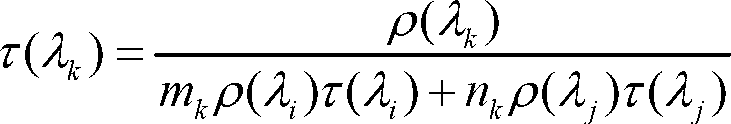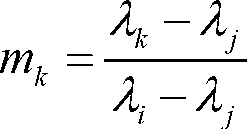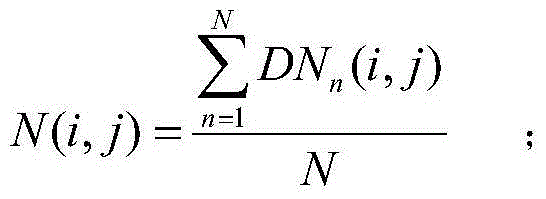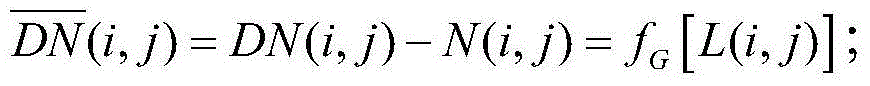Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
916 results about "Calibration coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
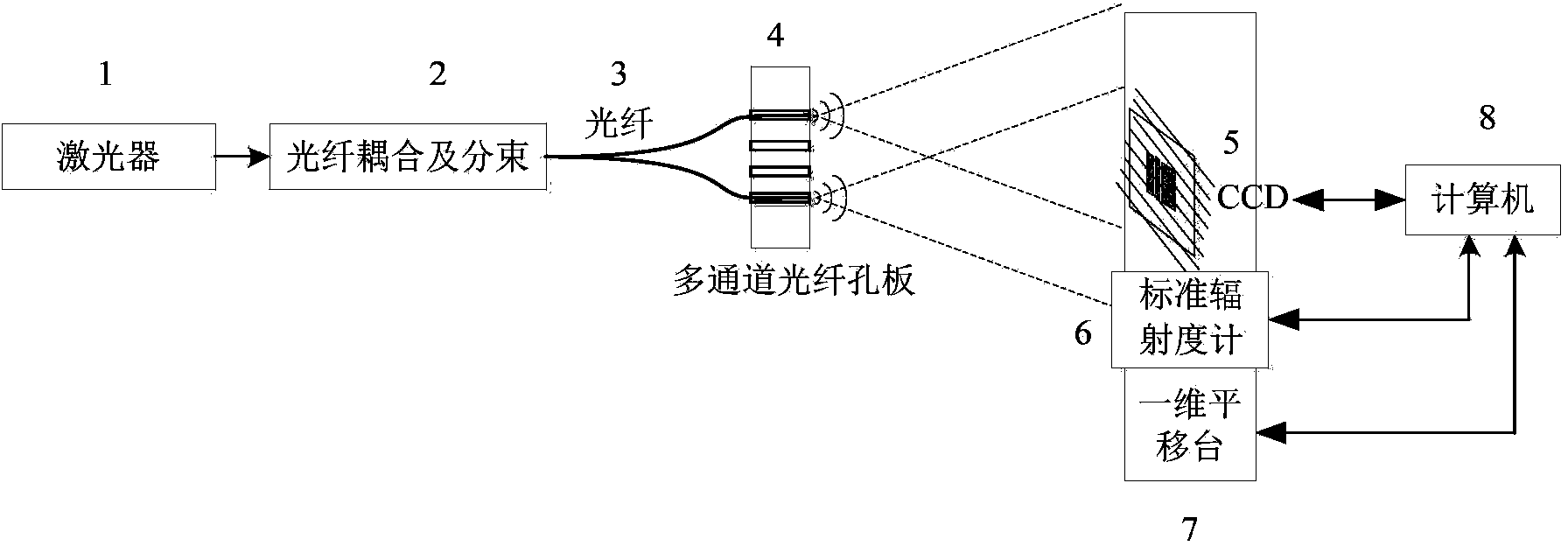
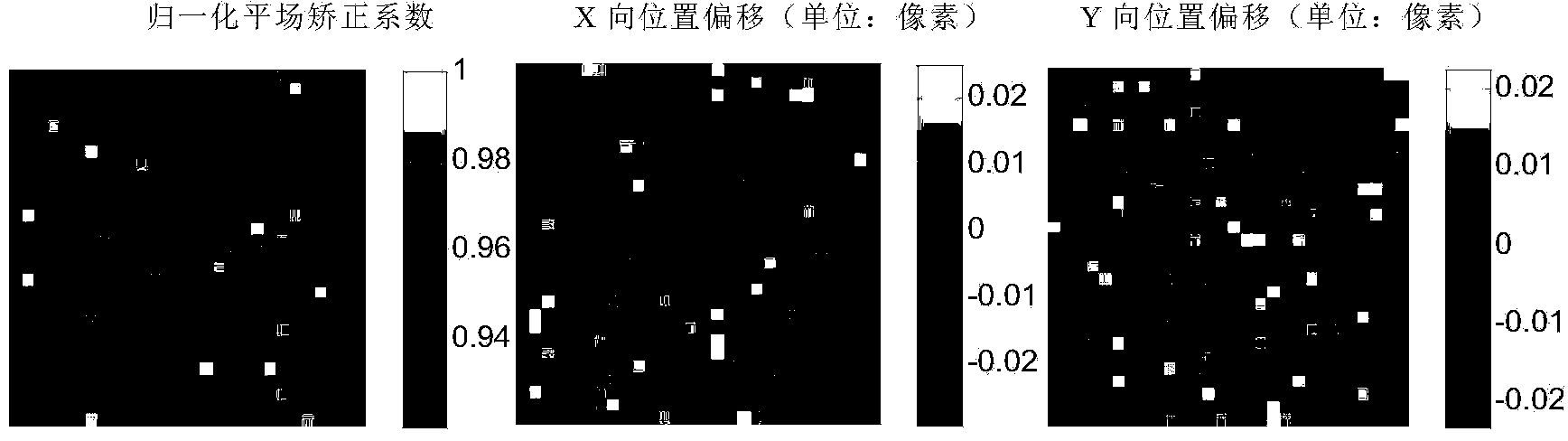
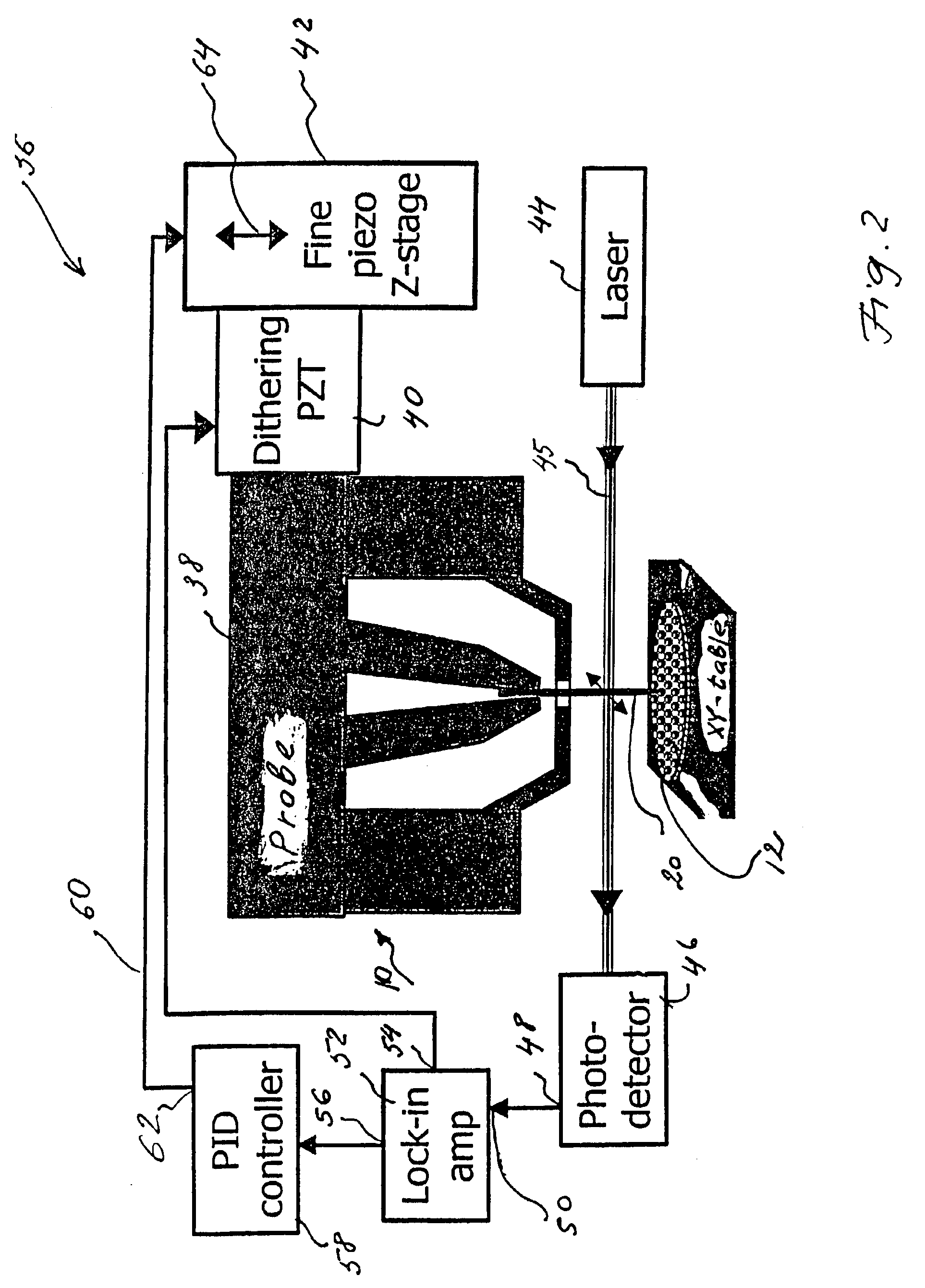
The Calibration Coefficients Computation for IR Channels process calculates the calibration offset and gain that describes the linear relationship between pixel count and radiances for the thermal IR channels.
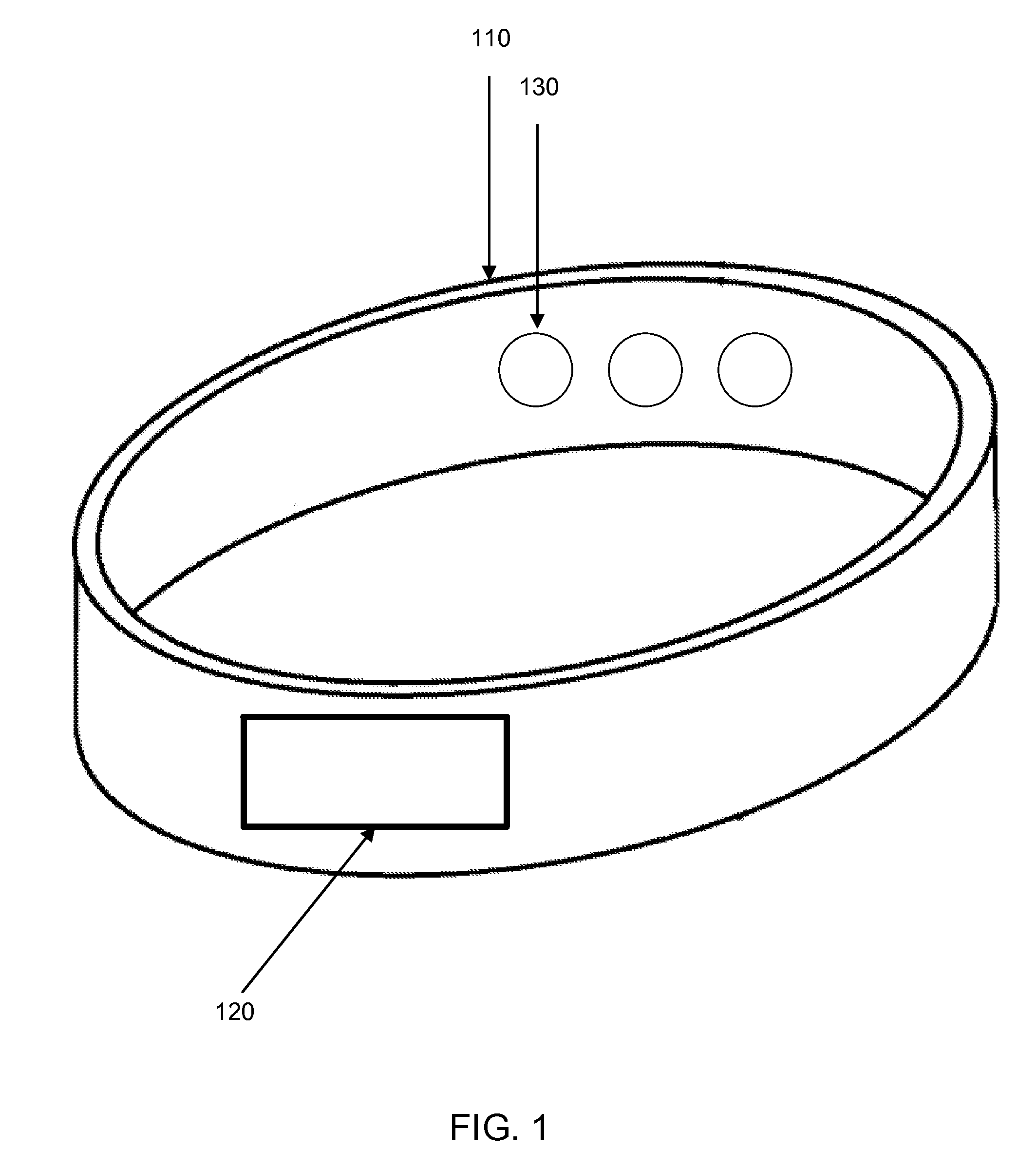
Calibration of a wearable medical device
A technology for a wearable medical device for monitoring medical parameters. Medical measurement data can be received at the wearable medical device from a medical measurement sensor attached to the wearable medical device or a medical measurement sensor in communication with the wearable medical device. A calibration coefficient can be determined for calibrating the wearable medical device based on the medical measurement data. The wearable medical device can be calibrated based on the calibration coefficient.
Owner:HALO WEARABLES LLC
Mutual coupling method for calibrating a phased array
A method for calibrating a phase array antenna comprises performing initial measurements of array antenna elements to ensure that calibration measurements are within the linear dynamic range of receive elements contained within the array. The method includes deriving calibration coefficients from a direct measurement of a forced out of phase condition and detection of deep nulls through adjustment of amplitude and phase settings over a range of frequencies of interest.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
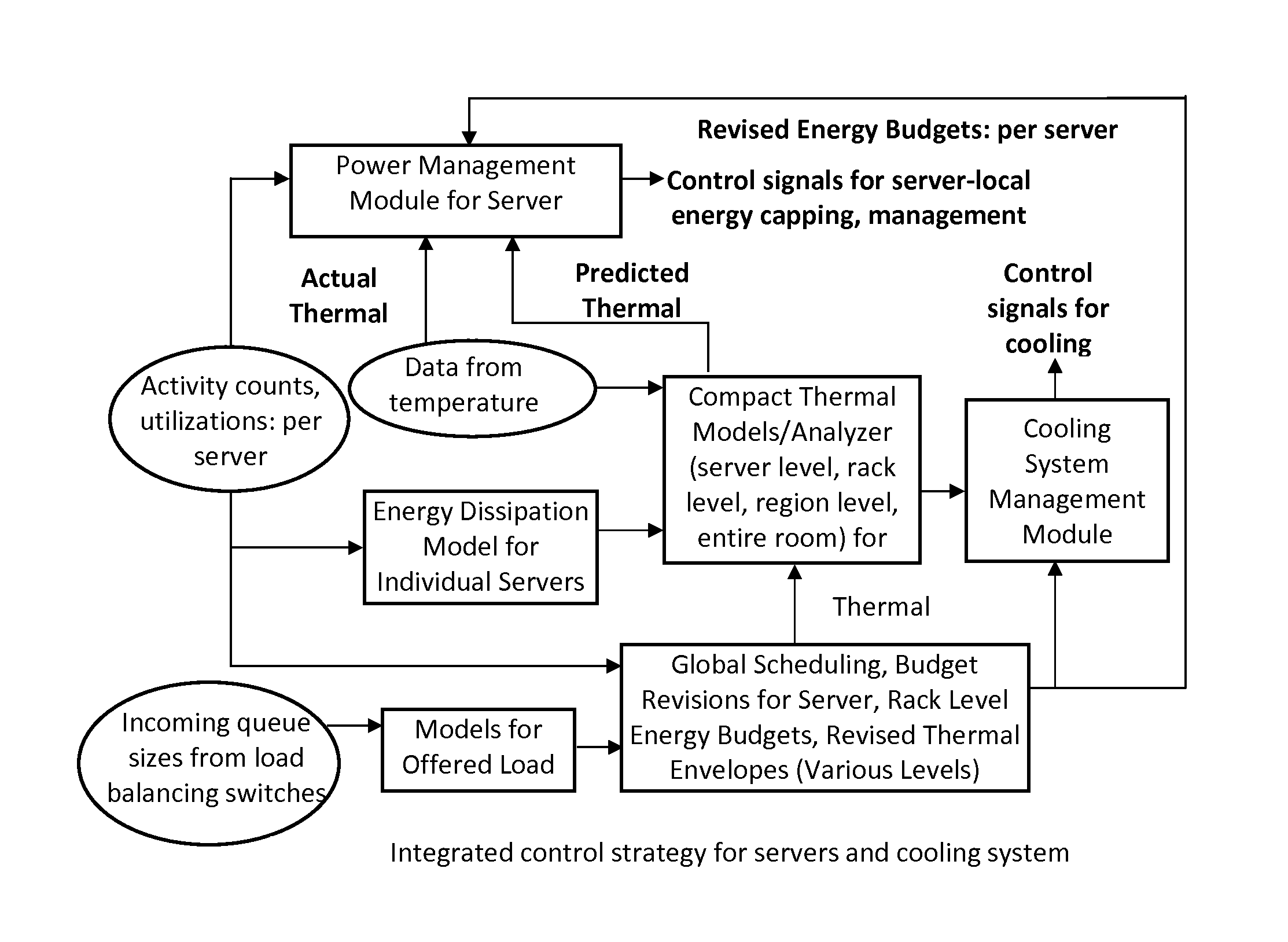
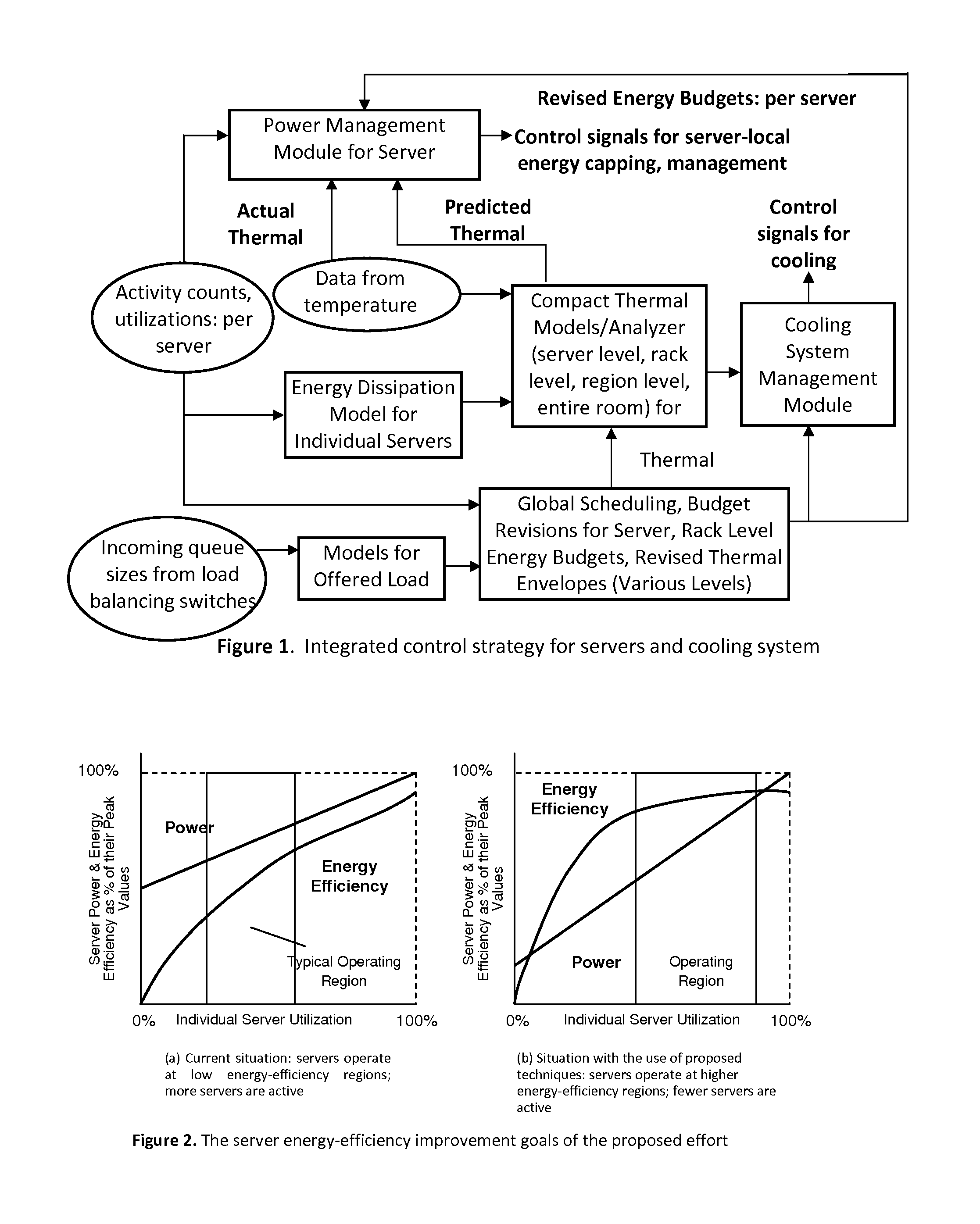
Apparatus and method for efficient estimation of the energy dissipation of processor based systems
ActiveUS8397088B1Maintain working temperatureImprove energy efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsOperational systemProcessor register
A system and method of scheduling tasks, comprising receiving activity and performance data from registers or storage locations maintained by hardware and an operating system; storing calibration coefficients associated with the activity and performance data; computing an energy dissipation rate based on at least the activity and performance data; and scheduling tasks under the operating system based on the computed energy dissipation rate.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
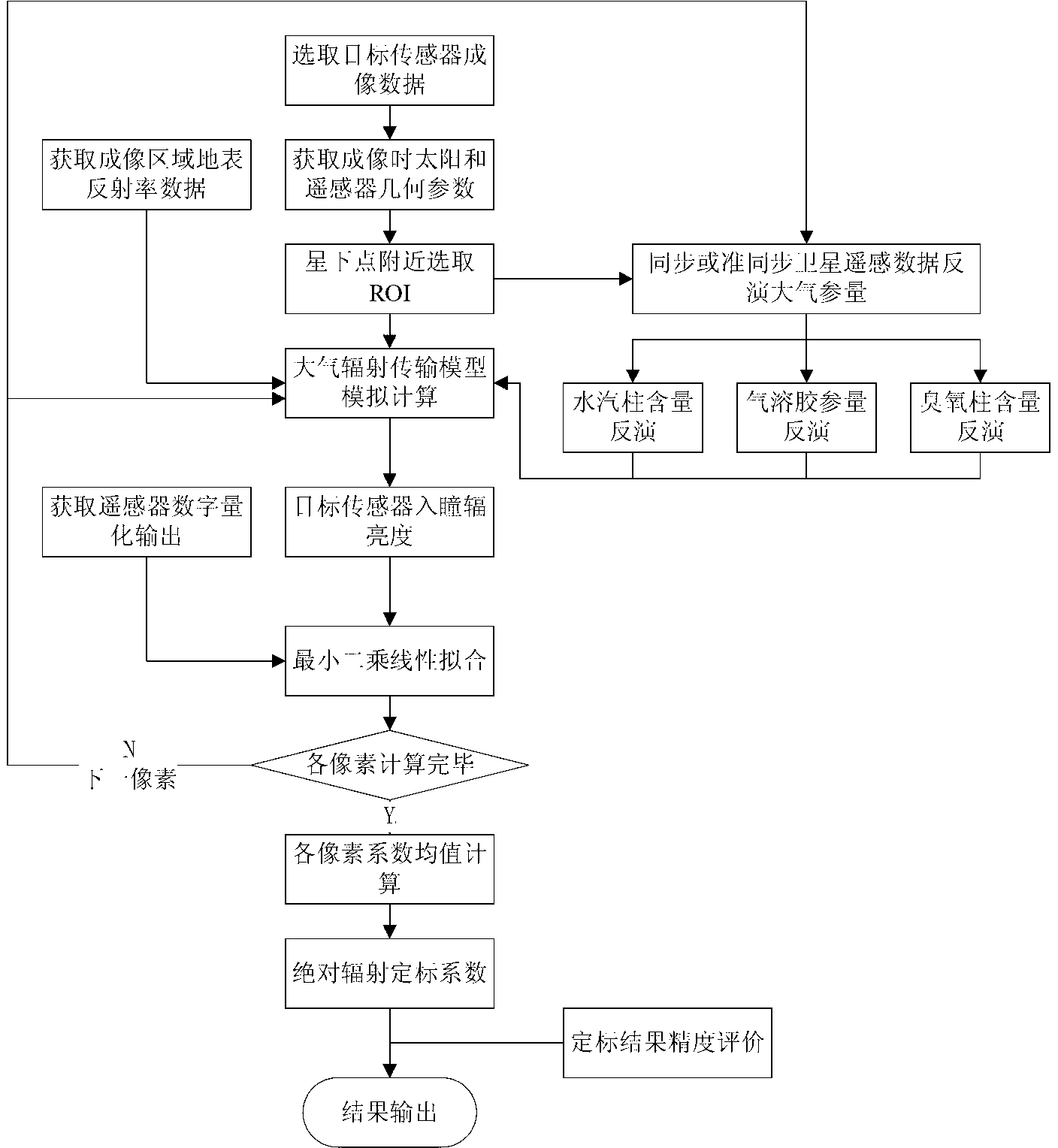
Satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval
InactiveCN103018736ASimulation is accurateAccurate entrance pupil radianceWave based measurement systemsMeteorological satelliteEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval. The method includes nine steps. A surface reflectance is obtained through ground synchronous actual measurement during satellite crossing or historical data, imaging time and observation geometry parameters are obtained through remote sensing data head files, atmospheric parameters during imaging of synchronous crossing meteorological satellite sensors or related load retrieval remote sensors are utilized, the entrance pupil radiance of the remote sensors is calculated by an atmospheric radiation transmission model according to retrieval results of the atmospheric parameters, a calibration coefficient is calculated through a radiation calibration model, and thereby the on-orbit radiation calibration for a satellite-borne remote sensor is achieved. The satellite-borne remote sensor radiation calibration method based on the atmospheric parameter remote sensing retrieval is a pixel-level calibration method and has the advantages that the accuracy is high, the costs are low, simultaneously, the high frequency calibration can be achieved, historical remote sensing data can be calibrated, and the method has a wide application prospect to remote sensing data processing methods and application technical fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
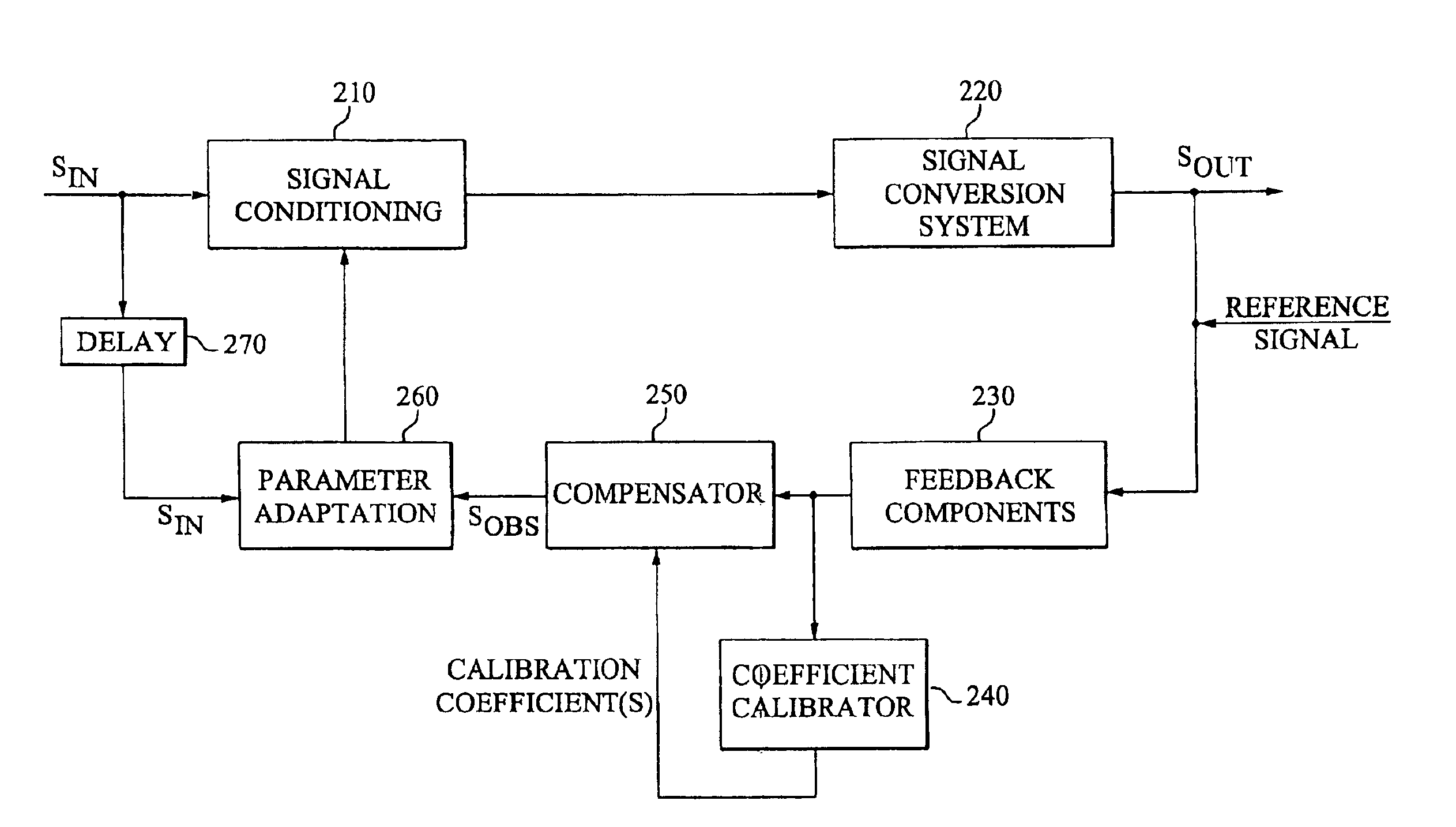
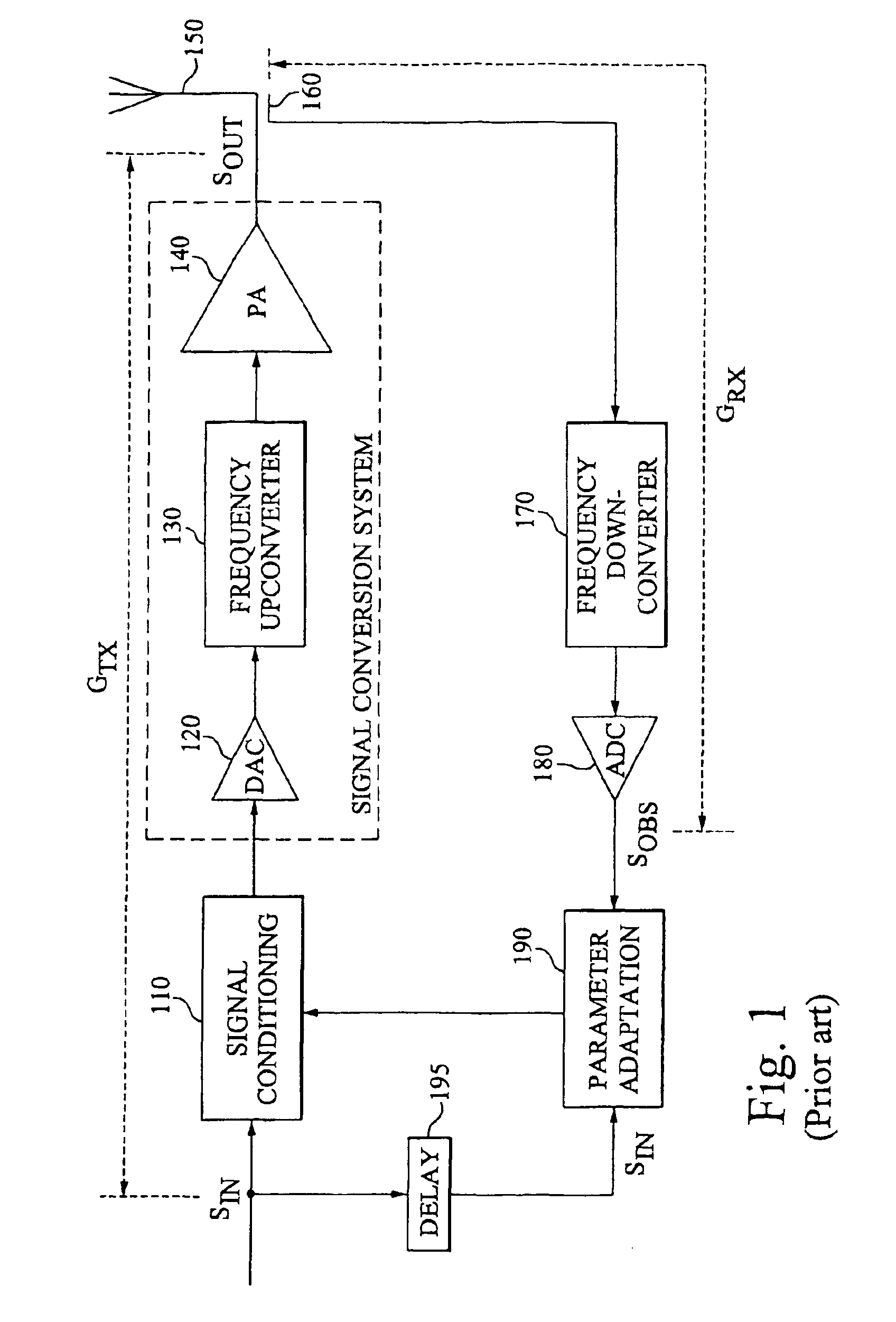
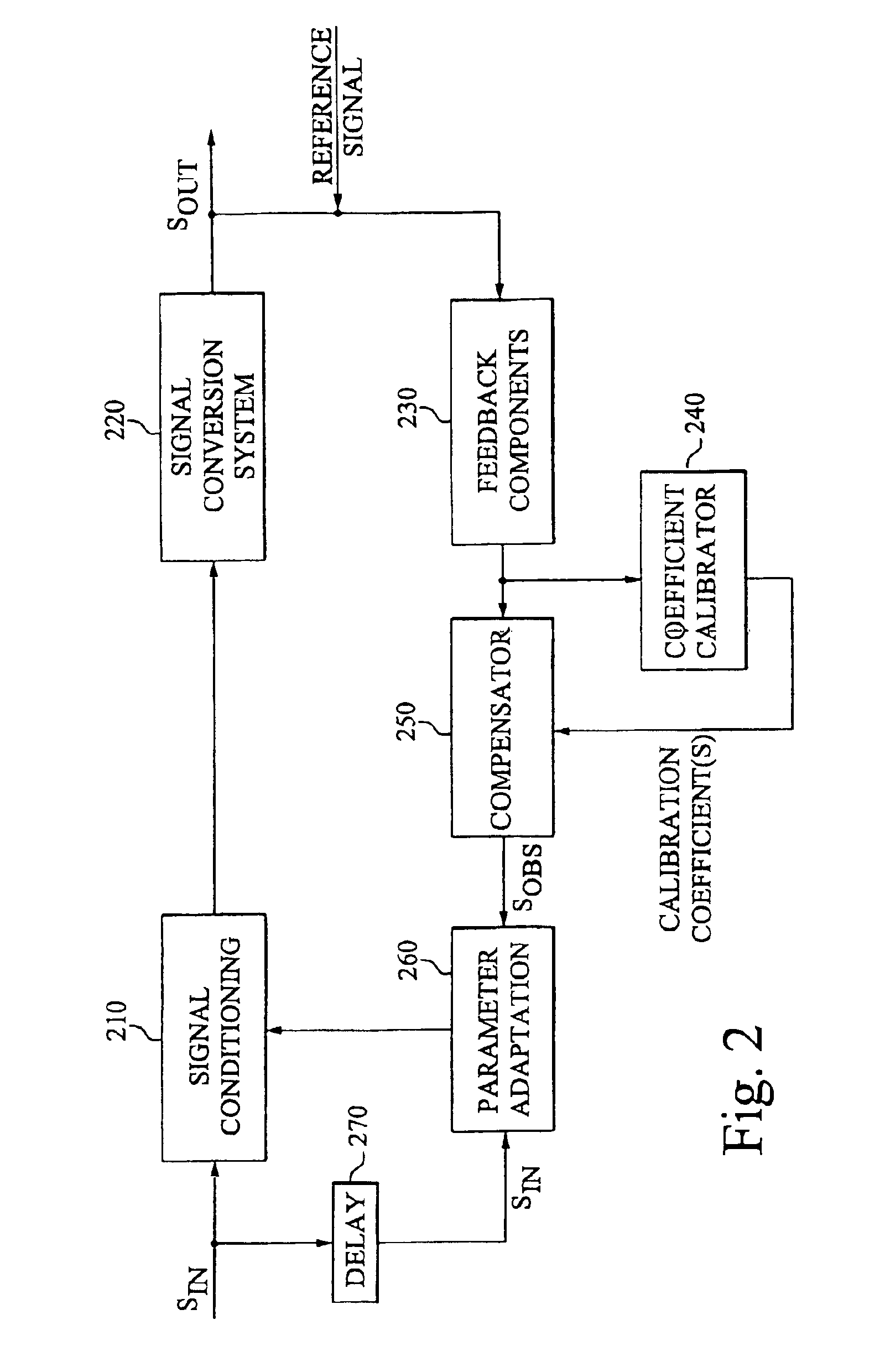
Calibration of an adaptive signal conditioning system
InactiveUS6943627B2Robust and efficient calibrationAccurate conditionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric devicesSignal conditioningEngineering
The invention provides robust and non-invasive calibration of an adaptive signal conditioning system having a signal conditioning block in the signal path to a signal conversion system, and a feedback path with a number of feedback components for enabling adaptation, by means of a parameter adaptation block, of the parameters used in the signal conditioning. In order to calibrate the feedback path, a well-defined reference signal is inserted into the feedback path, and an appropriate calibration coefficient is then determined by a coefficient calibrator in response to the received reference signal. The calibration coefficient is provided to a compensator, which effectively compensates for changes in the transfer characteristics of the feedback path due to factors such as variations in ambient temperature and component aging. Accordingly, the feedback signal transferred over the calibrated feedback path will be an accurate representation of the output signal of the signal conversion system, thus allowing accurate adaptive signal conditioning.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Indoor surveying apparatus and method
InactiveUS20150116691A1Optical rangefindersActive open surveying meansSurveyorCalibration coefficient
An indoor surveying apparatus comprises a light source, a color imaging system, a memory storing calibration coefficients, and a computing device for determining coordinates of 3D intersection points of the emitted light with objects using calibration coefficients and images captured by the imaging system. A method of using the surveying apparatus comprises the steps of capturing first image of a scene illuminated by the light source, capturing second image of the scene without the illumination by the light source, comparing the two images to identify locations of the 3D intersection points in the first image, using the set of calibration coefficients and the locations of the 3D intersection points in the first image to compute 3D coordinates of the intersection points, whereby surveying information collected by the apparatus comprises the coordinates of 3D intersection points and the color photographic images captured from known poses relative to the 3D intersection points.
Owner:PLANITAR INC
Robot tail end positioning deviation correction method and system
The invention provides a robot tail end positioning deviation correction method and system. The present includes the following steps that: 101, a camera calibration system is set; 102, the relative positions of the tail end of a manipulator and the center of a camera are calibrated; 103, the camera photographs the images of all mark points in a calibration plate and analyzes the images so as to obtain a series of deviation quantity data under the condition that the tail end of the manipulator drives the camera to move and traverse different Z values; and 104, a space deviation distribution table is constructed; and 105, the deviation of the tail end of the robot can be obtained based on the space deviation distribution table. According to the method and system of the invention, the calibration coefficient of the camera is calibrated; the relative positions of the tail end of the manipulator and the center of the camera are calibrated; the camera photographs the images of all the mark points in the calibration plate and analyzes the images so as to obtain deviation quantity under the condition that the tail end of the manipulator drives the camera to move and traverse different Z values, and the deviation correction table is stored; and manipulator positioning is compensated through searching the deviation correction table, and the manipulator can move to a set position.
Owner:深圳市大族机器人有限公司
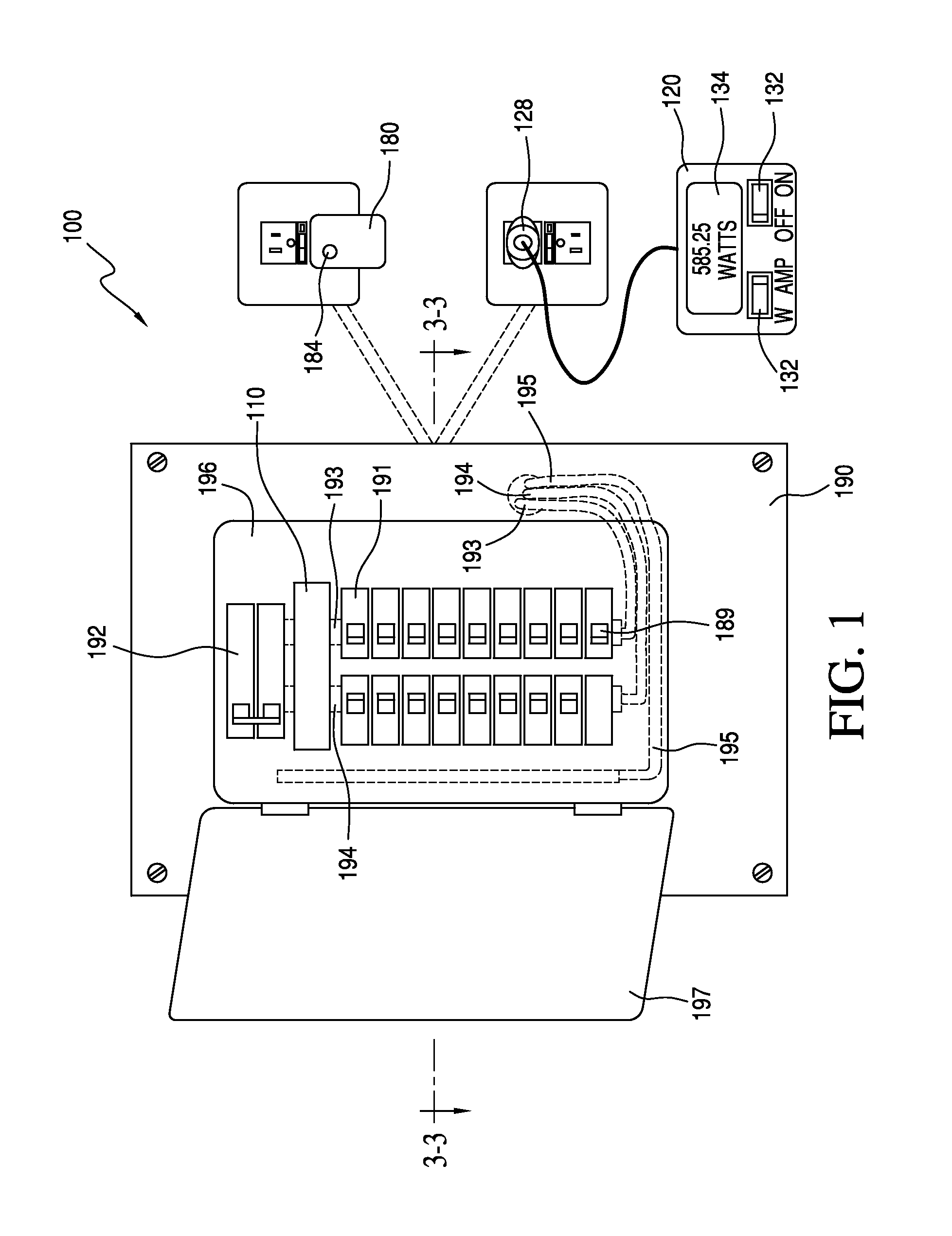
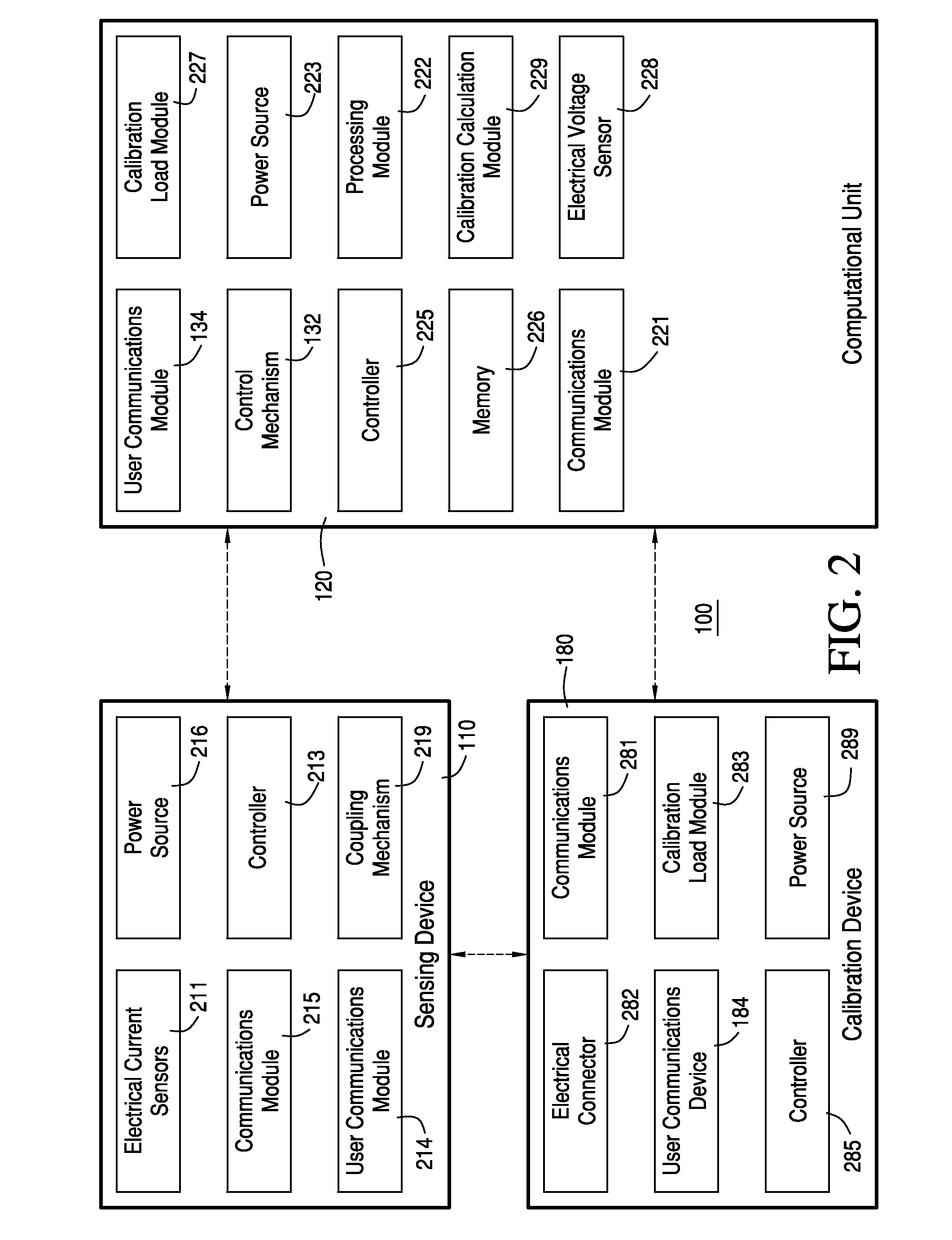
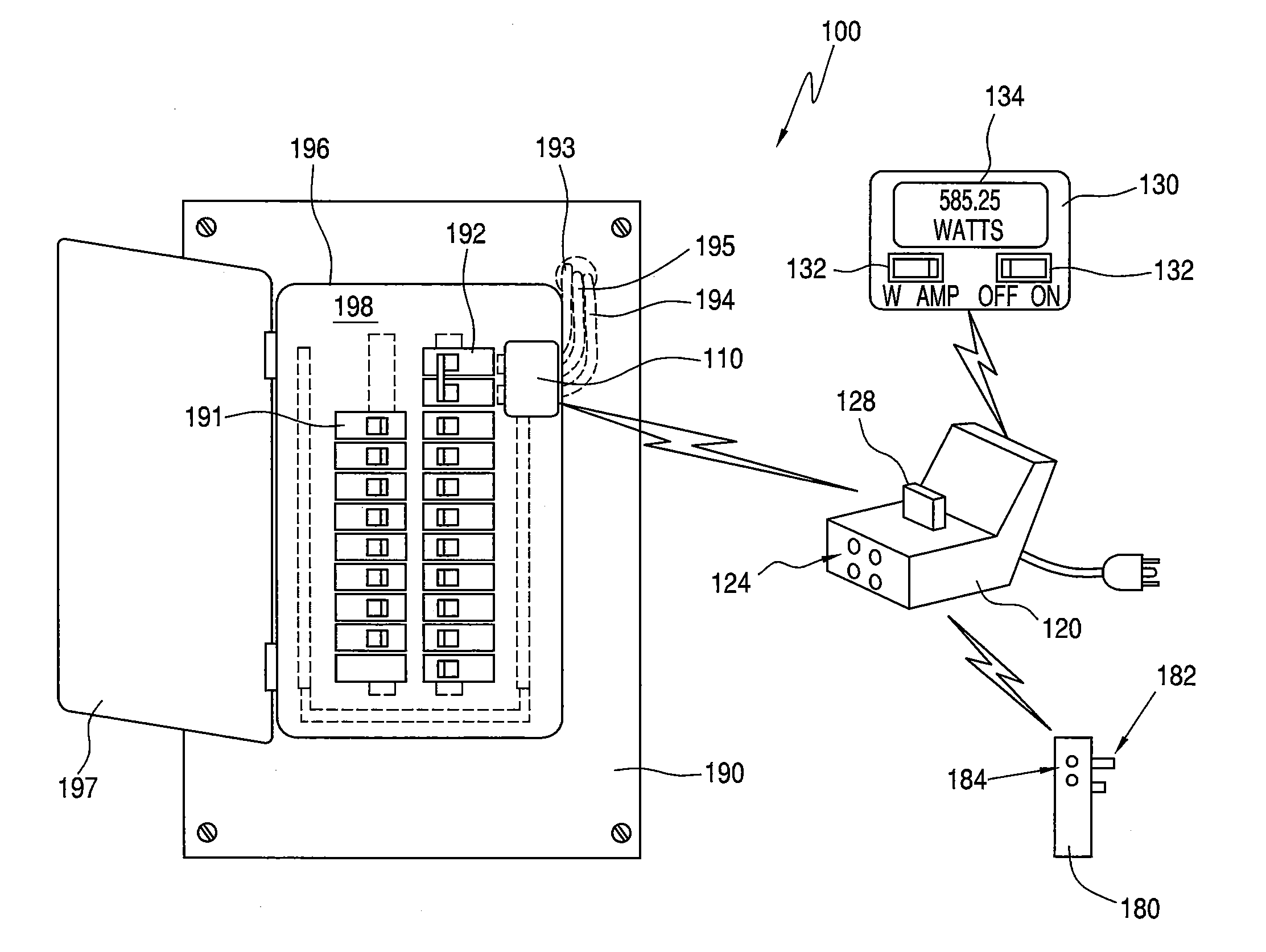
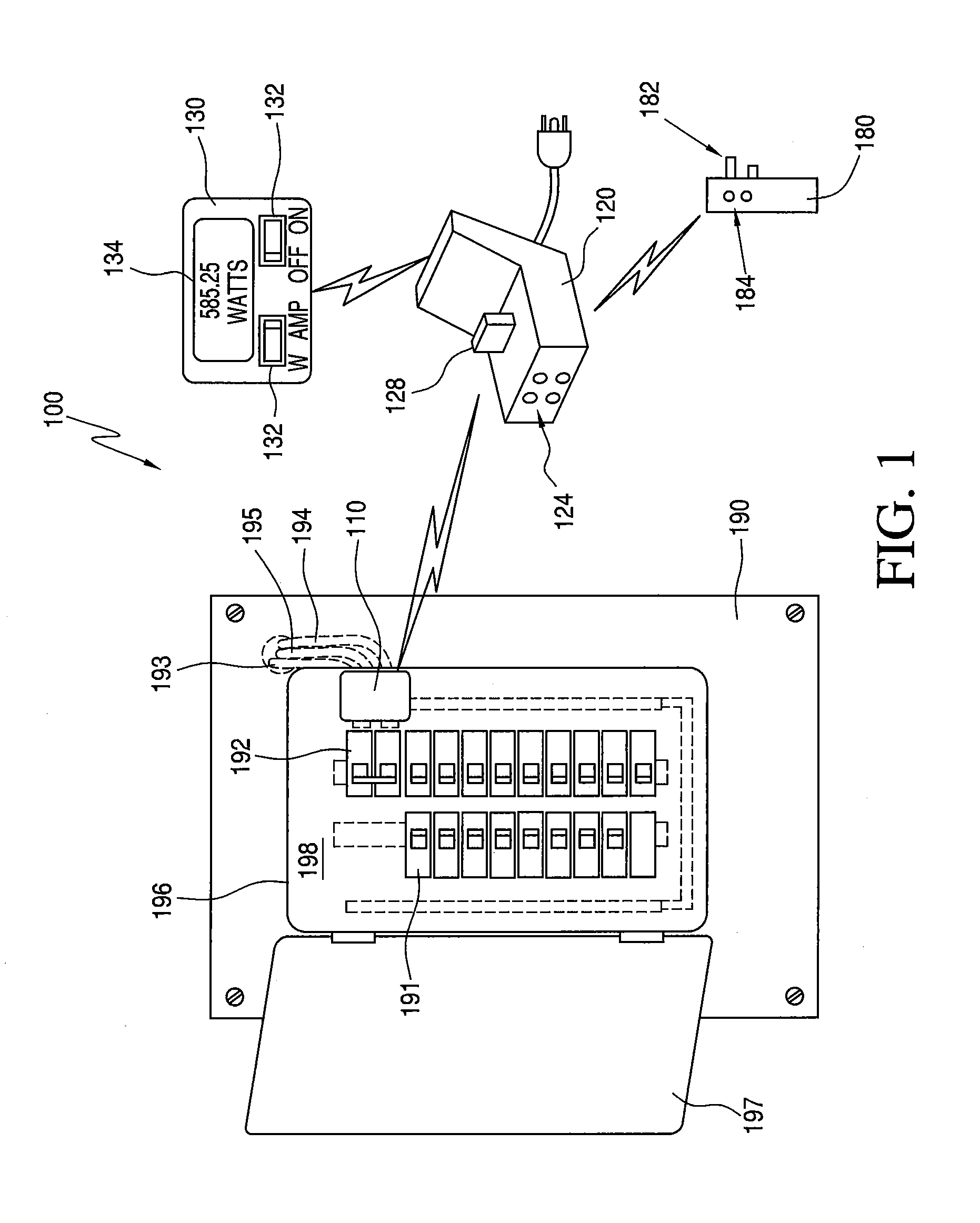
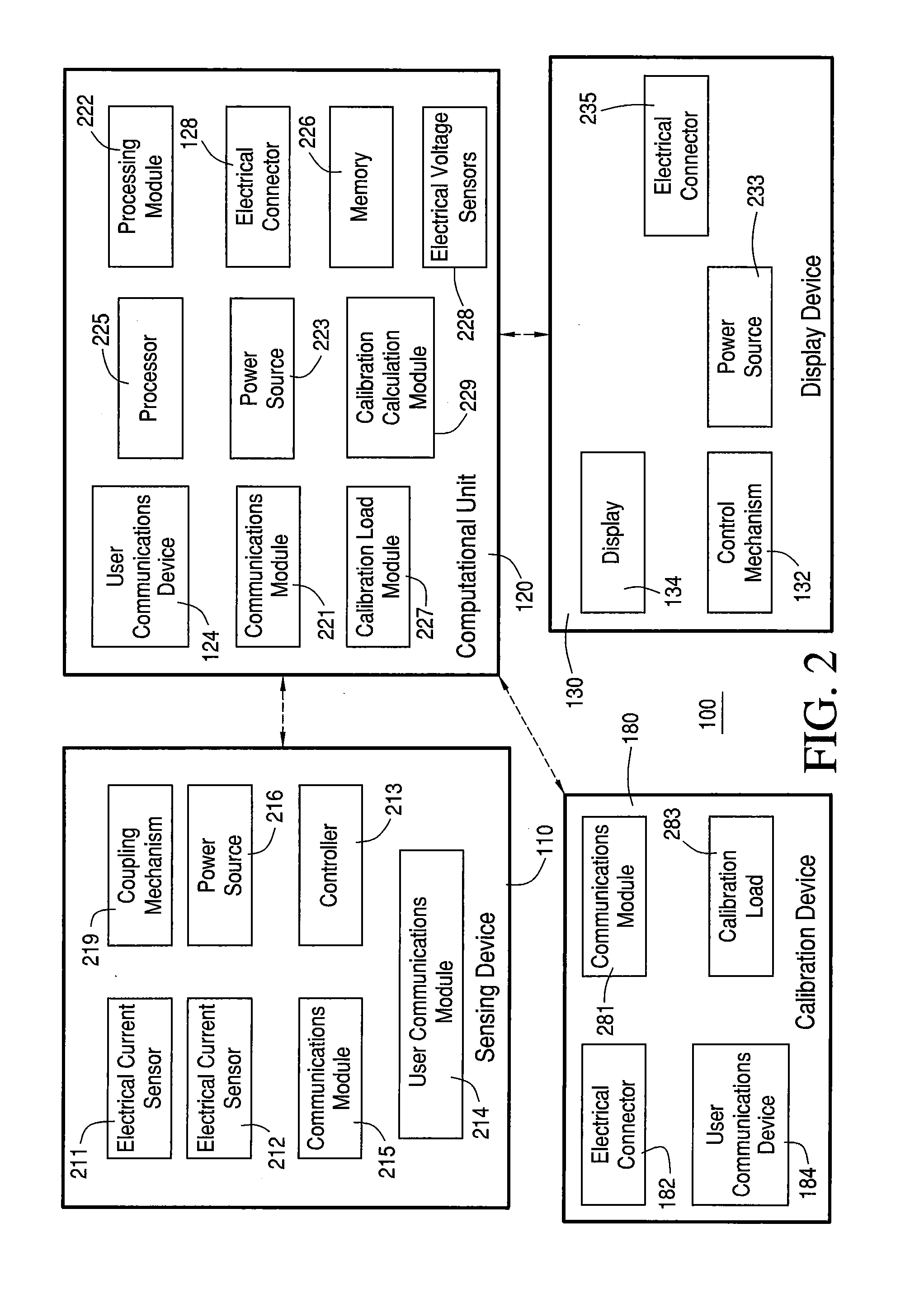
Systems and Methods for Measuring Electrical Power Usage in a Structure and Systems and Methods of Calibrating the Same
ActiveUS20120068692A1Magnetic measurementsDynamo-electric motor metersElectricity infrastructureMeasurement device
Some embodiments can concern a method of using a power consumption measurement device. The power consumption measurement device can be mechanically coupled to a surface of a circuit breaker box overlying at least part of one or more main electrical supply conductors for an electrical power infrastructure of a structure. The method can include: determining one or more first magnetic field readings from the one or more main electrical supply conductors using one or more sensors in the power consumption measurement device; after determining the one or more first magnetic field readings, electrically coupling a first calibration load to the electrical power infrastructure; while the first calibration load remains electrically coupled to the electrical power infrastructure, determining one or more second magnetic field readings from the one or more main electrical supply conductors using the one or more sensors in the power consumption measurement device; calibrating the power consumption measurement device using at least in part the one or more first magnetic field readings and the one or more second magnetic field readings, after calibrating the power consumption measurement device, determining one or more third magnetic field readings from the one or more main electrical supply conductors using the one or more sensors in the power consumption measurement device; and determining an electrical power used by the electrical power infrastructure of the structure using at least the one or more third magnetic field readings and the one or more calibration coefficients. Calibrating the power consumption measurement device can include determining one or more first calibration coefficients for the power consumption measurement device using at least in part the one or more first magnetic field readings and the one or more second magnetic field readings. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:BELKIN INT
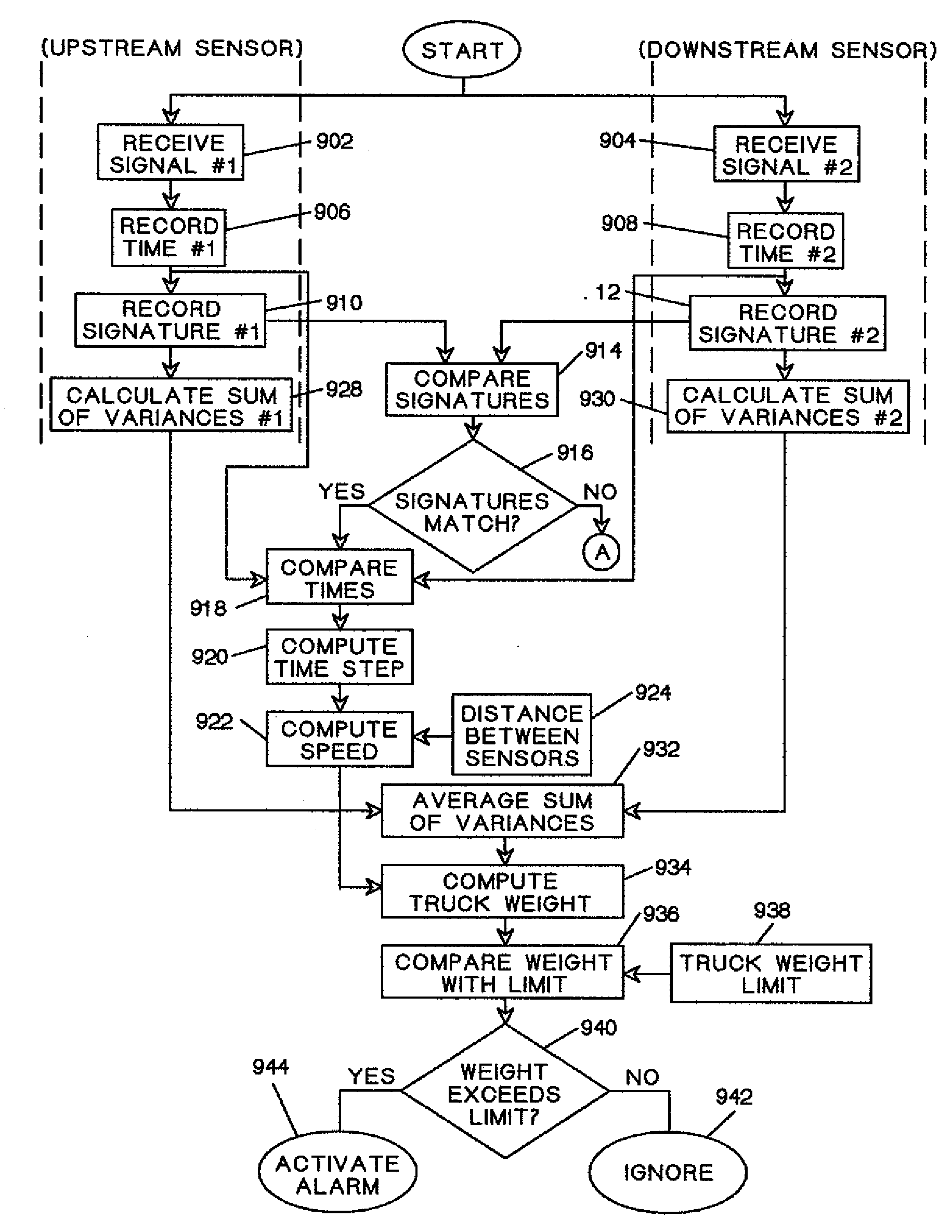
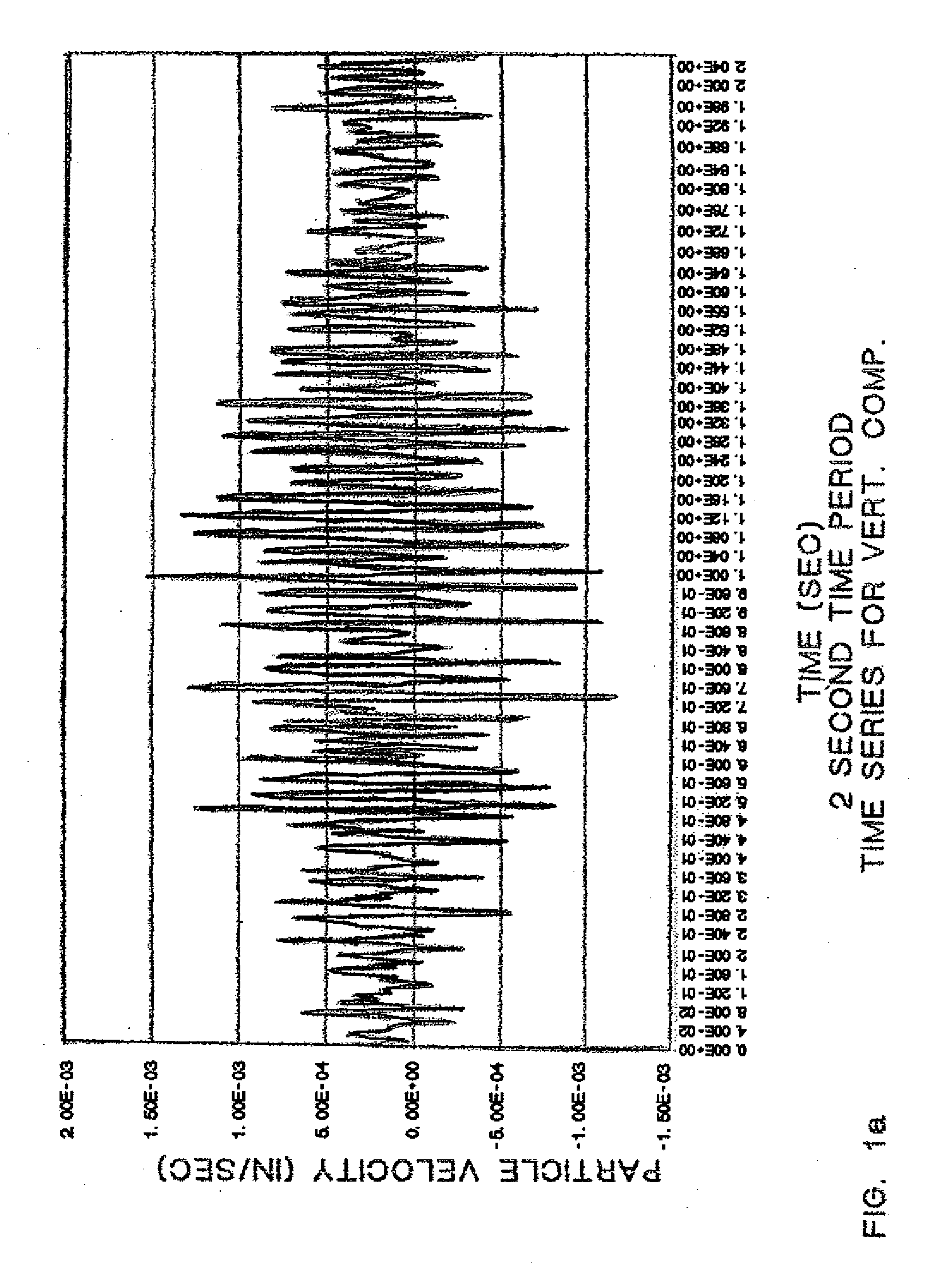
Method for weighing vehicles crossing a bridge
A method for weighing vehicles moving on a bridge deck pavement is provided. At least one vibration sensor is mounted on a lower side of the pavement to sense low frequency pavement vibrations generated by moving vehicle wheels and propagated in waves in the pavement. Vibration sensor output signals are provided to a computing device. Sensed vibration energy rate is computed and, with signals from vibration sensors mounted at two locations separated by a known longitudinal distance, vehicle speed is also computed. The weight of the vehicle is determined as the product of a calibration coefficient and the ratio of sensed vibration energy rate to velocity. Using vibration sensor signals indicative of wheel generated vibrations in the very near field and summing vibration energy rates computed from these signals during vehicle passage over the vibration sensors the weight of individual vehicles is computed when other moving vehicles are present.
Owner:TATOM FR B +1
Mutual coupling method for calibrating a phased array
A method for calibrating a phased array antenna comprises performing initial measurements of array antenna elements to ensure that calibration measurements are within the linear dynamic range of receive elements contained within the array. The method includes deriving calibration coefficients from a direct measurement of a forced out of phase condition and detection of deep nulls through adjustment of amplitude and phase settings over a range of frequencies of interest.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
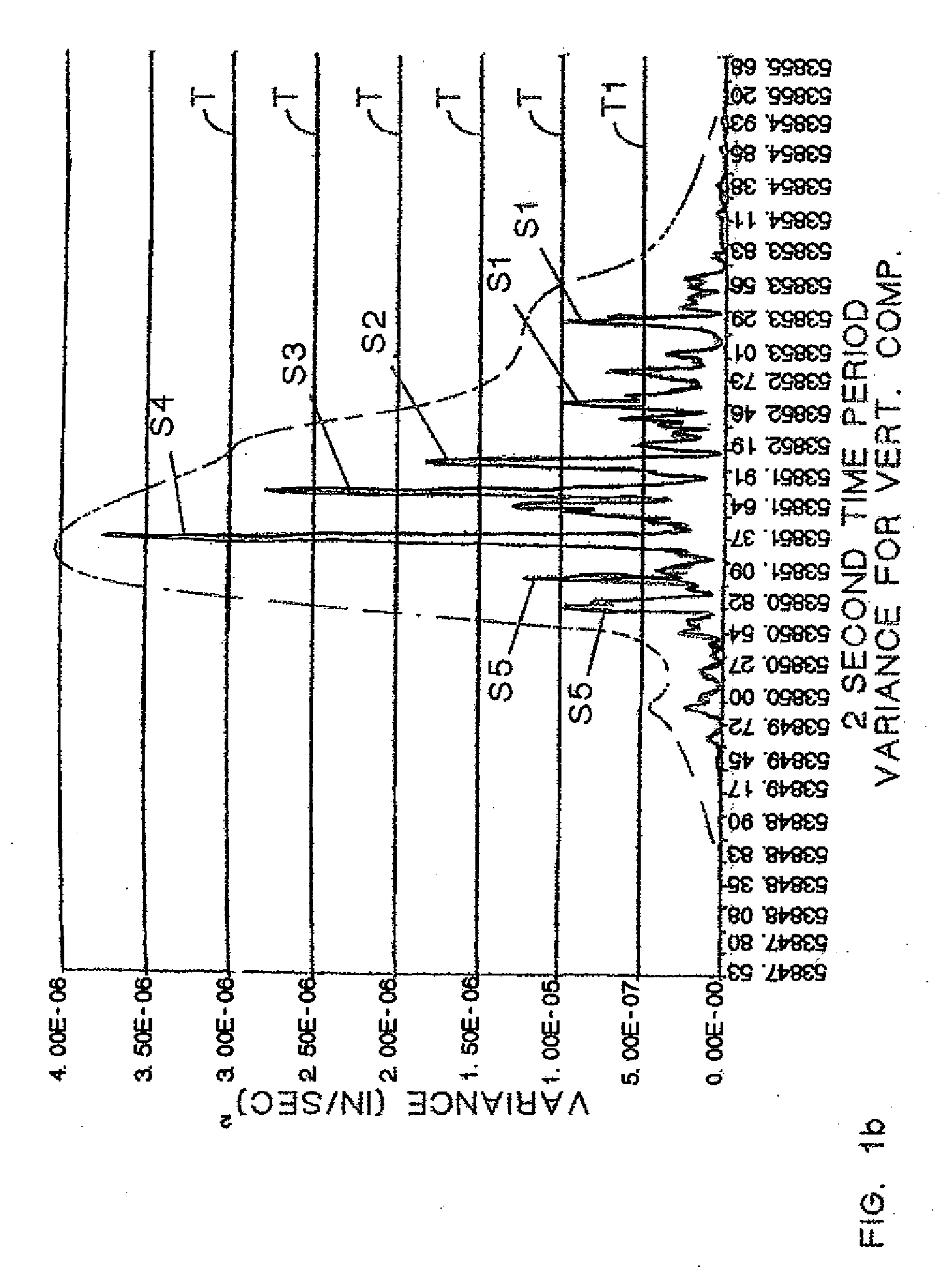
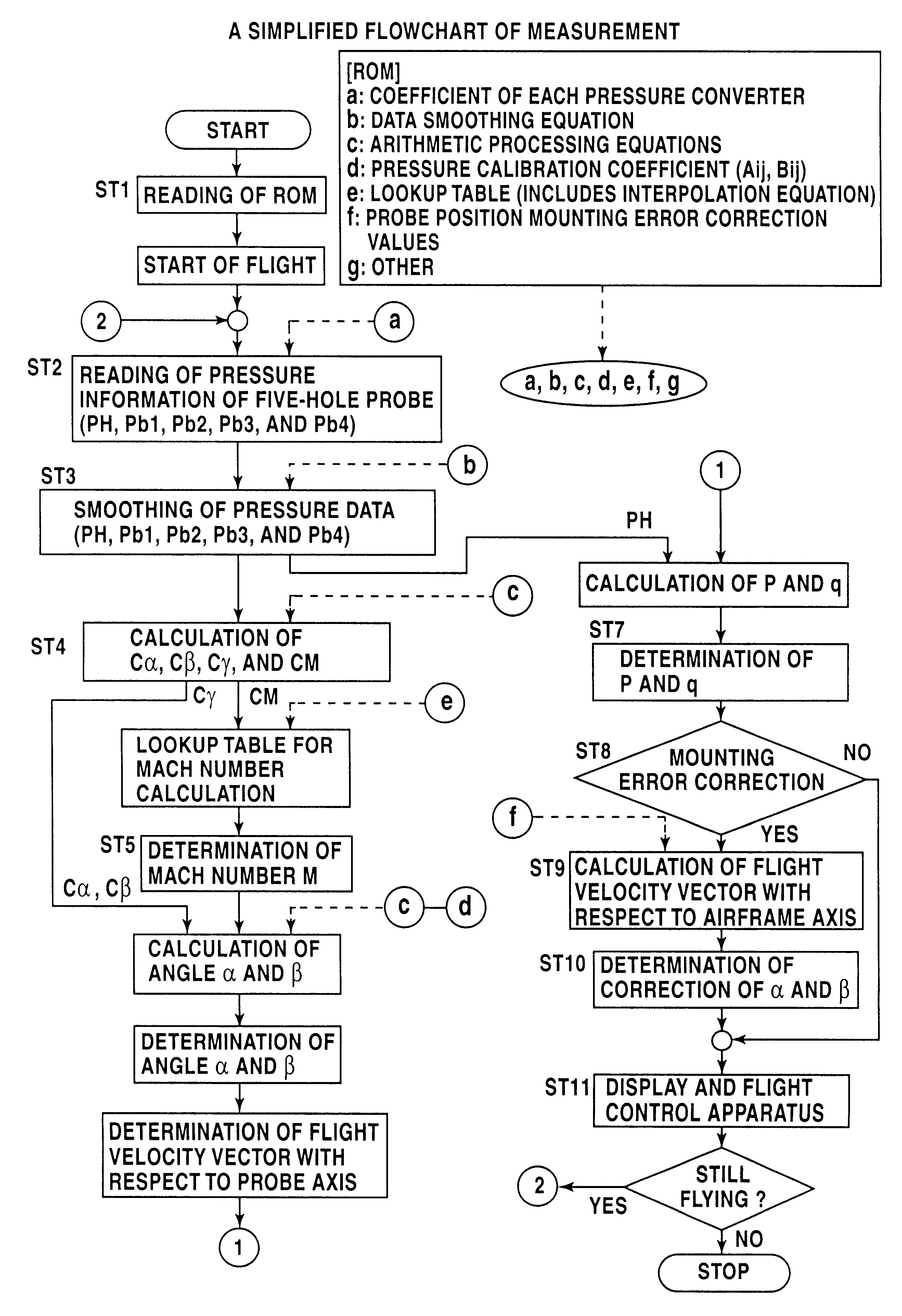
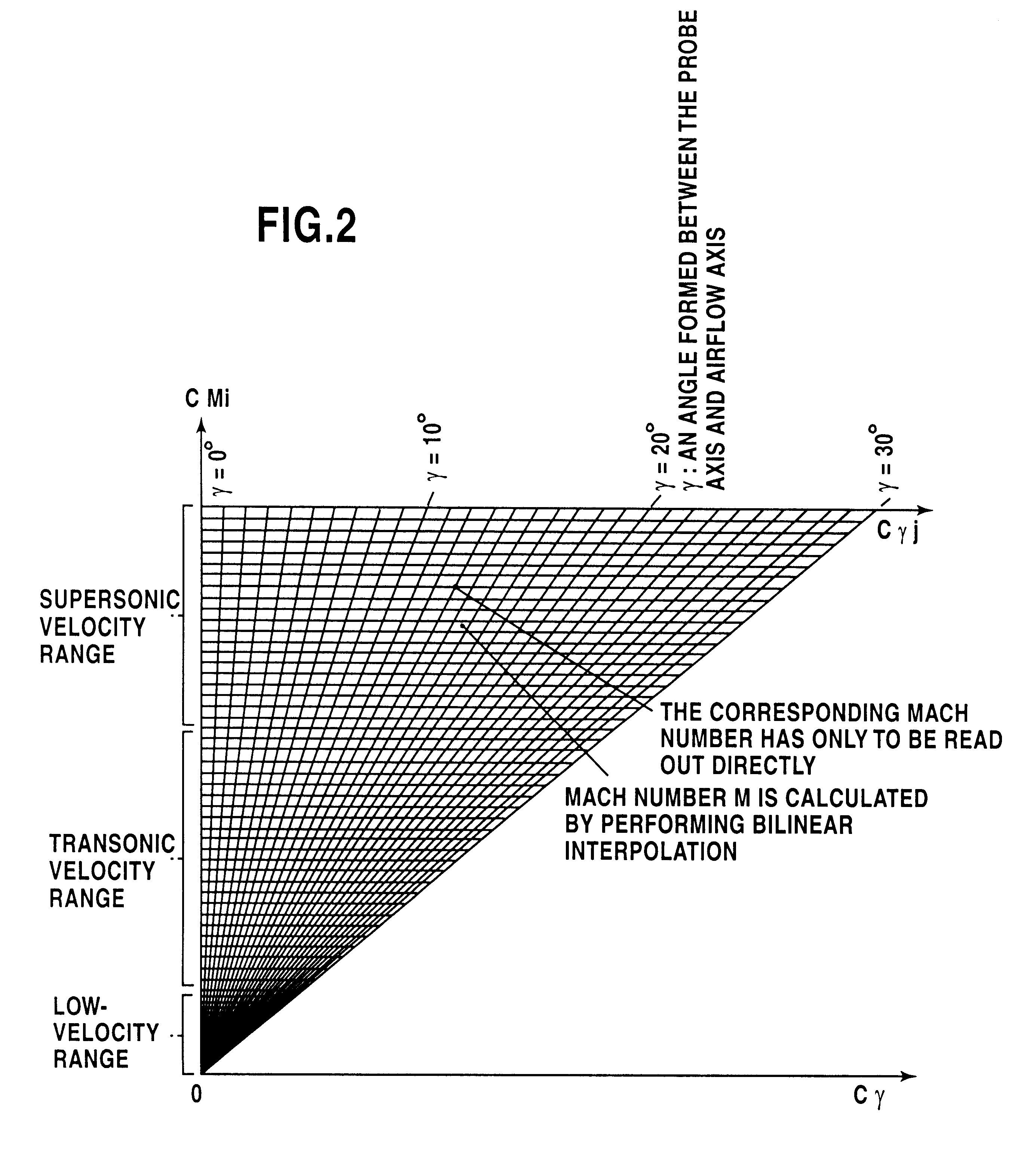
Arithmetic processing method and system in a wide velocity range flight velocity vector measurement system using a square truncated pyramid-shape five-hole pitot probe
InactiveUS6336060B1Digital data processing detailsVolume/mass flow measurementTime responseEquation of the center
An arithmetic processing method and system in a wide velocity range flight velocity vector measurement system using a square truncated pyramid-shape five-hole Pitot probe. Approximation equations that determine attack angle alpha and sideslip angle beta in the form of third-order equations concerning attack angle pressure coefficient Calpha and sideslip angle pressure coefficient Cbeta, which are known numbers, are expressed in the form of a polynomial equation concerning Mach number M, where the coefficients are obtained from a lookup table. Coefficient calculations in the polynomial equation, and attack angle a and sideslip angle beta, calculations may be performed as simple calculations by specifying and applying known numbers into the approximation equation without solving third-order equations, with calibration coefficients that form the basis of coefficient calculation with the polynomial equation first being stored in memory in advance as a table for each wide velocity range on the basis of wind tunnel testing. A Mach number may be calculated instantly from a lookup table by specifying Mach pressure coefficient CM and angle to airflow pressure coefficient Cgamma. Wide velocity range flight velocity vector measurement with a high update rate which is capable of real time response in flight control as demanded by aircraft is obtained.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
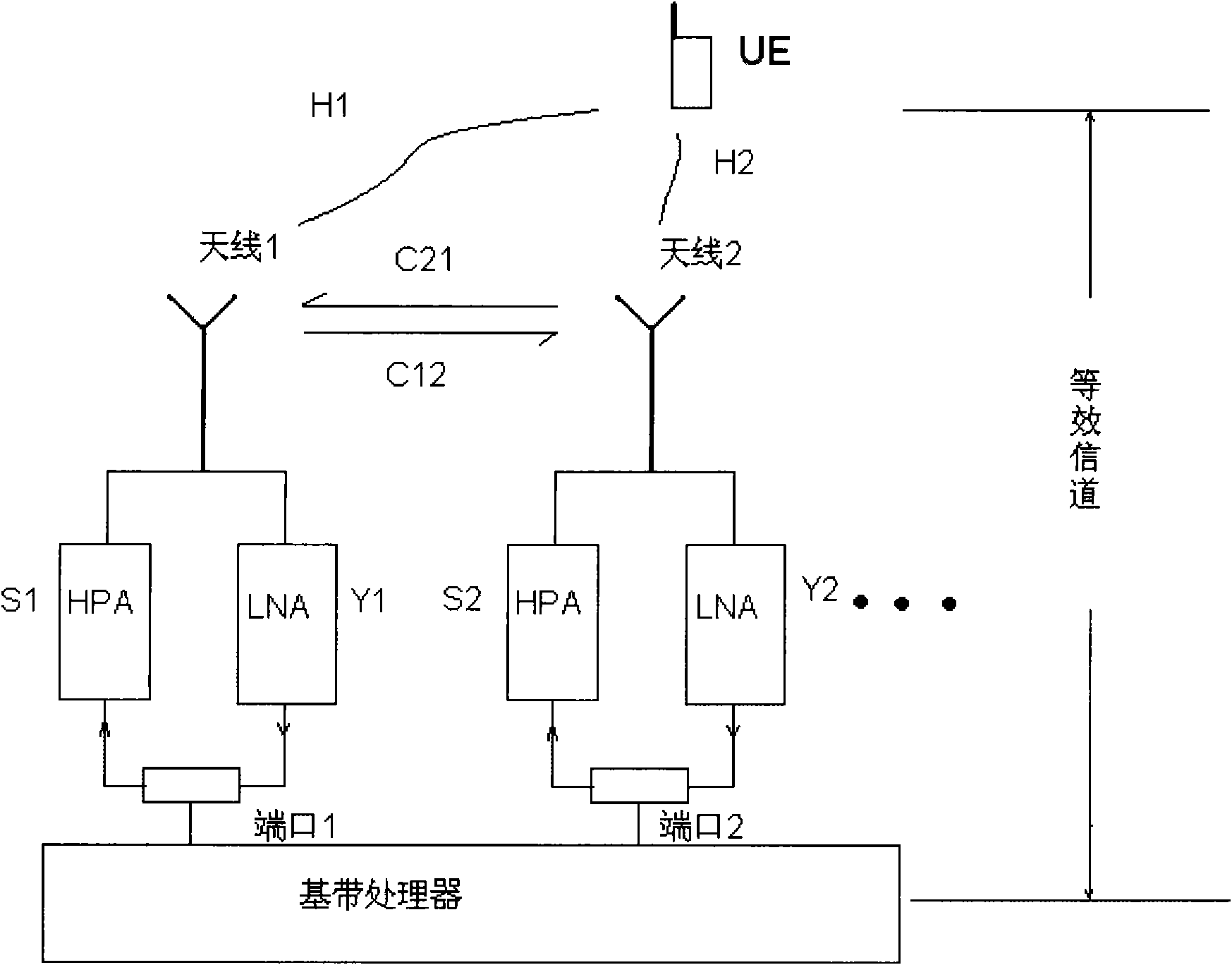
Statistical calibration of wireless base stations
InactiveUS6983127B1Easy CalibrationTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringRadio receptionRadio receiver
The present invention allows a radio receiver or a transmitter, with a plurality of antennas configured into an array, to be calibrated. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving a plurality of signals from a plurality of remote transmitters at the antenna array, sampling the signals received at at least two antennas of the array, computing a relative phase and amplitude of the sampled signals for each antenna, and computing calibration coefficients based on the relative phase and amplitude for the plurality of sampled signals from the plurality of remote transmitters for each antenna.
Owner:INTEL CORP
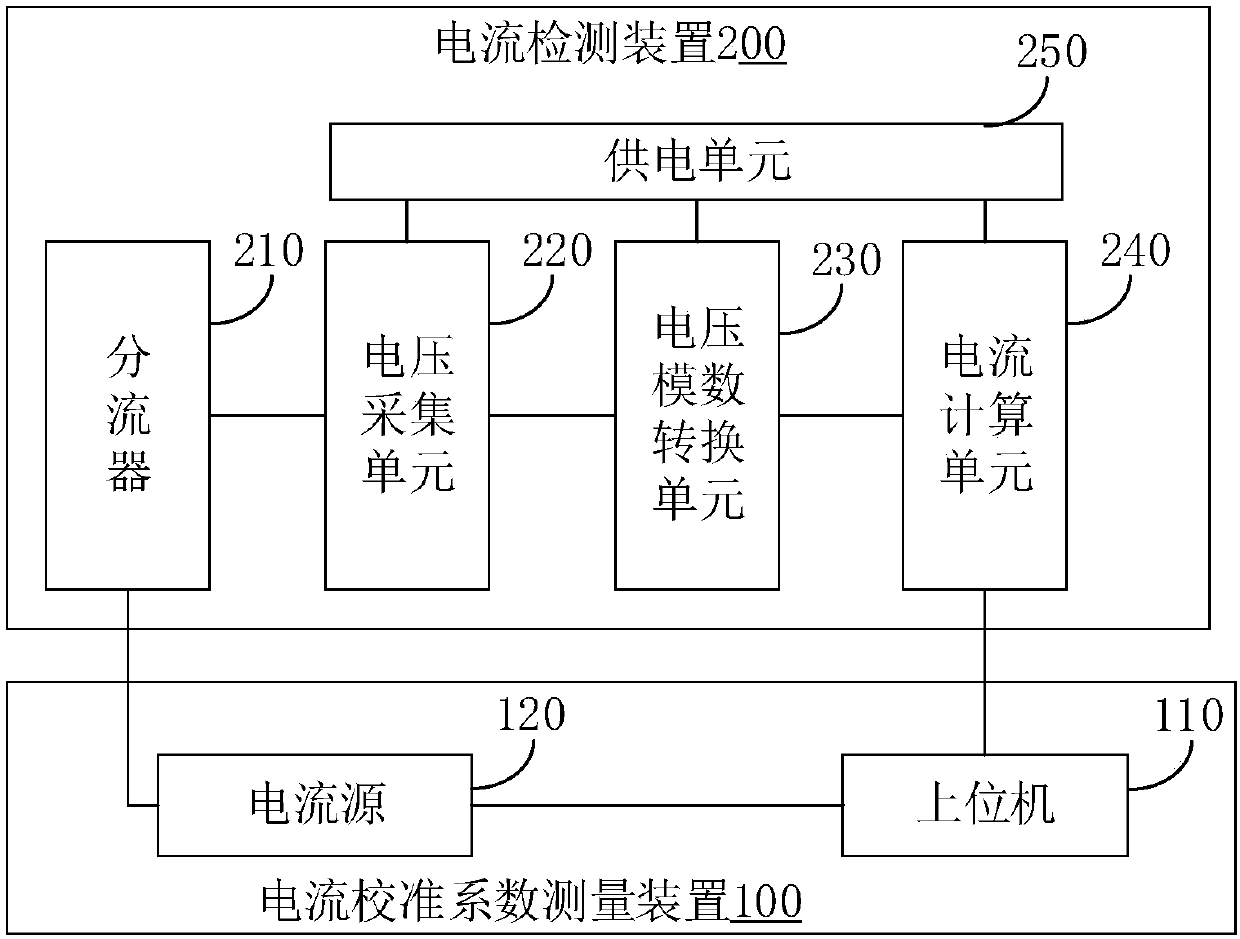
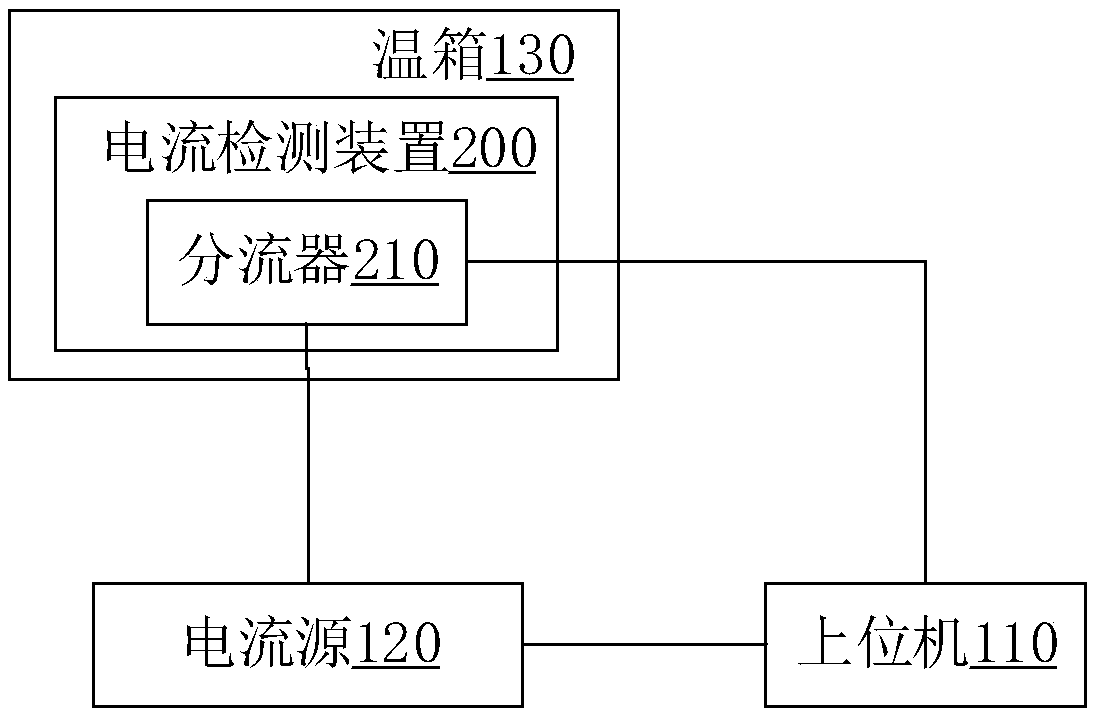
Current calibration coefficient measurement device, measurement method, current detection device and detection method
ActiveCN107728094AReduce mistakesImprove accuracyElectrical measurement instrument detailsMeasurement using digital techniquesShunt DeviceMeasurement device
The invention discloses a current calibration coefficient measurement device, a measurement method, a current detection device and a detection method. The measurement device comprises an upper computer and a current source, wherein the current source is serially connected with a shunt of a to-be-calibrated current detection device. The current detection device also comprises a voltage acquisitionunit for acquiring voltage analog signals at two ends of the shunt, a voltage analog-digital conversion unit for carrying out analog-digital conversion on the voltage analog signals to obtain a voltage value and a current calculation unit for calculating a detection current value according to the voltage value and the nominal resistance of the shunt. The upper computer is used for controlling thecurrent source to output current at a specified current value, and according to the specified current value and the detection current value calculated by the current calculation unit, a current calibration coefficient is calculated and obtained. According to the measurement device disclosed in the embodiment of the invention, a brand new current detection device current calibration coefficient measurement scheme is provided, a current calibration basis is provided for current detection by the current detection device, and the current detection precision is improved.
Owner:컨템포러리엠퍼렉스테크놀로지씨오리미티드
Apparatus and Methods Thereof for Error Correction in Split Core Current Transformers
ActiveUS20140200843A1Power measurement by digital techniqueVoltage/current isolationElectricityCalibration coefficient
Apparatus and methods are provided for electrical parameter measurements at points of interest, such as circuit breakers, machines, and the like. The devices which comprise of components that may require corrections, such as the errors induced by, but not limited to, the use of a split core mounted around a current carrier, and hence calibration coefficients are provided based on test, measurements and / or calculations respective of the devices. These coefficients may be stored in a database for retrieval when calibration of measurements received from a measuring device. In one embodiment at least one of the calibration coefficients is stored on the measuring device.
Owner:PANORAMIC POWER
System and method for monitoring electrical power usage in an electrical power infrastructure of a building
ActiveUS20130119972A1Dynamo-electric motor metersPower measurement by digital techniqueKaiman filterPower flow
Some embodiments can concern a method of using an electrical sensor device. The method can include: determining a first current measurement of a first current in an electrical power infrastructure and a first phase angle measurement of the first current; determining that a first load is coupled to the electrical power infrastructure; while the first load is coupled to the electrical power infrastructure, determining a second current measurement of a second current in the electrical power infrastructure and a second phase angle measurement of the second current; and using a Kalman filter to determine one or more first calibration coefficients for the electrical sensor device at least in part using the first current measurement, the second current measurement, the first phase angle, and the second phase angle. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:BELKIN INT
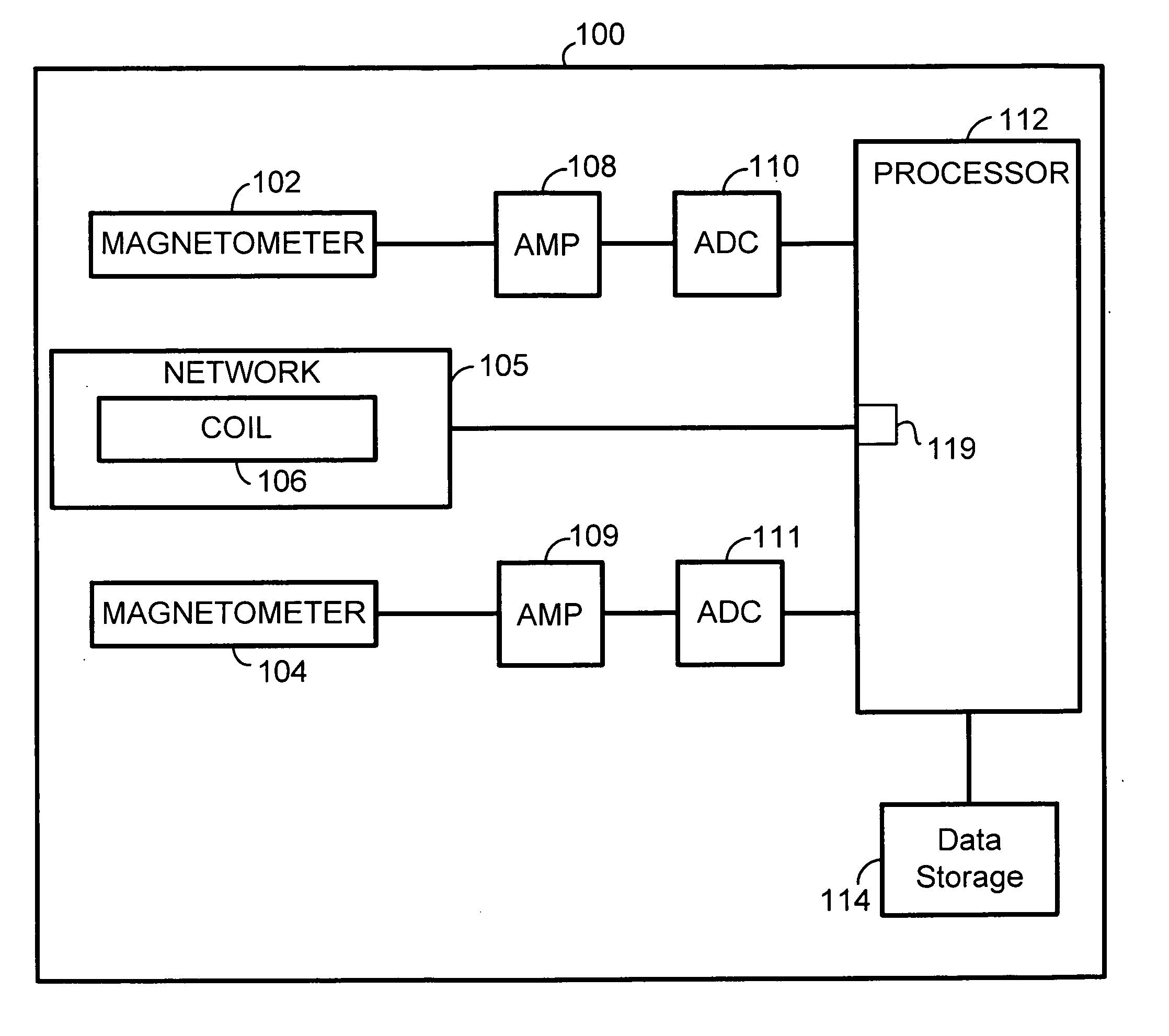
Method and system for electronic compass calibration and verification
ActiveUS20060152217A1Magnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCompassesMagnetic tension forceCalibration coefficient
A method and system for calibrating a magnetic compass and / or verifying a compass calibration, using a calibration magnetic field produced by a field-generating coil within the magnetic compass is described. The field-generating coil is located near magnetometers within the magnetic compass. Passing a self-trimming current through the coil produces a magnetic field that acts on the magnetometers. Samples of an output signal from each magnetometer are taken to obtain digital values that indicate the output signal from each magnetometer. The digital values are used by a processor to determine one or more calibration coefficient for using calibrating the magnetic compass. The samples of the output signals are taken when a self-trimming current is passing through the coil and when the self-trimming current is not passing through the coil. Calibration of the compass occurs by applying the one or more calibration coefficients to subsequent signals that indicate the output signals of one or more of the magnetometers.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
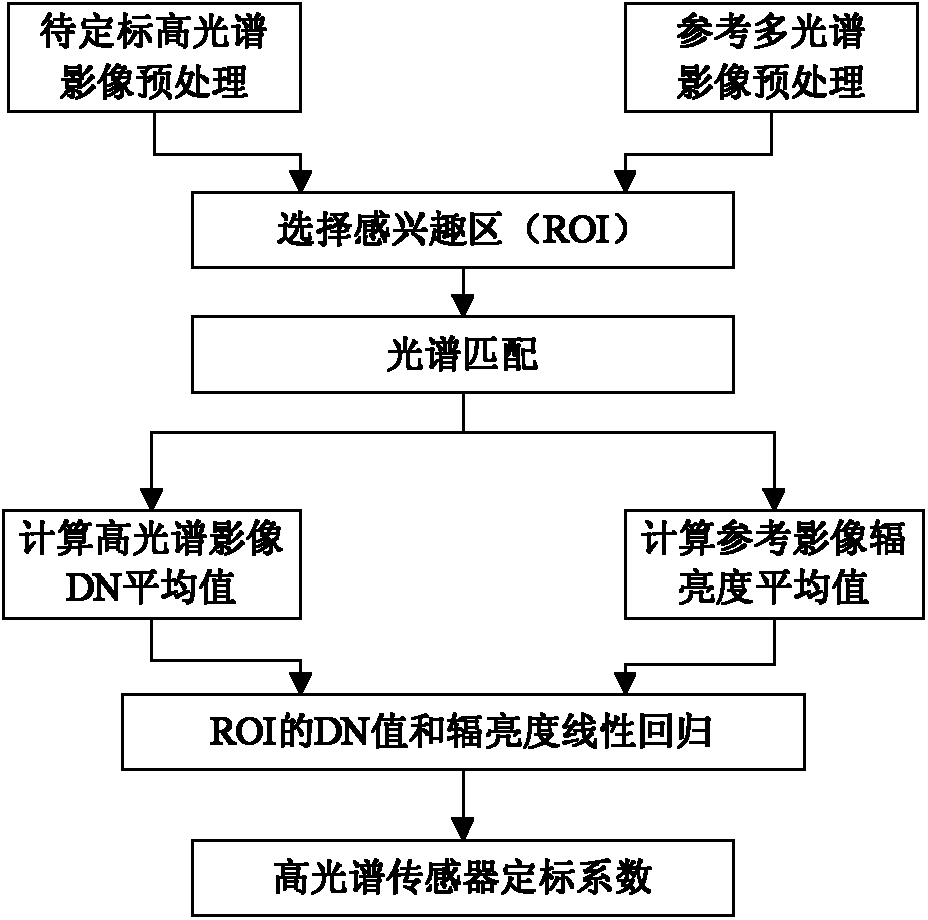
A cross-radiation calibration method for hyperspectral sensors based on multispectral sensors
InactiveCN102279393AAchieving Cross Radiation CalibrationReduce mistakesWave based measurement systemsLightnessEntrance pupil
The invention discloses a cross radiometric calibration method of a hyper-spectral sensor based on a multi-spectral sensor. The method is used for solving the cross radiometric calibration problem of the hyper-spectral sensor without a matched reference hyper-spectral image. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting cloudless hyper-spectral image data; selecting a multi-spectral reference image according to the hyper-spectral data; selecting a uniform ground object on the image as an interesting region; performing geometric precise correction of the two images; calculating entrance pupil radiances of various types of wave bands of the two sensors by using an atmospheric radiation transmission model; solving spectrum matching factors of various types of corresponding wave bands according to a certain rule; solving the entrance pupil radiances of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor by using the spectrum matching factors and the multi-spectral data; and linearly fitting pixel DN (Digital Number) values in the interesting region of the hyper-spectral image to be calibrated and the radiances of corresponding pixels of the multi-spectral reference image after being corrected through the spectrum matching factors to obtain calibration coefficients of the various types of wave bands of the hyper-spectral sensor. The method has the advantages of good stability, high reliability, high precision and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Centralized calibration coefficients for sensor based measurements
InactiveUS20060106561A1Save powerAccurate operationData processing applicationsTesting/calibration apparatusData retrievalCalibration coefficient
Disclosed is a methodology for reducing data processing time for data retrieved from a condition responsive sensor. During sensor manufacture, the manufacturer determines and stores calibration data for individual sensors in a database that associates sensor identification data and calibration data. The calibration data is later associated with a sensor data reading device that retrieves the calibration data based on reading the sensor device identification data and employs the retrieved calibration data to compensate raw condition responsive data read from the sensor device.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
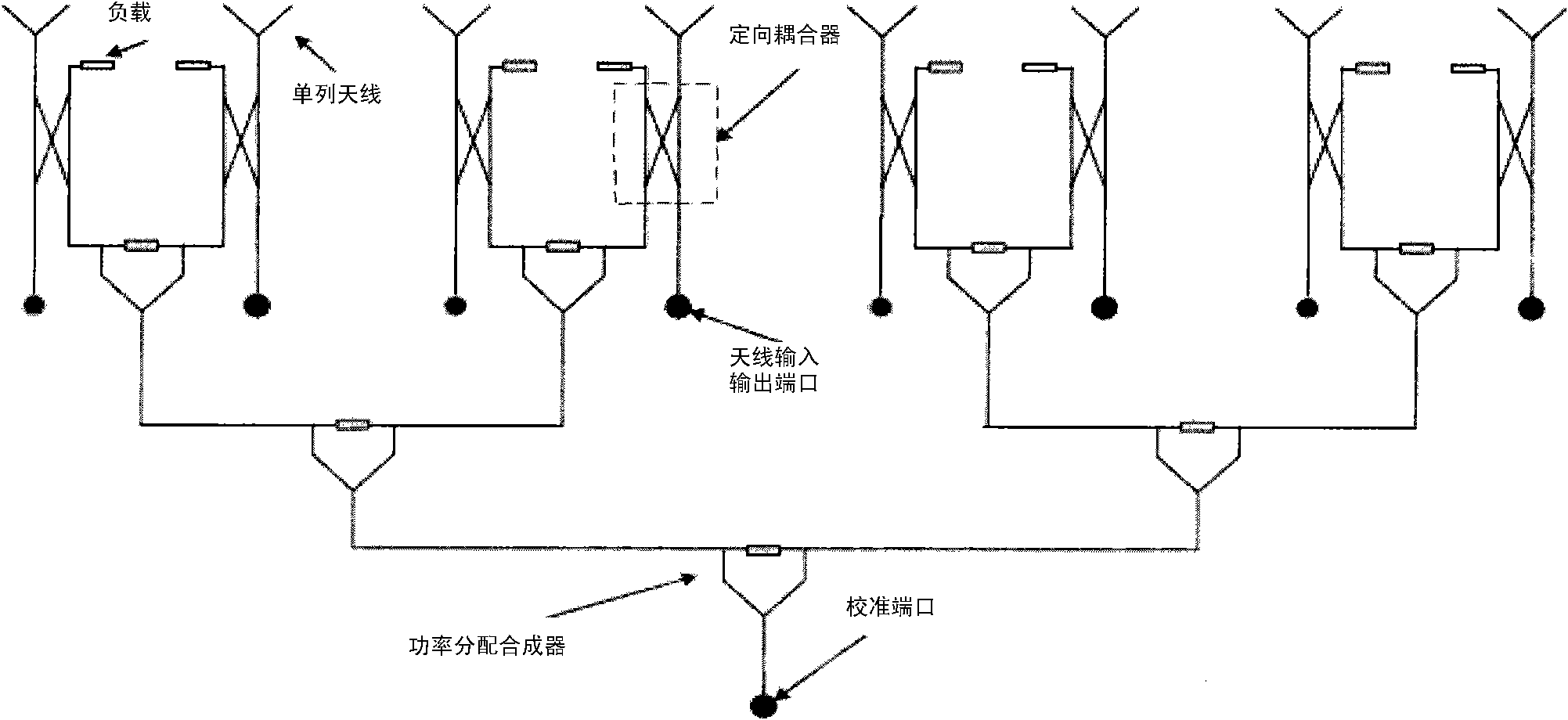
Antenna calibration method and device
ActiveCN102195695AImprove calibration accuracyImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityCouplingData memory
The embodiment of the invention discloses an antenna transmission calibration method, which comprises that: a baseband signal processor transmits a calibration sequence by a transmission radio frequency channel, and a calibration signal processor receives the calibration sequence by a calibration channel; the calibration signal processor judges whether errors of coupling networks are required to be compensated or not according to the accuracy of a receiving coupling network, calculates a calibration coefficient by the received calibration sequence, and transmits the calculated calibration coefficient to the baseband signal processor; and the baseband signal processor performs coefficient compensation according to the calibration coefficient. The embodiment of the invention also discloses an antenna transmission calibration device, which comprises the baseband signal processor, the calibration signal processor, a coupling signal processor and a coupling data memory. The embodiment of the invention can take the errors among channels of the coupling networks into account in calibration, perform the error compensation on the coupling networks, and effectively improve the antenna calibration accuracy, thereby improving beamforming performance.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
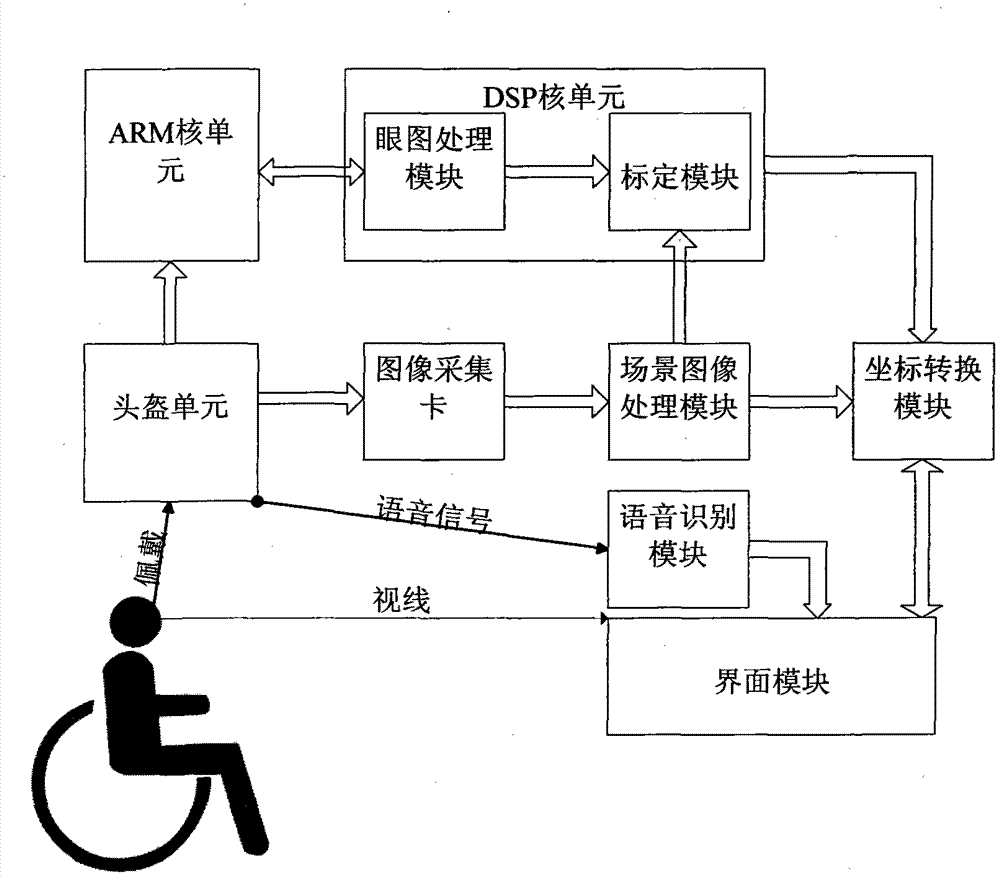
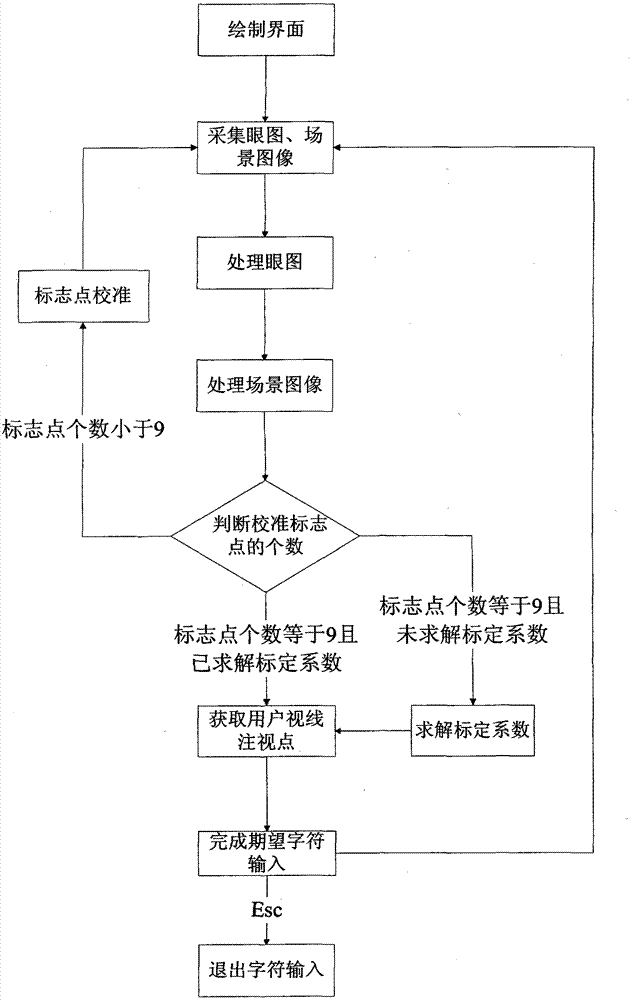
Character input device and method based on eye-gaze tracking and speech recognition
InactiveCN103076876APrecise positioningOvercome the disadvantage of low gaze precisionInput/output for user-computer interactionSpeech recognitionFixation pointSpeech identification
The invention discloses a character input device and method based on eye-gaze tracking and speech recognition. The device comprises a helmet unit, an ARM (advanced RISC machine) core unit, an image acquisition card, a voice identification module, a DSP (digital signal processor) core unit, a scene image processing module, a coordinate conversion module and an interface module. The method comprises the following steps of: on the basis of collecting and processing an eye pattern, a scene image and a user voice signal, calibrating to obtain a calibration coefficient; solving a two-dimensional calibration equation and a coordinate transformation matrix to obtain the coordinate value of a user sight fixation point in an interface coordinate system; finally, obtaining a character which is expected to be input; and cooperating with the user voice information to finish the operations of character input and the four arithmetic operation. The invention has the advantages of high character input fixation precision, big head moving range, simpleness in operation and good practicality and maneuverability.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
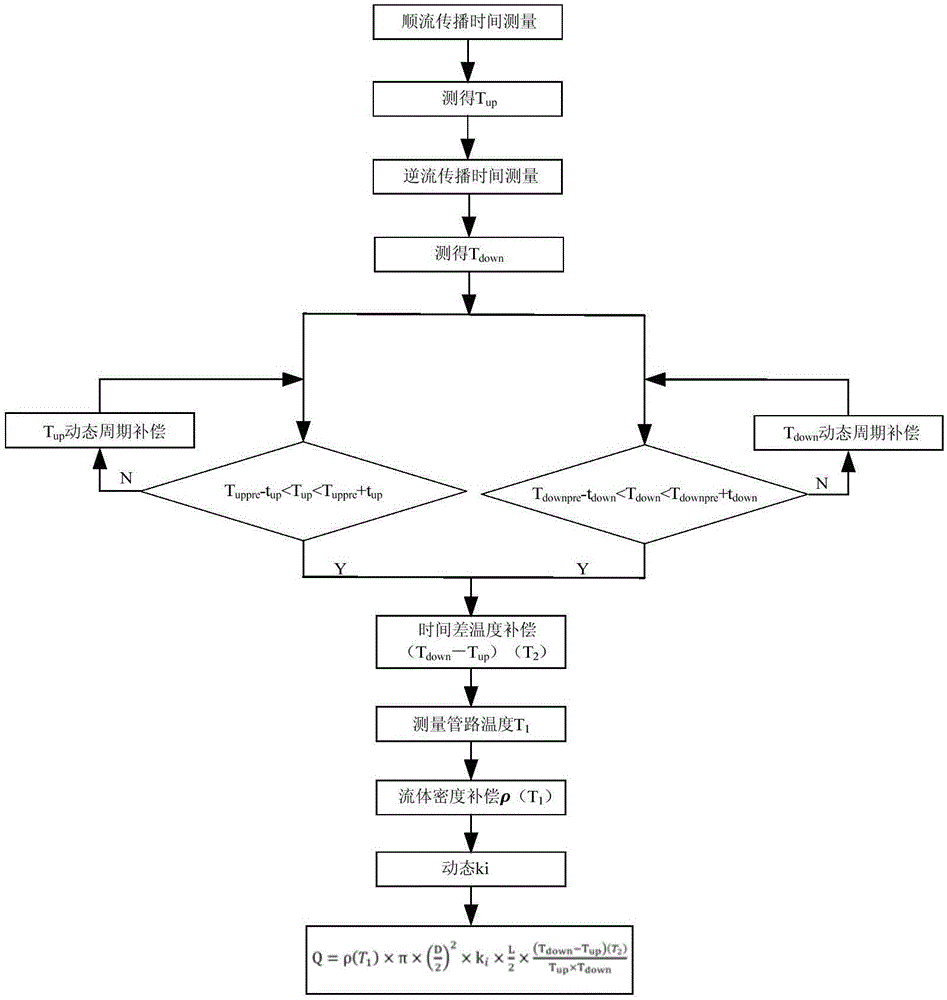
Dynamic compensation method for ultrasonic flow meter
ActiveCN105091970AEliminate calculation biasImprove calculation accuracyTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementLiquid densityLookup table
The invention discloses a dynamic compensation method for an ultrasonic flow meter. The dynamic compensation method comprises the step of measuring time dynamic period compensation and further comprises the step of conducting fluid density compensation, the step of conducting time difference temperature compensation of ultrasonic countercurrent spreading time and ultrasonic fair current spreading time, the step of looking up a calibration coefficient dynamically according to a calibration coefficient lookup table established in advance and the step of calculating the flow of multistage dynamic compensation, and therefore measuring time dynamic period compensation is conducted on the problem that ultrasonic spreading time measurement has deviation due to the water attack effect brought by instant opening and closing of a valve or residual bubbles in a pipeline; furthermore, compensation is conducted on the liquid density change caused by the temperature; temperature compensation is conducted on the time difference benchmark treating the influences of the temperature change of an element in a circuit box, the lookup table is established on the calibration coefficient without a constant value, and dynamic looking-up is conducted during flow calculation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
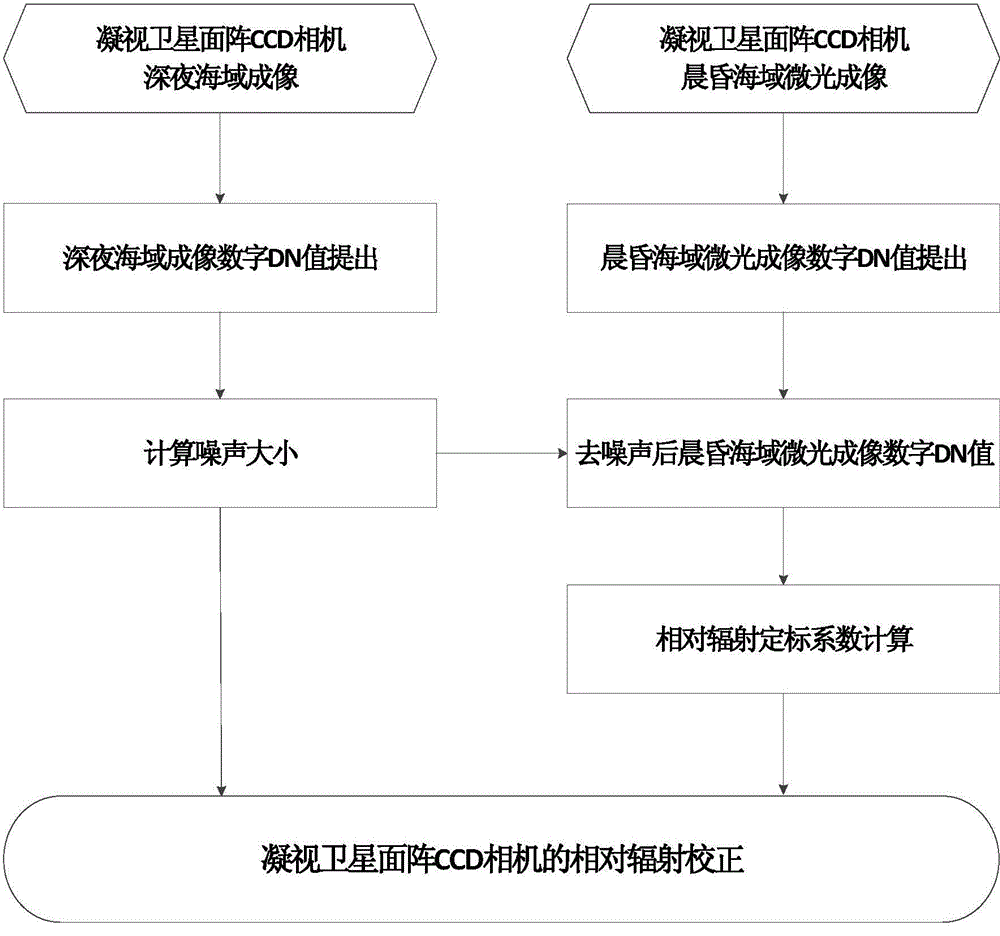
Relative radiation correction method of staring satellite area array CCD camera
ActiveCN104065892AControl for differences in the time domainControl varianceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCcd cameraCalibration coefficient
A relative radiation correction method of a staring satellite area array CCD camera is provided. The methods is characterized by, to begin with, establishing a radiation response model of detection elements of the area array CCD camera; then, utilizing the staring satellite area array CCD camera to carry out real-time and fixed-point observation on large-area deep sea far away from the land at the late night without moonlight, determining the amplitude of the noise through the remote sensing images obtained for many times, and carrying out denoising to obtain remote sensing image data without noise; then, in the morning and at dusk, utilizing the staring satellite area array CCD camera to carry out continuous imaging on the large-area deep sea far away from the land under the weak and uniformly-scattered skylight, and calculating relative radiation calibration coefficients through the remote sensing images which are obtained for many times and are denoised; and at last, obtaining a relative radiation correction image of the staring satellite area array CCD camera. The method helps to solve the technical problem of no relative radiation correction method is provided for the staring satellite area array CCD camera in in-orbit operation.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Aberration-free image reconstruction method based on CCD array pixel response function frequency domain calibration
InactiveCN104320598ARich calibration parametersThe calibration result is accurateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionFourier optics
The invention discloses an aberration-free image reconstruction method based on CCD array pixel response function frequency domain calibration, and belongs to the technical field of detectors. A frequency domain model of pixel response functions is established, same-frequency lasers with high stability are utilized for generating sinusoidal interference fringes in a far field, fringe light fields at different spatial frequencies are acquired by changing the relative positions of the same-frequency lasers, frequency domain calibration is conducted on the pixel response functions, calibration coefficients in all orders of all the pixel response functions are acquired respectively, on the basis and in combination with a Fourier optics method, CCD imaging reconstruction is achieved, and aberration-free imaging of a CCD detector can be achieved. According to the method, the pixel frequency domain response functions can be calibrated, meanwhile, tiny offset of the relative positions of all pixels can be calibrated, reconstructed images are free of sample blurs, modulation transfer functions (MTF) approach 1, the contrast ratio is not decreased, and the aberration-free image reconstruction method has the advantages of being high in calibration accuracy and wide in application prospect.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
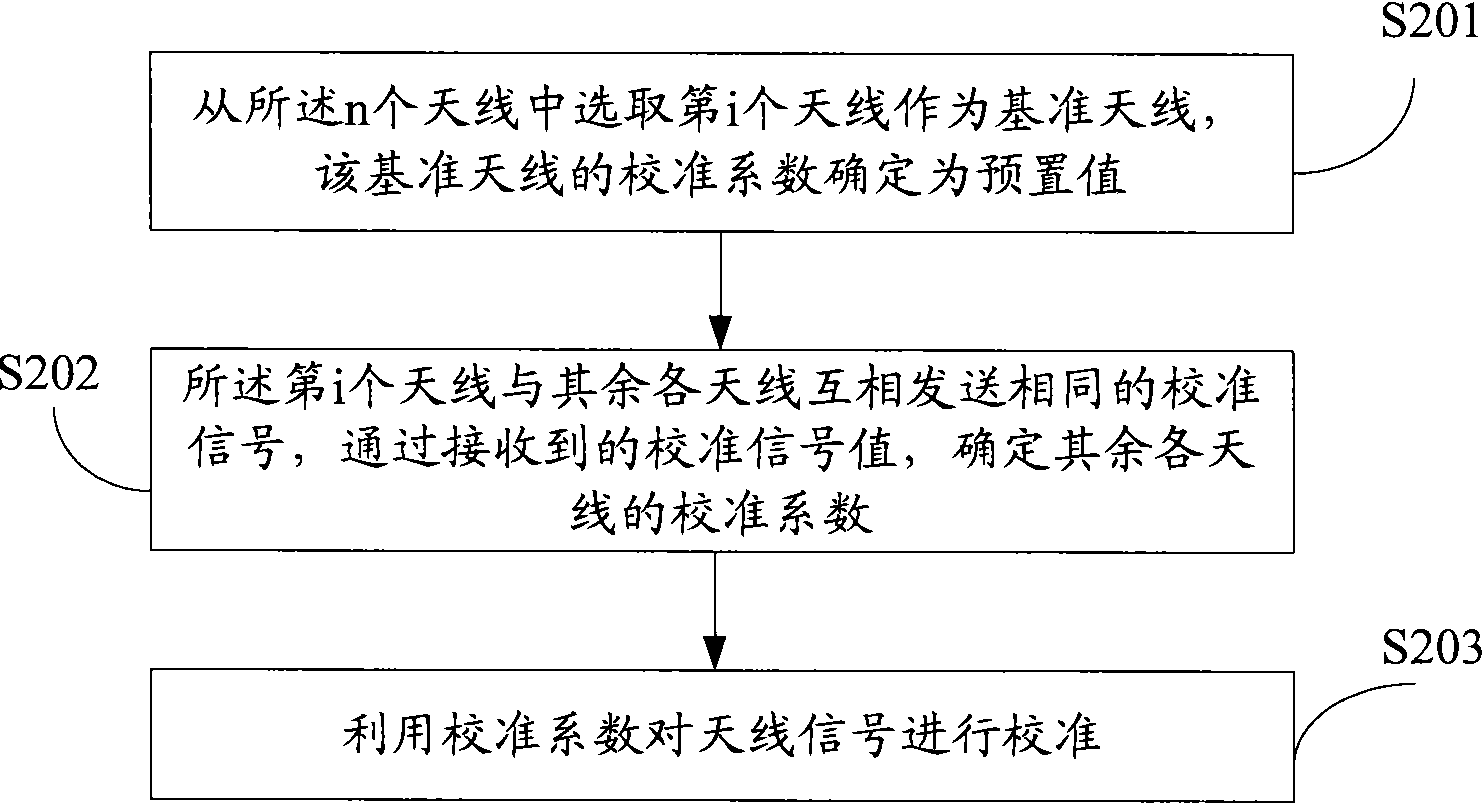
Method and device for calibrating antennae
InactiveCN101674140ALow costAvoid difficultyTransmission control/equalisingDiversity/multi-antenna systemsReference antennaEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for calibrating antennae, which are used for calibrating n antennae, wherein n is more than or equal to 2. The method comprises the following steps: selecting the ith antenna from the n antennae as a reference antenna, and determining the calibration coefficient of the reference antenna as a preset value; sending the same calibrating signals between the ith antenna and the rest antennae, and determining the calibration coefficients of the rest antennae according to the received values of the calibration signals; and using the calibration coefficients to calibrate antenna signals. The method and the device need no calibration networks, in short, connections are unnecessary to be established between the antennae, namely a unified calibration portis not needed for receiving and sending the calibration signals, thereby avoiding the problems that the prior scheme has high cost and large implementation difficulties caused by the calibration networks.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
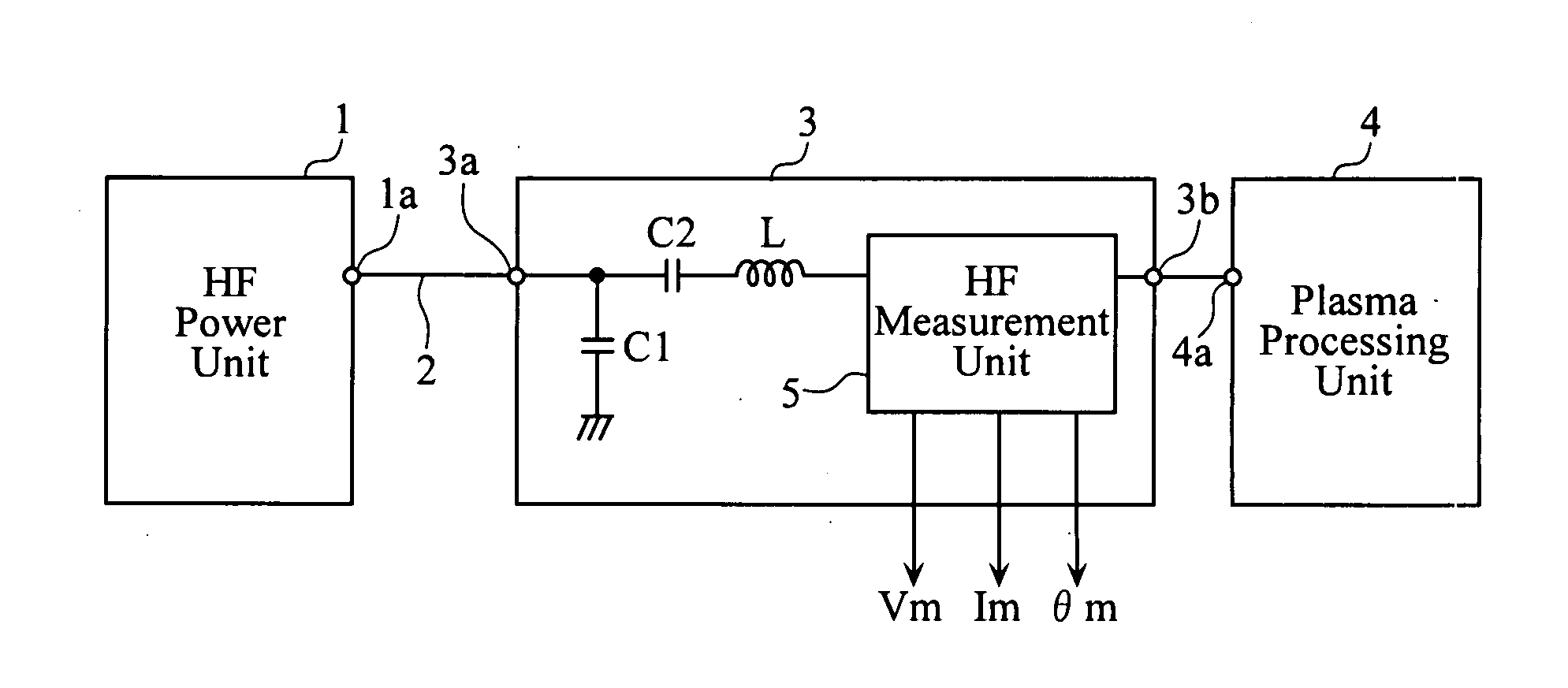
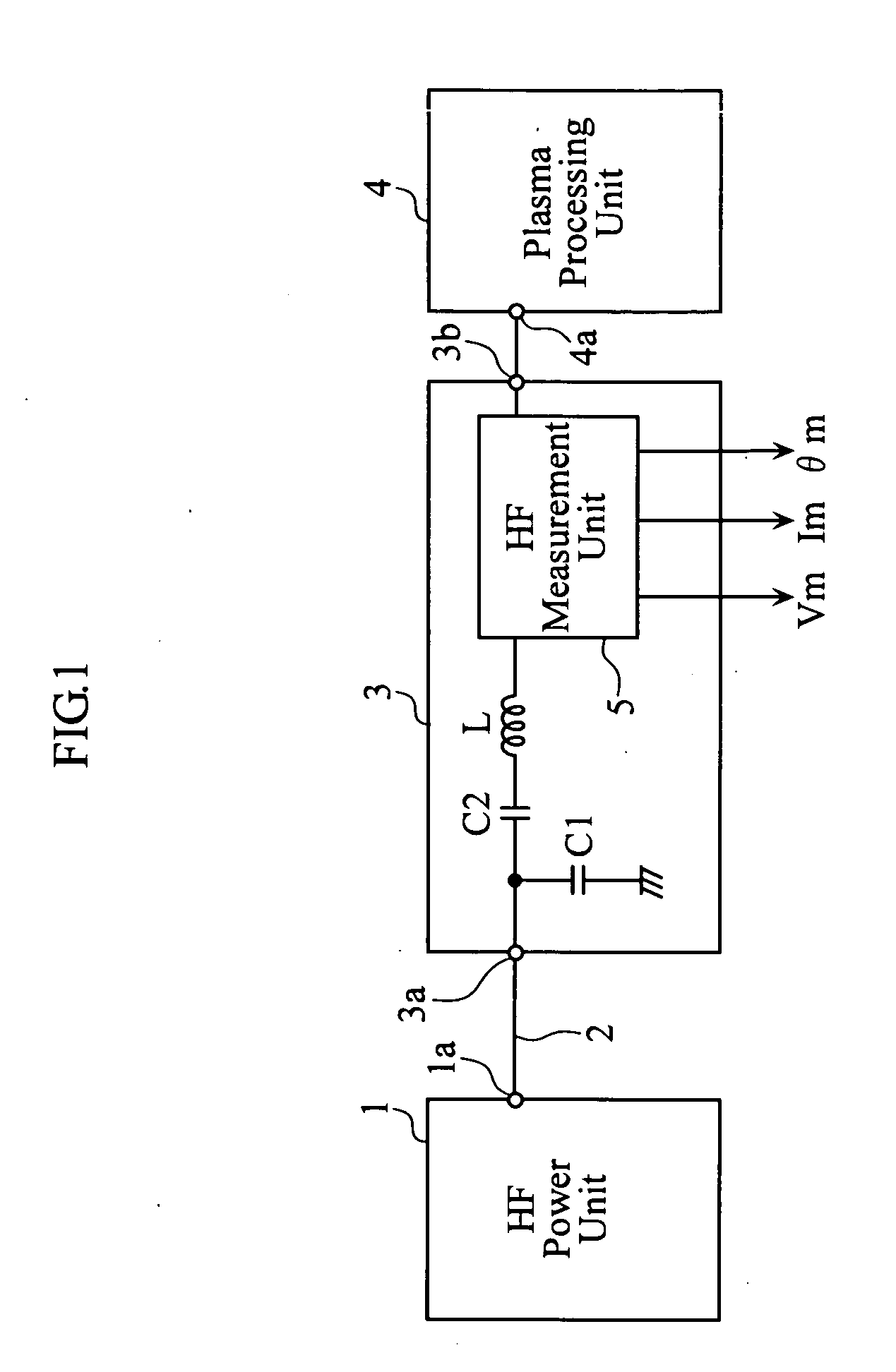
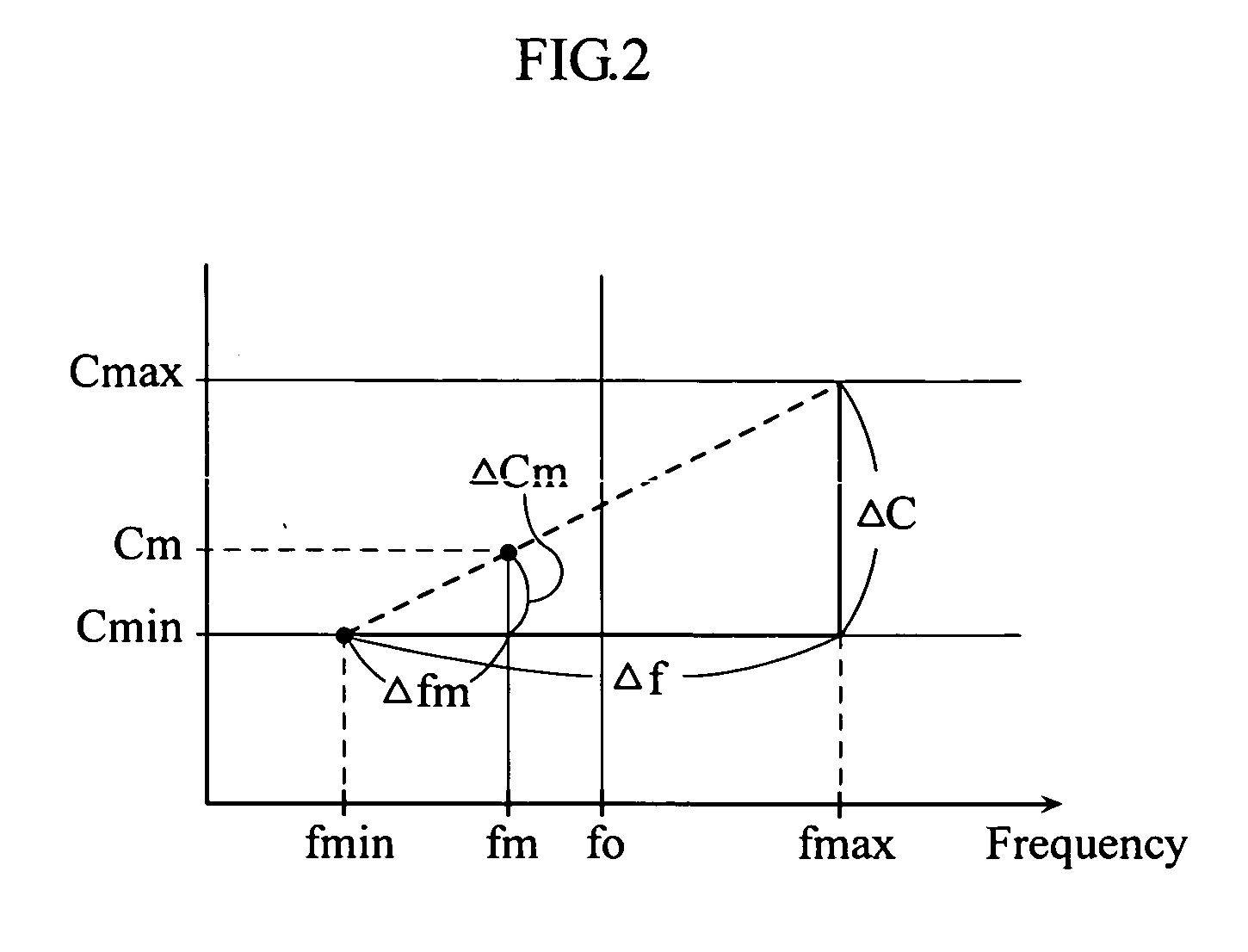
Plasma processing system
ActiveUS20070152678A1Easy to set upEasy to checkElectric devicesElectric discharge tubesLower limitSignal detector
A high-frequency measurement unit includes a signal detector for detecting a high-frequency signal, and a calibration coefficient storage for storing calibration coefficients Cmin and Cmax used to calibrate a value Amin detected at the lowest limit frequency fmin and a value Amax detected at the uppermost limit frequency fmax to a proper measurement value Asmin and to a proper measurement value Asmax, respectively. The high-frequency measurement unit further includes a frequency detection unit for detecting a frequency fm of the high-frequency signal, a calibration coefficient calculation unit for calculating a calibration coefficient Cm for the frequency fm, and a calibration unit for calibrating the value Am detected by the signal detector to a proper measurement value Asm by using the calibration coefficient Cm calculated by the calibration coefficient calculation unit.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
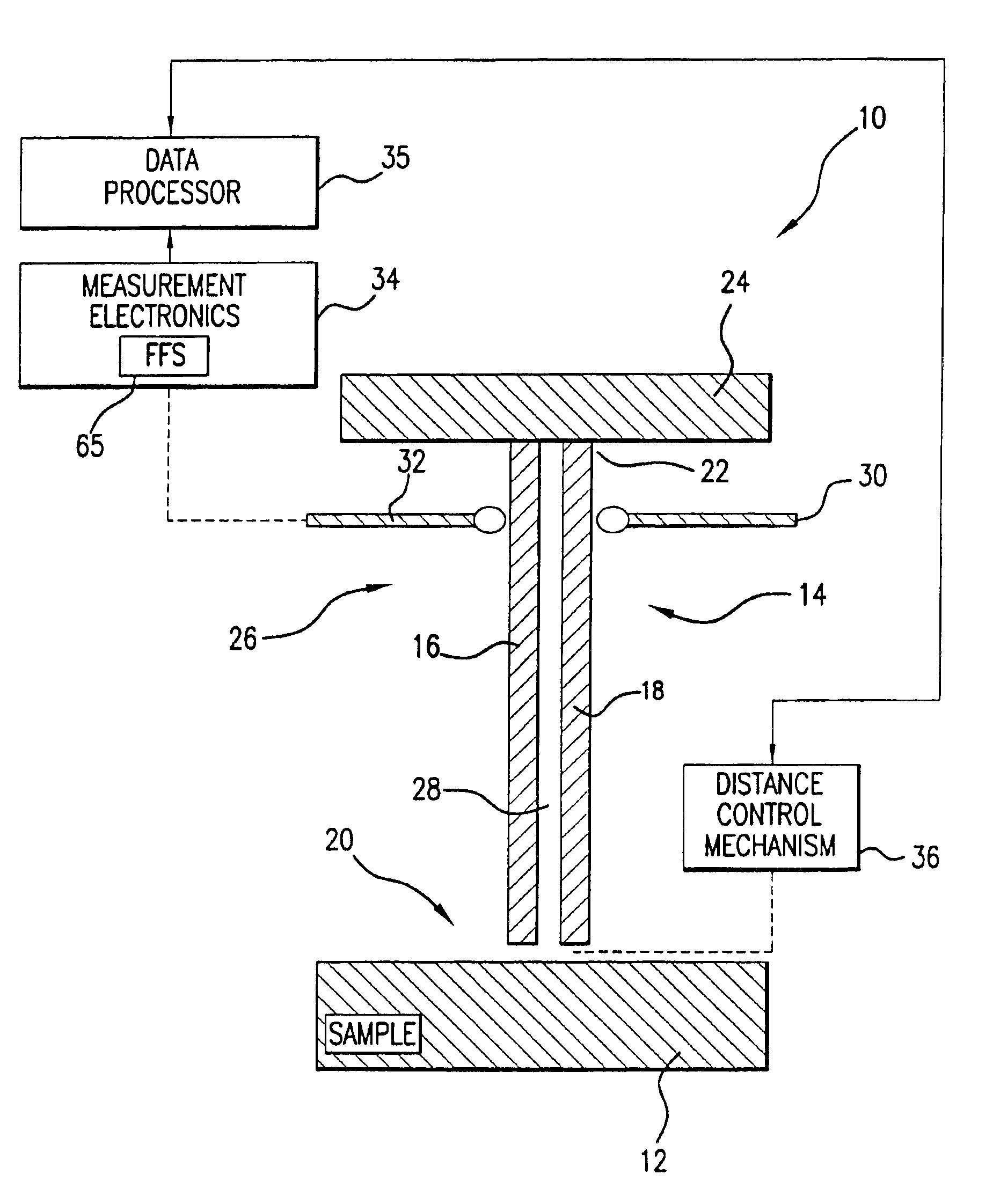
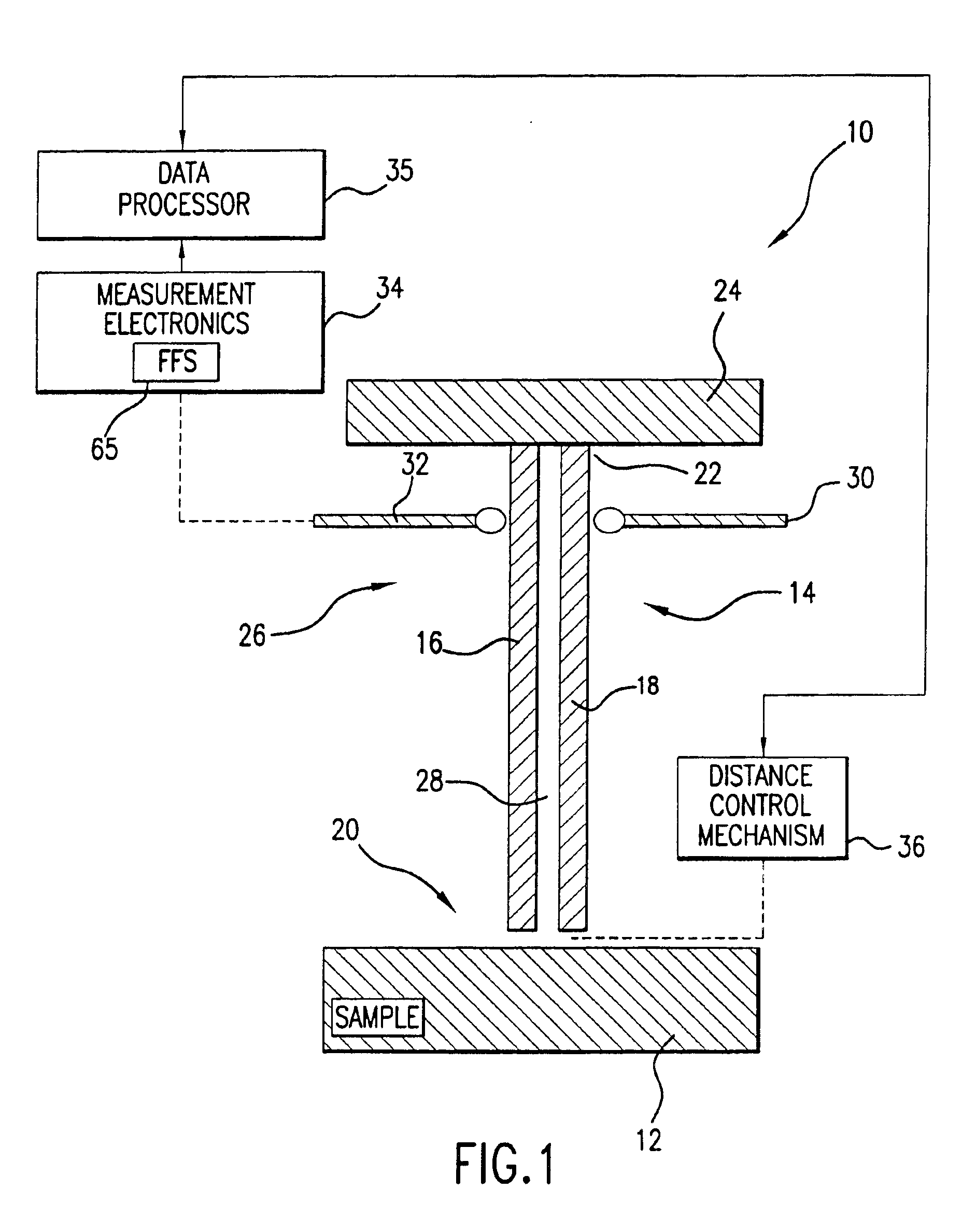
System and method for quantitative measurements of a material's complex permittivity with use of near-field microwave probes
InactiveUS6856140B2High precision measurementEasily controlled for modificationResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansFigure of meritFrequency shift
A method for measuring a material's complex permittivity is provided where a near-field microwave probe is positioned a predetermined distance from a first and a second standard sample for measuring a relative resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave probe for standard samples. Based on measurements, calibration coefficients are calculated. A relative resonant frequency shift of the near-field microwave probe for a sample under study is measured by fast frequency sweep technique while the distance between the tip of the probe and the sample under the study is maintained nominally at the distance between the tip of the probe and each standard sample during a calibration procedure by a shear-force based distance control mechanism. Also, the change in the quality factor of the probe for unloaded and loaded resonator is measured. The dielectric constant of the sample under study is calculated using the resonant frequency shift and the change in the quality factor of the near-field microwave probe for the sample under study and the calibration coefficients obtained during the calibration procedure.
Owner:SEMICON PHYSICS LAB
Exhaust gas measuring instrument
InactiveUS6460400B1Eliminate disadvantagesPossible to obtainEngine testingWithdrawing sample devicesDifferential pressureMeasuring instrument
An exhaust gas measuring instrument has a mini-dilution tunnel (22) in which a part of exhaust in the exhaust pipe (15) of an engine is introduced through sampling tube (30) and diluted with air. The exhaust gas is diluted in the mini-dilution tunnel (22), a high response differential pressure type extracted gas flow meter (31 and 40) measures the exhaust gas flow rate (Qs) in the sampling tube (30). A high response differential pressure type bypassed gas flow meter (29 and 39) measures the exhaust gas flow rate (Qb) in the exhaust pipe (15). The flow rate split ratio R=Qb / Qs is obtained by dividing the exhaust gas flow rate (Qb) by the exhaust gas flow rate (Qs). A calibration coefficient (k) of the flow rate split ratio is obtained and the calibrated flow rate split ratio (k.R) is calculated by multiplying the flow rate split ration by the calibration coefficient.
Owner:HINO MOTORS LTD
Calibration method and calibration apparatus for calibrating mismatch between I-path and Q-path of transmitter/receiver
ActiveUS9008161B1Transmitters monitoringAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFinite impulse responseFrequency spectrum
A method for calibrating mismatches of an in-phase signal path and a quadrature signal path of a transmitter, including: additionally configuration at least one mixer calibration coefficient at a transmitting part of the transmitter; obtaining at least one mixer testing signal from the transmitting part via loopback for spectrum analysis to derive at least one mixer spectrum analysis result; adjusting the mixer calibration coefficient of the transmitting part according to the mixer spectrum analysis result; and additionally utilizing an in-phase signal path finite impulse response filter and a quadrature signal path finite impulse response filter to calibrate mismatches between a low pass filter of the in-phase signal path of the transmitting part of the transmitter and a low pass filter of the quadrature signal path of the transmitting part of the transmitter. A similar mismatch calibration operation may be applied to a receiver.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Relative radiometric correction method for star-load TDICCD camera
ActiveCN101226639ASolve the problem of different nonlinearity of light intensity responseSolve for uniformityImage analysisWave based measurement systemsCalibration coefficientLinear fitting
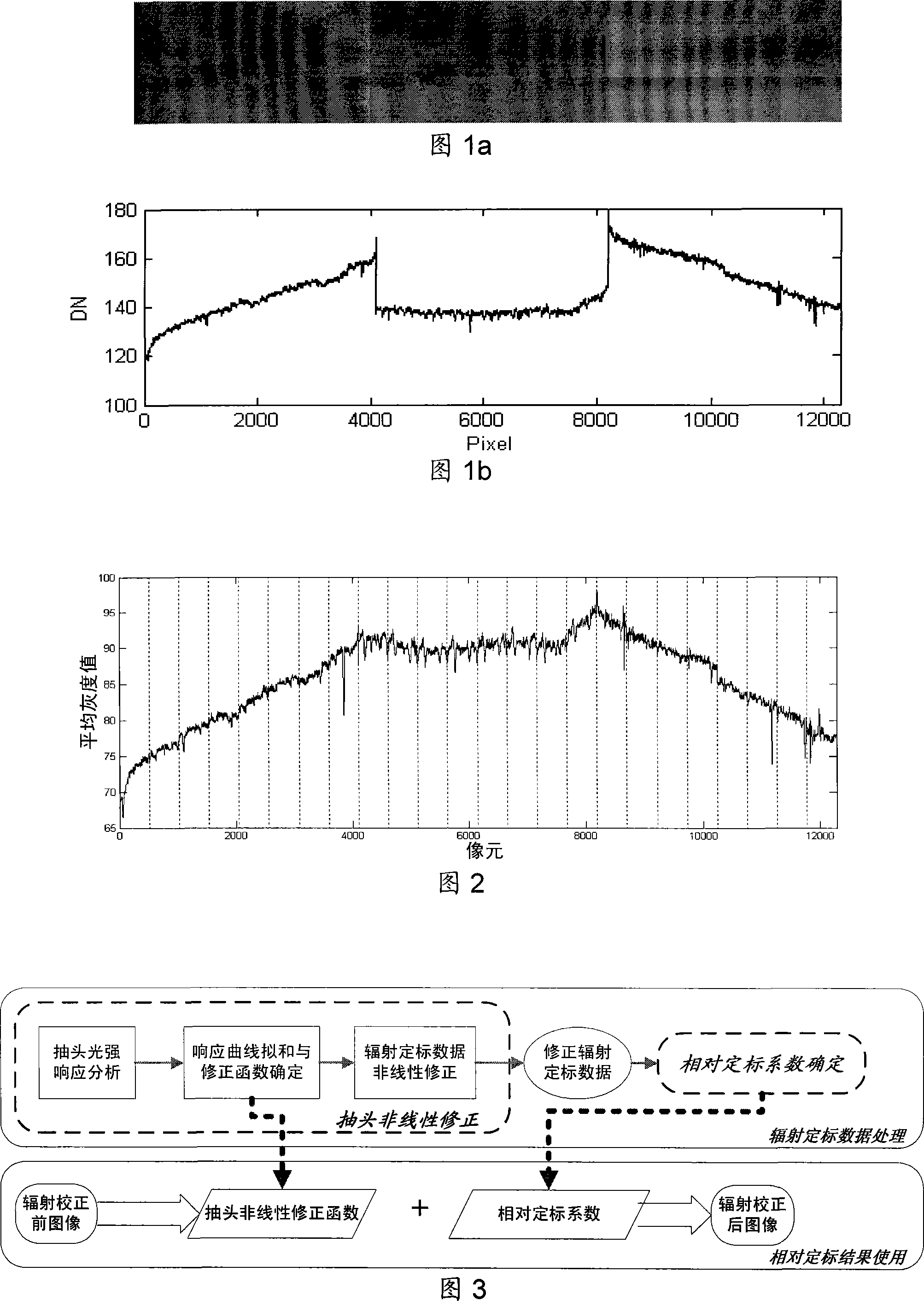
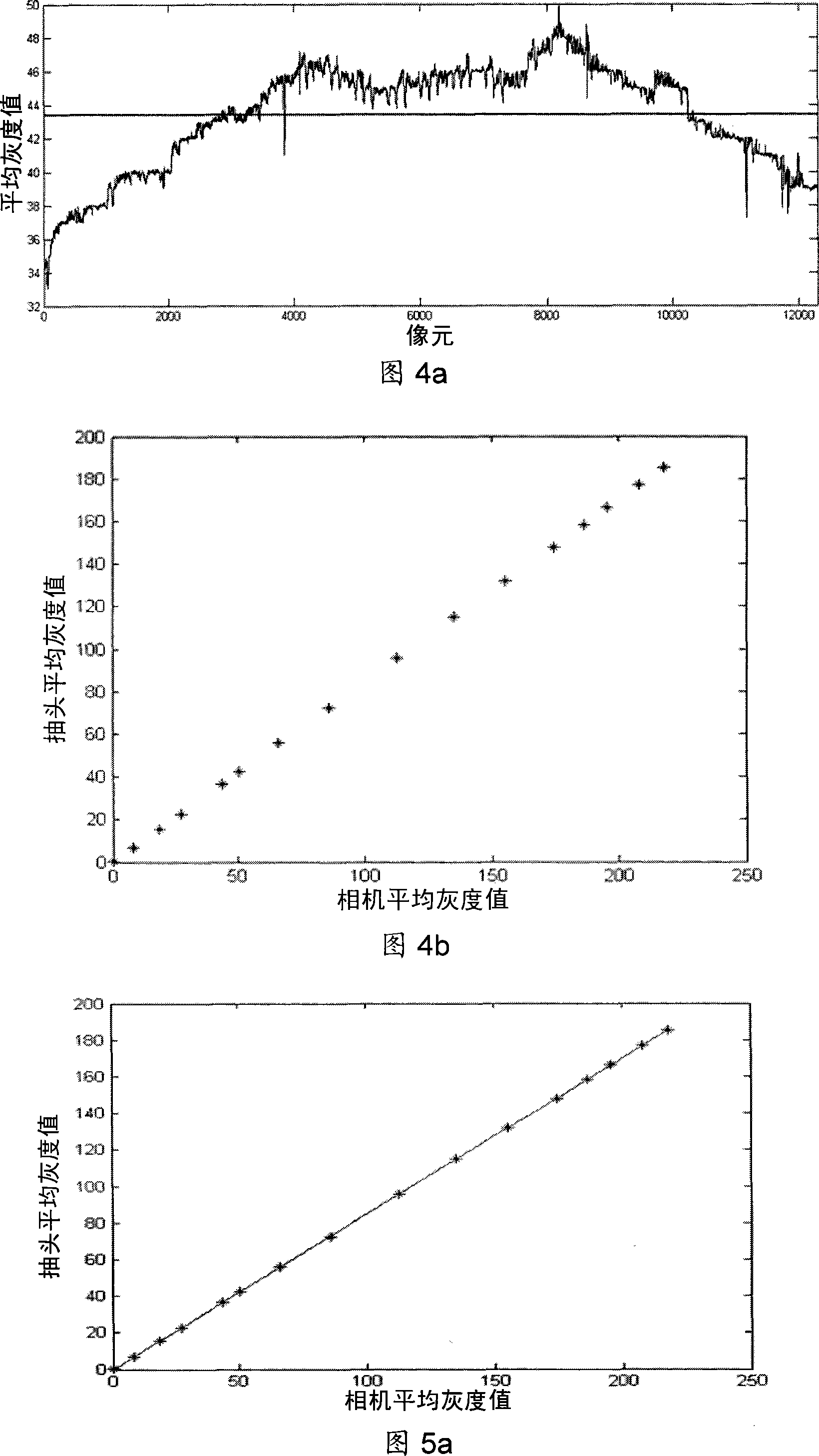
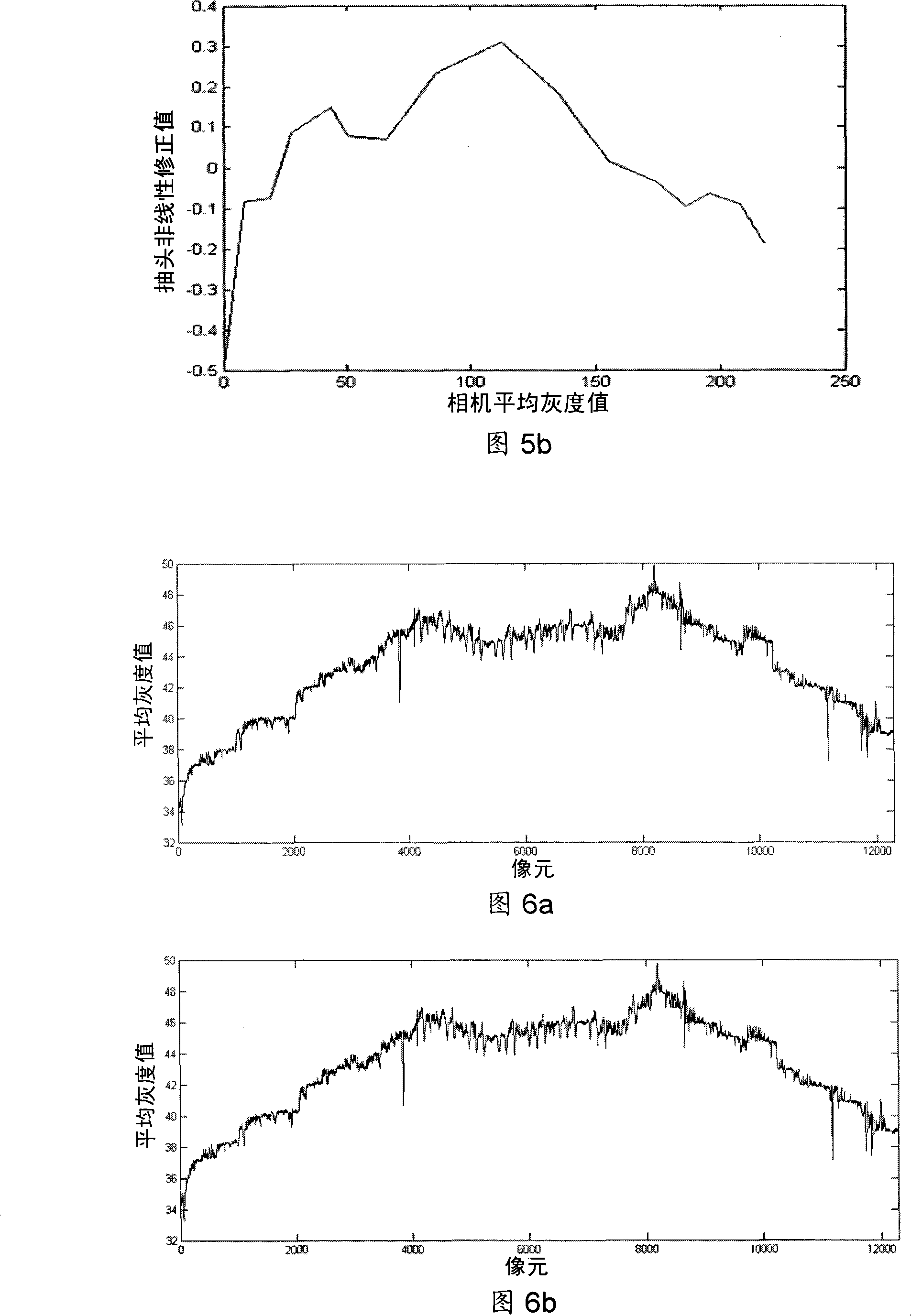
Disclosed is a relative radiometric correction method for the satellite-borne TDICCD camera. The steps comprises (1) analyzing the response output of a tapping under different light intensities and acquiring a scatter diagram of tapping light intensity response, (2) carrying out linear fitting to the scatter diagram of tapping light intensity response, then carrying out linear interpolation to the scatter diagram to obtain an interpolation curve, subtracting the interpolation curve of each tapping from respective fitting line to obtain a non-linear modified function of the tapping to light intensity, (3) using the non-linear modified function to carry out non-linear modification one after another to tapping of radiometric calibration data, and obtaining modified radiometric calibration data, (4) processing the modified radiometric calibration data and obtaining a modified inter- calibration coefficient, (5) carrying out radiation homogeneousness correction to arbitrary image produced by TDICCD via using the non-linear modified function and the modified inter- calibration coefficient. The invention resolves the problem that non-linear response to light intensity of the tapping can not be corrected in existing radiometric calibration method, and can increase relative radiometric calibration accuracy.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Splicing bright/dark line compensation method
The invention puts forward a splicing bright / dark line compensation method comprising the following steps: (i) shooting an image displayed by an LED display screen through an image acquisition device under control to get a correction image; (ii) processing the correction image to get the brightness compensation values of multiple LED lamp points needing correction at a splicing gap in the LED display screen; and (iii) sending the brightness compensation values of the multiple LED lamp points needing correction at the splicing gap to the LED display control system hardware of the LED display screen all at once so as to update the brightness and chrominance calibration coefficients corresponding to the multiple LED lamp points in the original brightness and chrominance calibration coefficients in the LED display control system hardware. Therefore, secondary correction of the bright / dark lines of an LED display screen can be realized without an original database file, the brightness compensation values can be sent all at once to the LED display control system hardware by generating a two-dimensional image, and the method is quick and efficient.
Owner:XIAN NOVASTAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com