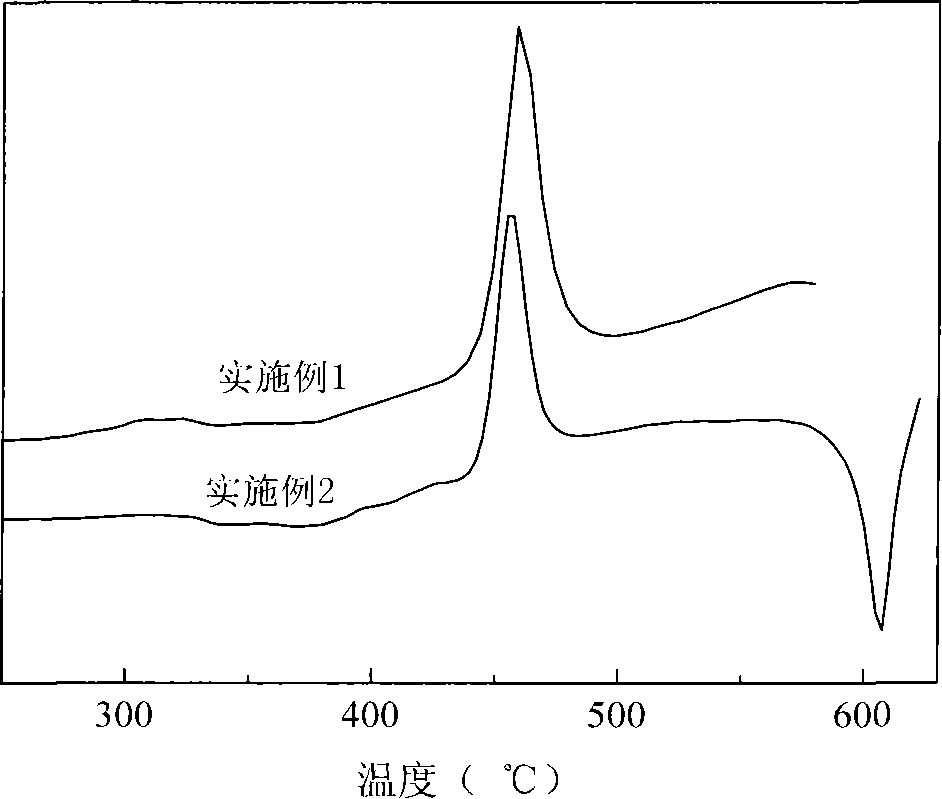
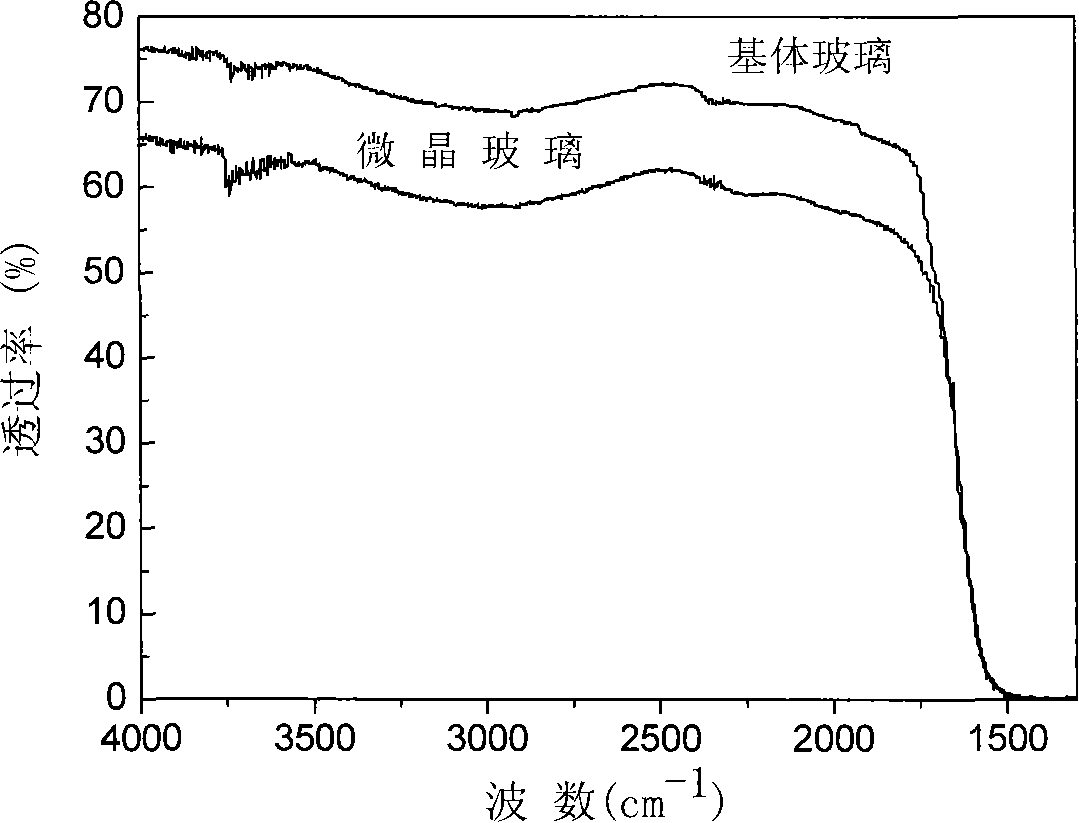
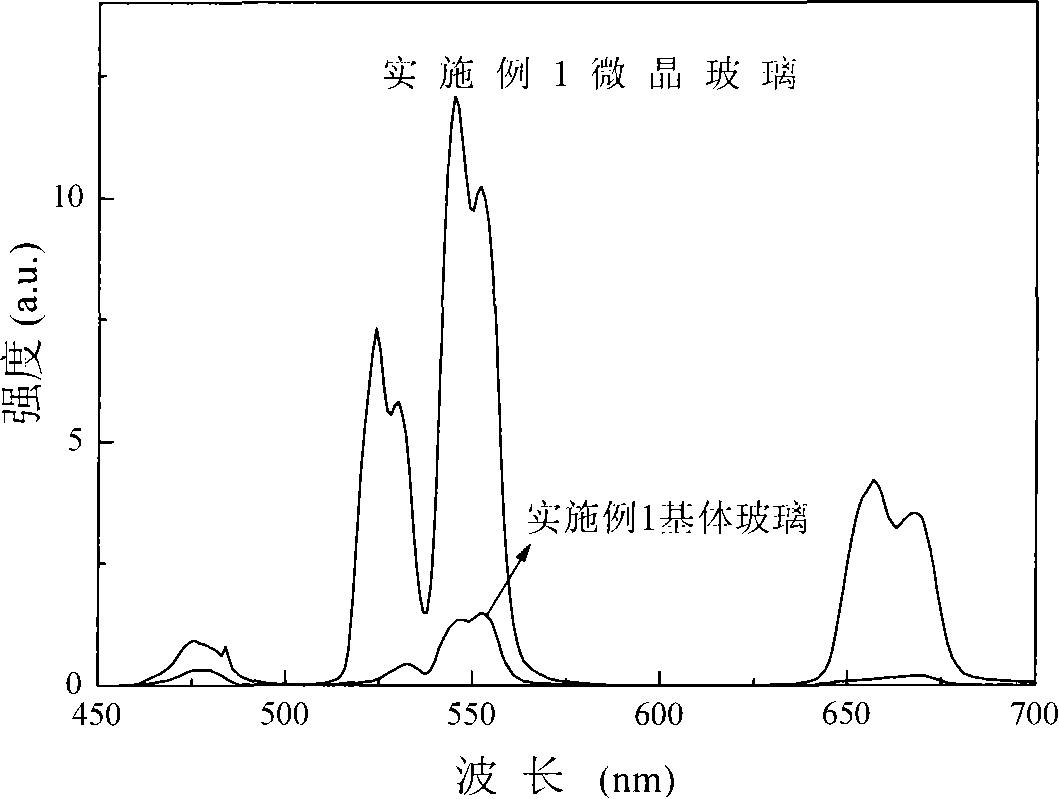
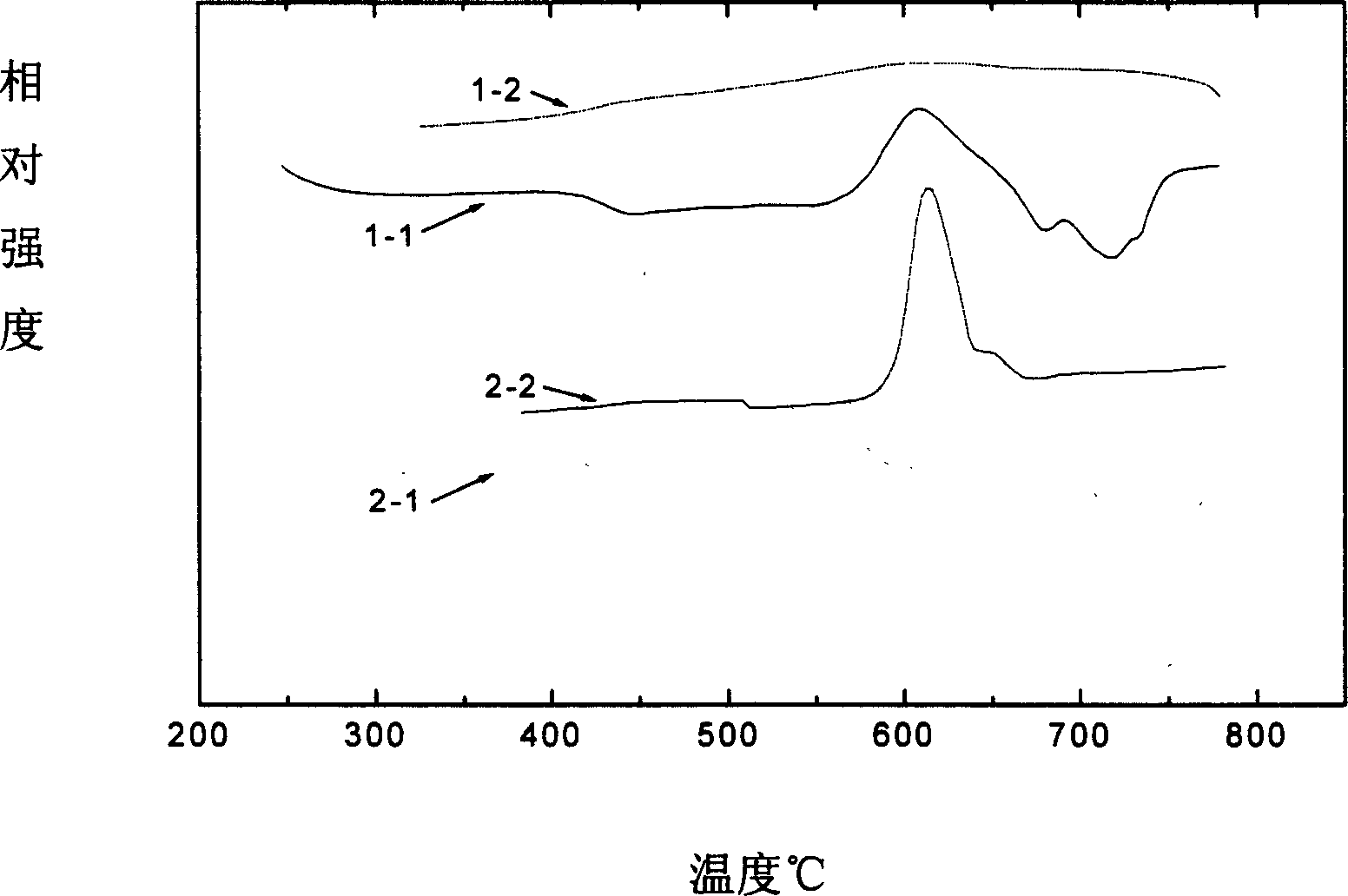
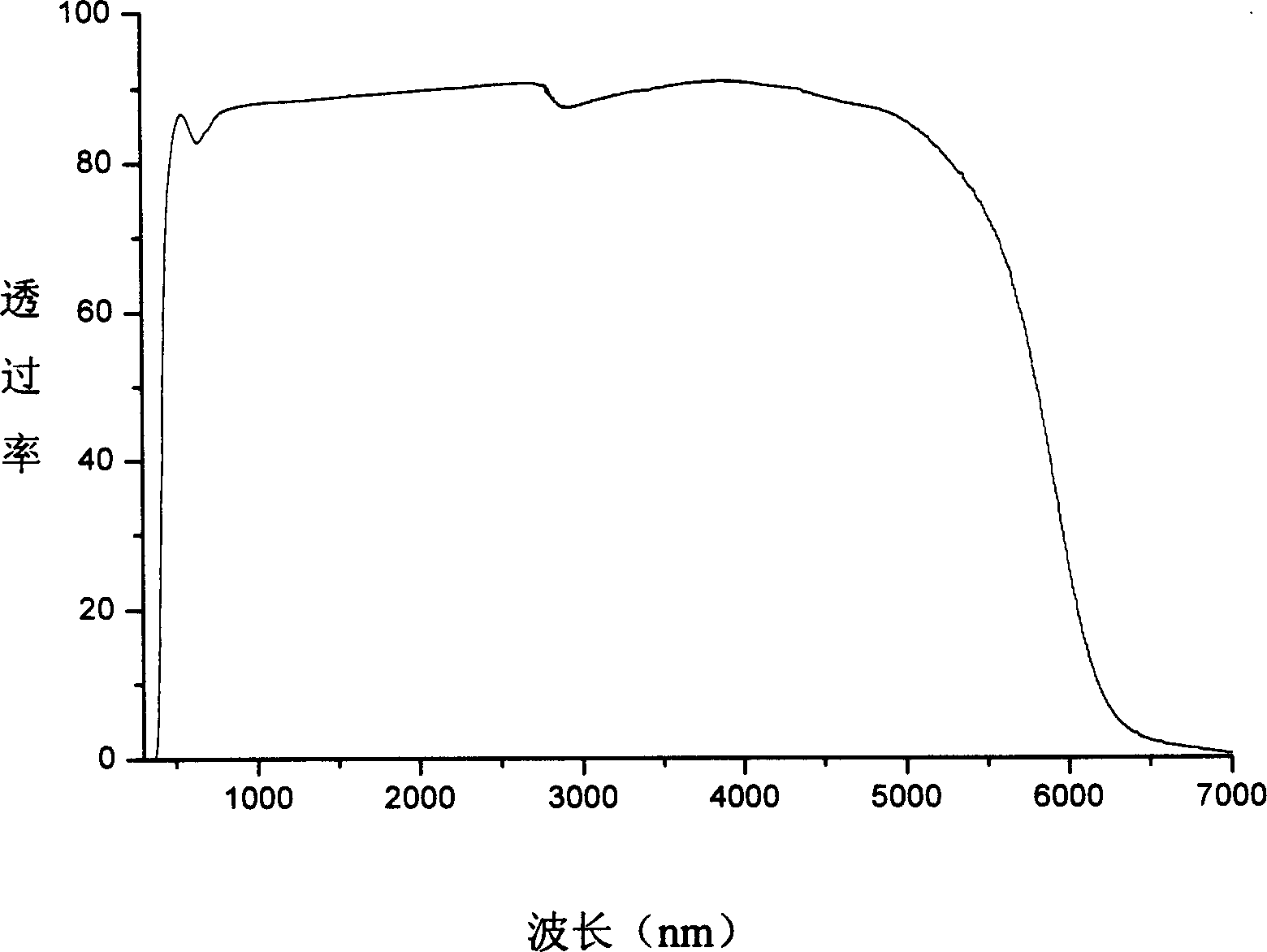
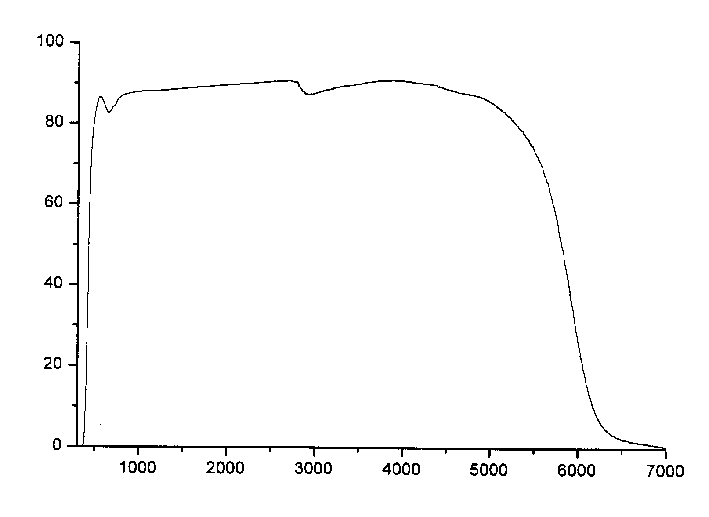
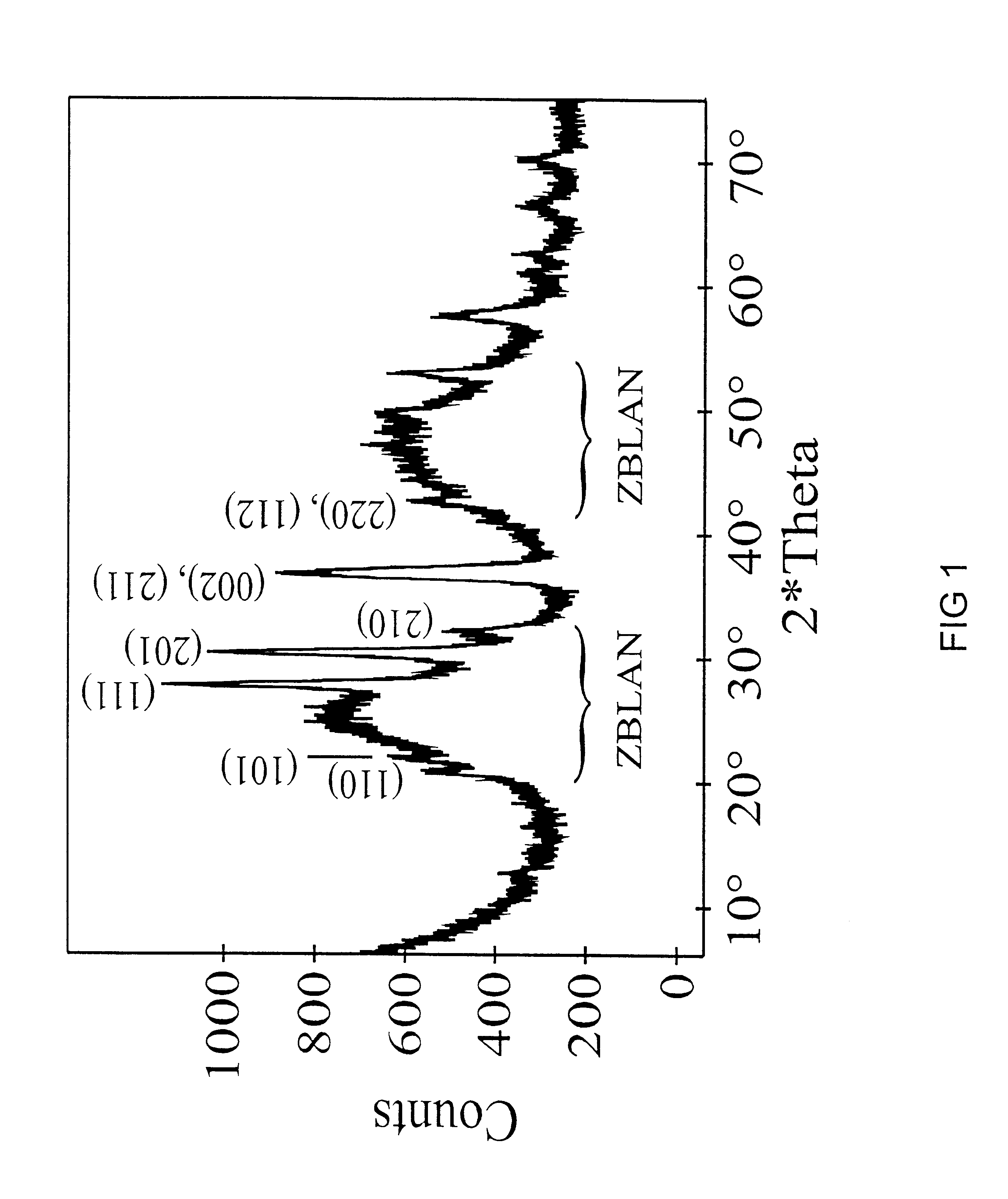
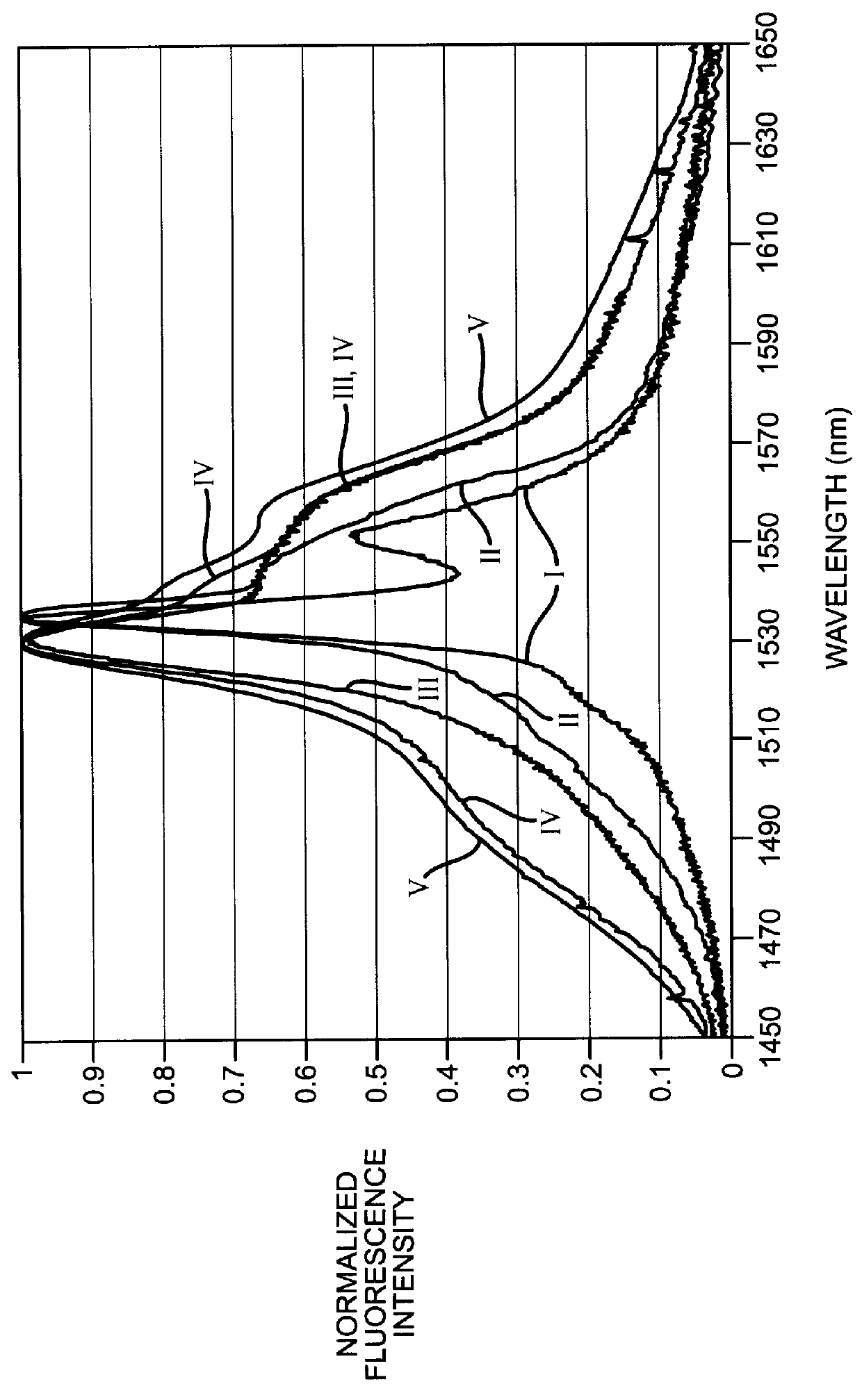
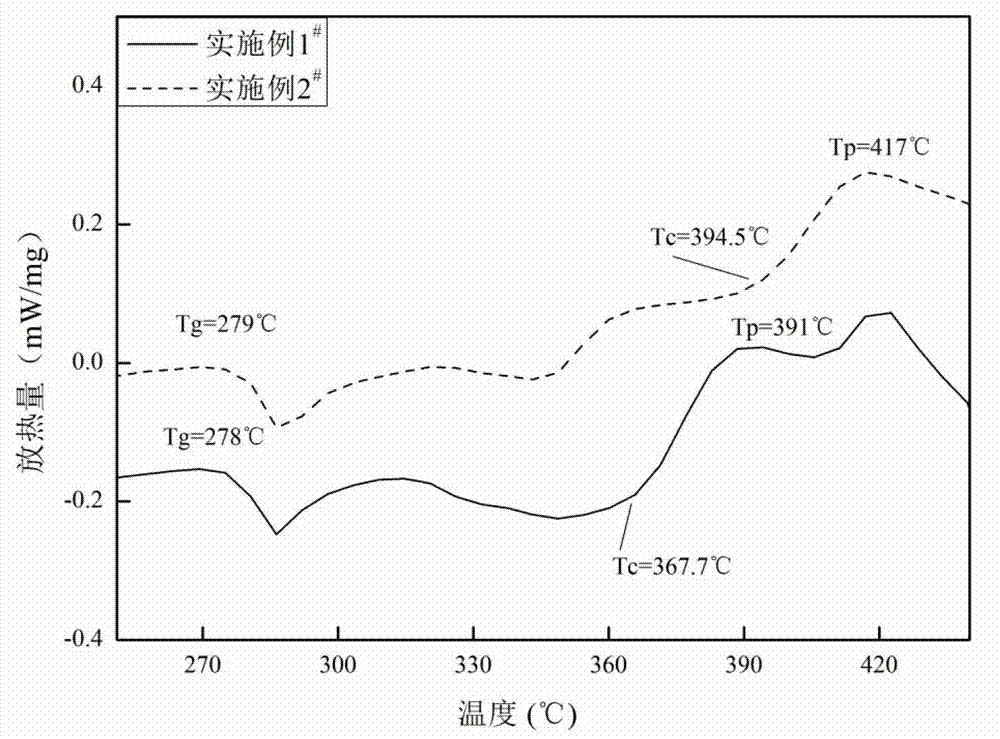
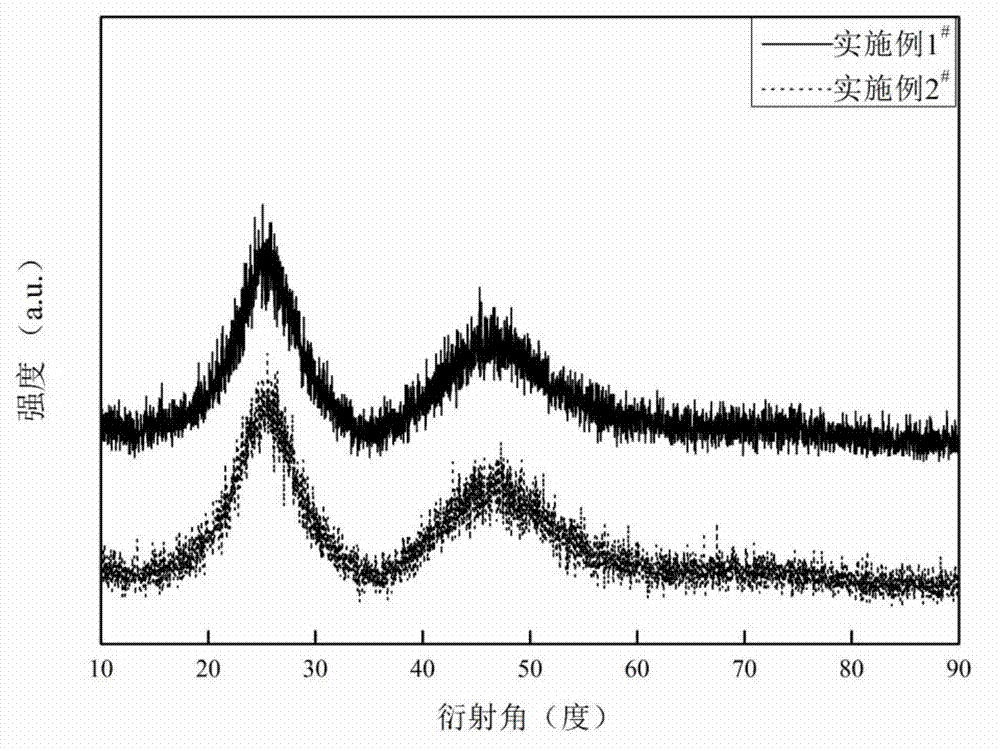
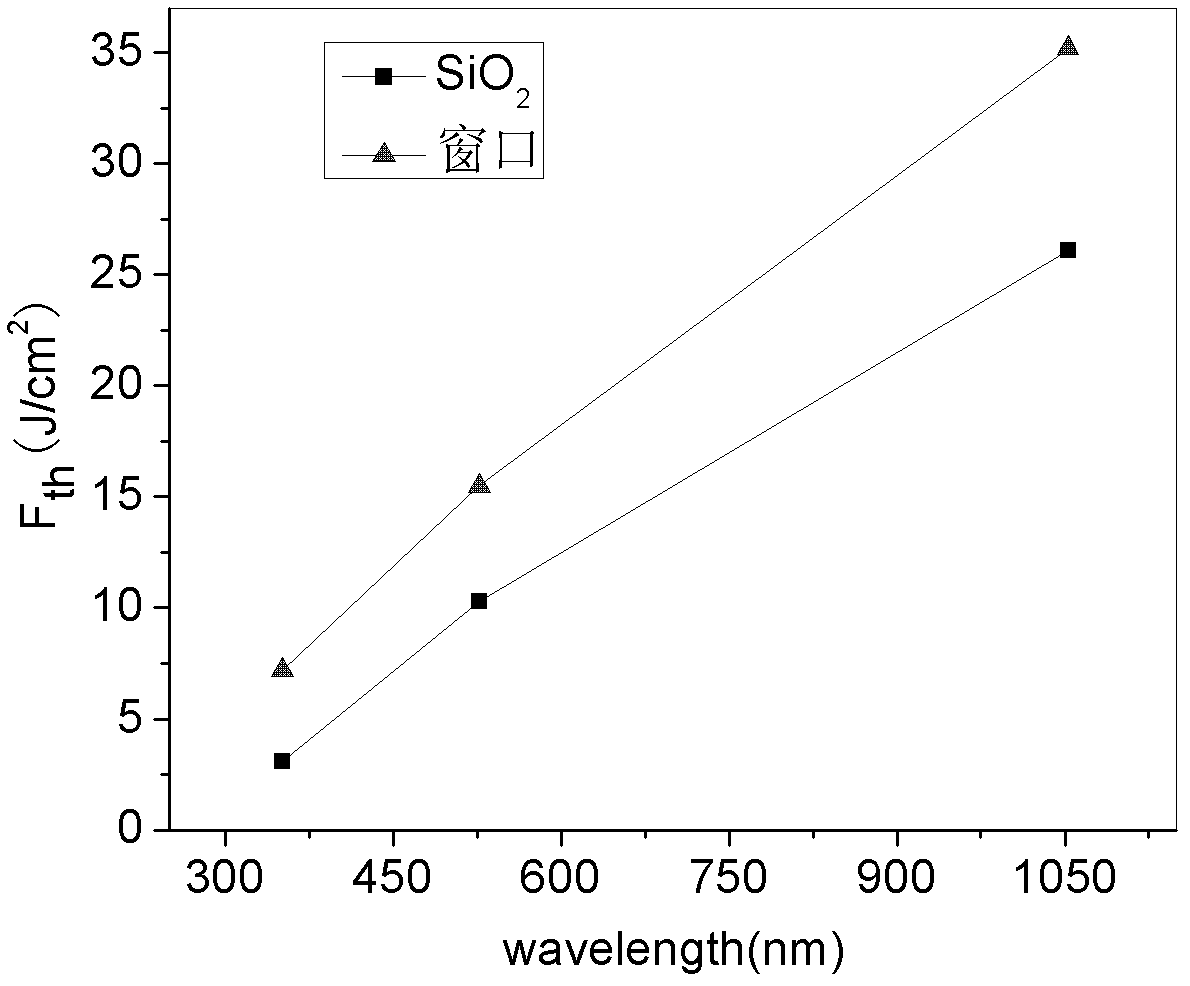
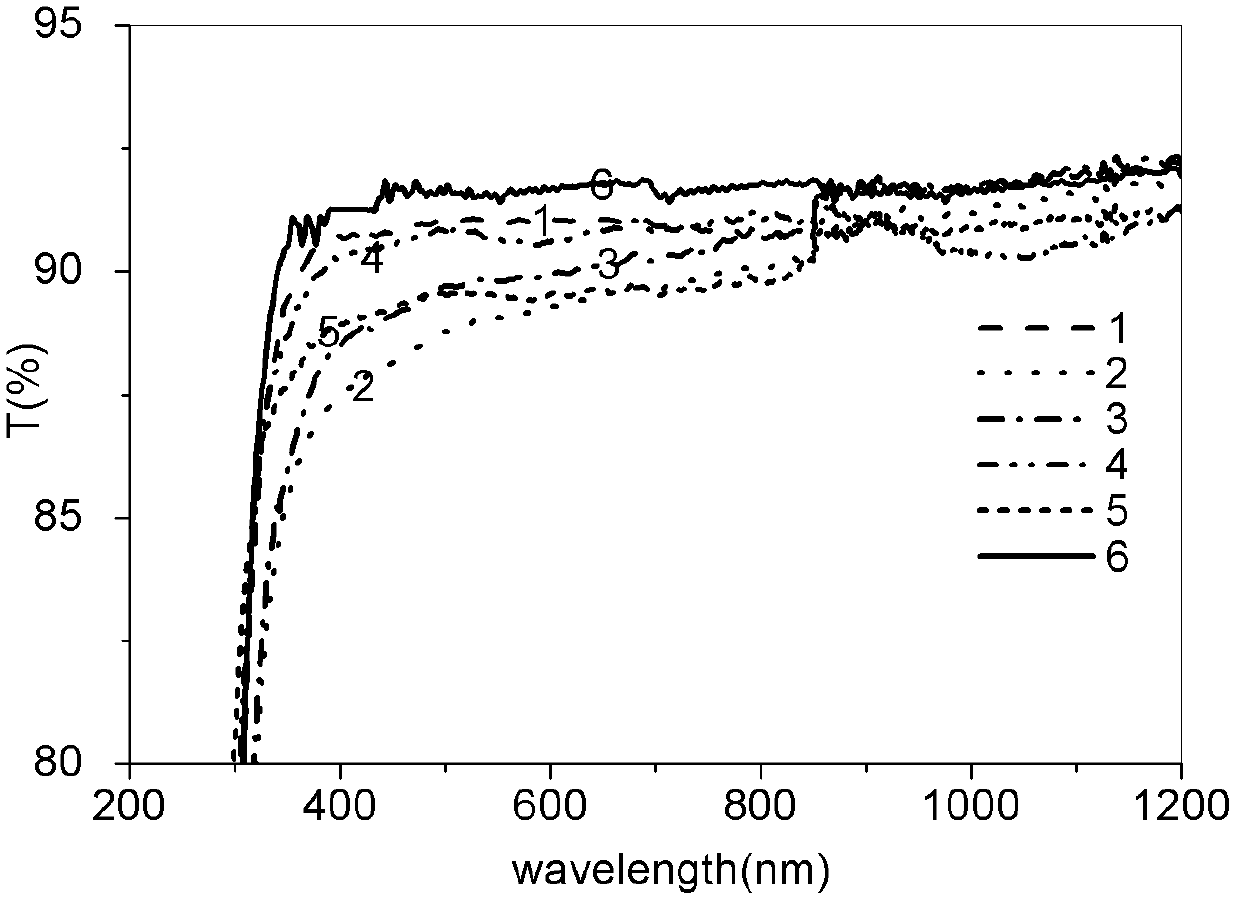
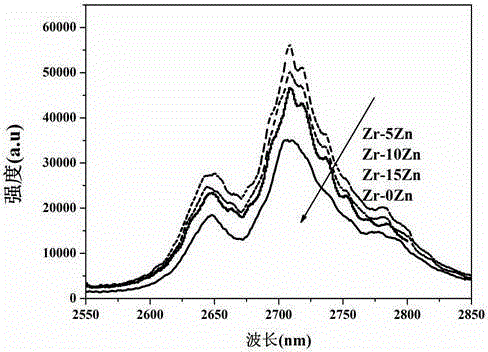
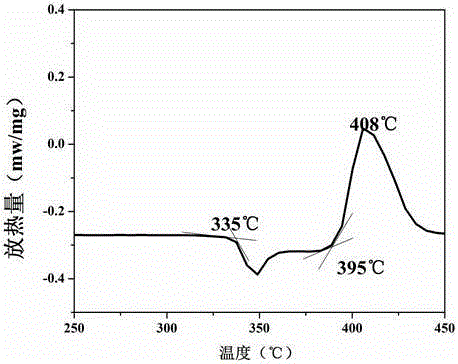
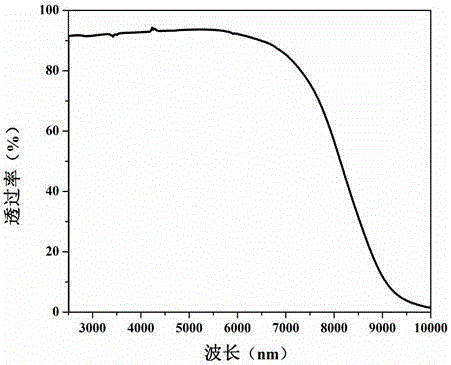
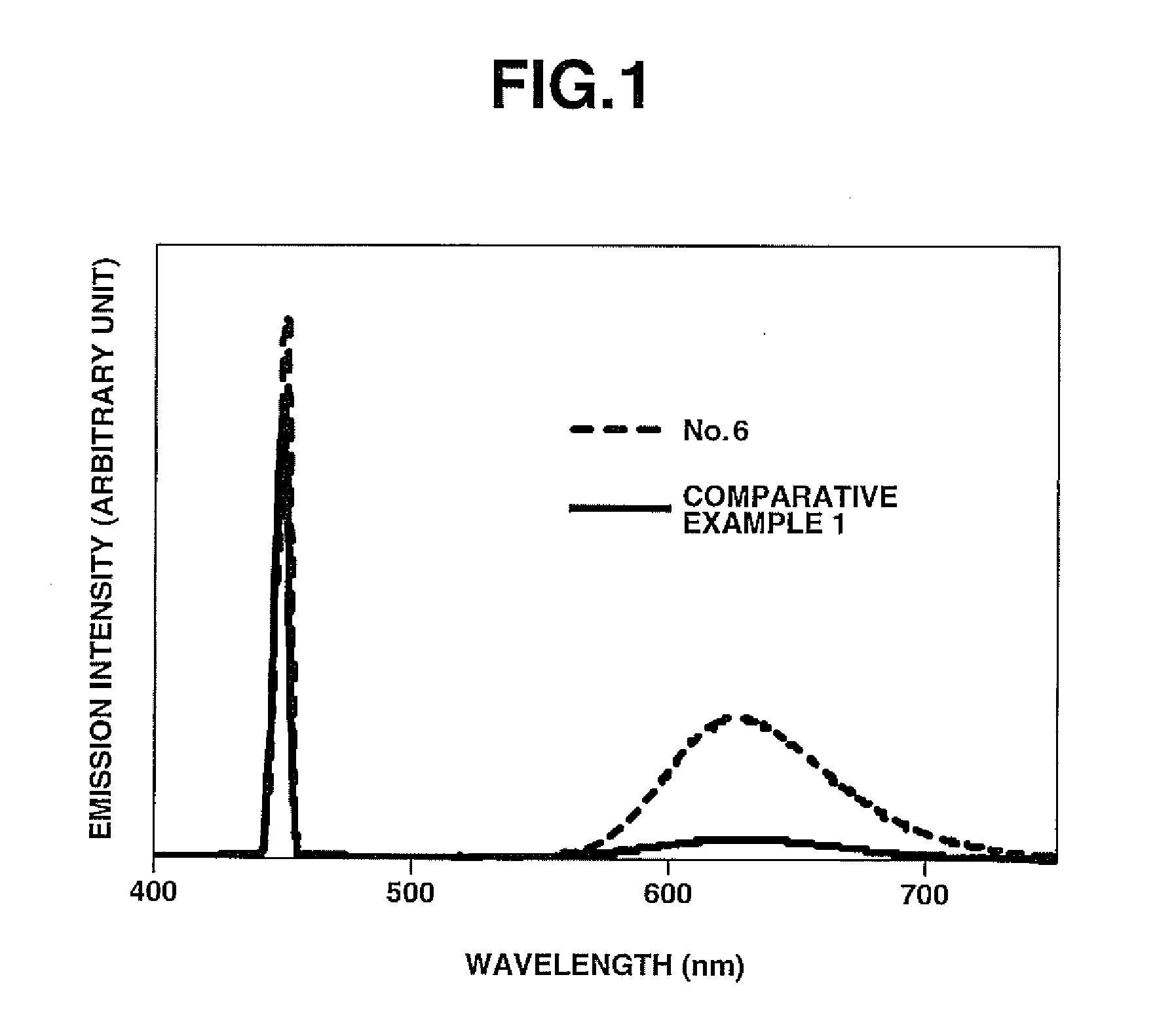
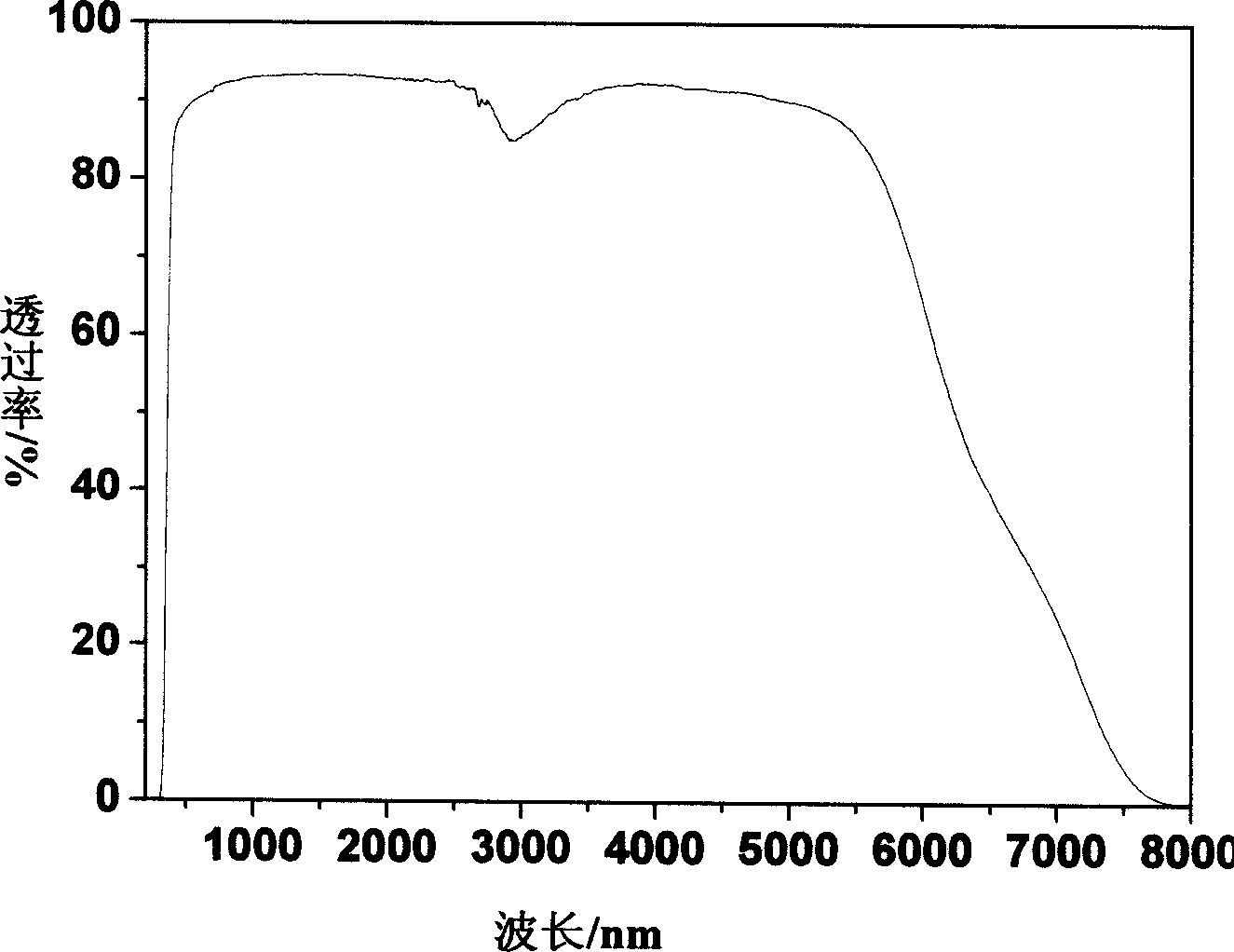
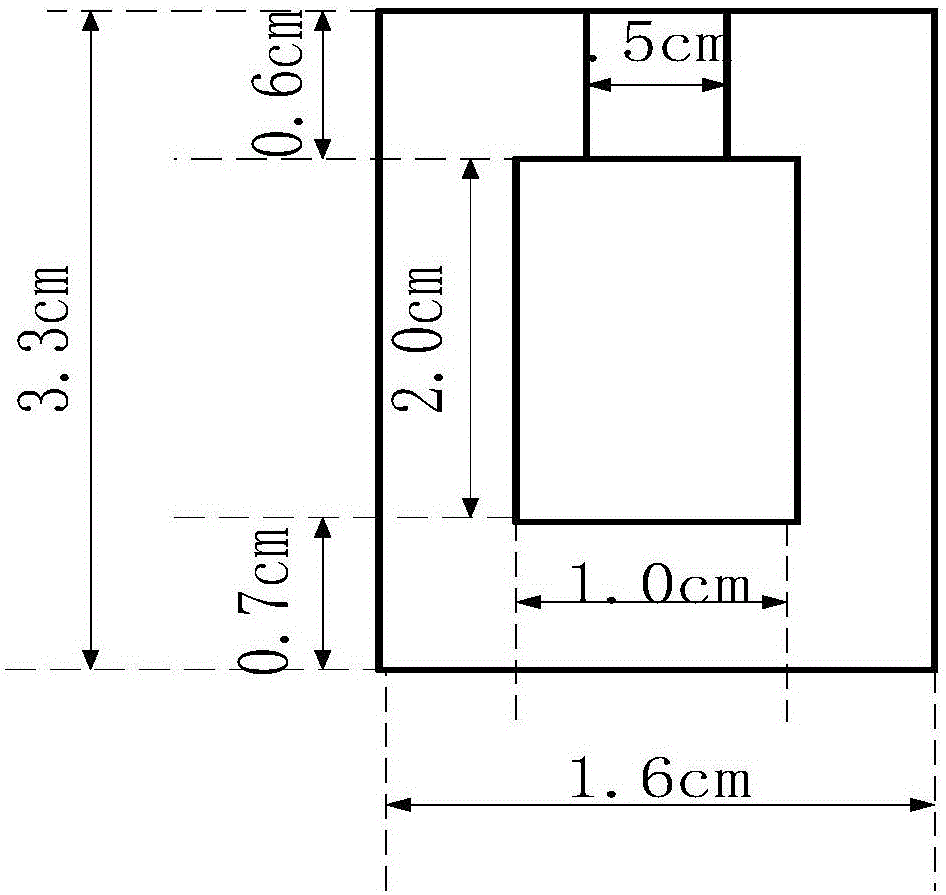
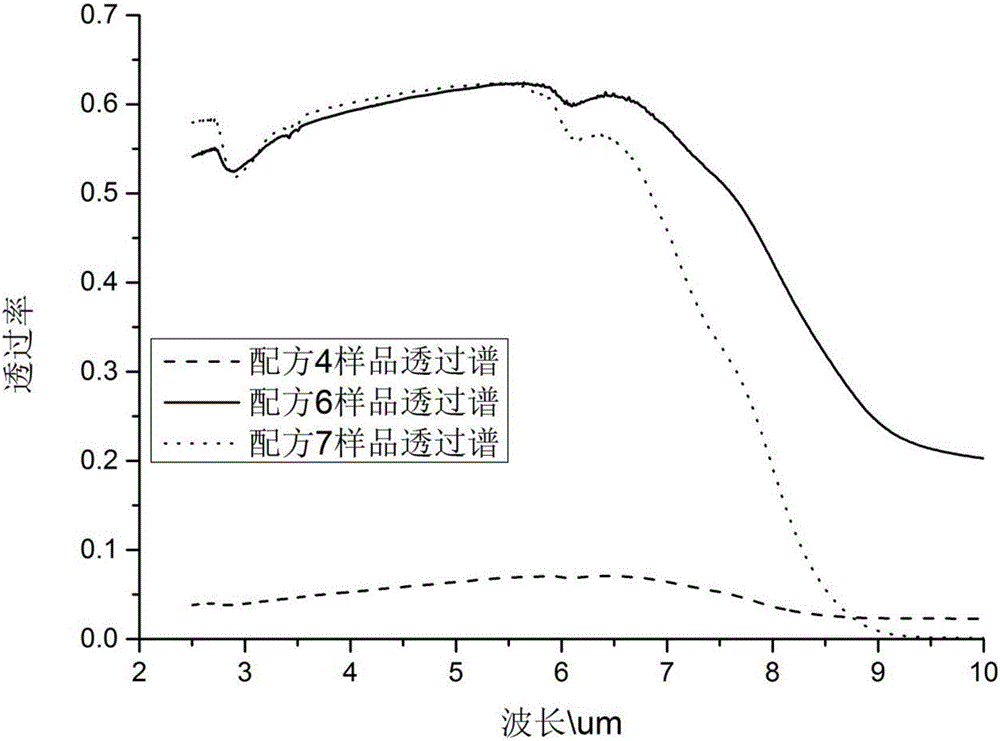
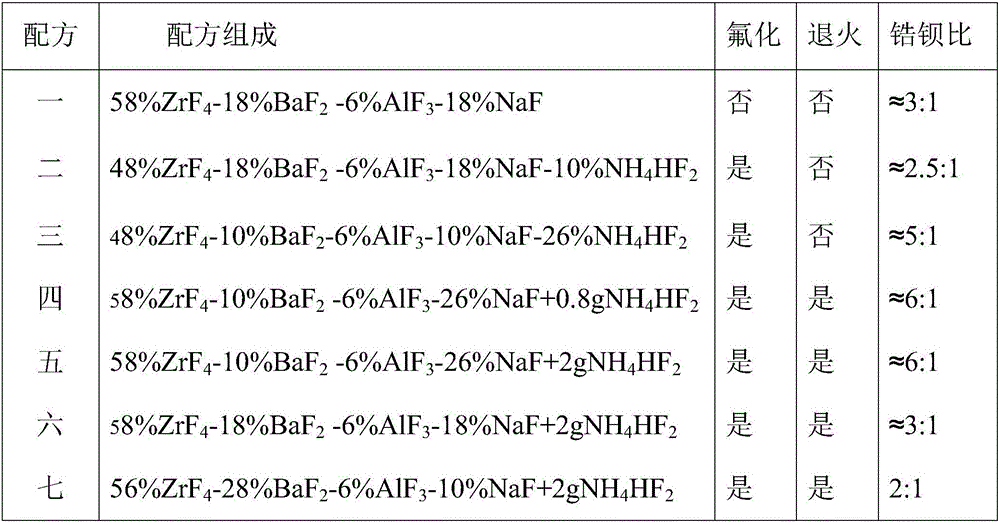
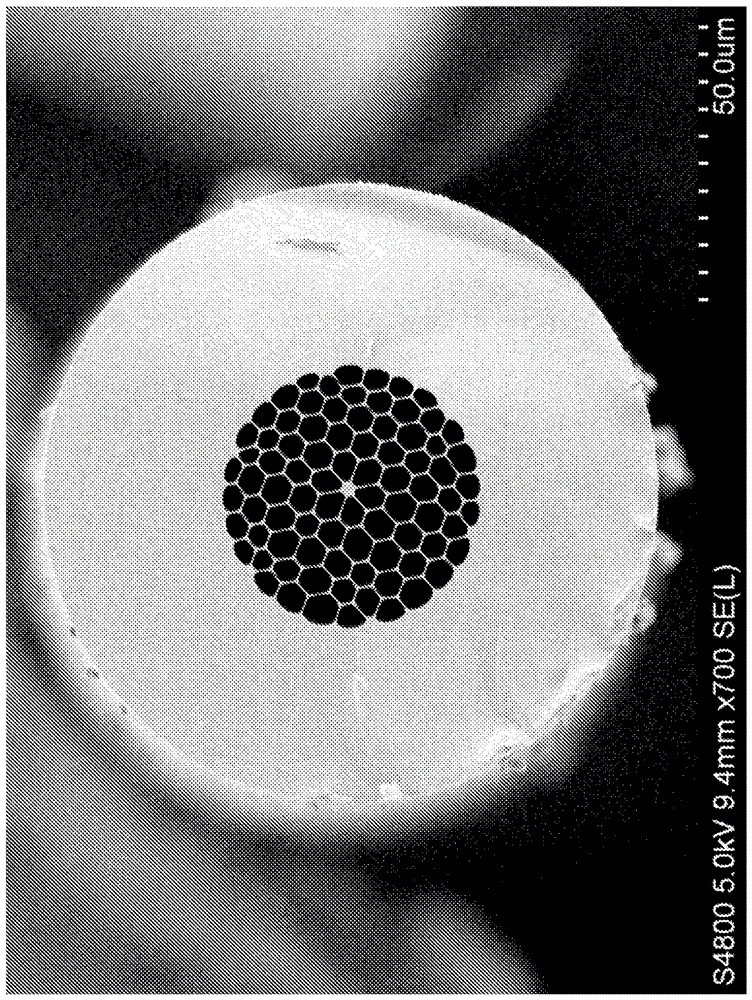
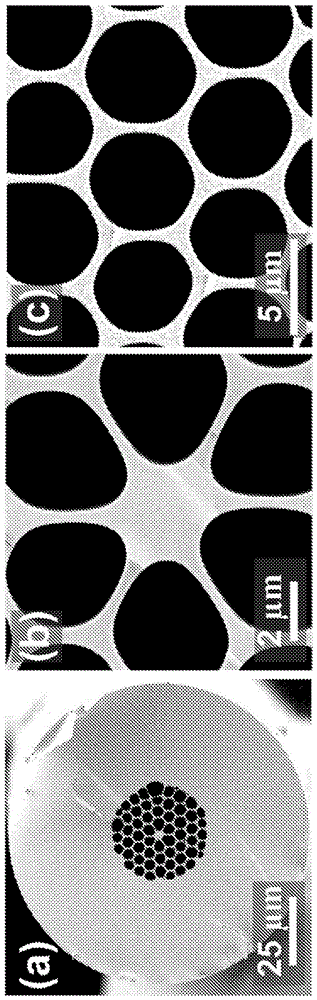
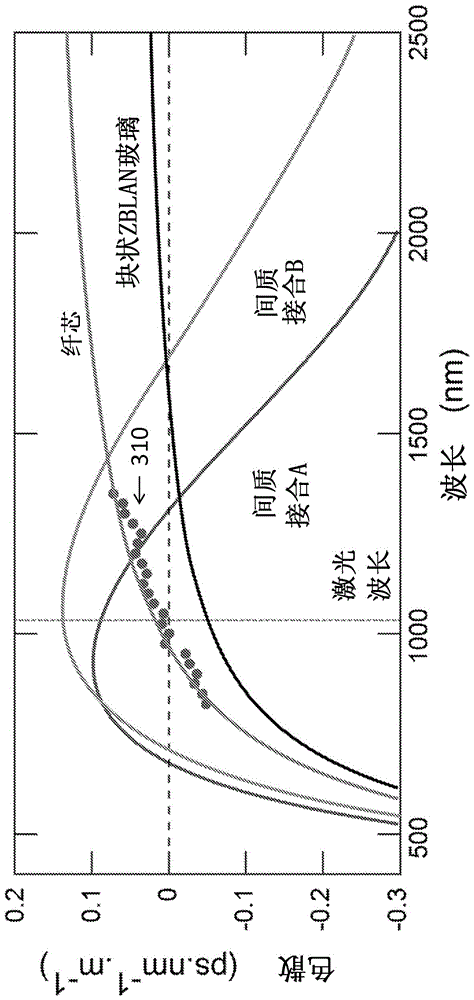
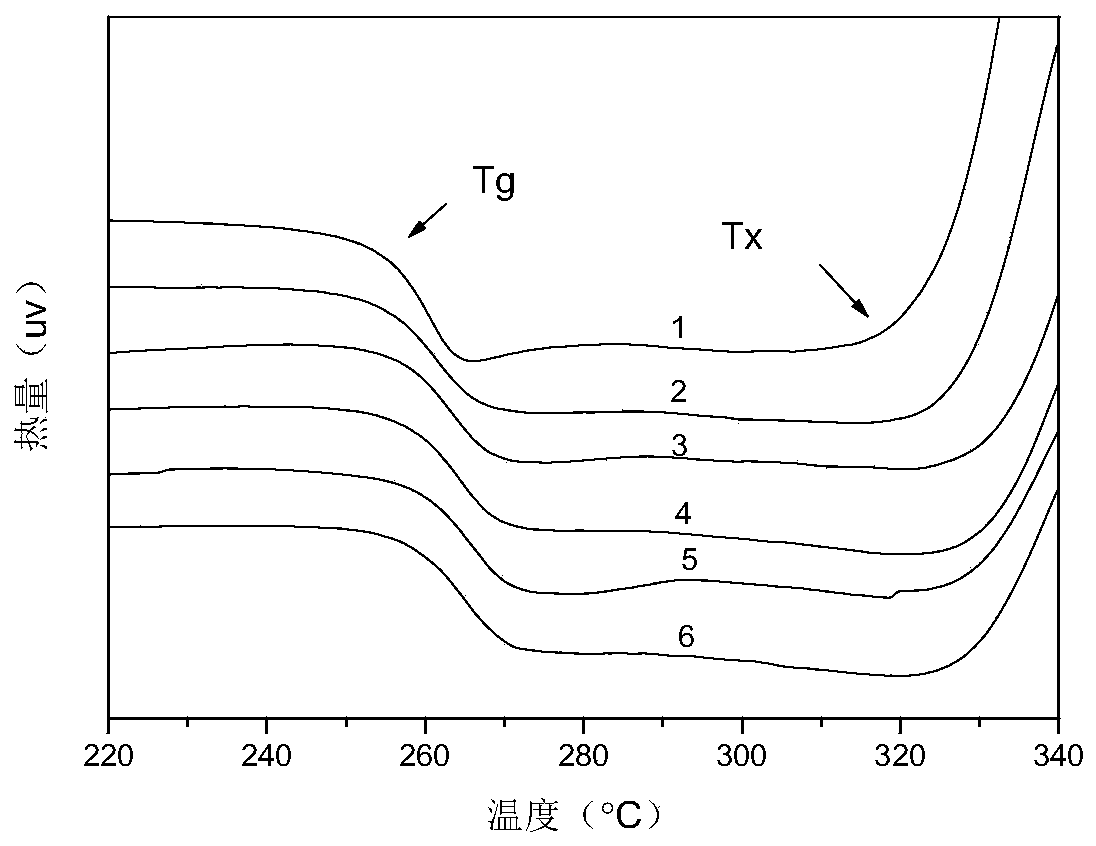
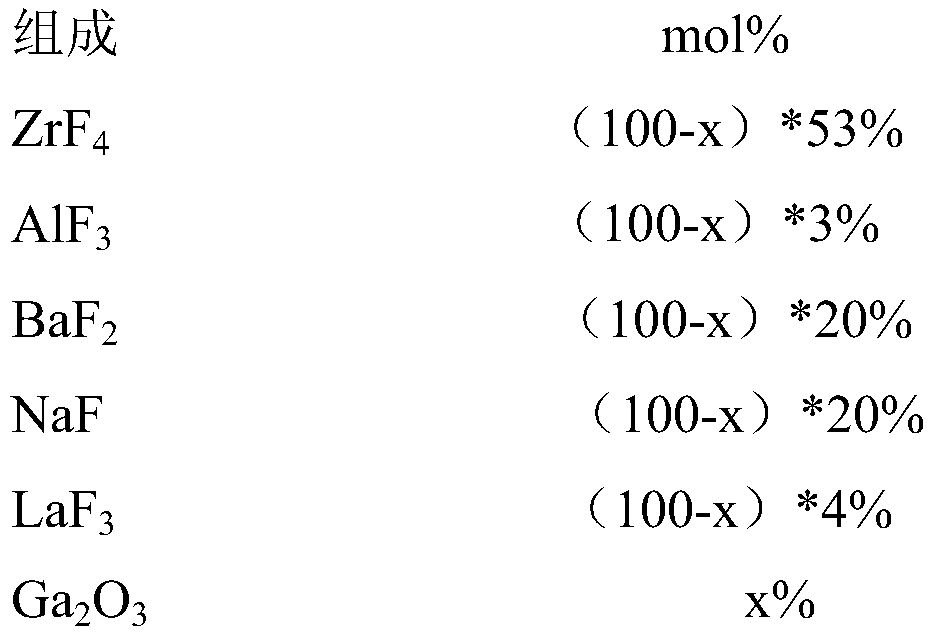Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
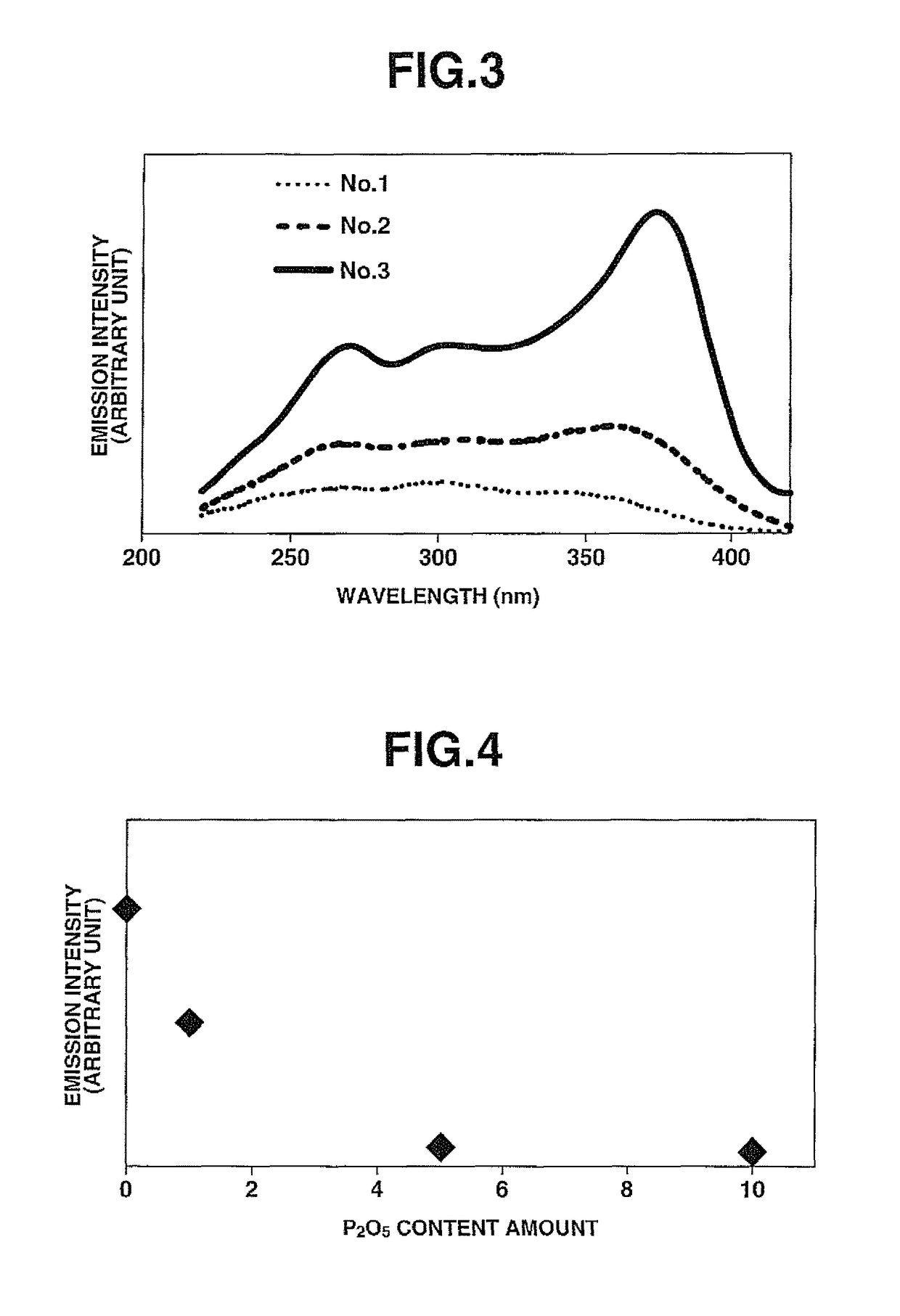
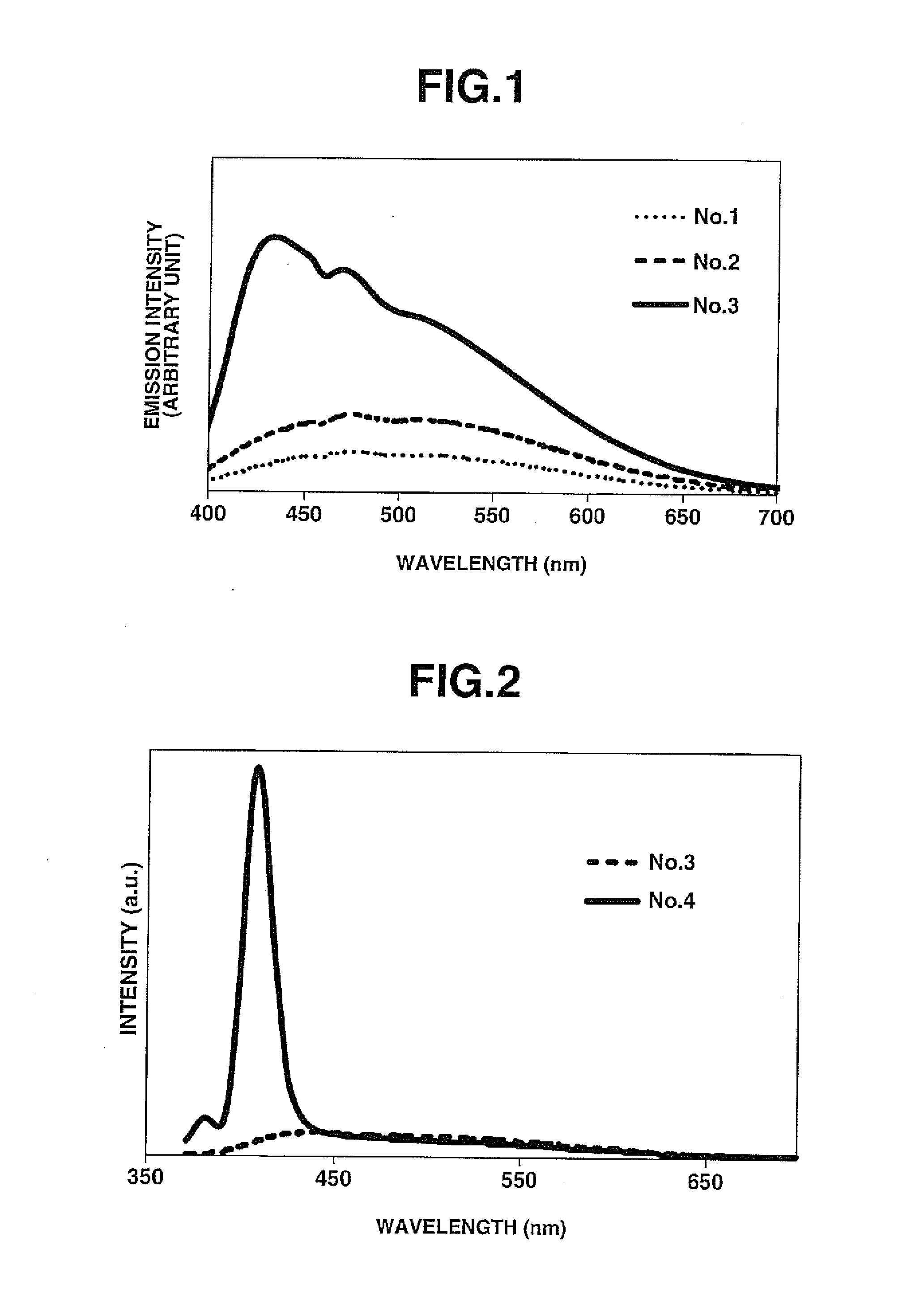
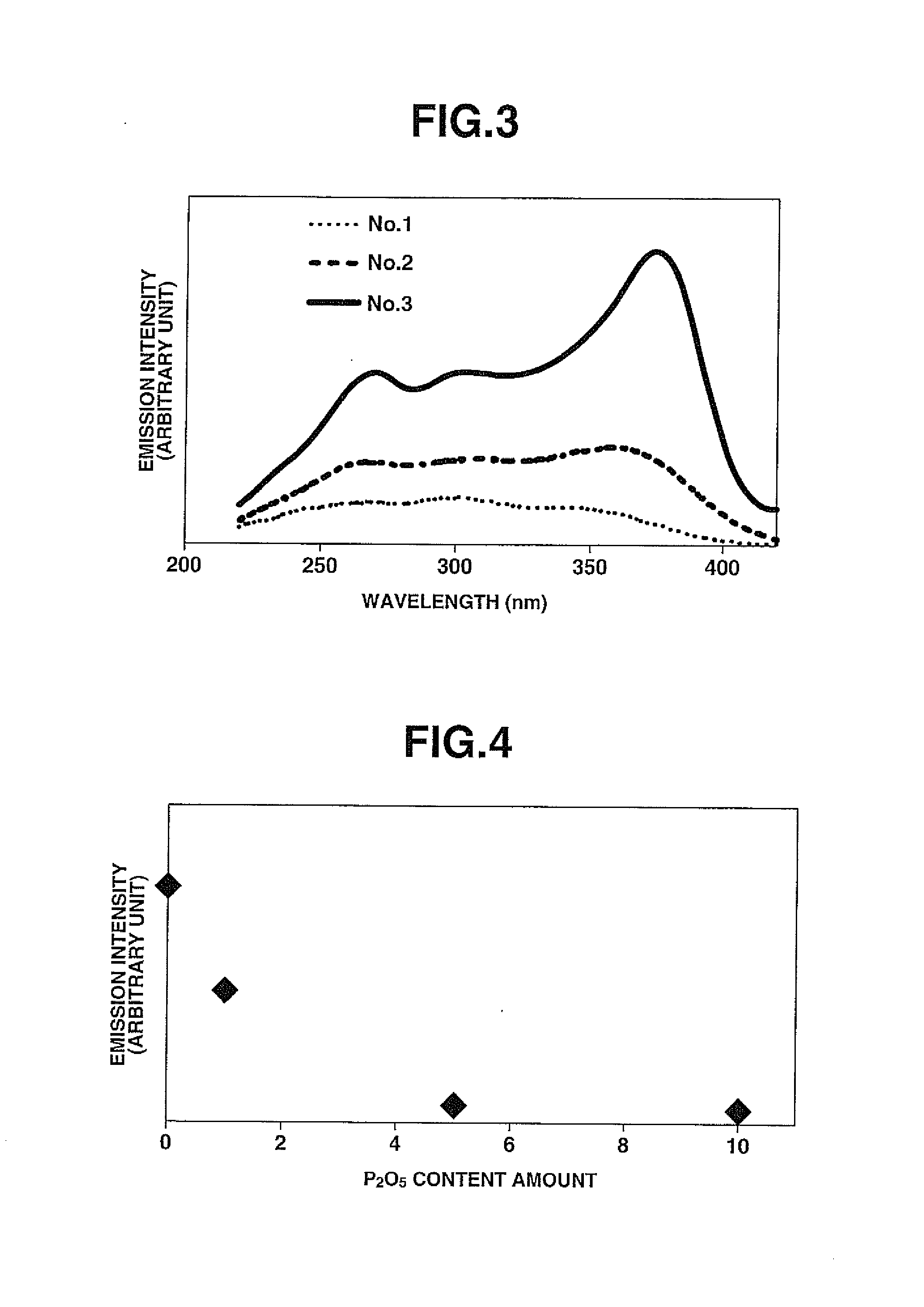
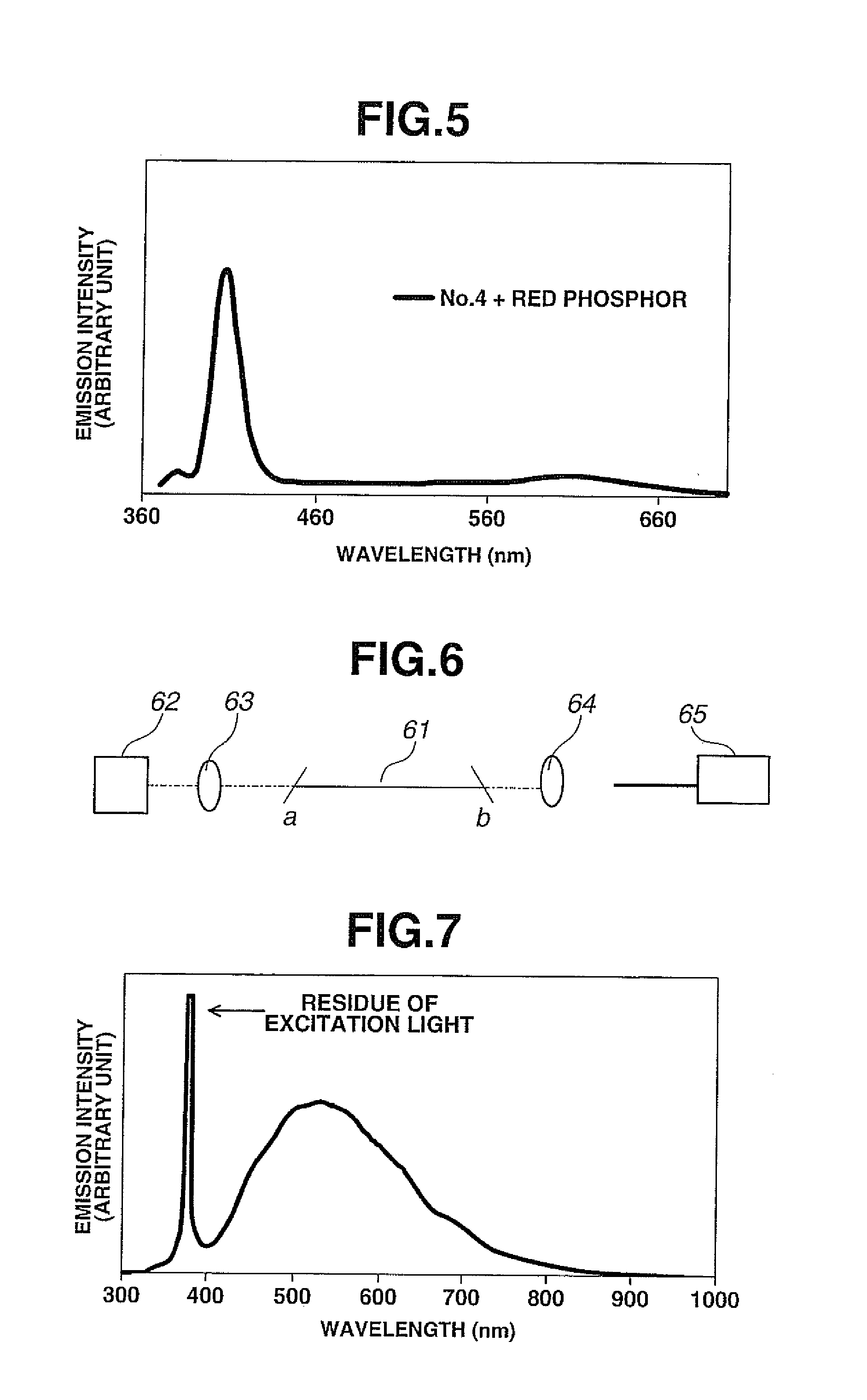
56 results about "Fluoride glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rare earth doped glass frequency conversion luminous material and preparation method thereof
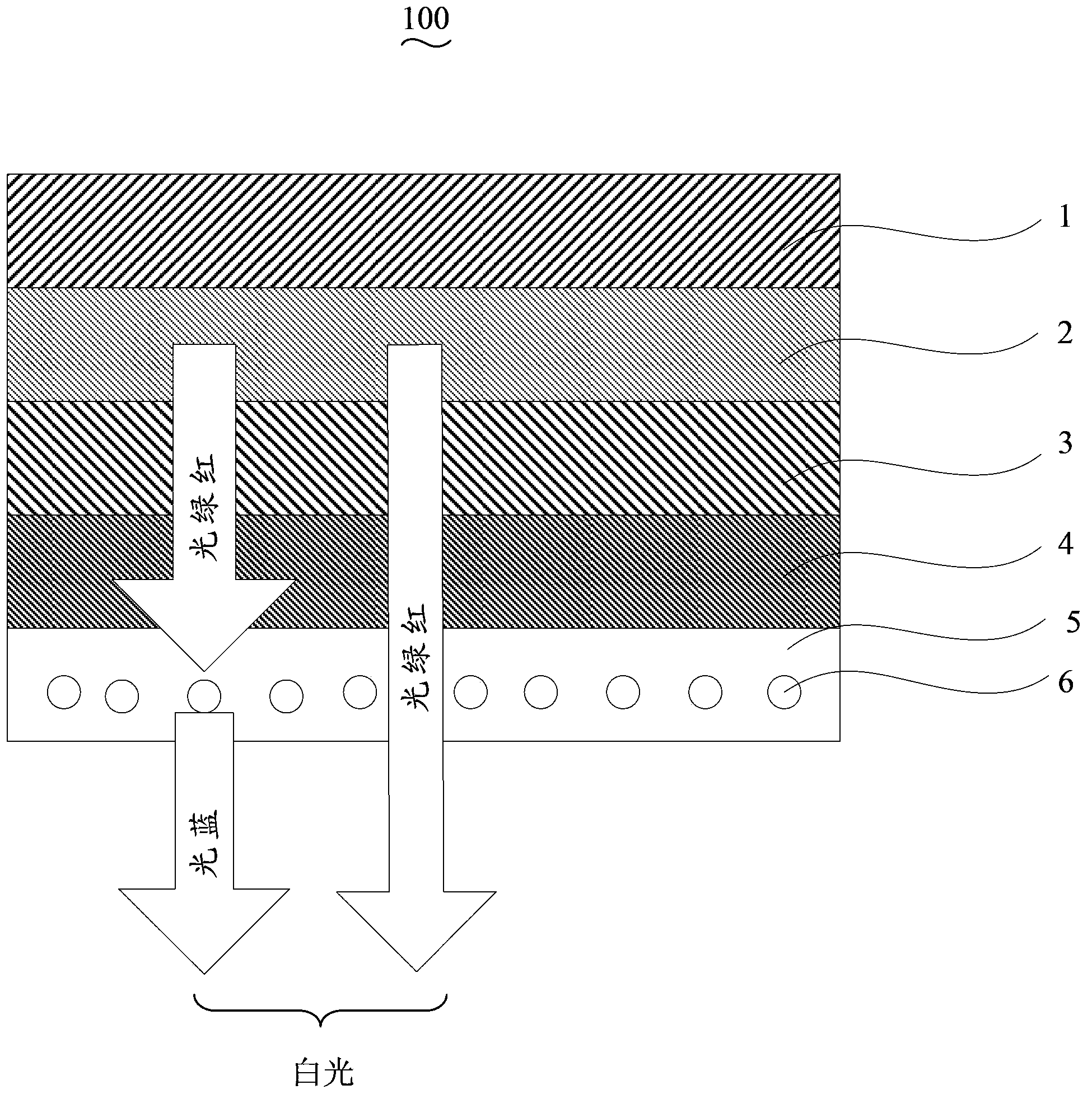
InactiveCN103666475AControl Particle SizeGood light transmissionLuminescent compositionsIon exchangeMaterials science
The invention discloses a rare earth doped glass frequency conversion luminous material and a preparation method thereof. The luminous material is formed by fluoride glass ceramics containing rare earth ions and silver nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the steps of firstly preparing glass containing rare earth ions, secondly preparing the glass into the glass ceramics containing fluoride crystals through the heat treatment technology, and thirdly soaking the glass ceramics in a mixed salt melt containing silver nitrate to undergo ion exchange, thus obtaining the rare earth doped frequency conversion luminous material jointly enhanced by the silver nanoparticles and fluoride microcrystals. The obtained luminous material has the beneficial effects that the luminous material has good optical property and thermal stability; through irradiation of exciting light, by utilizing the local field enhancement effect of the silver nanoparticles, the rare earth ions in a low phonon energy environment created by the fluoride microcrystals achieve high frequency conversion luminous efficiency which can be maximally enhanced by 30 times, thus effectively making up for the problem of low rare earth ion doped glass frequency conversion luminous efficiency.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
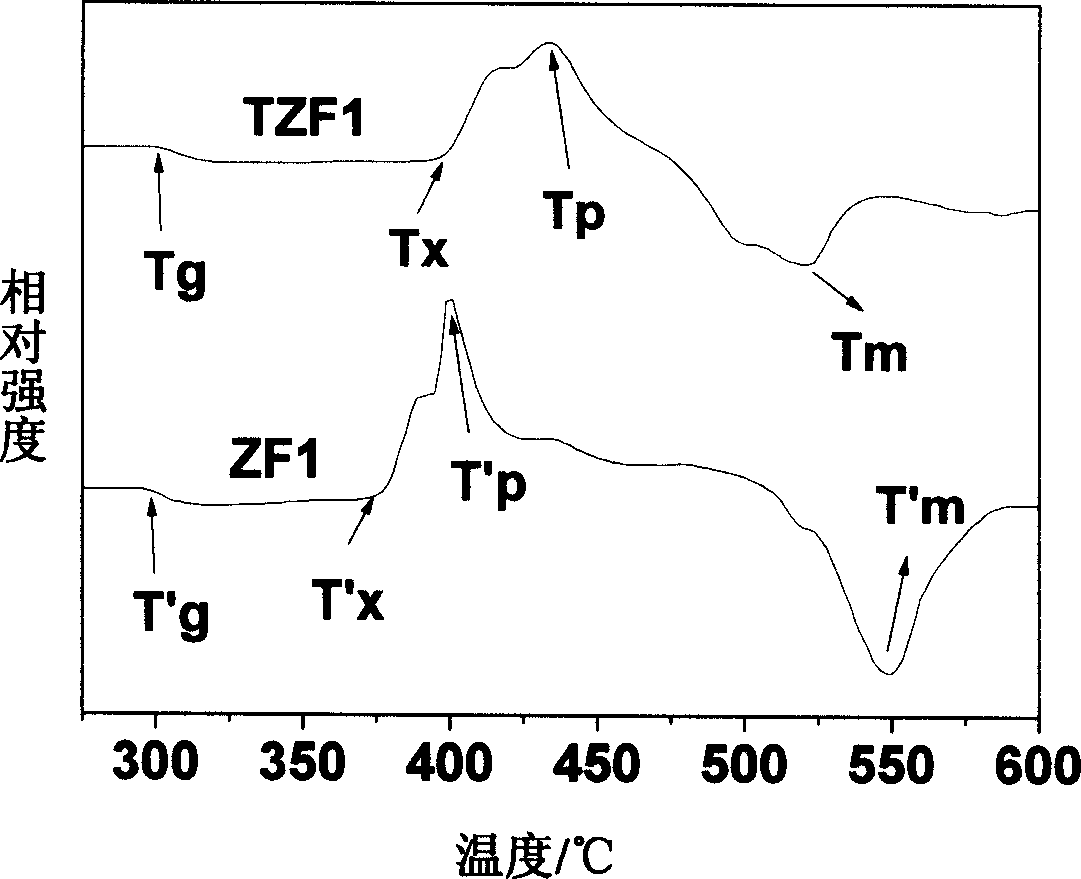
Rear earth doping oxygen-fluorine tellurate microcrystalline glass and preparation method thereof
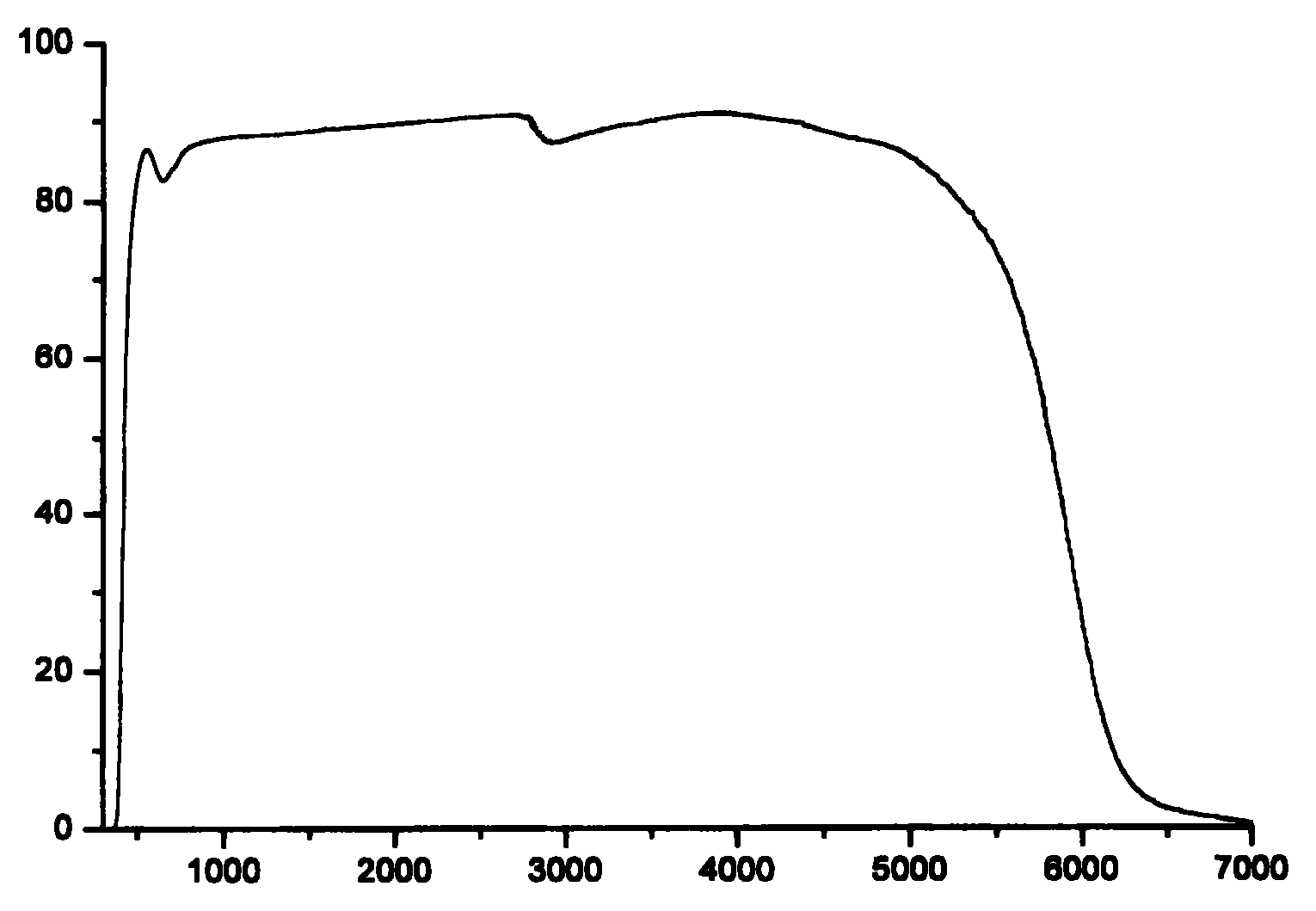
The present invention relates to a rare earth doping oxyfluoride tellurite nucleated glass and the preparing method thereof, and the mol percentage of the nucleated glass is as follows: TeO2: 68-73%, ZnO: 15-18%, ZnF2: 7-10%, RF3(R is a rare earth element): 3-5%. The preparing method is firstly preparing oxyfluoride tellurite glass with a melting method, then through an accurate heat processing technique the substrate glass is heat treated for crystallization to obtain a transparent oxyfluoride tellurite nucleated glass. The prepared oxyfluoride tellurite nucleated glass is excellent and has excellent infrared transmitting property and the dimension of the crystal phase in the nucleated glass is tens in nano-scale. The preparing method of the nucleated glass of the invention is simple relatively, comparing with the fluoride glass the stability of the glass is better and the heat treating blooming process can be controlled more easily. The nucleated glass is suitable for applying in the optical window material of the mid-infrared waveband, and is used for high intensity upper converting luminous material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Infrared permeating oxide fluoride glass
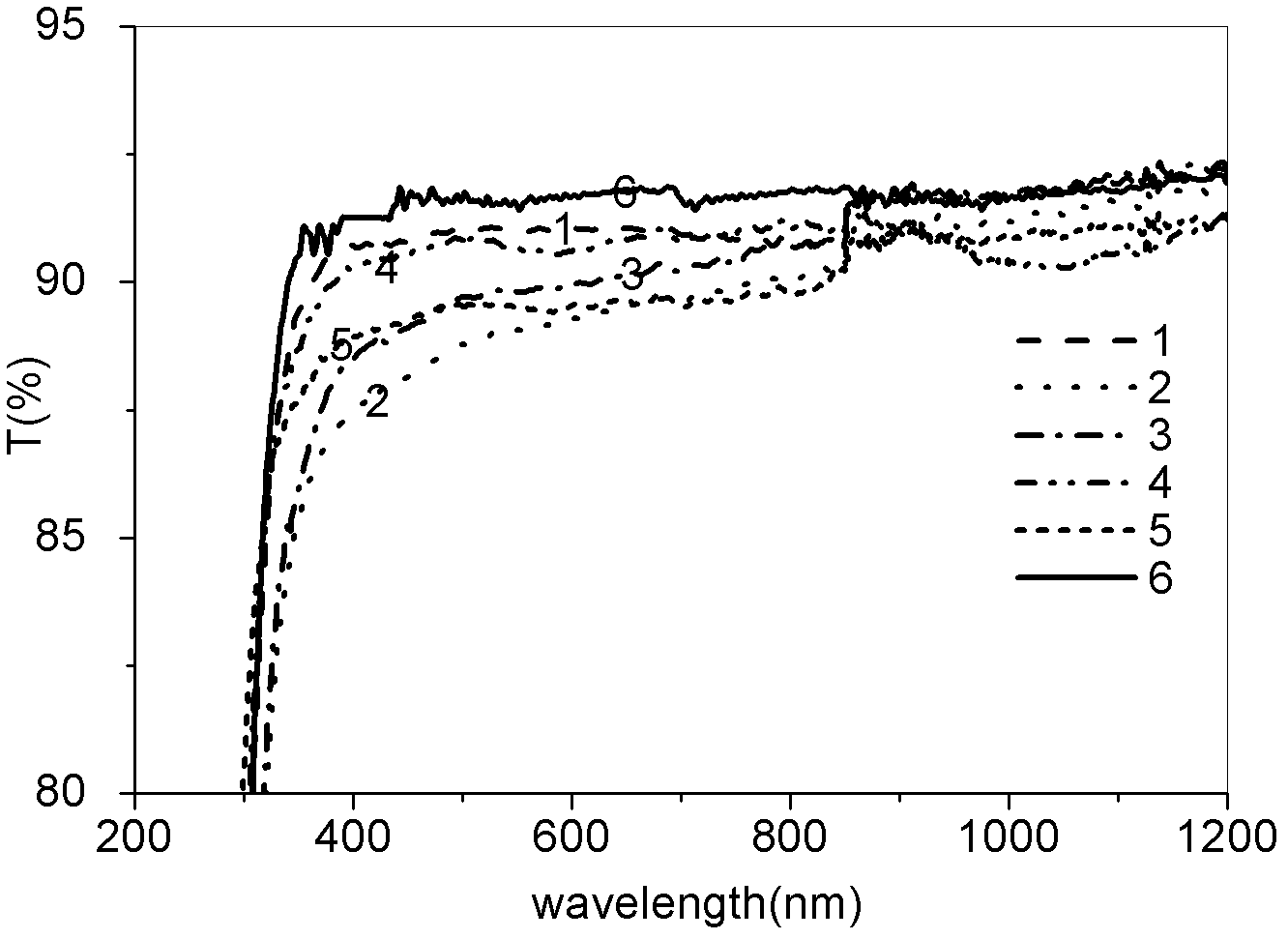
The present invention relates to an infrared transmitting oxyfluoride glass. It is characterized by that in the AlF3-MeF2-MF3 fluoride glass composition the TeO2 or tellurite is added, the range of the composition is as follows: (component, mol%) TeO2 3-50, AlF3 20-55, MgF2+CaF2+SrF2+BaF2 25-60, LaF3+YbF3+YF3 0-40. Said glass composition has good glass-forming property, and is suitable for large size material, and has good transmittance of near ultraviolet and middle infrared wave band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
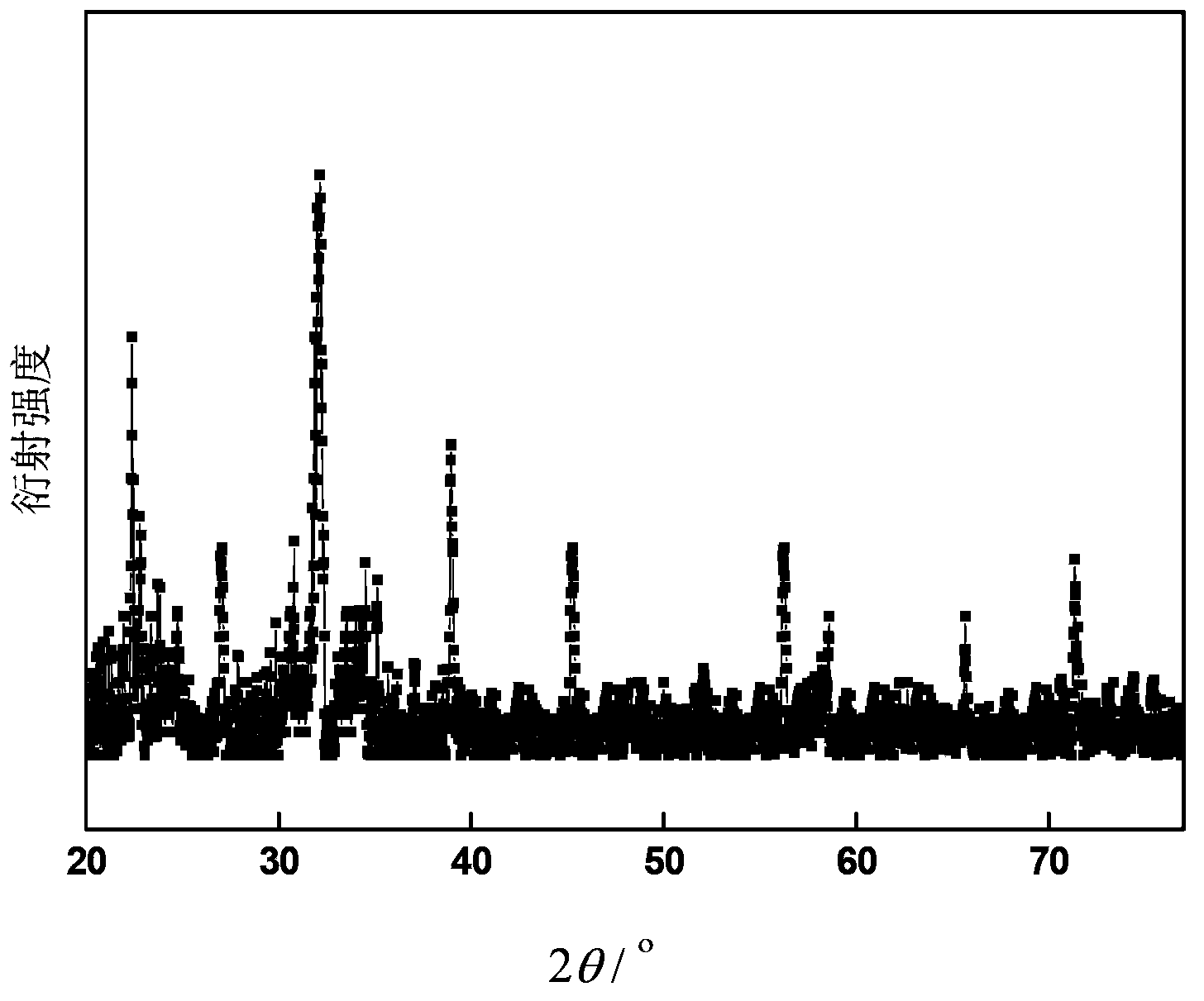
Fluoro glass ceramic showing photostimulable properties
InactiveUS6352949B1Good environmental stabilityReduce scatterLuminescent compositionsAlkali ionsRare earth
A glass ceramic material for storing energy of X-rays and releasing said energy by photo-stimulation comprising a fluoride glass matrix containing micro-crystalline particles, said particles having an average particle size, d, so that d<2 mum and said glass ceramic shows in a XRD spectrum a continuous spectrum of said glass matrix and discrete peaks superimposed on said continuous spectrum. Said glass matrix contains preferably zirconium ions and ions selected from the group consisting of alkali ions and alkaline earth ions, at least 5 mole % of the fluoride ions is replaced by bromide and / or chloride ions and at least 0.01 mole % of cations selected from the group consisting of transition metal ions, rare earth metal ions, In+, Ga+, Tl+, and Pb2+ is present.
Owner:SPAETH JOHANN MARTIN +2
SPCVD silicate glasses
InactiveUS6077799AImproved Gain FlatnessIncrease heightActive medium materialFibre transmissionFiberFluorescence
These glasses incorporate a combination of F and Al2O3 to achieve even wider fluorescence and improved gain flatness. In addition, SPCVD incorporates large amounts of N into low-loss fiber whose high charge has an impact on rare earth behavior. The Surface Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (SPCVD) produces fiber preforms with high levels of F, Al2O3, and N. These heavily fluorinated glasses provide much broader Er3+ emission than Type I or Type II silica for enhanced multichannel amplifiers. SPCVD successfully fluorinates silica with losses below 5 dB / km and increased Er3+ emission width.
Owner:CORNING INC
Infrared transparent fluozirconate microcrystalline glass and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1927752AGood resistance to devitrificationGood physical and chemical propertiesGlass furnace apparatusSmelting processFluoride glass
The present invention is infrared transmitting fluorozirconate microcrystal glass and its preparation process, and features that LaF3 is added into ZrF4-BaF2-YF3-AlF3 fluoride glass components to form the fluorozirconate microcrystal glass in the molar composition of: ZrF4 50-55 mol%, BaF2 15-33 mol%, YF3 10-22 mol%, AlF3 3-7 mol%, and LaF3 2-8 mol%. The preparation process includes the first smelting process to prepare fluorozirconate glass and the subsequent precise heat treatment to microcrystallize the base glass into infrared transmitting fluorozirconate microcrystal glass. The preparation process is simple, and the prepared fluorozirconate microcrystal glass has excellent resistance to transparency loss and higher mechanical performance than fluoride glass. The fluorozirconate microcrystal glass is suitable for use as the optical window material in medium infrared band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Erbium ion doped intermediate infrared luminous fluorine tellurate glass
InactiveCN103030275AEnhanced fluorescence emissionImprove thermal stabilityFluorescenceHeat stability
The invention provides an erbium ion doped intermediate infrared luminous fluorine tellurate glass. In terms of mol percentage, the glass comprises the following components by mole percent: 43-53 % of ZrF4, 18-22 % of CaF2, 3-5 % of YF3, 2-4 % of AlF3, 18-22 % of NaF, 0-5 % of TeO2, 0-5 % of GeO2, 0-5 % of Bi2O3 and 2-8 % of ErF3. The glass is prepared by using a covered platinum crucible and a silicon carbide rod electric furnace melting method. According to the invention, after heavy metal oxide is introduced, a fluoride glass is still transparent without crystallization, the infrared transmission rate of the glass is 85 % near intermediate infrared 2.7 microns, the heat stability of the glass is improved and the chemical stability of the glass is also improved; under laser diode pumping with wavelength of 980 nm, obviously enhanced intermediate infrared 2.7 microns fluorescence can be obtained; and the erbium ion doped intermediate infrared luminous fluorine tellurate glass provided by the invention is suitable for preparing and using erbium ion doped special glass and optical fiber materials which are luminous at intermediate infrared wave band of 2.7 microns.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
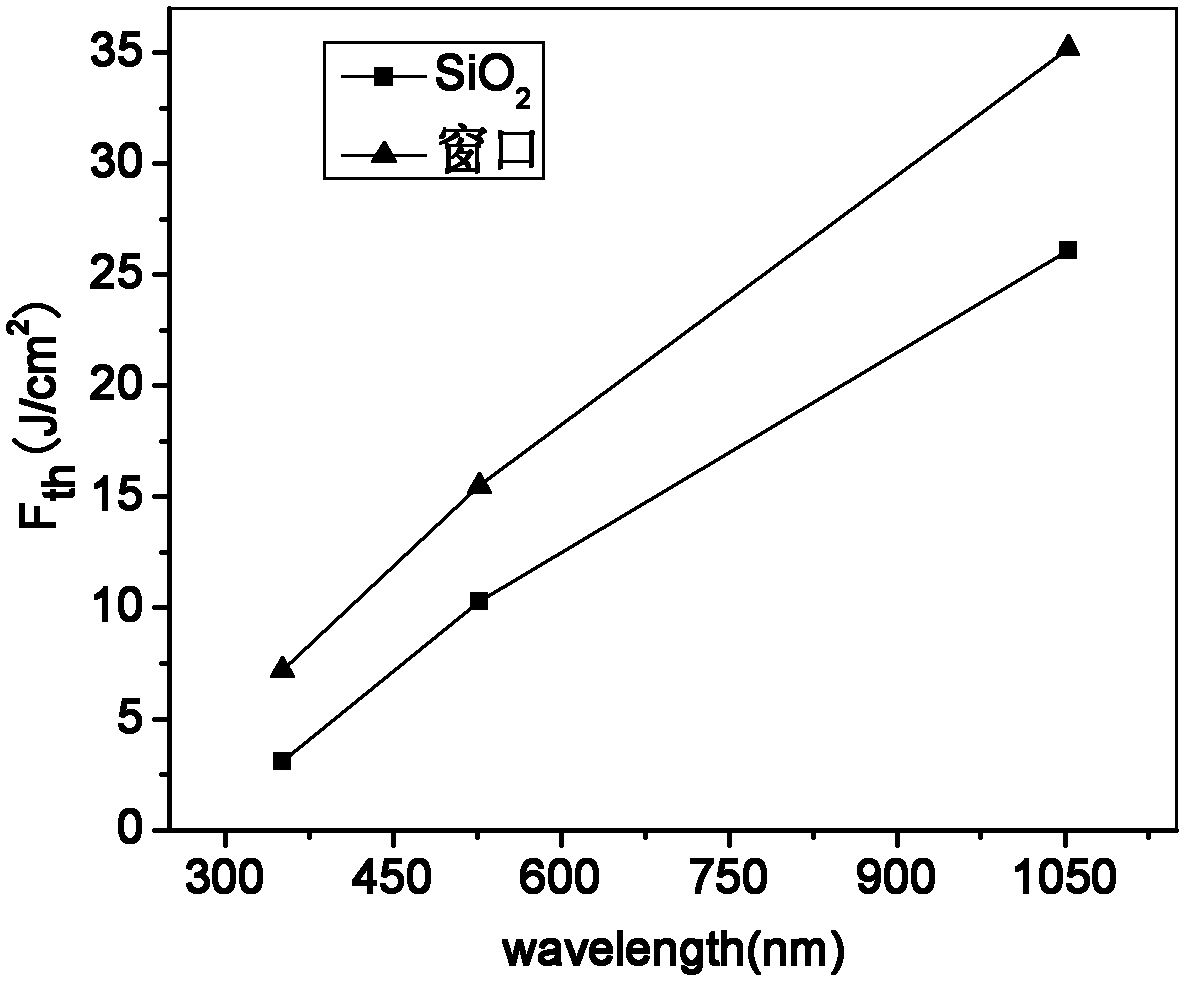
Method for preparing high-damage-threshold laser window material
ActiveCN102557430ASolve easy devitrificationSolve the problem of poor glass formationDevitrificationAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a novel method for preparing a high-damage-threshold laser window material, which is stable in chemical properties and high in damage-threshold. The technical scheme is that novel large-size high-damage-threshold laser window glass is obtained through the fact that an oxide accessory ingredient capable of improving glass forming properties and materialization properties of the material is introduced in fluoride glass. The method solves the problem that the fluoride glass is easy in devitrification, poor in glass forming and difficult in large-size production. Simultaneously, the damage-threshold is obviously improved, and the method can be used in a high-energy laser for improving load capacity and has important functions on smooth advancement of inertial confinement fusion (ICF).
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
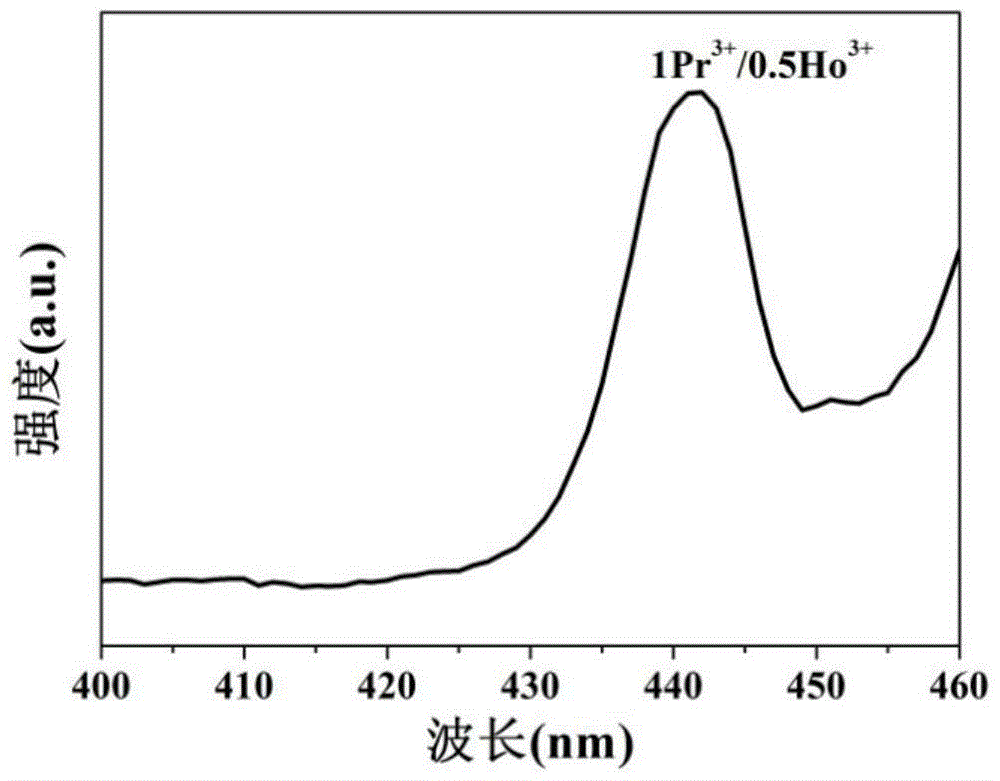
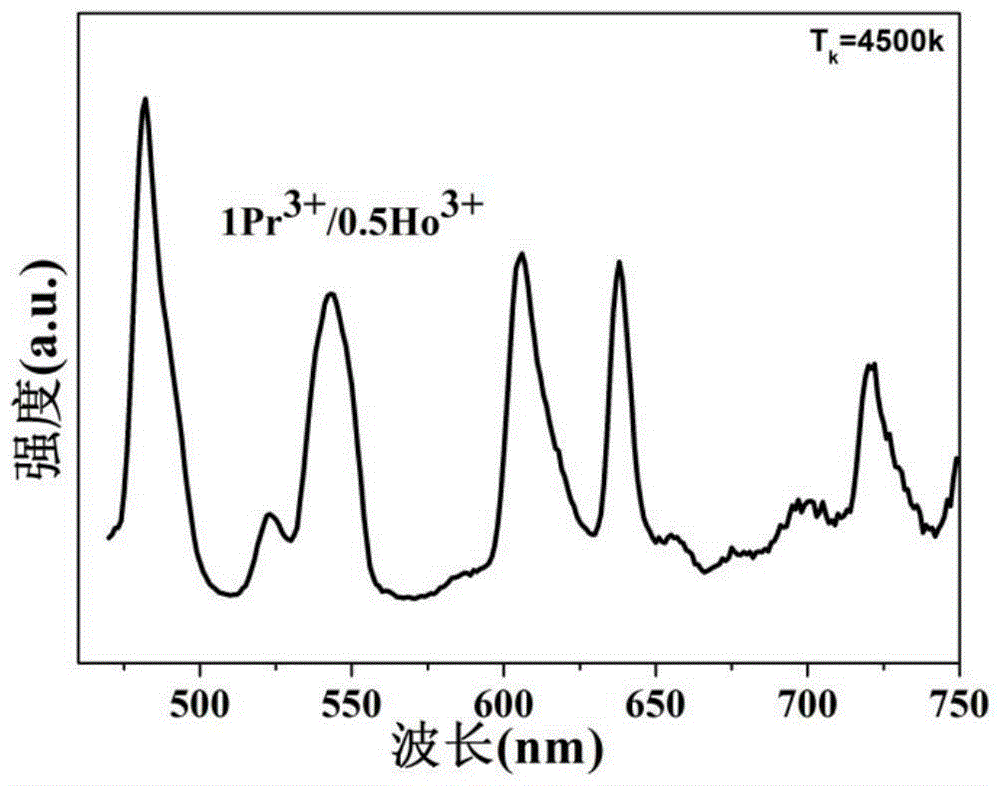
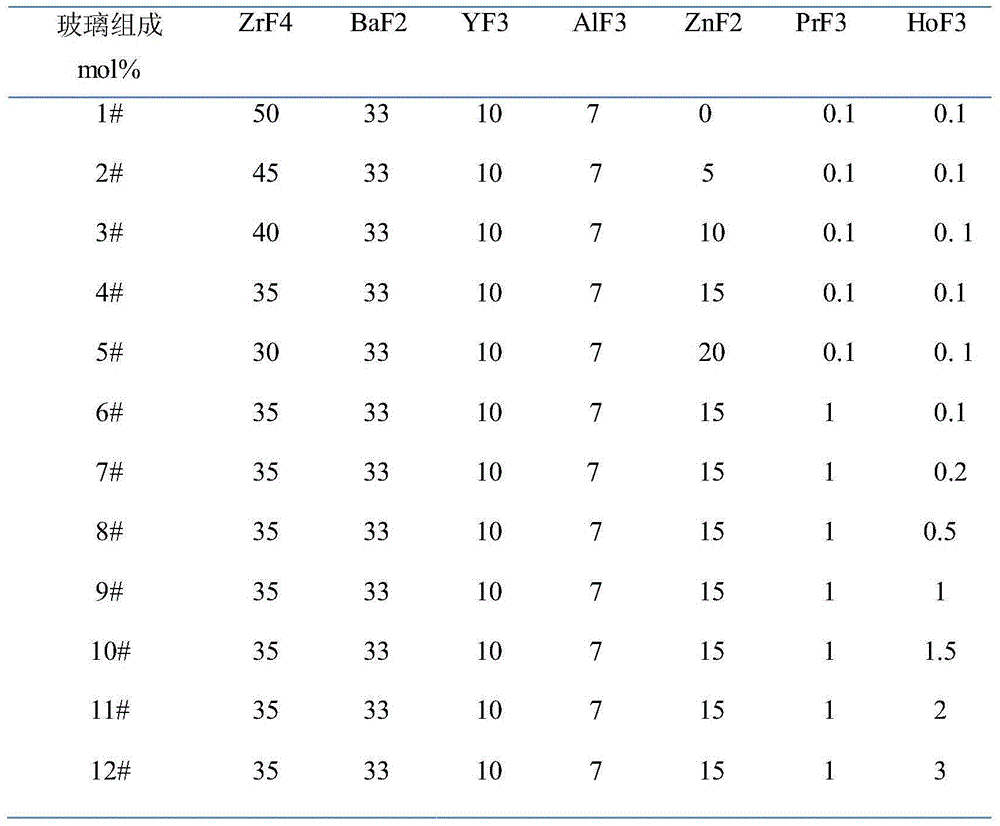
Rear earth-doped luminescent glass for white light emitting diode and preparation method therefor
A rear earth-doped luminescent glass for a white light light emitting diode and a preparation method therefor. The method uses rare earth Pr<3+> and Ho<3+> as main uminescent ions that are co-doped in a fluoride glass substrate, and are coordinated with a 445 nm blue LED to excite and emit a white light. The preparation method for the glass comprises three steps: obtaining raw materials, mixing glass batch materials, and melting the glass. The glass provided by the present invention can be excited by a blue light emitting diode to output a white light. The rear earth-doped luminescent glass is a multicomponent ZrF4-ZnF2 glass, and compared with ZBLAN glass, the glass provided by the present invention has the advantages of a higher glass transition temperature, better chemical and mechanical properties and a high luminous efficiency, and the like. Compared with YAG: Ce fluorescent powder, the glass provided by the present invention has the advantages that the preparation method is simple in process, easy to operate, low in cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Efficient cooling large-mode-area mid-infrared photonic crystal optical fiber and laser device thereof
ActiveCN104808288AReduce the refractive index differenceImprove enduranceOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingActive medium shape and constructionErbium dopingRefractive index
Disclosed is an efficient cooling large-mode-area mid-infrared photonic crystal optical fiber laser device. The efficient cooling large-mode-area mid-infrared photonic crystal optical fiber laser device is in a structural design of double-cladding photonic crystal fiber, wherein the internal cladding is fluoride glass; a fiber core is made of high erbium-doped fluoride glass and provided with a plurality of air holes, which are with a diameter of d and spaced at a pitch of lambda. According to the efficient cooling large-mode-area mid-infrared photonic crystal optical fiber laser device, by adjusting the structure of the air holes of the photonic crystal optical fiber, the refractive index difference between the fiber core and the inner cladding can be reduced, the mode field diameter of the optical fiber can be increased. The efficient cooling large-mode-area mid-infrared photonic crystal optical fiber laser device comprises an efficient cooling device, inert gas is fed into the air holes, the air holes can provide cooling channels to increase the specific surface area for cooling, so that heat generated inside the photonic crystal optical fiber, particularly inside the fiber core, can be rapidly guided out of the optical fiber. Therefore, the cooling problem of large-core-diameter fiber can be solved, and possibility for achieving hectowatt-scale 2.7 mm single-mode laser output can be obtained.
Owner:杭州光学精密机械研究所
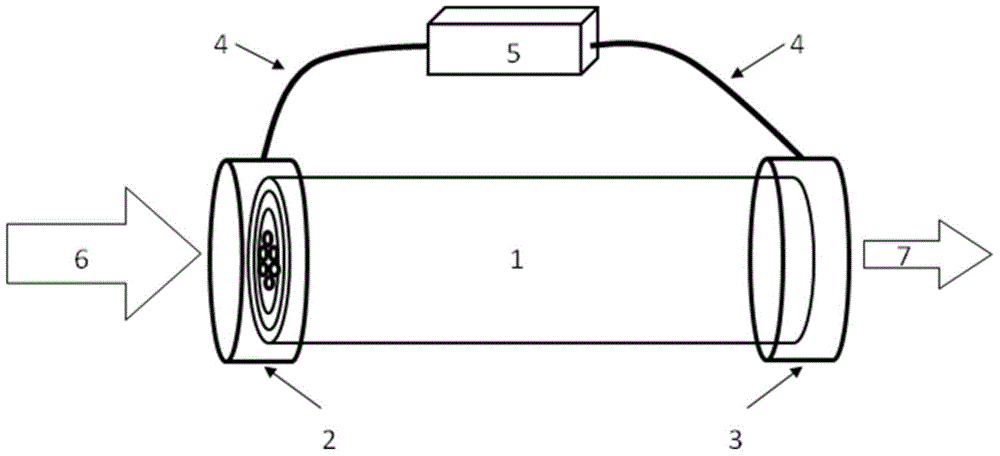
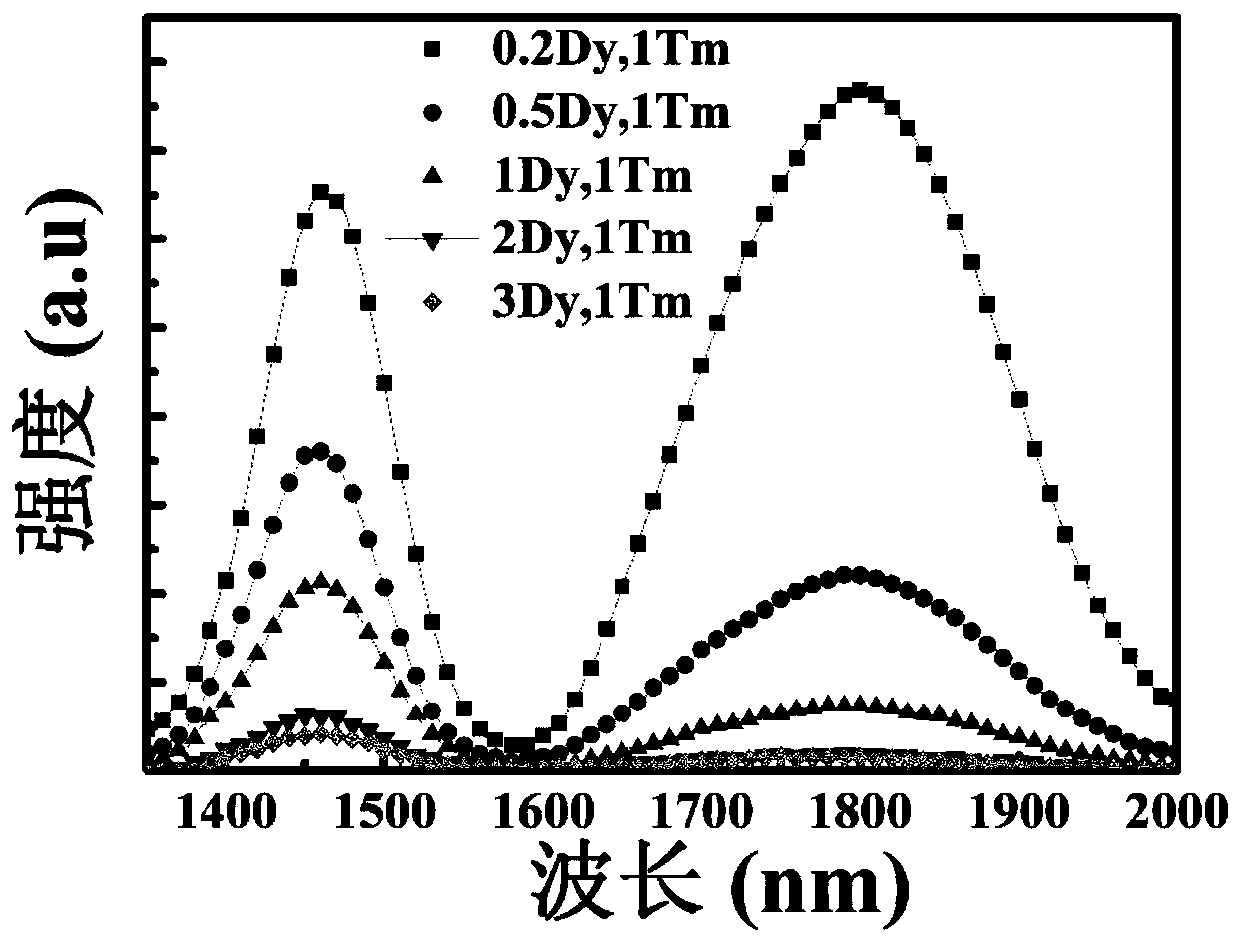
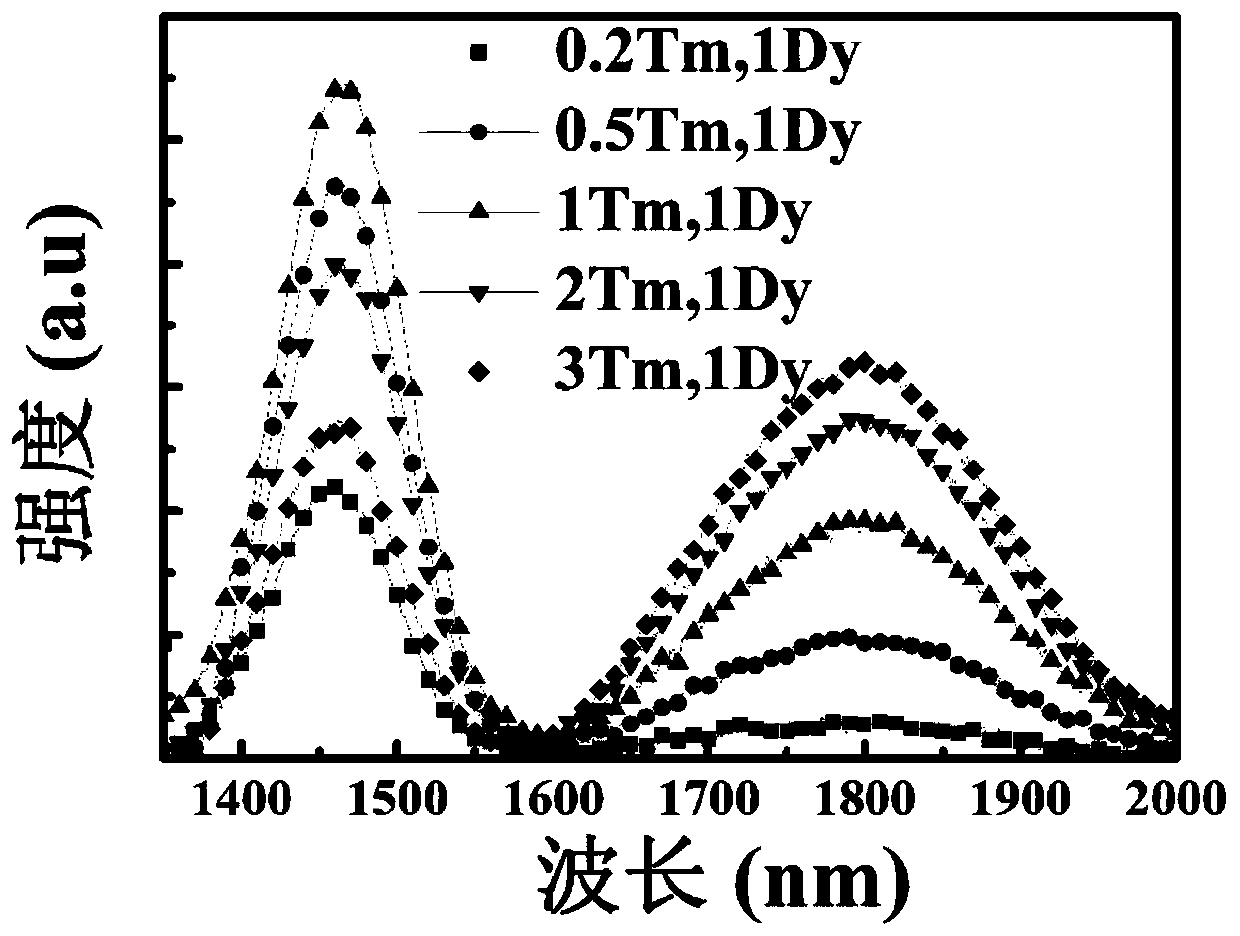
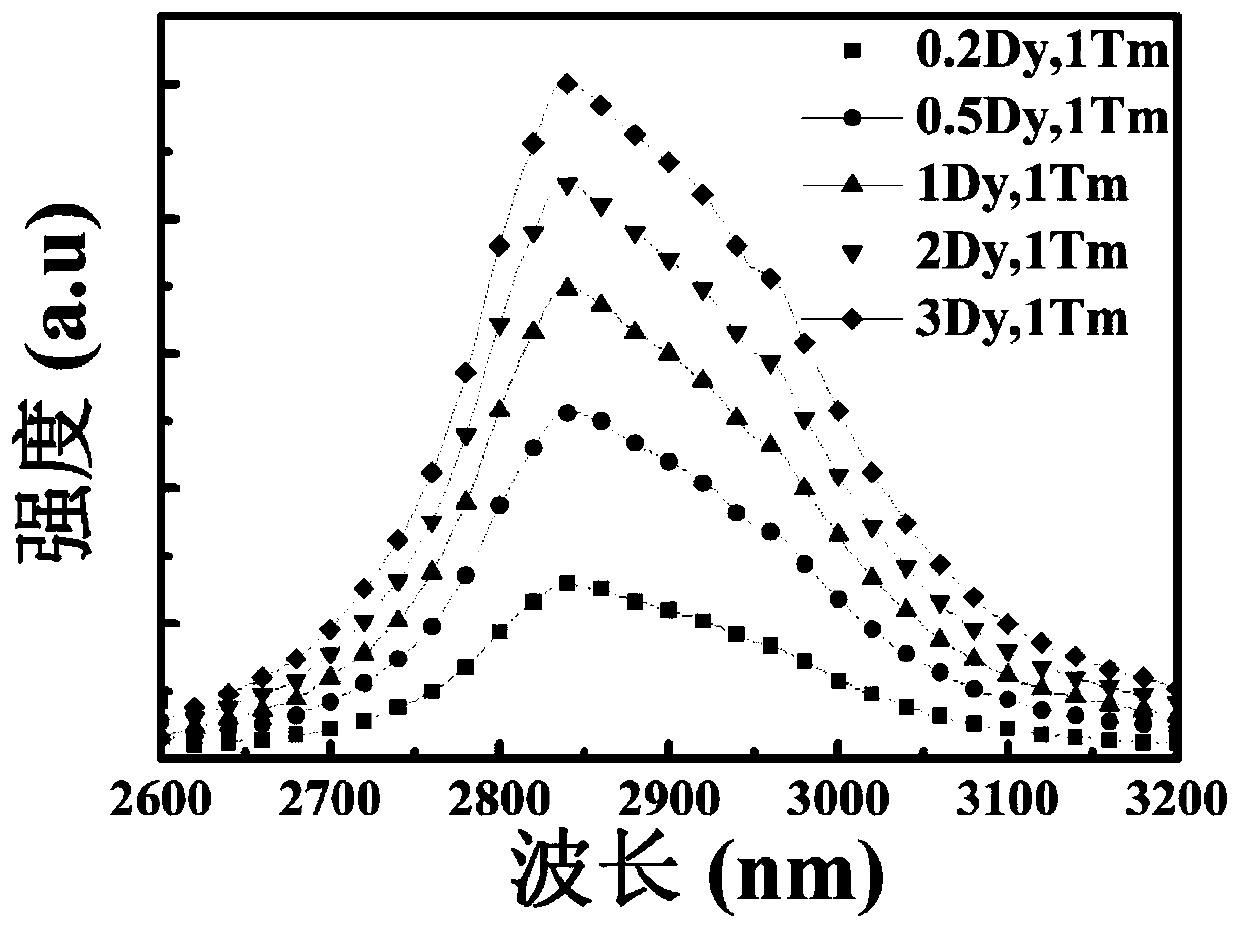
ZBYA fluoride glass and preparation method thereof
The invention provides ZBYA fluoride glass and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of solid laser devices. Near-infrared and intermediate infrared wave-band fluorescent light can begenerated through preparing a Dy<3+> and Tm<3+> co-doped ZBYA fluoride glass matrix; the mol percent of the matrix and co-doping ions meets the following ratio: when Dy<3+> ions are doped, the formulais 50ZrF4-33BaF2-(9-x)YF3-7AlF3-1TmF3-xDyF3; when Tm<3+> ions are doped, the formula is 50ZrF4-33BaF2-(9-x)YF3-7AlF3-1DyF3-xTmF3; and x is equal to 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2 and 3. The ion-doped glass preparedby the invention has high glass transparency and high luminous efficiency and also has good chemical stability; and a preparation technology is simple and the ion-doped glass can be used as a gain medium of a near-infrared and intermediate infrared wave-band optical fiber laser device.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Tm3+ doping-based fluoride glass microsphere laser
InactiveCN109768465ALower the thresholdRaise the thresholdActive medium materialMicro nanoMicrosphere
The invention relates to a Tm3+ doping-based fluoride glass microsphere laser, which belongs to the field of solid lasers and mainly comprises a micro-nano optical fiber, a fluoride glass microsphereof the ZYA doped with Tm3+, a pump source and a spectrometer. The pump source, the micro-nano optical fiber, the fluoride glass microsphere of the ZYA doped with Tm3+ and the spectrometer are coupledby a single-mode optical fiber in sequence. The method adopts a CO2 laser micromachining mode to prepare the fluoride glass microsphere of the ZYA doped with Tm3+, and realizes the 2-micron laser output of the fluoride glass microsphere of the ZYA doped with Tm3+. The laser in the invention has the characteristics of low threshold value and high Q value; and the structure is simple, the miniaturization and integration of the laser can be realized under a low threshold value, and a new matrix material is provided for the laser technology. The 2-micron laser obtained by the invention can be applied to the fields of integrated photonics, low-threshold laser, high-sensitivity biosensing, cavity photodynamics and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Double wave-length laser therapeutic apparatus
InactiveCN1618409AFast gasificationOptical resonator shape and constructionSurgical instrument detailsEr:YAG laserLaser cutting
A dual-wavelength laser therapy apparatus has the Er:YAG laser system and the Nd:YAG laser system for outputting the 2940 nm and 1064 nm laser beams, which are transmitted via a single optical fibre made of sapphire or fluoride glass. Its laser cutting function has high gasifying speed, resulting in high staltic effect.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Erbium-doped mid-infrared luminescent zirconium fluoride zinc-based glass and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105271727ATransparent optical quality is goodEnhanced fluorescence emissionGlass shaping apparatusFluorescenceErbium doping
The invention discloses erbium-doped mid-infrared luminescent zirconium zinc-based fluoride glass. Zirconium zinc-based glass which is transparent and better in optical quality is obtained by introducing ZnF2 into erbium-doped mid-infrared luminescent fluorozirconate ZBYAN glass, the infrared transmittance of the zirconium zinc-based glass is kept at a higher level near mid-infrared 2.7 microns, fluorescence emission which is obviously enhanced at mid-infrared 2.7 microns can be obtained under pumping of a laser diode with 980 nm wavelength, and a preparation method is suitable for preparation and application of mid-infrared 2.7 micron laser glass and optical fiber materials.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Phosphor-Dispersed Glass and Method for Producing Same
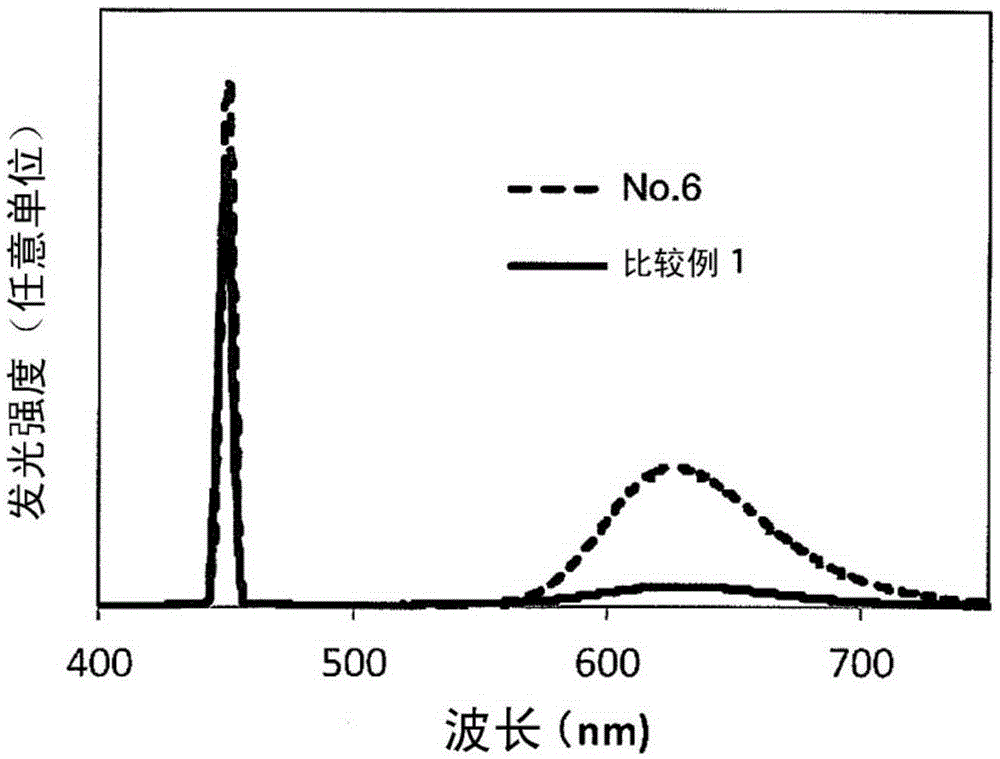
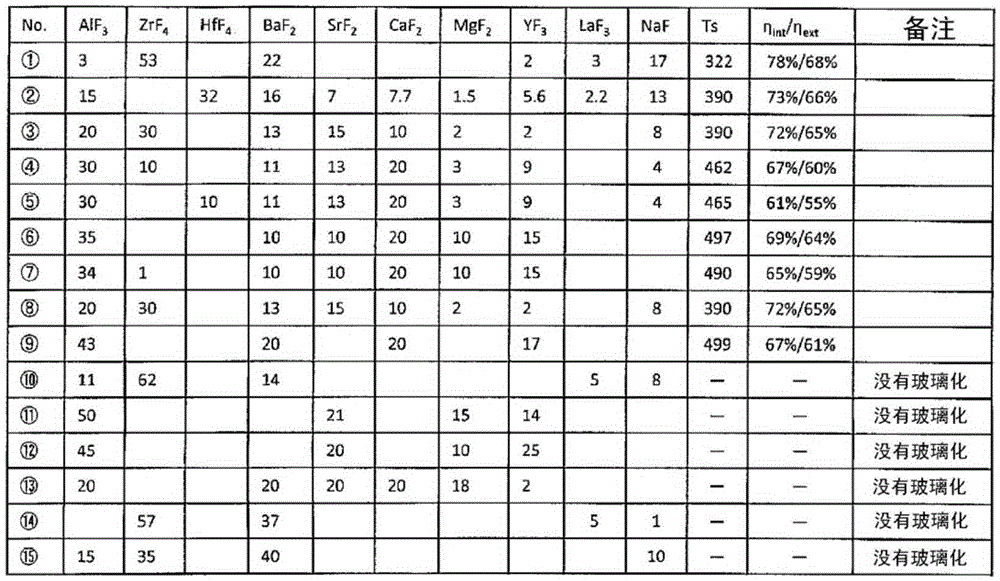
InactiveUS20160152515A1Avoid inactivationImprove efficiencyLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesAlkaline earth metalPhosphor
A phosphor-dispersed glass according to one aspect of the present invention includes phosphor particles and a phosphor encapsulant, wherein the phosphor encapsulant is a fluoride glass material containing 1 to 45 mol % of AlF3, 30 to 60 mol % of a sum of a fluoride of Hf and a fluoride of Zr, 20 to 65 mol % of alkaline earth fluorides in total, 2 to 25 mol % in total of at least one fluoride of element selected from the group consisting of Y, La, Gd and Lu and 0 to 20 mol % in total of at least one fluoride of element selected from the group consisting of Na, Li and K. It is feasible in this phosphor-dispersed glass to suppress deactivation of the phosphor particles regardless of the kind of the phosphor.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Phosphor-dispersed glass and method for producing same
InactiveCN105392746AAvoid inactivationImprove efficiencyLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesPhosphorAlkali metal
This phosphor-dispersed glass comprises phosphor particles and a phosphor sealing material. The phosphor-dispersed glass is characterized in that the phosphor sealing material is a fluoride glass and the fluoride glass composition consists of 1-45 mol% of AlF3, a total of 30-60 mol% of Hf fluoride and Zr fluoride, a total of 20-65 mol% of alkaline earth fluoride, a total of 2-25 mol% of a fluoride of at least one element selected from the group consisting of Y, La, Gd, and Lu, and a total of 0-20 mol% of a fluoride of at least one alkali metal selected from the group consisting of Na, Li, and K. With this phosphor-dispersed glass, it is possible to prevent deactivation of the phosphor, regardless of the type of phosphor used.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Mid-infrared electro-optical modulator based on black phosphorus fluoride waveguide
InactiveCN105807454AHigh electron mobilityReduce light lossNon-linear opticsMid infraredBlack phosphorus
The invention discloses a mid-infrared electro-optical modulator based on a black phosphorus fluoride waveguide, belongs to a mid-infrared electro-optical modulator in the field of optical communication, and aims to provide the mid-infrared electro-optical modulator based on the black phosphorus fluoride waveguide. Fluoride glass is used as a waveguide material, so that a modulation rate of the mid-infrared electro-optical modulator is effectively improved. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the mid-infrared electro-optical modulator comprises a substrate layer; a groove is formed on the upper surface of the substrate layer; a first optical waveguide is arranged in the groove; a first isolation dielectric layer, a first black phosphorus layer, a second isolation dielectric layer, a second black phosphorus layer and a third isolation dielectric layer are sequentially laminated on the upper surface of the first optical waveguide from bottom to top; a second optical waveguide is arranged on the upper surface of the third isolation dielectric layer; the first black phosphorus layer extends out of the left side of the first optical waveguide and is connected with a first electrode; the second black phosphorus layer extends out of the right side of the first optical waveguide and is connected with a second electrode. The invention is applicable to the mid-infrared electro-optical modulator.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low-fluorine phosphate frequency-doubled laser color separation glass and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106477880ASolve easy devitrificationSolve the problem of poor glass formationPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusDevitrificationPhosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser glass materials, and particular relates to low-fluorine phosphate frequency-doubled laser color separation glass and a preparation method thereof. The low-fluorine phosphate frequency-doubled laser color separation glass comprises, by mol mass, 1.5-10% of Li2O, 0.8% of Na2O, 0-15% of K2O, 1.5-10% of MgO, 0-5% of CaO, 0.2% of SrO, 1-6% of BaO, 1-9% of Al2O3, 2-10% of ZnO, 55-75% of P2O5, 1-2% of YF3, 0.5-2% of LaF3 and 0.1-2% of Co3O4. The low-fluorine phosphate frequency-doubled laser color separation glass has the advantages that the problems that fluoride glass and a high-fluorine glass system are prone to devitrification, poor in glass formation tendency, high in volatilization, difficult for producers to remove strips uniformly, difficult to shape in large-size glass due to low viscosity and the like are solved; under the same testing conditions, the laser-damaged threshold value of the low-fluorine phosphate frequency-doubled laser color separation glass is remarkably larger than that of a fused quartz glass material, so that the low-fluorine phosphate frequency-doubled laser color separation glass can be used to replace the fused quartz glass material and applied to a high-energy superpower laser to improve the laser loading capability of a system.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
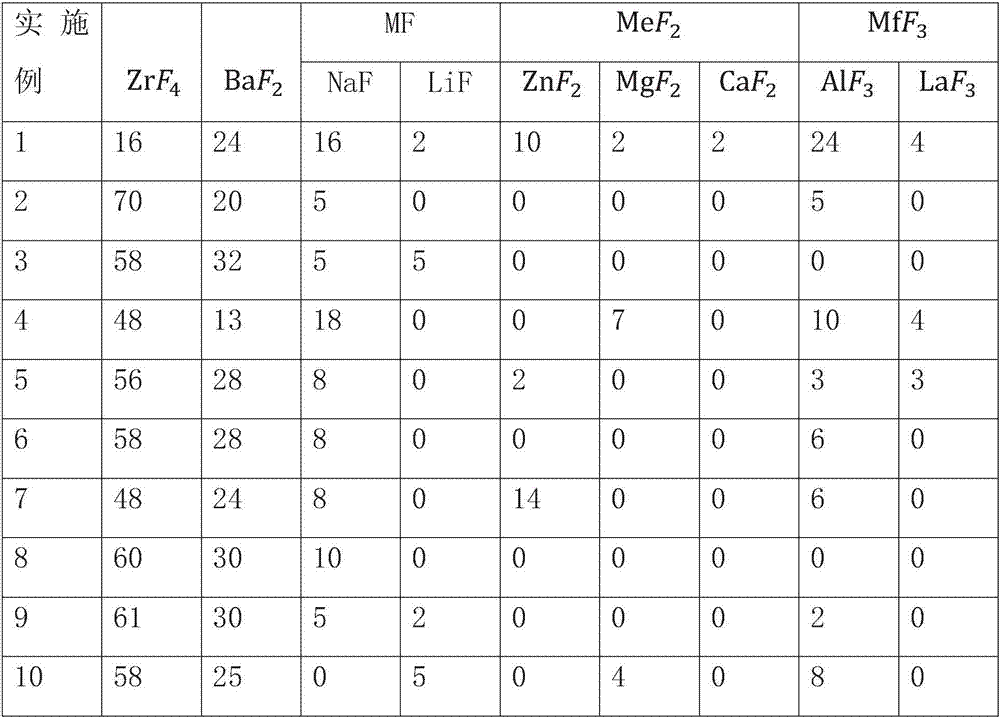
Fluoride glass and a preparing method thereof
Fluoride glass and a preparing method thereof are disclosed. The fluoride glass includes, in mole percentages, 16-70% of ZrF4, 13-32% of BaF2, 5-18% of MF, 0-14% of MeF2 and 0-28% of MfF3, wherein the M is one or two selected from Na and Li, the Me is one or more selected from Zn, Mg and Ca, and the Mf is one or two selected from Al and La. The fluoride glass has a low cost and is suitable for applications in optical windows of near ultraviolet to middle-infrared wavebands. The cutoff wavelength of the prepared glass is greater than 6 [mu]m. The glass has good glass forming capacity, and is suitable for preparing matrix glass of infrared laser fibers and fiber optic amplifiers and other optical materials. The glass has good glass forming capacity, good chemical stability, and low theoretical loss and is suitable for preparing matrixes of low-loss fluoride fibers and doped fibers.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
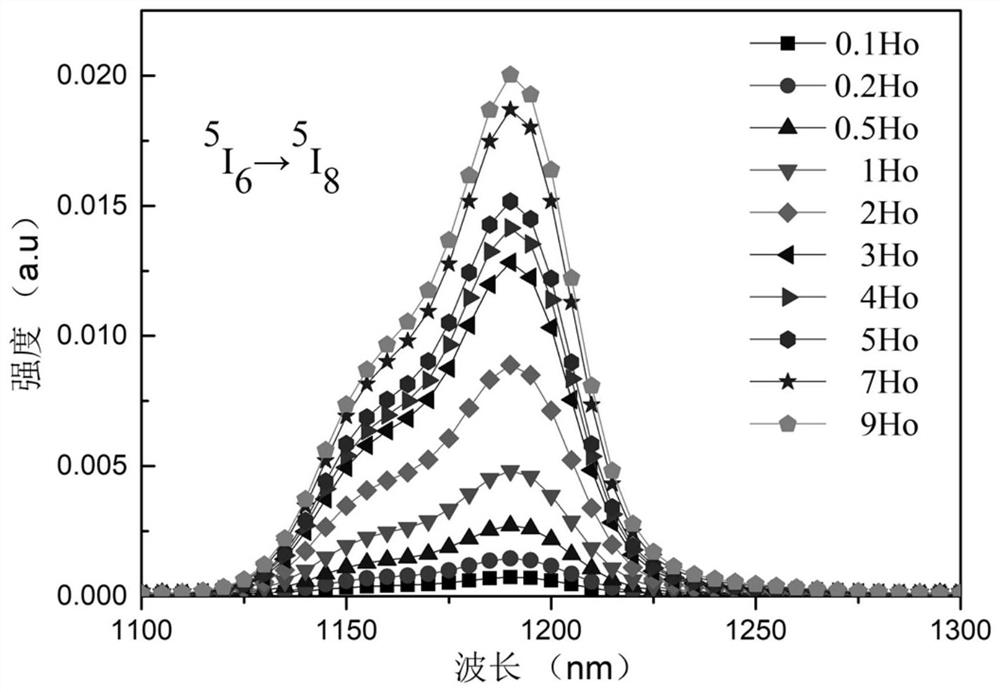
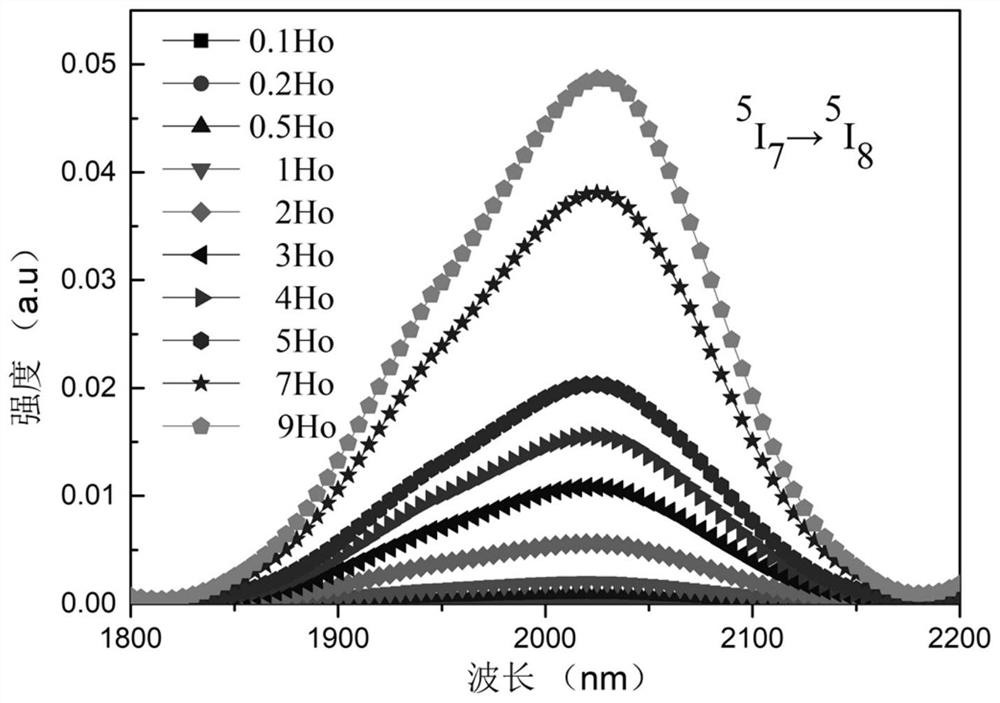
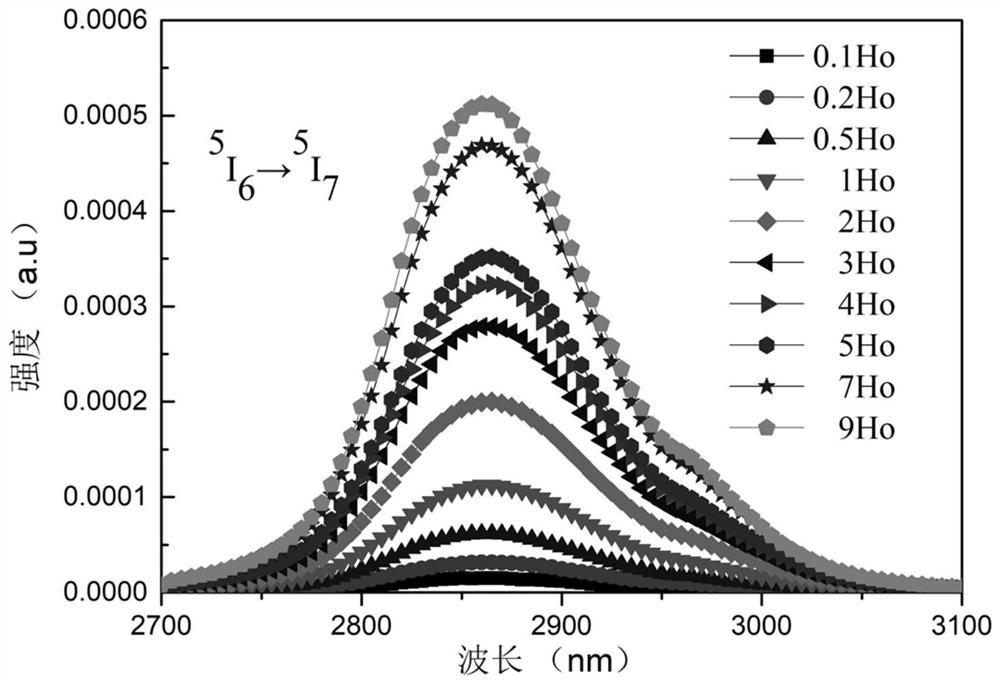
Ho<3+> doped ZBYA fluoride glass
InactiveCN111925117AEfficient infrared fluorescence outputGlass pressing apparatusFluorescenceMaterials science
The invention provides Ho<3+> doped ZBYA fluoride glass. The molar percentage of the concentration of the raw materials to the concentration of the doping ions is 50ZrF4-33BaF2-(10-x)YF3-7AlF3)-xHoF3(x=0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9). The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing the high-purity raw materials according to the proportion; putting the mixture into a platinum crucible, putting the platinum crucible into a high-temperature furnace (850 DEG C) in a glove box for melting; pressing the molten glass into a precursor glass sample; placing the sample in an annealing furnace for an annealing treatment so as to eliminate stress in the glass, and cooling to the room temperature to obtain Ho<3+> doped ZBYA fluoride glass. The provided glass generates farthest 3.9 [mu]m mid-infrared band fluorescence under the excitation of 888 nm laser, and the wavelength has an important application value in the fields of spectroscopy, remote sensing, medical treatment, environmental protection, military affairs and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
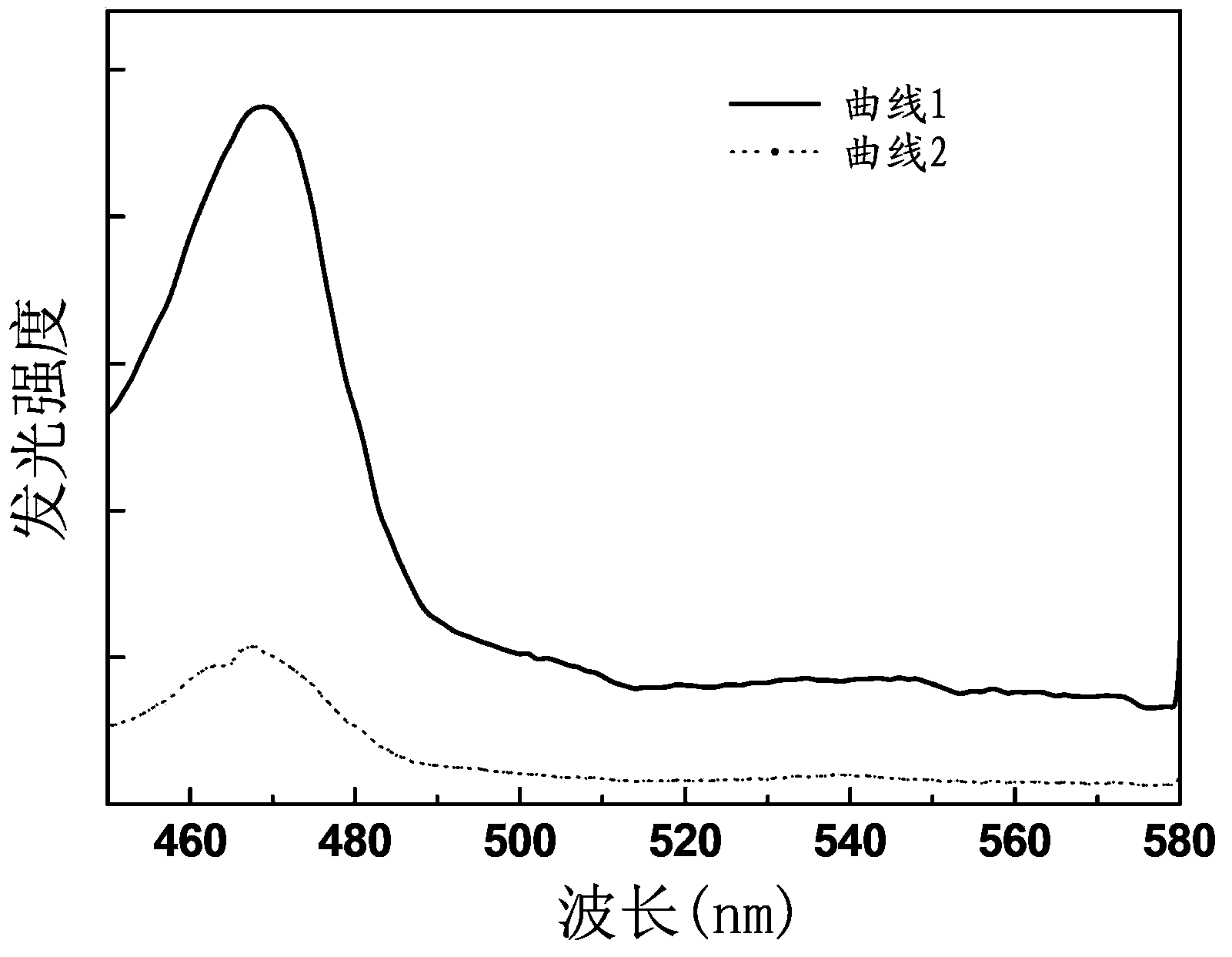
Neodymium-and-ytterbium-codoped alkaline earth fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104099091ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoluminescenceTransition radiation
The invention provides a neodymium-and-ytterbium-codoped alkaline earth fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material. The chemical formula of the luminescent material is MeF2: xYb3+,yNd3+, wherein x is in a range of 0.005 to 0.05, y is in a range of 0.002 to 0.03, and Me is one selected from the group consisting of magnesium, calcium, strontium and barium. In the photoluminescence spectrum of the neodymium-and-ytterbium-codoped alkaline earth fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material, the excitation wavelength of the neodymium-and-ytterbium-codoped alkaline earth fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material is 586 nm, and in the wavelength zone of 469 nm, a luminescence peak is formed by transition radiation of Nd3+ ions from 2P3 / 2 to 4I15 / 2; and the material can be used as a blue-light luminescent material. The invention further provides a preparation method for the neodymium-and-ytterbium-codoped alkaline earth fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material and an organic light-emitting diode using the neodymium-and-ytterbium-codoped alkaline earth fluoride glass up-conversion luminescent material.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Fluorozirconate glass containing tellurium dioxide
The fluorozirconate glass containing tellurium dioxide has the main components of TeO2 2-12 mol%, ZrF4 45-60 mol%, BaF2 25-35 mol%, and LaF3+AlF3+YF3 5-11 mol%. This kind of glass has very high transparency in the wavebands from near ultraviolet to middle infrared. Compared with available fluoride glass, the present invention has better chemical stability and better formation performance, and is suitable for making large size infrared material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-cost ZBAN quaternary system fluoride optical glass and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses low-cost ZBAN quaternary system fluoride optical glass and a preparation method thereof. The glass provided by the invention is prepared from quaternary fluoride systems ZrF4, BaF2, AlF3 and NaF; good ventilation characteristics are realized in near-infrared to medium infrared waveband; the fluoride glass transmission rate at the 4 to 6 mum waveband can reach 60 percent. The invention also provides the preparation method of the glass. The preparation method mainly comprises modified melting, shaping and annealing processes. The glass and the preparation method are based on simple preparation conditions; the drying and oxygen-free environment in the raw material melting process is ingeniously realized through methods of low-temperature fluorination and the like; the experiment cost is reduced; the requirements on experiment requirements is reduced; the process is simple; the material cost is low; the optical glass cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Supercontinuum system with microstructured photonic crystal fibers based on fluoride glass
InactiveCN105849986AActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsGlass fiberPhotonic crystal
A fiber-based supercontinuum system including: a pump laser; a ZBLAN or other fluoride-based microstructured glass fiber; and control electronics; wherein the control electronics control the pump laser to generate laser pulses into the ZBLAN or other fluoride-based microstructured glass fiber. The fabrication of a ZBLAN photonic crystal fiber with sub-micron features and large air- filling fraction and the use of the fiber to generate a stable supercontinuum (200 to 2500nm) from 140fs, 1nJ pulses at 1042nm are disclosed.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Infrared-transmission fluorozirconate glass containing gallium oxide and preparation method of glass
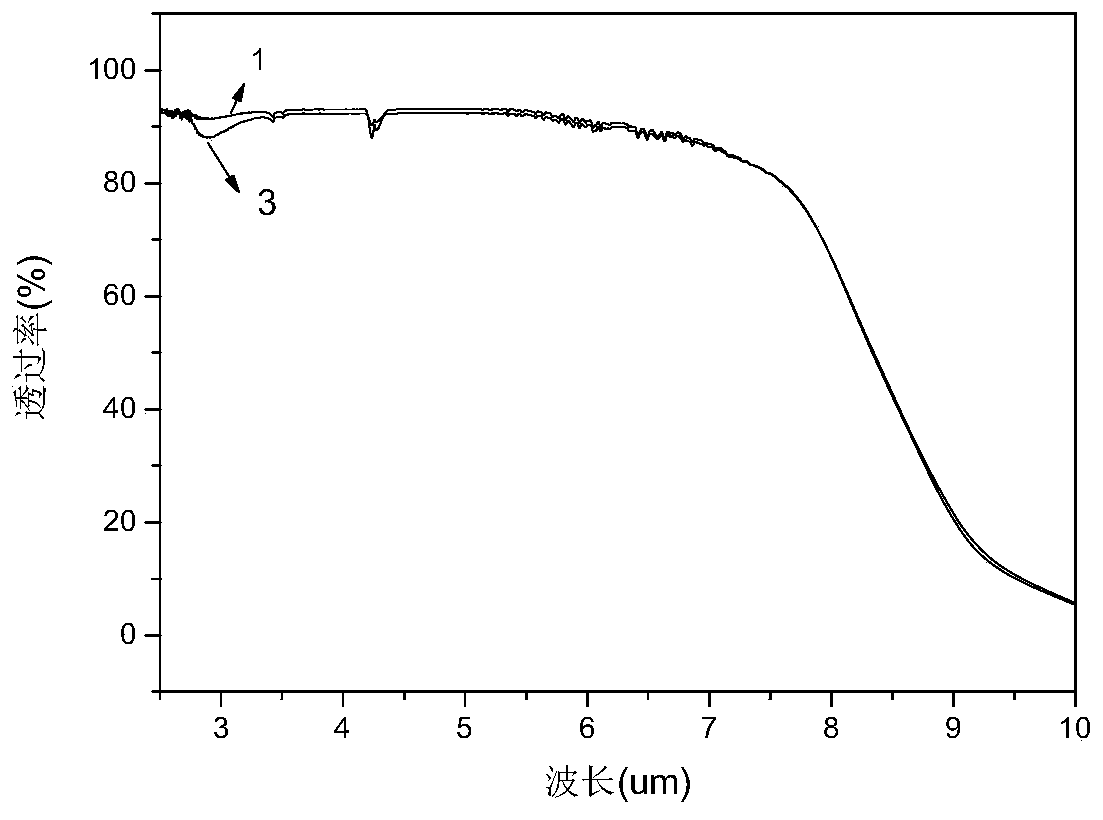
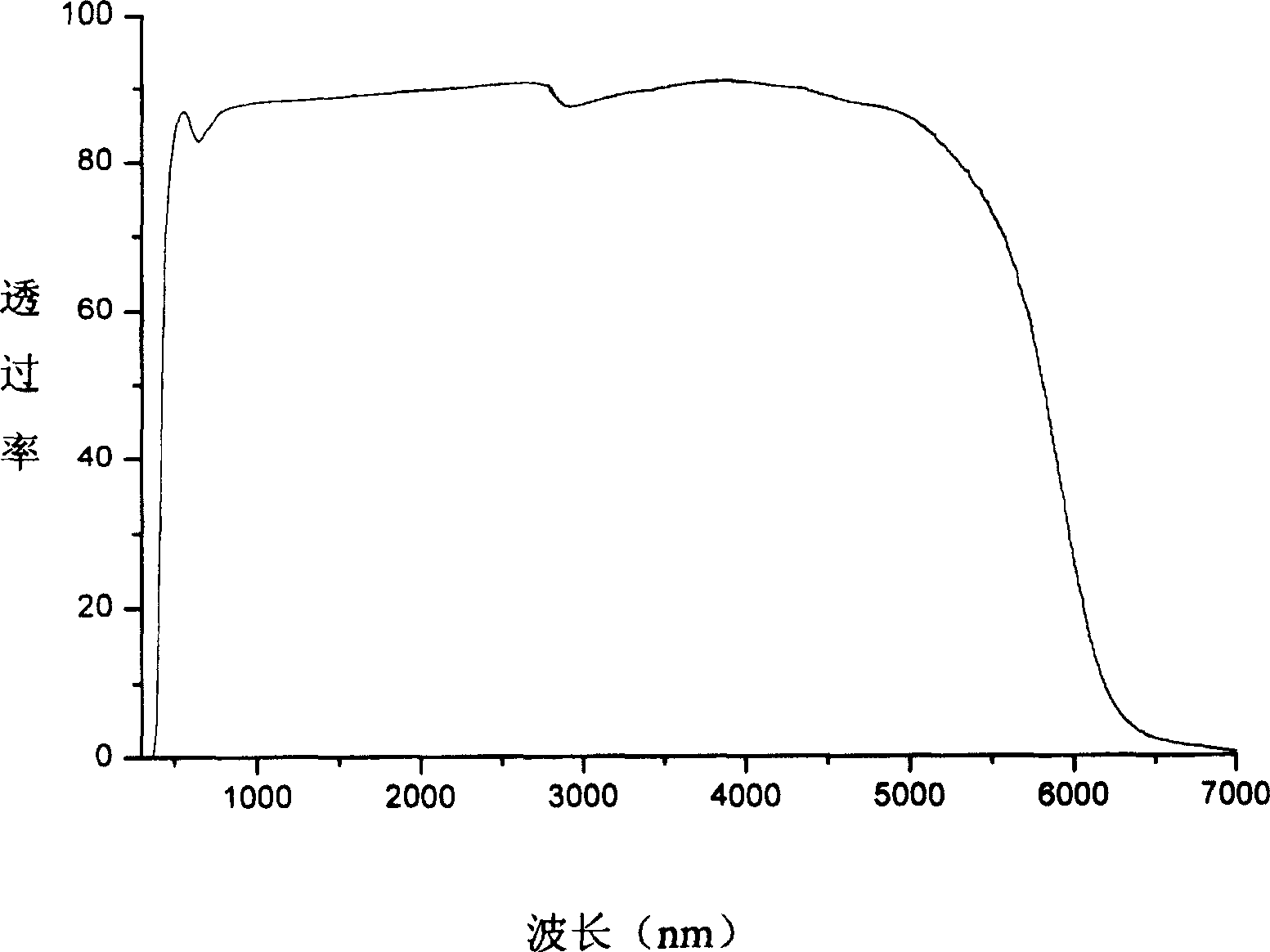
InactiveCN110156322AImprove thermal stabilityGood for large size productionGlass shaping apparatusMiddle infraredTransmittance
The invention relates to infrared-transmission fluorozirconate glass containing Ga2O3. The gallium oxide is introduced into composition of ZrF4-BaF2-LaF3-AlF3--NaF(ZBLAN) fluoride glass, and the fluorozirconate fluoride glass is modified by the gallium oxide, and the fluorozirconate glass containing the gallium oxide comprises the following raw materials, in percentages by molar: (100-x)(ZrF4-AlF3-BaF2-NaF-LaF3)-xGa2O3. The fluorozirconate glass containing the gallium oxide is prepared by adopting a melt cooling method, and the prepared glass is transparent, has no crystallization, and has very good transmittance equivalent to that of fluorozirconate glass in the middle infrared wave band from 3[mu]m to 5 [mu]m; and the fluorozirconate glass containing the Ga2O3 has better thermal stability (delta T) than ZBLAN glass and very good middle-infrared transmission performance, and is particularly suitable for use as a window material in the middle-infrared wave band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Infrared permeating oxide fluoride glass
The present invention relates to an infrared transmitting oxyfluoride glass. It is characterized by that in the AlF3-MeF2-MF3 fluoride glass composition the TeO2 or tellurite is added, the range of the composition is as follows: (component, mol%) TeO2 3-50, AlF3 20-55, MgF2+CaF2+SrF2+BaF2 25-60, LaF3+YbF3+YF3 0-40. Said glass composition has good glass-forming property, and is suitable for large size material, and has good transmittance of near ultraviolet and middle infrared wave band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
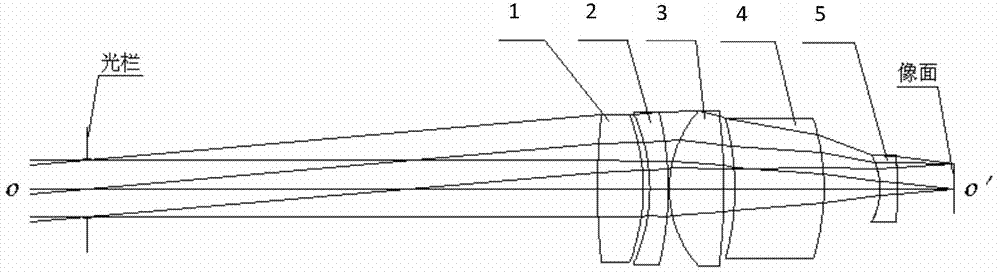
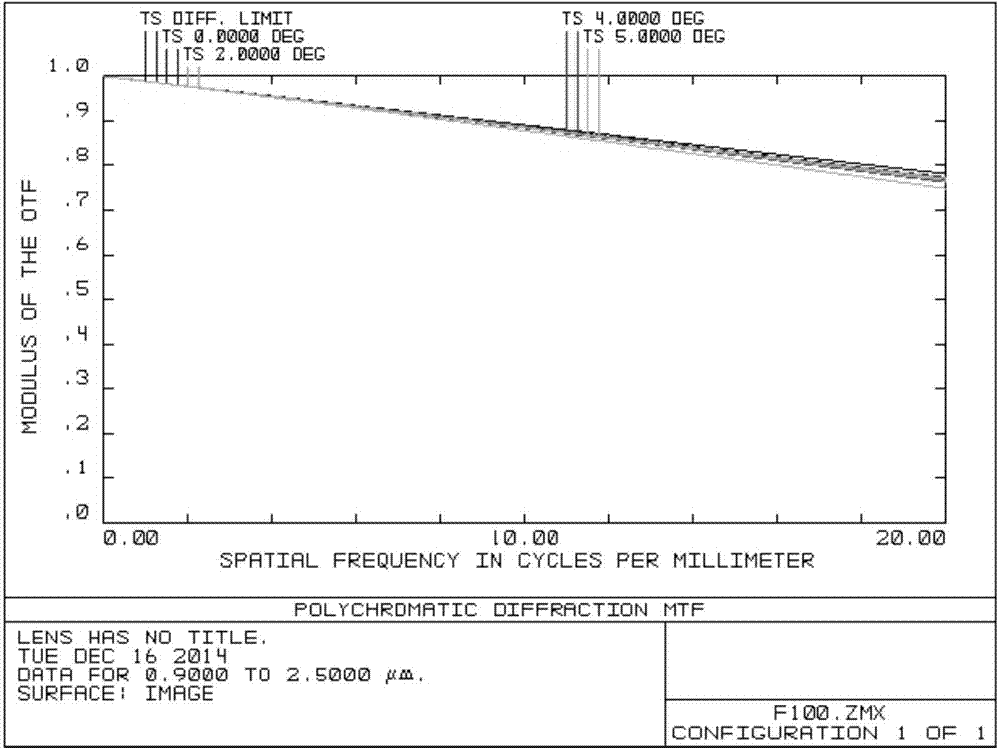
Long-pupillary-distance and shortwave infrared spectral imaging objective lens
InactiveCN104730694AIncreased field of view capabilitySatisfy the telecentric requirementsOptical elementsPupillary distanceShortwave infrared
The invention discloses a long-pupillary-distance and shortwave infrared spectral imaging objective lens. The objective lens comprises five optical lenses which are sequentially arranged on a system optical axis from a light bar to an image surface. An achromatism glass pair with the focal power of positive, negative and negative is formed by the first three optical lenses. A very good achromatism capability is achieved on the short wave infrared outer section through the combination of fluoride glass and dense flint glass, and meanwhile a high spectrum transmittance rate is achieved. The fourth optical lens is used for balancing astigmatism and the curvature of field of the system to increase the view field capability of the imaging objective lens. The fifth optical lens is used for further compensating for the astigmatism of the objective lens and meanwhile is used for meeting the requirement of the imaging objective lens for telecentric performance in image space. Finally, the requirement for the achromatism in the long papillary distance and shortwave infrared band can be met.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing high-damage-threshold laser window material
The invention provides a novel method for preparing a high-damage-threshold laser window material, which is stable in chemical properties and high in damage-threshold. The technical scheme is that novel large-size high-damage-threshold laser window glass is obtained through the fact that an oxide accessory ingredient capable of improving glass forming properties and materialization properties of the material is introduced in fluoride glass. The method solves the problem that the fluoride glass is easy in devitrification, poor in glass forming and difficult in large-size production. Simultaneously, the damage-threshold is obviously improved, and the method can be used in a high-energy laser for improving load capacity and has important functions on smooth advancement of inertial confinement fusion (ICF).
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Broadband emission material and white light emission material
ActiveUS9663397B2Good colorAccelerate emissionsMechanical apparatusLight guides with fluorescent dopantsAlkaline earth metalRare earth ions
A broadband emission material according to the present invention includes: a fluoride glass containing 20 to 45 mol % of AlF3, 25 to 63 mol % of alkaline-earth fluorides in total and 3 to 25 mol % of at least one fluoride of element selected from the group consisting of Y, La, Gd and Lu; and ytterbium ions incorporated in the fluoride glass as divalent rare-earth ions so as to serve as a luminescent center, wherein the fluoride glass includes 1 to 15 mol % of at least one halide of element selected from the group consisting of Al, Ba, Sr, Ca and Mg and element selected from the group consisting of Cl, Br and I; and wherein the alkaline-earth fluorides includes 0 to 15 mol % of MgF2, 7 to 25 mol % of CaF2, 0 to 22 mol % of SrF2 and 0 to 5 mol % of BaF2.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Broadband Emission Material and White Light Emission Material
ActiveUS20160090322A1High emission intensityGood colorMechanical apparatusLight guides with fluorescent dopantsAlkaline earth metalRare earth ions
A broadband emission material according to the present invention includes: a fluoride glass containing 20 to 45 mol % of AlF3, 25 to 63 mol % of alkaline-earth fluorides in total and 3 to 25 mol % of at least one fluoride of element selected from the group consisting of Y, La, Gd and Lu; and ytterbium ions incorporated in the fluoride glass as divalent rare-earth ions so as to serve as a luminescent center, wherein the fluoride glass includes 1 to 15 mol % of at least one halide of element selected from the group consisting of Al, Ba, Sr, Ca and Mg and element selected from the group consisting of Cl, Br and I; and wherein the alkaline-earth fluorides includes 0 to 15 mol % of MgF2, 7 to 25 mol % of CaF2, 0 to 22 mol % of SrF2 and 0 to 5 mol % of BaF2.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com