Secretory expression method for exoinulinase from Kluyveromyces marxianus
An exo-inulinase, secreted expression technology, applied in the field of exo-inulinase expression, can solve the problems of inability to form natural inulinase molecules and affect the biological activity of recombinant inulinase, and achieve the goal of a good enzymatic tool Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Cloning and sequence determination of Kluyveromyces marxii gene with signal peptide inulinase
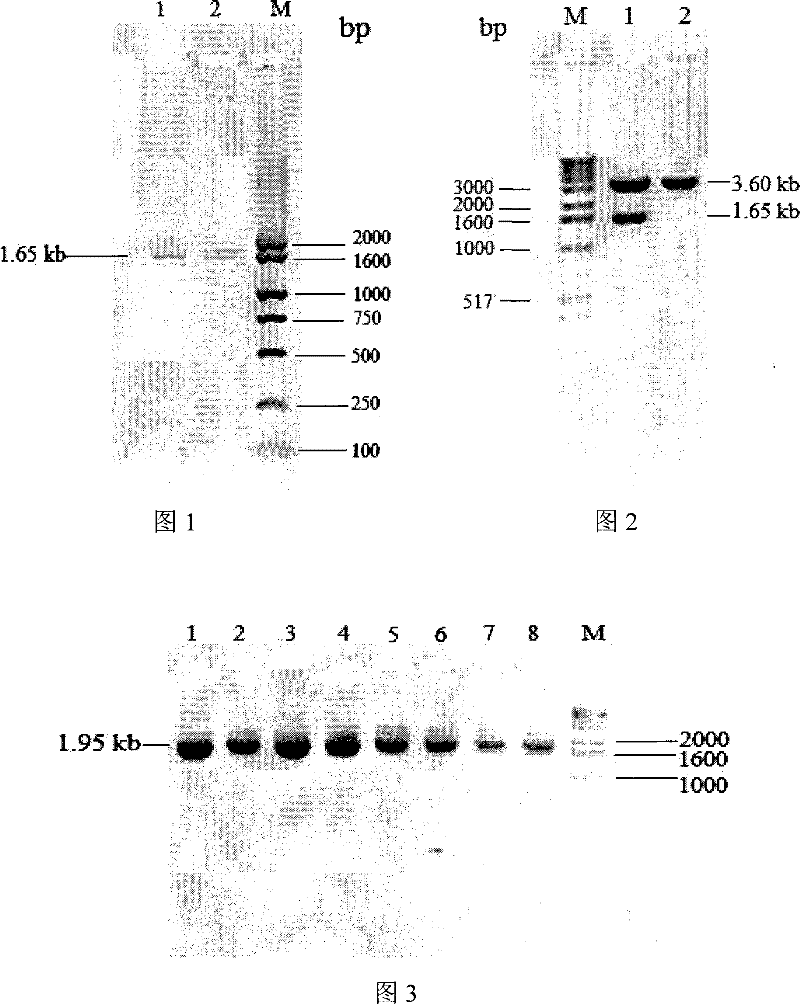
[0029] Kluyveromyces marxianus K. marxianus CBS6556 genomic DNA was extracted with reference to the method described in "Refined Molecular Biology Experiment Guide" (Fourth Edition, Osper et al., Yan Ziying et al. Translated, published by Science Press), V- 530 ultraviolet / visible light / near infrared spectrometer (JASCO) to measure its OD 260 / OD 280 Value = 1.76, frozen at -20°C for later use. Using the genomic DNA of K. marxianus CBS6556 as a template, using two specific primers inu-ORF-p1: 5'-ATGAAGTTAGCATACTCCCTCTTGC-3' and inu-ORF-p2: 5'-TCAAAGGTTAAATTGGGTAACGTT-3', according to the conventional method (molecular The third edition of Cloning Experiment Guide, written by Sam Brook, translated by Huang Peitang, published by Science Press) for polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR system: 10×PCR buffer (Dalian TakaRa) 5.0μl, dNTPs (10mmol / l, TaKaRa) 1.0μl, inu-...
Embodiment 2
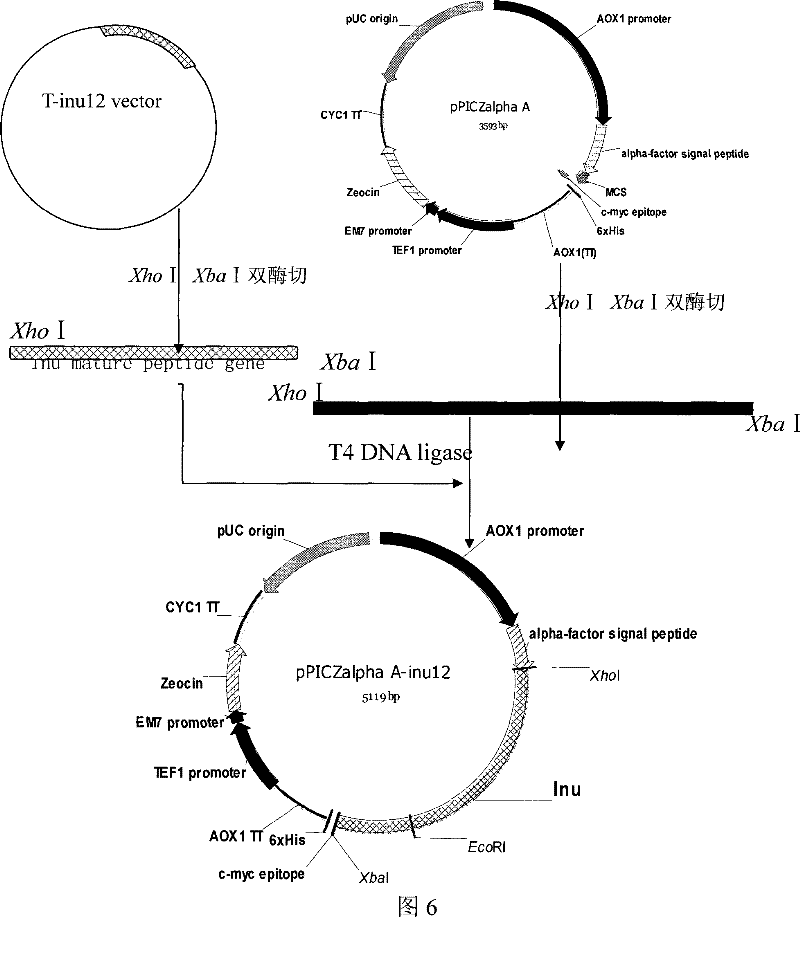
[0058] Example 2: Construction of recombinant Pichia pastoris expression vector pPICZαA-inu12
[0059] According to the two-terminal sequence of the mature protein encoded by the K.marxianus CBS6556 inulinase gene and the polyclonal restriction site sequence information of the Pichia pastoris expression vector pPICZαA (purchased from Invitrogen), a pair of specific primers were designed with the following sequences:
[0060] Inu-p1: 5'-TC GATGGTGACAGCAAGGCCAT-3' (the underlined part is the Xho I restriction sequence, and the boxed part is the coding sequence of the Kex2 signal peptidase recognition site)
[0061] Inu-p2: 5'-CTC AAGGTTAAAATTGGGTAACGTT-3' (the single underlined part is the Xba I restriction sequence, and the double underlined part is the stop codon sequence)
[0062] Using the T vector carrying the K.marxianus CBS6556 inulinase gene obtained in Example 1 as a template, using primers Inu-p1 and Inu-p2, the coding of the inulinase mature peptide was amplified ...
Embodiment 3
[0120] Example 3: Transformation of Pichia pastorii strains and screening of positive clones
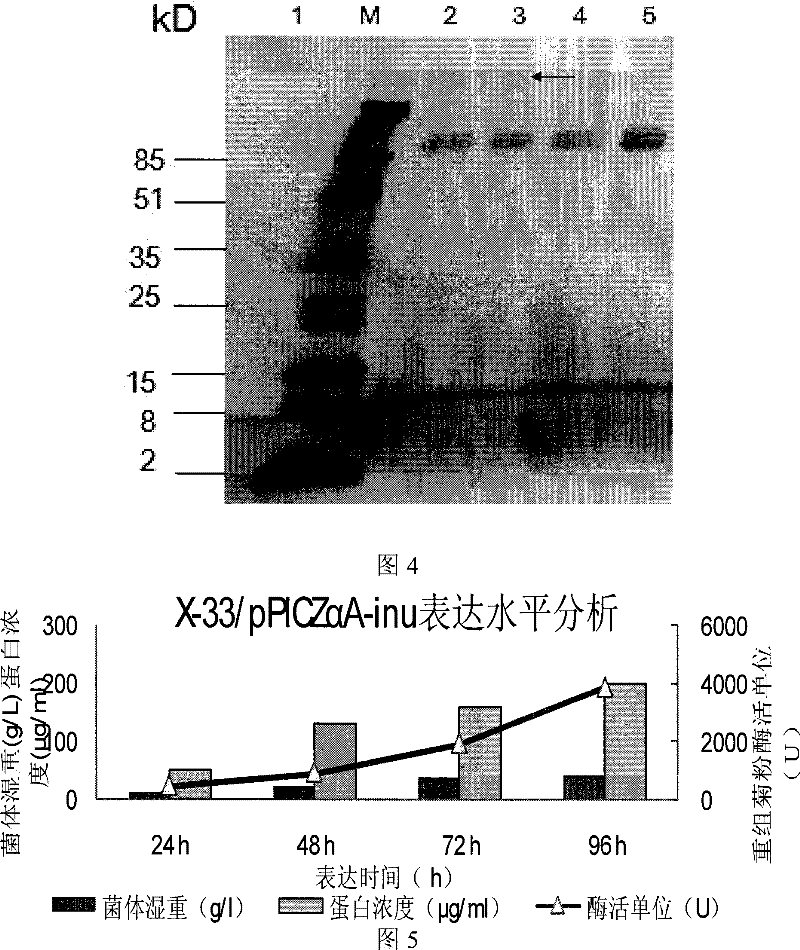
[0121] Recombinant expression plasmid inulinase was single-digested with sac I (Dalian TakaRa) and linearized, extracted with phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol to remove protein, added 1 / 10 volume of 3mol / l sodium acetate solution (pH5.2) and 2 Double the volume of absolute ethanol, precipitate and recover the linearized carrier, and the concentration of the purified linearized carrier is 995 ng / μl as determined by a V-530 mol / l ultraviolet / visible light / near-infrared spectrometer (JASCO). 10 μl of the purified linear vector was taken and transformed into Pichia pastoris X-33 (purchased from Invitrogen) by electroporation, and transformed into the linearized pPICZαA empty vector as a control. Electric shock conversion parameters: Electric shock parameters: 0°C, 1.5kv, 200Ω, 25μF, electric shock time: 4.5-10ms, see the operation process instructions for the preparation of competent ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com