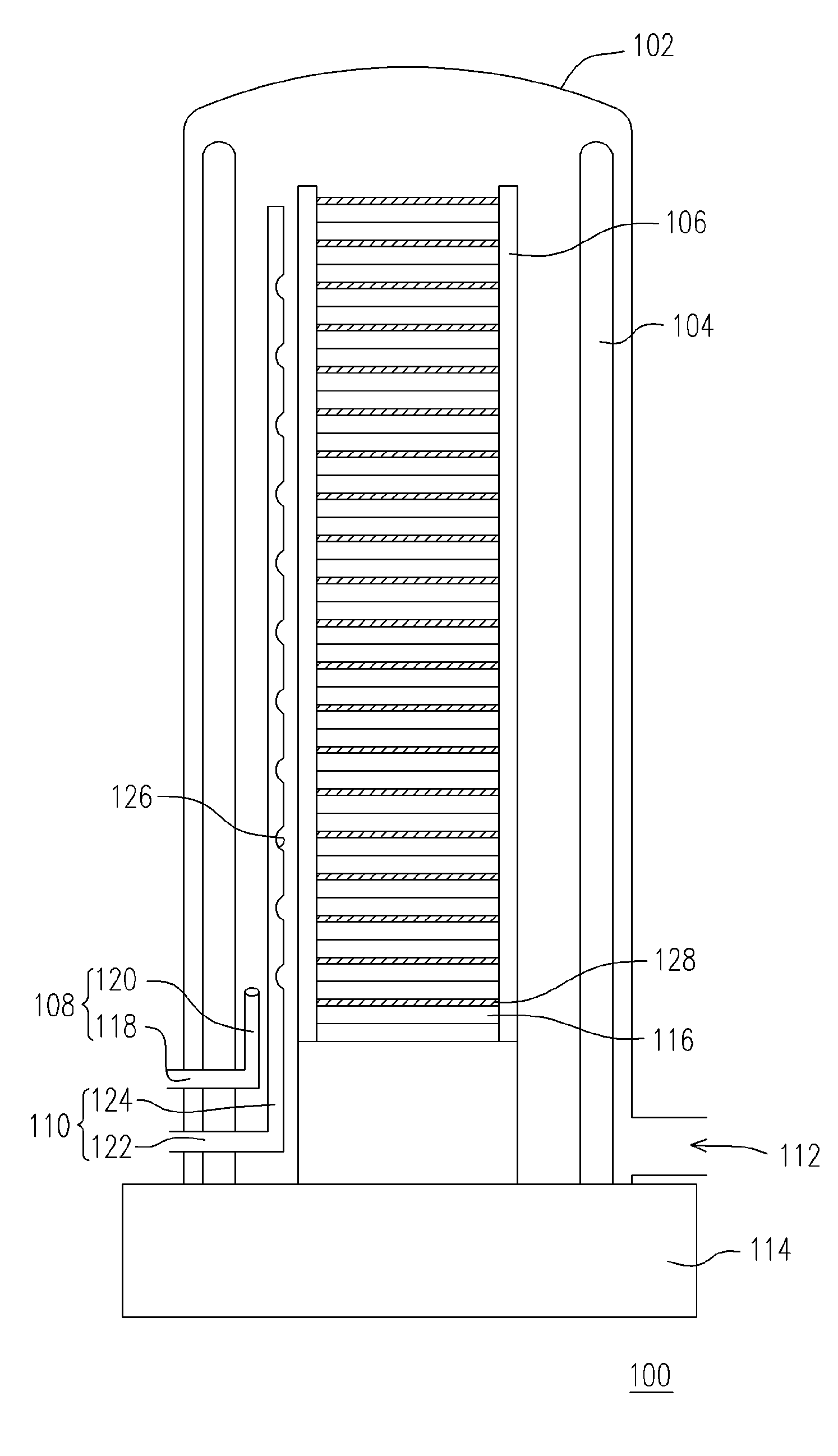
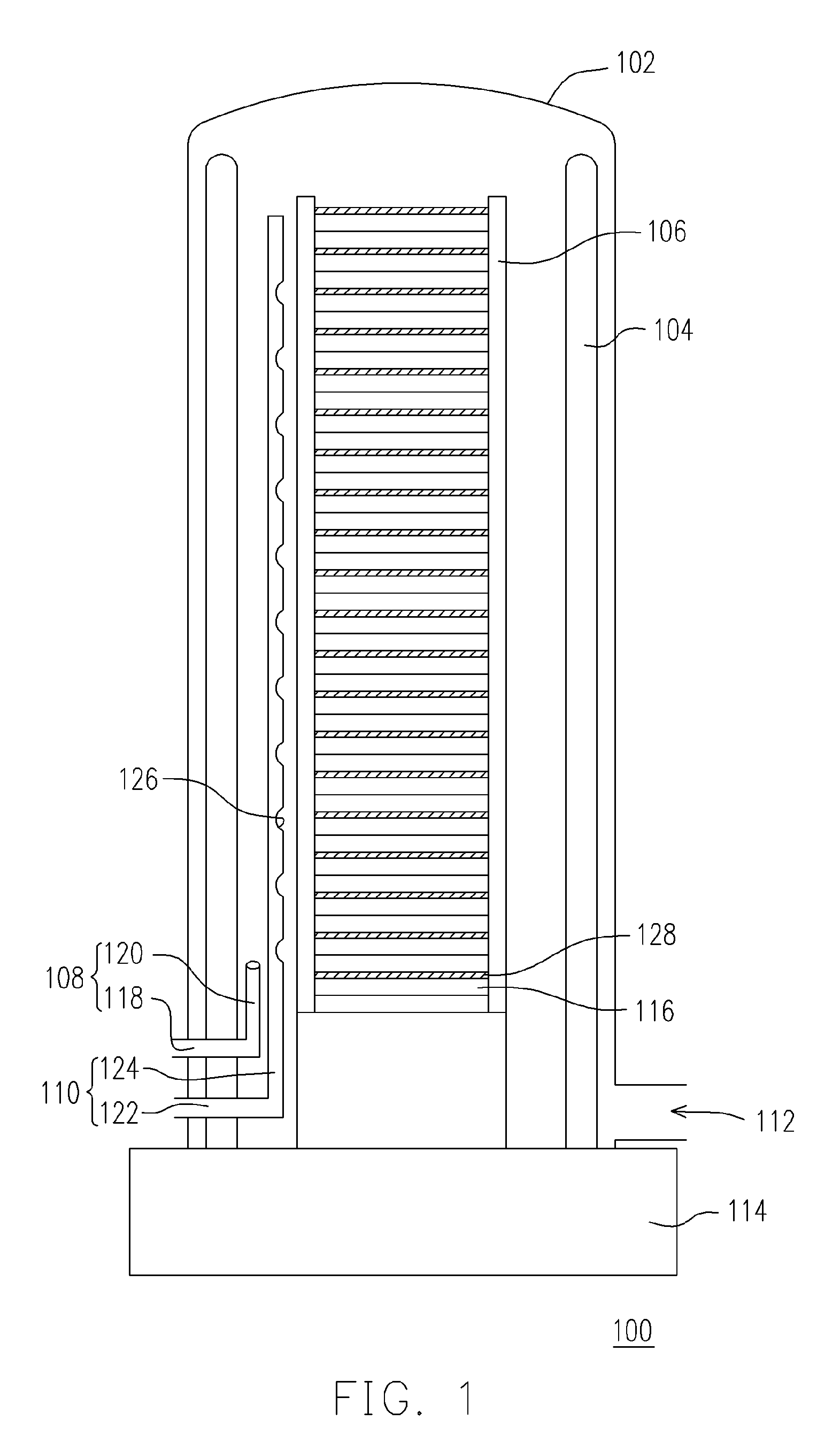
An apparatus (100) and method are provided for thermally processing substrates (108) held in a carrier (106). The apparatus (100) includes a vessel (101) having a top (134), side (136) and bottom (138), and a heat source (110) with heating elements (112-1, 112-2, 112-3) proximal thereto. The vessel (101) is sized to enclose a volume substantially no larger than necessary to accommodate the carrier (106), and to provide an isothermal process zone (128) extending throughout. In one embodiment, the bottom wall (138) includes a movable pedestal (140) with a bottom heating element therein (112-1), and the pedestal can be lowered and raised to insert the carrier (106) into the vessel (101). The apparatus (100) can include a movable shield (146) that is inserted between the pedestal (140) and the carrier (106) to shield the substrates (108) from the heating element (112-1) and to maintain pedestal temperature. A magnetically coupled repositioning system (162) repositions the carrier (106) during processing of the substrates (108) without use of a movable feedthrough into the volume enclosed by the vessel (101), and without moving the bottom heating element (112-1) in the pedestal (140).
Owner:DU BOIS DALE R +4
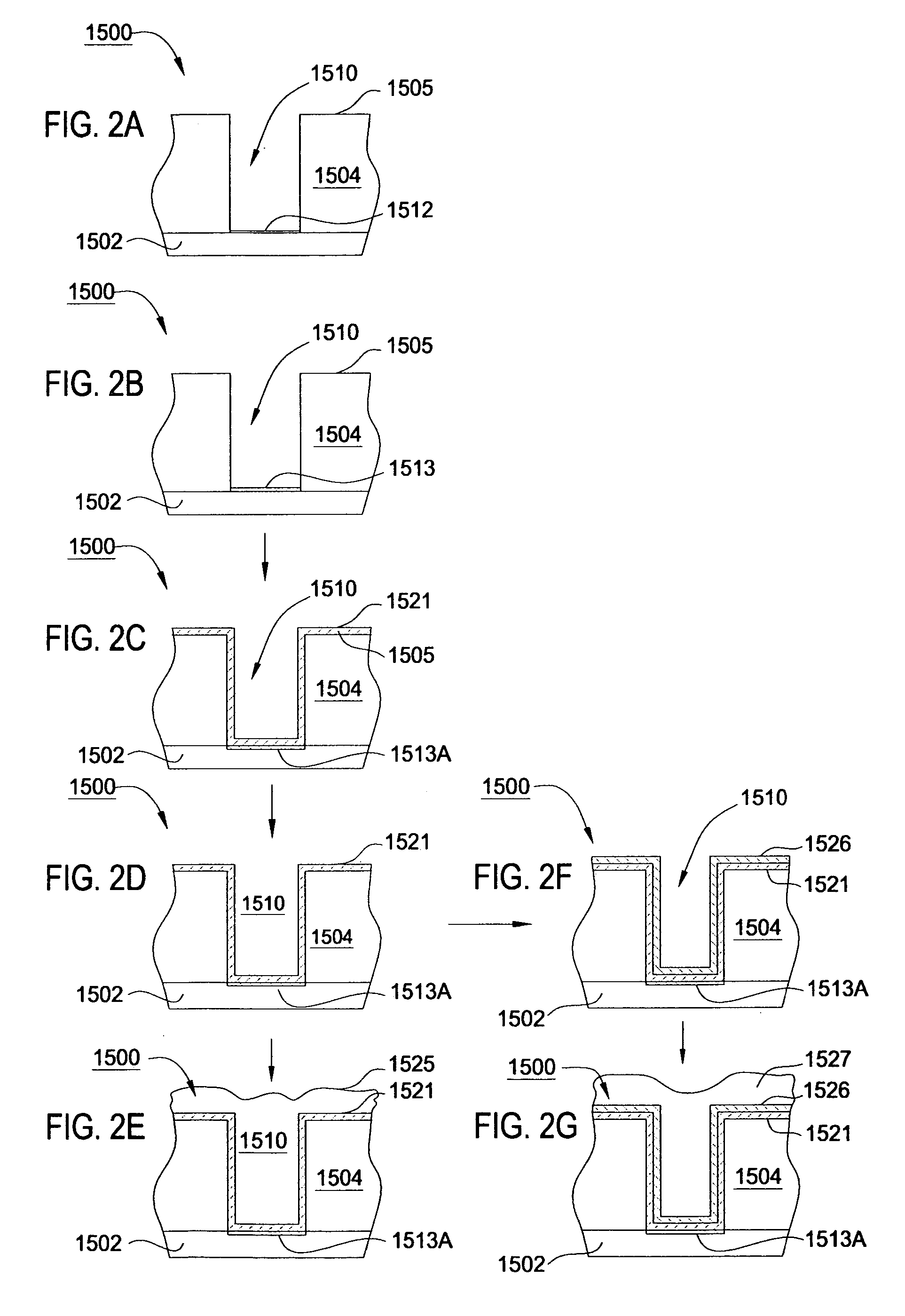
Method to minimize wet etch undercuts and provide pore sealing of extreme low k (k<2.5) dielectrics
ActiveUS20110092077A1Constant ratePrevents undercuts and CD lossVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin layerNitrogen
Methods of processing films on substrates are provided. In one aspect, the methods comprise treating a patterned low dielectric constant film after a photoresist is removed form the film by depositing a thin layer comprising silicon, carbon, and optionally oxygen and / or nitrogen on the film. The thin layer provides a carbon-rich, hydrophobic surface for the patterned low dielectric constant film. The thin layer also protects the low dielectric constant film from subsequent wet cleaning processes and penetration by precursors for layers that are subsequently deposited on the low dielectric constant film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
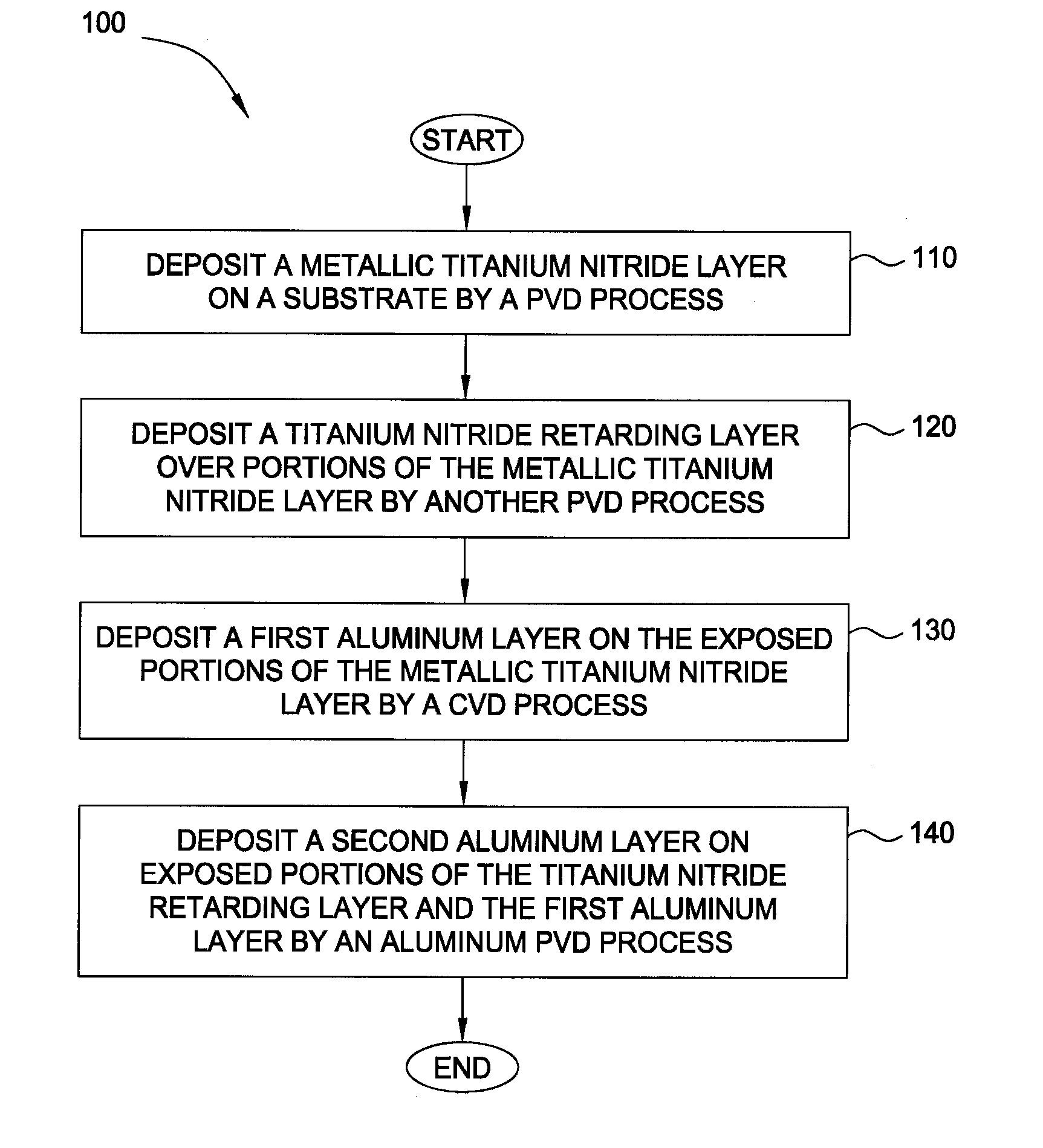
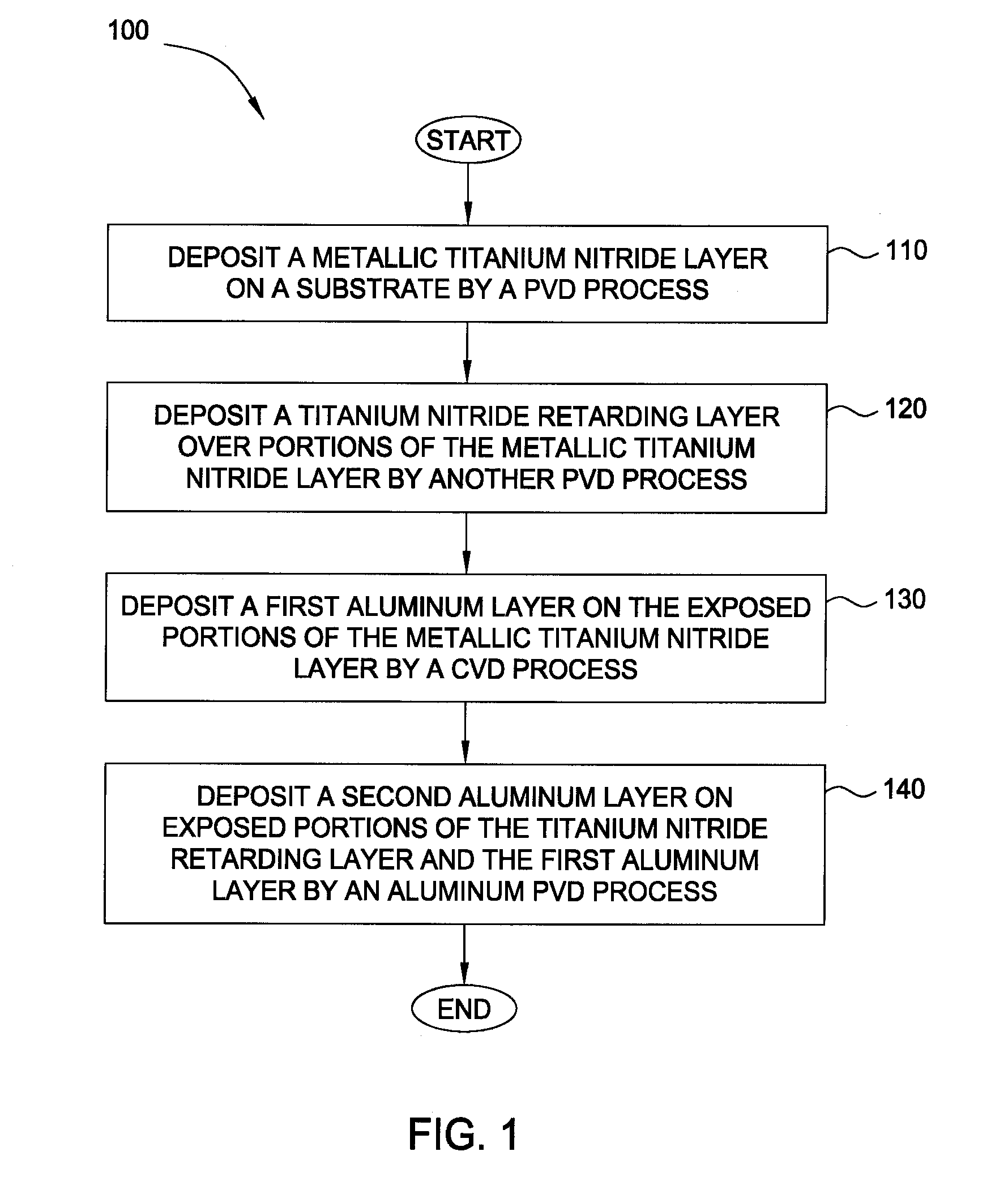
Deposition processes for titanium nitride barrier and aluminum
InactiveUS20090087585A1Increasing nitrogen gas flowDecrease DC powerSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTitanium nitrideDeposition process
Embodiments described herein provide a method for forming two titanium nitride materials by different PVD processes, such that a metallic titanium nitride layer is initially formed by a PVD process in a metallic mode and a titanium nitride retarding layer is formed over a portion of the metallic titanium nitride layer by a PVD process in a poison mode. Subsequently, a first aluminum layer, such as an aluminum seed layer, may be selectively deposited on exposed portions of the metallic titanium nitride layer by a CVD process. Thereafter, a second aluminum layer, such as an aluminum bulk layer, may be deposited on exposed portions of the first aluminum layer and the titanium nitride retarding layer during an aluminum PVD process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
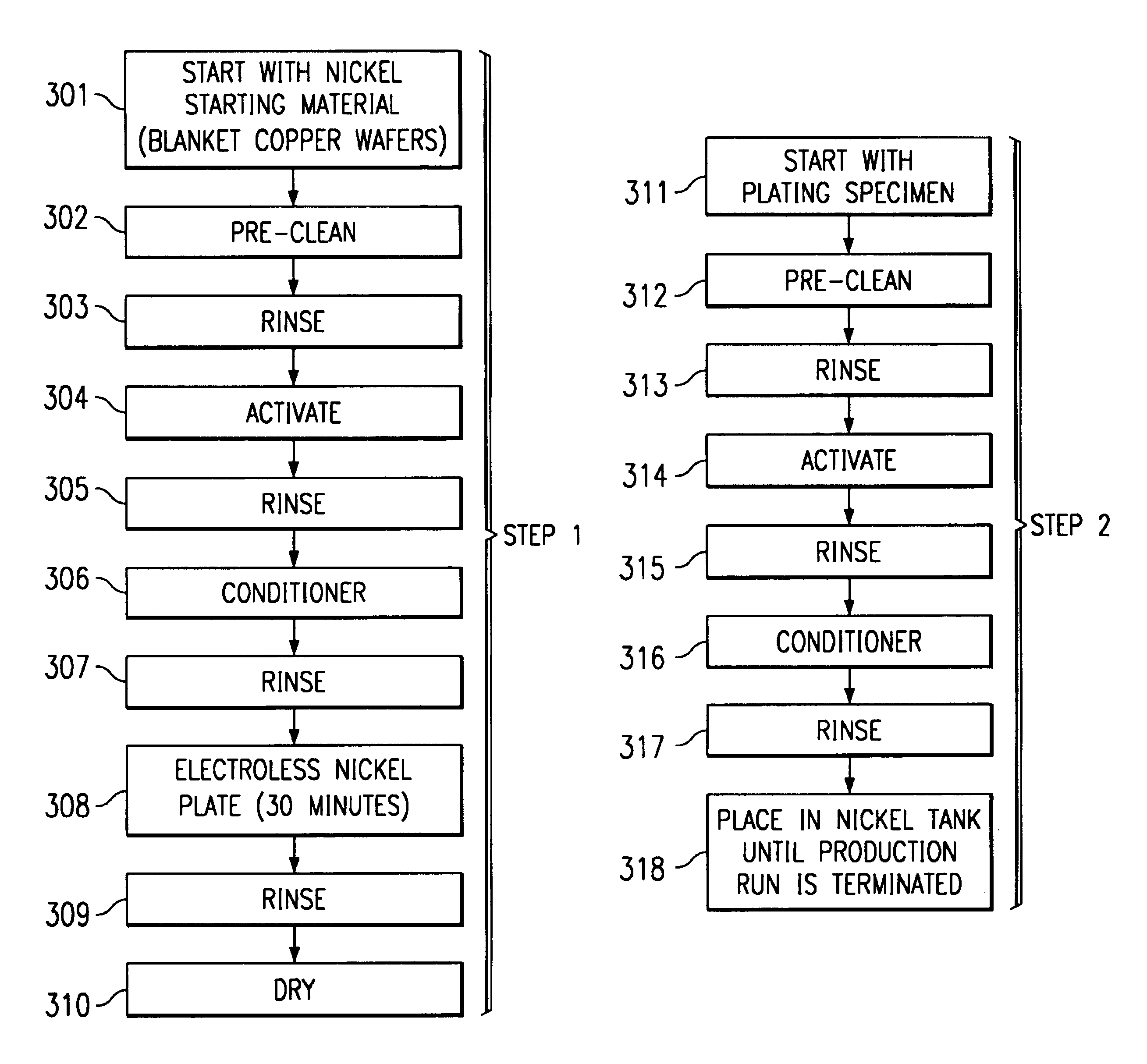
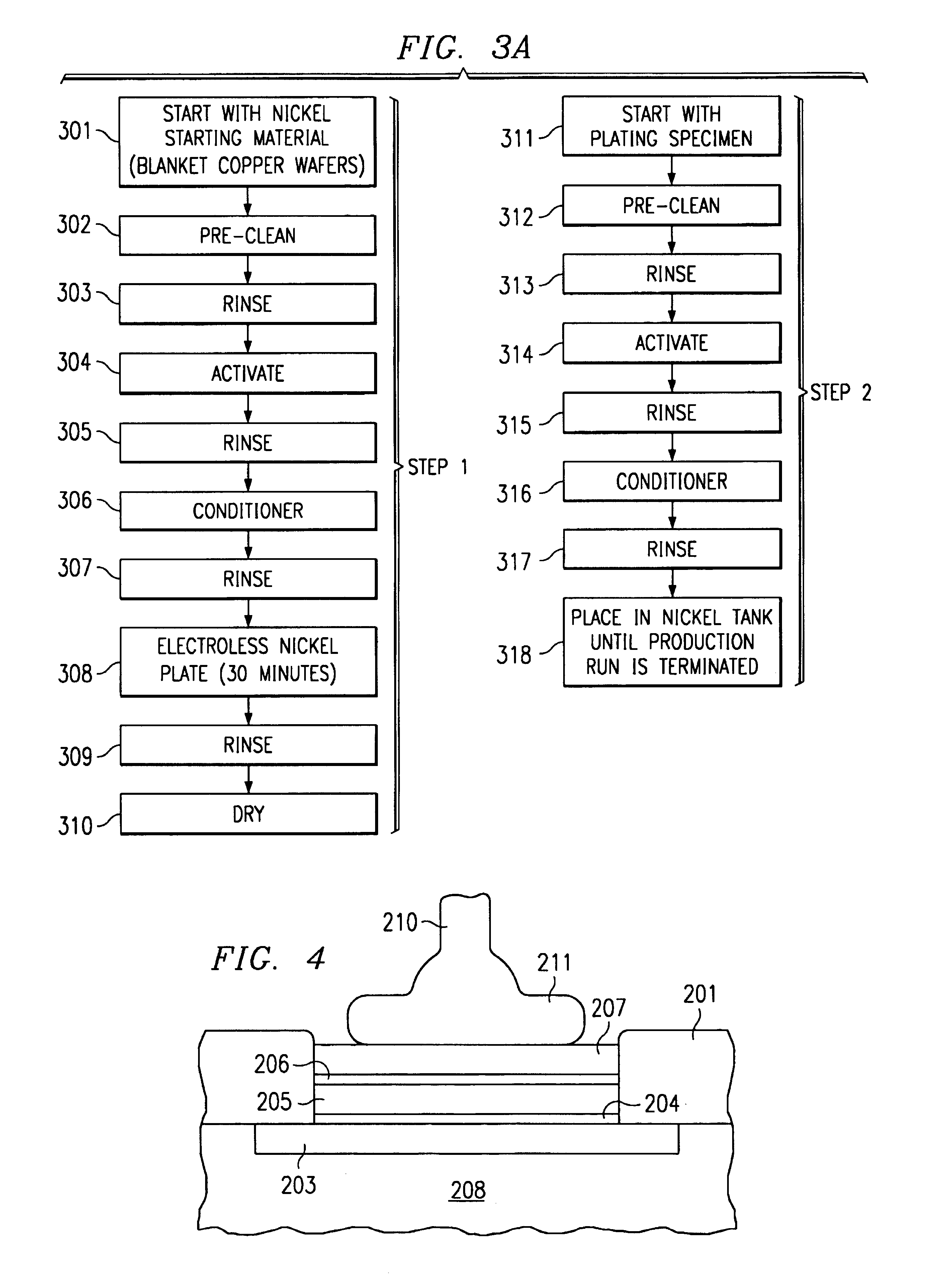
Method to achieve continuous hydrogen saturation in sparingly used electroless nickel plating process
InactiveUS6616967B1Maintain saturationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogenCopper
An improved wire bonding process for copper-metallized integrated circuits is provided by a nickel layer that acts as a barrier against up-diffusing copper. In accordance with the present invention the nickel bath is placed and remains in hydrogen saturation by providing a piece of metal that remains in the nickel plating tank before and during the plating process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
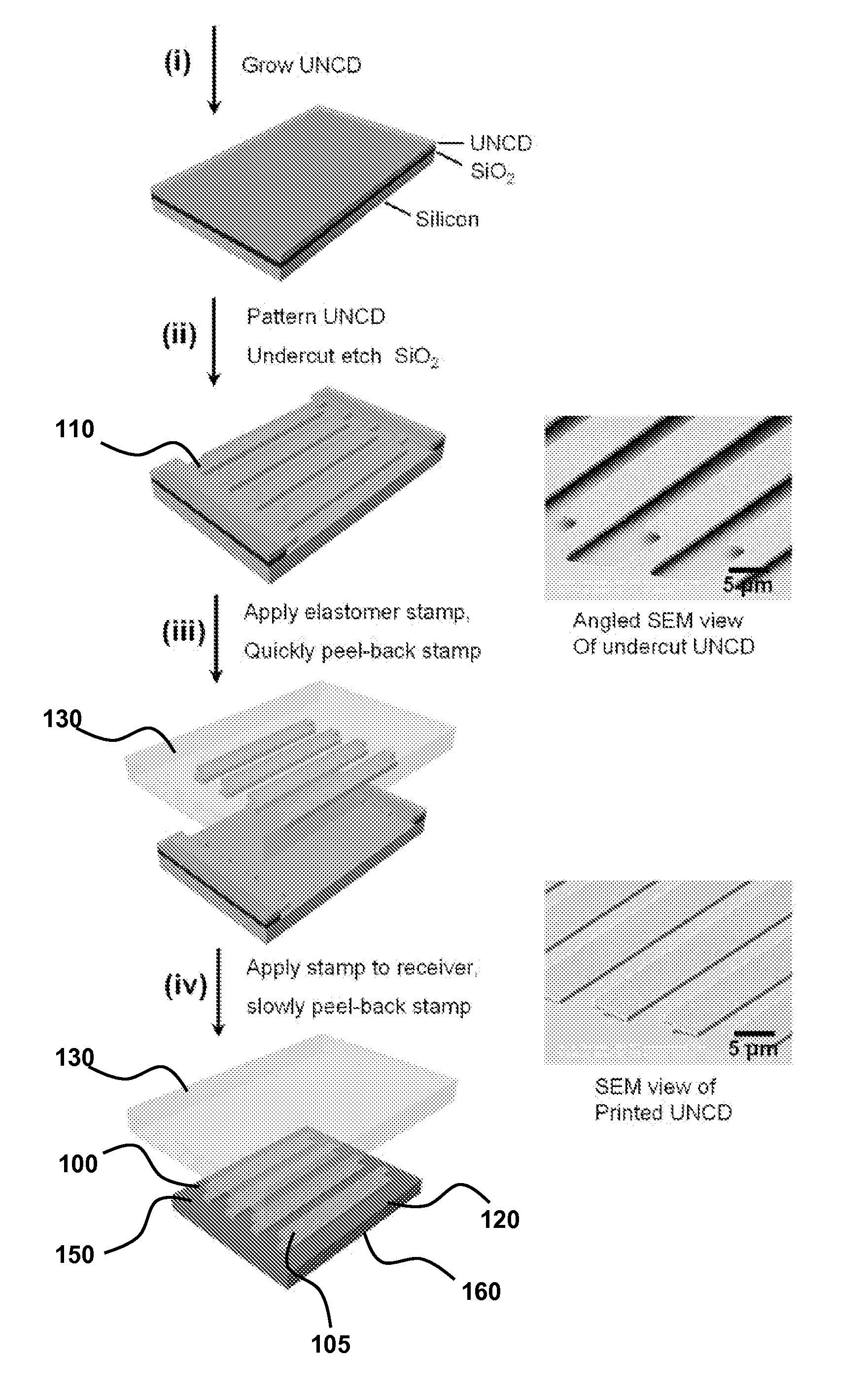
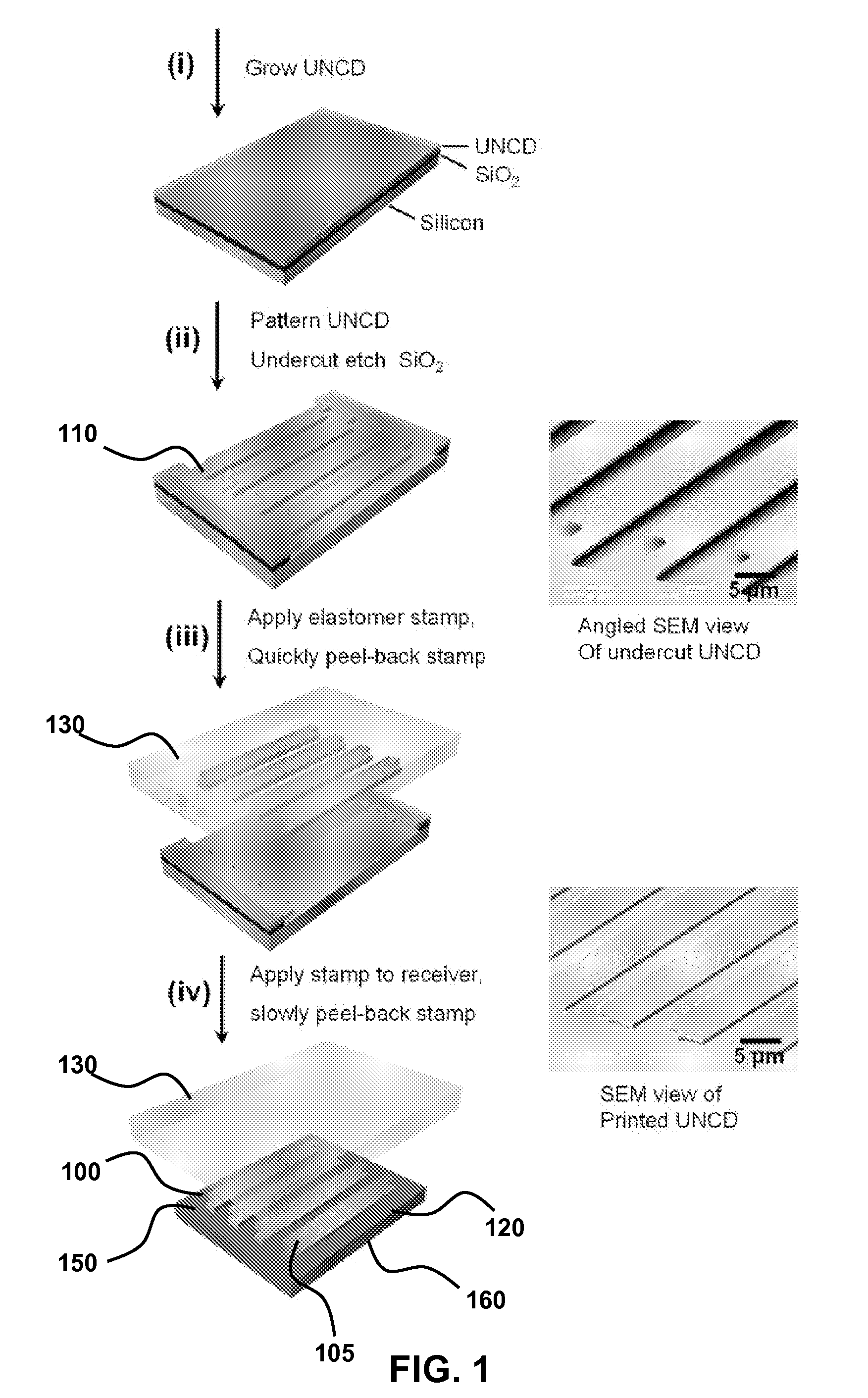
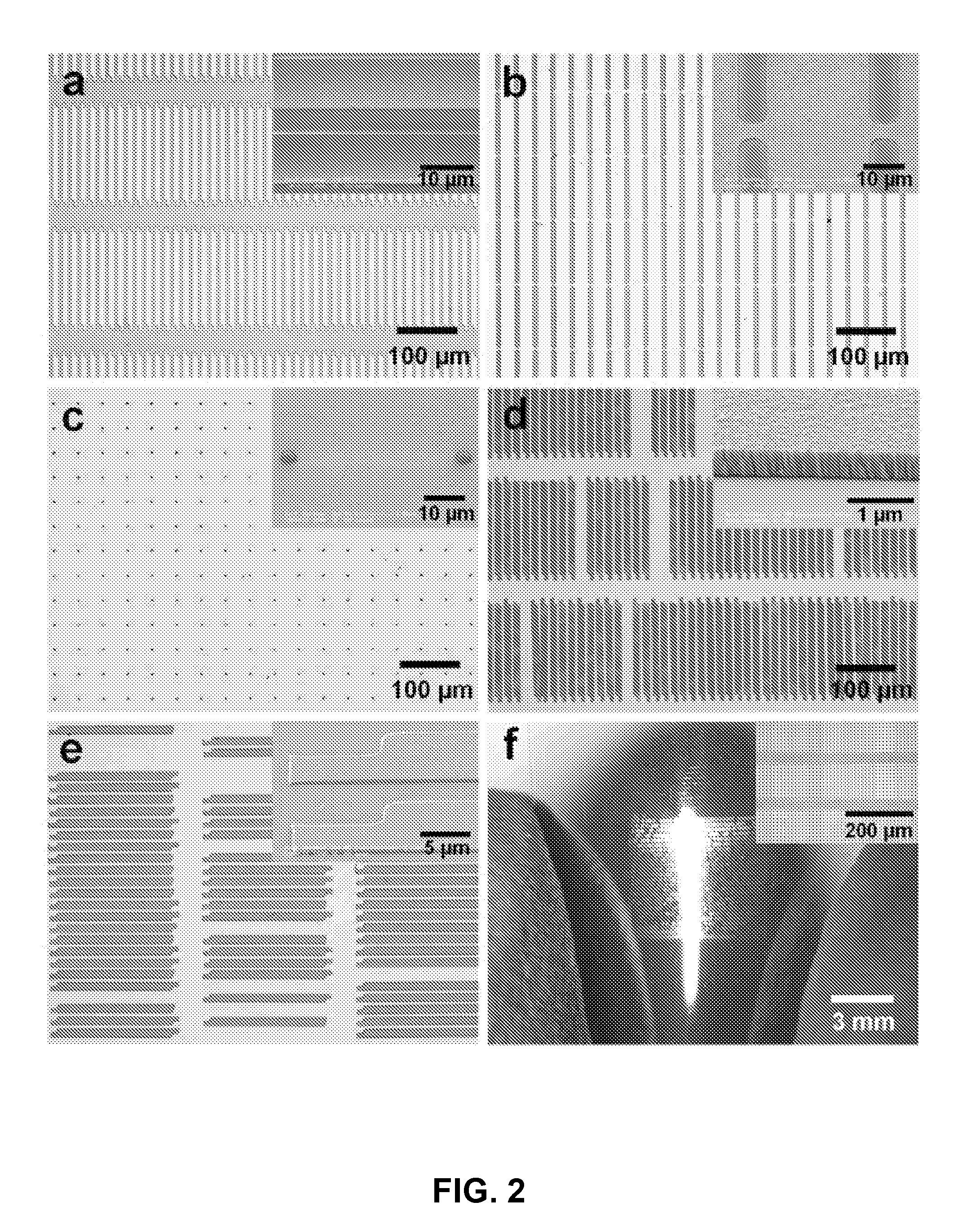
Printable, flexible and stretchable diamond for thermal management
InactiveUS8470701B2Reduce the amount requiredHeat dissipationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFlexible electronicsHeat sink
Owner:JOHN CRANE INC +2
Method and apparatus for forming device features in an integrated electroless deposition system
InactiveUS20070071888A1Growth inhibitionPrinted circuit aspectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial removalEngineering
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a cluster tool that is configured to electrolessly fill features formed on a substrate. More particularly, embodiments of the invention are used to integrate the filling of an interconnect or contact level feature using an electroless fill process and material removal steps. A typical sequence for forming an interconnect includes depositing one or more non-conductive layers, etching at least one of the layer(s) to form one or more features therein, depositing a barrier layer in the feature(s) and depositing one or more conductive layers, such as copper, to fill the feature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
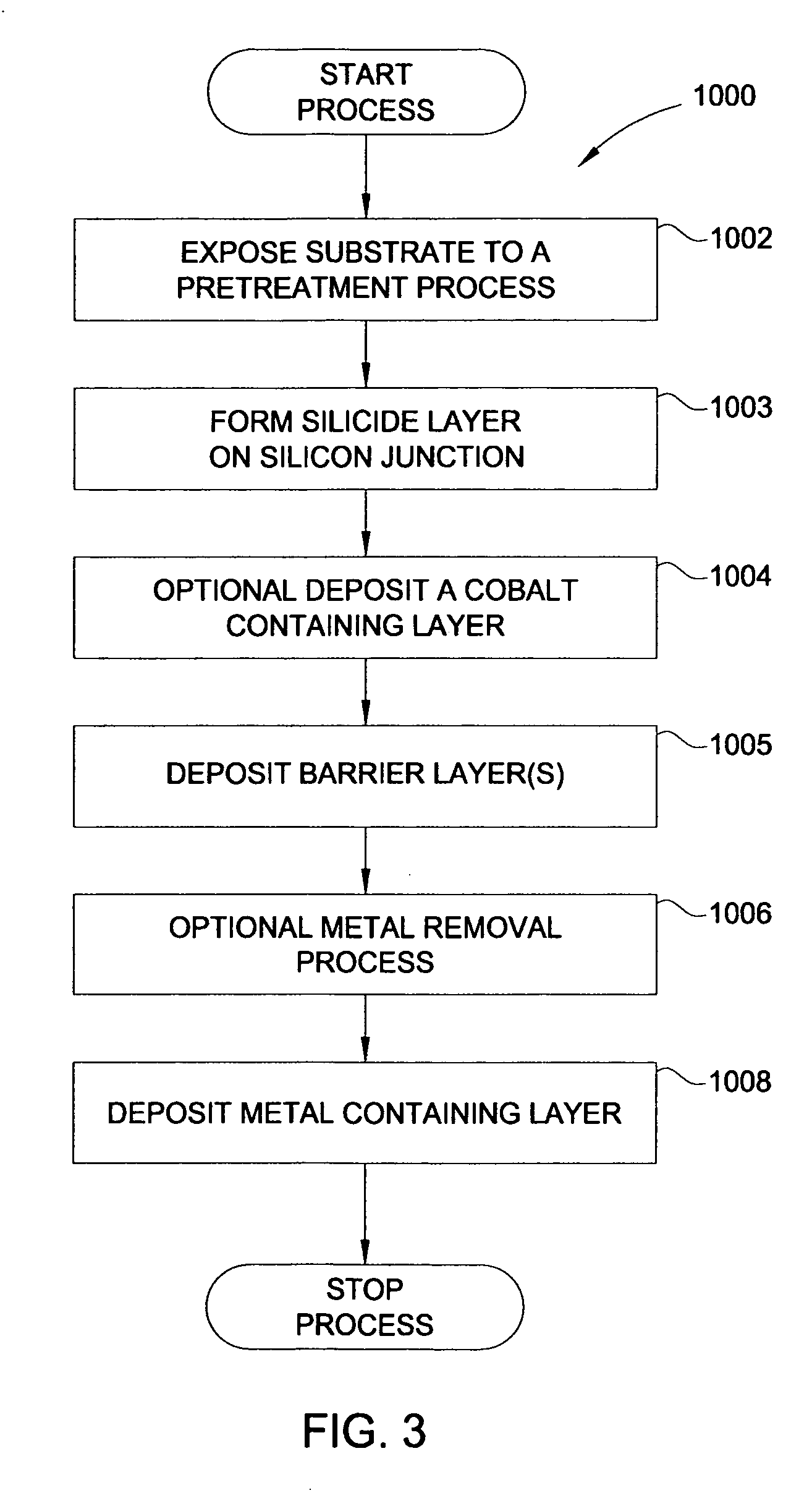
Electroless deposition process on a silicide contact
InactiveUS20060246217A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideElectroless deposition
Embodiments as described herein provide methods for depositing a material on a substrate during electroless deposition processes, as well as compositions of the electroless deposition solutions. In one embodiment, the substrate contains a contact aperture having an exposed silicon contact surface. In another embodiment, the substrate contains a contact aperture having an exposed silicide contact surface. The apertures are filled with a metal contact material by exposing the substrate to an electroless deposition process. The metal contact material may contain a cobalt material, a nickel material, or alloys thereof. Prior to filling the apertures, the substrate may be exposed to a variety of pretreatment processes, such as preclean processes and activations processes. A preclean process may remove organic residues, native oxides, and other contaminants during a wet clean process or a plasma etch process. Embodiments of the process also provide the deposition of additional layers, such as a capping layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
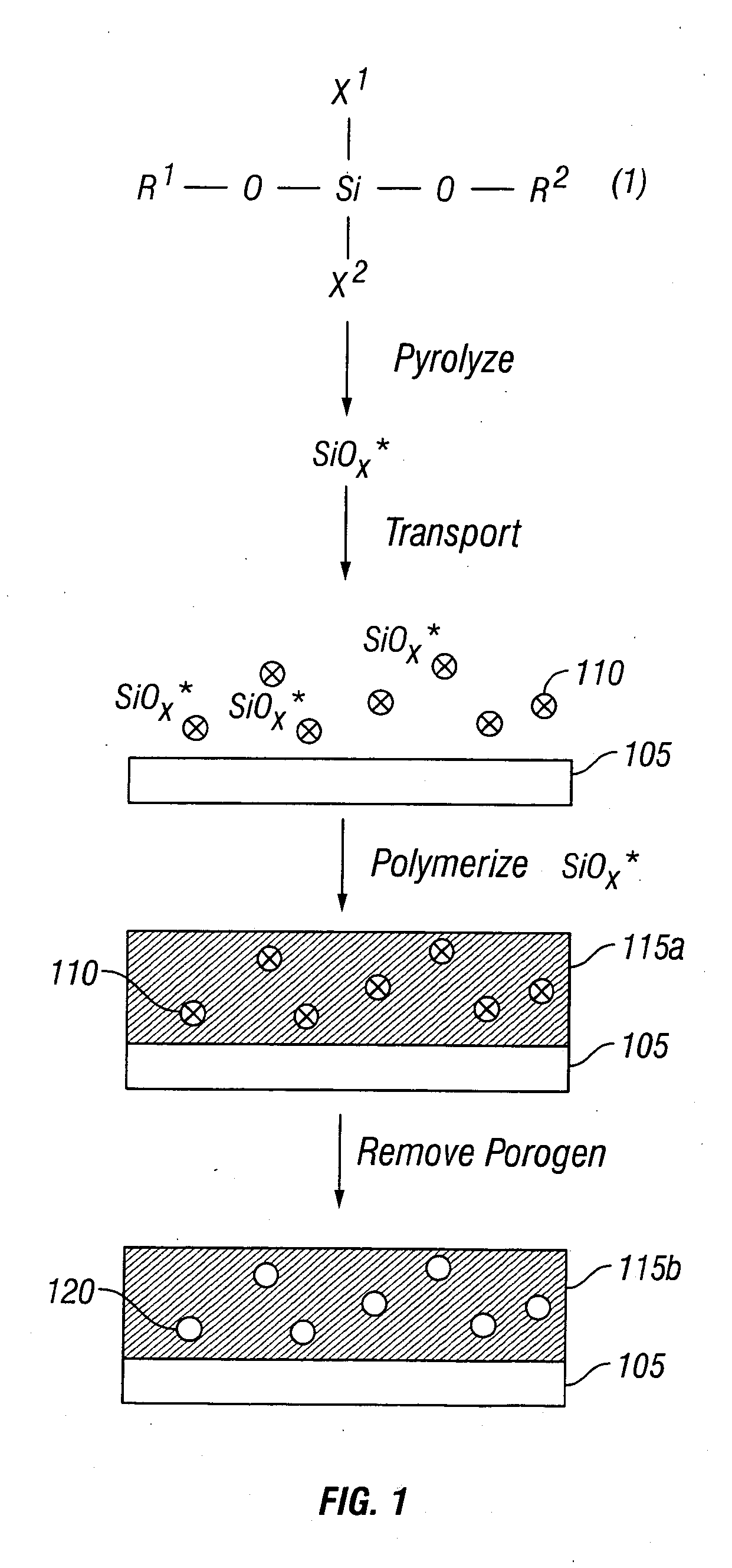
Apparatus, precursors and deposition methods for silicon-containing materials
A method for making a Si-containing material comprises transporting a pyrolyzed Si-precursor to a substrate and polymerizing the pyrolyzed Si-precursor on the substrate to form a Si-containing film. Polymerization of the pyrolyzed Si-precursor may be carried out in the presence of a porogen to thereby form a porogen-containing Si-containing film. The porogen may be removed from the porogen-containing Si-containing film to thereby form a porous Si-containing film. Preferred porous Si-containing films have low dielectric constants and thus are suitable for various low-k applications such as in microelectronics and microelectromechanical systems.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Sub-quarter-micron copper interconnections with improved electromigration resistance and reduced defect sensitivity
InactiveUS6069068ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseInterconnection
A method of providing sub-half-micron copper interconnections with improved electromigration and corrosion resistance. The method includes double damascene using electroplated copper, where the seed layer is deposited by chemical vapor deposition, or by physical vapor deposition in a layer less than about 800 angstroms.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of depositing films by using carboxylate complexes
InactiveUS6010969AVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesSemiconductor structureCarboxylic salt
A method of forming a film on a substrate using chemical vapor deposition techniques and carboxylate complexes. The complexes and method are particularly suitable for the preparation of semiconductor structures.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
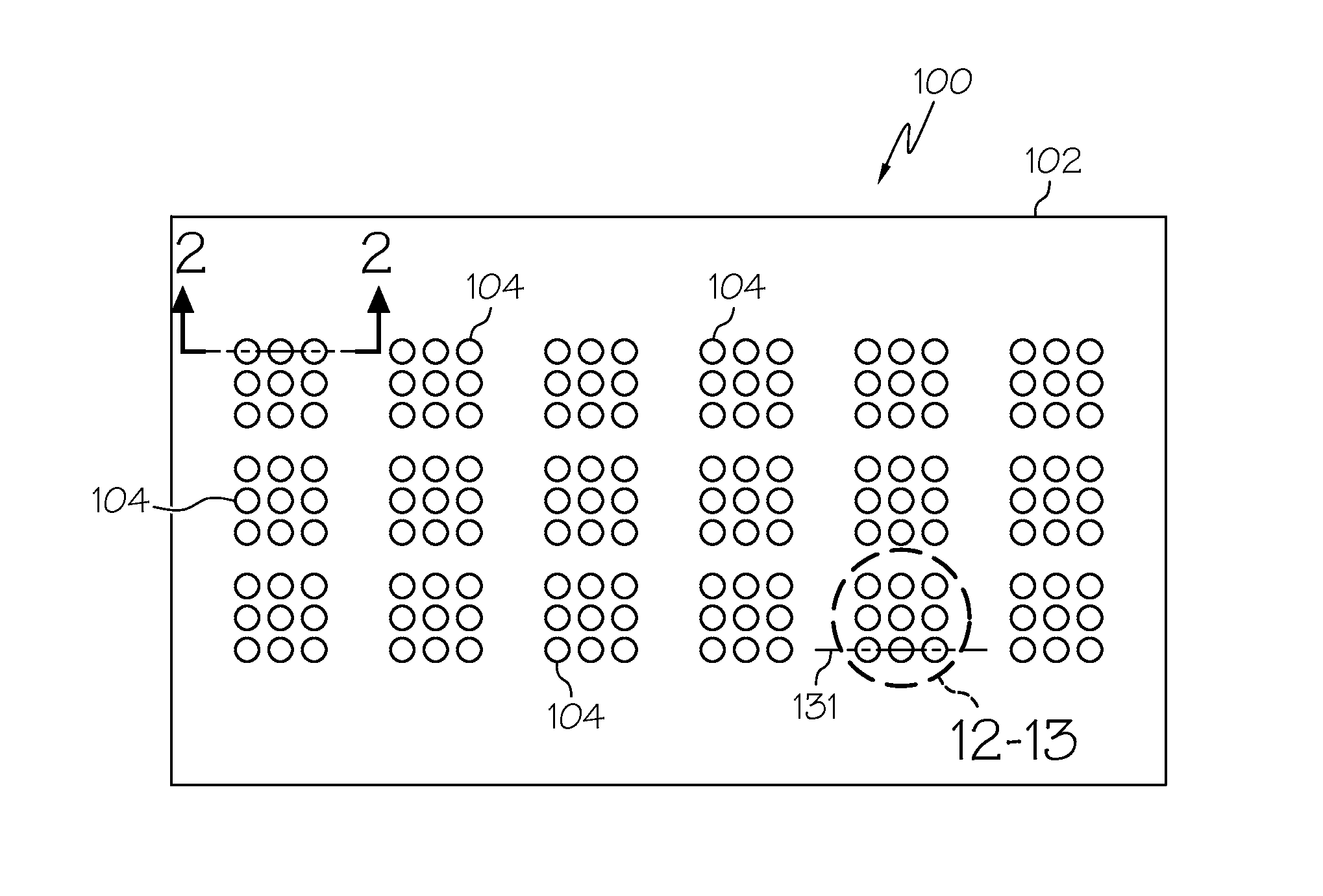
Glass Interposer Panels And Methods For Making The Same
InactiveUS20120048604A1Line/current collector detailsPrinted circuit detailsInterposerSecondary layer
Glass interposer panels and methods for forming the same are described herein. The interposer panels include a glass substrate core formed from an ion-exchangeable glass. A first layer of compressive stress may extend from a first surface of the glass substrate into the thickness T of the glass substrate core to a first depth of layer D1. A second layer of compressive stress may be spaced apart from the first layer of compressive stress and extending from a second surface of the glass substrate core into the thickness T of the glass substrate core to a second depth of layer D2. A plurality of through-vias may extend through the thickness T of the glass substrate core. Each through-via is surrounded by an intermediate zone of compressive stress that extends from the first layer of compressive stress to the second layer of compressive stress adjacent to a sidewall of each through-via.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of forming a silicon nitride layer
ActiveUS7229502B2Uniform thicknessReduce internal stressVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNitrogenEngineering
A method of forming a silicon nitride layer is provided. A deposition furnace having an outer tube, a wafer boat, a gas injector and a uniform gas injection apparatus is provided. The wafer boat is positioned within the outer tube for carrying a plurality of wafers. The gas injector is positioned between the outer tube and the wafer boat. Similarly, the uniform gas injection apparatus is positioned between the outer tube and the wafer boat. Gas injected into the uniform gas injection apparatus is uniformly distributed throughout the entire deposition furnace. To form a silicon nitride layer on each wafer, a silicon-containing gas is passed into the deposition furnace via the gas injector and a nitrogen-mixed carrier gas is passed into the deposition furnace via the uniform gas injection apparatus.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Method for manufacturing build-up multi-layer printed circuit board by using yag laser
A method for manufacturing a build-up multi-layer printed circuit board is disclosed in which a YAG laser is used upon the formation of a via hole in the multi-layer printed circuit board, such that it can have the following advantages: the manufacturing process would become simple; the component packaging density and freedom for the design of the board would be improved; and a high speed of signal process would be ensured. The method for manufacturing a build-up multi-layer printed circuit board includes the steps of: forming a first printed circuit pattern on a copper clad laminate (CCL) by applying a general photo-etching process, the CCL having a copper foil on the one face thereof; stacking a resin-coated (on one face) copper foil (RCC) on the CCL with the first printed circuit pattern formed thereon, and heating and pressing this structure; irradiating a YAG laser to the board with said RCC stacked so as to form a via hole at a predetermined position by removing said RCC; carrying out an electroless and electro copper plating on the board with the via hole formed therein to form a plated layer; and forming a second printed circuit pattern on said plated layer to electrically connect the layers on which the first and second printed circuit patterns are formed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
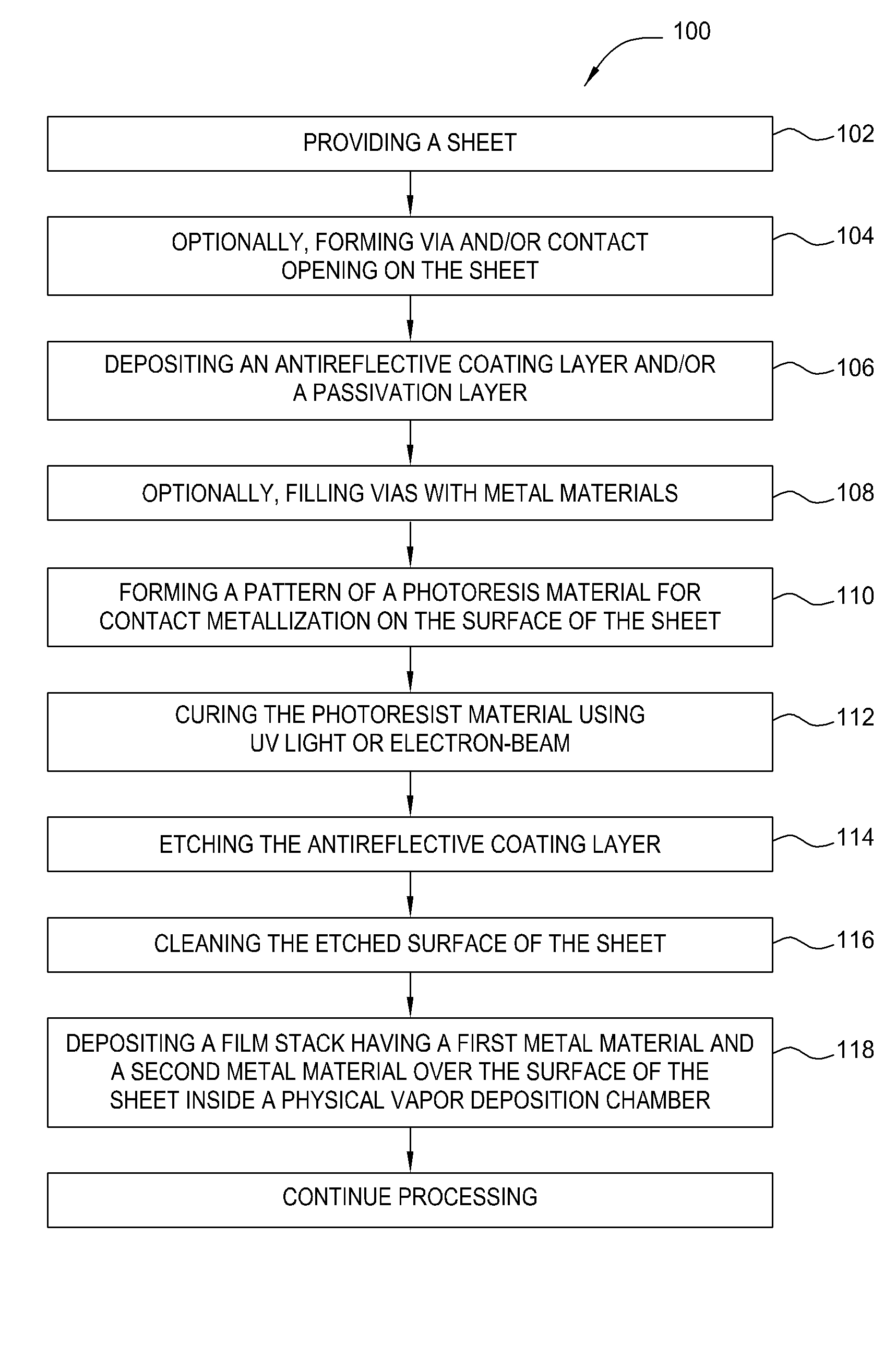
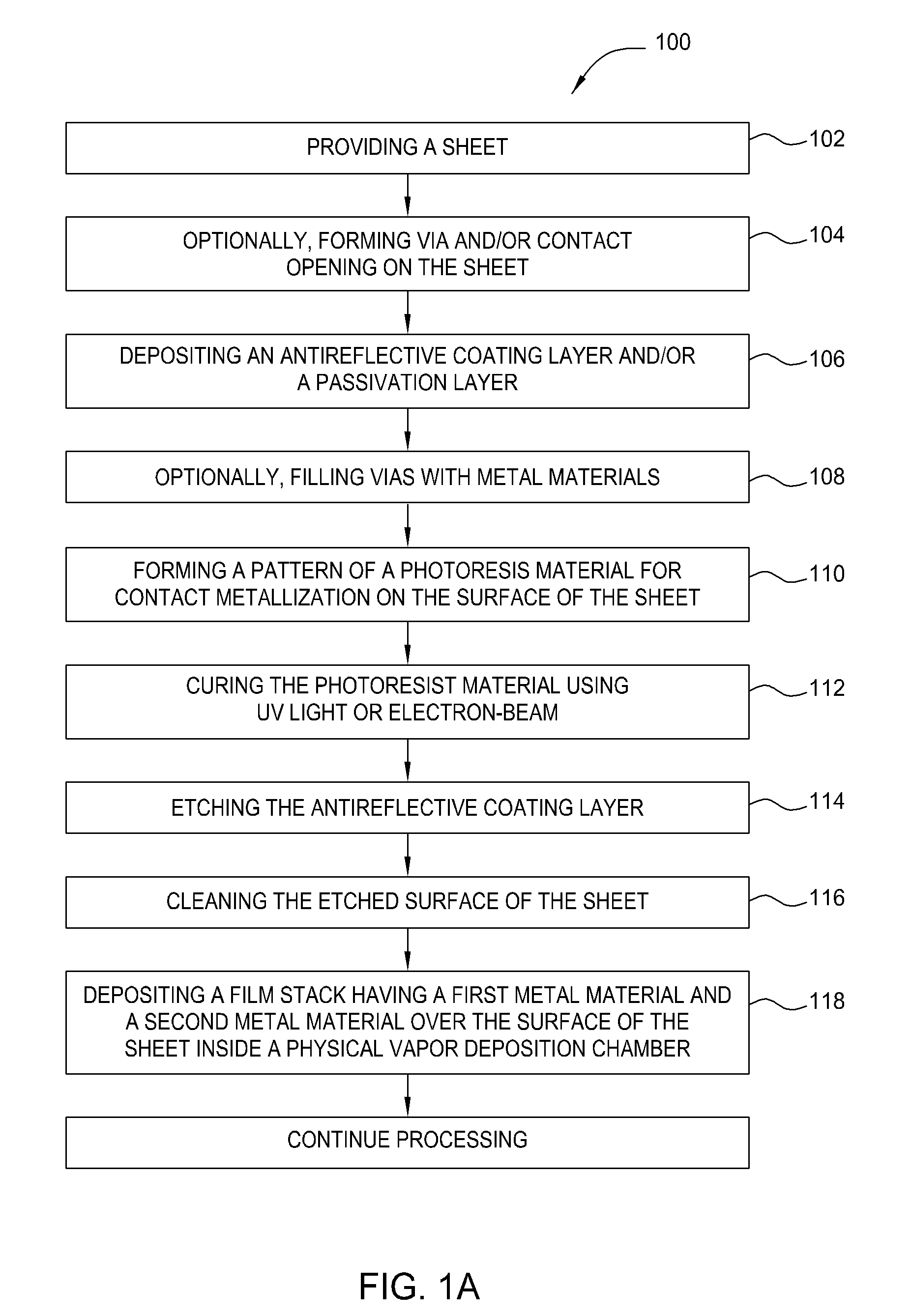
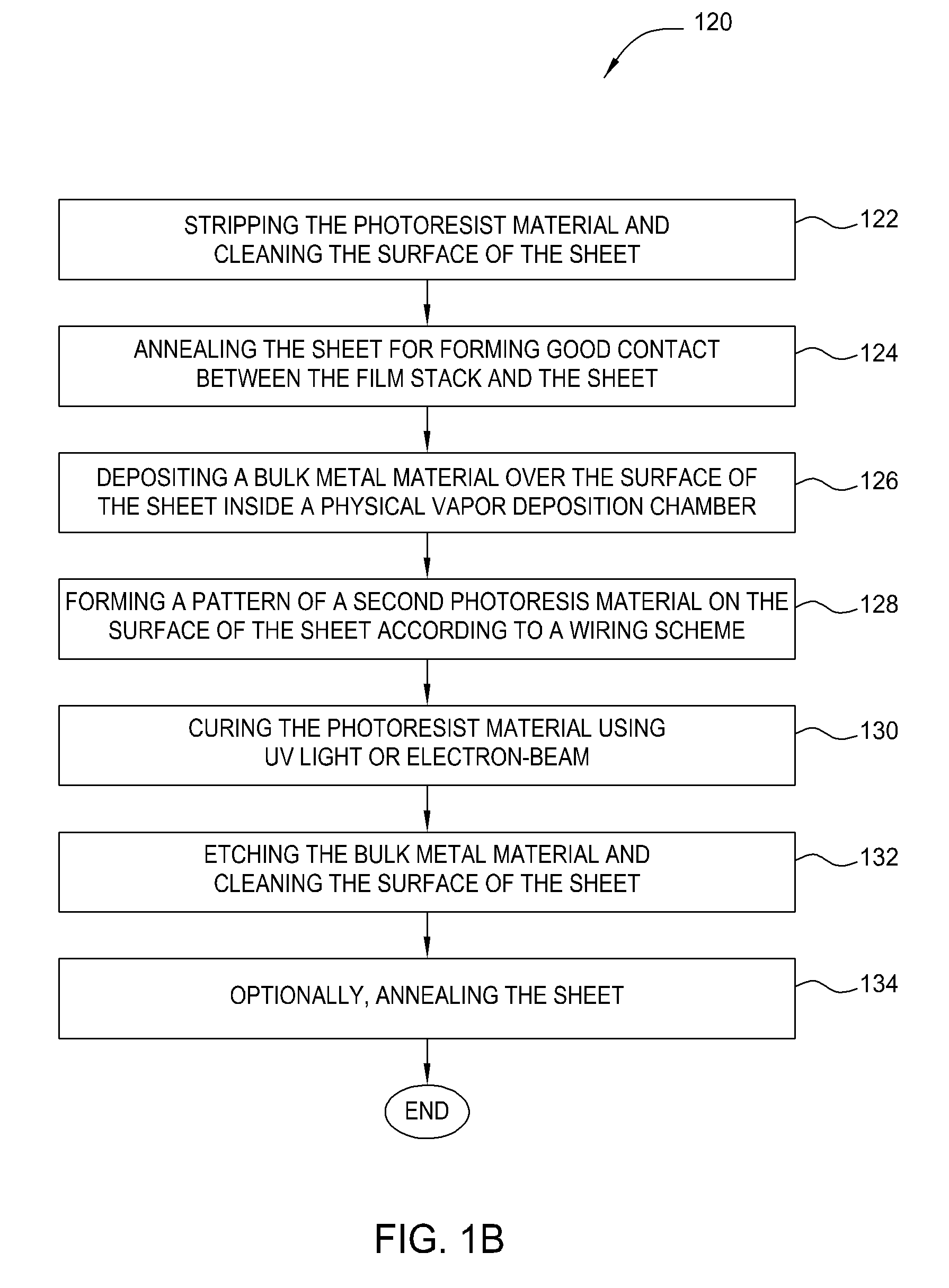
Photovoltaic contact and wiring formation
InactiveUS20070148336A1Reduce contact resistanceEnhanced vapor depositionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEtchingGas phase
A method and apparatus for fabricating a solar cell and forming metal contact is disclosed. Solar cell contact and wiring is formed by depositing a thin film stack of a first metal material and a second metal material as an initiation layer or seed layer for depositing a bulk metal layer in conjunction with additional sheet processing, photolithography, etching, cleaning, and annealing processes. In one embodiment, the thin film stack for forming metal silicide with reduced contact resistance over the sheet is deposited by sputtering or physical vapor deposition. In another embodiment, the bulk metal layer for forming metal lines and wiring is deposited by sputtering or physical vapor deposition. In an alternative embodiment, electroplating or electroless deposition is used to deposit the bulk metal layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Printed wiring board having highly reliably via hole and process for forming via hole
InactiveUS6280641B1Improve reliabilityImprove productivityLight absorption dielectricsDecorative surface effectsBond energyConductive coating
Disclosed are a printed wiring board having micro-via holes highly reliable for conduction and a method of making the micro-via hole by providing a coating or sheet of an organic substance containing 3 to 97% by volume of at least one selected from a metal compound powder, a carbon powder or a metal powder having a melting point of at least 900° C. and a bond energy of at least 300 kJ / mol on a copper foil as an outermost layer of a copper-clad laminate having at least two copper layers, or providing a coating or sheet of the same after oxidizing a copper foil as an outermost layer, irradiating the coating or sheet with a carbon dioxide gas laser at an output of 20 to 60 mJ / pulse, thereby removing a micro-via-hole-forming portion of at least the copper foil as the outermost layer, then irradiating micro-via-hole-forming portions of the remaining layers with a carbon dioxide gas laser at an output of 5 to 35 mJ / pulse to make a micro-via hole which does not penetrate through the copper foil in a bottom of the micro-via hole, and electrically connecting the copper foil as the outermost layer and the copper foil in the bottom of the micro-via hole with a metal plating or an electrically conductive coating composition.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
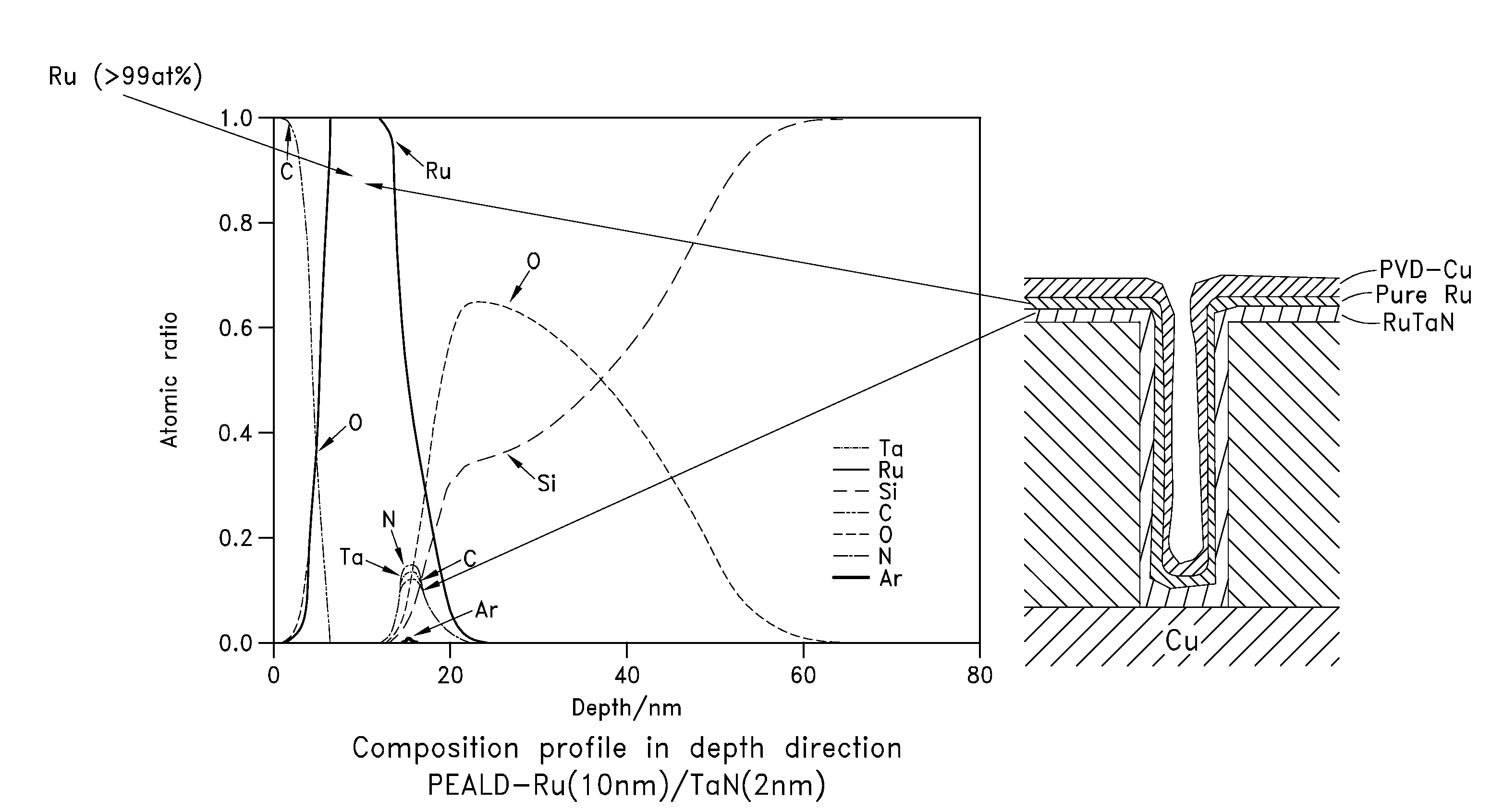
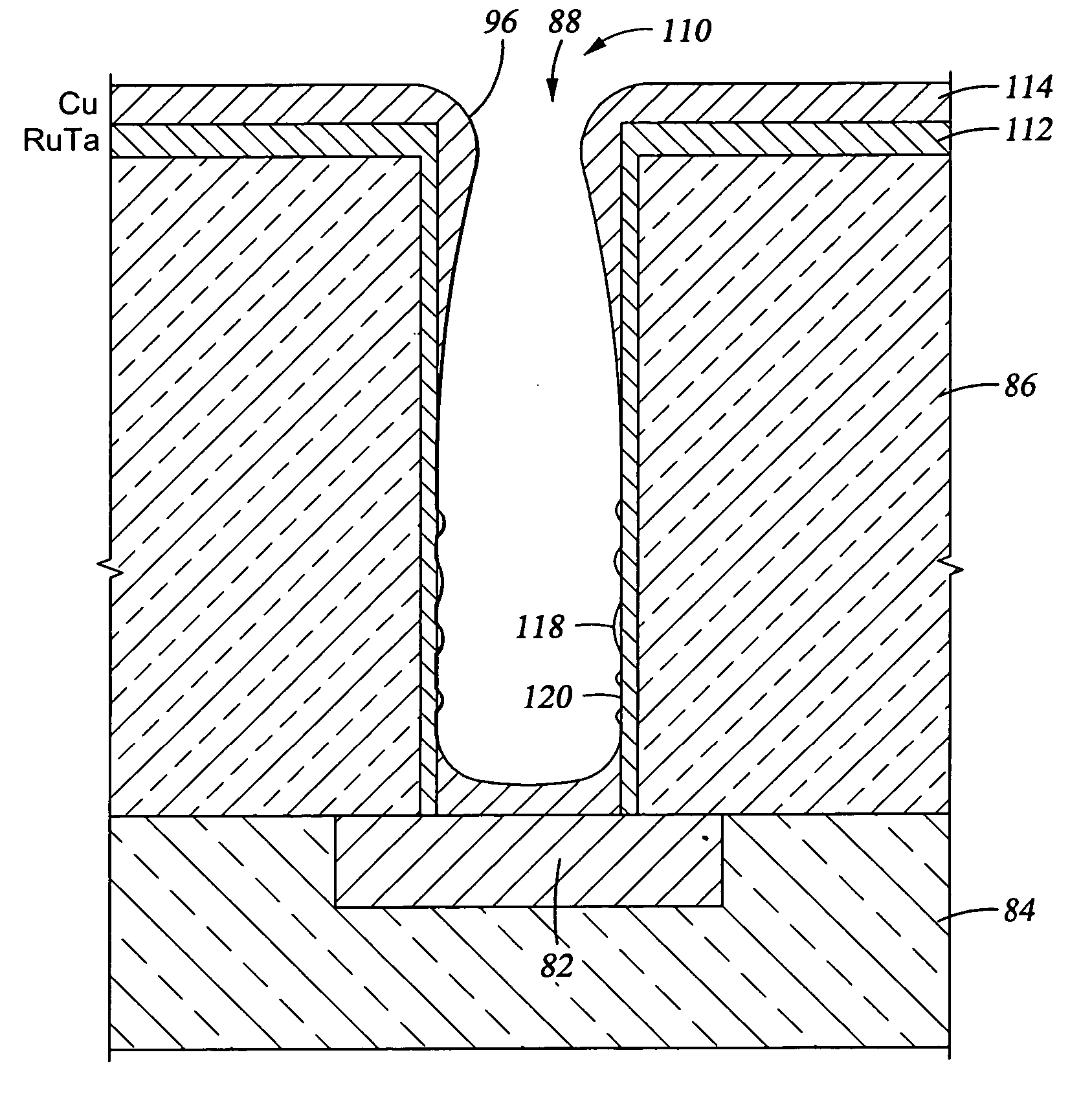
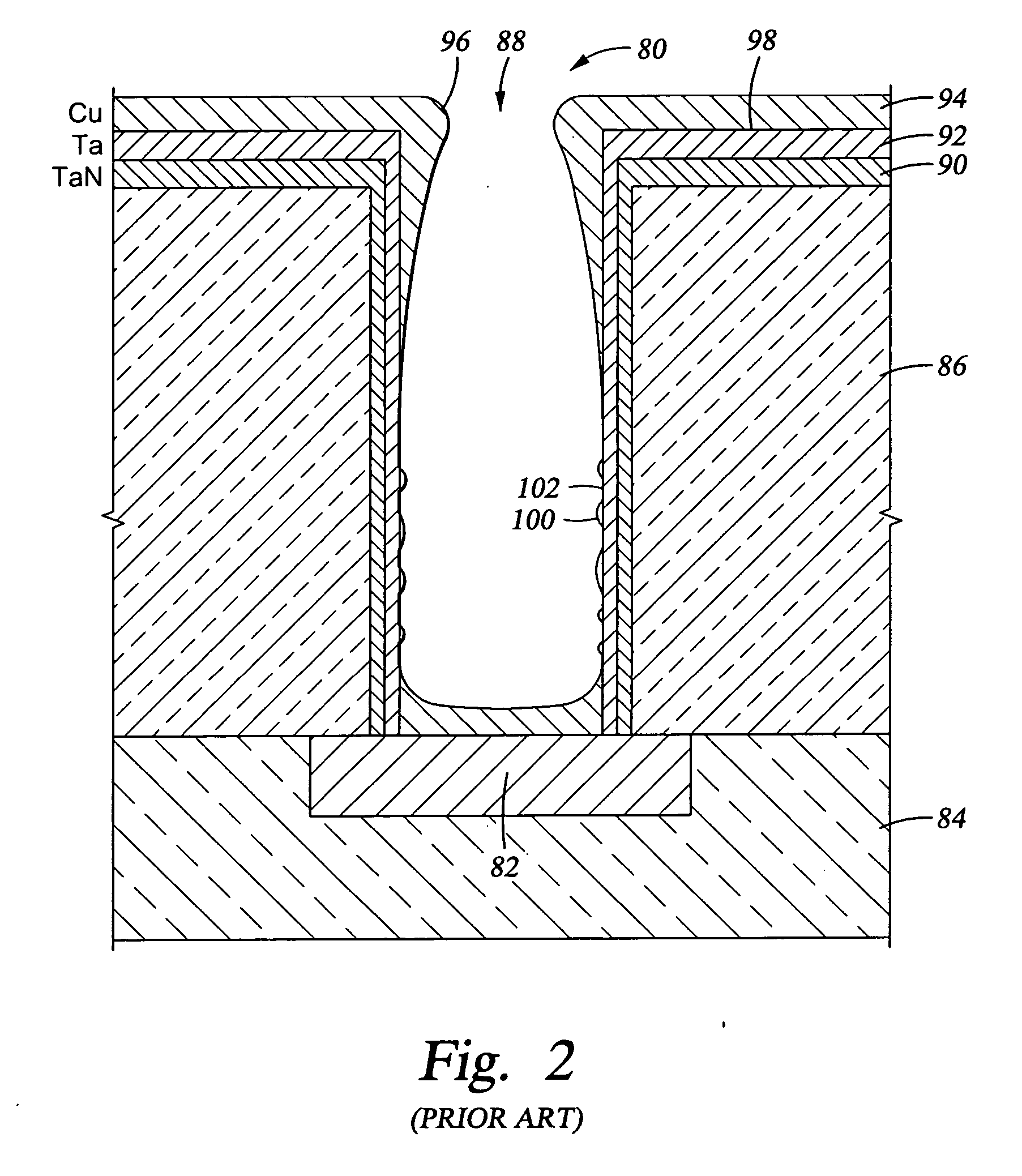
Integrated process for sputter deposition of a conductive barrier layer, especially an alloy of ruthenium and tantalum, underlying copper or copper alloy seed layer
InactiveUS20070059502A1Effective interfacial barrierGood suitSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingMoisture barrierRefractory metals
A fabrication method and a product for the deposition of a conductive barrier or other liner layer in a vertical electrical interconnect structure. One embodiment includes within a a hole through a dielectric layer a barrier layer of RuTaN, an adhesion layer of RuTa, and a copper seed layer forming a liner for electroplating of copper. The ruthenium content is preferably greater than 50 at % and more preferably at least 80 at % but less than 95 at %. The barrier and adhesion layers may both be sputter deposited. Other platinum-group elements substitute for the ruthenium and other refractory metals substitute for the tantalum. Aluminum alloying into RuTa when annealed presents a moisture barrier. Copper contacts include different alloying fractions of RuTa to shift the work function to the doping type.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
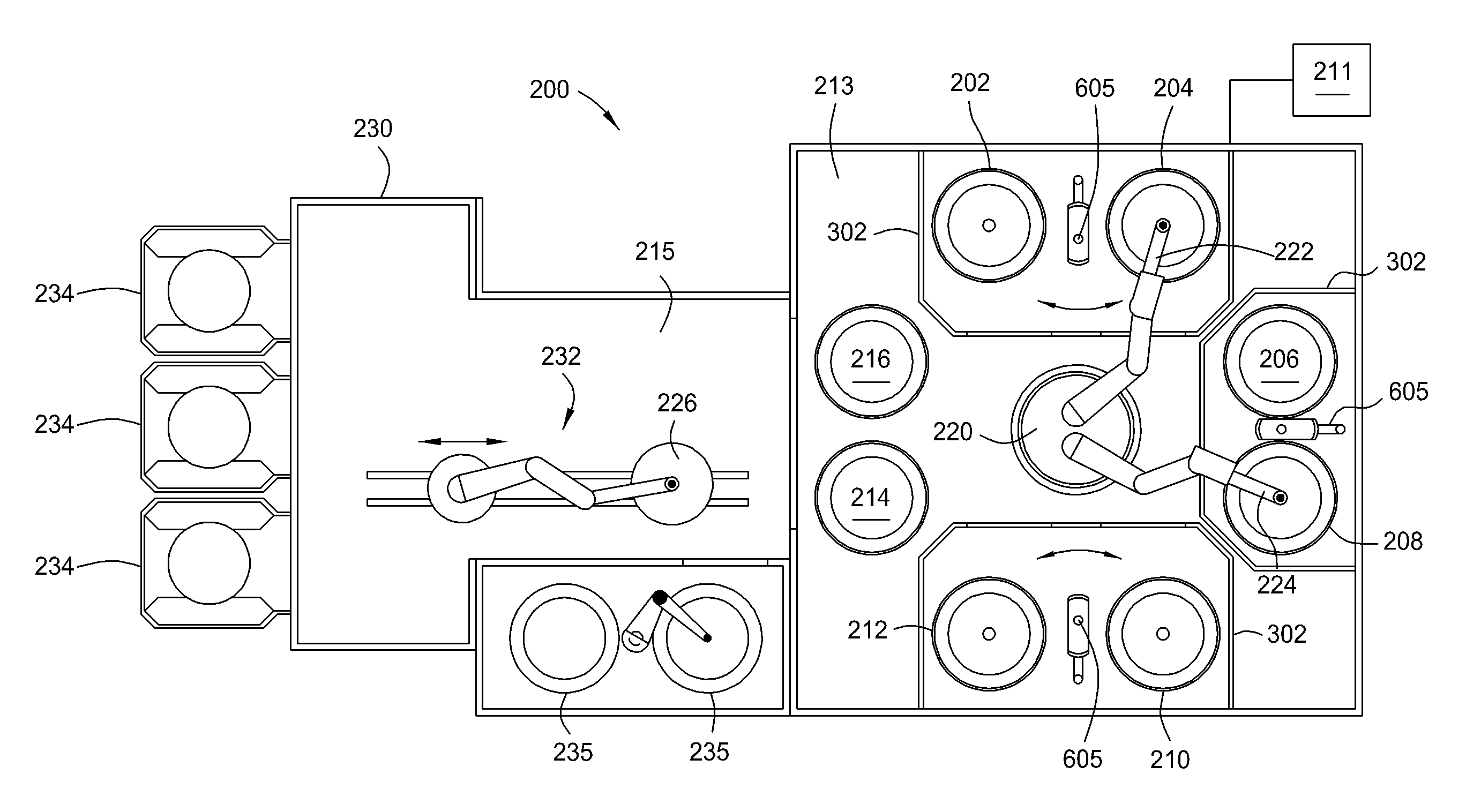
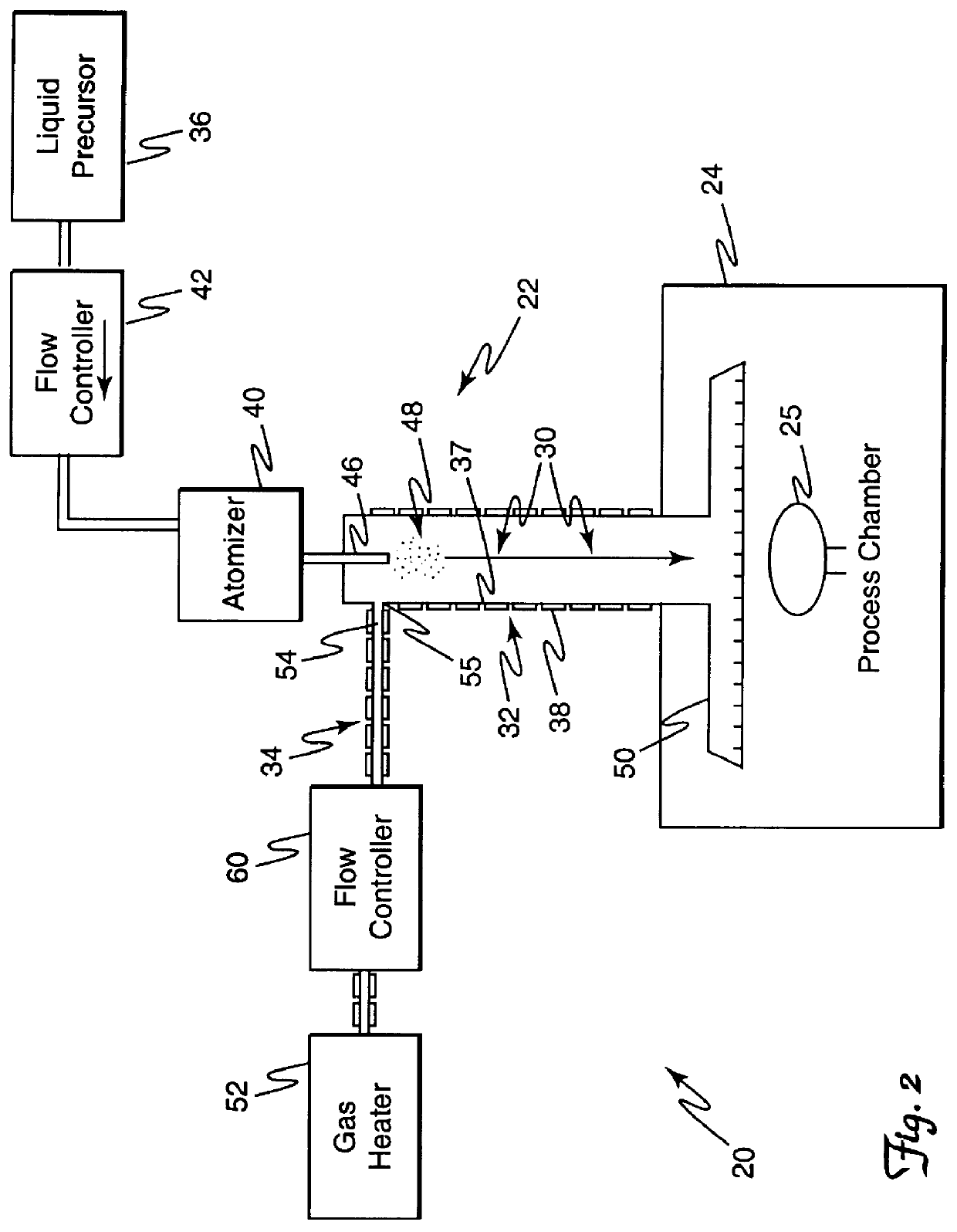
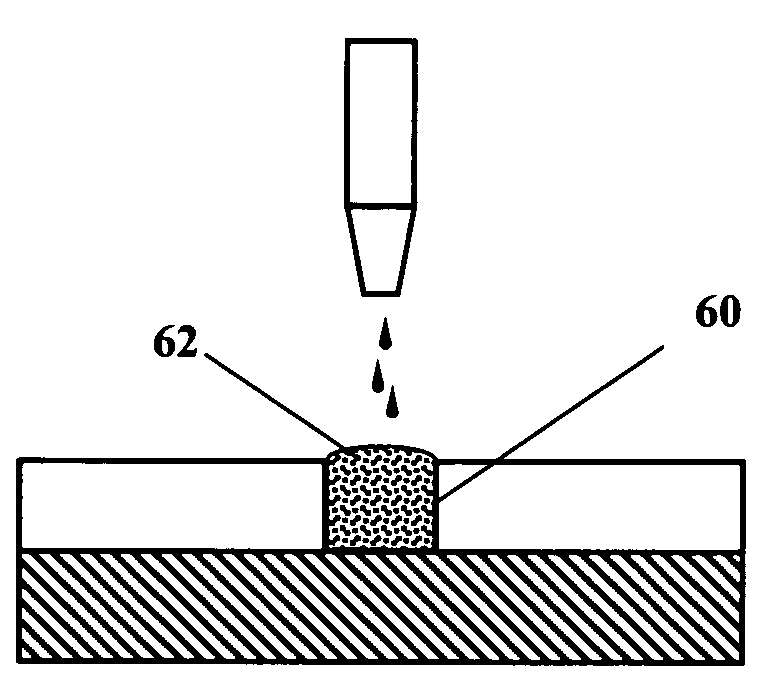
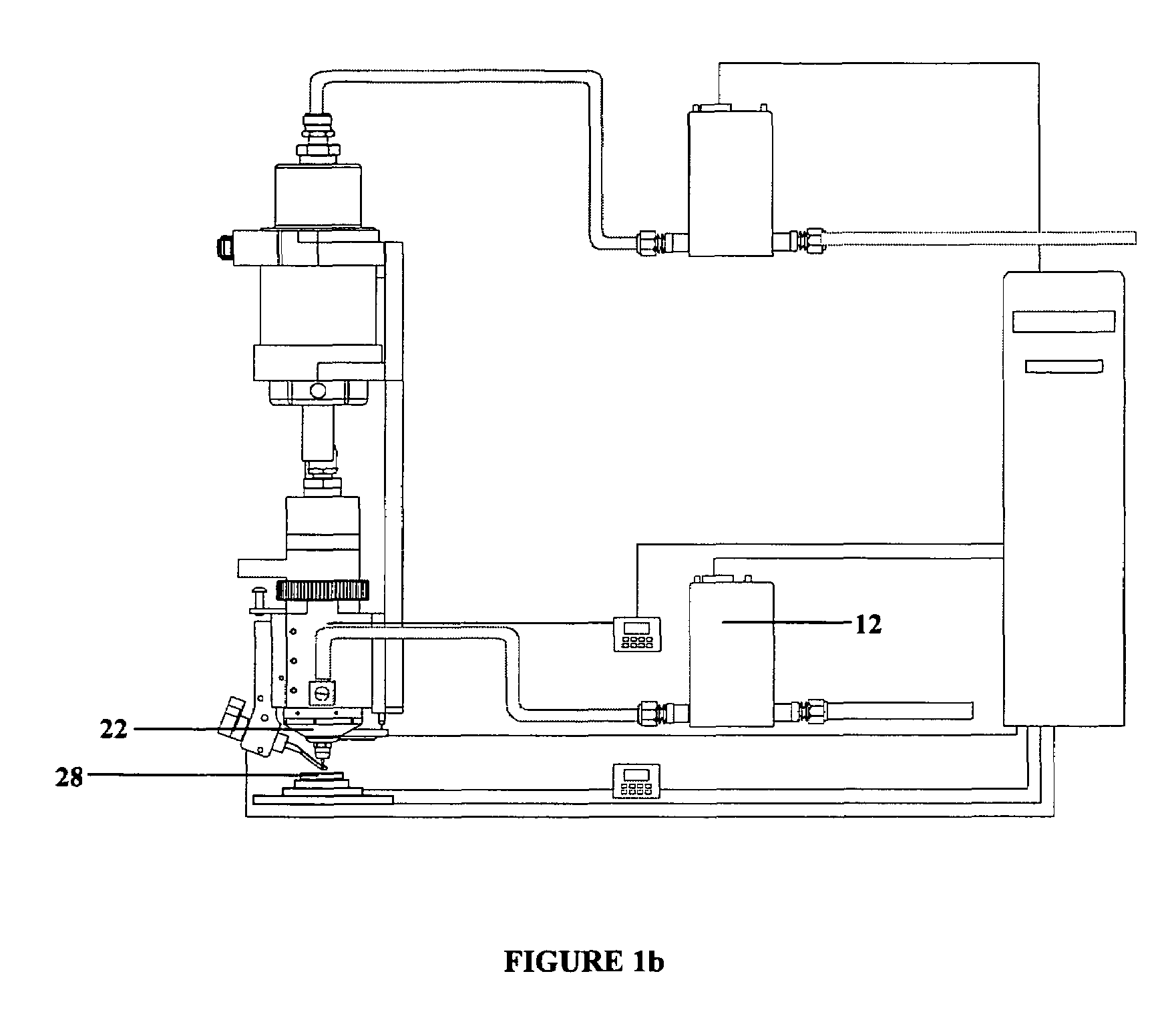
Aerodynamic jetting of aerosolized fluids for fabrication of passive structures
InactiveUS7674671B2Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical propertyDirect writing
Method and apparatus for direct writing of passive structures having a tolerance of 5% or less in one or more physical, electrical, chemical, or optical properties. The present apparatus is capable of extended deposition times. The apparatus may be configured for unassisted operation and uses sensors and feedback loops to detect physical characteristics of the system to identify and maintain optimum process parameters.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Dual damascene metallization
InactiveUS6207222B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper wireDielectric layer
The present invention generally provides a metallization process for forming a highly integrated interconnect. More particularly, the present invention provides a dual damascene interconnect module that incorporates a barrier layer deposited on all exposed surface of a dielectric layer which contains a dual damascene via and wire definition. A conductive metal is deposited on the barrier layer using two or more deposition methods to fill the via and wire definition prior to planarization. The invention provides the advantages of having copper wires with lower resistivity (greater conductivity) and greater electromigration resistance than aluminum, a barrier layer between the copper wire and the surrounding dielectric material, void-free, sub-half micron selective CVD Al via plugs, and a reduced number of process steps to achieve such integration.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for manufacturing touch panel, touch panel, display device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20100171718A1Reduce manufacturing costLow costLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPrinted circuit manufactureTouchpadDisplay device
A method for manufacturing a touch panel including a substrate, a first electrode, and a second electrode, the first and second electrodes being formed on one side of the substrate in a plural numbers and extending in directions intersecting with each other, the method includes forming the first electrode and electrode films on the substrate, forming an insulating film by a printing method on at least an intersection of the first electrode with the second electrode, and forming a bridge wiring line connecting the electrode films over the insulating film by the printing method. In the method, each of the electrode films has a shape obtained by cutting off the second electrode at the intersection.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for the fabrication of conductive electronic features
InactiveUS20100112195A1Reduce settlementGood dispersionPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronMaterials science
Owner:CABOT CORP
Multilayer ceramic capacitor with terminal formed by electroless plating
InactiveUS20080158774A1High strengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic capacitorElectroless deposition
A terminal to, most commonly, a ceramic capacitor, most commonly a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), is formed by electroless plating, also known as electroless deposition or simply as electrodeposition. In the MLCC having a multiple parallel interior plates brought to, and exposed at, at least one, first, surface, an electrically-conductive first-metal layer, preferably Cu, is electrolessly deposited upon this first surface directly in contact with, mechanically connected to, and electrically connected to, the edges of these interior plates. Lateral growth of the electrolessly-deposited first-metal is sufficient to span from exposed plate to exposed plate, electrically connecting the plates. One or more top layers, preferably one of Ni and one of Sn and Pb, are deposited, preferably by plating and more preferably by electrolytic plating, on top of the electrolessly-deposited Cu.
Owner:PRESIDIO COMPONENTS
Method for producing a tube
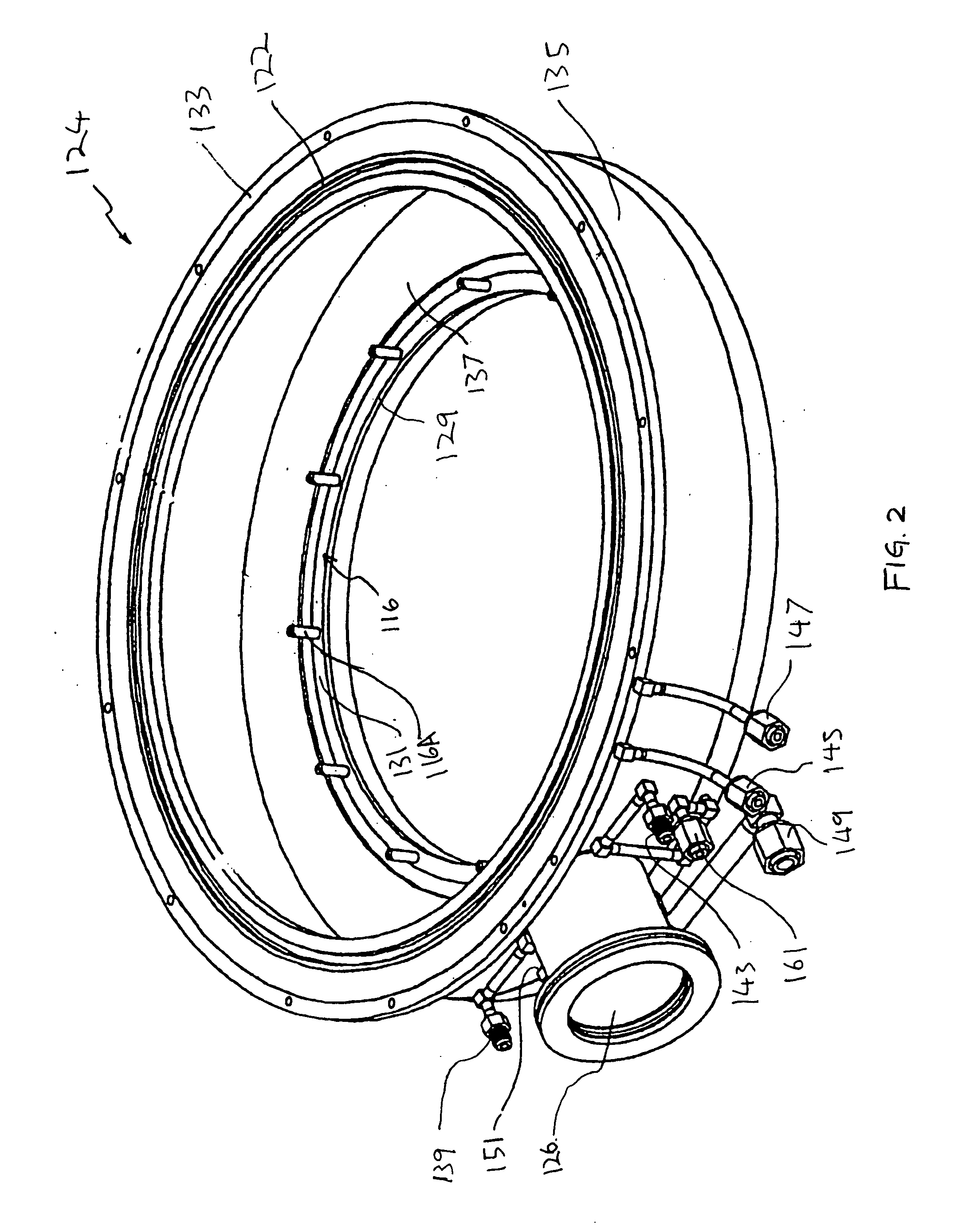
ActiveUS7155812B1Printed circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsElectrical conductorDrift tube
A method is described for producing tubular substrates having parallel spaced concentric rings of electrical conductors that can be used as the drift tube of an Ion Mobility Spectrometer (IMS). The invention comprises providing electrodes on the inside of a tube that are electrically connected to the outside of the tube through conductors that extend between adjacent plies of substrate that are combined to form the tube. Tubular substrates are formed from flexible polymeric printed wiring board materials, ceramic materials and material compositions of glass and ceramic, commonly known as Low Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic (LTCC). The adjacent plies are sealed together around the electrode.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com