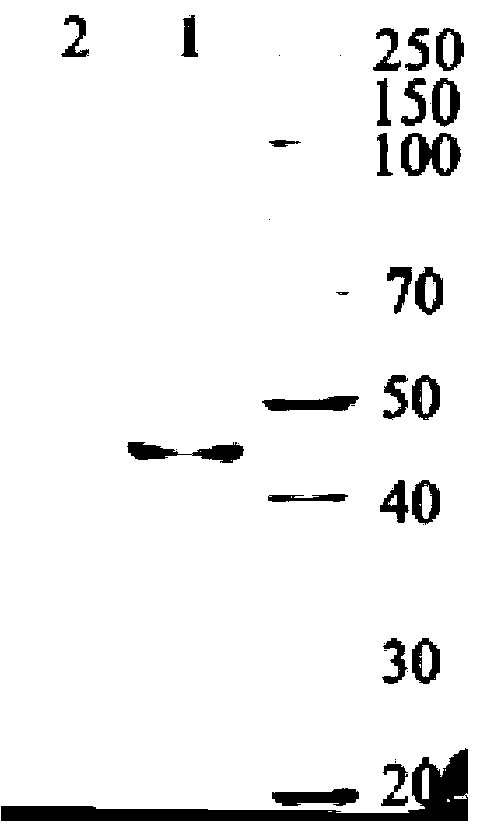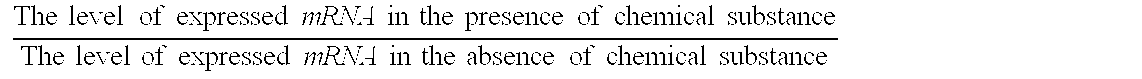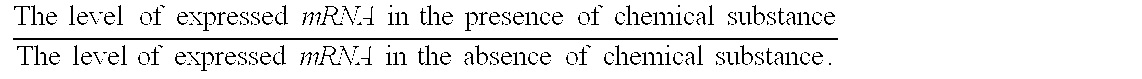Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Yeast gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for producing poly-unsaturated fatty acids by oleaginous yeasts
The present invention is directed to a process of producing novel fatty acids in oleaginous yeast by producing oleaginous yeast by introducing into the yeast genes coding for enzymes selected from the group consisting of D5-desaturase, D6-desaturase, D12-desaturase, D15-desaturase and elongase; and culturing the yeast in the medium containing high levels of carbon sources. The present invention is further directed to a residue or fatty acid that is obtained from pressing the oleaginous yeast produced by the process of the invention.
Owner:YEASTERN BIOTECH
Yeast arrays, methods of making such arrays, and methods of analyzing such arrays
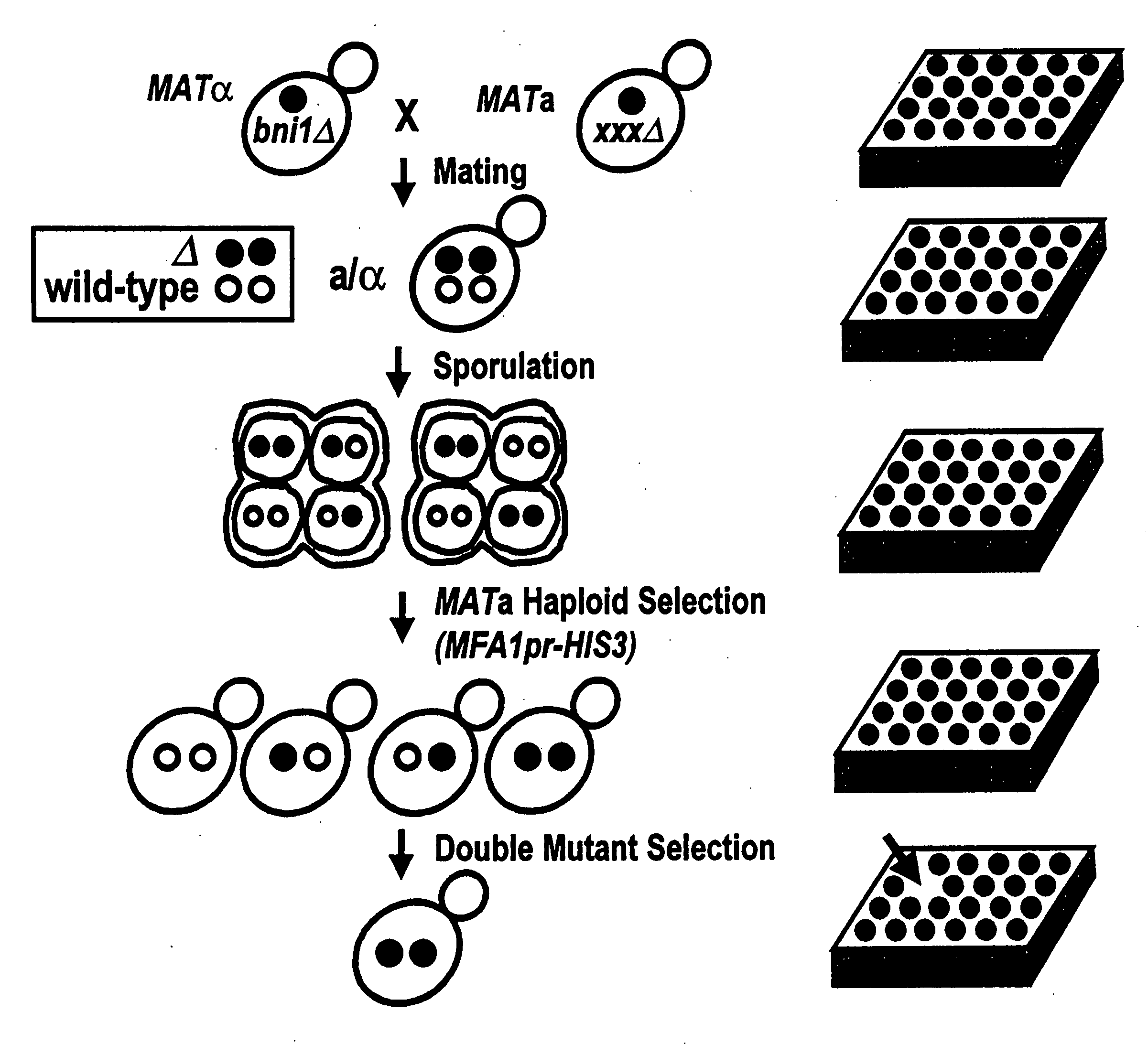
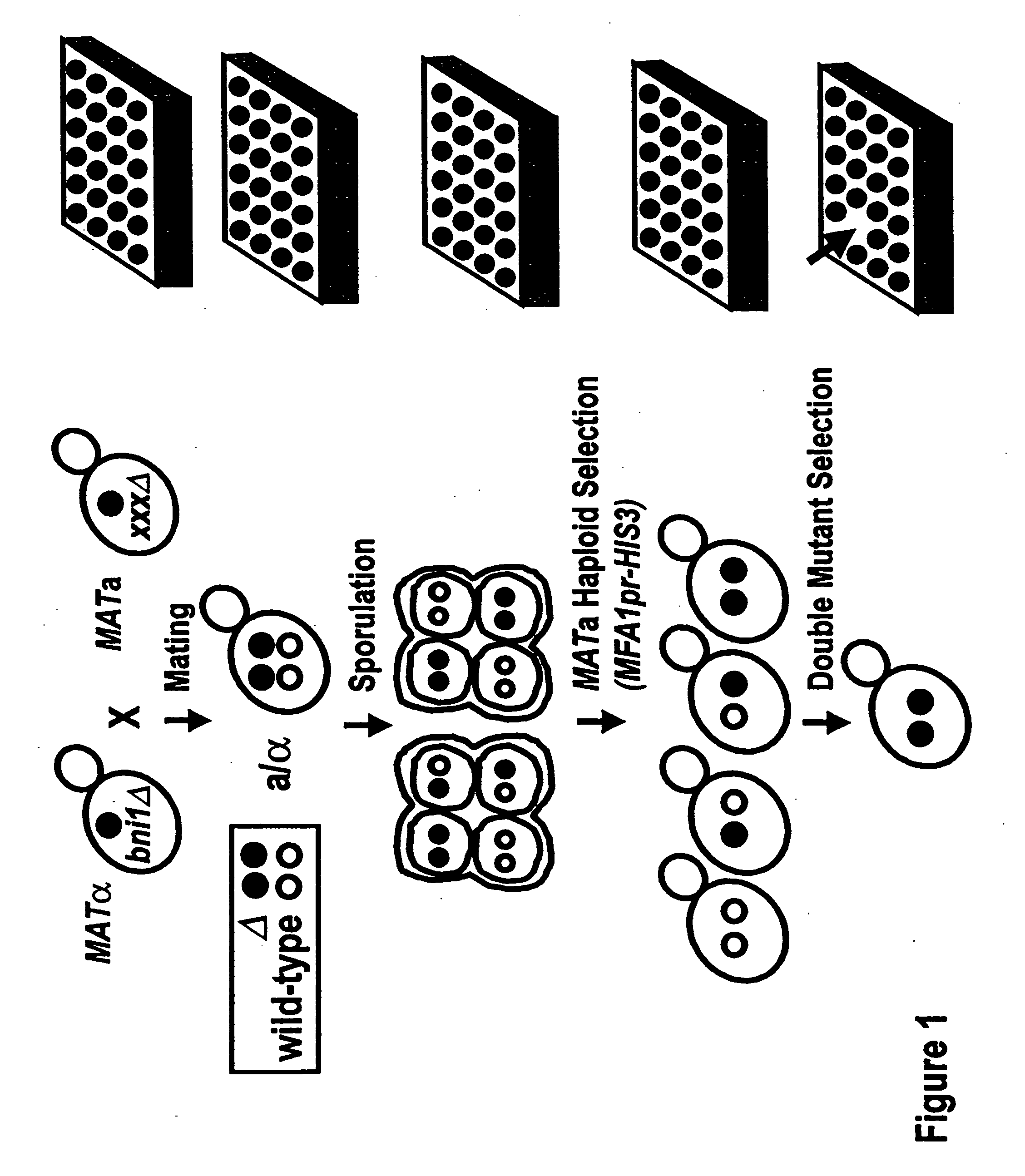
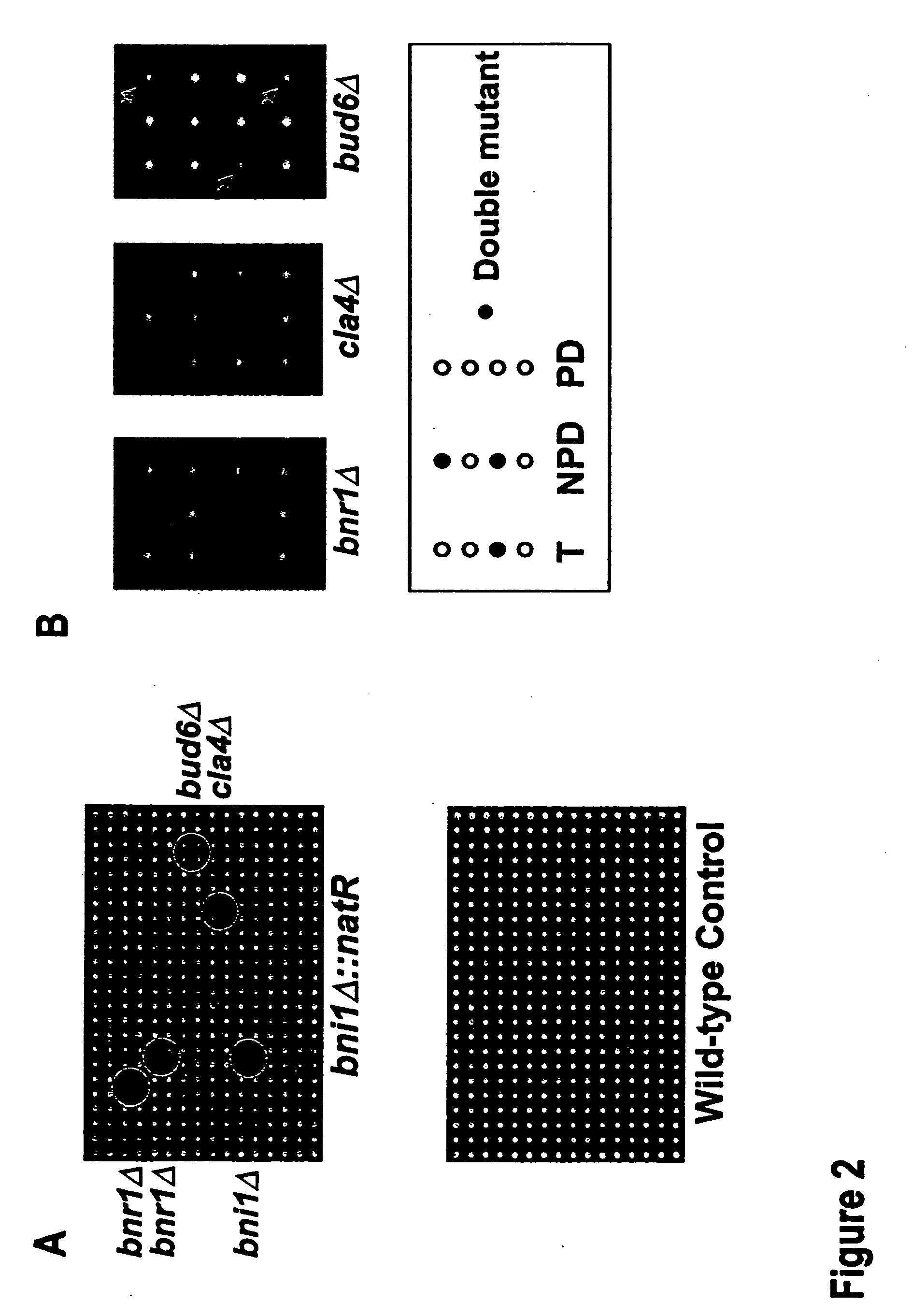
This patent describes a novel method of detecting genetic interactions in yeast. This method can also be used to screen for function of biological effectors on yeast. The method encompasses crossing yeast strains with genetic alterations to acquire double mutants. The phenotypes of these double mutants are then checked to detect genetic interactions between the double mutants. This method can be used to assign function to yeast genes and their viral, prokaryotic, and eukaryotic homologs, and aptamers. It can also be used to study yeast two hybrid interactions and to find genes that regulate certain yeast promoters.
Owner:BOONE CHARLES
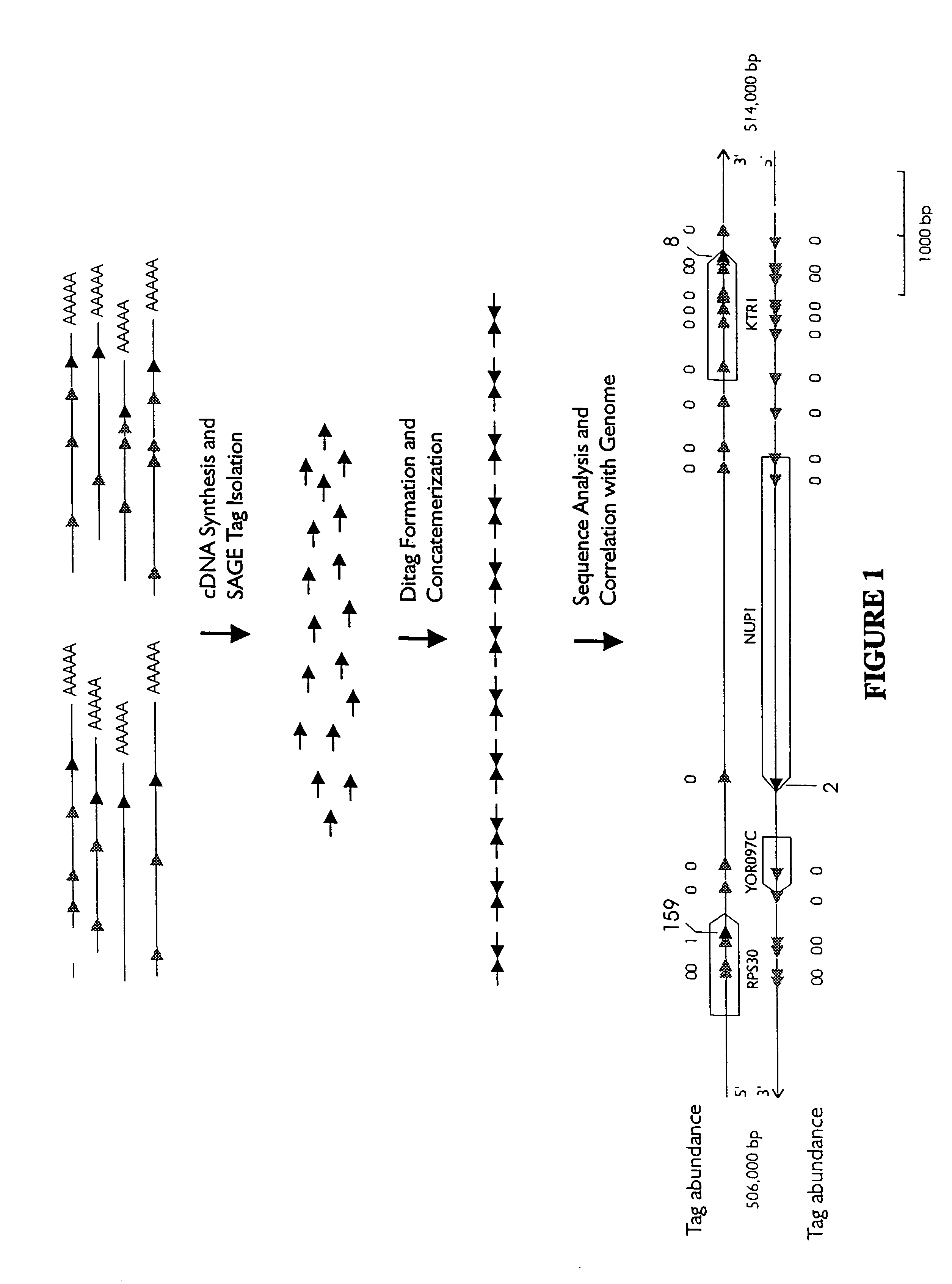
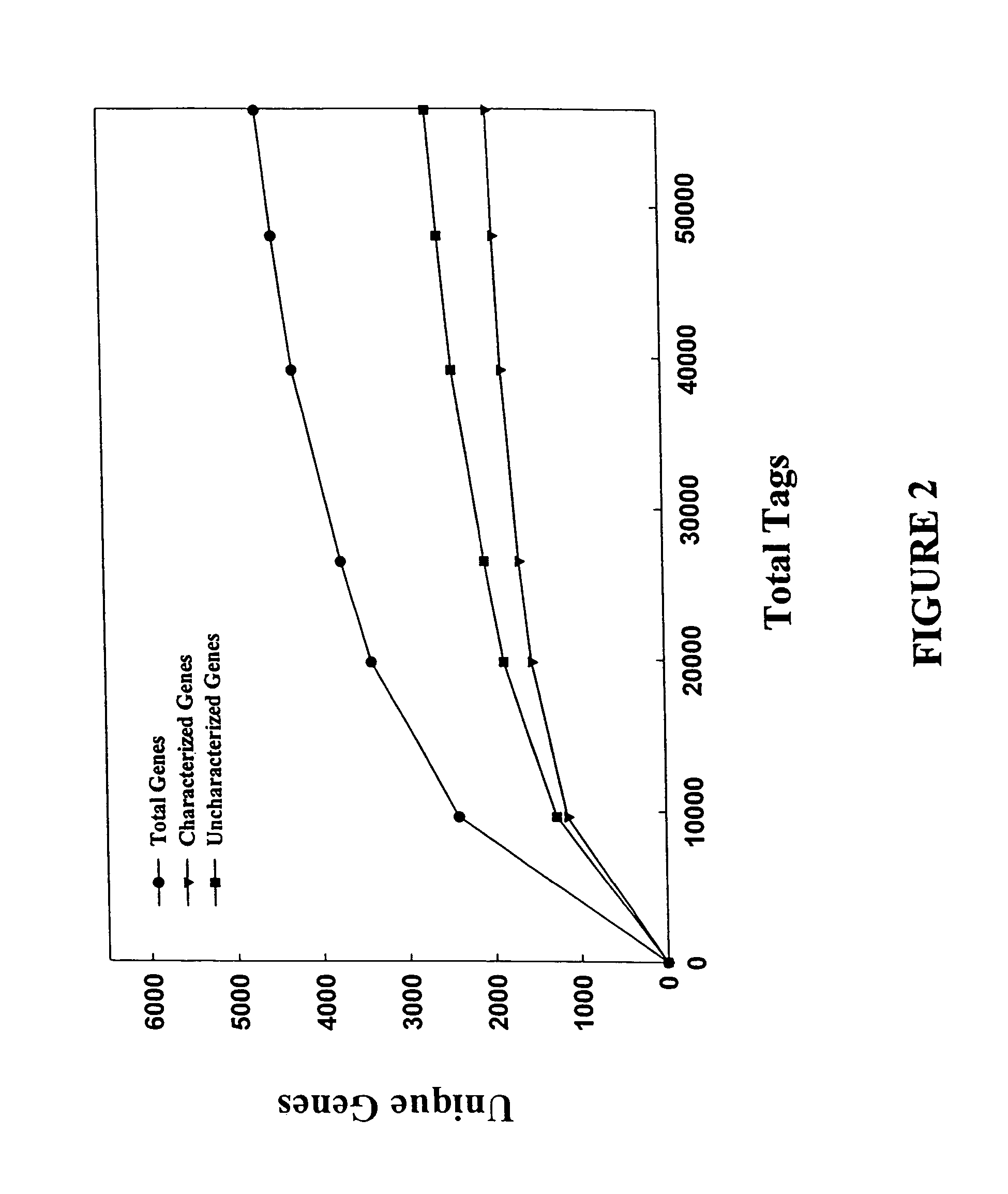
Characterization of the yeast transcriptome
Yeast genes which are differentially expressed during the cell cycle are described. They can be used to study, affect, and monitor the cell cycle of a eukaryotic cell. They can be used to obtain human homologs involved in cell cycle regulation. They can be used to identify antifungal agents and other classes of drugs. They can be formed into arrays on solid supports for interrogation of a cell's transcriptome under various conditions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High temperature and strong alkali resistant xylanase improved gene, genetic engineering bacterial strain thereof and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101392266AImprove thermal stabilityEasy extractionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisXylanase
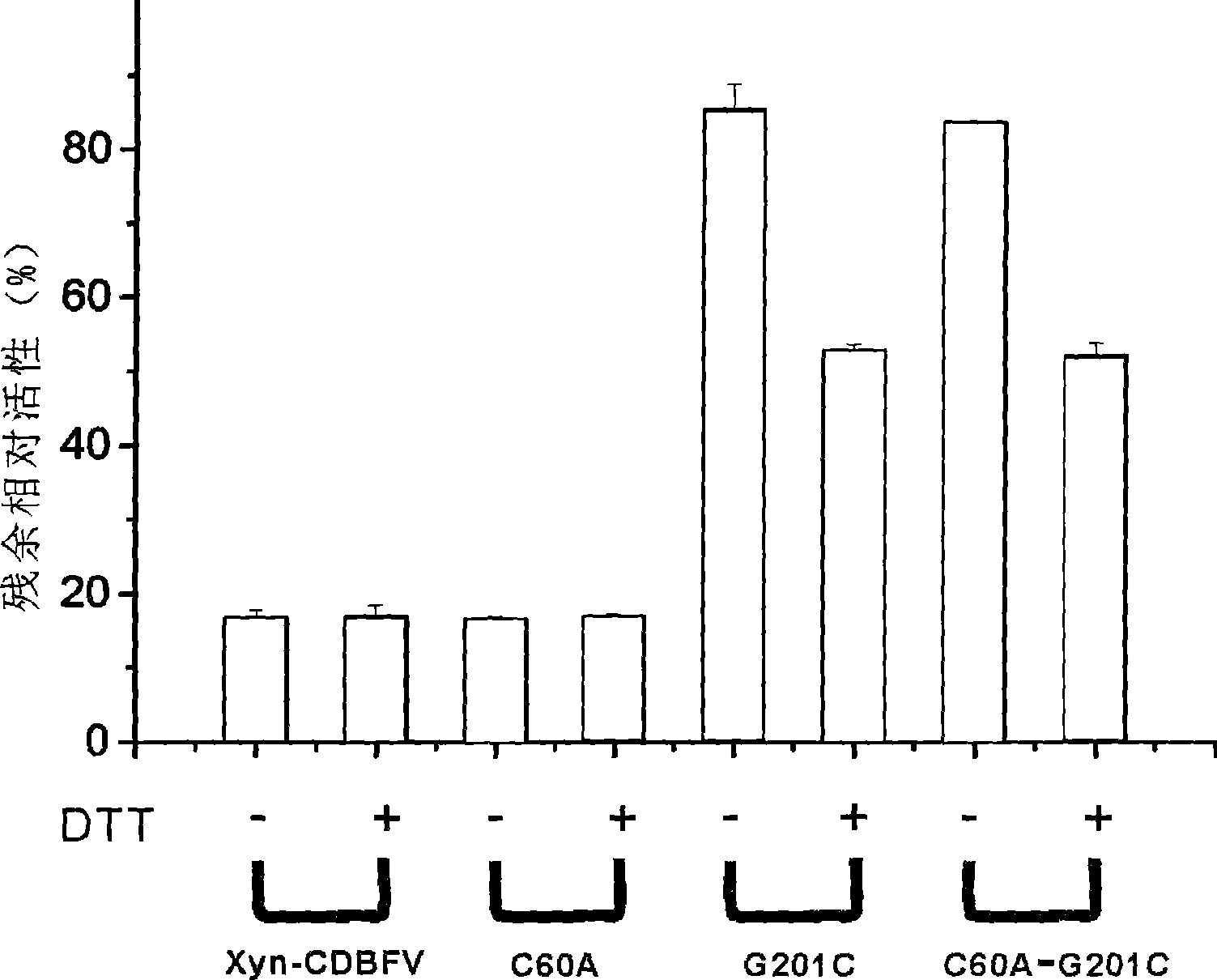
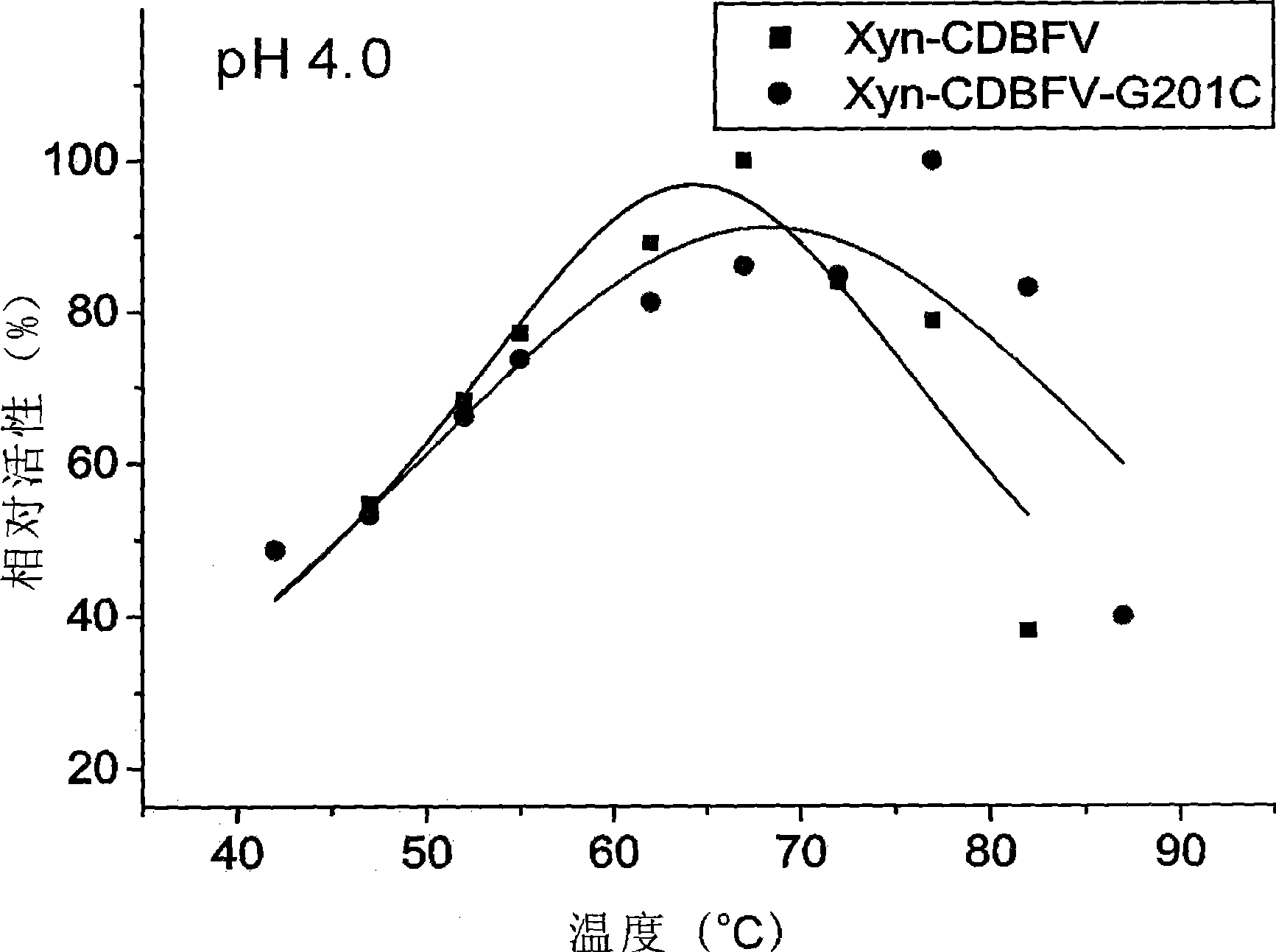
The invention provides a modified coding gene of xylanase that has high activity in the condition of high temperature and strong alkali, a recombinant plasmid thereof, a yeast recombination genetic engineering strain containing the gene and a preparation method of the gene. Compared with the original xylanase, the modified xylanase is mutated into cysteine from glycin of the 201 site of amino acid sequence of the original xylanase; and the modified xylanase has higher heat stability, after being processed for 10 minutes at the temperature of 75 DEG C, the residual activity of the modified xylanase reaches 80 percent, while that of the original xylanase is only 15 percent. The activity of the modified xylanase is 1.5 to 2 times of that of the original xylanase at the environment with high temperature and strong alkali and can decompose xylan for a long time at high temperature. The invention also provides the Pichia pastoris yeast recombination genetic engineering strain containing the modified gene. The modified xylanase can be widely applied to industries of paper making, feedstuff and food.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Characterization of the yeast transcriptome
InactiveUS20070031851A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesYeast geneYeast form
Yeast genes which are differentially expressed during the cell cycle are described. They can be used to study, affect, and monitor the cell cycle of a eukaryotic cell. They can be used to obtain human homologs involved in cell cycle regulation. They can be used to identify antifungal agents and other classes of drugs. They can be formed into arrays on solid supports for interrogation of a cell's transcriptome under various conditions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
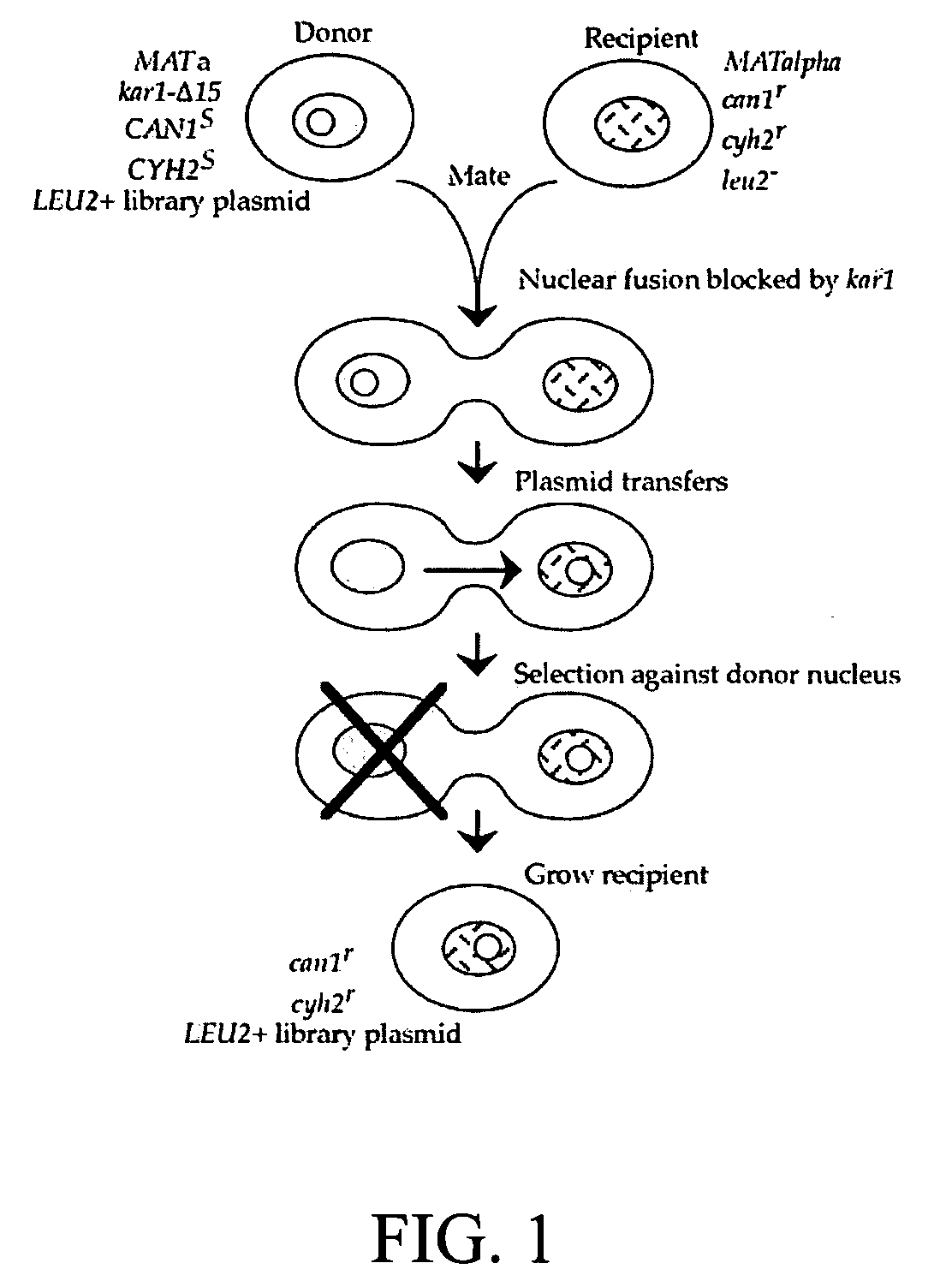
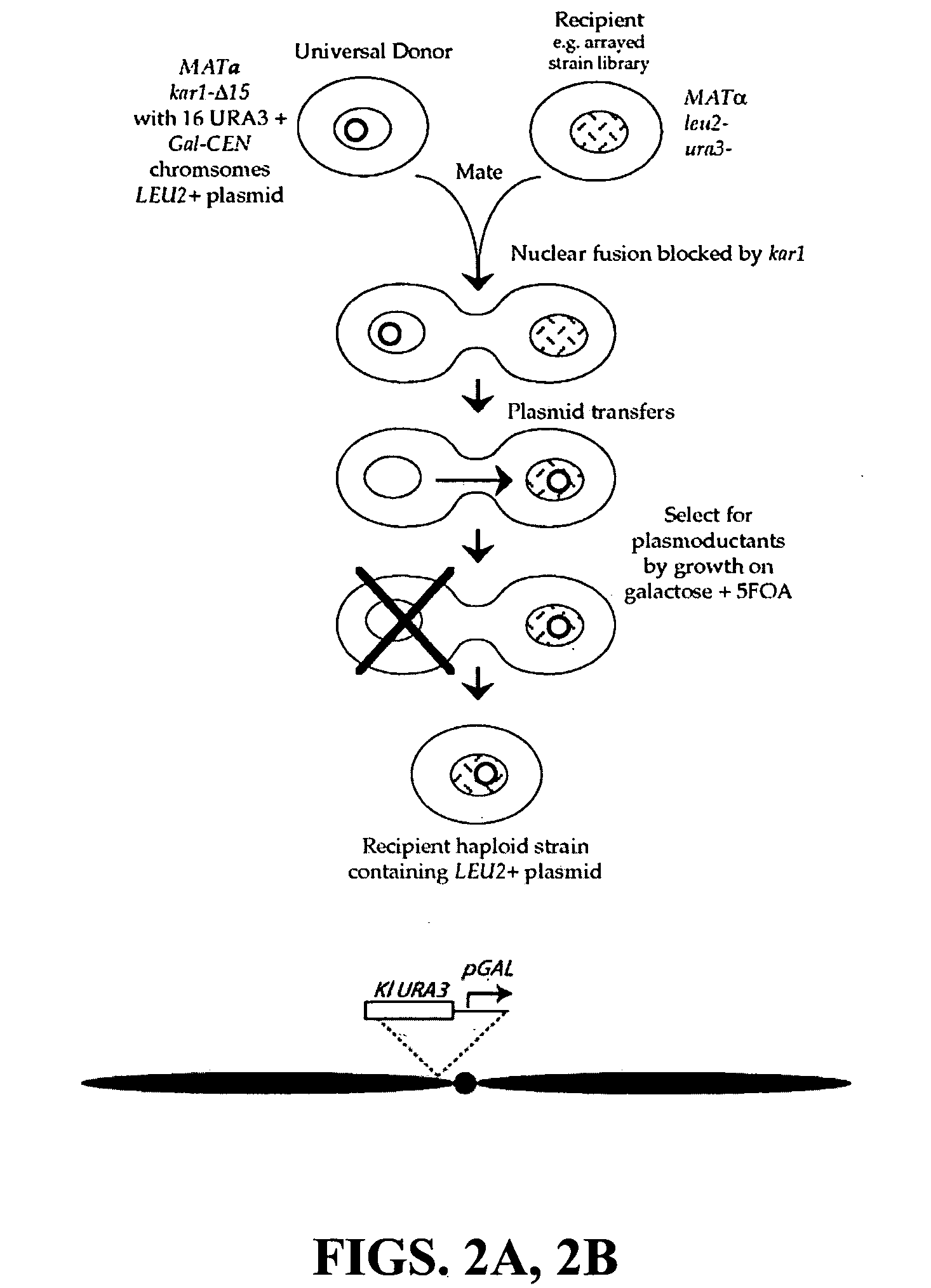
Donor yeast strain for transfer of genetic material
InactiveUS20060105361A1Reduce needSimple methodFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsBiotechnology
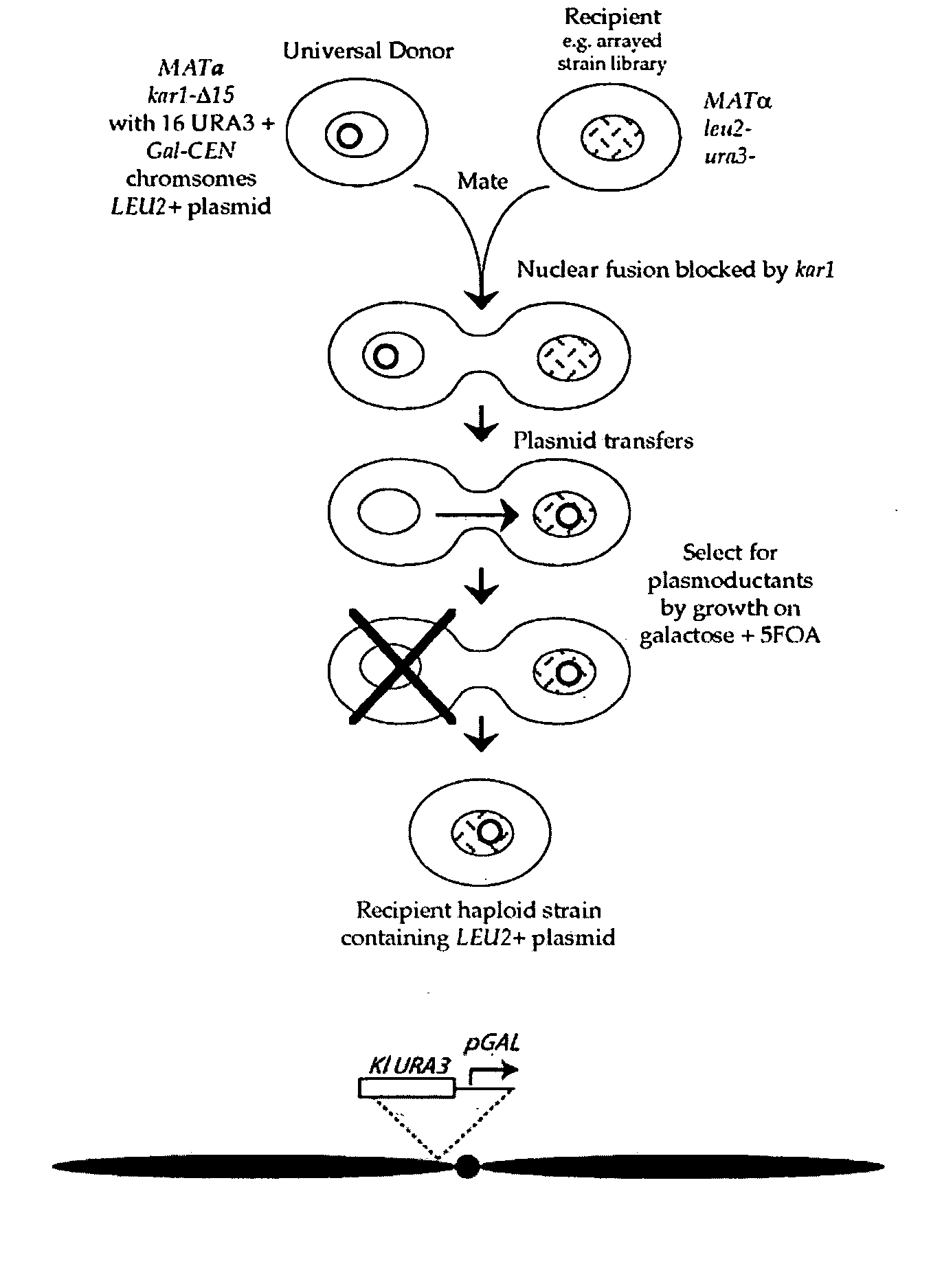
The invention provides a universal yeast donor strain that contains a conditional centromere and a URA3 allele on every chromosome. This strain was constructed in four rounds of crosses of individual conditional chromosome strains using a novel tetrad-based screen to identify segregants in which all marked chromosomes were contained in the same spore. The invention also provides an improved high efficiency method to transfer extrachromosomal genetic material such as plasmid DNA into any Saccharomyces strain for use with the current gene disruption libraries. The method of transfer is mating-based method which uses a kar1 plasmid donor strain that can initiate mating but cannot form a diploid and allows plasmid transfer (plasmoduction) between nuclei in the heterokaryon. kar1 matings have been used to transfer YACs between yeast strains, but previous methods required specialized genetic backgrounds in the recipient strains and suffered from high rates of spurious chromosome transfer (Hugerat, Y., et al. 1994. Genomics 22:108). Plasmoduction with the universal donor strain only requires that the recipient strain be ura3, GAL+ and have another marker available for selection of the transferred plasmid. Counterselection against every donor chromosome also limits the amount of spurious allele transfer. The universal donor strain and the method of the invention are used to screen the yeast gene disruption library with plasmid-based dominant negative alleles of various genes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Yeast gene engineering fungus and beta mannosan enzyme preparation and production method of manna oligose
InactiveCN1478887AHigh purityReduce manufacturing costFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyTransformation efficiency
A genetically engineered yeast Pichia pastoris (GS115 / HBMO47) able to effectively express beta-mannase is prepared through screening beta-mannase gene from the environmental microbes, cloning it to the expression carrier of Pichia yeast, introducing the carrier to Pichia yeast, and screening. The process for preparing the high-activity beta-mannase and the high-purity oligomannosan from said Pichia pastoris is also disclosed.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Modified methylotrophic Pichia pastoris yeast which secretes human growth hormone
In the present system an adequate expression system for the production and secretion of biologically active human growth hormone (HGH) in its natural form in which a methylotrophic yeast such as Pichia pastoris is used as host organism has been developed. This invention includes a methylotrophic yeast transformed with at least one copy of a functional cDNA sequence encoding HGH, which is functionally associated with a second DNA sequence encoding the S. cerevisae alpha factor pre-pro sequence (including the proteolytic processing site: lys-arg), and in which both DNA sequences are under the regulation of a methylotrophic yeast gene promoter which is inducible with methanol. Methylotrophic yeasts containing in their genome at least one copy of the DNA sequence efficiently produce and secrete mature, correctly processes and biologically active HGH, into the culture medium.
Owner:UNIV AUTONOMA DE NUEVO LEON
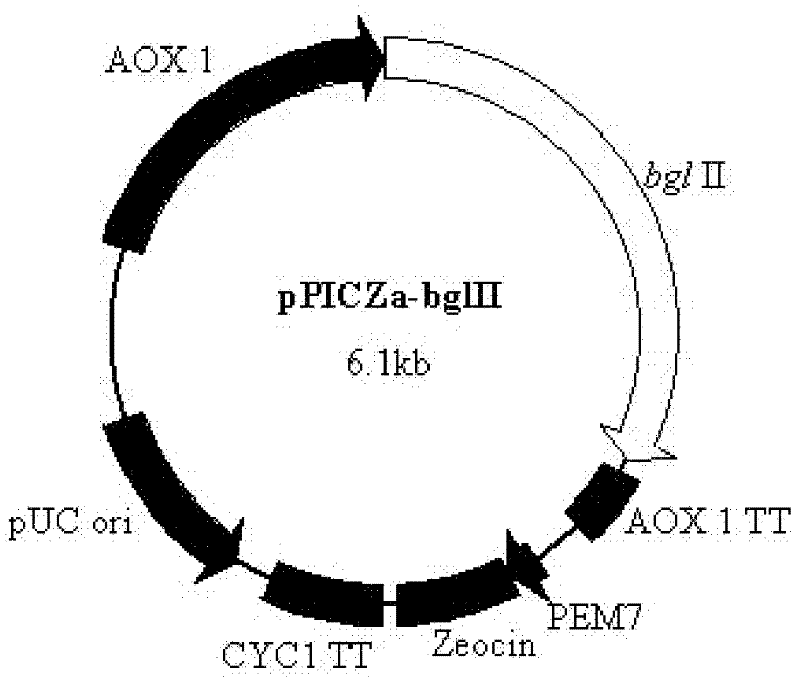
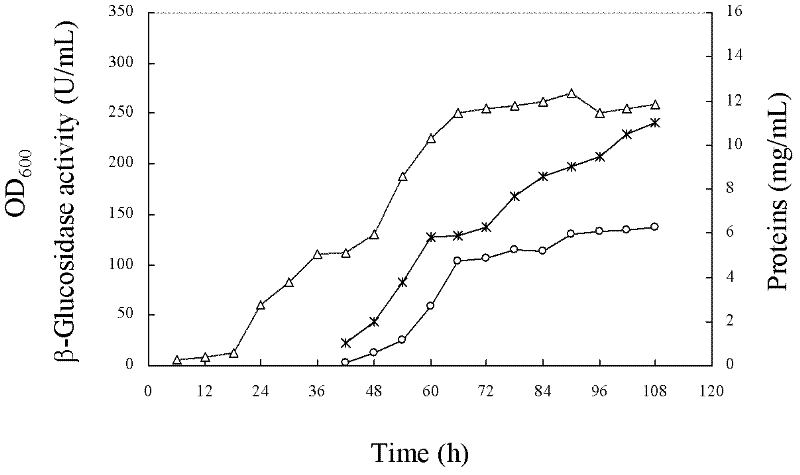
Improved beta-glucosidase gene and preparation of recombinase thereof
The invention relates to an improved beta-glucosidase gene and preparation of a recombinase thereof. The improved beta-glucosidase gene bgl II has an anucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Meanwhile, the invention provides a method for expressing the beta-glucosidase by the recombinant bacterium with a basic salt culture medium. Through artificial evolution and high density fermentation ofthe gene, the expression level of the improved aspergillus niger beta-glucosidase gene bgl II in Pichia pastoris is enhanced by 36 times compared with the original gene bgl I. The improved beta-glucosidase gene and preparation of a recombinase thereof in the invention can be used for molecular modification of beta-glucosidase gene and high density fermentation of its recombinant Pichia pastoris gene engineering bacterium, and can substantially improve the expression level of beta-glucosidase.
Owner:江苏好多收农业科技有限公司
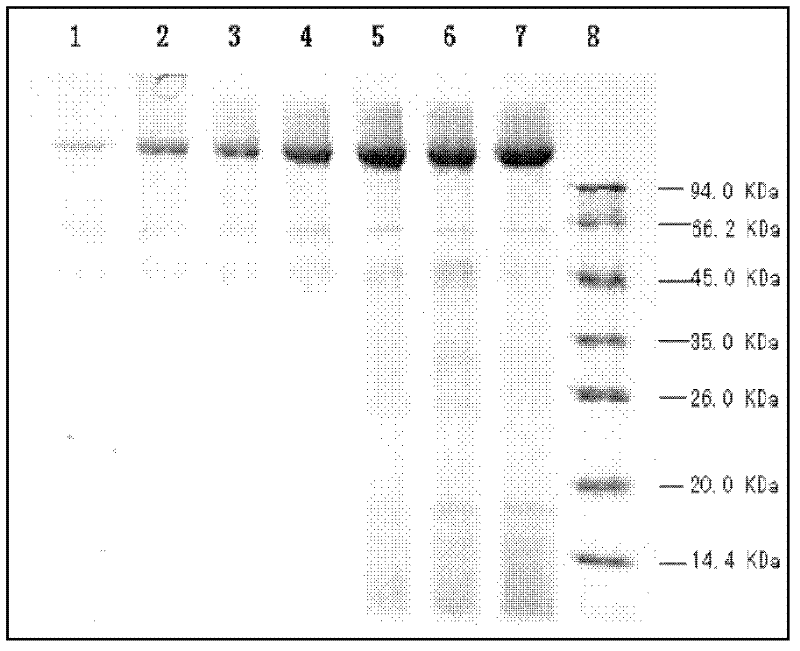
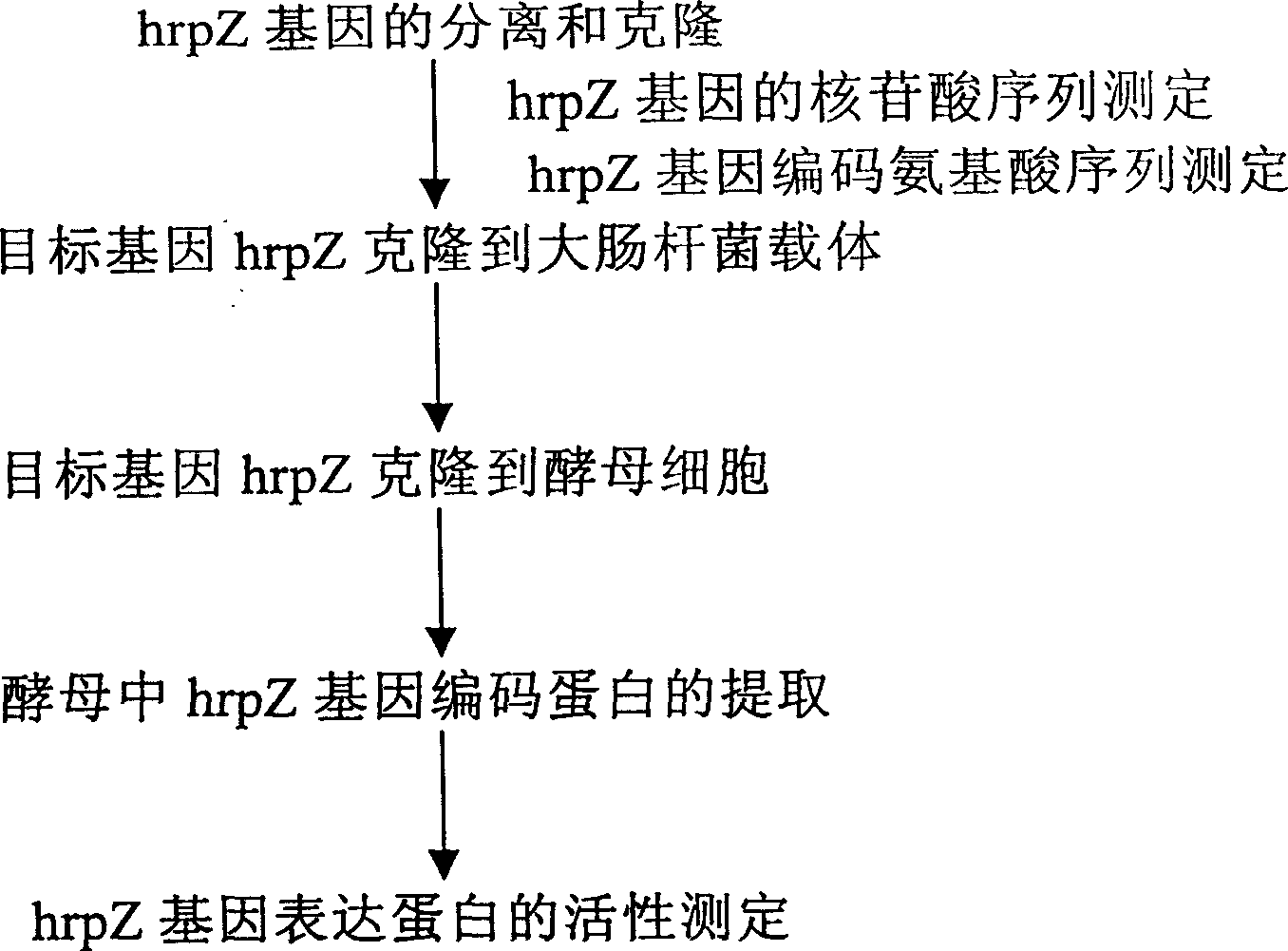
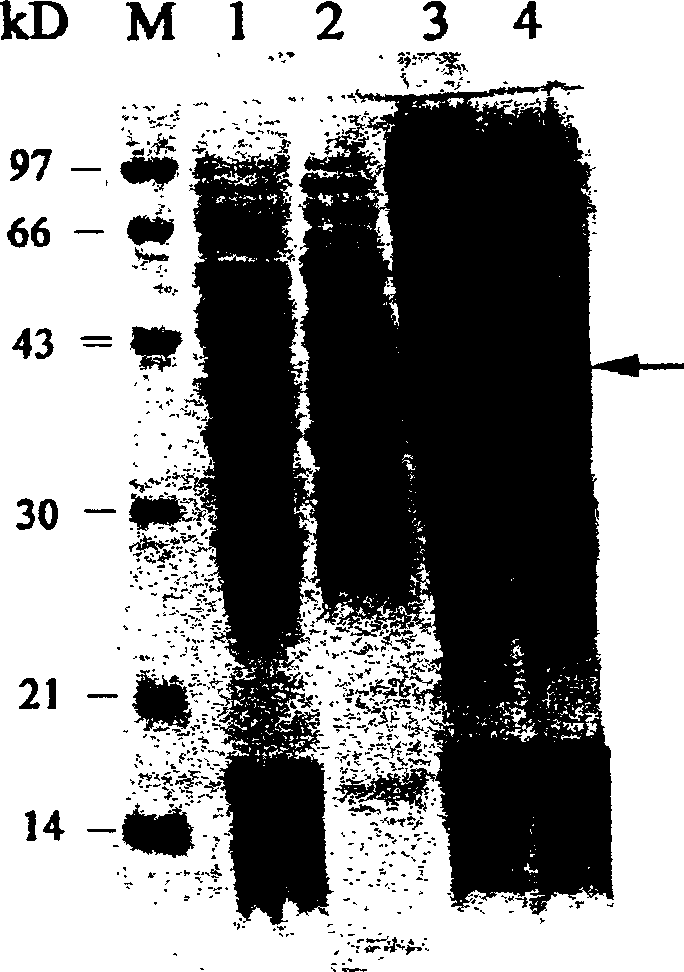
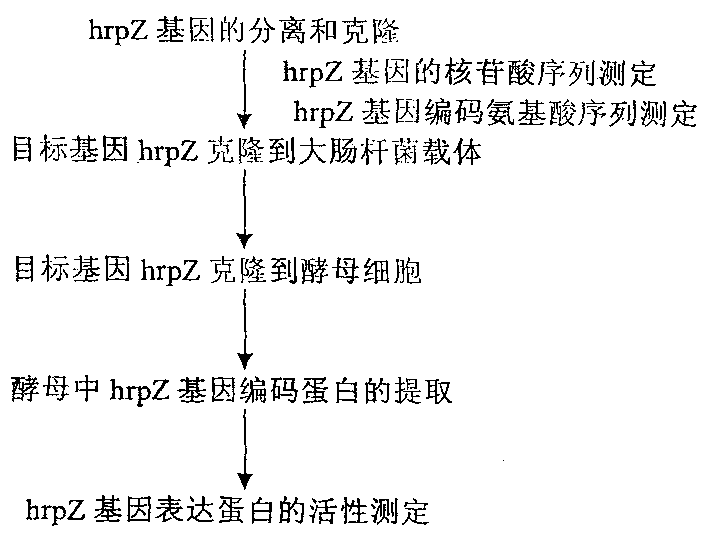
Yeast genetically engineered strain expressing hrp gene and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN1454989AStrong reactionImprove biological activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyBio engineering
The present invention relates to a yeast gene engineering strain capable of expressing hrp gene and its construction method. The name of said strain is Saccharomyces cerevisiae hrp Z, its number is CCTCC No:M203004. Its construction method includes: extraction of pseudomonas syringae genome DNA; using genome DNA as template PCR primer to make construction of hrp Z recombinant yeast gene engineering strain; hrpZ gene contained yeast conversion and induction. The gene engineering harpin protein produced by said strain can induce plant hypersensitive reaction, activate internal self-defense function of plant and promote plant growth. so that it can raise yield and quality of crops.
Owner:WUCAI FINE CHEM JIANGSU
Beta-mannase gene and amino acid sequence of its coded product and preparation method
InactiveCN1807644AExpand genetic resourcesEnrich excellent candidate genesHydrolasesRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses an amino acid sequence of beta-mannase gene and coding making method in the biological domain, which is characterized by the following: extracting Armillariella tabescens main RNA of high activity by konjaku flour evoking; using consanguinity sequence of Genebank to design degenerate primer; carrying on PCR expanding to protectorate by primer; designing gene specificity primer to carry on 3'RACE and 5'RACE; cloning total long cDNA of beta-mannase gene; constructing eucaryon expressing carrier with pichia; building-up yeast gene engineering bacterial strain.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
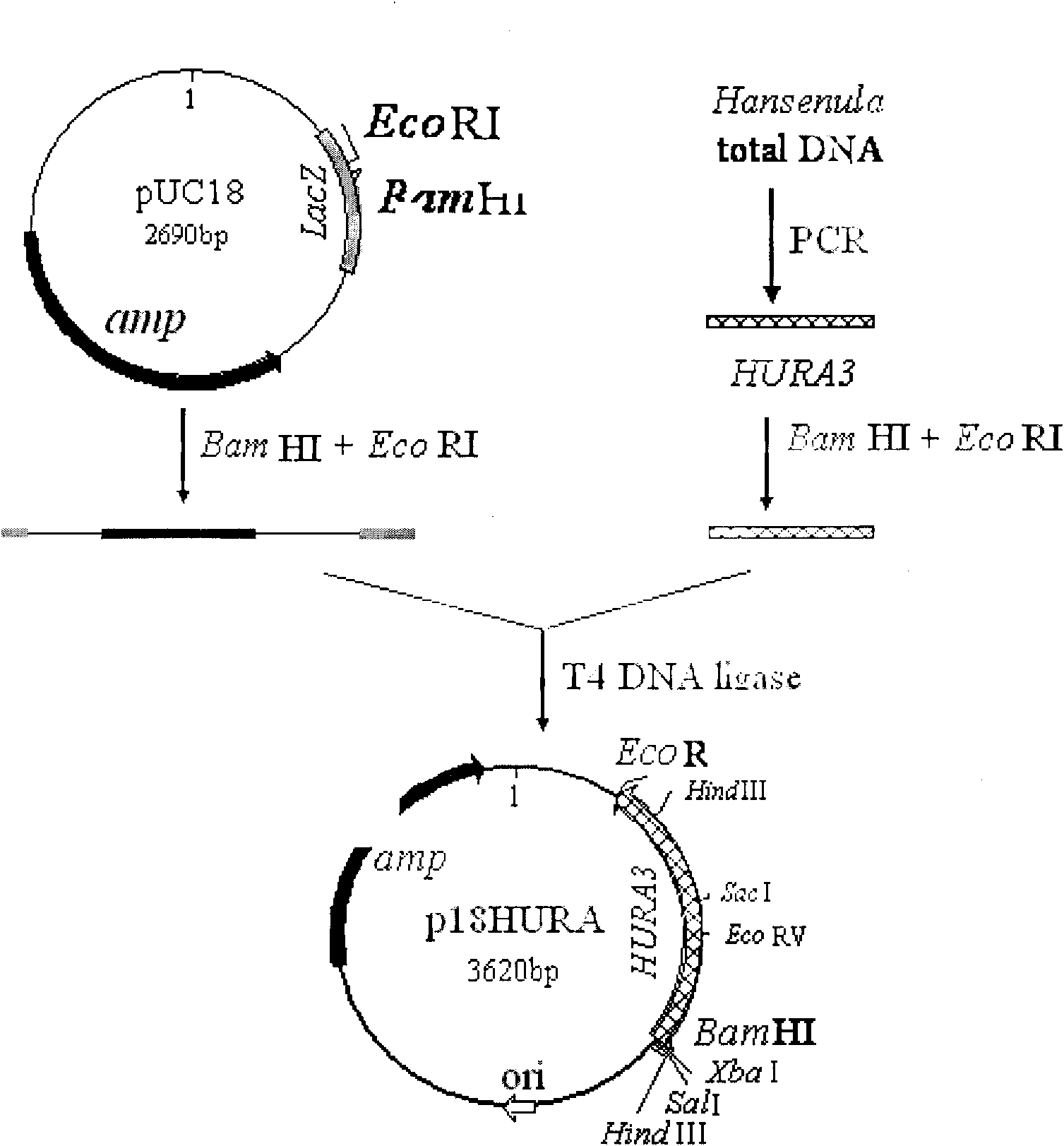
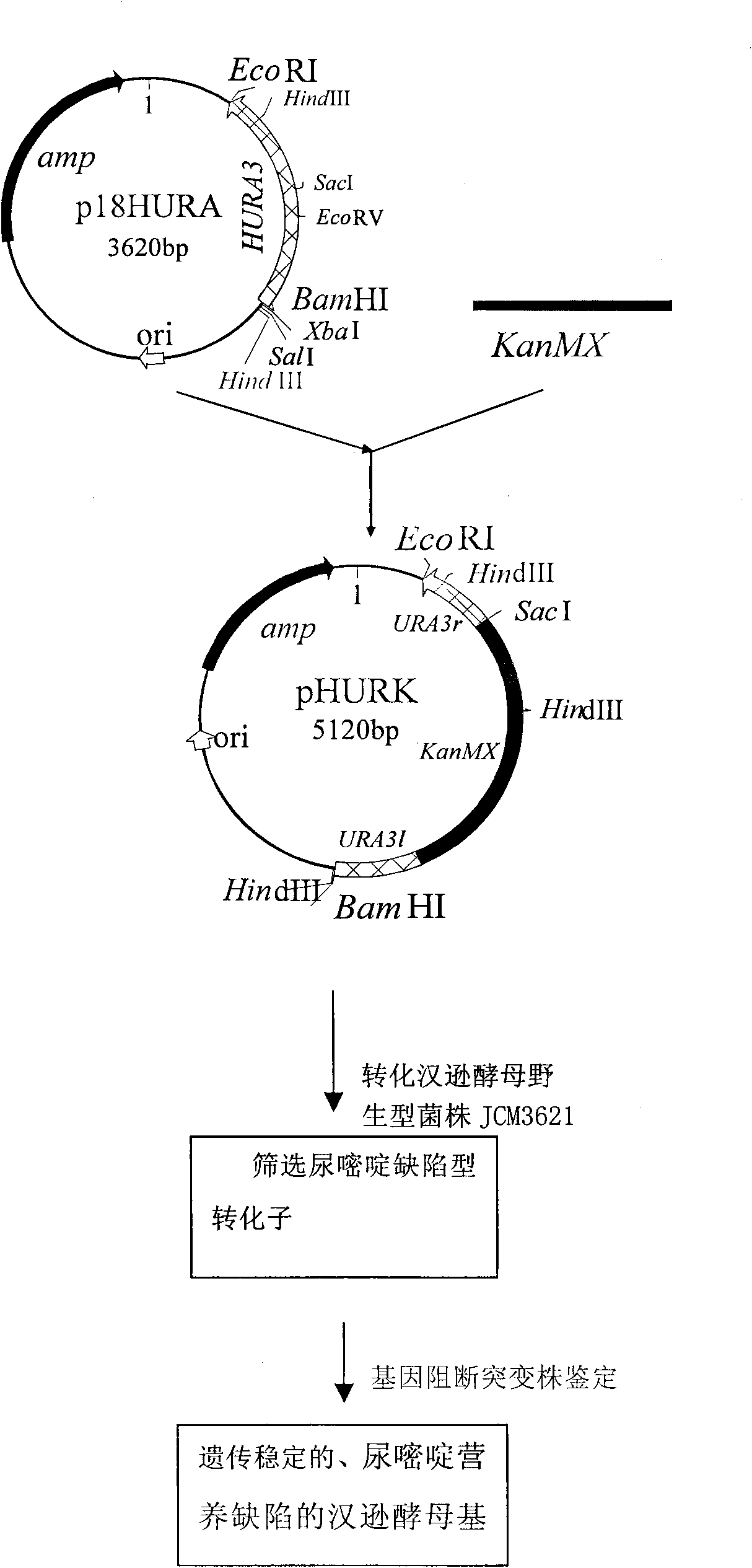
Uracil auxotroph Hansenula yeast, construction method thereof and application thereof
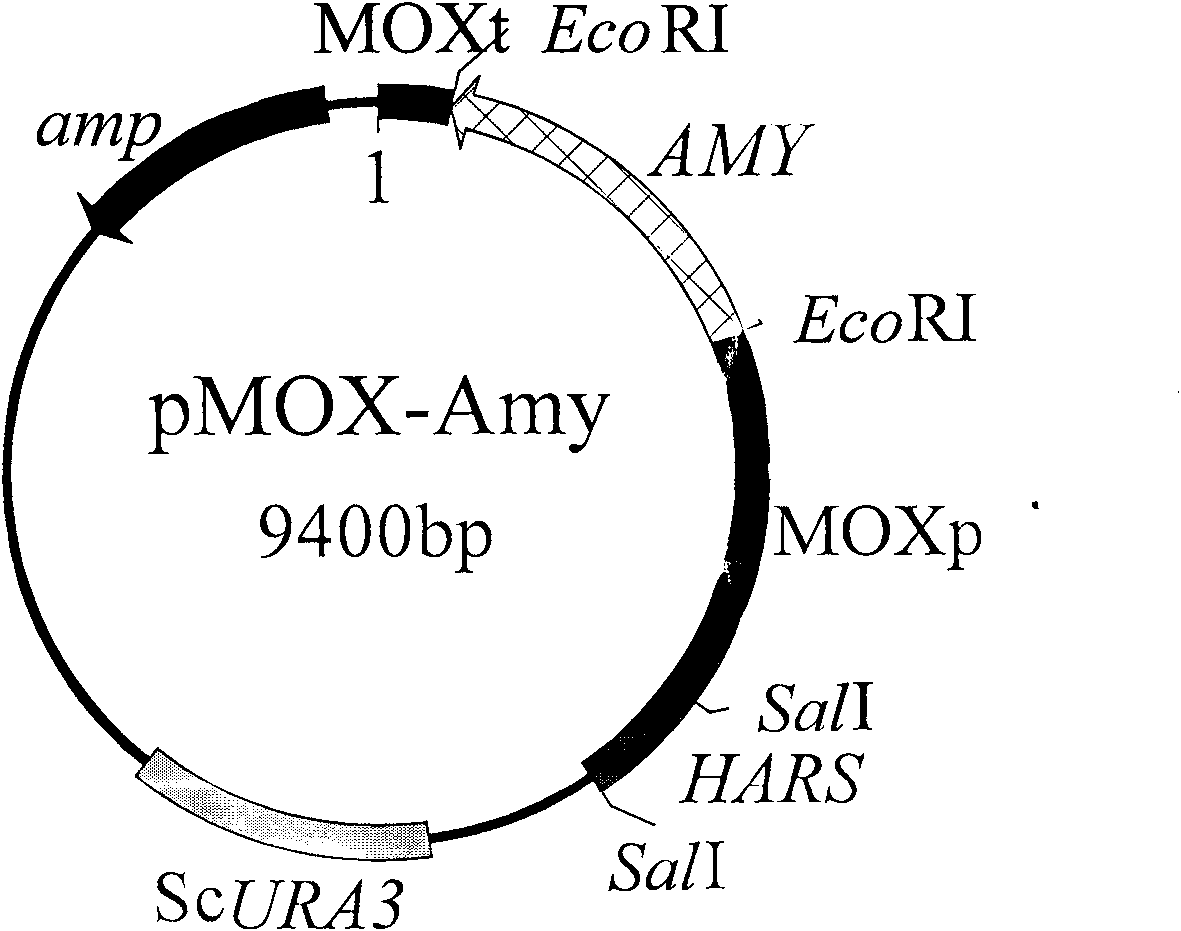
The invention discloses uracil auxotroph Hansenula yeast gene engineering host strain Hansenula yeast YH-11 CGMCC NO.2976 with stable heredity, and simultaneously provides a construction method for the Hansenula yeast. The construction method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing recombinant plasmid p18HURA containing orotidine-5-phosphate decarboxylase gene (HURA3) of the Hansenula yeast; and 2) constructing recombinant plasmid pHURK for the HURA3 with disrupted gene; and converting the plasmid pHURK of step 2) into the Hansenula yeast by using a yeast whole cell conversion method, and obtaining the uracil auxotroph strain through screening. The invention further discloses application of the constructed uracil auxotroph Hansenula yeast gene engineering host strain Hansenula yeast in producing foreign protein.
Owner:元昊
Yeast gene engineering bacteria and heat resistant alkali resistant xylanase preparation and application method
A genetically engineered yeast GS115 / HB705 able to effectively express the high temp and alkali resistant xylanase is disclosed, which can be used to prepare said xylanase through culture, separation and purifying, and in turn the oligoxylose.
Owner:桂林精成生物科技有限公司
Beta-mannase, coding gene as well as producing strain and application thereof
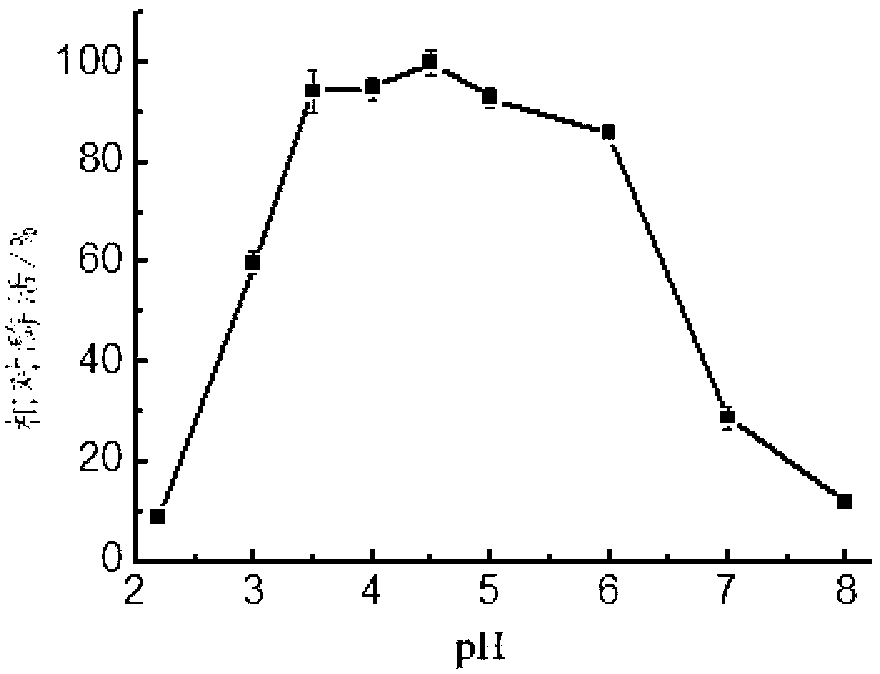
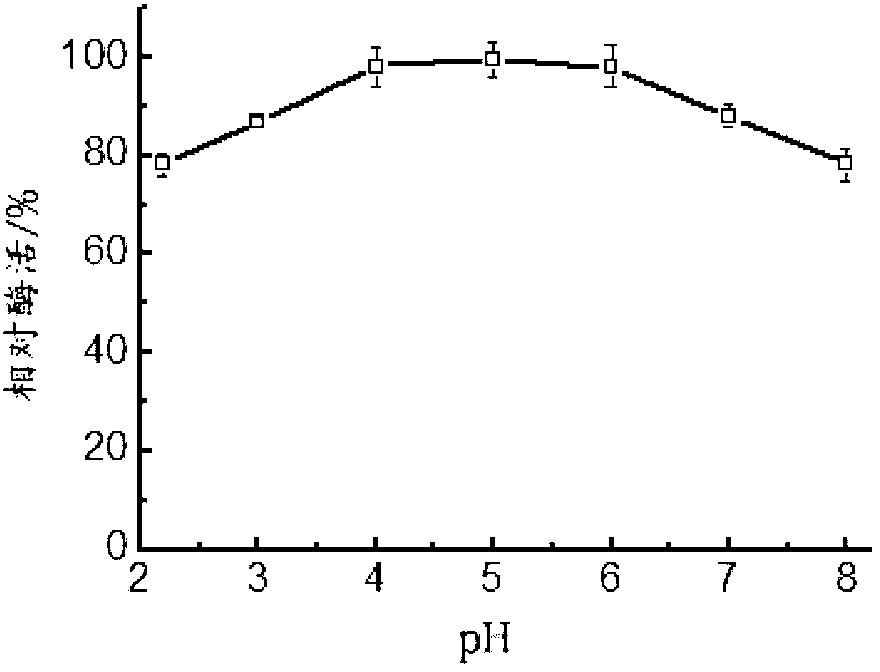
ActiveCN103255118AWide pH range of actionWide pH rangeFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses beta-mannase, a coding gene as well as a producing strain and application thereof. The fungus of the high-temperature beta-mannase is Aspergillus sp.T16 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2013122. The novel high-temperature mannase gene manT16 obtained by cloning the fungus has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or 3. The beta-mannase obtained by coding has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, as well as a recombinant vector for coding the mannase gene and yeast genetically engineered bacterium. The mannase has an optimum temperature of 75 DEG C and an optimum pH value of 3.5-5.0, and is tolerable to the high temperature of 75 DEG C and stable under the pH value of 2.2-8.0. Moreover, as novel high temperature enzyme, the beta-mannase has a great production application value and extensive application prospect in industries of feed, food, medicines, wine brewing, energy and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Yeast gene engineering bacterium and endoinulase preparation and its application method
The present invention provides a yeast gene engineering bacterium Pichia pastoris GS115 / HY005 which is an endo inulase gene obtain by screening strain from Aspergillus by means of PCR method or DNA library hybridization method. It can be cloned and inserted into Pichia yeast integration expression vector, then the obtained expression vector containing endoinulase gene is introduced into Pichia yeast, then a yeast gene engineering bacterium capable of high-effectively expressing endoinulase can be screened. The enzyme activity of the endoinulase prepared with said yeast gene engineering bacterium can be up to above 300 u / ml, and the reaction time for hydrolyze inulin with it is short, and its conversion rate is high, so that it can high-effectively economically convert and prepare oligofructose.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Expression system
The present invention relates to methods for increasing the secretion of a protein of interest (POI) from a eukaryotic cell comprising co-expression of a POI and of at least one protein that enhances protein secretion, said enhancing protein being selected from the group consisting of BMH2, BFR2, C0G6, C0Y1, CUP5, IMH 1, KIN2, SEC31, SSA4 and SSE1. The invention further relates to a yeast promoter sequence, in particular to a promoter sequence of the PET9 gene of P. pastoris, having, under comparable conditions, an increased promoter activity relative to a promoter sequence of the GAP protein. The invention further relates to an expression vector comprising such a promoter sequence and to the use of such an expression vector for expression of a POI in a host cell. The invention further relates to new yeast promoter sequences of genes from P. pastoris, which are useful for expression of a POI in yeast.
Owner:POLYMUN SCI IMMUNBIOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNG
Novel adenovirus vector and production method for same
ActiveCN103146753AImprove recombination efficiencyShorten the timeMicroorganism librariesFermentationYeastYeast gene
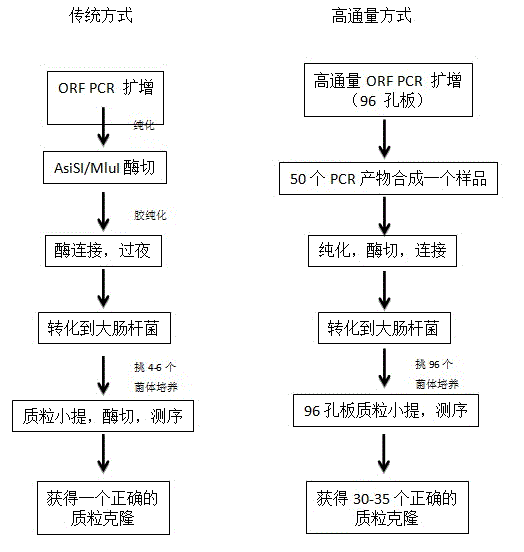
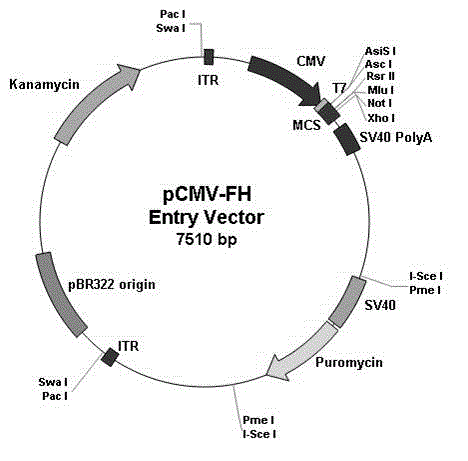
The invention relates to a novel adenovirus vector and a production method for the same. The production method comprises two main steps of: 1, cloning exogenous genes in shuttle vectors; and 2, recombining the shuttle vectors with adenovirus framework vectors. According to the novel adenovirus vector and the production method disclosed by the invention, the shuttle vectors used are -pCMV-FH improved on the basis of pShuttle-CMV carriers; the adenovirus framework vectors are formed by cloning a yeast gene for expressing ISceI in the existing adenovirus framework vectors; and a recombination strain used is SW102. Both of the method for cloning the shuttle vectors, and the method for recombining the shuttle vectors with the adenovirus framework vectors disclosed by the invention adopt high-flux production methods, and 99% of shuttle vectors can be recombined in the adenovirus framework vectors by repeatedly operating the high-flux method for cloning the shuttle vectors and the high-flux method for recombining to the fifth round. The recombining efficiency of the high-flux method for producing the adenovirus framework vectors is up to 85-90%, the experimental steps are greatly simplified, the time is greatly shortened, and the experimental cost is obviously decreased.
Owner:SHANDONG VIGENE BIOSCI
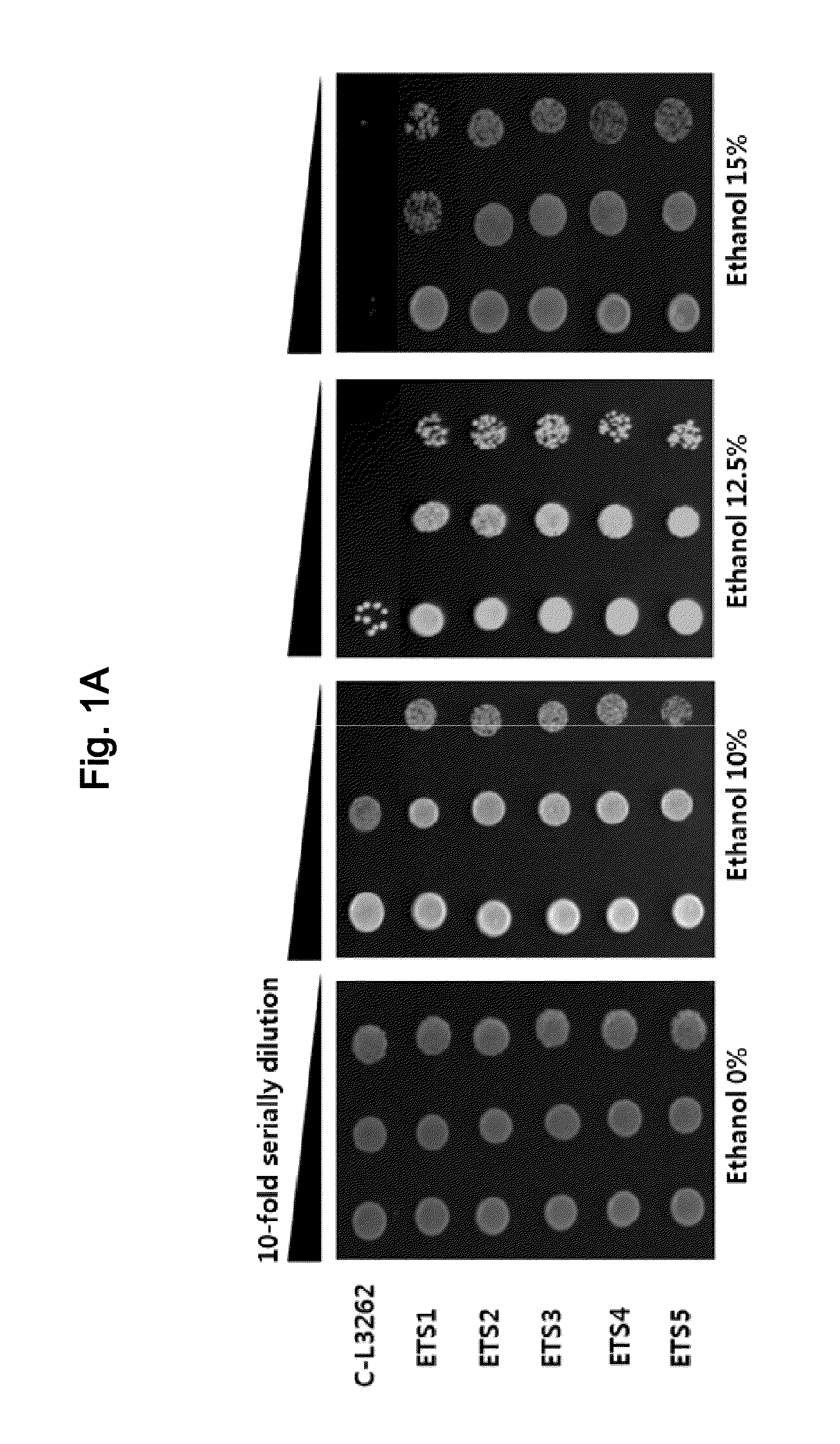
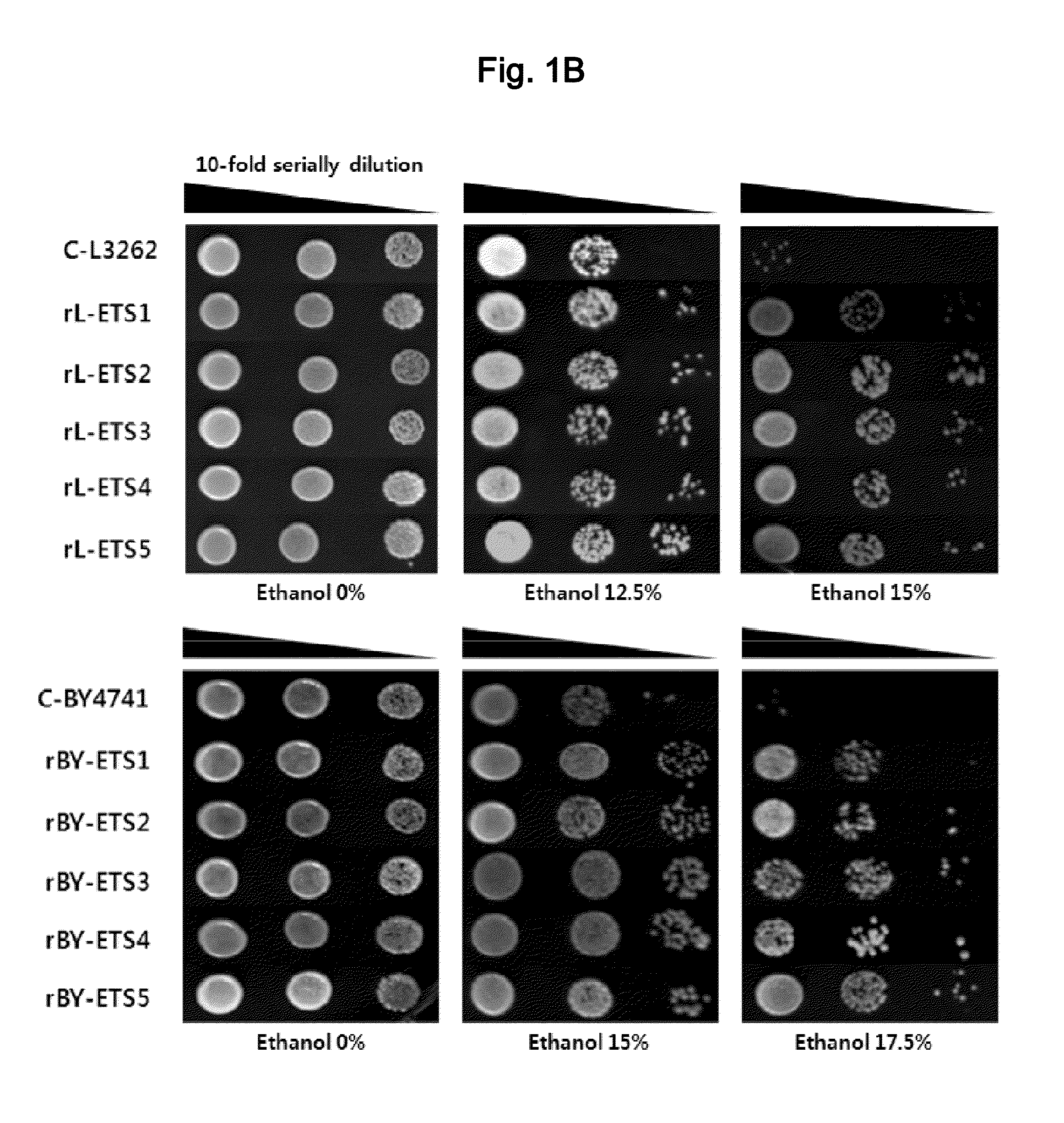
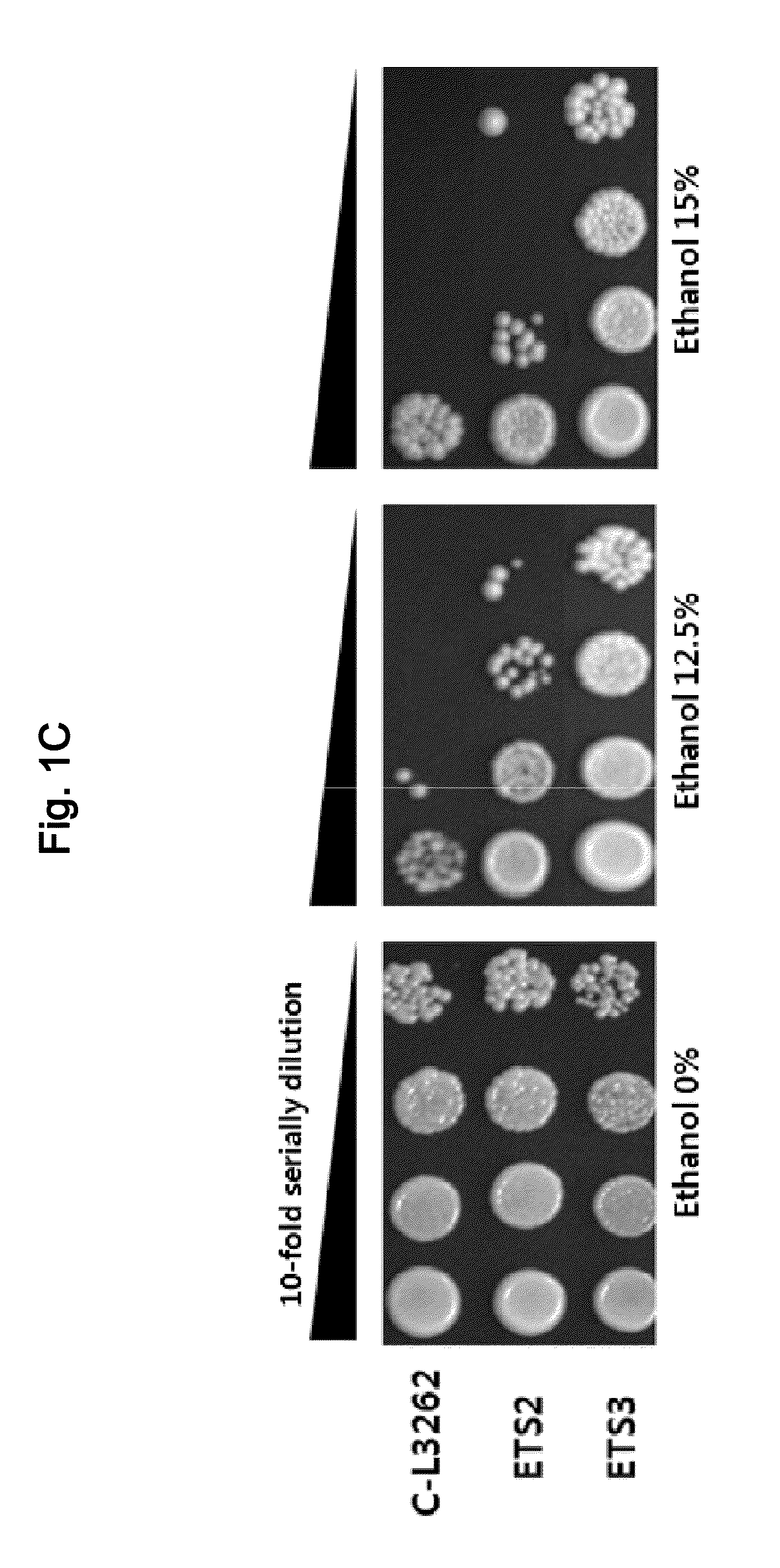
Ethanol-Resistant Yeast Gene, and Use Thereof
The present invention relates to a gene associated with ethanol tolerance, and yeast strains and uses using the same. The yeast strain of this invention may growth under the condition not only with high-concentration ethanol, preferably 6-15% ethanol, but also in high osmotic pressure, preferably 30-40% glucose or sucrose. The present inventors developed yeast strains resistant to high-concentration glucose and ethanol, suggesting that they would be valuably applied to much effective ethanol production, and also be utilized as a superbacteria having tolerance to various stresses for ethanol production with high efficiency.
Owner:EWHA UNIV IND COLLABORATION FOUND
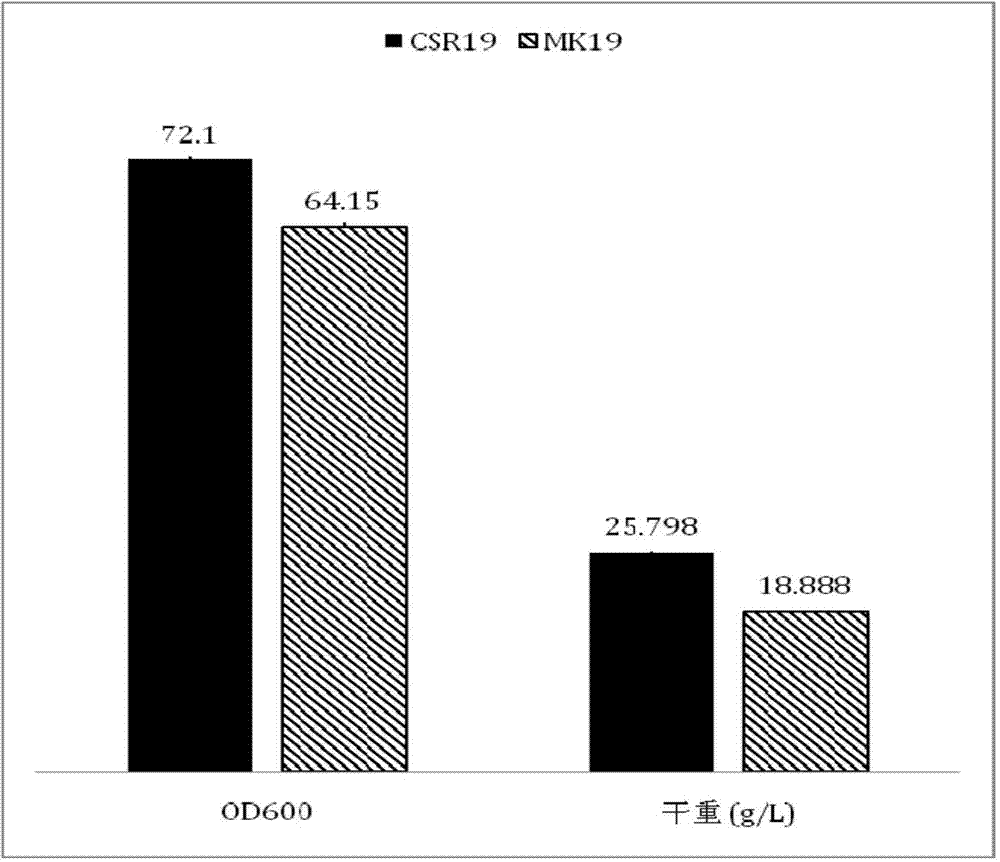
Phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene
InactiveCN104278015AImprove conversion efficiencyIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBinding site
The invention discloses a phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently an over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. The invention provides a phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield, obtained by over-expressing an endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. A phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain (MK19-pGBKT7crtS) capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield is obtained by over-expressing the astaxanthin synthetase gene crtS by virtue of free plasmids and the strain is named CSR19. An endogenous ribosome bind site sequence (Rbs. sequence for short) exists in front of the crtS gene expressed by the strain. By virtue of fermentation cultivation and in comparison with a receptor strain MK19, the astaxanthin yield of the engineering strain is increased by 33.5%, and the engineering strain is good in stability, and thus, the phaffia rhodozyma strain has a good application prospect in the feed industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
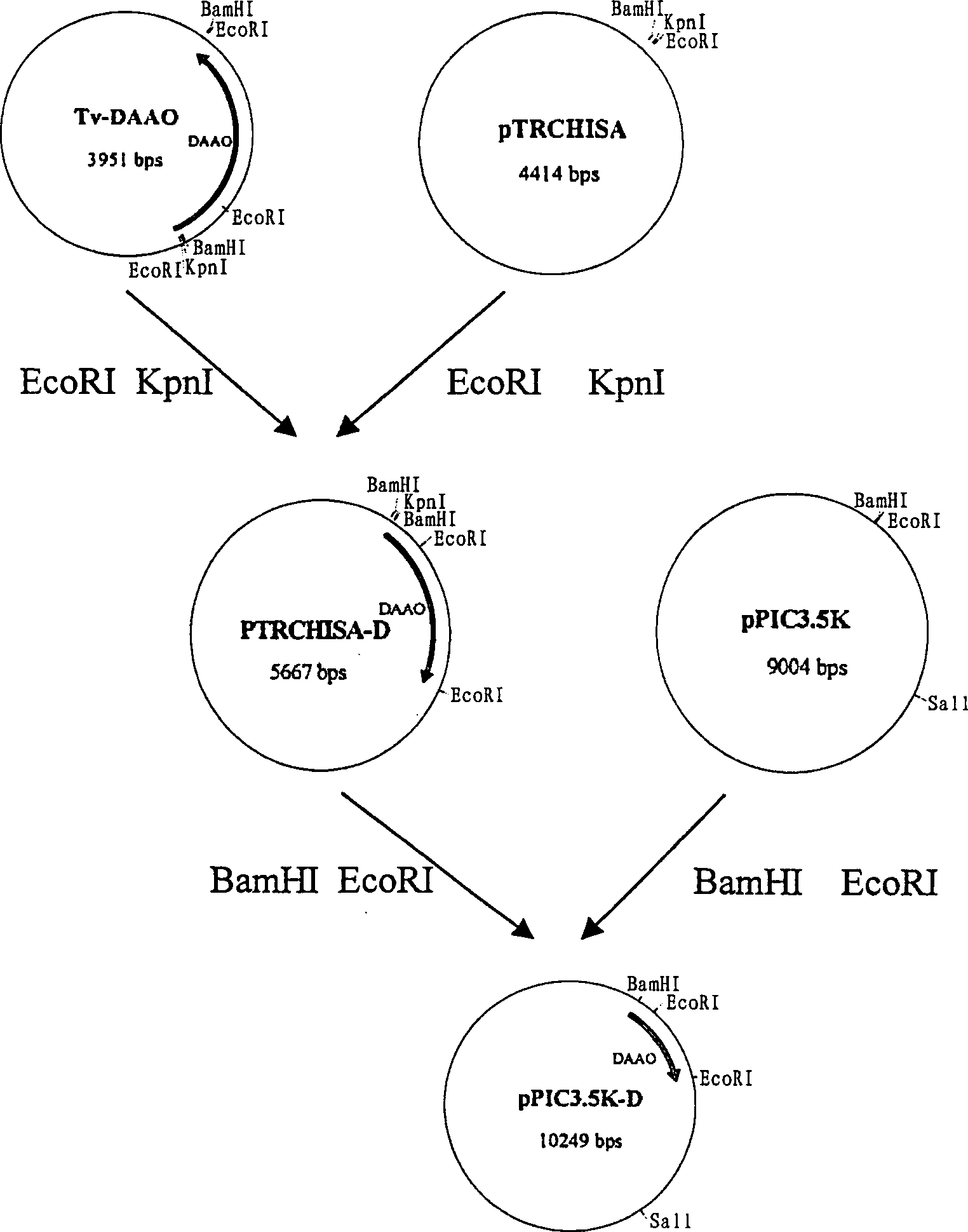
High-efficient expression D-amino acid oxidase methanol yeast, its construction and fermentation method
InactiveCN1385521ASimple fermentation conditionsLow costFungiFermentationYeastD-Amino-Acid Oxidase Gene
The present invention discloses a methanol yeast gene engineering bacterium strain SIBAS 0111 originated from high-effective expression D-amino acid oxidase, its D-amino acids oxidase gene is originated from trigonopsis vriabllis. Said inventions is characterized by that it utilizes the construction, transformation and screening of recombinant expression plasmid pPIC 3.5K-DAAO to obtain recombinant gene engineering bacterium strain of high-yield D-amino acid oxidase. After fermentation expression the expression level of D-miano acid oxidase in fermentation liquor can be upto 23000 U / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder, feed additive, premix and batch
The invention belongs to the field of animal feed and particularly relates to porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder, feed additive containing the porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder, premix and batch. A preparation method of the porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder includes fermenting bacterial strain, which carries porcine beta defensin-2 gene, of yeast genetic engineering, taking supernatant for ultrafiltration, sequentially adding protective agent, wall material and carrier to ultrafiltrate, and performing spray drying. The porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder expressed by Pichia pastoris having antibacterial activity, and activity of porcine beta defensin-2 can be stored to a maximum extent by combining a spray-drying method and an encystation technology. In addition, the porcine beta defensin-2 is not damaged after invitro-simulation of artificial gastric juice, and released porcine beta defensin-2 has high activity.
Owner:宿迁大北农饲料有限责任公司 +2
Yeast gene engineering bacteria and heat resistant alkali resistant xylanase preparation and application method
A genetically engineered yeast GS115 / HB705 able to effectively express the high temp and alkali resistant xylanase is disclosed, which can be used to prepare said xylanase through culture, separation and purifying, and in turn the oligoxylose.
Owner:桂林精成生物科技有限公司
Novel expression enzyme yeast gene engineering system
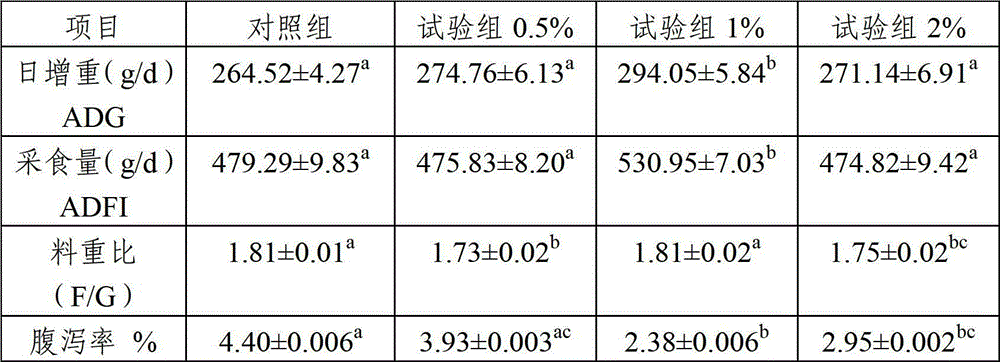
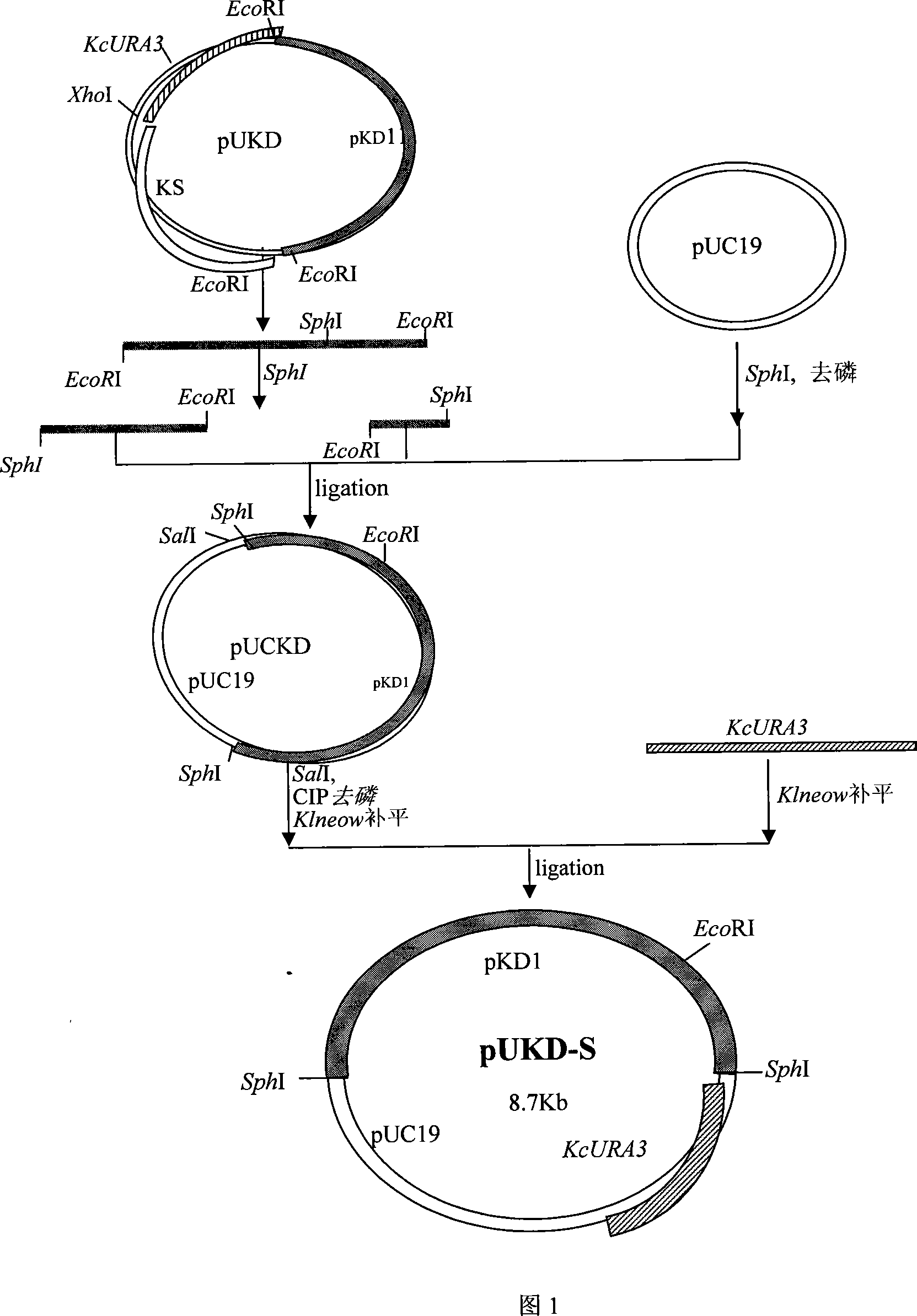
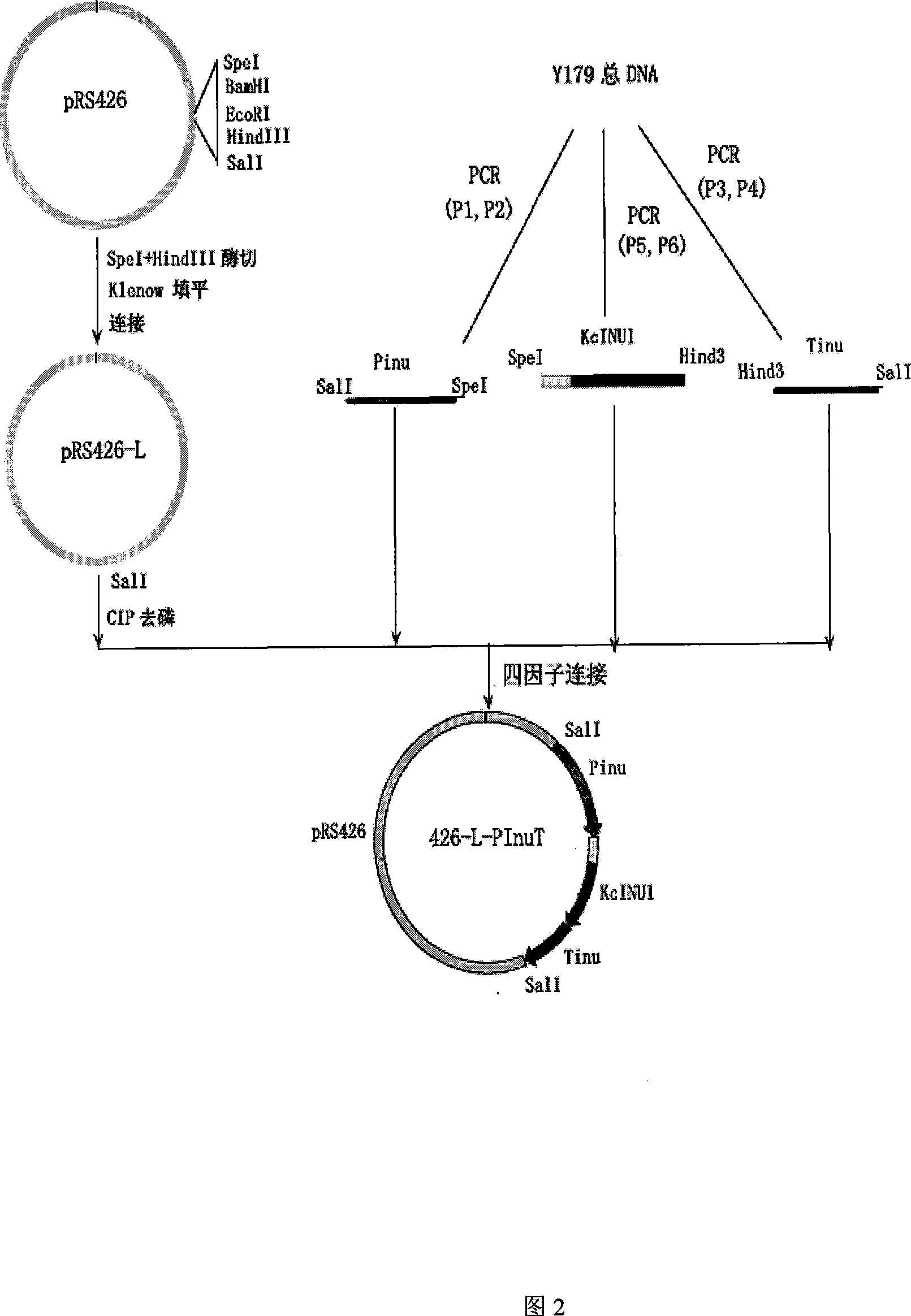
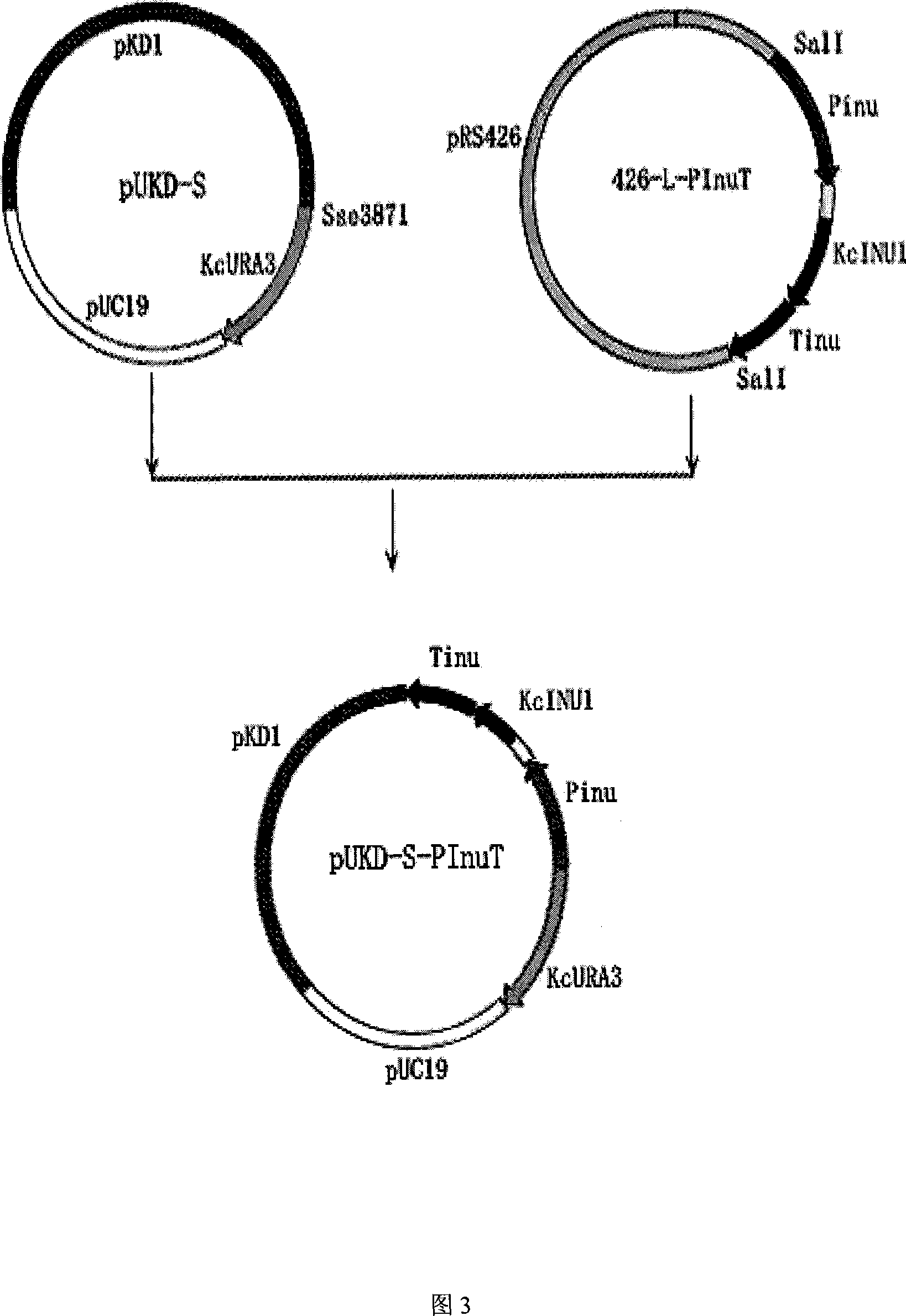
The invention pertains to the biological gene engineering technical field, in particular to a yeast gene engineering system of expressing enzyme which comprises the construction of an expression box which consists of Bengal grain kluyveromyces promoter, terminator and inulase gene with signal peptide, the construction of high-stable inulase gene expression plasmid by inserting the expression box into a carrier pUKD-S, the construction of gene engineering bacteria of expressing inulase with high efficiency by importing Bengal grain kluyveromyces host Y179ura3- and the production of inulase by using the constructed Bengal grain kluyveromyces gene engineering bacteria. The invention could also be used for expressing and producing other endogenetic, exogenous, natural and recombinant enzymes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
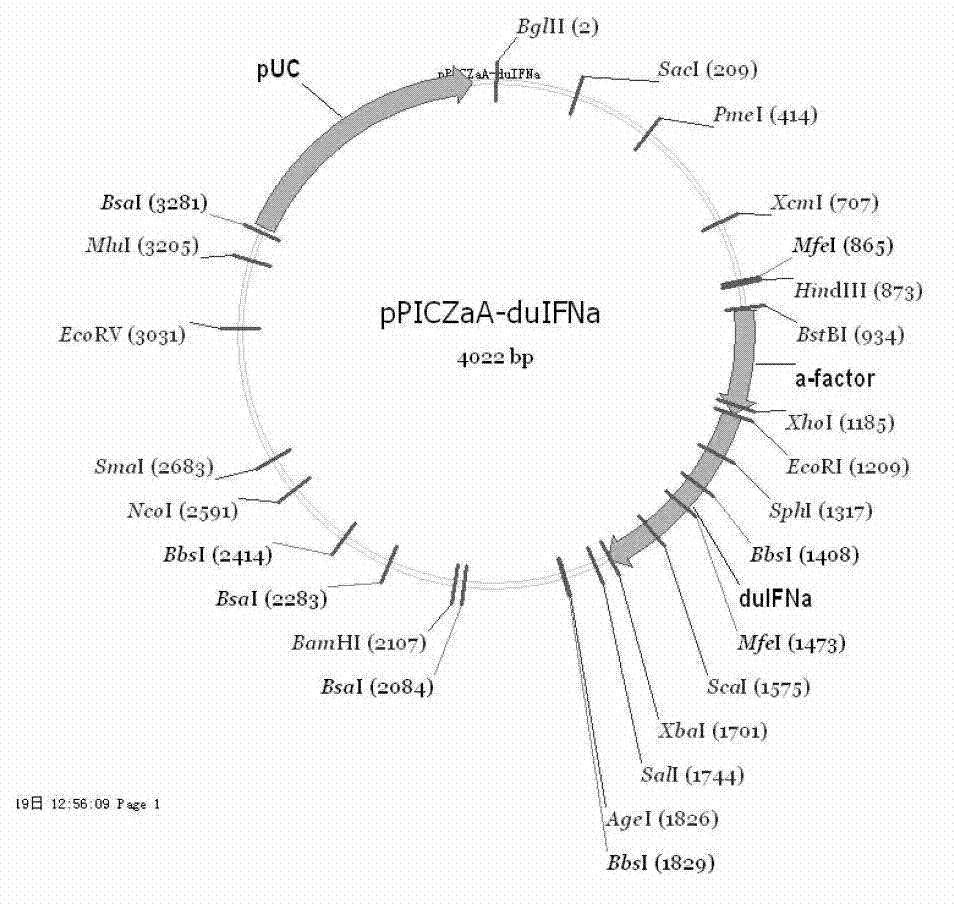
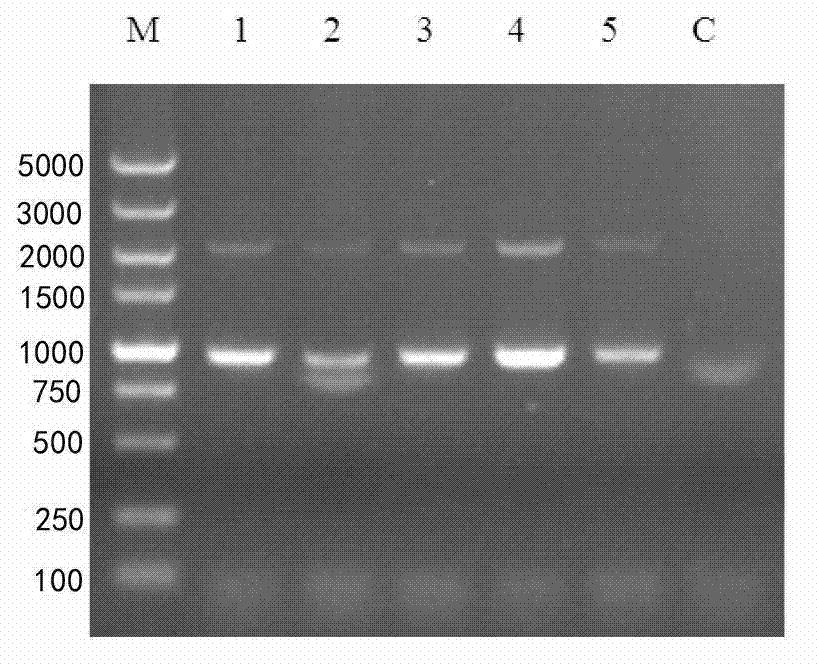
Complex duck interferon-alpha gene, and recombinant vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a complex duck interferon-alpha gene, and a recombinant vector and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the complex duck interferon-alpha gene is disclosed as SEQ ID NO:1. The optimized complex duck interferon-alpha gene can be expressed in Pichia yeast gene engineering bacteria to produce complex duck interferon-alpha. The obtained complex duck interferon-alpha has the following advantages: high purity: the thin-layer chromatography scanning on the yeast-expressed duck interferon-alpha SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) result indicates that the target ribbons of the recombinant yeast duck interferon-alpha account for more than 80% of the total expression proteins; and high antivirus action: compared with the yeast-expressed natural duck interferon-alpha, the protein expressed by the novel genome has higher antivirus activity, and the action of resisting 100TCID50VSV virus infection on duck embryo fibroblasts is enhanced by 40 times. The complex duck interferon-alpha gene can be used for preparing drugs for treating poultry virus diseases.
Owner:广东省农业科学院兽医研究所
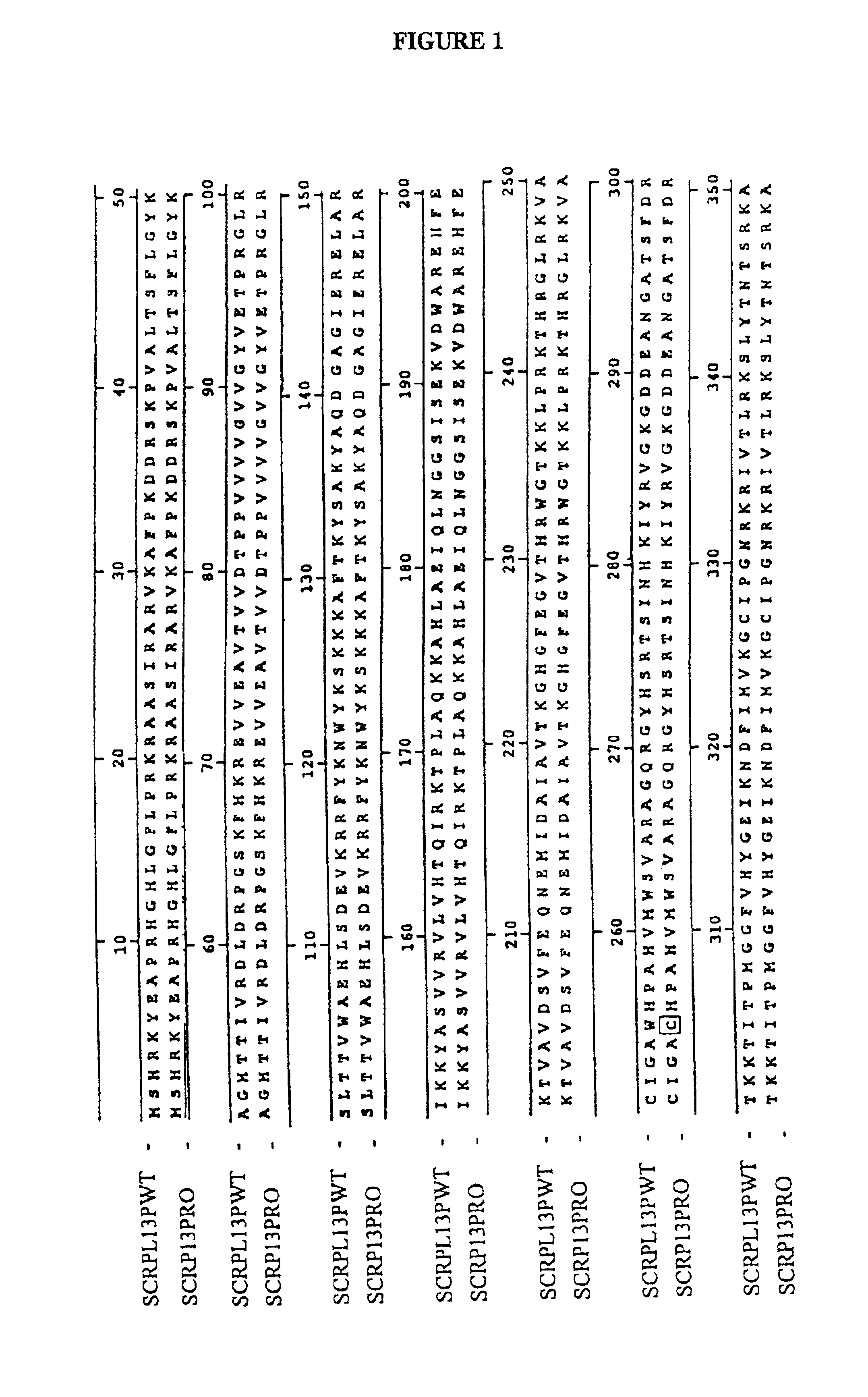
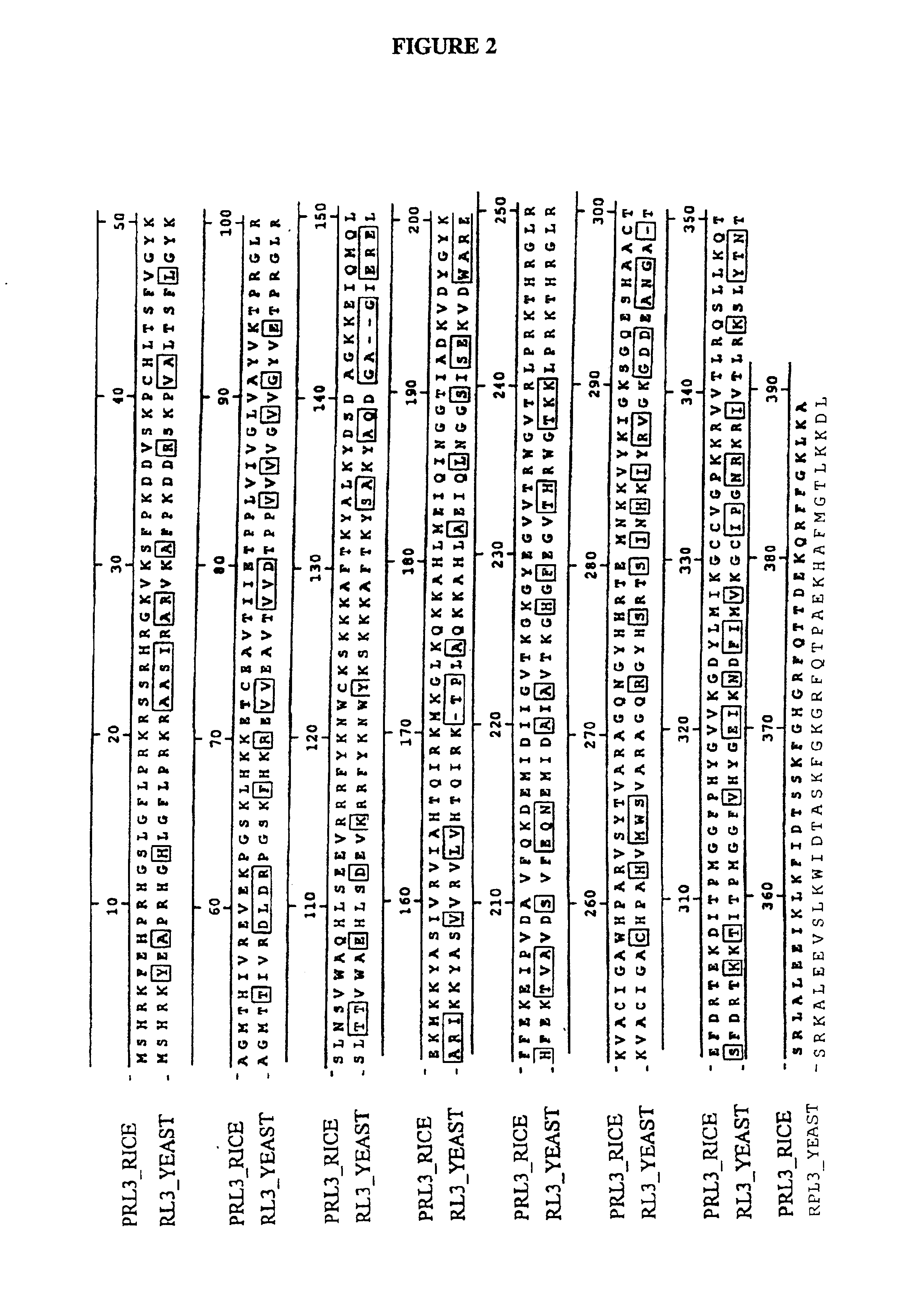
Tolerance of trichothecene mycotoxins in plants through the modification of the ribosomal protein L3 gene
InactiveUS6855872B2Inhibit protein synthesisPreventing initiationSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFungal toxinTriticeae
Fusarium graminearum is a plant pathogen, attacking a wide range of plant species including corn (ear and stalk rot), barley, and wheat (head blight). Fusarium epidemics result in millions of dollars of losses in crop revenues. Fusarium graminearum infection in the cereals reduces both grain yield and quality. Mycotoxins are produced by many fungal Fusarium species and thus the grain becomes contaminated with these mycotoxins, such as the trichothecenes. The major trichothecene produced by F. graminearum is deoxynivalenol (abbreviated as DON, also known as vomitoxin). Trichothecenes are potent protein synthesis inhibitors and are quite toxic to humans and livestock. A yeast gene has been identified which confers upon yeast tolerant of the trichothecene, trichodermin. A corresponding plant gene has been prepared, which has been used to transform plants. These transformed plants have an increased resistance to Fusarium infestation.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD +1
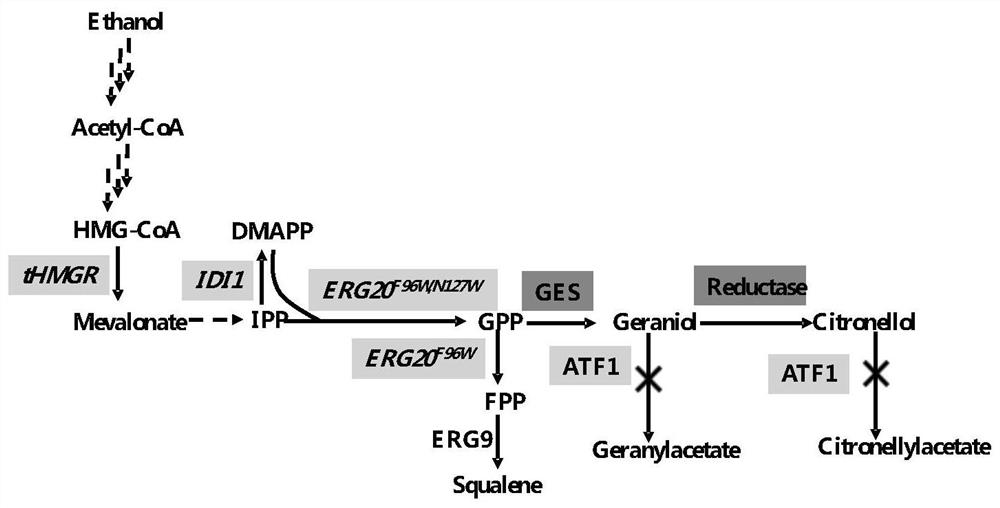
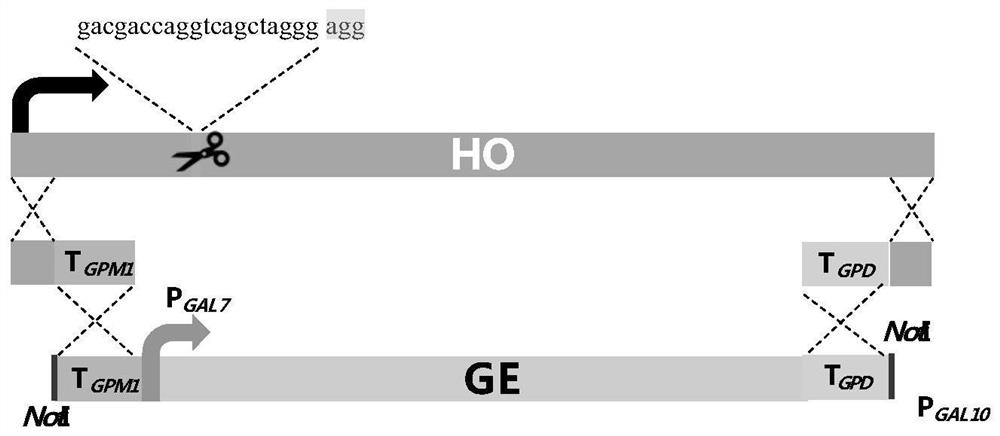
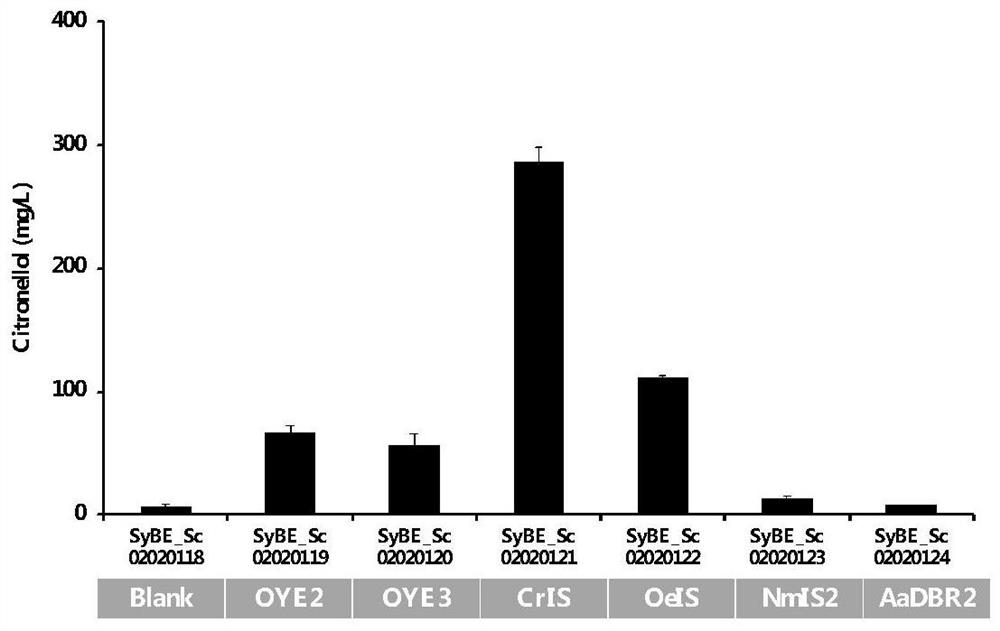
Yeast genetically engineered strain for high yield of citronellol as well as construction method and fermentation method of yeast genetically engineered strain
The invention relates to the technical field of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain construction and fermentation, in particular to a yeast genetically engineered strain for high yield of citronellol as well as a construction method and fermentation method of the yeast genetically engineered strain. The transformation of the yeast genetically engineered strain comprises the following steps: transferring one or more of CrIS, NmIS2, OeIS, OYE2 and OYE3 genes; mutating ERG20 of a yeast chassis strain into ERG20F96W; and introducing a protein scaffold consisting of SH3, PDZ and GBD while isomerase IDI1, reductase CrIS and fusion protein GE are expressed, so that a protein complex is assembled. Compared with the prior art, the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is more environmentally-friendly and low in cost, and a green and efficient method is provided for citronellol production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Gene traceless editing carrier and application of gene traceless editing carrier to organism gene editing
ActiveCN108676811AIndustrial Production SafetyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCell wall
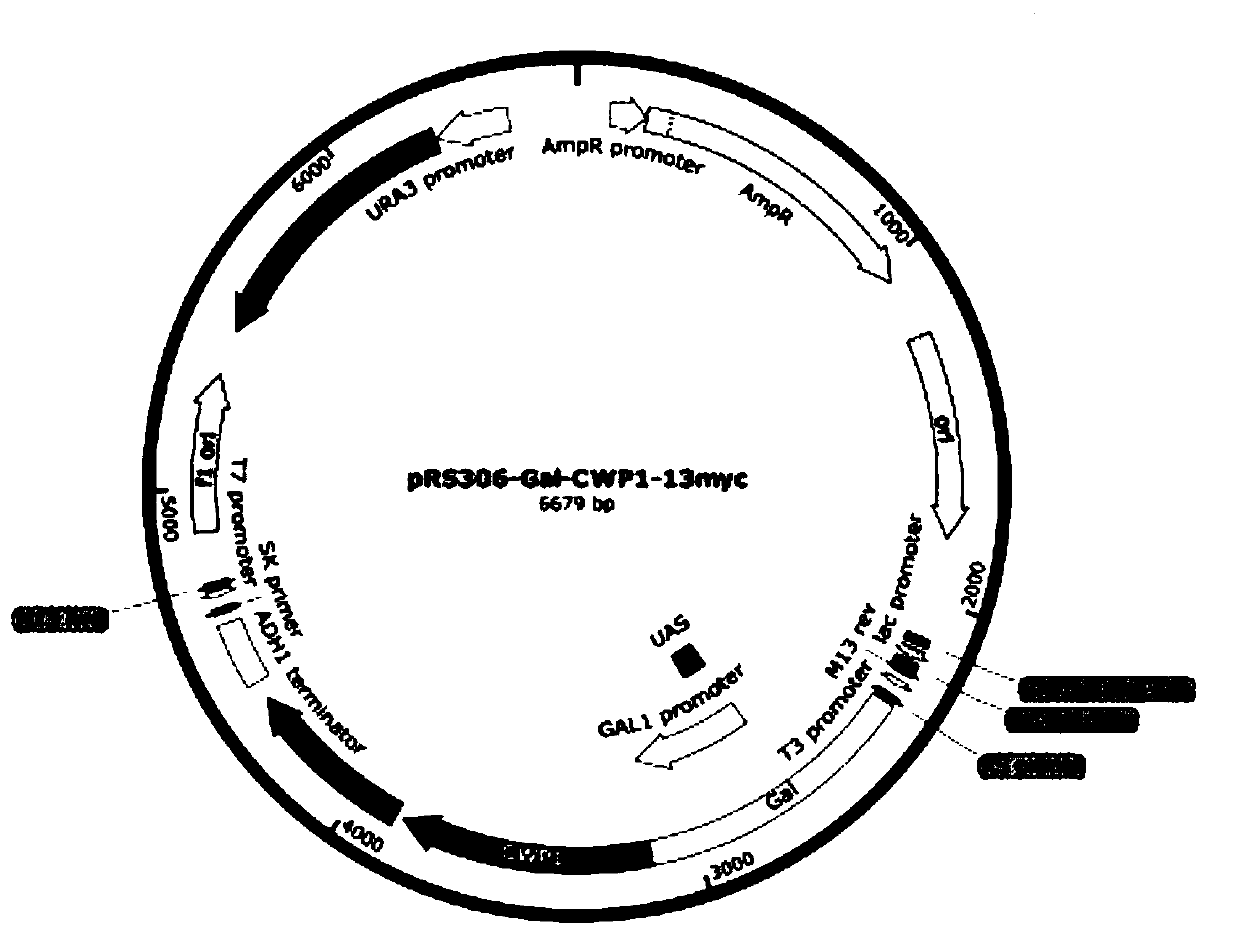
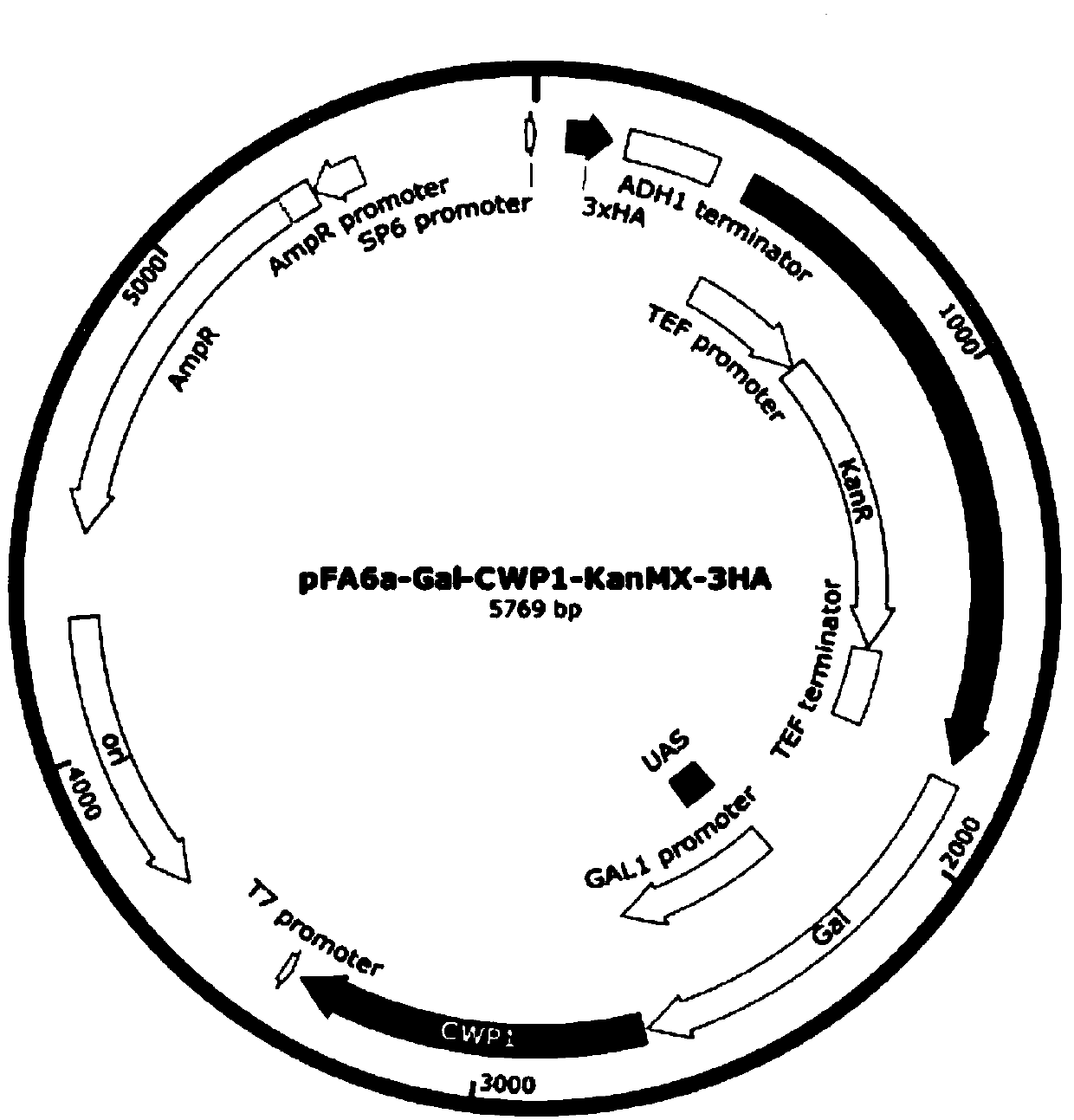
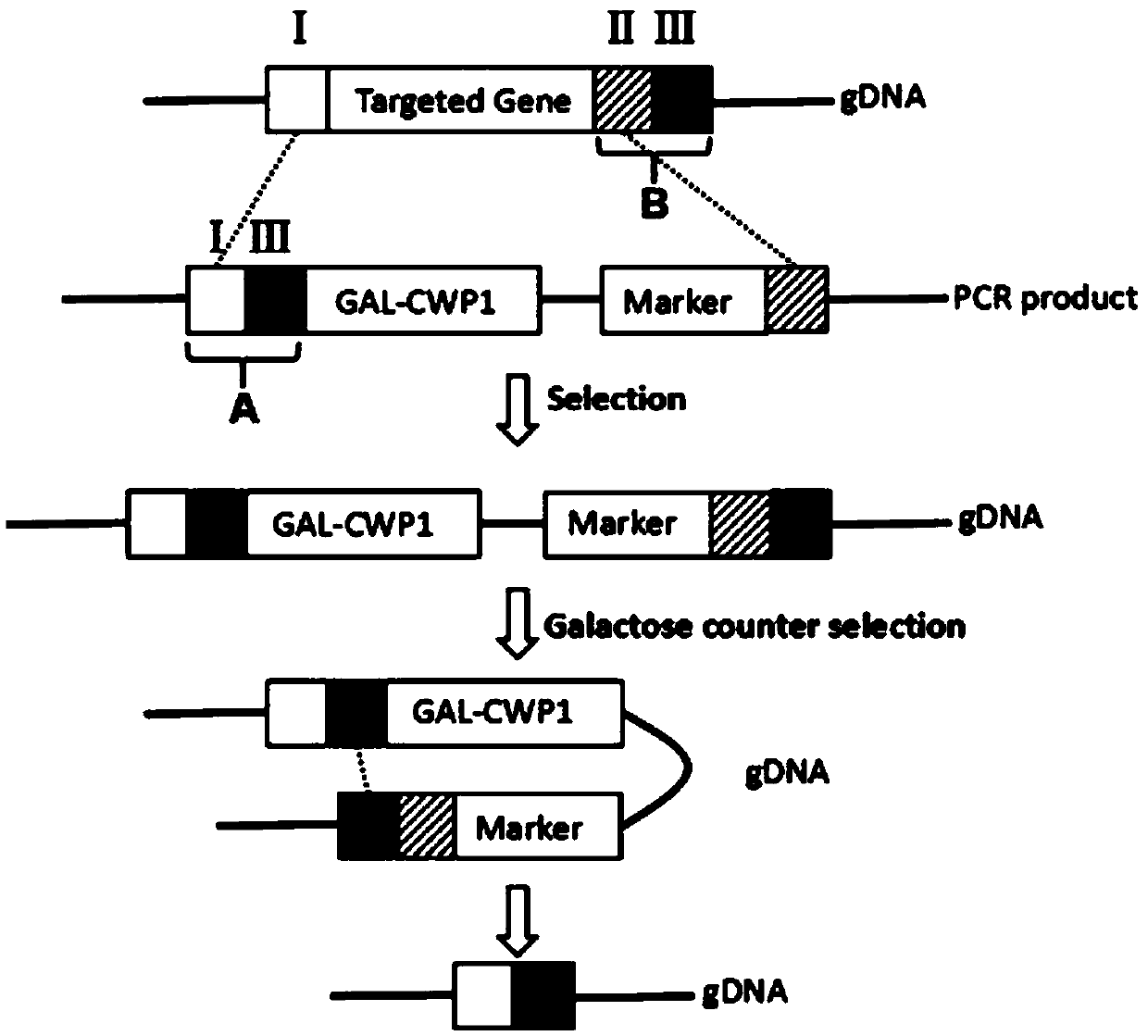
The invention discloses a gene traceless editing carrier and application of the gene traceless editing carrier to organism gene editing. The gene traceless editing carrier consists of a genome homology sequence A, a promoter sequence, a cell wall protein CWP1 gene sequence, a resistance screening report gene sequence and a genome homology sequence B. By aiming at the problems that during the saccharomyces cerevisiae traditional gene knockout, screening markers are remained, the multigene knockout research is inconvenient, and the exogenous gene is remained, the invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae efficient gene traceless editing method. The method can be used for saccharomyces cerevisiae gene editing and can also be applicable to other microorganisms of the gene editing principle. The gene traceless editing carrier can be used for studying the function and metabolic mechanism of the yeast gene; no any exogenous gene is remained at an obtained mutant strain; the gene tracelessediting carrier can be safely used for industrial production.
Owner:河北福赛农业科技有限公司
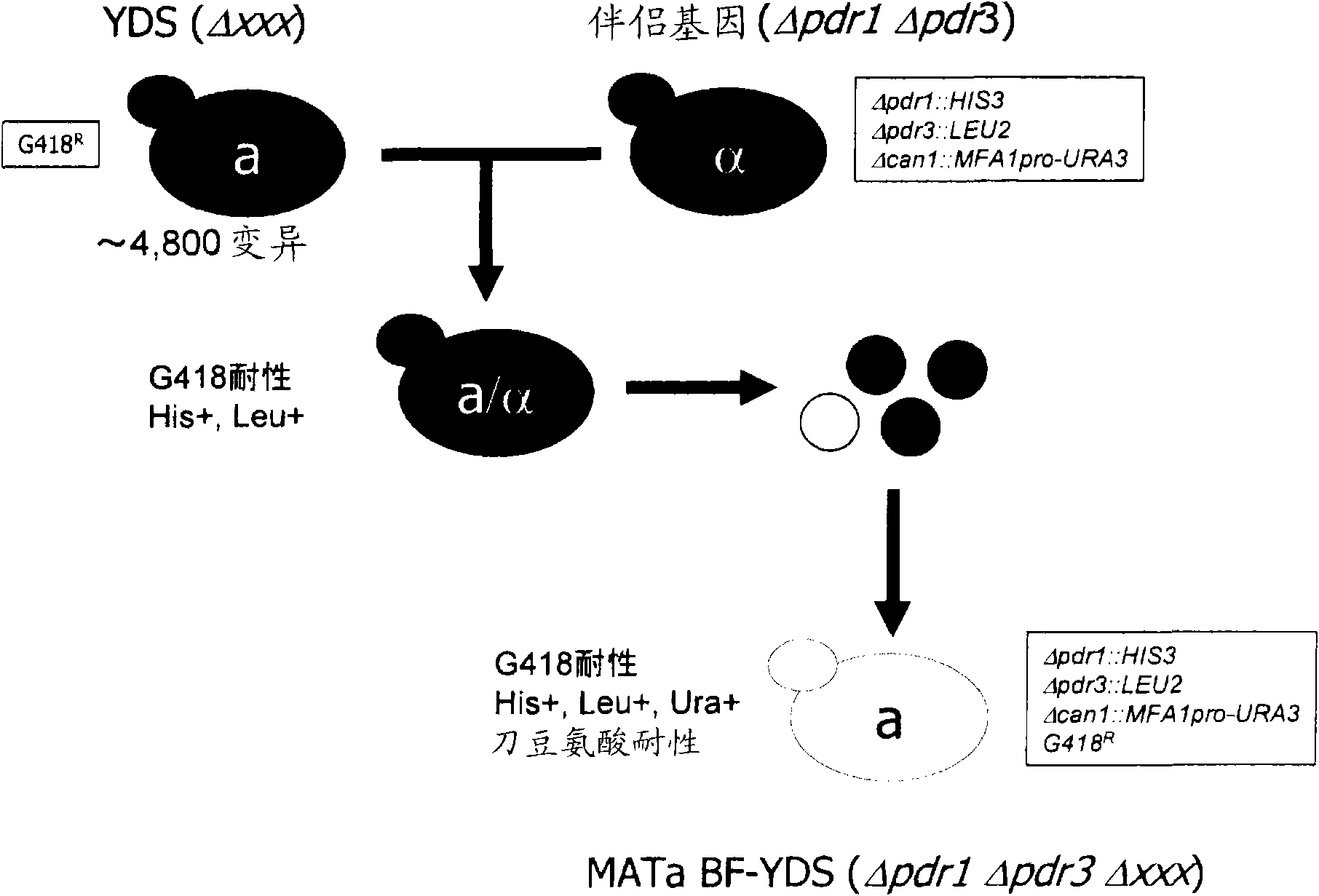
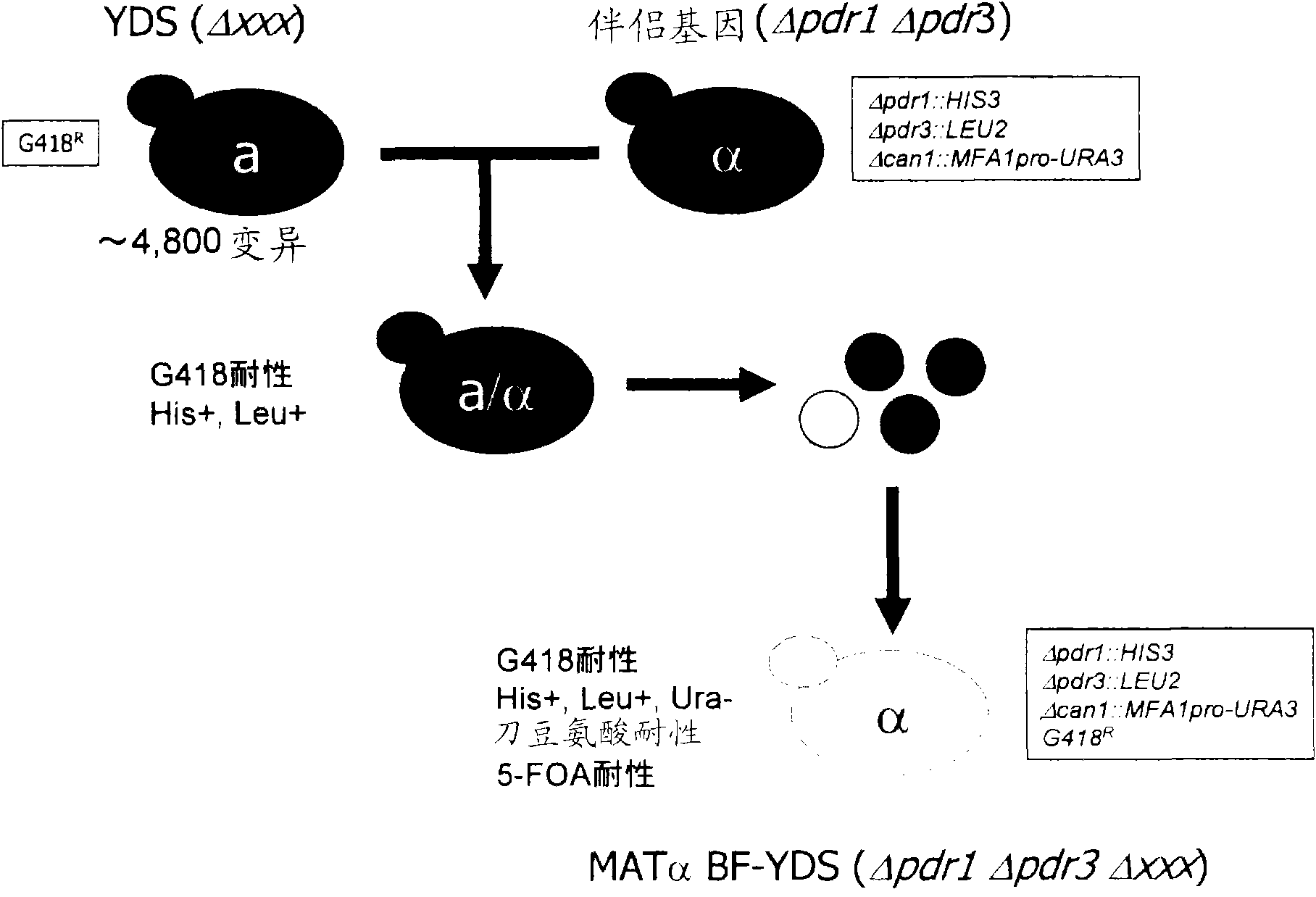
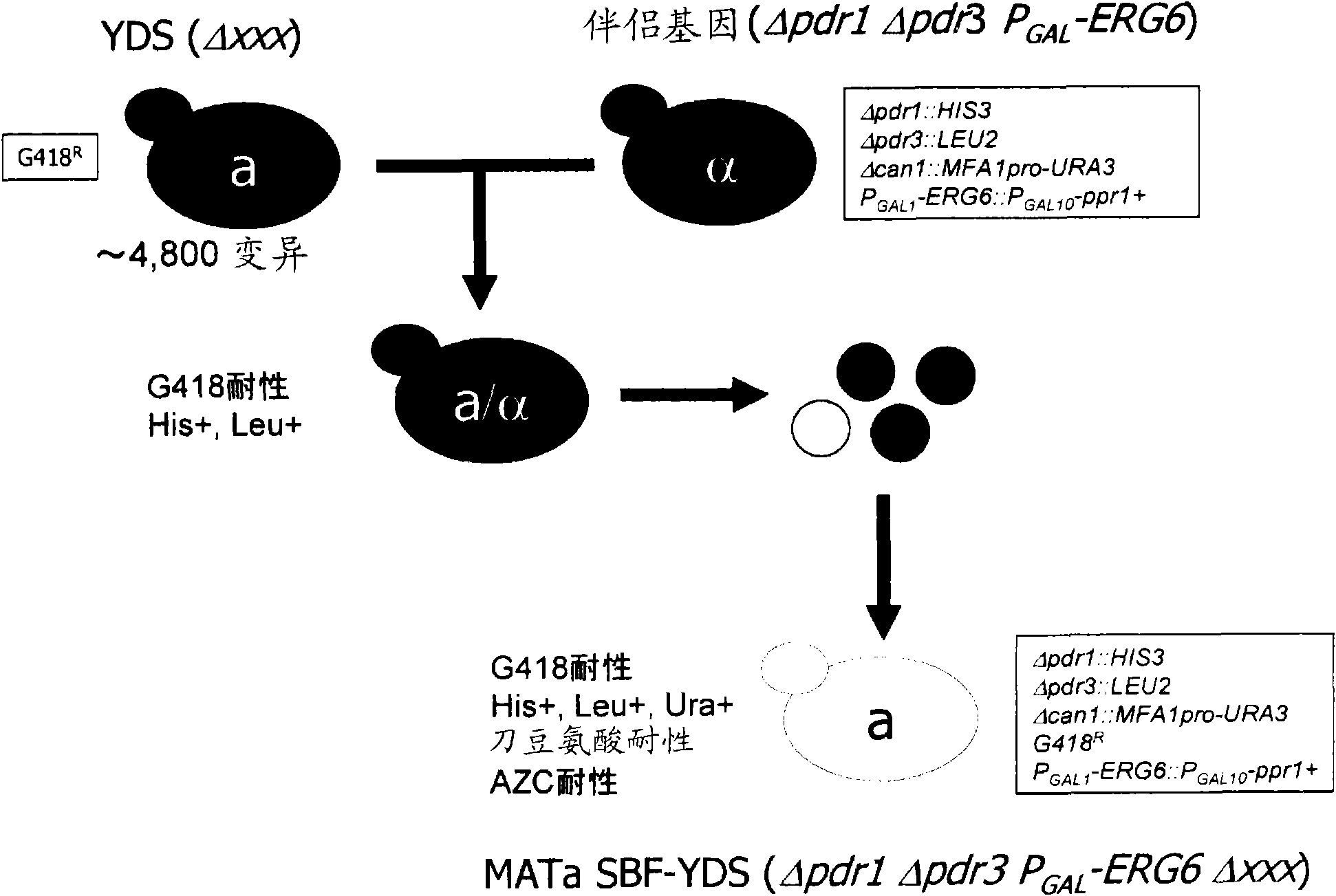
Set of yeast cells, method of identifying target candidate molecule, method of analyzing action mechanism and screening method
InactiveCN101688199AIncrease drug sensitivityImprove high sensitivityCompound screeningFungiBiotechnologyYeast
It is intended to provide a set of yeast gene knockout strains whose drug sensitivity has been significantly improved. A set of yeast cells of the invention is a set of yeast cells comprising two or more species of yeast cells, wherein at least one mutually different gene has been deleted or mutated in each of the two or more species of yeast cells, and all the two or more species of yeast cells are drug hypersensitive yeast cells in which the expression of at least one drug sensitivity-related gene has been regulated.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Overexpressed phosphorylcholine cytidine transferase saccharomyces cerevisia genetically engineered bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107488603AImprove permeabilityThe biotransformation process is convenient and fastFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyPhosphorylcholine
The invention relates to overexpressed phosphorylcholine cytidine transferase saccharomyces cerevisia genetically engineered bacteria as well as a construction method and application thereof. The construction method comprises the steps of cloning saccharomyces cerevisia sourced gene cct capable of encoding phosphorylcholine cytidine transferase to a pYES2.0-Kanmx carrier so as to construct recombinant plasmid pYES2.0-Kanmx-cct, and transferring the recombinant plasmid pYES2.0-Kanmx-cct into S.cerevisiae HG, so as to obtain the saccharomyces cerevisia genetically engineered bacteria. The yield of a solid matter of the strain to fermentable sugar is 50%-56%, the strain can be used for manufacturing a citicoline product from 5'-cytidine monophosphate and phosphorylcholine through bioconversion, and after the strain reacts for 7 hours, the molar conversion ratio reaches up to 73%. The yield of the strain in a fermentation system for producing and culturing the strain is high. When applied to the production of citicoline, the strain has the advantages of low cost and manufacturing energy consumption, short reaction period and the like.
Owner:NANTONG QIUZHIYOU BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Processes for detecting toxic substances
InactiveUS20070287155A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiotechnologyYeast gene
Biology-based processes for detecting toxic substances are provided. The processes comprise detecting mRNA that is expressed in the presence of toxic substances by a cell comprising a yeast gene as followed, or a gene that is homologous to the yeast genes and is derived from other species, wherein the mRNA corresponds to said yeast gene or said homologous gene thereof.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com