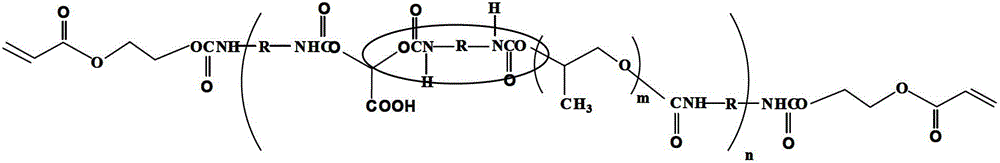
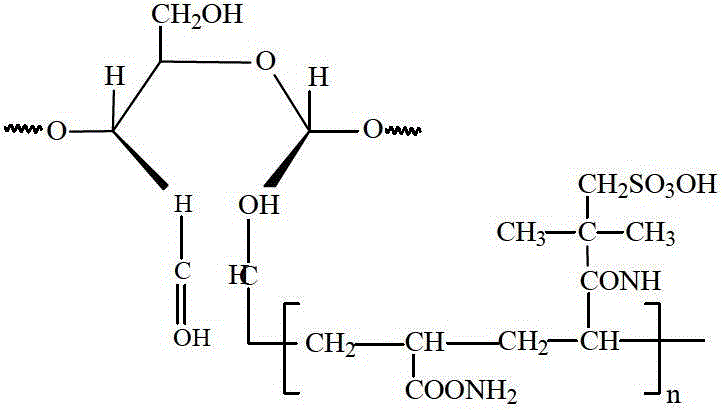
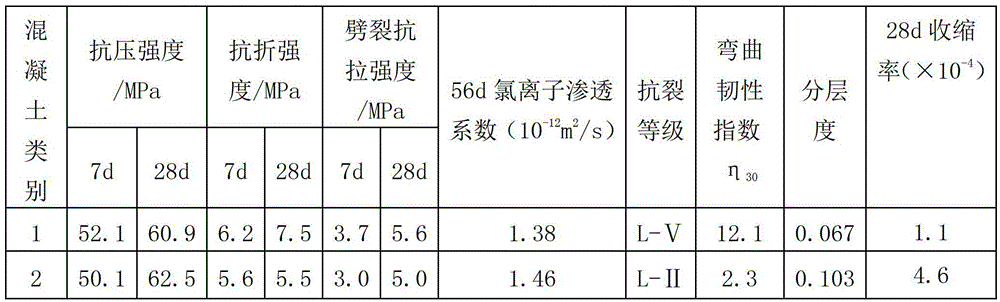
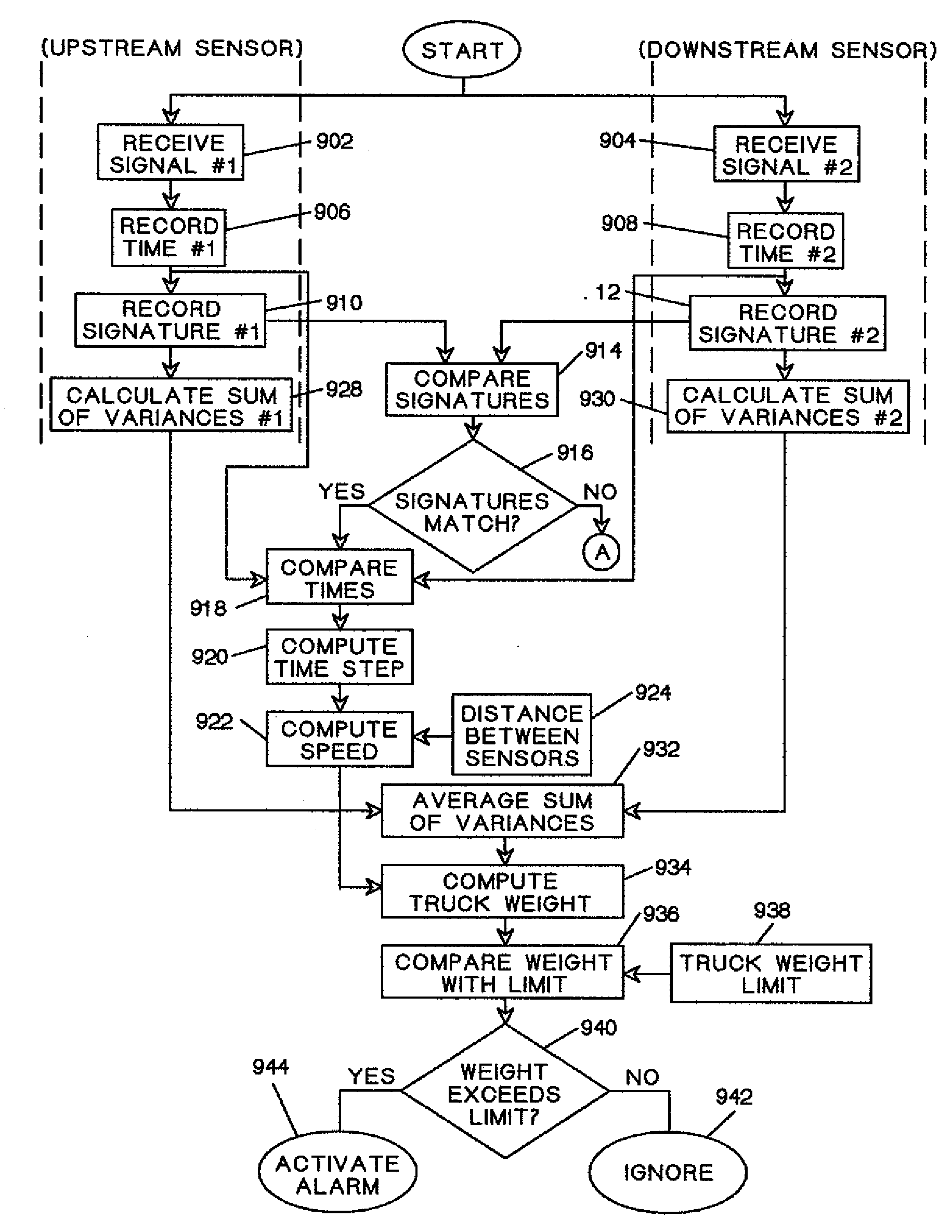
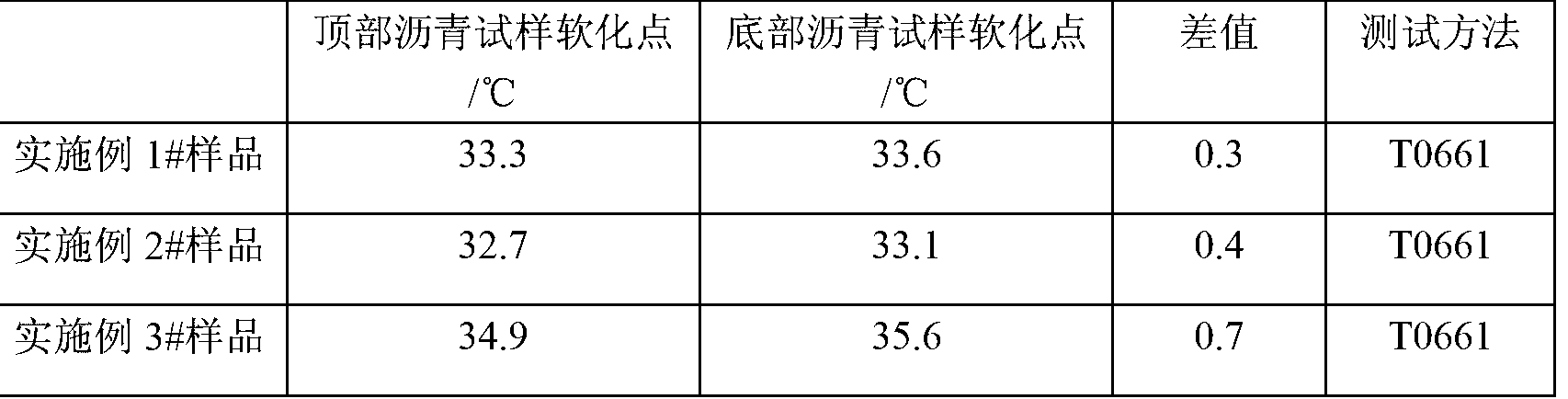
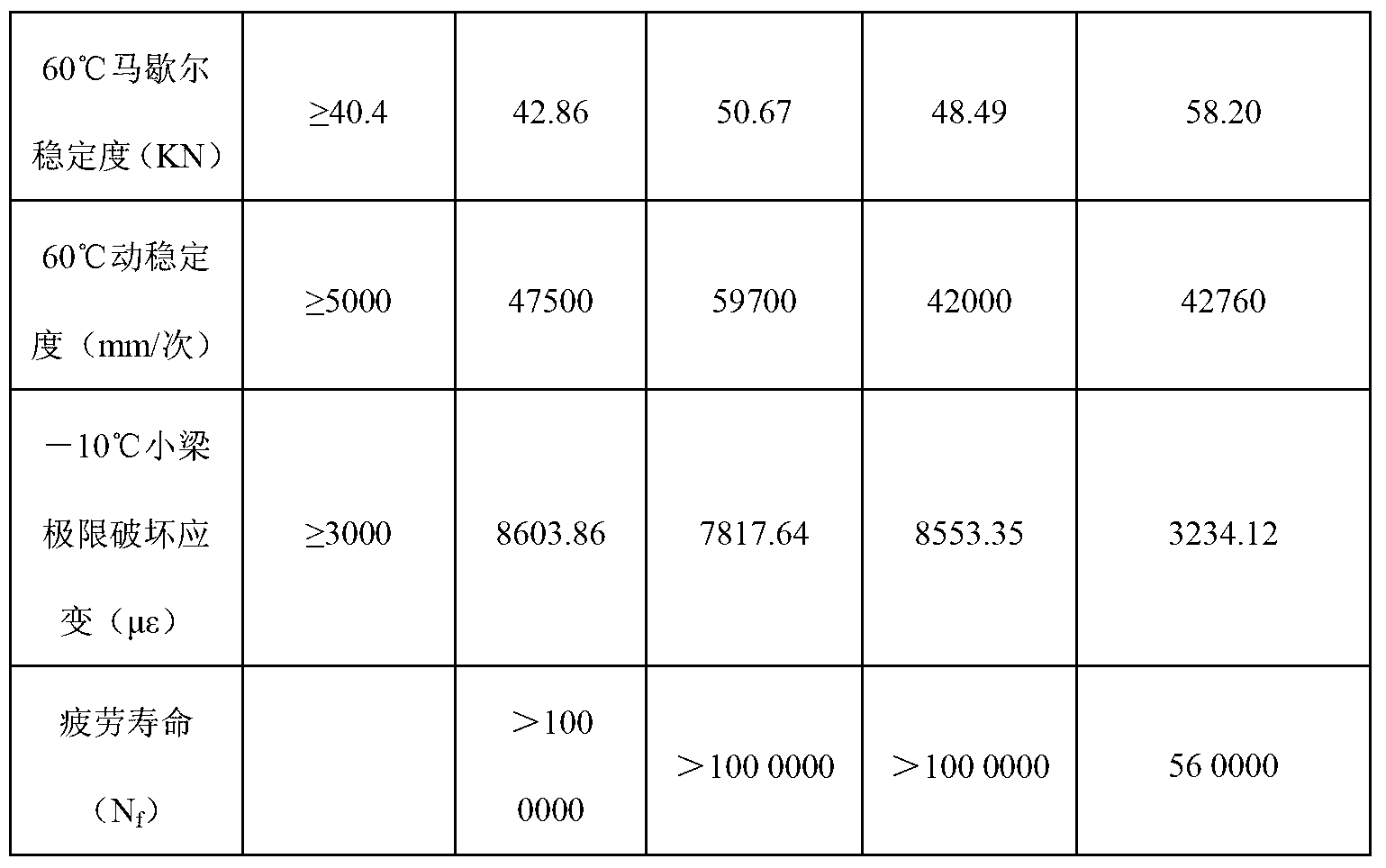
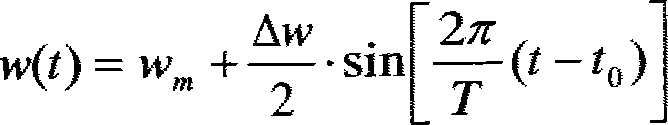Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5080 results about "Bridge deck" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
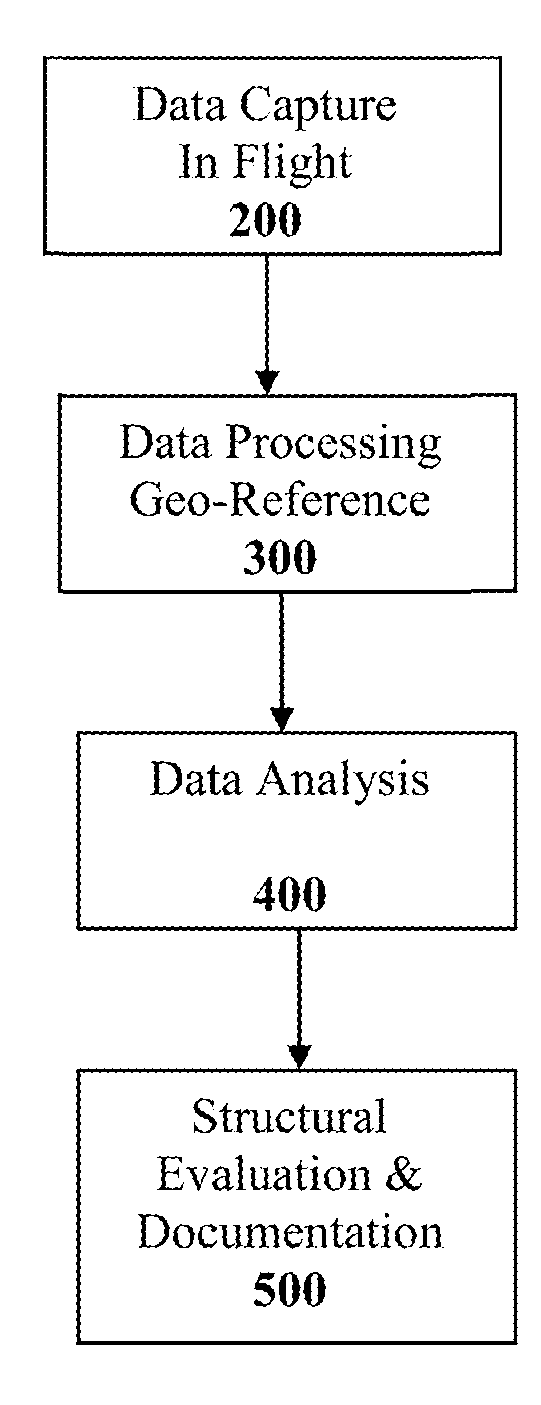
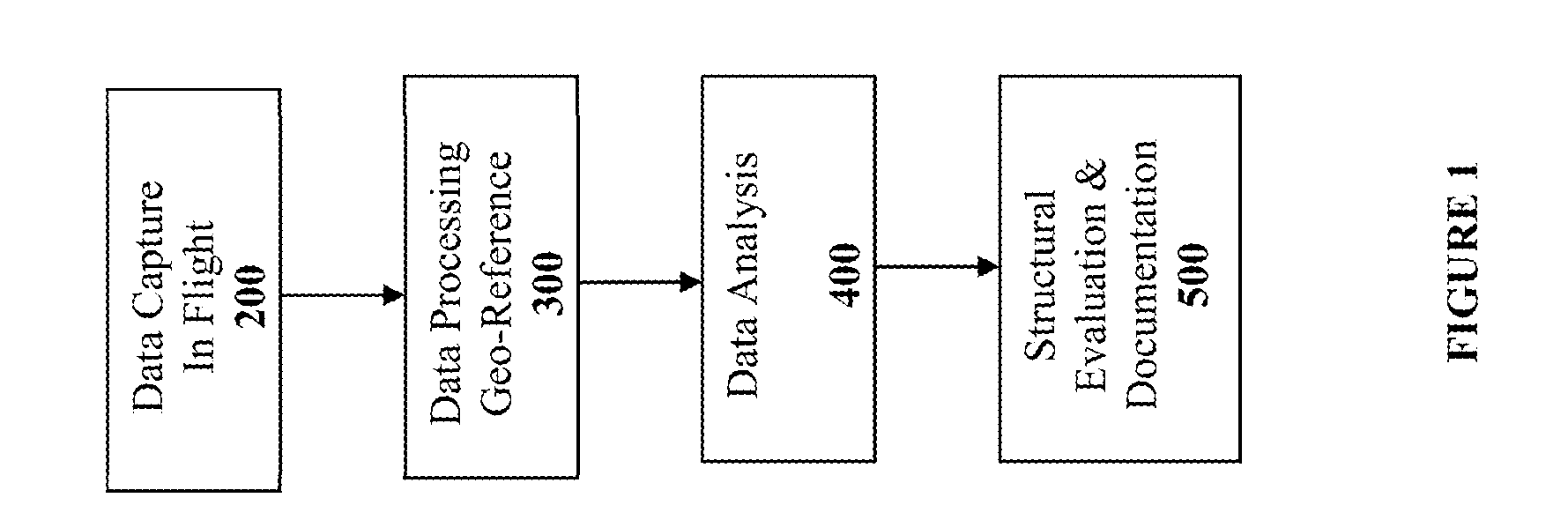
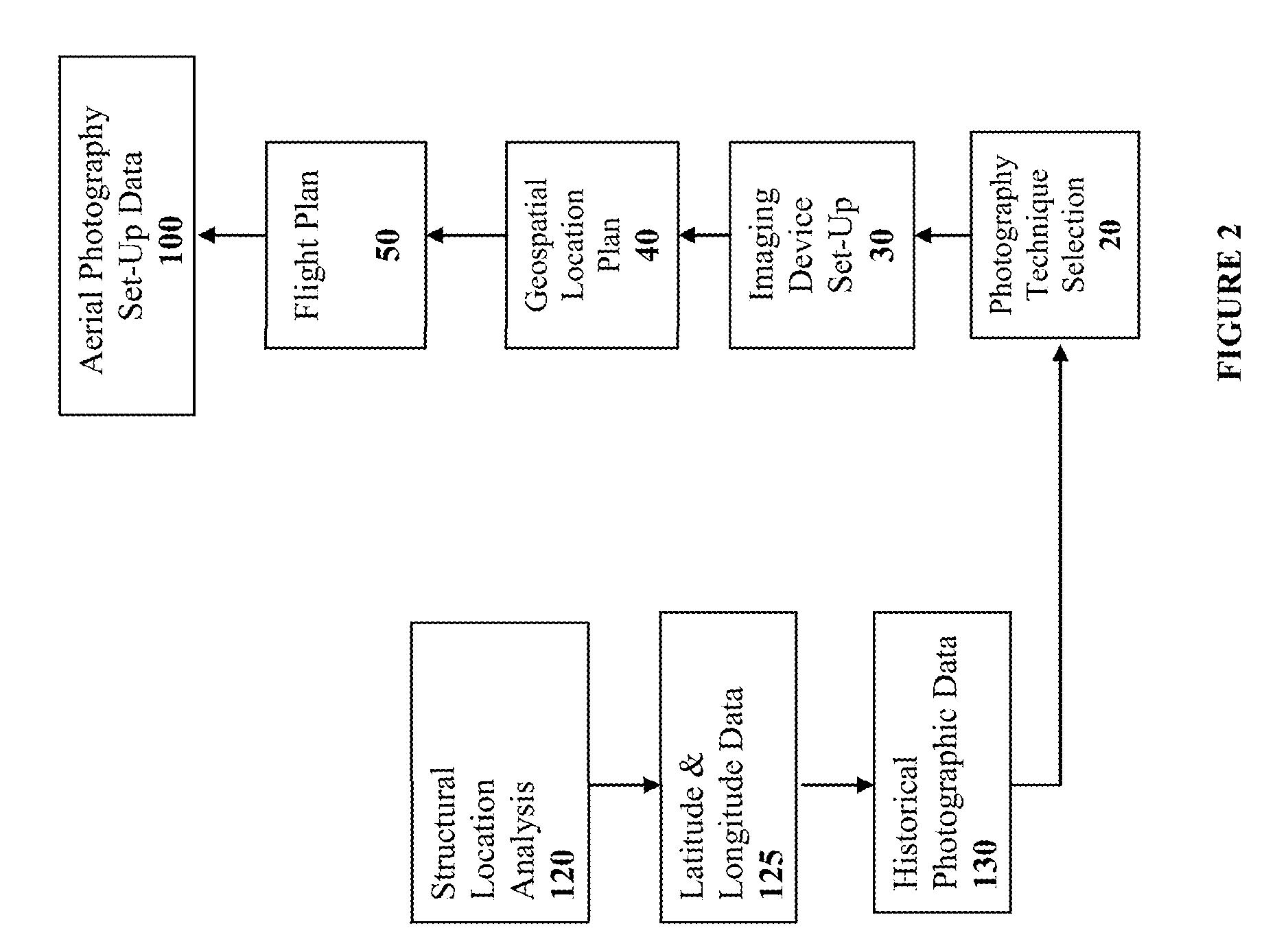
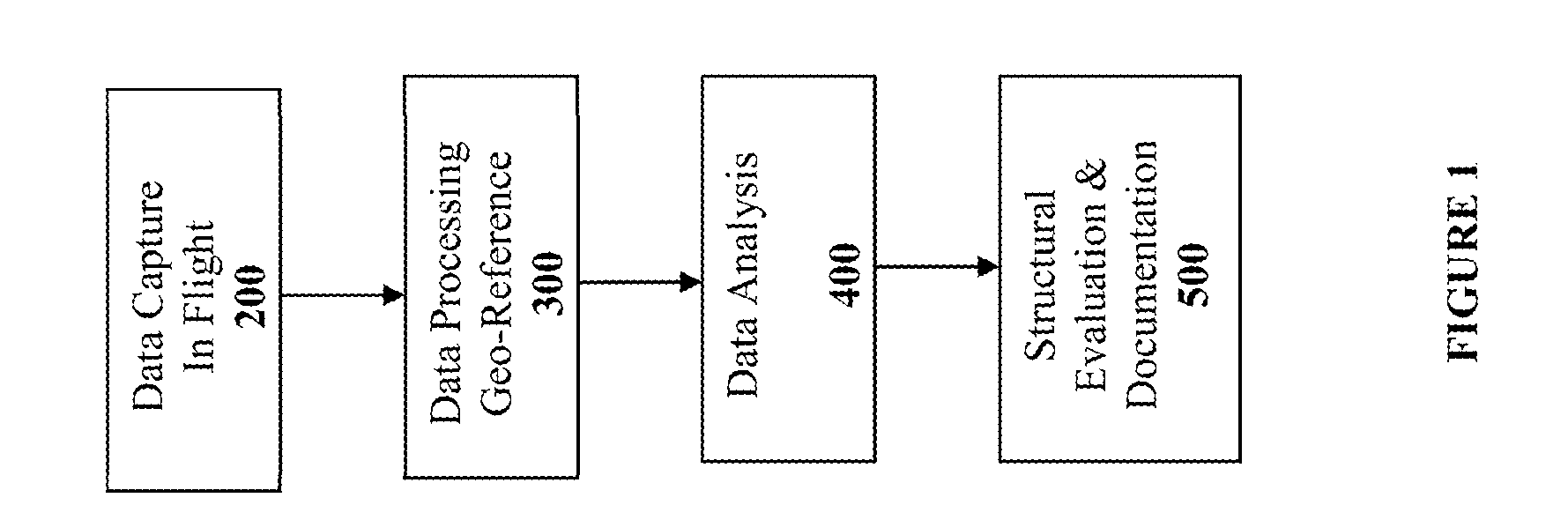
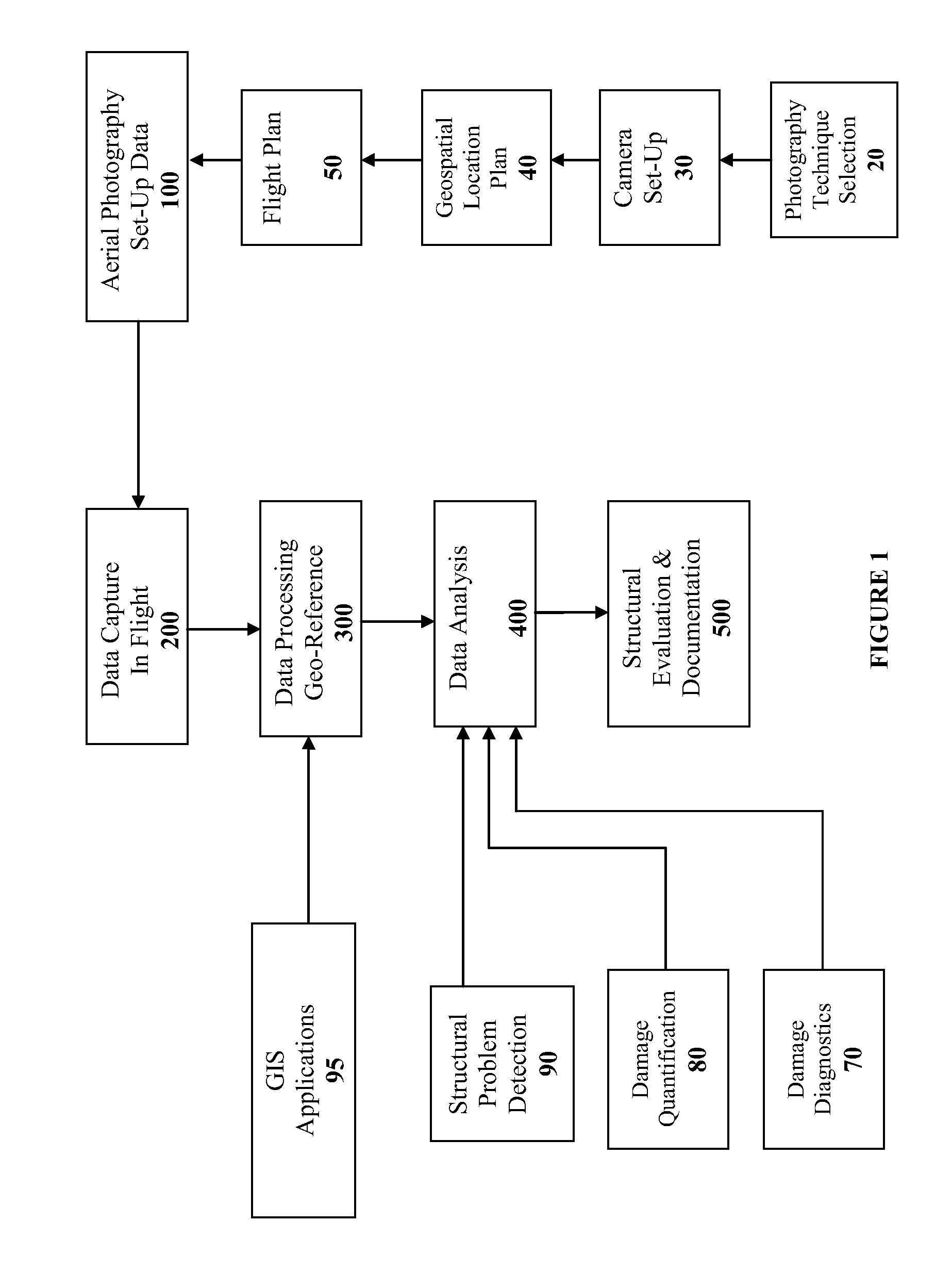
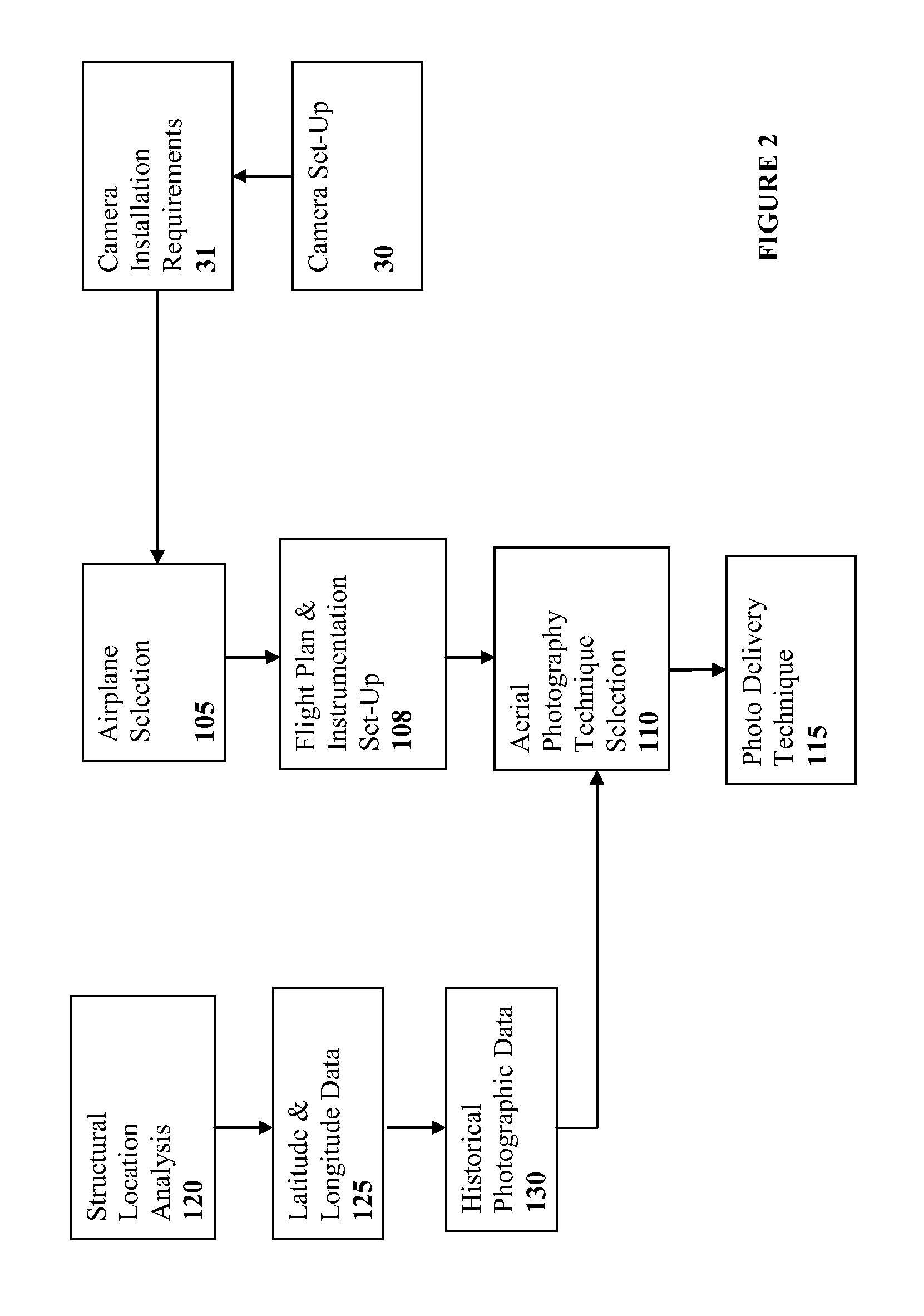
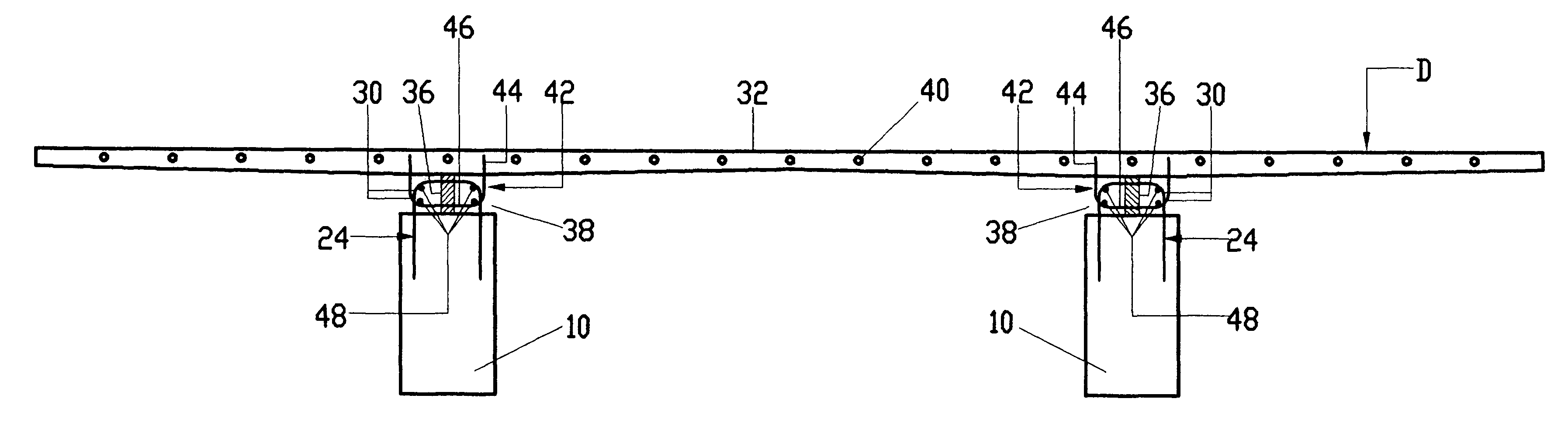
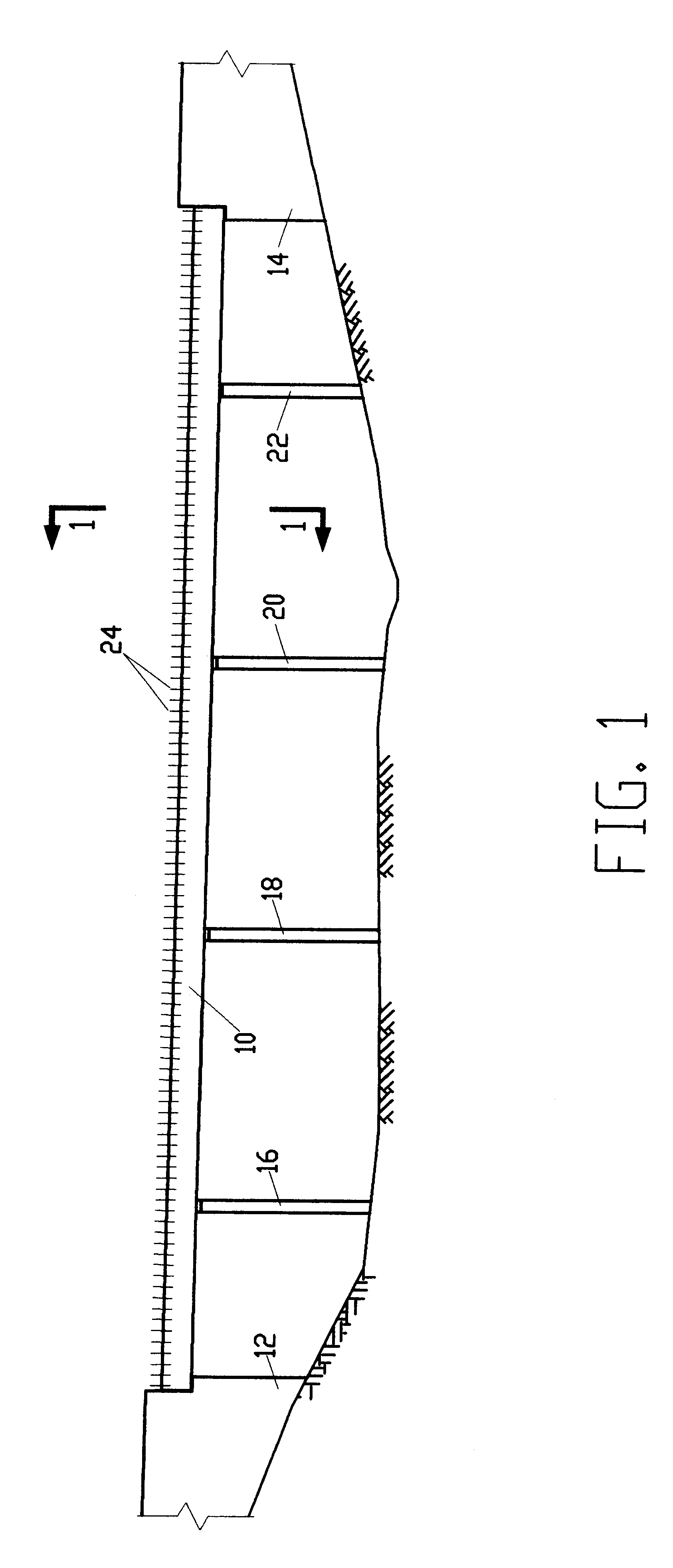
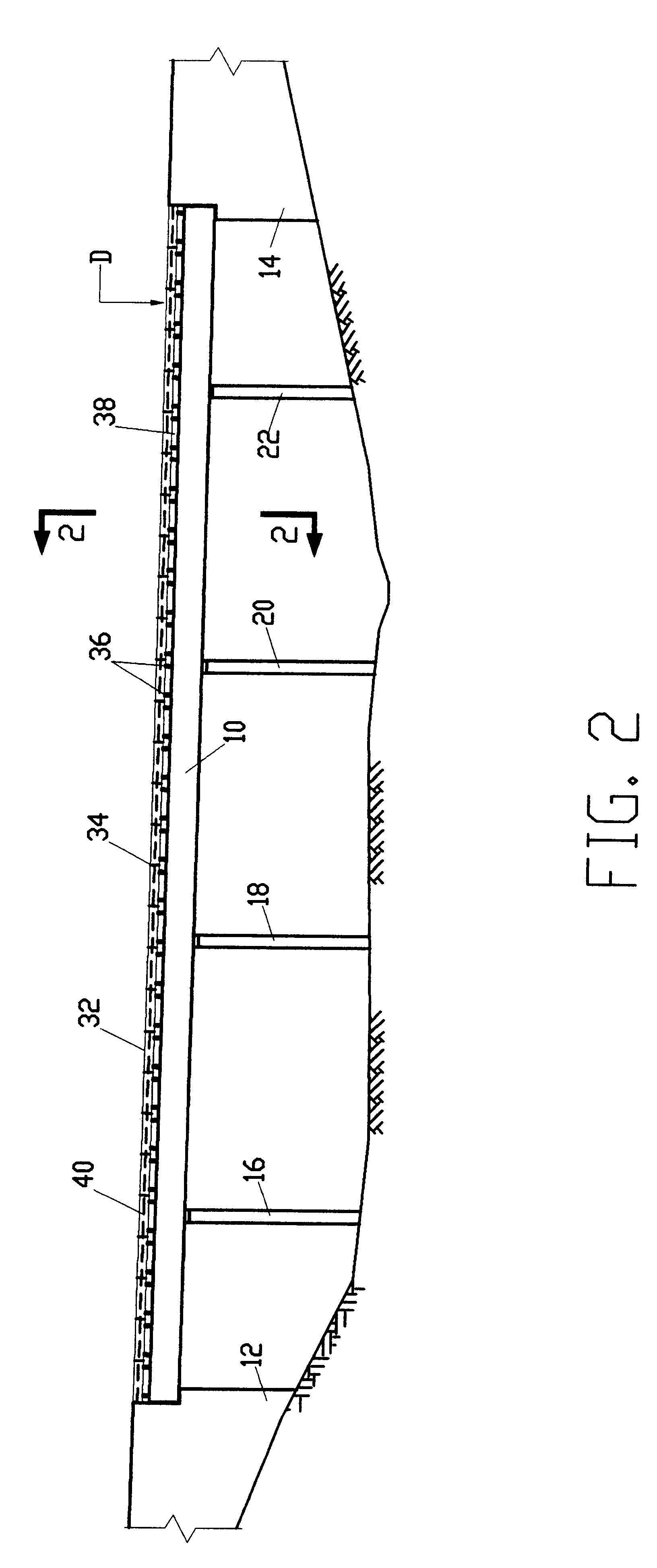
Method and System for Remotely Inspecting Bridges and Other Structures
ActiveUS20130216089A1Facilitating spatial integrationFacilitating automated damage detectionImage enhancementImage analysisJet aeroplaneOn board
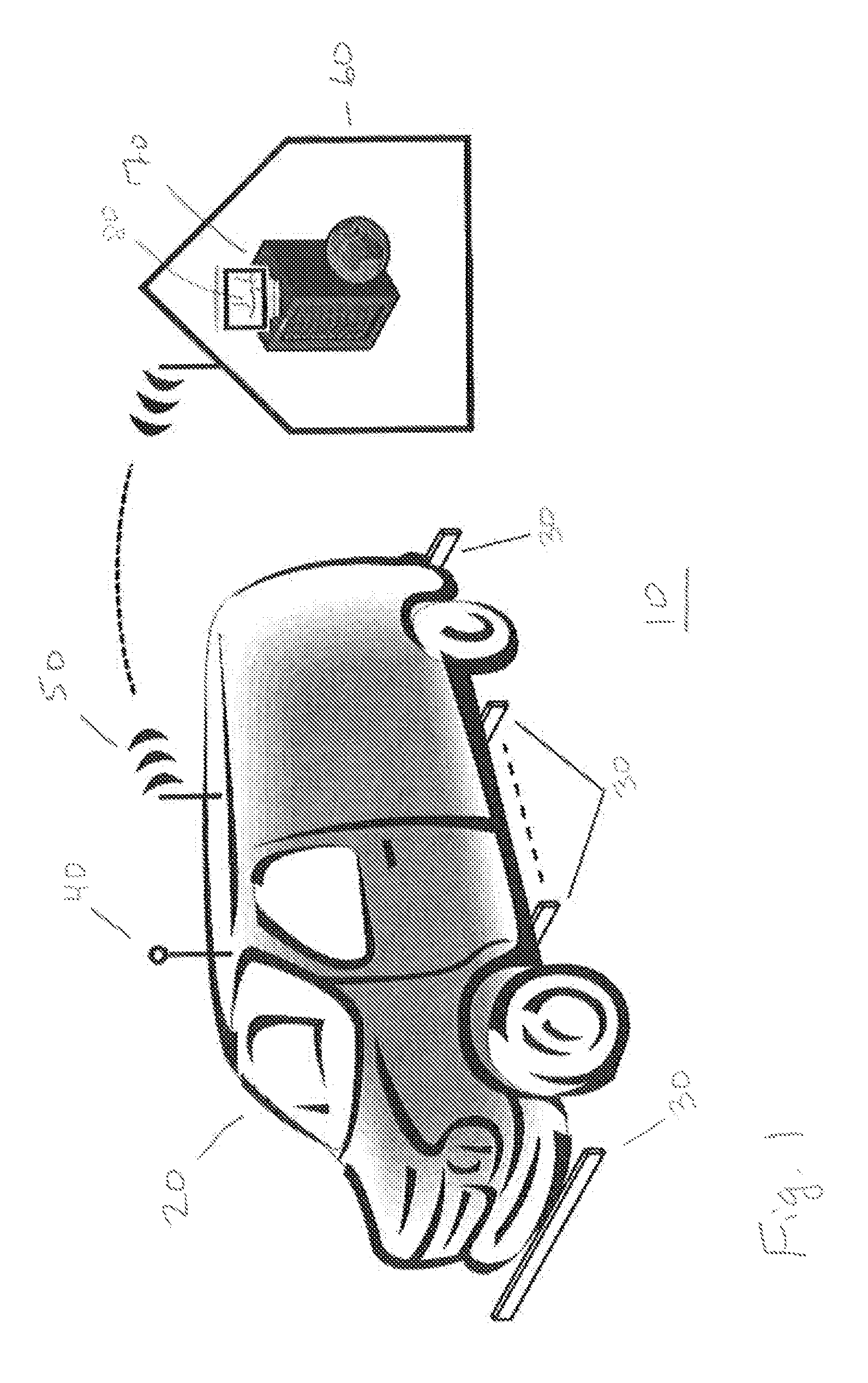
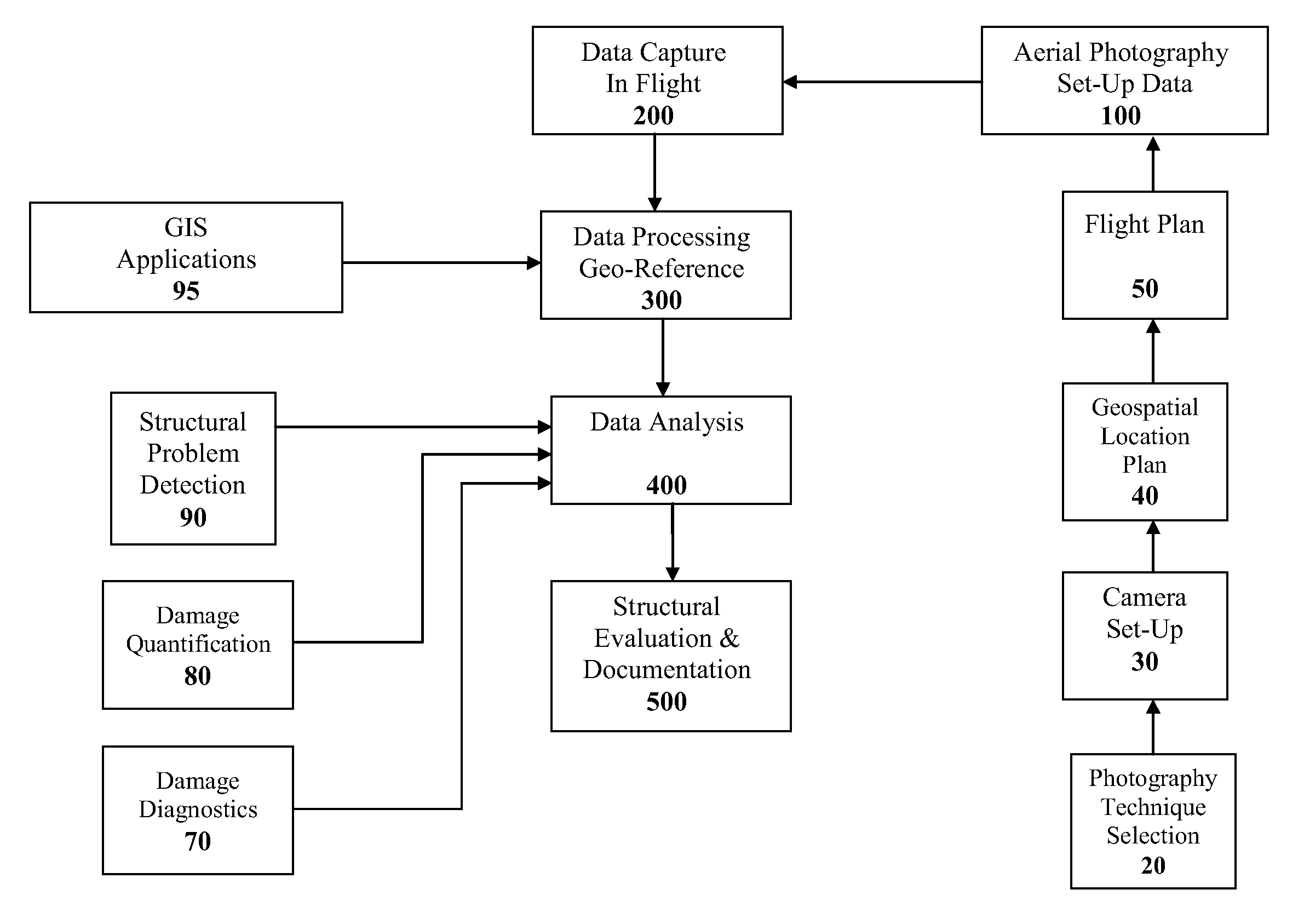
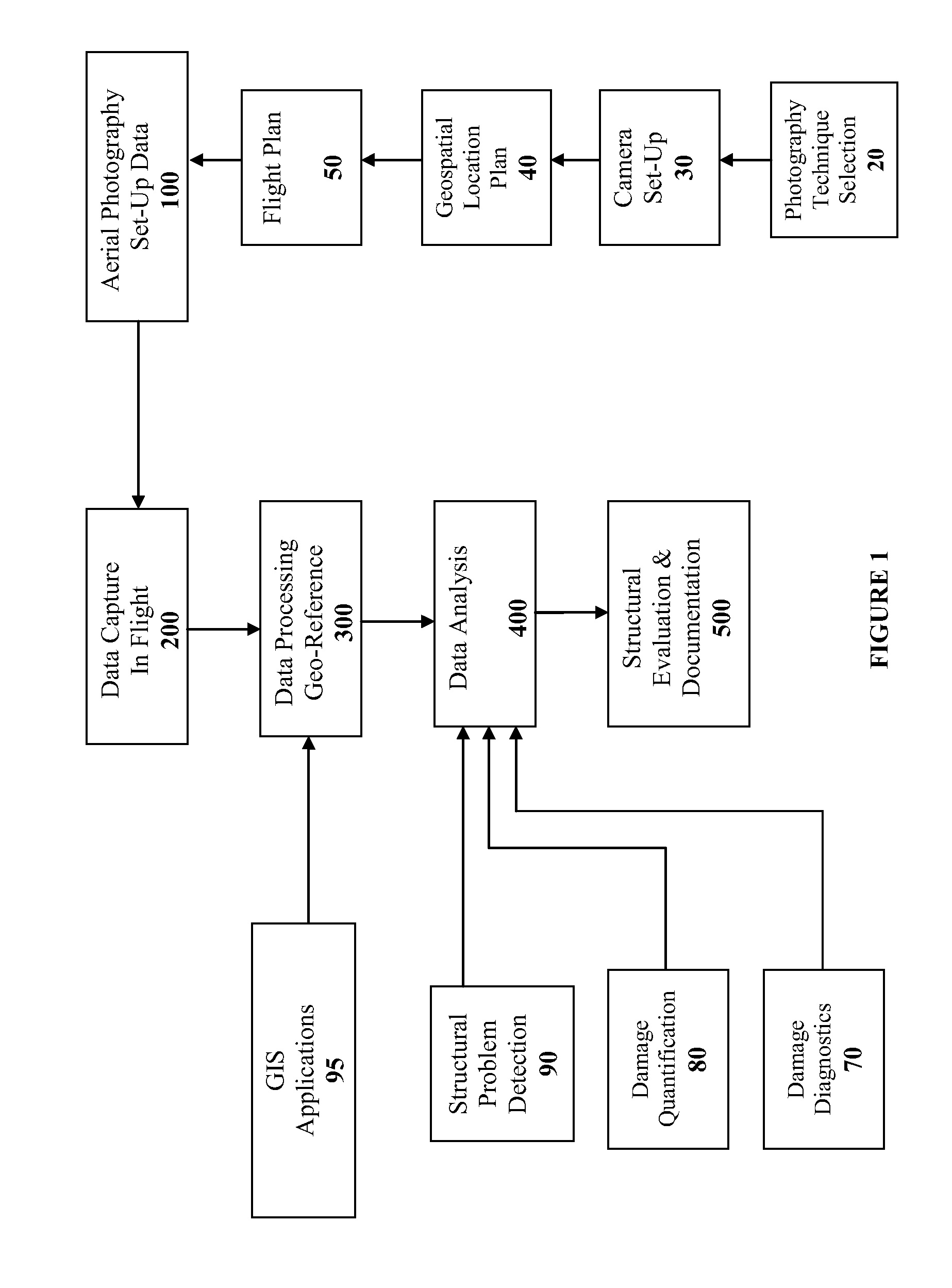
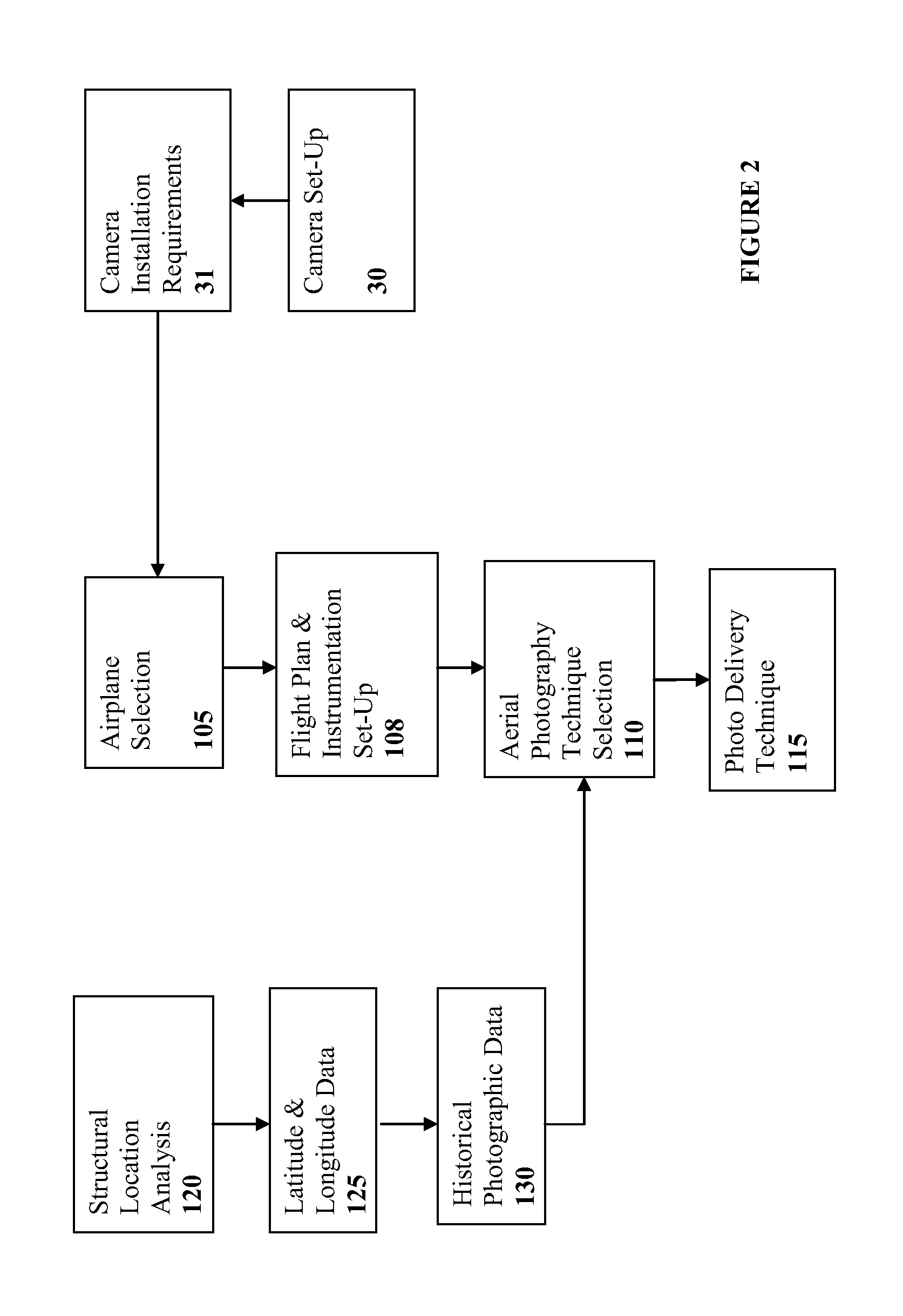
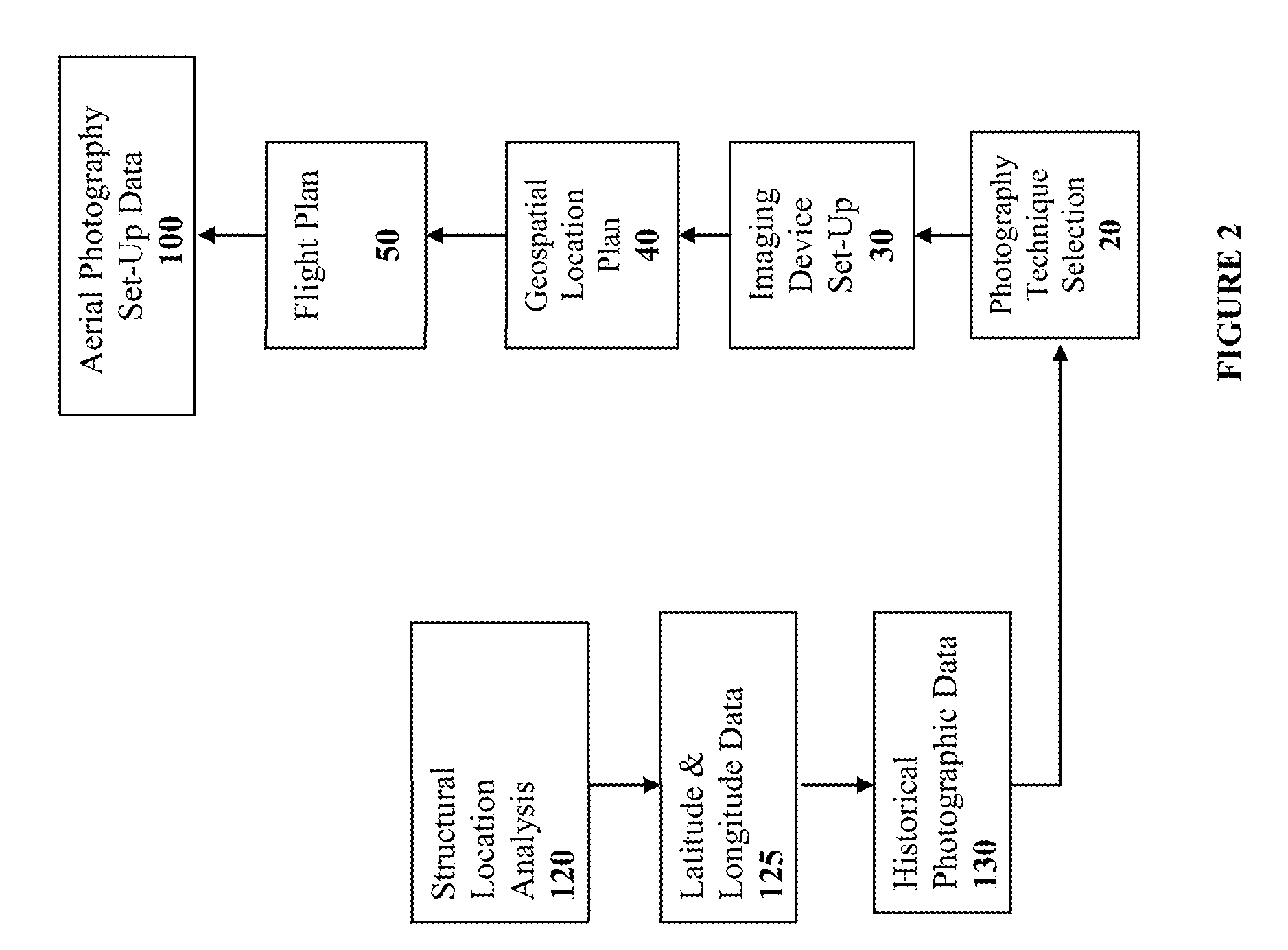
Spatially Integrated Small-Format Aerial Photography (SFAP) is one aspect of the present invention. It is a low-cost solution for bridge surface imaging and is proposed as a remote bridge inspection technique to supplement current bridge visual inspection. Providing top-down views, the airplanes flying at about 1000 feet can allow visualization of sub-inch (large) cracks and joint openings on bridge decks or highway pavements. On board Global Positioning System (GPS) is used to help geo-reference images collected and facilitate damage detection. Image analysis is performed to identify structural defects such as cracking. A deck condition rating technique based on large crack detection is used to quantify the condition of the existing bridge decks.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
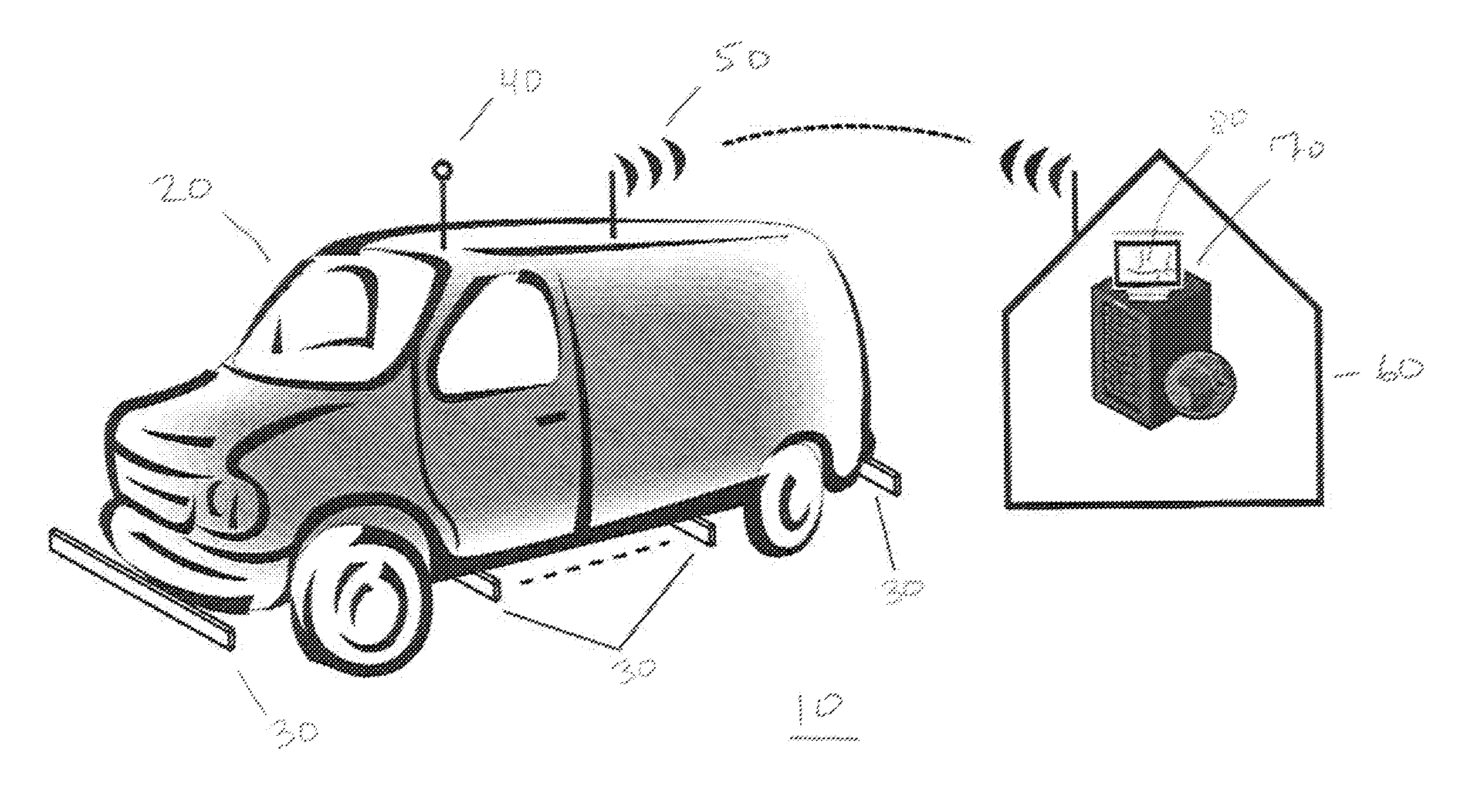
Roaming Mobile Sensor Platform For Collecting Geo-Referenced Data and Creating Thematic Maps
ActiveUS20130018575A1Improve securityTraffic can be stoppedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlRebar corrosionBridge deck
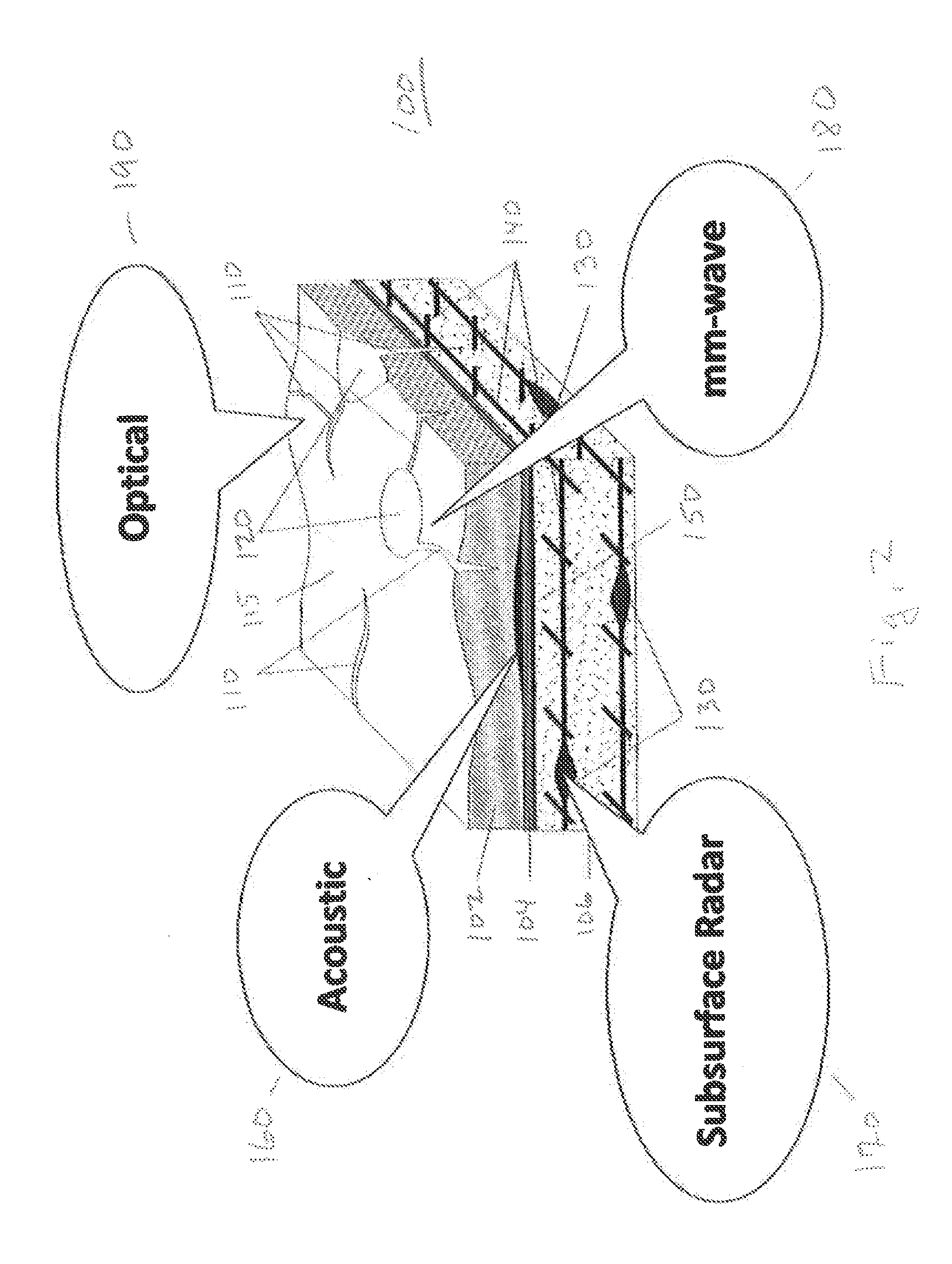
A roaming sensor system collects data on the condition of roads and bridge decks and identifies and maps defects, including cracks, potholes, debonding, tracking, delamination, surface ice, surface water, and rebar corrosion. Data are collected by a vehicle or a fleet of vehicles driven at normal traffic speeds. The vehicle is outfitted with sensors that collect data using acoustic surface waves, ground penetrating radar, mm wave surface radar, and / or video images. The data are transmitted to a control center for analysis and distribution.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Spatially integrated aerial photography for bridge, structure, and environmental monitoring
Spatially Integrated Small-Format Aerial Photography (SFAP is one aspect of the present invention. It is a low-cost solution for bridge surface imaging and is proposed as a remote bridge inspection technique to supplement current bridge visual inspection. Providing top-down views, the airplanes flying at about 1000 ft, can allow visualization of sub-inch (large) cracks and joint openings on bridge decks or highway pavements. On board Global Positioning System is used to help geo-reference images collected and allow automated damage detection. A deck condition rating technique based on large crack detection is used to quantify the condition of the existing bridge decks.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Travel way measurement system
ActiveUS8306747B1Maximize data samplingEnhance system resolutionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlSoftwareBridge deck
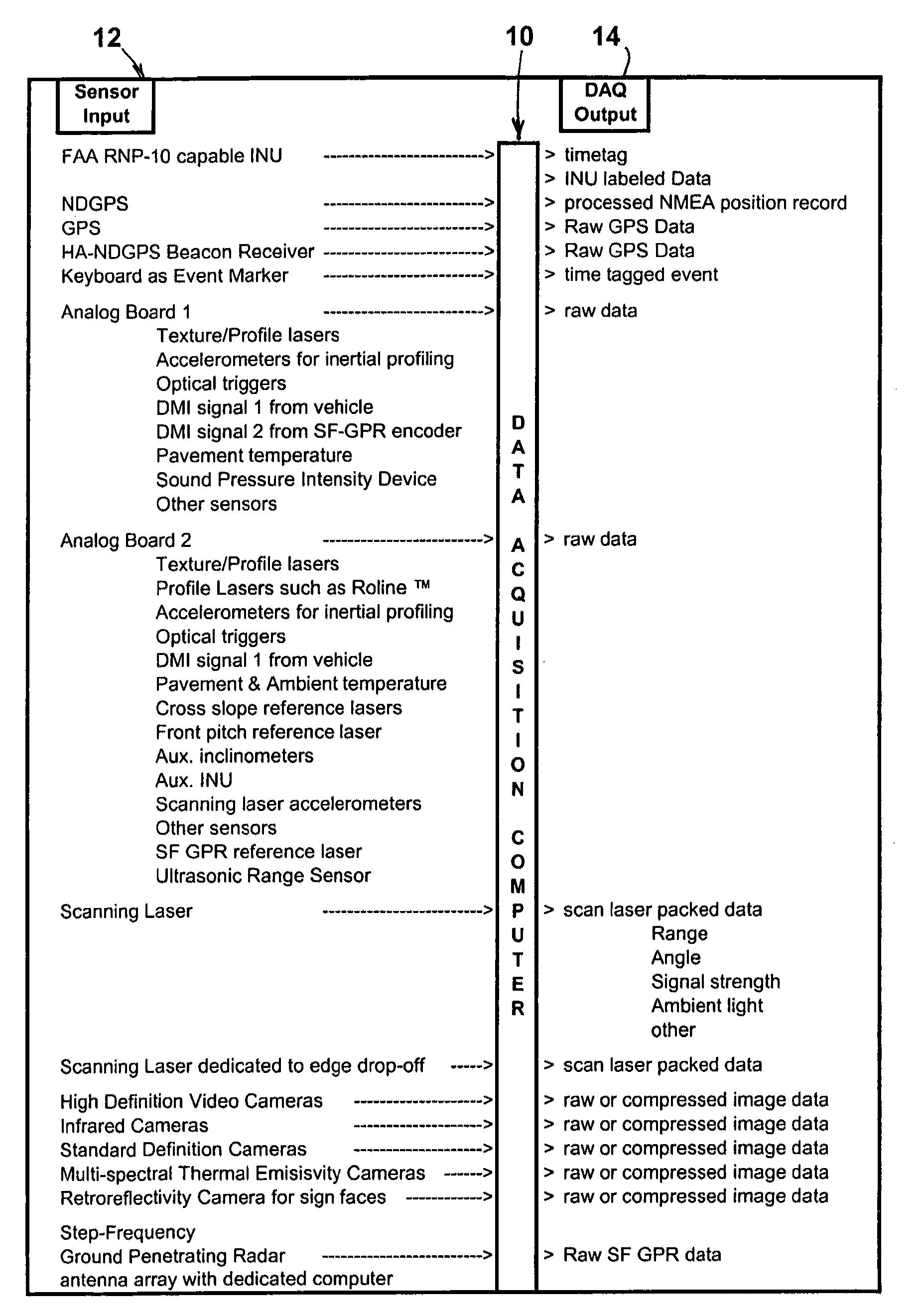
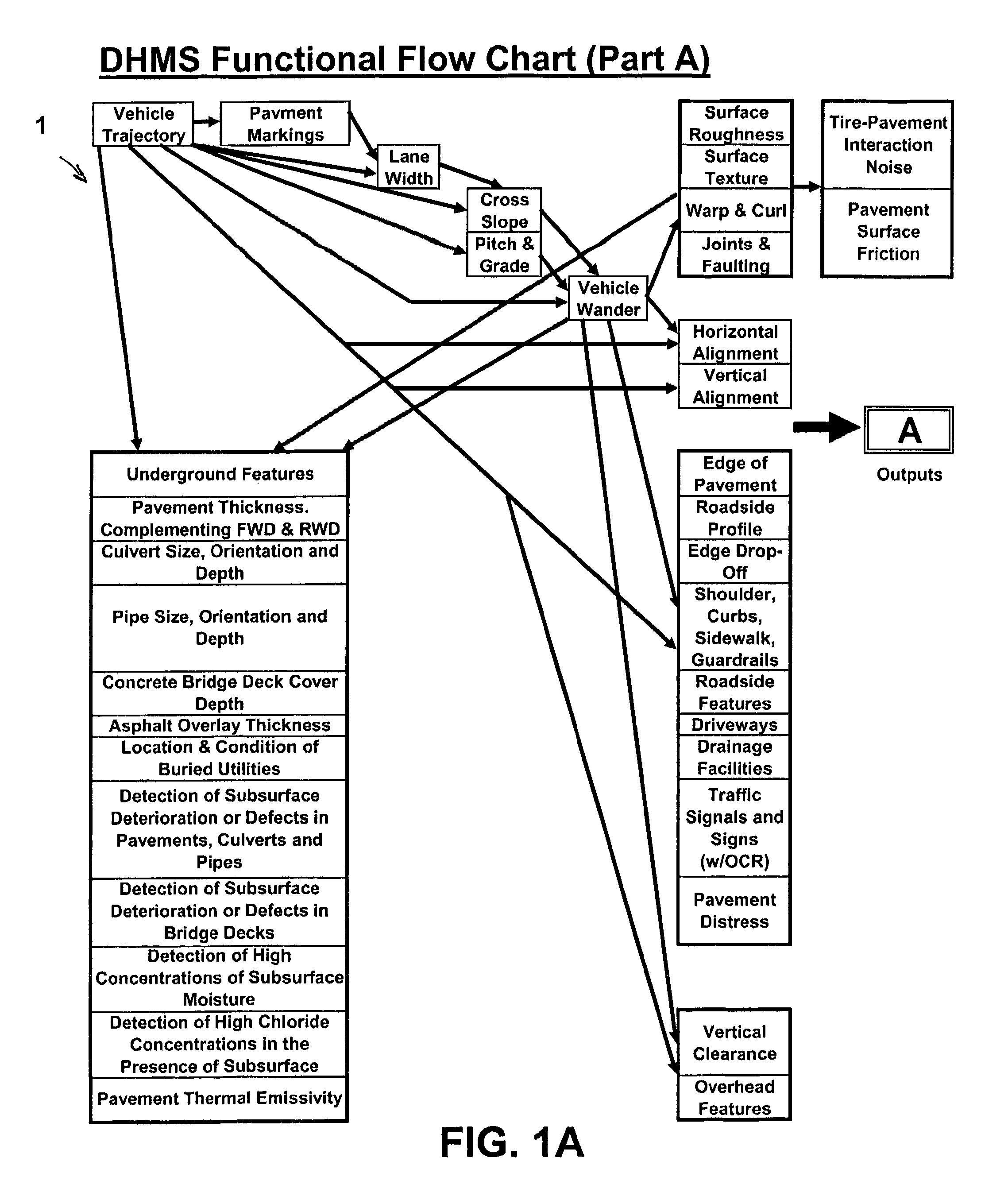
A mobile platform, sensors mounted on the mobile platform, computers, data storage devices, power system, data acquisition hardware, and software form a Travel Way Measurement System. The mobile platform with sensors mounted within and upon it, moves along a surface travel way and records data to determine an accurate location and geometry of the travel way surface, surface features, transverse profile and features along side the travel way surface, structures, signs, and other features above the travel way surface, and utilities, pavement thickness and properties, pavement condition, and bridge deck properties and condition below the travel way surface. The mobile platform and sensors can travel and collect data at up to 60 miles per hour or more. The data acquisition hardware and software protocols permit the synchronization of all the sensor outputs in the temporal and spatial domain or in any other domain resulting from numerical transformation of sensor outputs.
Owner:STARODUB
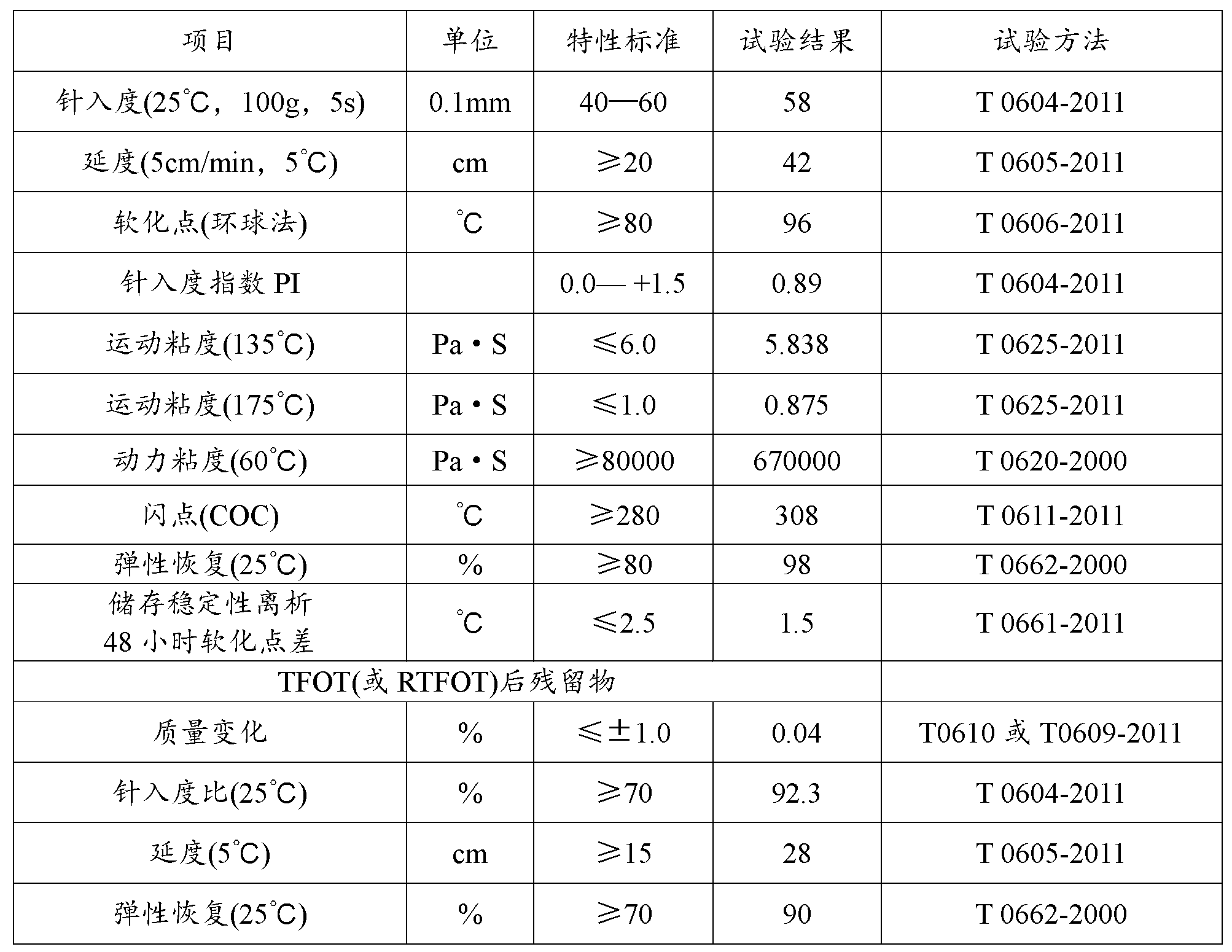
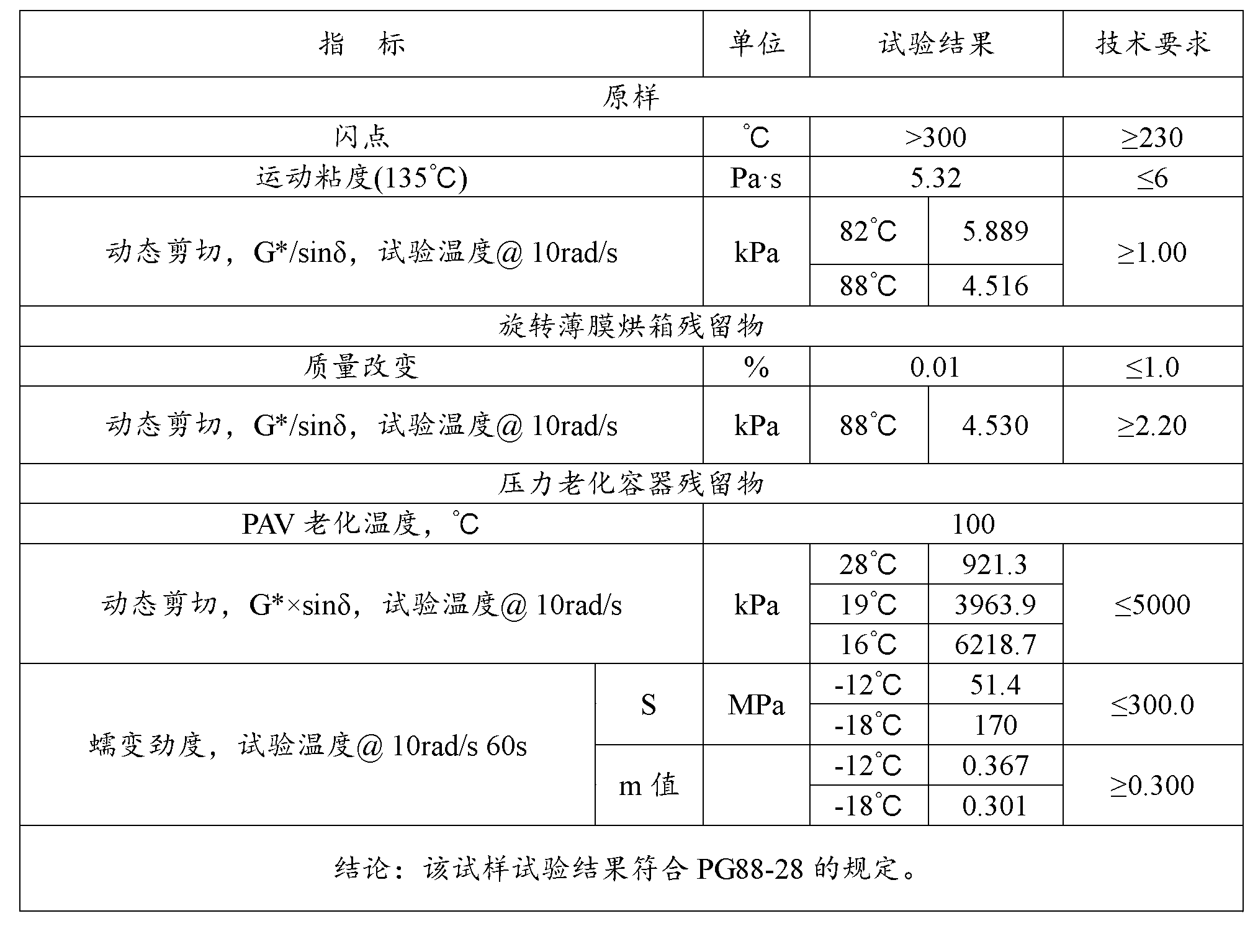
Asphalt modifier, modified asphalt and asphalt mixture
ActiveCN102838874AExcellent Adhesive PropertiesImprove low temperature 60°C viscosityIn situ pavingsBuilding insulationsRoad engineeringBridge deck
The invention belongs to the field of road engineering, and particularly relates to a hyperviscous and high-elastic asphalt modifier applicable to steel bridge deck pavement. The asphalt modifier comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-10 parts of junked tire rubber powder, 3-10 parts of polyethylene wastes, 3-8 parts of styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer, 1-5 parts of styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer, 1-5 parts of terpene resin, 5-10 parts of solvent naphtha, and 0.3-0.7 part of alcohol ether carboxylate adhesion agent. In addition, a modified asphalt and amodified asphalt mixture are prepared on the basis of the modifier, the 60 DEG C dynamic viscosity of the modified asphalt prepared by applying the modifier can reach more than 300000Pa.s, and the performance grading reaches PG 88-28; and the asphalt mixture has favorable water stability, higher dynamic modulus, higher track dynamic stability and low temperature failure strain, and can resist complicated mechanics and temperature environment of a steel bridge deck.
Owner:山东高速交通建设集团股份有限公司
Method and system for remotely inspecting bridges and other structures
ActiveUS9036861B2Damage detectionIntegration damageImage enhancementImage analysisJet aeroplaneOn board
Spatially Integrated Small-Format Aerial Photography (SFAP) is one aspect of the present invention. It is a low-cost solution for bridge surface imaging and is proposed as a remote bridge inspection technique to supplement current bridge visual inspection. Providing top-down views, the airplanes flying at about 1000 feet can allow visualization of sub-inch (large) cracks and joint openings on bridge decks or highway pavements. On board Global Positioning System (GPS) is used to help geo-reference images collected and facilitate damage detection. Image analysis is performed to identify structural defects such as cracking. A deck condition rating technique based on large crack detection is used to quantify the condition of the existing bridge decks.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
A kind of steel truss bridge and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN102277825AImprove stabilityImprove securityTruss-type bridgeBridge structural detailsBridge deckEngineering
The invention discloses a steel truss bridge and a method for fabricating the same. The steel truss bridge comprises a steel box girder bridge deck, a main truss composed of two steel trusses, and a steel portal frame. The steel truss comprises an upper chord member, a lower chord member, and a web member which is connected with the upper chord member and the lower chord member through bolts. A sidewalk bracket is arranged outside each steel truss. The lower chord member is connected to the steel box girder bridge deck and the sidewalk bracket, respectively. Besides, the two steel trusses are connected through the steel portal frame. During fabrication, all the sections of the steel trusses, the steel portal frame and the bridge deck are independently fabricated, respectively; all the sections of the upper and lower chord members of the steel truss are pre-assembled circularly with the corresponding web members, and all the sections of the steel box girder bridge deck are pre-assembled with the corresponding lower chord members by an orthotectonic method, respectively; and the steel portal frame is pre-assembled with the steel trusses. The steel truss bridge disclosed by the invention completely meets the design requirements so that the stability and safety factor of the bridge can be enhanced; and by employing the fabricating method, positioning is accurate so that the risks during the field assembling can be reduced; and the construction period can be shortened.
Owner:JIANGSU JINGHU HEAVY IND
Piezoresistance/piezoelectric composite material, manufacturing method of material, sensor utilizing material and manufacturing method of sensor
InactiveCN102924020AImprove structural toughnessGood compatibilityConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyFiberBridge deck
The invention relates to a piezoresistance / piezoelectric material system and production and application methods of the piezoresistance / piezoelectric material system. The piezoresistance / piezoelectric composite material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of cement, 105-500 parts of micro / nano grade piezoelectric ceramic powder body, 10-30 parts of fly ash, 15-50 parts of water, 0.01-2 parts of super plasticizer, 0.1-10 parts of toughness fiber and 0.01-15 parts of conductive fillers. A sensor utilizing the piezoresistance / piezoelectric composite material comprises a piezoresistance / piezoelectric composite material layer, wherein the upper surface and the lower surface of the piezoresistance / piezoelectric composite material layer are respectively provided with one electrode, the piezoresistance / piezoelectric composite material layer and the electrodes are coated in a package shell, the upper electrode and the lower electrode are connected by an electromagnetic shielding wire passing through the package shell, and the sensor is arranged between a bracket and a support bridge deck unit or is embedded in the support bridge deck unit. The sensor utilizing the material, disclosed by the invention, has intrinsic structure toughness and synchronous monitoring capability of covering a whole-frequency-domain static / dynamic traffic and structure parameters.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
High-polymer modified pitch, its water-proof roll material and use thereof
ActiveCN101070434AImprove standardsHigh standard waterproof functionOther chemical processesRoof covering using flexible materialsPolymer modifiedCrack resistance
The invention provides a polymer modified asphalt, and the weight of the components comprising as follows :45-55% matrix asphalt, 4 - 8% blend oil, 12 - 14% of SBS ,5-9 % APAO, 2-7% of High-temperature improvement and 15-20% filler. It also offers polymer modified asphalt, which made of waterproof membrane and the railway bridge, highway bridge deck waterproofing project applications. The invention of these waterproofing membrane have a high standard of waterproof function, it can withstand high intensity of railway bridge and particularly high stress dynamic load .It also have excellent performance on water-resistance, high and low temperature resistance, adhesion, crack resistance, fatigue resistance and other aspects .it can be used for railway bridge and the road deck waterproofing works.
Owner:JINZHOU DONGFANG YUHONG BUILDING MATERIALS +1
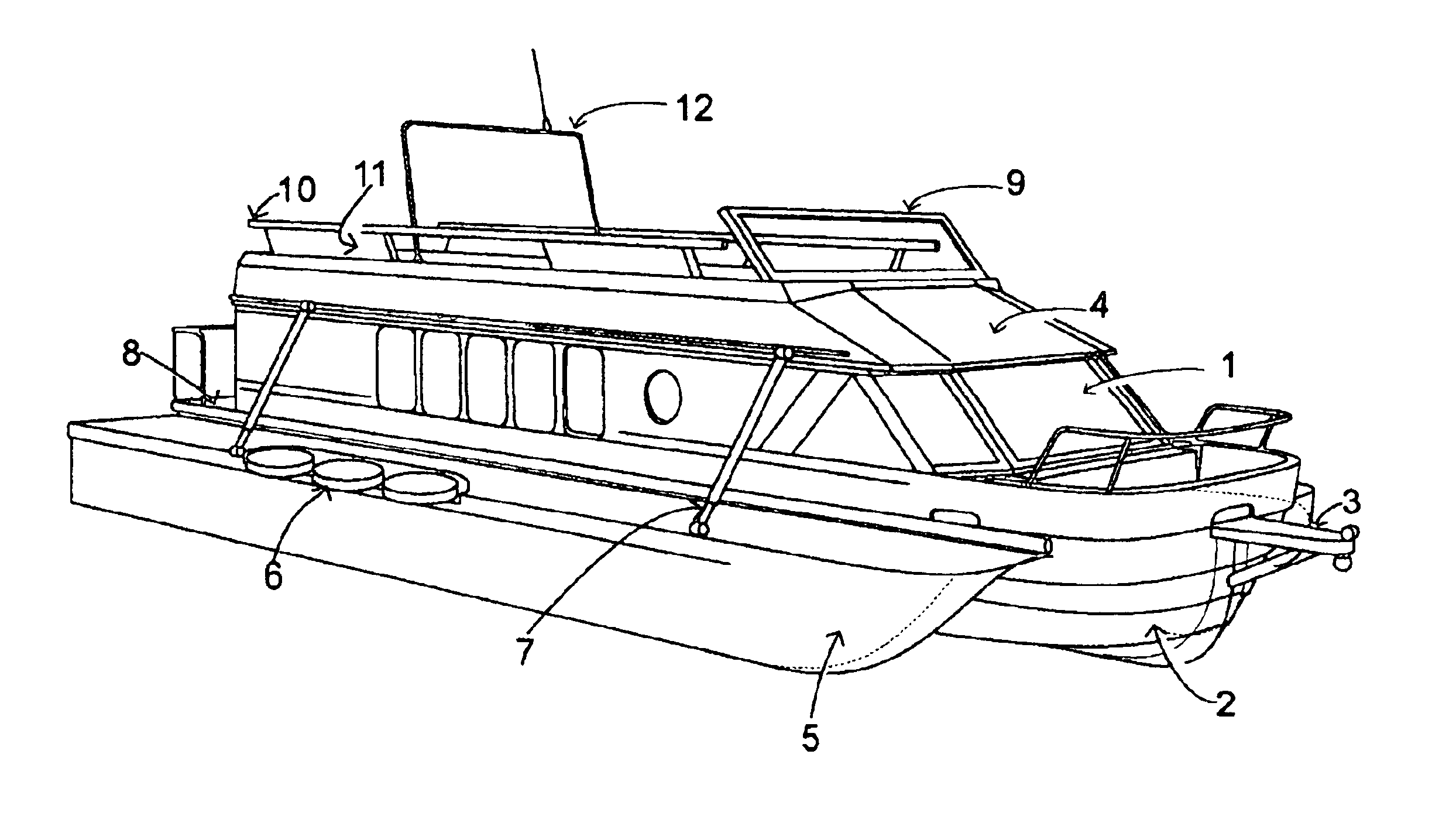
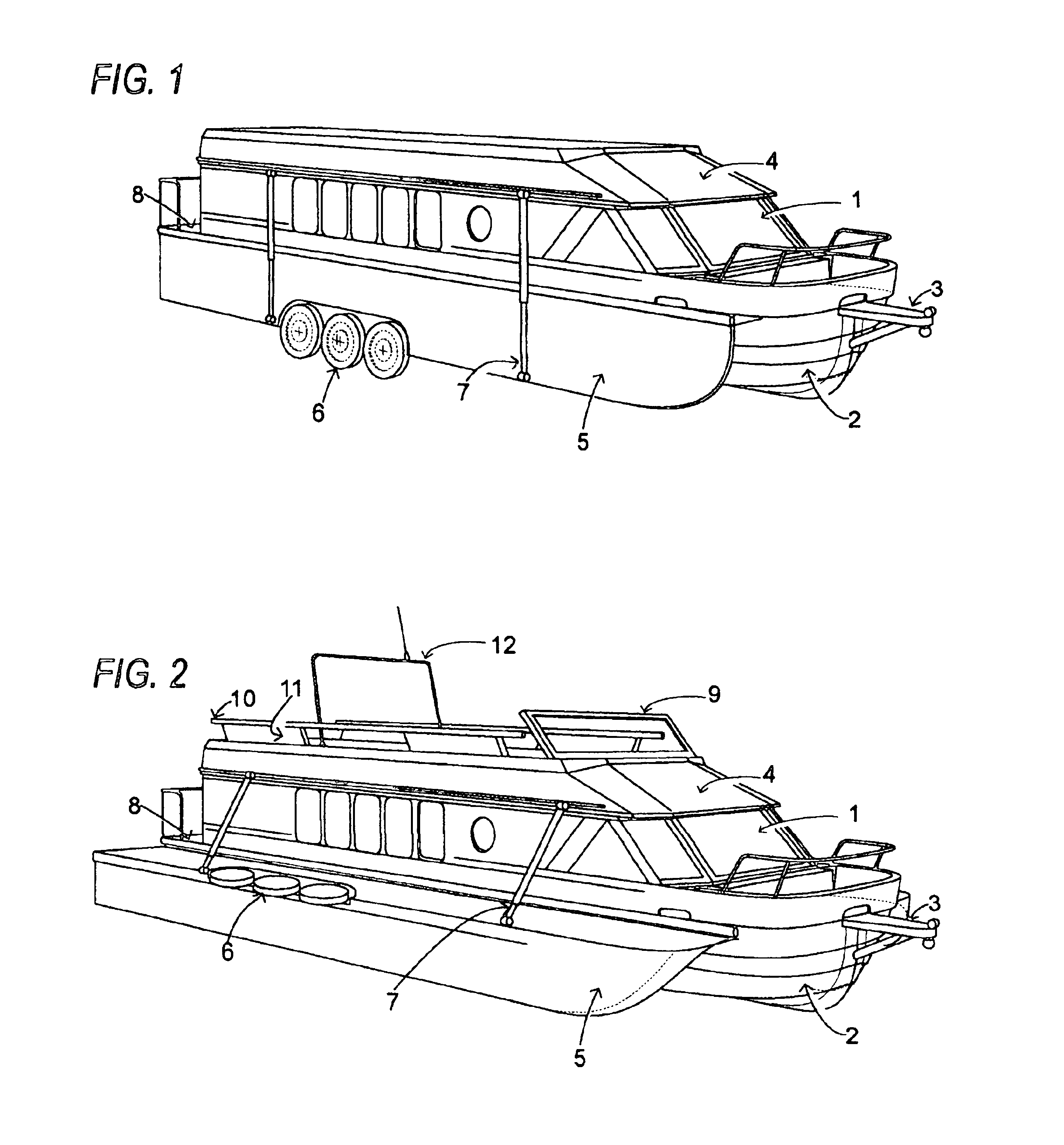
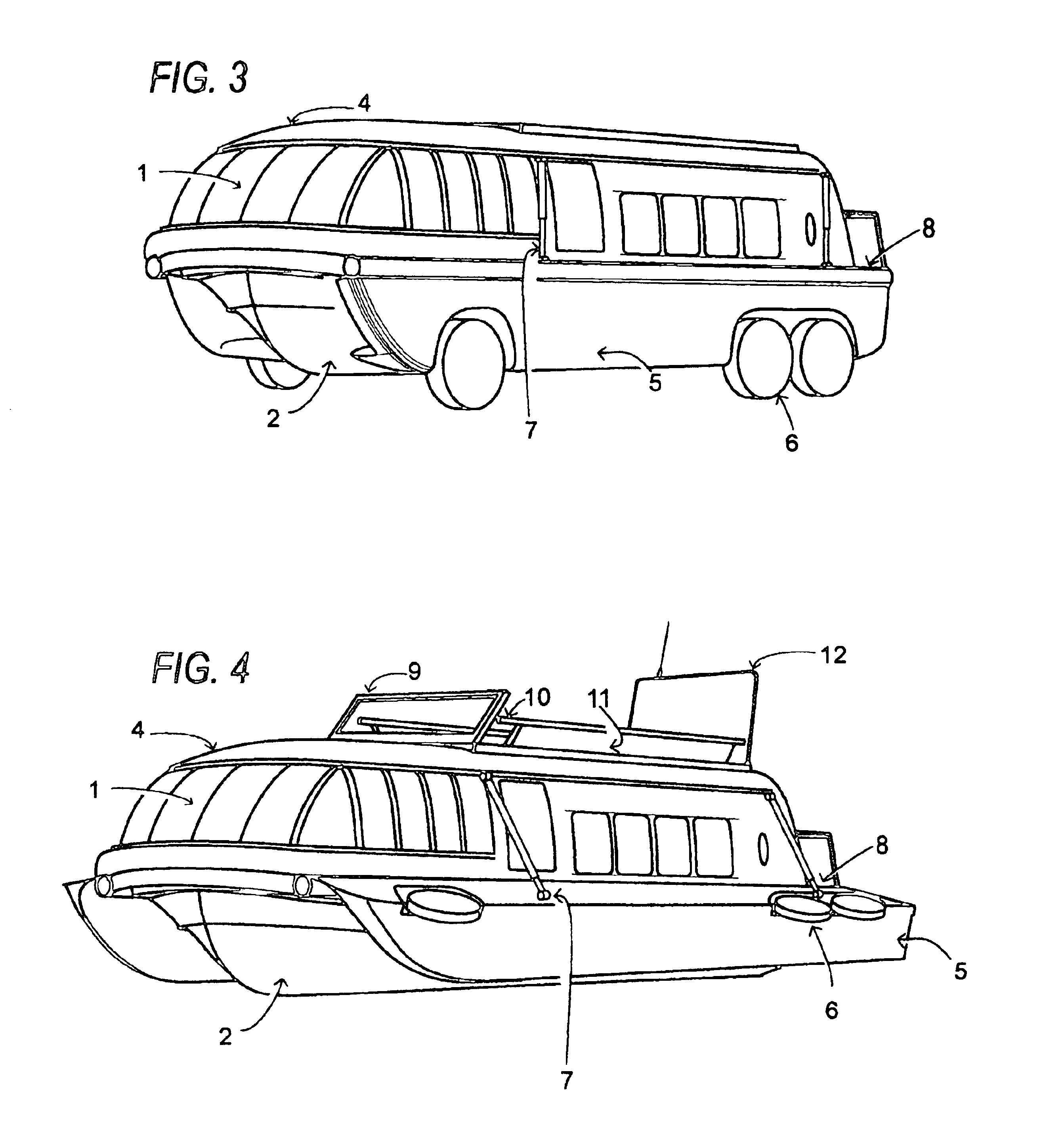
Amphibious recreational vehicle
InactiveUS6840825B1Easy to planEliminate parasite dragAmphibious vehiclesVehicle with living accommodationNacelleWater vapor
An amphibious recreational vehicle (motorhome, trailer, SUV, and the like) of conventional RV height, width, and length restricted dimensions necessary to travel on highways and roads, and which upon entering the water, the bottom of the vehicle expands outwardly and upwardly to form a fast planing, wide-beam, ground effects cathedral type double-tunnel hull. The hull makes use of a dynamic air cushion to augment the planing of the hulls, owing to the ground effect created by compression of the ram air stream (and water vapor) rushing through the two tapered tunnels separating the three hulls. The wheels of the vehicle are simultaneously raised out of the water to eliminate parasite drag. The resultant hull is substantially wider than the cabin, providing substantial ocean-going stability for the craft. The folded elements incorporated within the cabin rooftop, raise upward to form a traditional yacht flying bridge, complete with a windshield, steering station, seating, mast, and safety rails. The resultant watercraft closely approximates the off-shore speed, seaworthiness, performance, stability, cabin space, main deck space, and elevated flying bridge deck attributes of conventional yachts. And when on land, the craft is a fully functioning traditional recreational vehicle suited for fast highway travel, driving about towns, staying in RV parks, and camping in the wilderness. This amphibious recreational vehicle is an interrelated component divided from the inventor's previous Comprehensive Vehicle Construction And Hybrid Electric Drive System application.
Owner:MESSANO FR
High-ductility low-shrinkage anti-cracking concrete for bridge deck pavement and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of concrete structural materials, and discloses a preparation method for high-ductility low-shrinkage anti-cracking concrete for bridge deck pavement. The high-ductility low-shrinkage anti-cracking concrete for bridge deck pavement is characterized by comprising the following components in proportion: 135-155 kg / m<3> of water, a cementing material, 600-800 kg / m<3> of fine aggregate, 950-1150 kg / m<3> of coarse aggregate, 2.0-3.0 kg / m<3> of shrinkage-reducing ductility-increasing component,10-20 kg / m<3> of internal curing agent, 3.0-5.0 kg / m<3> of water reducing agent and hybrid fiber, wherein the cementing material comprises 320-380 kg / m<3> of cement and 20-40 kg / m<3> of coal ash in proportion; and the hybrid fiber comprises 0.8-1.0 kg / m<3> of organic polymer fiber and 40-50 kg / m<3> of steel fiber in proportion. According to the concrete and the preparation method for the concrete disclosed by the invention, reinforcement meshes on the bridge deck pavement layer can be cancelled.
Owner:SICHUAN DEPT OF TRANSPORTATION HIGHWAY PLANNING PROSPECTING & DESIGN RES INST
Method for weighing vehicles crossing a bridge
A method for weighing vehicles moving on a bridge deck pavement is provided. At least one vibration sensor is mounted on a lower side of the pavement to sense low frequency pavement vibrations generated by moving vehicle wheels and propagated in waves in the pavement. Vibration sensor output signals are provided to a computing device. Sensed vibration energy rate is computed and, with signals from vibration sensors mounted at two locations separated by a known longitudinal distance, vehicle speed is also computed. The weight of the vehicle is determined as the product of a calibration coefficient and the ratio of sensed vibration energy rate to velocity. Using vibration sensor signals indicative of wheel generated vibrations in the very near field and summing vibration energy rates computed from these signals during vehicle passage over the vibration sensors the weight of individual vehicles is computed when other moving vehicles are present.
Owner:TATOM FR B +1
Fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite panel
InactiveUS20080078038A1Increased durabilityHigh fatigueSynthetic resin layered productsBridge structural detailsGlass fiberFilling materials
A fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite panel is described. One use of the panel is to construct bridge decks although the panel may have several other uses. It comprises two flat plates formed of commingled glass fiber reinforced polypropylene secured in spaced parallel relationship to a core. The core is formed by either two corrugated sheets interconnected together along connecting ridge sections or else by a plurality of elongated FRP channel members disposed transversely between the flat plates. The corrugated sheets or channel members form hollow core spaces between the two flat plates and the core material and these hollow spaces are filled with a filler material to add stability to the panel. Both the flat plates and the core material are formed of commingled glass fiber reinforced polypropylene (FRP).
Owner:BORAZGHI HOSSEIN
Pavement structure and testing device for bridge deck pavement bonding interface shearing-resistance characteristic
InactiveCN101620054AEffective simulationRational engineering designMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesStress conditionsBridge deck
The invention relates to a pavement structure and a testing device for bridge deck pavement bonding interface shearing-resistance characteristic, which are based on mechanics principle and indoor test, effectively simulate road surface and simulate stress conditions, can realize continuous change with 0-80 degrees of shearing angle, meet needs of different working conditions and are suitable for the design and research of the pavement structure, the indoor test and engineering test. The testing device comprises an upper part and a lower part, each part comprises a bearing board, a rolling shaft, an arc base, a semi-circular clamp, an internal collet and a clamp fixing device. The whole device also comprises an angle dial scale and an angle pointer and other attached parts which are used for indicating the size of the angle. A square testing piece is arranged in the internal collet, the semi-circular clamp and the base can rotate relatively, after the shearing angle is set, the clamp and the base are fixed by the clamp fixing device. The horizontal surface of the other side of the base is contacted with the bearing board in a rolling way by the rolling shaft, so as to lead the device loading to generate vertical displacement and to move horizontally at the same time.
Owner:张磊
Single plate force-bearing reinforcing method of hollow slab bridge
InactiveCN103061271AAvoid destructionImprove reliabilityBridge erection/assemblyBridge strengtheningWhole bodyBridge deck
The invention relates to a single plate force-bearing reinforcing method of a hollow slab bridge. The single plate force-bearing reinforcing method includes that the original bridge deck pavement is shoveled, hinge joint concrete is removed, defects and cracks of the original hollow slab bridge beam body are processed, strip-shaped steel plates are transversely pasted on the upper surface and the lower surface of the hollow slab bridge in the longitudinal bridge direction at certain intervals, split screws penetrate through drilled holes at the hinge joint position, a counter-force frame is arranged, a wedge-shaped block is embedded between the counter-force frame and the steel plates, and the steel plates are pressurized and pasted in sealing mode and then are positioned and fixed; the counter-force frame is demounted after sticky steel glue is cured; cavities in beam joints are subjected to pressure grouting, shear reinforcements are placed into the top surface of a hollow slab, a reinforcement mesh is reconstructed, and the bridge deck reinforcement mesh and the implanted reinforcements are connected in binding or point welding mode to form a whole body; steel fiber reinforced concrete is poured and waterproof coatings are sprayed; and bituminous concrete is paved. The single plate force-bearing reinforcing method improves transverse load distribution, steel plate pasting reliability and bridge integral force-bearing performance on the premise of preventing hollow slab beam body damage, not changing a structural force-bearing system and not interrupting the traffic.
Owner:CHINA MAJOR BRIDGE ENERGINEERING
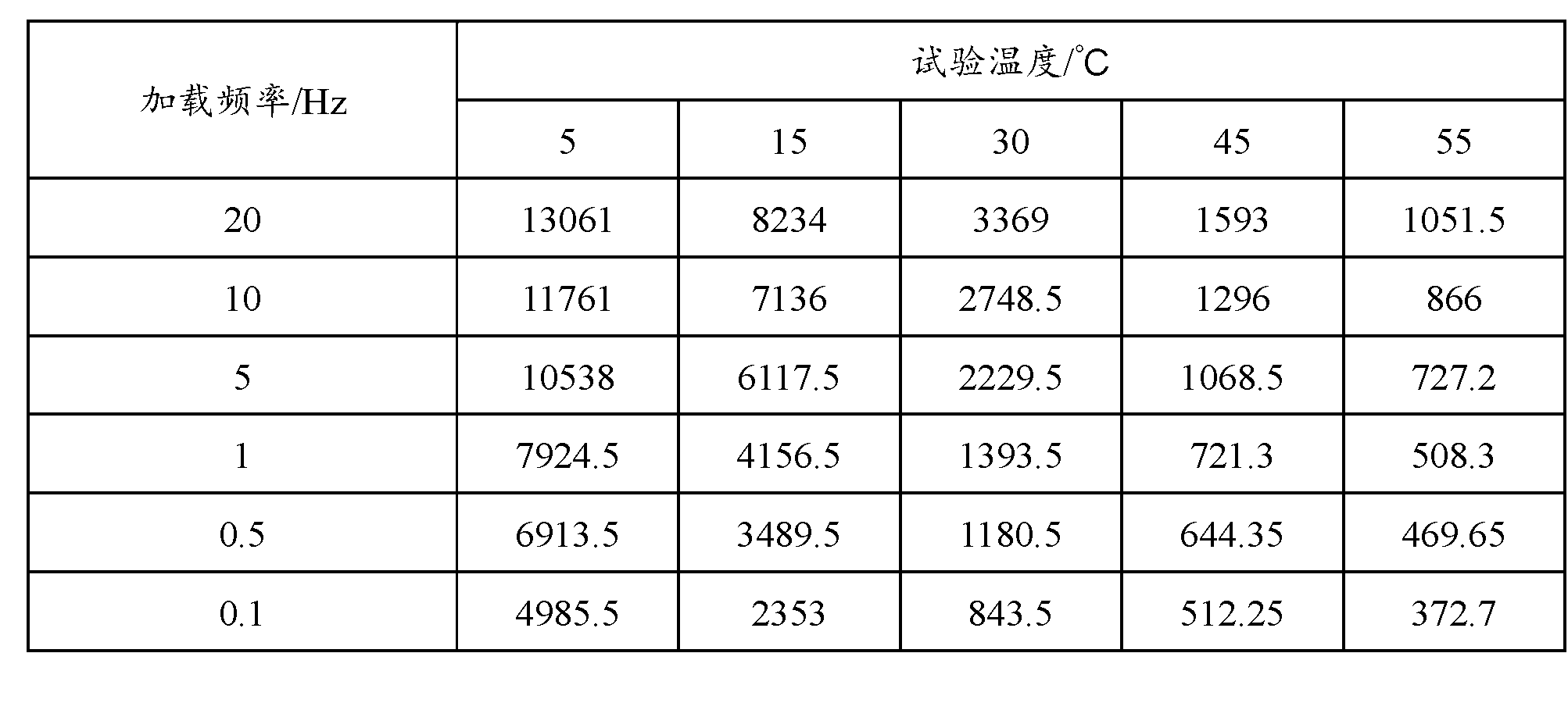
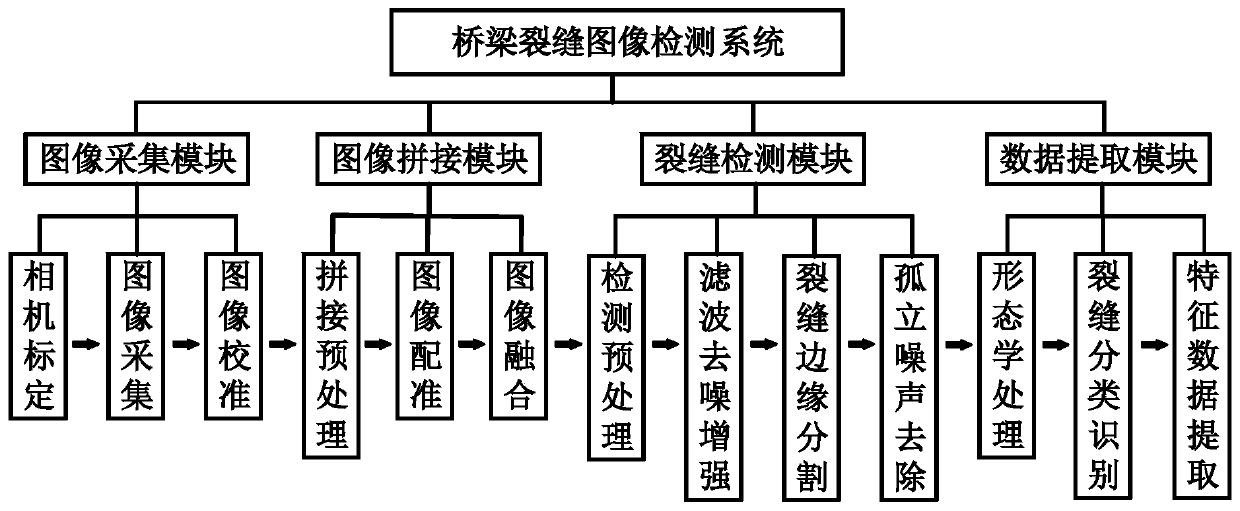
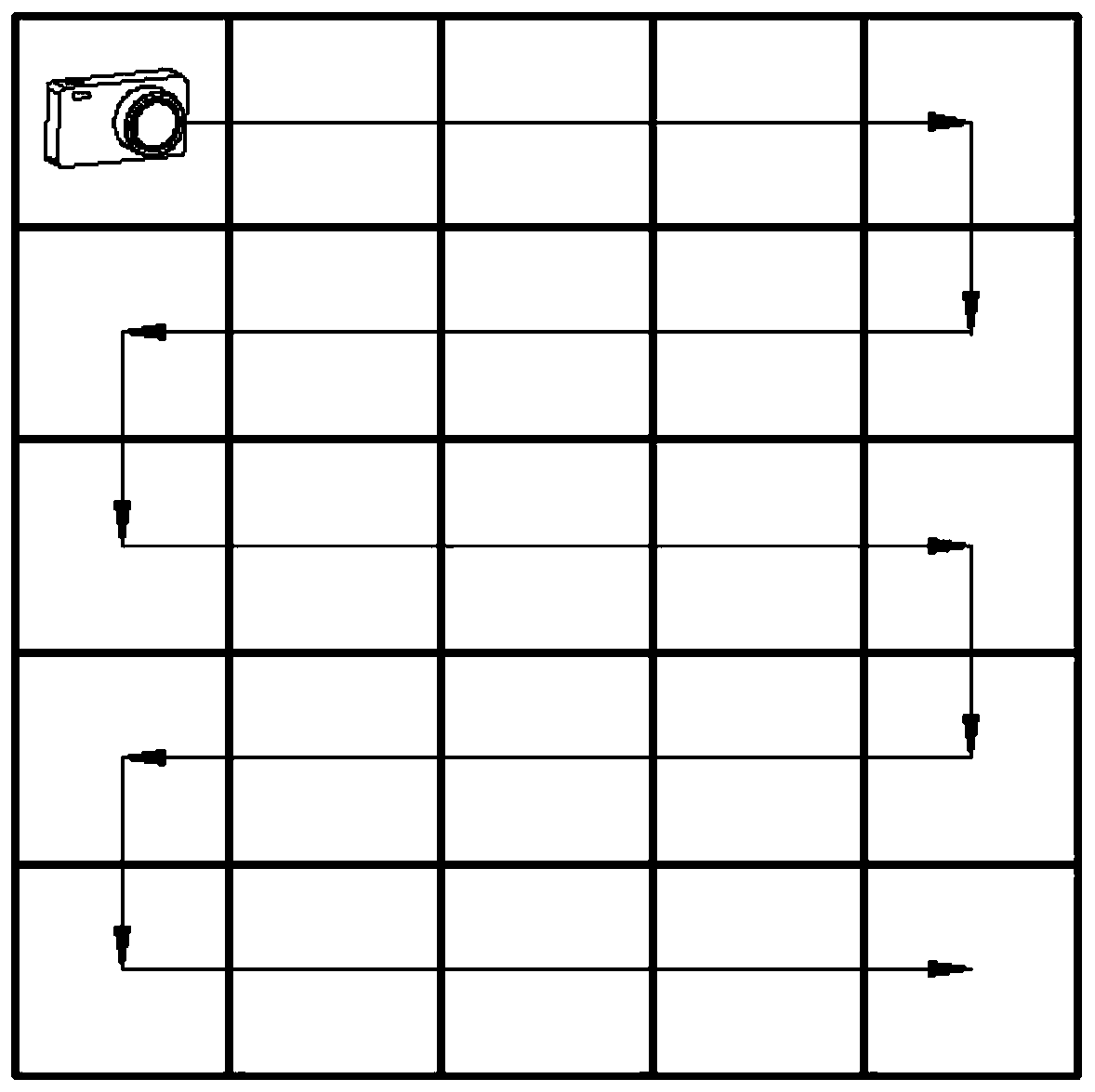
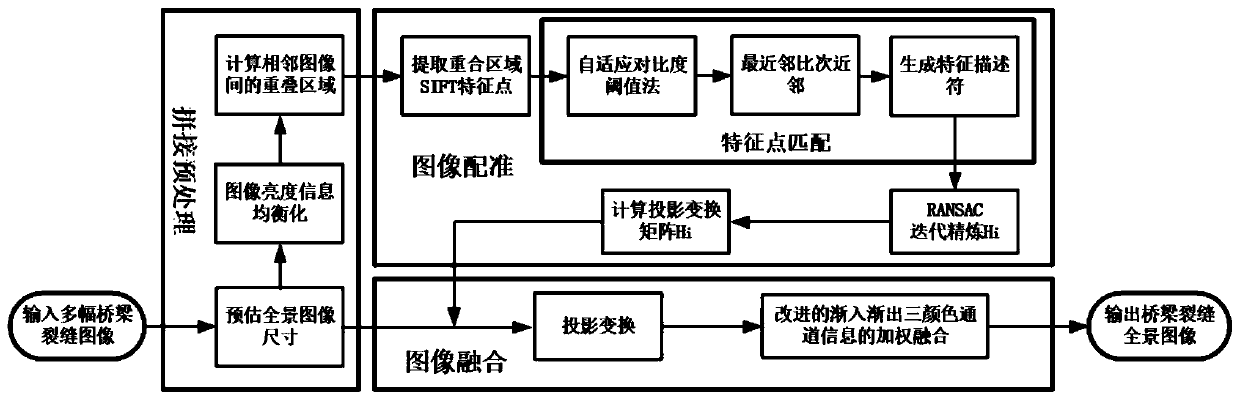
Bridge crack detection method
ActiveCN110378879AImprove mobilityIncrease flexibilityImage enhancementImage analysisTerrainBridge deck
The invention discloses a bridge crack detection method. Due to the fact that manual marking has certain subjectivity, the pavement crack detection precision depends on experience knowledge of experts, and experience lacks objectivity in quantitative analysis. The method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting images of a detected bridge floor one by one to obtain a bridge floor image set; 2,splicing images; 3, detecting crack; 4, extracting crack parameter. According to the invention, the image acquisition and processing technology replaces human eyes to complete automatic nondestructive detection of the bridge crack, and has very important practical significance for research of the bridge crack detection technology in a complex terrain environment. On one hand, the construction safety is enhanced, and on the other hand, the operation maneuverability and flexibility are improved. According to the invention, fidelity splicing of multiple groups of bridge deck images is realized,the image splicing precision and efficiency are improved, a working foundation is laid for subsequent bridge crack image detection, and a technical reference is provided for image splicing detection in other fields.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
High-performance thermosetting epoxy resin adhesive for roads and bridges and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103160234AIncreased durabilityFast curing reactionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesEpoxyBridge deck
The invention provides a high-performance thermosetting epoxy resin adhesive for roads and bridges. The adhesive comprises a component A and a component B, wherein, the component A comprises the following components in parts by mass: 100 parts of epoxy resin, 25 to 33 parts of flexibilizer, and 5 to 10 parts of diluent; the component B comprises the following components in parts by mass: 80 to 120 parts of curing agent, 5 to 10 parts of accelerant, 0.5 to 2 parts of coupling agent, 1 to 10 parts of reinforcing agent, and 0.2 to 0.5 part of antifoaming agent; and the ratio of the component A to the component B is 100:100-100:120. According to the adhesive, a flexible long-chain aliphatic amine serving as the curing agent has a curing reaction with the epoxy resin to form a solid crosslinking structure, so that the epoxy resin adhesive is high in adhesion capability and water resistance; The toughness of the epoxy asphalt adhesive is improved by adopting the soybean oil-based polyurethane to be adapted to the flexibility of a steel plate, and the soybean oil-based polyurethane containing massive hydroxyl has good compatibility with the epoxy resin. The adhesive is applicable to adhesion and waterproofing of steel bridge decks, viaducts, cement concrete bridge decks, tunnels, expressways and other decks. The invention discloses a preparation method of the high-performance thermosetting epoxy resin adhesive.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
High-iron special flame-resistant polyurethane waterproof coating and preparation method thereof
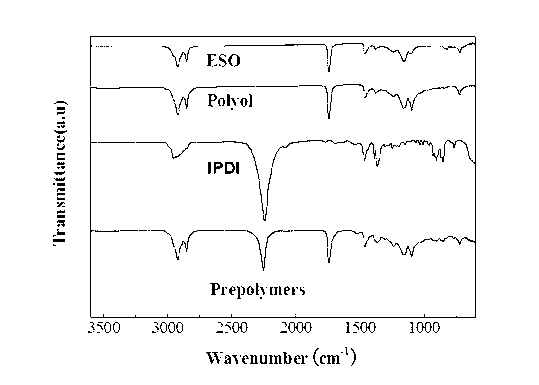
InactiveCN101619193ALow volatilityLow vapor pressureFireproof paintsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPrepolymerHigh intensity
The invention discloses a high-iron special flame-resistant polyurethane waterproof coating and a preparation method thereof. The high-iron special flame-resistant polyurethane waterproof coating comprises an A component of an isocyanate group terminated polyurethane prepolymer and a B component of a dense cure-crosslinking agent. The prepared double-component high-strength flame-resistant polyurethane waterproof coating has tensile strength of 3.5-10MPa, at-break elongation of 450-600 percent and concrete interface boning strength greater than 2.5MPa and is used by uniformly mixing the A component and the B component according to a certain proportion and coating the mixture on a concrete waterproof plane to solidify into an integral waterproof coating with elasticity, firmness and durability. The coating is suitable for concrete ballast bridge floors and non-ballast bridge floors of high-iron passenger special line bridges and railway bridge culvert waterproof engineering and is suitable for the waterproofness of other buildings and constructions with higher requirements on waterproof performance.
Owner:天津市耀新科技发展有限公司
Mounting method for underbeam segment of large-stride steel box girder stayed-cable bridge
ActiveCN101476294AEasy to installThe installation method is safe and reliableBridge erection/assemblyCable stayedBridge deck
The invention relates to a large span steel box girder cable-stayed bridge tower lower beam segment mounting method, belonging to the bridge construction steel box girder construction technology field. The construction method comprises the steps: (1) setting up a masts type crane lifting tower area steel box girder by means of the upper crossbeam of the cable tower and the construction wind; (2) mounting the bridge deck crane in on the tower area steel box girder and lifting the first standard beam segment immediately adjacent to the tower area steel box girder; (3) mounting the bridge deck crane symmetrically on the mounted first standard beam segment, and starting the standard beam segment symmetrical hanging on both the river side and the bank side. The method in the invention achieves the advantages of simple, practical, safe, reliable, economic, convenient less limited by the construction condition, solves the problems in present large span steel box girder cable-stayed bridge construction process.
Owner:SICHUAN ROAD & BRIDGE GRP
Composite modified asphalt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103232717AGood compatibilityHigh temperature and low temperature performanceBuilding insulationsEpoxyBridge deck
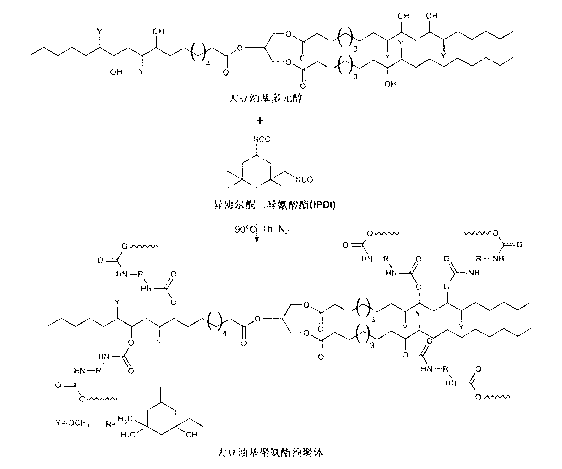
The invention relates to composite modified asphalt. The composite modified asphalt is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 23.1-45.5% of polyurethane modified epoxy resin, 5-10% of compatibilizer, 5-10% of plasticizer, 5-10% of curing agent and 40-60% of road petroleum asphalt, wherein the polyurethane modified epoxy resin is terminal-amino polyurethane modified epoxy resin, terminal-isocyanato polyurethane modified epoxy resin or imidazolyl-terminal-capped polyurethane modified epoxy resin, the compatibilizer is naphthalene oil, asphalt tar or a mixture of naphthalene oil and asphalt tar, the plasticizer is dioctyl phthalate, dibutyl phthalate or a mixture of dioctyl phthalate and dibutyl phthalate, the curing agent is a modified aromatic amine curing agent, and the road petroleum asphalt is 70# petroleum asphalt, 90# petroleum asphalt or 110# petroleum asphalt. The road performance of concrete adopting the polyurethane epoxy resin composite modified asphalt further meets the requirements of technical specifications and surpasses that of the similar imported product Japan Epoxy, so that the composite modified asphalt can be widely applied to the construction of steel bridge deck pavement, and has great significance in opening a market for domestic epoxy asphalt materials.
Owner:重庆市智翔铺道技术工程有限公司
Method for paving resin filling type asphalt concrete steel box-beam bridge deck combined structure
ActiveCN101200873AHigh strengthChemically stableBridge structural detailsBuilding insulationsSheet steelSurface layer
The present invention relates to a paving method of the paving layer of the bridge deck of a steel box girder bridge. A resin infusion type paving method of the composite structure of the asphalt concrete steel box girder bridge deck includes three steps: (1) the sand blasting and the derusting of the steel plates of the steel box girder bridge deck; (2) the preparation of materials: (a) the preparation of high-viscosity modified asphalt; (b) mineral aggregate gradation; (c) the preparation of large pored asphalt concrete; (d) the preparation of thermoset resin grouting material; (3) The pavement of the paving layer of the bridge deck: (a) The large pored asphalt concrete is paved on the steel plates of the steel box girder bridge deck, the pavement thickness is 2cm to 4cm, and after final pressure, a large pored asphalt concrete skeleton layer is formed; (b) While the large pored asphalt concrete skeleton layer is still in a hot state, the thermoset resin grouting material is grouted into the large pored asphalt concrete skeleton layer; (c) After the maintenance of three days, a layer of bonding oil is sprinkled, and an asphalt abrasion surface layer with the thickness of 4cm is paved. The paving method is characterized in good interface cohesive property and simple and convenient construction process.
Owner:WUHAN MUNICIPAL CONSTR GROUP
Steel-super high performance concrete composite beam based on ribbed plate type bridge deck and construction method
InactiveCN104831617AReasonable forceHigh strengthBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyCrack resistanceBridge deck
The invention discloses a steel-super high performance concrete composite beam based on a ribbed plate type bridge deck and a construction method. The construction method includes the following steps that step1, steel beams are machined, manufactured and installed; step2, shearing force connecting parts are welded; step3, the super high performance concrete bridge deck is constructed; step4, a guardrail or an anti-collision wall is constructed; step5, bridge deck pavement is constructed, wherein the super high performance concrete bridge deck and the steel beams are fixed through the shearing force connecting parts, the cross section or / and the longitudinal section of the super high performance concrete bridge deck is / are of a ribbed plate structure, and pre-stressed reinforcements can be arranged on a longitudinal rib region or / and a transverse rib region. The composite beam is reasonable in stress, high in strength and capable of substantially reducing the structure dead weight, effectively avoiding defects at a hogging moment region of a composite continuous beam and bringing tensile strength, compressive strength and high durability of super high performance concrete into full play; the composite beam has the advantages of being small in building height, high in rigidity, small in dead weight, good in durability, crack resistance and fatigue resistance and the like, and has great practical value and good economic benefits.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fiber reinforced polymer composite bridge deck of tubular profile having vertical snap-fit connection
InactiveUS7131161B2Quality improvementImprove workabilitySingle unit pavingsTemporary pavingsBridge deckEngineering
Owner:LEE SUNG WOO
Spatially integrated aerial photography for bridge, structure, and environmental monitoring
ActiveUS9014415B2Damage detectionIntegration damageImage enhancementImage analysisAviationJet aeroplane
Spatially Integrated Small-Format Aerial Photography (SFAP) is one aspect of the present invention. It is a low-cost solution for bridge surface imaging and is proposed as a remote bridge inspection technique to supplement current bridge visual inspection. Providing top-down views, the airplanes flying at about 1000 feet can allow visualization of sub-inch (large) cracks and joint openings on bridge decks or highway pavements. On board Global Positioning System (GPS) is used to help geo-reference images collected and allow automated damage detection. A deck condition rating technique based on large crack detection is used to quantify the condition of the existing bridge decks.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Steel and ultra-high performance concrete combined bridge deck structure
InactiveCN101858052AChange structureChange work statusBridge structural detailsBridge materialsBridge deckRebar
The invention relates to a bridge deck structure of a steel bridge, in particular to a steel and ultra-high performance concrete combined bridge deck structure, comprising a steel bridge deck, an ultra-high performance concrete layer is coated above the steel bridge deck, a bridge deck pavement layer is coated above the ultra-high performance concrete layer, and the ultra-high performance concrete layer is internally provided with reinforced bars. The steel and ultra-high performance concrete combined bridge deck structure has the advantages of small construction height, large stiffness, good binding performance between combined layers, good durability, good fatigue resistance, little vehicle impact and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Flexible protective shed-tunnel and method for designing same
InactiveCN102493328AImprove flexibilitySimple structureProtective constructionBridge structural detailsBridge deckDesign methods
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Composite bridge superstructure with precast deck elements
InactiveUS6470524B1Good ride qualitySaving maintenance costBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyPre stressCrack free
A method for constructing a composite bridge superstructure of simple precast elements. According to the method, the bridge superstucture is comprised of one or more prestressed beams aligned substantially parallel to the bridge longitudinal axis. On top of the prestressed beams, there is placed a plurality of full width, precast deck slabs forming the bridge deck, with the precast deck slabs being transversely disposed side by side, with adjacent slabs attached by joints to complete the bridge deck structure. The deck slabs are spaced from the beams by spacing devices, such that a gap is left between the beams and the deck slabs and the bridge deck structure is prestressed separately from the beams. Subsequent to the prestressing of the deck structure and the beams, the bridge deck structure is connected to the beams by a concrete layer cast in situ in the gap between the bottom face of the precast deck slabs and the top face of the prestressed beams. The concrete is preferably of the low shrinkage type but normal shrinkage concrete may also be employed. The connection is further reinforced by a plurality of shear stirrups. The method is characterized by separate prestressing of the deck structure and the beams and by natural compression of the connecting concrete layer resulting in significant savings of construction time and costs. The construction sequence according to the method enables the deck structure as well as the cast in place concrete layer connecting the deck structure to the beams to undergo a natural compressing process due to time dependent creep and shrinkage contraction of the beams relative to the connecting layer and the deck structure, thereby eliminating the need to apply additional prestressing. In addition, the substantially separate longitudinal prestressing of the deck structure and the beams is highly effective, achieving considerable saving of prestressing steel. The natural compressing of the deck structure and the cast-in-place concrete layer result in crack-free condition and better riding quality of the deck, thereby eliminating the well known drawbacks of additional prestressing, and saving maintenance costs.
Owner:MAIRANTZ BENJAMIN
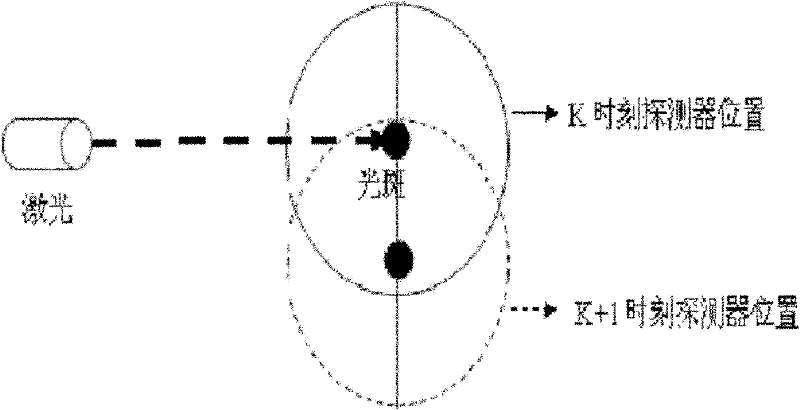
Method for testing deflection/longitudinal displacement change of bridge based on four-quadrant position detector
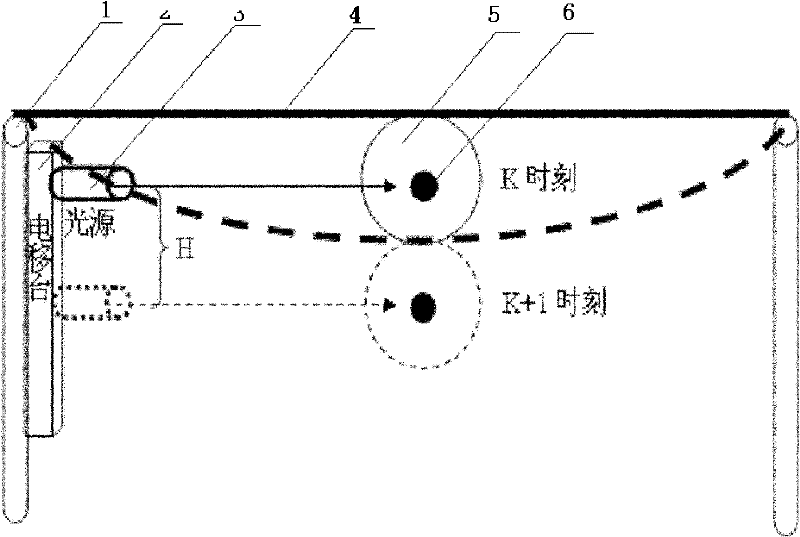
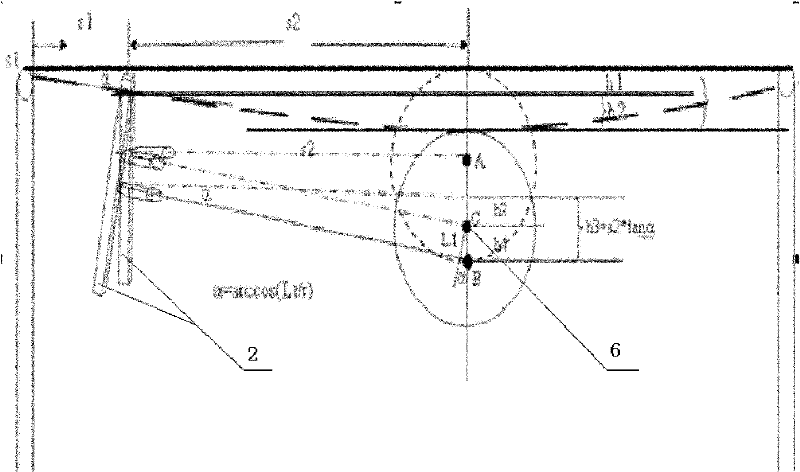
InactiveCN102564323AHigh precisionReal-time monitoring of security statusUsing optical meansFour quadrantsLight spot
The invention discloses a method for testing a deflection / longitudinal displacement change of a bridge based on a four-quadrant position detector. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, the four-quadrant position detector is installed in the centre of the bridge or other points to be tested at the bottom of a bridge deck; a laser source is installed on a pier and / or a certain point below the bridge deck through an electric displacement table; then, testing is carried out by matching the four-quadrant detector with the laser source, so that the light spot of laser is over against the centre of the detector; when the deflection of the bridge deck changes, the four-quadrant detector longitudinally moves together with the point to be tested; the light spot position, formed on the four-quadrant detector, of the laser moves oppositely relative to the detector; and different position coordinates of the light spot on the detector before and after the deflection of the bridge changes and light spot position variable quantity on the four-quadrant detector, namely deflection position variable quantity of the point to be tested on the bridge deck can be calculated. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, good controllability and high precision and is capable of realizing real-time online test of the deflection / longitudinal displacement of the bridge.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Construction process for using bridge girder erection machine to remove T-shaped cantilever continuous rigid frame box girders
InactiveCN103243663ALow costGuaranteed normal shippingBuilding repairsArchitectural engineeringBridge deck
The invention discloses a construction process for using bridge girder erection machines to remove T-shaped cantilever continuous rigid frame box girders. The process is characterized by including the steps of A, mounting the bridge girder erection machines; B, performing trial hanging by the bridge girder erection machine; C, drilling and cutting; D, removing girder sections; E, chiseling girder sections; F, transversely moving the bridge girder erection machine; and G, removing the bridge girder erection machines; wherein the removing equipment includes two 50m-span bridge girder erection machines, and girder turning is achieved by modifying hanging hooks of the bridge girder erection machines; the bridge girder erection machines are heightened by adding Berea groups and pouring concrete strip foundation below support legs of the bridge girder erection machines to realize that the removed girders are delivered out between two main trusses of the bridge girder erection machines through a bridge face. All girder section removing includes girder section prehanging, girder section cutting, girder section turning, girder section transferring, and girder section chiseling. The construction process is low in used equipment, short in construction period, and small in influence on the society, box girders are removed safely while cost is saved a lot and normal operation of channels or passages below a bridge is unaffected, and safe and environment-friendly T-shaped cantilever continuous rigid frame box girder removing is achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL CHANGDA HIGHWAY ENG
Double-deck bridge floor combined trussed girder bridge
InactiveCN101158143AIncrease capacityOpen sightTruss-type bridgeBridge structural detailsLow noiseBridge deck
A combined truss bridge of double bridge decks relates to a novel bridge structure and the combined truss bridge of double bridge decks consists of an upper concrete bridge deck, a steel structure web member and a lower concrete bridge deck. The upper and lower bridge decks are used for bearing the load of vehicles and are used as an upper chord part and a lower chord part to share the global stress with the global structure. The steel structure web member consists of a slant web member and a vertical web member, and combines the upper and the lower concrete bridge decks as a whole to be used for resisting the shearing force of the truss bridge. The upper concrete bridge deck and the lower concrete bridge deck in tensile areas are provided with vertically stressed steel bars or section steel. The invention, compared with traditional single bridge deck combined girder bridges, enjoys greater traffic capacity and higher traffic comfort; compared with steel truss bridges, the invention remarkably reduces steel consumption by using concrete bridge decks as compression chords, and has the advantages of low noise, easy maintenance, good durability and so on.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com