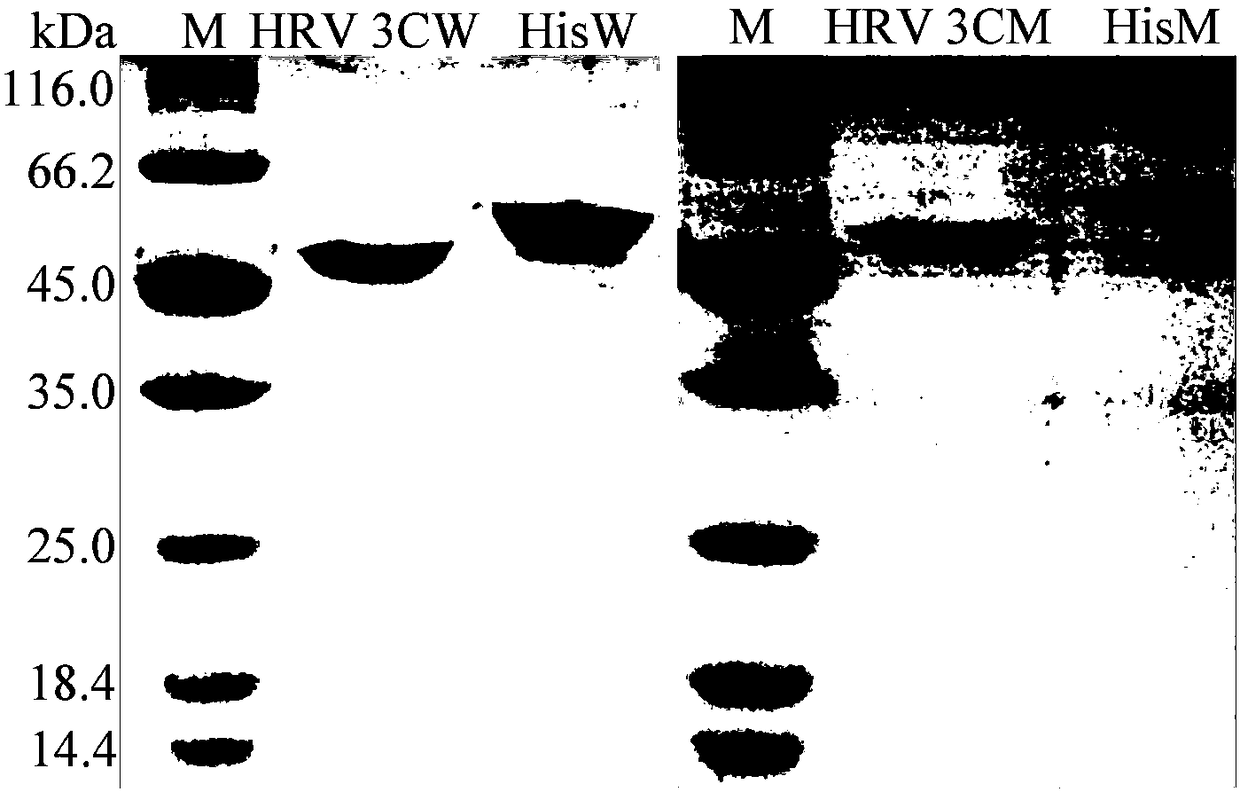
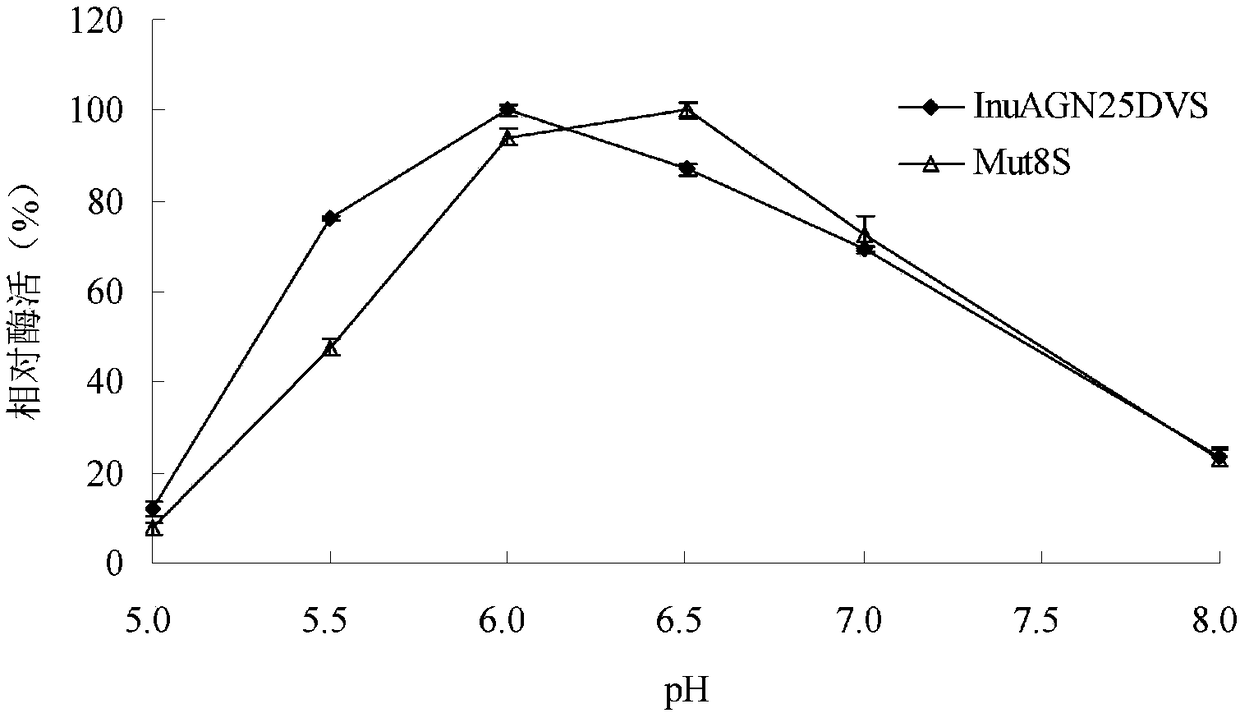
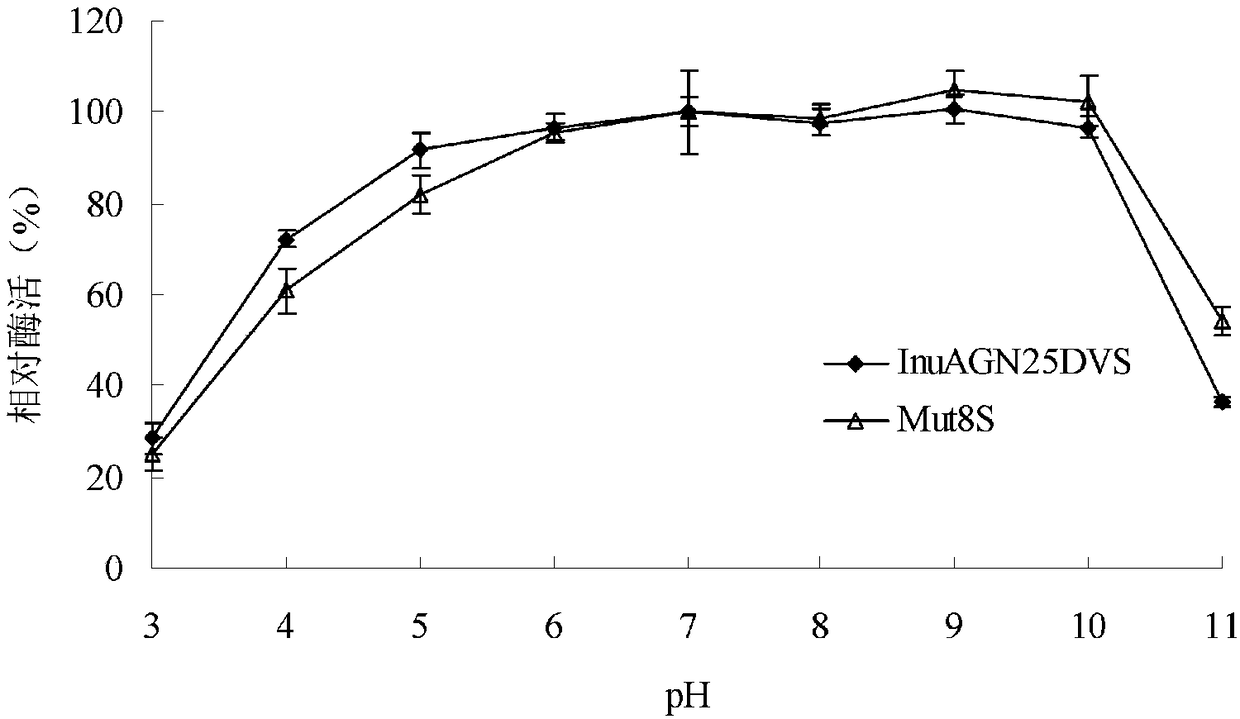
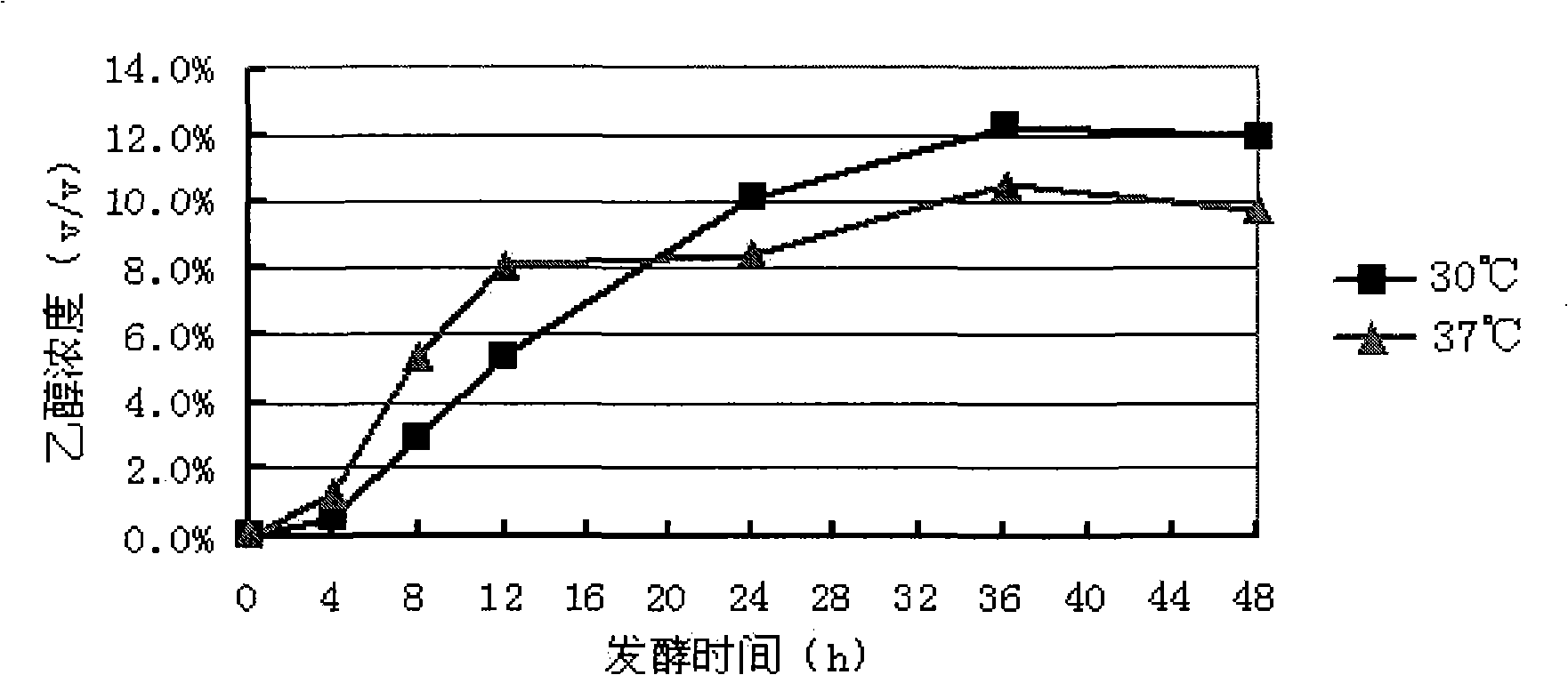
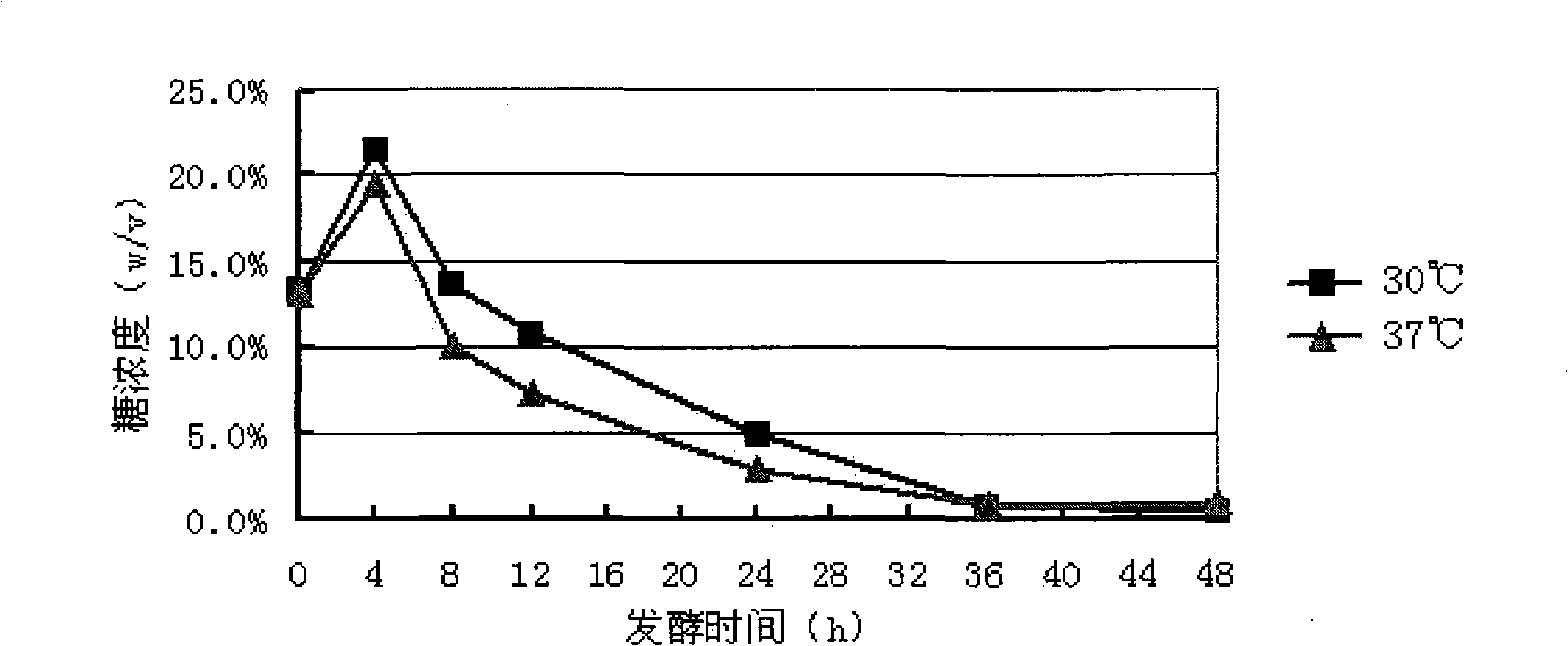
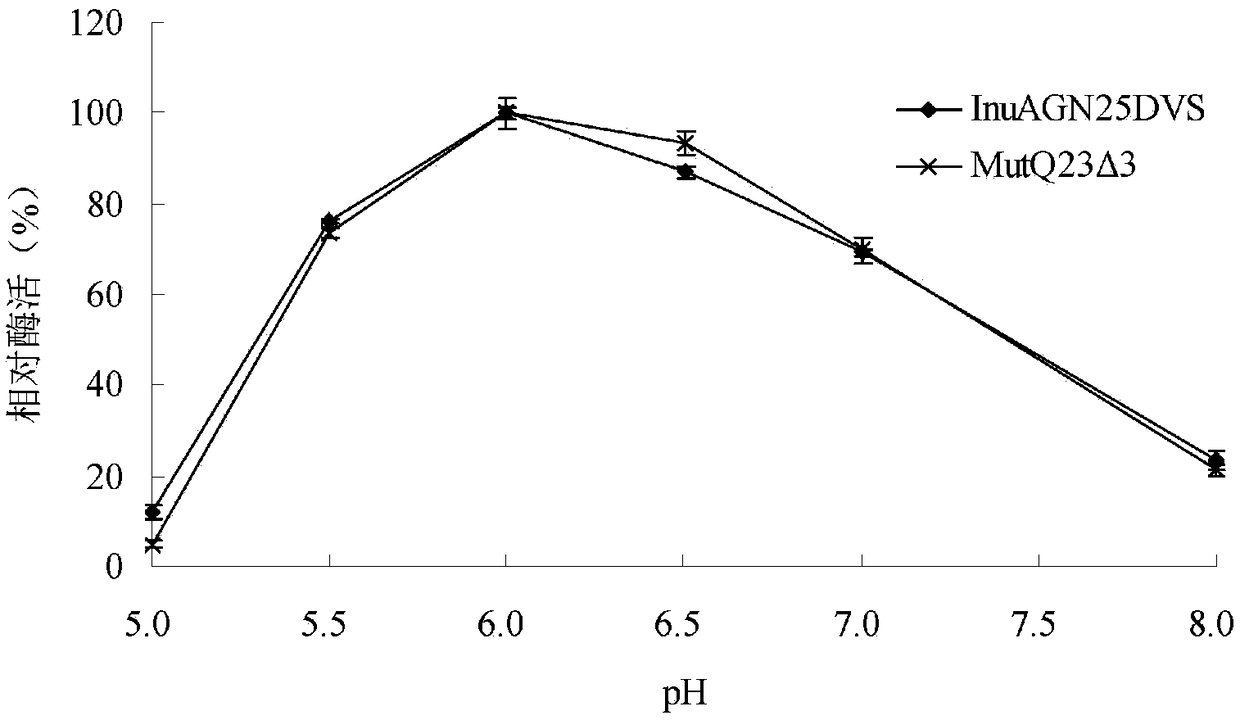
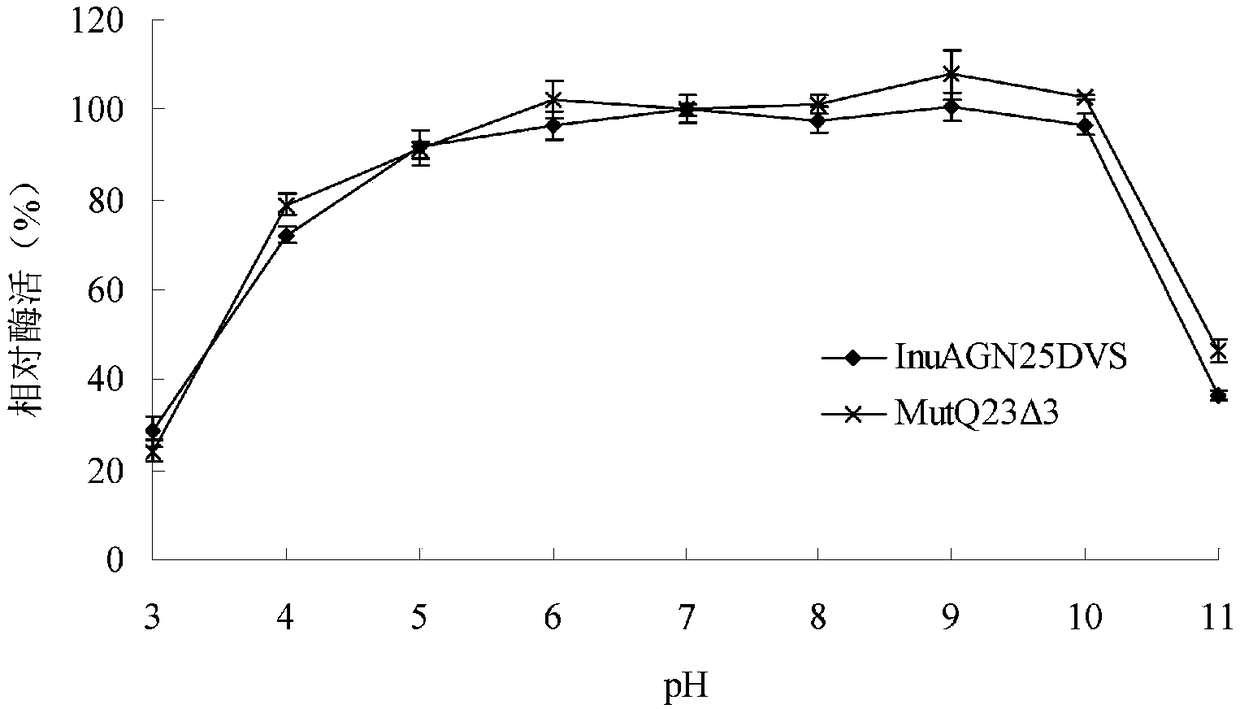
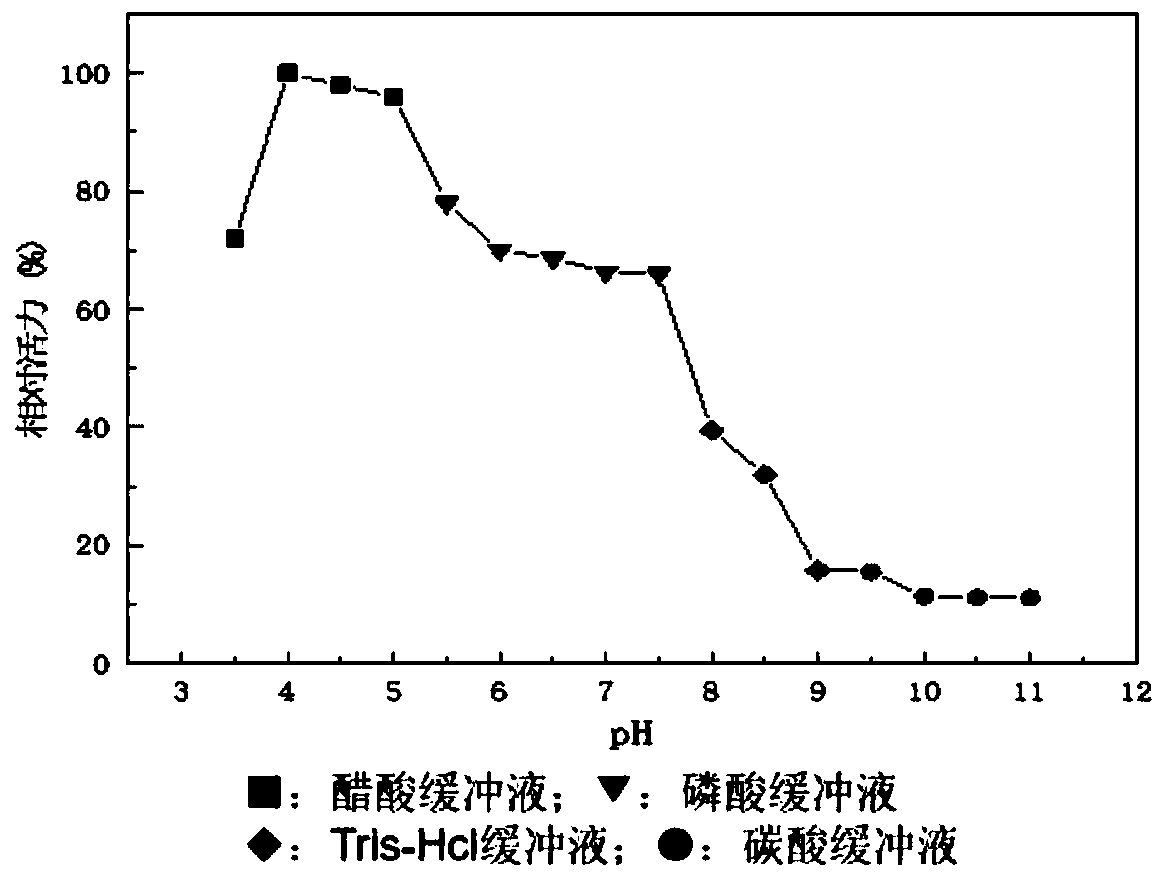
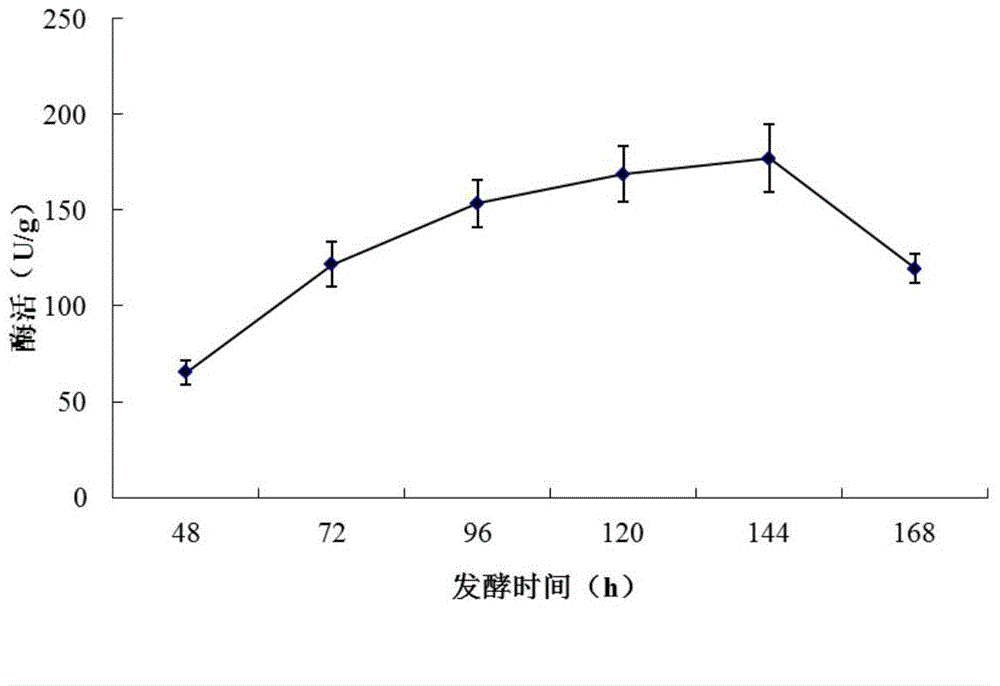
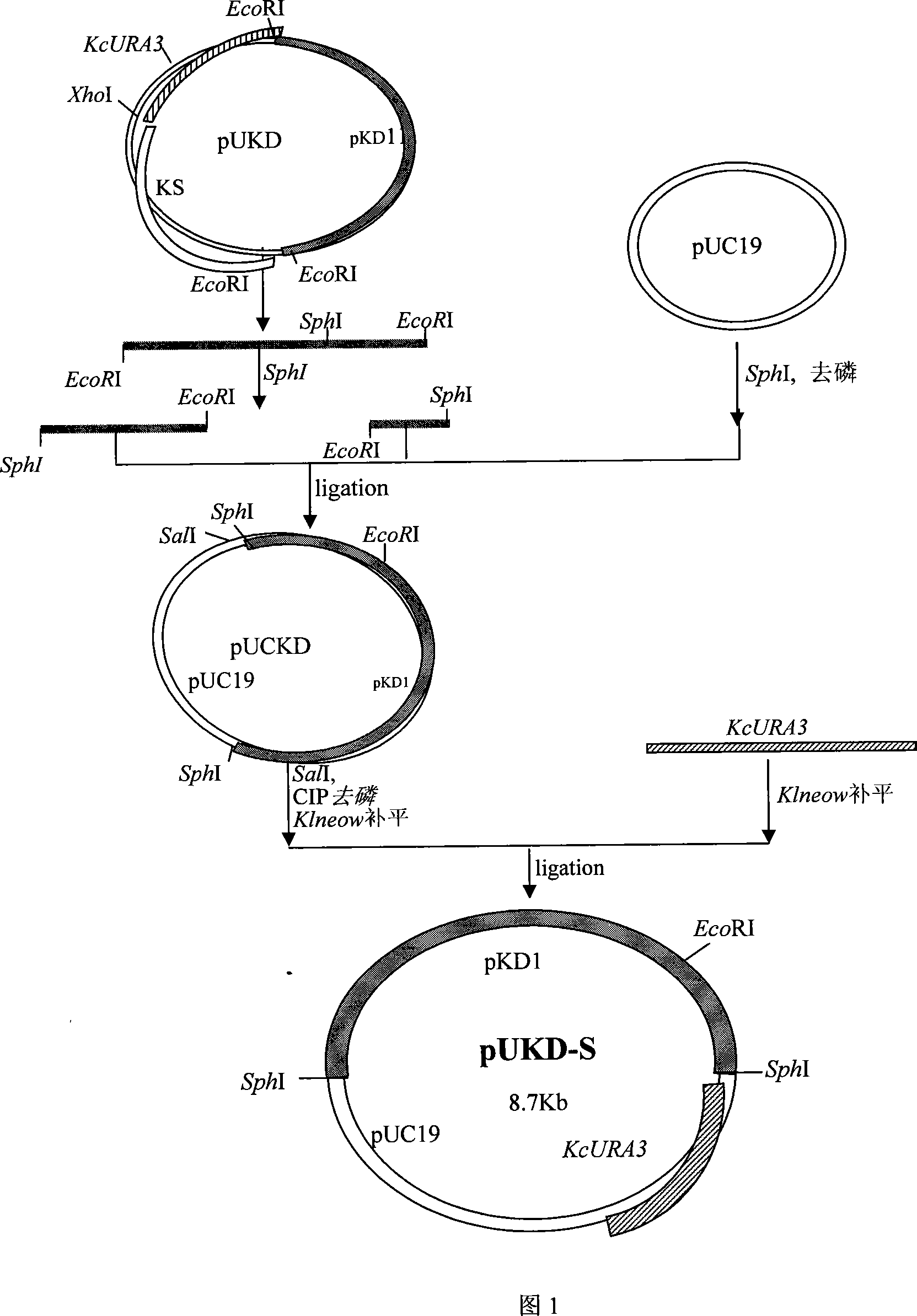
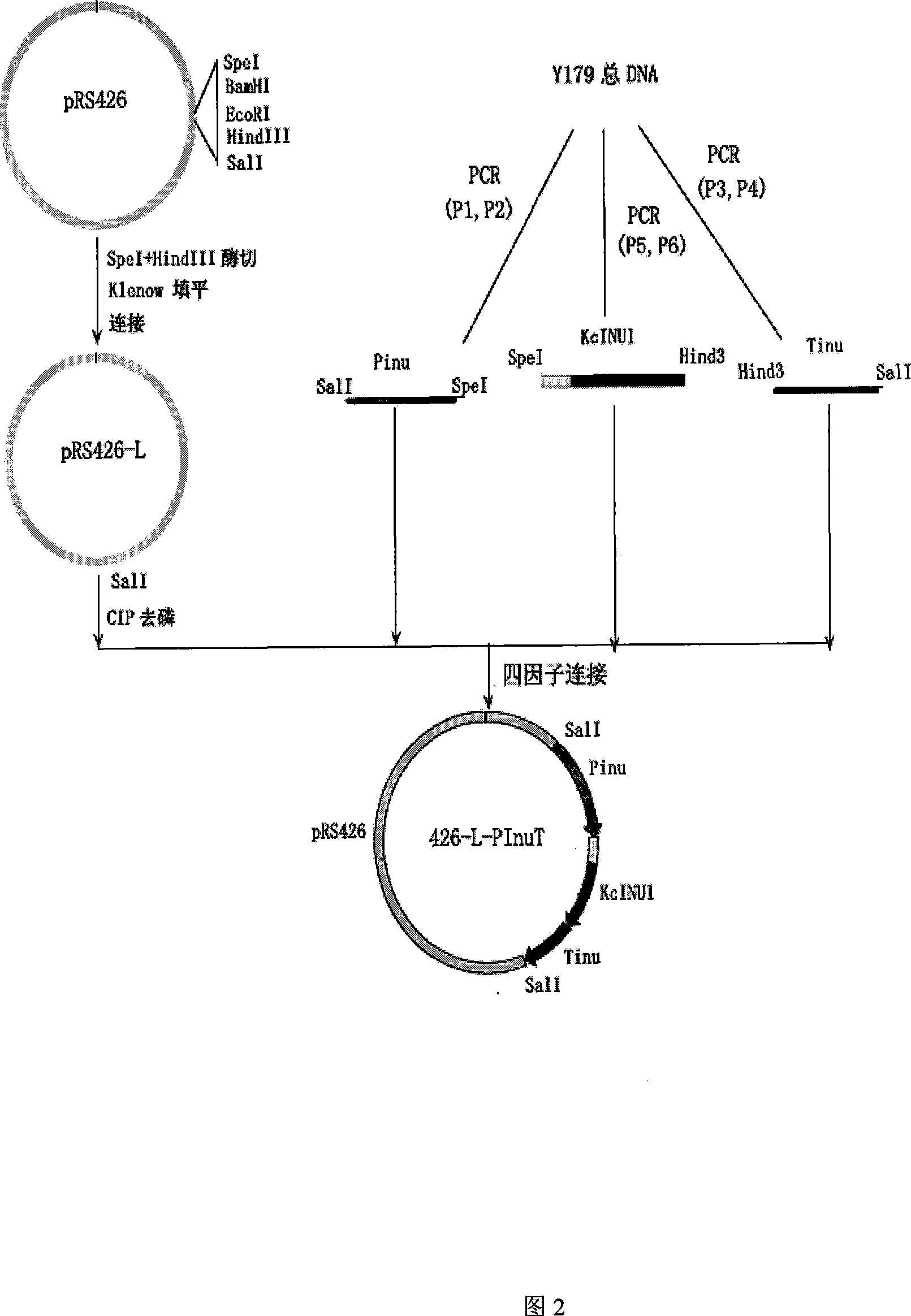
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85 results about "Inulinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inulinase (EC 3.2.1.7, inulase, endoinulinase, endo-inulinase, exoinulinase, 2,1-beta-D-fructan fructanohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-beta-D-fructan fructanohydrolase.
Low-temperature exoinulinase mutant Mut8S with improved heat stability
ActiveCN108504644AChange thermal stabilityIncreased thermal activityFermentationGlycosylasesBiotechnologyGenetically engineered
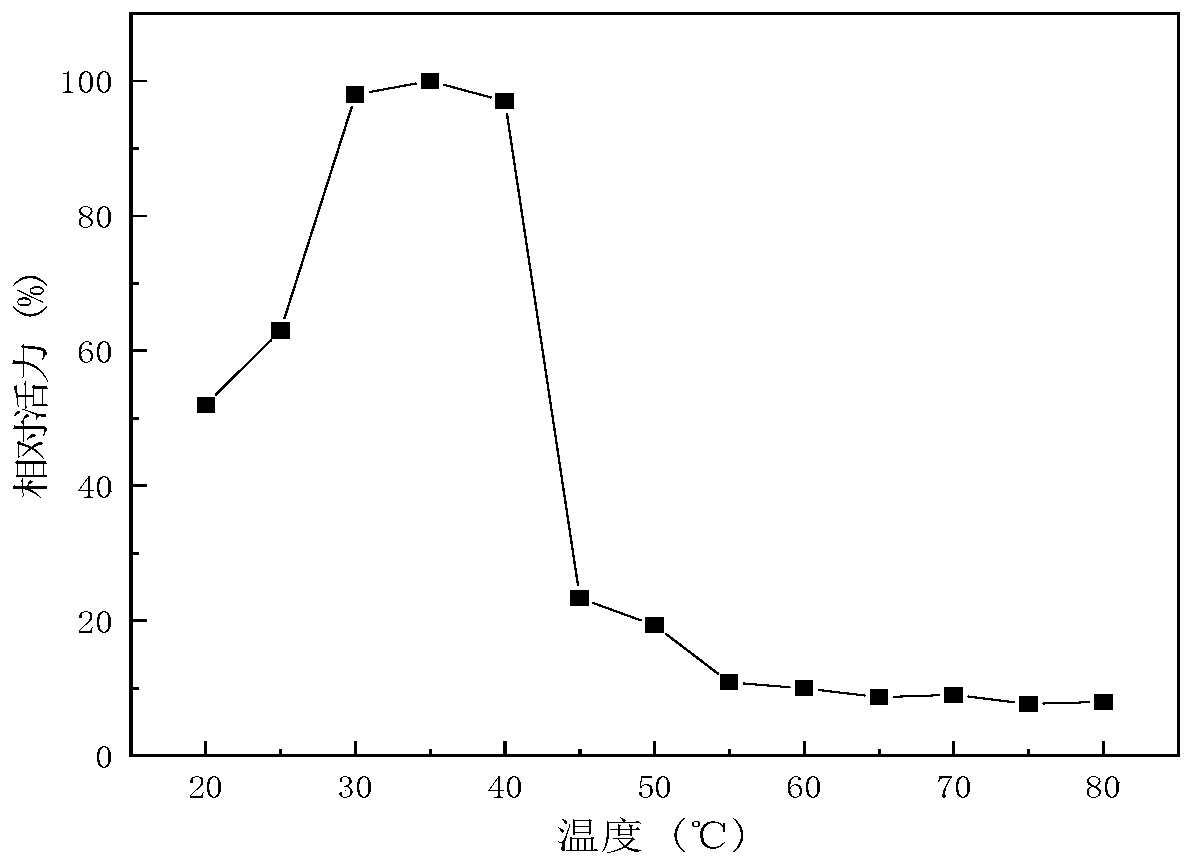
The invention relates to the technical fields of genetic engineering and protein modification and particularly relates to a low-temperature exoinulinase mutant Mut8S with the improved heat stability.The amino acid sequence of the mutant Mut8S is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The optimal pH value of the Mut8S is 6.5; the optimal temperature of the Mut8S is 40 DEG C, and the Mut8S respectively has the enzyme activities of 16%, 27%, 51%, 76% and 78% at the temperatures of 0 DEG C, 10 DEG C, 20 DEG C, 30 DEGC and 50 DEG C; and after being processed at 50 DEG C for 60 minutes, the Mut8S still preserves 100% of the enzyme activity; and the enzyme can be used for hydrolyzing inulin so as to generate fructose. The low-temperature exoinulinase mutant Mut8S with the improved heat stability can be applied to the industries of foods, wine brewing, biological energy sources and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for producing ethanol by synchronously saccharifying and fermenting Jerusalem artichoke raw material
InactiveCN101265485AReduce fermentation costsBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
New method for purifying fructo oligosaccharide in chicory
The invention belongs to the field of natural organic chemistry, and relates to a method for purifying fructo oligosaccharide in chicory by using an Aspergillus niger endo-inulinase-microwave extraction combined technology, macroporous resin decolorization and impurity removing, and combination of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration. The method has the following advantages that: 1, the Aspergillus niger endo-inulinase-microwave extraction combined technology is adopted so as to substantially improve the yield of the fructo oligosaccharide, greatly reduce the extraction time, and improve the extraction speed; the macroporous resin is selected so as to substantially improve the active ingredient content, and achieve the large-scale production, wherein the macroporous resin provides a large absorption amount for pigment, and the inulin loss is low during the decolorization process; and 3, the ultrafiltration and nanofiltration equipment is adopted, such that the extraction purity of the fructo oligosaccharide is high, the separation effect is significant, and the permeation flux of the membrane can be restored after the membrane is washed. By combining the Aspergillus niger endo-inulinase-microwave extraction combined technology, the macroporous resin decolorization and impurity removing, and the ultrafiltration and nanofiltration filtration process, the final product fructo oligosaccharide with the content more than 98% can be obtained. With the present invention, disadvantages of long time, existing of impurities, and high active ingredient loss of the conventional inulin extraction method are overcome.
Owner:DAXINGANLING LINGOBERRY BOREAL BIOTECH CO LTD
Exo-inulinase mutant MutDR121EH9 with improved low-temperature activity
The invention discloses an exo-inulinase mutant MutDR121EH9 with improved low-temperature activity, which has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the thermal activity and the thermal stability of the mutant MutDR121EH9 are changed, so that the mutant MutDR121EH9 has higher activity at low temperature, the thermal stability is reduced and the low-temperature activity is increased, and the use amount of enzyme is reduced or the reaction time is shortened during a low-temperature reaction; meanwhile, the degraded thermal stability makes the enzyme reaction process to be controlled through thermal treatment, wherein optimal temperature of the wild enzyme InuAMN8 is 35 DEG C, and the optimal temperature of the mutant enzyme MutDR121EH9 is 20 DEG C; after treatment at 50 DEG C, the enzyme activity of the wild enzyme InuAMN8 keeps 81% or above, and the enzyme activity of the mutant enzyme MutDR121EH9 is reduced from 32% to 14%. The mutant MutDR121EH9 disclosed by the invention can be applied to the industries of food, wine brewing, washing and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Heat-resistant low temperature exo-inulinase mutant MutQ23 delta 3
ActiveCN108715840AImprove thermal stabilityImprove heat resistanceHydrolasesFermentationAfter treatmentHeat resistance
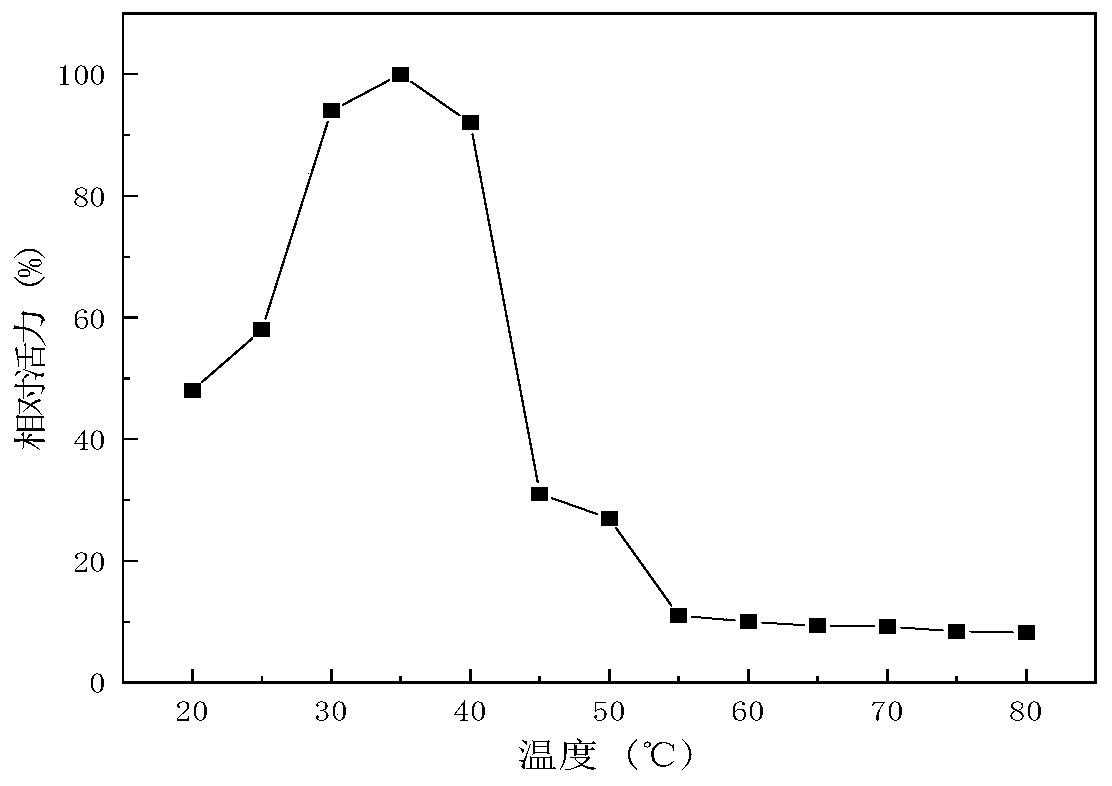
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering and protein modification, in particular to a heat-resistant low temperature exo-inulinase mutant MutQ23 delta 3. Amino acid sequence ofthe mutant MutQ23 delta 3 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the optimum pH of the MutQ23 delta 3 is 6.0, and the optimum temperature is 45 DEG C; the mutant MutQ23 delta 3 respectively contains 14%, 24%, 46% and 75% of enzyme activity at the temperature of 0 DEG C, 10 DEG C, 20 DEG C and 30 DEG C; the MutQ23 delta 3 still maintains 100% of enzyme activity after treatment for 60 minutes at the temperature of 50 DEG C; the enzyme can hydrolyze inulin to produce fructose. The heat-resistant low temperature exo-inulinase mutant MutQ23 delta 3 has the advantages of being applicable to industries such asfood, brewing and bioenergy.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
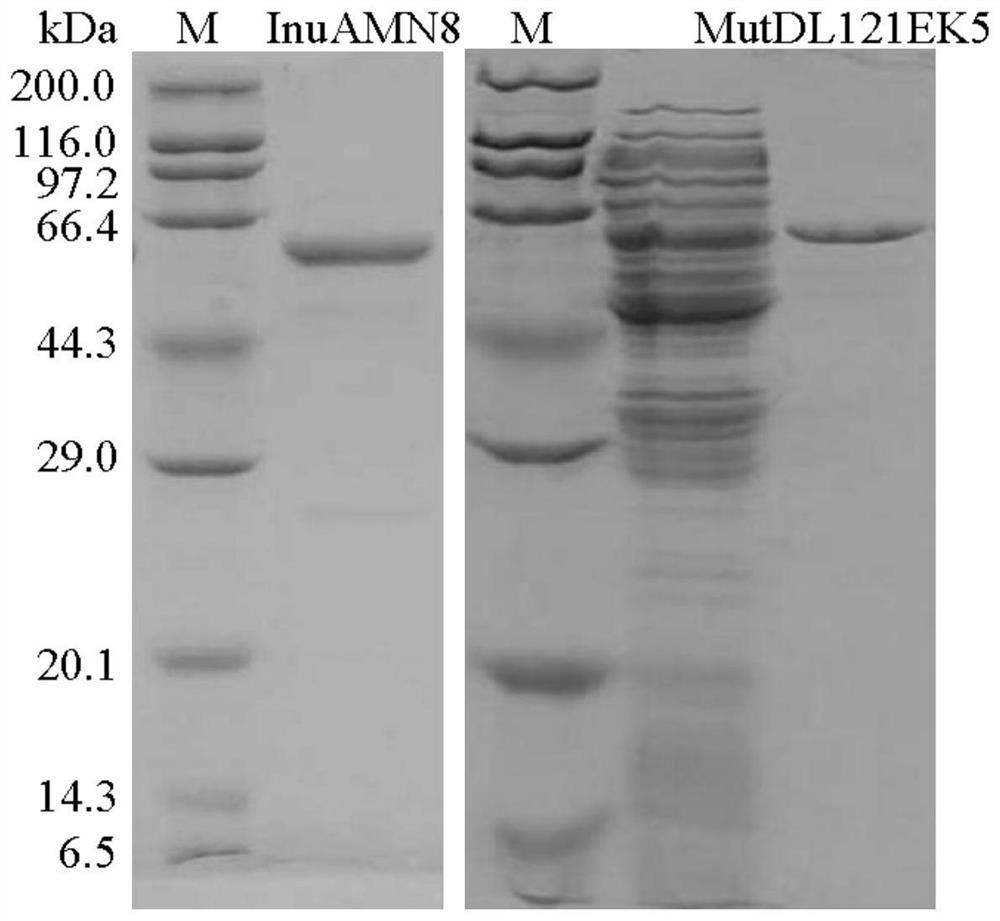
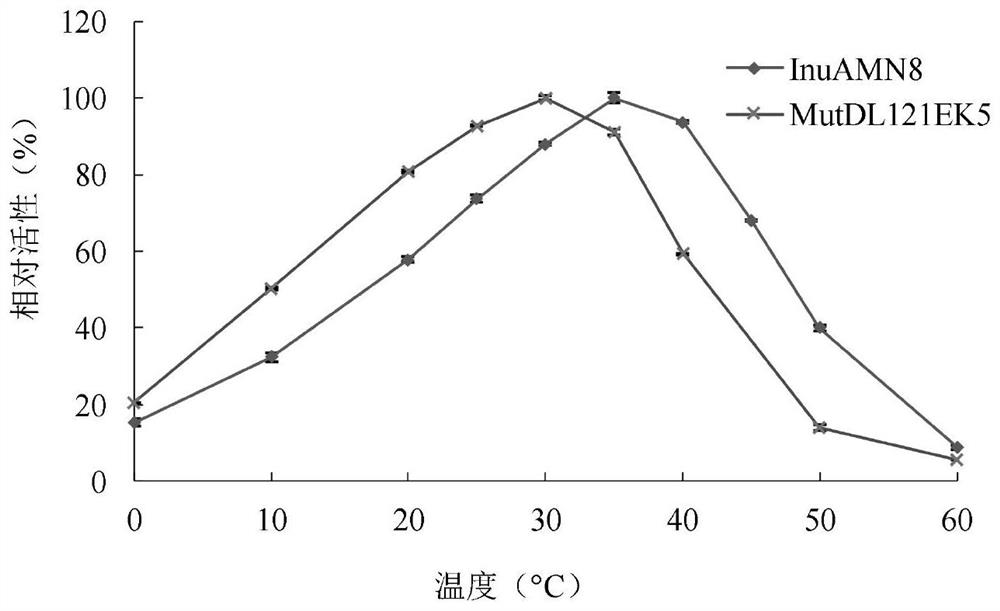
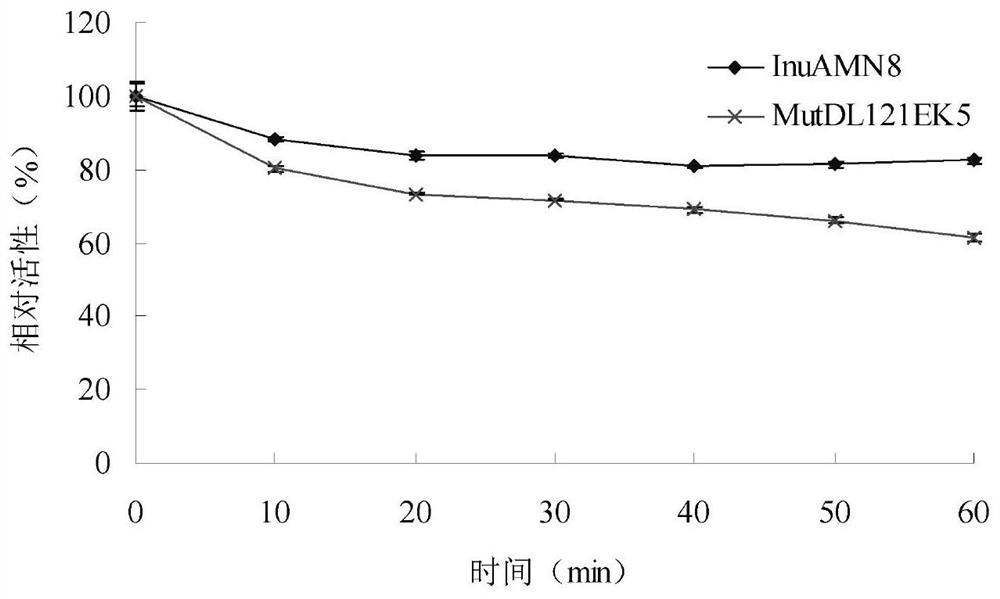
Low-temperature exoinulinase mutant MutDL121EK5 with improved low-temperature adaptability and application thereof
ActiveCN112852782AChange thermal stabilityHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThermal denaturation
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering and protein modification, and discloses a low-temperature exoinulinase mutant MutDL121EK5 with improved low-temperature adaptability and application thereof, the amino acid sequence of the mutant MutDL121EK5 is obtained by replacing DAAPL from the 121st site to the 125th site of wild exoinulinase InuAMN8 with five amino acids EEDRK, and the sequence of the MutDL121EK5 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. Compared with a wild enzyme InuAMN8, the mutant enzyme MutDL121EK5 has the advantages that the low-temperature activity is improved, the mutant enzyme MutDL121EK5 is more easily subjected to thermal denaturation, the improvement of the low-temperature activity is beneficial to reducing the dosage of the enzyme or shortening the reaction time during low-temperature reaction, and the easy thermal denaturation is beneficial to controlling the reaction process of the enzyme through thermal treatment. The low-temperature exoinulinase mutant MutDL121EK5 disclosed by the invention can be applied to the industries of food, wine brewing, washing and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Process for preparing inslin and oligofructose using xuelianguo fruits as raw material
The invention relates to a producing process of the inulin and the oligo fructose produced from the fruit of the snow lotus. The process is mainly that the fresh fruit of the snow lotus is cleaned, chipped, expressed juice, filtrated, dried, crushed characterized in that the slicing is dipped into the color fixative 1-3 hour and the inulin is purified by adding the 10% confected inulinase and the water and is fermented 48-72 hour in the aerobic atmosphere of the temperature of 20-30. The snow lotus inulin and the glucosidase fructose can be used for the health products, the food additive.The using of it as the health products has many merits of the low consumption of taking medicine, the good curative effect, taking conveniently, transporting and storing conveniently. So it can be added into the food such as the drink, the cake and the candy to form the functional food. The invention has some merits of the advance arts and crafts, the high quality.
Owner:昆明瑞鹏生态农业科技有限公司
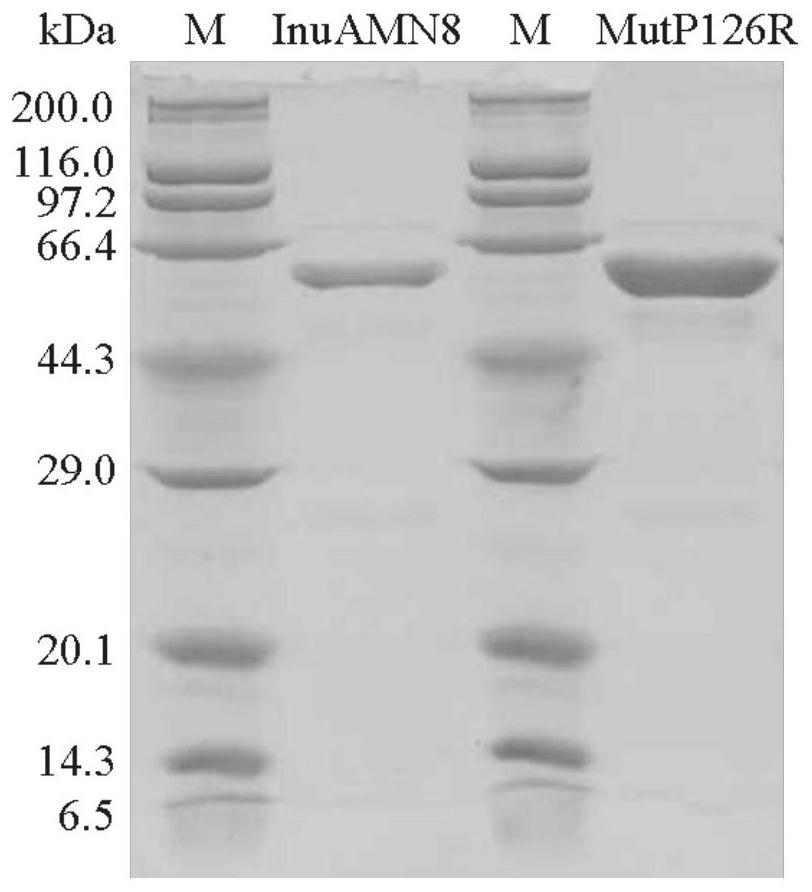
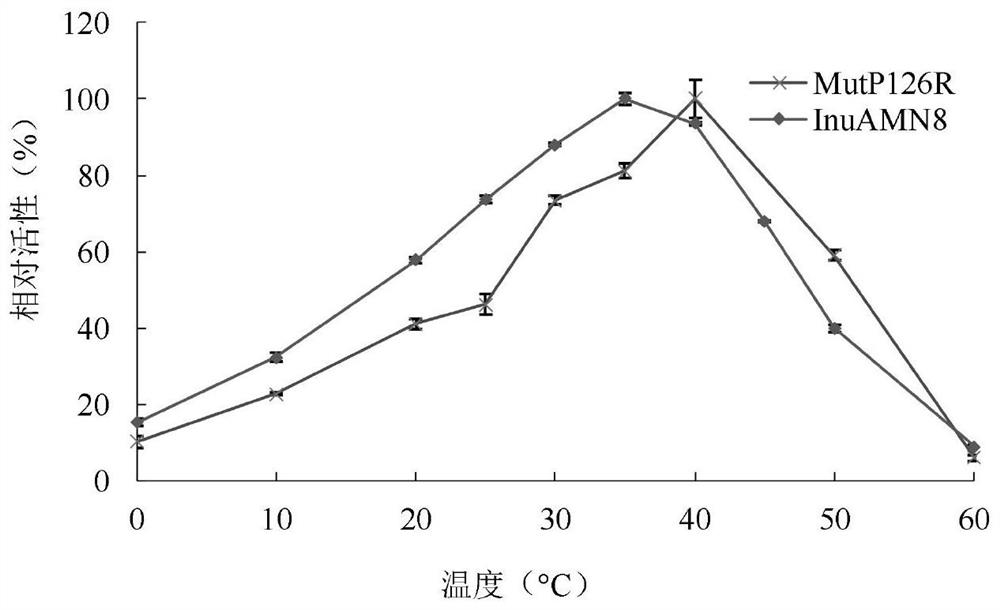
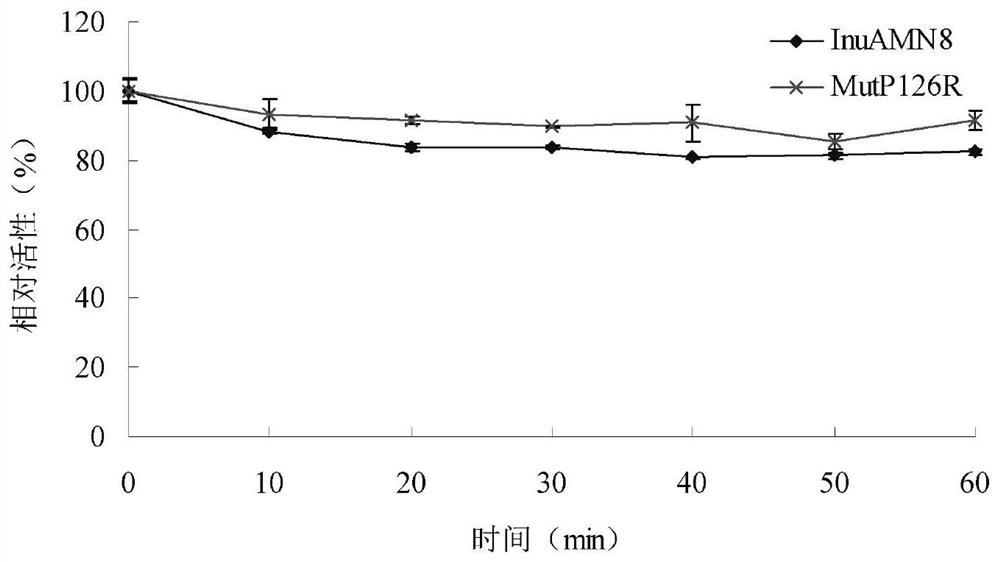
Low-temperature excision inulase mutant MutP126R stable at medium temperature
ActiveCN112725309AEasy to produceEasy to storeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutant enzymeAmino acid
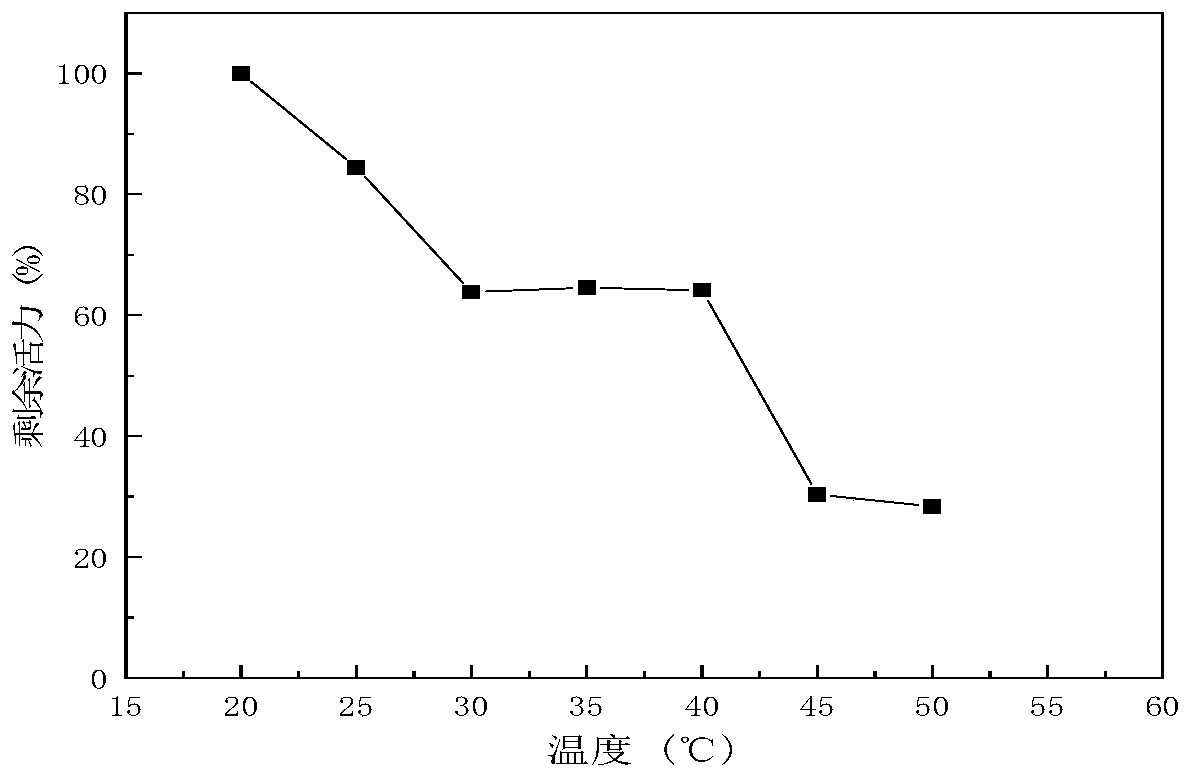
The invention discloses a low-temperature exoinulinase mutant MutP126R stable at medium temperature, the mutant MutP126R has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the thermal activity and thermal stability of the mutant MutP126R are changed, the optimal temperature is increased, the thermal stability is better, and the mutant MutP126R is beneficial to production, storage, transportation and the like of enzymes. The optimum temperature of the purified wild enzyme InuAMN8 is 35 DEG C, and the optimum temperature of the mutant enzyme MutP126R is 40 DEG C; after the wild enzyme InuAMN8 is treated at 55 DEG C for 10-60 minutes, the enzyme activity of the wild enzyme InuAMN8 is reduced from 70% to 17%, and the enzyme activity of the mutant enzyme MutP126R is reduced from 70% to 26%. The low-temperature excision inulase mutant MutP126R disclosed by the invention can be applied to the industries of food, wine brewing, biological energy and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for improving expression level of recombinant protein in kluyveromyces
InactiveCN101386868AHigh expressionReduce manufacturing costFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyProtein target
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to a technical proposal used to improve the expression level of recombinant protein. In the method, a promoter, alpha-signal peptide, target protein of an inulase gene are orderly connected with a terminal subcode sequence of the inulase gene first; then the sequence is inserted into a Kluyveromyces lactis expression vector; finally the Kluyveromyces lactis is transformed and fermented, and a fermented supernatant is taken and separated. The method can accelerate the remarkable growth of the yield of the recombinant protein expressed in the Kluyveromyces lactis. The technical proposal can be used to improve the expression amount of various proteins and provide a new method for reducing production cost and enlarging production scale.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Secretory expression method for exoinulinase from Kluyveromyces marxianus
InactiveCN101469325AFor precise cuttingHigh purityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyProtein target
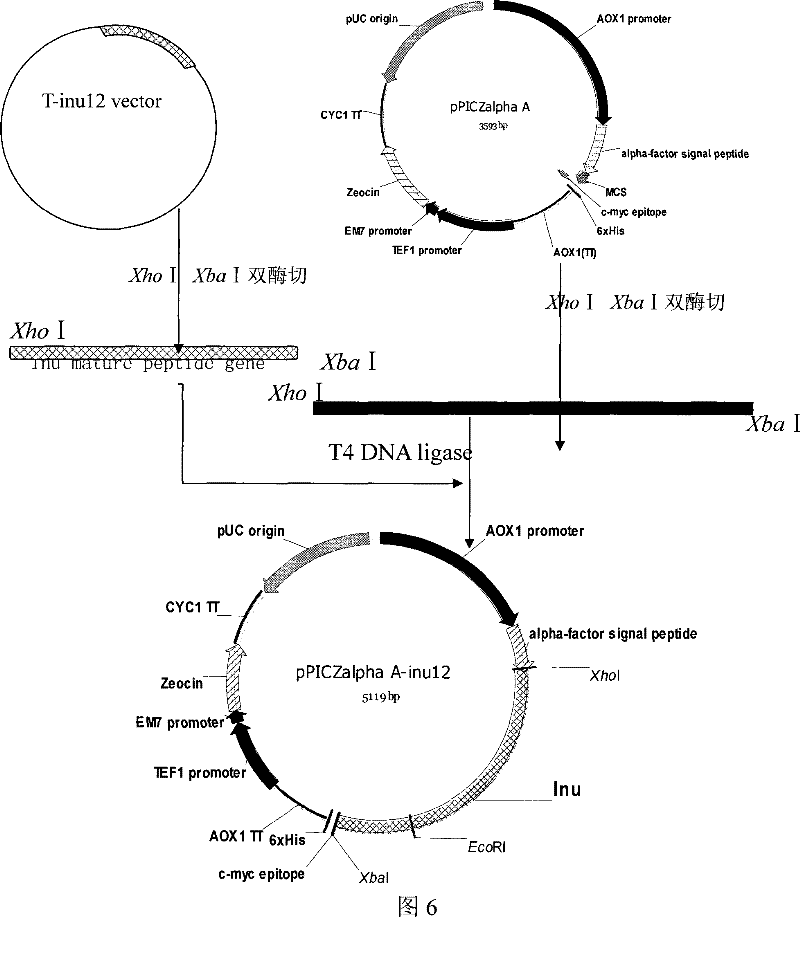
The invention relates to a eukaryon expression method for exoinulinase, which mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, connecting a nucleotide sequence (as shown in SEQ ID No: 1) of the exoinulinase of Kluyveromyces marxianus with pichia expression plasmids pPICZ alpha A through a restricted enzyme site, and obtaining a recombinant expression vector; and secondly, introducing the recombinant expression vector into a thermococcus host strain X-33 or SMD1168, and expressing target proteins (the Kluyveromyces marxianus exoinulinase) through induction fermentation. The eukaryon expression method for the exoinulinase lays a foundation for developing the exoinulinase with industrial application value.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for fermenting carbohydrate-rich crops
A method for fermenting carbohydrate-rich crops is provided. Sugar beet, sugar cane, sweet sorghum, tropical maize hybrids and fruits are rich in simple sugars; potato, sweet potato, cassava and yam are rich in starch; and Jerusalem artichoke is rich in inulin. This method uses vacuum infusion to infuse yeast into the intercellular space (apoplast) of the parenchyma tissue. The simple sugars diffuse into the apoplast, come into contact with the yeast and produce ethanol. Ethanol can be extracted from the crop by vacuum stripping or crushing or can be left inside the starchy crop to preserve it. In some variants, pectinase enzymes degrade the parenchyma cell walls to speed up diffusion of simple sugars to the yeast, speed up diffusion of amylase to starch granules or speed up diffusion of inulinase to insoluble inulin.
Owner:HAMRICK EDWARD BRIAN
Bacterial strain producing L-lactic acid and method for producing L-lactic acid by using the same through synchronous diastatic fermentation
InactiveCN101418272AFar-reaching societyFar-reaching economyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGramBatch fermentation
The invention relates to a strain for producing L-lactic acid and a method for producing the L-lactic acid through saccharifying and fermenting Jerusalem artichoke simultaneously with the strain, which belongs to the technical fields of biological energy source and conversion technology, enzymes and metabolic regulation and control technology, as well as related fermentation engineering. The method uses aspergillus niger and lactobacillus to convert the Jerusalem artichoke into the L-lactic acid through a novel process of synchronous saccharification and fermentation. An aspergillus niger strain SL-09 with high inulinase vitality and a lactobacillus G-02 for producing the L-lactic acid with high optical purity are obtained from the natural world; when the two strains are mixed for culture, the inulinase vitality of the aspergillus niger is improved significantly due to the obvious synergy; in a lactic acid fermentation process, the Jerusalem artichoke powder is used as a substrate; and with a feed-batch fermentation process and after 36 hours of fermentation, the concentration of the L-lactic acid is 120.5 grams per liter and the conversion rate is improved to 94.5 percent. The invention provides a basis for the industrialization of the transformation of the Jerusalem artichoke to the lactic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Double-promoter multi-copy recombinant pichia pastoris strain for highly producing endo-inulinase
InactiveCN103981112AImprove conversion efficiencyGood business valueFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisMicroorganism
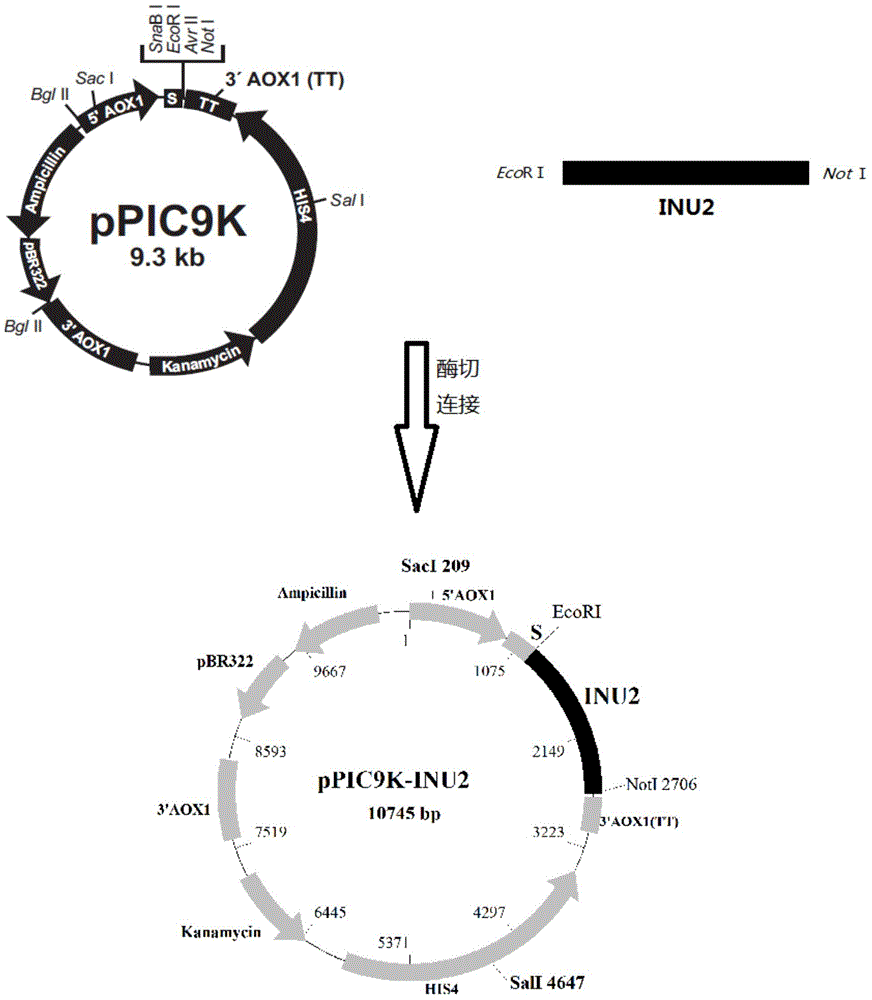
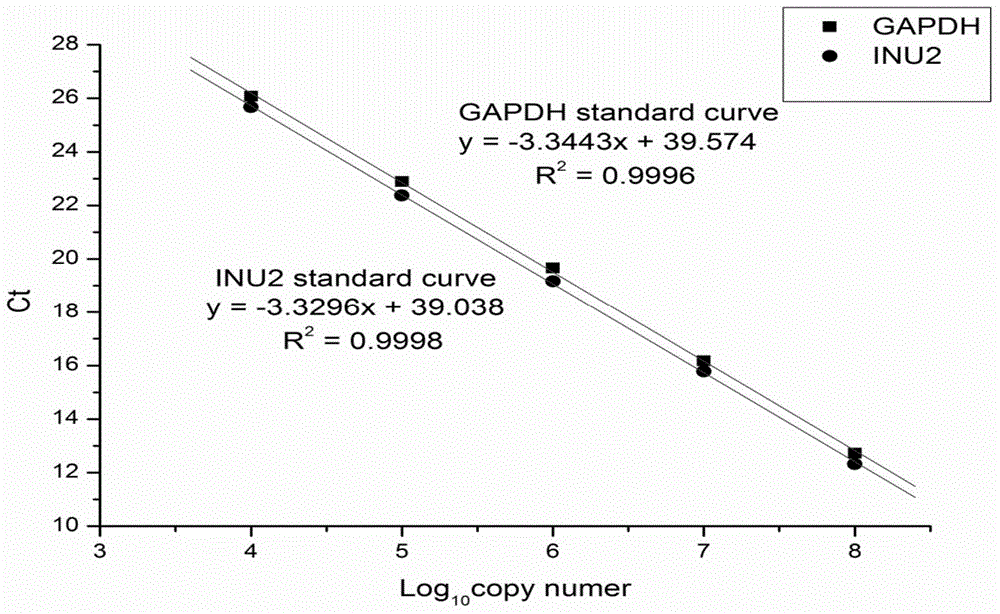
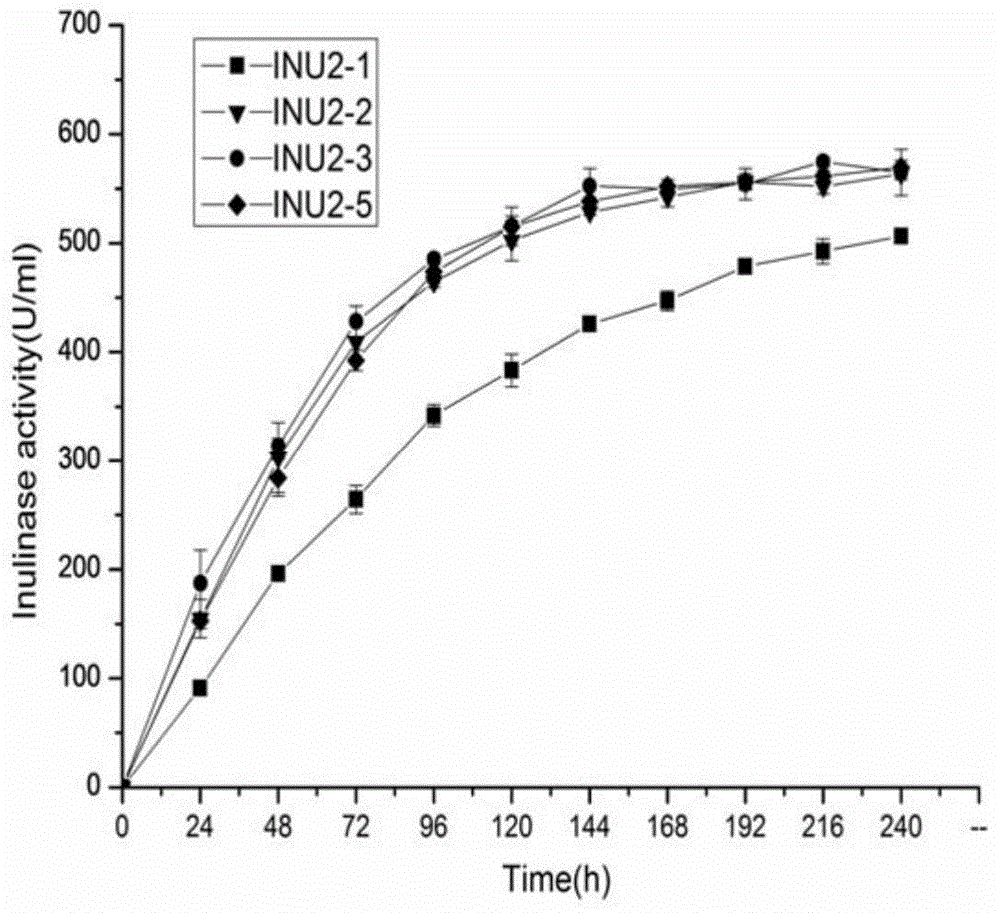
The invention discloses a double-promoter multi-copy recombinant pichia pastoris engineering strain for highly producing endo-inulinase INU2. The strain is named pichia pastoris GS115-A3-G2, and is preserved in the general microbiology center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on April 16th, 2014, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO:9049. According to the strain disclosed by the invention, the endo-inulinase gene INU2 multi-copy is integrated into pichia pastoris GS115 genome by two plasmids pPIC9K and pGAPZaA, and the double-promoter multi-copy recombinant pichia pastoris engineering strain for efficiently expressing the endo-inulinase is obtained in a screening manner. The experiment proves that the inulinase enzyme activity can be up to 3006U / ml in 3L high-density fermentation, simply purified crude enzyme can be directly applied to hydrolysis of inulin, so as to generate fructo-oligose, the conversion efficiency is high, production of the fructo-oligose by using inulin enzymatic hydrolysis in industry is achieved, and the double-promoter multi-copy recombinant pichia pastoris engineering strain has great practical value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Levulose group fermentation raw material and uses thereof
InactiveCN101245353AWide variety of sourcesReduce manufacturing costBeer fermentationEnzymesInulinaseSpray drying
The invention relates to a fructosyl fermented raw material and the application, 1) an inulin-rich organ of an inulin plant is dried, smashed into powder by a smashing machine, screened by 50 to 200 meshes and produced into powder; 2) the powder is dissolved by water at 45 to 70 DEG C to be made into the solution with a weight concentration of 10 to 20 percent, an inulin powder enzymolysis reaction liquid is prepared according to the proportion of each liter solution added with 1000U to 100000U units of inulinase, the pH value is regulated to 4.2 to 6.5, the reaction is carried out in a reactor at 45 DEG C to 70 DEG C for 3 to 9 hours, a fructose inulin powder liquid is formed after the enzymolysis reaction, or the fructose inulin powder is prepared by further spray drying. The production cost is low, the sources of the raw material are wide, the technique is simple, the technical route is mature and the industrial implementation can be realized.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of endo-inulinase
InactiveCN105505899AEasy post-processingImprove conversion efficiencyNucleic acid vectorGlycosylasesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
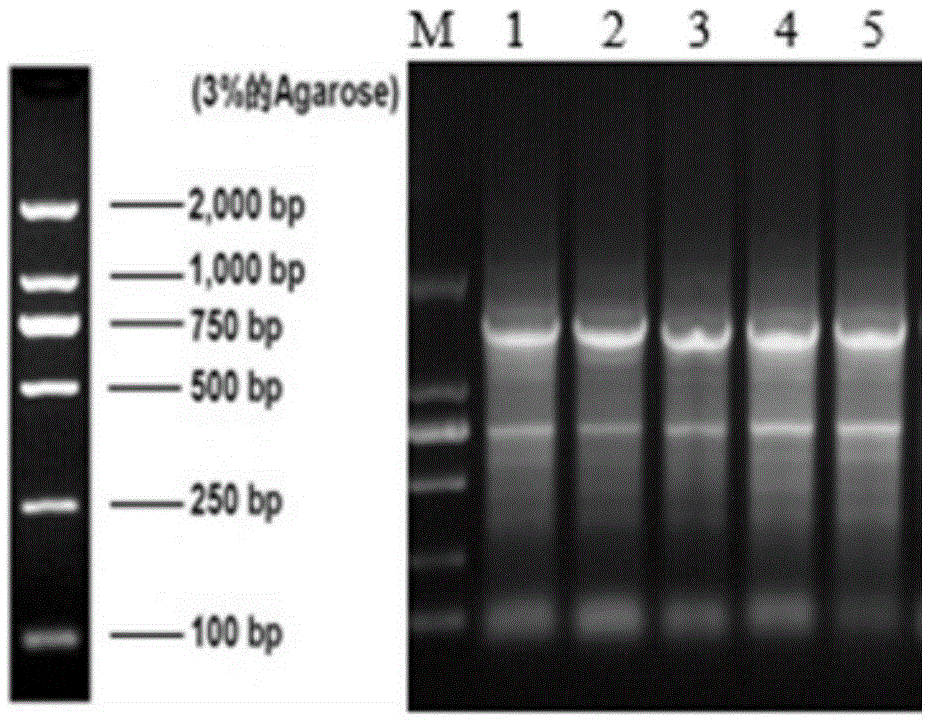
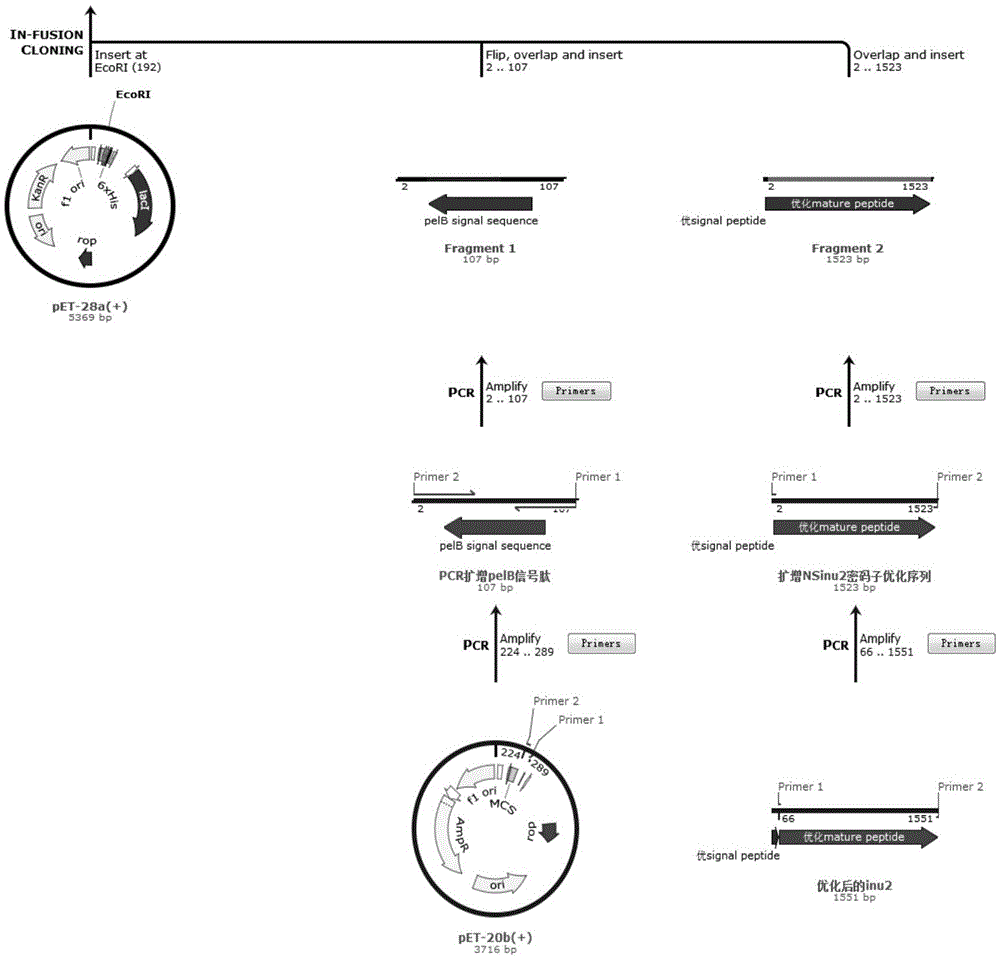
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of endo-inulinase. An endo-inu2 gene of Aspergillus ficuum ATCC 16882 serves as the source sequence, the gene sequence is optimized through the gene engineering technology, the optimized gene sequence of encoded endo-inulinase is cloned to a carrier pET-28a(+), and recombined Escherichia coli BL21pET28a-pelB-NSinu2 for efficiently secreting and expressing endo-inulinase is established. Recombined Escherichia coli serves as a fermenting strain, endo-inulinase is efficiently secreted and expressed, and finally prepared endo-inulinase is purified and successfully used for hydrolyzing inulin to prepare fructo-oligose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Yeast gene engineering bacterium and endoinulase preparation and its application method
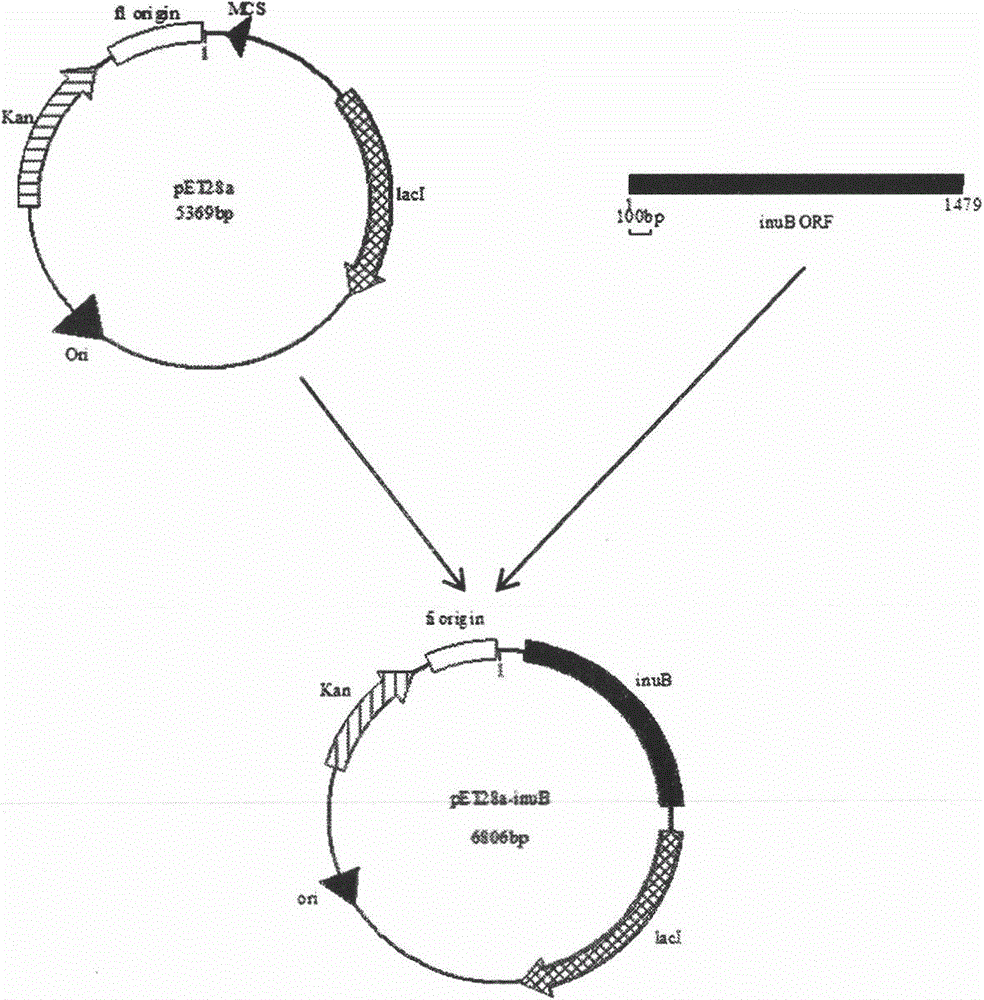
The present invention provides a yeast gene engineering bacterium Pichia pastoris GS115 / HY005 which is an endo inulase gene obtain by screening strain from Aspergillus by means of PCR method or DNA library hybridization method. It can be cloned and inserted into Pichia yeast integration expression vector, then the obtained expression vector containing endoinulase gene is introduced into Pichia yeast, then a yeast gene engineering bacterium capable of high-effectively expressing endoinulase can be screened. The enzyme activity of the endoinulase prepared with said yeast gene engineering bacterium can be up to above 300 u / ml, and the reaction time for hydrolyze inulin with it is short, and its conversion rate is high, so that it can high-effectively economically convert and prepare oligofructose.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Heat-resisting alkali-resisting and salt stable inulase exonuclease, and coding gene and application thereof
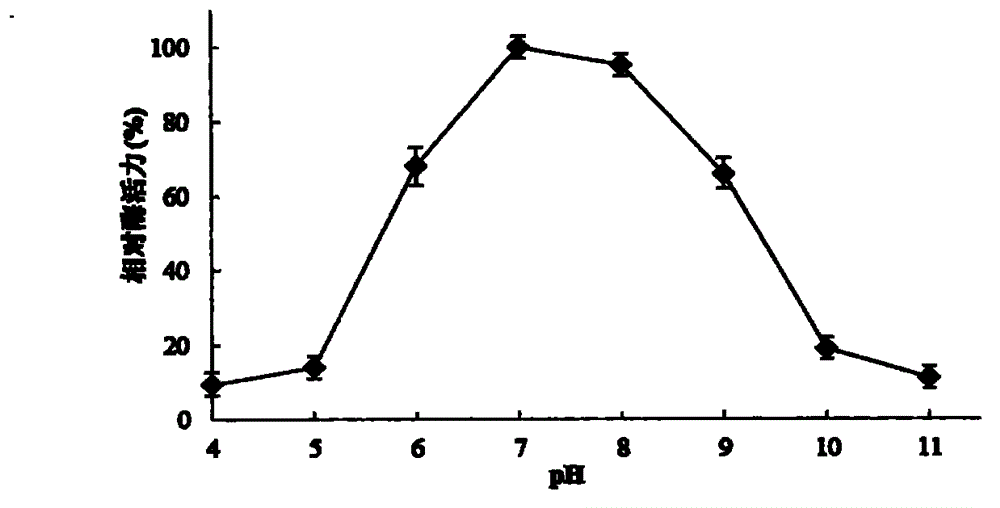
The invention discloses an amino acid sequence and a nucleotide sequence of a heat-resisting alkali-resisting and salt stable inulase exonuclease, and construction and application of an inulase exonuclease recombinant expression vector. Results of enzymatic property research show that the optimum reaction conditions of the inulase exonuclease are as below: pH 7.0, 50 DEG C and 10% NaCl. The enzyme can catalyze the hydrolysis of inulase, levan, sucrose, raffinose, kestose, nystose and Kestopentaose. In a catalysis process using inulase as a substrate, only generation of fructose is detected rather than oligosaccharide or other carbohydrates. The inulase exonuclease provided by the invention can be applied to the field of food industry and biological energy source as a novel biocatalyst for fructose production.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for continuously preparing fructo-oligosaccharide by using immobilized enzyme microreactor
The invention discloses a method for continuously preparing fructo-oligosaccharide by using an immobilized enzyme microreactor. The method comprises the steps of fixing endo-inulinase in the microreactor, injecting a substrate, namely an inulin aqueous solution into the microreactor, wherein the flow rate of the substrate is 0.1-1mL / min, and the reaction temperature is 55-65 DEG C, the retention time of circulation and continuous flow of reaction feed liquid in the microreactor is 2-6 hours, and degrading the inulin solution to the fructo-oligosaccharide. The method has the advantages that the microreactor is used for enzymatic hydrolysis of inulin to generate the fructo-oligosaccharide, the reaction efficiency is greatly improved, and the energy consumption is reduced; meanwhile, the content of nystose in the product can be remarkably increased by controlling operating conditions, and the effects of the fructo-oligosaccharide on prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases are improved. A micro-reaction chip of the microreactor can be replaced, the microreactor is simple in structure, as long as the number of the microreactor is increased, the production capacity can be expanded in an equal proportion manner, and therefore, the method has good industrialization prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Fructo-oligosaccharide producing method with fossilized endoinulinase in bacterial cellulose
InactiveCN104928330AImprove adsorption capacityIncrease contentOn/in organic carrierFermentationBuffer solutionOligosaccharide
The invention discloses a fructo-oligosaccharide producing method with fossilized endoinulinase in bacterial cellulose. The fructo-oligosaccharide producing method with the fossilized endoinulinase in bacterial cellulose is characterized in that the fructo-oligosaccharide producing method comprises the steps that 1 pretreatment is conducted on the surface of a bacterial cellulose film, the surface hole size of the bacterial cellulose film is enlarged, and modified bacterial cellulose film is acquired; 2 the modified bacterial cellulose film is added into the endoinulinase solution, and the endoinulinase is fixed to the surface of the bacterial cellulose film; 3 washing is conducted through 0.5 mol / L Tris-HCI buffer solution, and bacterial cellulose film which fossilizing the endoinulinase is obtained; 4 the bacterial cellulose film which fossilizing the endoinulinase is placed into inulin solution, the endoinulinase is used for resolving the inulin, and fructo-oligosaccharide solution is obtained; 5 purification is conducted on the obtained fructo-oligosaccharide solution, and fructo-oligosaccharide with the purity over 90% is obtained. According to the fructo-oligosaccharide producing method with fossilized endoinulinase in bacterial cellulose, the prepared fructo-oligosaccharide is high in purity and little in impurity, the content of the fructo-oligosaccharide is over 99%, and significant industrial application prospect is possessed.
Owner:WEIDE QINGHAI BIOTECH
Lactobacillus plantarum for generating acid inulase and application of lactobacillus plantarum for generating acid inulase
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum 3-2 for generating acid inulase and an application of the lactobacillus plantarum 3-2 for generating acid inulase. The srtain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 25 November 2019, wherein the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2019972. The Lactobacillus plantarum 3-2 is screened from Guangxi Zhuang nationality traditional foods namely cold pressing rice powder, and in a fermentation medium that inulin is used as a carbon source and a beef extract is used as a nitrogen source, the lactobacillus plantarum 3-2 can growwell, and is high in acid resistance. After the acid inulase generated by the strain is placed under the condition that the pH is 4.5 for 1h, the survival rate is 96%, and the lactobacillus plantarum3-2 has the capacity for degrading inulin and levan substances and preparing high fructose syrup. For the first time, the lactobacillus plantarum for generating the acid inulase is reported, and a new strain and inulase thereof are provided for industrial degradation of the inulin and levan substances and preparation of the high fructose syrup.
Owner:南宁中诺生物工程有限责任公司
Leuconostoc citreum for producing acid inulase and application
InactiveCN110804575AImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh fructose
The invention discloses leuconostoc citreum for producing acid inulase and application. The strain is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on November 25, 2019 and has thecollection number of CCTCC NO:M 2019971. The leuconostoc citreum 1-1 is a lactobacillus strain 1-1 selected from traditional food raw-pressed rice noodles in a Guangxi Zhuang nationality region and having inulase producing capacity, inulin serving as a carbon source, beef extract serving as a nitrogen source and the like form a fermentation medium for fermentation production of the acid inulase,the strain grows well on the fermentation medium and has high acid resistance, the acid inulase produced by the strain has the survival rate of 96% after 1 h at the pH of 4.0, and has capacity of degrading inulin and fructan substances and preparing high fructose syrup through detection after fermentation.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method of producing exoinulinase with utilization of solid state fermentation of streptomyces grisepoplanus S501
ActiveCN104611311AHigh activityOvercome the disadvantage of high costMicroorganism based processesGlycosylasesFreeze-dryingWheat Brans
The invention provides a method of producing exoinulinase with utilization of solid state fermentation of streptomyces grisepoplanus S501 and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a bacterial suspension by freeze-dried powder of a strain S501 and aseptic water on a selective medium, culturing for 3-5d at the temperature of 28 DEG C, scraping spores, putting the spores into the aseptic water, diluting until the concentration of a spore suspension is 106cfu / mL, inoculating to a solid state culture medium, and carrying out static culture for 3-6d at the temperature of 28 DEG C; and after fermentation, adding deionized water, carrying out oscillating extraction for 1h, filtering, carrying out centrifugation on a filtrate for 20 minutes at the temperature of 4 DEG C and the rotational speed of 8000rpm / min to obtain a supernatant containing the exoinulinase, and treating the supernatant by virtue of the conventional freeze-drying method to prepare an inulinase preparation. According to the method provided by the invention, with wheat bran as a solid fermentation matrix and garlic husk powder which is cheap and easily acquired as a carbon source, the strain S501 is induced to produce the exoinulinase, the enzyme activity of the exoinulinase reaches up to 209.63 + / - 0.96U / g, and the defects of high cost, time and labor consumption in a liquid state fermentation method and non suitability in industrial production in the prior art with inulin as a carbon source are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
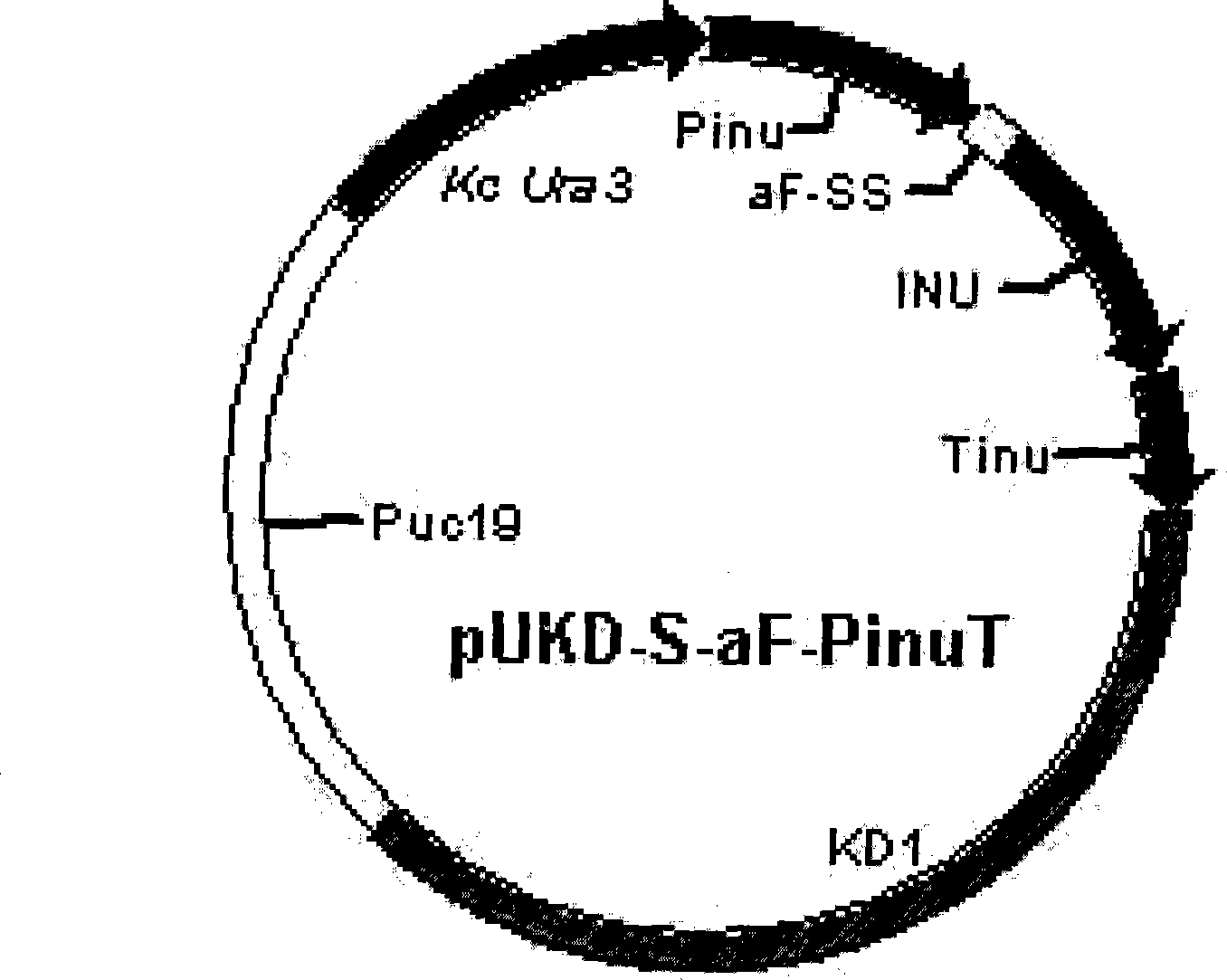
Novel expression enzyme yeast gene engineering system
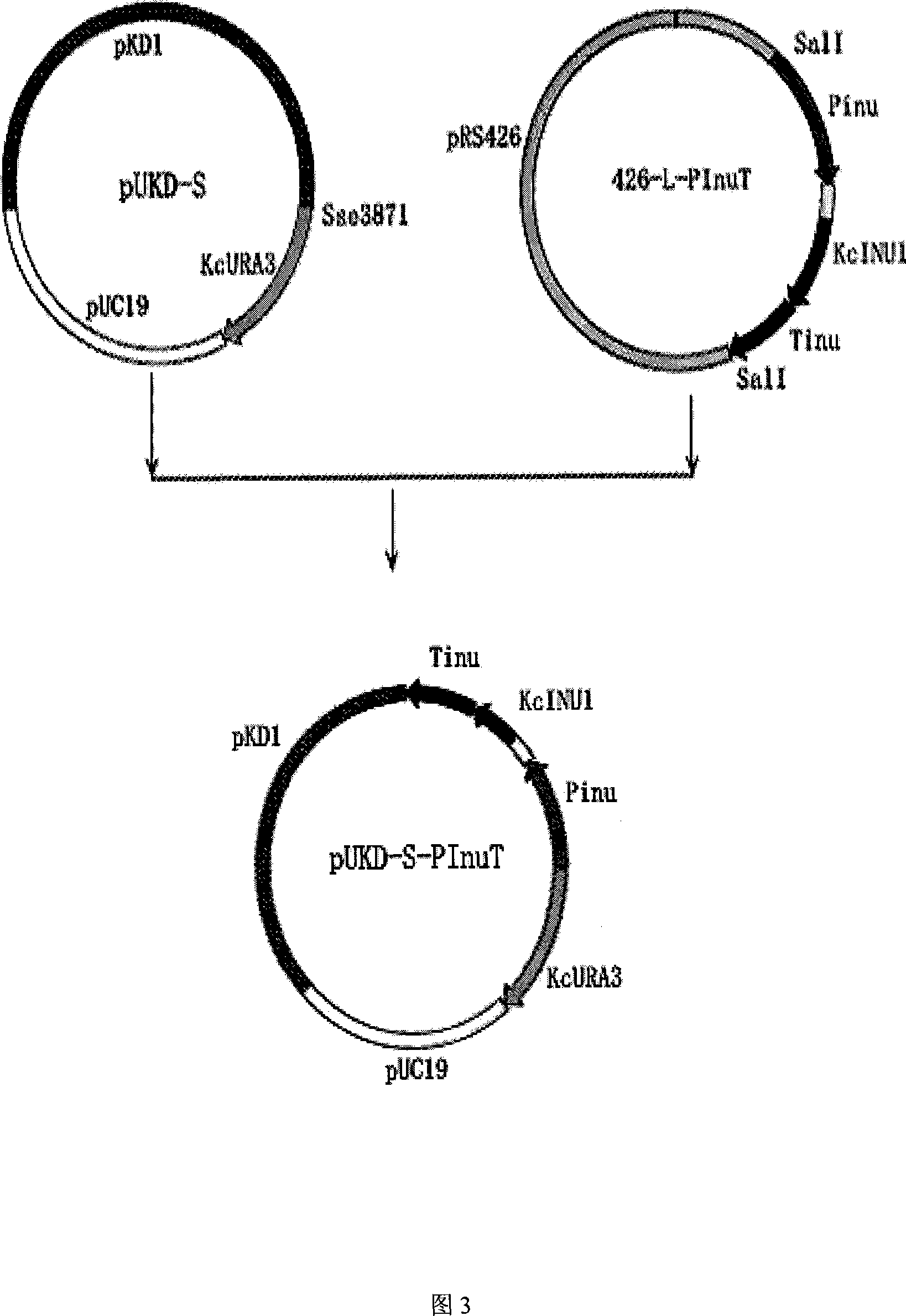
The invention pertains to the biological gene engineering technical field, in particular to a yeast gene engineering system of expressing enzyme which comprises the construction of an expression box which consists of Bengal grain kluyveromyces promoter, terminator and inulase gene with signal peptide, the construction of high-stable inulase gene expression plasmid by inserting the expression box into a carrier pUKD-S, the construction of gene engineering bacteria of expressing inulase with high efficiency by importing Bengal grain kluyveromyces host Y179ura3- and the production of inulase by using the constructed Bengal grain kluyveromyces gene engineering bacteria. The invention could also be used for expressing and producing other endogenetic, exogenous, natural and recombinant enzymes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Secretory expression method for exoinulinase from Kluyveromyces marxianus
InactiveCN101469325BShorten the fermentation cycleFor precise cuttingHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPichia henricii
The invention relates to a eukaryon expression method for exoinulinase, which mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, connecting a nucleotide sequence (as shown in SEQ ID No: 1) of the exoinulinase of Kluyveromyces marxianus with pichia expression plasmids pPICZ alpha A through a restricted enzyme site, and obtaining a recombinant expression vector; and secondly, introducing the recombinant expression vector into a thermococcus host strain X-33 or SMD1168, and expressing target proteins (the Kluyveromyces marxianus exoinulinase) through induction fermentation. The eukaryon expression method for the exoinulinase lays a foundation for developing the exoinulinase with industrial application value.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
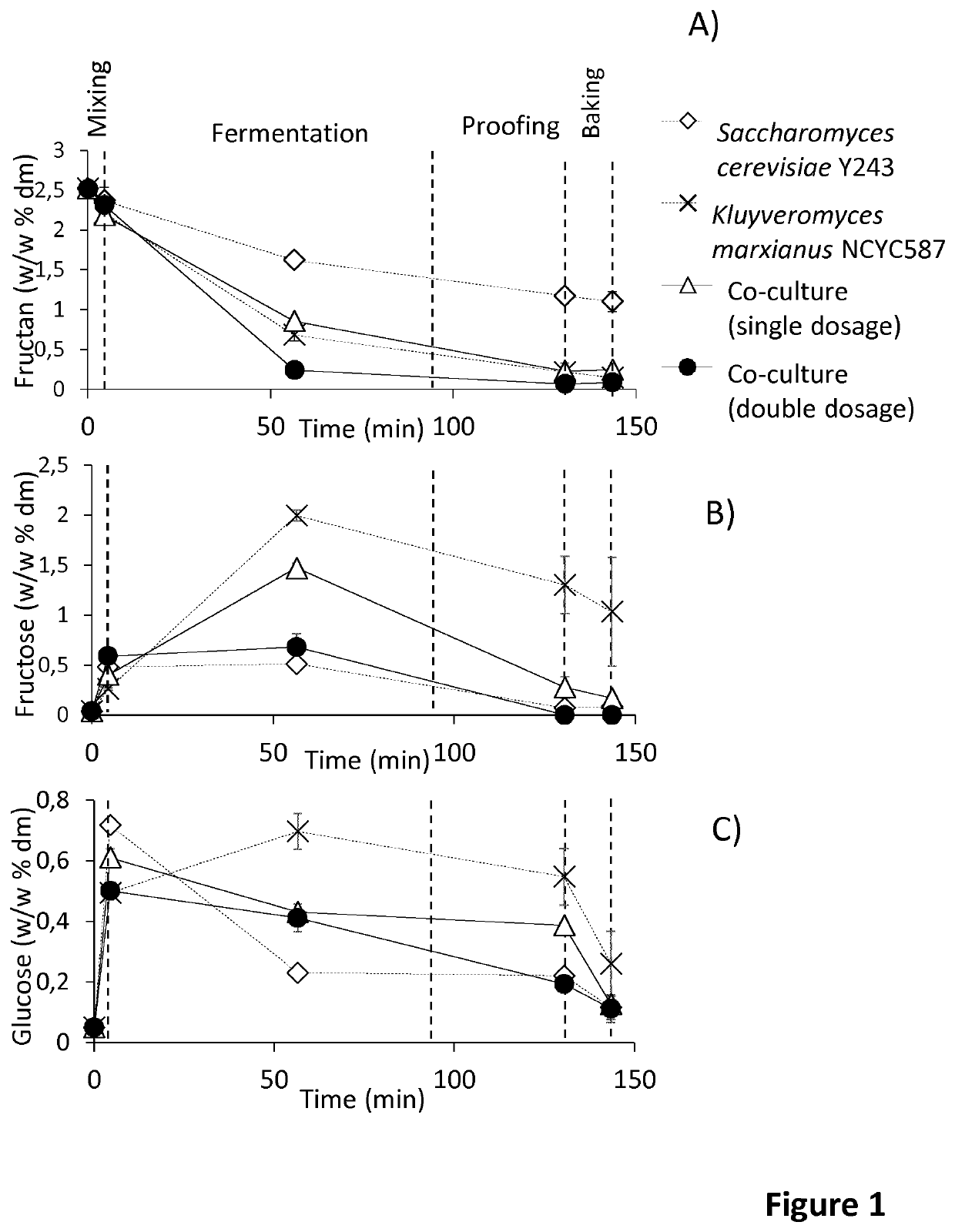
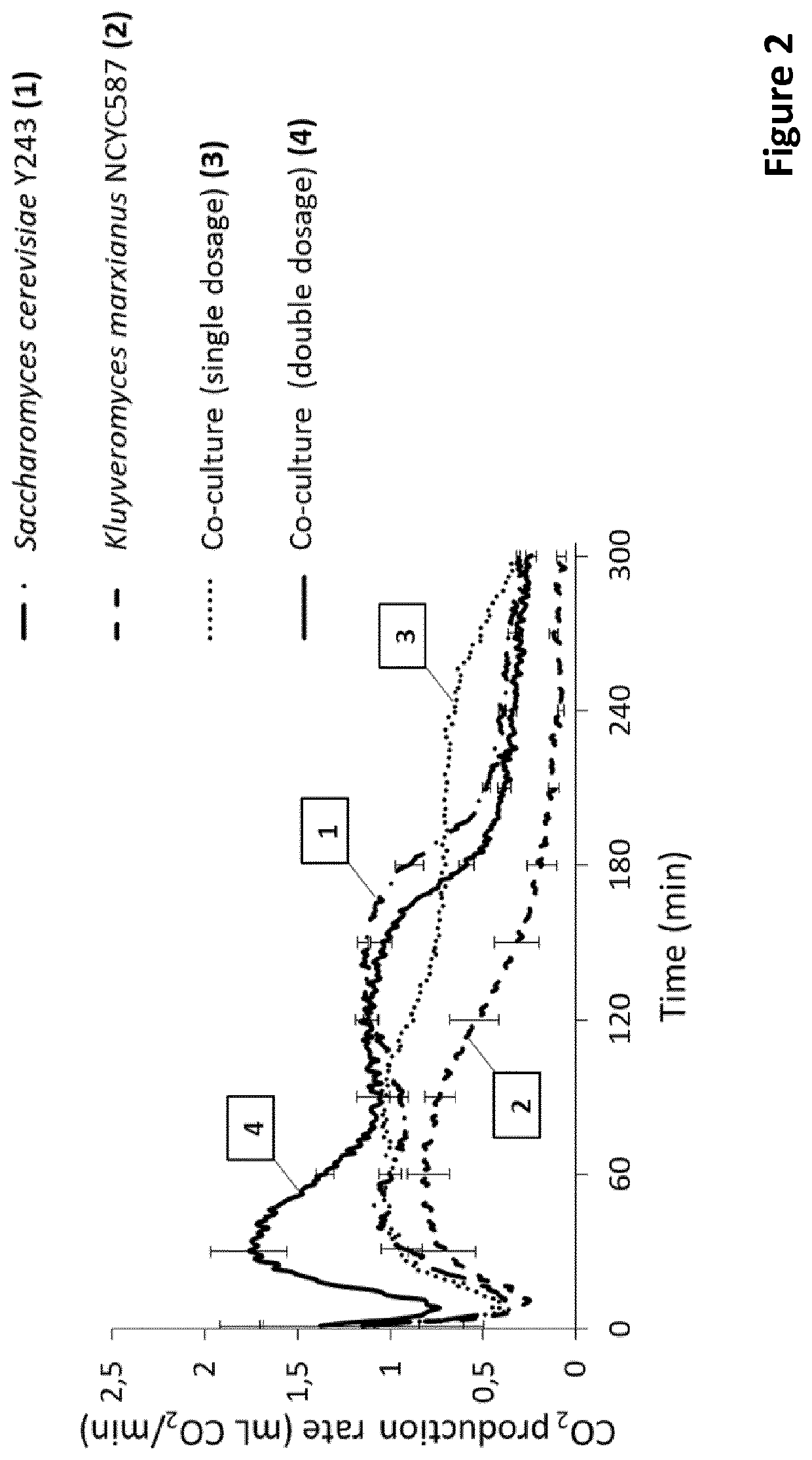
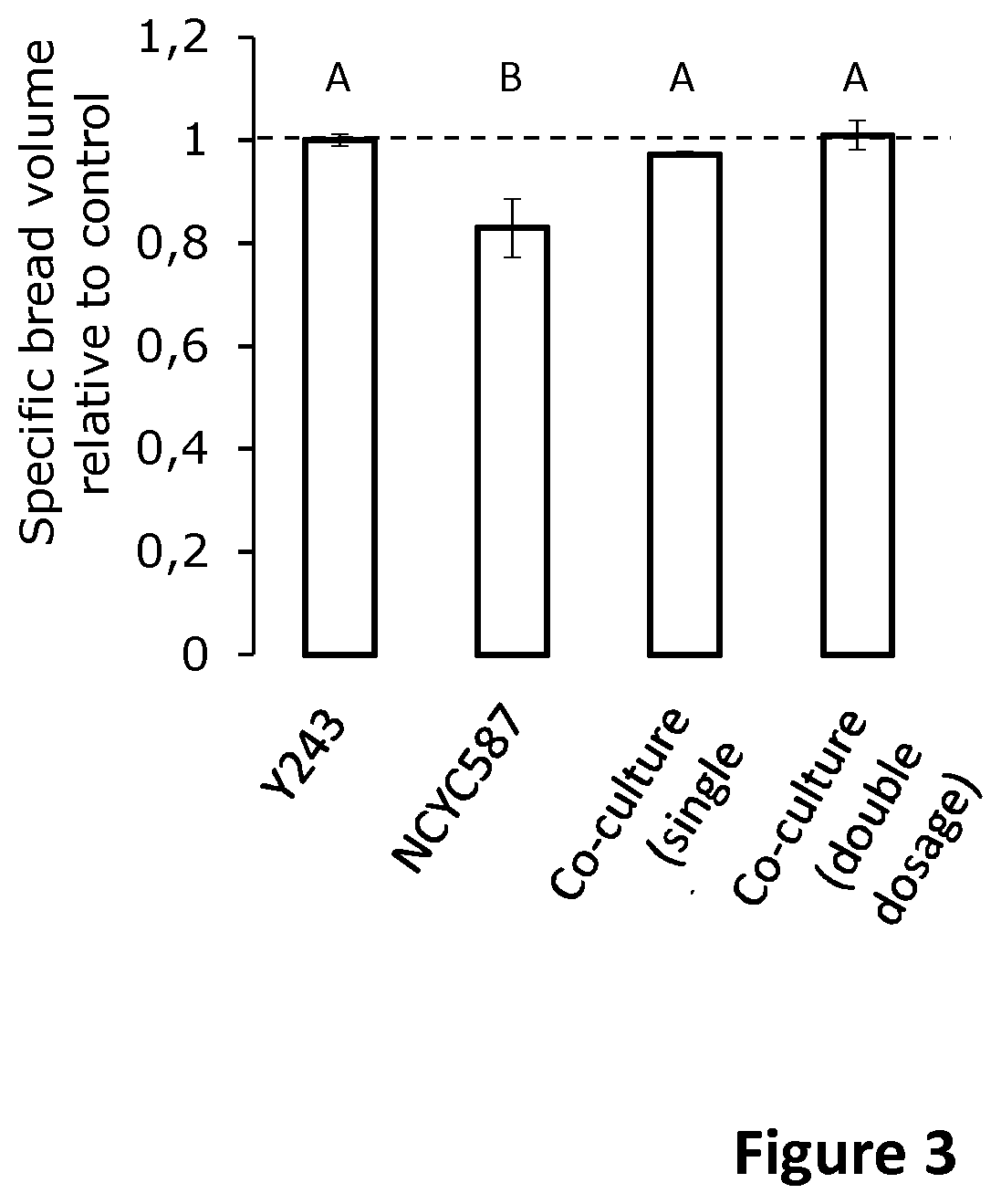
Wholemeal bread with reduced fodmap content
PendingUS20200205425A1Lower Level RequirementsReduction of FODMAP levelDough/pre-mixesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyFructan
The invention relates to the use of inulinase for reducing FODMAP (Fermentable oligo-, di-, monosaccharides and polyols) content in wholemeal bread or whole-meal dough. The invention further relates to wholemeal yeast fermented bread with a FODMAP content of maximum 0.2 gram fructans per 50 g of bread on dry matter base. The invention relates to methods of preparing a wholemeal yeast fermented bread with reduced FODMAP content, comprising the steps of mixing wholemeal and inulinase into a dough, allowing the dough to ferment and baking the dough. The invention further relates to methods of preparing a wholemeal dough with reduced FODMAP content in a wholemeal dough, comprising the steps of mixing wholemeal and inulinase into a dough, allowing the dough to ferment. Yeasts such as Kluyveromyces marxianus can be used as source of inulinase.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Method for producing fructooligosaccharides by fermenting inulase mutants
The invention discloses a method for producing fructooligosaccharides by fermenting inulase mutants. An enzymolysis technology for producing the high-quality fructooligosaccharides includes the optimal adding quantity of jerusalem artichoke, the optimal pH, the optimal concentration of a buffer solution, the optimal adding quantity of enzymes, the optimal temperature, the optimal stirring speed and the optimal stirring time. The formed enzymolysis technology can achieve the efficient production process in which the fructooligosaccharides account for more than 95.78% of the total sugar content. Inulase adopted in the technology is the novel inulase mutants and has high enzyme activity, the enzyme activity of fermentation liquor in a 30-m<3> system can be 60,000 U / ml, the production efficiency of the inulase can be remarkably improved, and production cost can be reduced. The formed enzymolysis technology for the fructooligosaccharides is a new technology; when the fructooligosaccharides are prepared with the technology, operation difficulty can be greatly lowered, and economic cost can be saved.
Owner:福建福大百特生物科技有限公司
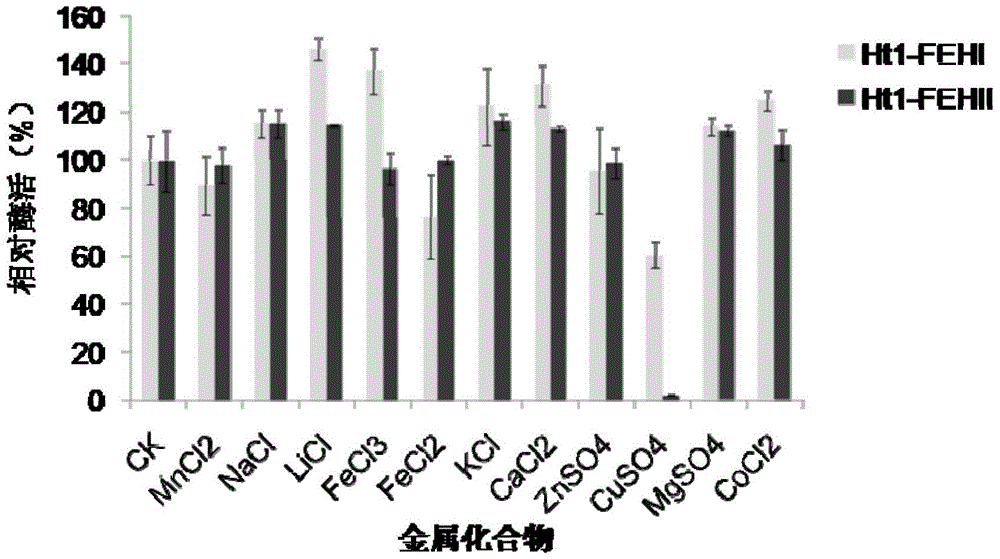
Recombinant vector containing Jerusalem artichoke fructan 1-exohydrolase gene and application thereof in producing alcohol by fermentation
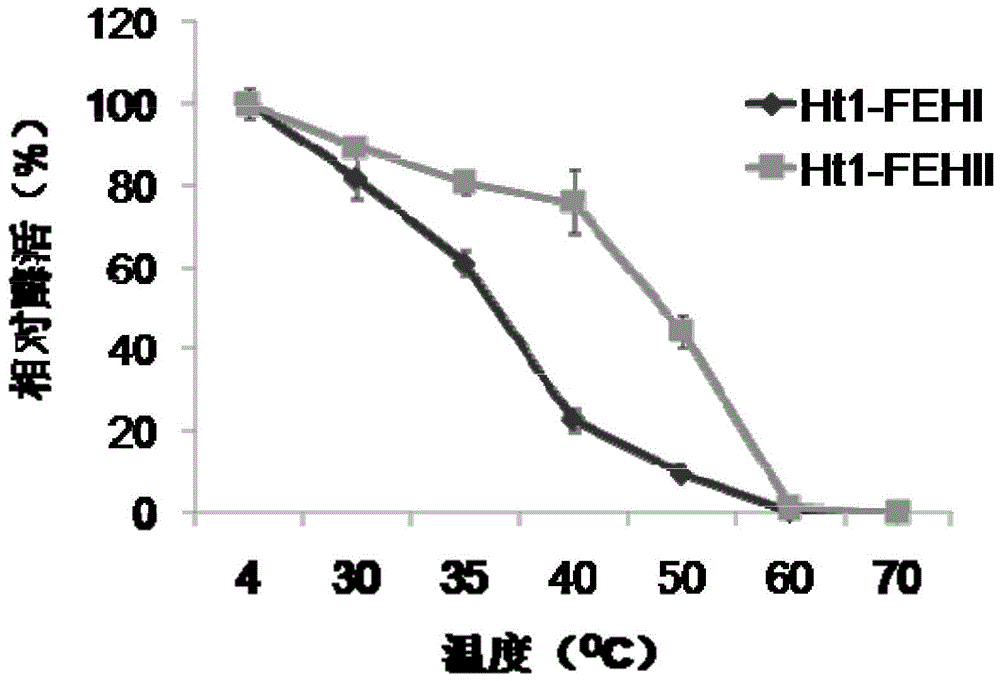
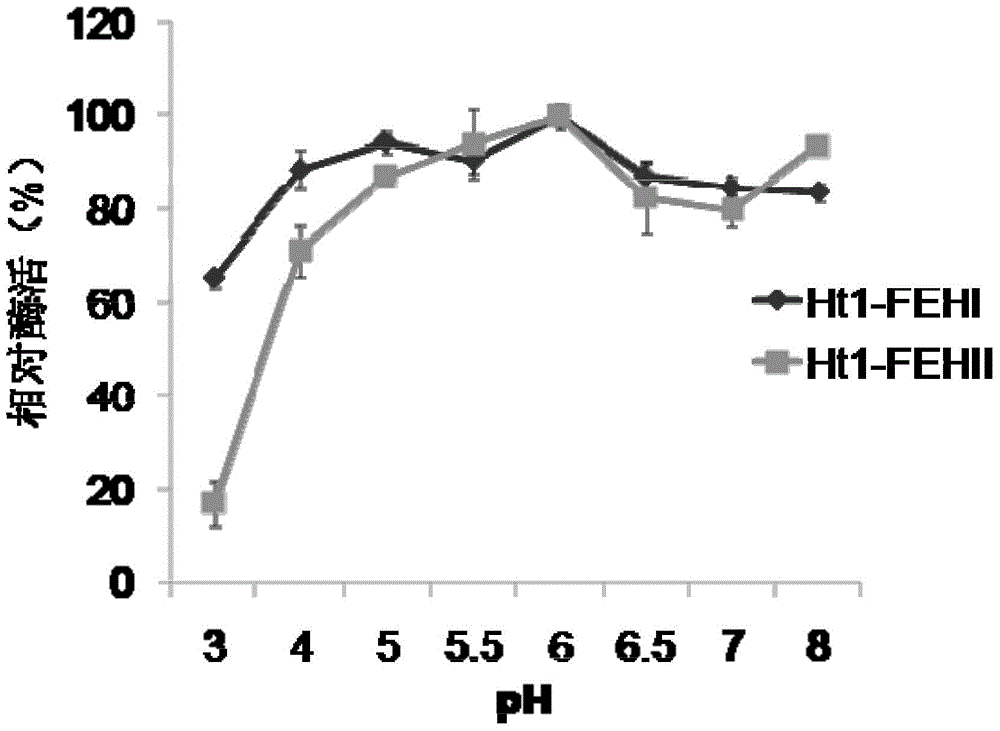
The invention discloses a recombinant vector containing Jerusalem artichoke fructan 1-exohydrolase gene and application thereof in producing alcohol by fermentation. The recombinant plasmid is prepared by the following steps: inserting a Saccharomyces cerevisiae 3-phosphoglyceric kinase gene PGK1 promoter between EcoRV and SpeI enzyme digestion sites of an expression vector pUG6, inserting a CYC1-terminator-fused Jerusalem artichoke fructan 1-exohydrolase gene Ht 1-FEHs between SpeI and HpaI enzyme digestion sites of the expression vector pUG6, and inserting an 18SrDNA sequence segment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome between XbaI and BstEII enzyme digestion sites of the expression vector pUG6. The invention also discloses application of the recombinant plasmid in producing alcohol by fermentation. The Jerusalem artichoke inulase genes Ht-FEHI and Ht-FEHII can promote fermentation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce alcohol, thereby providing a new method for enhancing the alcohol yield of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Protein stabilization by domain insertion into a thermophilic protein
ActiveUS8592192B2Improve dynamic stabilityCompromise in its activityEnzyme stabilisationImmunoglobulinsProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
A strategy to improve protein stability by domain insertion. TEM 1 beta-lactamase (BLA) and exo-inulinase, as model target enzymes, are inserted into a hyperthermophilic maltose binding protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMBP). Unlike conventional protein stabilization methods that employ mutations and recombinations, the inventive approach does not require any modification on a target protein except for its connection with a hyperthermophilic protein scaffold. For that reason, target protein substrate specificity was largely maintained, which is often modified through conventional protein stabilization methods. The insertion was achieved through gene fusion by recombinant DNA techniques.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Protein stabilization by domain insertion into a thermophilic protein
ActiveUS20100227374A1Improve dynamic stabilityImprove stabilityEnzyme stabilisationImmunoglobulinsProtein targetProtein insertion
A strategy to improve protein stability by domain insertion. TEM 1 beta-lactamase (BLA) and exo-inulinase, as model target enzymes, are inserted into a hyperthermophilic maltose binding protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMBP). Unlike conventional protein stabilization methods that employ mutations and recombinations, the inventive approach does not require any modification on a target protein except for its connection with a hyperthermophilic protein scaffold. For that reason, target protein substrate specificity was largely maintained, which is often modified through conventional protein stabilization methods. The insertion was achieved through gene fusion by recombinant DNA techniques
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Production method for preparing inulase
InactiveCN101717758AImprove permeabilityPromote growthHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesSporeSalting out
The invention relates to a production method for preparing inulase. The method comprises the following four steps of: the preparation of a spore suspension, the preparation of liquid seeds, the preparation of an aspergillus niger fermentation liquor and the preparation of an inulase product. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: inoculating aspergillus niger stains on a slant culture medium to culture the spore suspension; inoculating the spore suspension into a liquid seed culture medium at a temperature of 28-30 DEG C to culture so as to obtain the liquid seeds; inoculating the liquid seeds into an aspergillus niger fermentation medium to ferment according to an inoculation quantity of 3-7 percent in a volume ratio under an aseptic condition; within a period of time of 0-60h under a certain fermentation condition, opening an ultrasonic transmitting device to carry out ultrasonic irradiation culture on the aspergillus niger fermentation medium and the liquid seeds; after the ultrasonic irradiation culture, continuously carrying out ultrasonic irradiation culture to obtain the aspergillus niger fermentation liquor; precipitating inulase from the aspergillus niger fermentation liquor by adopting a salting-out method; and filtering waste liquid through a filter press and drying a filter cake to obtain an inulase product. The production method is simple and stable, saves the production cost, and improves the output of the inulase.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com