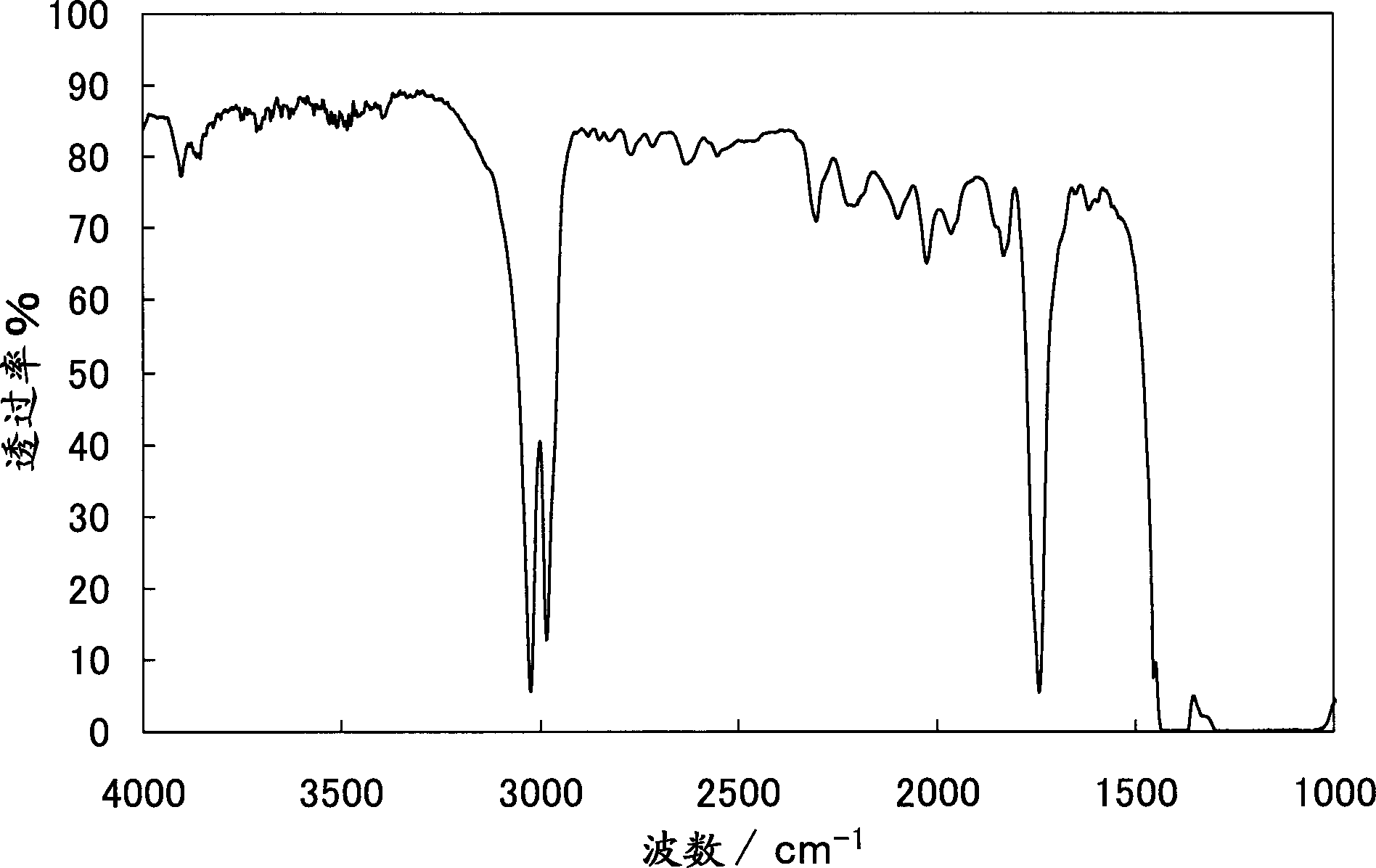
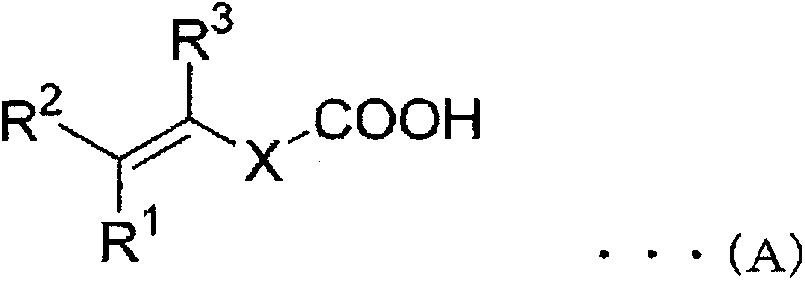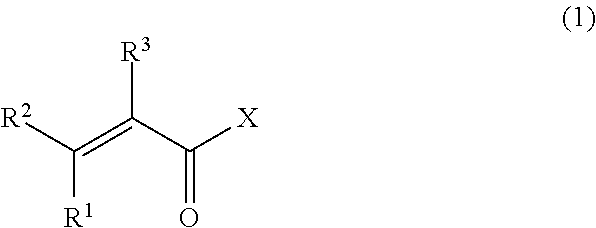Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "1,1-Difluoroethylene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
1,1-Difluoroethylene, also known as vinylidene fluoride, is a hydrofluoroolefin. It is a flammable gas. Global production in 1999 was approximately 33,000 metric tons. It is primarily used in the production of fluoropolymers such as polyvinylidene fluoride.
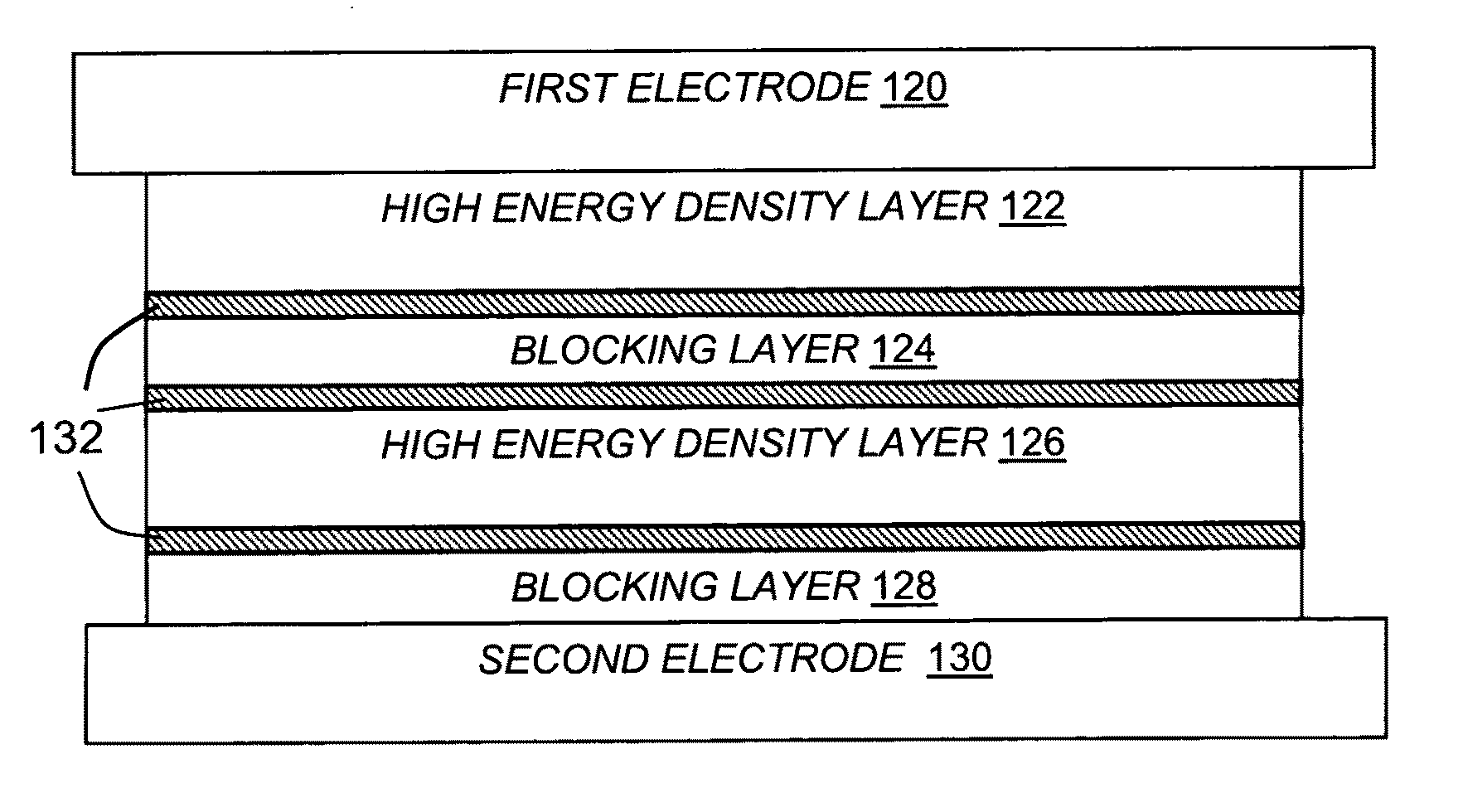
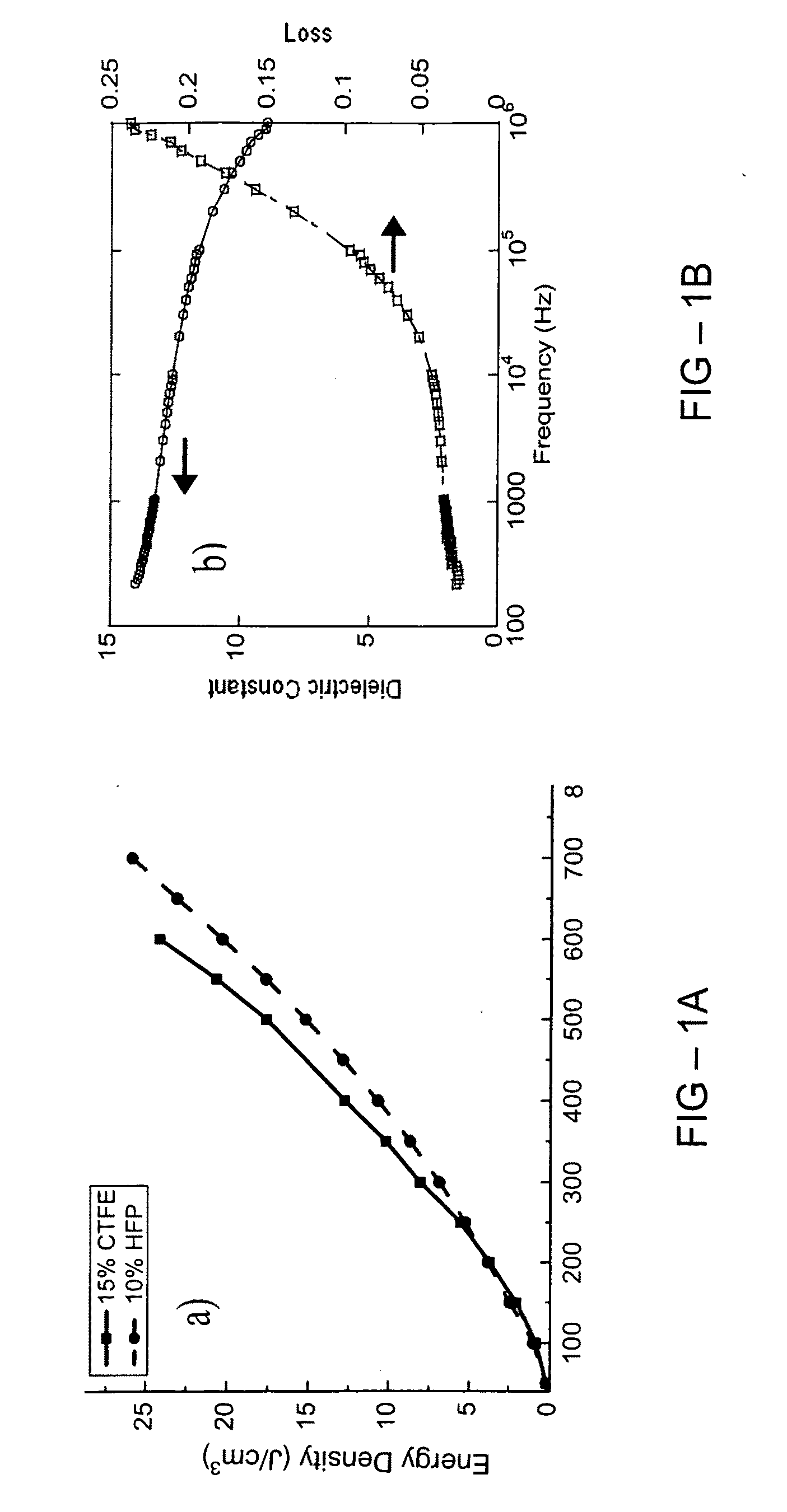
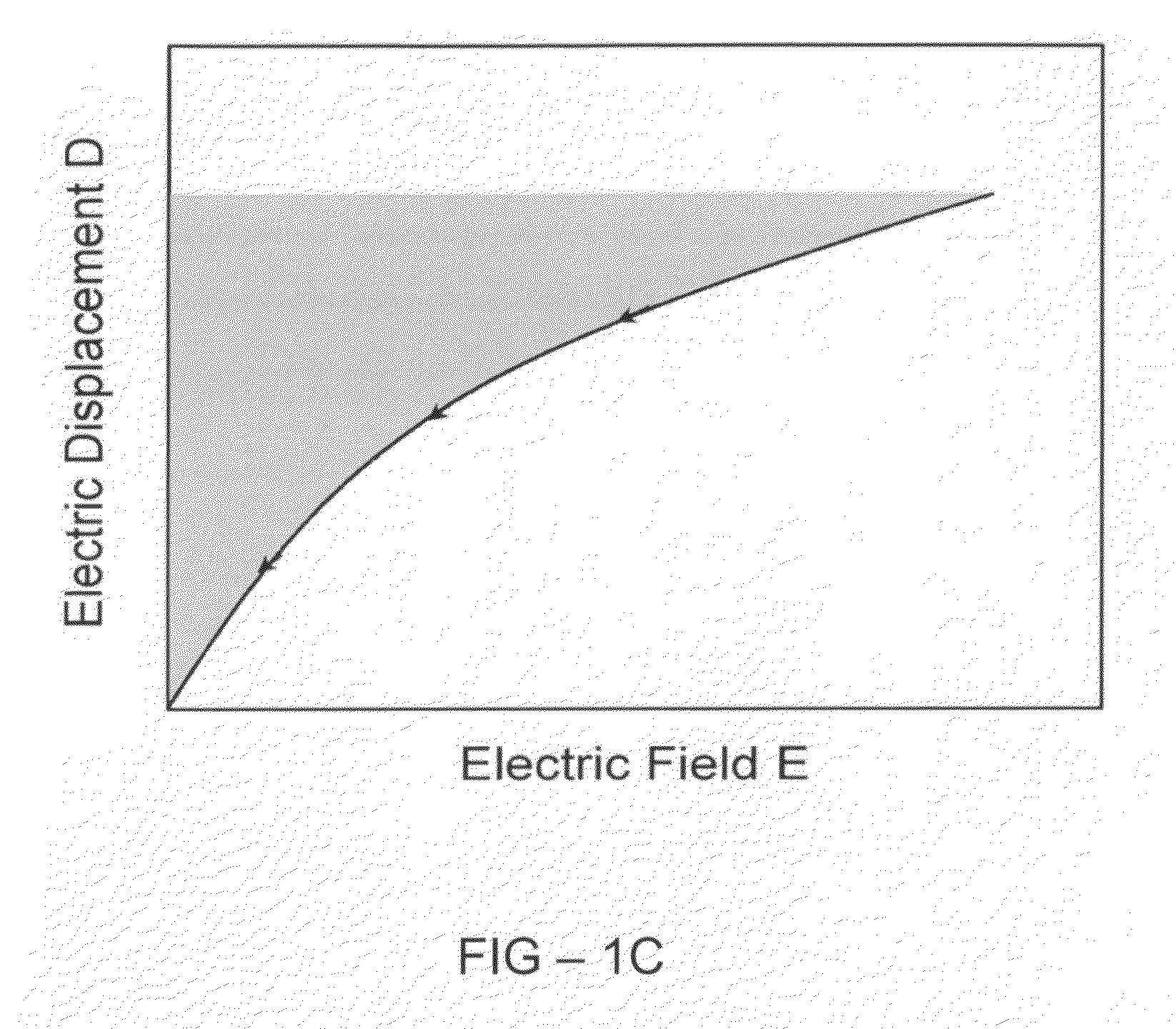
Methods to improve the efficiency and reduce the energy losses in high energy density capacitor films and articles comprising the same
InactiveUS20110110015A1Reduce conduction lossHigh breakdown strengthThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitanceDielectric loss
A multilayer film useful for capacitive applications comprises a high energy density layer and a dielectric blocking layer. In some embodiments, a conducting film is located between the high energy density layer and the blocking layer. The high energy density layer may be a fluoropolymer, such as a polymer or copolymer of poly-1,1-difluoroethene or a derivative thereof. The multilayer film may have high energy density (for example,. >8 J / cm3) and low dielectric loss, for example less than 2%, and preferably less than 1%.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Vinylidene-fluoride-based copolymer and application of said copolymer
ActiveCN103261247AGood adhesionHigh peel strengthCell electrodesFinal product manufactureHydrogen atomMetal foil
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Vinylidene fluoride copolymer, method for producing the same, gel electrolyte, and non-aqueous battery
ActiveUS20170015772A1Improve balanceSecondary cellsElectrolye immobilisationAtomic groupHexafluoropropylene
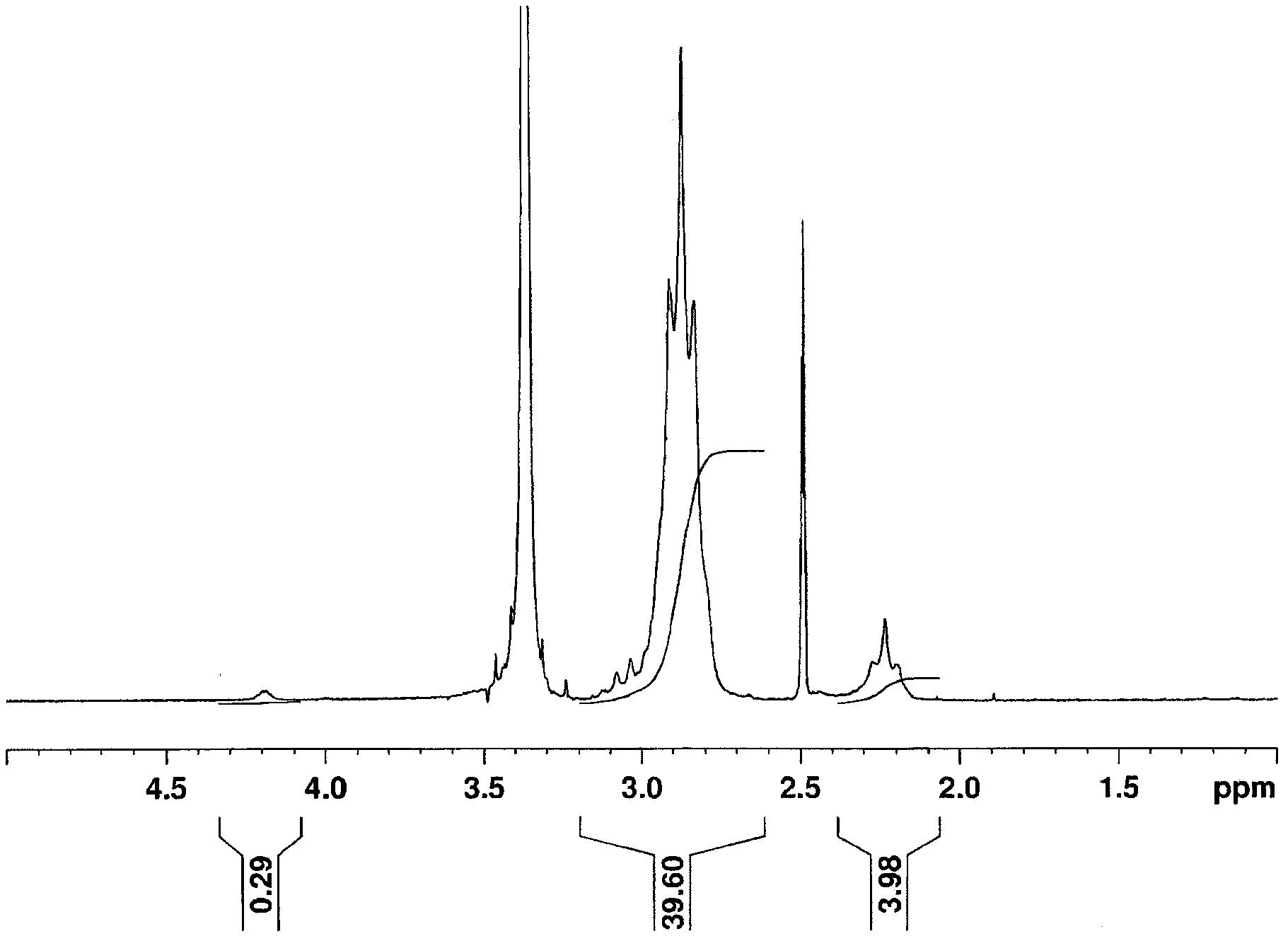
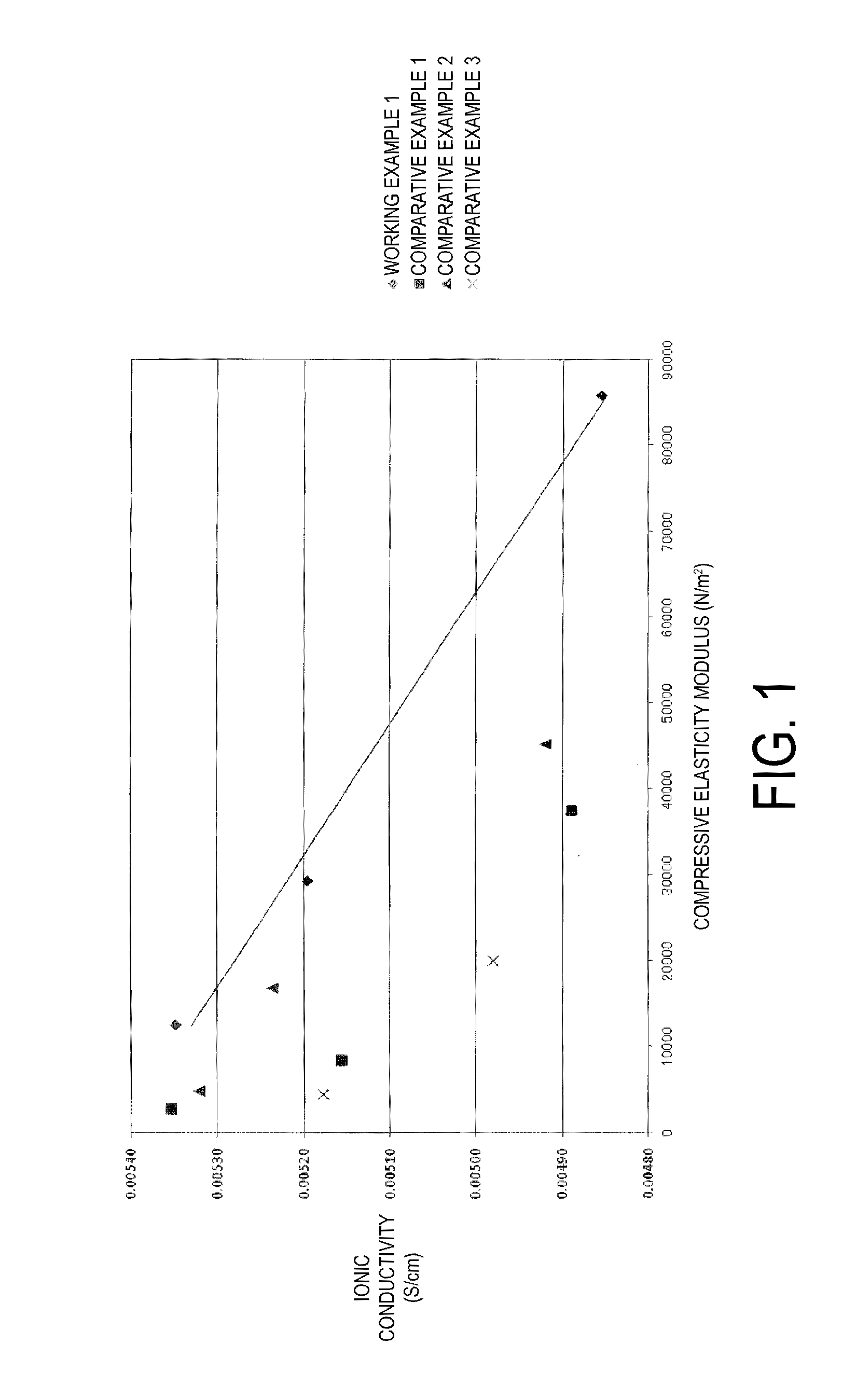
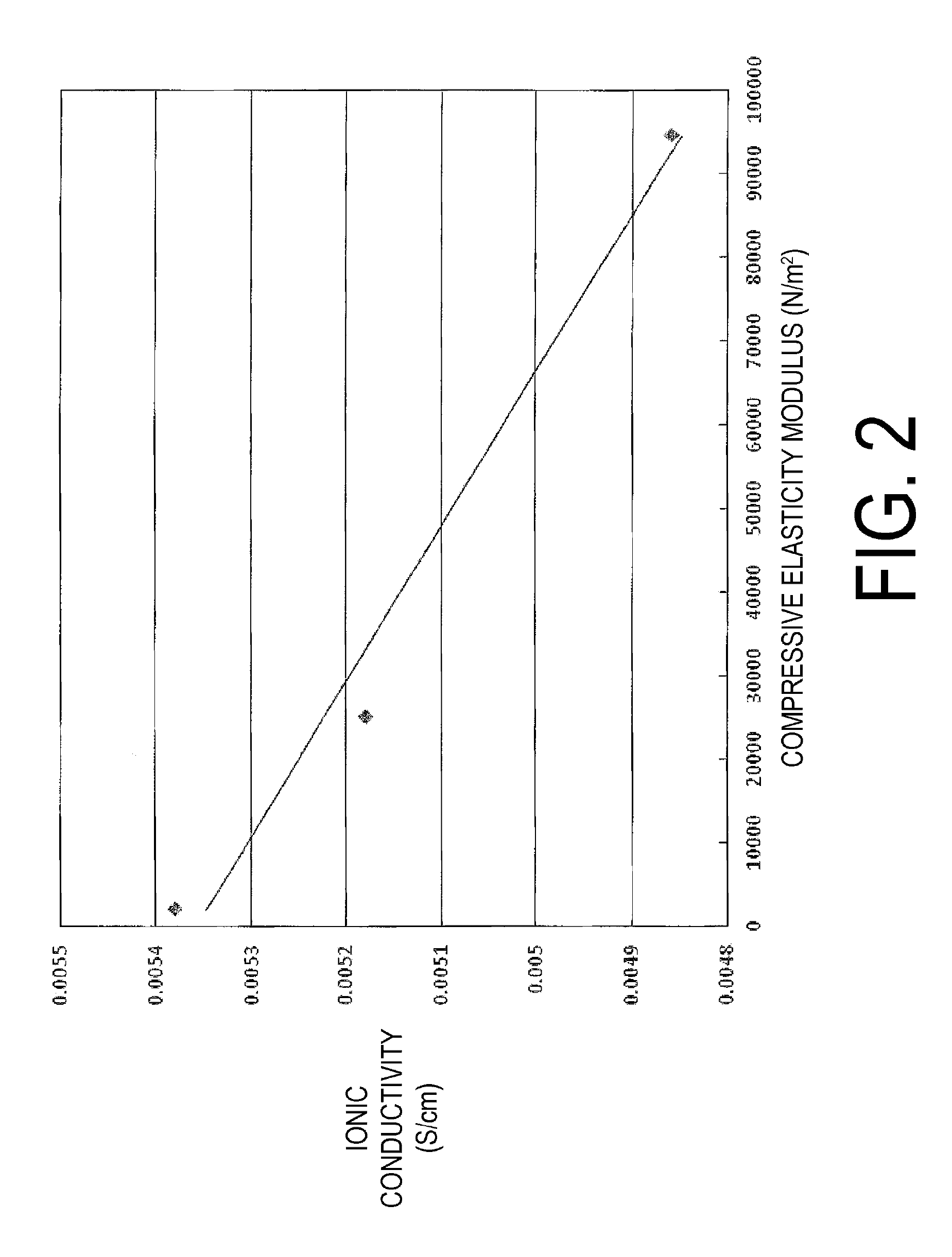
The vinylidene fluoride copolymer of the present invention is a polymer obtained by copolymerizing at least one type of fluorine-based monomer selected from hexafluoropropylene and chlorotrifluoroethylene, vinylidene fluoride, and a compound represented by formula (1) (wherein X is an atomic group having a hydroxyl group or a carboxyl group and having a molecular weight of not greater than 517 with a main chain having from 1 to 19 atoms) and is obtained by adding the compound represented by formula (1) to the fluorine-based monomer and vinylidene fluoride in divided portions or continuously during copolymerization. The gel electrolyte of the present invention contains the vinylidene fluoride copolymer and a non-aqueous electrolyte solution, and the gel electrolyte has an excellent balance of ionic conductivity and gel strength.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Preparation method of 1,1-difluoroethylene
ActiveCN109180420AIncrease added valueRaw materials are cheap and easy to getPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offCatalyst activation/preparationGas phaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of 1,1-difluoroethylene. The preparation method comprises following steps: a composite catalyst is introduced into a tubular reactor, 1, 1-difluoro-1-chloroethane or 1, 1-difluoro-2-chloroethane is taken as a raw material and is introduced into the tubular reactor for gas phase catalytic cracking so as to obtain 1,1-difluoroethylene. The composite catalyst is a metal composite fluoride. The method is low in reaction temperature, high in product selectivity, high in yield, mild in operation technical conditions, and simple in operation, and the reproducibility of the adopted catalyst is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for fabricating semiconductor devices
ActiveUS9460935B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface treatment compositionsThiolSemiconductor
The invention relates to a method for fabricating a semiconductor device. The method comprises forming a first etching layer and a second etching layer stacked on a substrate, and forming a recess region by etching the first and second etching layers under plasma generated from an etching gas including a compound. The compound comprises at least one of 1,1,1,2,3,3-hexafluoropropane, 2,2,2-trifluoroethane-1-thiol, 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane, 1,1,2,2,3-pentafluoropropane and 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoro-1-iodoethane, 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene and 1,1-difluoroethene.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Porous vinylidene fluoride resin membrane and process for producing same
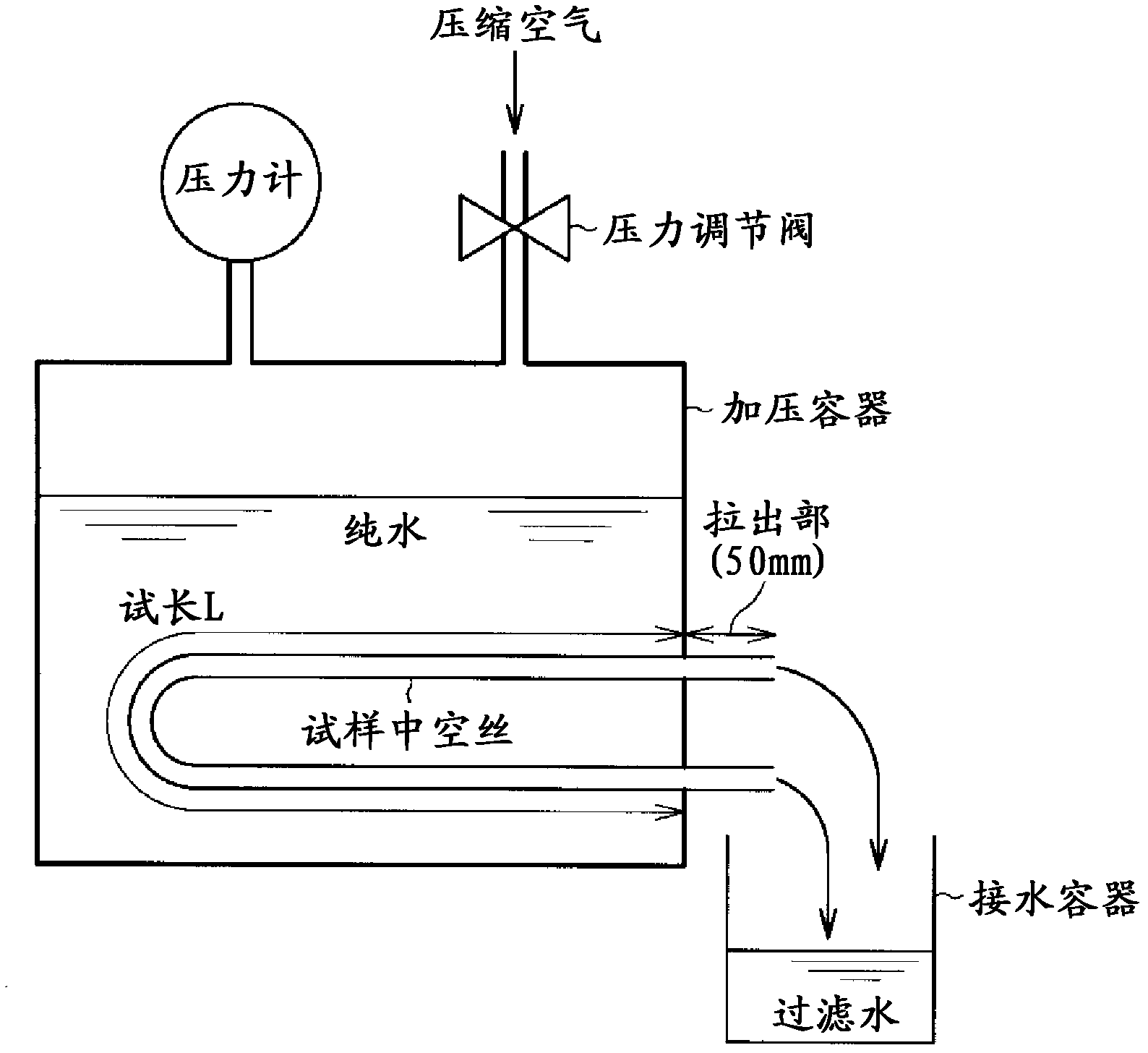
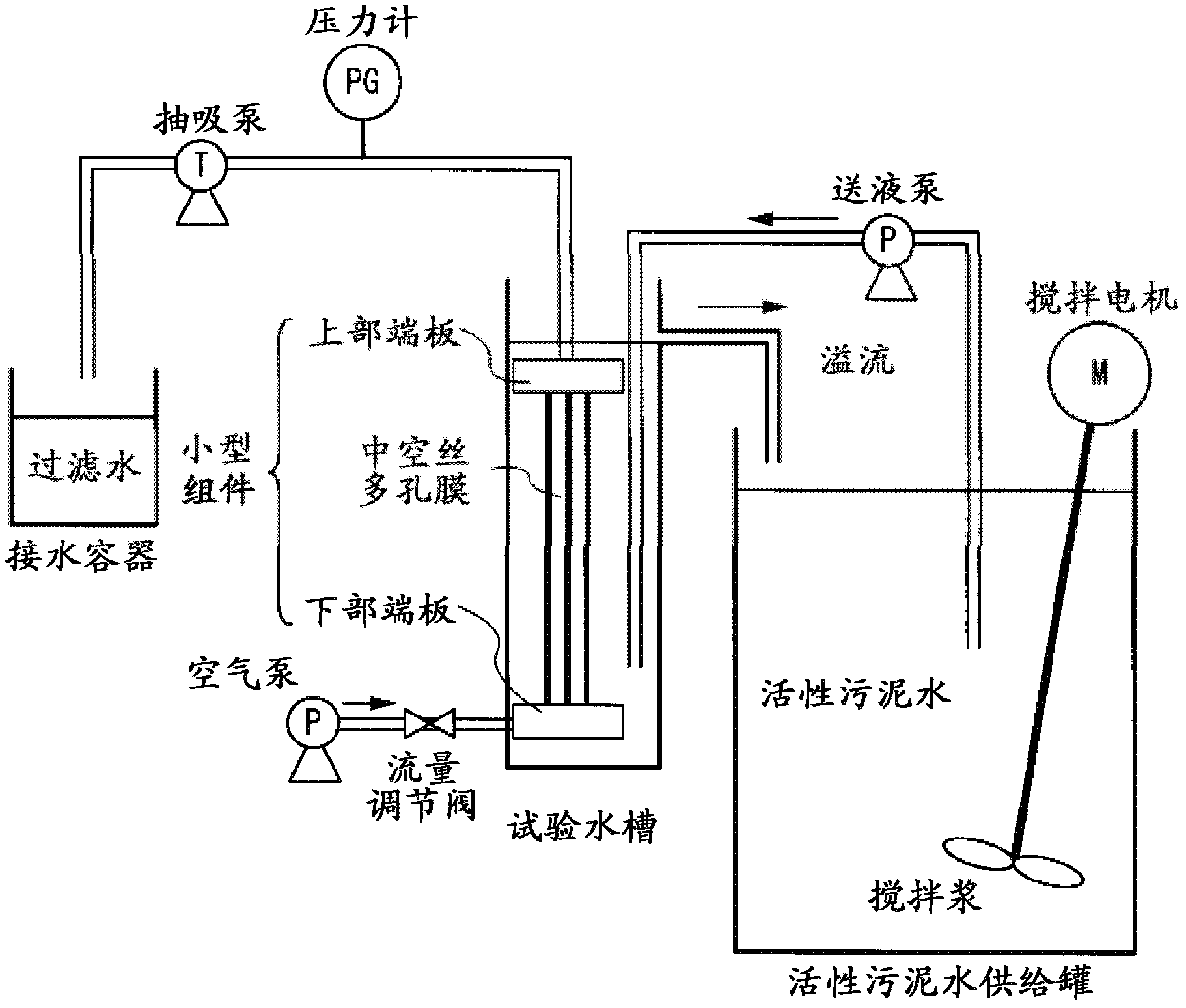
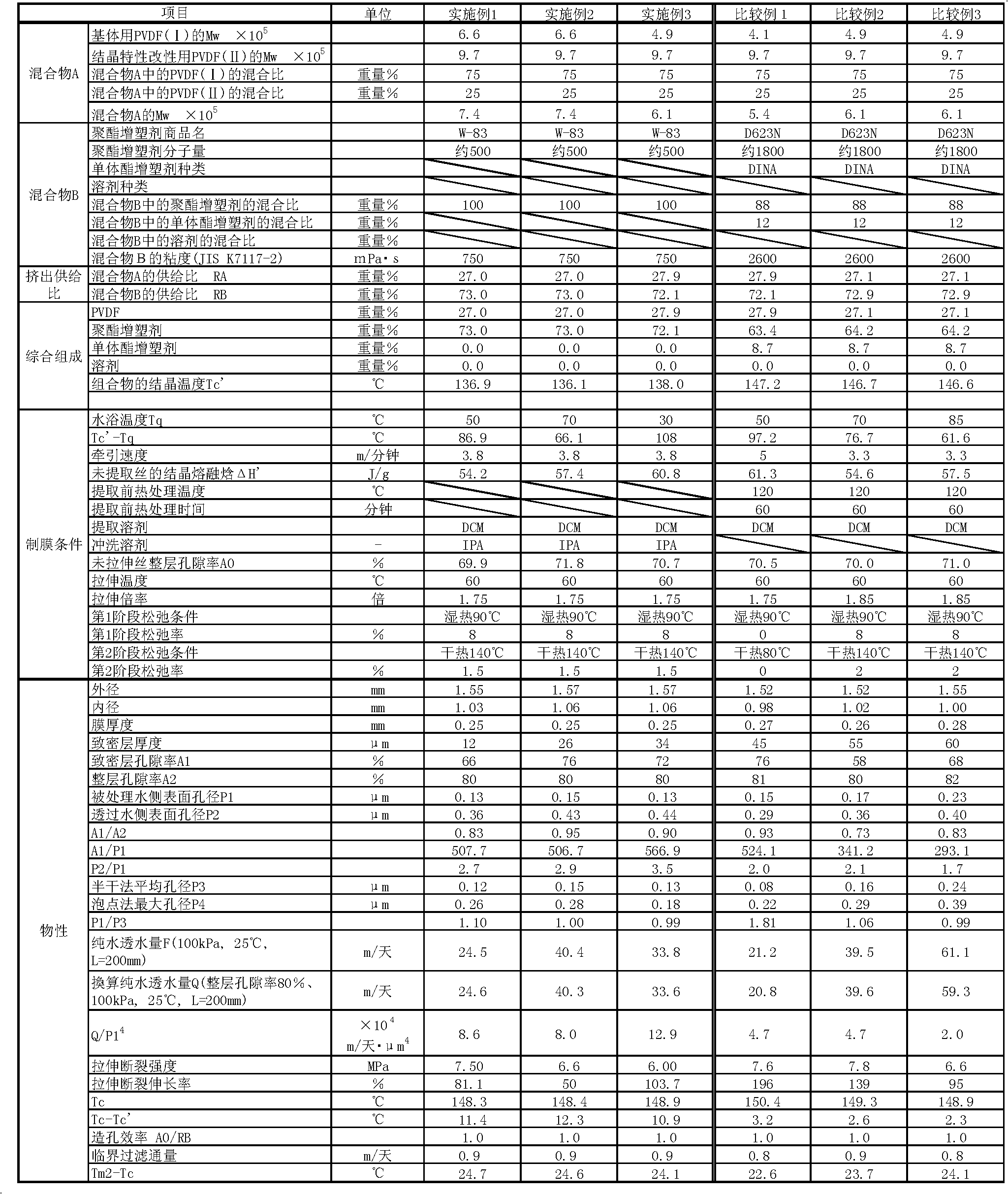
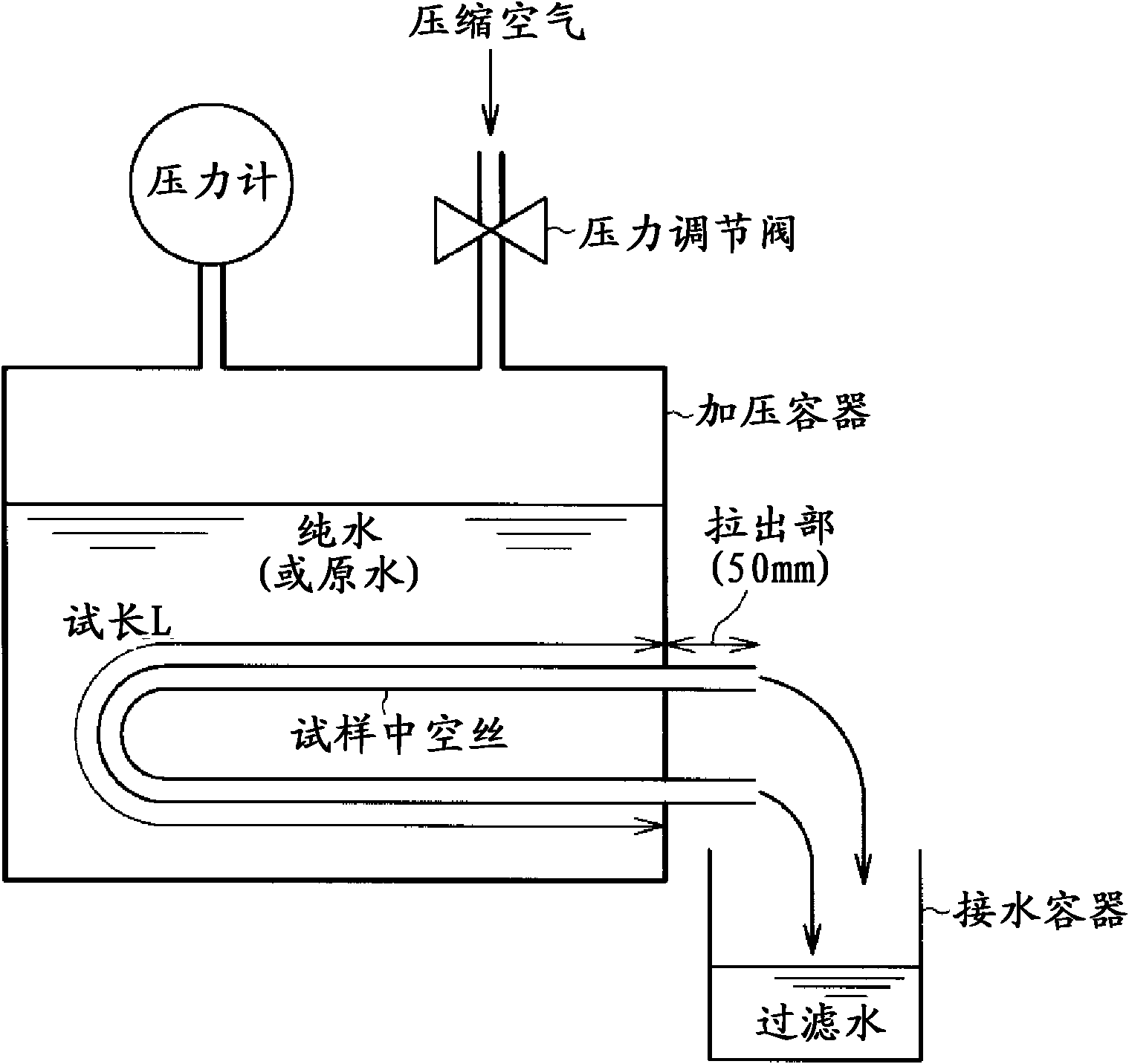
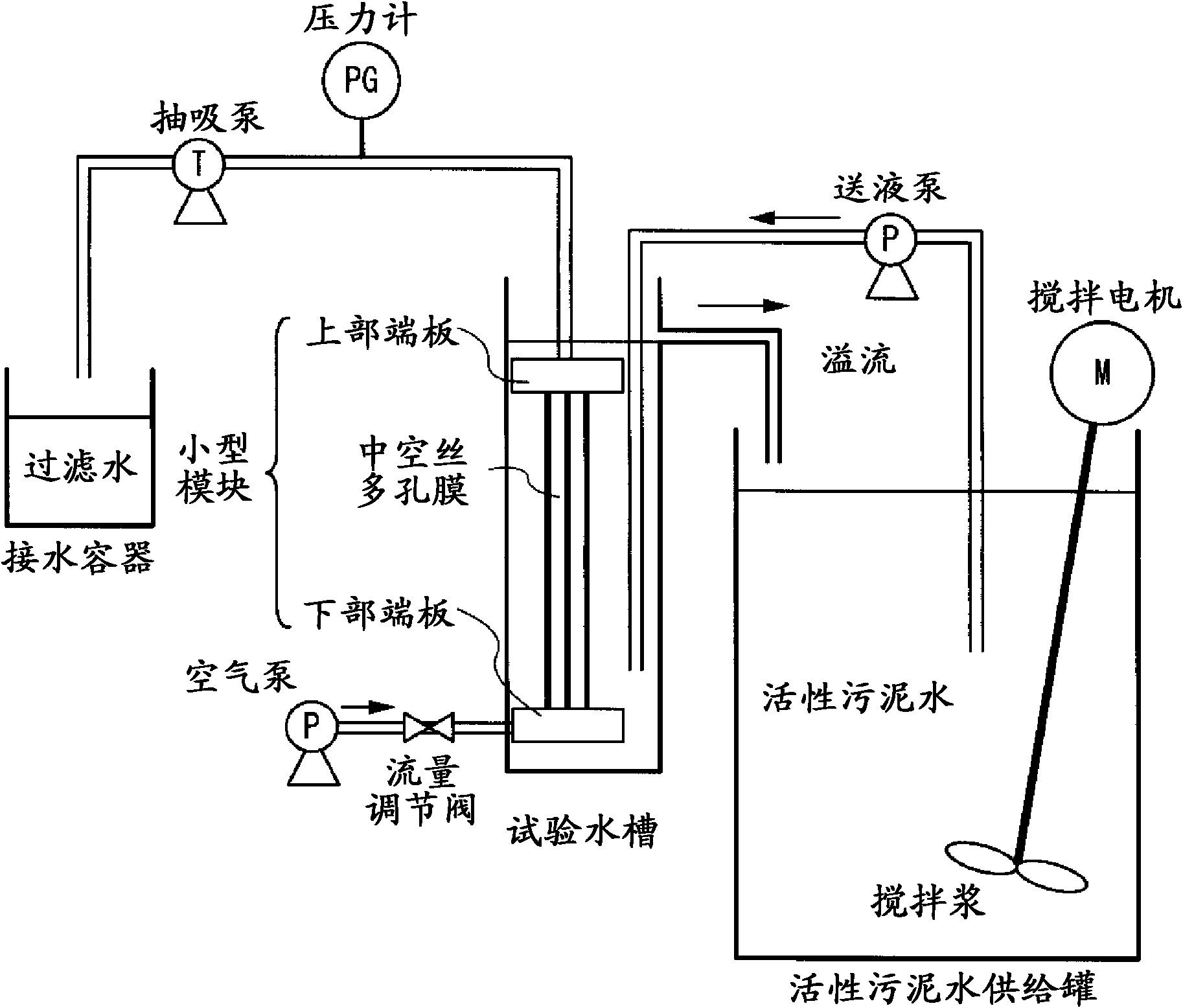
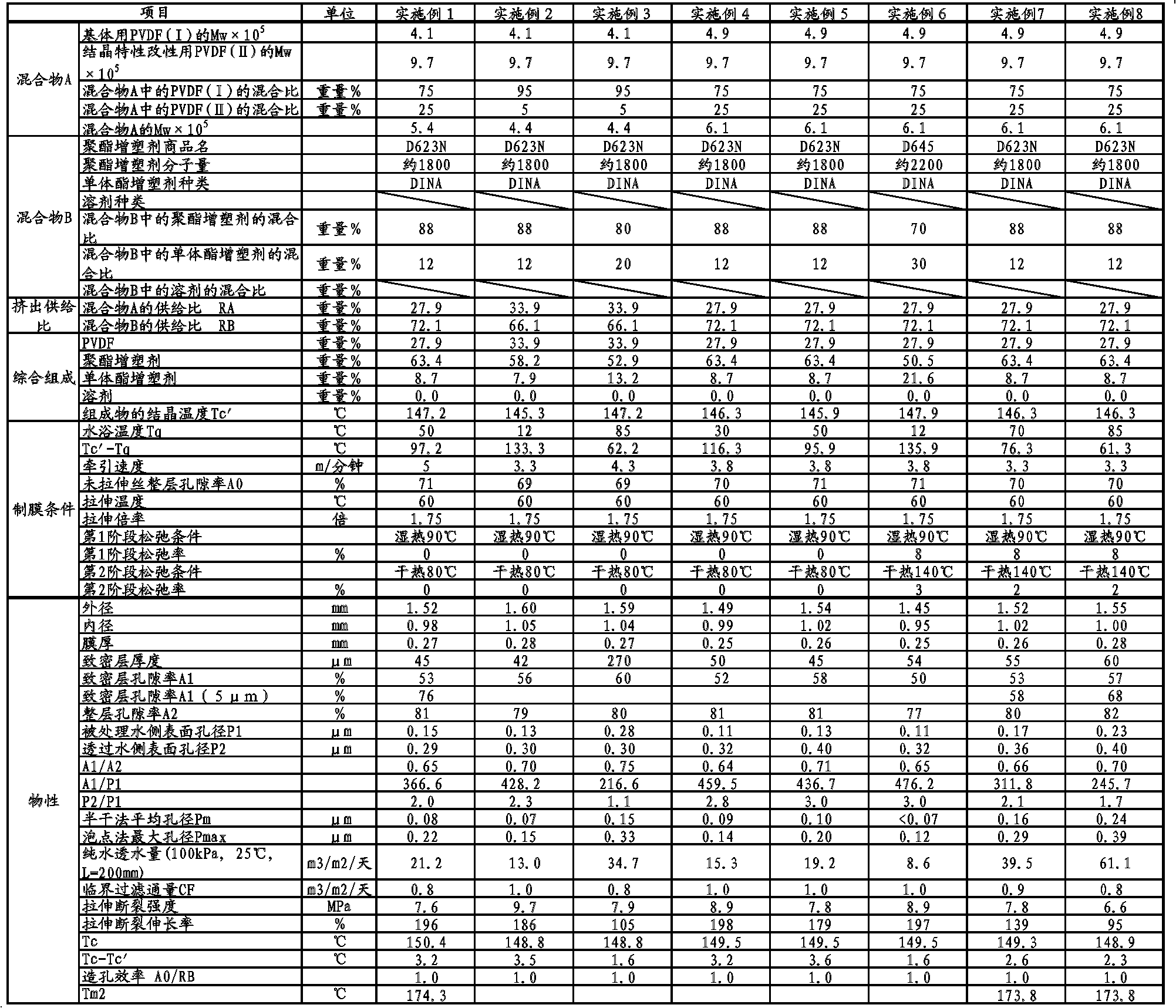
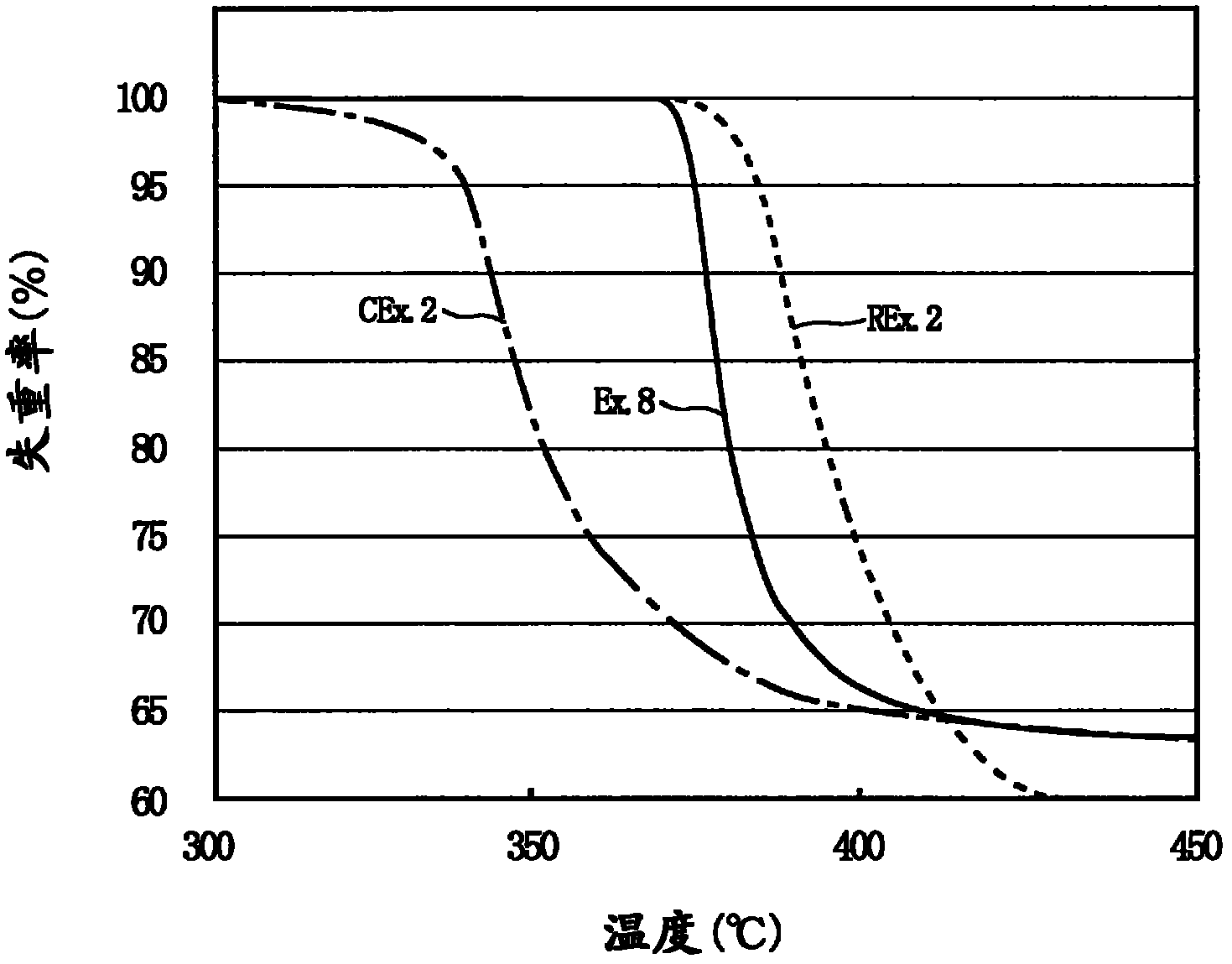
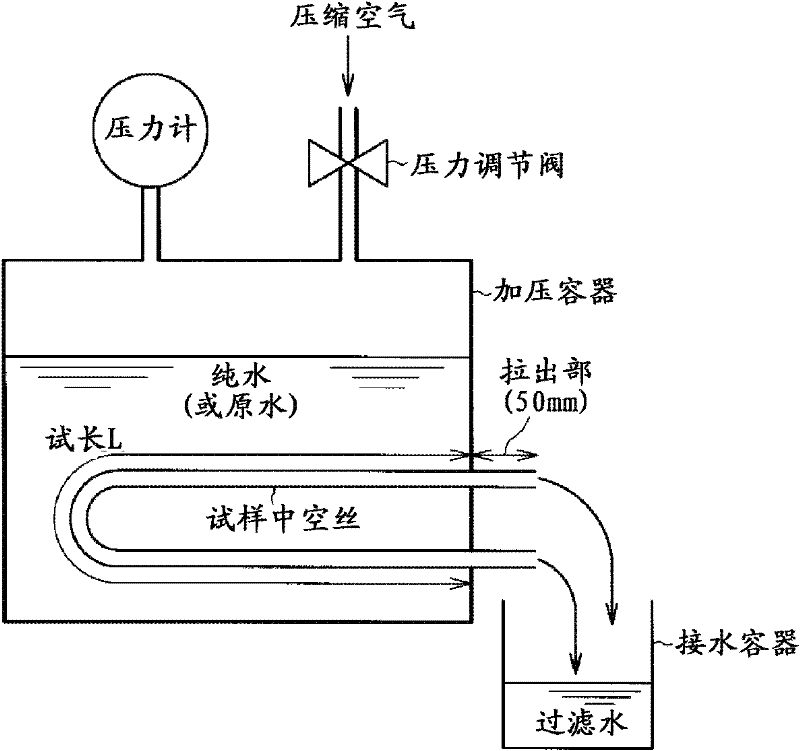
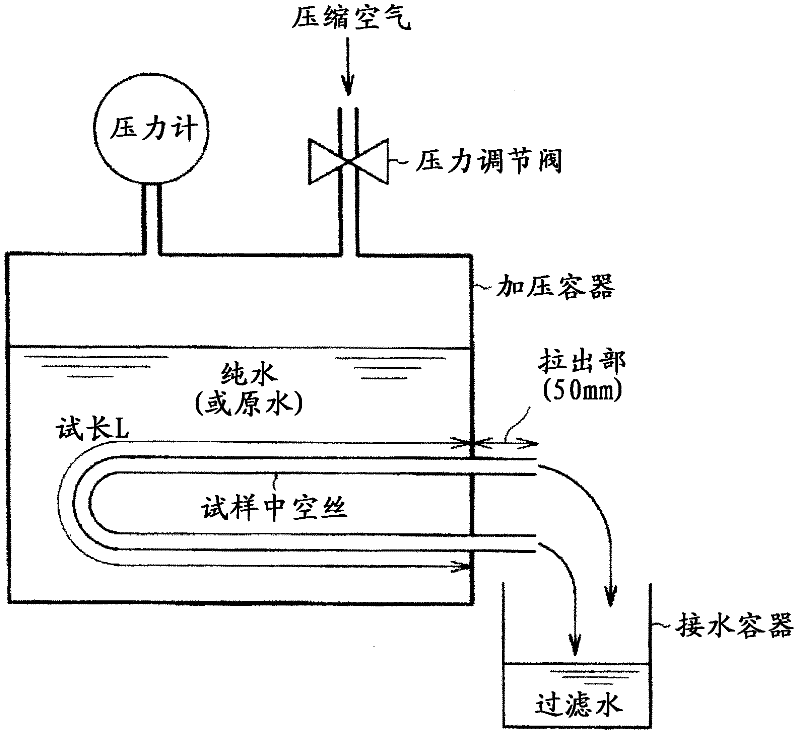
Disclosed is a porous vinylidene fluoride resin membrane characterized by having two main surfaces, between which a certain thickness is sandwiched, and by having, on the side thereof facing one of the main surfaces, a dense layer that has a small pore diameter and governs the filtration performance, having an asymmetric gradient network structure in which the pore diameter increases continuously from the surface toward the other surface, and satisfying the following requirements (a) to (c): (a) the part of the dense layer which has a thickness of 5 [mu]m and extends continuously from the surface has a porosity (A1) of 60% or higher; (b) the surface has a surface pore diameter (P1) of 0.30 [mu]m or smaller; and (c) the ratio of the amount of water which has passed through in a test length (L) of 200 mm under the conditions of a differential pressure of 100 kPa and a water temperature of 25 DEG C, the water amount being a converted value (Q (m / day)) calculated for an overall porosity (A2) of 80%, to the fourth power of the surface pore diameter (P1) of the surface (P1<4> ([mu]m<4>)), Q / P1<4>, is 5*10<4> (m / day.[mu]m<4>) or higher.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Process for producing 1,1-difluorovinyl cycloaliphatic compounds
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of 1,1-difluoroolefins, e.g., difluorovinyl cycloaliphatic compounds such as difluorovinylcyclohexane and derivatives by the dehydrofluorination of a trifluoromethyl-substituted cycloaliphatic compound and the resulting compositions. This method utilizes a “sterically hindered super-base” system represented by the formula M+−NRR−; where M is Na or K and R is a secondary, or tertiary alkyl or cycloalkyl group of amines for effecting dehydrofluorination of the trifluoromethyl group leading to the difluorovinyl based cycloaliphatic compounds. The sterically hindered super base can be formed by the, in situ, reaction of a sodium or potassium alkoxide, e.g., KtBuO with a lithium dialkylamide where the lithium is bonded to nitrogen atom of an amine bearing secondary or tertiary aliphatic groups.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Polyvinylidene fluoride resin film, multilayer film, backsheet for solar cell module, and film manufacturing process
InactiveCN103582671AExcellent mechanical propertiesNo thermal wrinklesSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentCrystal structurePolyvinylidene difluoride
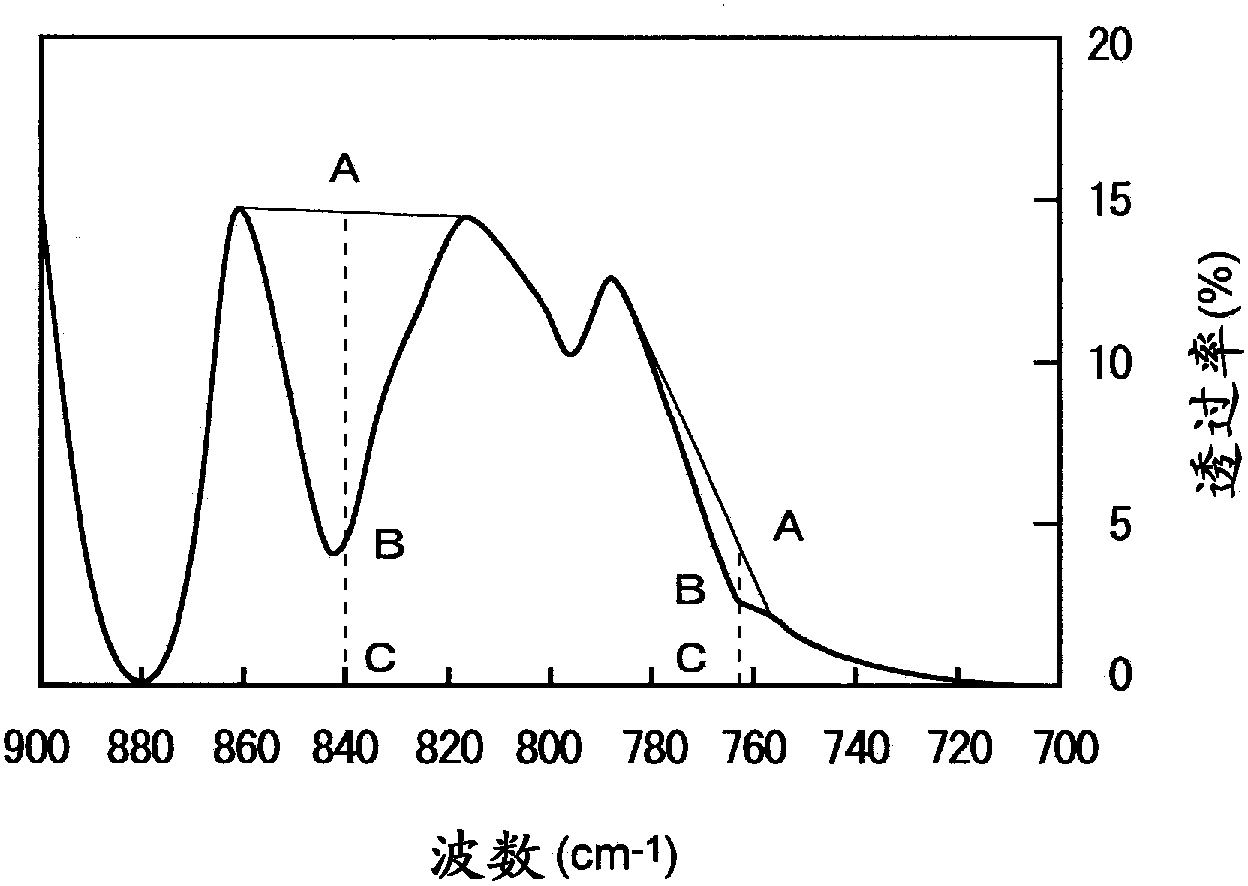
The invention provides a polyvinylidene fluoride resin (PVDF) film which has a crystal structure such that the [Beta]-crystal content is 10% or more relative to the sum total of [Alpha]-crystal and [Beta]-crystal as calculated from the absorbances observed in the infrared absorption spectrum and which preferably exhibits either a tensile modulus in TD of 90MPa or less at 120 DEG C or a ratio of (tensile modulus in TD at 100 DEG C) / (tensile modulus in TD at 23 DEG C) of 4% or less and is particularly preferably produced by extrusion molding; a multilayer film; a backsheet for a solar cell module, being provided with the film; and a film manufacturing process which comprises subjecting a sheet-shaped PVDF material obtained by melt extrusion to rapid cooling at 5 to 70 DEG C and, preferably, then heat treatment.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
1, 1-polyvinylidene floride copolymer and use thereof
ActiveCN102731707AImprove adhesionHigh peel strengthFinal product manufactureNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesSulfurOrganic group
The present invention provides a 1, 1-Polyvinylidene Floride copolymer which can be excellently bonded with material such as metal material, and also provides a battery electrode containing the 1, 1-Polyvinylidene Floride copolymer, a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery mixture, an electrode for the non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery, obtained through using the mixture, and a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery with the electrode. The 1, 1-Polyvinylidene Floride copolymer is provided with a structure unit represented by a 80-99.95 mol% formula a, a structure unit represented by a 0-19.99 mol% formula b, and a structure unit represented by a 0.01-20 mol% formula c. in the formula b, RCOOH is an organic group containing a carboxyl, and RN and S are respectively an organic group of at least one heteroatom selected from nitrogen and sulfur.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Vinylidene fluoride resin porous film and manufacturing method therefor
Disclosed is a vinylidene fluoride resin porous film that has two primary surfaces which sandwich a prescribed thickness therebetween, having a dense layer which governs filtration performance on one surface side and having a sparse layer which provides strengthening support on the reverse surface side, and having an asymmetrical reticular inclined structure whereby the pore diameter continuously increases from the one surface toward the reverse surface, with the porosity (A1) (%) of a 7 [mu]m-thick portion of the dense layer that touches the one surface side being 50% or greater, and the surface pore diameter (P1) on one surface side being 0.30 [mu]m or less. This vinylidene fluoride resin porous film generally is useful as a porous film used for separation, and exhibits excellent ability to maintain permeability with respect to the continuous filtration of turbid water. This vinylidene fluoride resin porous film is manufactured with a method whereby a polyester plasticizer, which is compatible with a large molecular weight vinylidene fluoride resin and which in mixture with the vinylidene fluoride resin provides a crystallization temperature that is virtually identical to the crystallization temperature of vinylidene fluoride resin alone, is added in a relatively large amount to obtain a melt extrusion film that is preferentially cooled from one side and hardened, after which the plasticizer is extracted.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
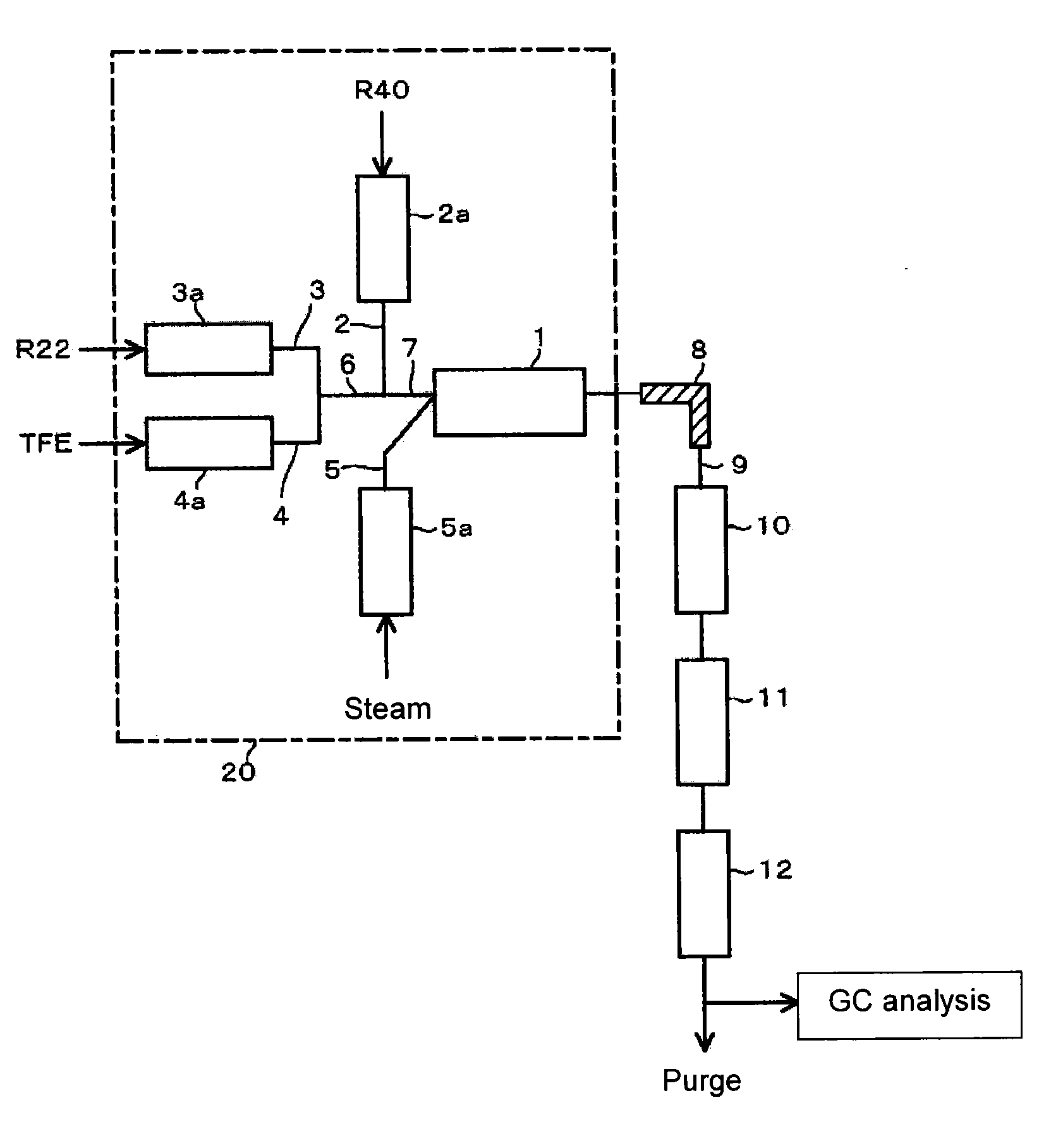
Process for producing 2, 3, 3, 3-tetrafluoropropene and 1, 1-difluoroethylene
ActiveUS20150005538A1High yieldLow costPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHFO-1234yf1,1-Difluoroethylene
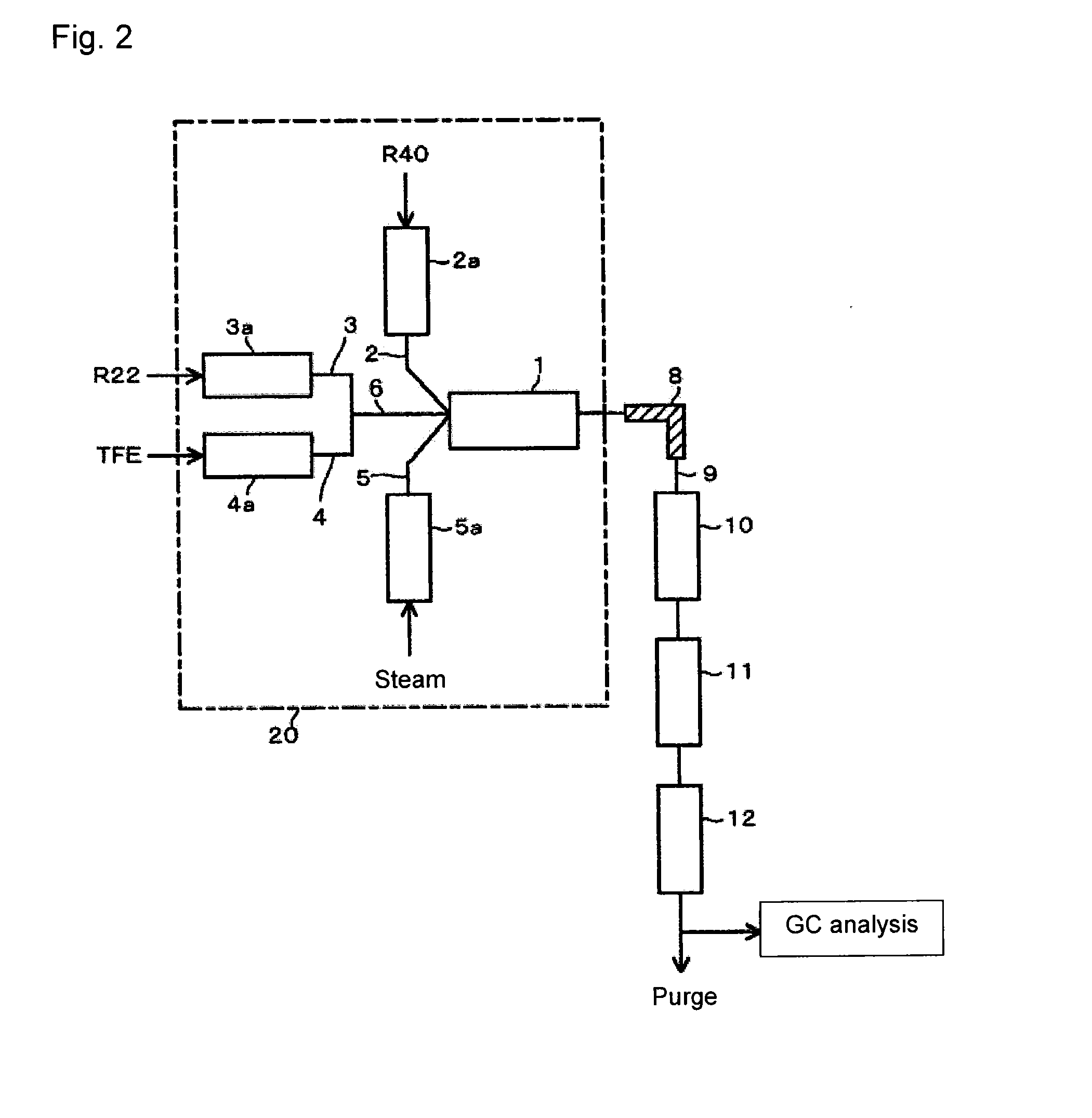
To provide an economically advantageous process for producing HFO-1234yf useful as a new refrigerant in sufficiently high yield by one reaction involving thermal decomposition. A process for producing HFO-1234yf and VdF from raw material containing R22, R40 and TFE, by a synthetic reaction involving thermal decomposition, which comprises (a) a step of supplying the R22, the R40 and the TFE to a reactor, as preliminarily mixed or separately, (b) a step of supplying a heat medium to the reactor, and (c) a step of bringing the heat medium in contact with the R22, the R40 and the TFE in the reactor to form the HFO-1234yf and the VdF.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Solar photovoltaic panel protective film
ActiveCN104553209AImprove transmittanceNo effect on light transmittanceSynthetic resin layered productsTectorial membranePolyethylene oxide
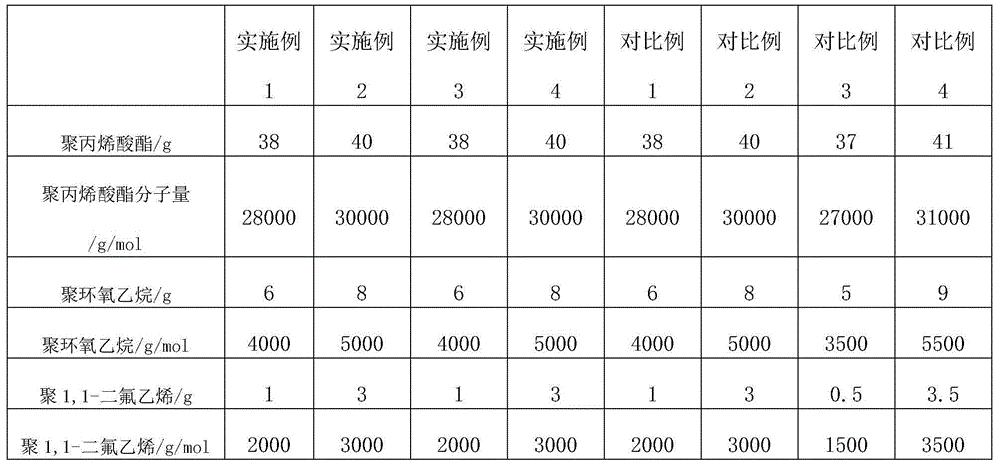
The invention discloses a solar photovoltaic panel protective film. The solar photovoltaic panel protective film comprises an optical PET layer and a protective coating which is arranged on the surface of the optical PET layer, wherein the protective coating consists of following materials in parts by weight: polyacrylate, polyethylene oxide, 1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluo-1-propylene, poly(1,1-vinyl-difluoride), cerium oxide and lithium fluoride. The polyacrylate is used as a main material, so that the high transmittance of the protective film can be guaranteed; by adding little fluorine-containing polymer, not only is the transmittance of the protective film under the sun exposure and non-sun exposure not affected, but also the corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance of the protective film can be improved; by adding the trace metal compound, the chemical and physical performance of the protective film can be obviously improved, on the basis of not affecting the high transmittance of the film, the low reflectance and low radiation absorption rate can be guaranteed, and the weather resistance, aging resistance and low temperature and high temperature resistance of the film also can be improved.
Owner:南京君弘新材料有限公司
Polyvinylidene fluoride resin composition, white resin film, and backsheet for solar cell module
InactiveCN102395624AAvoid thermal decompositionGood lookingPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesCarboxylic acidSolar cell
Disclosed is a polyvinylidene fluoride resin composition which contains a polyvinylidene fluoride resin and titanium oxide. The titanium oxide is contained in an amount of 5-100 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the polyvinylidene fluoride resin. The polyvinylidene fluoride resin composition also contains, as a heat stabilizer, at least one compound that is selected from the group consisting of polyhydroxy monocarboxylic acid calcium salts, aliphatic carboxylic acid calcium salts having 5-30 carbon atoms, calcium carbonate, calcium hydroxide, zinc oxide and magnesium oxide, in an amount of 0.1-20 parts by weight. The weight ratio of the titanium oxide to the heat stabilizer is from 100:1 to 3:1.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
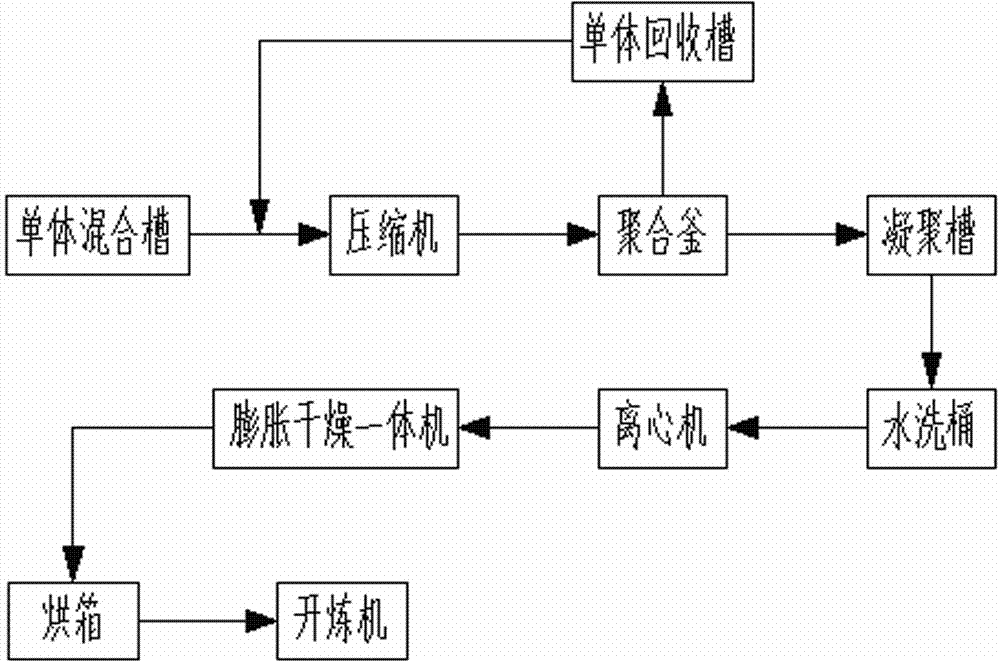
Method for making 1,1-difluoroethylene polymer
The invention provides a method for making a 1,1-difluoroethylene polymer to obtain the 1,1-difluoroethylene polymer being high in bulk density without increasing auxiliary devices and the scale covering in a polymerization system. The method for making the 1,1-difluoroethylene polymer comprises that a monomer taking the 1,1-difluoroethylene polymer as the main content is dispersed in an aqueous medium containing suspension to be subjected to suspension polymerization. Therefore, the method is characterized in that the suspension polymerization is carried out under the existing of polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester having a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance value (HLB) in the range of 1-8.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
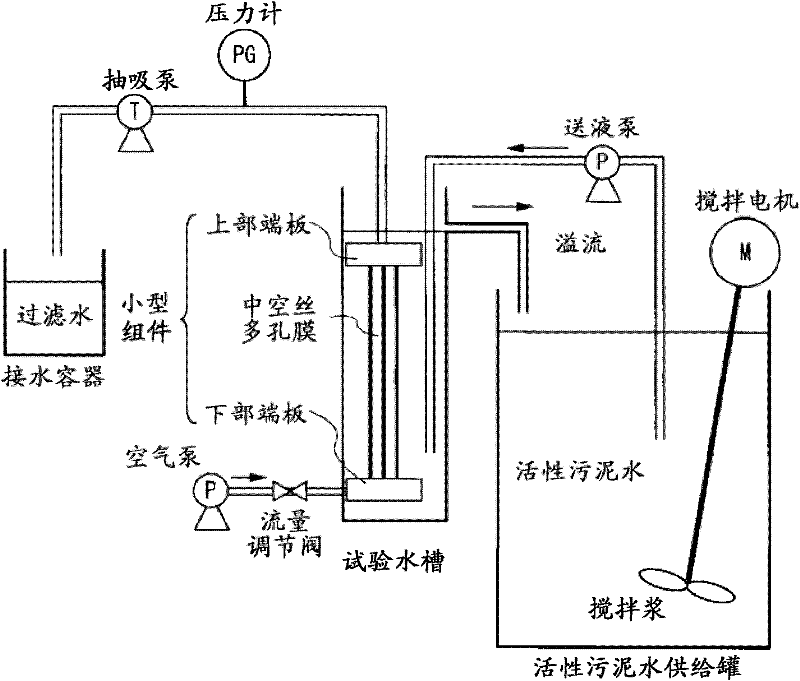
Vinylidene fluoride resin porous membrane, manufacturing method therefor, and method for manufacturing filtrate water
Provided is a vinylidene fluoride porous membrane characterized in that in a continuous area of thickness 10 [mu]m from one surface, as measured by a focused ion beam / scanning electron microscope, the mean diameter of netlike resin fibers is at most 100 nm and the porosity (A1) is at least 60%; also, the surface pore diameter (P1) at the aforementioned surface is at most 0.3 [mu]m. In addition to having a small surface pore diameter suitable for water filtration, the provided porous membrane comprises extremely thin netlike resin fibers and has a treated-water-side surface layer with extremely high porosity, thereby excelling at preventing particulate penetration and also being extremely reusable and resistant to contamination. The provided porous membrane is manufactured through a method wherein a melt-extruded membrane is obtained by adding a comparatively large amount of a polyester plasticizer which is compatible with a high-molecular-weight vinylidene fluoride resin and which, when kneaded together with the vinylidene fluoride resin, causes the crystallization temperature to be nearly equal to that of the vinylidene fluoride resin alone. After the melt-extruded membrane is preferentially cooled from one side and solidified, the plasticizer is extracted, the surface is partially wetted, and the membrane is stretched.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Vinylidene fluoride copolymer and preparation method therefor
Provided in the present invention is a vinylidene fluoride copolymer. Same is acquired via a polymerization reaction taking place at conditions of 30-100° C. and 2-7 MPa with vinylidene fluoride, tetrafluoroethylene, and perfluorinated dioxole or C1-4 alkoxy-substituted perfluorinated dioxole as raw materials, with an initiator added into an emulsion consisting of water, fluorinated emulsifier, a chain transfer agent, a pH regulator, and an antifouling agent, and then via steps of separation, purification, refinement, condensation, washing, drying, and granulation, where the molar ratio of vinylidene fluoride, tetrafluoroethylene, and perfluorinated dioxole or C1-4 alkoxy-substituted perfluorinated dioxole is 13-17:2-4:1-3. The vinylidene fluoride copolymer of the present invention provides excellent transparency, flexibility, and solubility, is widely applicable in optical apparatus such as lenses, and is for use in specialty films in the fields of solar panels and of capacitors as a fuel cell membrane, a transparent and tough coating, and a large-sized blown object.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
Preparation method of high-strength fluorine-containing polymer
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-strength fluorine-containing polymer. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding water and an emulsifier to a reactor, and evacuating until the oxygen content is smaller than or equal to 50ppm; 2) continuing to add a pH regulator and a chain transfer agent; 3) heating the reactor to 40-60 DEG C, and adding a mixed monomer composed of 1,1-difluoroethylene, tetrafluoroethylene and trifluorochloroethylene; 4) adding an initiator, beginning polymerization reaction, and lastingly adding the mixed monomer to maintain the pressure inside the reactor constant in the polymerization reaction; and 5) finishing the polymerization reaction when the solid content of a polymer emulsion achieves 25-35% by mass, freezing and condensing the emulsion, washing and drying, so as to obtain the fluorine-containing polymer which is relatively high in strength, good in ageing resistance, and good in mechanical property and has the molecular weight of 150,000-300,000. The preparation method of the fluorine-containing polymer, which is disclosed by the invention, is fewer in raw materials, simple in technology, and applicable to large-scale popularization.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
Low-temperature resistant fluorubber, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103755857AImprove low temperature resistanceAdapt to the requirements of low temperature sealingChemical industryHexafluoropropylene
The invention relates to a low-temperature resistant fluorubber, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of fluorine chemical industry and high molecular material technology. The preparation method comprise following steps: 1) alcohols containing fluorine, such as tetrafluoro-1-Propanol, octafluoropentyl alcohol, and H,1H,7H-dodecafluoro-1-heptanol are taken as initial fluorine-containing materials, and are subjected to condensation with pentafluoro bromopropylene in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst so as to obtain a fluorine-containing ether containing carbon-carbon double bonds; 2) a monomer mixture is prepared from 1,1-difluoroethylene, hexafluoropropylene, and fluorine-containing alkyl pentafluoropropene ether according to a certain molar ratio, and is stored for further treatment; and 3) the monomer mixture is delivered into a polymerization vessel, and is subjected to emulsion polymerization in the presence of an emulsifier, an initiator, and a chain transferring agent, and latex obtained via polymerization is subjected to coacervation, washing, and drying, and is made into low-temperature resistant fluorubber sheets using a open mill. The preparation method is capable of improving low-temperature resistance of fluorubber effectively, so as to satisfy requirements on low-temperature sealing; the raw materials are easily available; preparation processes are easy to realize; and the preparation method is beneficial for popularization and application.
Owner:江苏梅兰化工有限公司
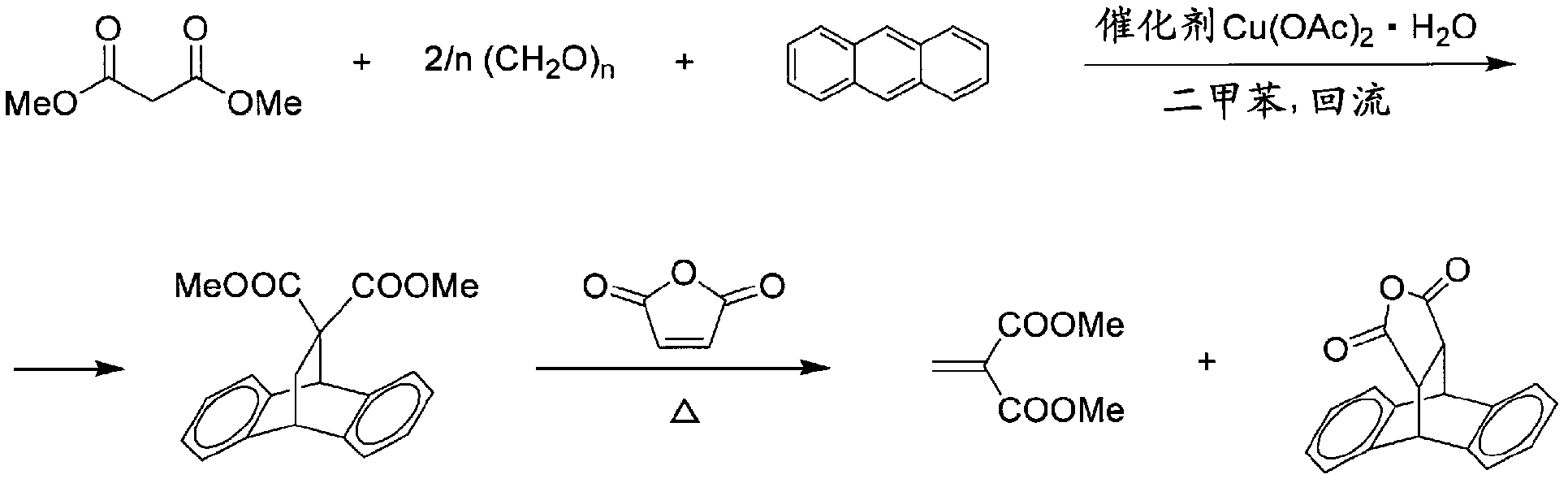
Novel vinylidene fluoride copolymers and processes for production thereof
A vinylidene fluoride copolymer which comprises 99.9 to 90mol% of vinylidene fluoride monomer units, 0.1 to 10mol% of methylidenemalonic ester monomer units, and 0 to 10mol% of other monomer units and which has a weight-average molecular weight of 200,000 or more; a vinylidene fluoride copolymer as described above, which is modified by hydrolyzing 10 to 90% of the total number of the ester groups of the methylidenemalonic ester monomer units; and processes for the production of the copolymers.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Preparation method of 2-bromo-1,1-difluoroethylene
ActiveCN109369323ASimple methodSimple post-processingHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationN-BromosuccinimideOrganic solvent
The invention provides a preparation method of 2-bromo-1,1-difluoroethylene. The preparation method comprises the following step: under a copper catalyst, taking N-bromosuccinimide and vinylidene fluoride to react in the presence of alkali and an organic solvent to obtain the 2-bromo-1,1-difluoroethylene. According to the preparation method, the N-bromosuccinimide and the vinylidene fluoride are used as raw materials of the reaction to prepare the 2-bromo-1,1-difluoroethylene; the method is simple, post-treatment is simple and no wastewater is produced; byproducts are directly filtered and recycled so that the preparation method is environmentally friendly; the purity of a prepared product is relatively high. The raw material vinylidene fluoride is an industrial product and is cheap and easy to obtain. An experiment result shows that the purity of the 2-bromo-1,1-difluoroethylene prepared by the method is 99.5 percent or more.
Owner:湖南有色郴州氟化学有限公司
1,1-Difluoroethylene-based copolymer, and use of the copolymer
ActiveCN102731707BImprove adhesionHigh peel strengthFinal product manufactureNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesCarboxyl radicalGeneral equation
PURPOSE: A fluoride vinylidene-based copolymer with superior adhesive force with a substrate and uses of the copolymers are provided to enhance adhesive force with substrates and release strength of current collector and compound layer. CONSTITUTION: A fluoride vinylidene-based copolymer has 80-99.95 mol% of component represented by chemical formula a, 0-19.99 mol% of component represented by chemical formula b, and 0.01-20 mol% of component represented by chemical formula c. In the chemical formula b, RCOOH is an organic group containing carboxy group, R^1, R^2, and R^3 are respectively hydrogen, halogen, and carboxyl group or the derivative, or C1-5 alkyl group. In a general equation c, R_(N,S) is an organic radical containing one or more hetero atoms, R^4, R^5, and R^6 are respectively hydrogen, halogen, carboxyl group or the derivative, or C1-5 alkyl group.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
1,1-difluoroethylene copolymer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a 1,1-difluoroethylene copolymer and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of fluorine chemicals. The 1,1-difluoroethylene copolymer is a heterogeneous polymer containing a plurality of continuous phases and is prepared from (a) 60 to 80 percent of first continuous polymer phase which contains 95 to 100 percent of vinylidene fluoride monomeric unit and 0 to 5 percent of other fluorine-containing monomeric units and (b) 20 to 40 percent of second continuous polymer phase which contains 65 to 85 percent of the vinylidene fluoride monomeric unitand 15 to 35 percent of comonomer unit, wherein a comonomer is one or two of hexafluoropropylene and perfluoropropyethyl ether. The 1,1-difluoroethylene copolymer disclosed by the invention has excellent low-temperature flexibility and high melting temperature. The invention also provides a simple and feasible preparation method, which improves the crystallinity of polyvinylidene fluoride and improves flexibility; meanwhile, the copolymer has high melting temperature and good solvent resistance.
Owner:SHANDONG HUAXIA SHENZHOU NEW MATERIAL
Preparation method of low-temperature-resistant binary fluorine rubber
ActiveCN102329402BReduce manufacturing costLower glass transition temperatureVinyl etherChemical industry
The invention relates to a preparation method of low-temperature-resistant binary fluorine rubber, belonging to the technical field of fluorine chemical industry. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) mixing 1,1-difluoroethylene, hexafluoropropylene and perfluoro methyl vinyl ether in a molar ratio of (60-80):(15-30):(2-8) to obtain a monomer mixture forlater use; and 2) reacting the monomer mixture in an aqueous dispersion form under the action of an initiator, an emulsifier and a chain transfer agent in a reaction kettle, adjusting the temperatureto 60-95 DEG C, pressure to 1.0-3.0MPa and stirring rate to 400-700 r / min, and carrying out copolymerization reaction for 3-7 hours to obtain a finished product. The preparation method of the low-temperature-resistant binary fluorine rubber has the advantages that the preparation process is simple, the use amount of expensive perfluoro methyl vinyl ether in the reaction is low, and the productioncost is greatly lowered; and the glass transition temperature of the prepared fluorine rubber can be effectively reduced by 2-7 DEG C and the brittleness temperature is reduced by 10-18 DEG C, thereby being suitable for low-temperature sealing requirements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FLUORINE CHEM NEW MATERIAL
Novel vinylidene fluoride copolymers and processes for production thereof
The present invention relates to a product having 99.9 to 90 mol% of vinylidene fluoride monomer units, 0.1 to 10 mol% of methylene malonate monomer units, and 0 to 10 mol of monomer units other than the above-mentioned monomer units %, 1,1-difluoroethylene copolymer with a weight average molecular weight of 200,000 or more, and a modified product obtained by hydrolyzing 10 to 90% of the total number of ester groups contained in the methylene malonate monomer unit , 1-difluoroethylene copolymers, and methods for their manufacture.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Polyvinylidene fluoride films and laminates thereof
A fluoropolymer film useful in a laminate construction comprising a fiberglass reinforced substrate and a high temperature resistant film comprising a fluoropolymer layer formed from a composition comprising (a) a polyvinylidene fluoride polymer; (b) a hydroxyl functional acrylic polymer; and (c) a crosslinking agent is provided.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Method for making 1,1-difluoroethylene polymer
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Method for preparing 1,1-difluoroethylene by cracking of 1,1,1-difluoro-1-chloroethane
The invention discloses a method for preparing 1,1-difluoroethylene by cracking of 1,1,1-difluoro-1-chloroethane. The method includes steps of uniformly mounting inner metal components with catalysis effect in a cracking tube made of an inert material according to the filling quantity that the surface area of the inner metal components in each cubic meter of cracking tube is 100-500 square meters; placing the cracking tube into an electric heating furnace, controlling the temperature of the cracking tube within the range of 500-580 DEG C, leading 1,1,1-difluoro-1-chloroethane and retaining the same in a reaction section of the cracking tube for 20-400 seconds; quenching reaction products at an outlet of the cracking tube to below 100 DEG C through a water cooler, absorbing acid gas such as hydrogen chloride therein through a secondary washing absorption tower and a primary alkali cleaning absorption tower, freezing and drying to obtain cracked products. The method has the advantages that crack reaction temperature is low, conversion rate of raw materials is high, reaction selectivity is good, the service life of the cracking tube is long, and the method is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:LINHAI LIMIN CHEM +1
Vinylidene fluoride resin hollow fiber porous membrane and process for producing same
Disclosed is a vinylidene fluoride resin hollow fiber porous membrane characterized by comprising a vinylidene fluoride resin porous membrane in the form of hollow fibers, and having a ratio of the maximum pore diameter (Pmax) to the average pore diameter (Pm) (i.e., a Pmax / Pm ratio) of 2.0 or less as measured by a half-dry / bubble-point method (ASTM F316 and ASTM E1294), a Pm of 0.13 to 0.25 [mu]m, a coefficient of variation in pore diameter on the outer surface of 70% or less, and a porosity of 75 to 90%. In the hollow fiber porous membrane, the average pore diameter is proper, the pore diameter distribution on the whole and the outer surface is uniform, and the porosity is high. Therefore, the hollow fiber porous membrane has good permeability to pure water, as well as an ability to maintain good permeability during the continuous filtration of muddy water. The hollow fiber porous membrane can be produced by a process comprising melt-extruding a vinylidene fluoride resin together with a plasticizer and a good solvent for the vinylidene fluoride resin into follow fibers, cooling the resulting product, shaping the cooled material into a membrane, extracting the plasticizer and the good solvent from the membrane, and stretching the membrane at a temperature ranging from 80 to 95 DEG C, which is higher and limited compared with the temperatures employed in the conventional processes, without carrying out any heat treatment for crystallization.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Vinylidene fluoride copolymer and preparation method therefor
ActiveUS9708430B2Good flexibilityWide range melting processing temperatureTetrafluoroethyleneSolubility
Provided in the present invention is a vinylidene fluoride copolymer. Same is acquired via a polymerization reaction taking place at conditions of 30-100° C. and 2-7 MPa with vinylidene fluoride, tetrafluoroethylene, and perfluorinated dioxole or C1-4 alkoxy-substituted perfluorinated dioxole as raw materials, with an initiator added into an emulsion consisting of water, fluorinated emulsifier, a chain transfer agent, a pH regulator, and an antifouling agent, and then via steps of separation, purification, refinement, condensation, washing, drying, and granulation, where the molar ratio of vinylidene fluoride, tetrafluoroethylene, and perfluorinated dioxole or C1-4 alkoxy-substituted perfluorinated dioxole is 13-17:2-4:1-3. The vinylidene fluoride copolymer of the present invention provides excellent transparency, flexibility, and solubility, is widely applicable in optical apparatus such as lenses, and is for use in specialty films in the fields of solar panels and of capacitors as a fuel cell membrane, a transparent and tough coating, and a large-sized blown object.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
Special material for ultraviolet resistant communication optical cable protective casing and preparation method of special material
InactiveCN104312127AImproves UV resistanceImprove anti-agingPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsDimethyl methylphosphonatePhosphate
The invention discloses a special material for an ultraviolet resistant communication optical cable protective casing and a preparation method of the special material. The special material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 56-74 parts of bisphenol A polycarbonate, 1-2 parts of 2,2',4,4'- tetrahydroxyl benzophenone, 5-8 parts of shea butter, 9-16 parts of zinc dihydrogen phosphate, 24-38 parts of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene terpolymer, 4-8 parts of pentachloro methyl stearate, 2-3 parts of neodymium iso-octanate, 10-15 parts of titanium dioxide, 18-26 parts of copolymer of 1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoro-1-propylene, 1,1-polyvinylidene floride and tetrafluoroethylene, 2-4 parts of tri(thioglycollic acid n-butyl ester) antimony, 3-6 parts of behenamide, 15-20 parts of organobentonite, 6-12 parts of dimethyl methylphosphonate, 5-10 parts of ammonium tetramolybdate, 2-3 parts of hydroquinone monomethyl ether, 1.5-2.5 parts of 2-phenyl benzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid and 3-6 parts of aids. The special material for the protective casing has excellent ultraviolet resistance, aging resistance, solar irradiation resistance, excellent mechanical property and electrical insulation property and high wear resistance, heat resistance and corrosion resistance, the optical cable protective casing can be kept from fading for a long time under sunshine and is prevented from being aged and cracked, and the service life of the protective casing is prolonged.
Owner:安徽电信器材贸易工业有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com