Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Laser bonding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laser bonding is a marking technique that uses lasers to bond an additive marking substance to a substrate. First invented in the mid 1990s by Paul W. Harrison, the founder of TherMark, LLC, this patent protected and patent pending technology produces permanent marks on metal, glass, ceramic and plastic parts for a diverse range of industrial and artistic applications, ranging from aerospace and medical to the awards and engraving industries. It differs from the more widely known techniques of laser engraving and laser ablation in that it is an additive process, adding material to the substrate surface instead of removing it.
Membrane-integrated energy exchange assembly
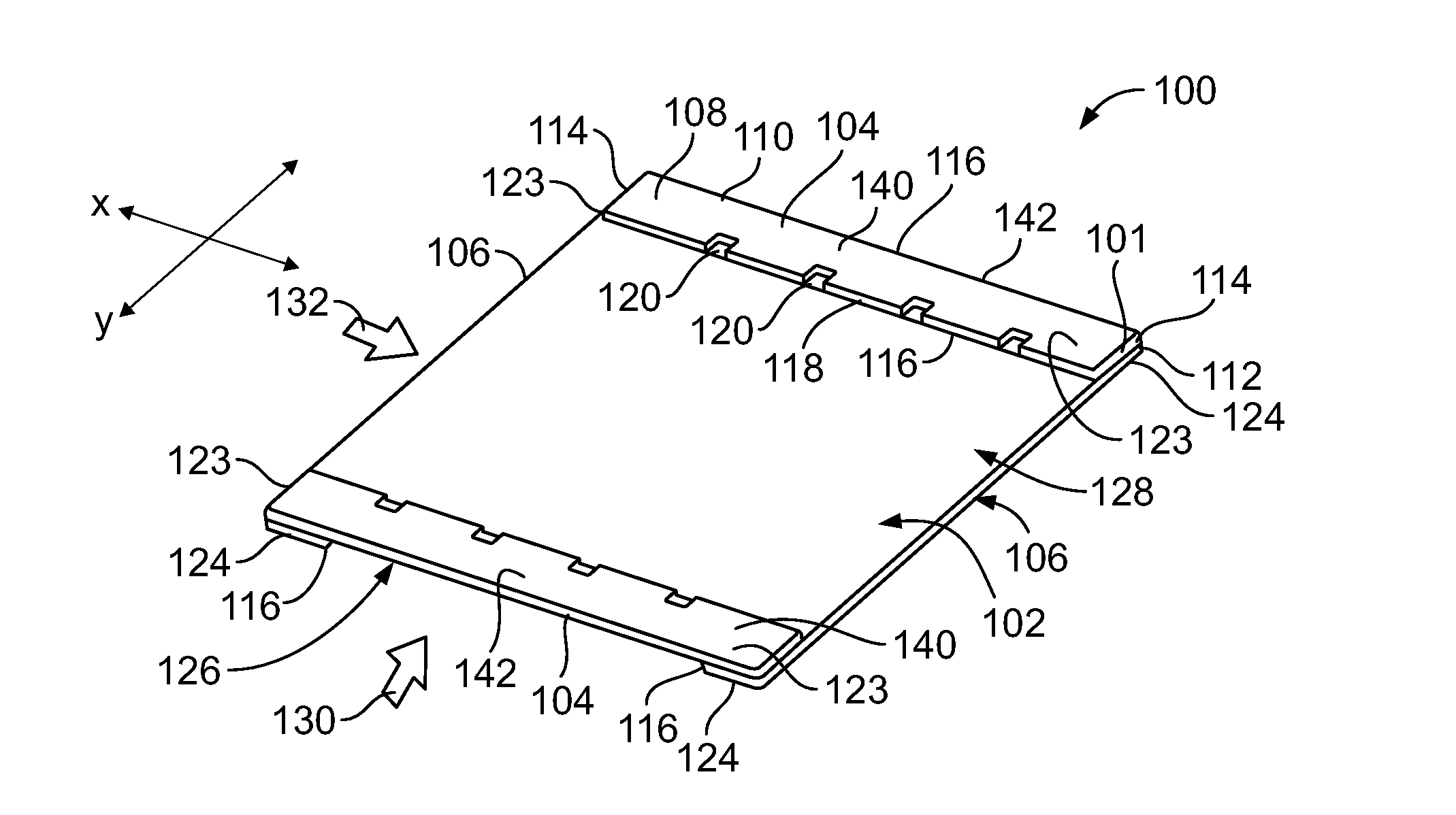
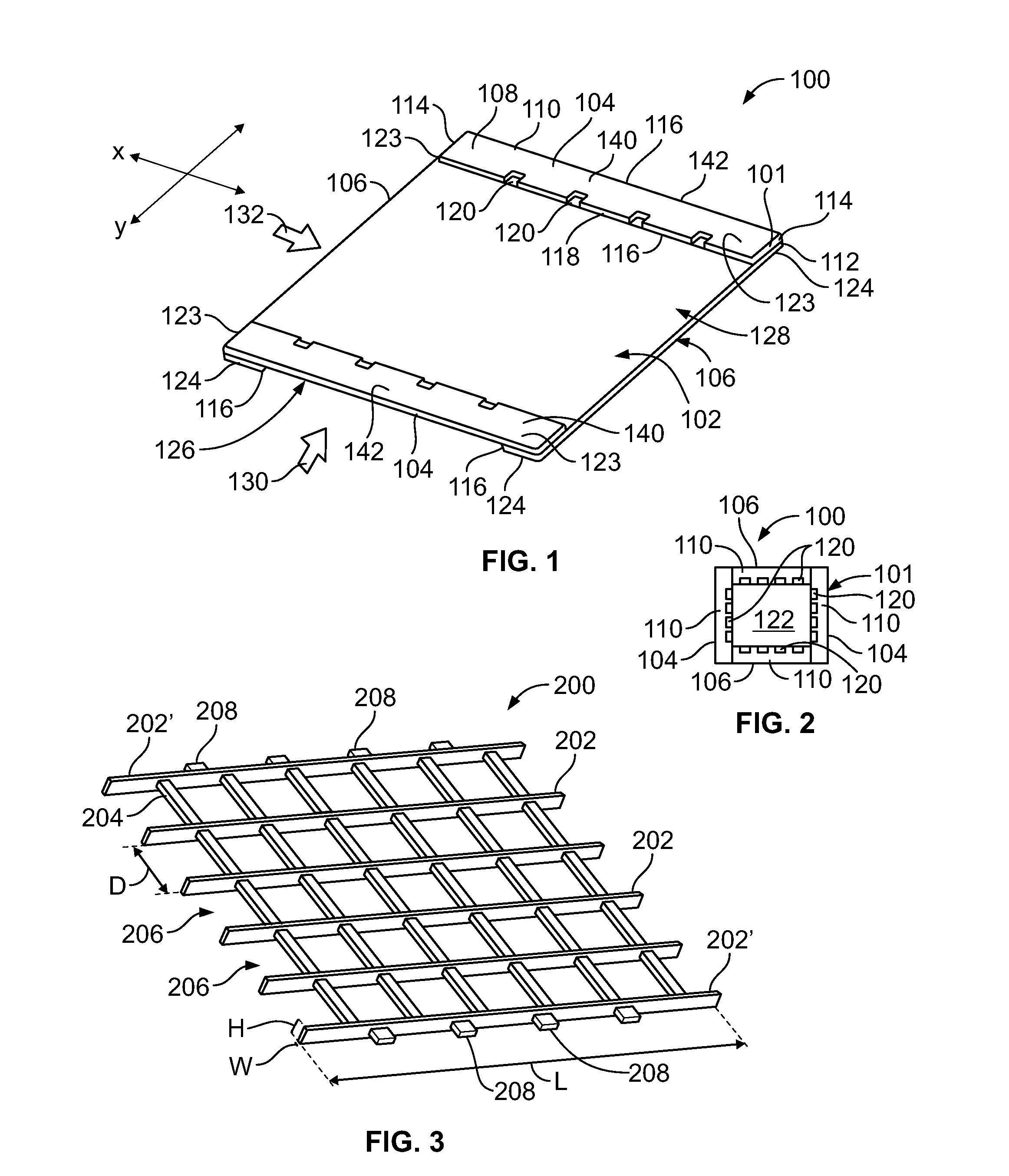
A method of forming a membrane panel configured to be secured within an energy exchange assembly may include forming an outer frame defining a central opening, and integrating a membrane sheet with the outer frame. The membrane sheet spans across the central opening, and is configured to transfer one or both of sensible energy or latent energy therethrough. The integrating operation may include injection-molding the outer frame to edge portions of the membrane sheet. Alternatively, the integrating operation may include laser-bonding, ultrasonically bonding, heat-sealing, or the like, the membrane sheet to the outer frame.
Owner:NORTEK AIR SOLUTIONS CANADA INC
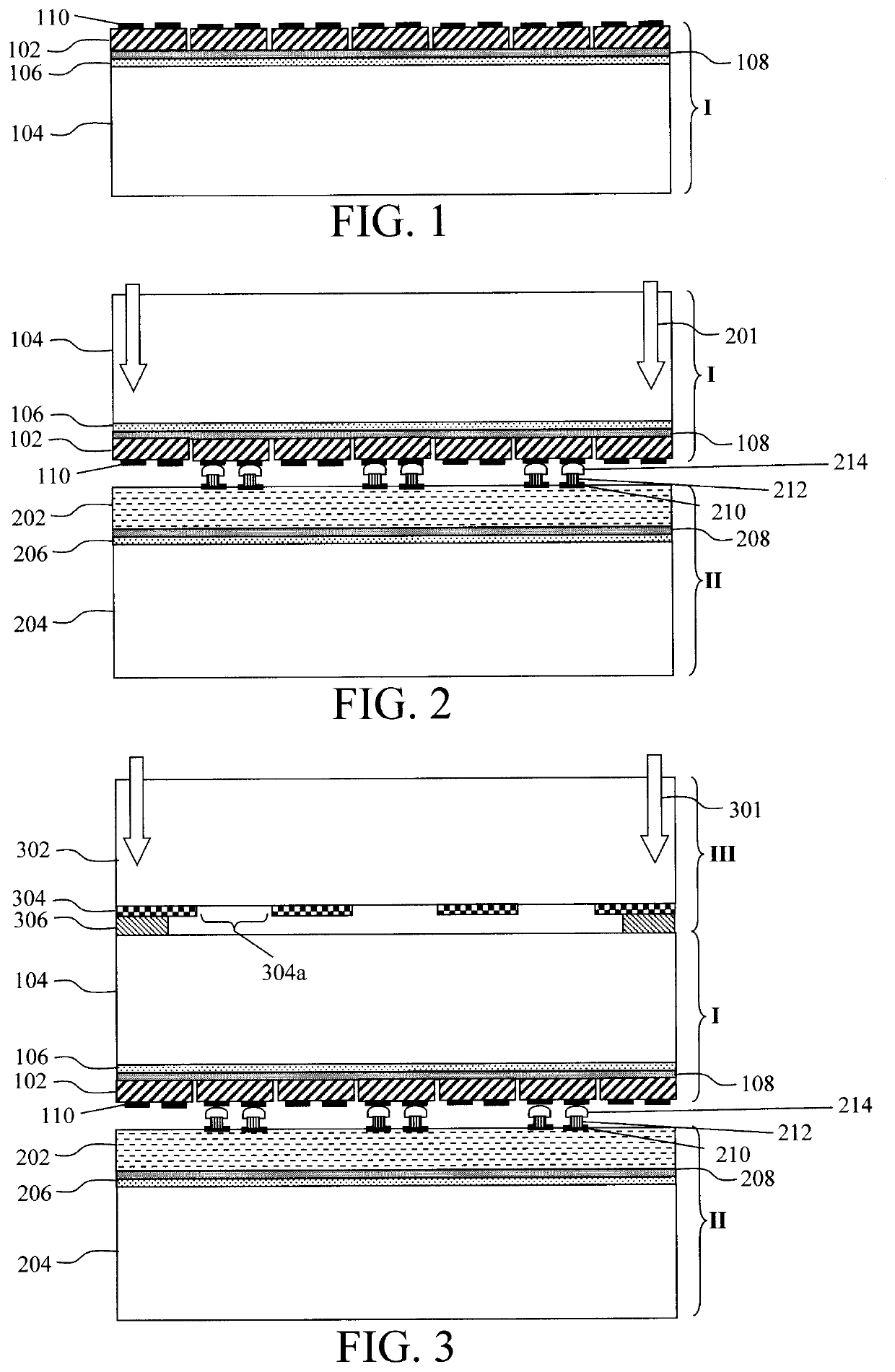
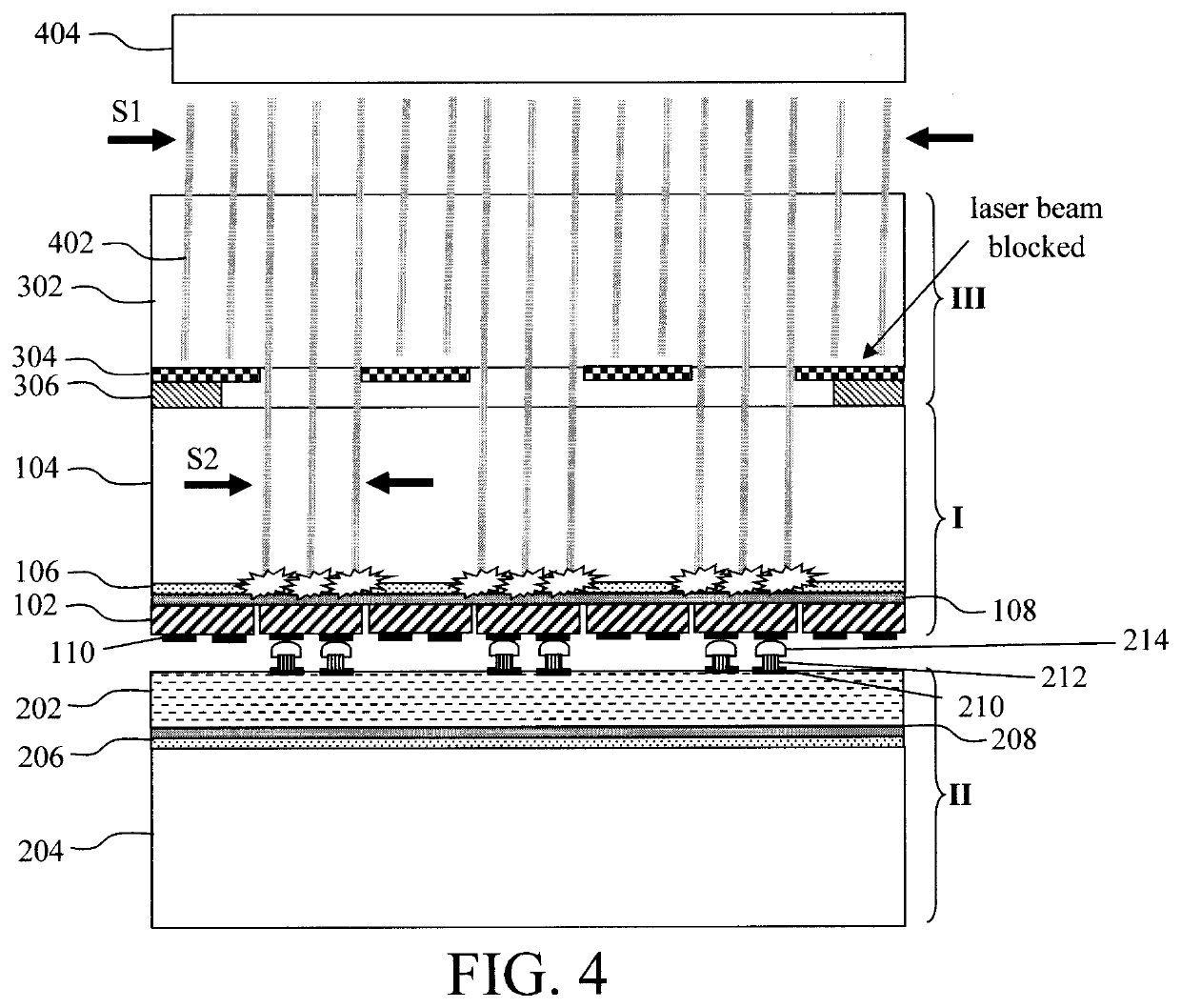
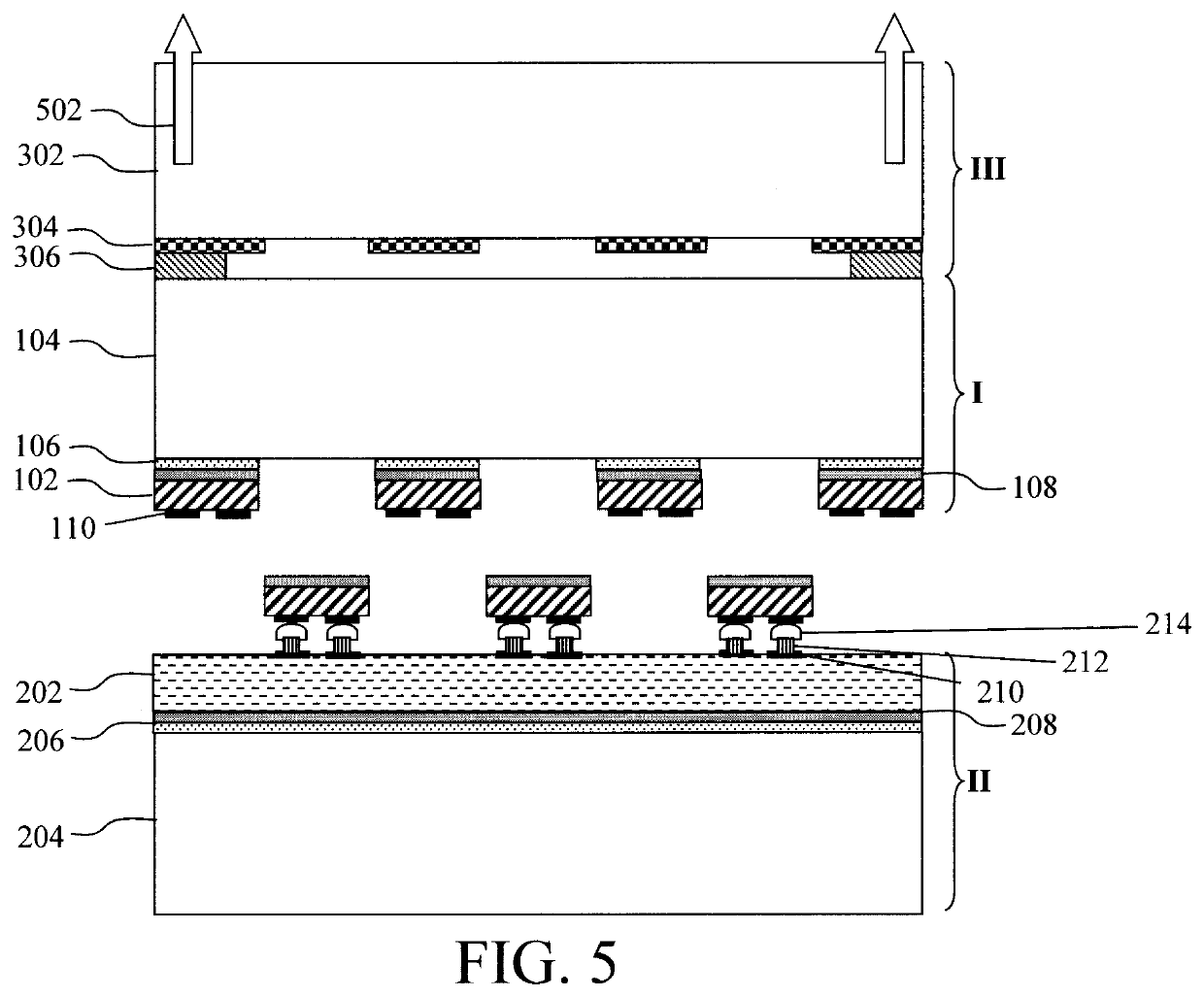
Pulse-Laser Bonding Method for Through-Silicon-Via Based Stacking of Electronic Components
ActiveUS20090243046A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLaser bondingEngineering
There is described a method of forming a through-silicon-via to form an interconnect between two stacked semiconductor components using pulsed laser energy. A hole is formed in each component, and each hole is filled with a plug formed of a first metal. One component is then stacked on another component such that the holes are in alignment, and a pulse of laser energy is applied to form a bond between the metal plugs.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Wire harness
InactiveCN101542640ASuppression of localized heatingIncrease contact areaCoaxial cables/analogue cablesLine/current collector detailsLaser bondingCoaxial cable
A wire harness using a coaxial cable, in which a ground bar and the shield of the coaxial cable are connected at a connection section in an environmentally friendly process and in a manner providing the harness with good electric characteristics. The ground bar (10) is made of a material having a lower melting point than the shield (16). For example, the ground bar (10) is made of brass or aluminum having a lower melting point than copper that forms the shield (16). The ground bar (10) and the shield (16) are connected together by applying a laser beam to the ground bar (10) and laser bonding them together by spots (30). Since the shield (16) has a higher melting point than the ground bar (10), melting of the shield (16) is suppressed because of the use of the laser bonding and, further, thermal damage to an inner dielectric layer under the shield (16) is suppressed. The environment is less affected because solder is not used.
Owner:PHOETON CORP
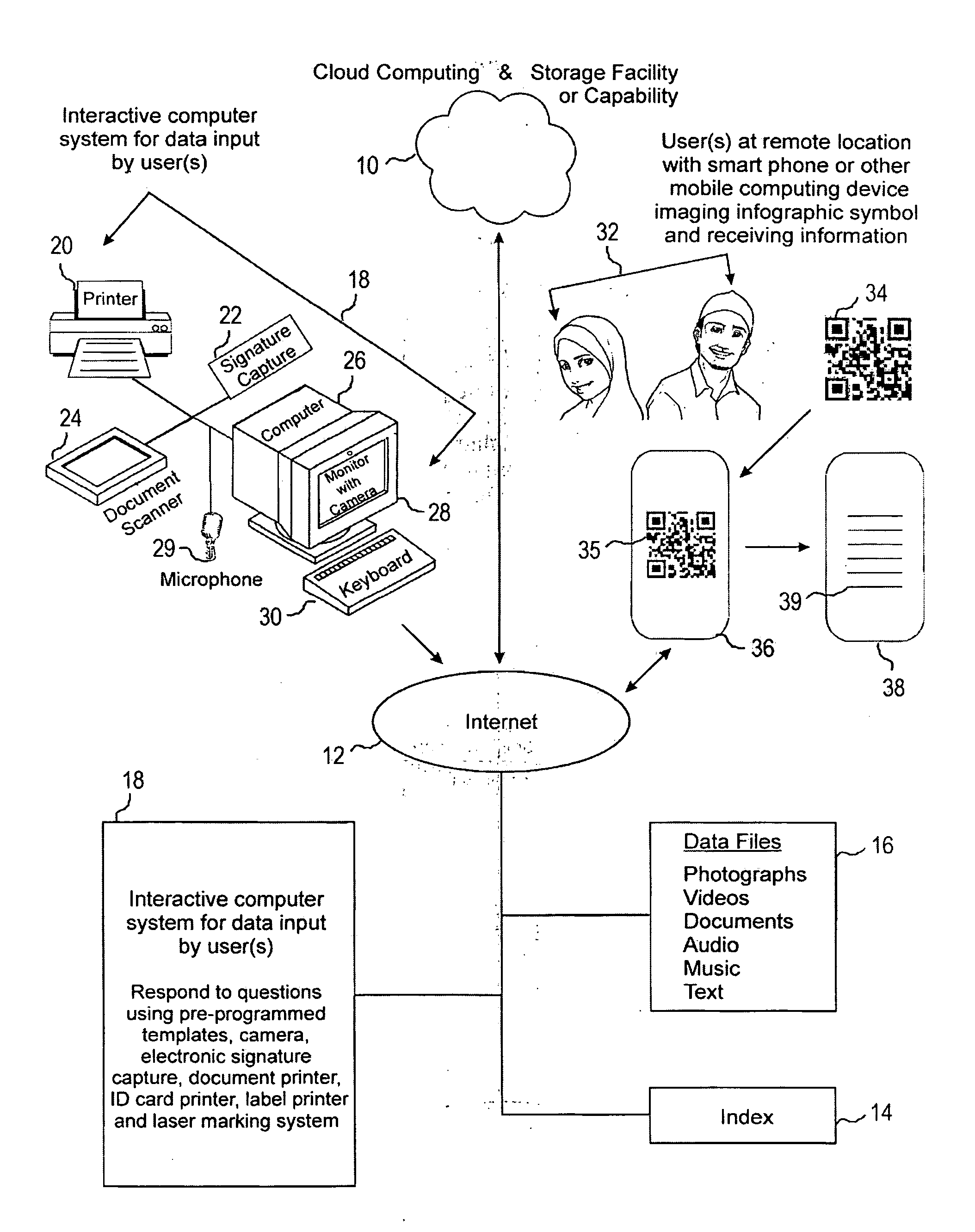
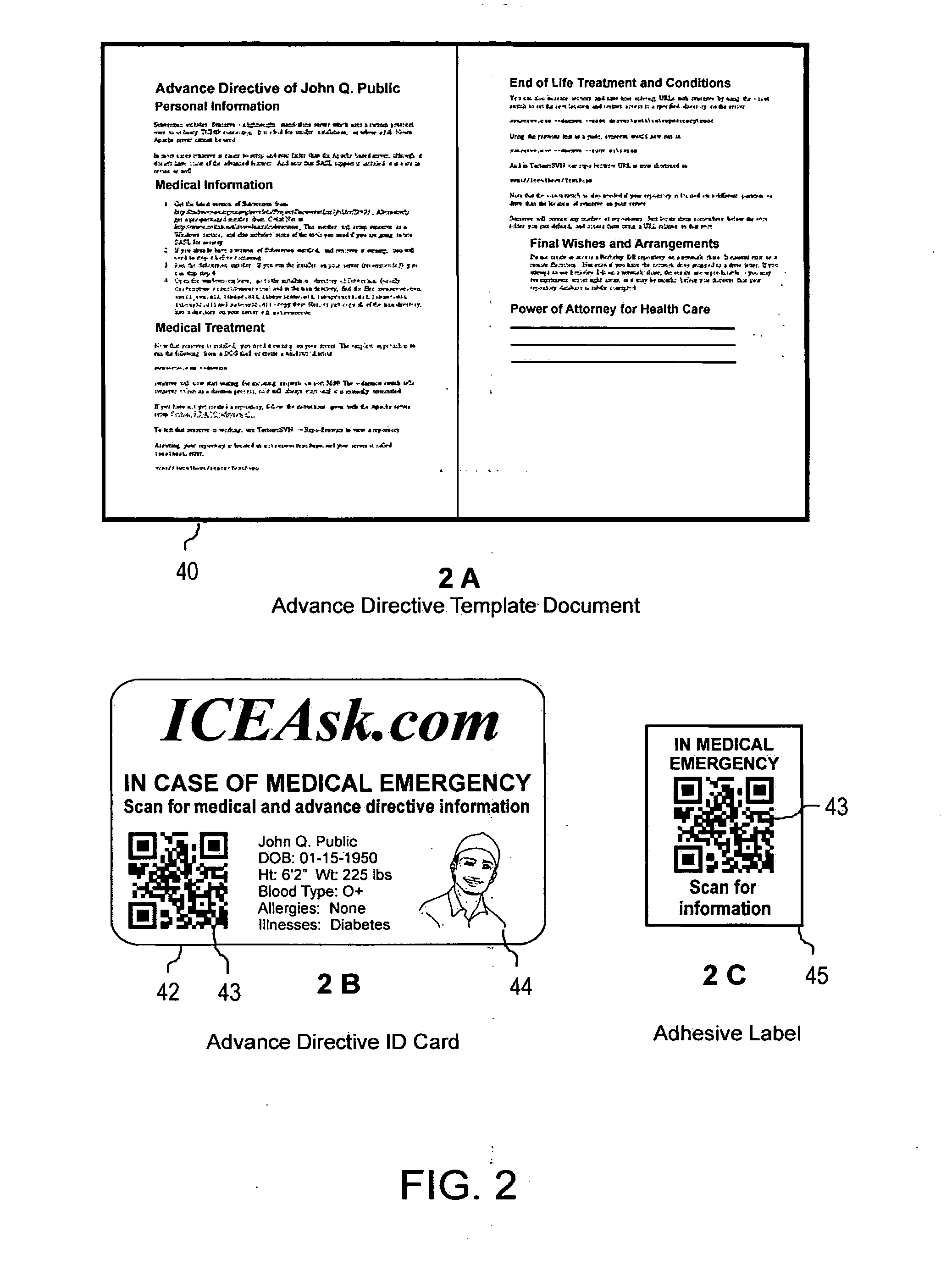
Systems and methods for the creation, transmission and storage of information and subsequent retrieval by a user
ActiveUS20140299662A1Easy to seeEasily captured and imaged and decodedDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsLaser bondingOperational system
Systems and methods for the creation, transmission and storage of information related to a specific person, animal, place or object and subsequent retrieval of information by a user positioned at remote locations are disclosed. The systems and methods comprise information; data input computer equipment, an operating system, software and methods for the electronic recording, scanning or creation of information; a remote electronic memory storage facility or capability, commonly known as “cloud computing and / or storage”; unique infographic symbols and a mobile computing device equipped with a camera capable of retrieving information via a communications link to the Internet and displaying the information at a remote location. The infographic symbol can be a QR code or other code laser bonded to the surface of a substrate.
Owner:HARRISON FAMILY TRUST
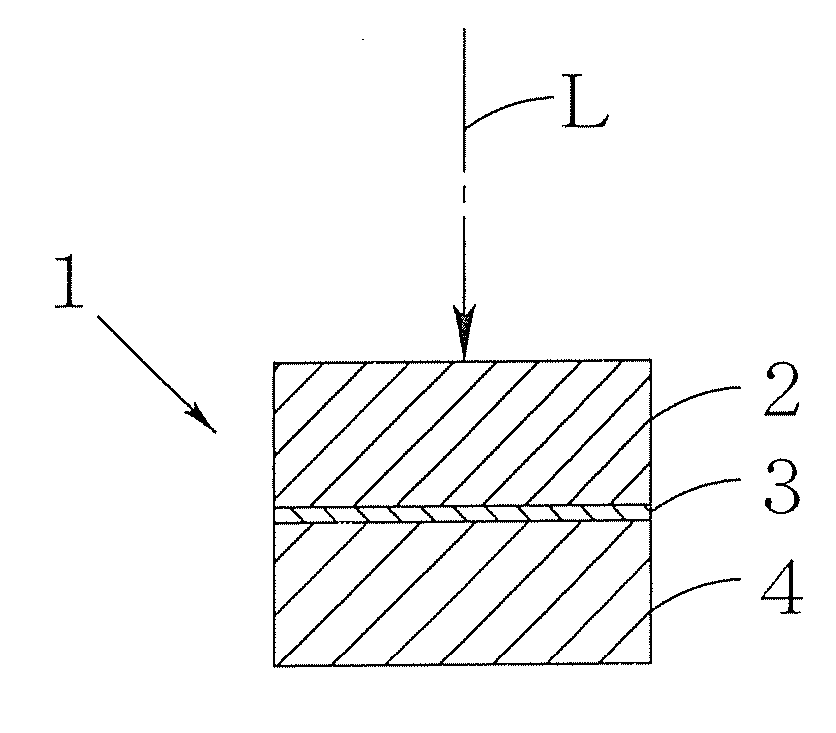
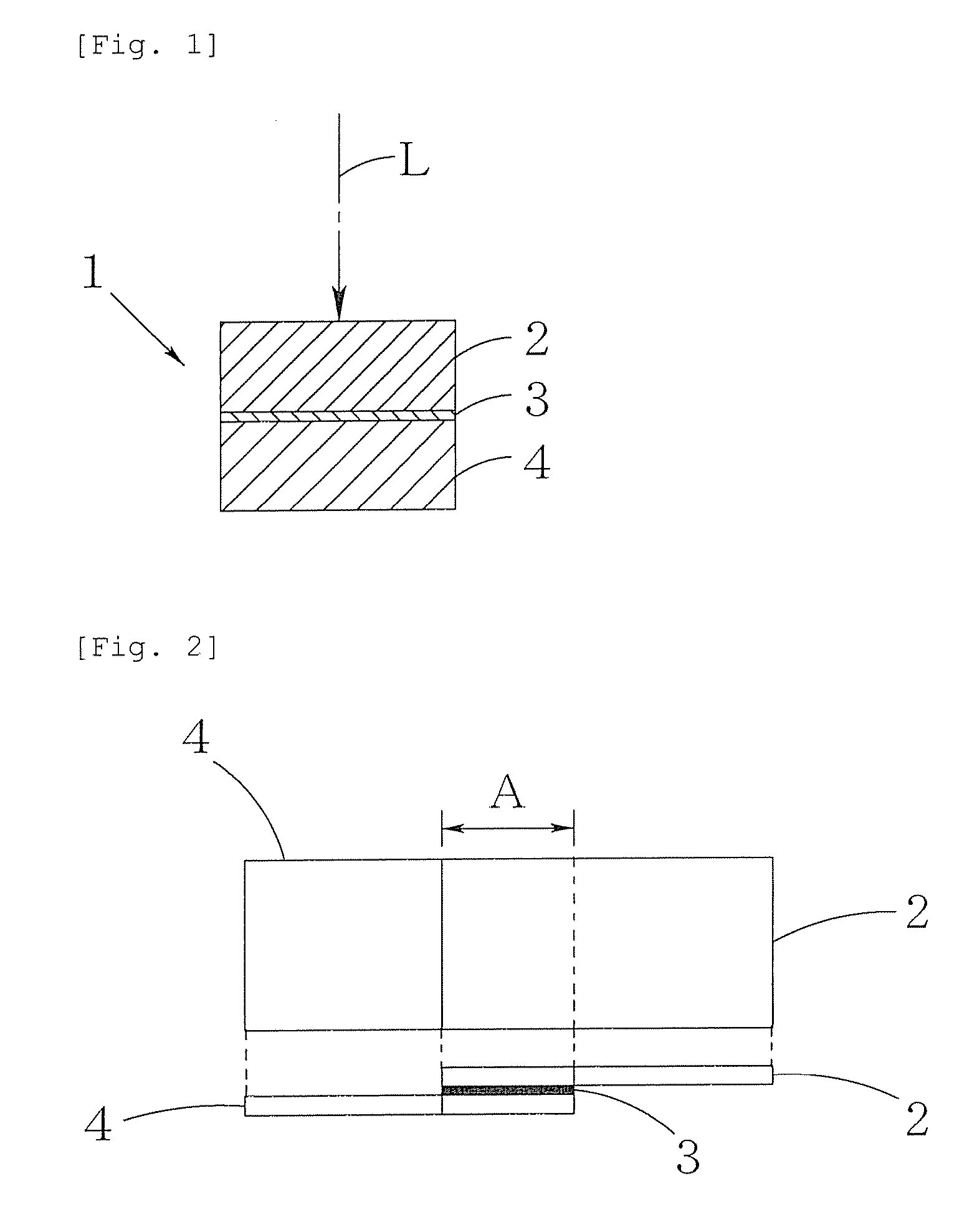
Intermediate member for laser bonding and method of bonding using the same
InactiveUS20100009150A1High bonding strengthEasy to operateAdhesive processesLamination ancillary operationsLaser bondingEngineering
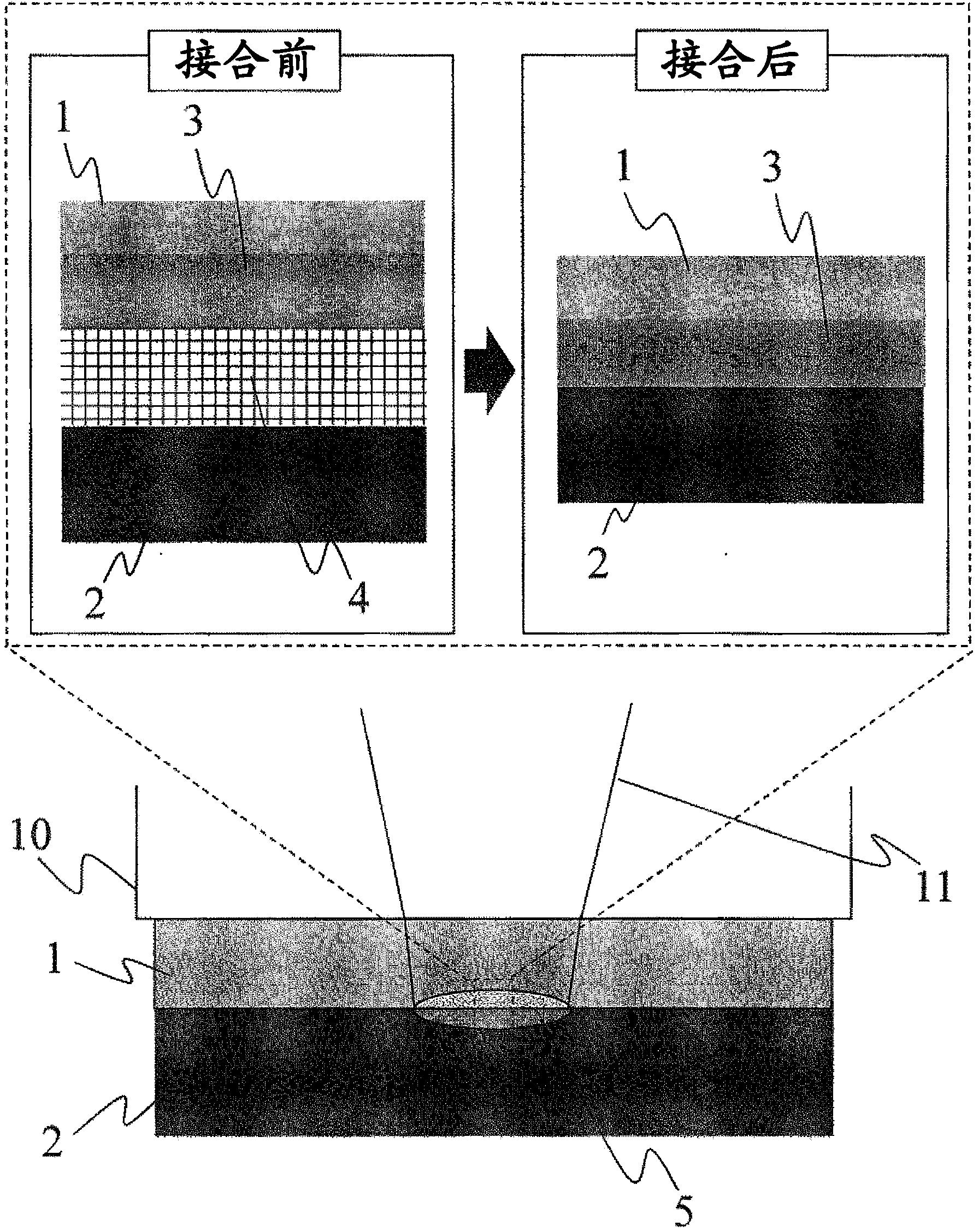
An intermediate member for laser bonding (3) to be sandwiched, in order to bond a first member (2) and a second member (4) using a laser welding method, between the first member (2) made of a material capable of transmitting laser beams and the second member (4) made of a material which is the same as or different from that of the first member (2) before irradiation with laser beams, the intermediate member for laser bonding (3) having tackiness. This intermediate member for laser bonding (3) can be used for bonding of various materials, and thus a high bonding strength can be attained.
Owner:OKAYAMA PREFECTURAL GOVERNMENT +1
Systems and Methods for Laser Bonding Catheter Components
InactiveUS20080135170A1Increase fluid pressureReduce tensionStentsBalloon catheterLaser bondingMedicine
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Membrane-integrated energy exchange assembly
A method of forming a membrane panel configured to be secured within an energy exchange assembly may include forming an outer frame defining a central opening, and integrating a membrane sheet with the outer frame. The membrane sheet spans across the central opening, and is configured to transfer one or both of sensible energy or latent energy therethrough. The integrating operation may include injection-molding the outer frame to edge portions of the membrane sheet. Alternatively, the integrating operation may include laser-bonding, ultrasonically bonding, heat-sealing, or the like, the membrane sheet to the outer frame.
Owner:NORTEK AIR SOLUTIONS CANADA INC
High Speed Handling of Ultra-Small Chips by Selective Laser Bonding and Debonding
ActiveUS20190348392A1Increase speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSoldering apparatusComputer control systemLaser bonding
Techniques for high speed handling of ultra-small chips (e.g., micro-chips) by selective laser bonding and / or debonding are provided. In one aspect, a method includes: providing a first wafer including chips bonded to a surface thereof; contacting the first wafer with a second wafer, the second wafer including a substrate bonded to a surface thereof, wherein the contacting aligns individual chips with bonding sites on the substrate; and debonding the individual chips from the first wafer using a debonding laser having a small spot size of about 0.5 μm to about 100 μm, and ranges therebetween. A system is also provided that has digital cameras, a motorized XYZ-axis stage, and a computer control system configured to i) control a spot size of the at least one laser source and ii) adjust a positioning of the sample to align individual chips with a target area of the laser.
Owner:IBM CORP
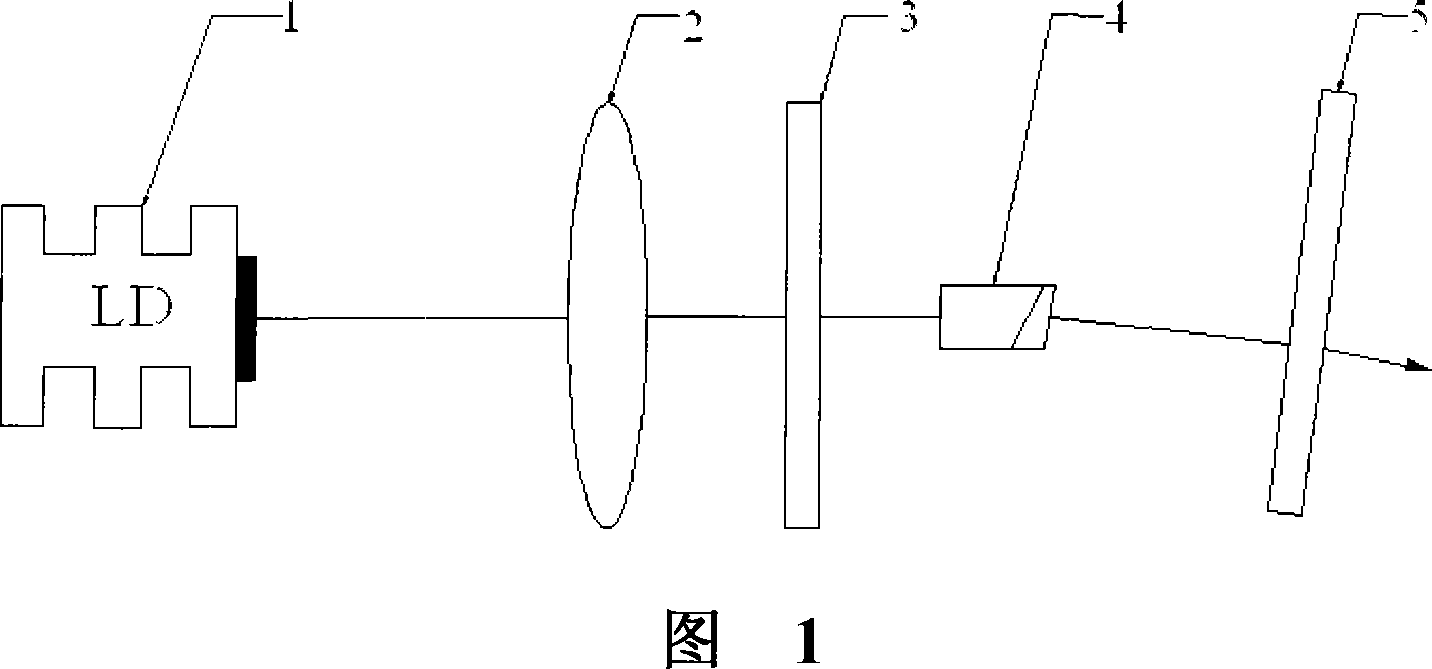
Medium infrared solid laser of semiconductor laser pump
InactiveCN101060228ADon't worry about low gain factorSimple structureActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionResonant cavityLaser bonding
The IR solid laser for semi-conductor laser pumping comprises: at one light path, a semi-conductor laser bonded with Tm:YAP and Cr:ZnSe crystal, a focus lens, an input lens, a laser medium, and an output lens, wherein the bonded crystal interface forms a Brewster angle with the laser resonant cavity. This invention uses simple structure to output higher power.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser bonding tool with improved bonding accuracy
A bonding tool for use in a laser bonding apparatus comprises an elongated body portion and a foot portion coupled thereto. The foot portion extends substantially transversely from the body portion and has a laser aperture and a guide channel therethrough. The guide channel is disposed between the body portion and the laser aperture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
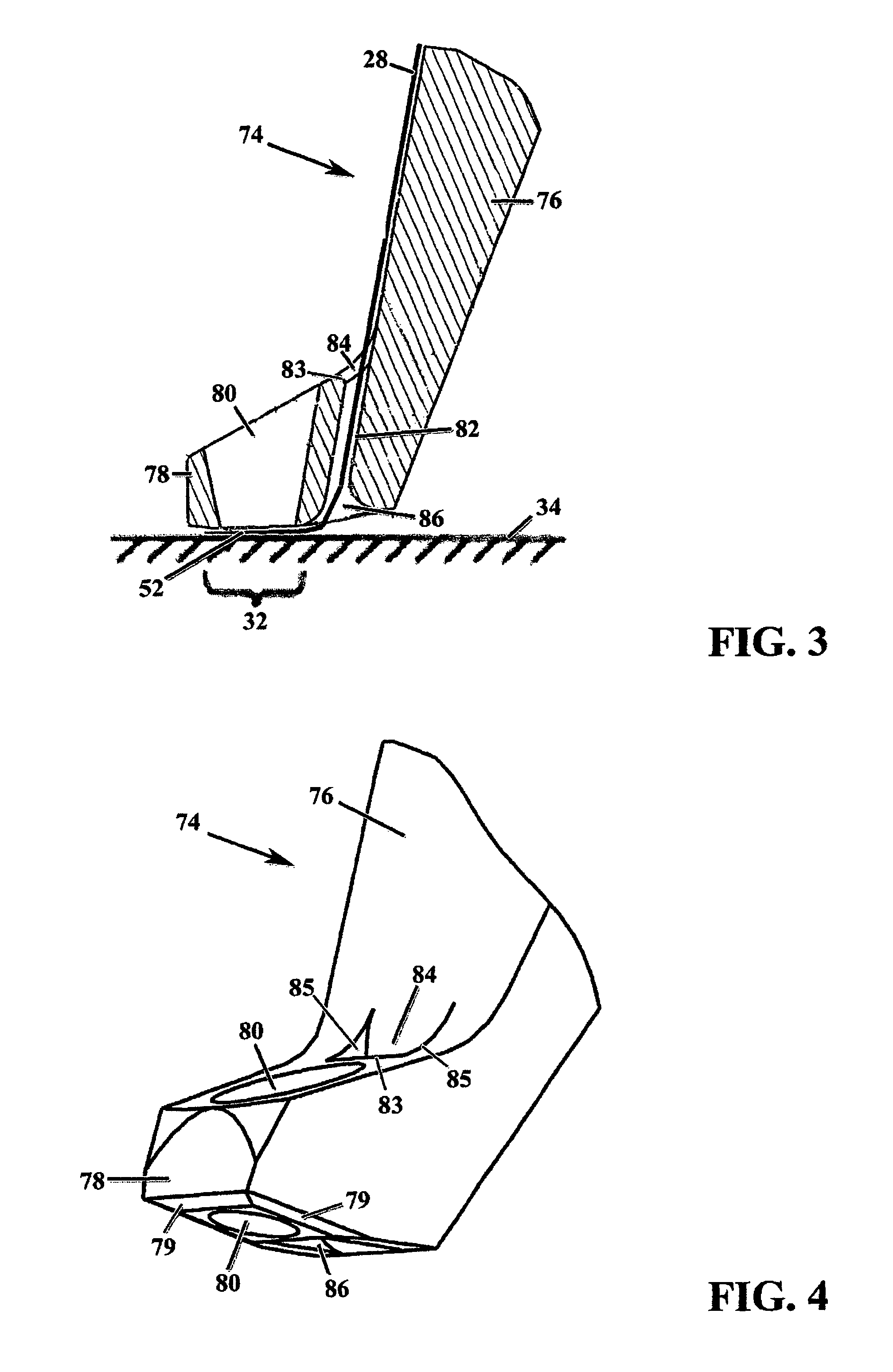
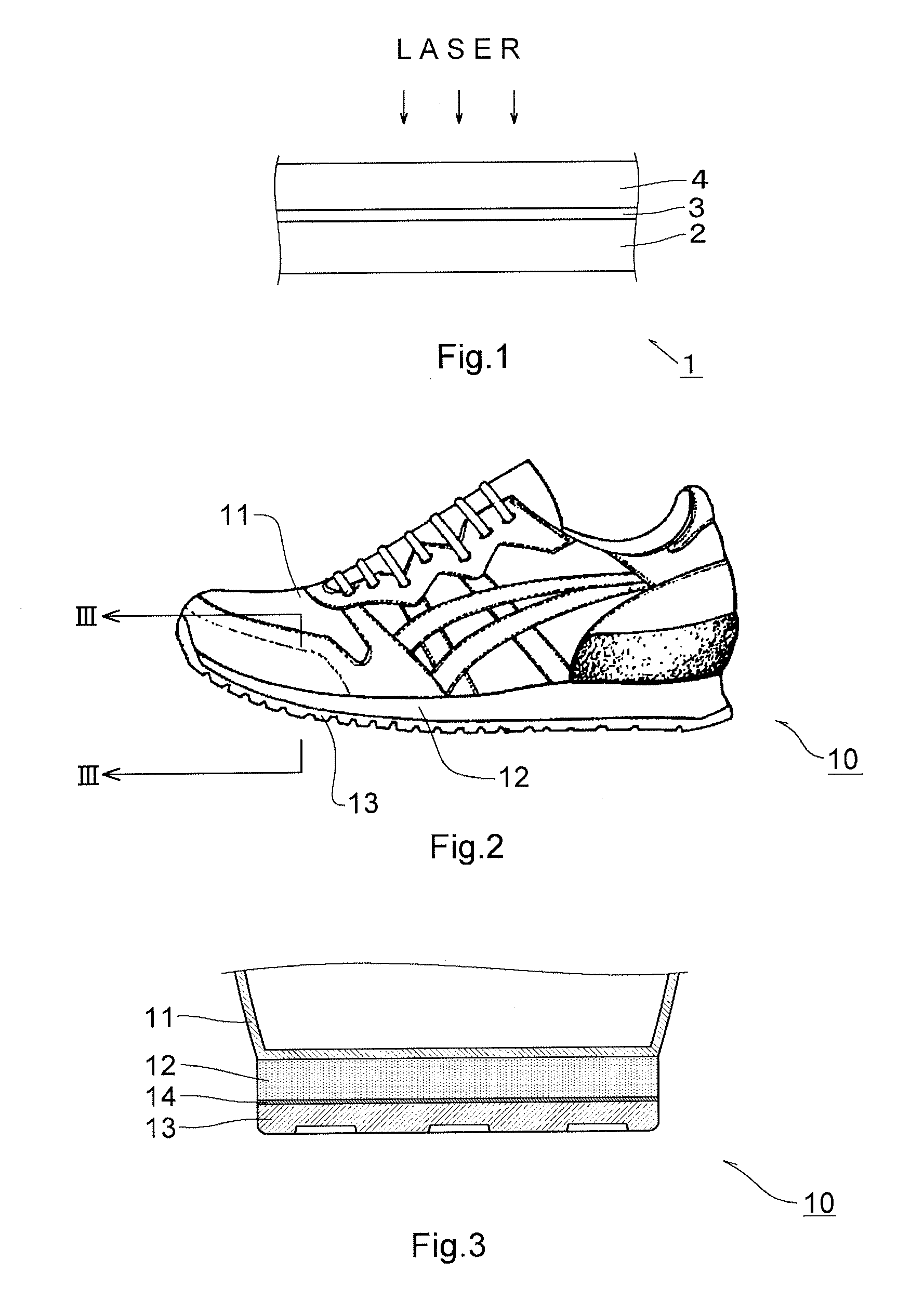
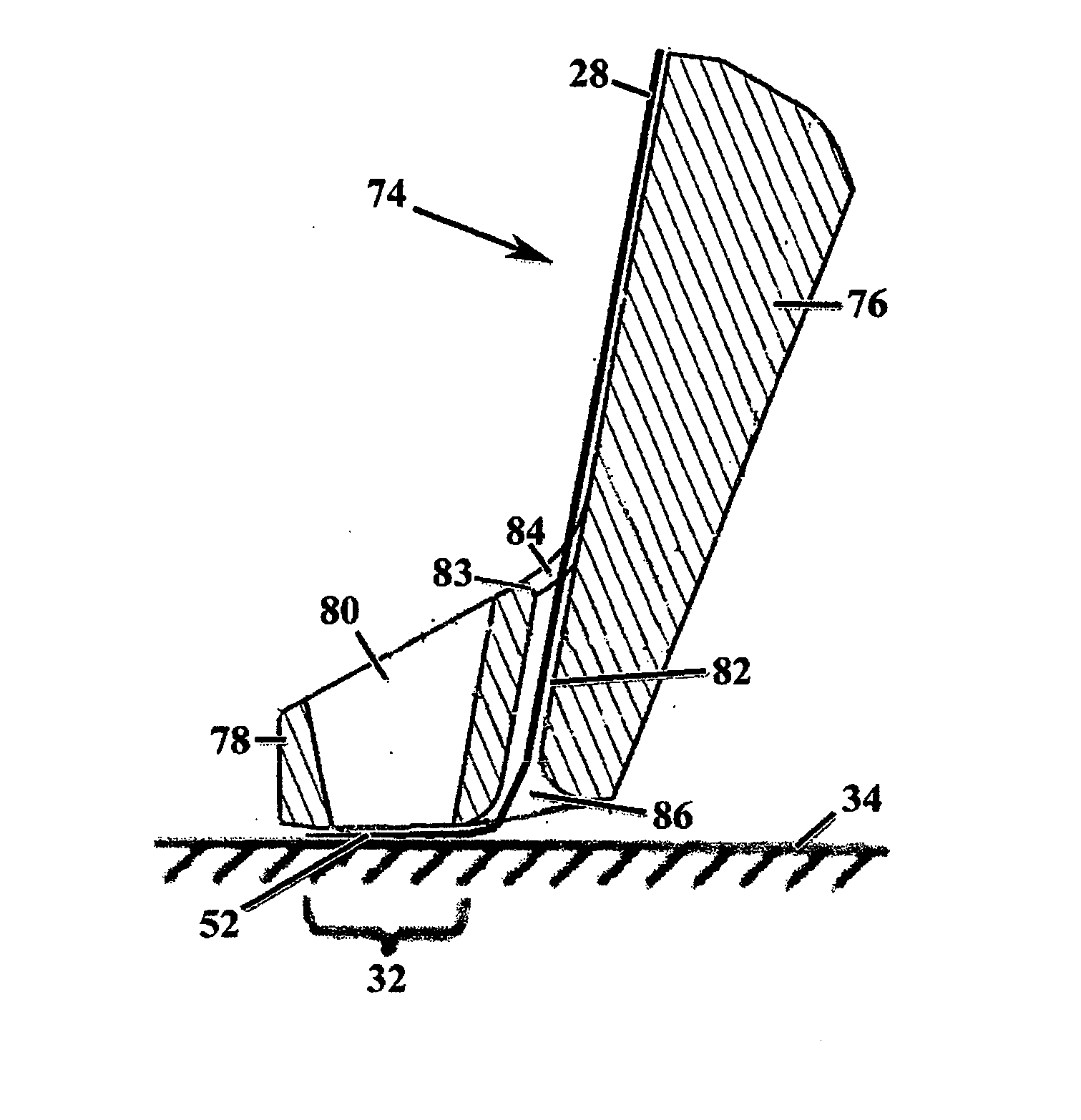
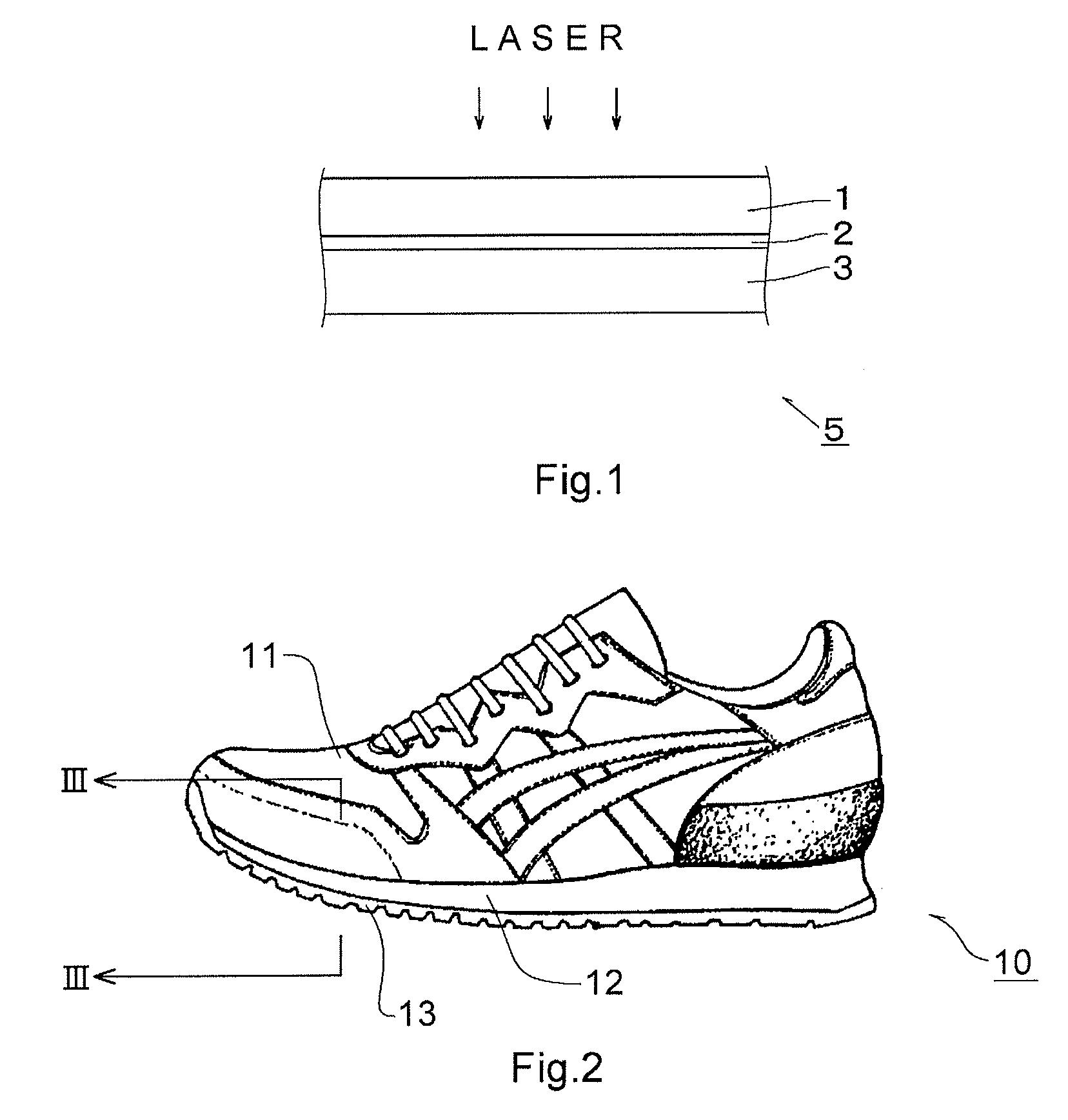
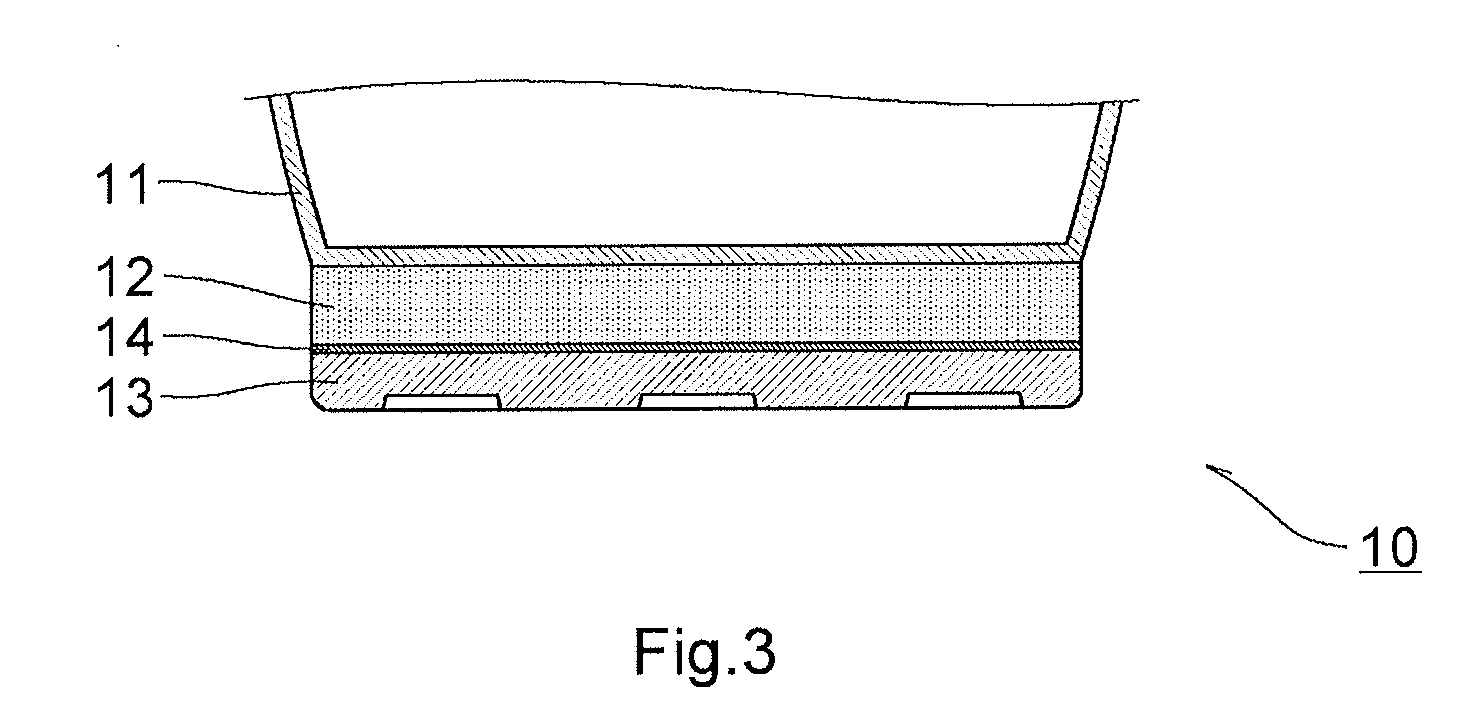
Layered product for laser bonding, shoe, and process for producing shoe
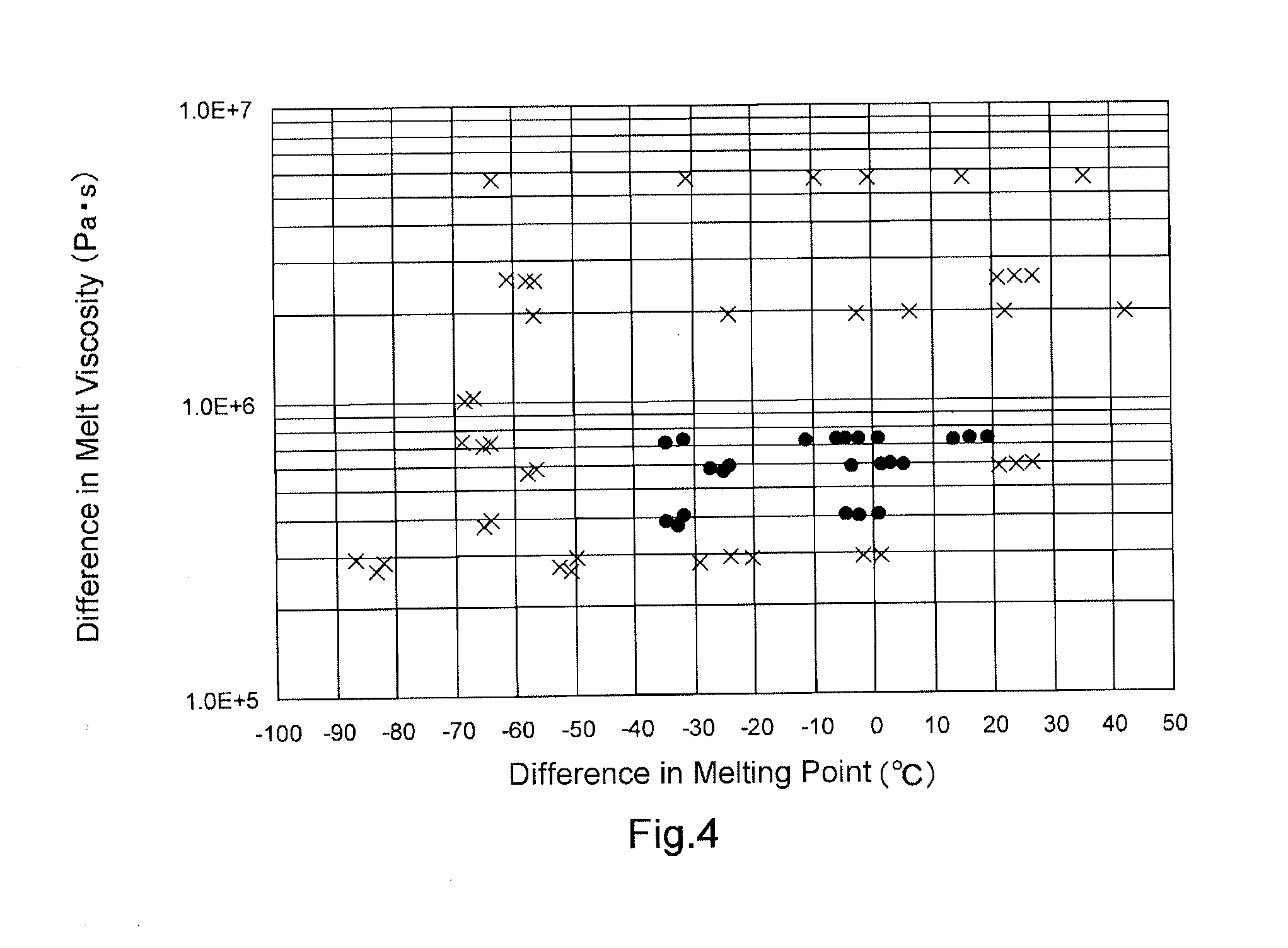
A laminate for laser bonding of the present invention contains a bonding sheet that is melted by irradiation of laser light and a first member laminated on one surface of the bonding sheet and formed of a thermoplastic foam. The difference between the melting point of the first member (Mfoam) and the melting point of the bonding sheet (Msheet) (Mfoam−Msheet) is −50° C. to 20° C. and the difference between the melt viscosity of the first member (Vfoam) and the melt viscosity of the bonding sheet (Vsheet) (Vfoam−Vsheet) is 3.0×105 Pa·s to 8.0×105 Pa·s. Preferably, the laminate for laser bonding contains a second member having transparency to laser light laminated on the other surface of the bonding sheet.
Owner:ASICS CORP
Laser bonding tool with improved bonding accuracy
A bonding tool for use in a laser bonding apparatus comprises an elongated body portion and a foot portion coupled thereto. The foot portion extends substantially transversely from the body portion and has a laser aperture and a guide channel therethrough. The guide channel is disposed between the body portion and the laser aperture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Square-wave laser bonding
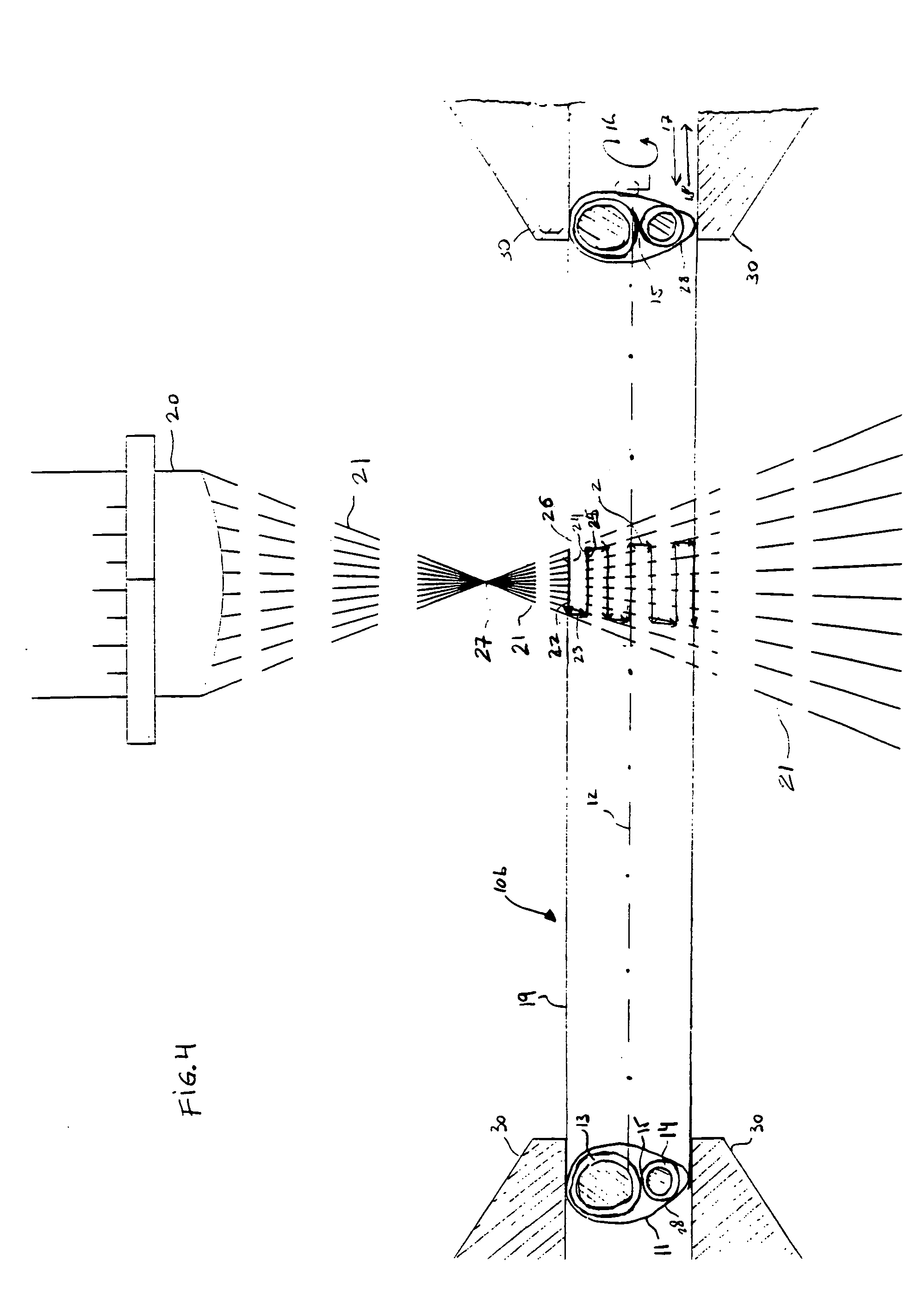
The present invention provides a square-wave laser seal pattern made by first directing a laser beam onto an shaft while the shaft is moving in a horizontal direction relative to a laser device so as to create a horizontal laser seal bond segment. Next, with the shaft rotating about a shaft longitudinal axis, the laser beam is directed onto the shaft so as to create a vertical laser seal bond segment. By alternately creating and coupling together a plurality of horizontal and vertical laser seal bond segments, a square-wave laser seal is formed around a circumference of the shaft. The shaft's movement in a horizontal direction relative to a laser beam may be either at a constant speed or a variable speed so as to control the amount of laser energy heat impacting the shaft material.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
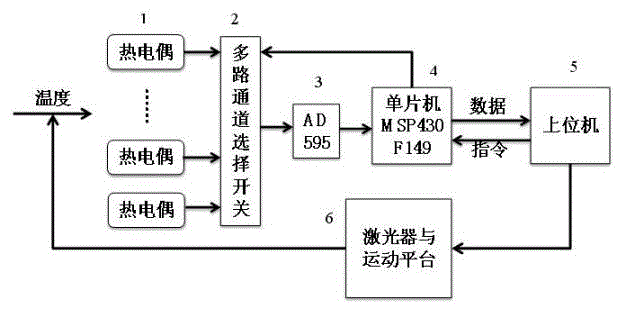
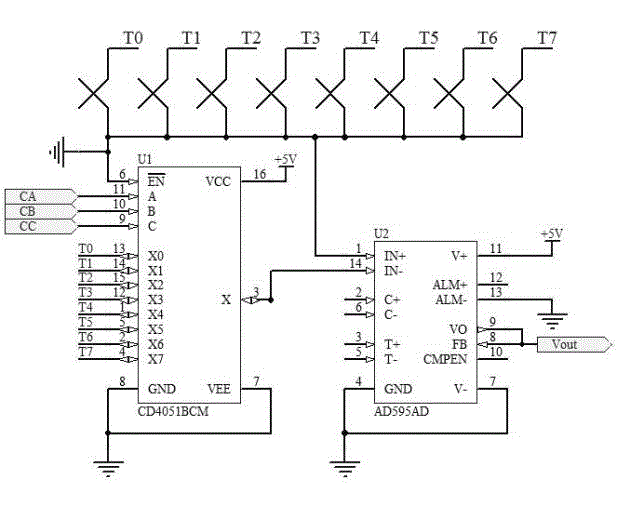
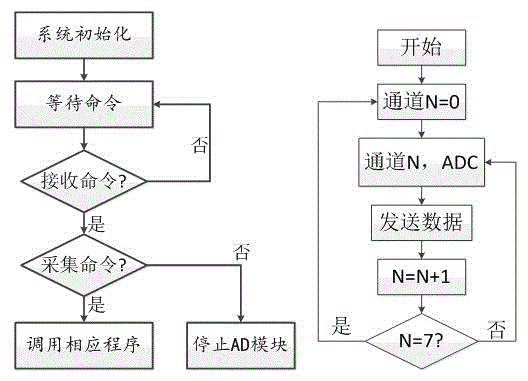
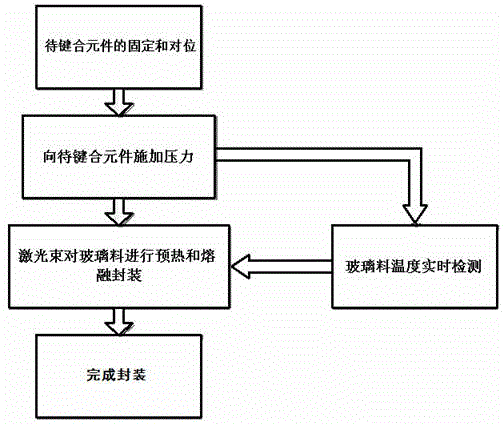
Photoelectric device encapsulation and laser bonding temperature collection and control system and method
The invention relates to a photoelectric device encapsulation and laser bonding temperature collection and control system and method. The laser bonding encapsulation adopts K-type thermocouple to collect the temperature. Collected temperature signals are selected by a multipath channel selector switch before AD (analogue-digital) conversion; converted signals are led into a single chip MSP430F149 for processing; and processed data is transmitted to an upper computer for communication and control to automatically regulate the power of laser or the scanning speed of a laser head so as to stabilize the temperature in a laser bonding process of a glass material within a certain range. The control system is mainly applied to photoelectric devices such as organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays and MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical systems) encapsulated by the glass material, taking the OLED devices as an example for exposition.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for preparing cobalt-substituted prealloying powder from regenerated metal
The invention discloses a method for preparing cobalt-substituted prealloying powder from regenerated metal. The method comprises the process steps: compounding raw materials, electrolyzing at a room temperature, crushing, screening, detecting and packaging; using the regenerated metal, such as recycled synthetic diamond waste powder accelerant, and the like, as a main raw material; supplementing a suitable amount of metal cobalt and metal iron to an anode basket together; and rinsing, purifying in vacuum after the room-temperature electrolysis step in the process steps and reducing hydrogen at 400 DEG C to 650 DEG C. More than 10 percent of particles in a final product have a sponge appearance, and an electrolyte used in the room-temperature electrolysis step in the process steps can be recycled. The invention has the advantages: 1, the production cost is lower than that of a chemical coprecipitation method by more than 50 percent, and the product quality is stable; 2, the powder appearances comprises the sponge appearance so as to have a large specific surface area; 3, the powder can be applied to laser bonding; 4, the strength is high, and the anti-abrasion performance is good; and 5, the sintering temperature is low, and the range is wide. The method is suitable for being adopted by industrial and mining plants producing the cobalt-substituted prealloying powder.
Owner:HUNAN FORLONG ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Spotting plate and process for its production
InactiveUS20130237443A1Easy and more specific bindingHigh binding capacitySequential/parallel process reactionsLibrary screeningLaser bondingMicrotiter plate
A process for the production of a reaction chamber assembly, wherein a flat substrate and bottomless reaction chambers are provided, the substrate is first loaded with a biological agent and then the bottomless reaction chambers are bonded glue-free to the substrate, in particular through laser bonding, and liquid-tight reaction chambers, for instance individual wells, individually connected wells, such as strips, or wells in the form of a microtiter plate, are obtained. The present invention further provides a kit comprising a substrate suitable for being loaded with at least one biological agent and at least one bottomless reaction chamber, wherein the kit is suitable for glue-free bonding of the bottomless reaction chamber to the substrate.
Owner:SCIENION GMBH +1
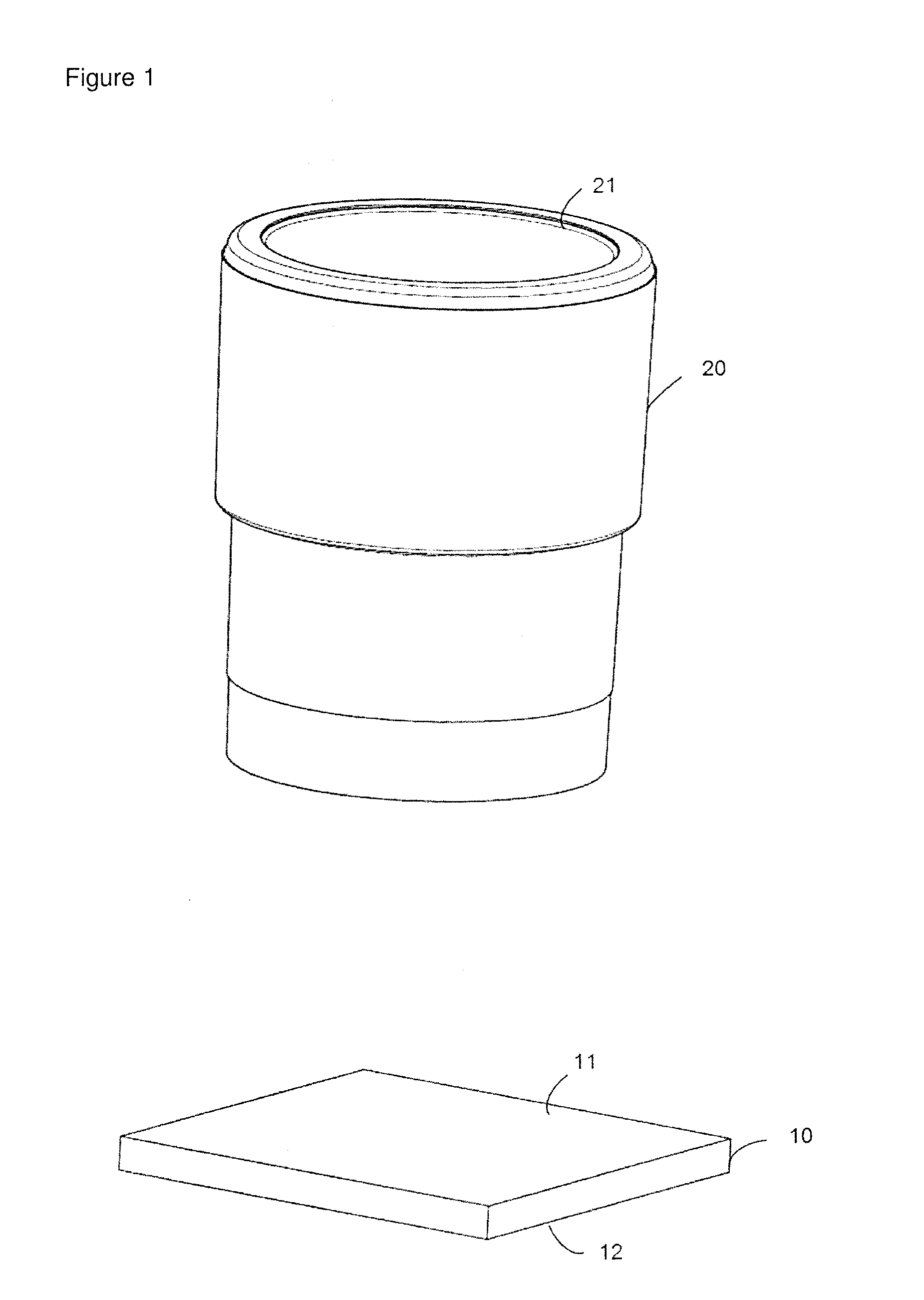
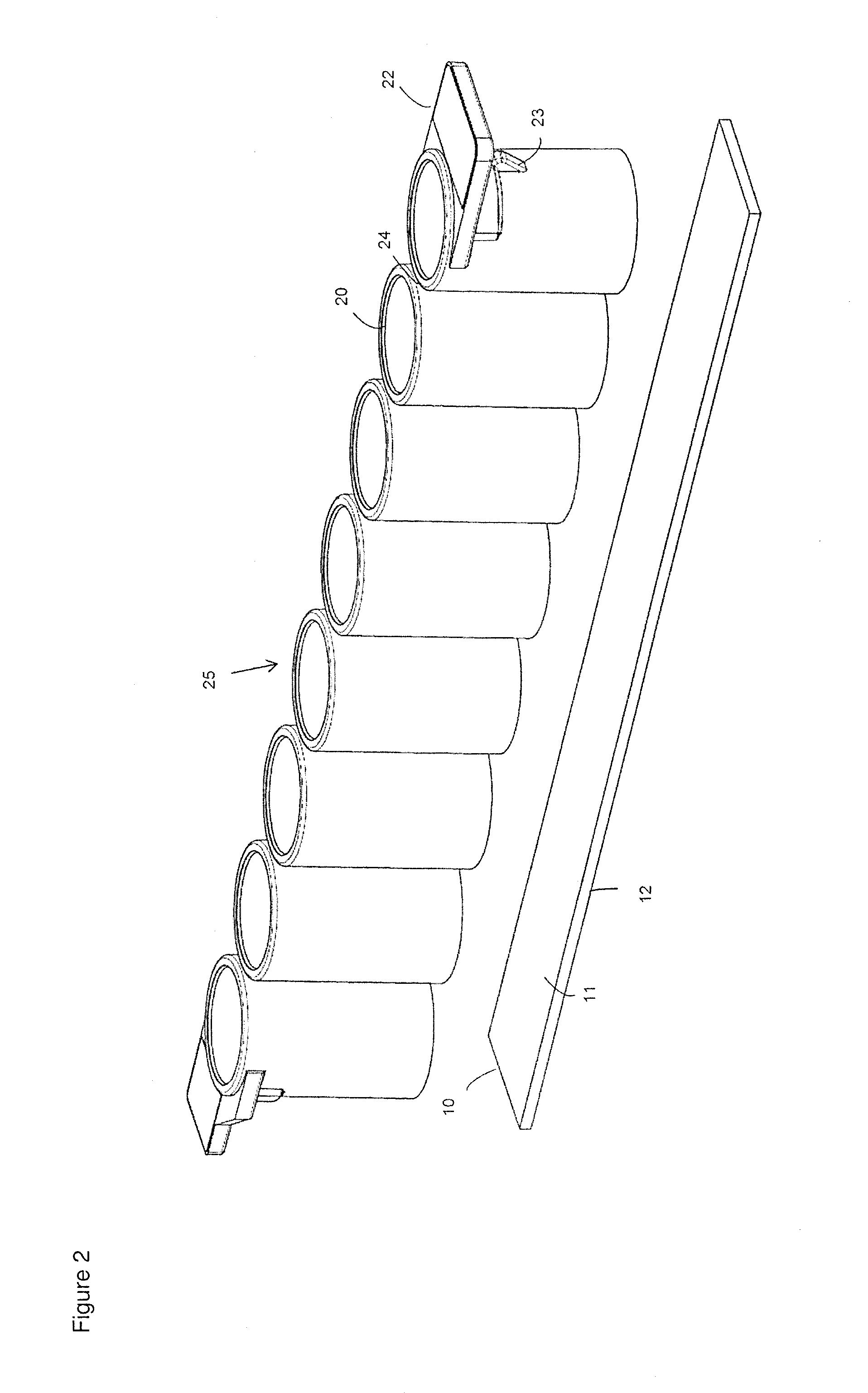
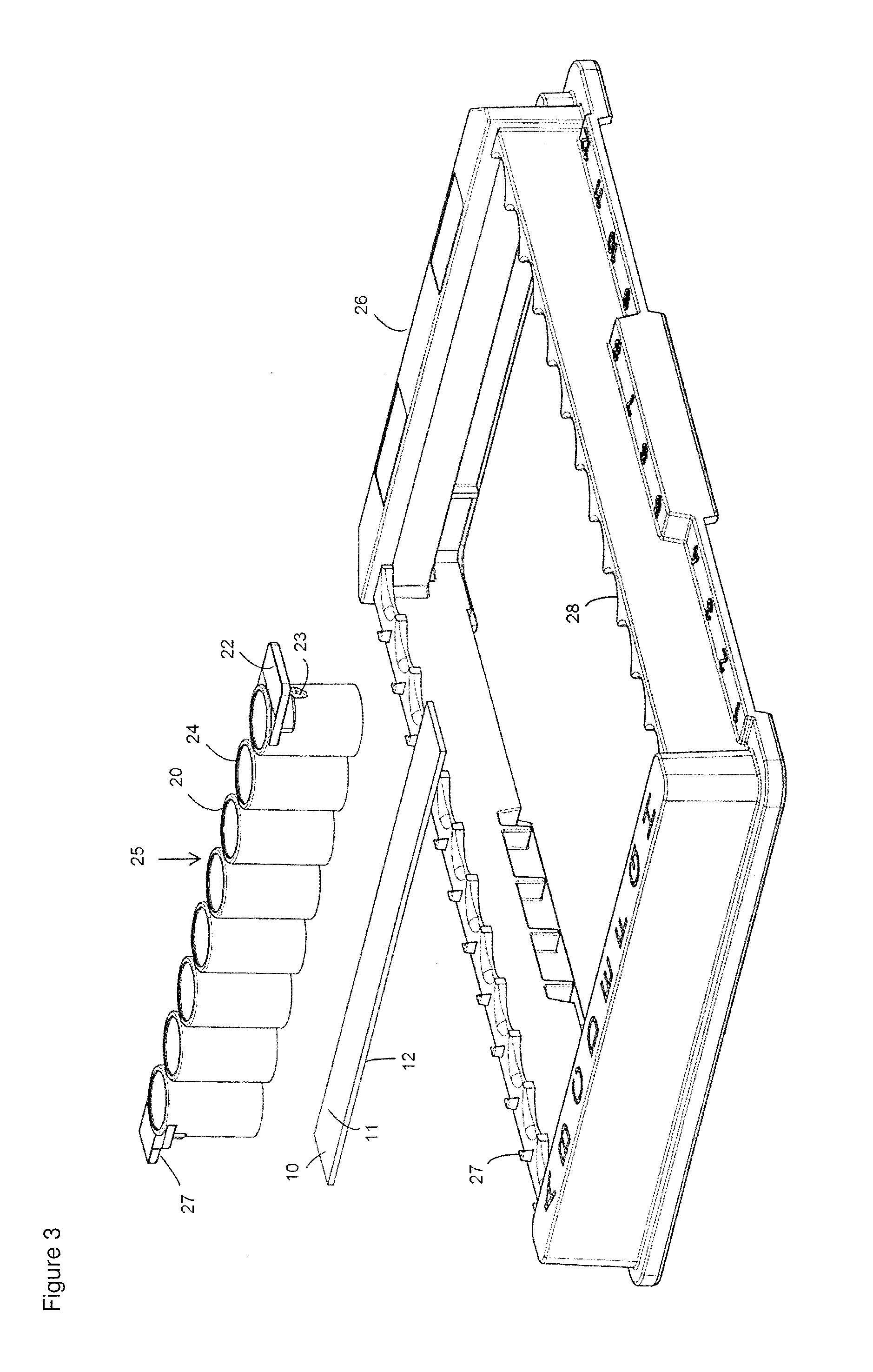
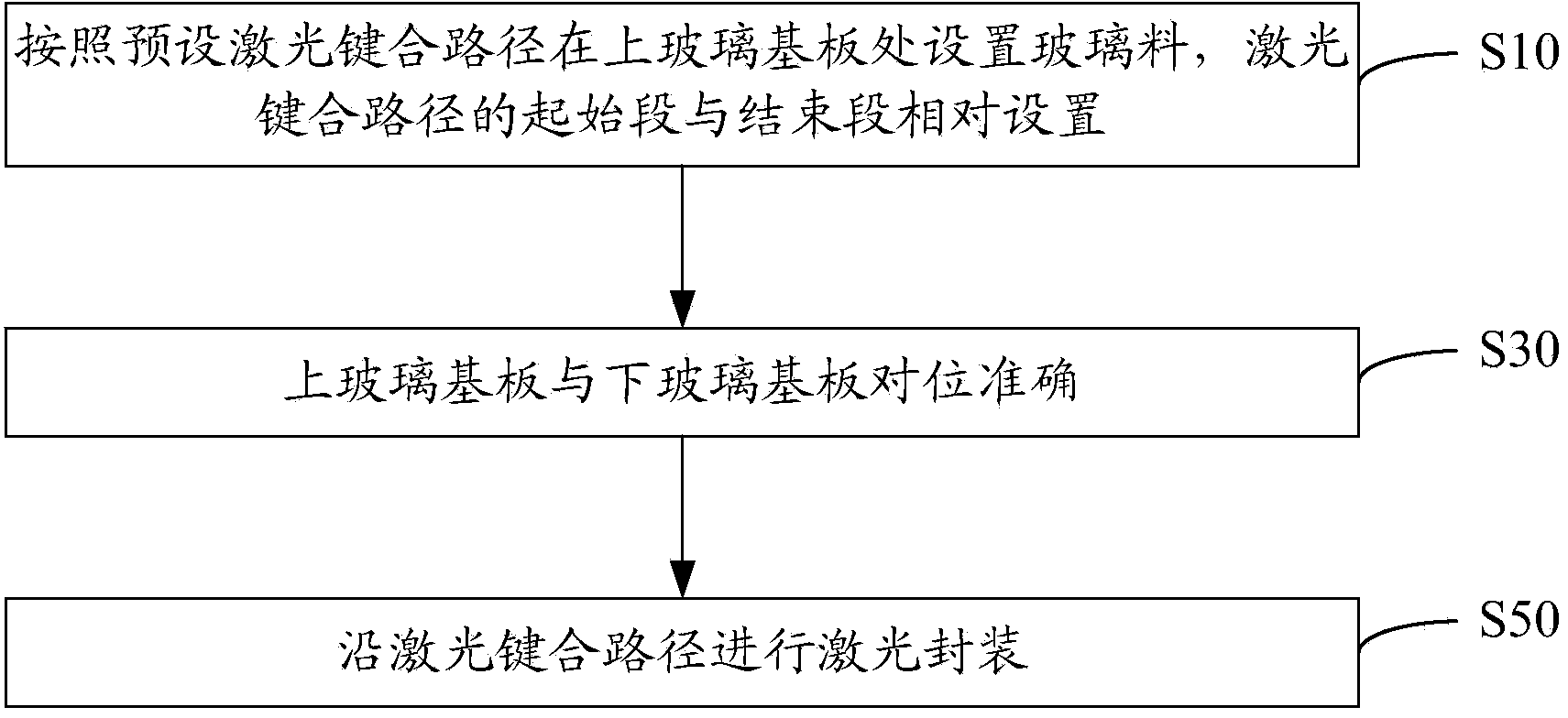
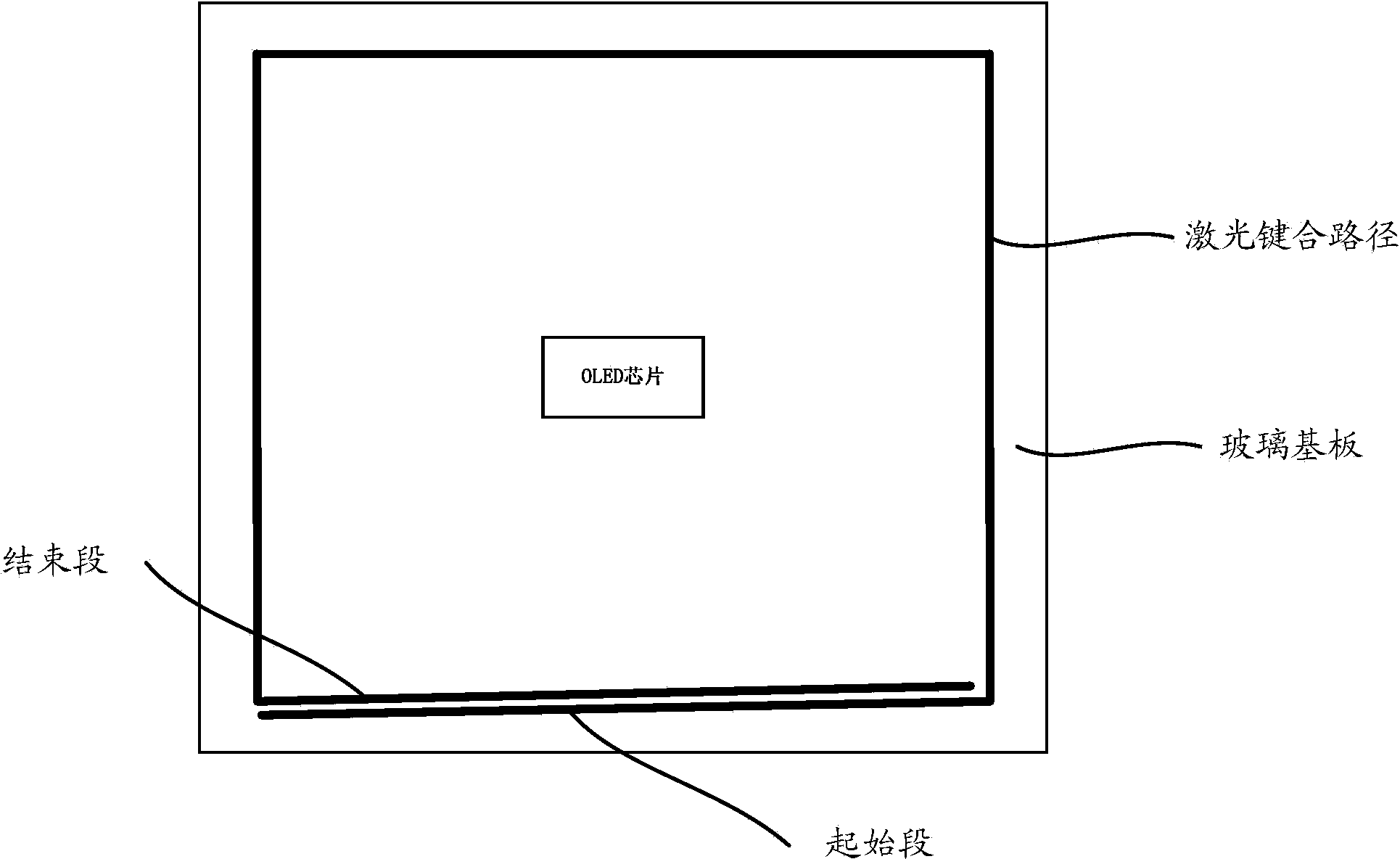
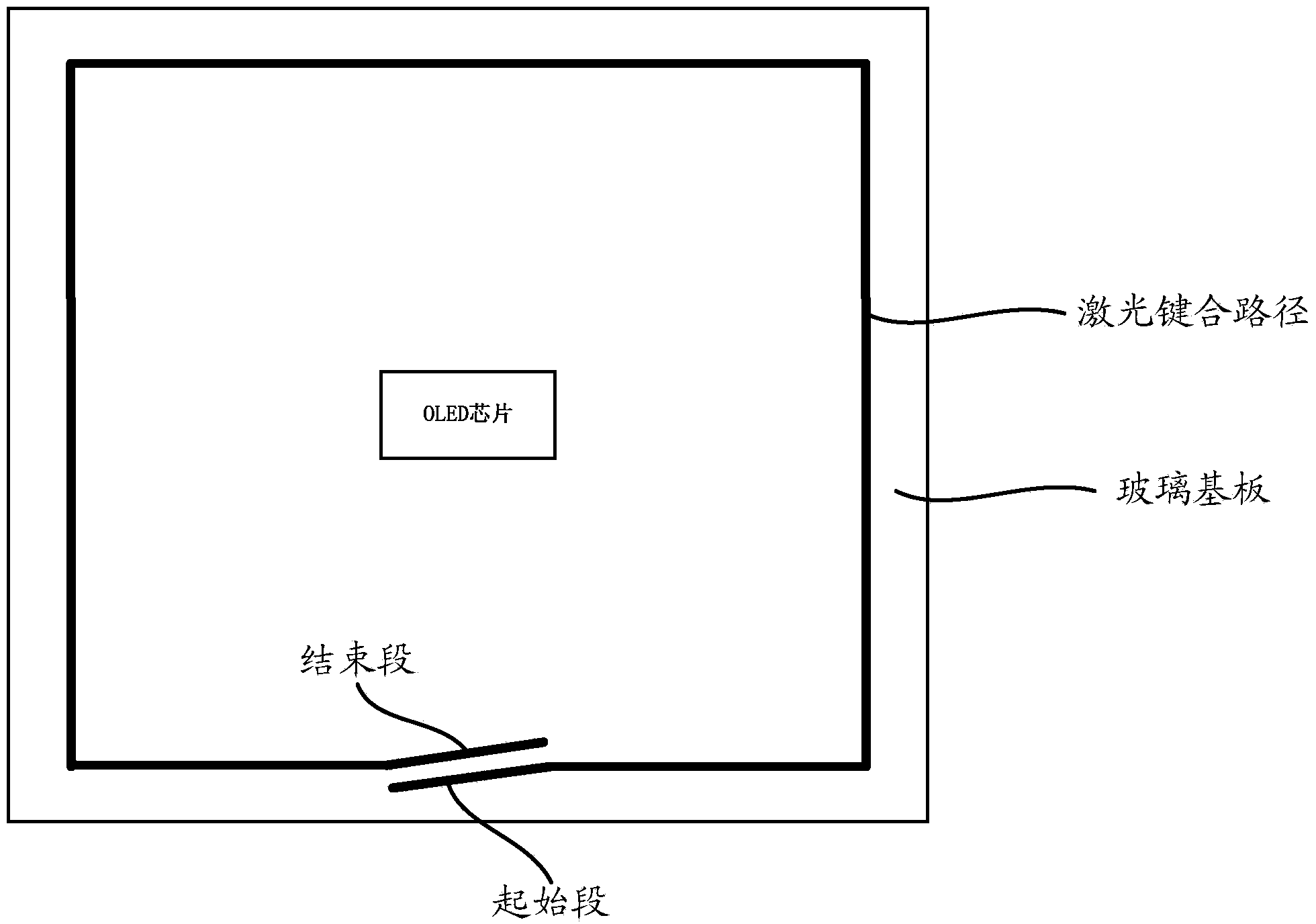
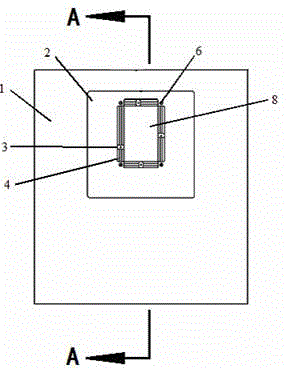
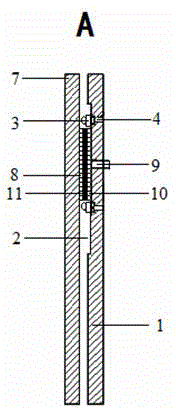
Laser bonding method
ActiveCN103531726AImprove sealingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser bondingOptoelectronics
A laser bonding method comprises the steps as follows: a frit is arranged in the position of an upper glass substrate according to a preset laser bonding path, wherein a starting section and an ending section of the laser bonding path are arranged oppositely; the upper glass substrate and a lower glass substrate are aligned accurately; and laser encapsulation is conducted along the laser bonding path. With the adoption of the method, the starting section and the ending section of the frit are staggered and arranged oppositely, by the aid of the mobility of the frit in a fused state, the starting section is attached to the ending section, and the starting section and the ending section are attached in a 'line-line' manner instead of closed in a 'point-point' manner, so that the sealing performance of the upper and lower glass substrates can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Double light path optical-fiber laser bonding machine for plate-type solar thermal absorber
InactiveCN101380695AQuality improvementFast welding speedLaser beam welding apparatusLaser bondingEngineering
The invention relates to a laser welding machine. The invention discloses a double-light path fiber laser welding machine used for a plate solar heat absorber which includes a laser, a fiber and a focusing system. The laser is connected with the focusing system by the fiber. The invention also includes a base device and a goal-post device; wherein, the goal-post device is arranged on the base device; the focusing device is arranged on the goal-post device for inducing the laser emitted by the laser between the goal-post device and the base device. Aiming at the position of a workpiece to be welded, the focusing system can move along the three directions of X, Y and Z; wherein, X and Y refer to a horizontal direction parallel to the ground; Z refers to a direction vertical to the ground. The welding machine solves the welding difficulty between a copper tube and an aluminum plate and changes the manufacturing technique flow of a solar heat absorber, thus leading the quality of the solar heat absorber to be greatly improved.
Owner:武汉楚天激光(集团)股份有限公司
Sealing shell for connector and electrical connector
InactiveCN102368579APrevent immersionPrevent intrusionCouplings bases/casesFixed connectionsLaser bondingEngineering
The invention provides a sealing shell for a connector and an electrical connector, which can reliably prevent water from intruding from the joint part of the sealing shell due to capillarity. The sealing shell of a connector is inserted into the outer circumferential wall of an electrically-insulating connector housing provided with an electrical connector contact for electromagnetic shield. The sealing shell (1) for the connector is formed into a tubular shape in a way to bend a metal sheet material with a preset size and thickness in a tubular way so as to form inside a hollow hole (12) capable of making the connector housing inserted and make the two ends of the metal sheet material docked. Laser bonding is performed on the docked joint part (1b'). At least one end is made open.
Owner:JST MFG CO LTD
Coaxial laser bonding wire fixture device
InactiveCN105428993AAchieve precise positioningEasy to operateLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsLaser bondingEngineering
The invention provides a coaxial laser bonding wire fixture device, which comprises a substrate base and a positioning cover plate, wherein the substrate base is provided with a bottom surface with a cavity to enable the substrate base to be matched with the original equipment working platform, and negative pressure through holes are uniformly distributed between the surface of the substrate base and the cavity; two sides of the positioning cover plate are provided with positioning mechanisms, the size of the positioning cover plate and the size of the substrate base are matched, the two are fixed via the positioning mechanisms, and the positioning cover plate is uniformly distributed with loading through holes corresponding to the negative pressure through holes in the substrate base. The device is simple to operate; seamless fixing between the positioning cover plate and the substrate base is realized through the positioning mechanisms; during a batch production process, the production efficiency is improved; accurate positioning of a semiconductor emitting laser device can be realized, and the processing precision is improved; scratching, peeling and other phenomena generated due to mechanical fixing of the device can be avoided, and integrity, stability and consistency of the product appearance can be ensured.
Owner:CHONGQING BEIHUA TECH
Flip chip laser bonding process
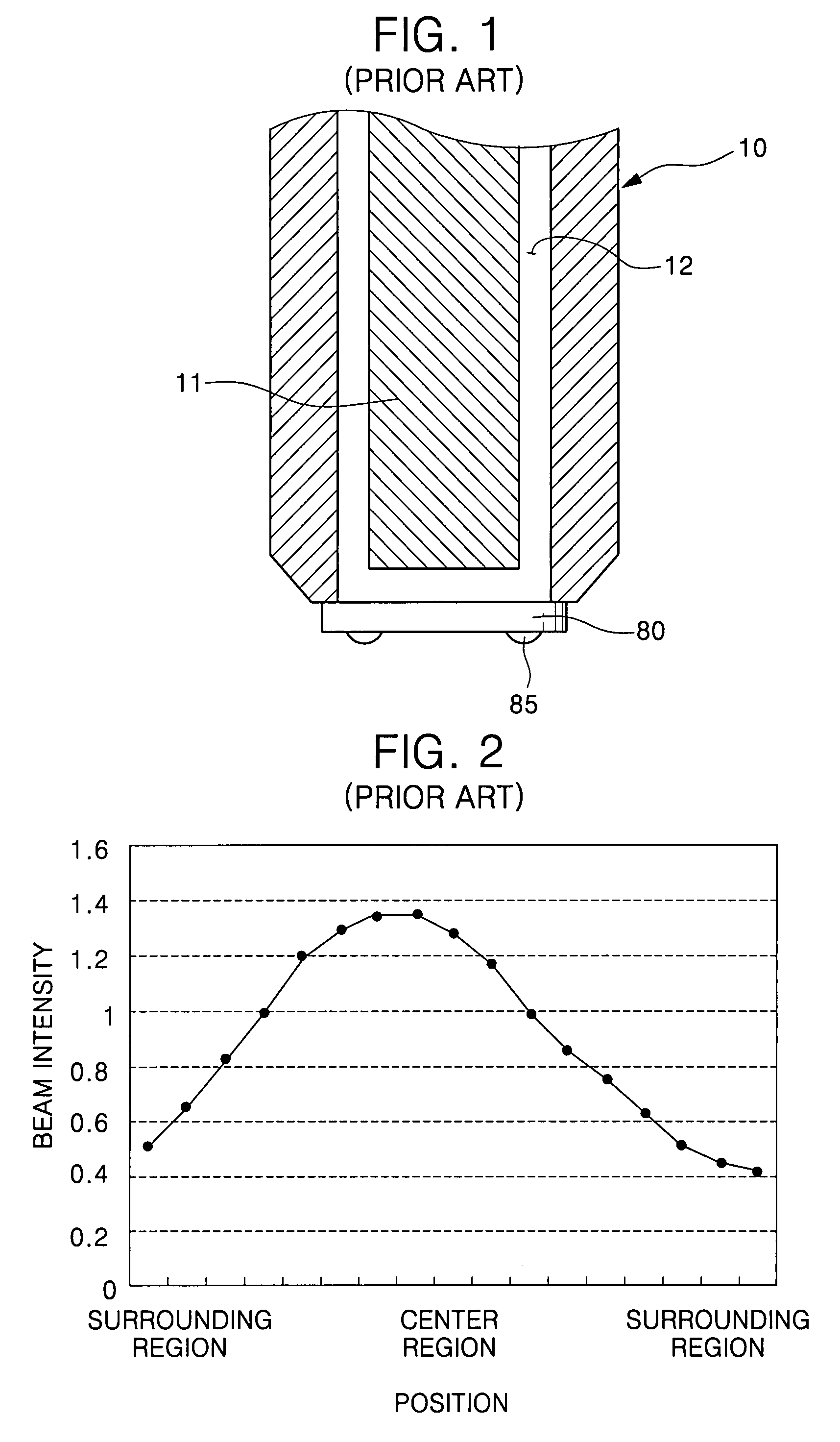
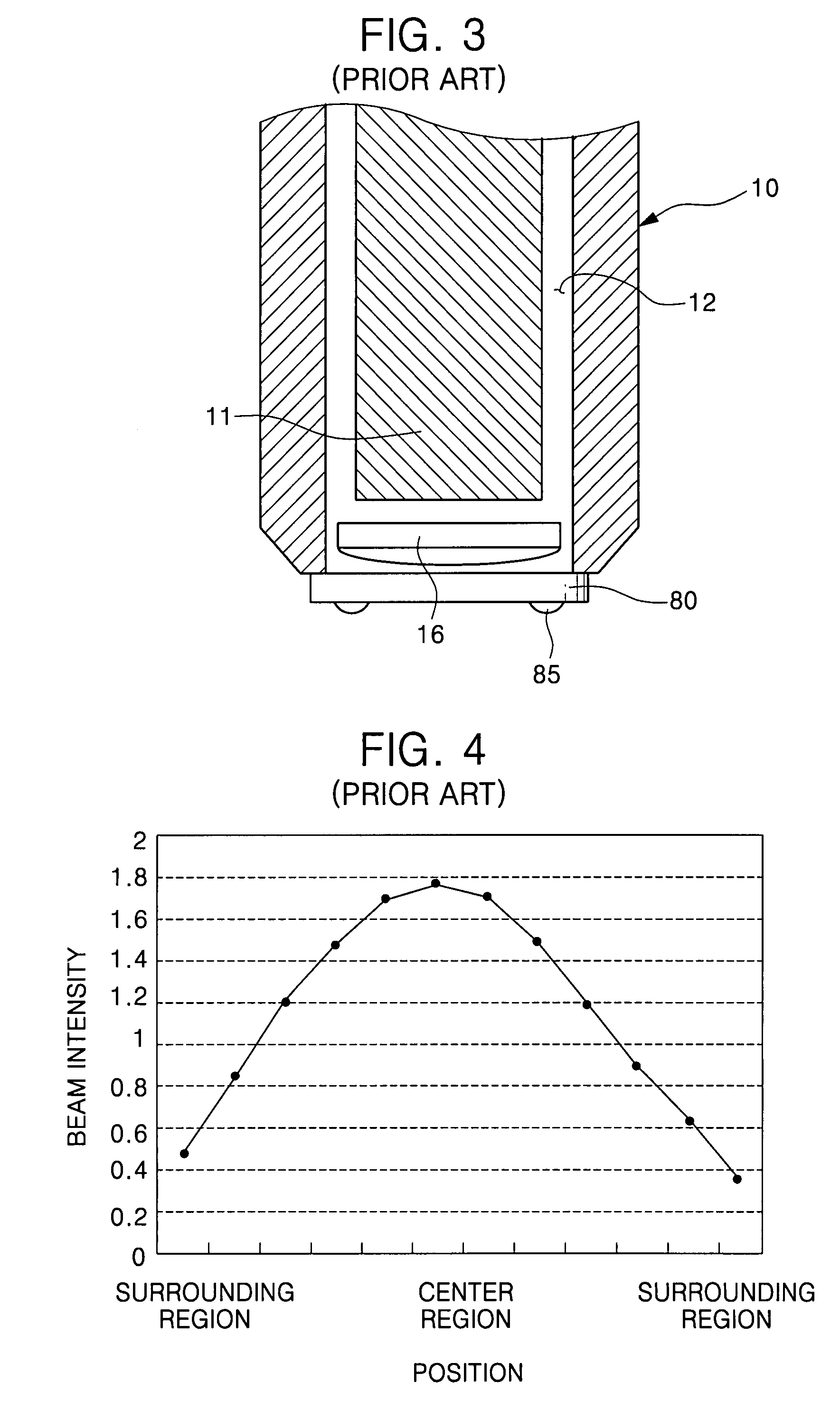
An apparatus for heating a chip includes: a laser generator for emitting a laser beam to a semiconductor chip to heat the semiconductor chip; and a beam intensity adjuster disposed on a laser emission path between the semiconductor chip and the laser generator to equalize the intensity of the laser beam to be emitted to the semiconductor chip. A flip chip bonder having the chip heating apparatus, and a method for bonding a flip chip using the same are also provided.
Owner:HANWHA AEROSPACE CO LTD
Pulse-laser bonding method for through-silicon-via based stacking of electronic components
ActiveUS8138577B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLaser bondingEngineering
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Laser bonding temperature acquisition system for photoelectric device packaging and method for photoelectric device packaging
ActiveCN102865939AEasy to measureSimple structureThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesLaser bondingEngineering
The invention discloses a laser bonding temperature acquisition system for photoelectric device packaging, which comprises a temperature sensor and locating elements thereof, wherein the locatingelements comprise a fixed-position locating element and a variable-position locating element; the temperature sensor, which is used for fixed point temperature measurement, of the fixed-position locating element is fixed onto a corresponding position corresponding to a glass sealing strip, and is used for testing fixed point temperature of the glass sealing strip; a movable part of the variable-position locating element is fixedly connected with other temperature sensors, so that the temperature sensors are limited to move along the periphery of the glass sealing strip; and temperature testing on different points of the glass sealing strip is realized through controlling positions of test points of the temperature sensor. The invention discloses a method for photoelectric device packaging, and through carrying out real-time fixed point temperature acquisition and real-time non-fixed point temperature acquisition on temperature of the glass sealing strip, the output power, the laser beam movement speed and the direction of a laser are controlled. According to the invention, the temperatures at different positions of glass material bonding parts can be simply and conveniently measured in real time, the structure is simple, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Multiple Laser Optical Assembly
A multiple laser optical assembly comprises two laser subassemblies with two lasers bonded on two bases respectively, a polarization beam combiner (PBC), a lens, a mechanical housing and an optical fiber. The two subassemblies are configured to have orthogonal polarization directions from the two lasers and are assembled coaxially. The PBC combines the orthogonal polarized beams from the two lasers. The lens focuses the combined beam and couples into the optical fiber. With such a two laser optical assembly as a building block and a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) filter to combine the beams from two of such type of two laser optical assembly, one can further build a four laser optical assembly and extend to even more channel multiple laser optical assembly by adding more WDM filters and more similar two laser optical assemblies.
Owner:LIU BIN
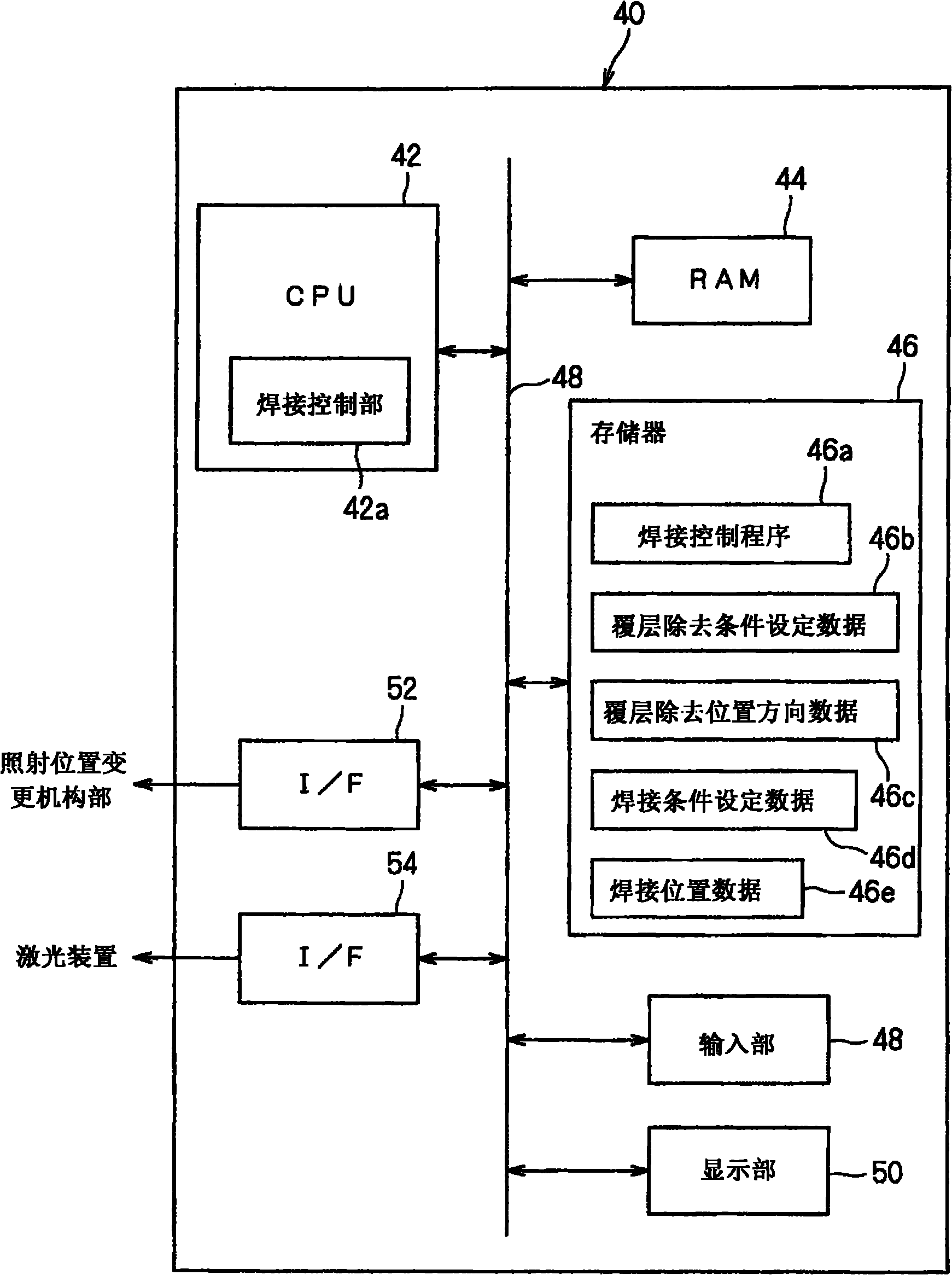
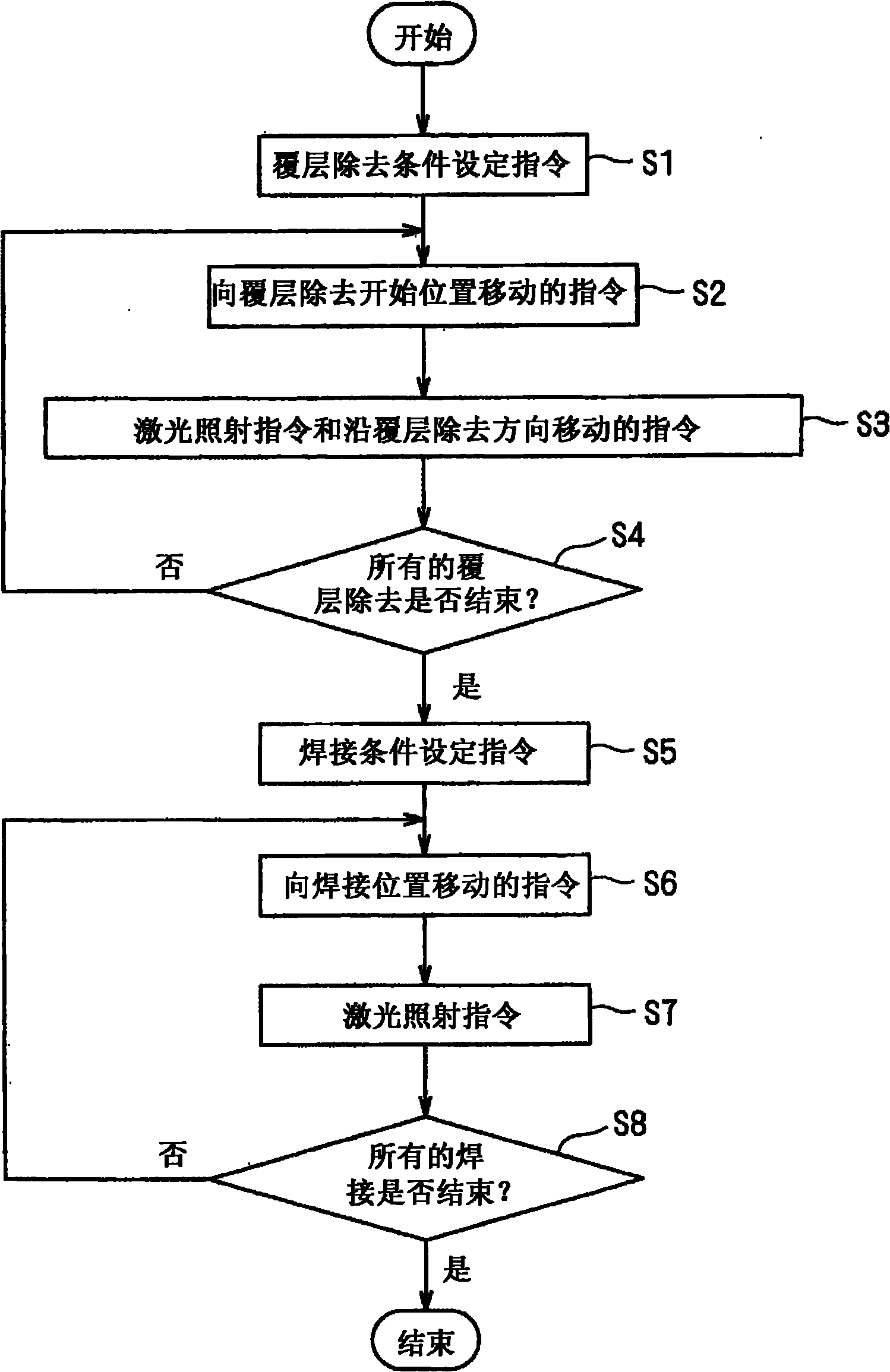
Laser bonding device
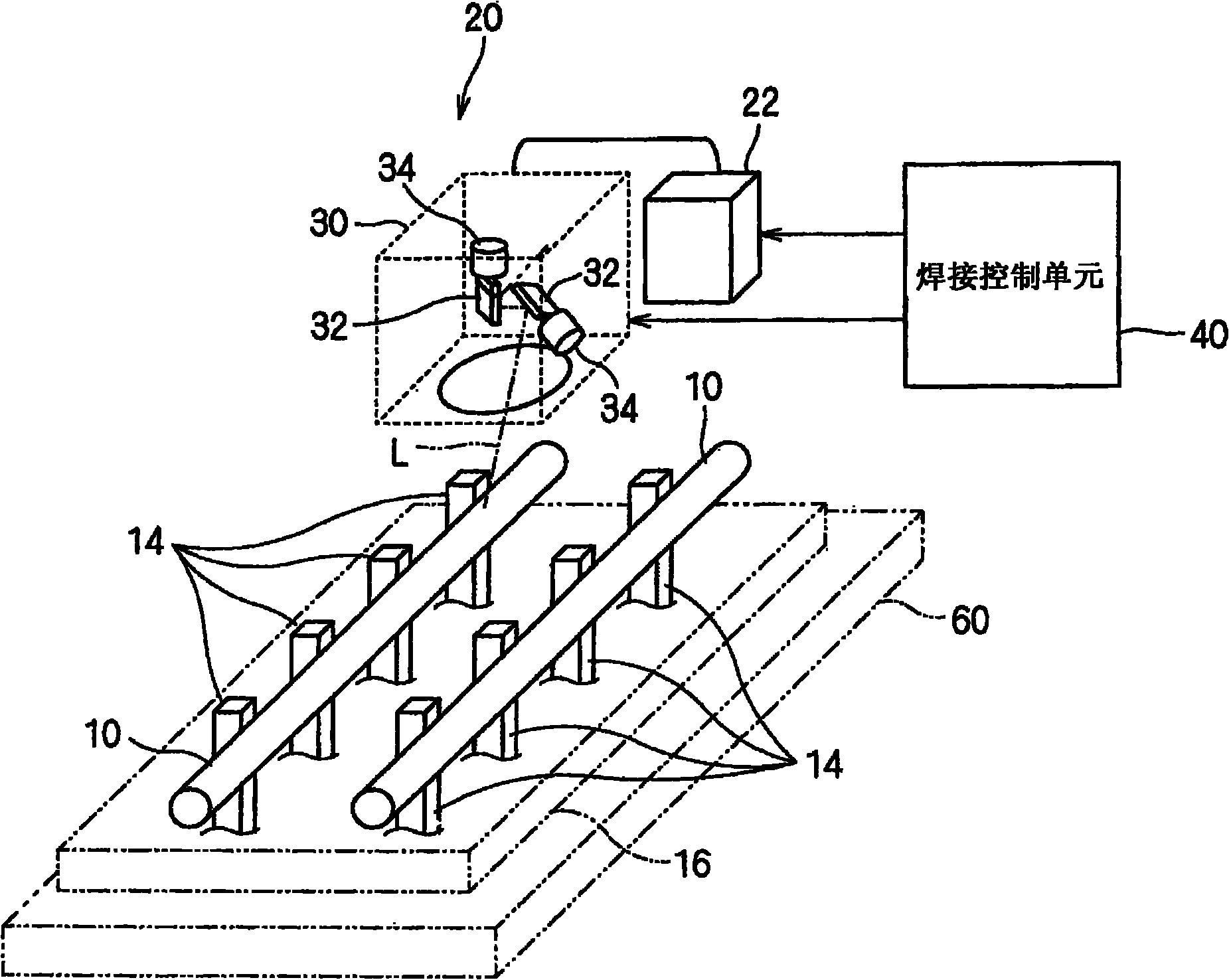
InactiveCN101872931AQuick and easy removalRemove appropriateLine/current collector detailsLaser detailsLaser bondingObject point
A laser bonding device can rapidly and conveniently remove a cover layer on a lead with cover layer and perform the laser bonding on the lead and a terminal. The laser bonding device can perform laser bonding on the lead with cover layer (10) and the terminal (14). The laser bonding device (20) is provided with a laser device (22) for generating a laser (L), an illuminating position exchanging mechanism (30) for changing the illumination position of the laser (L), and a bonding control unit (40) for controlling the illuminating position exchanging mechanism (30) to illuminate the laser (L) from the laser device (22) to a bonding area surface of the lead with cover layer (10), so as to illuminate the bonding object points of the lead with cover layer (10) and the terminal (14) through the laser (L) from the laser device (22) after covering the bonding area surface and perform the laser bonding on the lead with cover layer (10) and the terminal (14).
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Rubber member for laser bonding and shoe
ActiveUS20120198722A1High transparencyHigh mechanical strengthSolesSpecial tyresLaser bondingTransmittance
A rubber member for laser bonding of the present invention containing a rubber ingredient and silica, wherein the silica has an average particle size of more than 50 nm and 120 nm or less, and the amount of the silica is 10 parts by mass to 50 parts by mass based on 100 parts by mass of the rubber ingredient, the rubber member has a laser light transmittance of 30% or more, provided that the laser light transmittance is a transmittance when the rubber member has a thickness of 2 mm and is irradiated with laser light having a wavelength of 808 nm. The silica preferably includes silica having an average particle size of more than 50 nm and 120 nm or less and silica having an average particle size of 5 nm to 50 nm, and the amount of the silica having an average particle size of more than 50 nm and 120 nm or less is 10 parts by mass to 50 parts by mass based on 100 parts by mass of the rubber ingredient and the amount of the silica having an average particle size of 5 nm to 50 nm is 10 parts by mass to 50 parts by mass based on 100 parts by mass of the rubber ingredient.
Owner:ASICS CORP
High-temperature glass solder and its uses
The amorphous and / or partially crystalline glass solders are particularly suitable for high-temperature applications, e.g. in fuel cells or sensors in the exhaust gas stream of internal combustion engines. The glass solder is characterized by a linear coefficient of thermal expansion in the temperature range from 20° C. to 300° C. of 8.0×10−6 K−1 to 11.0×10−6 K−1 and a hemisphere temperature of 820° C. to 1100° C. and is suitable for laser bonding.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method for laser bonding
InactiveCN103561937AExcellent adhesionImprove reliabilityLaser beam welding apparatusLaser bondingOxygen
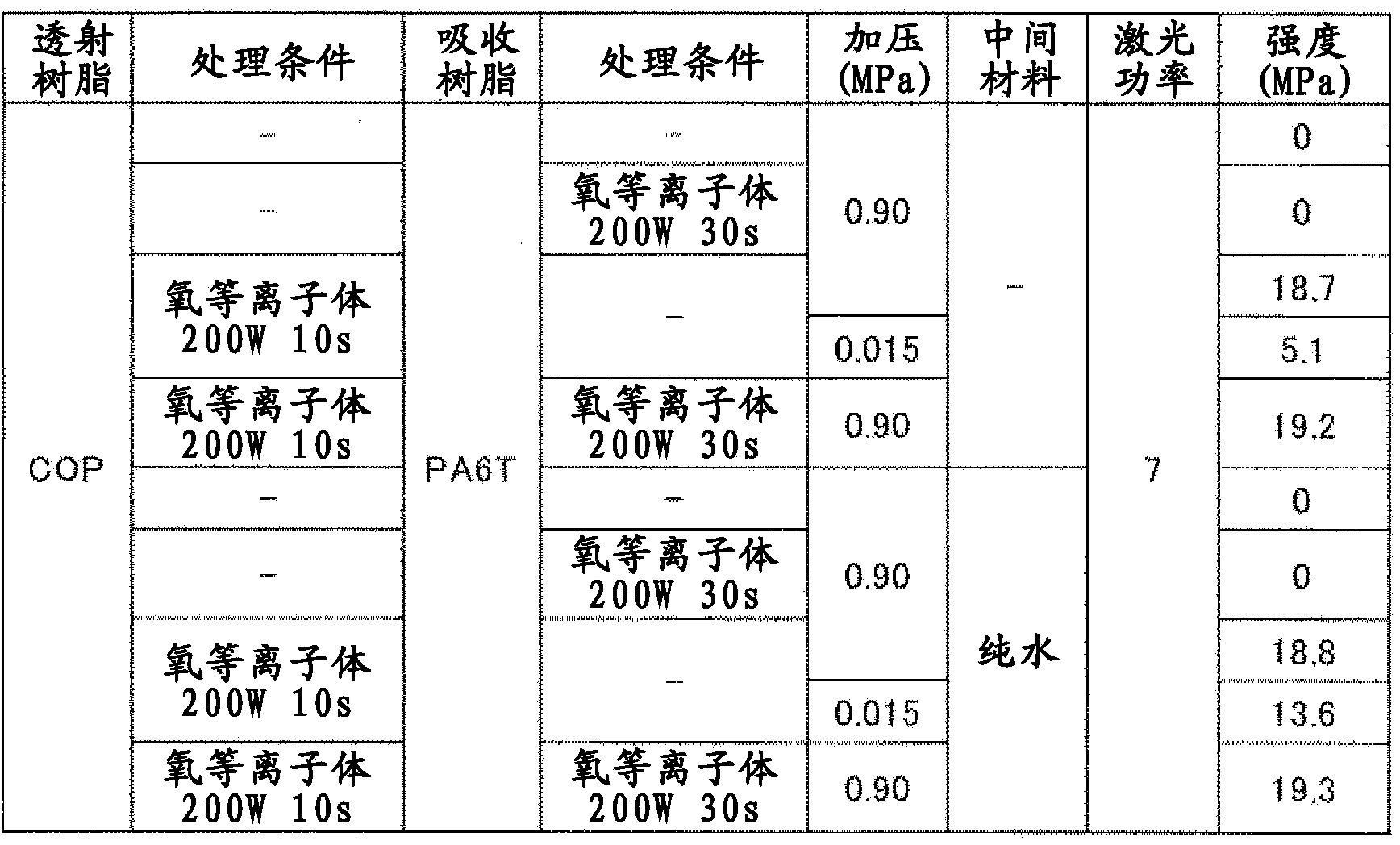
A method for laser bonding is provided in which interfacial strength between two thermoplastic resins or between a resin and a metal is heightened to render tenacious bonding possible, and bonding failures due to a remaining space can be significantly diminished. In order to solve the problem, the method includes, before bonding, a step in which the bonding surface of at least a first thermoplastic resin is subjected to a surface modification treatment to thereby form an oxidized layer that contains a larger number of oxygenic functional groups than in the bulk thermoplastic resin. A liquid intermediate material is interposed between the first thermoplastic resin and a second thermoplastic resin or a metal, and the stack in this state is pressed and bonded by laser irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for electrically connecting several solar cells and photovoltaic module
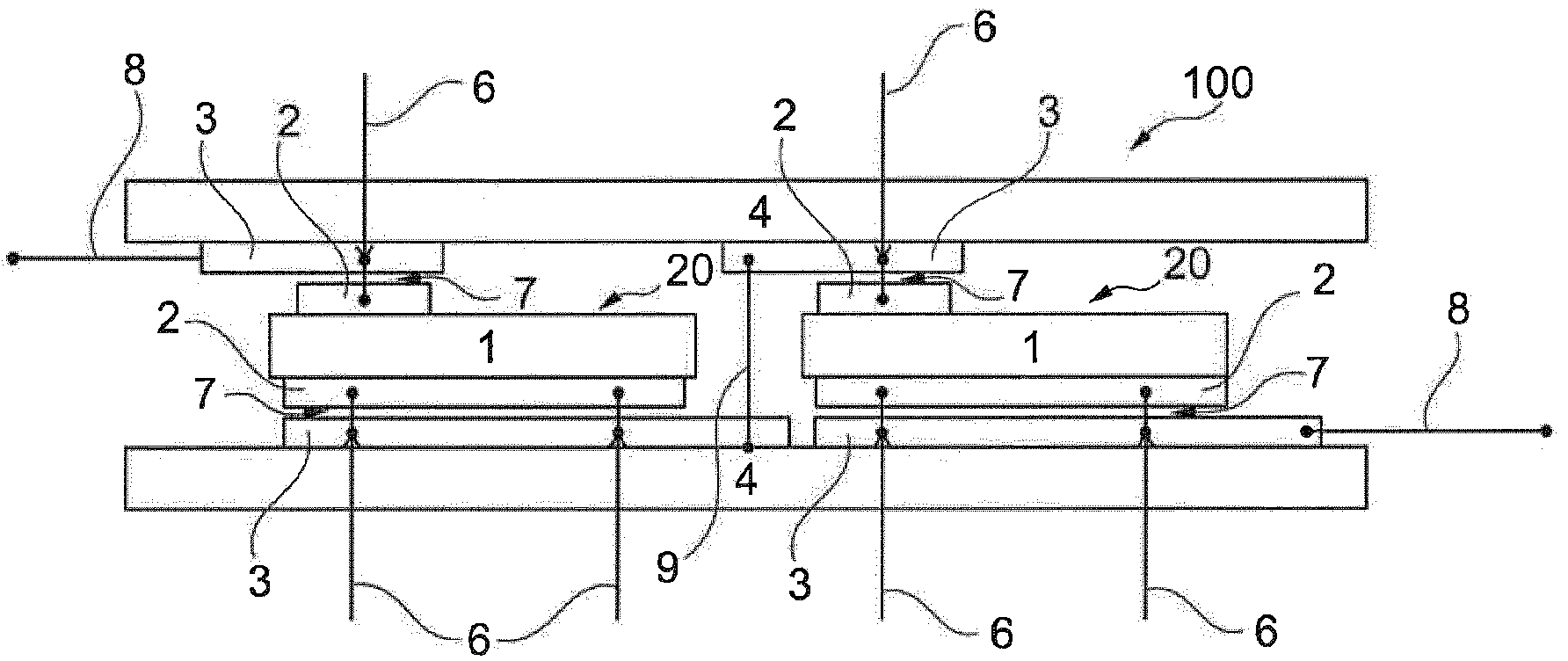
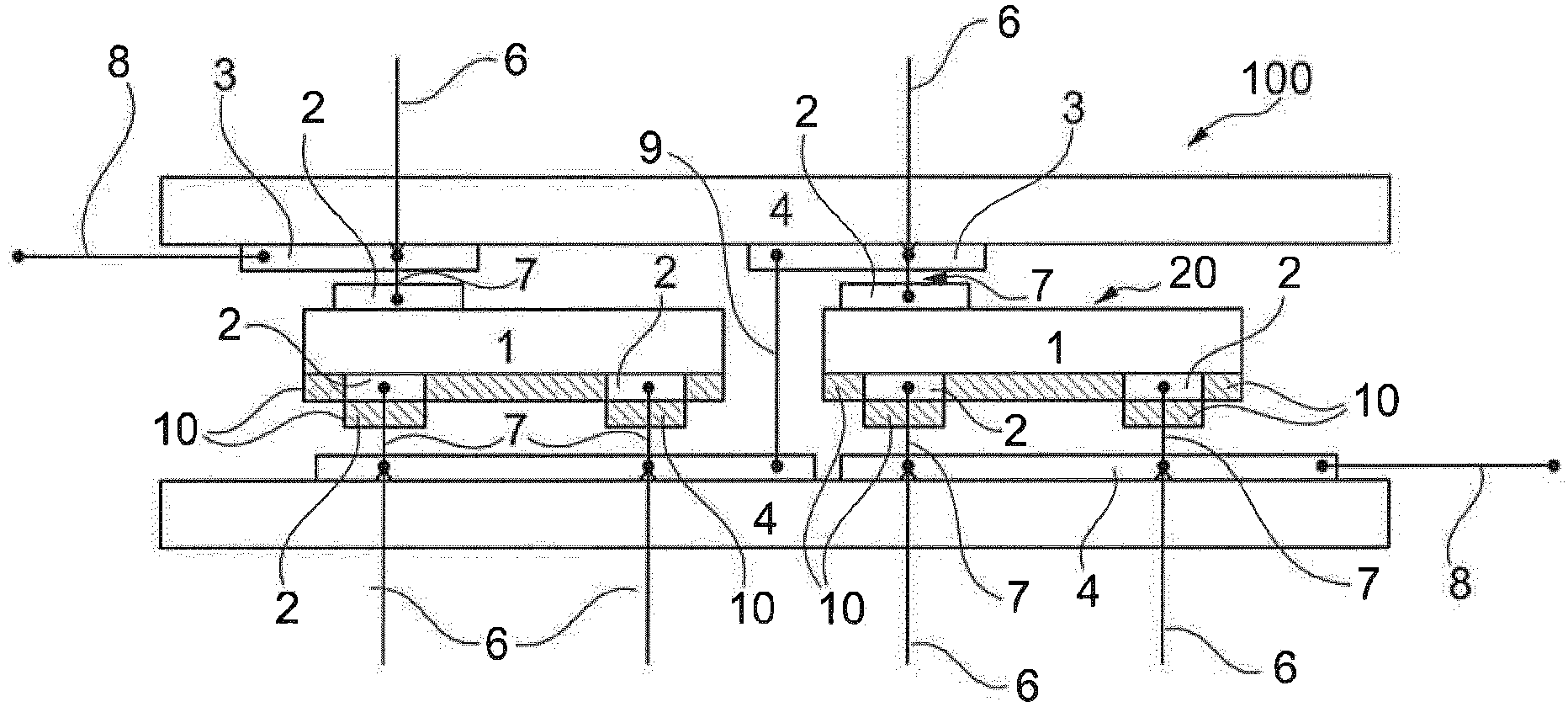
InactiveCN103748691ASimple processGood lateral conductivitySolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationLaser bondingElectricity
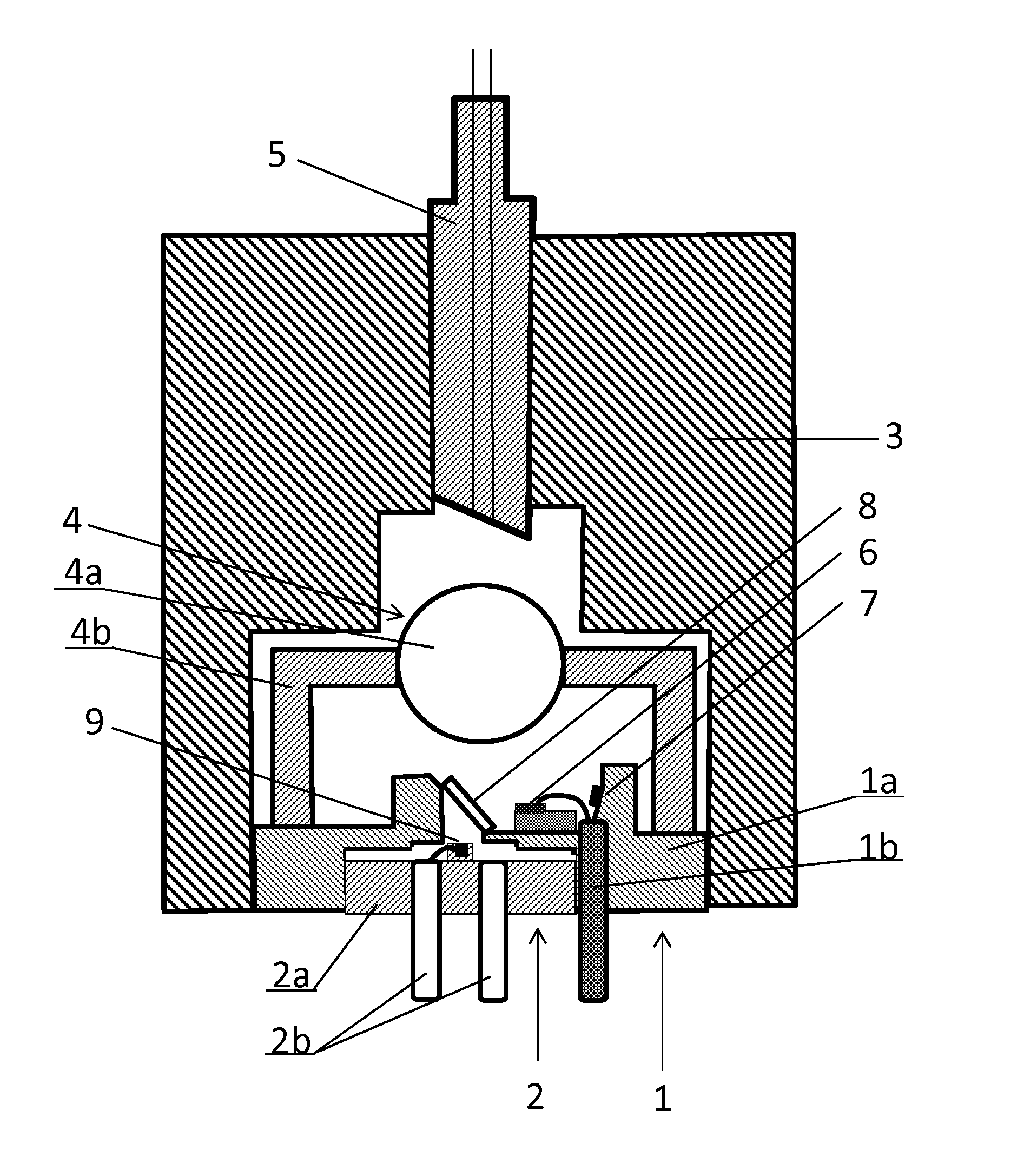
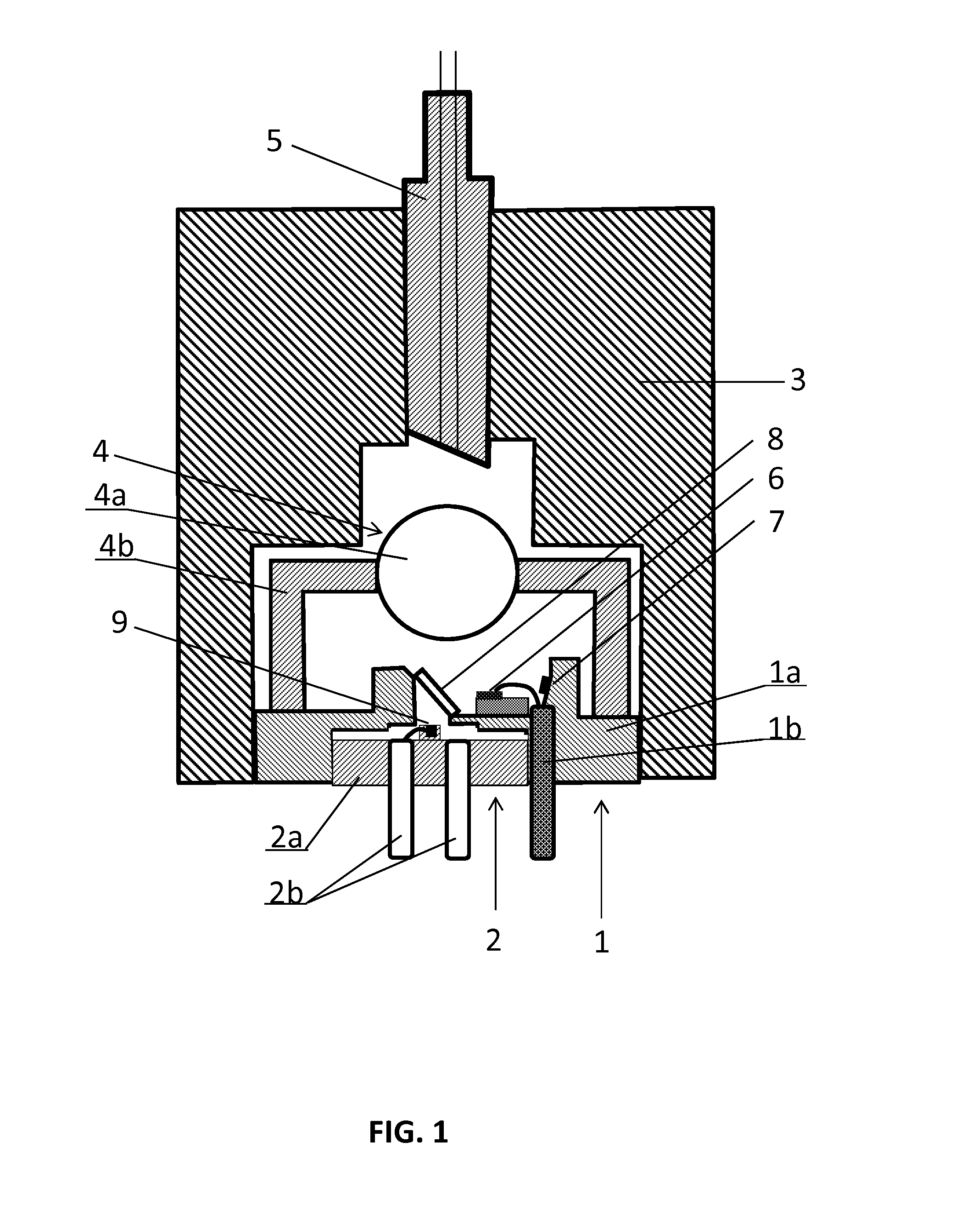
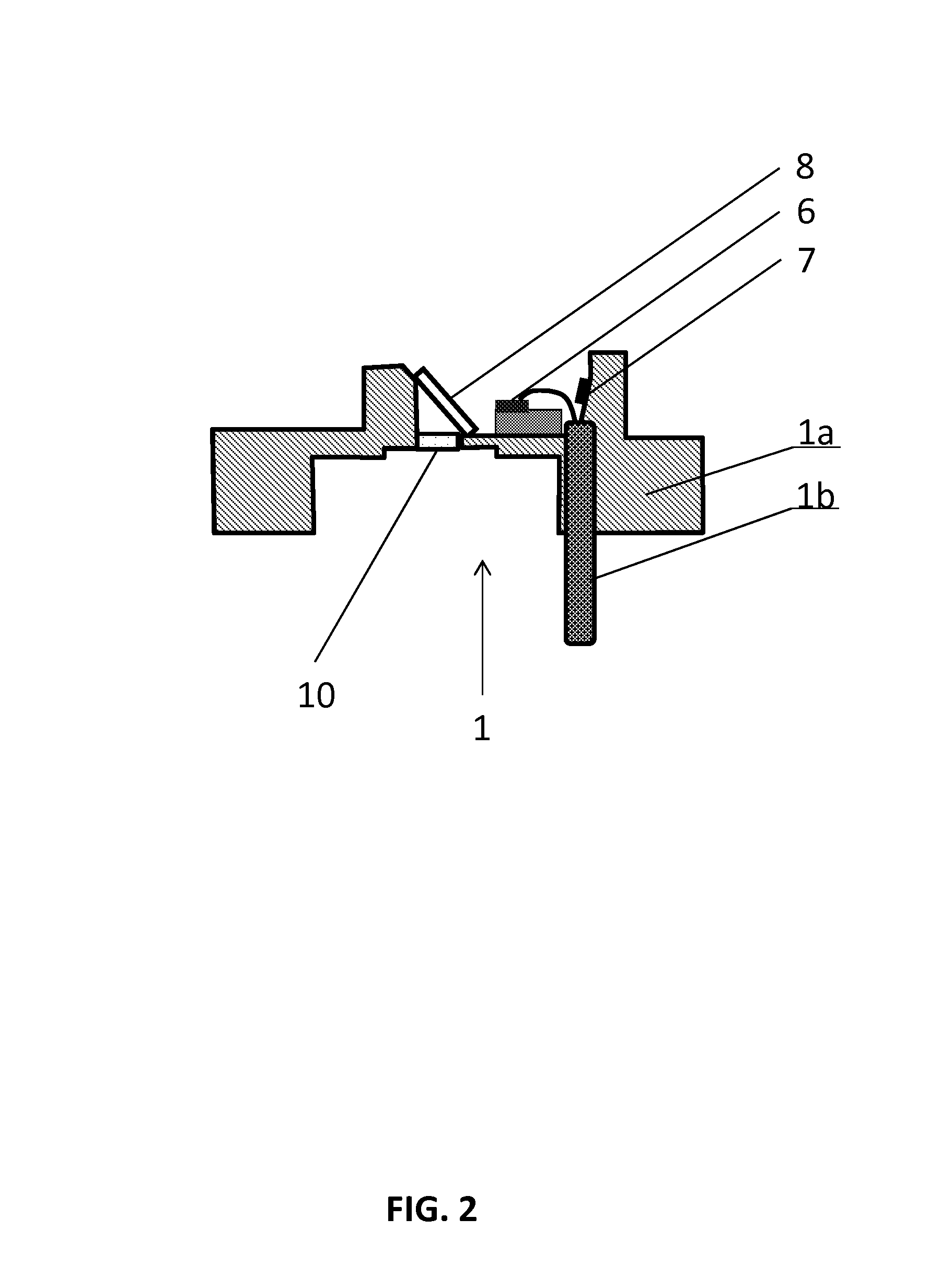
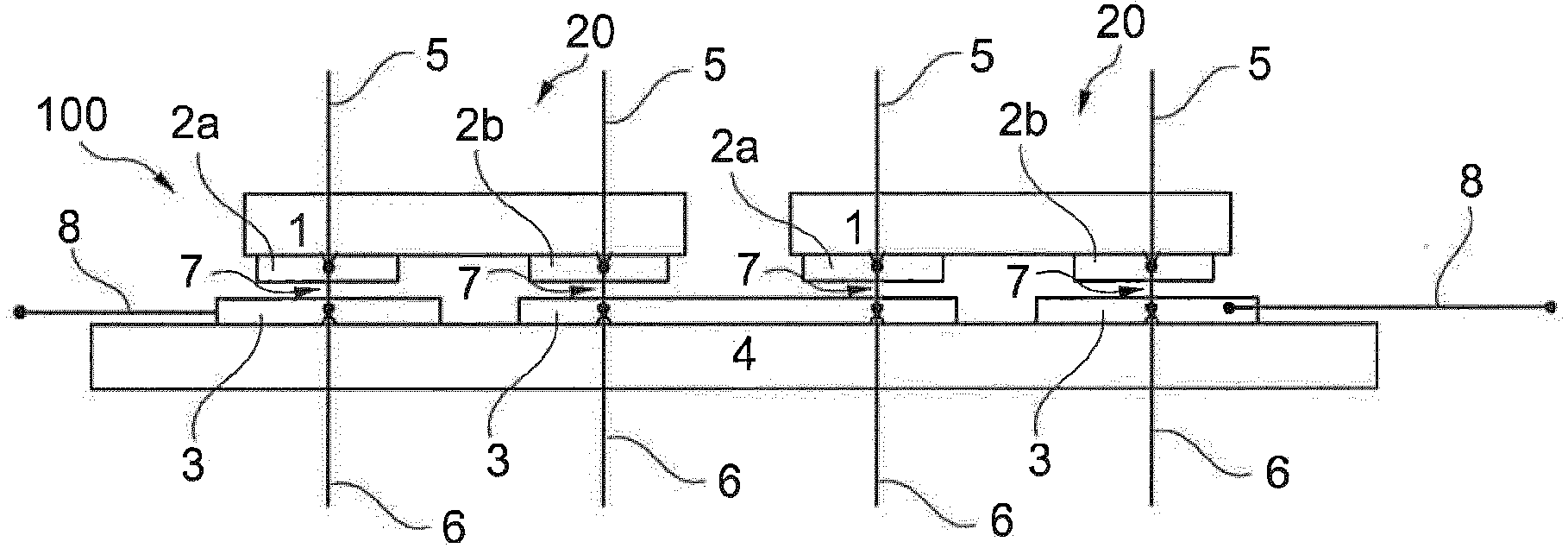
The invention relates to a method for metallizing and connecting solar cell substrates (1) and to a photovoltaic module (100) made of several metallized solar cells (20) that are electrically connected to one another. According to the invention, a solar cell substrate (1), in which second metal layers (2a, 2b) forming electrical metal contacts are optionally provided, is attached to a carrier substrate (4), on the surface of which at least one first metal layer (3) is formed in a suitable pattern. By localized irradiation of the metal layer (2, 3) with laser radiation (5, 6) through the solar cell substrate (1) or the carrier substrate (4), energy is introduced such that the metal layer (2, 3) is heated by absorbed laser radiation (4, 5) for an irreversible bonding to the adjacent surface of the solar cell substrate (1). By the laser bonding of the metal layer (3) on the carrier substrate (4) to the solar cell substrate (1), solar cells can be connected to form a photovoltaic module, wherein conventional soldering of adjacent solar cells via metal bands is no longer required. Non-solderable, cost-effective, in particular silver-free metal layers (2a, 2b) can thus be used for contacting the solar cell substrates (1) of the solar cells (20).
Owner:INST FUR SOLARENERGIEFORSCHUNG
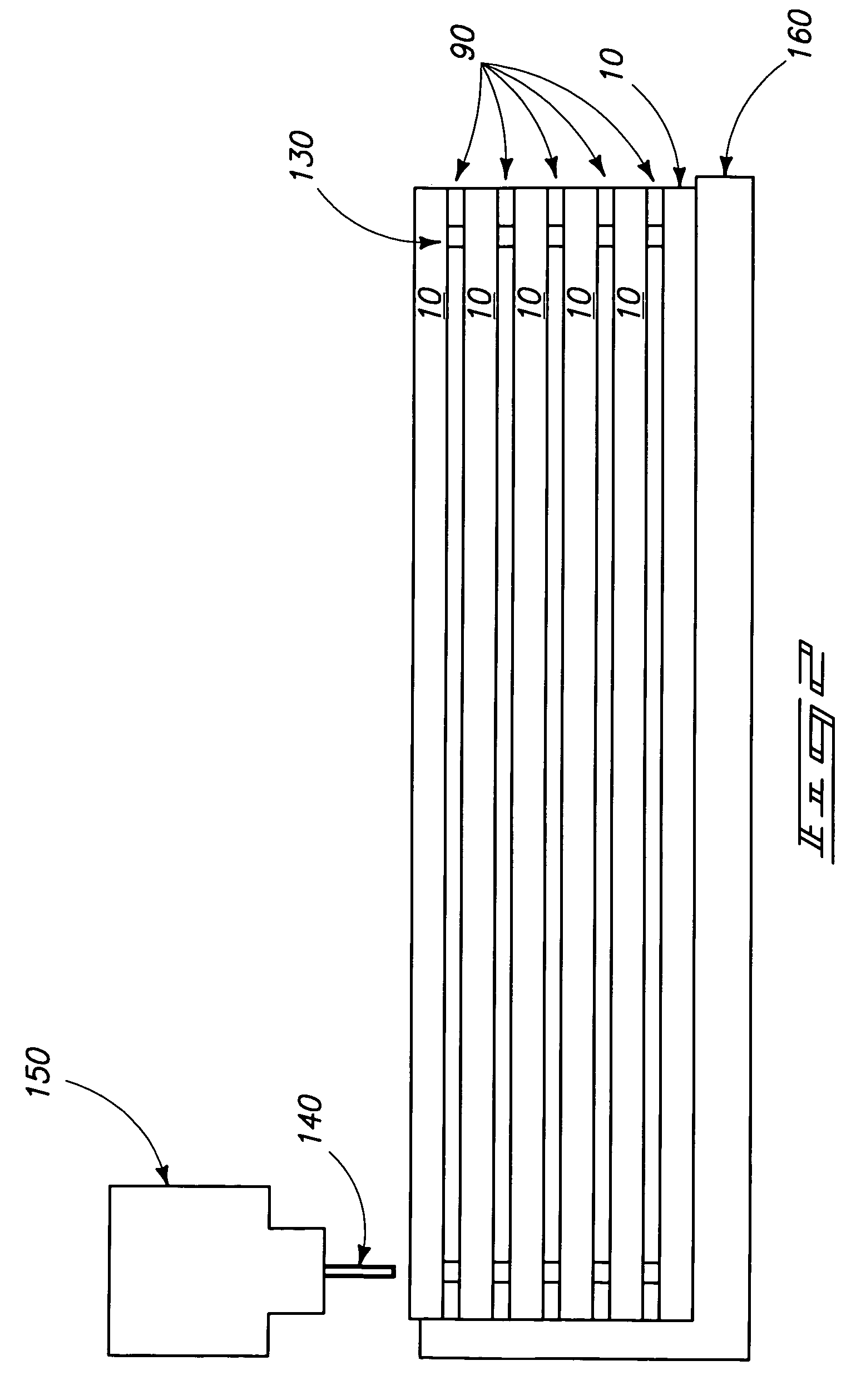
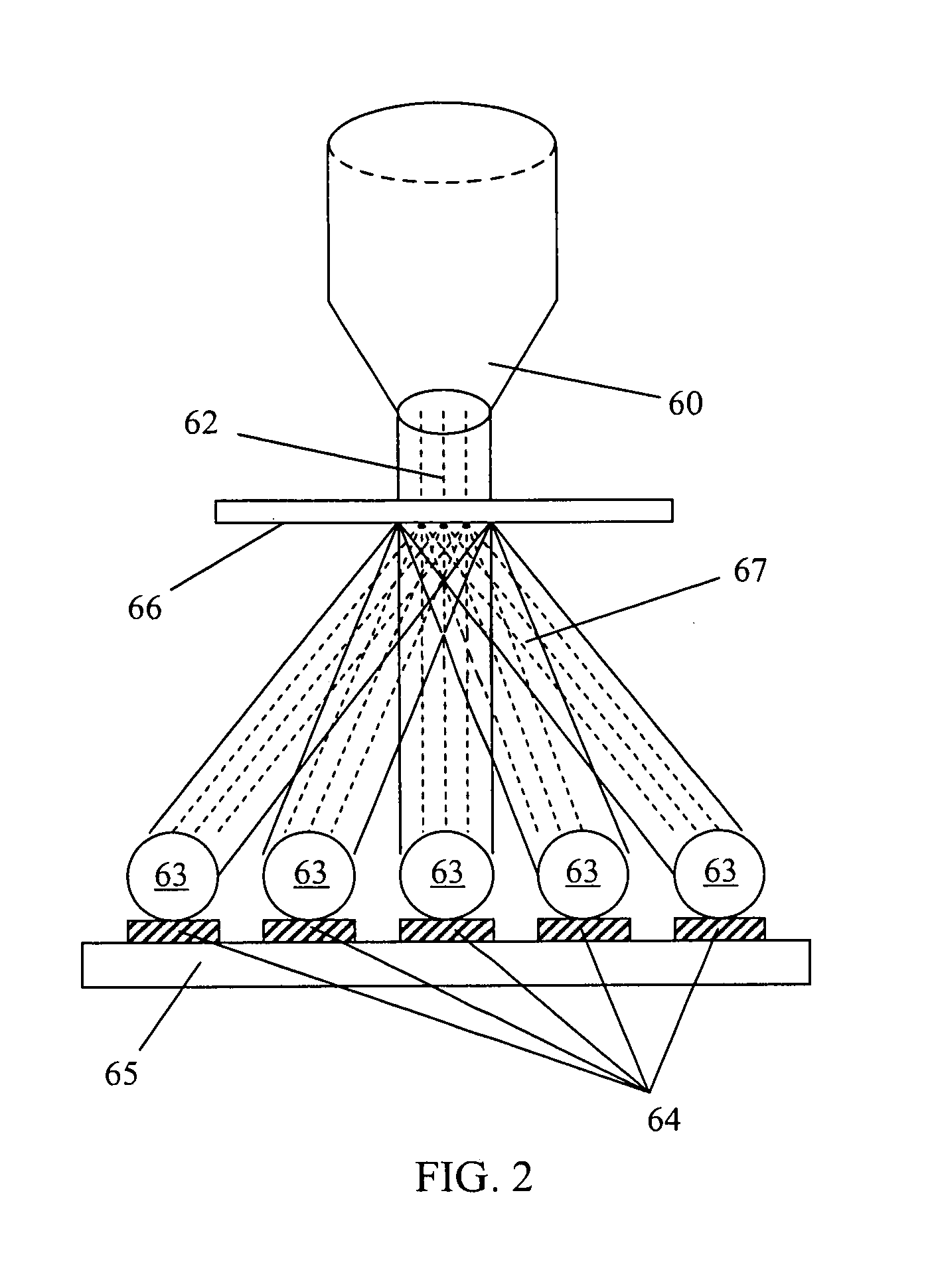
Multi-beam laser bonding apparatus and bonding method using the same
InactiveUS20090127235A1Bonding efficiency is dramaticallyAvoid mistakesSoldering apparatusSolid-state devicesLaser bondingOptoelectronics
A multi-beam laser bonding apparatus includes a laser beam irradiation unit for irradiating a unique laser beam and an optical instrument. The bonding apparatus is for bonding parts by a plurality of bonding media which are separated from each other at a predetermined distance. The optical instrument is positioned on a path of the unique laser beam for splitting the unique laser beam into a plurality of laser beams and focusing the plurality of laser beams onto the respective bonding media. The present invention also discloses a multi-beam laser bonding method with this bonding apparatus.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com