Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "Phenocopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
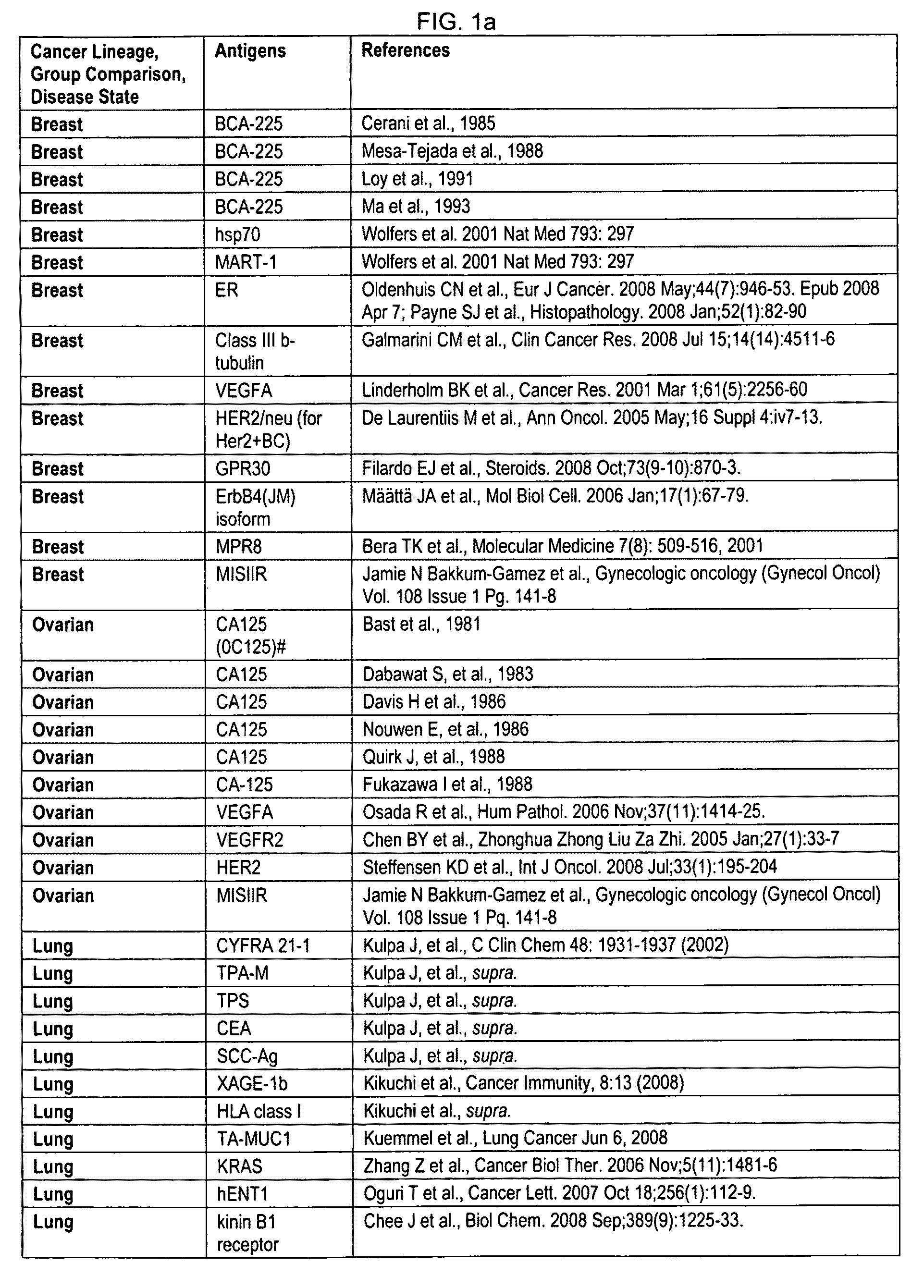
A phenocopy is a variation in phenotype (generally referring to a single trait) which is caused by environmental conditions (often, but not necessarily, during the organism's development), such that the organism's phenotype matches a phenotype which is determined by genetic factors. It is not a type of mutation, as it is non-hereditary.
Methods and systems of using exosomes for determining phenotypes
InactiveUS7897356B2High sensitivityStrong specificityMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementTherapy relatedBiomarker (petroleum)
Exosomes can be used for detecting biomarkers for diagnostic, therapy-related or prognostic methods to identify phenotypes, such as a condition or disease, for example, the stage or progression of a disease. Cell-of-origin exosomes can be used in profiling of physiological states or determining phenotypes. Biomarkers or markers from cell-of-origin specific exosomes can be used to determine treatment regimens for diseases, conditions, disease stages, and stages of a condition, and can also be used to determine treatment efficacy. Markers from cell-of-origin specific exosomes can also be used to identify conditions of diseases of unknown origin.
Owner:CARIS LIFE SCI LUXEMBOURG HLDG
Method of genotyping by determination of allele copy number
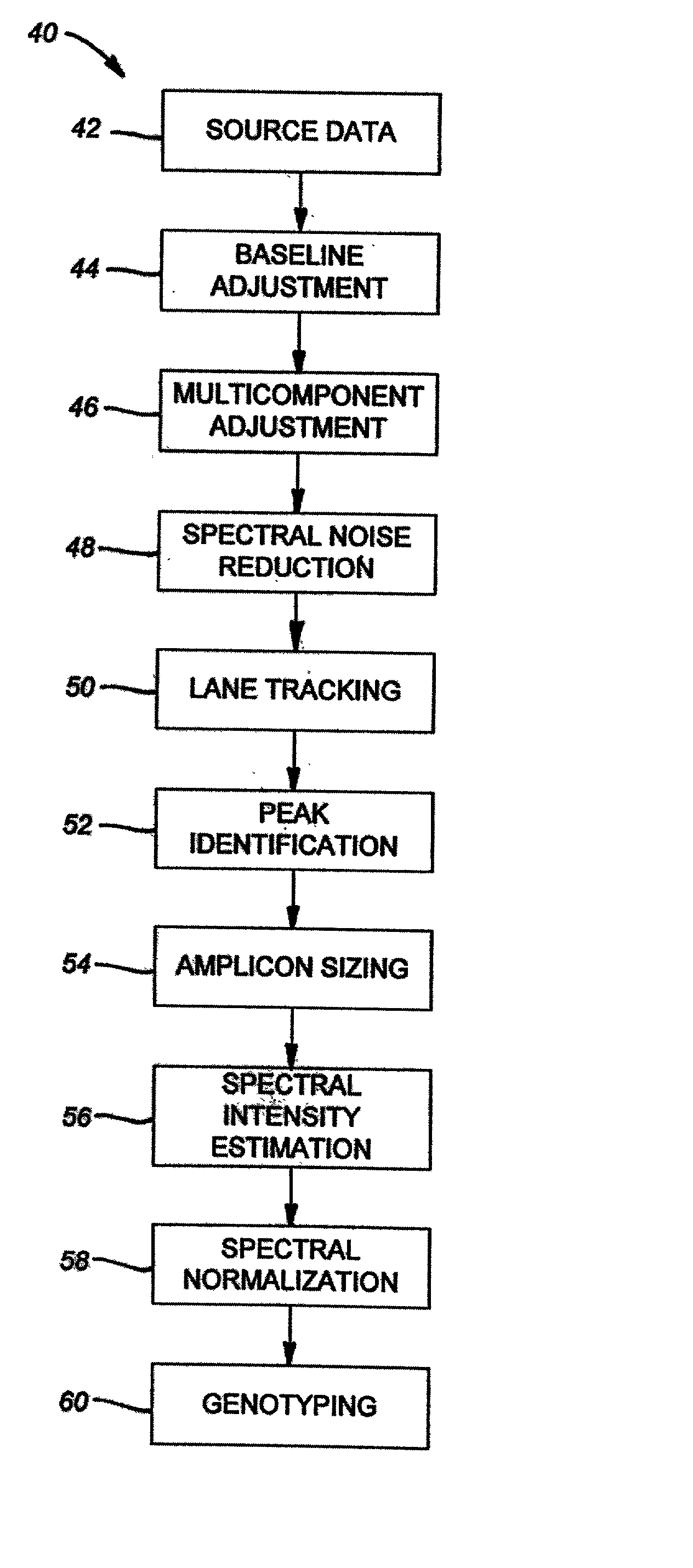
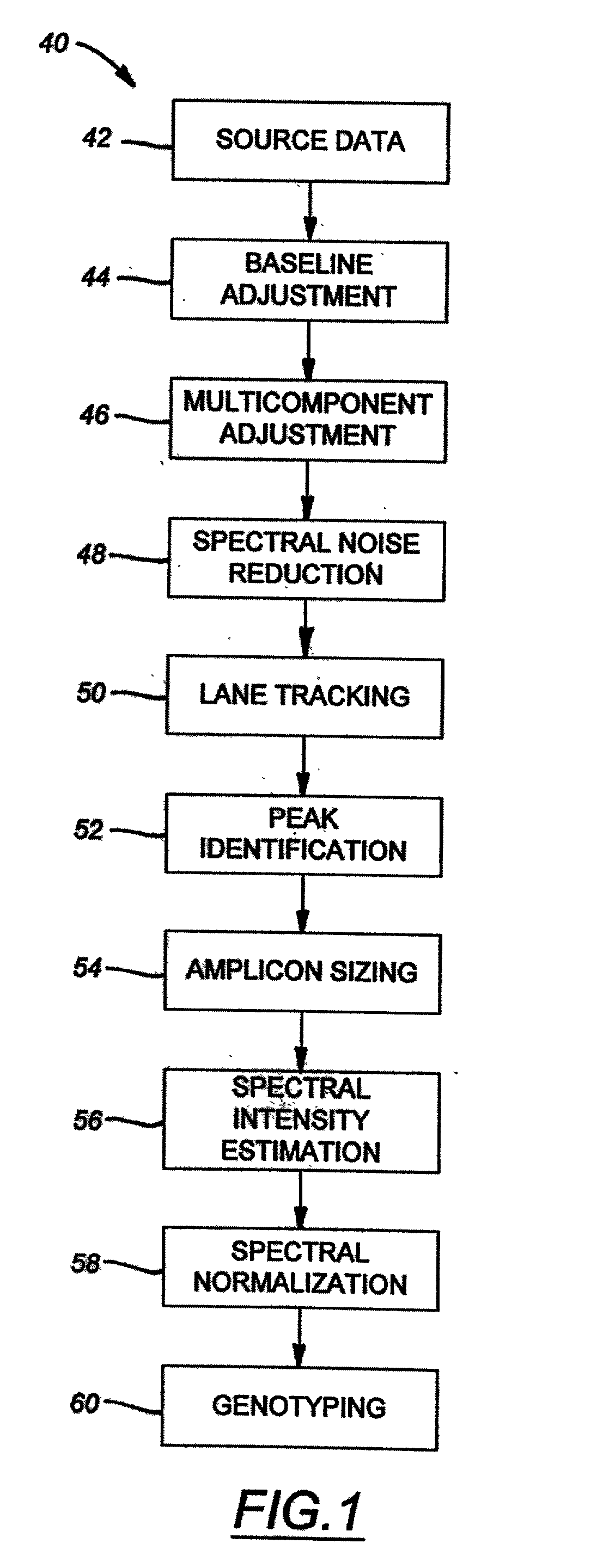
The majority of PCR-based fingerprinting technologies generate dominant genetic markers; homozygote present and heterozygote genotypes cannot be distinguished using conventional detection methods. In contrast, codominant genetic markers provide an unambiguous distinction among each genotype. A genotyping method is described that includes procedures implemented in software. This method quantifies allele copy number and enables recovery of codominant genotypes from markers expressing ostensibly dominant phenotypes. These procedures are designed and implemented to (1) greatly reduce variability attributable to sample assay and detector noise, (2) accurately estimate allele size and copy number, (3) provide normalization criteria for intra- and inter-marker comparisons, and (4) scale the resulting data to determine the genotype of individual markers.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
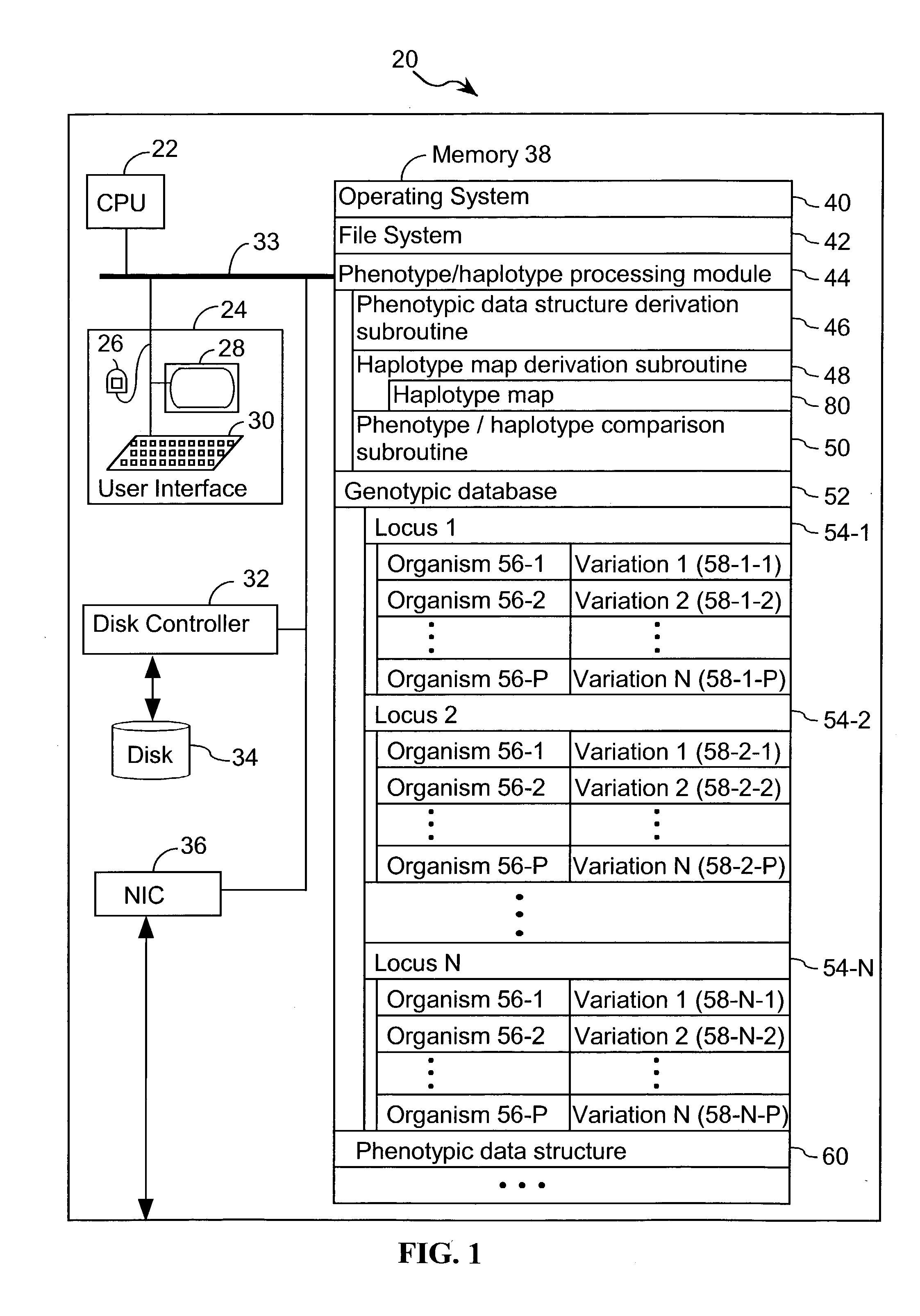
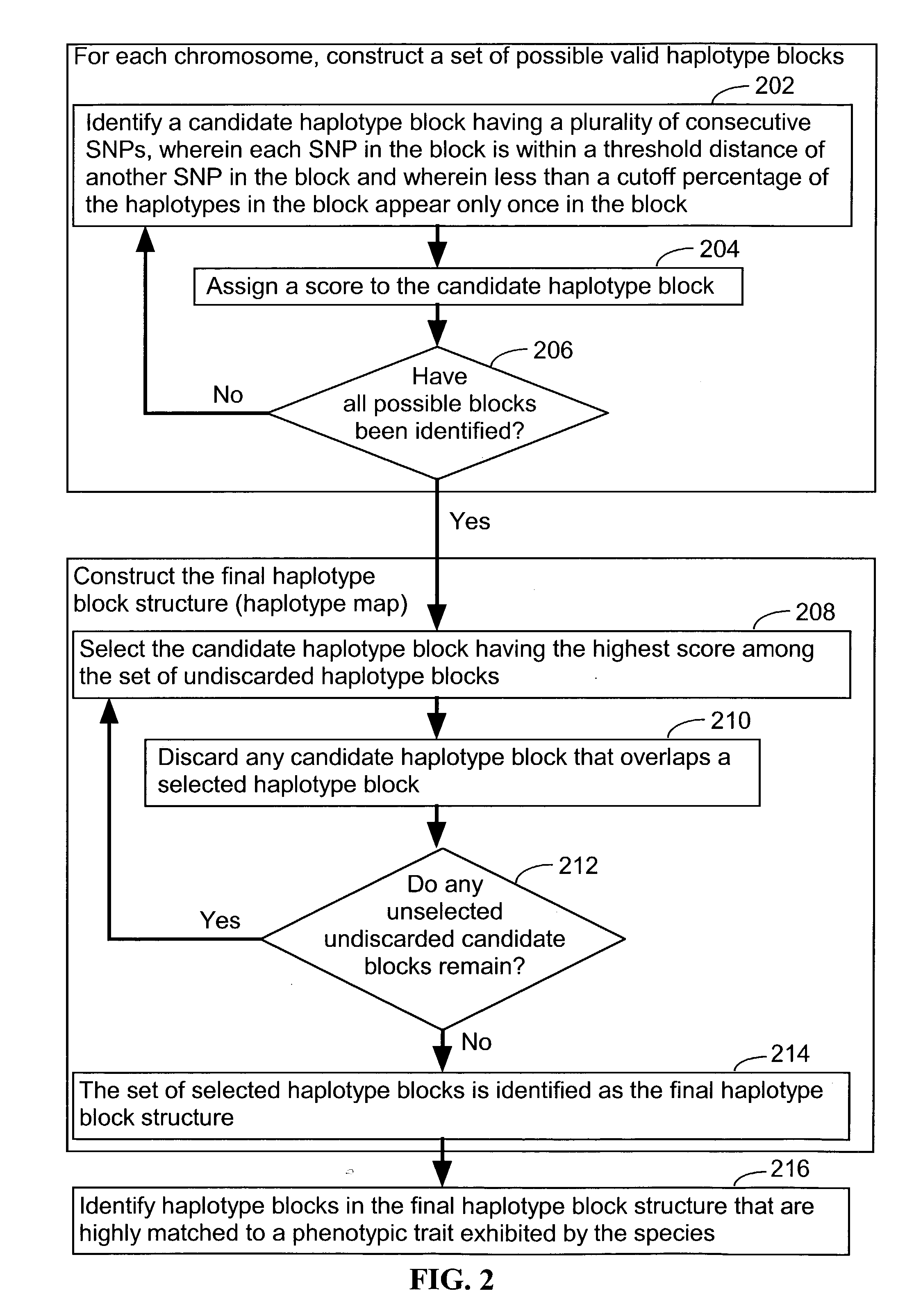
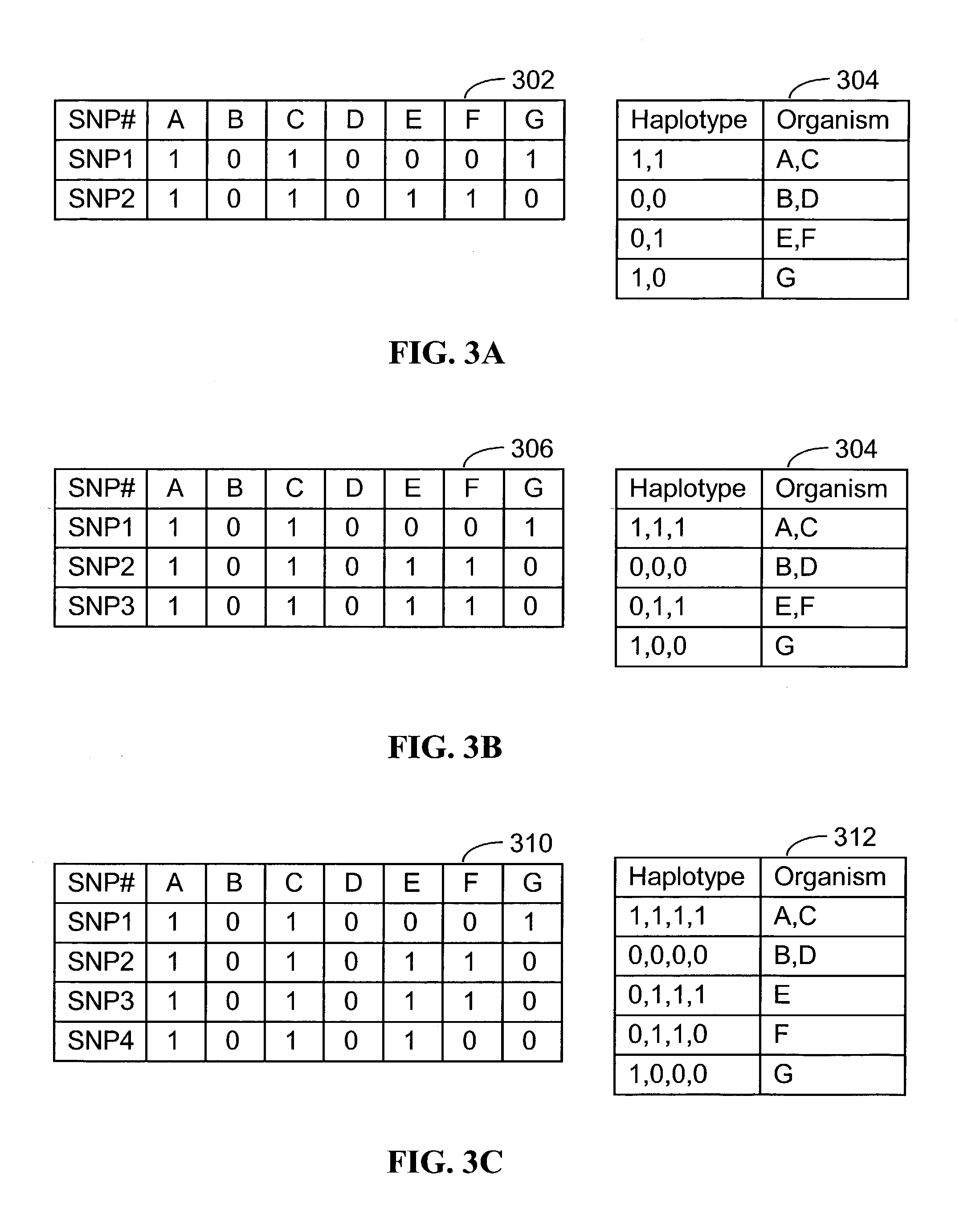
Systems and methods for predicting specific genetic loci that affect phenotypic traits
A database of genetic variations is analyzed to produce a haplotype map of the genome for strains of a single species. A computational method is used to rapidly map complex phenotypes onto the haplotype blocks within the haplotype map. The specific genetic locus regulating three different biologically important phenotypic traits in mice is identified using these systems and methods.
Owner:SANDHILL BIO CORP +1
Methods for genetic interpretation and prediction of phenotype
InactiveUS20040091933A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsHereditary MutationComputerized system
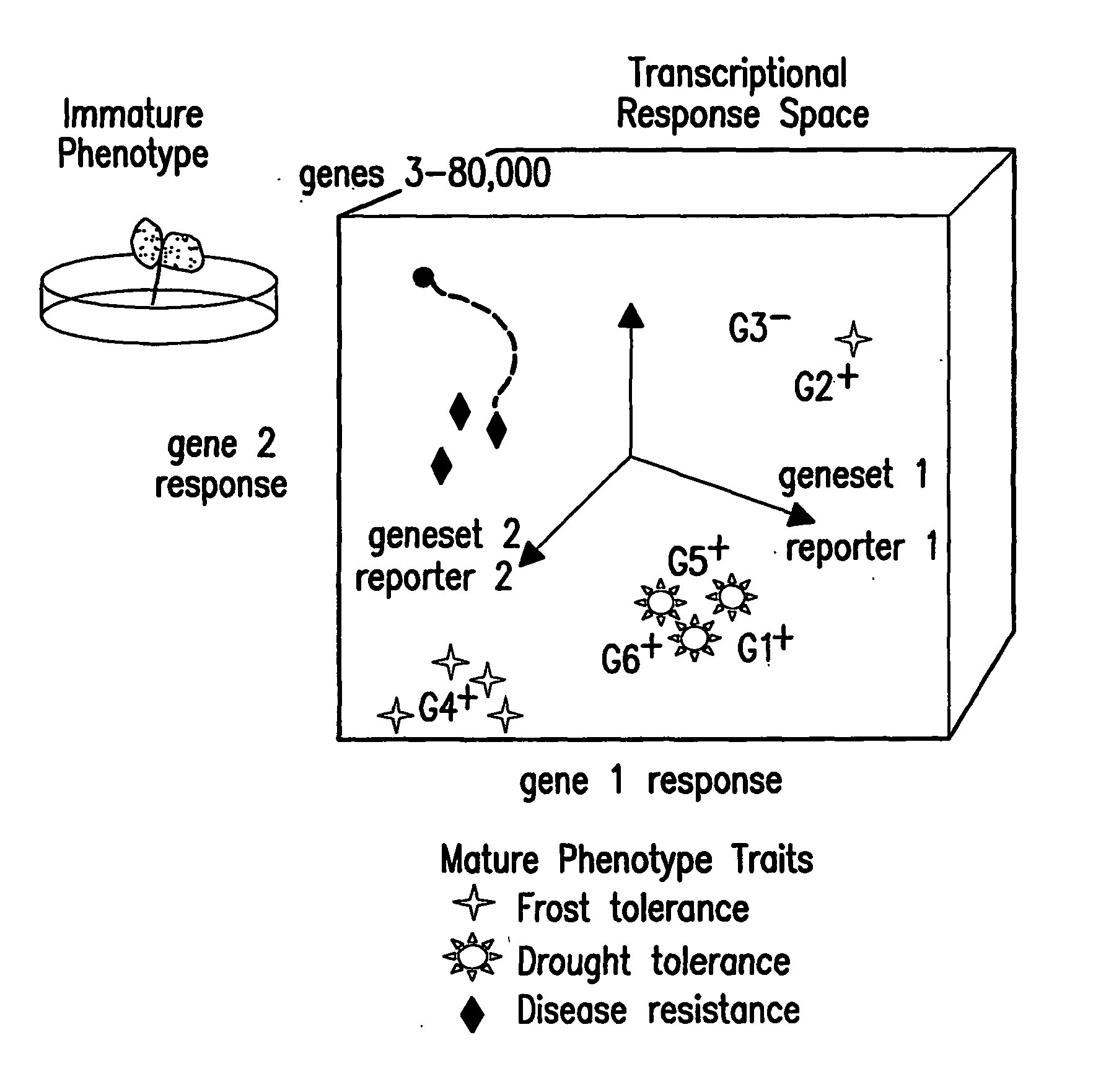
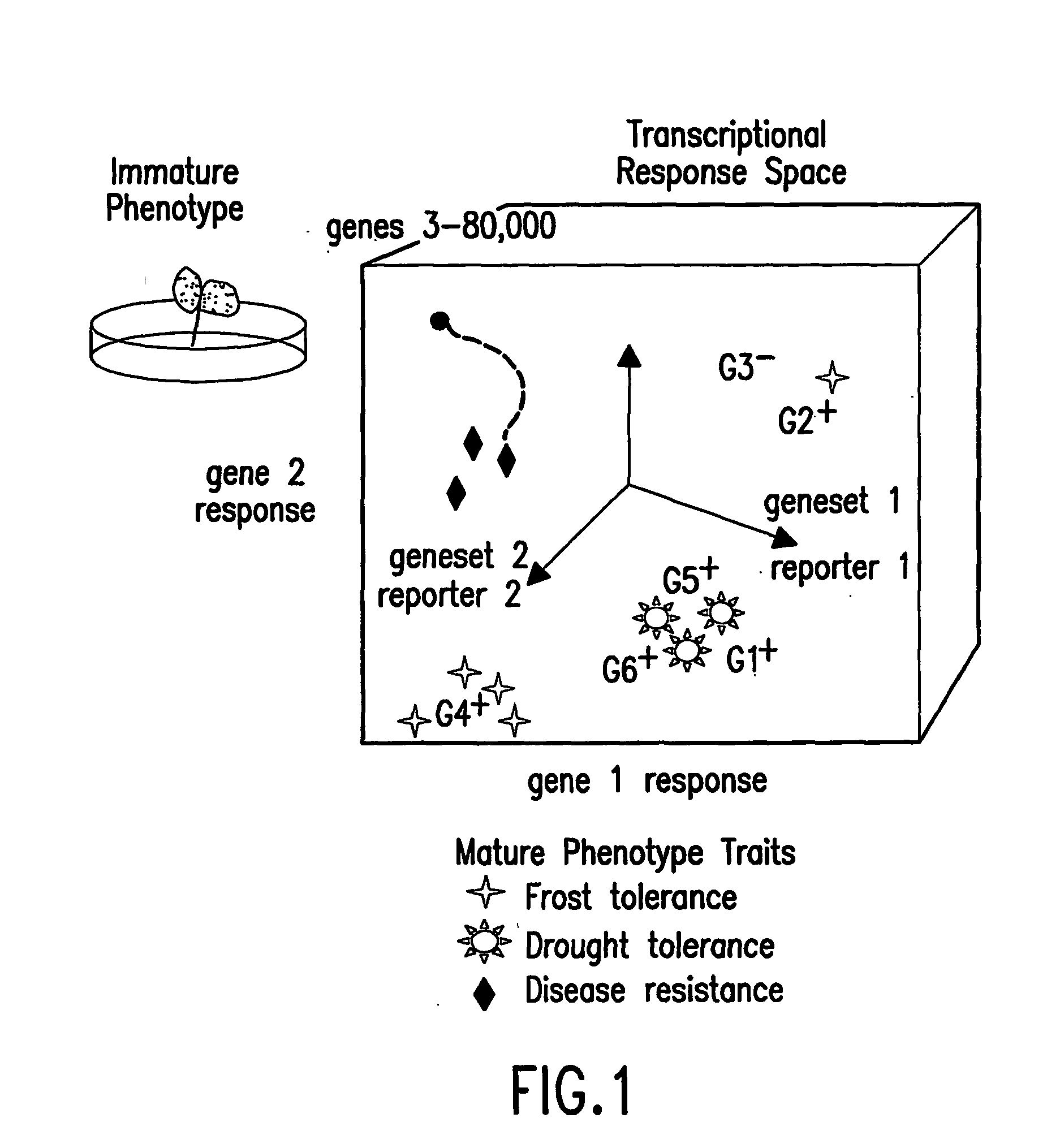
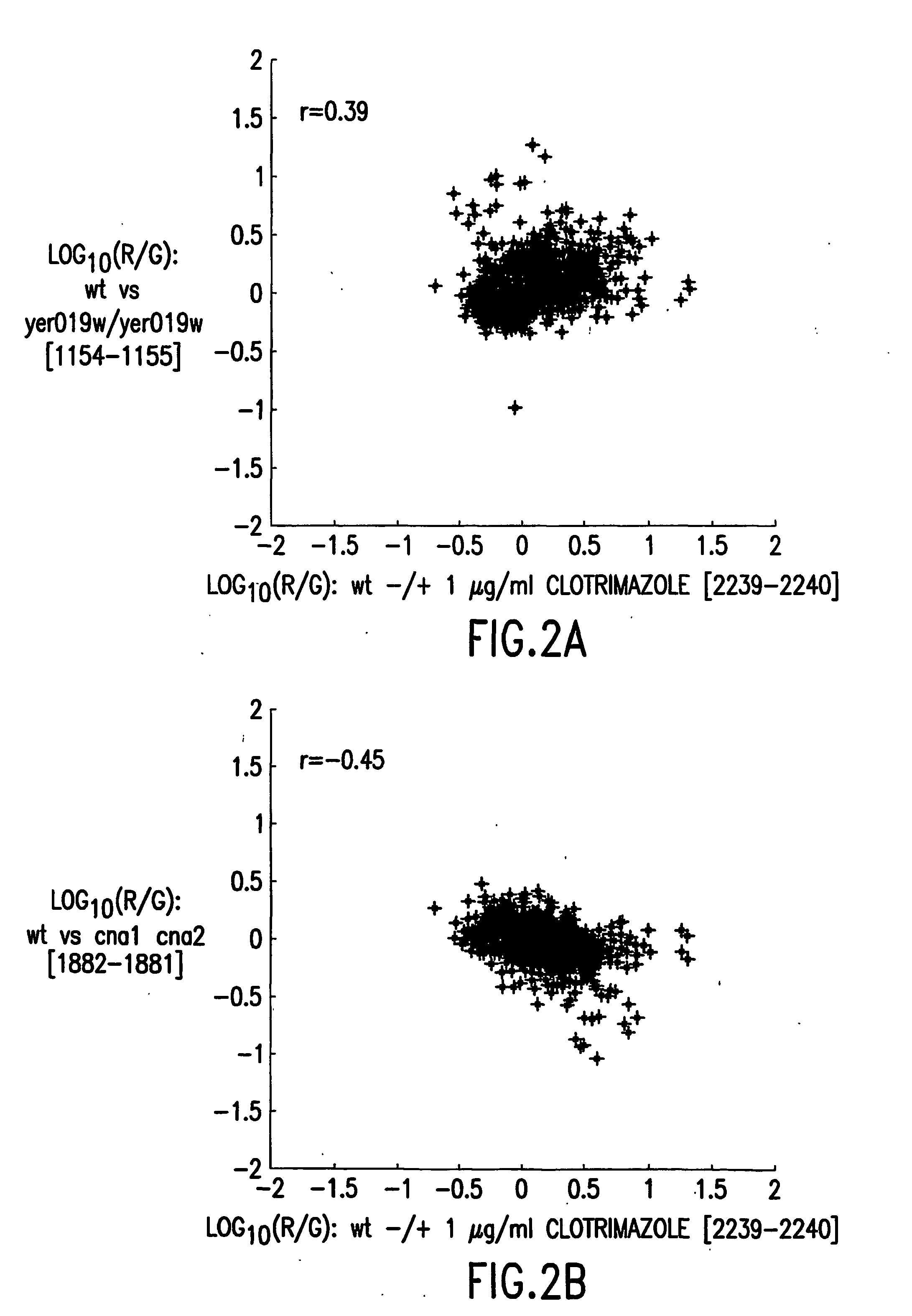
The present invention relates to methods for determining the genetic causes of certain phenotypes. The present invention further relates to methods for predicting the phenotype of a organism from its genotype. In particular, the methods of the invention relate to the use of compendia of biological response profiles of cells having known genetic mutations for comparisons with the biological response profiles of cells having unknown phenotypes and genotypes. The methods of the present invention are particularly useful for monitoring the success of genetic engineering and cross-breeding of crops and livestock. The present invention further relates to a computer system for comparing biological response profiles to a compendium of biological response profiles and to kits for relating the phenotype of a cell type to its genotype or for predicting the phenotype of a cell type.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
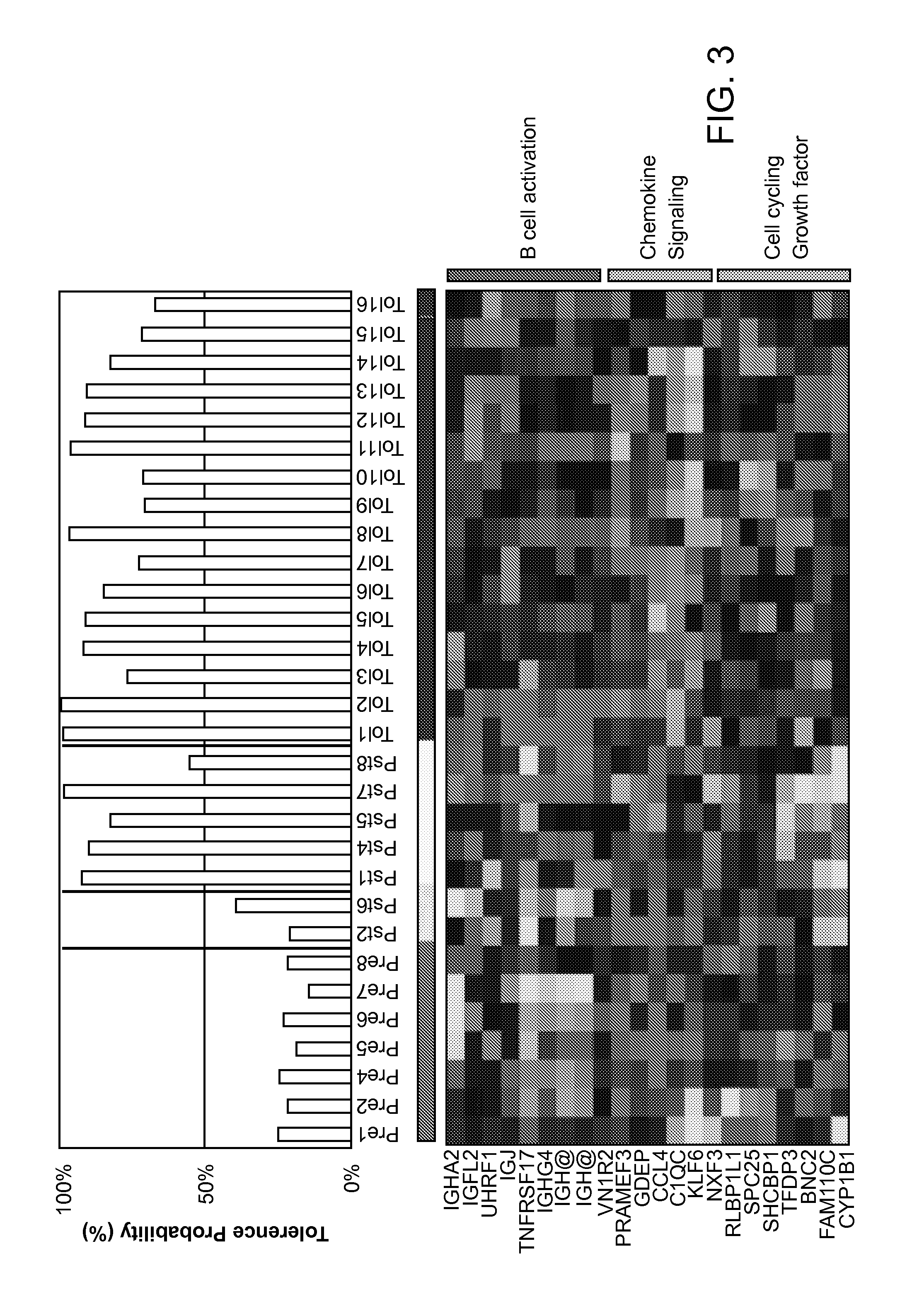
Biomarkers for Determining an Allograft Tolerant Phenotype
Methods are provided for determining whether a subject has a graft tolerant phenotype. In practicing the subject methods, the expression level of one or more gene in a sample from the subject, e.g., a blood sample, is assayed to obtain a gene expression result, where the gene expression result includes a result for a biomarker of graft tolerance. The obtained gene expression result is then employed to determine whether the subject has a graft tolerant phenotype. Also provided are compositions, systems and kits that find use in practicing the subject methods. The methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications, including the determination of an immunosuppressive therapy regimen.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
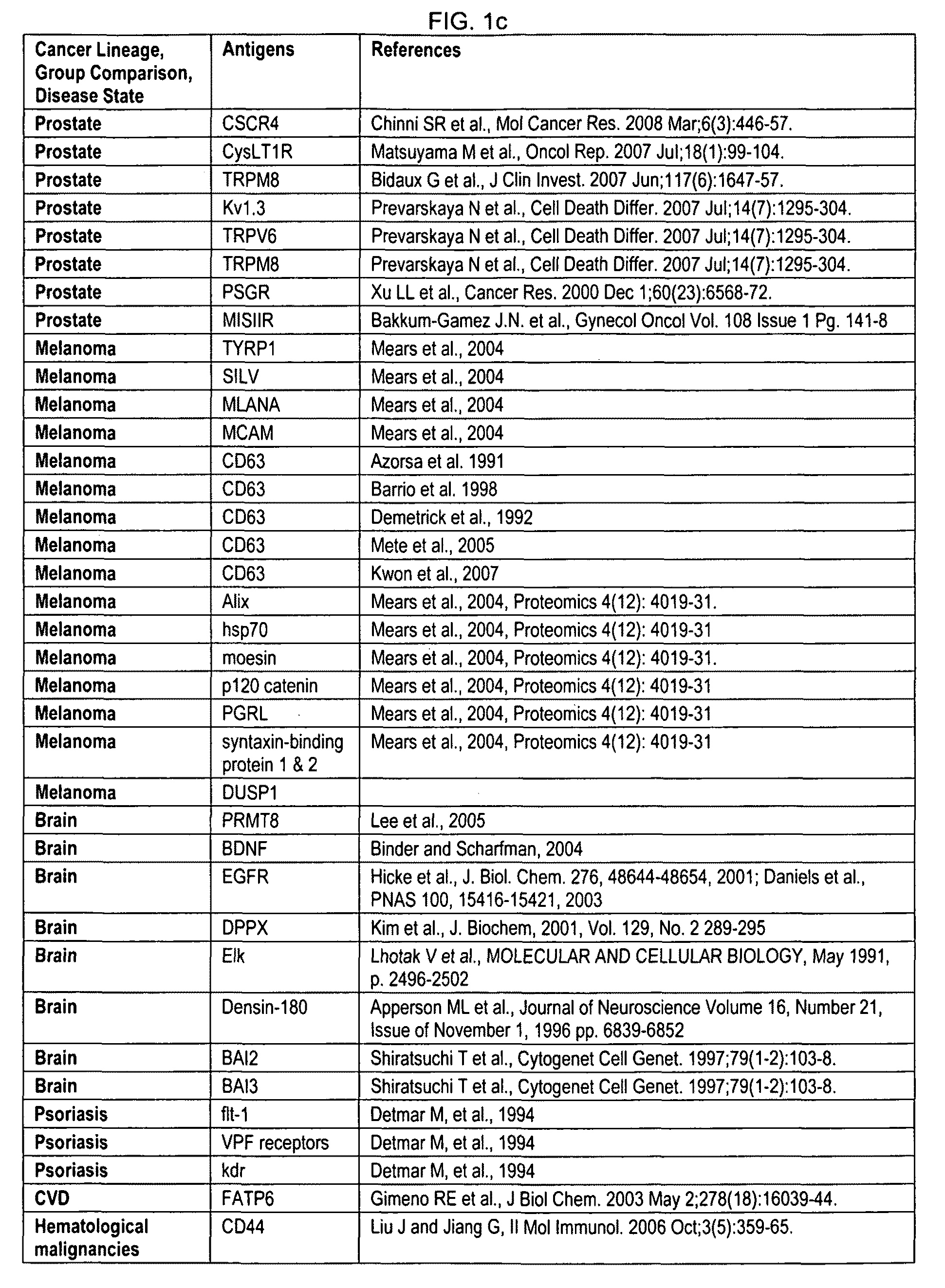
Method for detecting cancers
The invention provides for the production of several humanized murine antibodies specific for the antigen LK26, which is recognized by the murine antibody LK26. This antigen is expressed in all choriocarcinoma, teratocarcinoma and renal cancer cell lines whereas it is not expressed on cell lines of leukaemias, lymphomas, neuroectodermally-derived and epithelial tumour cell lines (excepting a small subset of epithelial cell lines). Furthermore, whereas renal cancer cell lines express the LK26 antigen, normal renal epithelial cells do not. Similarly, with the exception of the trophoblast, all normal adult and fetal tissues tested are negative for the LK26 phenotype. The invention also provides for numerous polynucleotide encoding humanized LK26 specific antibodies, expression vectors for producing humanized LK26 specific antibodies, and host cells for the recombinant production of the humanized antibodies. The invention also provides methods for detecting cancerous cells (in vitro and in vivo) using humanized LK26 specific antibodies. Additionally, the invention provides methods of treating cancer using LK26 specific antibodies.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Yeast arrays, methods of making such arrays, and methods of analyzing such arrays
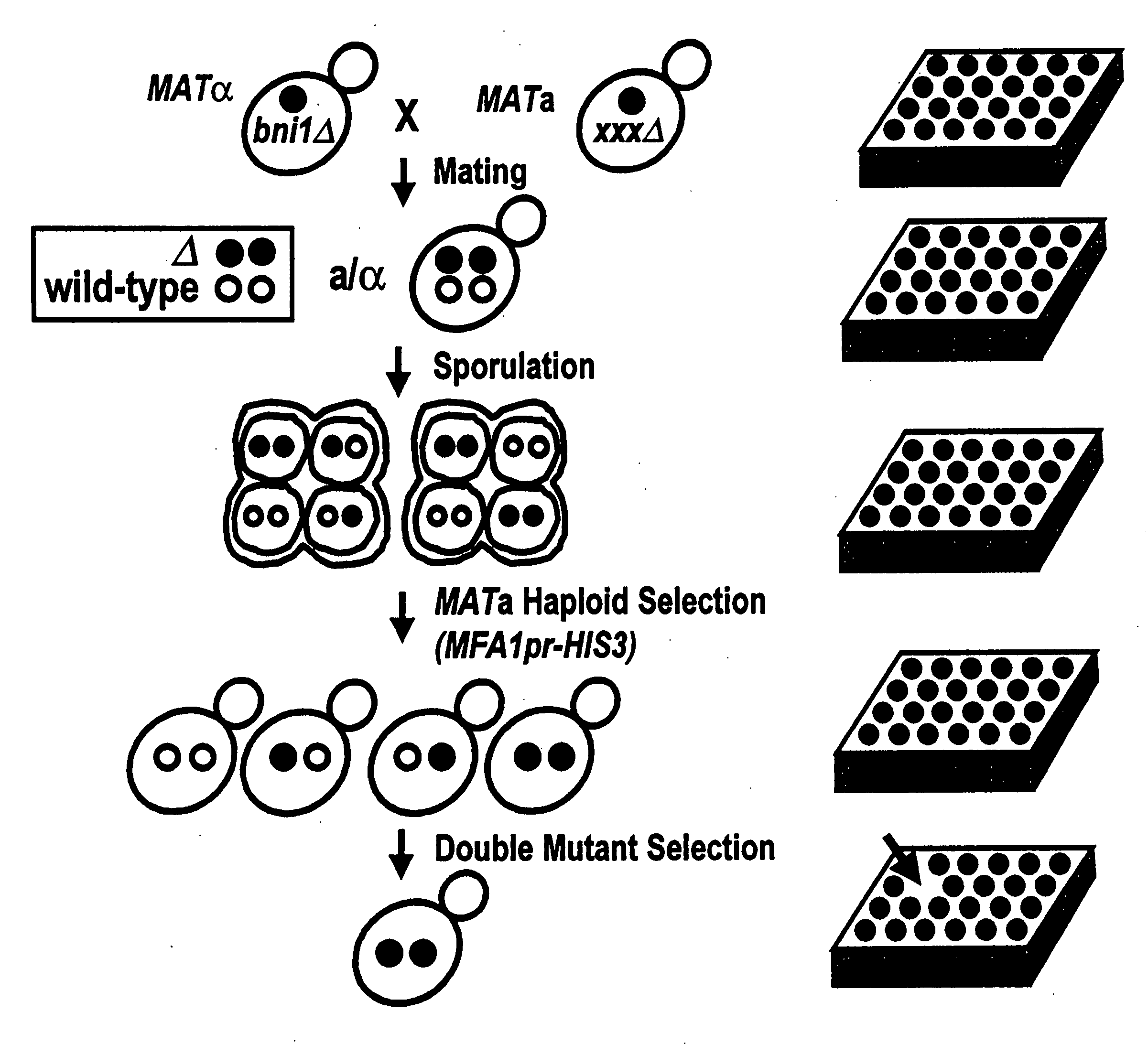
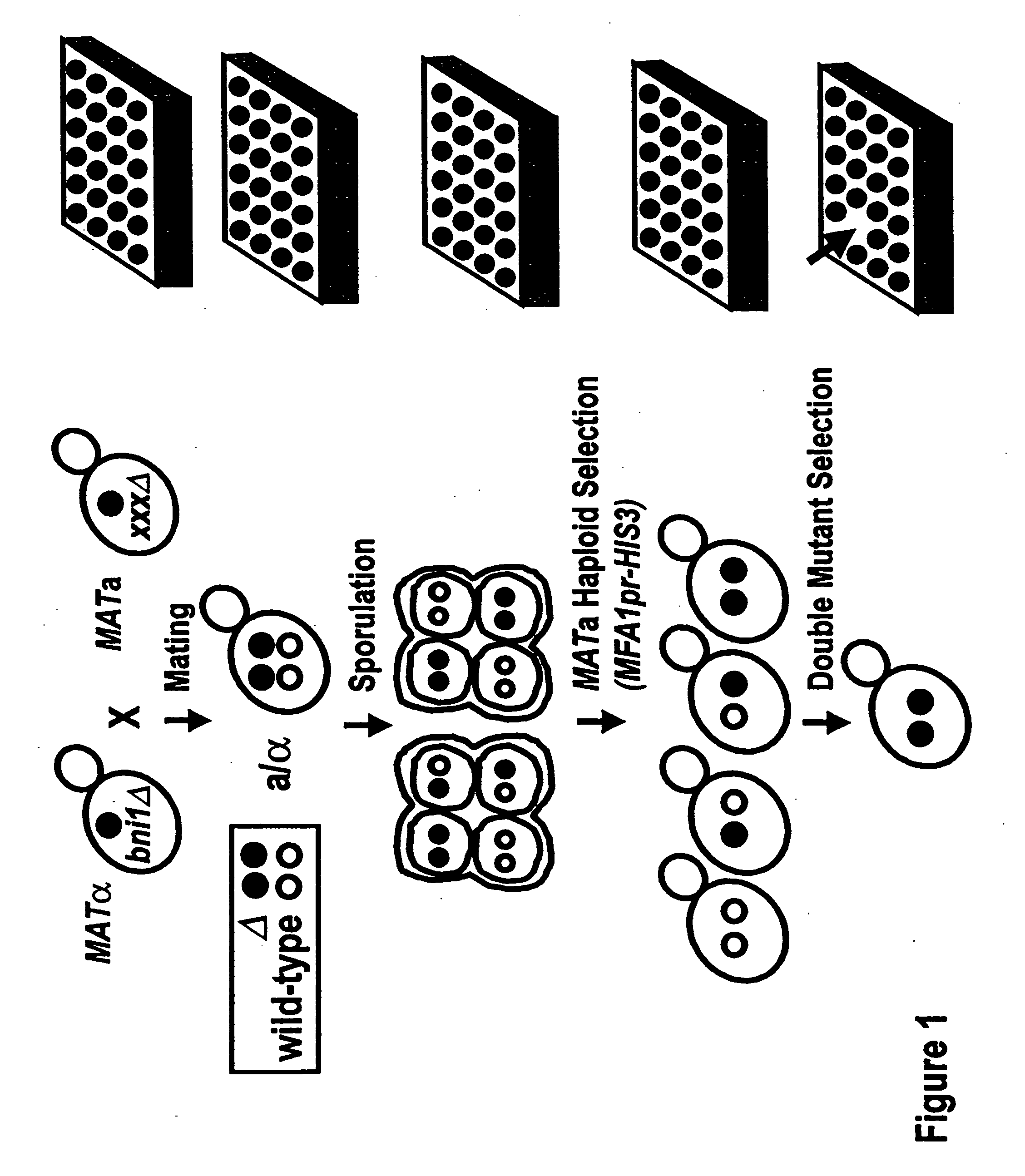
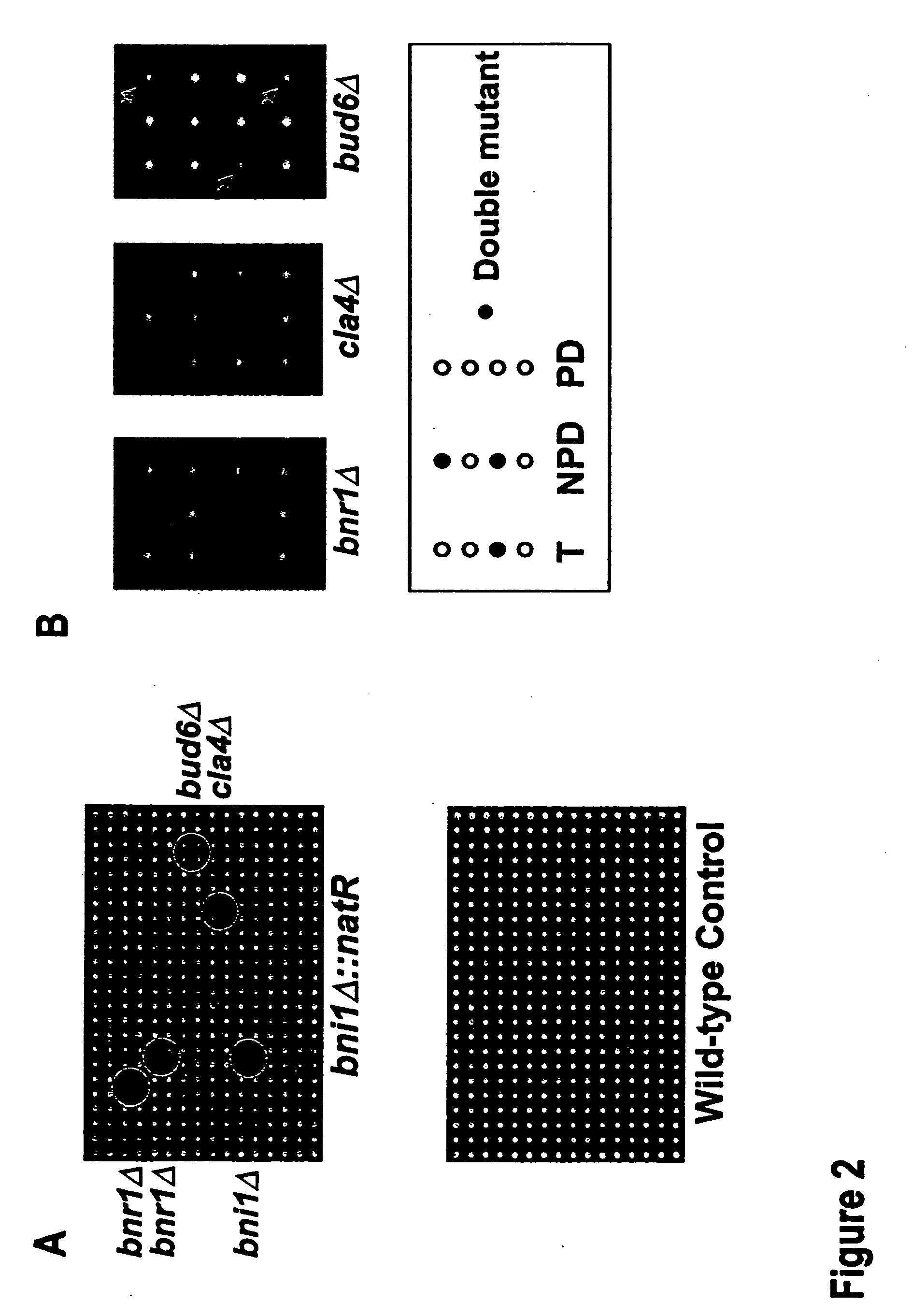
This patent describes a novel method of detecting genetic interactions in yeast. This method can also be used to screen for function of biological effectors on yeast. The method encompasses crossing yeast strains with genetic alterations to acquire double mutants. The phenotypes of these double mutants are then checked to detect genetic interactions between the double mutants. This method can be used to assign function to yeast genes and their viral, prokaryotic, and eukaryotic homologs, and aptamers. It can also be used to study yeast two hybrid interactions and to find genes that regulate certain yeast promoters.
Owner:BOONE CHARLES
Method for risk assessment for polygenic disorders
InactiveUS20040115701A1Reduce riskIncrease powerMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsPolygenic diseaseGenotype
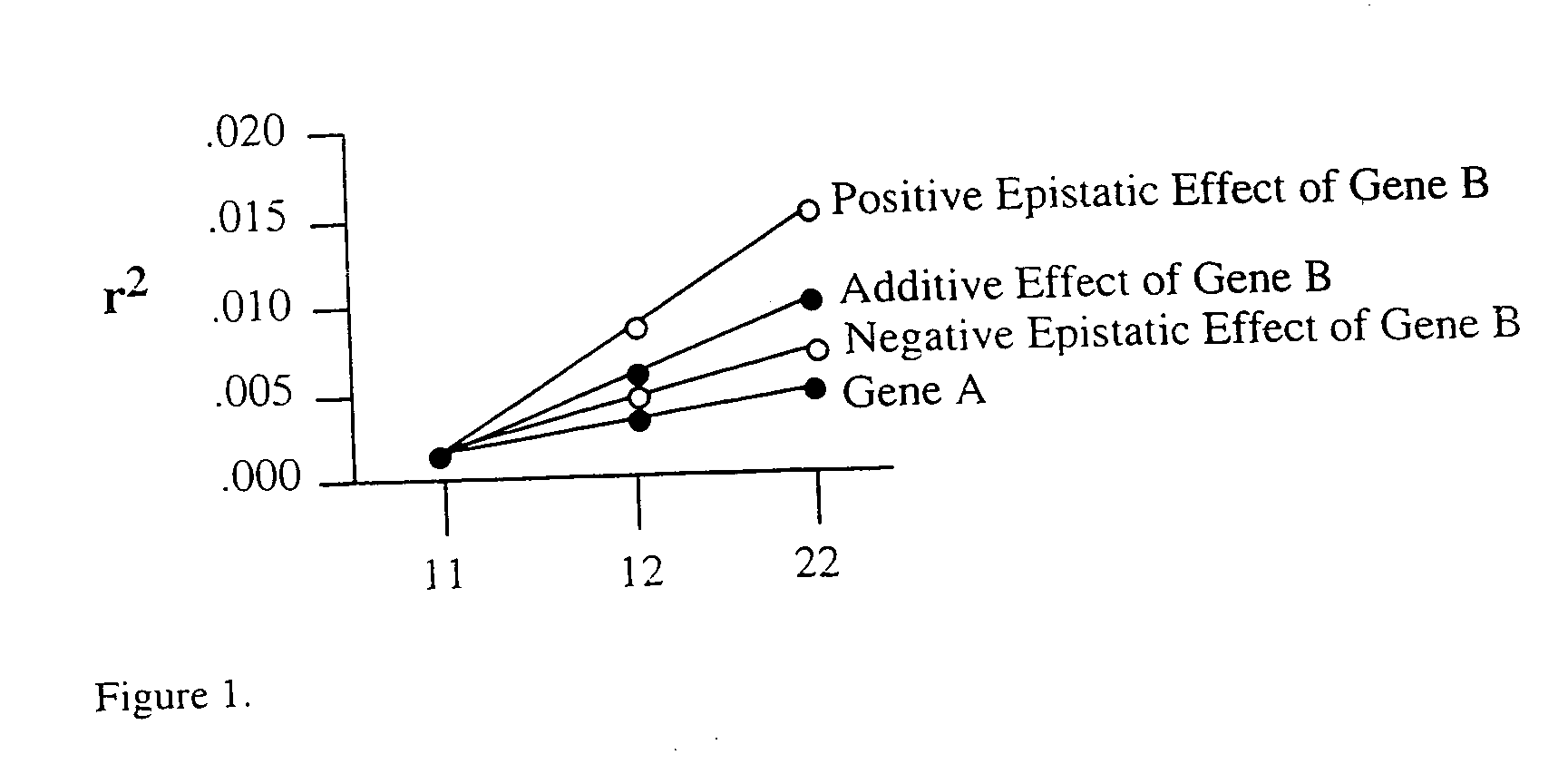
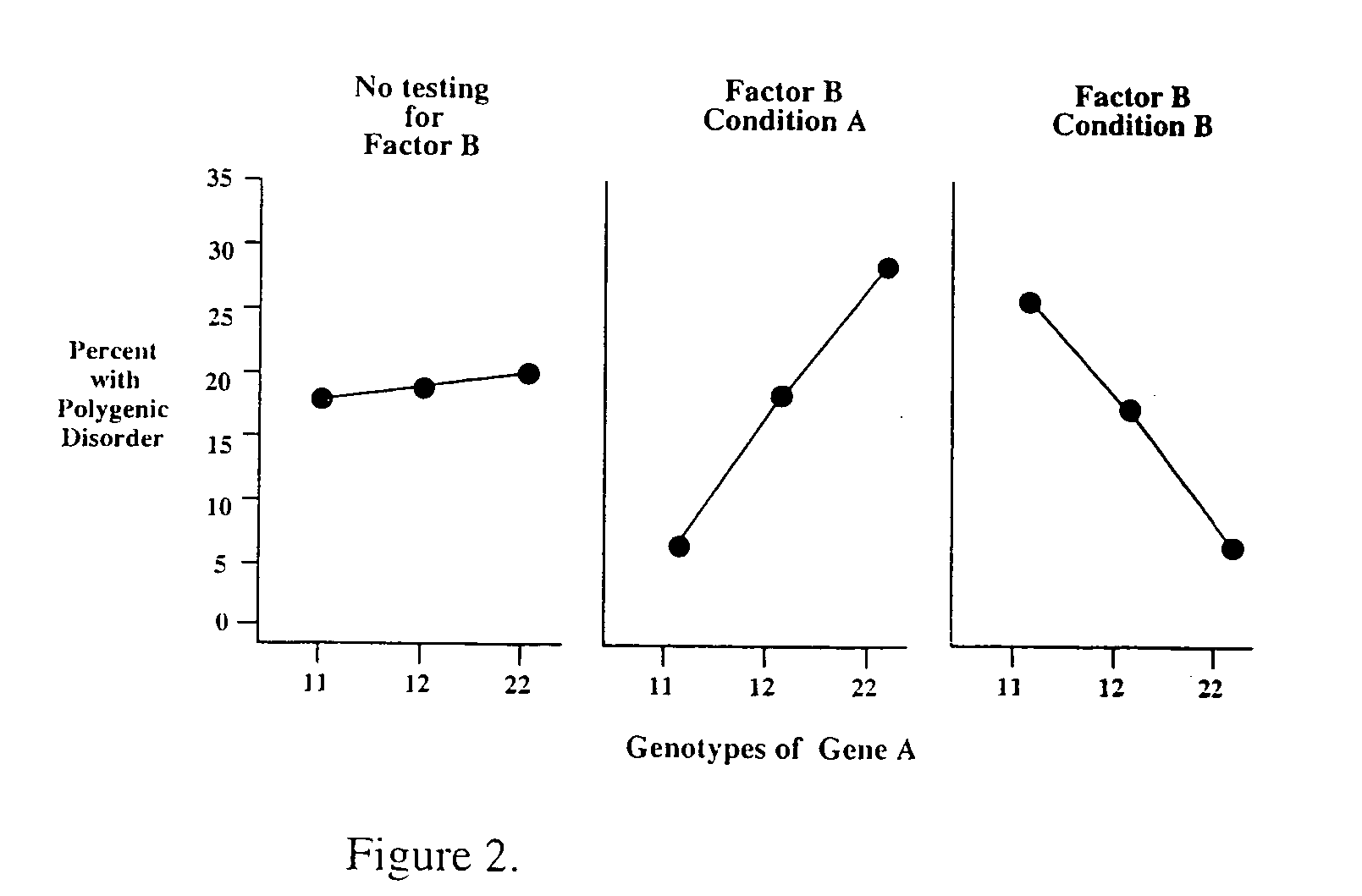
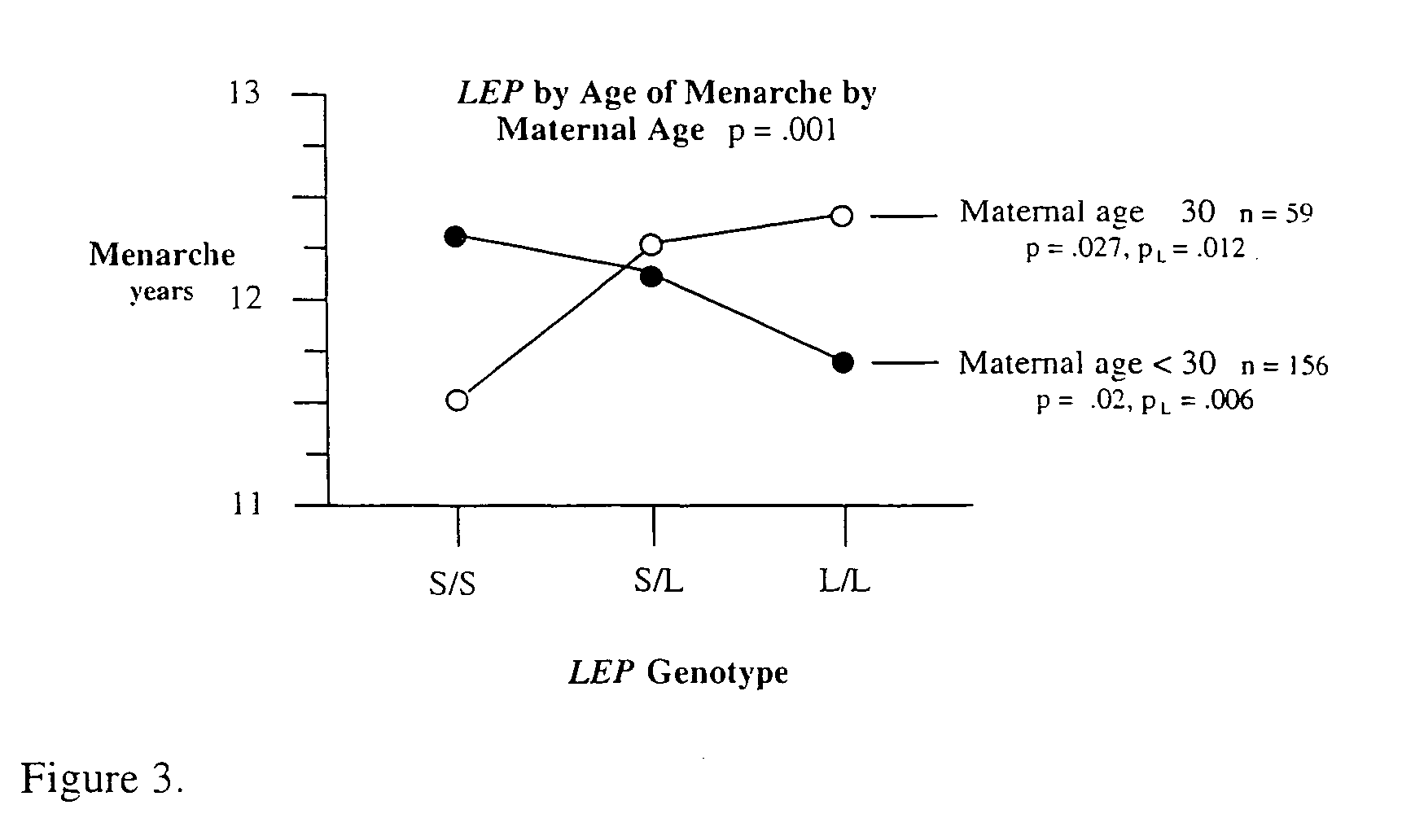
The present invention is directed to the identification of genostatic factors, methods of determining the association of a plurality of genes with polygenic disorders, and method of assessing the sensitivity and specificity of the risk of polygenic disorders. In particular, the present invention discovers that the association between a polygenic disorder phenotype and polygenes may be masked. Incorporating genostatic factor, such as maternal age, birth disorder, the androgen receptor gene, gender, and age, into the statistical analysis of the association between phenotypes and genotypes reveals statistically significant relationship between the two. Accordingly, the present invention provides novel methods in determining the association of a plurality of genes with a polygenic disease and the likelihood of having the polygenic disease.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
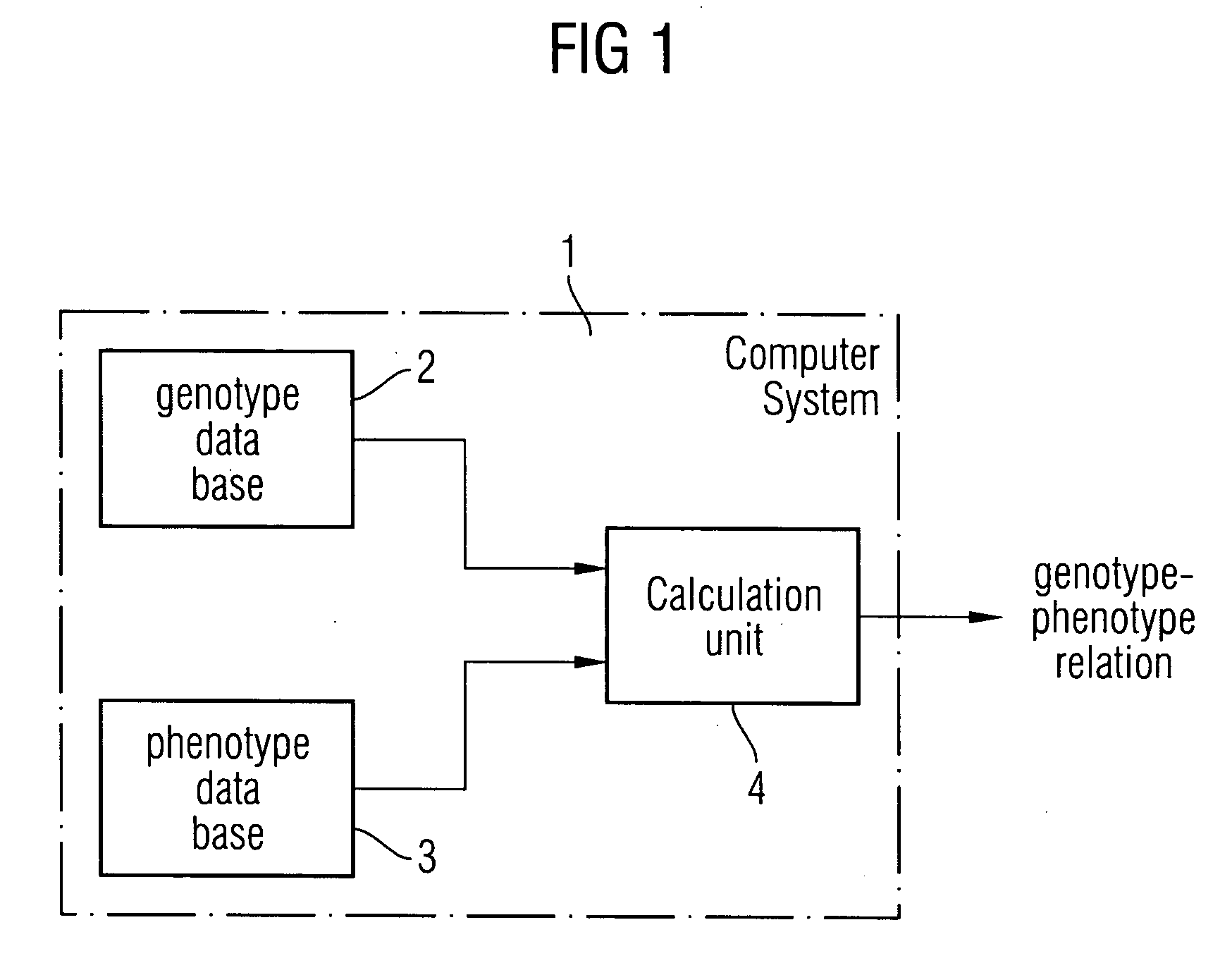
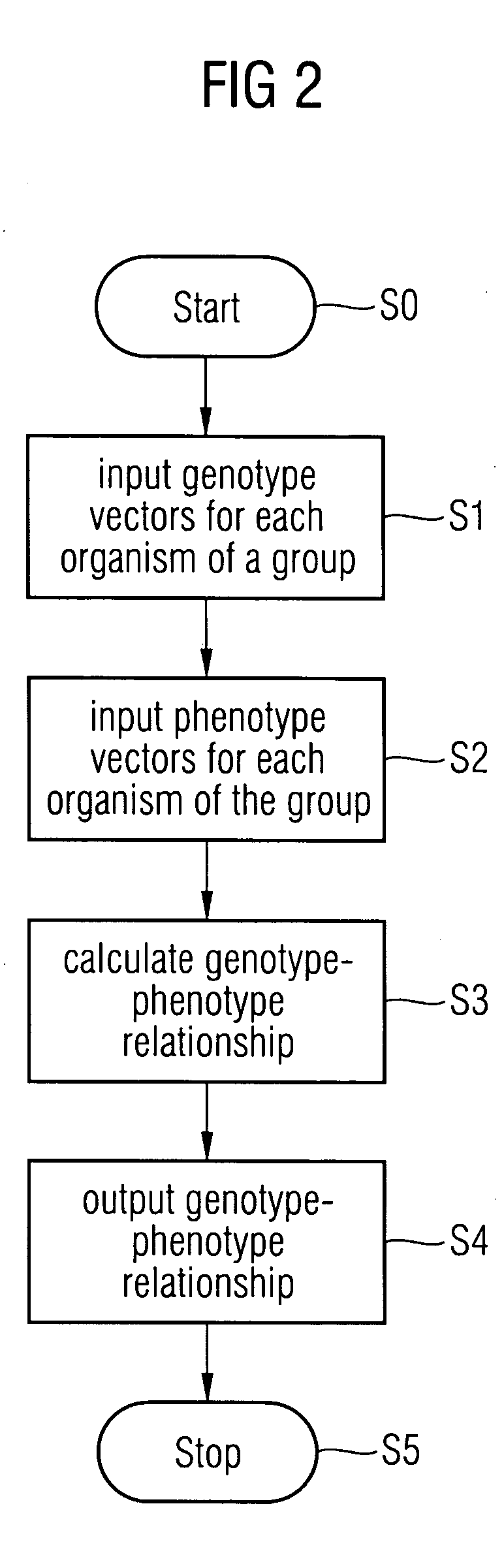
Method and a system for extracting a genotype-phenotype relationship
At least one genotype-phenotype relationship is extracted based on genotype data of a group of genes for different organisms of a group of organisms. A first database stores genotype data of each organism of the group of organisms. For each organism a genotype vector is stored having a vector component for each gene of the group of genes. A second database stores phenotype data of each organism of the group of organisms. For each organism a phenotype vector is stored having a vector component for each phenotype feature of a group of phenotype features of the organism. A calculation unit uses a machine learning process to classify organisms with different phenotypes depending on the genotype vectors stored in the first database and the phenotype vectors stored in the second database to extract the genotype-phenotype relationship.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Somatic hypermutation systems
InactiveUS20120028301A1Avoid problemsDecrease and increase in rateImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminaseIn vivo
The present application relates to somatic hypermutation (SHM) systems and synthetic genes. Synthetic genes can be designed using computer-based approaches to increase or decrease susceptibility of a polynucleotide to somatic hypermutation. Genes of interest are inserted into the vectors and subjected to activation-induced cytidine deaminase to induce somatic hypermutation. Proteins or portions thereof encoded by the modified genes can be introduced into a SHM system for somatic hypermutation and proteins or portions thereof exhibiting a desired phenotype or function can be isolated for in vitro or in vivo diagnostic or therapeutic uses.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
Multidimensional detection of aberrant phenotypes in neoplastic cells to be used to monitor minimal disease levels using flow cytometry measurements
ActiveUS7507548B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseMultidimensional scaling
A method for detecting aberrant phenotypes expressed by neoplastic cells includes the steps of: 1) staining one or more normal / reactive samples and one neoplastic sample with multiple combinations of monoclonal antibodies, 2) measuring fluorescence emissions associated to the stained cells, 3) storing two independent list mode data files of information on light scatter and fluorescence characteristics of each cell, 4) creating new data files by mixing list mode data from the data file containing information the neoplastic sample into the data file containing information on the normal samples, 5) defining corresponding to normal cells and areas corresponding to empty spaces in normal / reactive samples that may be occupied by tumor cells in neoplastic samples, 6) identifying events corresponding to neoplastic cells and events corresponding to normal cells coexisting in a multidimensional space, and 7) establishing the most relevant phenotypic aberrations displayed by the neoplastic cells as compared to their normal counterpart.
Owner:UNIV DE SALAMANCA
IL-1 gene cluster, insulin resistance and coronary artery disease associated polymorphisms and haplotypes and methods of using same
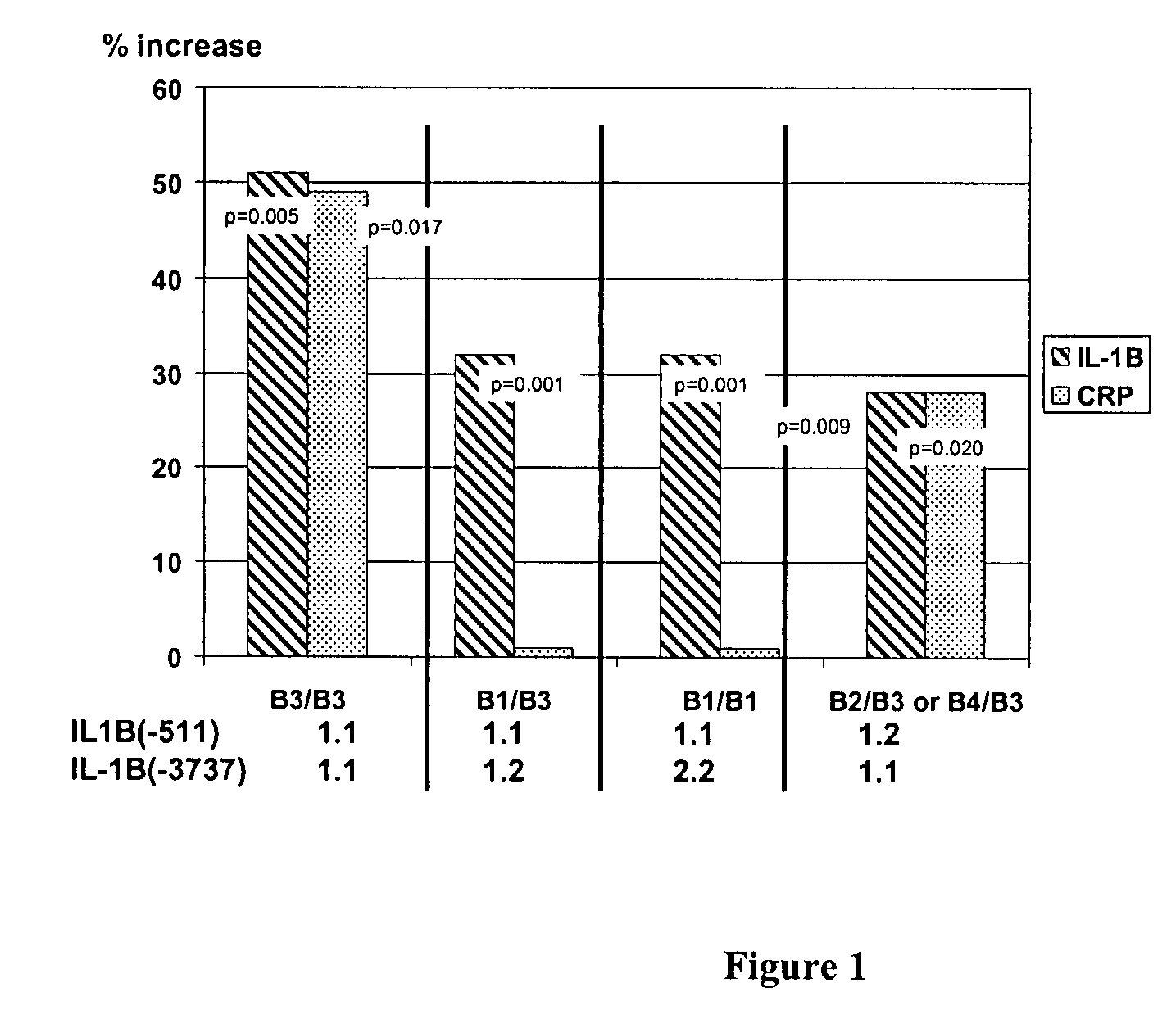
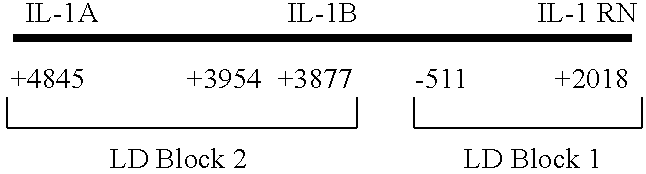
The invention provides methods and compositions relating to identification and use of genetic information from the IL-1 gene cluster—including the structure and organization of novel IL-1-like genes found within the IL-1 locus as well as polymorphisms and associated haplotypes within these genes. The invention thereby expands the repertoire of useful genetic information available from the IL-1 locus—which contains the previously-identified IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-1RN genes, for predicting IL-1 associated phenotypes (e.g. increased or decreased risks of insulin resistance associated pathologies) and for treating IL-1 haplotype associated insulin resistance associated pathologies.
Owner:SAPPHIROS LAB LLC
Uses of labeled hsp90 inhibitors
The disclosure provides evidence that the abundance of this particular “oncogenic HSP90” species, which is not dictated by HSP90 expression alone, predicts for sensitivity to HSP90 inhibition therapy, and thus is a biomarker for HSP90 therapy. The disclosure also provides evidence that identifying and measuring the abundance of this oncogenic HSP90 species in tumors predicts of response to HSP90 therapy. “Oncogenic HSP90” is defined herein as the HSP90 fraction that represents a cell stress specific form of chaperone complex, that is expanded and constitutively maintained in the tumor cell context, and that may execute functions necessary to maintain the malignant phenotype. Such roles are not only to regulate the folding of overexpressed (i.e. HER2), mutated (i.e. mB-Raf) or chimeric proteins (i.e. Bcr-Abl), but also to facilitate scaffolding and complex formation of molecules involved in aberrantly activated signaling complexes (i.e. STATS, BCL6).
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
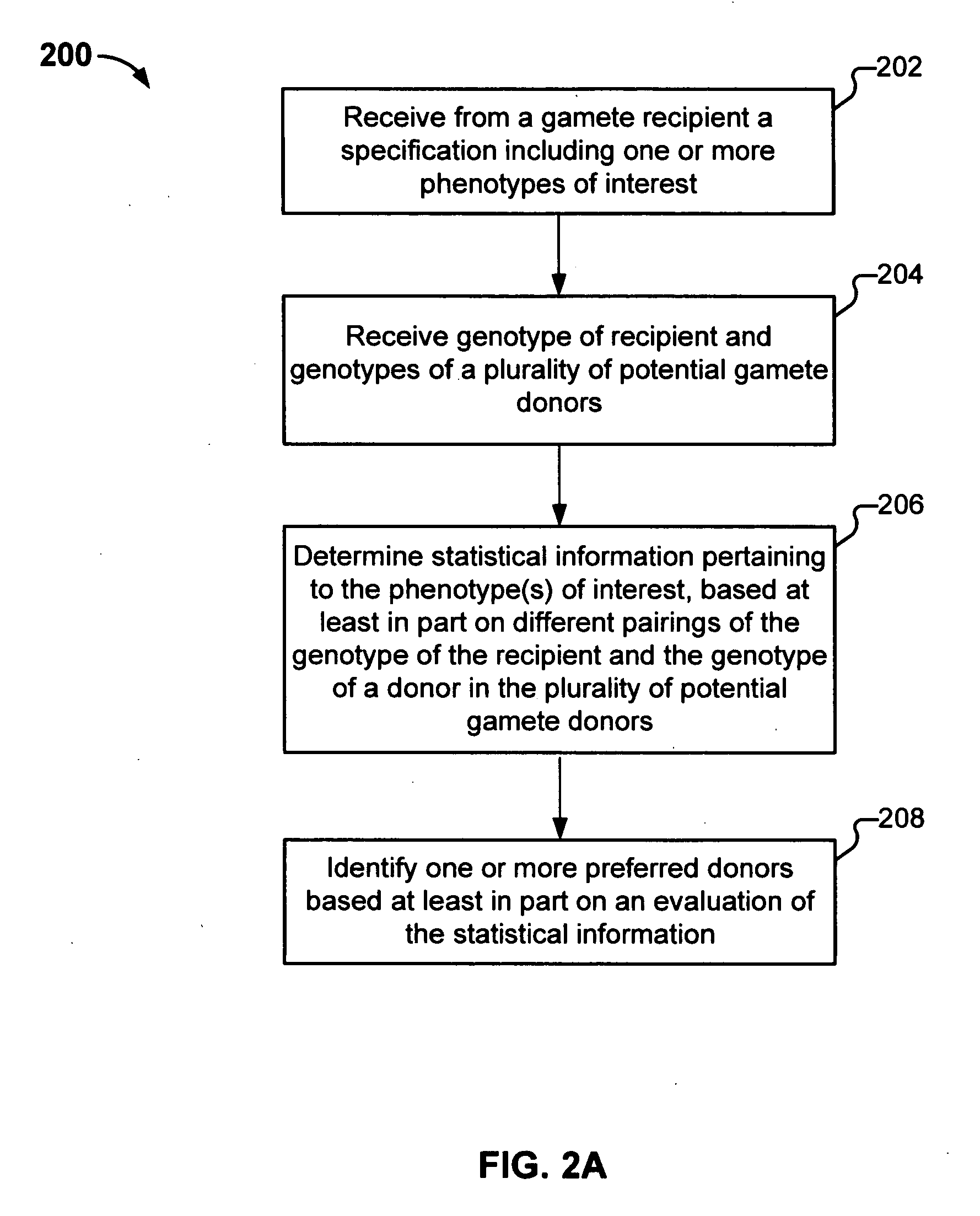
Gamete donor selection based on genetic calculations
Gamete donor selection includes receiving a specification including a phenotype of interest, receiving a genotype of a recipient and a plurality of genotypes of a respective plurality of donors, determining statistical information pertaining to the phenotype of interest based at least in part on different pairings of the genotype of the recipient and a genotype of a donor in the plurality of donors, and identifying a preferred donor among the plurality of donors, based at least in part on the statistical information determined.
Owner:23ANDME
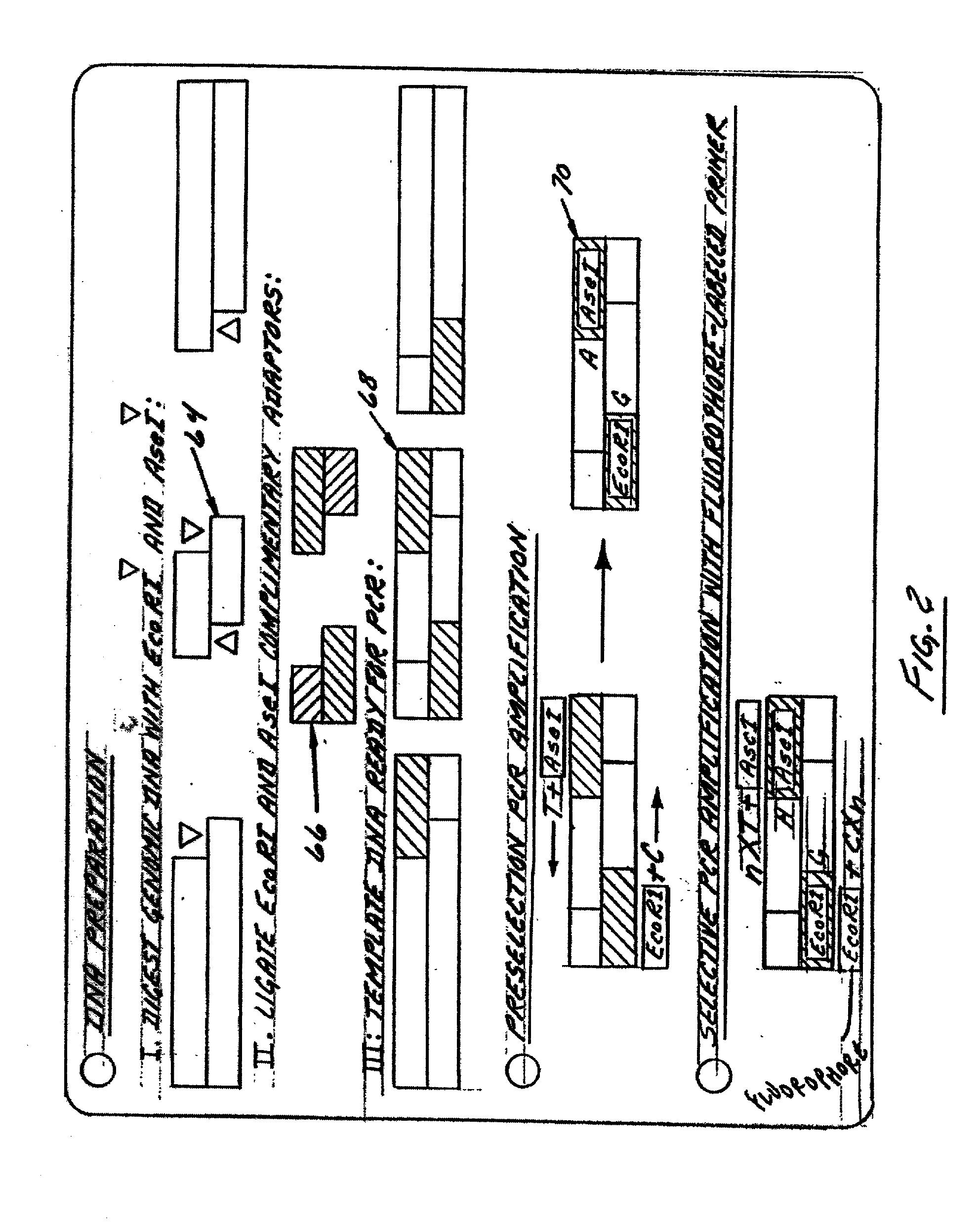
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker for evaluating growth performance of ctenopharyngodonidella, primer and evaluation method
ActiveCN106755527AEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic exchangeIntein
The invention provides an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker (comprising SNP1 and SNP4) for evaluating growth performance of ctenopharyngodonidella and a primer pair for amplifying a gene segment where an SNP locus is positioned by virtue of methods of molecular genetics and molecular biology. SNP1 is positioned at the 940th locus in a promoter of a complete sequence of a MyoD (myogenic determining factor) gene of the ctenopharyngodonidella, and a base T is inserted or deficient at the position; SNP4 is positioned in a 107th locus in a first intron of the complete sequence of the MyoD gene of the ctenopharyngodonidella, and a base at the position is A or T. The growth performance of the ctenopharyngodonidella is determined by detecting haplotypes of the two SNP loci. The adopted haplotypes are mutated according to bases generated in the MyoD gene, so that genetic exchange and further phenotype verification are avoided. By virtue of the haplotypes of the SNP marker, rapidly growing ctenopharyngodonidella can be simply and rapidly identified, and rapidly growing ctenopharyngodonidella of a new line can also be guided to be bred.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and using genetic, phentoypic and clinical data to make predictions
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, and also for predicting likely phenotypic outcomes using mathematical models and given genetic, phenotypic and / or clinical data of an individual, and also relevant aggregated medical data consisting of genotypic, phenotypic, and / or clinical data from germane patient subpopulations. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects.
Owner:NATERA
A method for estimating genomic breeding value integrating dominance effects
ActiveCN109101786AImprove accuracyIntroduce reasonableSpecial data processing applicationsHomozygous genotypeModel complexity
The invention discloses a genome breeding value estimation method for integrating dominant effect, which relates to the technical field of livestock and poultry genetic selection. The method comprisessteps identifying a reference group and a candidate group, the phenotype of the target traits of the reference population was determined, Genome-wide marker typing of reference population, quality control of gene marker of reference population, statistics of heterozygous marker deviation of reference population, formulation of genome marker re-coding rules, genome-wide marker typing of candidatepopulation, quality control of gene marker of candidate population, re-coding of genome marker and estimation of genome breeding value, etc. Based on the deviation degree between the phenotype of theheterozygous genotype and the phenotype of the homozygous genotype, the invention formulates coding rules, starts from the genomic marker end, re-codes the heterozygous genotype, causes the gene marker coding to include dominant effect, and then estimates the genomic breeding value. The invention is adapted to the needs of livestock and poultry genetic breeding, and can greatly improve the accuracy of genome estimation breeding value without increasing the complexity of the model.
Owner:ANIMAL SCI RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Concurrent two-phase completion genetic algorithm system and methods
InactiveUS7603325B2Efficient processingImprove accuracyDigital computer detailsBiological testingData setGenotype
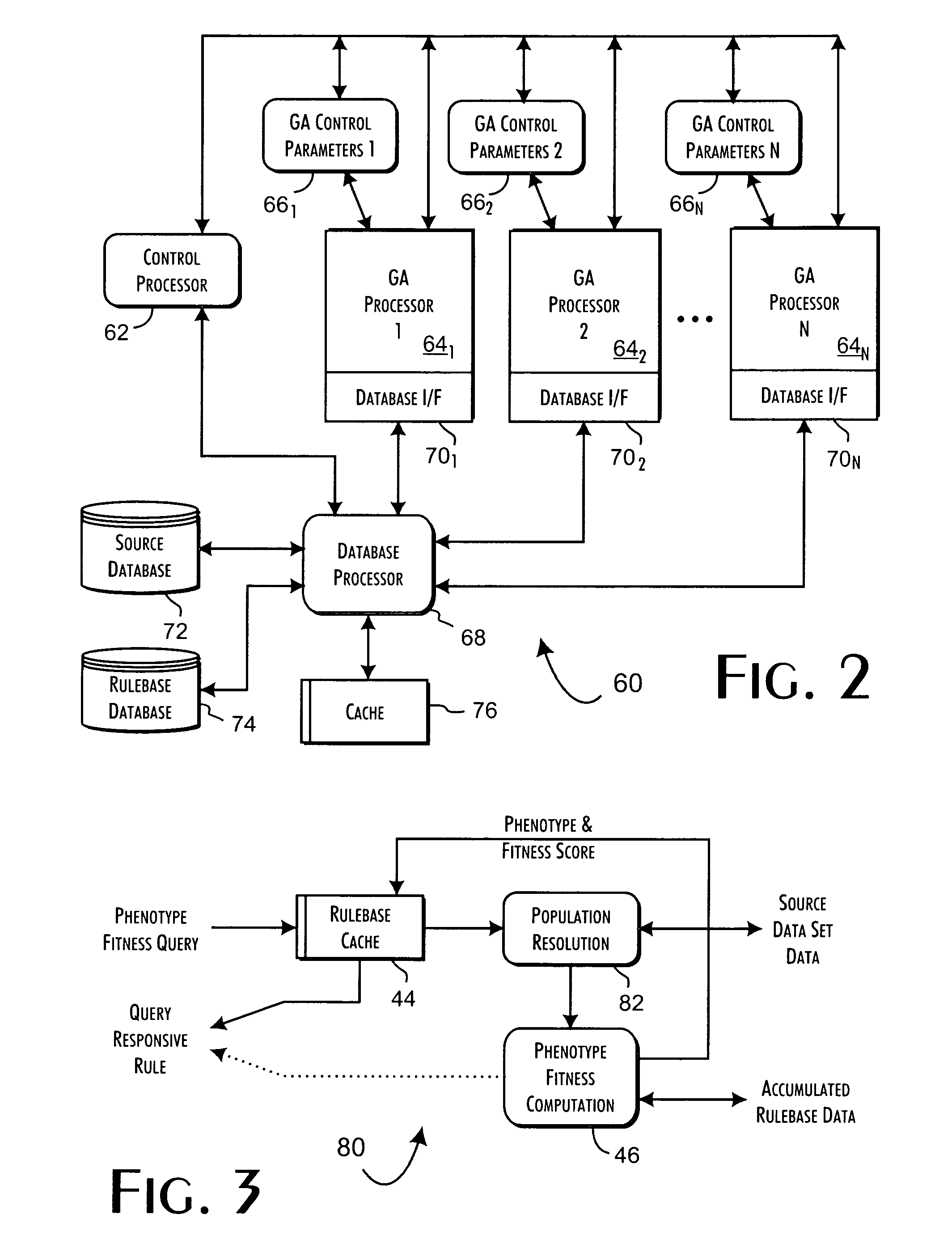
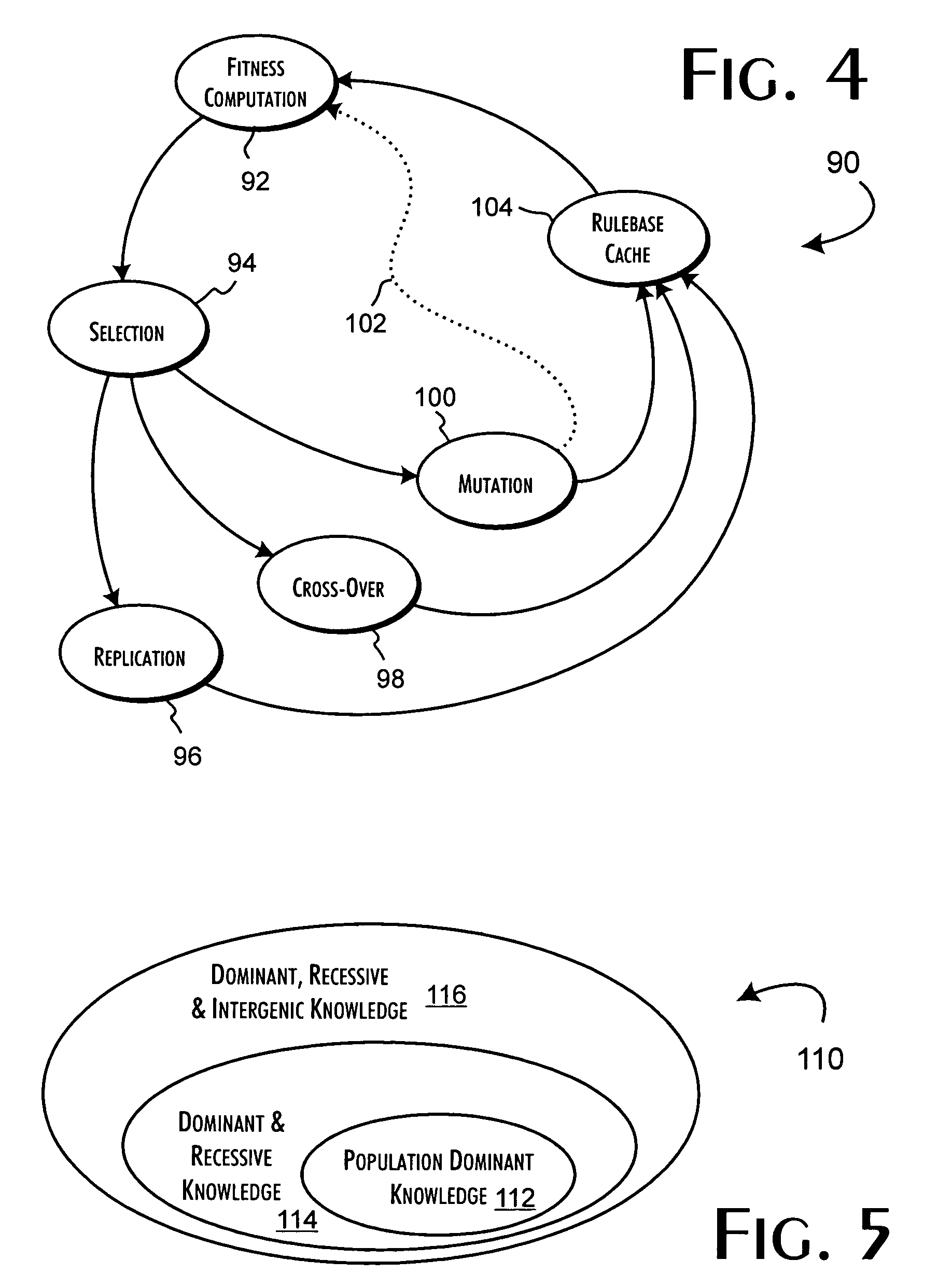
A genetic algorithm architecture implements a two-stage completion genetic algorithm with respect to an evolving current population data set. The two-stage completion genetic algorithm that includes genotype and phenotype completion loops. The genotype completion loop operates to compete the current population data set based on genotype field fitness scores. The genotype completion loop also implements a phenogenesis operator used to generate a current phenotype set. The phenotype completion loop operates, concurrently with the genotype completion loop, to evaluate the current phenotype set, constrained relative to the current population data set, against a fitness function to produce phenotype fitness scores. The phenotype completion loop implements a genotype reduction operator that then determines corresponding genotype fitness scores for use as the basis for competition in the genotype completion loop.
Owner:JACOBSON DAVID L
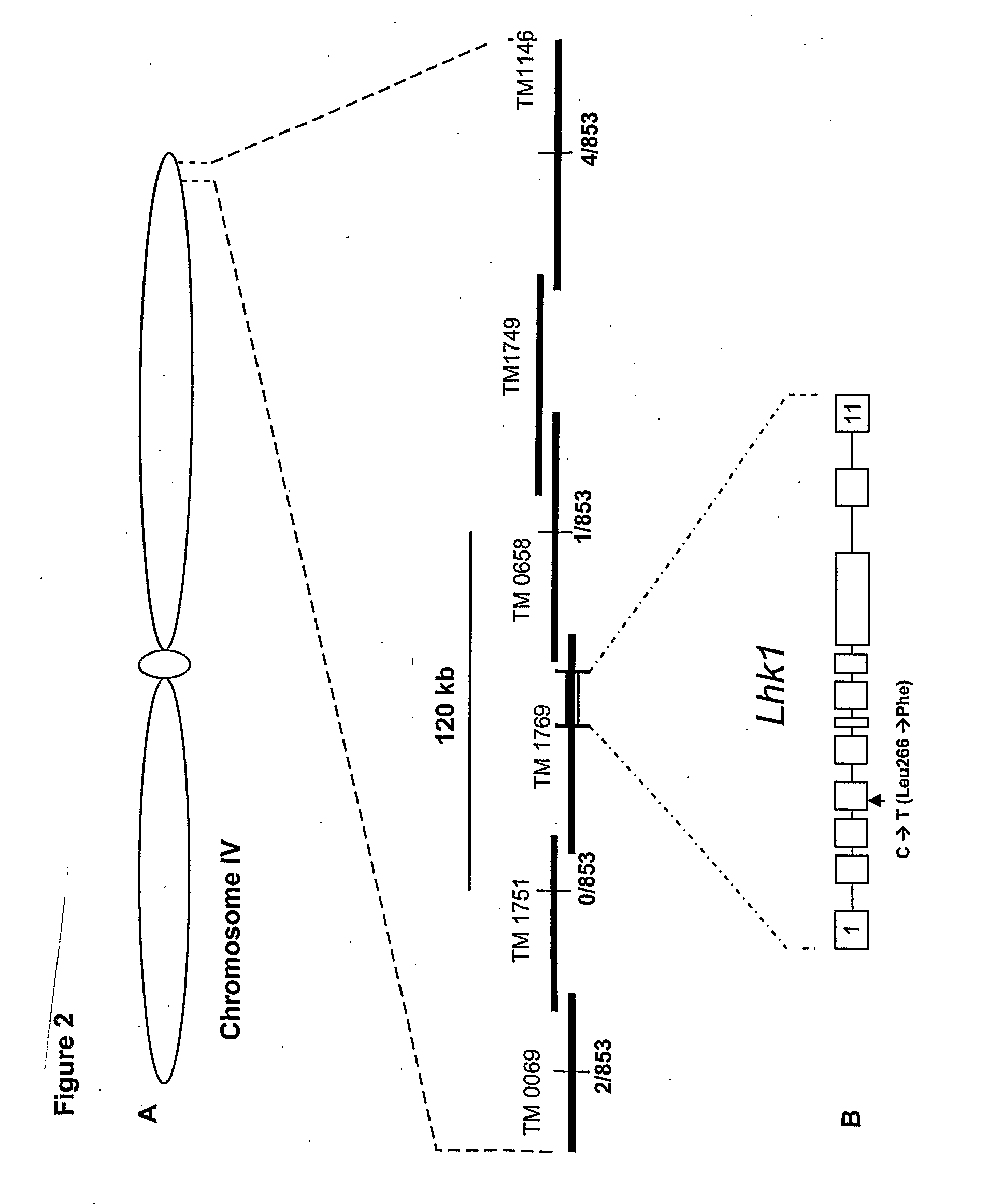
Mutant histidine kinase that confers spontaneous nodulation in plants
Formation of nitrogen fixing root nodules in legumes is induced by perception of lipochitin-oligosaccharide signal molecules secreted by compatible Rhizobium bacteria, which triggers a common symbiotic pathway. The present invention provides a spontaneous nodule formation (snf2) mutant, in which the formation of symbiotic nodules is spontaneous, leading to nodule development in the absence as well as in the presence of Rhizobium bacteria and / or exogenous rhizobial signals. The invention further provides an isolated DNA sequence encoding a mutant cytokinin-independent histidine kinase whose activity results in this ‘gain of function’ dominant phenotype of spontaneous nodule formation. Furthermore the snf2 gene is shown to confer a phenotype, characterised by regulated organogenesis of spontaneous nodules, to plants having a nodulation deficient genetic background. A gene of the invention, that confers this spontaneous nodulation phenotype, has 15 utility for the transfer and establishment of nitrogen fixing capability in non-nodulating plants, and thereby reducing the nitrogen fertiliser dependence of non-nodulating crop plants.
Owner:STOUGAARD JENS +5
Process for selecting individuals and designing a breeding program
InactiveUS20080216188A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesMethod selectionGenetics
The presently disclosed subject matter provides methods for improving the efficacy of a plant breeding program aimed at altering phenotypic traits for which associations with genetic markers can be established. Genome-wide genetic values of individuals are computed based on the individuals' marker genotypes and the associations established between genetic markers and phenotypic traits. Individuals and breeding schemes are then selected based both on the individuals' genome-wide genetic value and on the distributions of these genetic values for the potential progenies derived through the breeding schemes under evaluation. The presently disclosed subject matter also provides systems and computer program products for performing the disclosed methods as well as plants selected, provided, or produced by any of the methods herein and transgenic plants created by any of the methods herein.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data
InactiveUS6909971B2Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene mappingNucleotide
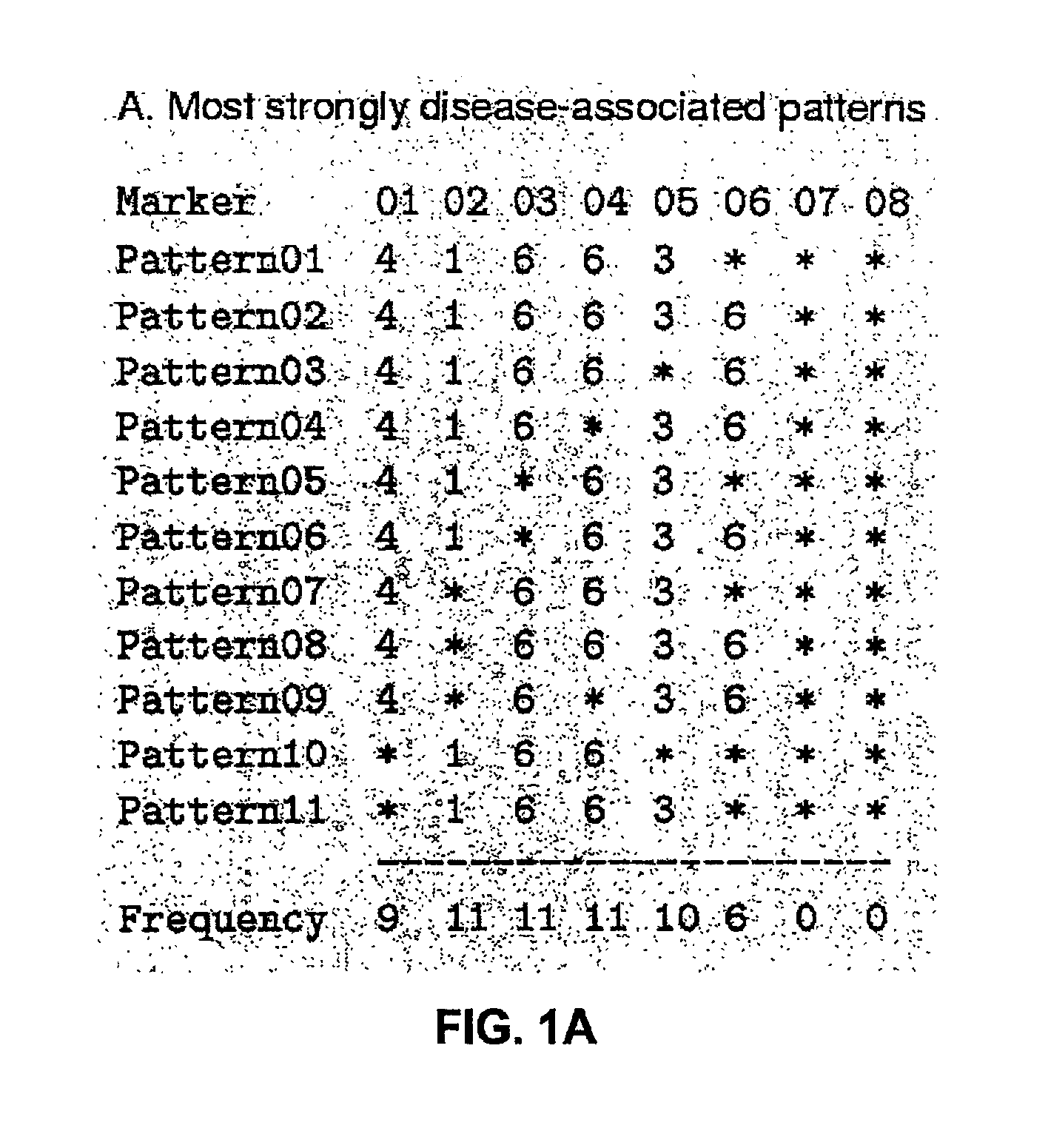
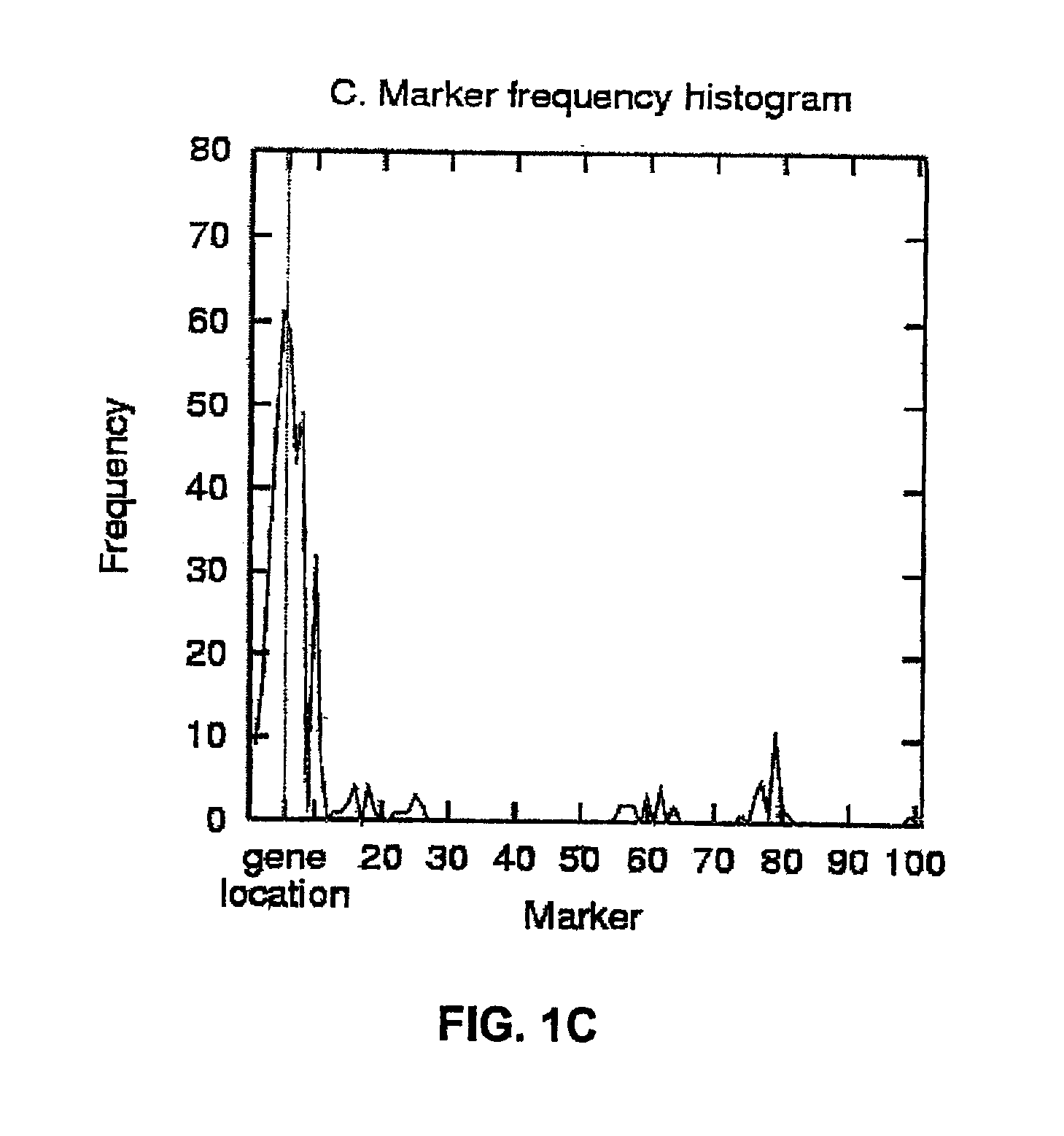
The present invention relates to a method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data, which utilizes linkage disequilibrium between genetic markers mi, which are polymorphic nucleic acid or protein sequences or strings of single-nucleotide polymorphisms deriving from a chromosomal region. All marker patterns P that satisfy a certain pattern evaluation function e(P) are searched from the data, each marker mi of the data is scored by a marker score and the location of the gene is predicted as a function of the scores s(mi) of all the markers mi in the data.
Owner:LICENTIA OY
Method of detecting phenotypic character related genes in nuclear genome
The invention discloses a method of detecting phenotypic character genes related in a nuclear genome. The method includes: S1) measuring a target phenotypic character of an F1-generation hybrid population and selecting an extreme target phenotypic character; S2) extracting RNA of the individuals with the extreme target phenotypic character, grouping by a BSA method, and constructing an expression gene chip; and S3) finding differentially expressed genes according to information of the expression gene chip, wherein the genes are the phenotypic character related genes in the nuclear genome. By application of the technical scheme, the target phenotypic character of the F1-generation hybrid population is screened by a plurality of times of measurement, the individuals with the stable extreme target phenotypic character are selected, mixing and grouping are performed by adoption of the BSA method and gene pools are constructed, thus highlighting differences of the target phenotypic character. A large number of genes are hybridized at the same time by combination of a gene chip technology. The differentially expressed genes related to the target phenotypic character are screened through analyzing chip results.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
High-throughput method for segregating quantitative character regulatory gene
InactiveCN101544974AAvoid false positivesImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTotal rnaCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a high-throughput method for segregating a quantitative character regulatory gene, which comprises the following steps of: 1) construction of a target character segregation population, in which the population is a population in two parent hybridization progenies (F2 and F3), a DH system and a RIL; 2) mixing of extreme samples and segregation of total RNA in the population, in which a progeny segregation population is divided into three categories according to character phenotype; 3) gene expression analysis, in which the difference and sameness of gene expressions between two extreme mixed samples are compared by utilizing a gene expression analysis method, namely one of chip, EST sequencing, subtraction, cDNA-AFLP, and the like; and 4) acquisition and verification of a candidate gene, in which a differential expression gene between the two extreme mixed samples is found and is a candidate regulatory gene related to target character, and the function of the gene is verified through transgene, gene expression, molecular marker correlation and a contribution rate analysis method to obtain a target gene with regulatory character phenotype. The method is suitable for the segregation of a certain quantitative character regulatory gene controlled by multigene of all organisms, and is a simple, quick, high-throughput and economical gene segregation method.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Phased Whole Genome Genetic Risk In A Family Quartet
An embodiment of the present invention is a methodology for prioritizing variants relevant to inherited Mendelian (“single gene”) disease syndromes according to disease phenotype, gene, and variant level information.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Dominant SCAR molecule mark for wild cabbage type cole self-incompatibility and uses thereof
InactiveCN101255461AReduce breeding workloadShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMolecular breeding
The invention belongs to the field of rape breeding, particularly relates to rape self-incompatibility complete linkage dominant SCAR labels and the application thereof. Cabbage type rape self-incompatibility S locus dominant SCAR molecular labels are produced artificially, which includes self-incompatibility S locus dominant labels and self-incompatible restorer line S locus dominant labels, wherein the self-incompatibility S locus dominant SCAR labels are named as SRKa, SEKb and SP11a, whose nucleotide sequences are displayed in sequence tables with SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 6; the self-incompatible restorer line S locus dominant SCAR labels are named as SLGa, SLGb and SLGc, whose nucleotide sequences are displayed in sequence tables with SEQ ID NO: 3, 4, 5. The molecular labels can differentiate homozygous-compatible, hybrid-compatible and homozygous-incompatible genes. The molecular labels are used to verify the cabbage type rape self-incompatibility phenotype. The invention provides practical labels and a usage method for rape molecular breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
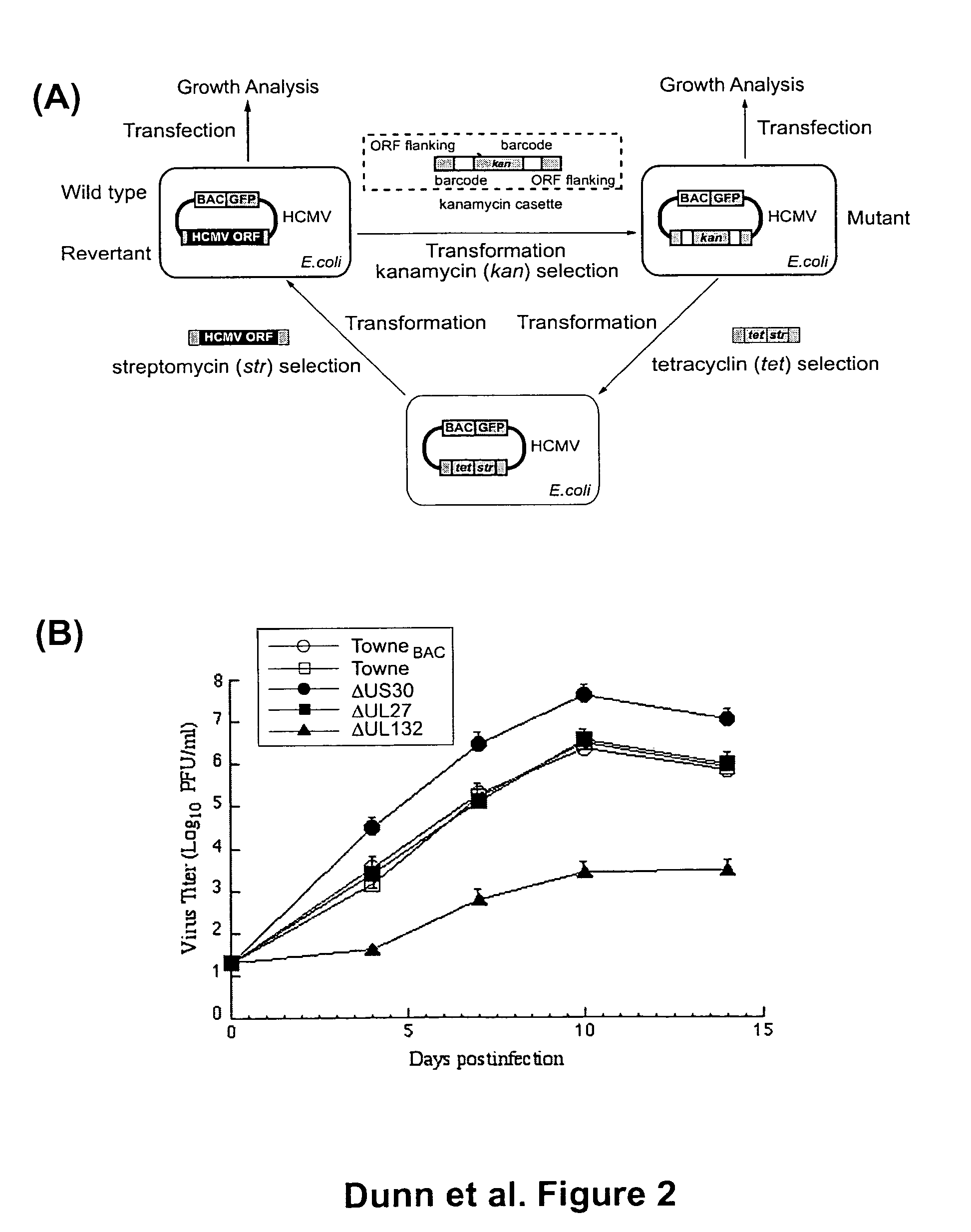
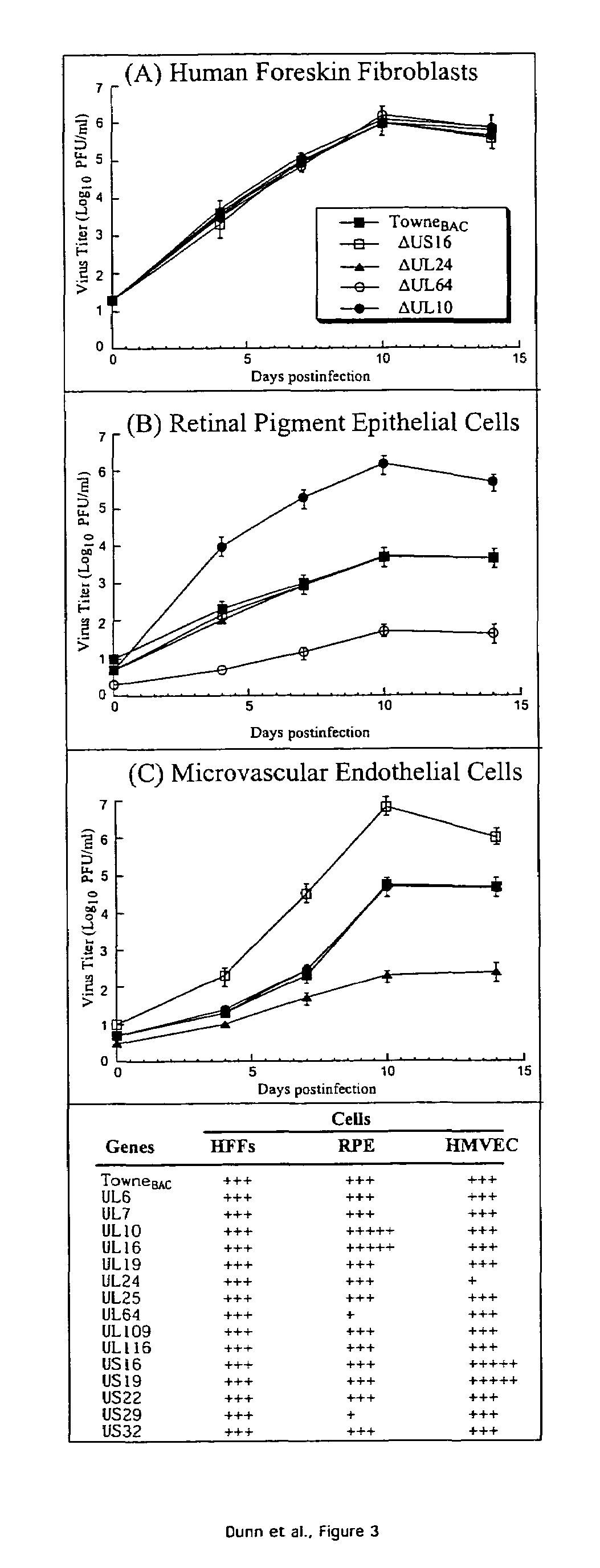
Cytomegalovirus gene function and methods for developing antivirals, anti-CMV vaccines, and CMV-based vectors
ActiveUS7407744B2Enhance their long-term survivabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSurvivabilityORFS
A global functional analysis of HCMV genes is performed by constructing virus gene-deletion mutants and examining their growth phenotypes in different natural HCMV host cells. This systematic analysis of the HCMV genome identified 45 viral ORFs essential for viral replication and characterizes of 115 growth-dispensable viral genes. Of particular interest is the finding that HCMV encodes genes (temperance factors) that repress its own replication on a cell type-specific basis. In addition to HCMV, pathogen temperance may be a strategy employed by other infectious agents to enhance their long-term survivability within their respective host population.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
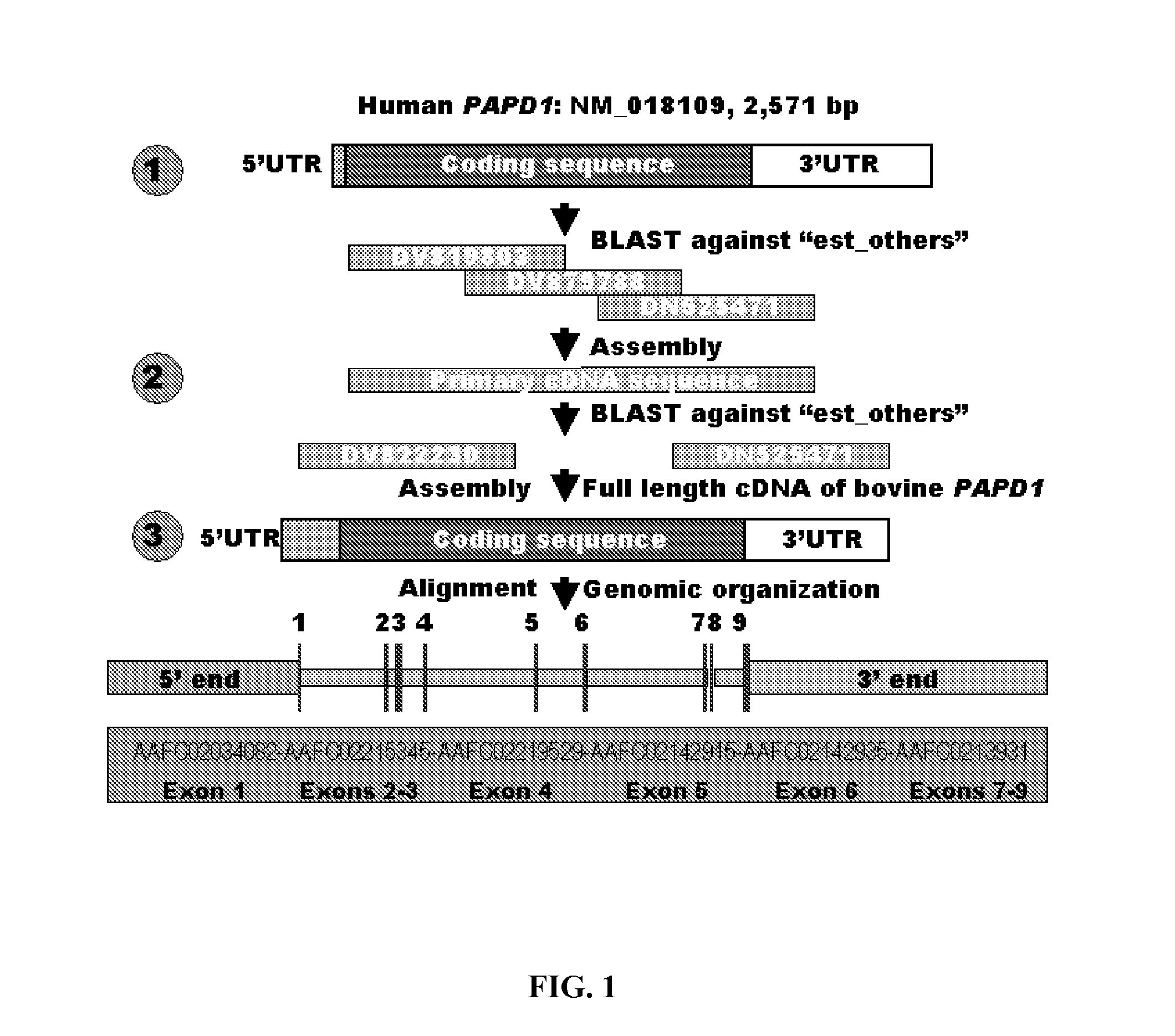
Involvement of a Novel Nuclear-Encoded Mitochondrial Poly(A) Polymerase PAPD1 in Extreme Obesity-Related Phenotypes in Mammals
InactiveUS20090024401A1Microbiological testing/measurementInstrumentsMarker-assisted selectionIntramuscular fat
Aspects of the present invention also provide novel compositions and methods based on novel PAPD1 single nucleotide polymorphisms selected from the group consisting of AAFC02034082.1:g.9224G>A, g.9330A>C, g.9367G>C, g.9419A>C, g.9435T>G, g.9409[(G)4]+[(G)5], g.10084T>C, g.10228G>T, c.10326C>T and c.10364A>G, which may provide novel markers for intramuscular fat deposition. Additional aspects provide for novel methods which may comprise marker-assisted selection or marker-assisted management to improve intramuscular fat deposition in cattle.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Method to Screen Plants for Genetic Elements Inducing Parthenogenesis in Plants
InactiveUS20130180005A1Fertilization of will not be preventedPromote generationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
Compositions and methods for producing a plant population lacking sexually derived embryos are provided. Compositions include suppression cassettes encoding polynucleotides and promoters resulting in parthenogenesis. Further provided are parthenogenesis genetic elements used to prevent sexual reproduction in self-reproducing plants.Methods include: utilizing maternal embryo defective recessive mutations which are maintained as a sterile inbred maintenance system, allowing generation of populations that are homozygous for recessive mutant alleles, but transgenically complemented. Methods include utilizing a toxin genes expressed via egg-cell specific promoters, creating a dominant, embryo-less phenotypes, non-transmittable through female gametes. Resultant hemizygous plants are transformed with egg-cell promoters driving the antidote, a pollen ablation PTU and a seed color marker for identification of transgenic seed. The generation of a plants 50% female fertile, having seed which when grown in the next generation will yield plants with 50% viable transgenic seed, and 50% non-viable embryo-less seed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Down syndrome 21 chromosome miRNA differential expression map model, modeling method and application
ActiveCN103045736AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseDistribution characteristic
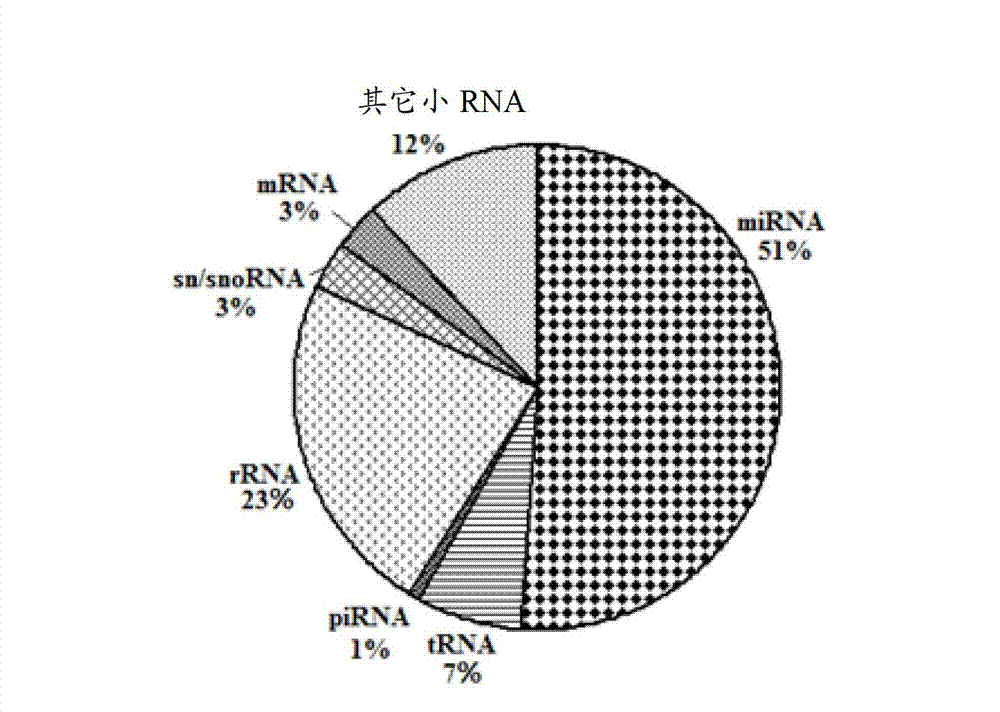
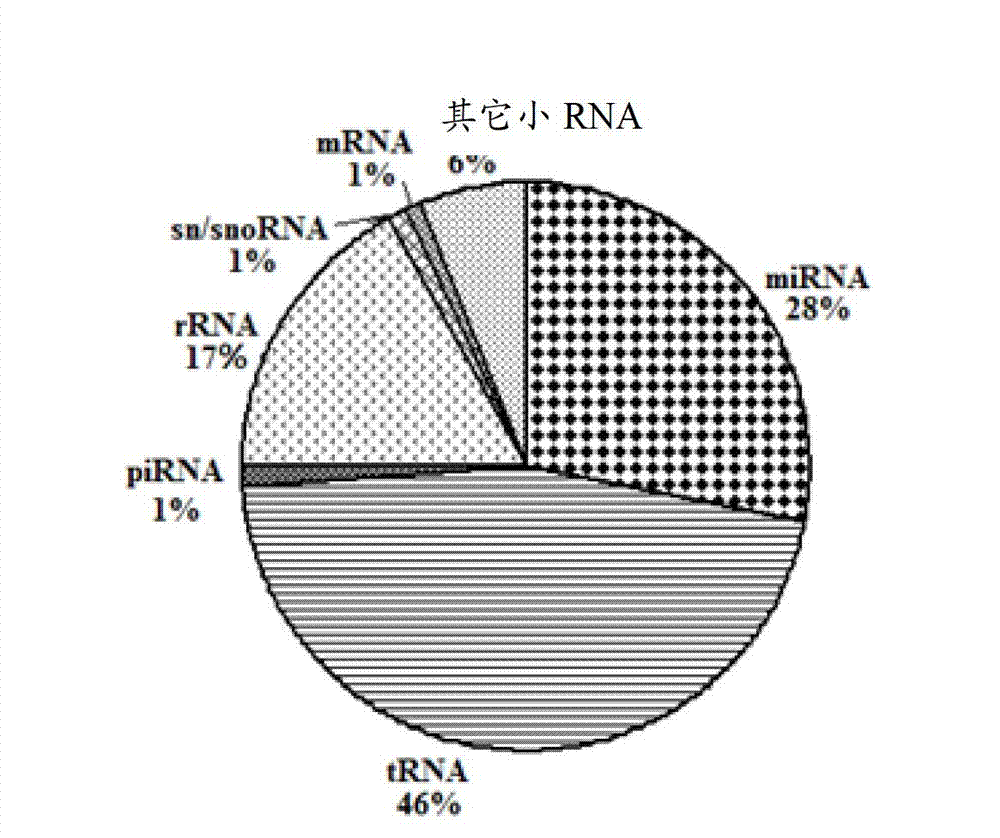
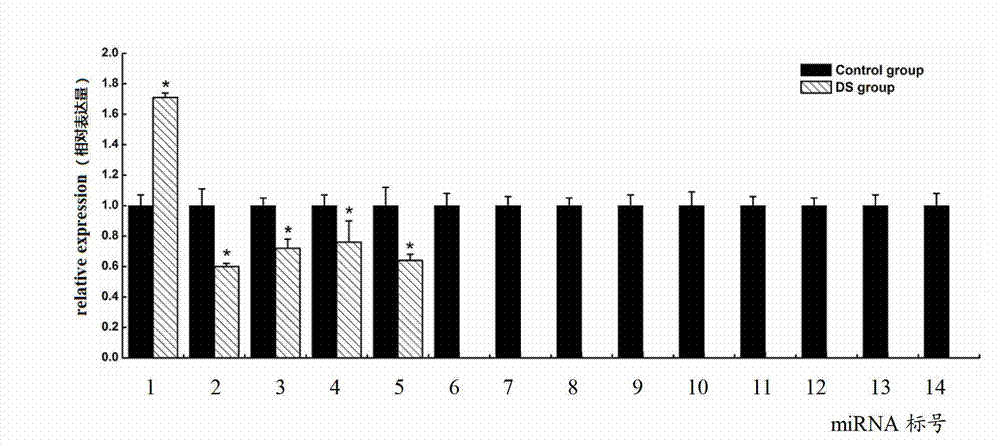
The expression map and the chromosome distribution characteristic of a DS (down syndrome) fetal genome-wide miRNAs are studied by an Illumina deep sequencing technology so as to obtain a down syndrome 21 chromosome-related miRNA differential expression map model, which consists of an up-regulated miRNA, four down-regulated miRNAs and 9 zero-expression miRNAs. miRNA molecules with significant difference and specific expression help to understand a molecular regulation mechanism for occurrence and development of a clinical phenotype of a DS disease and lay the foundation for further studying gene expression disorder of a DS patient genome-wide and a relationship between the gene expression disorder and relevant clinical symptoms.
Owner:徐勇
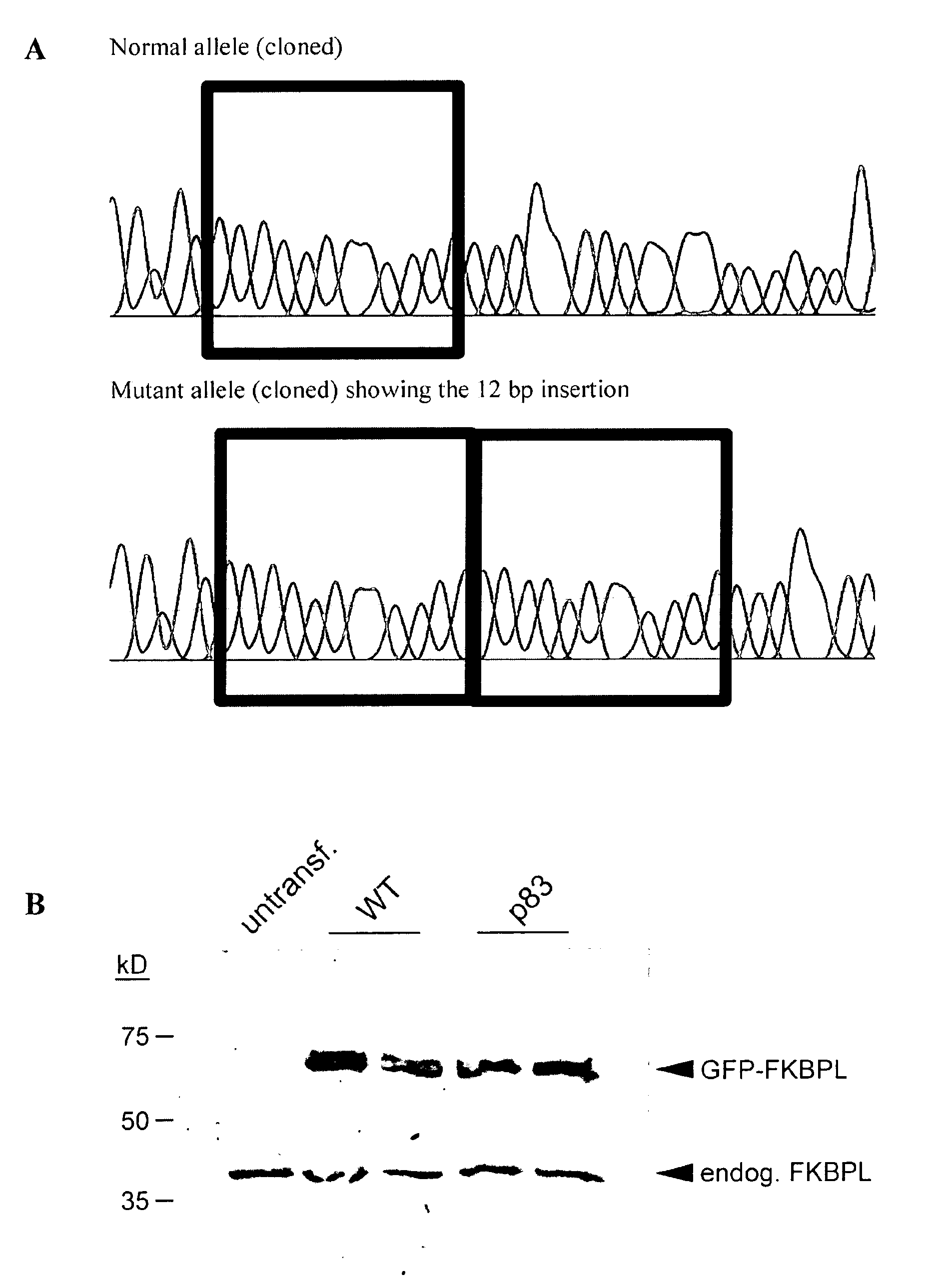
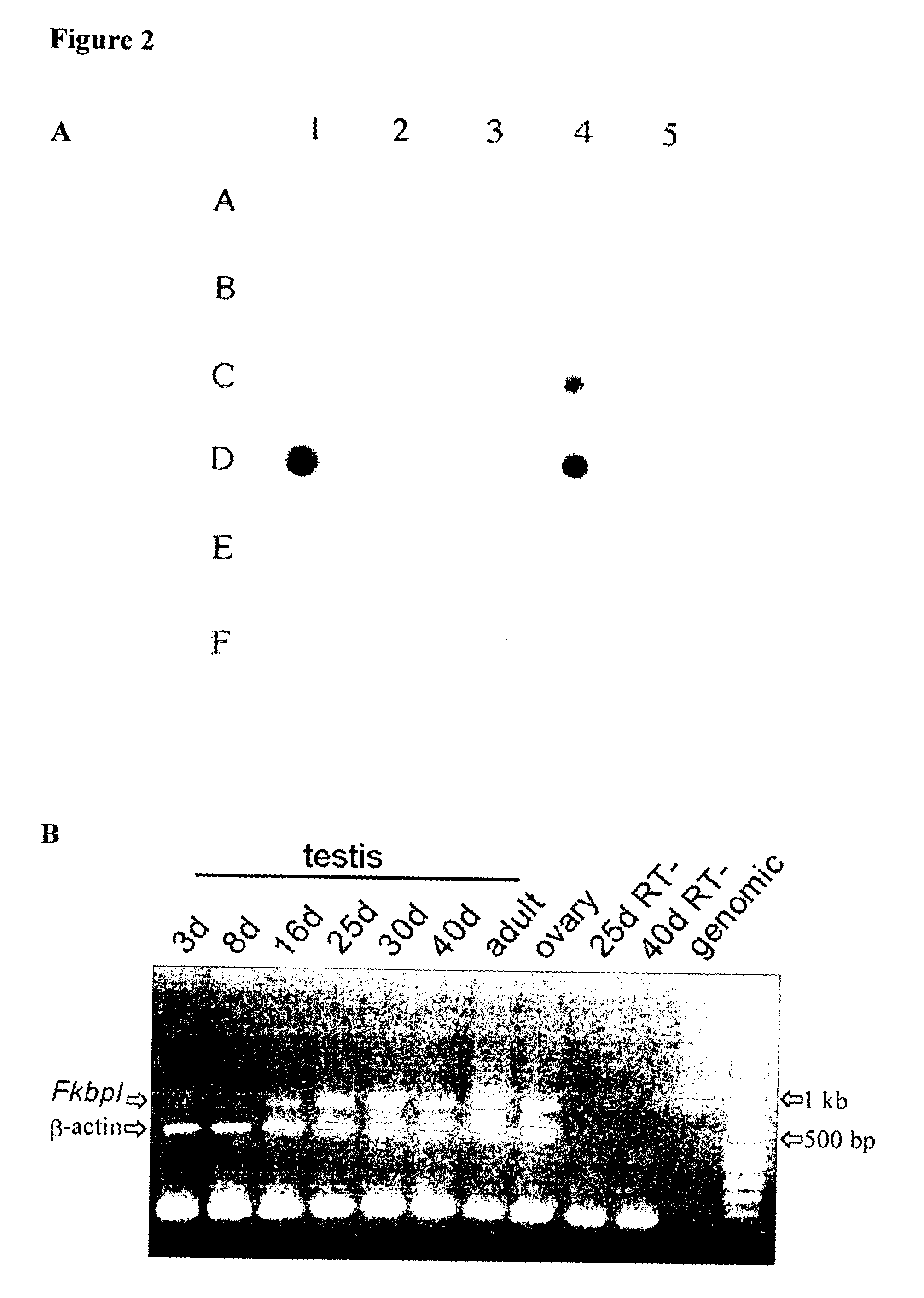
Use of FKBPL gene to identify a cause of infertility
InactiveUS20100305082A1High activityOrganic active ingredientsElectrolysis componentsGenotypeAnimal husbandry
Fertility problems affect (1 in 10) couples in Western society, making it one of the most common serious health issues. Despite this, little is known about the causes of infertility, and thus patient counseling and treatment are suboptimal. With infertility being such a common problem, identification of any cause would impact on a large number of patients, allowing better counseling, clearer diagnoses and the possibility of making more informed choices (e.g. adoption vs. IVF treatment). The present invention provides methods to identify a cause of infertility in a subject based on the genotype of the subject, in particular, by evaluating the status of the gene encoding FK506 binding protein-like (FKBPL). In particular, the present invention relates to use of the status of the gene encoding FK506 binding protein-like for identification of a cause of an infertile phenotype in a subject. Also provided, are methods method for identifying an infertile phenotype in a subject, and identifying a cause of an infertile phenotype in a subject. This diagnostic tool finds wide clinical utility in the identification of a cause of infertility, resultantly impacting on a large number of patients. Further aspects of the present invention relate to the targeting of FKBPL in order to temporarily and reversibly induce infertility in a subject. Such aspects of the present invention find utility in the development of a male contraceptive pill. Moreover, due to the high degree of homology between the human and mouse FKBPL gene, FKBPL can be targeted in order to induce infertility in mice (or other species) as a form of pest control or animal husbandry.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ULSTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com