Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "High labeling yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
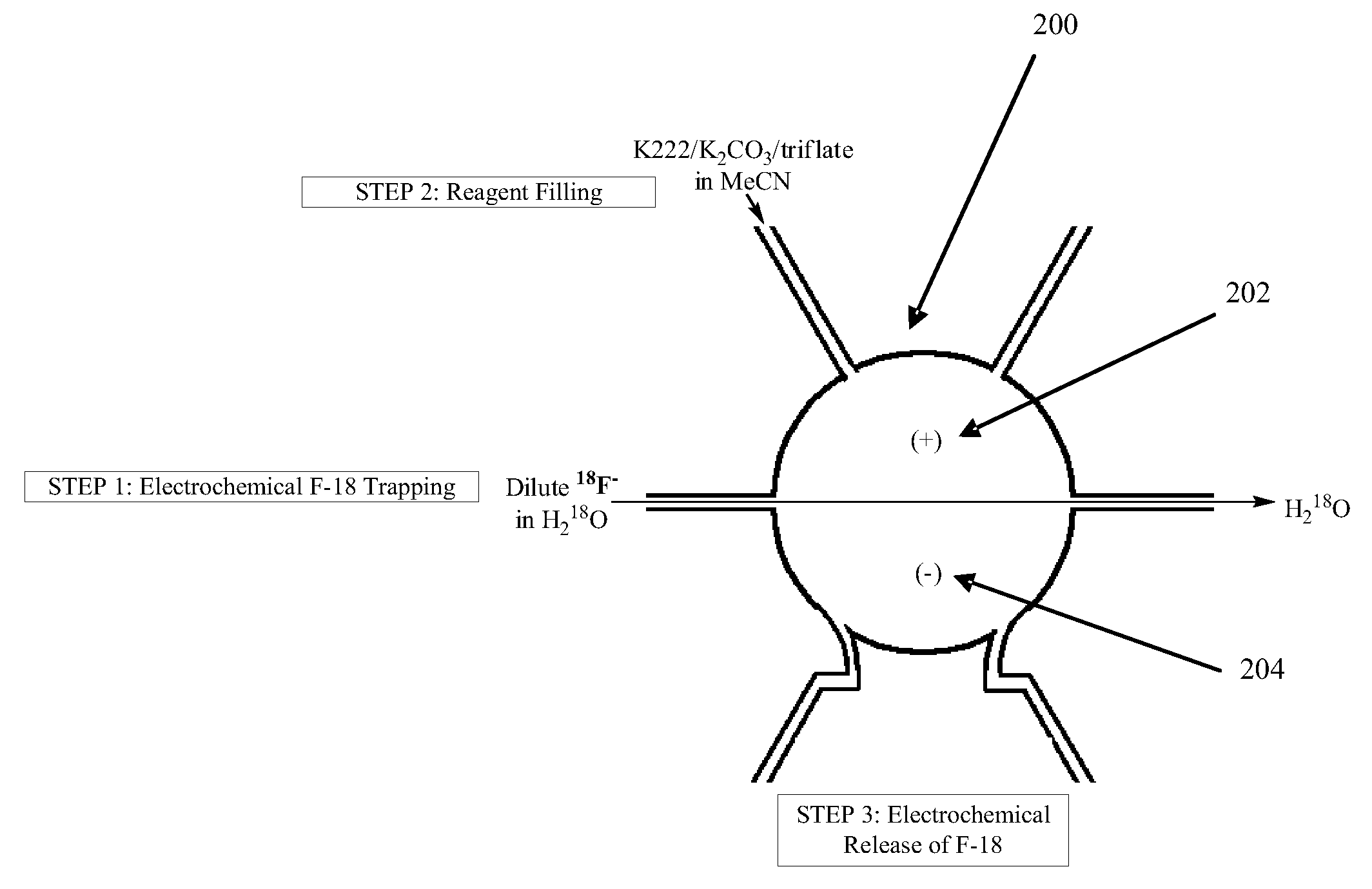
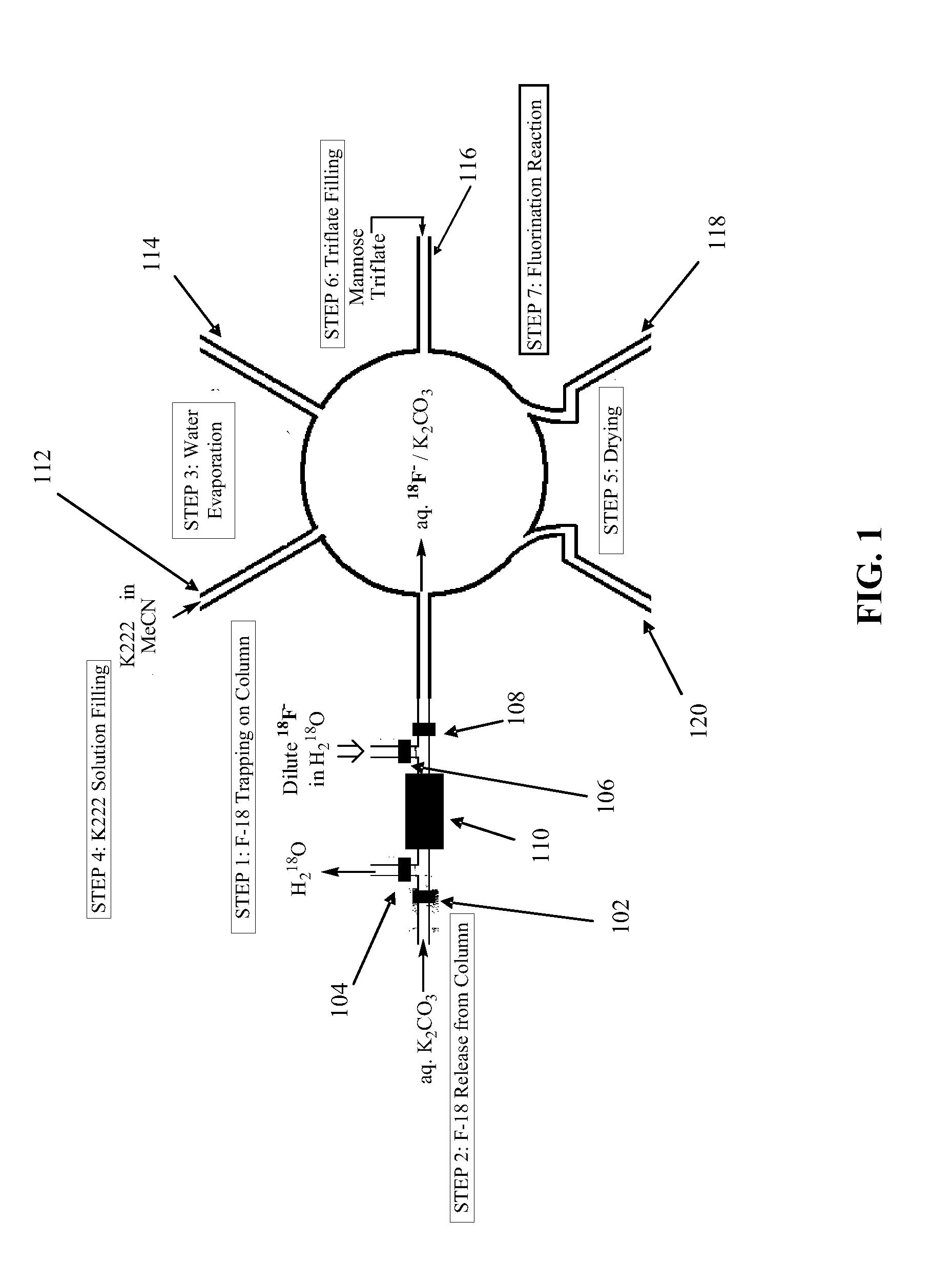
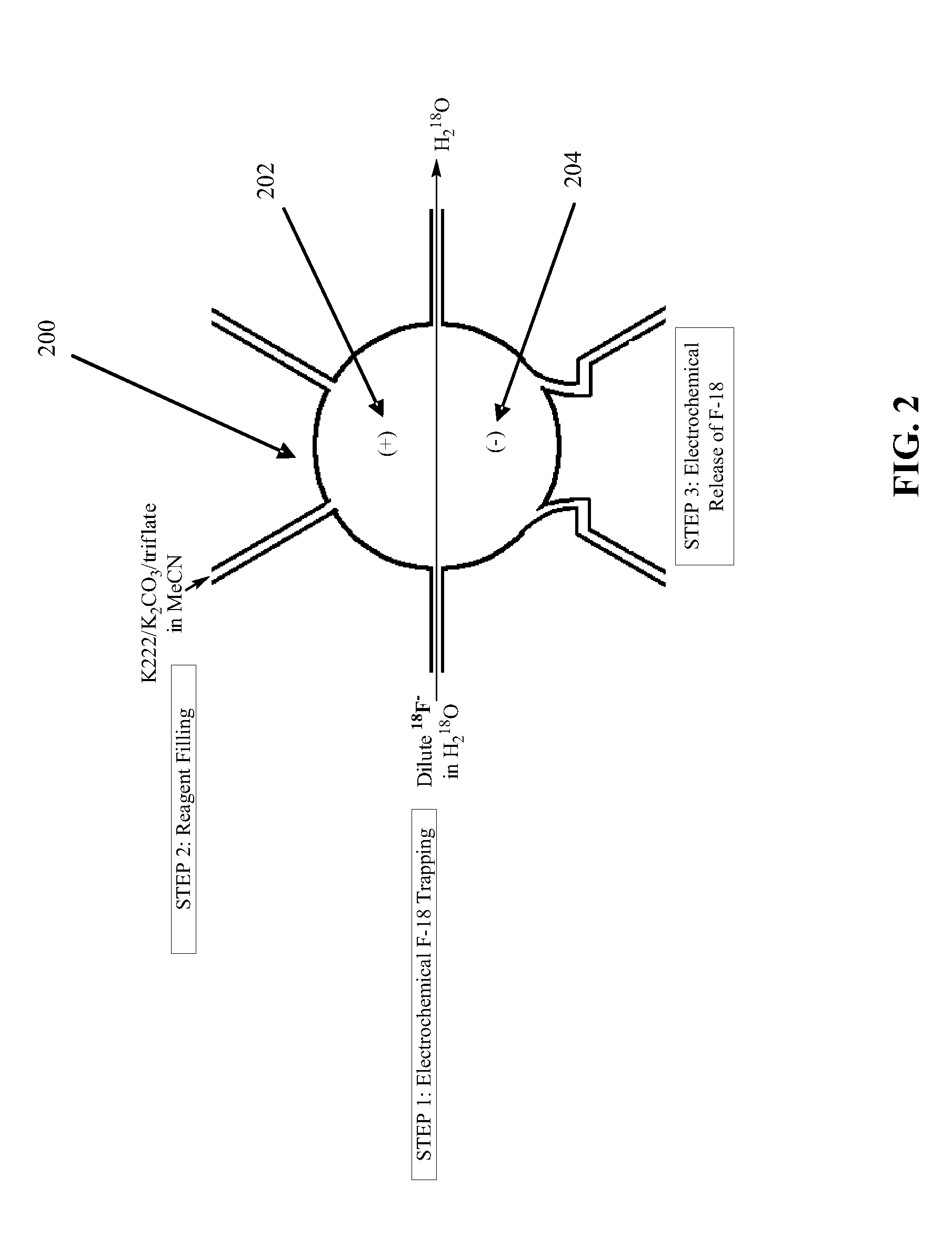
Microfluidic radiosynthesis of a radiolabeled compound using electrochemical trapping and release
InactiveUS20090095635A1Faster and robust operationHigh radiochemical labeling yieldCellsElectrolytic organic productionMicroreactorChemical synthesis
Methods and apparatus enable radiosynthesis of radiolabeled compounds using electrochemical trapping and release. The trapping and release of radioactive isotopes all occur inside a microreactor, a vial or similar device, thus eliminating the need for azeotropic drying and several dead-end filling steps, as well as the necessity to move concentrated radioisotopes from one compartment of the chip to another. These and other features allow radioisotope enrichment to be carried out internally within a radiochemical synthesis chip, providing faster and more robust operation, as well as producing very high radiochemical labeling yields.
Owner:CAL TECH +1
Radioactive label polypeptide coordination complex and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102911256APromote commercial applicationSimple radiolabeling methodRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsCoordination geometryRadioactive Label
The invention provides an RGD polypeptide coordination complex of a radioactive nuclide label. According to the structure of the coordination complex, the radioactive nuclide is selected from 64Cu, 68Ga, 111In, 62Cu, 67Cu, 67Ga, 86Y, 89Zr or 18F; the ligand is a ligand compound containing an RGD structure, which is shown in a formula (I). The coordination complex has stronger ligand stability and high target / non-target ratio, and the appetency of the ligand with integrin AlphavBeta3 is stronger. The invention further provides a preparation method of the coordination complex, and an application of the coordination complex in preparing tumor developers.
Owner:NANTONG SHIMEIKANG PHARMA CHEM
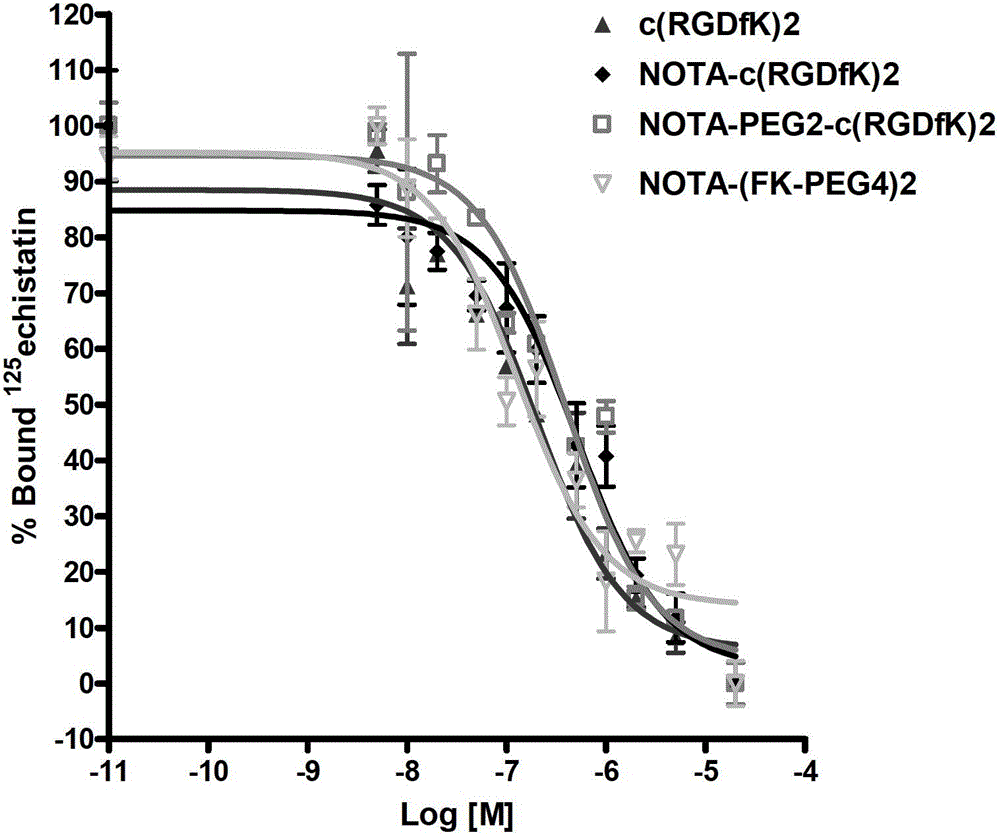
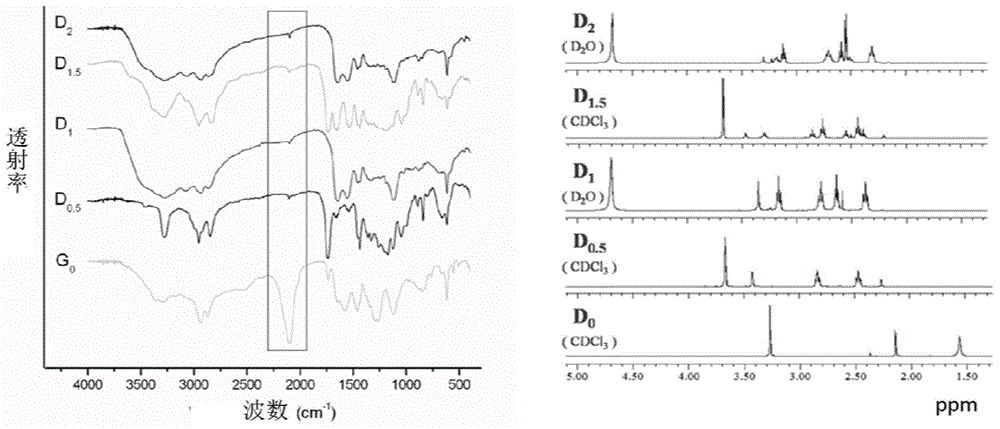
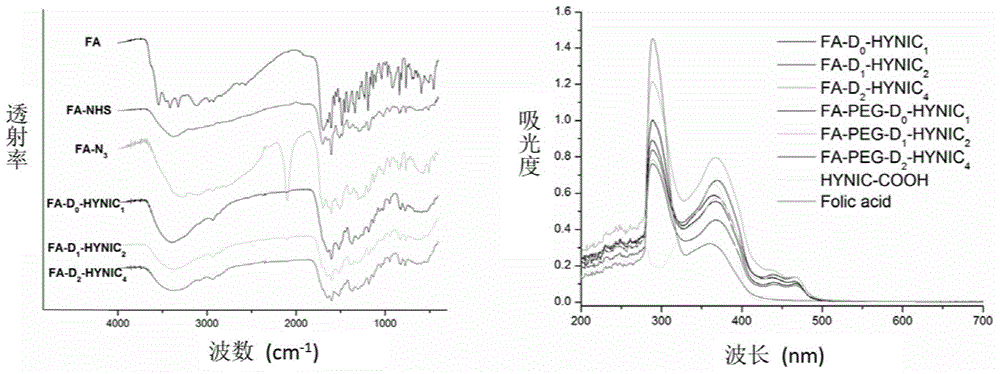
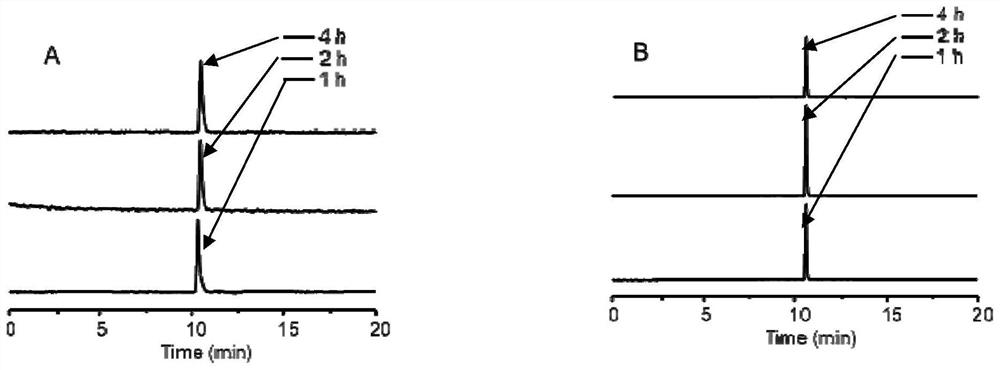
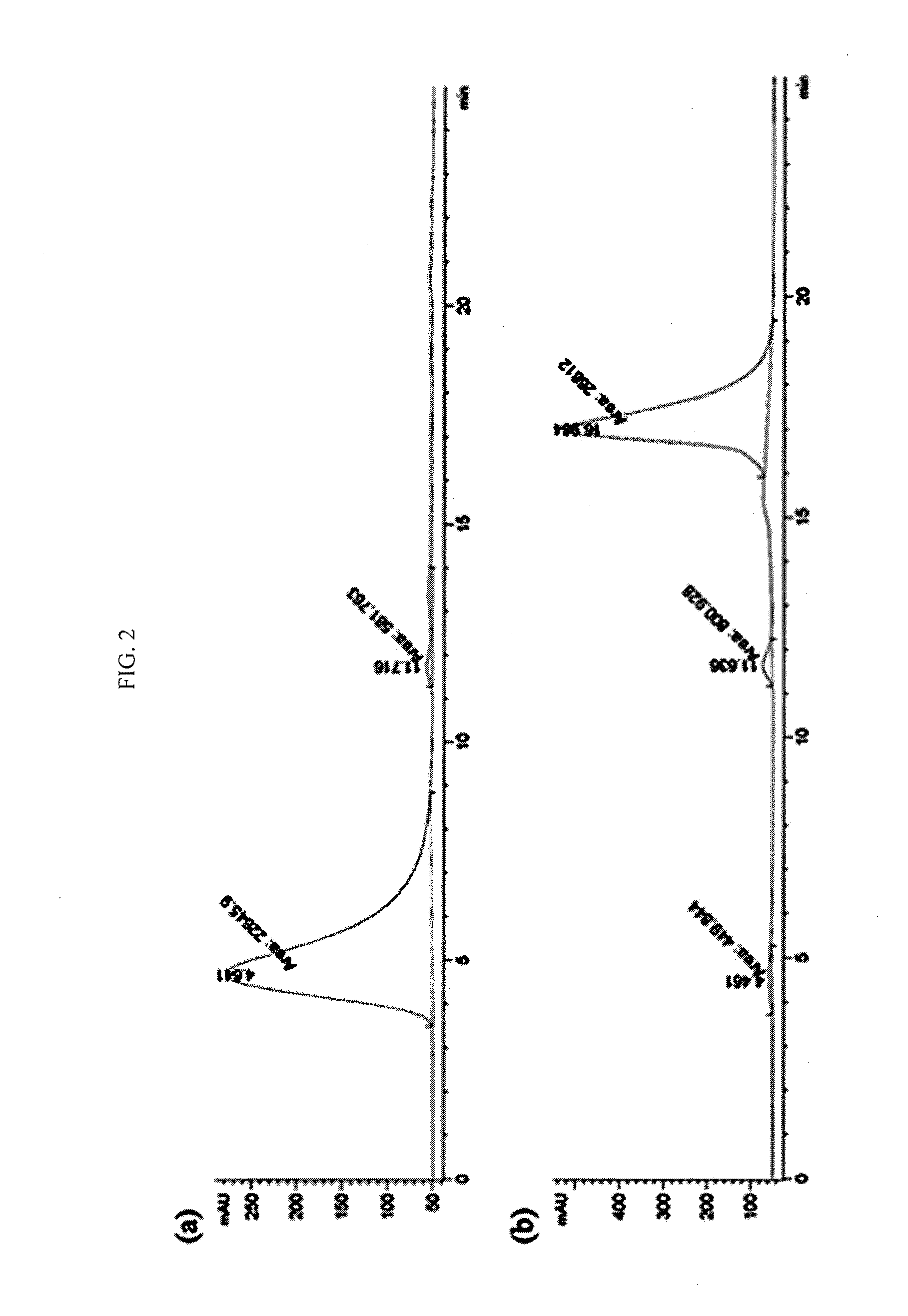
[<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104725473ADoes not affect biological activityDoes not affect pharmacokinetic propertiesPeptide preparation methodsIn vivoStructural formula
The invention discloses a [<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and a preparation method thereof. The probe comprises TMTP1 polypeptide and NOTA, which are connected together, and the structural formulae of the TMTP1 polypeptide and the NOTA are shown in the description. According to the [<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and the preparation method thereof, a glycine is added to the TMTP1, and a G-TMTP1 polypeptide is designed, so that the polypeptide does not influence the biological activity after being radioactively marked; furthermore, 18F is taken as a radionuclide, and the G-TMTP1 polypeptide is marked by utilizing a [<18>F] AlF-NOTA method, so that the obtained [<18>F] AlF-marked PET polypeptide probe has excellent pharmacokinetics properties, the background cleaning rate is high, the liver uptake rate is low, in-vivo stability is good, the uptake rate of tumor site is high, highly metastatic tumor can be diagnosed specifically, and the polypeptide probe can be applied to diagnosis or therapeutic evaluation of highly metastatic malignant tumor.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XIAMEN UNIV +1
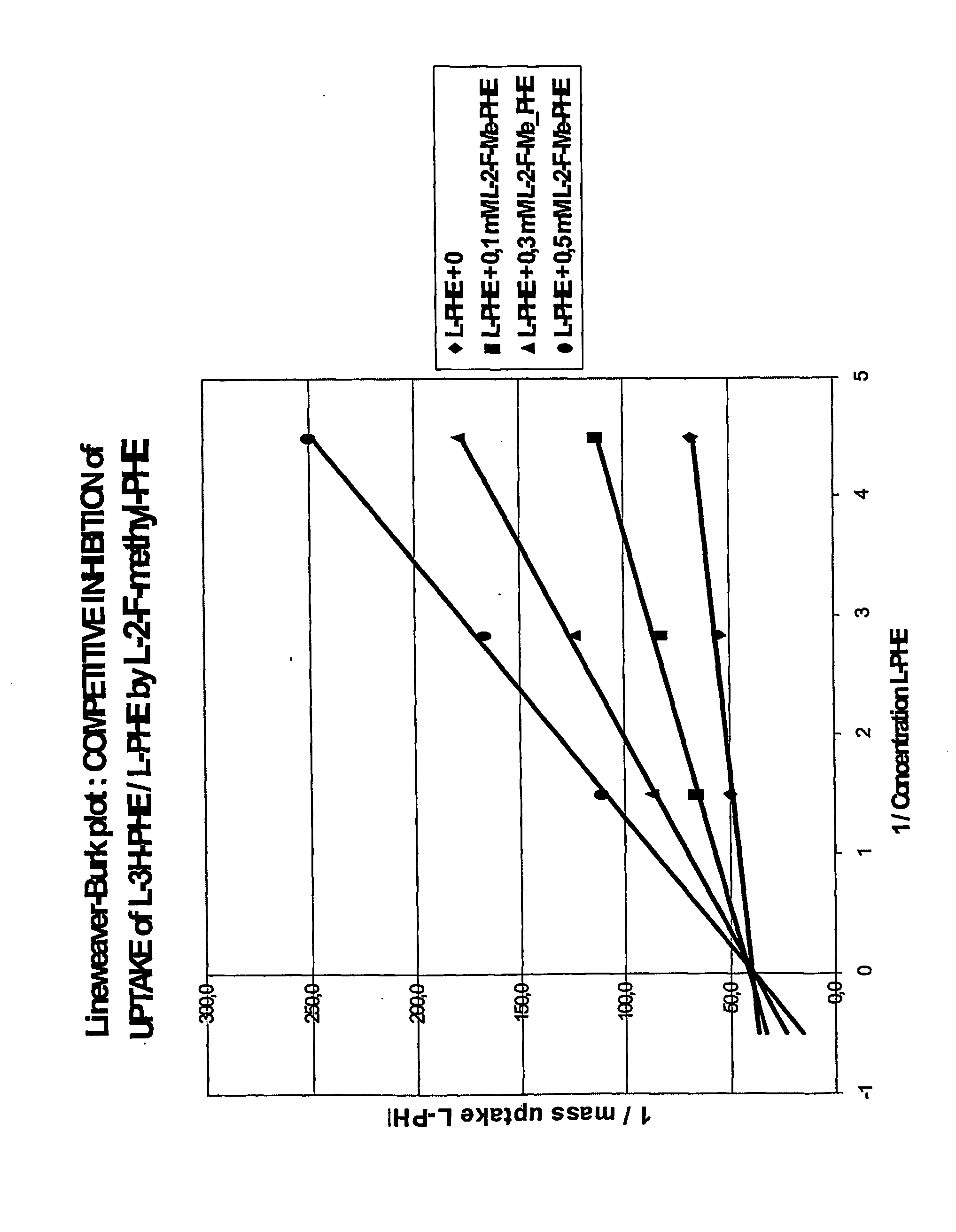
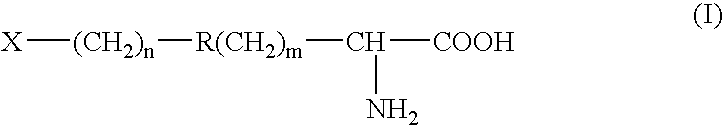
Radioactively labelled amino acid analogues, their preparation and use
InactiveUS20060127306A1Synthesis is simple and fastHigh labeling yieldBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHalogenCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to Halogenated amino acid analogues for use in diagnosis, which compounds have the genera formula (I) wherein: R is (C1-C6) alkyl optionally substituted with thioether or ether oxygen atom when n=0, or a substituted aromatic or heteraromatic ring when n=1-6; and m=0 or 1; and X is a halogen atom. The invention further relates to precursor compounds for these analogues, to a method of preparing these analogues, to a pharmaceutical composition comprising these analogues and to the use of these analogues and compositions in the diagnosis of cancer.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Targeted probe for nuclide labeling and preparation method and application of targeted probe
ActiveCN104830316AStrong marking abilityShort marking timeOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a targeted probe for nuclide labeling and a preparation method and an application of the targeted probe. A general structural formula of a complex is as shown in the specification, wherein R' is a nuclide chelating group; R is a targeted group; Dn is a molecular skeleton which is formed by repeated michael addition reaction and amidation reaction employing propargylamine as an initial reactant, the peripheral group is amino, n represents different algebras, and the numerical value of n is an integer greater than or equal to 0; and m is equal to 2n. A polymer in the targeted probe for nuclide labeling is beneficial to improvement of the specific activity; a high-quality developing result can be obtained by instrument scanning; the targeted probe can play a role in effectively monitoring tumors or inflammatory diseases; meanwhile, carrying of relatively many nuclides on a molecule is facilitated by the formed polymer; the nuclide concentration of focus location is improved; and the targeted probe plays a relatively good treatment role.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
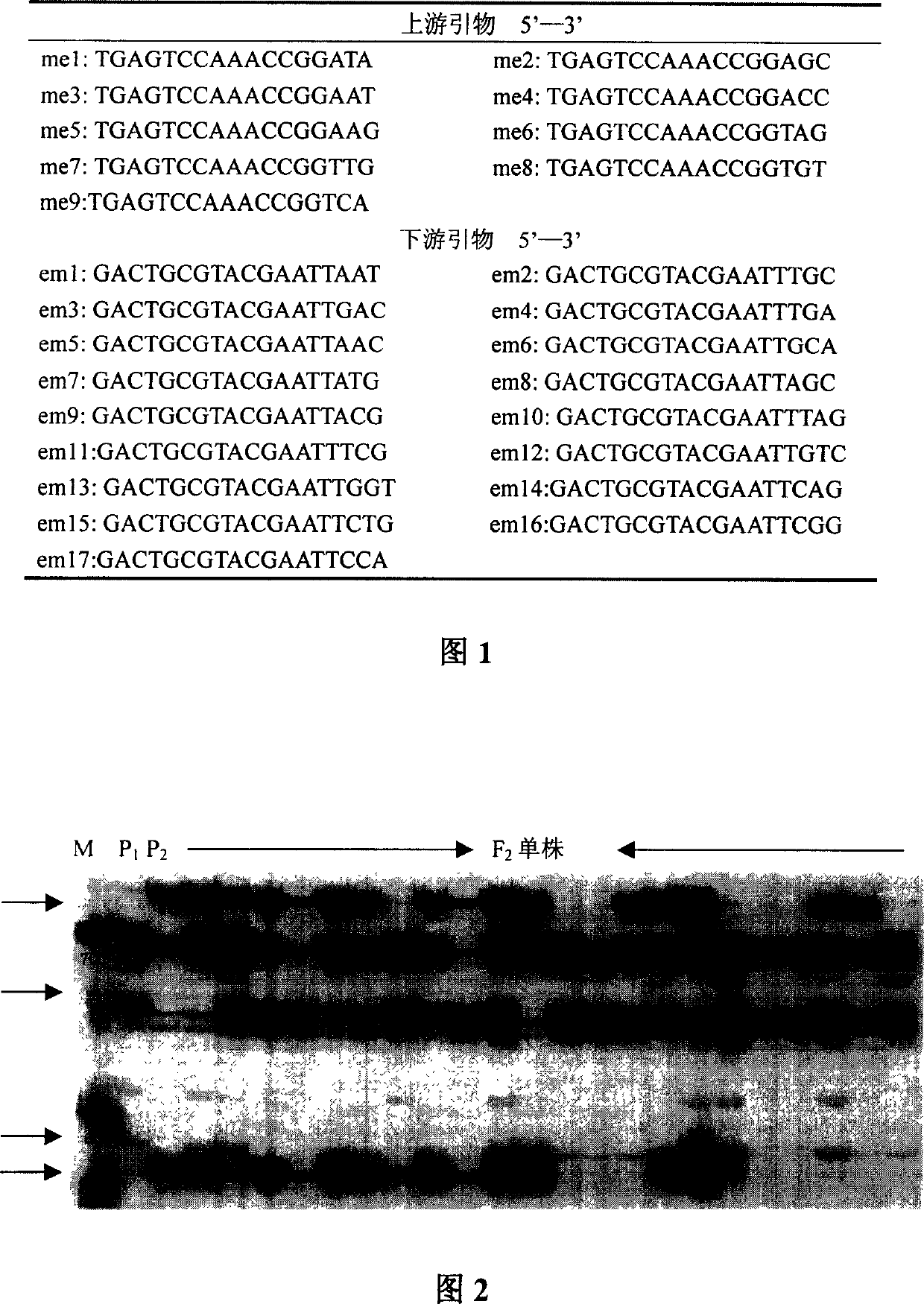
Molecular genetic linkage mapping method of cotton
InactiveCN1541514AOvercoming uneven marker distributionHigh labeling yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationPopulationAgricultural science
The present invention is linked inheritance mapping method utilizing SRAP molecular mark for cotton. The mapping population is hybridization between sea island cotton and upland cotton to generate F2 single plant. Applying SRAP molecular mark and PCR proliferation for detecting population polymorphism in inheritance mapping obtains 285 polymorphic bands in high yield. The 285 marks are used in constructing MAPMAKER linkage group, and 237 marks enter 39 linkage groups, each of which has 2-13 marks. All the linkage groups have the total length of 3030.7 cM, covers 65.4 % of the total cotton genome, and the average mark interval is 12.79 cM. The marks are distributed in the linkage groups relatively homogeneously. The specific molecule marking steps and electrophoresis parameters are also proposed.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
{0><}0{>Radio-labeled tumor developing agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105963724AStrong targetingIncrease polarityOrganic chemistry methodsRadioactive preparation carriersTumor targetAnimal body
{0><}0{>The invention discloses a radio-labeled tumor developing agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. <0}{0><}0{>The radio-labeled tumor developing agent structurally contains an alpha-amino acid derivate structure capable of labeling nuclide and a tumor-targeted folic acid molecule, wherein radionuclide is 18F, and the alpha-amino acid derivate structure and the folic acid molecule are connected in a specific chemical mode. <0}{0><}0{>The invention further relates to a preparation method of the compound and application of the compound serving as a tracing developing agent in PET development in a human body or an animal body. The radio-labeled tumor developing agent has the advantages of simplicity in preparation, low price and strong targeting property especially when serving as a tumor developing agent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Ready-to-use multi-probe hybridization slide, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN107904283AEasy to operateReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluorescence in-situ hybridization, and particularly relates to a ready-to-use multi-probe hybridization slide, and a preparation method and applicationthereof. The multi-probe hybridization slide consists of a probe-attached slide, probes, a hybridization buffer, and a sample-attached slide. The probes are attached to mutually independent probe attachment regions respectively in a lyophilized state. A sample is dropped on a sample attachment region. When the sample attachment region is attached to a probe attachment region, the sample in the sample attachment region is hybridized with the probe of the corresponding probe attachment region. Compared with the traditional FISH experiment, multiple sets of probes can be preset on one slide at atime, and detection of multiple probes can be achieved on the same slide, in this way, the operation steps of the conventional FISH are greatly simplified, the consumption of the probes is reduced, and the using cost of the probes is reduced. The ready-to-use multi-probe hybridization slide has a very high signal-to-noise ratio, specificity, and sample detection rate.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
Technetium-99m-labeledgraphene oxide nanoparticle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103965250AGood water solubilityGood biological adaptabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a technetium-99m-labeled graphene oxide nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: (1) enabling an alkynyl-modified ligand compound and azido-modified graphene oxide to have a Click reaction, and purifying coarse products to obtain a reactant A, wherein the ligand compound is a macrocyclic ligand compound; (2) evenly mixing the reactant A, a hydrochloric acid of stannous chloride and high-technetium acid radial ions in a solvent to obtain mixed liquor, adjusting the pH of the mixed liquor to 6.0-7.5, and performing a reduction coordination reaction to obtain the nanoparticle. The preparation method is high in reaction selectivity, mild in condition, simple to operate and higher in labeling yield. The technetium-99m-labeled graphene oxide nanoparticle is very good in biocompatibility and better in water solubility, can be used for studying the real-time distribution condition of graphene oxide in the cell level and the small animal level and provides more basic information for the application of the graphene oxide to organisms later.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel carbazole fluorescent thiol marking reagent as well as synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN108484478AQuick tagMark accuratelyOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzaldehydeSynthesis methods
The invention provides a novel carbazole fluorescent thiol marking reagent as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. The florescent marking reagent adopts carbazole as a fluorescent basering and activated C=C double bonds as reaction activity groups, is simple and convenient in synthesis step, easy to operate and can be synthesized in a large scale through two steps of reactions as follows: (1) enabling carbazole to react with 4-bromobenzaldehyde so as to obtain an intermediate (4-(9H-carbazole-9-yl) benzaldehyde; (2) enabling the intermediate (4-(9H-carbazole-9-yl) benzaldehydeto react with malononitrile so as to obtain a target product (4-(9H-carbazole-9-yl) benzaldehyde malononitrile, and performing recrystallization for three times with acetonitrile, thereby obtaining ayellow needle-shaped crystal. The chemical purity of the fluorescent marking reagent provided by the invention is up to 99%, and the fluorescent marking reagent is stable in chemical property. The novel carbazole fluorescent thiol marking reagent provided by the invention is capable of rapidly and accurately marking degradation thiol products of organic thiol ester insecticides under a gentle condition, and quantitative analysis on contents of organic thiol ester insecticides in reagent samples can be achieved.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Radioactively labelled amino acid analogues, their preparation and use
InactiveUS7189383B2Synthesis is simple and fastHigh labeling yieldBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHalogenMedicinal chemistry
The present invention relates to Halogenated amino acid analogues for use in diagnosis, which compounds have the general formula (I) wherein: R is (C1–C6) alkyl optionally substituted with thioether or ether oxygen atom when n=0, or a substituted aromatic or heteraromatic ring when n=1–6; and m=0 or 1; and X is a halogen atom. The invention further relates to precursor compounds for these analogues, to a method of preparing these analogues, to a pharmaceutical composition comprising these analogues and to the use of these analogues and compositions in the diagnosis of cancer
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
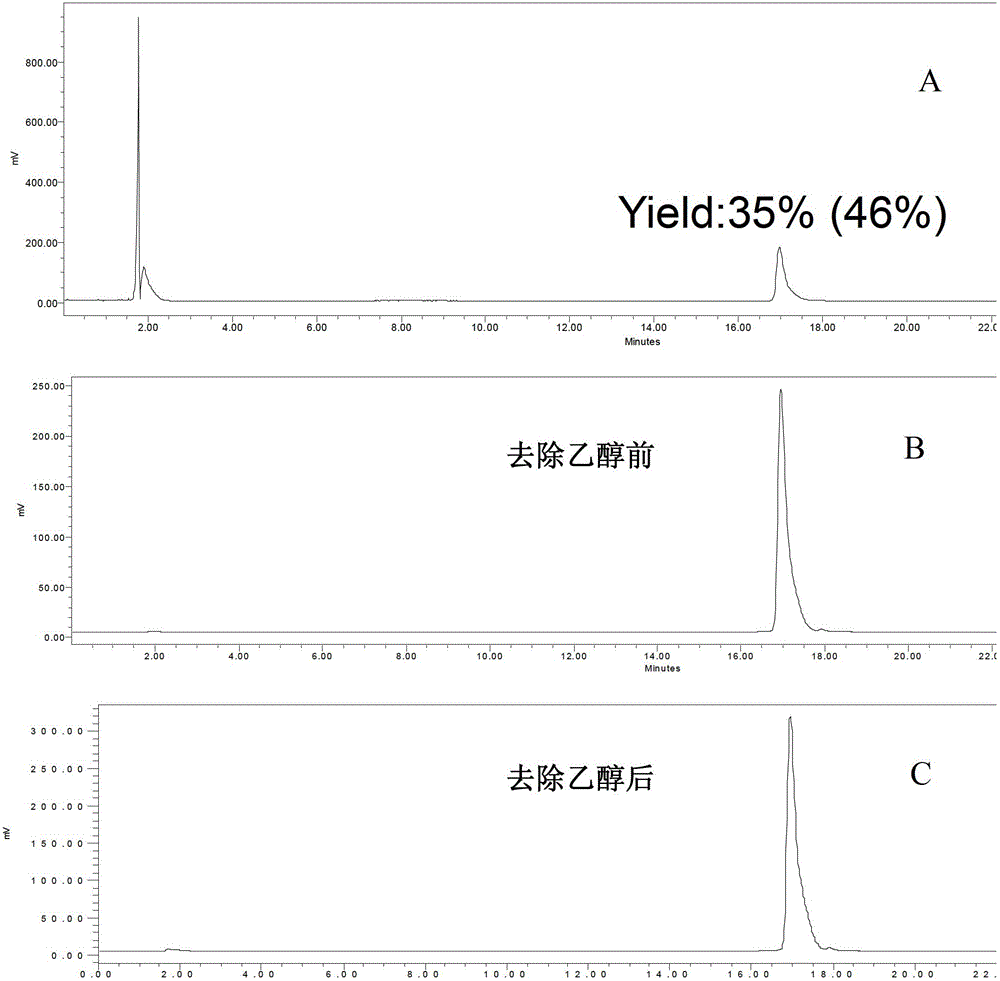
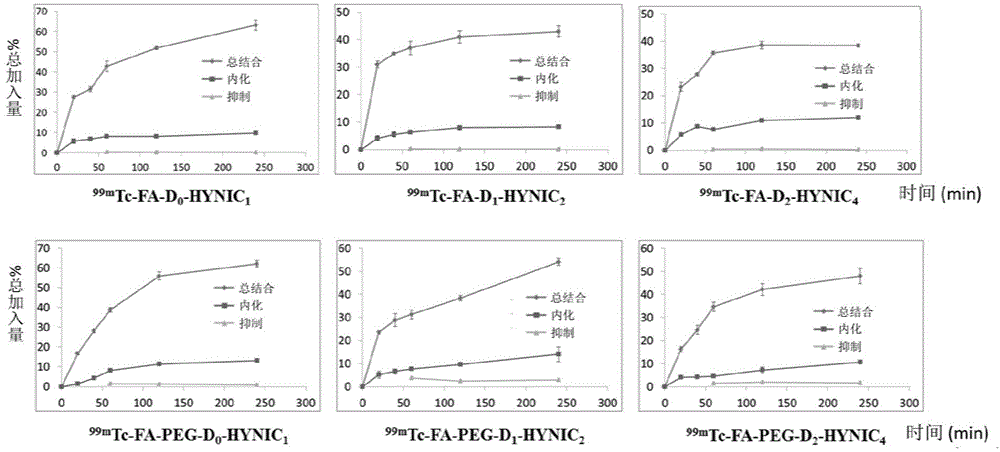
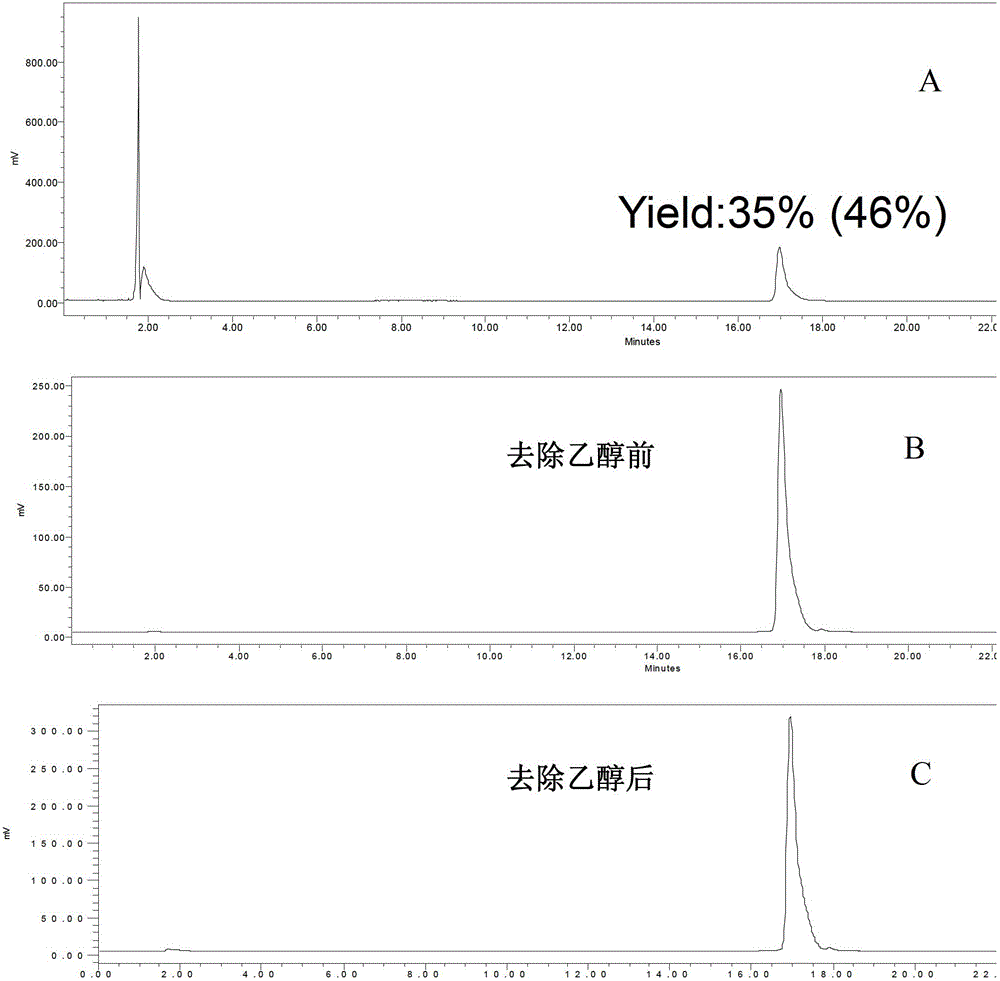
Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM
InactiveCN102516141ARaw materials are easy to obtainEasy to markSulfonic acid esters preparationIsotope introduction to organic compoundsBenzeneImaging agent
The present invention relates to a labeling method for a hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM. According to the method, a <18>F labeling treatment is performed on 1,3-di-p-toluenesulfonyl propane; the resulting labeled intermediate 1-fluoro(<18>F)-3-p-toluenesulfonyl propane reacts with 2-aminobenzene-(2-(N,N-dimethyl)-4-hydroxy)-phenylsulfide to obtain the [<18>F]-FPBM, wherein the reaction process is represented by the following. According to the present invention, the precursor compound 2-aminobenzene-(2-(N,N-dimethyl)-4-hydroxy)-phenylsulfide is firstly used for label of the FPBM, the results show that the compound provides good selectivity for the small molecular chain linking reaction, and the total labeling yield of the labeling method is 13-25%. With the present invention, the optimization of the radioactive synthesis process of the compound is solved, the labeling yield is improved, the automation synthesis is firstly achieved, and the basis is established for the clinical application of the [<18>F]-FPBM in the future.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Radioactive label tEB-TMTP1 compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109705193AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsProduction rateMetastasis tumor
The invention discloses a radioactive label tEB-TMTP1 compound. Through modification with DOTA and NOTA bifunctional chelating agents, DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 and NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 are synthetized, radioactive metal nuclides of radioactive nuclides 68Ga, 64Cu and 177Lu and the like are respectively labelled, and a nuclear medicine diagnosis and treatment probe of specific target high-metastasis tumors is synthetized. The probe designed and synthesized from the radioactive label tEB-TMTP1 compound disclosed by the invention has two advantages that firstly the labelling steps are simple, higher labelling production rate is achieved, and a foundation is laid for clinical application; secondly, the obtained DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe and the obtained NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe have excellent pharmacokinetics nature,the half life of the DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe and the obtained NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe in bodies can be notably prolonged, the DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe and the obtained NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe can circulate in thebodies for a long term, tumor part ingestion is increased, and target treatment on high-metastasis tumors can be realized.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XIAMEN UNIV
Interferon stimulating protein targeting compound, radiomarker thereof, and preparation method and application of interferon stimulating protein targeting compound and radiomarker
ActiveCN112920172AAccurate guide selectionAccurate Visual InspectionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryProtein targetChemical compound
The invention provides a dimeric amido benzimidazole compound. The structure of the dimeric amido benzimidazole compound is shown as a formula (I), wherein R0 is an integer of n from 0 to 5. The invention also provides a compound with anti-tumor activity and a radionuclide labeled compound targeted by interferon stimulating protein, wherein the compound is based on the dimeric amido benzimidazole compound. The dimeric amido benzimidazole compound has high affinity and high specificity to interferon stimulating protein, the compound with anti-tumor activity has the characteristic of activating an STING pathway in vitro, and the radionuclide labeled compound has the advantages that target uptake and non-target uptake are obviously compared, and the lipid solubility can be changed by introducing nuclides with different properties so that the application scene is greatly widened, and the compound can be combined with treatment nuclides for tumor treatment, and even can be used for immunotherapy.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Two-dimensional palladium-based probe with radioiodine labeling and preparation method and application of probe
ActiveCN110013560APromote commercial applicationStrong marking abilityRadioactive preparation carriersCardiovascular disorderHalogenNanocarriers
The invention discloses a two-dimensional palladium-based probe with radioiodine labeling and a preparation method and application of the probe. The probe comprises a two-dimensional palladium-based nanomaterial, a PEG linking molecule, a targeting group R and radioiodine, a thiol group is arranged at one end of the PEG linking molecule, a modifiable group is arranged at the other end of the PEG linking molecule, one end of the PEG linking molecule is linked to the two-dimensional palladium-based nanomaterial through the above thiol group, the other end is linked to the targeting group R through the modifiable group, and radioiodine is directly labelled on the two-dimensional palladium-based nanomaterial. According to the present invention, a plurality of radioiodine can be carried on a unit of nanocarrier based on the strong binding force between the two-dimensional palladium-based nanomaterial and halogen ions, the probe has the characteristics of strong labeling ability, short labeling time, high labeling yield and no need of subsequent purification before application, and is more conducive to commercial application and clinical promotion of markers.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparation of n-methyl-3-(2-tributylstannylphenoxy)-3-phenylpropanamine, and use therof
InactiveUS20110313183A1Simplify separationEasy to purifyTin organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationNorepinephrine transporterLeaving group
A method for preparation of N-methyl-3-(2-tributylstannylphenoxy)-3-phenylpropanamine is provided, which includes formation of N-methyl-3-(2-tributylstannylphenoxy)-3-phenylpropanamine, useful as a precursor of a norepinephrine transporter (NET) contrast label [123Iodine](R)—N-methyl-3-(2-iodophenoxy)-3-phenylpropanamine ([123I]MIPP) with a leaving group Bu3Sn.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
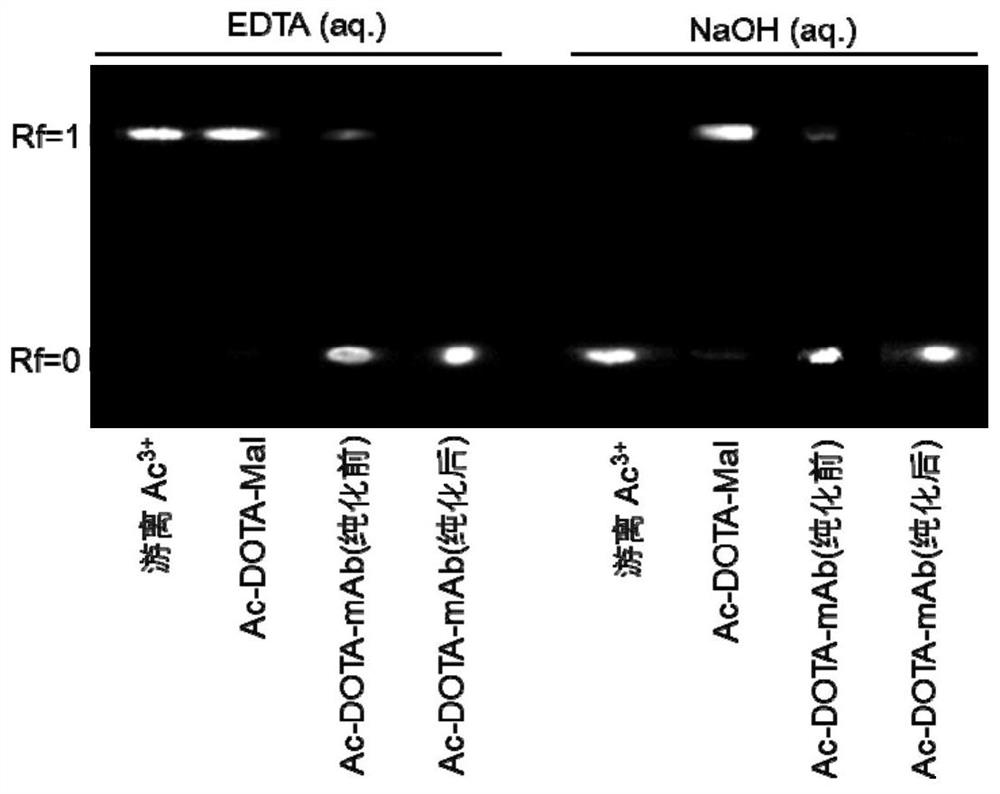
Method for radiolabeling biological compound
PendingCN111808161AImprove thermal stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide preparation methodsImideChemical compound
The invention relates to a method for radiolabeling a biological compound. The method comprises the following steps of performing chelation reaction on a bifunctional chelating agent modified with a maleimide group and radionuclide, and directly adding the biological compound to carry out coupling reaction, thereby obtaining the radiolabeled biological compound. The technical scheme adopts the maleimide group with excellent thermal stability, so that the bifunctional chelating agent can be chelated with radioactive metal ions under a high-temperature condition, the chelating reaction time is remarkably shortened, and the labeling efficiency is improved; and the product of the chelation reaction can be subjected to biological compound coupling without purification, and the method has the advantages of simple steps, convenience, high efficiency and high connection efficiency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
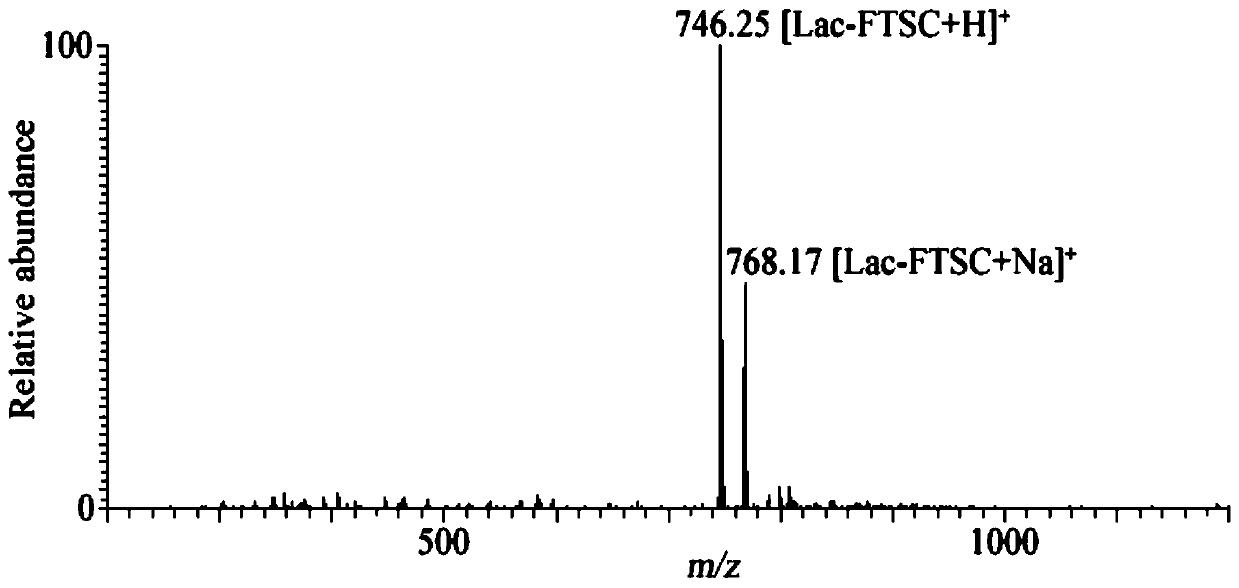
One-step fluorescence derivation method of reducing sugar and application thereof
InactiveCN110954517ASimplify the fluorescent labeling processHigh labeling yieldComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluorescence spectraThiourea
The invention discloses a one-step fluorescence derivation method of reducing sugar and application thereof. By adopting reducing sugar as a raw material, the reducing sugar and a fluorescence labeling reagent fluorescein-5-amino-thiourea are subjected to a stirring reaction at room temperature to generate a sugar-FTSC derivative so that and various types of sugar such as lactose, uronic acid, maltodextrin and traditional Chinese medicine source reducing polysaccharide are labelled. Mass spectrum structure analysis, fluorescence spectrum and microscopic living cell imaging research are performed on an obtained product. Results show that the carbohydrazone derivative obtained by labeling has good stability and high fluorescence yield, and can be used for fluorescence derivative labeling andmicroscopic fluorescence imaging detection of reducible neutral and acidic oligosaccharides. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high reaction yield and simple operation, and can be used for large-scale synthesis and preparation of functional oligosaccharide probes; meanwhile, the method is suitable for researching mass spectrometry, chromatography, fluorescence, microscopic fluorescence imaging, flow cytometry and the like of reductive oligosaccharides and polysaccharide molecules, and has a wide application prospect in the field of life science.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Technetium-99m labeled complex of gold nanoparticle-gold binding peptides, and method of making and using the same
InactiveUS20140314668A1High labeling yieldPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsNanoparticleImaging agent
There is provided a method for preparing a 99mTc labeled gold nanoparticles-gold binding peptide, including: (a) coating gold nanoparticles with a gold binding peptide; and (b) labeling a composed 99mTc tricarbonyl precursor on the gold binding peptide coated on the gold nanoparticles. The 99mTc labeled gold nanoparticles-gold binding peptide prepared by the method according to the present invention is expected to be usefully employed for manufacturing a molecular contrast agent (imaging agent) which is traceable in organisms using imaging apparatuses such as gamma imaging and single photon emission computed tomography due to high labeling yield and good in-vivo stability.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Stable isotope amino compound labeling reagent as well as synthesis method and application thereof
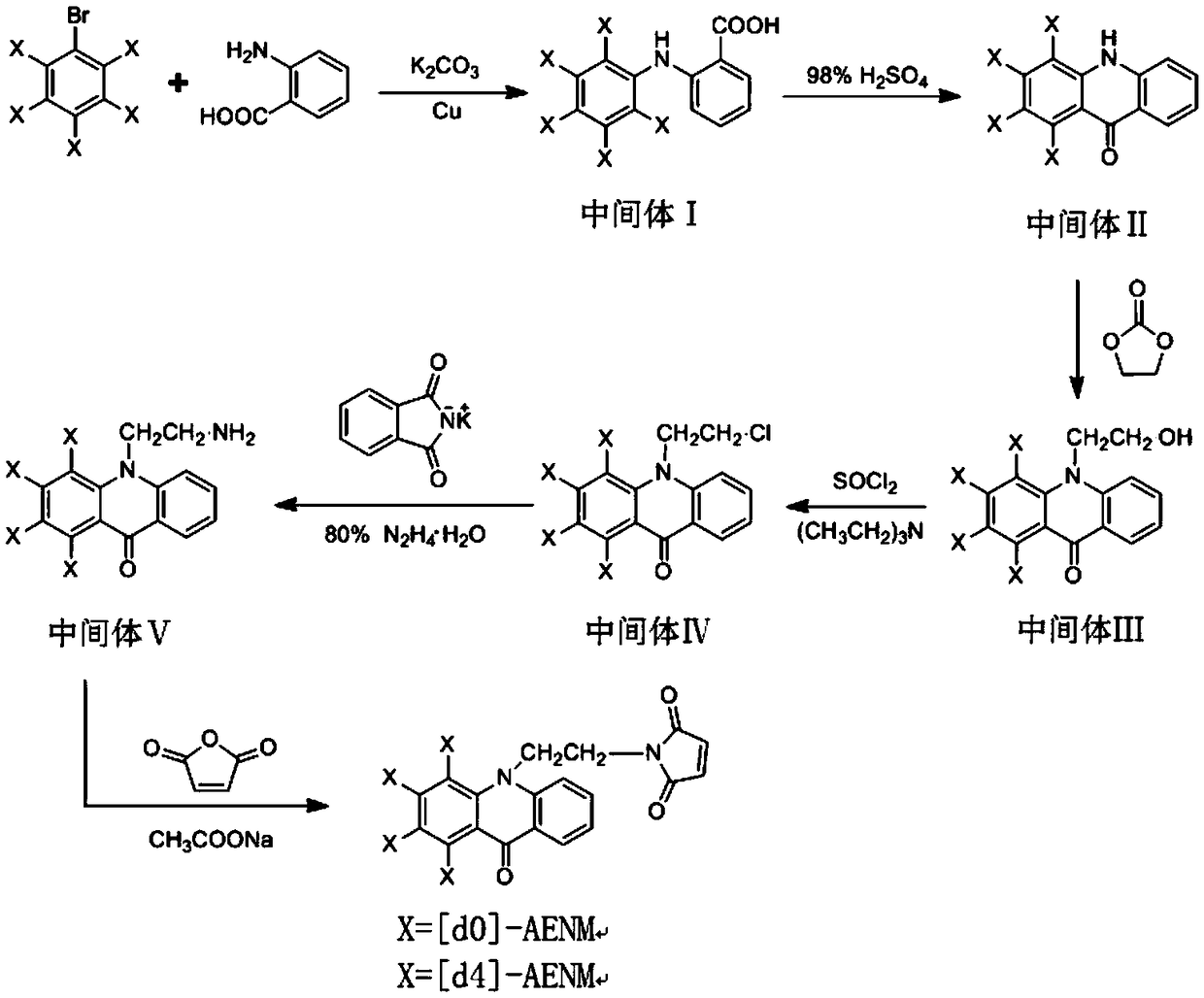
InactiveCN113402352AQuick selectionHigh selectivityIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsComponent separationEthyl chloroformateStable Isotope Labeling
The invention relates to the technical field of stable isotope labeling, in particular to a stable isotope amino compound labeling reagent and a synthesis method and application thereof. The chemical structural formula of the labeling reagent is as shown in formula 1 in the specification, wherein in the formula 1, X is D, and the labeling reagent is [d4]-2-(9-acridone)-ethyl chloroformate; and R is any one of F, Cl, Br, I and other elements, and n is equal to 2 or 3. The isotope labeling reagent provided by the invention takes acridone as a parent ring and an isotope labeling group and chloroformate as a reaction group, can selectively label an amino compound, and has the advantages of simple and convenient synthesis method, high labeling reaction rate, strong signal of a labeled product, high labeling yield and high amino selectivity; and the accuracy and the sensitivity of mass spectrometric detection of the amino compound are enhanced.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
[18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof
PendingCN109734720AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSimple manufacturing methodRadioactive preparation carriersIsotope introduction to organic compoundsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Chemistry
The invention discloses a [18F] DPA-174 derivative. The [18F] DPA-174 derivative is prepared by modifying the benzene ring structure of or prolonging the carbon chain structure of a [18]F DPA-174 imaging agent. The invention also discloses preparation and application methods of the [18F] DPA-174 derivative. The [18F] DPA-174 derivative is simple in preparation, easy to implement, high in labellingyield and good in repeatability and can help in real time observe and in vivo monitor the status of intracerebral neuroinflammation of an animal model as well as the changes of the major organs and tissues of the animal model; the prepared imaging agents can achieve imaging effects on neuroinflammation; the [18F] DPAF imaging agent can achieve a high signal-to-noise ratio on neuroinflammation lesions to provide possibility for further monitoring and assessing the diagnosis and treatment effects on neuroinflammation..
Owner:中国人民解放军东部战区总医院 +1
Novel gall bladder imaging agent and its preparation method
ActiveUS20140186262A1Suitable for use in diagnosisEfficient captureRadioactive preparation carriersRadiation therapyGlycineImaging agent
A novel gall bladder image agent which includes a radio-labelled MAG3-tri-galactosamine, and its preparation method, which includes reacting mercaptoacetyltriglycine (MAG3)-tri-galactosamine, SnF2 and Tc-99m in the presence of a phosphate buffer solution (at pH of from 10.0˜12.0) to obtain Tc-99m-MAG3-tri-galactosamine, when the MAG3-tri-galactosamine is MAG3-DCM-Lys(Gah-GalNAc)3 (where DCM represents a dicarboxymethyl group, and Gah represents a glycine-aminohexyl group), it obtains a labelling yield of at least 90%, and its specific radioactivity is at least 7.0×109 Bq / mg.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
A radiolabeled polypeptide complex and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102911256BPromote commercial applicationSimple radiolabeling methodPeptidesBulk chemical productionCoordination geometryRadioactive Label
The invention provides an RGD polypeptide coordination complex of a radioactive nuclide label. According to the structure of the coordination complex, the radioactive nuclide is selected from 64Cu, 68Ga, 111In, 62Cu, 67Cu, 67Ga, 86Y, 89Zr or 18F; the ligand is a ligand compound containing an RGD structure, which is shown in a formula (I). The coordination complex has stronger ligand stability and high target / non-target ratio, and the appetency of the ligand with integrin AlphavBeta3 is stronger. The invention further provides a preparation method of the coordination complex, and an application of the coordination complex in preparing tumor developers.
Owner:NANTONG SHIMEIKANG PHARMA CHEM
Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase
InactiveUS20210196842A1High degree of purityHigh labeling yieldTransferasesRadioactive preparation carriersProtein proteinChemistry
New methodologies for site-specifically radiolabeling proteins with the PET isotope [1SF] are required to generate high quality radiotracers for imaging in both the preclinical and clinical settings. The enzymatic radiofluorination overcomes many of the limitations encountered to date with purely chemical approaches. The bacterial enzyme lipoic acid ligase was used to conjugate [18F]-fluorooctanoic acid to both a small peptide and a Fab antibody fragment. Labeling was site-specific and highly efficient under mild aqueous conditions using small amounts of peptide / protein (1-10 nmol). The labeled construct retained full epitope binding affinity and was stable in mouse serum. Using an optimized reaction scheme, mCi quantities of [18F]-Fab were generated, an amount sufficient for human imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gall bladder imaging agent and its preparation method
ActiveUS9226982B2Suitable for use in diagnosisEfficient captureRadioactive preparation carriersRadiation therapyGlycineImaging agent
A novel gall bladder image agent which includes a radio-labelled MAG3-tri-galactosamine, and its preparation method, which includes reacting mercaptoacetyltriglycine (MAG3)-tri-galactosamine, SnF2 and Tc-99m in the presence of a phosphate buffer solution (at pH of from 10.0˜12.0) to obtain Tc-99m-MAG3-tri-galactosamine, when the MAG3-tri-galactosamine is MAG3-DCM-Lys(Gah-GalNAc)3 (where DCM represents a dicarboxymethyl group, and Gah represents a glycine-aminohexyl group), it obtains a labelling yield of at least 90%, and its specific radioactivity is at least 7.0×109 Bq / mg.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
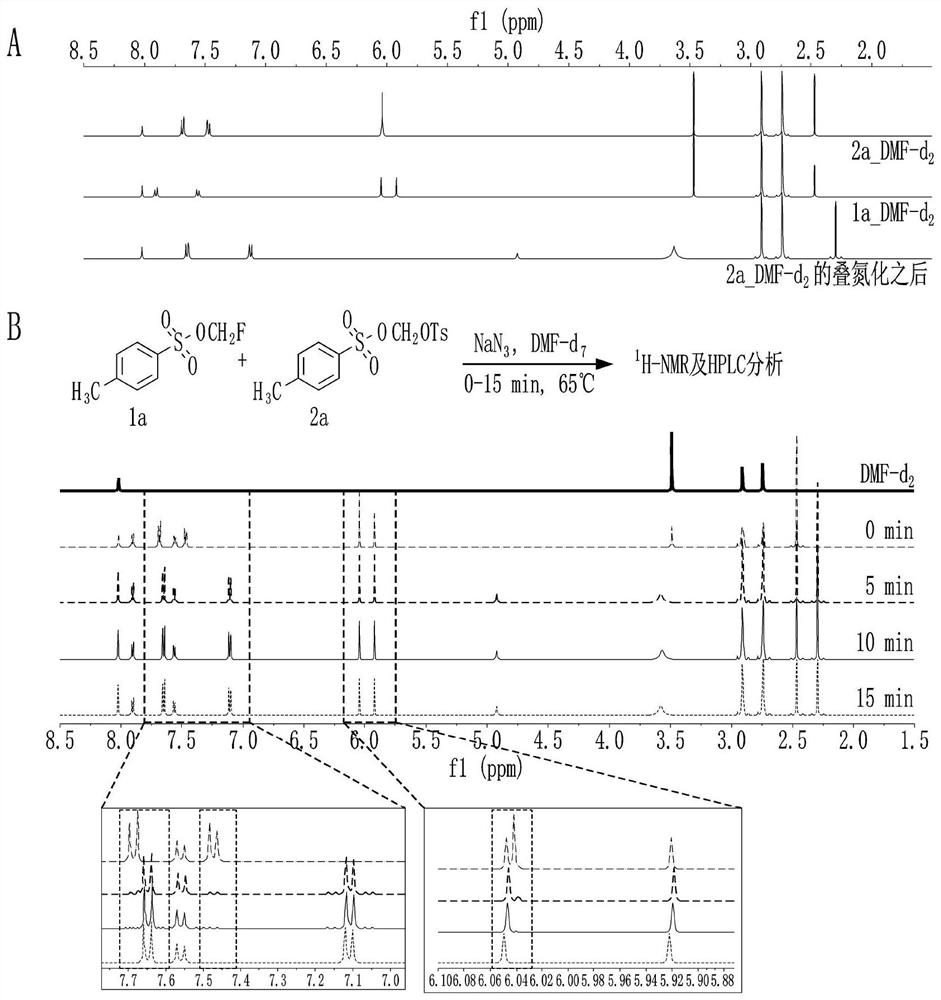
Method for preparing fluorine-18-labeled fluoromethyl-substituted radiopharmaceuticals using selective azide substitution reaction and precursor scavenging
InactiveCN112752740AShort manufacturing timeHigh purityRadioactive preparation carriersIsotope introduction to acyclic/carbocyclic compoundsMeth-Chemical compound
Owner:BIK治疗公司
A kind of carbazole fluorescent thymine drug labeling reagent, synthesis and application
ActiveCN108409635BImprove retention behaviorHPLC-Fluorescence detectionOrganic chemistryComponent separationCarbazoleFood safety
The present invention relates to carbazole fluorescent thymine drug labeling reagent, synthesis and application. Carbazole is used as fluorescent mother ring, benzyl chloride is used as reactive group, and its chemical name is: 4-(9H-carbazole-9- base) benzyl chloride. The novel stable carbazole-based fluorescent thymine drug labeling reagent described in the present invention can accurately, sensitively and rapidly label thymine drugs under mild conditions, thereby realizing the separation of micro and trace amounts of thymine drugs in complex systems It can be used in research fields such as environmental analysis and food safety, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV +1
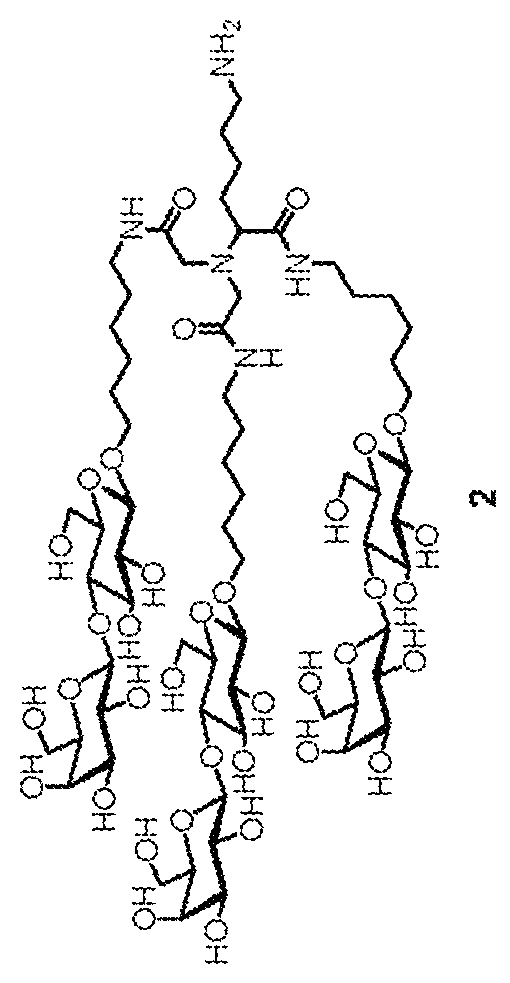
A kind of nuclide-labeled targeting probe compound and preparation method thereof
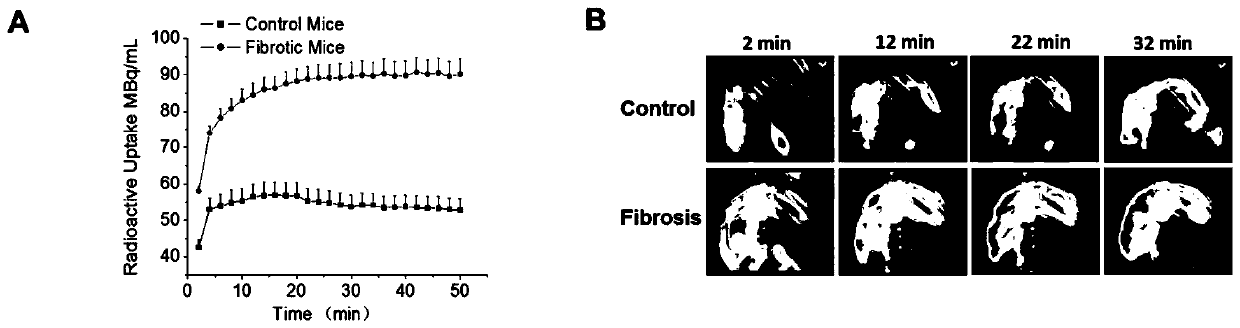
ActiveCN107253969BImaging time is shortImprove image qualityIsotope introduction to sugar derivativesSugar derivativesAnatomical structuresImaging quality
The invention discloses a nuclide-labeled targeted probe compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular weight of the nuclide-labeled targeted probe compound is 1kDa-50kDa, and the nuclide-labeled targeted probe compound comprises a polyethyleneimine skeleton and a targeted group derived from N-acetyl glucosamine or diacetyl chitobiose acid and is labeled through coordination of a radionuclide X label and an imino group on the polyethyleneimine skeleton. The nuclide-labeled targeted probe compound can be applied to in-vivo hepatic fibrosis detection, has the advantages of relatively short imaging time, relatively high imaging quality, relatively wide imaging depth, less kidney radioactive accumulation and the like, and is relatively beneficial to early hepatic fibrosis. Meanwhile, by combining with CT imaging, accurate anatomical structure signals and functional information can be obtained, thereby being beneficial to the evaluation and accurate staging of hepatic fibrosis.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Stable isotope mercapto compound labeling reagent and its synthesis method and application
InactiveCN106518846BStable marker positionHigh selectivityComponent separationOrganic chemistry methodsReaction rateSynthesis methods
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method
InactiveCN104725473BDoes not affect biological activityDoes not affect pharmacokinetic propertiesPeptide preparation methodsGlycineClearance rate
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XIAMEN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![[<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof [<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/13785fee-f1d4-4334-9714-3e2e39f3ae96/HDA0000568632230000011.PNG)
![[<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof [<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/13785fee-f1d4-4334-9714-3e2e39f3ae96/HDA0000568632230000012.PNG)
![[<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof [<18>F] AlF marked positron emission tomography (PET) polypeptide probe and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/13785fee-f1d4-4334-9714-3e2e39f3ae96/HDA0000568632230000021.PNG)













![Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/65e97cf1-7e30-4dc7-b892-92f616396211/HDA0000104892830000011.png)
![Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/65e97cf1-7e30-4dc7-b892-92f616396211/HDA0000104892830000012.png)
![Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM Labeling method for hydroxytamine transporter imaging agent [<18>F]-FPBM](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/65e97cf1-7e30-4dc7-b892-92f616396211/FDA0000104892810000011.png)

















![[18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof [18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e6434e2c-a450-4f29-a176-a2dd07cc6c9d/HDA0001959649660000011.png)
![[18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof [18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e6434e2c-a450-4f29-a176-a2dd07cc6c9d/HDA0001959649660000021.png)
![[18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof [18F] DPA-714 (N, N-diethyl-2-(2-(4-(2-[18]F-fluoroethyoxy)phenyl)-5, 7-dimethylpyrazolo[1, 5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)aceamide) derivative and preparation and application methods thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e6434e2c-a450-4f29-a176-a2dd07cc6c9d/HDA0001959649660000031.png)





![Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/196292b6-f3f6-4805-9da8-6c9458a4f7ad/US20210196842A1-D00001.png)
![Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/196292b6-f3f6-4805-9da8-6c9458a4f7ad/US20210196842A1-D00002.png)
![Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase Site-specific radiofluorination of peptides with 8-[18f]-fluorooctanoic acid catalyzed by lipoic acid ligase](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/196292b6-f3f6-4805-9da8-6c9458a4f7ad/US20210196842A1-D00003.png)










![A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/87dc7176-28d9-4f7d-aa89-b6af25cba93b/HDA0000568632230000011.png)
![A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/87dc7176-28d9-4f7d-aa89-b6af25cba93b/HDA0000568632230000012.png)
![A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method A [18f]alf-labeled pet polypeptide probe and its preparation method](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/87dc7176-28d9-4f7d-aa89-b6af25cba93b/HDA0000568632230000021.png)