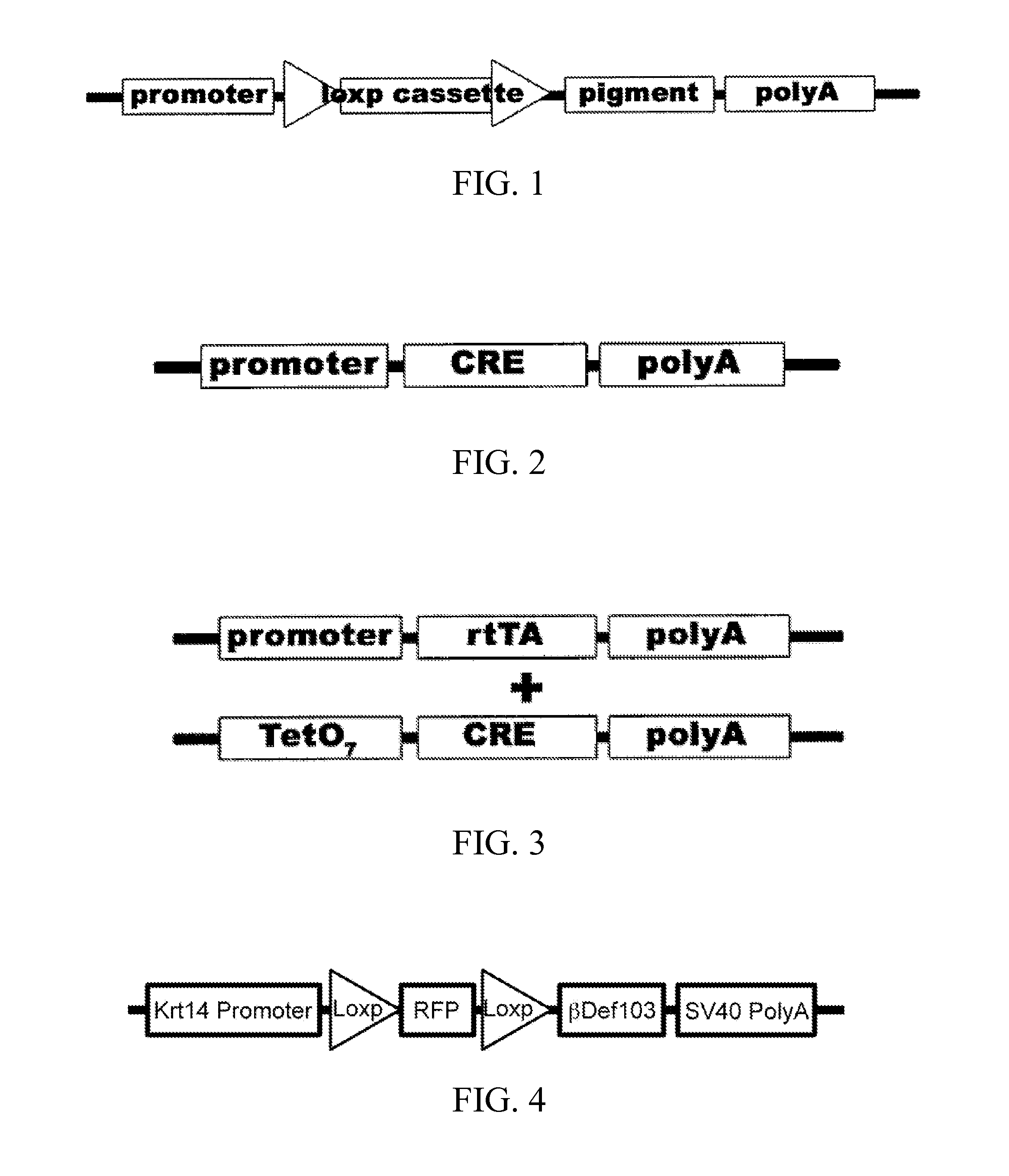
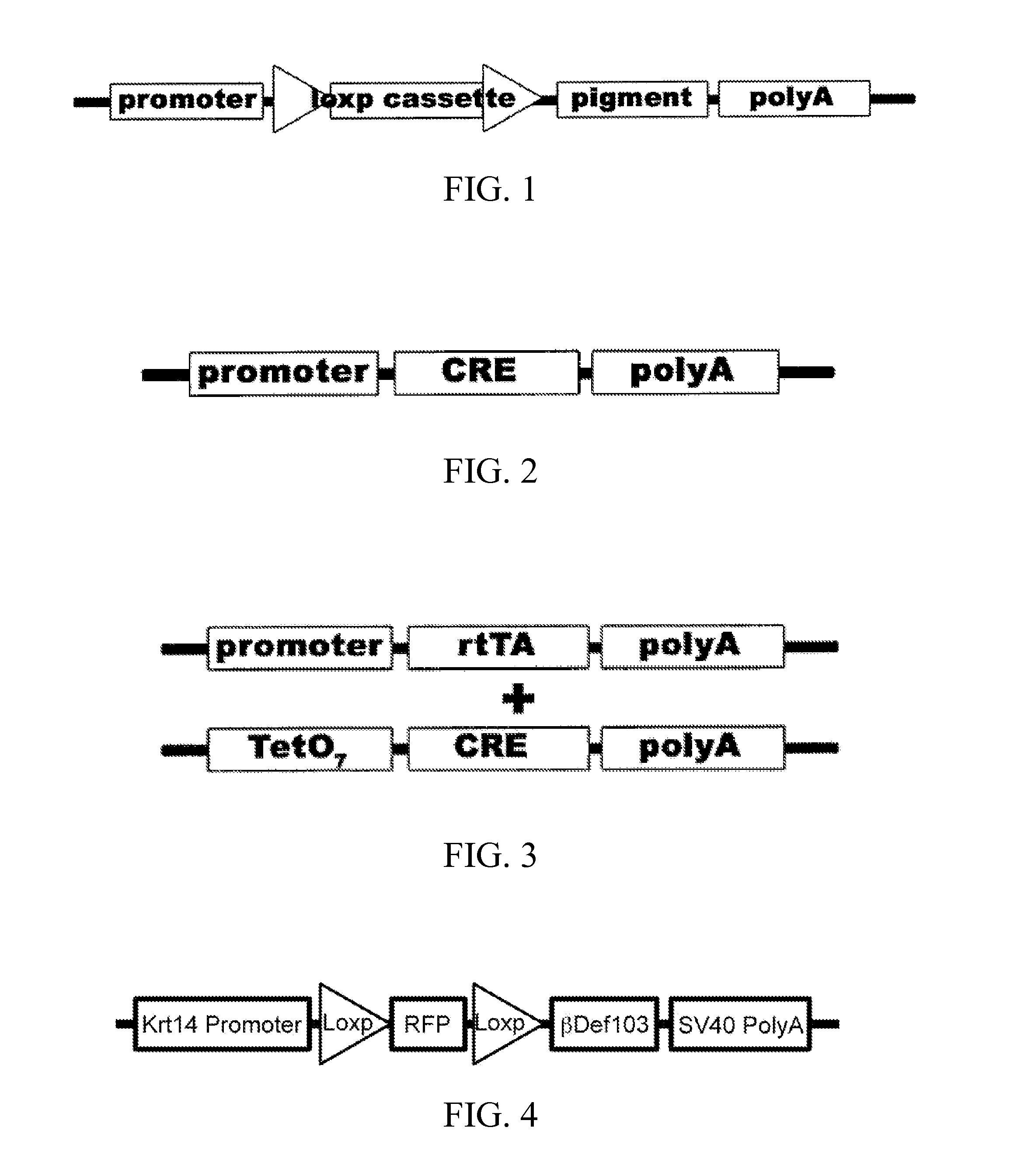
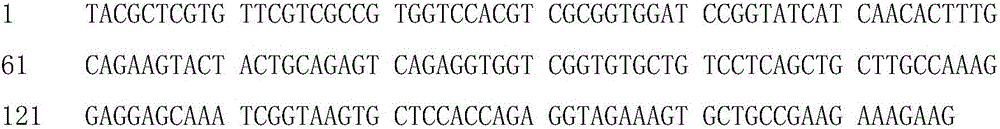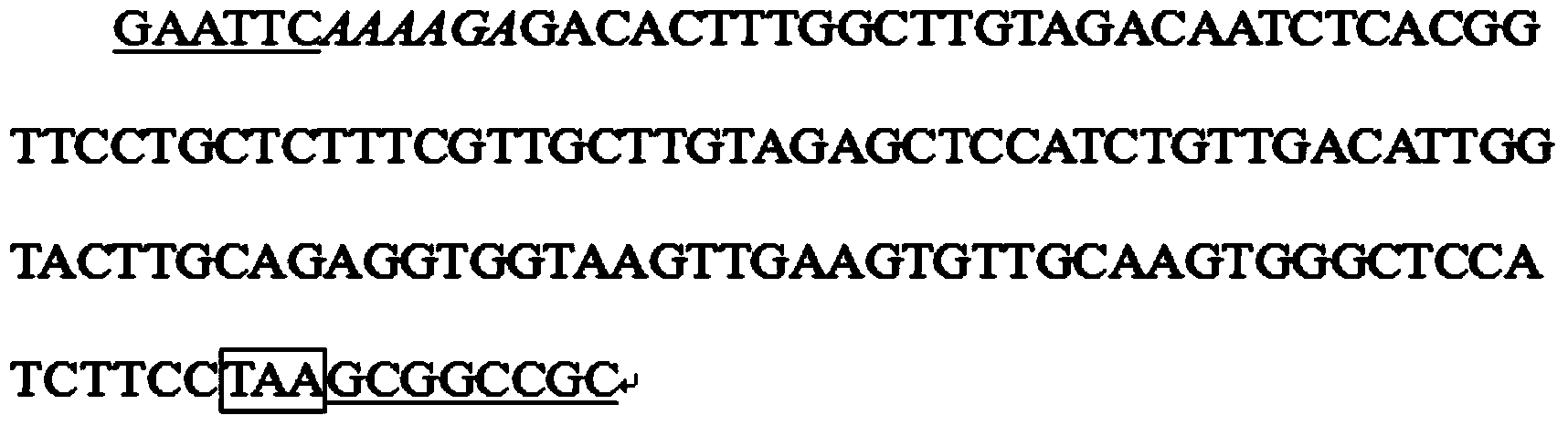Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Beta defensin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Beta defensins are a family of mammalian defensins. The beta defensins are antimicrobial peptides implicated in the resistance of epithelial surfaces to microbial colonization. Defensins are 2-6 kDa, cationic, microbicidal peptides active against many Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, fungi, and enveloped viruses, containing three pairs of intramolecular disulfide bonds. On the basis of their size and pattern of disulfide bonding, mammalian defensins are classified into alpha, beta and theta categories. Every mammalian species explored thus far has beta-defensins. In cows, as many as 13 beta-defensins exist in neutrophils. However, in other species, beta-defensins are more often produced by epithelial cells lining various organs (e.g. the epidermis, bronchial tree and genitourinary tract.
Active ingredients stimulating type 2 and/or type 3 human beta-defensins and cosmetic or pharmaceutical compositions containing such active ingredients
The invention relates to active ingredients capable of stimulating direct or indirect expression of type 2 human beta-defensins and / or type 3 human beta-defensins. The invention thus provides an active ingredient capable of stimulating direct or indirect expression of type 2 human beta-defensins and / or type 3 human beta-defensins, characterized in that said active ingredient does not cause any inflammatory, irritation or intolerance reactions. The invention also provides a screening method for the selection of such active ingredients. The invention is applicable to the preparation of cosmetic or pharmaceutical compositions containing such active ingredients.
Owner:YVES SAINT LAURENT PARFUMS SOCIETE ANONYME +1
Immunologic regulation by theta defensins
InactiveUS20080255052A1Deleterious effectInhibit microbial growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBeta defensinImmuno modulation
The invention provides a method of inhibiting undesirable microbial contamination, invasion, or growth in an individual by administering to the individual an effective amount of a theta defensin. The invention additionally provides a method of inhibiting deleterious effects resulting from microbial contamination, invasion, or growth in an individual by administering to an individual an effective amount of a theta defensin, whereby immune-mediated pathology is limited and immune function is improved.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antimicrobial peptide freeze-dried preparation for treating colpitis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104043098AStrong anti-inflammatory, anti-itch and anti-bacterialProtect physical and mental healthOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtozoaCancer cell
The invention provides a freeze-dried preparation for treating colpitis. The preparation includes an antimicrobial peptide freeze-dried powder and an antibacterial peptide basic liquid. The antibacterial peptide freeze-dried powder comprises the following components according to the total mass percentage: 0.1%-8% of an antibacterial peptide human beta defensin, 0.01%-0.2% of a low molecular weight heparin sodium and 1%-15% of a stabilizing agent; the antibacterial peptide basic liquid comprises the following components according to the total mass percentage: 0.01%-0.4% of hyaluronic acid, 0.5%-4% of menthoxypropanediol, 0.5%-5% of a honey extract, 0.5%-5% of PCA sodium, 0.5%-5% of dissolved protease, 0.3%-0.7% of 1,2 hexanediol, 1.5%-6% of oat beta dextran, 1%-5% soybean isoflavone, and the balance of deionized water or water for injection. The antimicrobial peptide freeze-dried preparation provided by the invention has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, and strong killing effect on bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa and cancer cells, and even can enhance immunity, accelerate wound healing process; in addition, the preparation has obvious curative effect, and no rebound or side effect.
Owner:广州舒泰生物技术有限公司
Antibacterial peptide GW13 and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN102827255ASimple experimental techniqueLow hemolytic activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBeta defensinCombinatorial chemistry
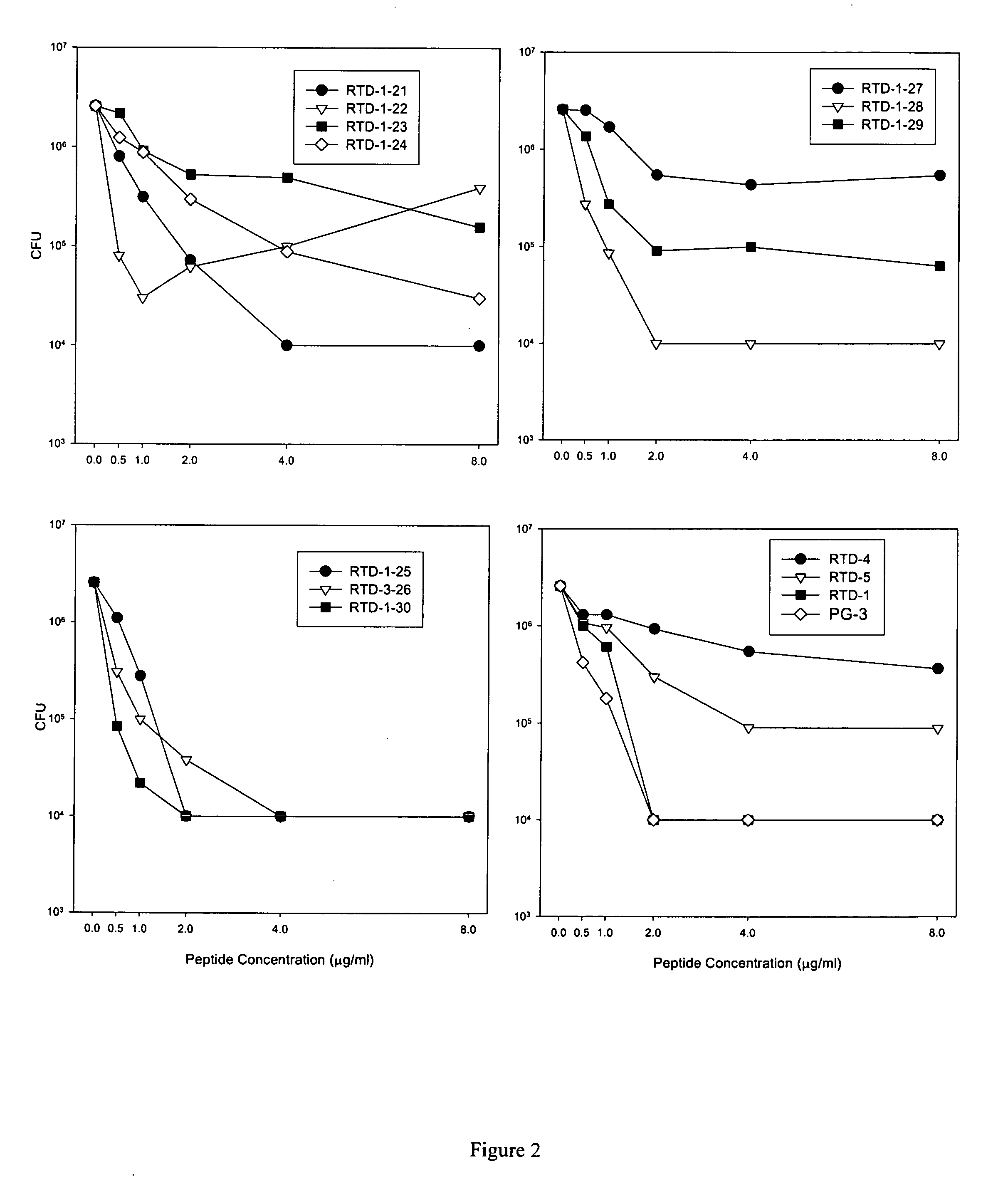
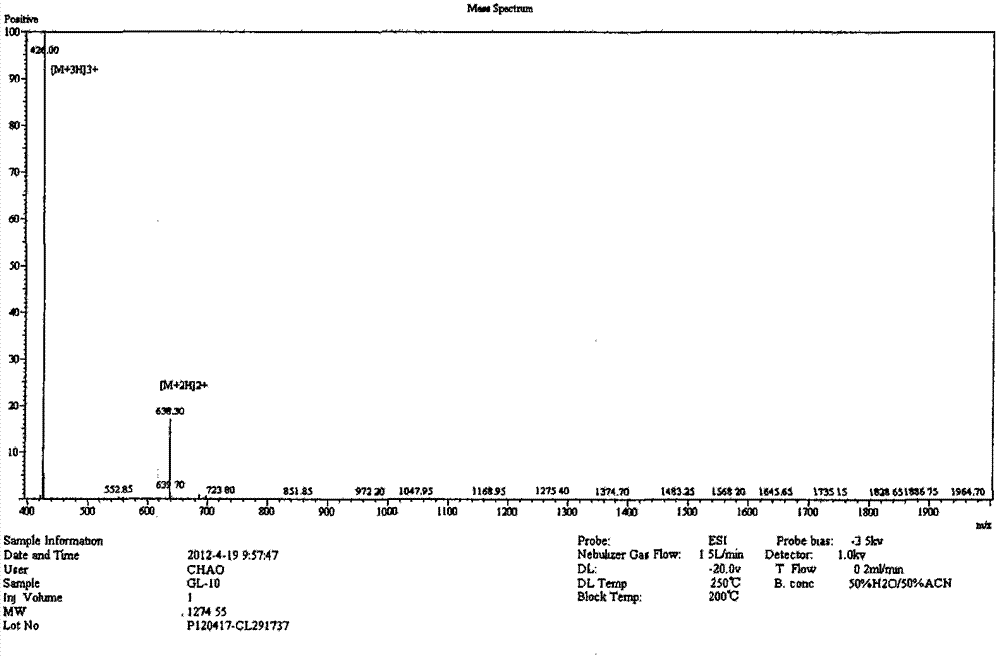
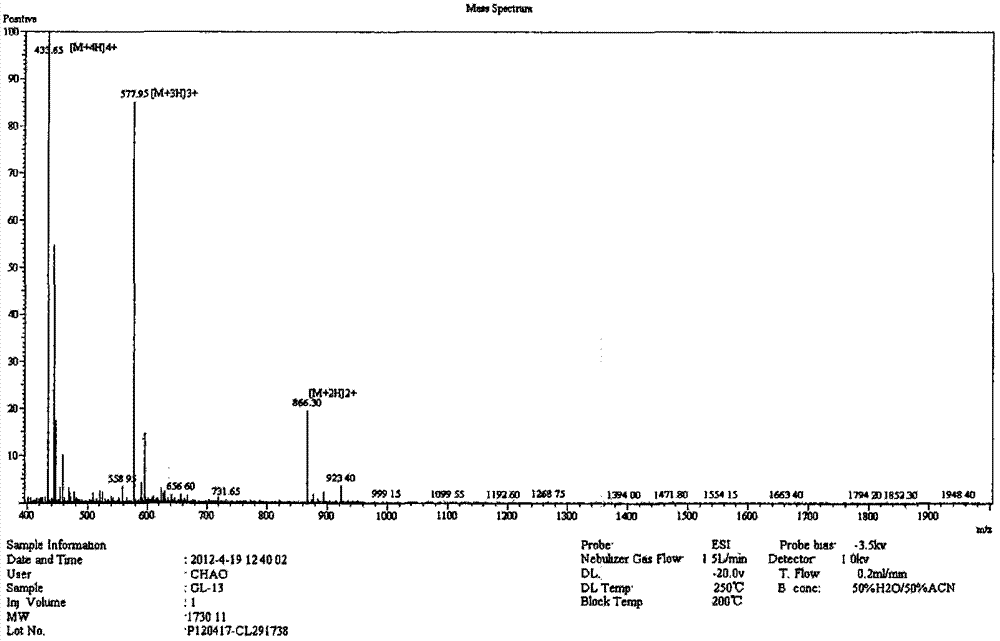
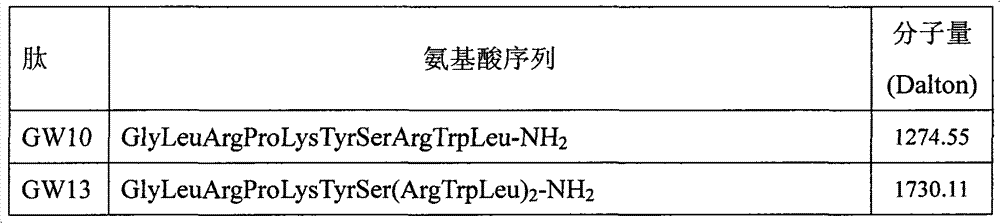
The invention relates to an antibacterial peptide GW13 and its preparation method and use. The antibacterial peptide GW13 has an amino acid sequence of GlyLeuArgProLysTyrSer(ArgTrpLeu)2-NH2. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, cutting out 13 amino acid fragments from a linear chicken beta-defensin 4 carboxyl end by a fixed-point amino acid fragment cutting method, removing disulfide bonds to obtain a GW10 (GlyLeuArgProLysTyrSerArgTrpLeu-NH2) fragment, and repeating connecting characteristic three-residue complexes ArgTrpLeu to obtain the antibacterial peptide GW13, and 2, synthesizing a peptide resin in a polypeptide synthesizer by a solid-phase synthesis method, carrying out TFA cutting to obtain a polypeptide, and carrying out reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography purification. The antibacterial peptide GW13 obtained by the preparation method has strong bacteriostatic activity, low hemolytic activity, the highest therapeutic index and a large development potential.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
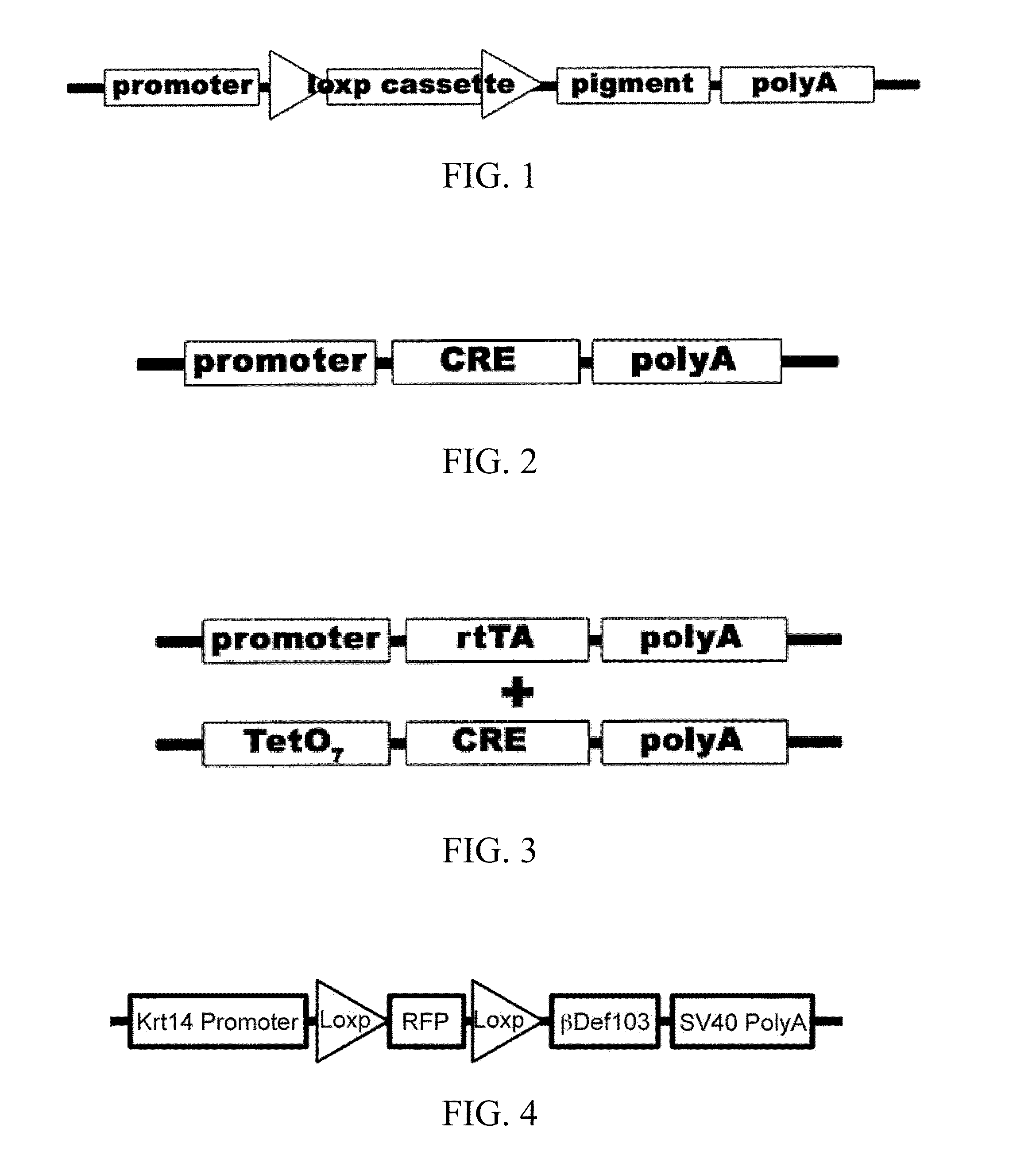
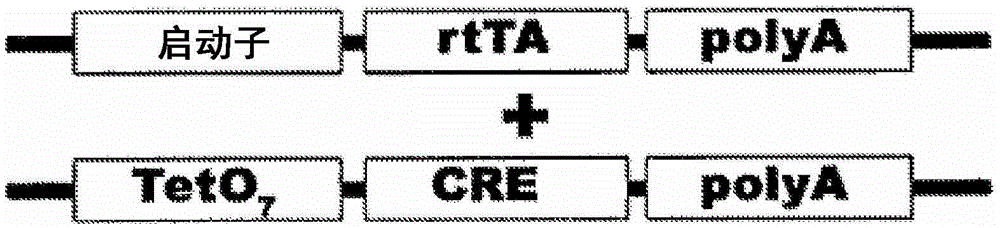
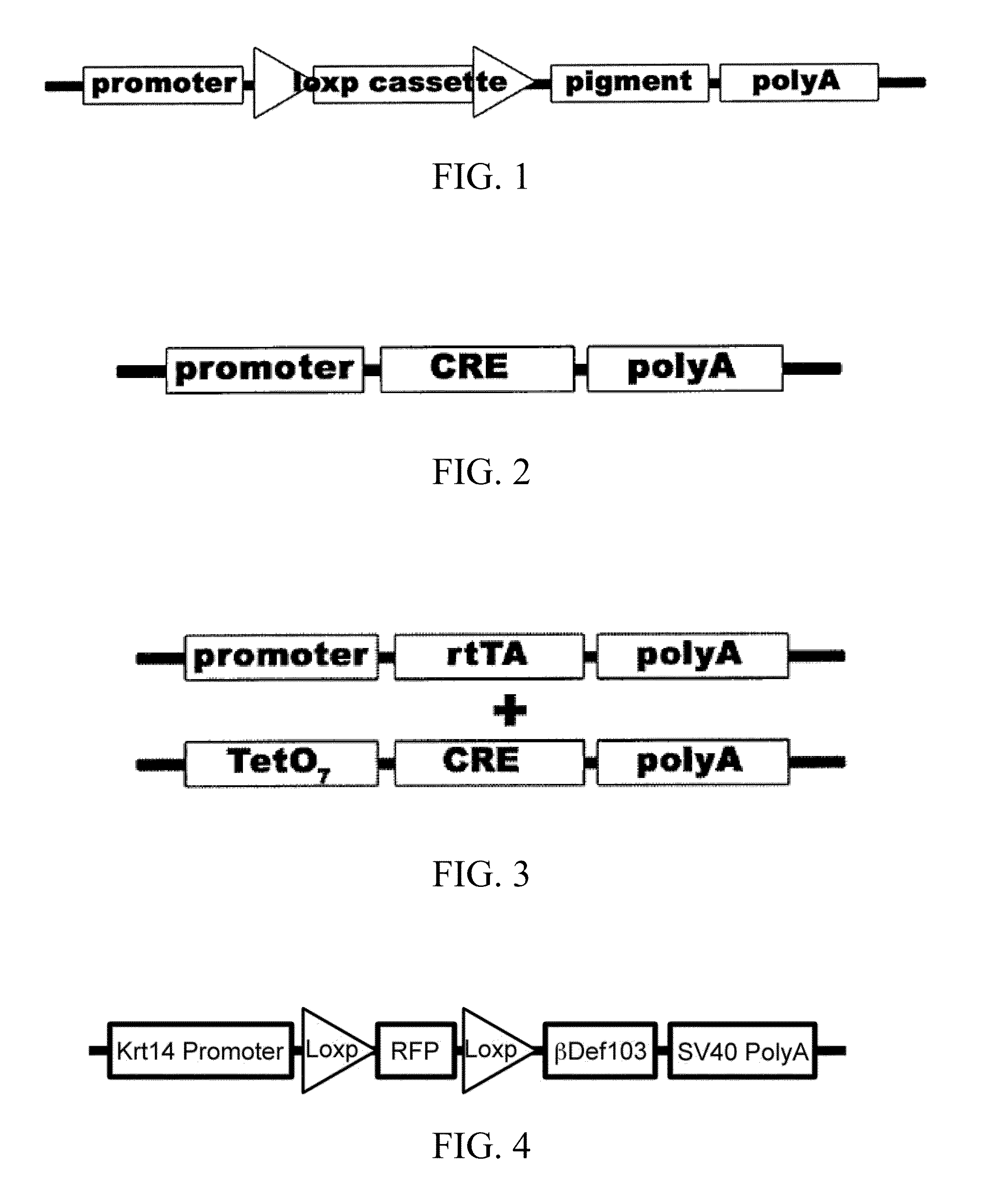
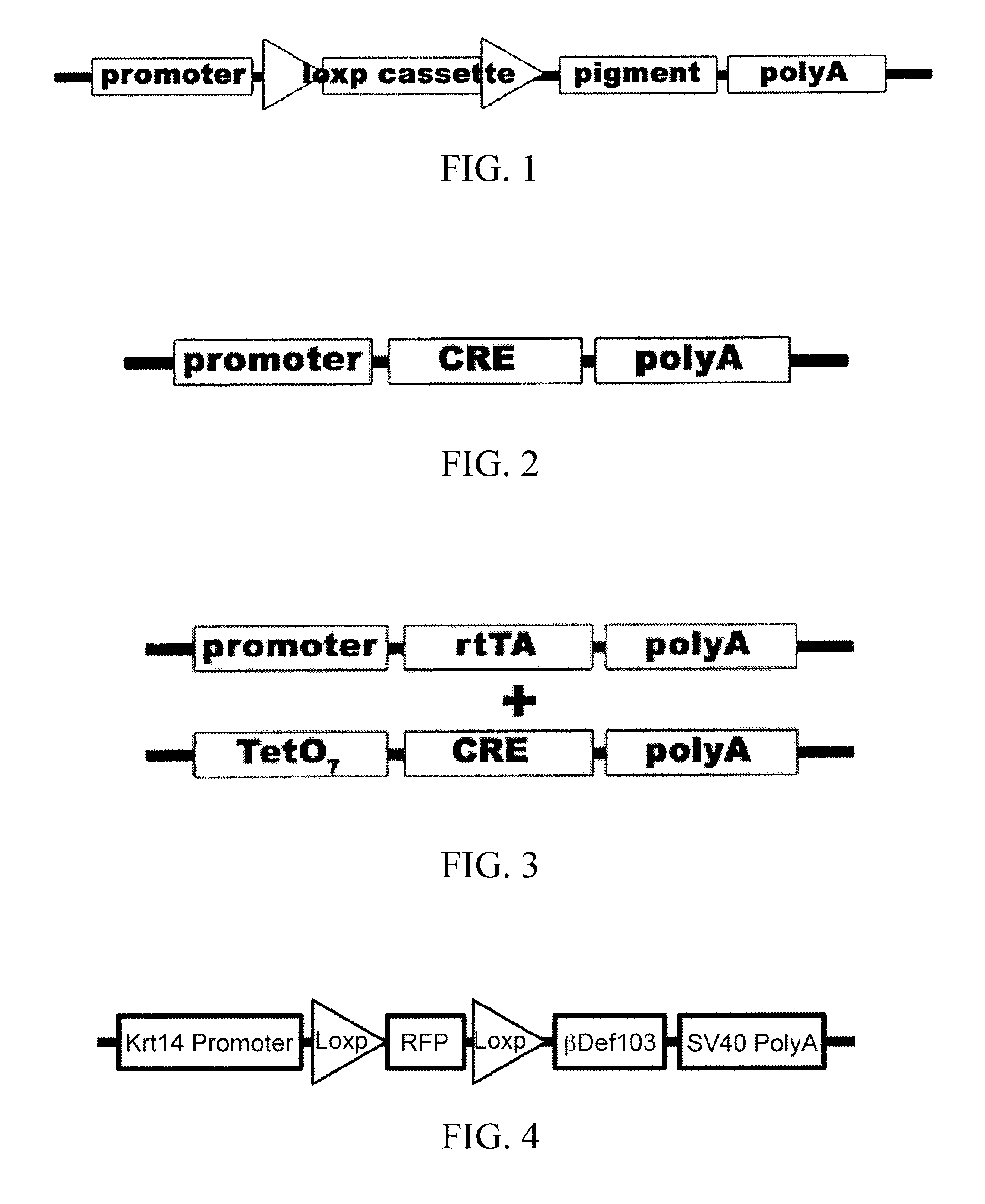
Transgenic animals with customizable traits
Disclosed are materials and methods for creating customizable traits in animals. In the demonstration of the principle of the subject invention, a keratin-14 specific promoter is used with, red fluorescent protein in the loxp cassette, dominant black (ΔG23) beta defensin 103 in the pigment cassette, and an SV40 (with intron) polyadenylation sequence. When Cre recombinase (or HTNCre) is applied to the animal's skin in a carrier base (e.g., lipid bilayers), fur is permanently genetically modified to turn black in the shape in which it was applied.
Owner:AGGENETICS
Methods for modulating intestinal microbiota
InactiveCN108778309AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntestinal structureOral medication
The present invention relates to methods for modulating the intestinal microbiota by administering one or more defensins and / or GLP-1 / GLP-1 analogs and methods for prevention or treatment of gut inflammation by oral administration of one or more defensins. GLP-1 analogs such as Liraglutide, as well as mammalian and poultry alfa and beta defensins can cause a change in the composition of the microbiota and metabolome in the intestine and can therefore be used to treat or prevent gut inflammation, colorectal cancer, metabolic syndrome, obesity, prediabetes and diabetes or as lean growth promoters in the meat production.
Owner:DEFENSIN THERAPEUTICS APS
Transgenic animals with customizable traits
InactiveUS20130212723A1Tissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionPolyadenylationBeta defensin
Disclosed are materials and methods for creating customizable traits in animals. In the demonstration of the principle of the subject invention, a keratin-14 specific promoter is used with red fluorescent protein in the loxp cassette, dominant black (ΔG23) beta defensin 103 in the pigment cassette, and an SV40 (with intron) polyadenylation sequence. When Cre recombinase (or HTNCre) is applied to the animal's skin in a carrier base (e.g., lipid bilayers), fur is permanently genetically modified to turn black in the shape in which the HTNCre was applied.
Owner:AGGENETICS
Transgenic animals with customizable traits
Disclosed are materials and methods for creating customizable traits in animals. In the demonstration of the principle of the subject invention, a keratin-14 specific promoter is used with, red fluorescent protein in the loxp cassette, dominant black (ΔG23) beta defensin 103 in the pigment cassette, and an SV40 (with intron) polyadenylation sequence. When Cre recombinase (or HTNCre) is applied to the animal's skin in a carrier base (e.g., lipid bilayers), fur is permanently genetically modified to turn black in the shape in which it was applied.
Owner:AGGENETICS
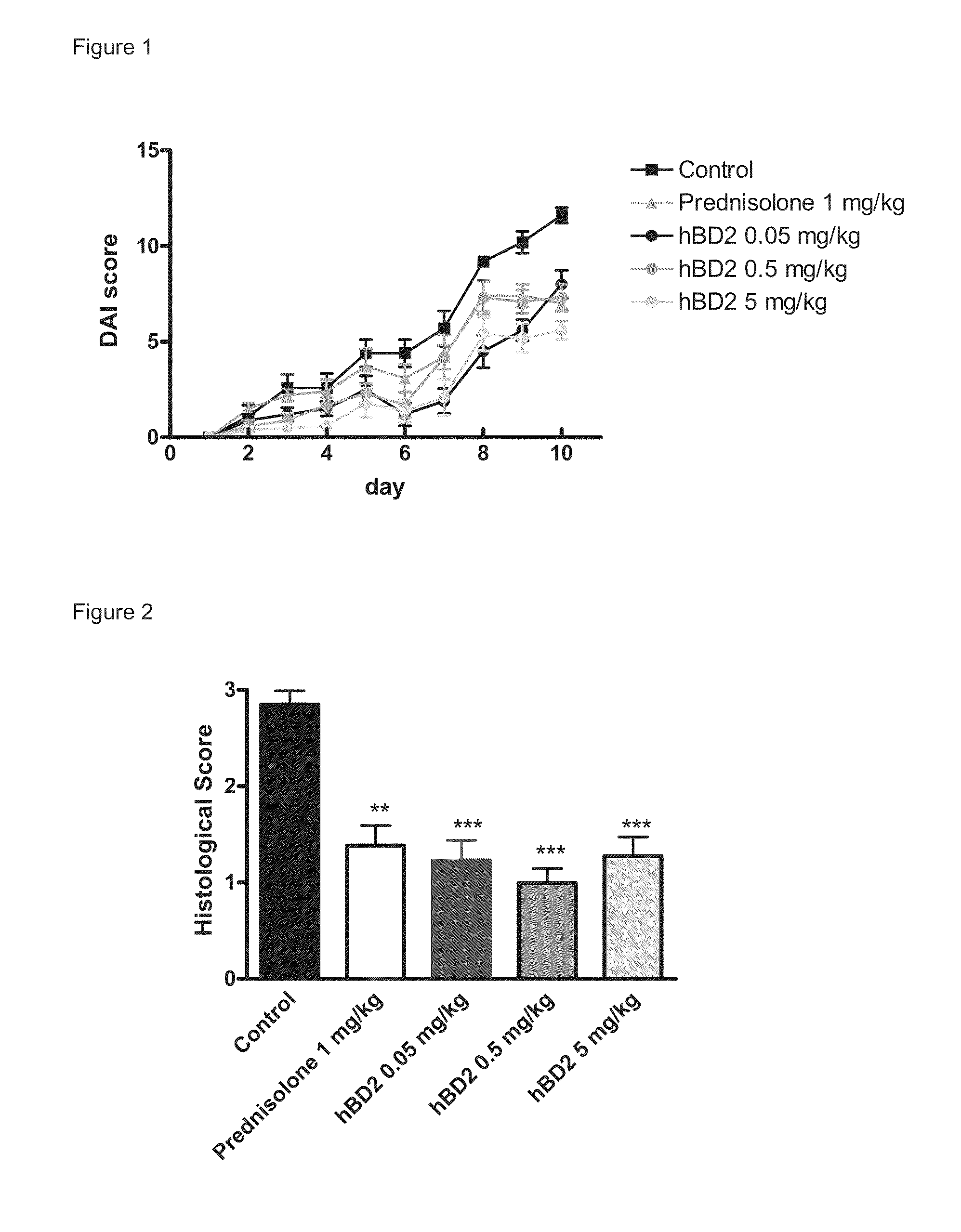
Oral treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
The present invention relates to treatment of an inflammatory bowel disease by simultaneous or successive parental and oral administration of a mammalian beta defensin.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
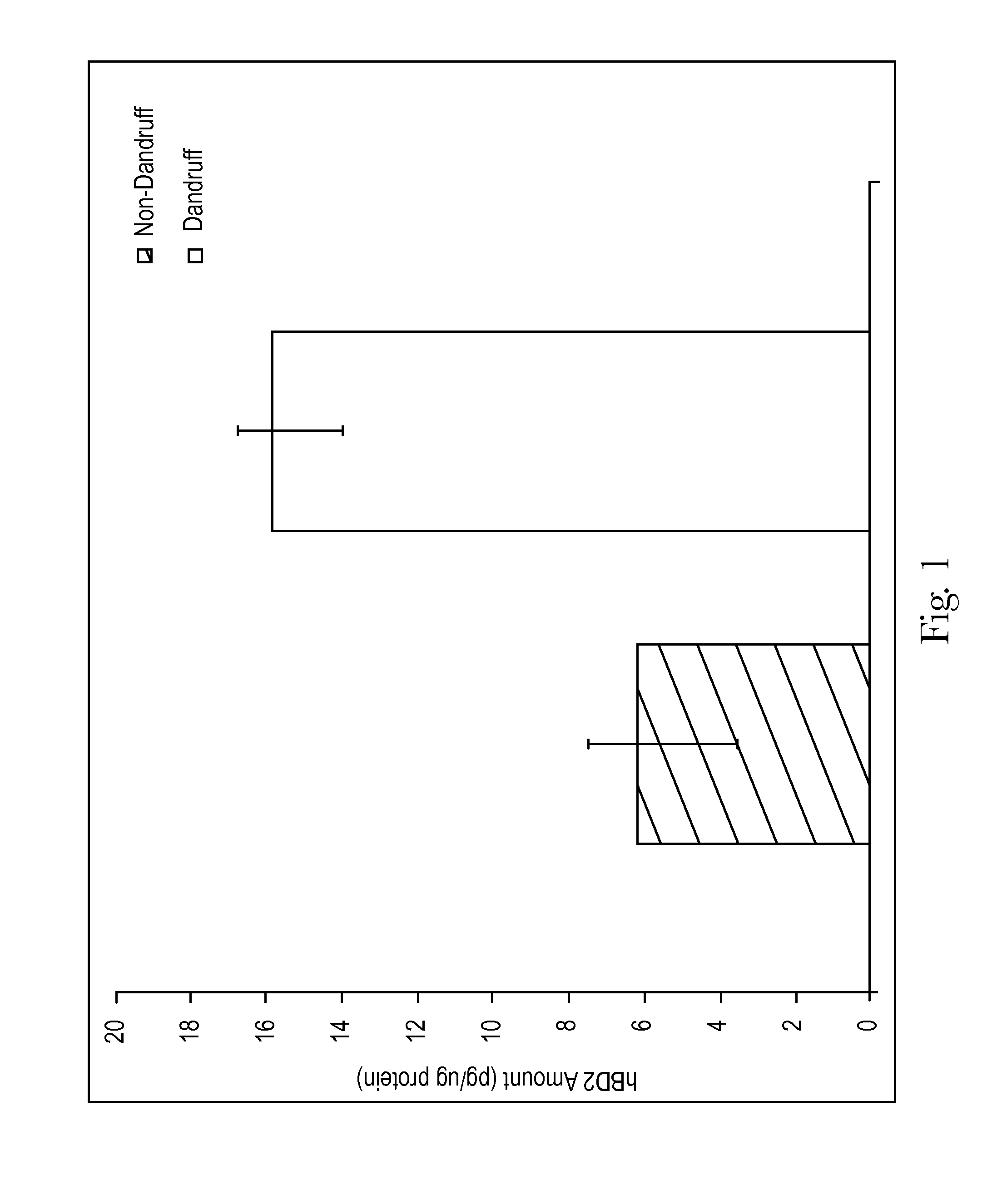
Noninvasive method for measuring antimicrobial peptides from skin as an objective measurement of natural protection from microbes
InactiveUS20140273065A1High speedRelieve symptomsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein S100-A9Cathepsin G
A noninvasive method for measuring skin health in a subject comprising collecting an epithelial cell / skin cell sample from the subject; detecting a level of one or more antimicrobial peptide biomarkers in the epithelial cell sample / skin cell sample; diagnosing the subject as having a defense mechanism due to microbial attack on skin or a measure of the system being in balance with environment homeostasis based on the level of one or more antimicrobial peptide biomarkers selected from the group consisting of Histone H2B type 1-M, Histone H2A, Histone H4, Protein S100-A7, Protein S100-A8, Protein S100-A9, Cathepsin G, Neutrophil defensin 3 (Defensin, alpha 3) (HNP-3), Dermcidin, Ribonuclease 7 (RNase 7), human beta-defensin -2 (nBD-2) and Beta-defensin 103 (hBD-3) and listed in Table 1 wherein the AMP families include bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (BPI), Defensin, Histone, Pore-forming toxin, S100 protein, Cytotoxin, Serine Protease 51, Dual Oxidase, transcription regulation, and mixtures thereof. Further, a noninvasive method for evaluating the efficacy of products for skin health.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
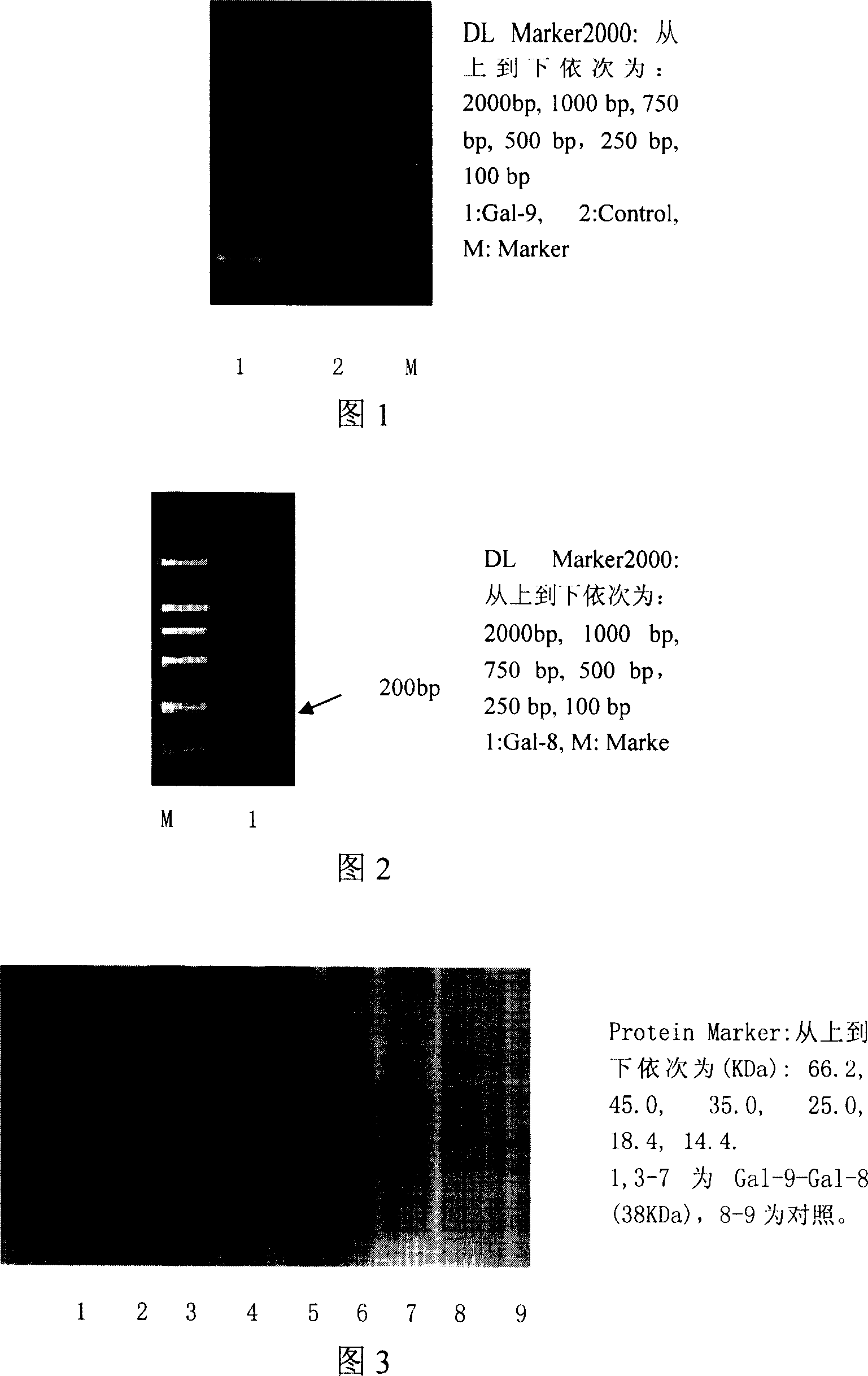
Natural antibacterial agent-recombinant chicken-beta alexin protein Gal-9 preparation method
The invention provides a method for preparing natural antibiotics- recombined chicken- beta Buchner's bodies Gal-9. The invention employs molecular biology technology to clone chicken- beta Buchner's bodies Gal-9 gene from chicken, and expresses chicken- beta Buchner's bodies Gal-9 protein outside chicken body by using proper expression host. It is found by further research that the chicken- beta Buchner's bodies Gal-9 possesses wide anti bacteria activity and immunologic enhancement. The recombined chicken- beta Buchner's bodies Gal-9 is characterized in that: (1) ir can inhibit and kill bacillus coli, salmonella, Micrococcus pyogenes and so on, (2) prevents avian infectious brunchitis virus, (3) increases antibody for avian infectious brunchitis virus concentration by 10- 20 % in dimefox after oral administration for one week by chicken, improves apleen lymphocyte blastogenesis by 40- 50%.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Transgenic animals with customizable traits
Disclosed are materials and methods for creating customizable traits in animals. In the demonstration of the principle of the subject invention, a keratin-14 specific promoter is used with red fluorescent protein in the loxp cassette, dominant black ([Delta]G23) beta defensin 103 in the pigment cassette, and an SV40 (with intron) polyadenylation sequence. When Cre recombinase (or HTNCre) is applied to the animal's skin in a carrier base (e.g., lipid bilayers), fur is permanently genetically modified to tum black in the shape in which theHTNCre was applied.
Owner:AGGENETICS
Methods for modulating intestinal microbiota
InactiveUS20190111107A1Reduce riskImprove glucose toleranceOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntestinal structureOral medication
The present invention relates to methods for modulating the intestinal microbiota by administering one or more defensins and / or GLP-1 / GLP-1 analogs and methods for prevention or treatment of gut inflammation by oral administration of one or more defensins. GLP-1 analogs such as Liraglutide, as well as mammalian and poultry alfa and beta defensins can cause a change in the composition of the microbiota and metabolome in the intestine and can therefore be used to treat or prevent gut inflammation, colorectal cancer, metabolic syndrome, obesity, prediabetes and diabetes or as lean growth promoters in the meat production.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
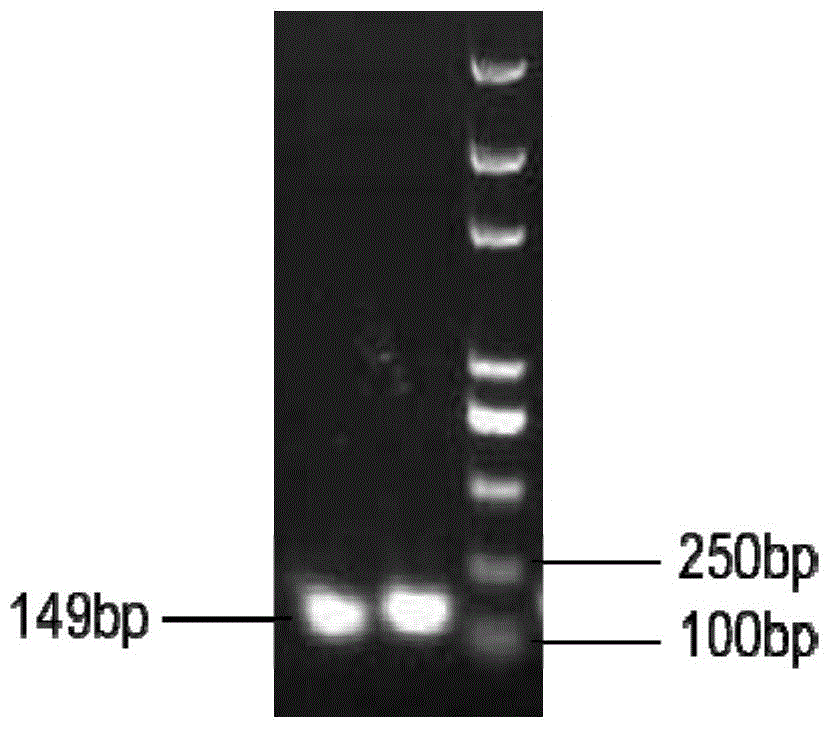
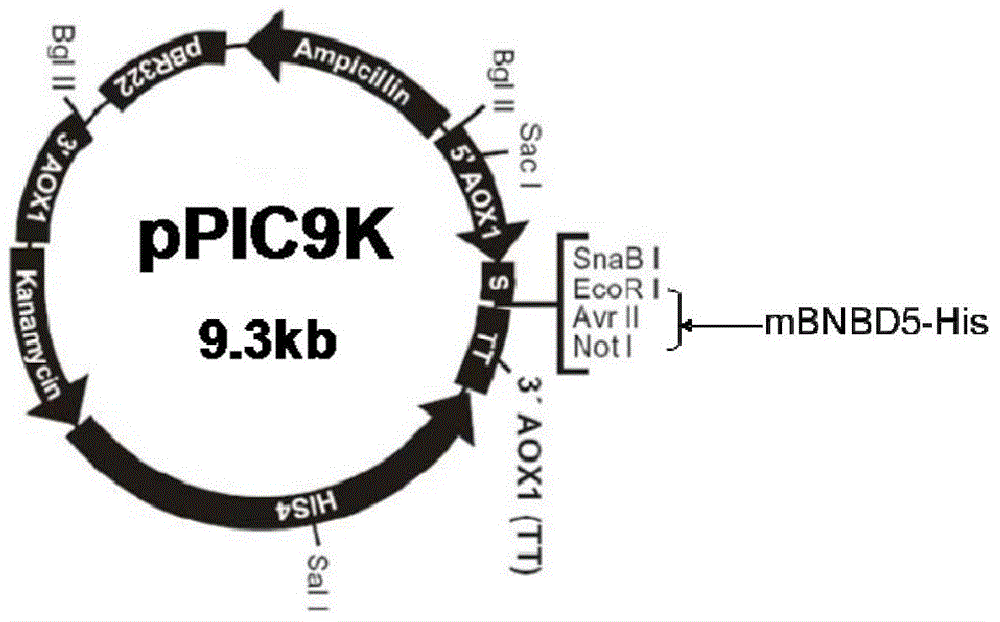
Preparation method of cattle beta-defensin 5 mature peptide, its recombinant bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN103981209AHas antibacterial activityKeep aliveFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The present invention relates to a technical field of animal medicine engineering, and provides an eukaryotic expression vector which is pPIC9K-mBNBD5 constructed by cattle beta-defensin 5 mature peptide gene and the eukaryotic expression vector pPIC9K, a nucleotide sequence of the cattle beta-defensin 5 mature peptide gene is shown as SEQ IDNO:1; and the invention also provides a recombinant bacteria and a preparation method of the cattle beta-defensin 5 mature peptide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1)preparing the cattle beta-defensin 5 mature peptide gene; 2)constructing the above eukaryotic expression vector; 3)preparing the vector; and 4)performing in vitro inducible expression on positive transformant of pichia pastoris. The recombinant cattle neutrophil granulocyte beta-defensin 5 mature peptide has antibacterial activity and has certain antituberculous activity, and is suitable for using in animal production and disease treatment, the production cost is low, and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
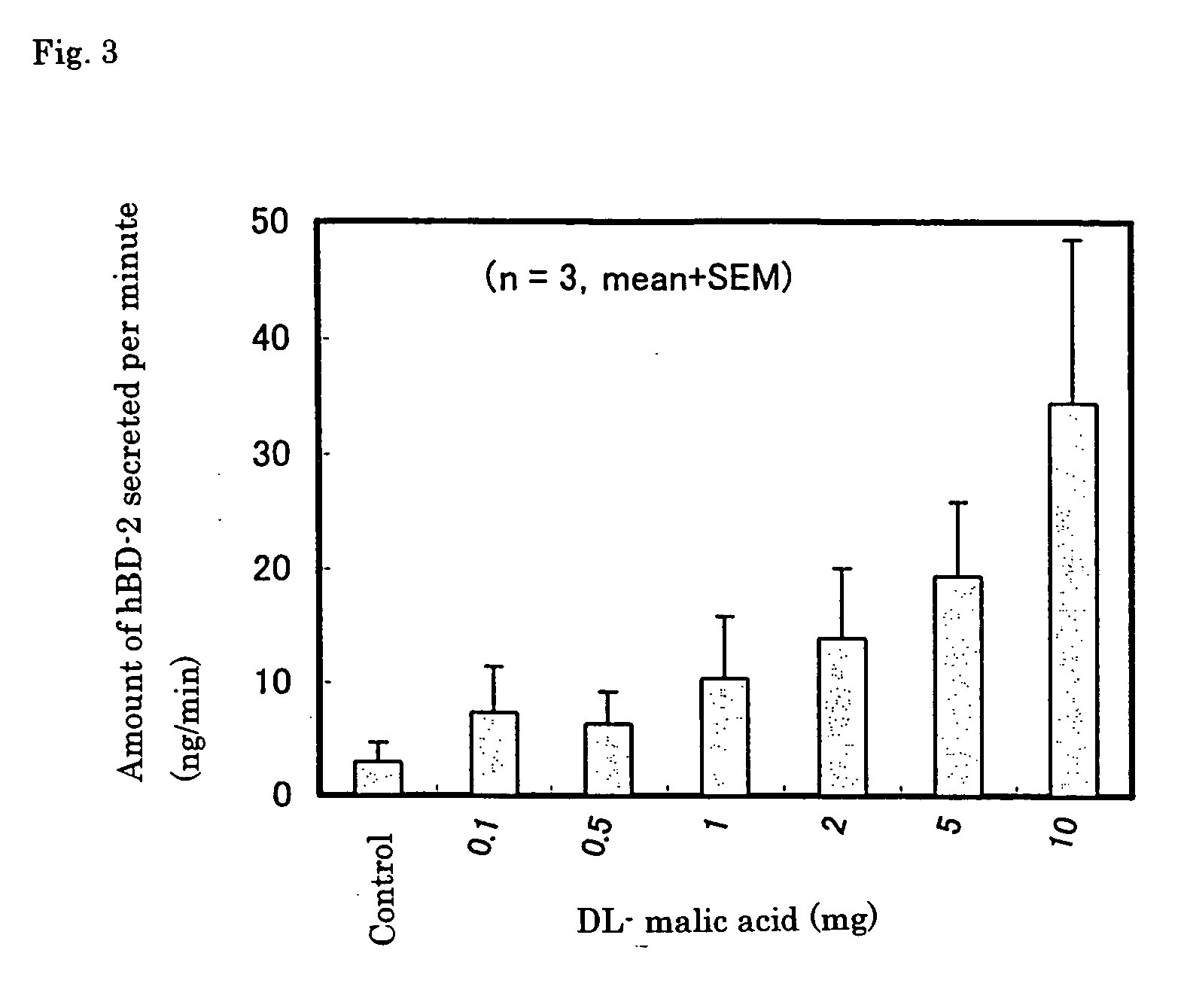
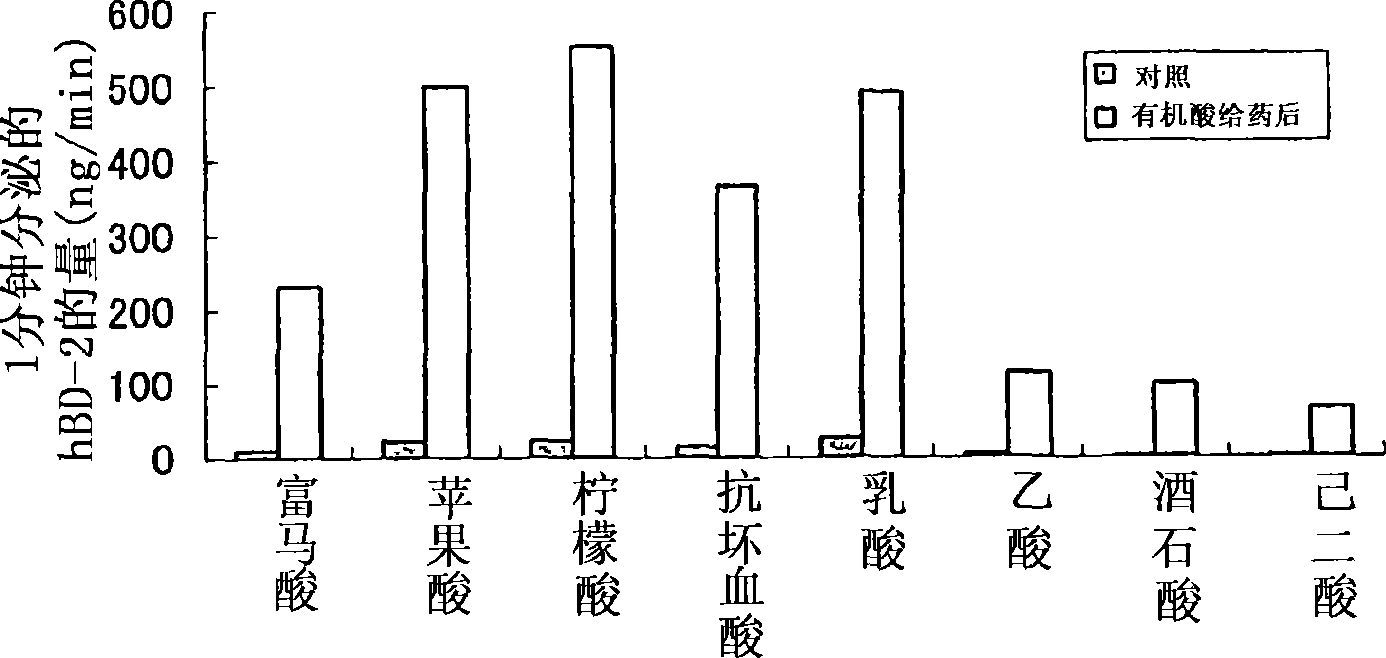
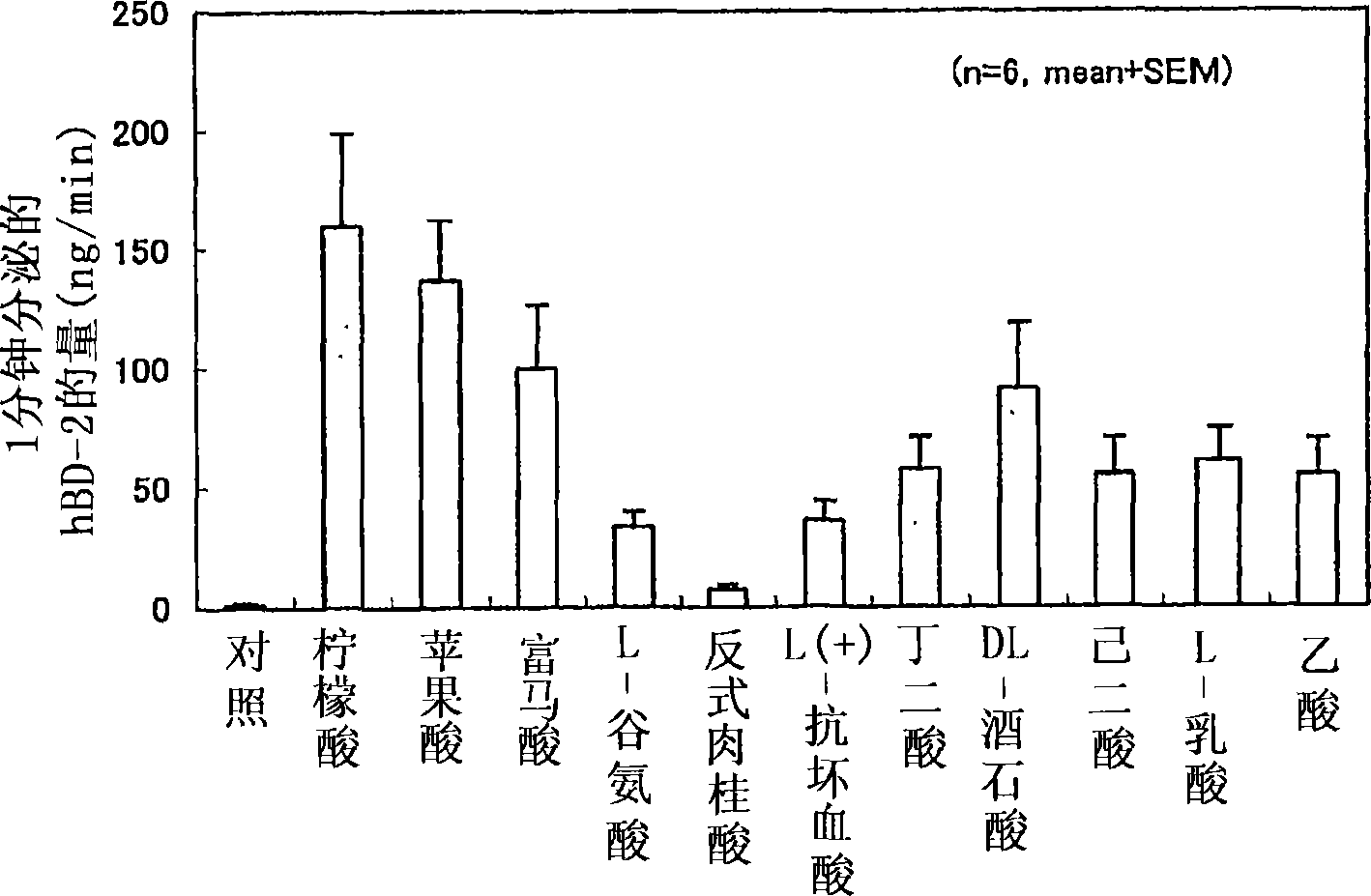
Human beta-defensin secretion promoter
InactiveUS20070093416A1Promote effectivePromote secretionAntibacterial agentsBiocideOrganic acidBeta defensin
The present invention provides a human β-defensin secretion promoter that can be used in various forms, such as external preparation, internal preparation, food, etc., and promotes human β-defensin secretion. An organic acid has an effect of promoting the secretion of human β-defensin, particularly human β-defensin-2, and therefore the organic acid is used as an active ingredient of a human β-defensin secretion promoter. Furthermore, by adding the human β-defensin secretion promoter to external preparations, internal preparations, or foods, a human β-defensin secretion promotion effect can be imparted thereto.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Natural antibacterial agent-recombinant chicken-beta defensins Gal-9-Gal-8 double-molecule protein preparation method
InactiveCN101007852APeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesEscherichia coliInfectious bronchitis virus Antibody
The invention provides a method for preparing natural antibacterial agent- recombination chicken- beta defensins Gal-9-Gal-8 bi-molecule protein. The invention employs molecular biology technology and colones chicken- beta defensins Gal- 8 and Gal-9 gene inside chicken and expresses defensins Gal-9-Gal-8 bi-molecule protein outside chicken body by employing proper expression host. The recombined chicken- beta defensins Gal-9-Gal-8 bi-molecule protein is characterized in that: (1) it can inhibit and kill bacillus coli, salmonella and salmonella and so on, (2) it can resist avian infectious brunchitis and newcastle disease virus, (3) it can increase the antibody for avian infectious brunchitis in dimefox by 10-20%, antibody for newcastle disease virus by 10-20% and increase chicken splenocyte lymphocyte conversion rate by 60-70%.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
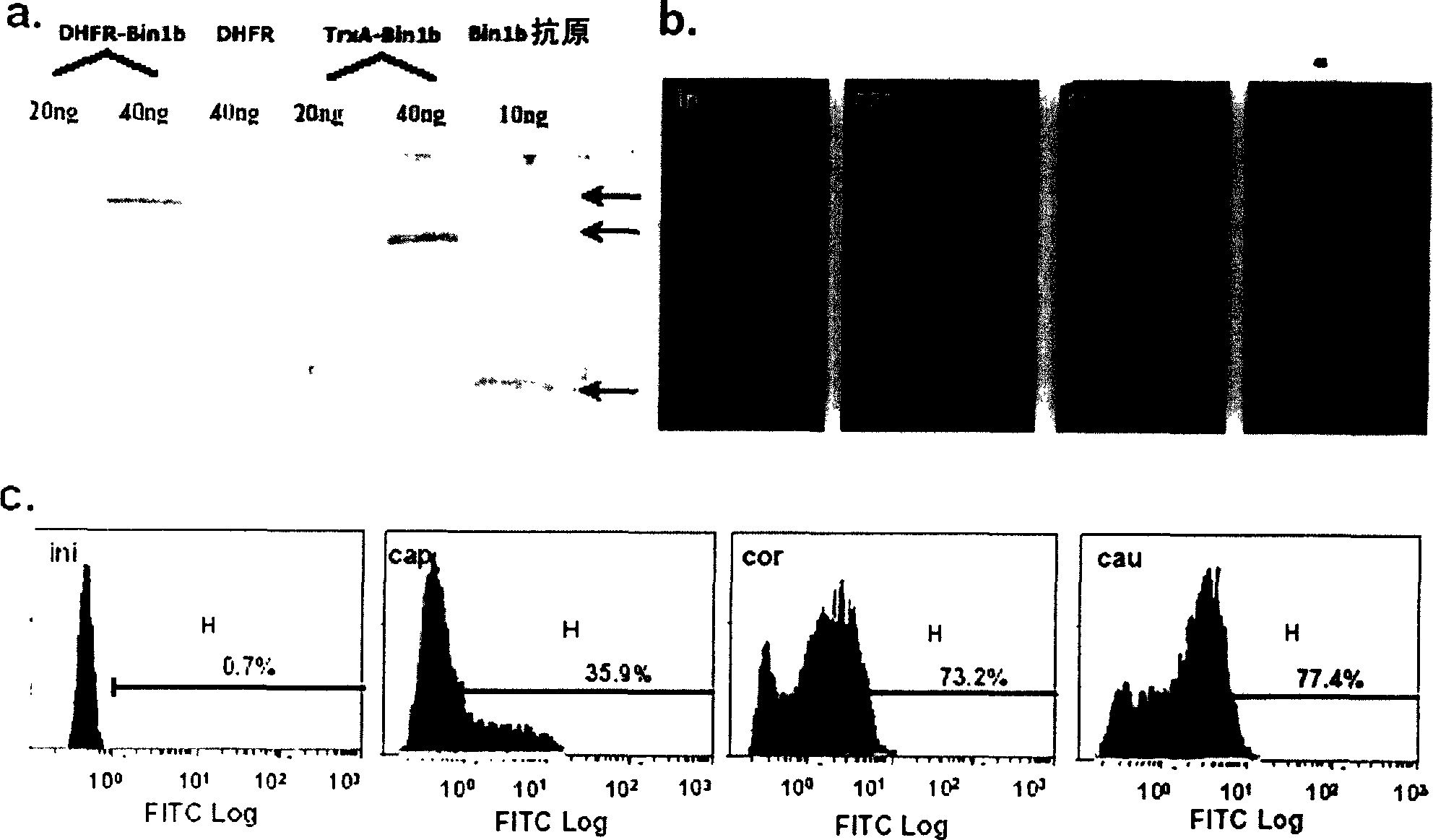
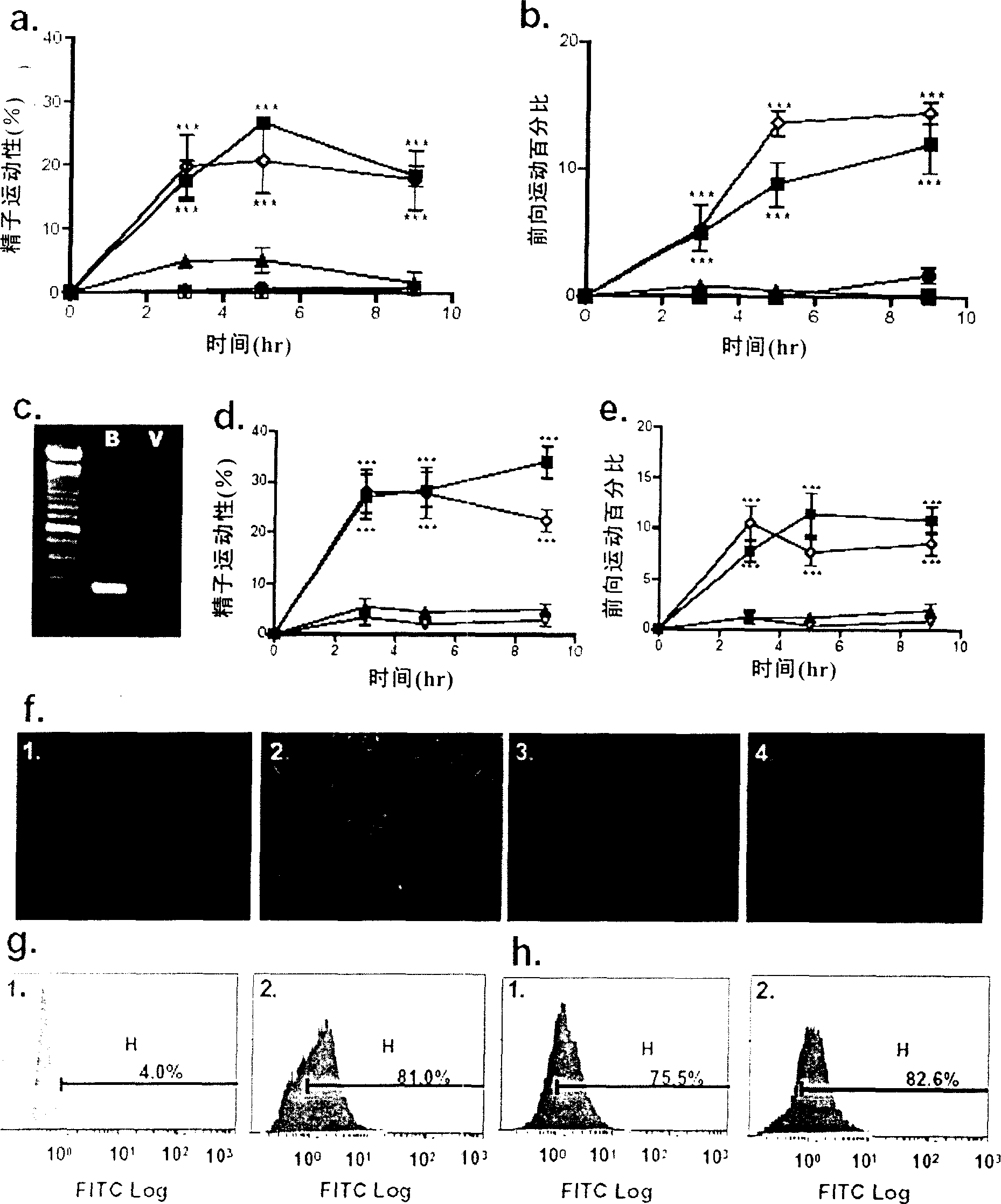
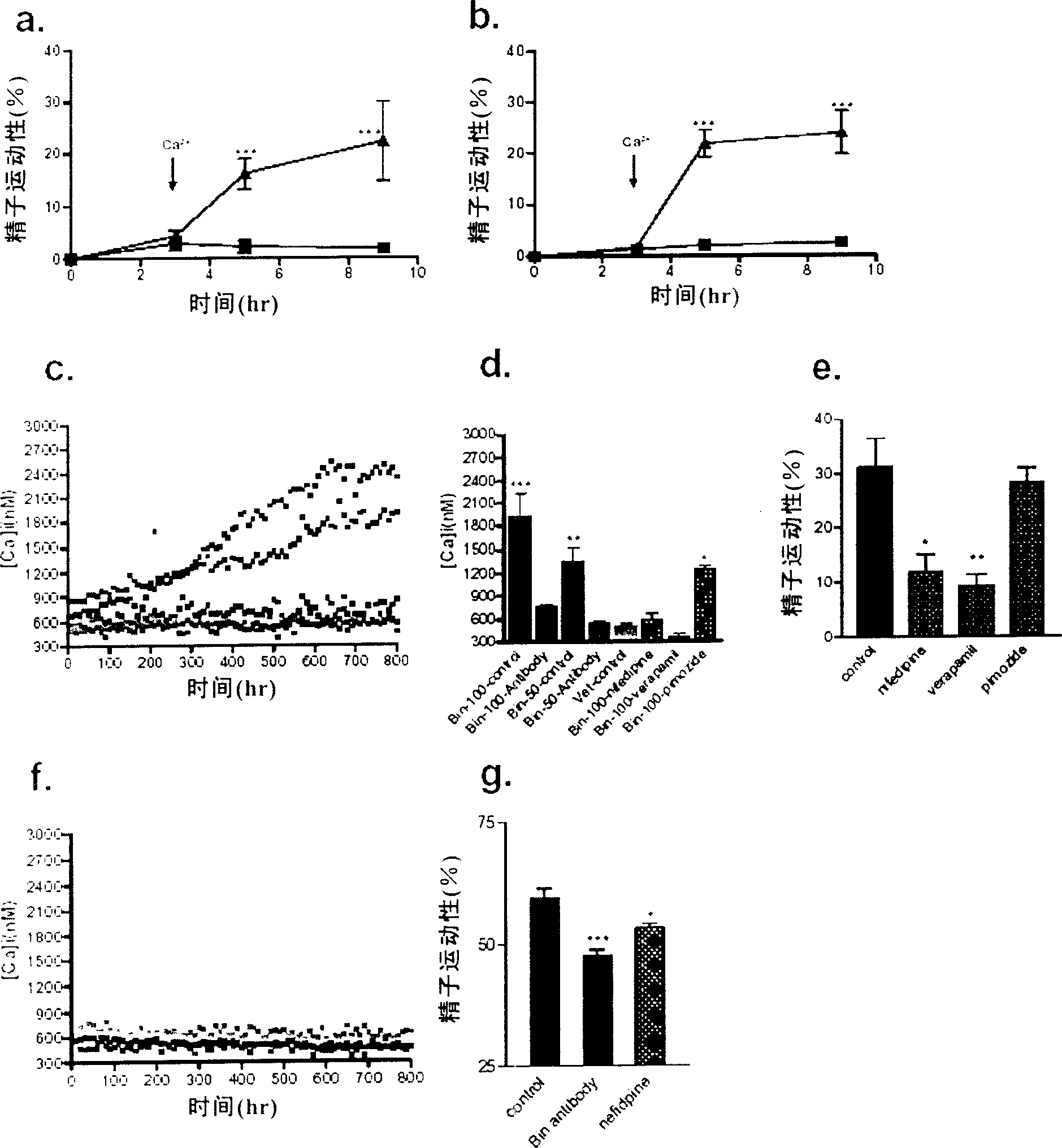
Purposes of epididymis characteristic antibiotic peptide Bin1b in spermiotiliosis
InactiveCN1689640AInhibition of maturationPeptide/protein ingredientsSexual disorderAntibiotic peptideBeta defensin
The present invention discloses the use of epididymis specific beta-defensins, which are used in preparing medicine for promoting the mature of sperm. The optimal beta-defensin is Bin1b. The present invention also provides the sperm mature promoting composition, which contains beta-defensin in safe and effective amount, calcium ion source and pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Amino acid sequence and polynucleotide sequence for chicken intestinal canal beta alexin and extraction method thereof
InactiveCN101210243ANo pollution in the processNo side effectsPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesSodium acetateAntibacterial activity
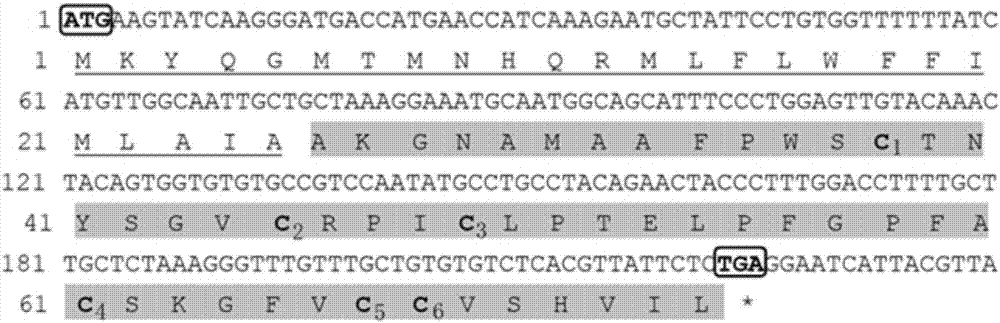
A chicken intestinal tract Beta-defensin cDNA is characterized in that the cDNA has the following sequence: tcagacagcc agctgtgcag gaacaaccat ggccactgcc ggaggctctg cttccacatg gagagctggg ctgggagctg catgaacggc cgcctgcgct gctgcaggtt ctccaccaag cagccctttt ccaaccctaa acattcagtg ctgcacacag cagagcagga cccttcccca agccttggag ggacgtga. The amino acid sequence of the Beta-defensin is Ser-Asp-Ser-Gln-Leu Cys-Arg-Asn-Asn-His Gly-His-Cys-Arg- Arg Leu-Cys-Phe-His-Met Glu- Ser-Trp-Ala-Gly Ser-Cys-Met-Asn-Gly Arg-Leu-Arg-Cys-Cys Arg-Phe-Ser-Thr-Lys-Gln Pro-Phe-Ser-Asn-Pro Lys-His-Ser-Val-Leu His-Thr-Ala-Glu-Gln Asp-Pro-Ser-Pro-Ser Leu-Gly-Gly-Thr. The extraction method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting broken mucosa cells of chicken intestinal tract; (2) breaking vesicles; (3) leaching with 5% acetic acid under stirring, centrifuging, collecting supernatant, removing sediment, subpackaging the supernatant and freeze-storing to obtain crude chicken intestinal tract Beta-defensin; (4) separating the supernatant with Sephadex G-100 gel column at low temperature, eluting with 0.2mol / L sodium acetate (constant flow pump speed 3*1), detecting with nucleic acid-protein detector, collecting the eluate with an automatic collector (1.5mL each tube), and recording with a recorder (speed 6cm / h, and range 20mV); (5) detecting the antibacterial activity of the liquid in each tube to Pasteurella with agarose diffusion method, collecting the eluate with bacteriostatic activity, and storing under vacuum freeze drying; (6) purifying the the eluate with bacteriostatic activity with Tricine-PAGE, PVDF membrane blotting the protein bands, and performing amino acid sequence analysis with Sanger partial hydrolysis method; and (7) deriving chicken intestinal tract Beta-defensin cDNA with BLAST software.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Human beta-defensin secretion promoter
InactiveCN1852708APromote secretionAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsOrganic acidBeta defensin
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Transgenic animals with customizable traits
Disclosed are materials and methods for creating customizable traits in animals. In the demonstration of the principle of the subject invention, a keratin-14 specific promoter is used with red fluorescent protein in the loxp cassette, dominant black (ΔG23) beta defensin 103 in the pigment cassette, and an SV40 (with intron) polyadenylation sequence. When Cre recombinase (or HTNCre) is applied to the animal's skin in a carrier base (e.g., lipid bilayers), fur is permanently genetically modified to turn black in the shape in which the HTNCre was applied.
Owner:AGGENETICS
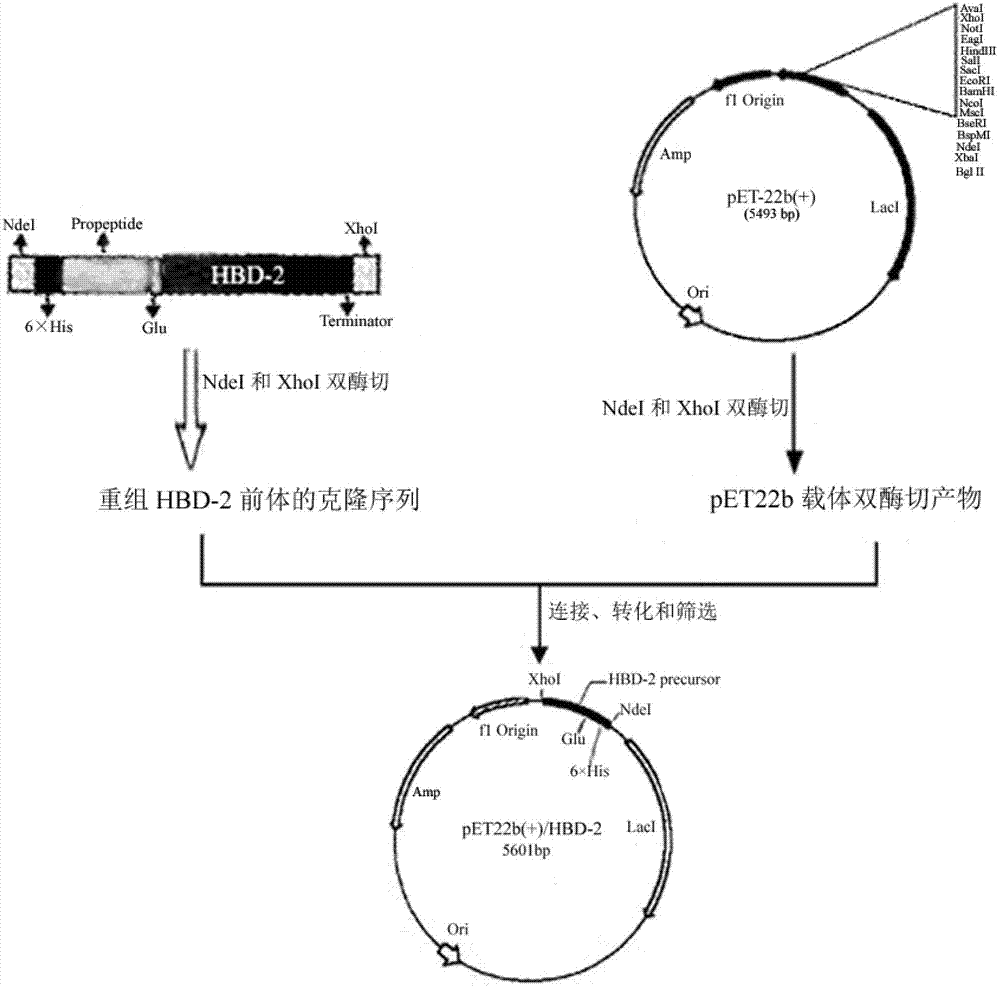
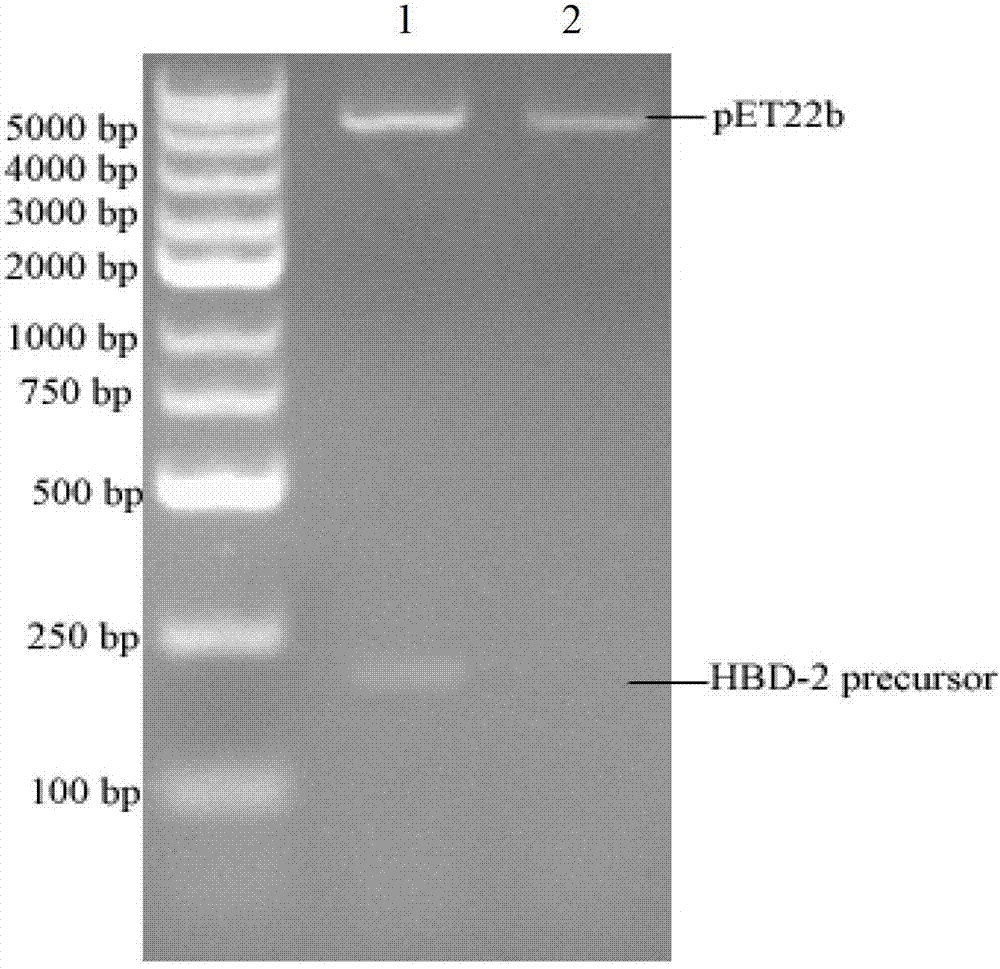
Mature human beta-defensin-2 (HBD-2) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103088050AEasy to buildStable expressionPeptide preparation methodsFermentationBacillus licheniformisBeta defensin
The invention discloses mature human beta-defensin-2 (HBD-2) and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing glutamic residue between mature sequence and propeptide of HBD-2, obtaining HBD-2 pre-pro-peptide through recombination expression, obtaining HBD-2 pre-pro-peptide with higher purity via nickel column affinity chromatography purification, carrying out enzymolysis by using recombined bacillus licheniformis glutamic specific endopeptidase with an His(histidine)-tag, removing the propeptide and the affinity tag and removing the recombined bacillus licheniformis glutamic specific endopeptidase and other impurities through the affinity chromatography again, wherein the mature HBD-2 with higher purity exists in the solution. The preparation method of the mature HBD-2, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost and simplicity in purification process and accordingly lays a foundation for the large-scale preparation and the application of the mature HBD-2.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pelteobagrus fulvidraco beta defensin gene, and beta defensin antibacterial peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN107022549AGood broad-spectrum antibacterial activity in vitroHelps reveal pathways of actionAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a pelteobagrus fulvidraco beta defensin gene, and beta defensin antibacterial peptide and application thereof. An in vitro recombinant expression technology is used for successfully expressing a pelteobagrus fulvidraco beta defensin recombinant protein PET-32a-Pf_BD, and antibacterial activity identification results show that the pelteobagrus fulvidraco beta defensin gene has a certain bacteriostasis for staphylococcus aureus in gram-positive bacterium, escherichia coli in gram-negative bacterium, aeromonas hydrophila, edwardsiella ictaluri and flavobacterium columnare. Therefore, a foundation is laid for application of the defensin recombinant protein, used as a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug, in aquaculture.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Oral Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
ActiveUS20140213521A1Reduce generationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemOral medicationBeta defensin
The present invention relates to treatment of an inflammatory bowel disease by simultaneous or successive parental and oral administration of a mammalian beta defensin.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
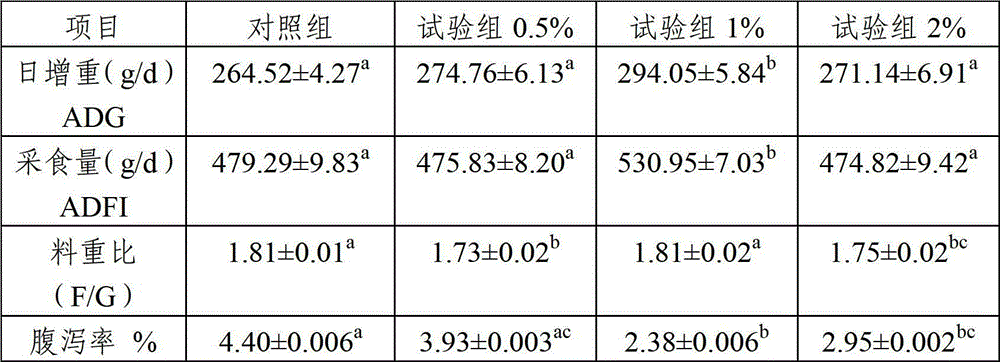
Porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder, feed additive, premix and batch
The invention belongs to the field of animal feed and particularly relates to porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder, feed additive containing the porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder, premix and batch. A preparation method of the porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder includes fermenting bacterial strain, which carries porcine beta defensin-2 gene, of yeast genetic engineering, taking supernatant for ultrafiltration, sequentially adding protective agent, wall material and carrier to ultrafiltrate, and performing spray drying. The porcine beta defensin-2 spray-dried powder expressed by Pichia pastoris having antibacterial activity, and activity of porcine beta defensin-2 can be stored to a maximum extent by combining a spray-drying method and an encystation technology. In addition, the porcine beta defensin-2 is not damaged after invitro-simulation of artificial gastric juice, and released porcine beta defensin-2 has high activity.
Owner:宿迁大北农饲料有限责任公司 +2
Human beta-defensin-3 (HBD-3), a highly cationic beta-defensin antimicrobial peptide
The present invention relates a novel antimicrobial peptide HBD-3 and derivatives thereof as well as the gene encoding the peptide. The invention further relates to methods of use of the HBD-3 peptide including a method of inhibiting microbial growth by administering an effective amount of the HBD-3 peptide alone or in combinination with other antimicrobial agents or antibiotics. In addition, the immunomodulatory properties of the HBD-3 peptide also facilitate the manipulation of the immune response, i.e., as a chemoattractant for immature dentritic cells or memory T cells.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Cell-penetrating peptide and human Beta-defensin 3 fusion protein and preparation method and application thereof
Cell-penetrating peptide and human Beta-defensin 3 fusion protein has 59 amino acids in full length, has a cell-penetrating peptide sequence at its nitrogen end and Beta-defensin 3 mature peptide sequence at its carbon end, and the two peptide segment are connected via double glycine and single serine and have molecular weight of 6.7 KD. The preparation method comprises the steps of acquiring a gene, constructing Pichia pastoris expression vector, constructing cell-penetrating peptide and human Beta-defensin 3 fusion protein Pichia pastoris genetically-engineered bacterium, fermenting cell-penetrating peptide and human Beta-defensin 3 fusion protein with Pichia pastoris, and purifying the cell-penetrating peptide and human Beta-defensin 3 fusion protein. Application of cell-penetrating peptide and human Beta-defensin 3 fusion protein in the preparation of bactericidal gels, application in the preparation of film cosmetics and application in the preparation of toner cosmetics are also provided.
Owner:SHAANXI HUIKANG BIO TECH CO LTD
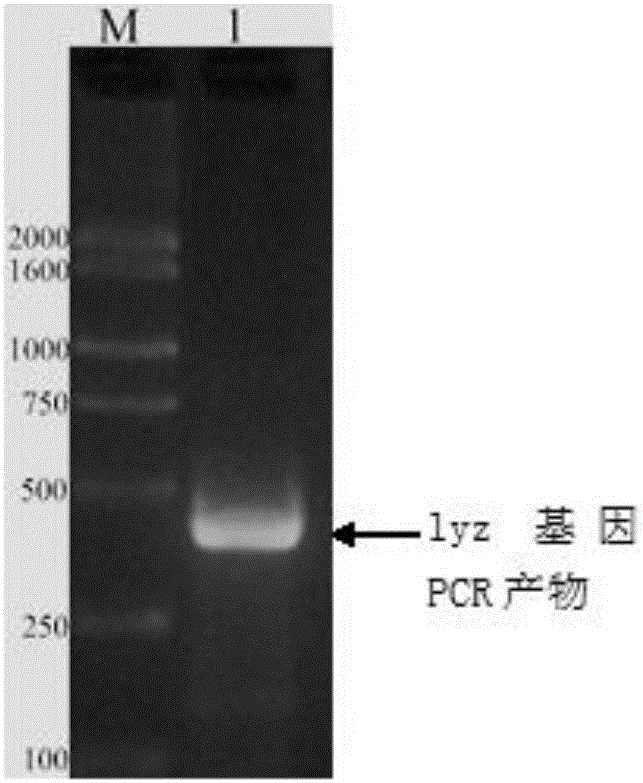
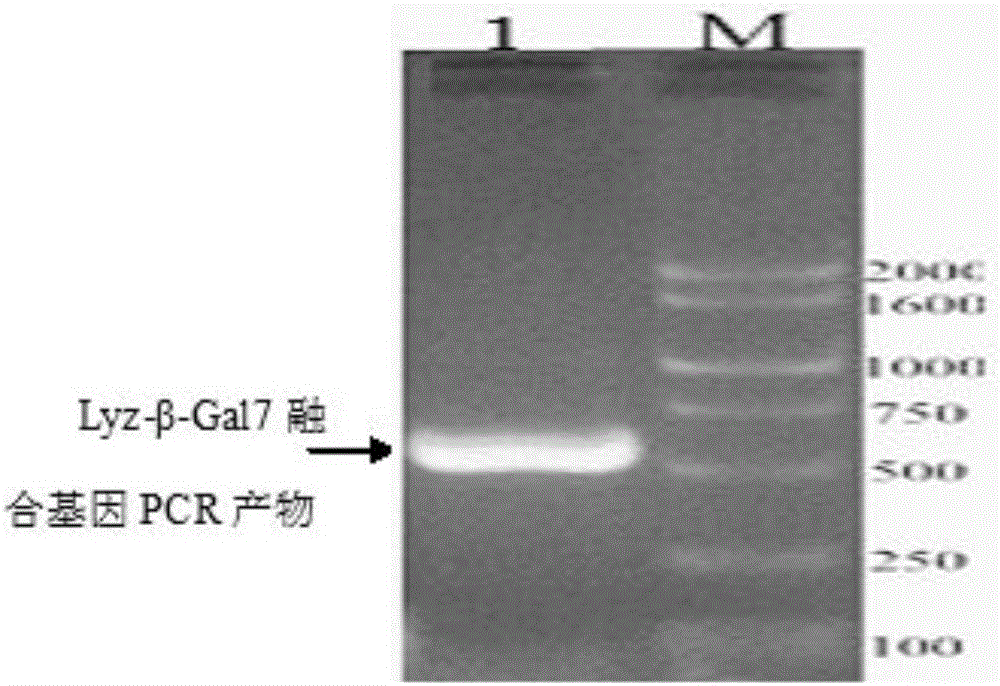
Chicken lysozyme and chicken beta-defensin 7 fused gene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106399340AHigh in proteinNo drug dependenceBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsStaphylococcus cohniiMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention discloses a chicken lysozyme and chicken beta-defensin 7 fused gene. The nucleotide sequence of the chicken lysozyme and chicken beta-defensin 7 fused gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. Fused protein encoded by the fused gene has the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The invention further discloses a construction method of an expression vector of the fused gene, the fused protein prepared by adopting the expression vector has the obvious bacteriostasis activity for staphylococcus aureus, and the minimal inhibitory concentration is lower than 4mg / ml.
Owner:易道生
Transgenic animals with cutomizable traits
Owner:AGGENETICS
Short beta-defensin-derived peptides
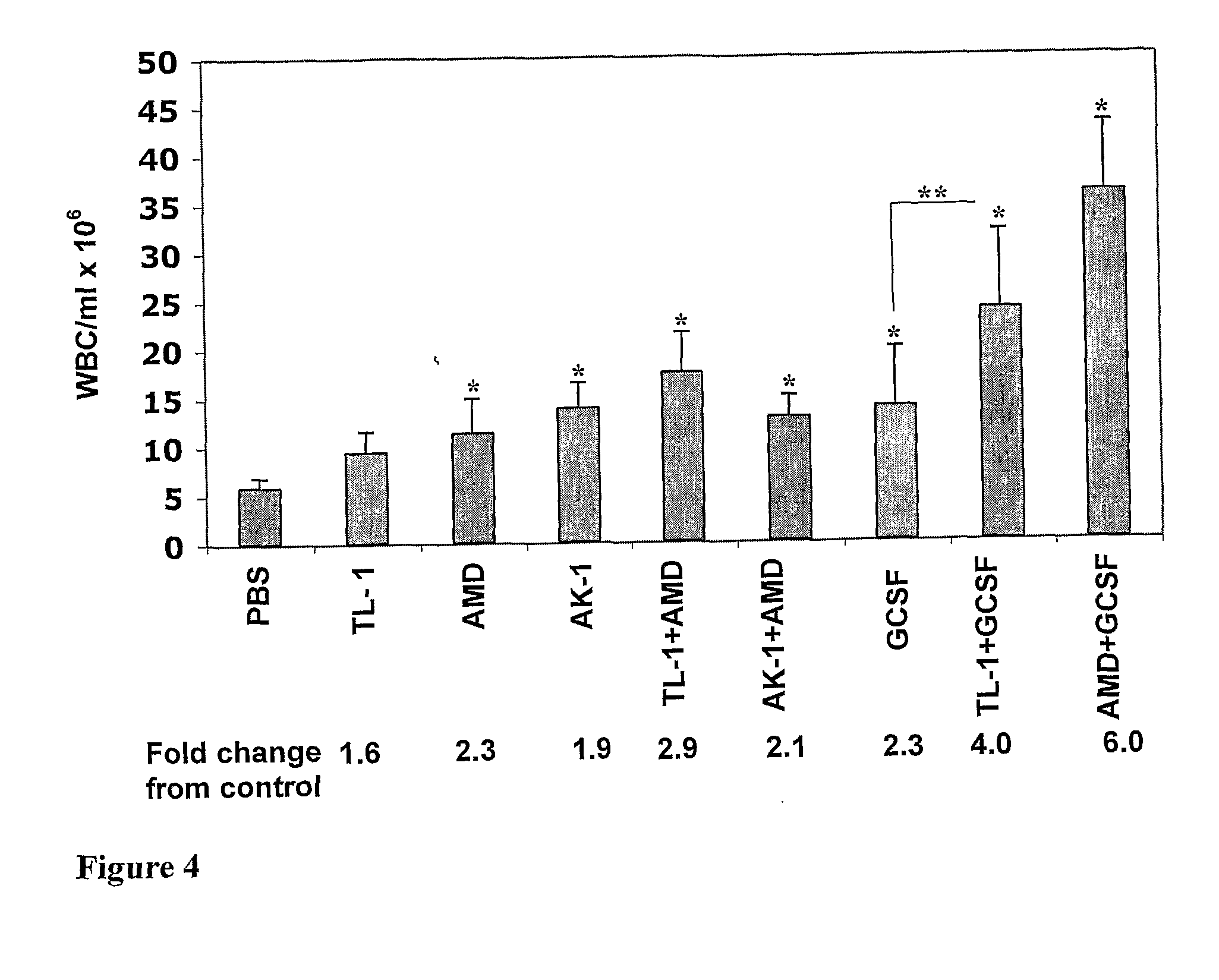
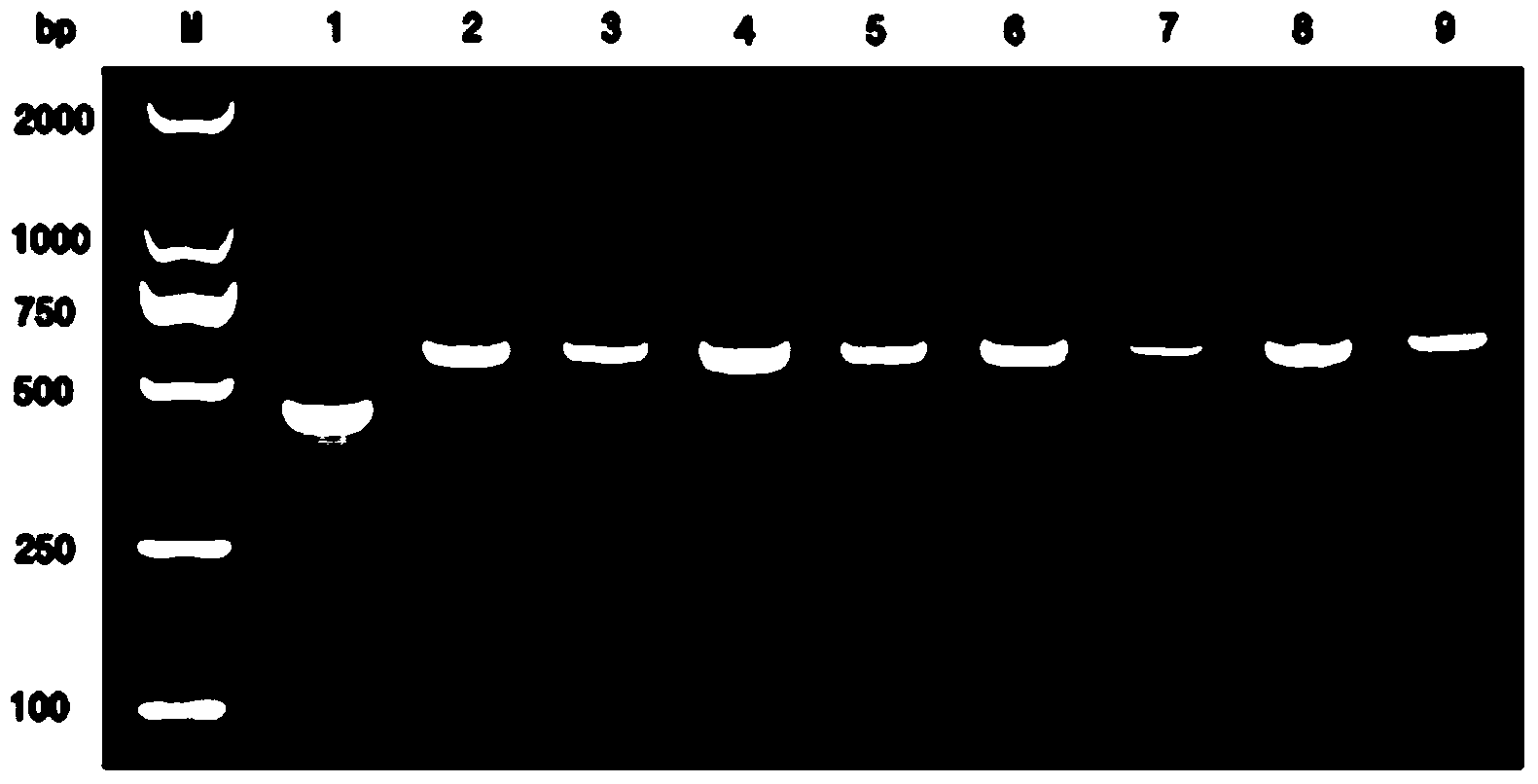
InactiveUS20120045411A1Improve accessibilityIncrease homingBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsProgenitorCXCR4
The invention is directed to beta-defensin-derived peptides and their use in modulating the activity of hematopoietic cells and other CXCR4-expressing cells. Specifically, the invention provides compositions and methods useful in the treatment of cancer. The invention further provides compositions and methods useful for promoting mobilization and transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Preparation and expression method of chicken beta-defensin 9 yeast engineered bacteria
InactiveCN103614380AEasy to chooseSelect operation shortcutFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention discloses preparation and an expression method of a chicken beta-defensin 9 yeast engineered bacteria, and belongs to the fields of biological technology and gene engineering pharmaceutical technology. The preparation process comprises: utilizing a pichia yeast consistently-used codon to optimize chicken beta-defensin 9 gene, adding a Kex2 restriction enzyme cutting site coding sequence at the front terminal of the gene, and artificially synthesizing the gene; then inserting the synthetic beta-defensin 9 gene sequence into a yeast constitutive expression vector, integrating into a the chromosome of a methylotrophy type pichia yeast by homologous recombination; and screening for multiple times to obtain the yeast engineered bacteria for producing chicken beta-defensin 9. The yeast engineered bacteria is capable of continuously performing high-level protein expression after fermentation and culturing, the expressed product is high in yield, is relatively close to the natural structure, is secreted in the broth, and also has relatively strong anti-foodborne pathogenic activity. The broth is subjected to preliminary separation and can be directly used as a forage additive after concentrated or dried, and the forage additive is applied to animal breeding industry, so that the production cost of defensin is reduced and the economic benefit of a production enterprise is improved. The technical scheme provided by the invention helps to establish a technological base for industrial large-scale production and application of beta-defensin 9 and development of poultry forage antibiotic additive substitutes.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com