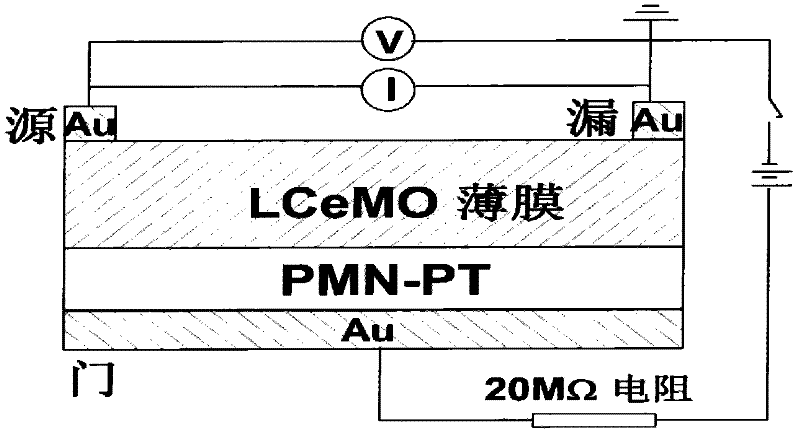
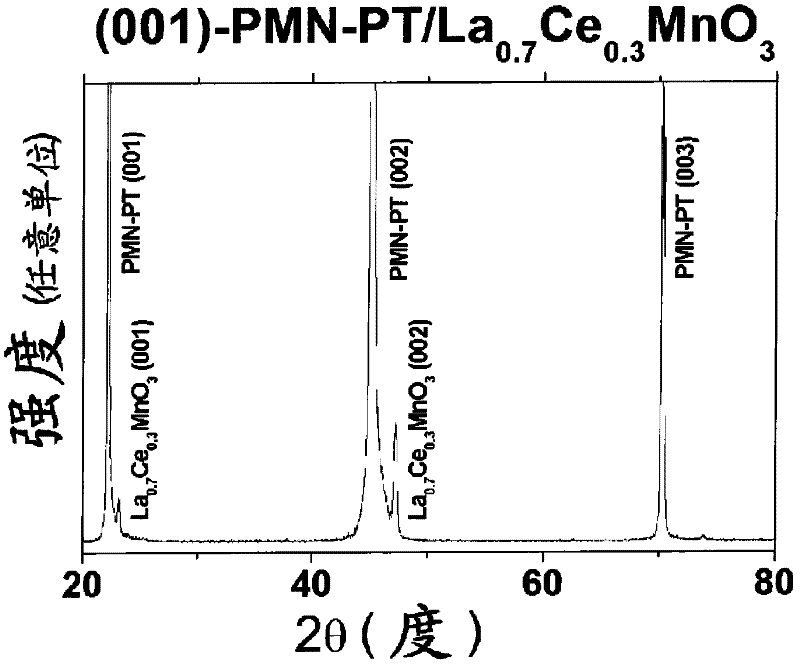
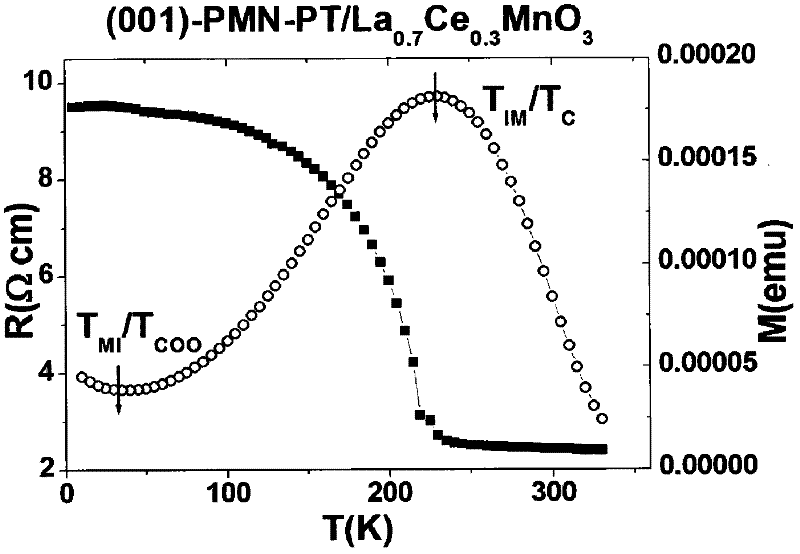
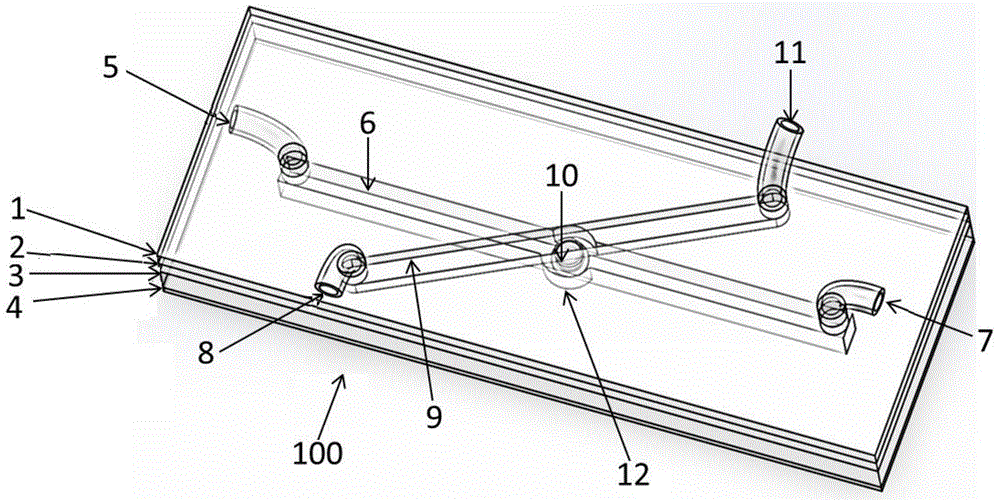
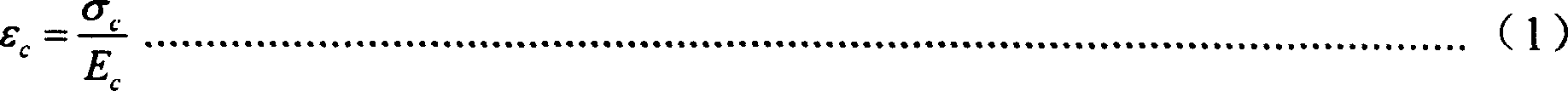Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Strain effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Most common effects include eye dryness, cotton mouth, increase in appetite, mood elevation, paranoia, energy boost and sedation. Of course, these effects vary from strain to strain and from person to person.
Process for predicting porosity and permeability of a coal bed
InactiveUS6860147B2Reduce contentIncrease contentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyPorosityGas composition
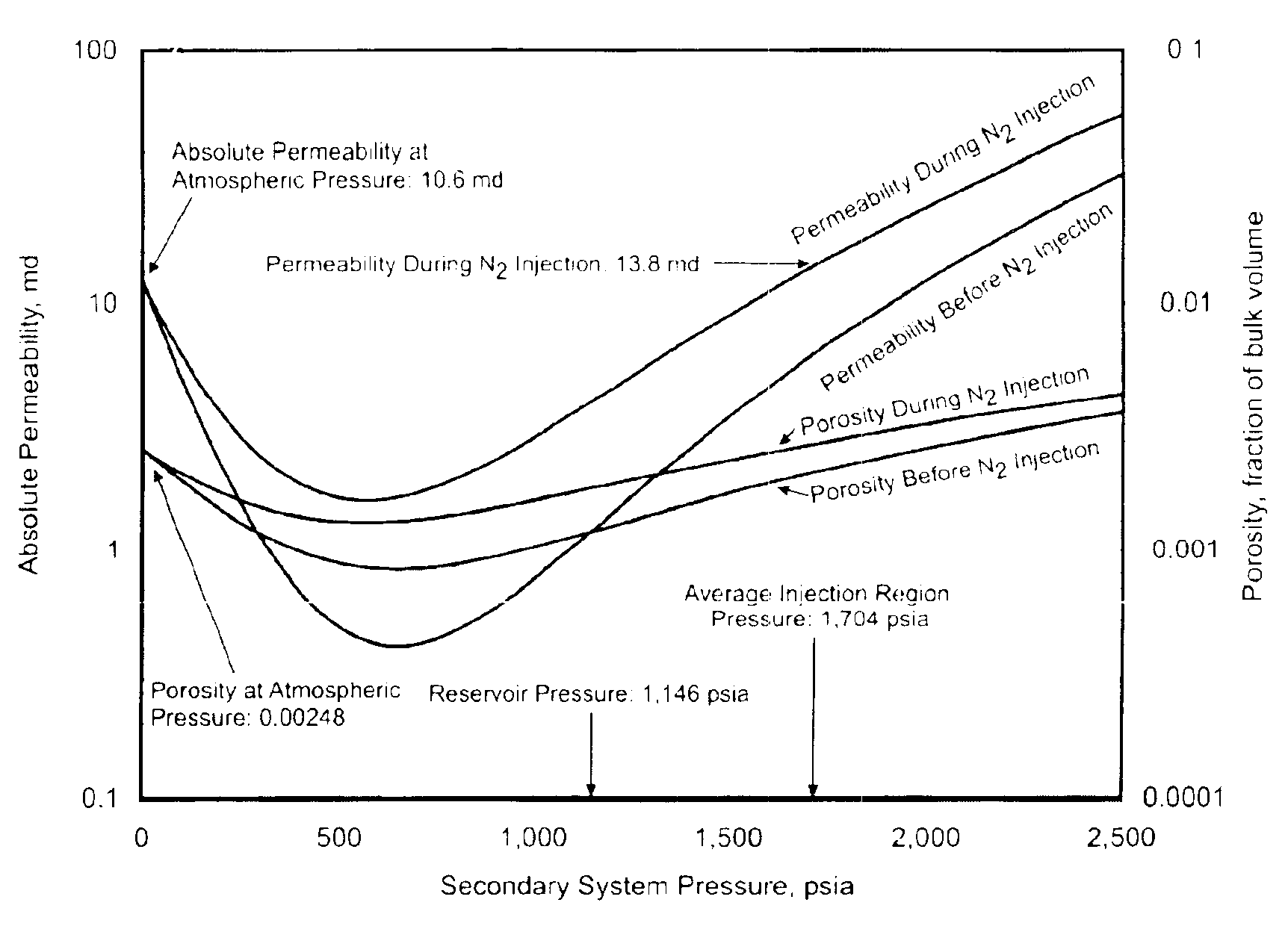
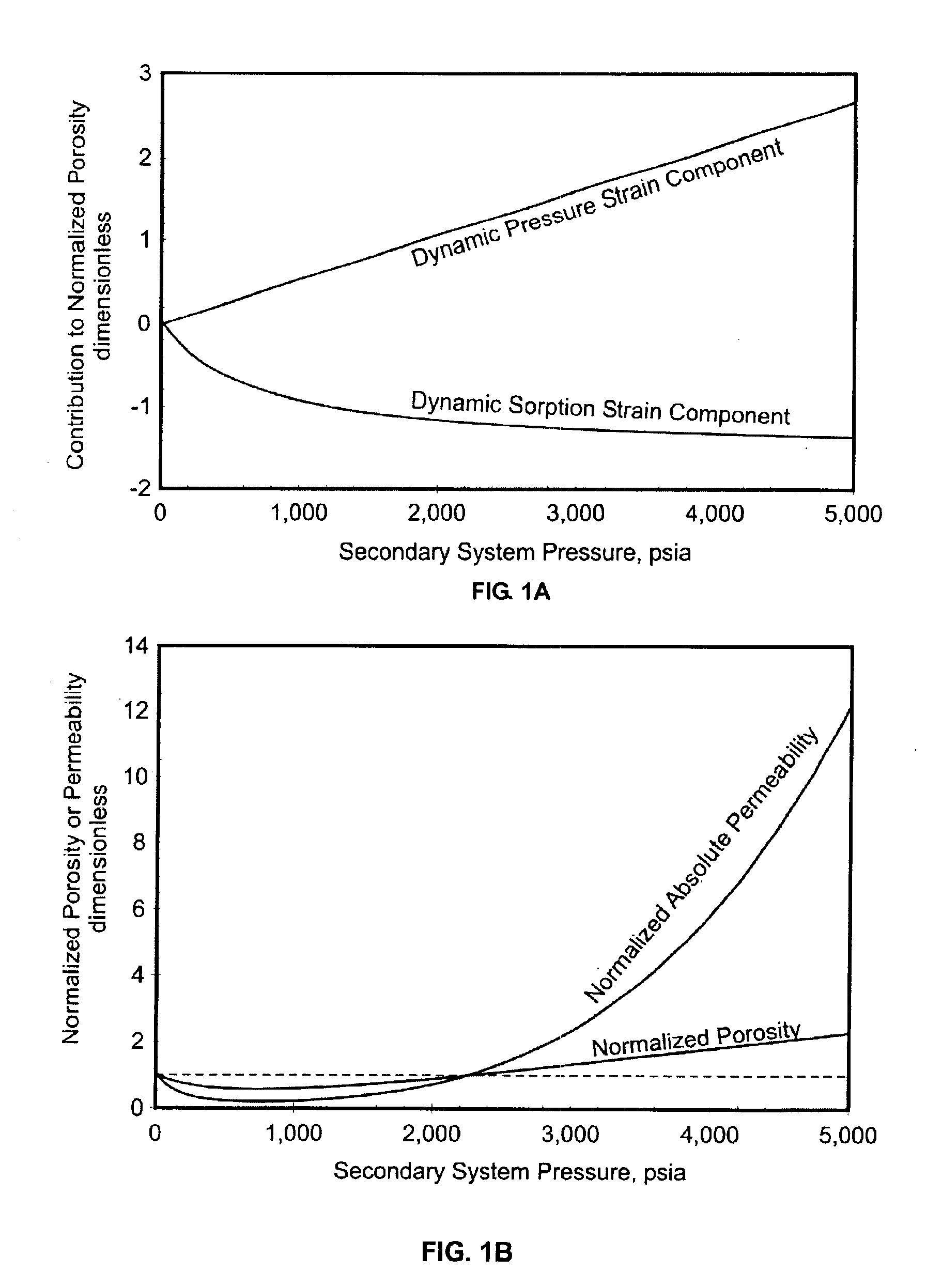
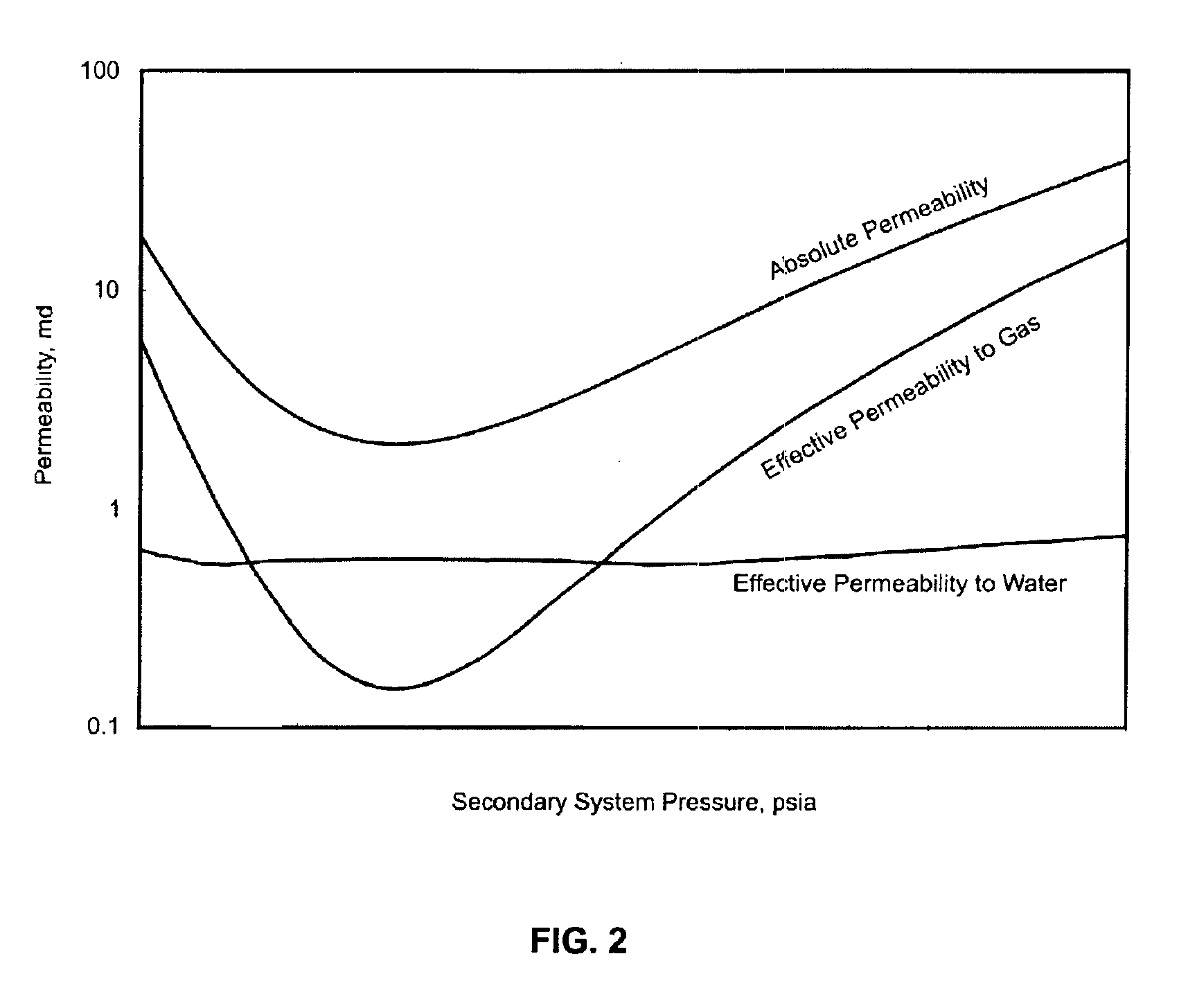
A method for predicting the secondary porosity system (SPS) porosity, and thereby permeability, of a coal bed involves determining an initial condition in the coal bed, including an initial SPS pressure and an initial sorbed gas composition, determining a pressure strain effect due to increasing the SPS pressure to a value greater than the initial SPS pressure, and determining a sorption strain effect due to changes in the sorbed gas composition resulting from decreasing the methane content and increasing the content of a stronger adsorbing fluid (SAG) relative to the initial sorbed gas composition. Preferably, the method uses data from test injections of water and / or a weaker adsorbing fluid (WAG) and a SAG. The data is used in the inventors' model to compute a SPS porosity and an absolute permeability at a reference SPS pressure and a reference sorbed gas composition. Preferably, the reference pressure is atmospheric pressure. The inventors' model accounts for both dynamic pressure strain and dynamic multicomponent sorption strain effects. As a result, a calibrated model can be produced for the coal bed for predicting the coal bed's SPS porosity, and thereby permeability, as a function of a pre-selected injection or production fluid's composition and / or SPS pressure conditions.
Owner:ALBERTA INNOVATES TECH FUTURES
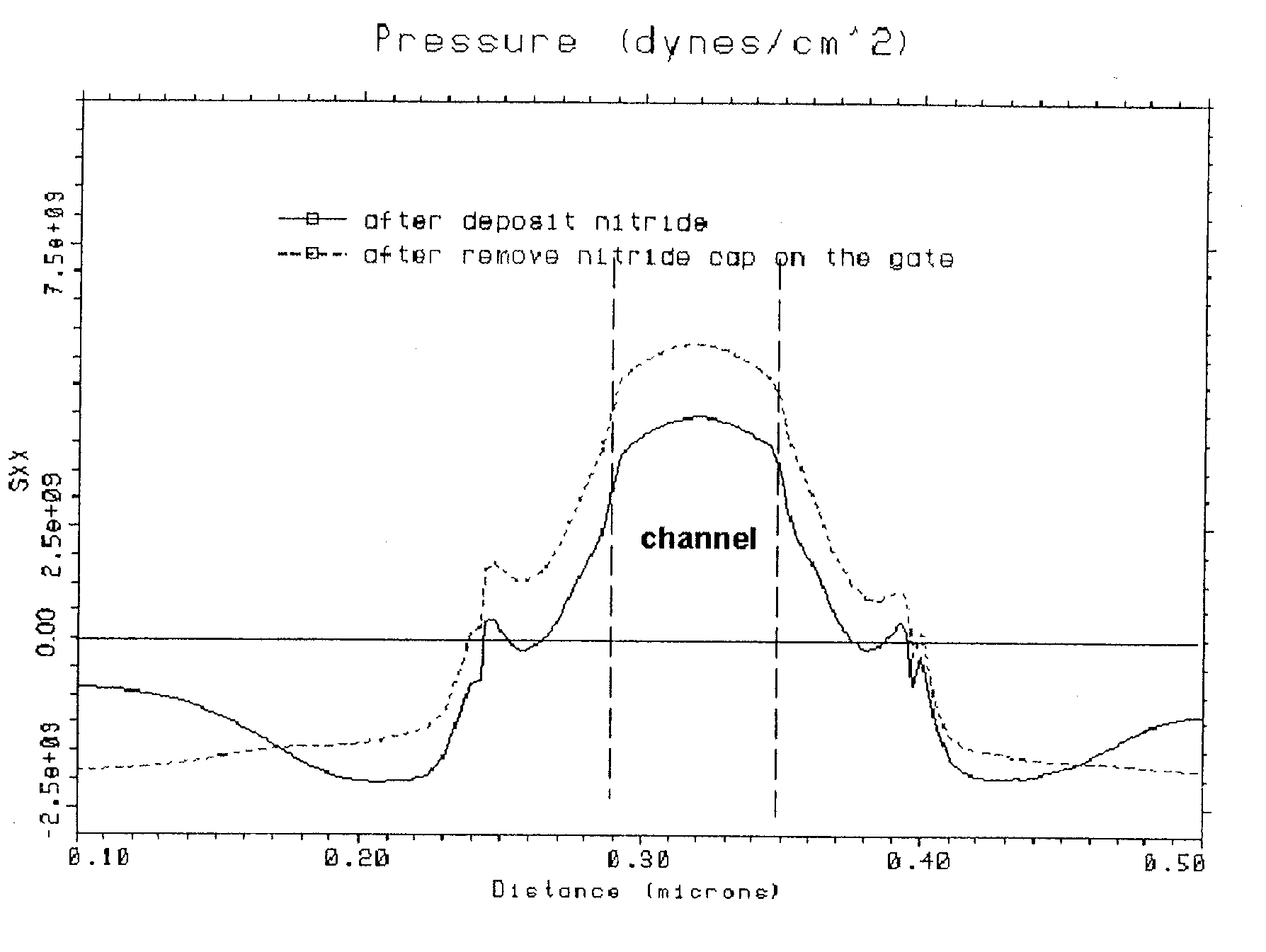
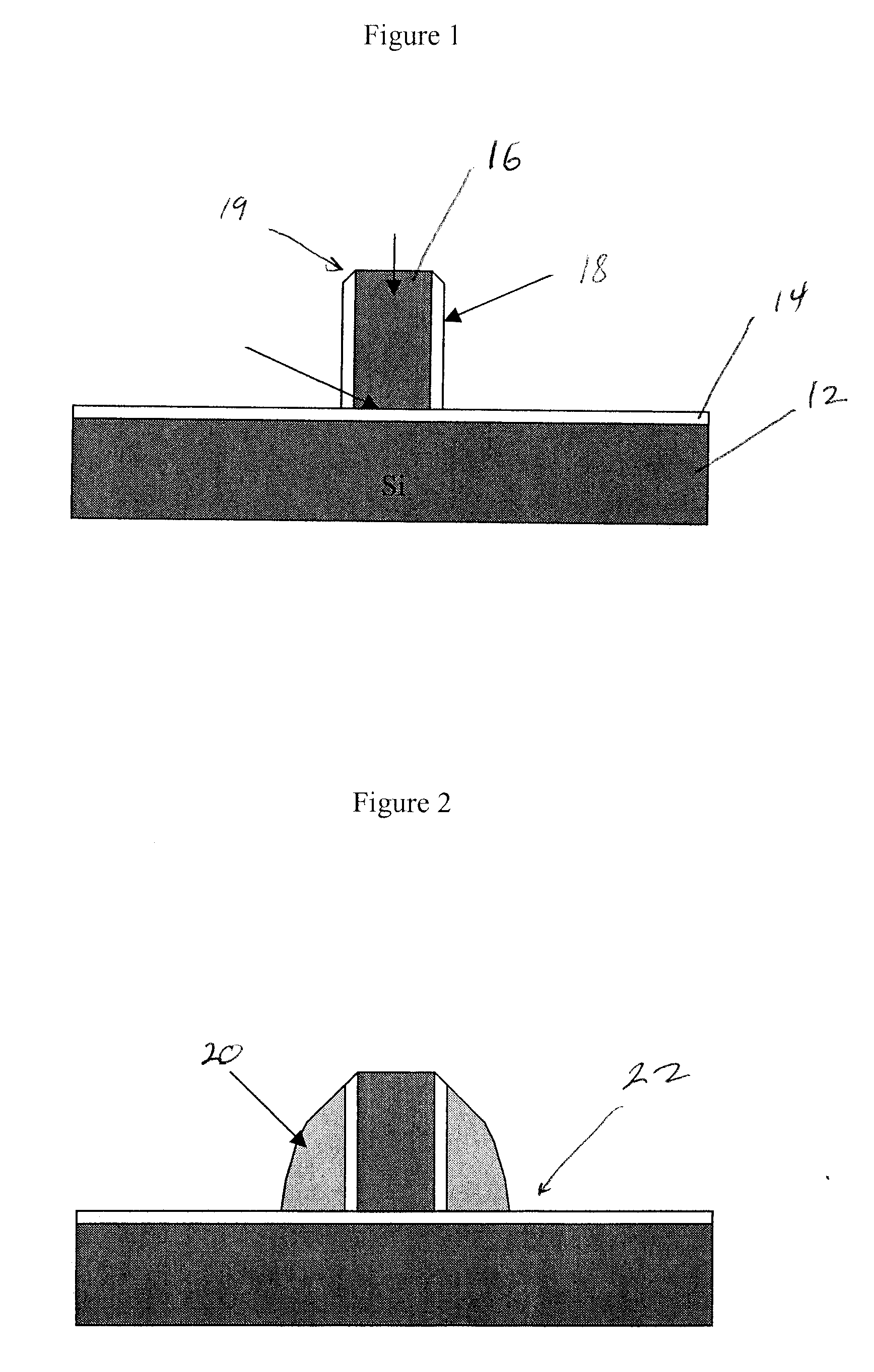
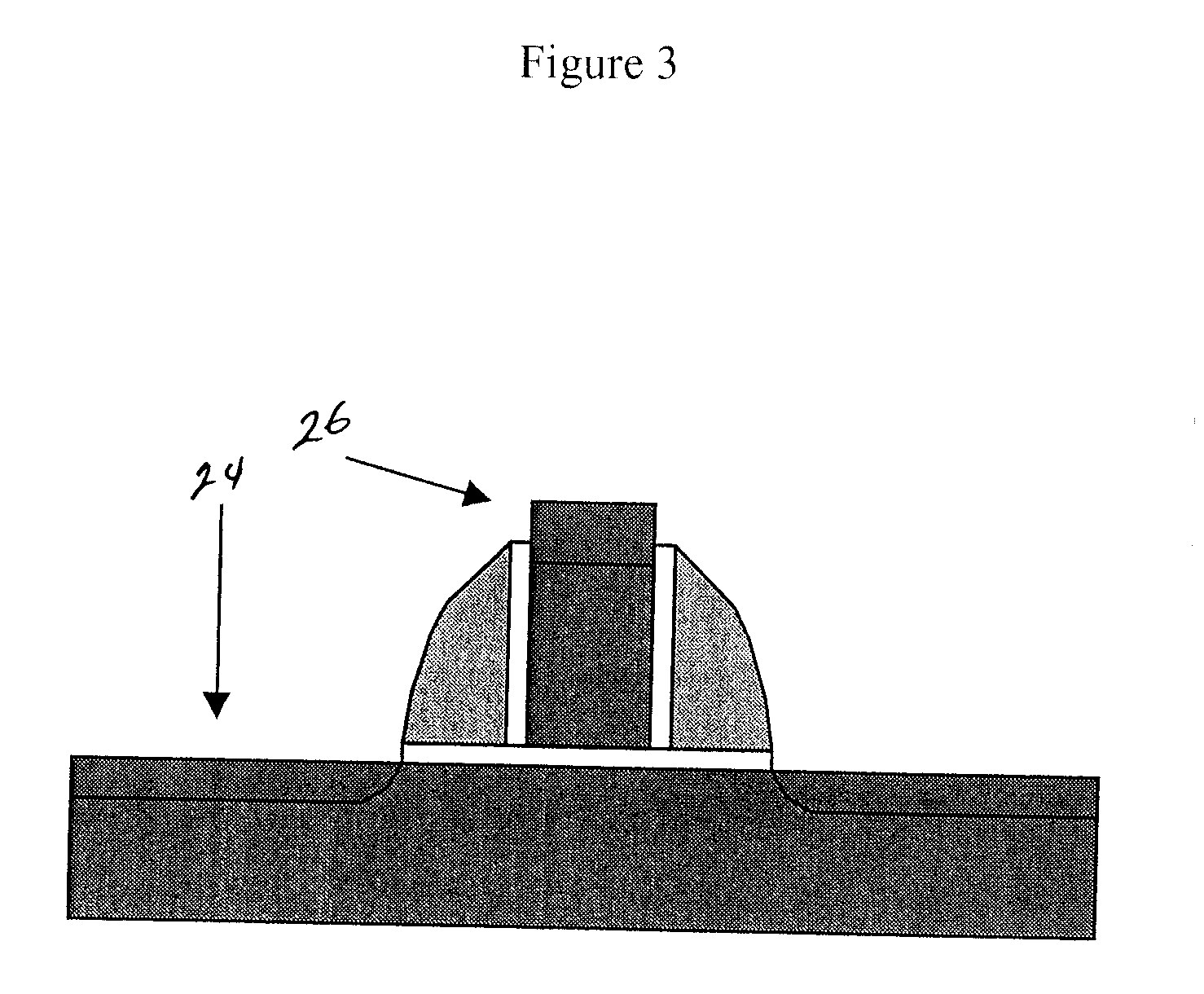
Method and apparatus to increase strain effect in a transistor channel
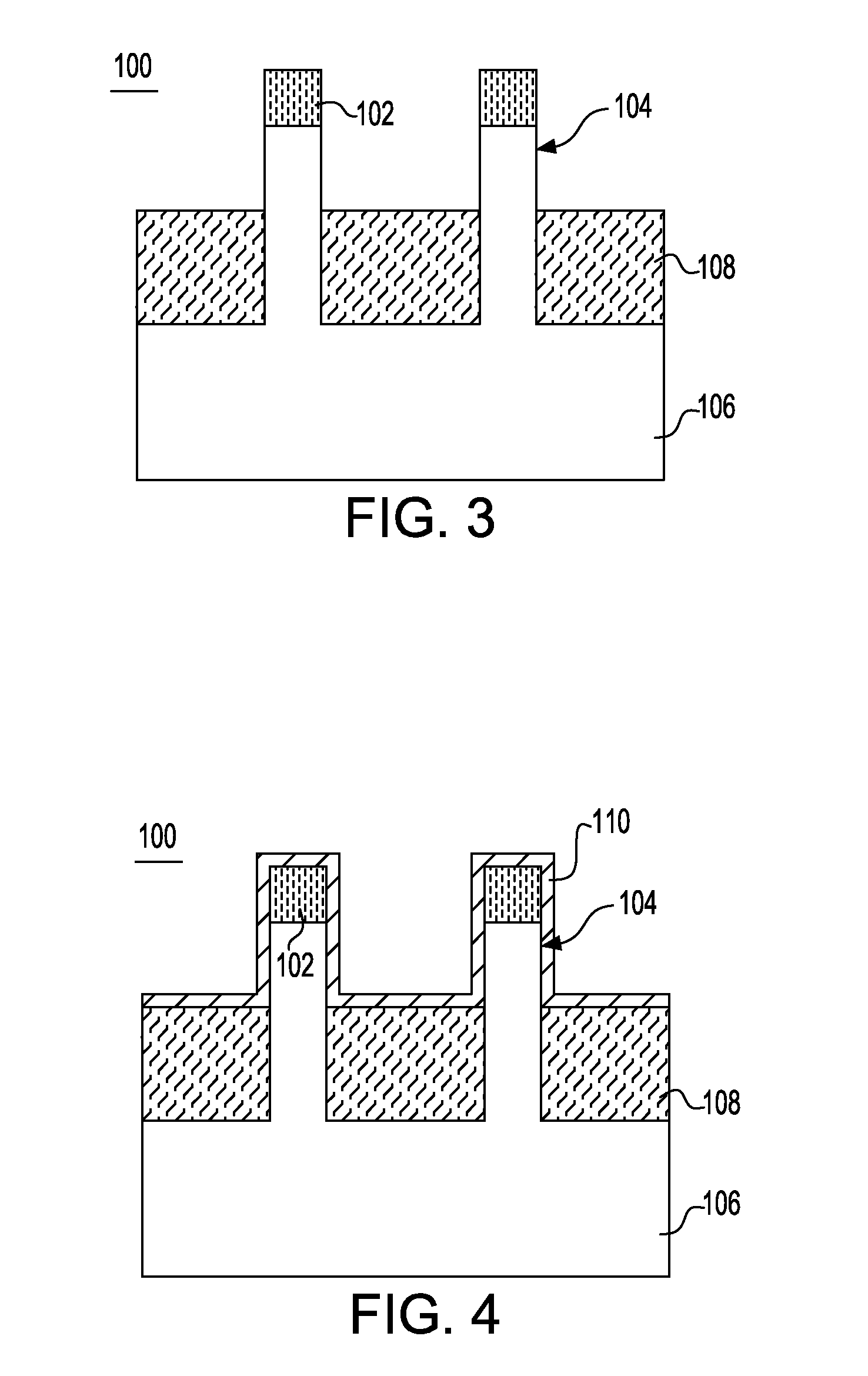
ActiveUS20050158955A1Increase pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackNitride
A semiconductor device having a transistor channel with an enhanced stress is provided. To achieve the enhanced stress transistor channel, a nitride film is preferentially formed on the device substrate with little to no nitride on a portion of the gate stack. The nitride film may be preferentially deposited only on the silicon substrate in a non-conformal layer, where little to no nitride is deposited on the upper portions of the gate stack. The nitride film may also be uniformly deposited on the silicon substrate and gate stack in a conformal layer, with the nitride film proximate the upper regions of the gate stack preferentially removed in a later step. In some embodiments, nitride near the top of the gate stack is removed by removing the upper portion of the gate stack. In any of the methods, stress in the transistor channel is enhanced by minimizing nitride deposited on the gate stack, while having nitride deposited on the substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and structure to enhance gate induced strain effect in multigate device
ActiveUS20150206953A1Increase currentImprove mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilityHigh stress
A FinFet formed by depositing a thin layer of polycrystalline silicon followed by depositing a stress containing material, including a high Ge percentage silicon germanium film and / or a high stress W film on top of a polycrystalline silicon film. Freeing space between fins allows stressor films to be deposited closer to the transistor channel, improving the proximity of the stress containing material to the transistor channel and enhancing the stress coupling efficiency by defining a ratio between stress level in the stressor film and stress transferred to the channel for a mobility enhancement. The stress level is enhanced by patterning by removing the n-type workfunction metal from the p-FinFET. After stripping off the soft or hard mask, the p-type workfunction metal is deposited in the n- and p-FinFET regions. The freed space specifically for p-FinFet between the fins achieves an even higher stressor coupling to further boost the carrier mobility.
Owner:IBM CORP
Metal hydrogen permeation behavior research device and method
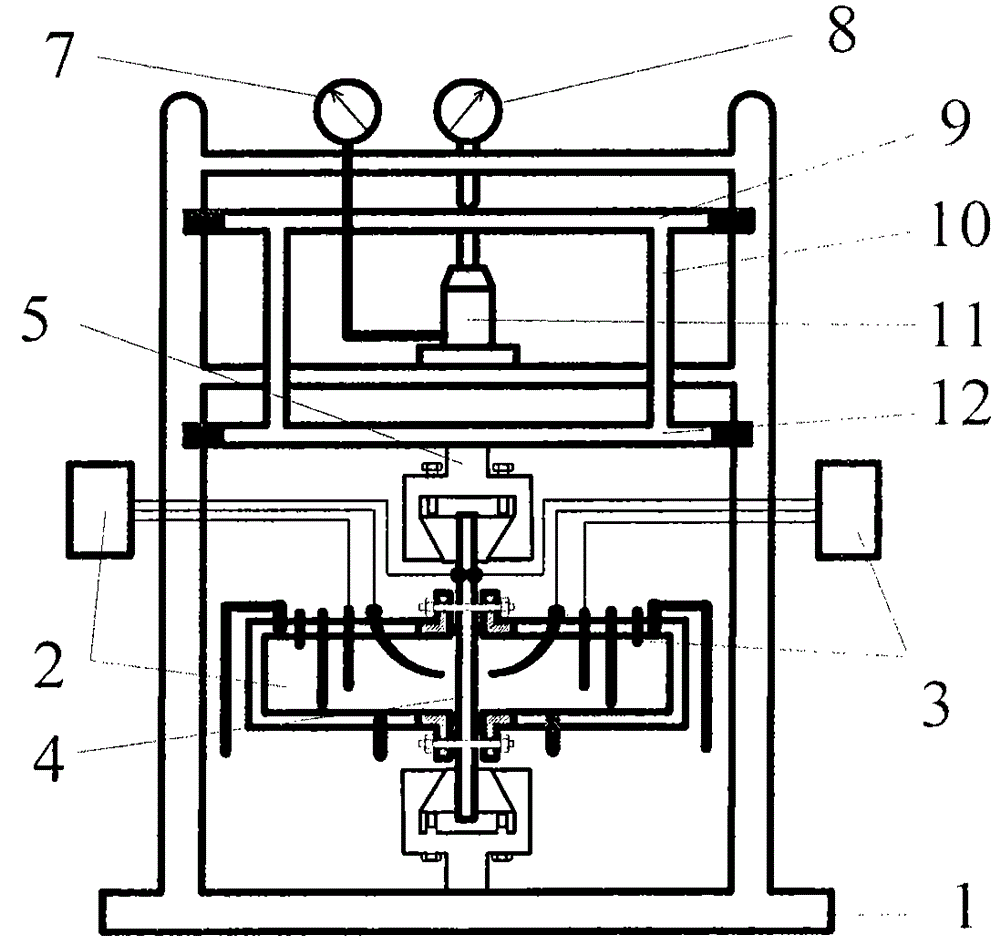
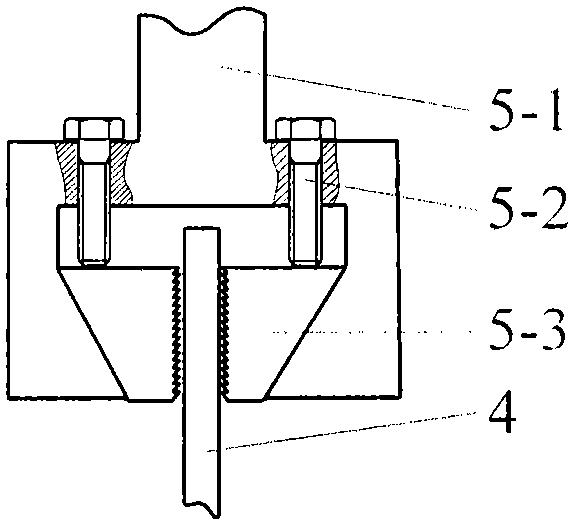
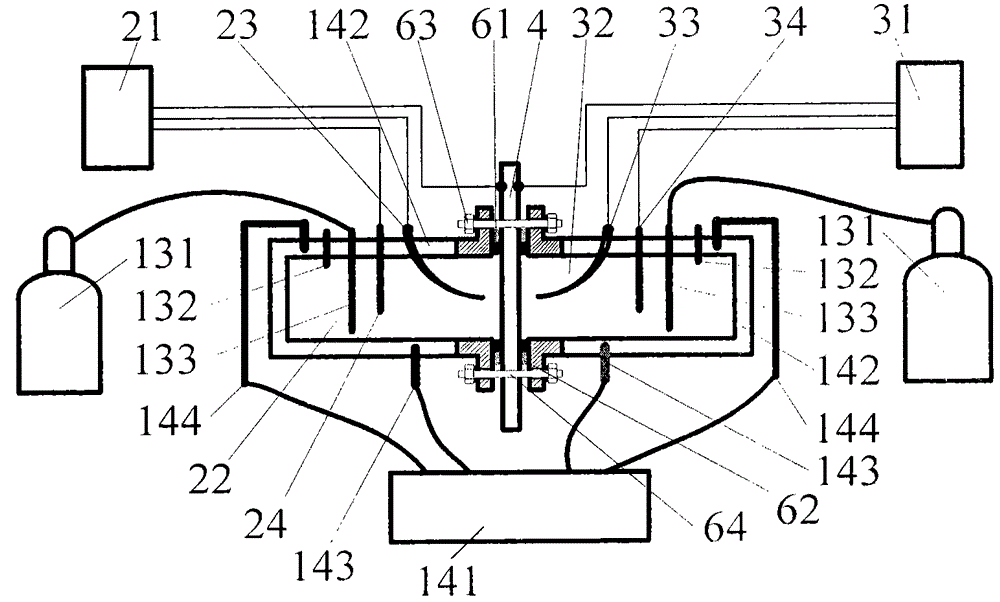
The invention discloses a metal hydrogen permeation behavior research device and method, the device includes a mechanical loading system, an electrochemical measurement system, a temperature control system and a gas drive system. The loading system provides tensile stress to a specimen by a jack via a middle transfer component. A hydrogen permeation electrolysis pool, a negative pole pool and a positive pole pool are made of nickel base alloy so as to improve the bearing capacity and corrosion resistance, a sealing component is adopted to realize strict sealing between the electrolytic pool and the specimen. An electrolyte solution and a high pressure gas are introduced into the negative pole pool, and a high-voltage reference electrode and an auxiliary electrode are arranged to simulate the mechanical chemical service environment of a metal structure. The metal hydrogen permeation behavior research device can be used for study on hydrogen permeation behavior of a metal structure in high hydrostatic pressure effect deep sea environment and downhole drilling device high pressure environment under the action of tensilc stress-strain effect, and the defect that in the prior art the hydrogen permeation cell can't measure the impact of stress state on metal hydrogen permeation behavior in high pressure environment can be compensated, and by introduction of the temperature control system and the gas drive system, the medium stability can be maintained, and the testing precision is increased.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
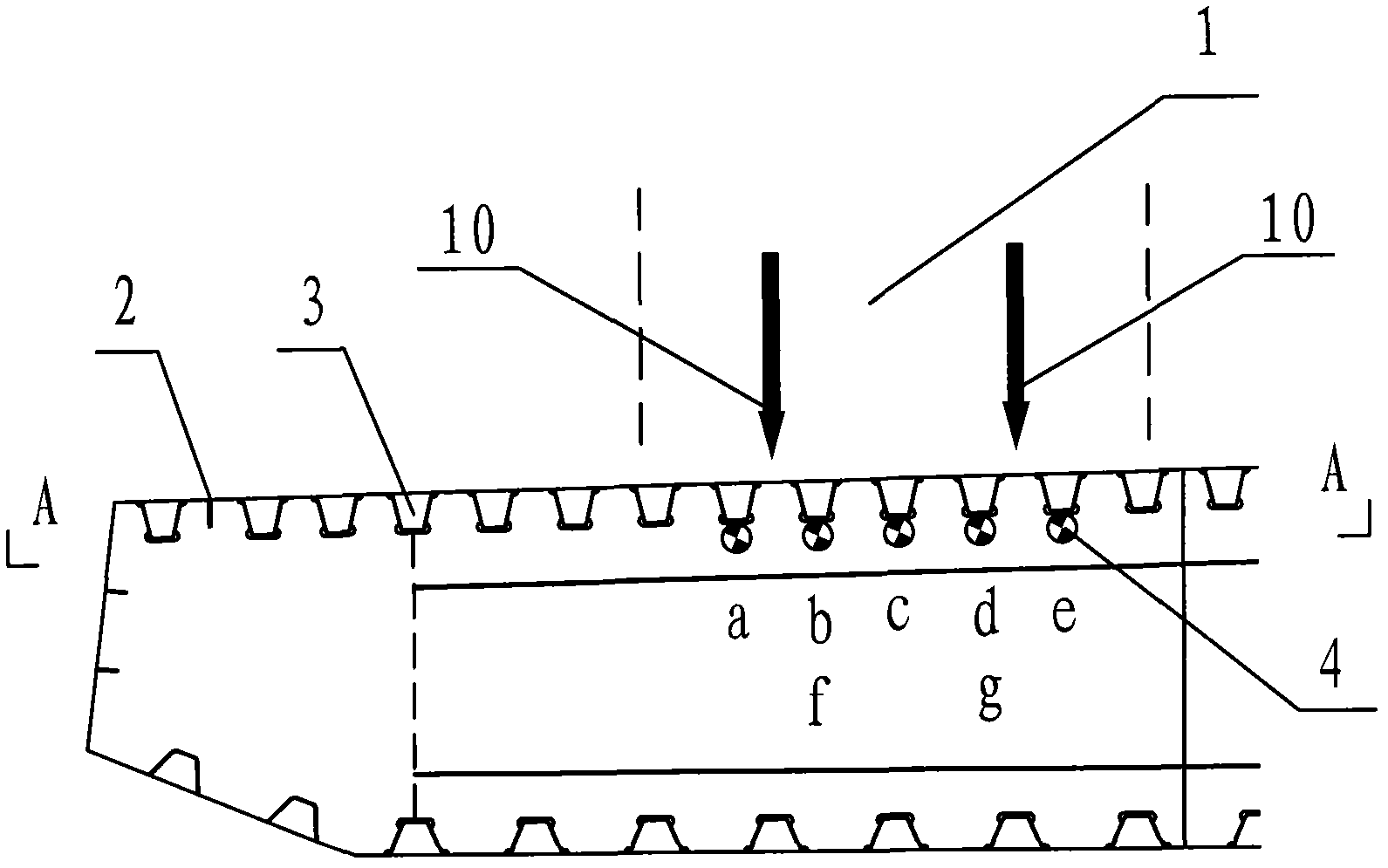
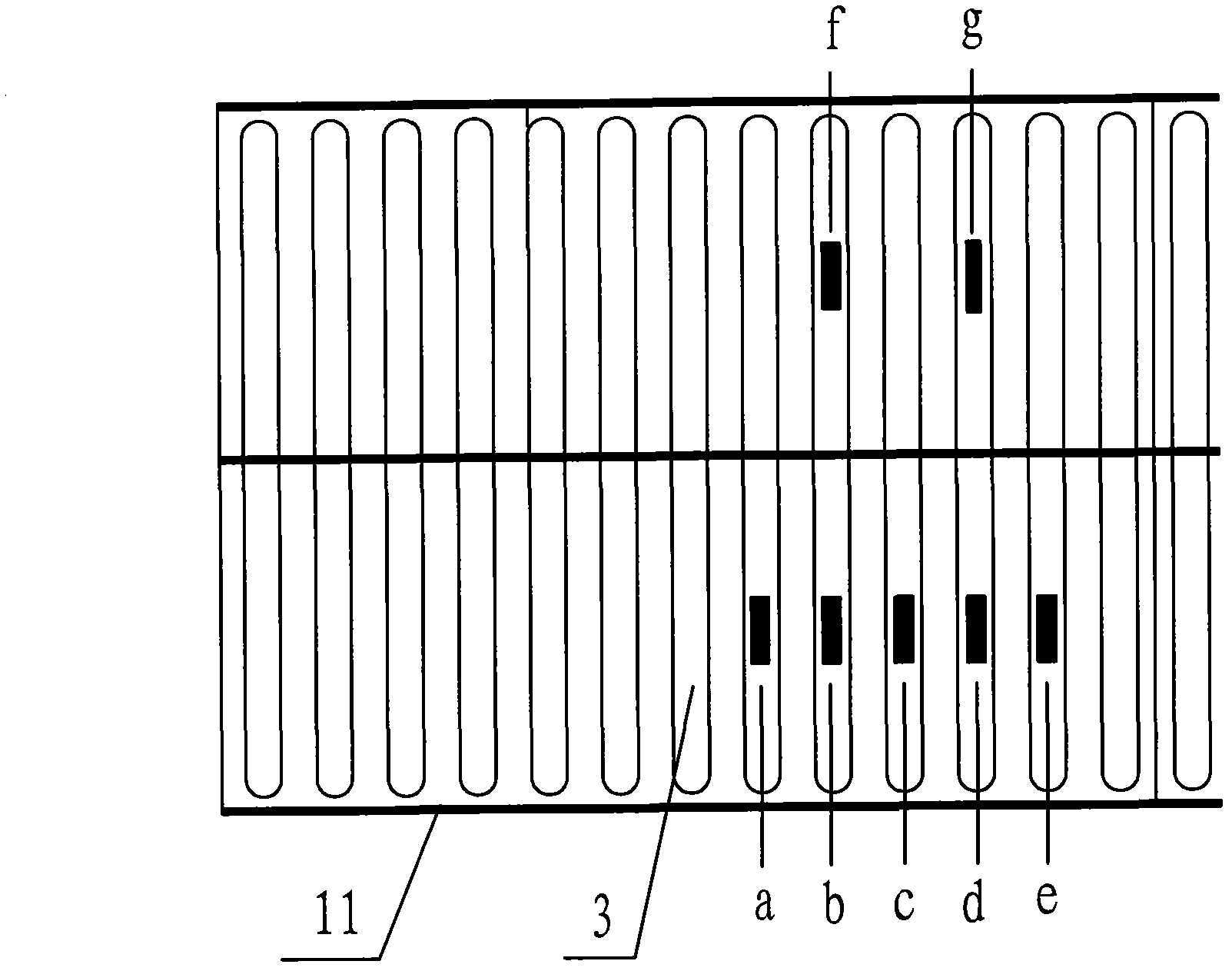
Vehicle load dynamic weighing method for orthotropic bridge deck steel box girder bridge
ActiveCN102628708ADoes not affect drivingHigh sampling frequencyUsing optical meansSpecial purpose weighing apparatusCross correlation analysisBridge deck
The invention discloses a vehicle load dynamic weighing method for an orthotropic bridge deck steel box girder bridge, which relates to the field of bridge health monitoring. The method comprises the following steps of: mounting a fiber grating strain sensor at the bottom of a U-shaped rib of an internal top plate of an orthotropic bridge deck steel box girder; measuring longitudinal bridge strain of the U-shaped rib when a vehicle passes through the position of the sensor; converting the strain into an optical signal by the sensor; demodulating the optical signal by using a fiber grating demodulator; carrying out cross-correlation analysis on actually measured strains of measuring points on the same U-shaped rib in the steel box girder at different sections so as to determine vehicle speed of the vehicle; analyzing actually measured strain area vectors of measuring points on different U-shaped ribs in the steel box girder at the same section; and carrying out angle Cosine distance analysis by using a strain effect linear area vector of the U-shaped rib of the steel box girder so as to figure out transverse acting position and weight of each vehicle on a running lane. The vehicle load dynamic weighing method for the orthotropic bridge deck steel box girder bridge, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of convenience for mounting, low manufacturing price, no need of interrupting transportation, no excavation or damage of the road surface and capability of achieving nondestructive and automatic dynamic weighing of the bridge vehicle load.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY BRIDGE SCI RES INST LTD +1
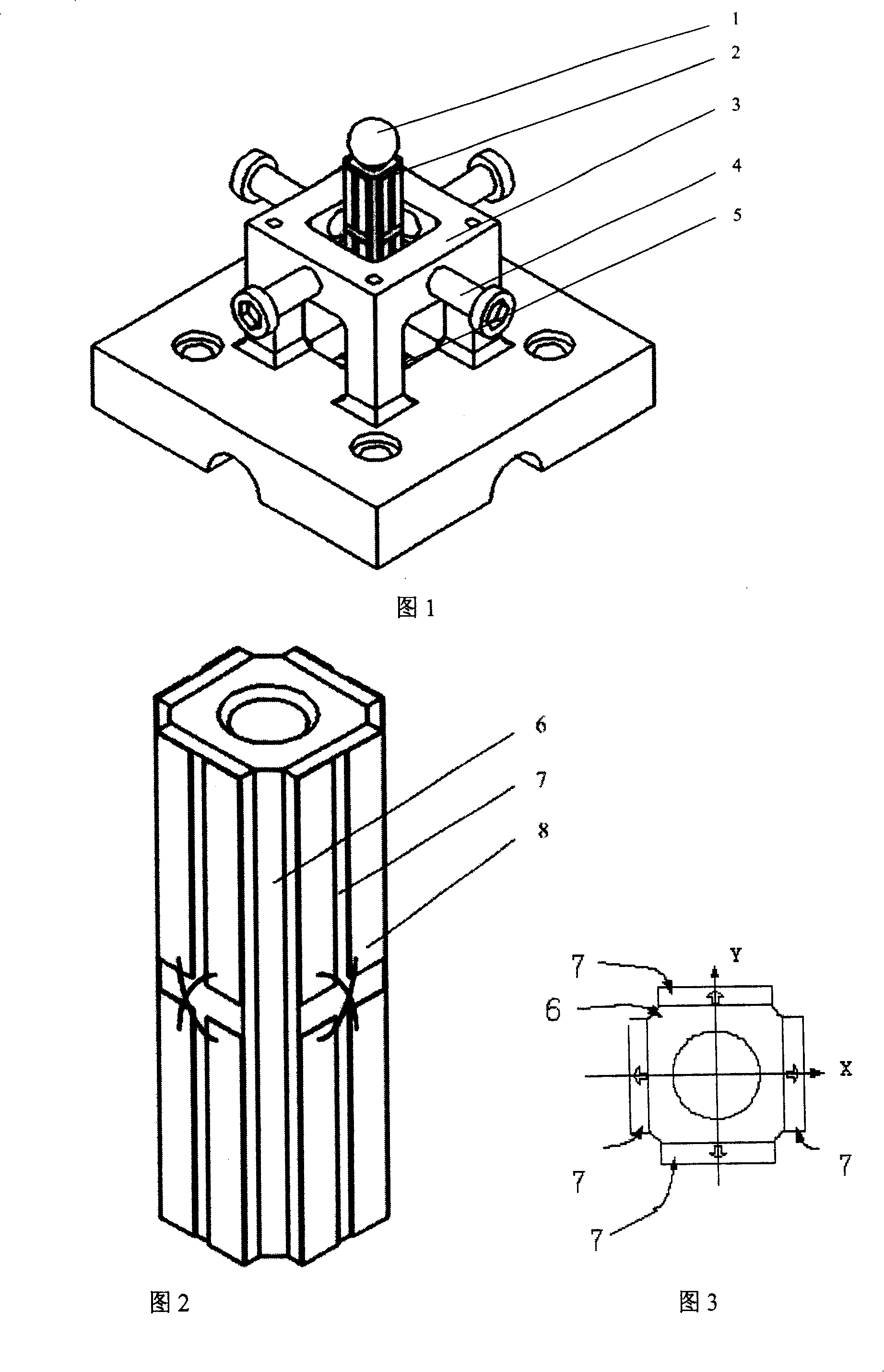
Novel fiber grating two-dimensional tilting angle sensor
InactiveCN101603827AEliminate the effects ofSimple structureIncline measurementConverting sensor output opticallyGratingCoupling
The invention relates to a novel fiber sensor which is used for measuring the size and the direction of a tilting angle and is manufactured by utilizing strain effect of a fiber grating and wavelength measuring technology based on the prior fiber Bragg grating. The system consists of a pedestal (1), a supporting column (2), a top disc (3), fiber gratings (4), a weight (5) and fibers (6). When the sensor tilts for a certain angle, the sensor causes three fiber gratings to have different stresses and utilizes the drifting amount of central reflective wavelength of the fiber grating measured by the wavelength measuring technology to reversely calculate the size and the direction of the tilting angle. A common fiber grating is sensitive to a temperature; and as the novel fiber sensor uses the three fiber gratings positioned in the same environment and the consistent drifting amount of the central wavelength caused by the temperature can be compensated in the angle analyzing and calculating process, the novel fiber sensor is insensitive to the temperature when measuring the tilting angle. The novel fiber sensor has a simple principle, has the characteristics of light mass, anticorrosion, electromagnetic interference resistance, safe and reliable use and the like, also has the unique advantages of small size, high sensitivity, easy coupling with fiber, small consumption, integration of sensing and transmission and easy wavelength division multiplex and the like and is convenient to realize; therefore, the novel fiber sensor can be used as a tilting angle sensor of various fields.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
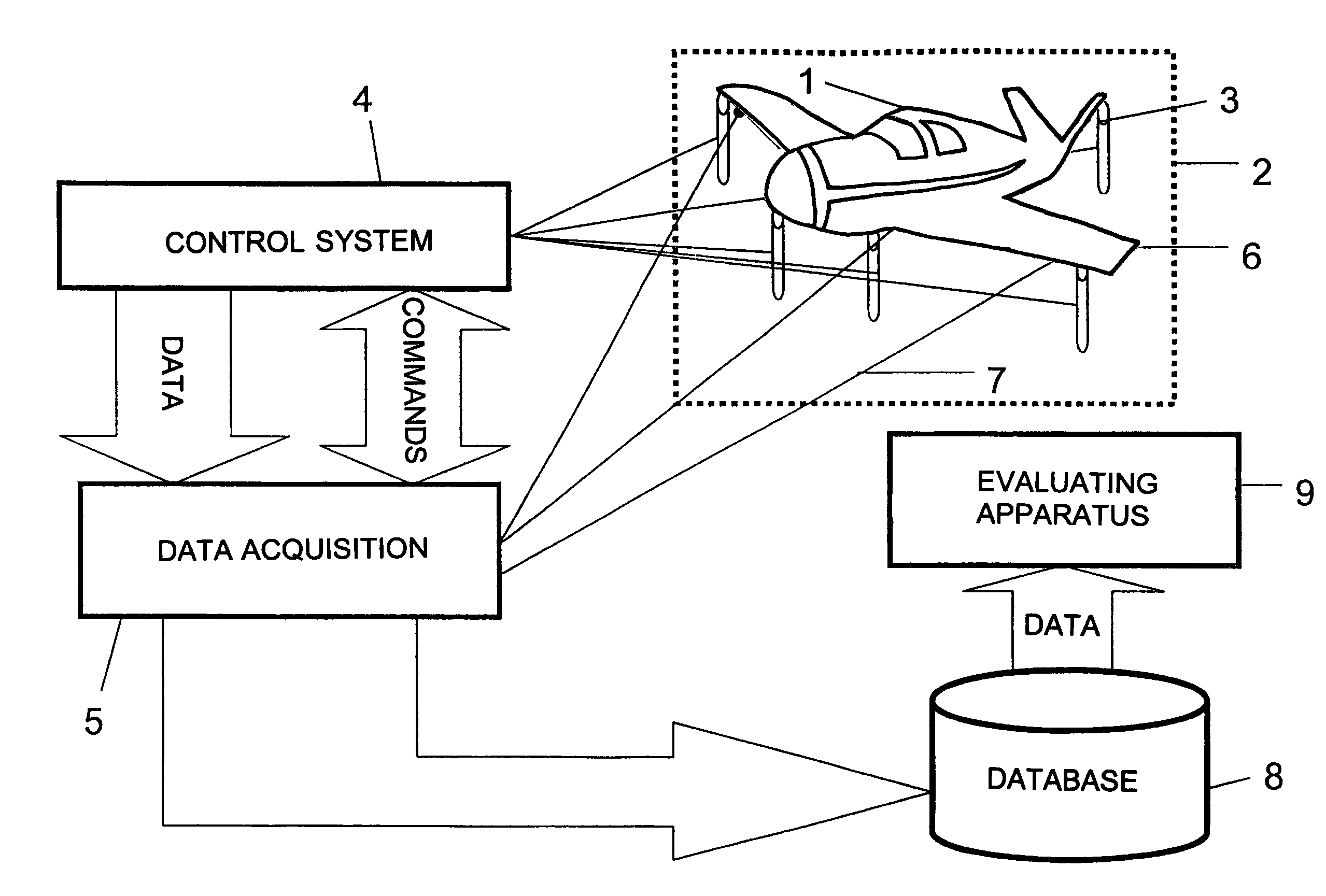
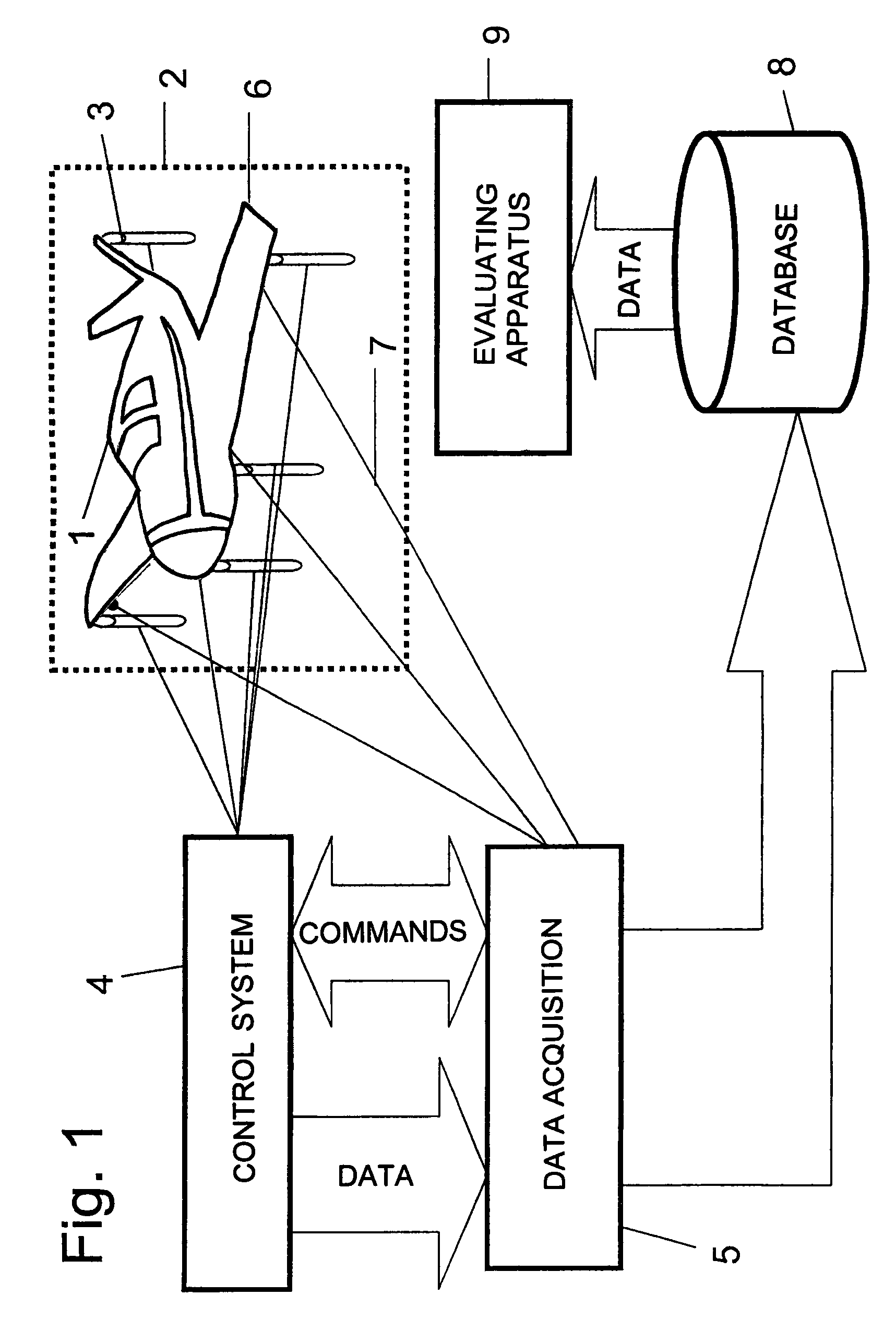
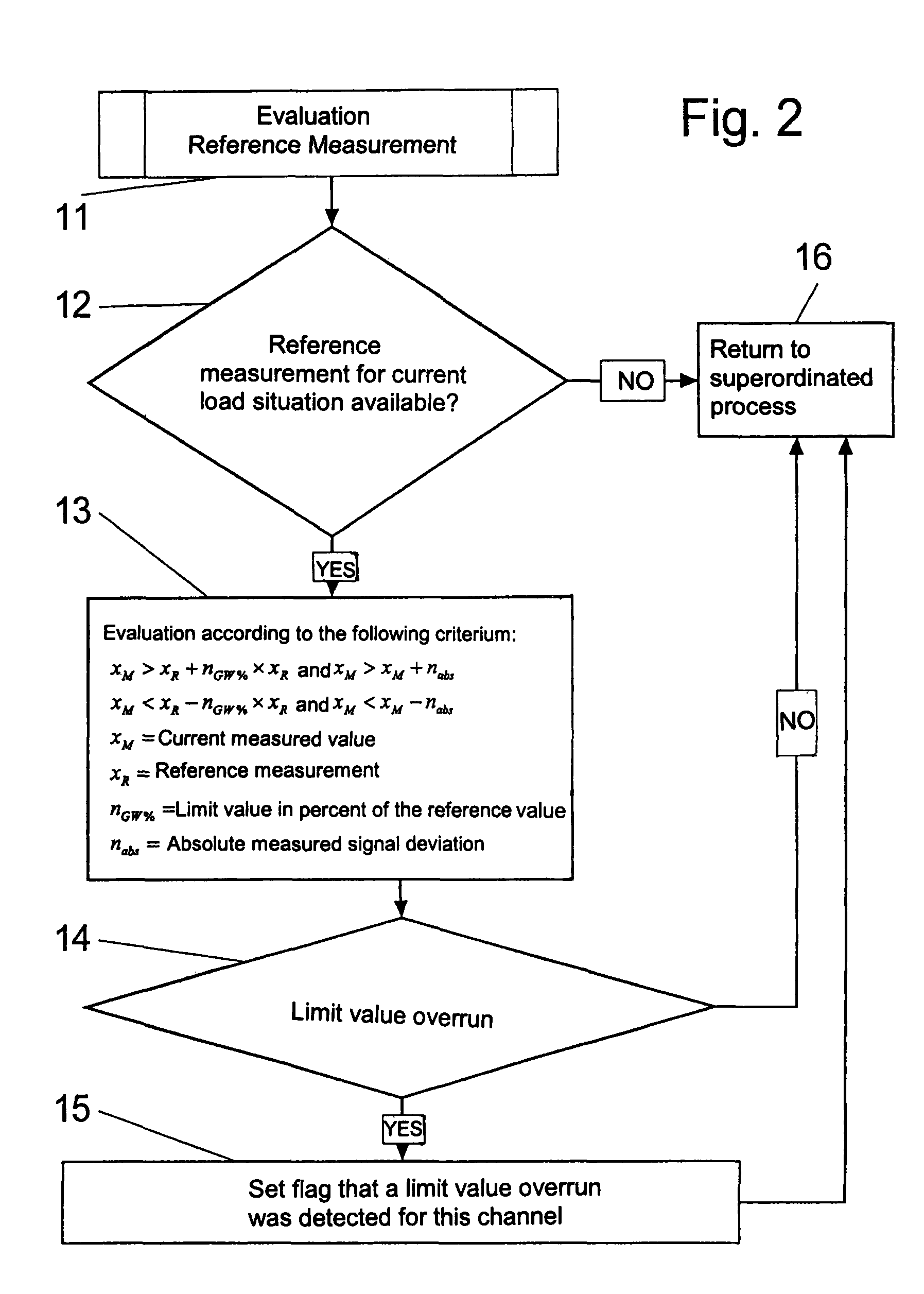
Method for evaluating measured values for identifying a material fatigue
InactiveUS7930112B2The process is fast and accurateAdvantageouslyPlug gaugesForce measurementEngineeringLimit value
In a method of evaluating measured values for recognizing defect conditions due to material fatigue on aircraft parts, strain sensors (6) are applied on the critical locations of an aircraft (1) and measured values of outputs of the strain sensors are detected at different loading conditions, amplified and stored through several measuring circuits. An evaluating apparatus (9) derives, signals or indicates a material fatigue by comparison of current measured values with previous measured values. The critical aircraft parts (1) are impinged on with prescribed loading conditions by loading elements (3). The strain effect caused thereby is detected by measuring circuits. The evaluating apparatus (9) forms, for at least each loading condition and each measuring circuit, an allocated reference value and a permissible limit value range. If current measured values exceed the limit value range, this represents a material fatigue manifestation.
Owner:HOTTINGER BRUEL & KJAER GMBH
Method and apparatus to increase strain effect in a transistor channel
ActiveUS7118999B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackNitride
A semiconductor device having a transistor channel with an enhanced stress is provided. To achieve the enhanced stress transistor channel, a nitride film is preferentially formed on the device substrate with little to no nitride on a portion of the gate stack. The nitride film may be preferentially deposited only on the silicon substrate in a non-conformal layer, where little to no nitride is deposited on the upper portions of the gate stack. The nitride film may also be uniformly deposited on the silicon substrate and gate stack in a conformal layer, with the nitride film proximate the upper regions of the gate stack preferentially removed in a later step. In some embodiments, nitride near the top of the gate stack is removed by removing the upper portion of the gate stack. In any of the methods, stress in the transistor channel is enhanced by minimizing nitride deposited on the gate stack, while having nitride deposited on the substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Dual Fiber Grating and Methods of Making and Using Same
A multiple-layer fiber-optic sensor is described with dual Bragg gratings in layers of different materials, so that the known temperature and strain response properties of each material may be utilized to simultaneously correct the sensor output for temperature and strain effects.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Flexible capacitive-type pressure sensor and preparation method therefor
PendingCN108731851AImprove dynamic rangeImprove linearityForce measurementFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationElectricityCapacitive pressure sensor
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
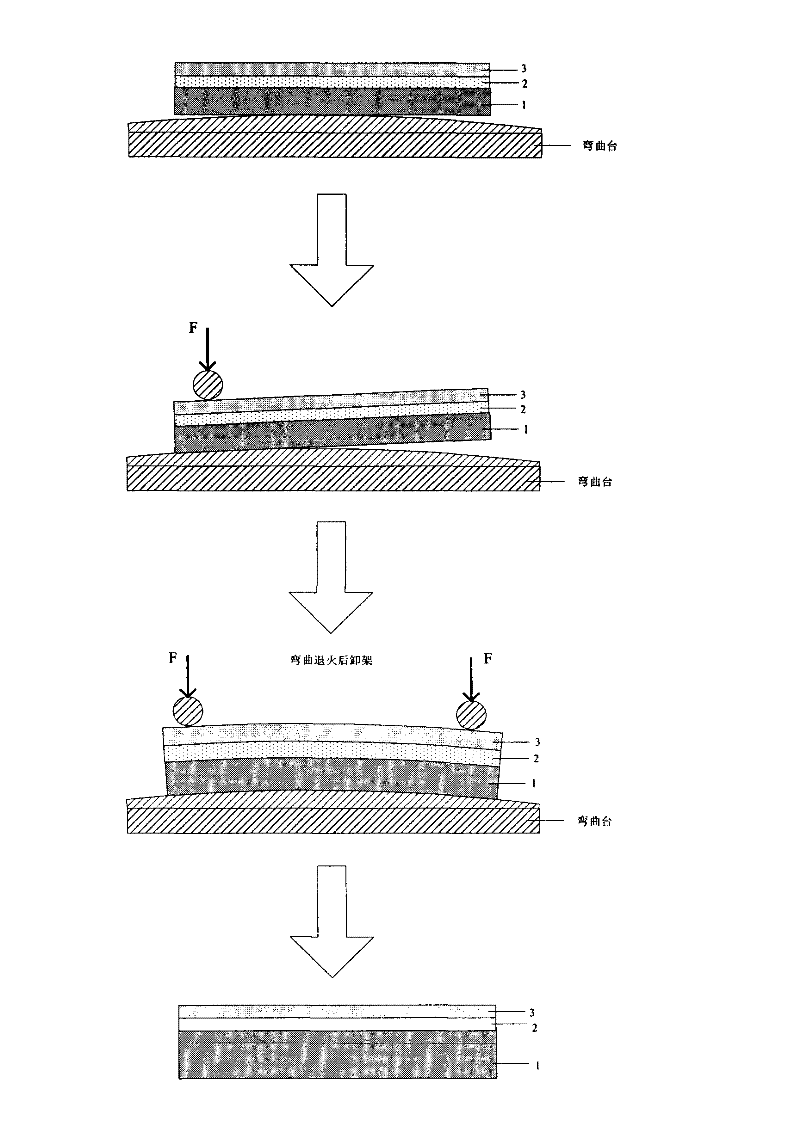
Manufacturing method of single-shaft strain GeOI wafer based on mechanical bending table
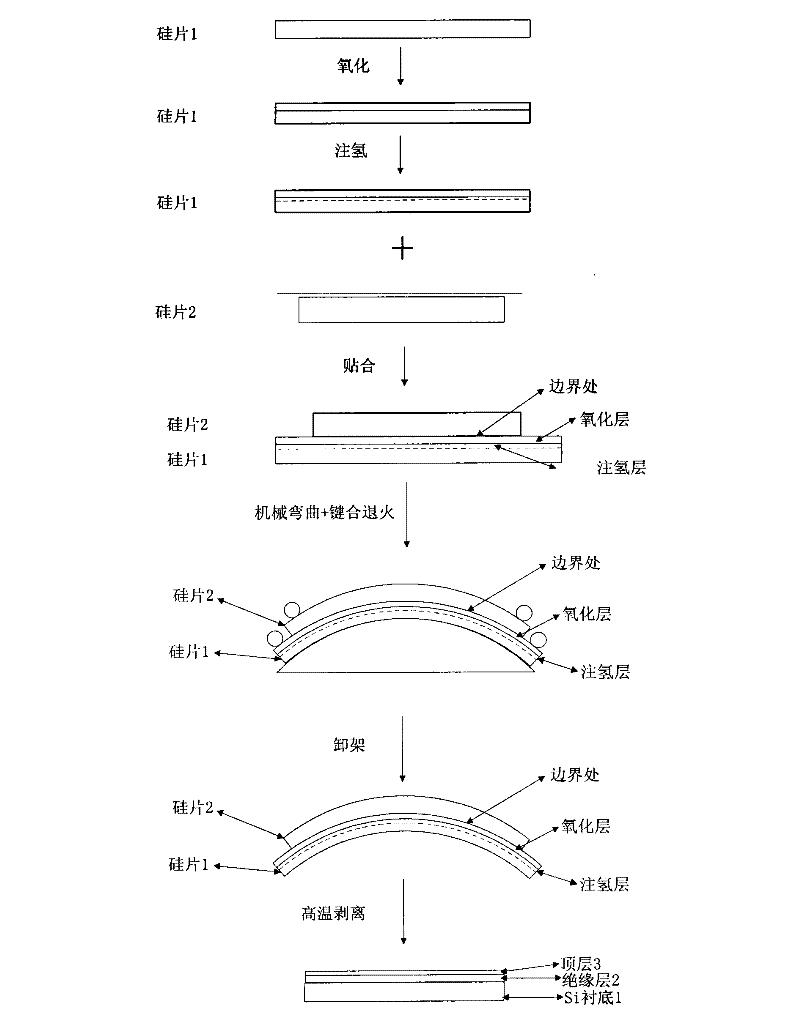
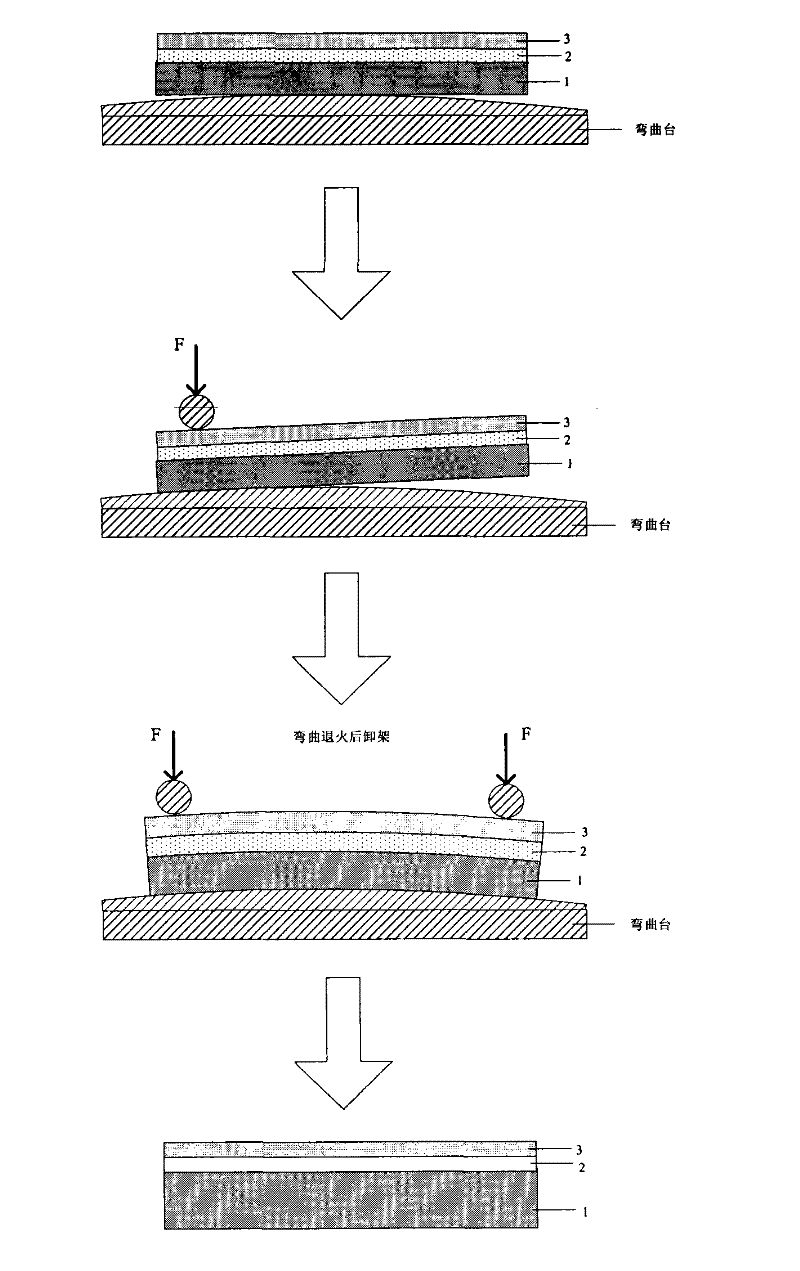
InactiveCN102403259ARaw materials are easy to getReduce process complexitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessRoom temperature
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a single-shaft strain GeOI wafer based on a mechanical bending table, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, placing a Ge layer surface on the top layer of the GeOI wafer on the arc-shaped bending table downwards or upwards; secondly, respectively and horizontally placing two cylindrical stainless steel pressing rods at the two ends of the GeOI wafer which is 1cm away from the edge of the GeOI wafer; thirdly, slowly rotating nuts of the connected pressing rods, so that the GeOI wafer gradually bends along an arc-shaped tabletop till to be completely fitted with the arc-shaped tabletop; fourthly, placing the arc-shaped bending table carried with the GeOI wafer into an annealing furnace for annealing; fifthly, slowly cooling to the room temperature after the completion of the annealing and taking out the arc-shaped bending table carried with the GeOI wafer; and sixthly, rotating the nuts of the connected pressing rods and slowly lifting the pressing rods till the bent GeOI wafer restores the original shape. The invention has the following advantages that firstly, the raw materials are easy to obtain; secondly, the manufacturing cost is low; thirdly, the manufacturing process is simple; fourthly, the process temperature range is wide; fifthly, the yield rate is high; sixthly, the surface roughness is small; seventhly, the strain effect is good; and eighthly, the thermal property is good.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Differential velocity cyclic extrusion forming method for high performance rare earth magnesium alloy billet
InactiveCN109909411AAchieve optimizationImprove mechanical propertiesExtrusion diesForging/hammering/pressing machinesRare earthShearing deformation
The invention discloses a differential velocity cyclic extrusion forming method for a high performance rare earth magnesium alloy billet, and relates to a billet making die for differential velocity cyclic extrusion of a high performance rare earth magnesium alloy. The billet making die comprises an upper die assembly, a "T"-shaped punch, a split concave die and a lower die assembly. The split concave die comprises an upper concave die and a lower concave die. The upper concave die is provided with an upper rectangular die cavity and an upper half polygons expansion die cavity. The lower concave die is provided with a lower cuboid die cavity and a lower half polygons expansion die cavity, the upper concave die and the lower concave die combine to form a polygons expansion die cavity, and differential velocity angles are arranged on both sides of the lower half polygons expansion die cavity, and the height of the differential velocity angle on both sides is different. A billet is extruded through multiple passes after upsetting, a metal flow state is changed by changing the structure of a concave die cavity, the shear deformation is introduced to realize the strain growth, the number of deformation is reduced, the strain effect is improved, the production efficiency is improved, the grain structure is refined, the second phase structure is optimized, and finally the magnesium alloy billet with remarkable mechanical properties is obtained.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Billet making die for differential velocity cyclic extrusion of high performance rare earth magnesium alloy
InactiveCN109909412AFully deformedIncreased cumulative strainExtrusion diesForging/hammering/pressing machinesRare earthShearing deformation
The invention discloses a billet making die for differential velocity cyclic extrusion of a high performance rare earth magnesium alloy. The billet making die for the differential velocity cyclic extrusion of the high performance rare earth magnesium alloy comprises an upper die assembly, a "T"-shaped punch, a split concave die and a lower die assembly. The split concave die comprises an upper concave die and a lower concave die. The upper concave die is provided with an upper rectangular die cavity and an upper half polygons expansion die cavity, the lower concave die is provided with a lowerrectangular die cavity and a lower half polygons expansion die cavity, and the upper concave die and the lower concave die combine to form a polygons expansion die cavity. Differential velocity angles are arranged on both sides of the lower half polygons expansion die cavity, and the height of the differential velocity angles on both sides is different. The lower die assembly comprises a first lower template of a solid body, a gasket block and a second lower template with a through hole. The first lower template is used for fixing at the bottom of the lower concave die during upsetting, and the gasket block blocks the lower rectangular die cavity. By changing the die cavity structures of the concave dies, the metal flow state is changed, the shear deformation is introduced, the strain growth is realized, the deformation times are reduced, the strain effect is improved, the production efficiency is improved, the grain structure is refined, and the second phase structure is optimized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
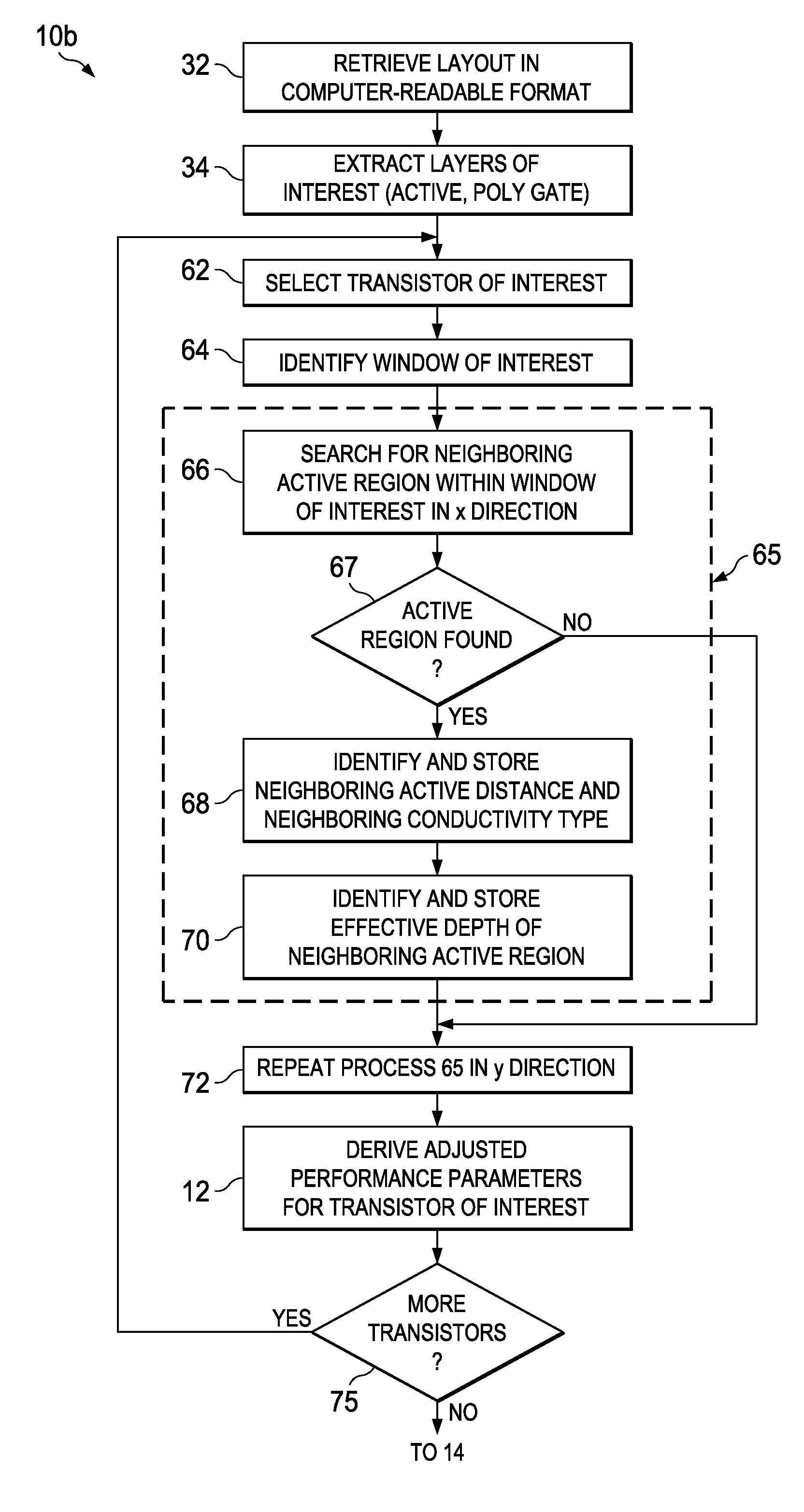
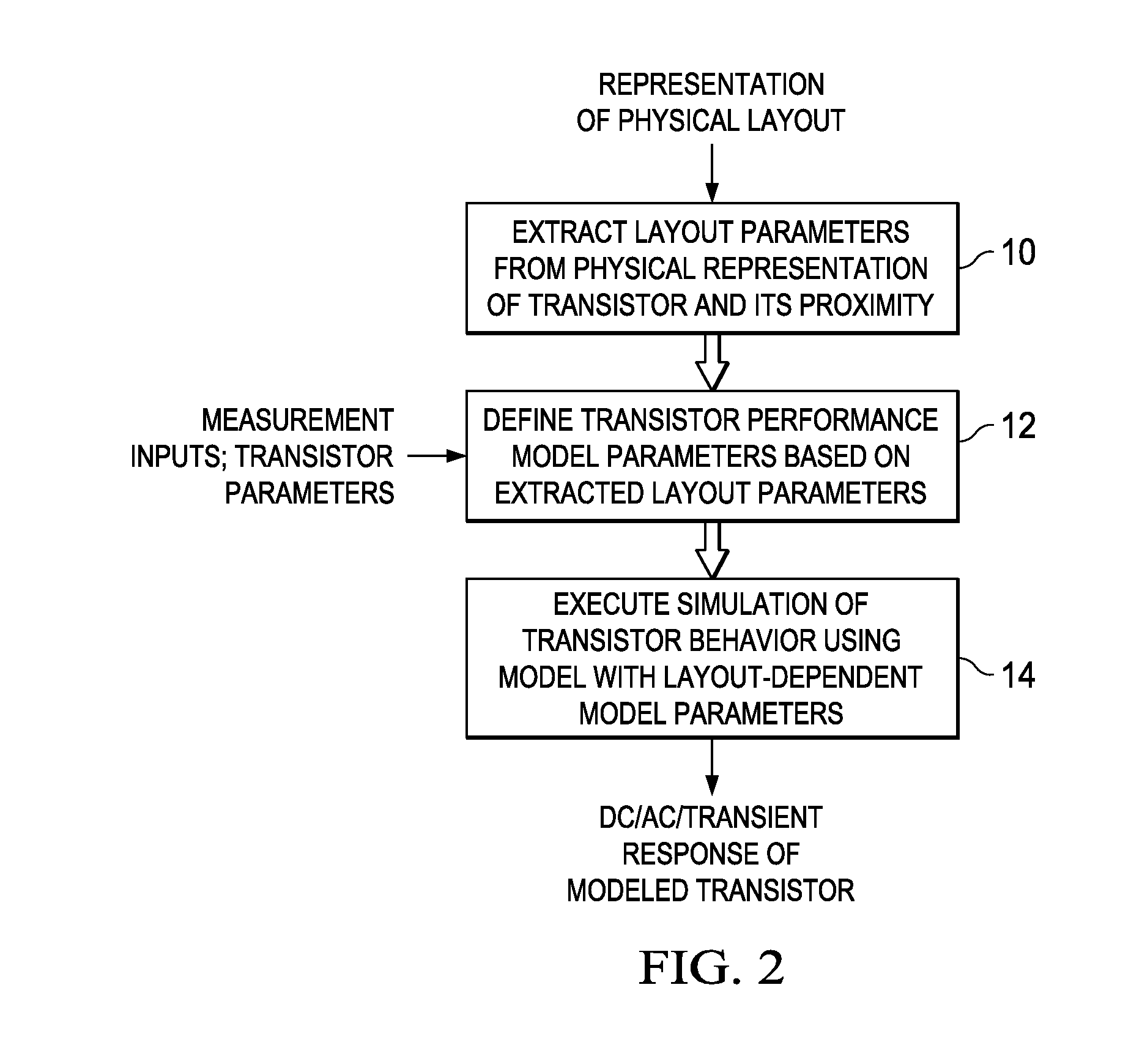
Automated Extraction of Size-Dependent Layout Parameters for Transistor Models
InactiveUS20120143569A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringIntegrated circuit layout
A system and method for determining transistor model parameters that account for layout-dependent features in the transistor being modeled, and also in neighboring devices in the same integrated circuit. A computer-readable expression of the integrated circuit layout is retrieved, and active and gate layers in that expression extracted. For a transistor being modeled, its active regions are analyzed to determine whether these regions have a complex shape. Model parameters are derived based on volume effects of the complex shaped active regions. Neighboring active regions that affect parameters of the transistor being modeled are also identified and their effective depth determined. Strain effects due to complex shaped active regions and neighboring elements are thus included in the transistor model.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-free degree ultrasonic wave electromotor based on piezoelectric porcelain cut strain
InactiveCN101170286ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerEngineering
The invention provides a multi-degree-of-freedom ultrasonic motor based on piezoelectric ceramic shear strain. It includes a rotor, a stator and a clamping base. The stator is composed of a vibrator column and four pieces of piezoelectric ceramics pasted on the four sides of the vibrator column. The electrodes on the upper layer of each piece of piezoelectric ceramics are composed of four equal parts, and the electrodes on the lower layer are integrated. The poles and stator are clamped on the base by clamping screws. In the present invention, the four-part piezoelectric ceramic is pasted on the vibrator column by glue to realize the necessary vibration modes of the multi-free ultrasonic motor, and by applying the excitation signal on the appropriate electrode, the shear strain of the piezoelectric ceramic is used. effect produces the vibrational modes described above. Therefore, under the effect of vibration superposition, the elliptical motion of the stator end particle pushes the rotor to produce independent rotations around the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis, and further rotation around any direction axis is realized by switching the above-mentioned orthogonal rotation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
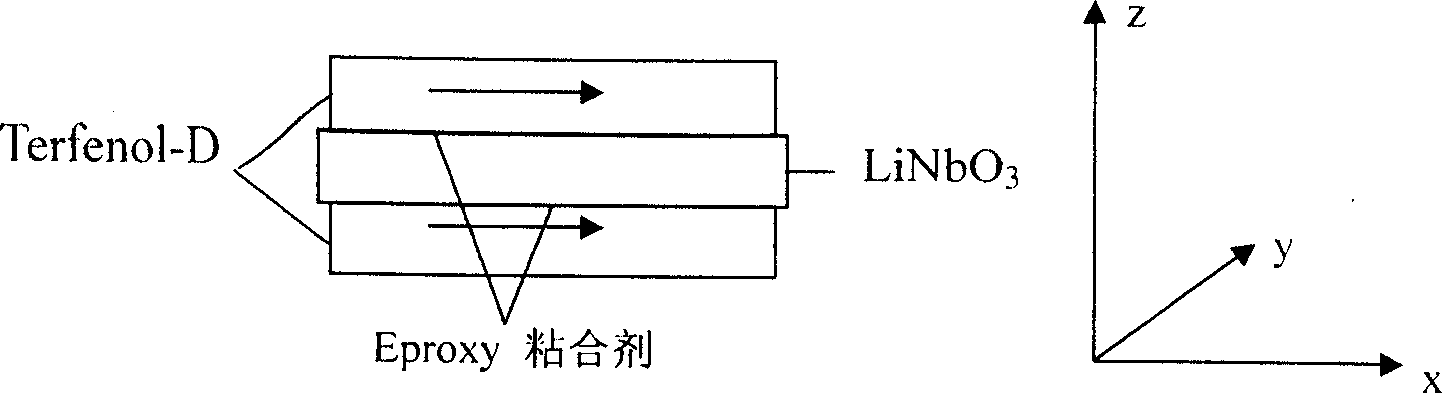
Method for improving magneto-electric effect of composite materials
InactiveCN1805165AIncrease magnetoelectric outputPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMagnetostrictive device manufacture/assemblySingle crystalPiezoelectric coefficient
The invention relates to a method for improving the magnetoelectric effect of composite material, which prepares the magnetic deformation and the piezoelectric material into sheet composite material while they are adhered. It designs the cutting shape of piezoelectric single crystal according to the vibration mode of magnetic deformation material under the direct current bias magnetic field and alternating excited magnetic field, to make the cut piezoelectric single crystal attain high piezoelectric output under the strain effect processed by the magnetic deformation material; selecting the cutting shape of standard cut piezoelectric single crystal to attain the maximum piezoelectric factors of crystal; processing coordinate transformation on the piezoelectric tensor matrix of standard piezoelectric single crystal to make the piezoelectric factor integrated valve used in the new cut piezoelectric factor matrix reach maximum, and the new cut piezoelectric single crystal attain maximum piezoelectric output at needed direction to attain the maximum magnetoelectric effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Micro cantilever beam driving member based on antiferroelectric thick film field induced phase transition strain effect
InactiveCN101590999AGuaranteed stabilityAction richDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro actuatorEngineering
The invention relates to a driving member for a micro actuator, in particular to a micro cantilever beam driving member based on an antiferroelectric thick film field induced phase transition strain effect, which solves the problems existing in the driving member of the prior actuator of slow response, small driving displacement and the like. The method for preparing the member adopts the following steps: (1) preparing a precursor sol of a lead based antiferroelectric material and a PbO sol; (2) preparing a thick film of the lead based antiferroelectric material on a Pt metallic layer of a supporting substrate; (3) spin-coating the PbO sol on the thick film of the lead based antiferroelectric material, and carrying out the annealing treatment; (4) sputtering a metallic layer on the thick film of the lead based antiferroelectric material, which is used as a top electrode, and a pressure welding point; and (5) corroding the back surface of the support substrate, and reducing the thickness of the middle of the support substrate; etching the thick film of the lead based antiferroelectric material and the front face of the middle part of the support substrate to form a peripheral substrate and a cantilever beam structure connected with the single end of the peripheral substrate. The driving member has the advantages of having a simple process and structure, realizing the application of the antiferroelectric material in the field of the driving members for the micro actuator, and providing a completely new idea for designing and manufacturing the micro driving member with quick response and large displacement.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Improved waveguide structure
InactiveUS20070122081A1Improved polarization crosstalk characteristicEliminates strain effectCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideCrosstalk
An improved waveguide structure employing blocks of waveguide core material positioned sufficiently close to a waveguide core thereby eliminating strain effects and its resulting undesirable polarization crosstalk. The improved structures are applicable to a variety of optical components including bent waveguides, directional and star couplers.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Semiconductor field effect structure and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102544093ASignificant Magnetic Modulation FeaturesSignificant inverse piezoelectric effectVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceSingle crystal substrate
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
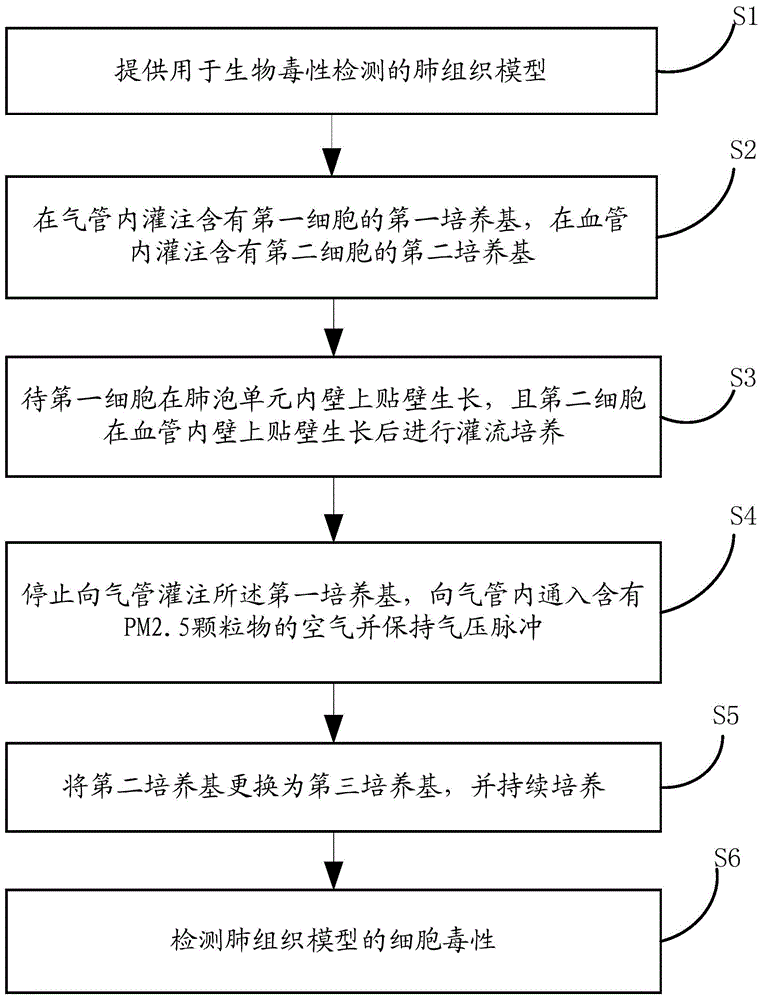
Lung tissue model for biotoxicity detection and biotoxicity detection method
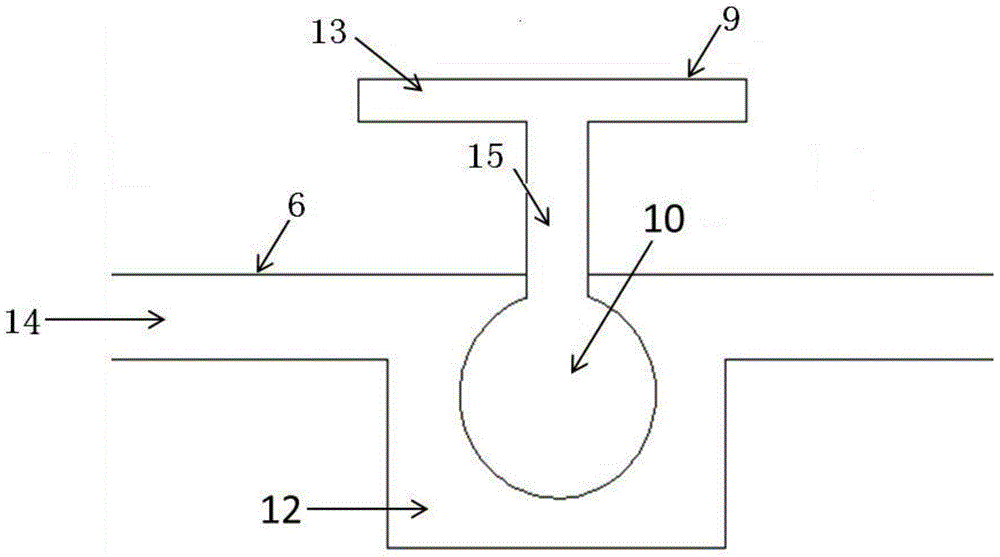
The invention discloses a lung tissue model for biotoxicity detection and a biotoxicity detection method. The lung tissue model comprises a trachea, a blood vessel and an alveolus pulmonis unit, wherein an air passage is defined in the trachea, and an air inlet and an air outlet, which are communicated with the air passage respectively are formed at two ends of the trachea; a blood passage is defined inside the blood vessel, and a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet which are communicated with the blood passage respectively are formed at the two ends of the blood vessel, a cavity is defined in the alveolus pulmonis unit, an elastic ventilate membrane is formed on the wall of the alveolus pulmonis unit, the alveolus pulmonis unit is arranged in the blood passage, and the cavity is communicated with the air passage. By adopting the lung tissue model, an air exchanging function and a breathing strain effect of the lung blood in the body can be simulated; through planting cells in the alveolus pulmonis unit, the structure and function of the alveolus pulmonis unit in a body and inflammation reaction of immune cells can be simulated in the subsequent culture process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
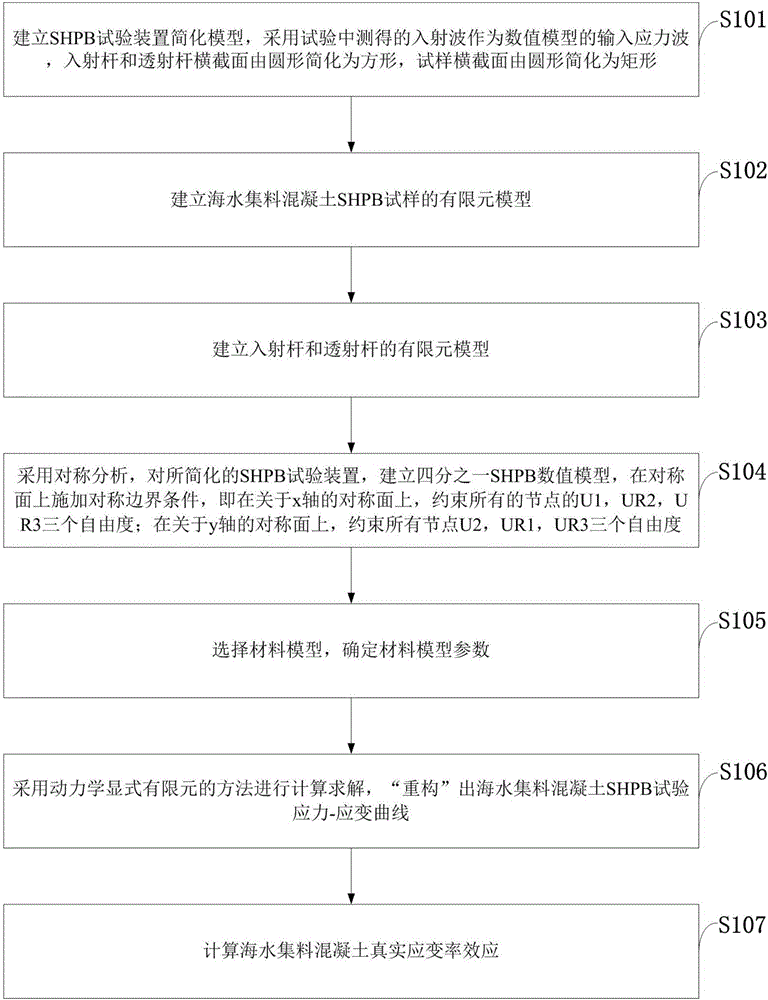
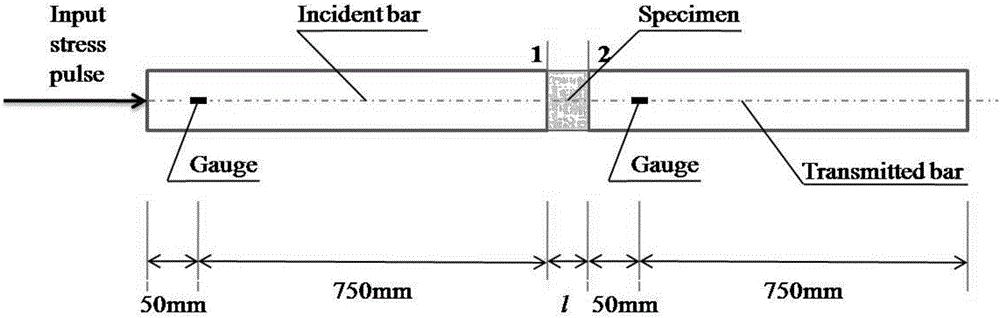
Computer dynamic simulation method of determining true strain rate effect of seawater aggregate concrete
ActiveCN106503372AAchieve separationAccurate Strain Rate Effect ParametersDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelIncident wave
The invention discloses a computer dynamic simulation method of determining a true strain effect of a seawater aggregate concrete. A disconnect-type Hopkinson compression bar test and a corresponding finite element analytical model of the seawater aggregate concrete are utilized. The method comprises the steps of using a measured compression bar incident wave as an input stress wave of the finite element model; selecting and using an extended Drucker-Prager model as a material model of the seawater congregate concrete basal body, wherein the strain rate effect is not set, and only simulating the increase of the strength of the seawater congregate concrete caused by a sidewise inertial confinement effect under a high strain rate; determining the true strain rate effect of the seawater congregate concrete according to the strain rate effect obtained through compression bar test and the strain rate effect caused by the sidewise inertial and end face friction. According to the computer dynamic simulation method of determining the true strain effect of the seawater aggregate concrete, the situation that a complicatedly designed test decouples the true strain rate effect of the seawater congregate concrete with a structure of an inner shell body and the strain rate effect caused by the sidewise restraint is avoided, the result is quick and accurate, and the computer dynamic simulation method of determining the true strain effect of the seawater aggregate concrete has better practical value.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Method for testing real stress of self-compensating concrete structure and concrete real stress gauge
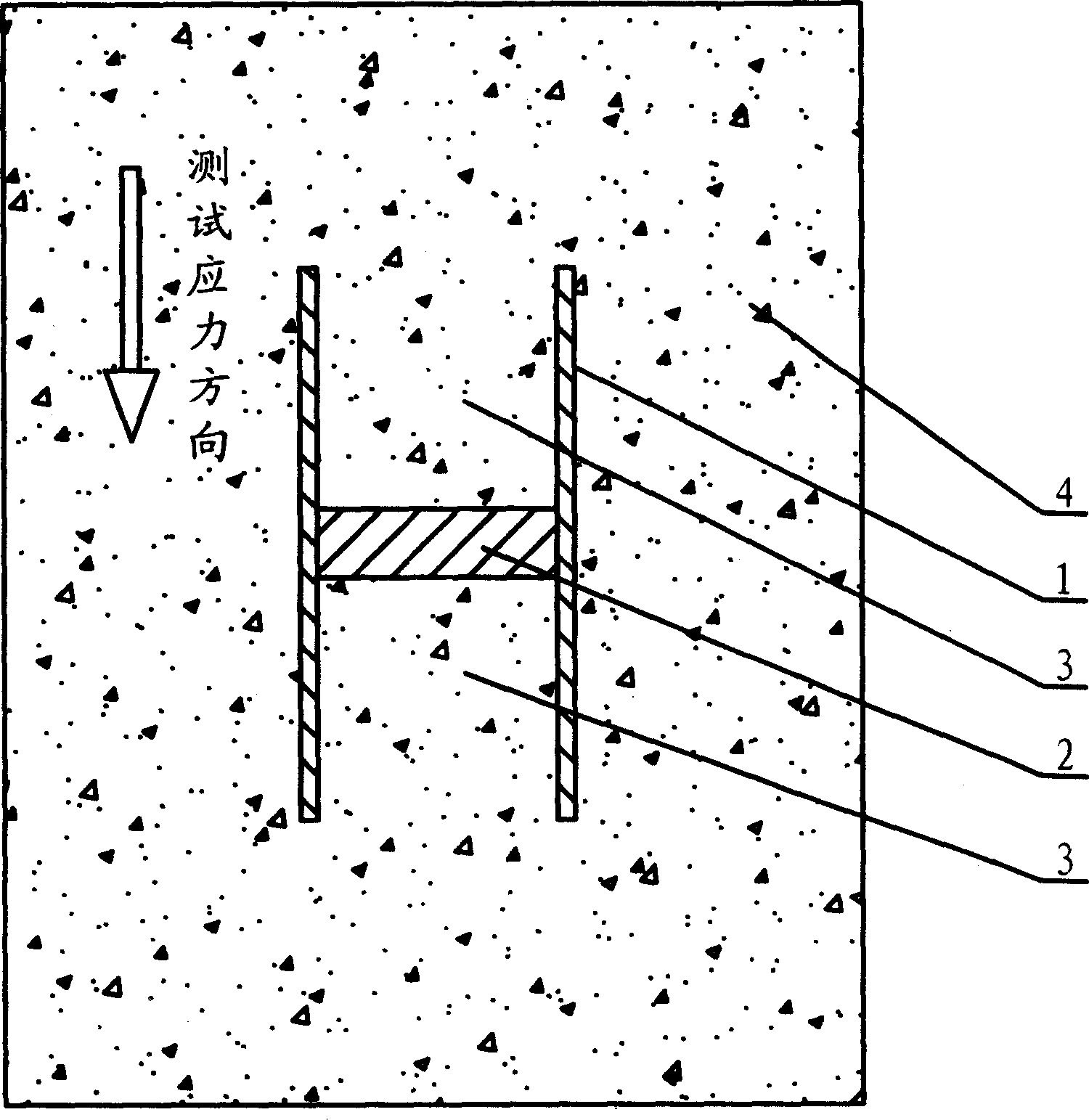
The related test method for true stress of concrete structure comprises: setting a equal-section insulator on test direction to isolate the concrete in and out of the device, using a force senor to test concrete column axial force in device to obtain the objective value. This invention eliminates non-spring strain effect, has reliable result and well practice.
Owner:郑万山 +2
Manufacture method of uniaxial strain silicon germanium on insulator (SGOI) wafer on aluminum nitride (AIN) embedded insulating barrier based on mechanical bending table
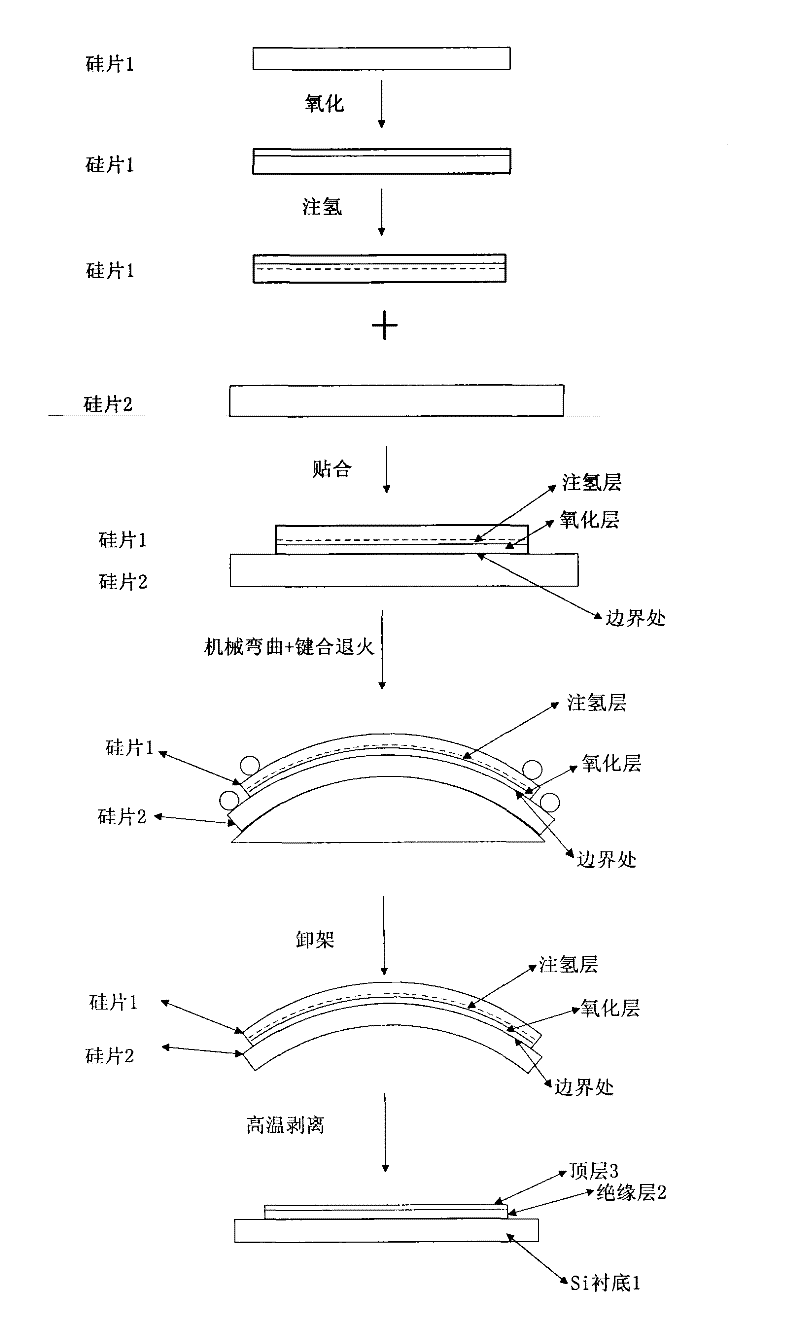
InactiveCN102543719AReduce manufacturing costSimple preparation processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStrain effectSilicon-germanium
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a uniaxial strain silicon germanium on insulator (SGOI) wafer on an aluminum nitride (AIN) embedded insulating barrier based on a mechanical bending table, which comprises the steps as follows, (1) a top layer silicon-germanium (SiGe) layer face of the SGOI wafer is upwards or downwards placed on the mechanical bending table; (2) two cylindrical stainless steel compression bars are respectively and horizontally placed at two ends of the SGOI wafer and 1cm away from the edge of the SGOI wafer; (3) a nut connected with the compression bars is slowly rotated to enable the SGOI wafer to bend gradually along an arc-shaped table face until the SGOI wafer is completely fitted with the arc-shaped table face; (4) the arc-shaped bending table loaded with the SGOI wafer is placed in an annealing furnace for annealing; (5) the temperature is reduced to the room temperature after completion of annealing, and the arc-shaped bending table loaded with the SGOI wafer is taken out; and (6) the nut connected with the compression bars is rotated to slowly life the compression bars until bending SGOI wafer is reinstated. The manufacture method has the following advantages of being (1) low in manufacture cost, (2) simple in manufacture equipment and process, (3) high in strain effect, (4) excellent in insulativity and thermal property, (5) high in rate of finished products, and (6) large in annealing temperature range.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for increase strain effect in a transistor channel
InactiveUS20060281272A1Increase pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackSemiconductor
Method of enhancing stress in a semiconductor device having a gate stack disposed on a substrate. The method utilizes depositing a nitride film along a surface of the substrate and the gate stack. The nitride film is thicker over a surface of the substrate and thinner over a portion of the gate stack.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
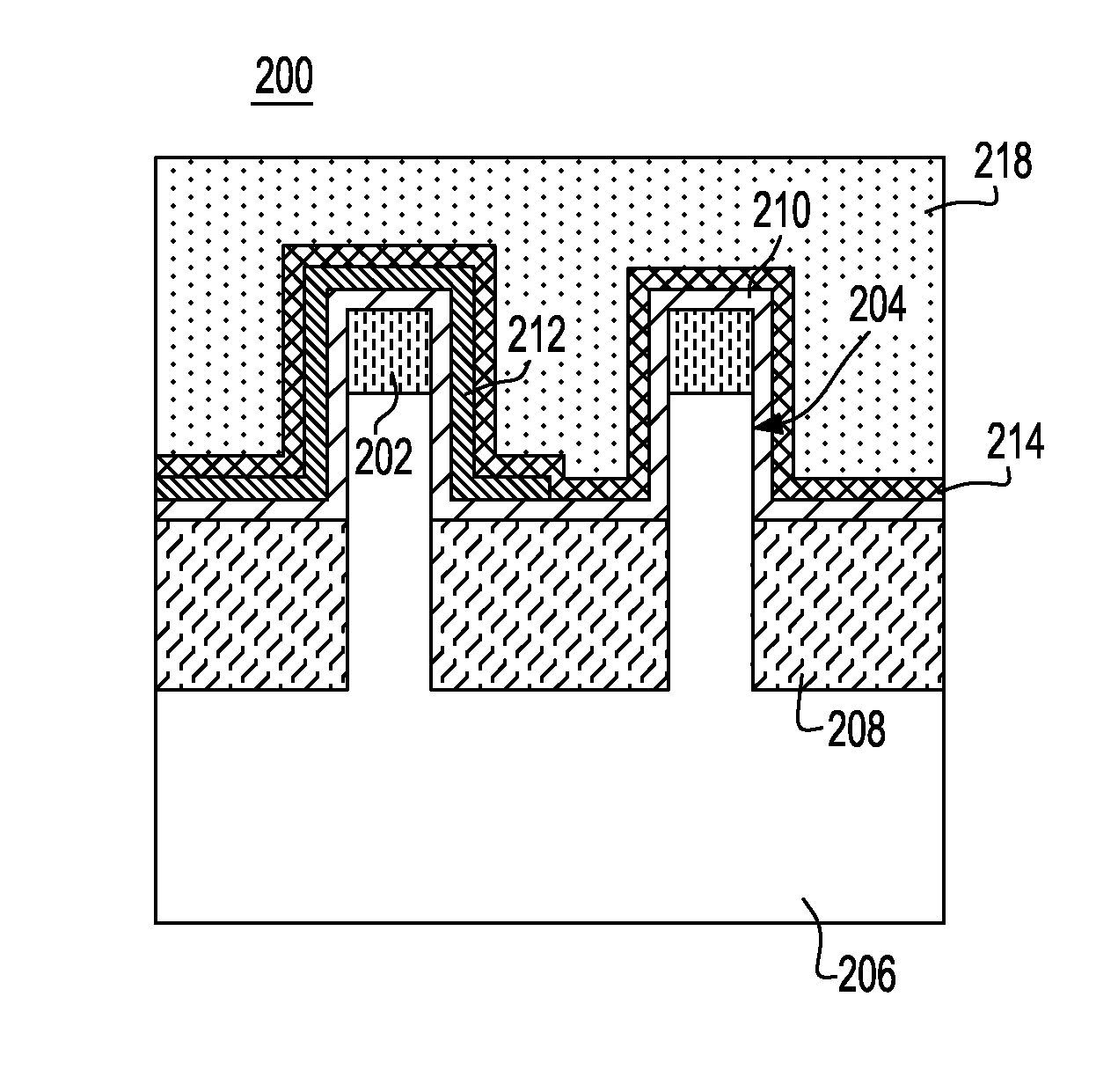
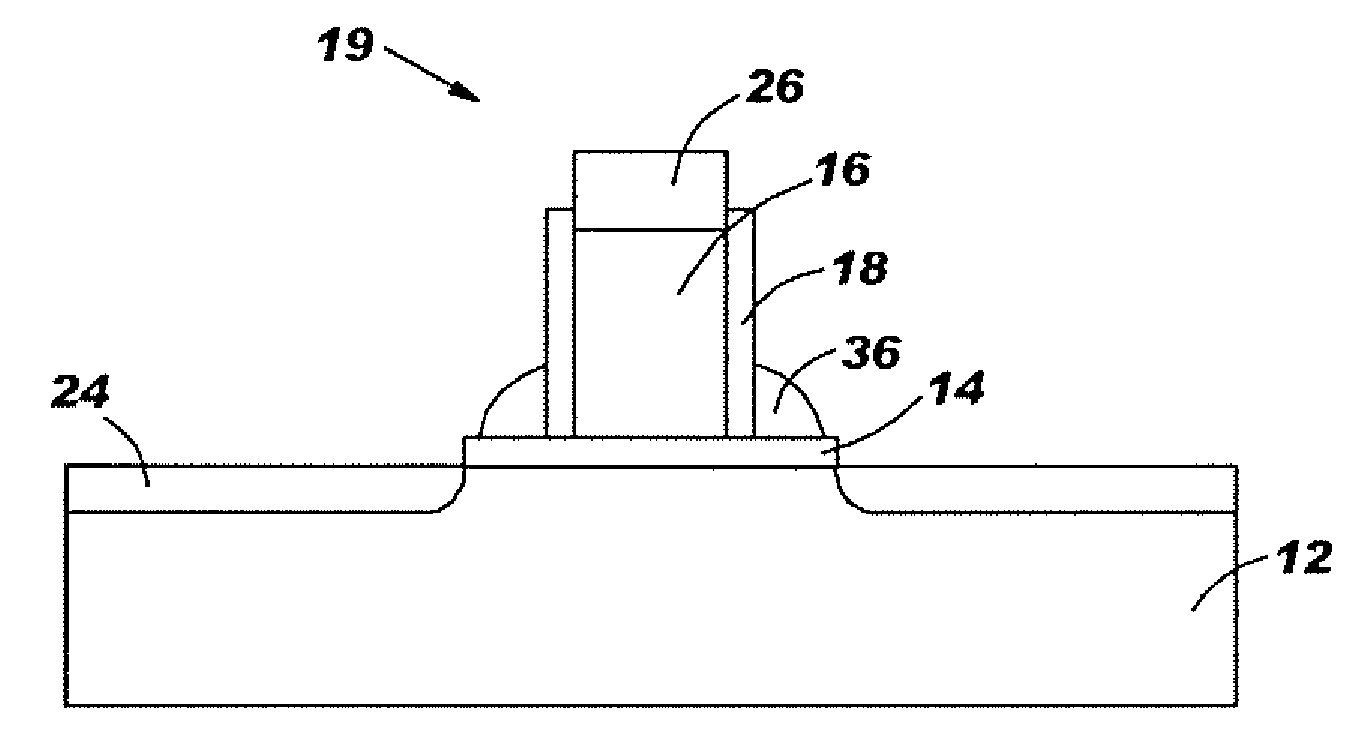
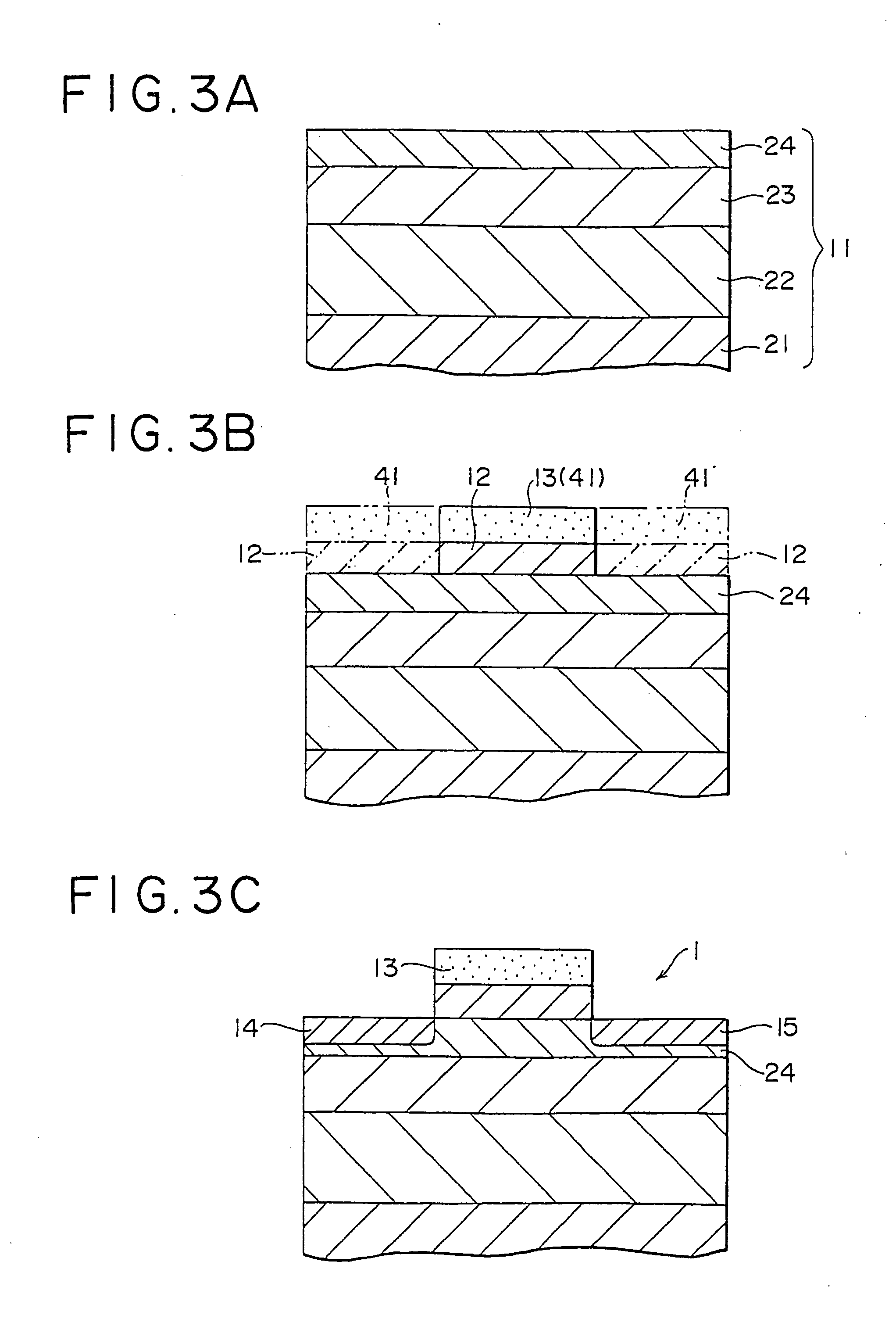
Field effect transistor and fabrication thereof, semiconductor device and fabrication thereof, logic circuit including the semiconductor device, and semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS20080176367A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorP channel
A method for forming a Field Effect Transistor (FET) within a strain effect semiconductor layer is disclosed, whereby the source and drain of the FET are formed only in the strain effect silicon layer. The FET may be formed as a gate electrode of a p-channel type field effect transistor, and a gate electrode of a n-channel type field effect transistor on the silicon layer which has the strain effect through a gate insulating film. The sources and drains of p- and n-type diffusion layers are then formed in the silicon layer having the strain effect, on both sides of the gate electrode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Inner-outer tube type gas flowmeter and flow detecting method
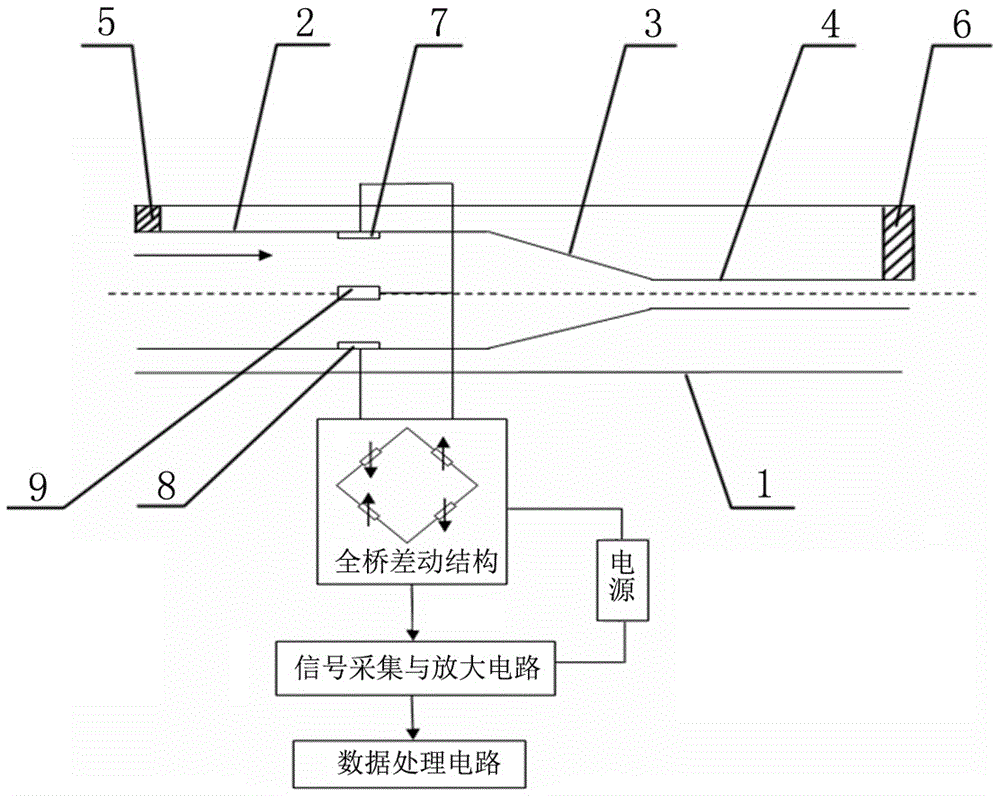
ActiveCN106768097AVerify rationalityVerify feasibilityVolume/mass flow by differential pressureFull bridgeDifferential pressure
The invention provides an inner-outer tube gas flowmeter and a flow detecting method. According to the inner-outer tube gas flowmeter, an inner tube of which the length is equal to that of an outer tube is arranged inside the outer tube, supports are arranged at the two ends of the inner tube so as to guarantee that in the measuring process, the inner tube is fixed and stays still, and the perturbation phenomenon of the inner tube is reduced; four pressure measuring holes are uniformly formed in the same cross section of the inner tube simultaneously, strain gages with positive stress are embedded into two oppositely-arranged pressure measuring holes, strain gages with negative stress are embedded into the other two pressure measuring holes, and the four strain gages form a full-bridge differential-motion structure, which is equivalent to the function of arranging a pressure sensor in the inner tube. When gas flows, the resistance values of the strain gages change due to strain effects, a voltage is loaded on the strain gages, the voltage value is obtained through signal acquisition and amplified circuit acquisition, the obtained voltage through acquisition reflects differential pressure information between the inner tube and the outer tube, and the flow of gas can be calculated through the differential pressure information. The inner-outer tube gas flowmeter is simple in structure and reasonable in design, and the final measuring result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
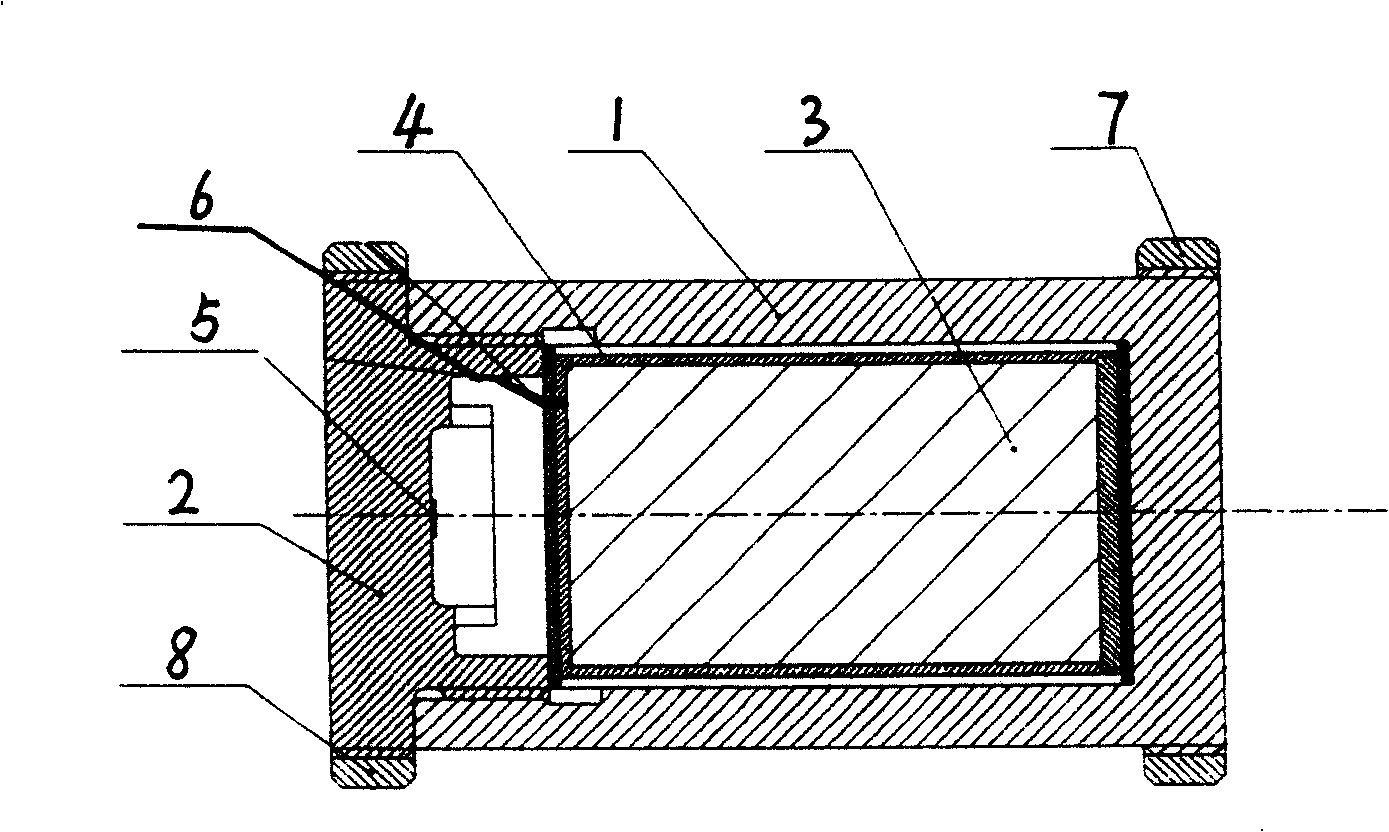
Integrated electric voltage detector based on strain effect
InactiveCN101245976ARealize integrationMiniaturizationFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationWeapon testingElectrical resistance and conductanceMetallic materials
The invention relates to an electronic pressure measuring device, in particular to an all-in-one electronic pressure measuring device based on the strain effect, and solves the problem that a pressure sensor that is configured in an existing electronic pressure measuring device has large volume, thus causing that the existing electronic pressure measuring device has an oversize whole volume and can not satisfy the use requirement of volume-constrained occasions. The all-in-one electronic pressure measuring device based on the strain effect comprises a barrel-shaped shell and an end cover that is fixed at the end of the barrel-shaped shell and made of elastic metallic materials, and a protective inner barrel is arranged inside the barrel-shaped shell and used for placing a measuring circuit; electrical resistance strain gages that are respectively used for sensing pressure change and temperature change are fixed in the middle and on the lateral wall of the inner surface of the end cover and connected with an input end of the measuring circuit. The all-in-one electronic pressure measuring device based on the strain effect has simple structure, small volume, low production cost, wide application range, and all the performance indexes that reach the testing requirements.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Bar V-shaped groove tip microcrack preparing method based on straightening mechanism
InactiveCN103658240ASimple structureEasy to automateMetal-working feeding devicesPositioning devicesEngineeringStrain effect
The invention relates to a bar V-shaped groove tip microcrack preparing method based on the straightening mechanism and belongs to the technical field of metal bar feeding. The method is based on a straightening machine which mainly comprises a driven material pulling mechanism, a driving material pulling mechanism, a straightening and transmission mechanism, a material conveying mechanism and a machine frame. The driven material pulling mechanism, the driving material pulling mechanism, the straightening and transmission mechanism and the material conveying mechanism are arranged on the machine frame. The driven material pulling mechanism and the driving material pulling mechanism are arranged at one end of the straightening and transmission mechanism. The material conveying mechanism is arranged at the other end of the straightening and transmission mechanism. According to the method, by screwing an adjusting bolt, a circulating strain effect can be conveniently used for forming microcrack in the tip end of a metal bar V-shaped groove, the structure is simple, and automatic operation can be achieved conveniently.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Field effect transistor and fabrication thereof, semiconductor device and fabrication thereof, logic circuit including the semiconductor device, and semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS7355214B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorP channel
A method for forming a Field Effect Transistor (FET) within a strain effect semiconductor layer is disclosed, whereby the source and drain of the FET are formed only in the strain effect silicon layer. The FET may be formed as a gate electrode of a p-channel type field effect transistor, and a gate electrode of a n-channel type field effect transistor on the silicon layer which has the strain effect through a gate insulating film. The sources and drains of p- and n-type diffusion layers are then formed in the silicon layer having the strain effect, on both sides of the gate electrode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Wind speed measuring device and method based on surface plasma resonance
ActiveCN109142781AEliminate the effects ofHigh temperature sensitivityFluid speed measurementICT adaptationDielectricResonance wavelength
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric detection and relates to a wind speed measuring device and method based on surface plasma resonance. The device includes a broad spectrumlight source, a heating light source, a fiber sensor, a spectrometer, a coupler, an isolator B, an isolator C, a circulator, a single mode fiber and a wind speed measuring pipeline, wherein the fibersensor is a fiber temperature sensor based on surface plasma resonance and strain compensation, a sensing fiber is formed through respectively plating metal films generating surface plasma resonance at inner walls of two dielectric holes at the center of opposite sides of a second hexagonal dielectric hole layer outwards, a medium hole plated with the metal film and two adjacent medium holes on the same layer are filled with a medium A, a media B is filled in all the media holes which are not filled with the media A, when the temperature of the fiber sensor changes, resonance wavelength changeof the metal films A and B is not consistent, a strain value is solved, the strain effect is eliminated, a temperature value is solved, and the fiber hotline wind speed is calculated on the basis.
Owner:辽宁省计量科学研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com