High temperature and strong alkali resistant xylanase improved gene, genetic engineering bacterial strain thereof and preparation method thereof
A technology for genetically engineered strains and xylanase, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and protein engineering, can solve the problems that the enzymatic properties cannot meet industrial production and application, and achieves the effects of satisfying the needs of industrial production and improving thermal stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Obtaining improved xylanase gene by directed evolution technique
[0035] Design PCR primers XynF1 and XynR1 as follows:
[0036] XynF1: GGC GGATCC ATGCAAAGTTTCTGTAGTTCAGCTTCTCAC (forward primer, the underlined sequence is the recognition sequence for BamHI digestion), that is, SEQ ID NO 3.
[0037] XynR1: GCG GCGGCCGC ATCACCAATGTAAACCTTTGCGTAT (reverse primer, the underlined sequence is the NotI restriction recognition sequence, without stop codon, the expression is terminated by using the stop codon on the vector), that is, SEQ ID NO 4.
[0038] Using the Xyn-CDBFV gene as a template, the GeneMorph II Random Mutation PCR Kit (Stratagene) was used to perform PCR amplification with the above primers, and the PCR product was recovered from the gel, digested with BamHI and NotI, and then ligated with the PET21a vector after the same digestion , transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), spread on LA plate (LB medium + 100 μg / ml ampicillin), and culture...
Embodiment 2
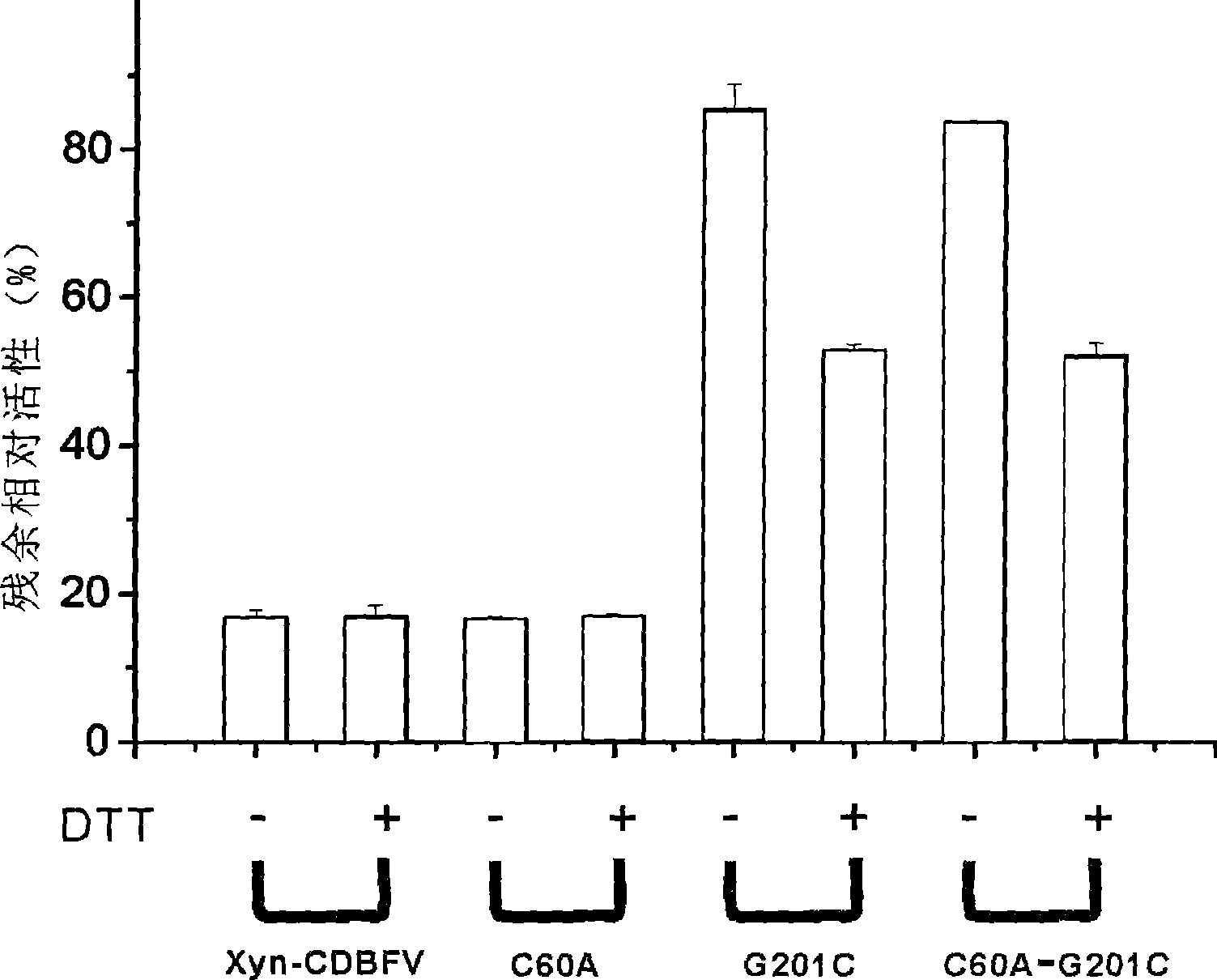
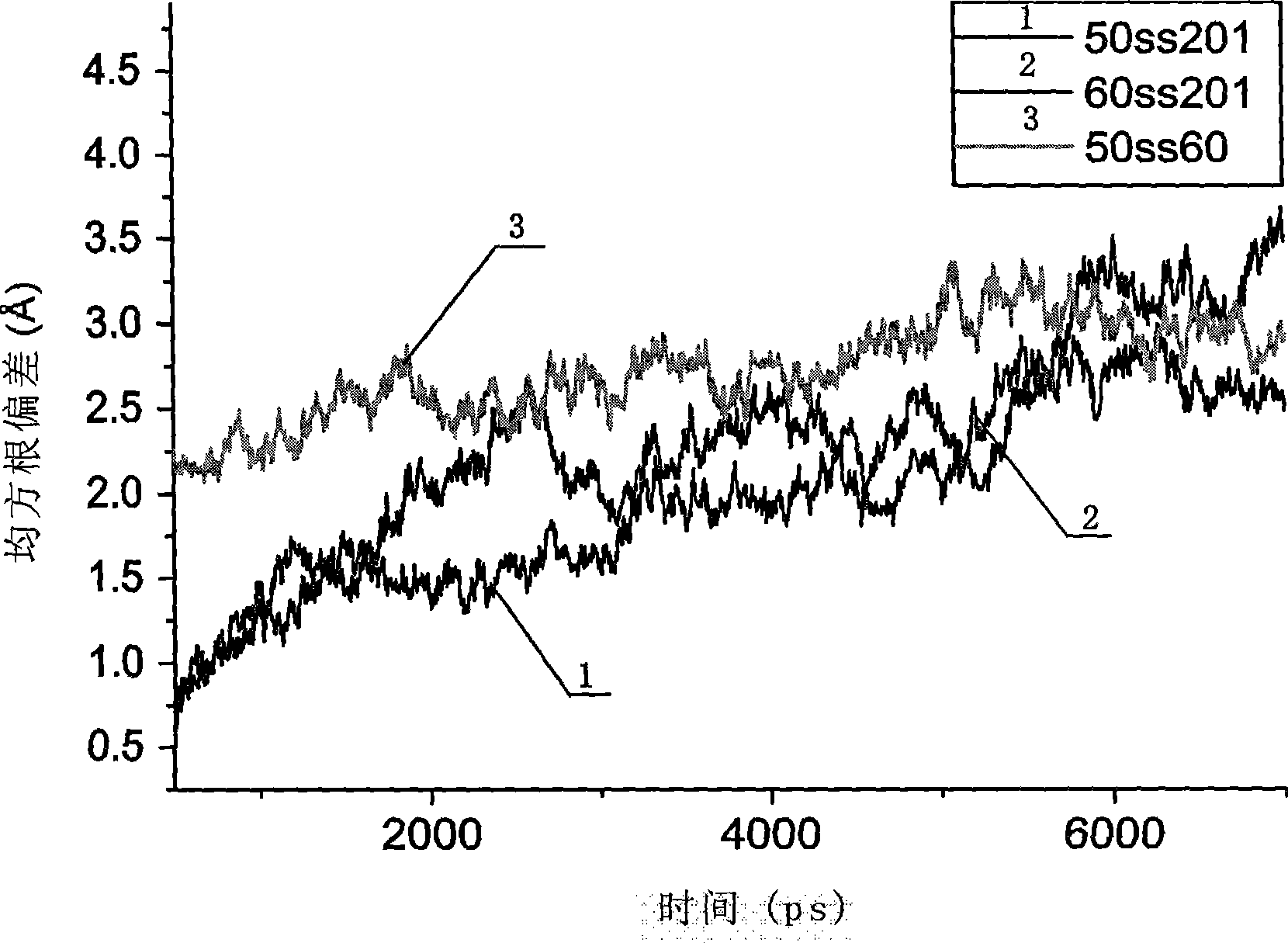
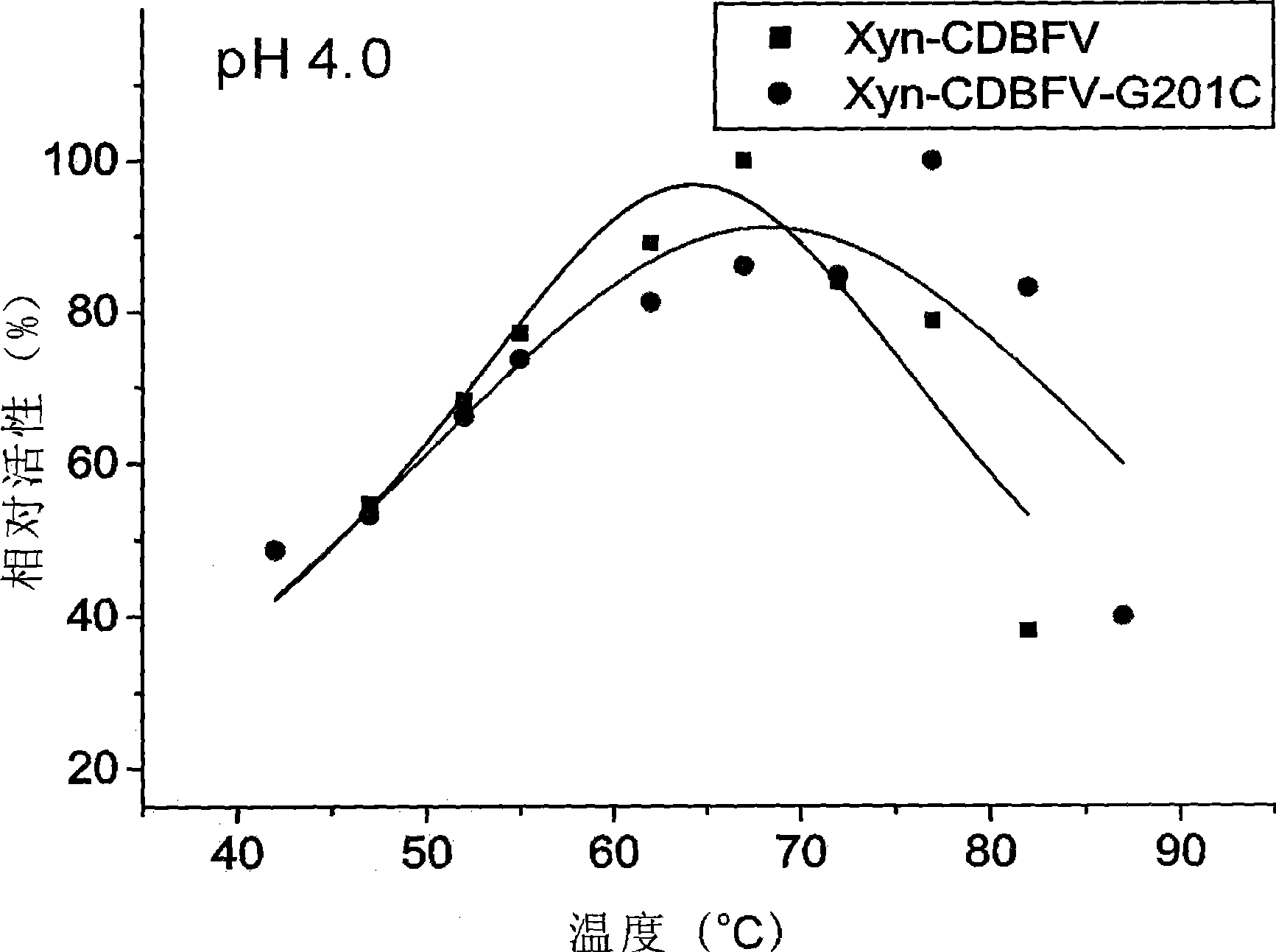
[0040] Example 2: Cysteine at position 201 and position 50 in the improved xylanase forms a disulfide bond
[0041] The improved thermostability of the improved xylanase is due to the formation of a new disulfide bond between the 201-position and the 50-position cysteine.
[0042] The homology modeling of the improved xylanase (Xyn-CDBFV-G201C) was carried out in SWISS-MODEL (http: / / swissmodel.expasy.org / ), and it can be seen that the cysteines at positions 50, 60 and 201 are in They are close to each other in space, and it is possible to form disulfide bonds with each other, but the spatial positions of cysteines at position 201 and 50 make them easier to form disulfide bonds, so site-directed mutations were carried out on the original and improved xylanases, The cysteine at position 60 was mutated to alanine. The original and improved xylanase genes and their C60A mutant genes were respectively cloned into PET21a, and these four enzyme proteins were prepared by recombin...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Construction of recombinant yeast expression vectors containing improved genes and acquisition of recombinant yeast genetically engineered strains
[0045] The plasmid used to construct the yeast expression vector is pPIC9K (with alpha factor secretion signal), and the PCR primers XynF2 and XynR2 are designed as follows:
[0046] XynF2: GGC GAATTC ATGCAAAGTTTCTGTAGTTCAGCTTCTCAC (forward primer, the underlined sequence is the EcoRI restriction recognition sequence), that is, SEQ ID NO 5.
[0047] XynR2: GCG GCGGCCGC ATCACCAATGTAAACCTTTGCGTAT (reverse primer, the sequence underlined is the NotI restriction recognition sequence, and the sequence in the box is the stop codon), that is, SEQ ID NO 6.
[0048] Using PET21a-Xyn-CDBFV-G201C plasmid DNA as a template, use high-fidelity Pfu polymerase to amplify the Xyn-CDBFV-G201C fragment, clone it into pPIC9k, and form a recombinant plasmid pPIC9k-Xyn-CDBFV-G201C, the enzyme gene is in the AOX1 promoter downst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com