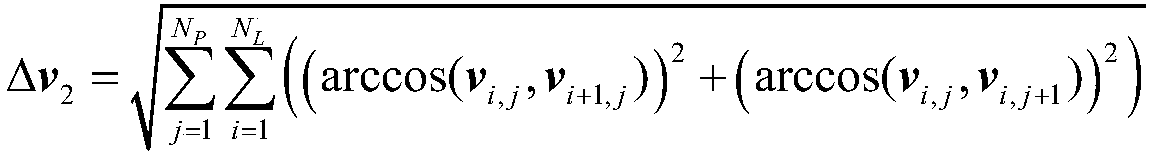Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94 results about "Eta squared" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
ETA Squared. In statistics, eta squared is used to measure the effect size (the size of the relationship between the two variables) in an analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical test. Eta squared measures the proportion of variance in a dependent variable (hyperlink?) that is explained by the independent variable.
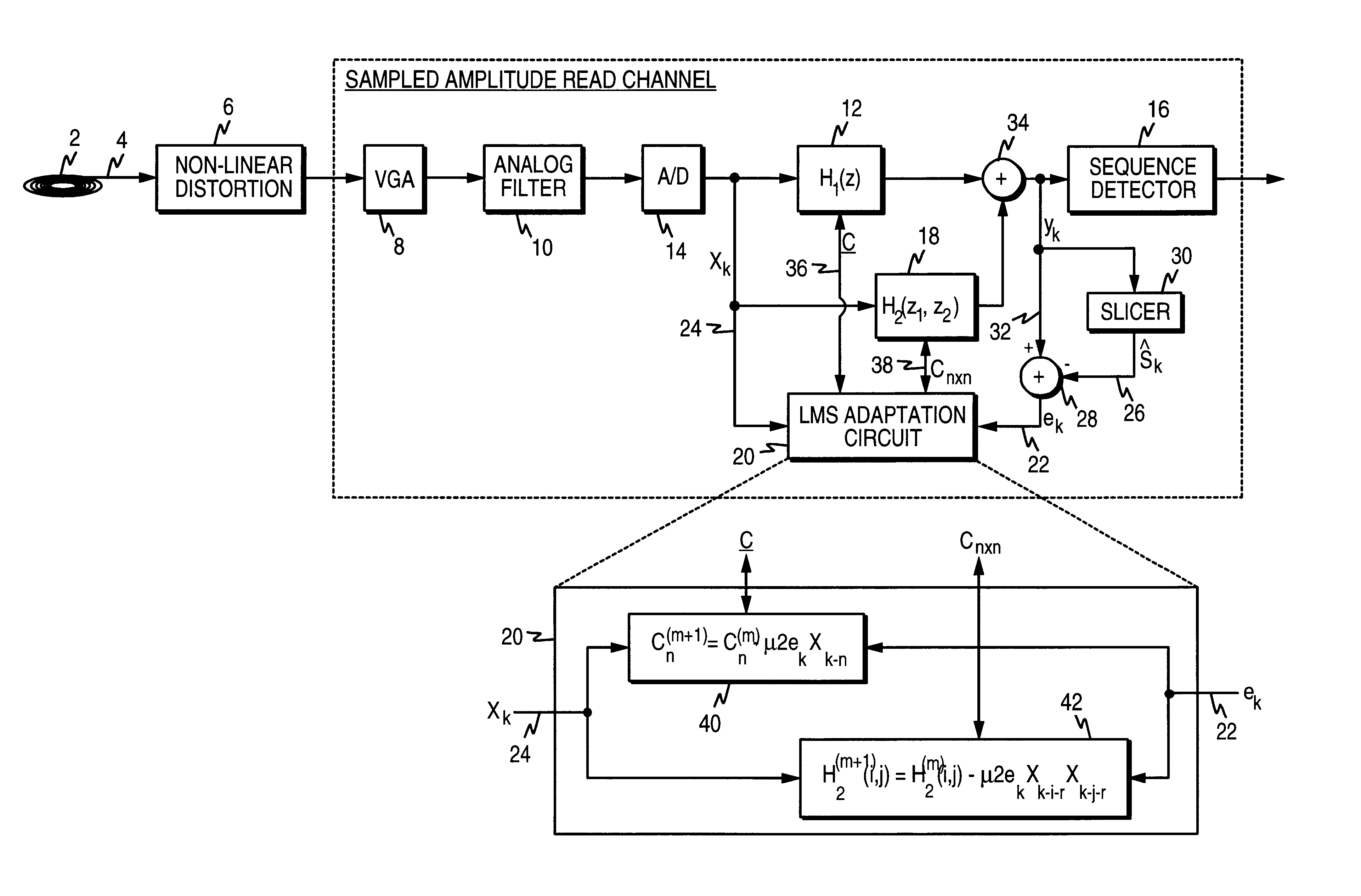
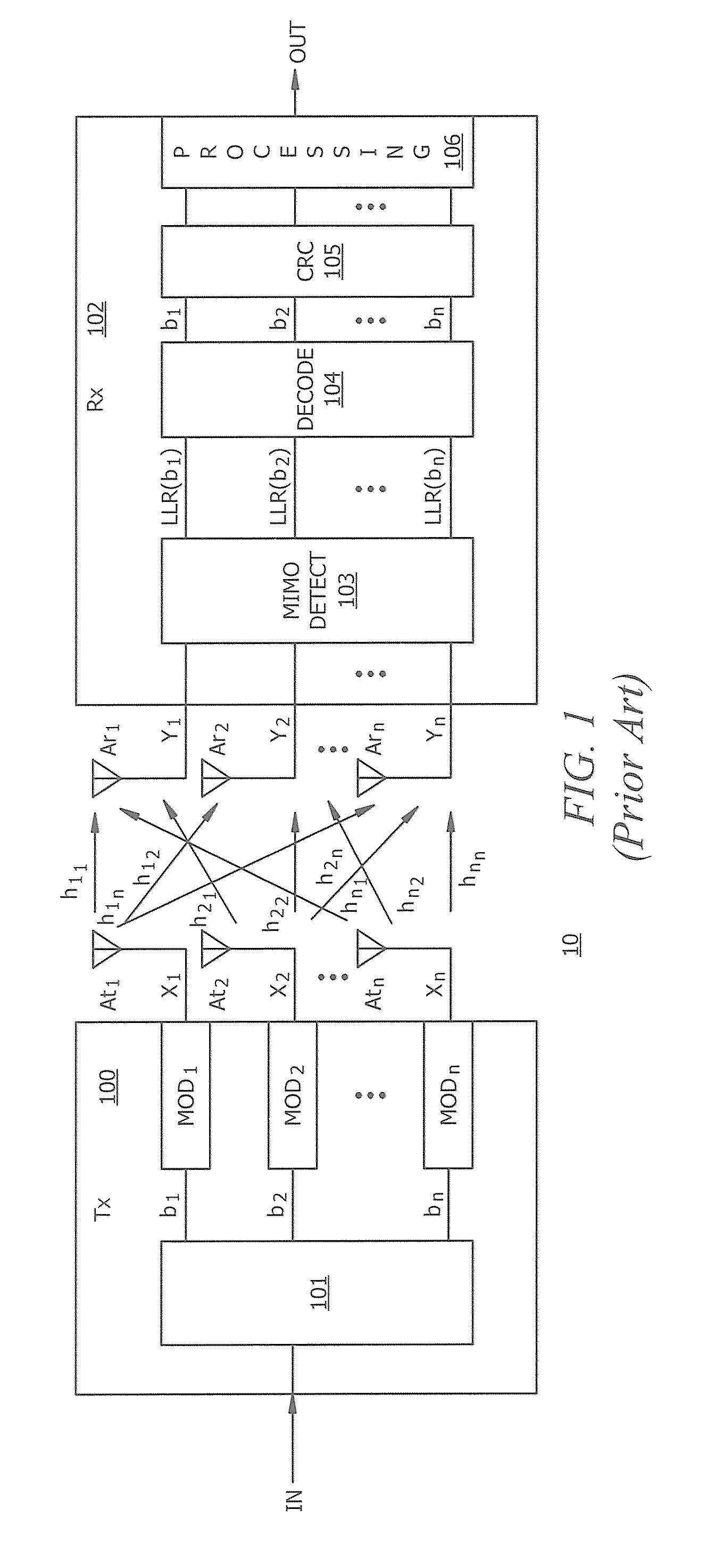
Sampled amplitude read channel employing an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in a read signal
InactiveUS7012772B1Minimize complexityLow costMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsNonlinear distortionAsymmetric head
A sampled amplitude read channel is disclosed for magnetic disk storage systems comprising an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in the read signal, such as asymmetry caused by the non-linear response of a magneto-resistive (MR) read head. The analog read signal is sampled and the discrete time sample values equalized into a desired partial response prior to sequence detection. The non-linear correction circuit is inserted into the read path prior to the sequence detector and adaptively tuned by a least-mean-square (LMS) adaptation circuit. In one embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit is a discrete-time Volterra filter comprising a linear response for implementing an equalizing filter, and a non-linear response for attenuating non-linear distortions in the read signal. The filter coefficients of both the linear and non-linear sections of the Volterra filter are adaptively adjusted by the LMS adaptation circuit. In an alternative embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit operates in the analog domain, prior to the sampling device, where the cost and complexity can be minimized. The analog correction circuit implements an inverse response to that of the non-linearity in the read signal, and the response is adaptively tuned using an LMS update value computed in discrete-time for a Volterra filter, without actually implementing a Volterra filter. Further, the LMS update value for the analog correction circuit can be implemented using a simple squaring circuit.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Automatic gain control of multiple antenna OFDM receiver
ActiveUS7277685B2Receivers monitoringAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTime domainAutomatic control
A method includes amplifying the plurality of received signals, generating a plurality of time domain samples of the amplified signals with at least an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), determining at least a candidate power according to root-mean-square (RMS) powers of a first group of symbols received at the receiver antennas, and setting the gain of the amplifier according to a selected candidate power with the processor. The received RMS power for one antenna is determined as the square root of the averaged product of each received symbol and its complex conjugate for all symbols of the first group. The candidate power can be determined considering a subgroup of antennas using an RMS value, an arithmetical mean value, or a geometric mean value of this subgroup.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
System and method for improving the accuracy of time of arrival measurements in a wireless ad-hoc communications network
ActiveUS7054126B2Improve accuracySynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCorrelation functionPeak value
A system and method for improved Time Of Arrival (TOA) distance measurements between nodes of a wireless ad-hoc network. Specifically, the present invention is a system and method of distance estimation using square-root raised-cosine pulse shaping and chip matched filters on direct sequence spreading waveforms, the multiplication of which produces raised-cosine filtered pulse responses. The responses are used to identify a time when a function is at a maximum, corresponding to the actual signal reception time. The system and method produces a raised-cosine filtered pulse response and an auto-correlation function based on a received signal. A peak value of the auto-correlation function is calculated based on a quadratic approximation, which is corrected using a signal sampling phase offset detected between the raised-cosine filtered pulse response and the calculated peak value. The calculated peak value is then corrected to represent an actual reception time for received signals.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Relative non-high-frequency leakage equivalent N-drop smooth spectrum analog deconvolution method
ActiveCN101201407AFit closelyImprove computing efficiencySeismic signal processingLow-pass filterFourier transform on finite groups
The invention belongs to the seismic data processing and relates to a method by utilizing an equivalent N point smooth spectrum for the simulation of deconvolution. The implementation steps are that the seismic data is collected; the Fourier transform is made for the seismic data at a certain time window; a low pass filter operator of the time domain with an interception frequency of FE and a sampling rate of DT is calculated, which is taken as the equivalent N point smooth operator; FE and DT satisfy the equation that FE*DT is equal to X*DF*1.024; the estimate value of the amplitude spectrum of the seismic wavelet and the reverse wavelet are obtained, which are convoluted with the original seismic data; and the deconvolution seismic data of the time window is obtained. The single peak hypothesis is not applied for the amplitude spectrum of the seismic wavelet in the invention, which suits for complex amplitude spectrum of the seismic wavelet; compared with the least square polynomial fitting, the shape of the simulated amplitude spectrum curve of the seismic record is not affected by the global influence; the invention has the advantages of high calculation efficiency, better stability and improved resolution of seismic profiles.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
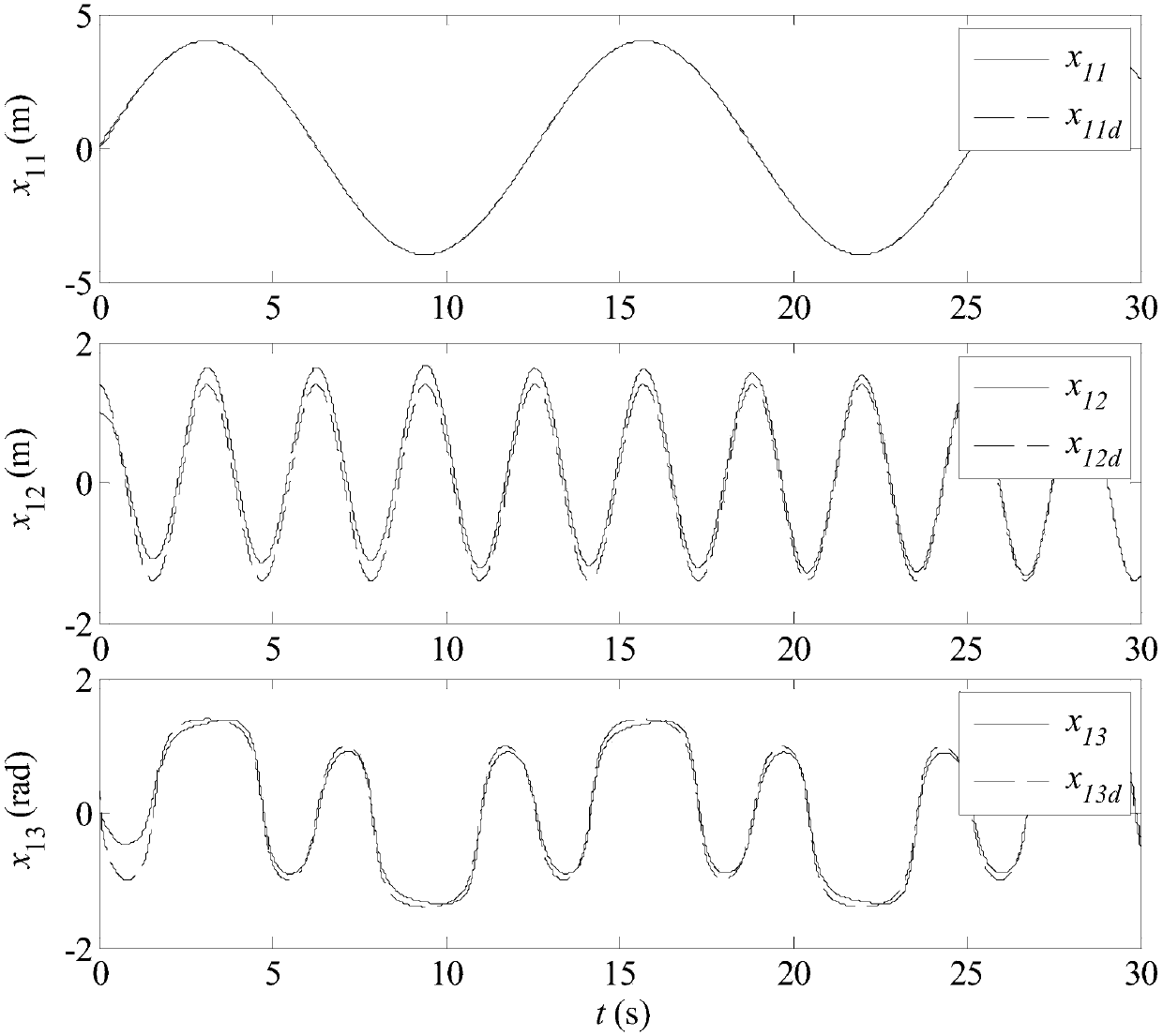
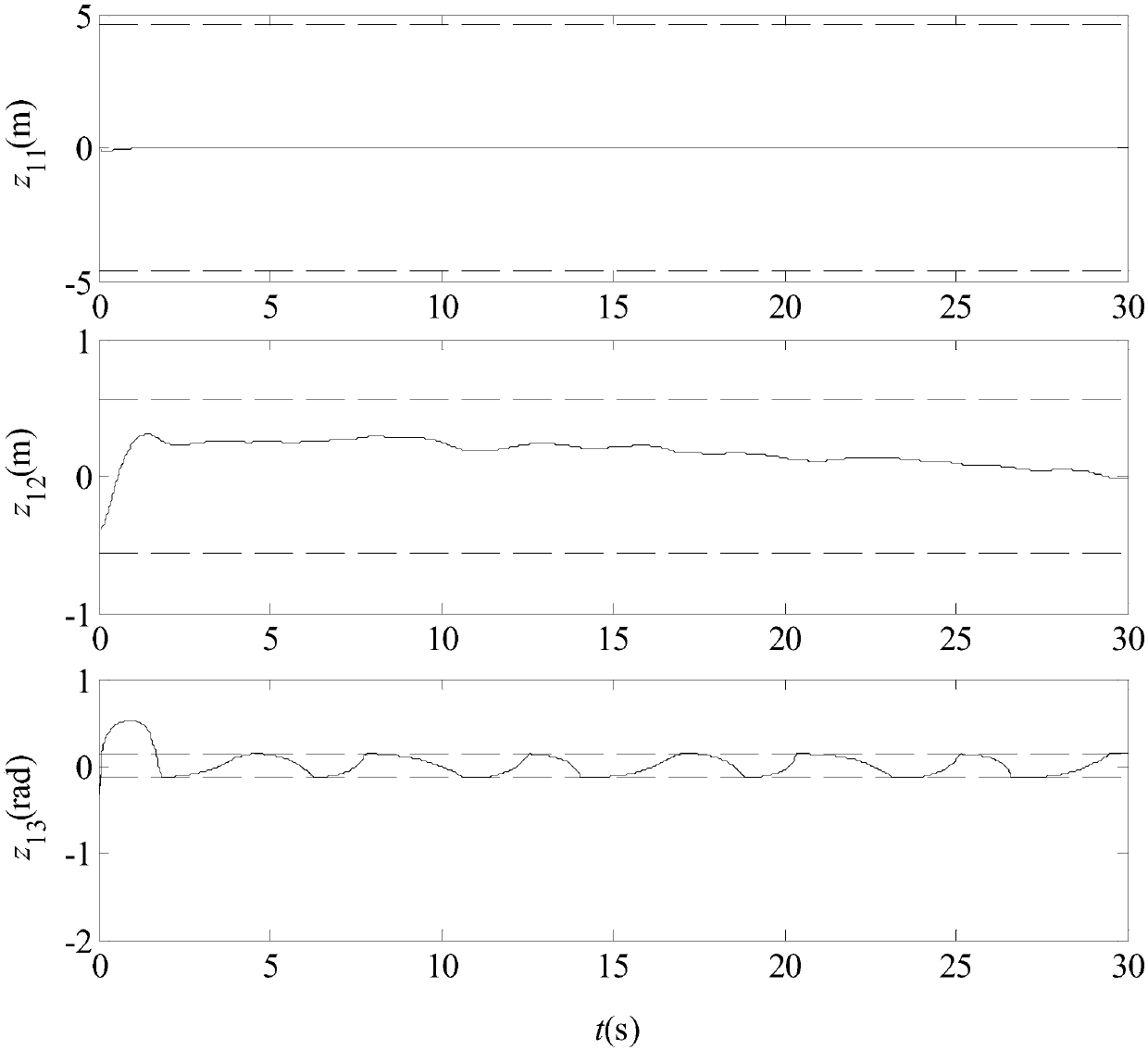
Input saturation-considered unmanned surface vehicle full-state constraint trajectory tracking control method
The invention discloses an input saturation-considered unmanned surface vehicle full-state constraint trajectory tracking control method, relates to an unmanned surface vehicle control method, and aims at solving the problem that existing unmanned surface vehicle trajectory tracking control-oriented control methods do not process state constraint and saturation problems. According to the method, akinetic model of a 3-degree of freedom and multiple-input-multiple-output unmanned surface vehicle; a saturated closed-loop system is established and a self-adaptive method is selected to estimate squares of unknown interference upper limits and control input difference upper limits; and self-adaptive laws are designed for unknown interferences and control inputs according to the self-adaptive method, and a controller is designed according to a pseudo-inverse condition so as to control the unmanned surface vehicle. The method is suitable for the control of unmanned surface vehicles.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
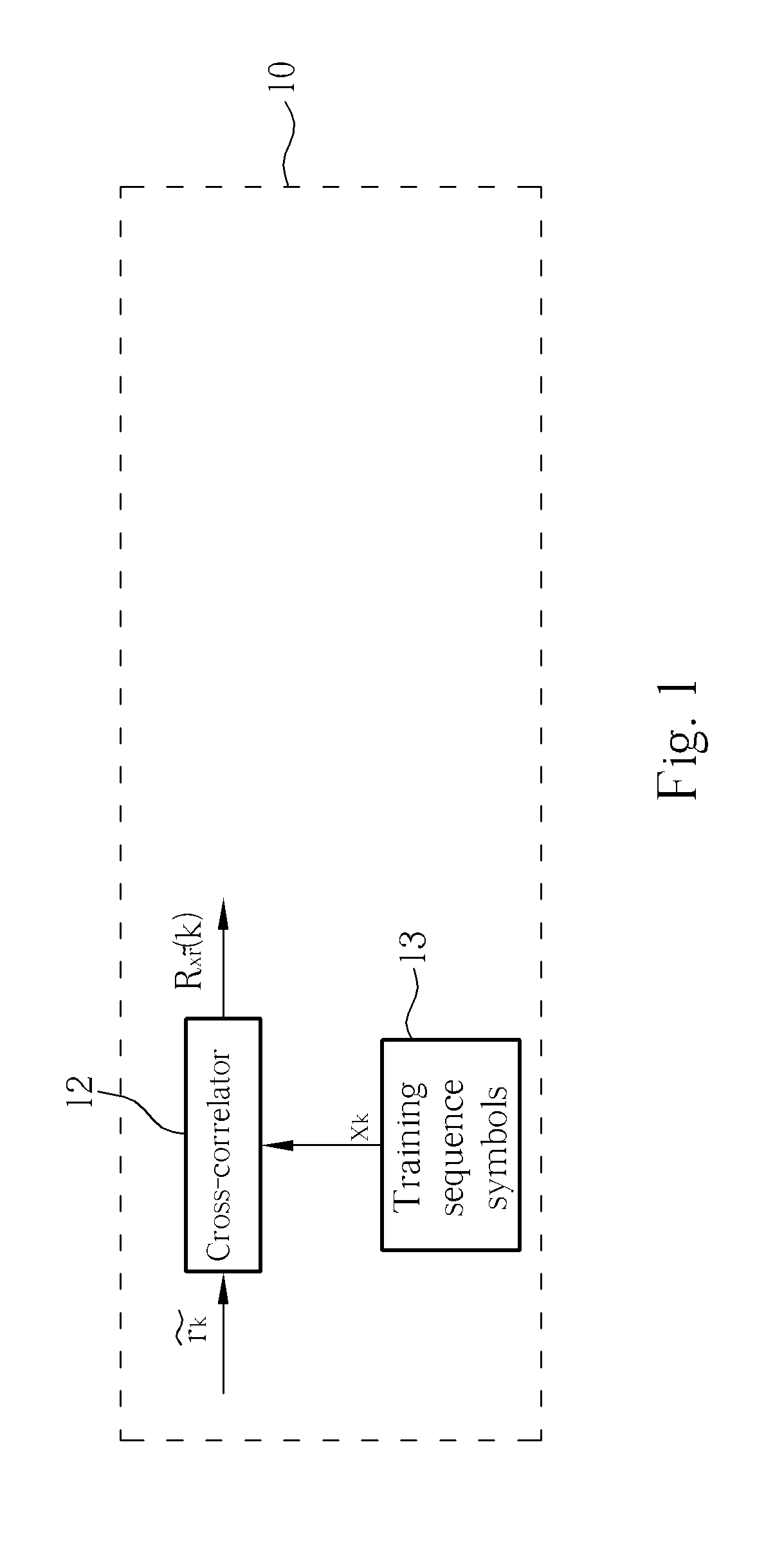
Method and apparatus for channel impulse response estimation in GSM systems
A method for estimating channel impulse response (CIR) in a communication system includes converting RF analog signals to obtain baseband digitized signals, sampling the baseband digitized signals according to the symbol period or bit period, cross-correlating at least part of the samples and a predetermined set of training sequence symbols, and calculating the ratio of the maximum square of the modulus (power) value and the second largest value among the outputs of the cross-correlations. If the ratio is larger than a first predetermined value, the method outputs the cross-correlation values as the CIR according to the time step index of the maximum power value, and if the ratio is not larger than the first predetermined value, the method calculates the energy of a predetermined window and outputs the cross-correlation values as the CIR according to the time step index of the maximum energy.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
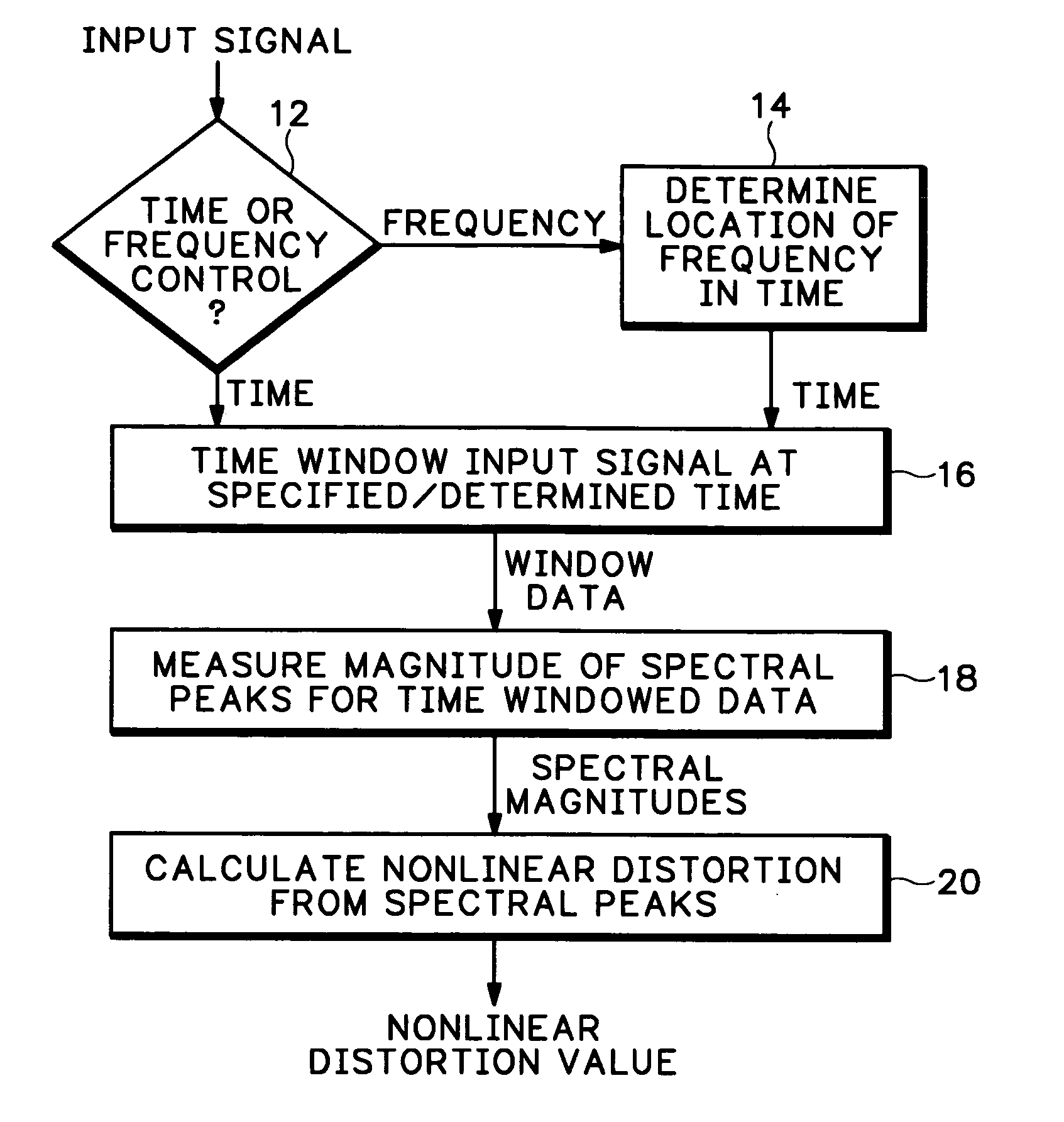
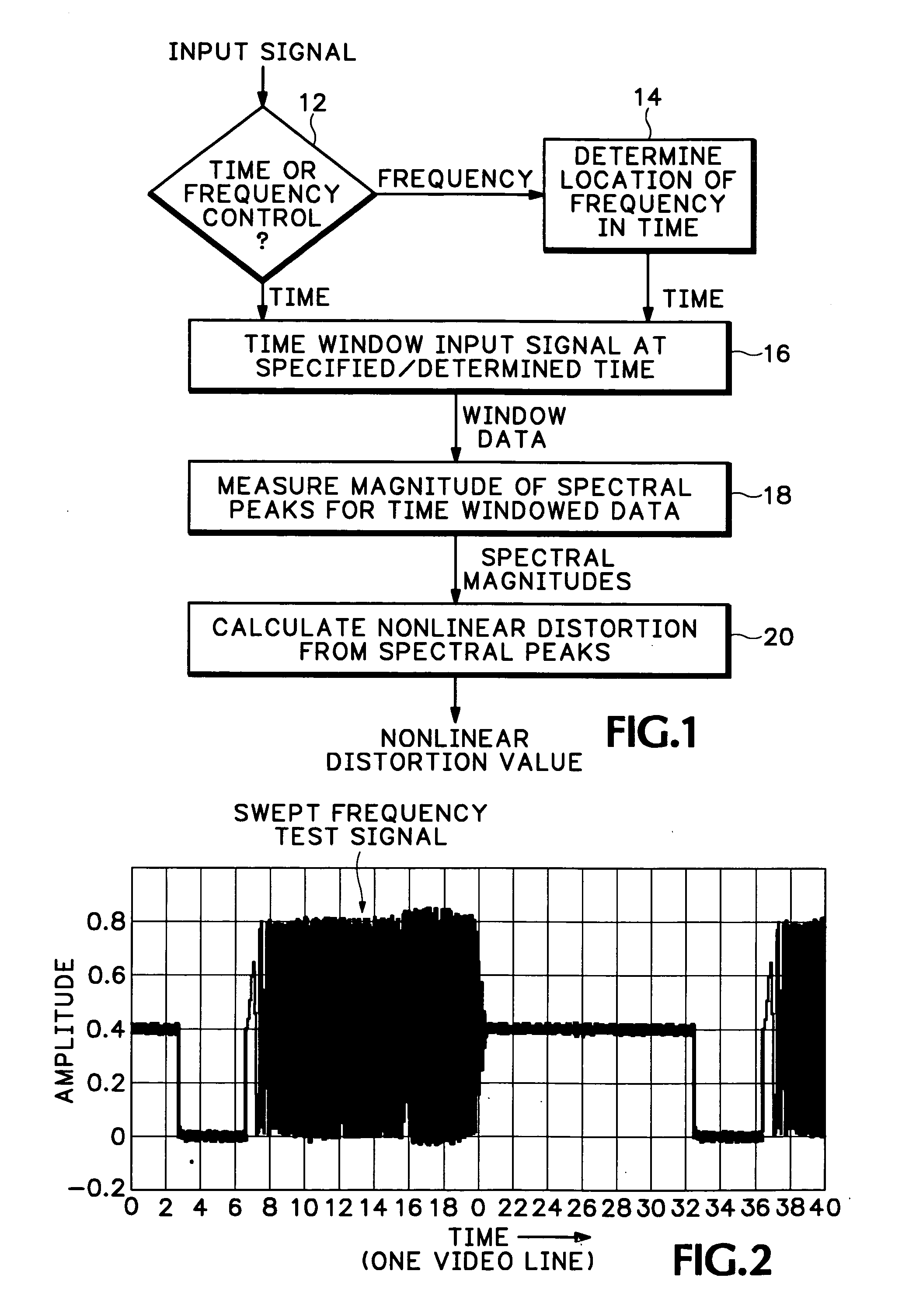
Measuring instantaneous signal dependent nonlinear distortion in response to varying frequency sinusoidal test signals
InactiveUS20050233702A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsNonlinear distortionFrequency spectrum
A method of measuring instantaneous signal-dependent nonlinear distortion in a system under test in response to a test signal having a varying frequency sinusoidal component, such as a swept frequency signal or a multi-burst signal, uses a time window to locate a frequency of interest in the corresponding varying frequency component of a signal output from the system under test. Once the location of the frequency of interest is located in the output signal, a spectrum of the portion of the output signal within the time window is generated and the magnitudes of the spectral peaks, including the spectral peak for the frequency of interest or nominal frequency and all isolated peaks representing distortion frequencies, are measured. The amount of distortion is calculated as a ratio of the square-root of the sum of the magnitudes of the distortion frequencies to the magnitude of the nominal frequency.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Apparatus for monitoring quality of picture in transmission
ActiveUS6943827B2Effective assessmentAccurate assessmentCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsMean squareLow speed
A first characteristic value extracting unit extracts a characteristic value from a picture transmitted from a transmission side, and a second characteristic value extracting unit extracts a characteristic value from a picture received on a reception side. These extracted characteristic values are supplied to a central monitoring unit through low speed lines, respectively. In the central monitoring unit, an MSE (mean square error) is assessed from the data by an MSE assessing unit. The first and second characteristic value extracting units divide an input picture into blocks, subject the blocks to an orthogonal transformation, or subject the blocks to PN sequence multiplication before the orthogonal transformation, and extract and output orthogonal transformation coefficients. The MSE assessing unit determines the differences between corresponding coefficients on the transmission side and the reception side and squares the differences, adds the squared differences for every coefficients or every blocks, and assess an MSE based on the added values referred to a table. With this operation, the MSE can be effectively assessed using a smaller amount of extracted data (accordingly, slower speed lines can be used in the central monitoring unit).
Owner:KDDI CORP
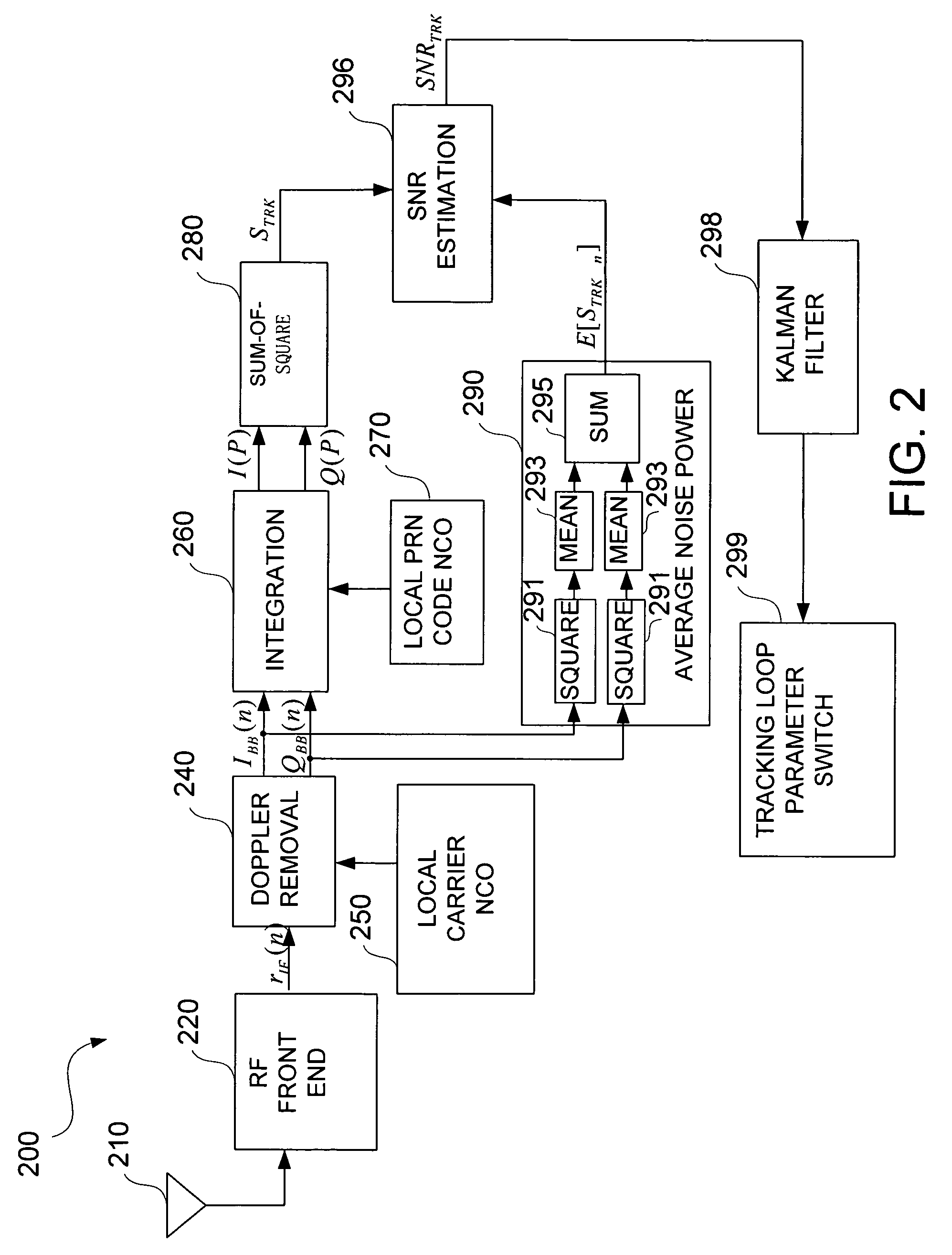
Apparatus and method for determining GPS tracking loop parameter based on SNR estimation
A method for estimating signal quality of a spread spectrum signal is provided. The method includes squaring a plurality of in-phase correlation results and a plurality of quadrature correlation results, summing each squared in-phase correlation result and the corresponding correlation result to obtain a plurality of sum-of-square values, detecting a peak value among the plurality of sum-of-square results, calculating an average of non-peak values among the plurality of sum-of-square results. The peak value is regarded as a signal power value, while the averaged non-peak values are regarded as an average noise power value. A signal-to-noise ratio is then calculated based on the signal power value and the average noise power value. A method for determining the parameters for the tracking loop is also provided. The method includes estimating the signal-to-noise ratio of the spread spectrum signal, and determining the tracking loop parameters based on the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
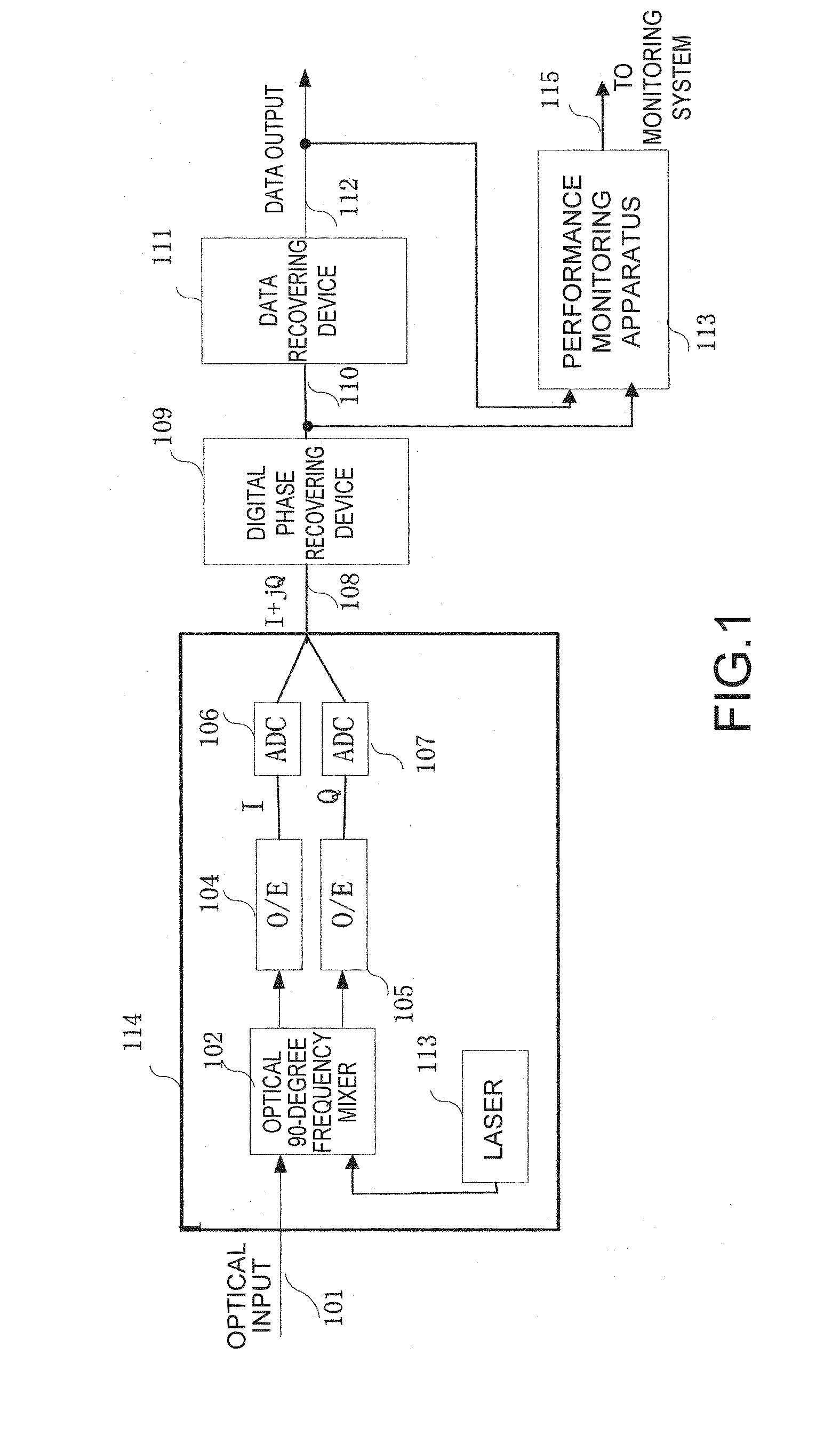
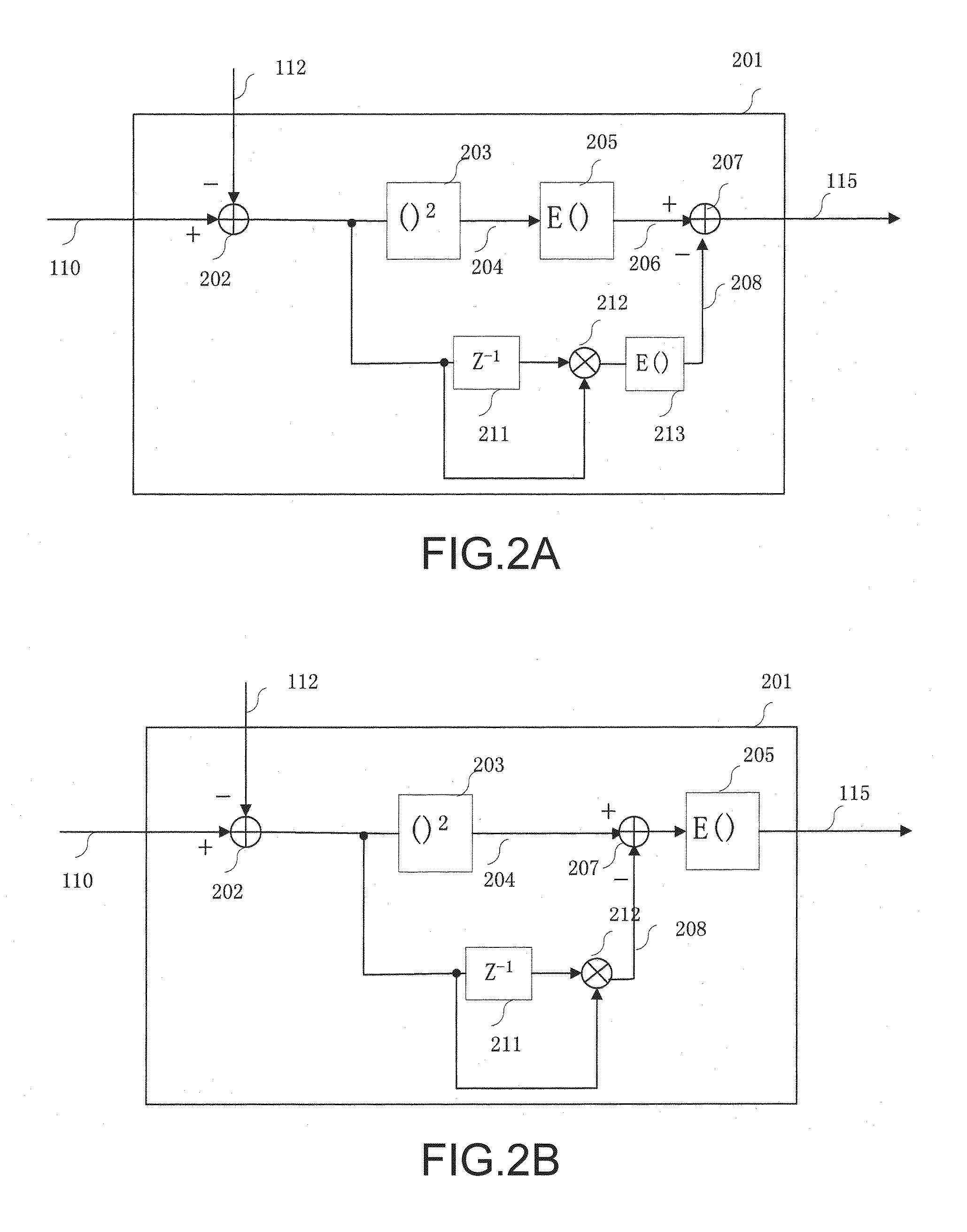
Optical coherent receiver, apparatus for and method of monitoring performance thereof
ActiveUS20100092168A1Quickly and precisely reflect change in performanceChange performanceOptical measurementsTransmission monitoringEngineeringEta squared
The present invention relates to an optical coherent receiver and an apparatus for and a method of monitoring performance thereof. The apparatus for monitoring performance of the optical coherent receiver makes use of a first signal and a second signal from the optical coherent receiver to monitor performance of the optical coherent receiver, and comprises a first subtracter, for subtracting the second signal from the first signal to obtain a first subtraction result; a squarer, for obtaining a square of the first subtraction result; a delayer, for delaying the first subtraction result; a multiplier, for multiplying the first subtraction result with the delayed first subtraction result; and a second subtracter, for subtracting the result of the multiplier from the result of the squarer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
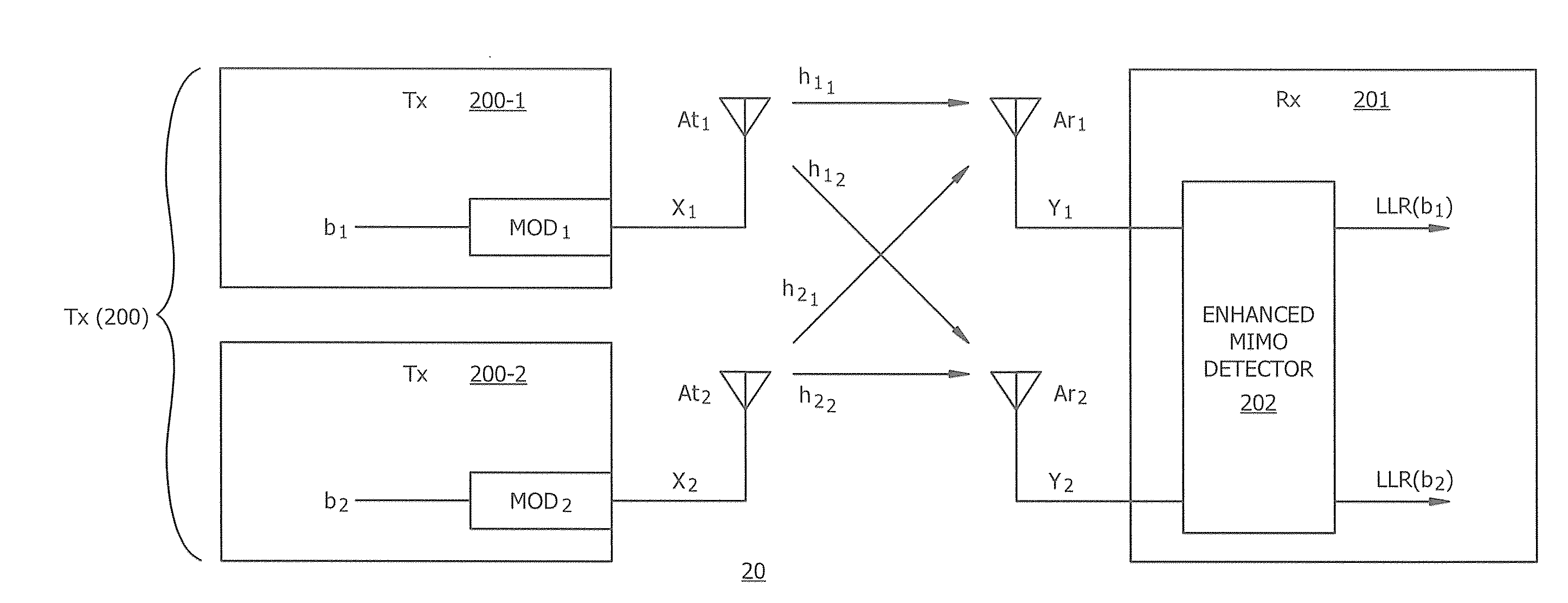
Multiple antenna spatial multiplexing optimal detection
ActiveUS20100329378A1Easy to useAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsComputer scienceSpatial multiplexing
MIMO detection is described that reduces the complexity of computations for finding the soft bit output. The detection process includes QR factorization splitting the distance calculations into two groups, subset lookup using a last cross constellation set (LCCS) lookup, and minimal distance lookup with soft bit output calculation. By grouping the distance calculations into a first group that has one antenna transmitting using a modulation scheme with a generally square constellation diagram and a second group for all of the other antenna constellation diagrams, the LCCS lookup process may be used which substantially reduces the number of calculations to be made in the detection process. Moreover, in the special case of 2×2 antenna, QR factorization is performed by applying a scaled Givens rotation to the channel matrix. The application of the scaled Givens rotation operator eliminates any square root operations that would be performed in a standard QR factorization.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
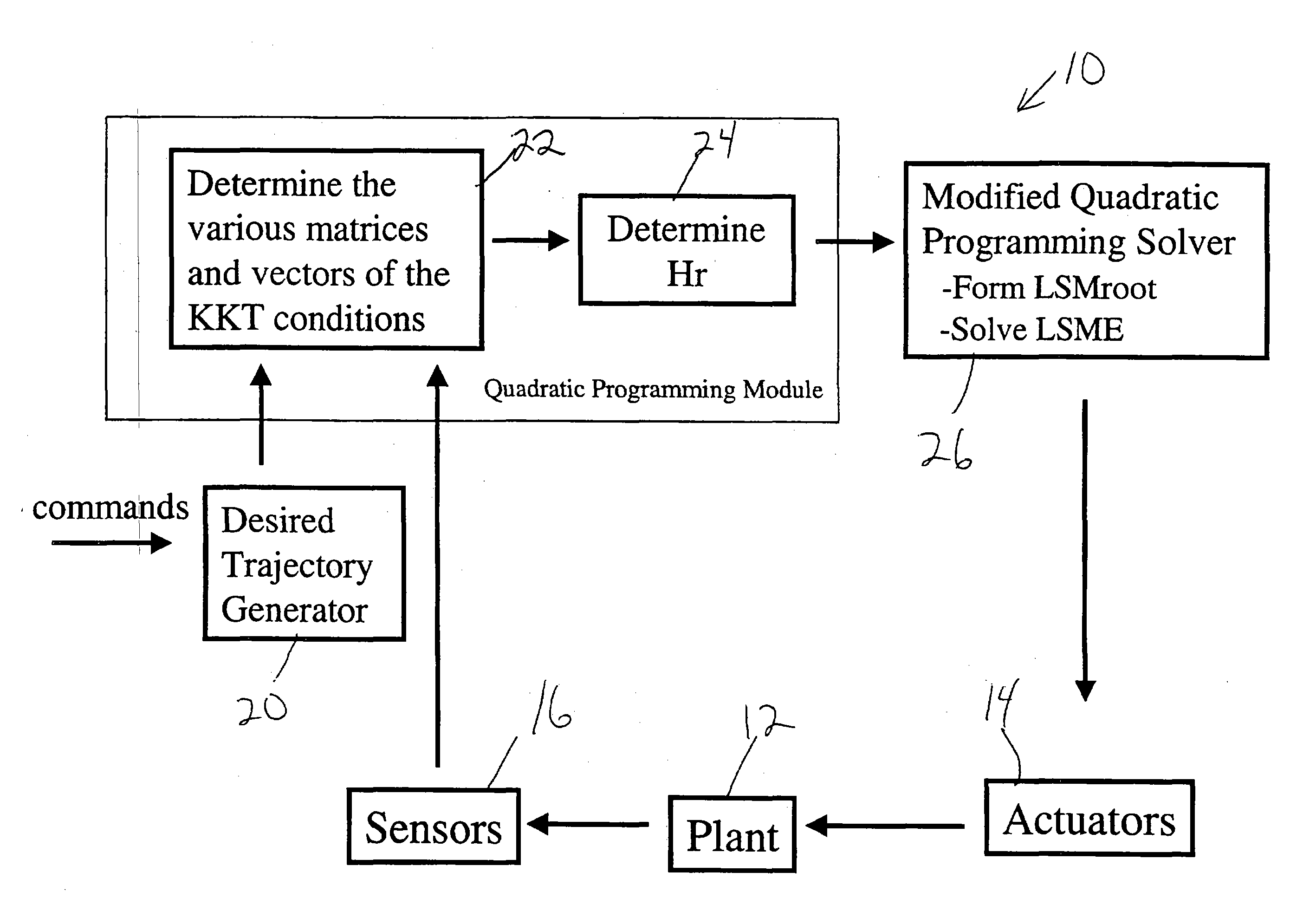
Square root method for computationally efficient model predictive control
ActiveUS20050015421A1Lighten the computational burdenFast dynamicsSimulator controlDigital computer detailsAlgorithmModel predictive control
An efficient method for solving a model predictive control problem is described. A large sparse matrix equation is formed based upon the model predictive control problem. The square root of H, Hr, is then formed directly, without first forming H. A square root (LSMroot) of a large sparse matrix of the large sparse matrix equation is then formed using Hr in each of a plurality of iterations of a quadratic programming solver, without first forming the large sparse matrix and without recalculating Hr in each of the plurality of iterations. The solution of the large sparse matrix equation is completed based upon LSMroot.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Undeniable digital signature scheme based on quadratic field
InactiveUS6976169B1Resolution problemPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureTheoretical computer science
An efficient undeniable digital signature scheme based on a quadratic field is disclosed. Public keys (D, P, k, t) and secret keys (D1, q) are defined by generating two primes p, q (p, q>4, p=3 mod 4, √{square root over (p / 3)}<q), computing D1=−p and D=D1q2, obtaining a bit length k of √{square root over (|D1|)} / 4 and a bit length t of q−(D1 / q) where (D1 / q) denotes Kronecker symbol, and generating a kernel element P of a map from a class group Cl(D) to a class group Cl(D1). Then the signature verification is realized by first checking whether a norm N(S) of the signature S is smaller than k bits or not, and judging that the signature S is illegal when the norm N(S) is larger than k bits, or generating a challenge C when the norm N(S) is not larger than k bits, by computing the message ideal M of the message m, generating a random integer r smaller than t bits, computing H=(M / S)r, generating a random ideal B whose norm is smaller than k−1 bits, and computing the challenge C=BH, at a verifier side; then computing a response W by mapping the challenge C to the class group Cl(D1) and pulling the mapped challenge C back to the class group Cl(D) and squaring a result of mapping and pulling back, using the secret keys (D1, q), at the signer side; and then checking whether W=B2 holds or not, and judging that the signature S is legal when W=B2 holds or that the signature S is illegal otherwise, at the verifier side.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a pseudorandom binary sequence using a linear feedback shift register
InactiveUS20070047623A1Quick and efficientEasy to operateDigital data processing detailsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemOperation mode
A method and apparatus are provided for generating a code by quickly computing a state of a Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) in a mobile communication system, in which a code for the communication system is generated including an n-stage LFSR and operating in sleep mode and active mode set at a preset time interval from the sleep mode. Current state values of the LFSR are combined with n different mask patterns such that the current state values are shifted by {20,21, . . . ,2n−1}. A combination result is provided as a new state value of the LFSR at an arbitrary time variably set in the sleep mode. To transform a current state value of the LFSR to a new state value after an arbitrary time, the code generation method employs a square and multiply algorithm without use of mask patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Excitation surge current fast identification method based on planar adjacent point distances formed by differential current adjacent order difference
ActiveCN103683198ADownsamplingShort time windowEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase differenceTransformer
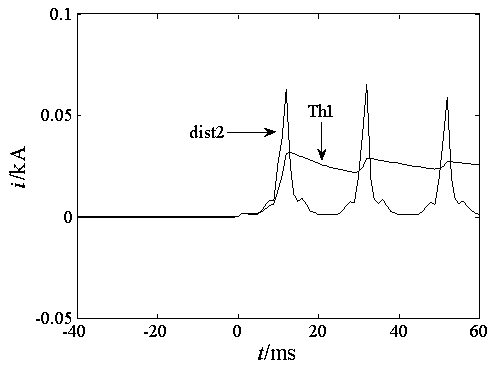
The invention relates to an excitation surge current fast identification method based on planar adjacent point distances formed by differential current adjacent order difference and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When an internal fault or excitation surge current of a transformer occurs, a protecting measuring device starts immediately, a measuring unit measures the three-phase difference current of the transformer, the three-phase difference current data recorded by the measuring unit is extracted, and the first difference and the second difference of each phase difference current are calculated according to the three-phase difference current; the second difference of each of the three phases is used as a horizontal axis, the first difference of the corresponding phase is used as a vertical axis, and three planes are constructed; calculating the quadratic sum of all adjacent point distances on the three constructed planes, calculating the maximum value dist2sum of the three quadratic sum, and calculating the standard deviation and average value of the square of the adjacent point distance corresponding to dist2sum; performing integration on the obtained standard deviation and average value to obtain Th1sum, and comparing the dist2sum and the Th1sum to distinguish the internal fault and excitation surge current inside the transformer.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
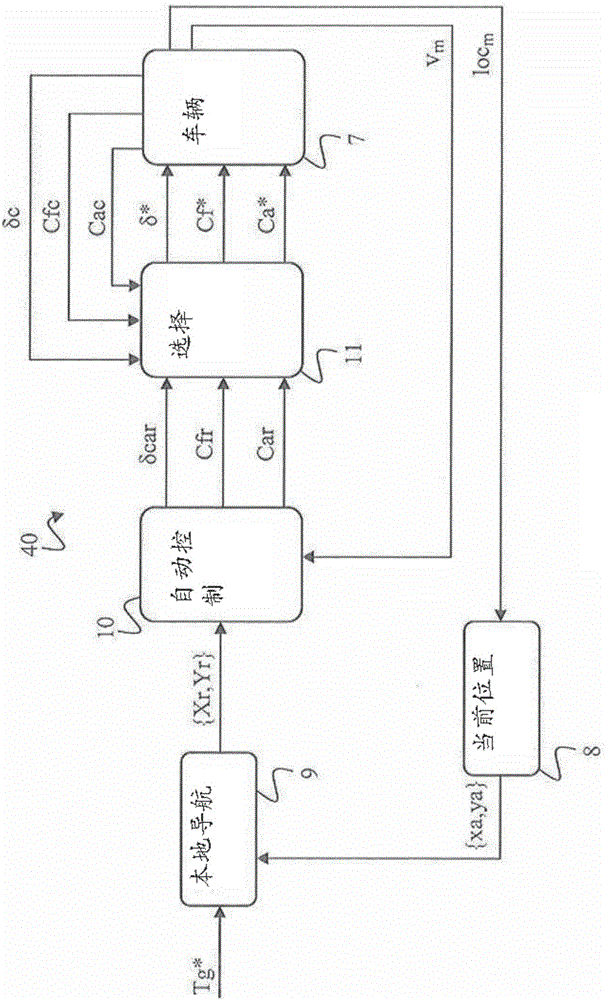
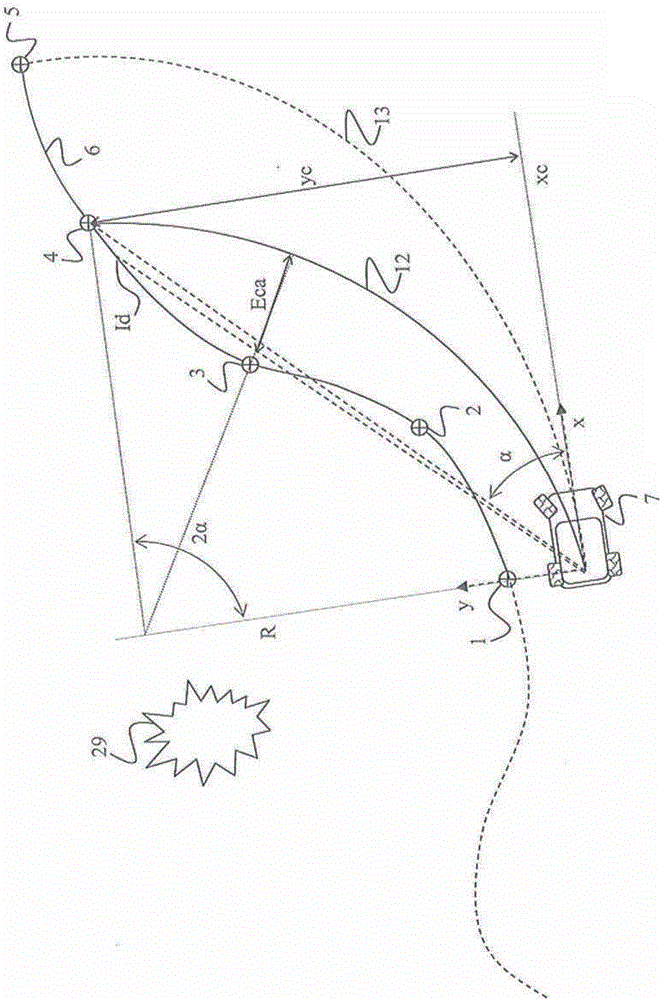
Method and device for automatically controlling a vehicle
The method for automatically controlling a vehicle comprises an initial step (100) in which a reference local path and a potential speed (v) of the vehicle are given. A step (120, 121, 140) of calculating a stirring angle automatic setpoint (delta car) makes it possible to calculate a lateral acceleration (aykin) proportional to the square of the potential speed (v) of the vehicle, making the vehicle describe an arc of a circle comprising a point of intersection with the reference local path at a distance (Id) from the vehicle. A step (181) consists in generating a speed setpoint (vr) set to a value equal to that of the potential speed (v) when the lateral acceleration (aykin) has a value lower than a maximum permissible lateral acceleration value (ay max) and an adjustment step (167) consists in decreasing the value of the potential speed (v) when the lateral acceleration (aykin) has a value higher than or equal to the maximum permissible lateral acceleration value (ay max) so as to calculate a reduced lateral acceleration (aykin) by repeating said calculation step (120, 121, 140).
Owner:RENAULT SA
Code assignment algorithm for synchronous DS-CDMA links with SDMA using estimated spatial signature vectors
InactiveUS7050480B2Increase system capacityAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemParallel computing
A method is disclosed for operating a synchronous space division multiple access, code division multiple access communications system. The method operates, within a coverage area of a base station (BS) or radio base unit (RBU) having a multi-element antenna array, for estimating a SSV for individual ones of a plurality of active subscriber stations (SSs) and assigns a spreading code to a subscriber station (SS) that minimizes the similarity of the determined SSVs of the SSs in a spreading code set. A metric used to measure the similarity of the spatial signature vectors of the SSs comprises the squared sum of the inner products of same code SSs' SSV with a current SS's SSV. The step of assigning includes calculating the magnitude of the squared inner product of the SSVs of all pairs of active SSs; using the calculated values for determining ξn(c) for each spreading code that is not already used some specified maximum number of times; and assigning to a SS the spreading code with a minimum ξn(c).
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
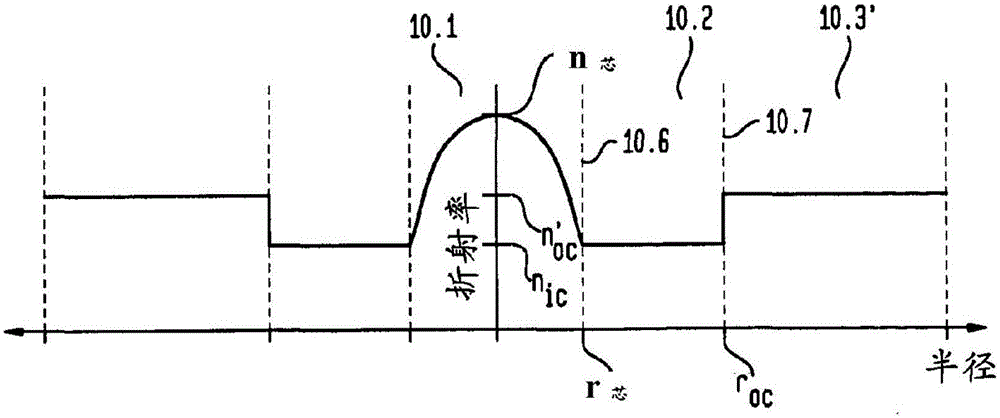
Design and manufacture of multi-mode optical fibers
ActiveCN105829928AOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideLength waveLambda
Described is a technique for the design and manufacture of MMFs. Designs are implemented so as to limit the maximum variation in z{r, Lambda) with respect to wavelength, where z(r. Lambda) is the dielectric constant weighted by the square of the vvaveiengih. MMFs for use in CWDM applications are specifically described.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Method and circuit for curvature correction in bandgap references with asymmetric curvature
ActiveUS20080164938A1Easy to correctIncrease temperatureElectric variable regulationRelative magnitudeLogit
A non-linear correction current ICTAT2 (current complementary to the square of absolute temperature) is generated from a current IPTAT (current proportional to absolute temperature) and a current ICTAT (current complementary to absolute temperature), both modified in a circuit having a topology and components which capitalize on the logarithmic relationship between transistor collector current and base-emitter voltage. The resulting ICTAT2 current (current complementary to the square of absolute temperature) is injected into a node of a bandgap reference circuit to compensate for non-linear temperature effects on output voltage. A more general correction circuit generates both IPTAT2 and ICTAT2, and applies each to a respective multiplier which, in a preferred embodiment, is a current DAC configured as a multiplier. Control inputs CTL1 and CTL2 to respective multipliers set the amplitudes of the modified IPTAT2 and ICTAT2 output currents, which are then summed to generate the compensating current Icomp which is injected to the appropriate node in the bandgap reference circuit as described above. By adjusting the relative amplitudes of the IPTAT2 and ICTAT2 currents, a wide range of compensating current versus voltage curves is produced, allowing the optimization of a wide range of bandgap reference circuits. An optimal value for CTL1 is determined by holding CTL2 constant, then measuring curvature at a plurality of CTL1 values. That CTL1 value closest to the interpolated value at which curvature is minimized is then used.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for calculating current reference value of three-phase four-wire grid-connected voltage source type pulse-width modulation (PWM) rectifier
The invention relates to a method for calculating a current reference value of a three-phase four-wire grid-connected voltage source type PWM rectifier. On the condition of unbalanced drop of grid voltage, the elimination of the active power fluctuation and the suppression of the direct current bus voltage fluctuation serve as the control target. According to the method, on the premise that the requirements of the control target are met, the maximum value in reference values of three-phase current amplitudes can be minimized simultaneously. The method comprises that firstly, three voltage sensors of the rectifier detect to obtain three-phase grid voltage ea, eb and ec, fundamental wave amplitudes Ea, Eb and Ec and fundamental wave phases phi a, phi b and phi c of the three-phase grid voltage can be obtained after processing by three single-phase phase-locked loop structures, and different current reference value calculation methods can be determined according to the criterion that whether the quadratic sum of any two phase amplitudes in grid voltage amplitudes is smaller than the square of the third phase amplitude.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
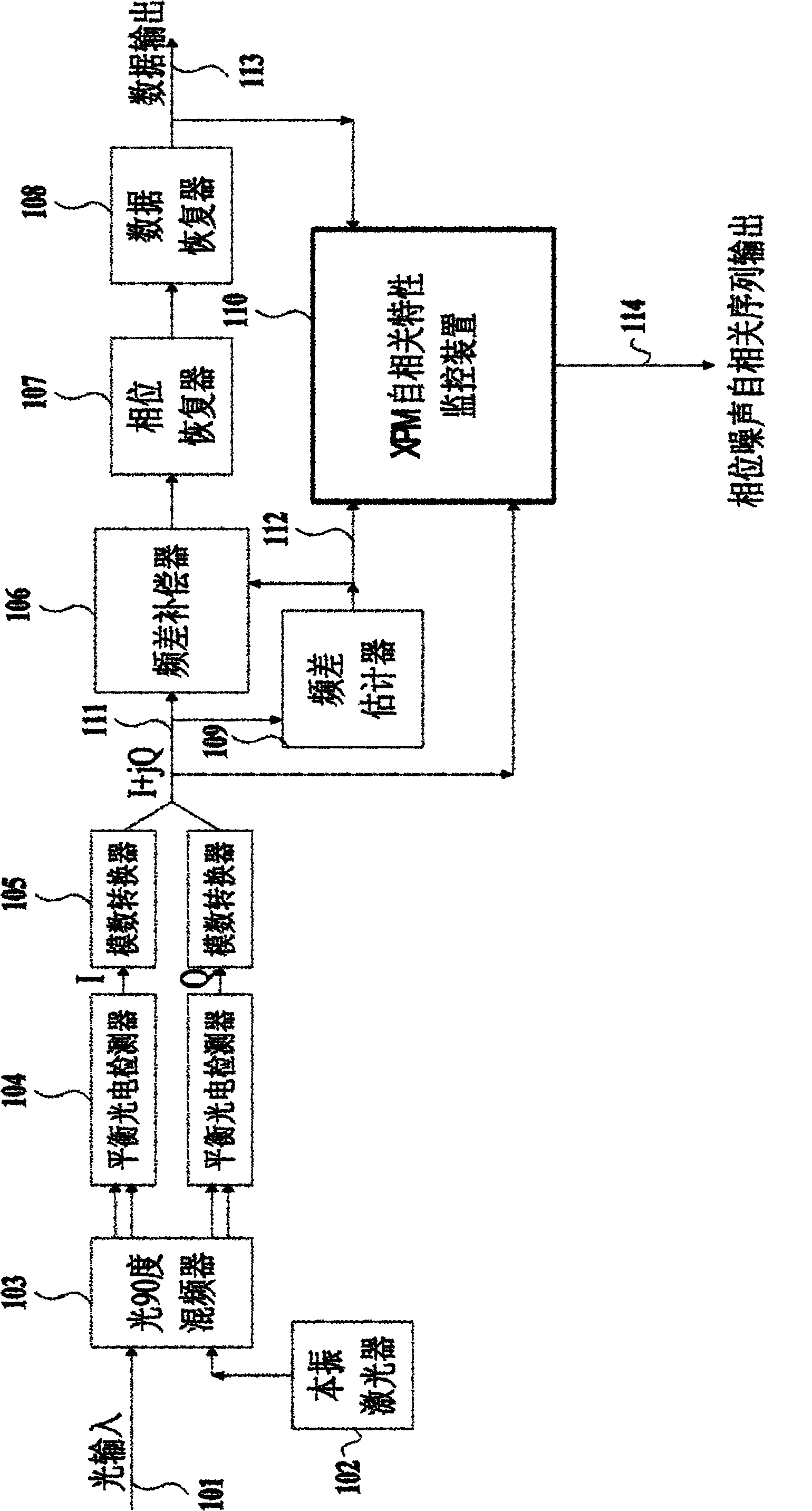
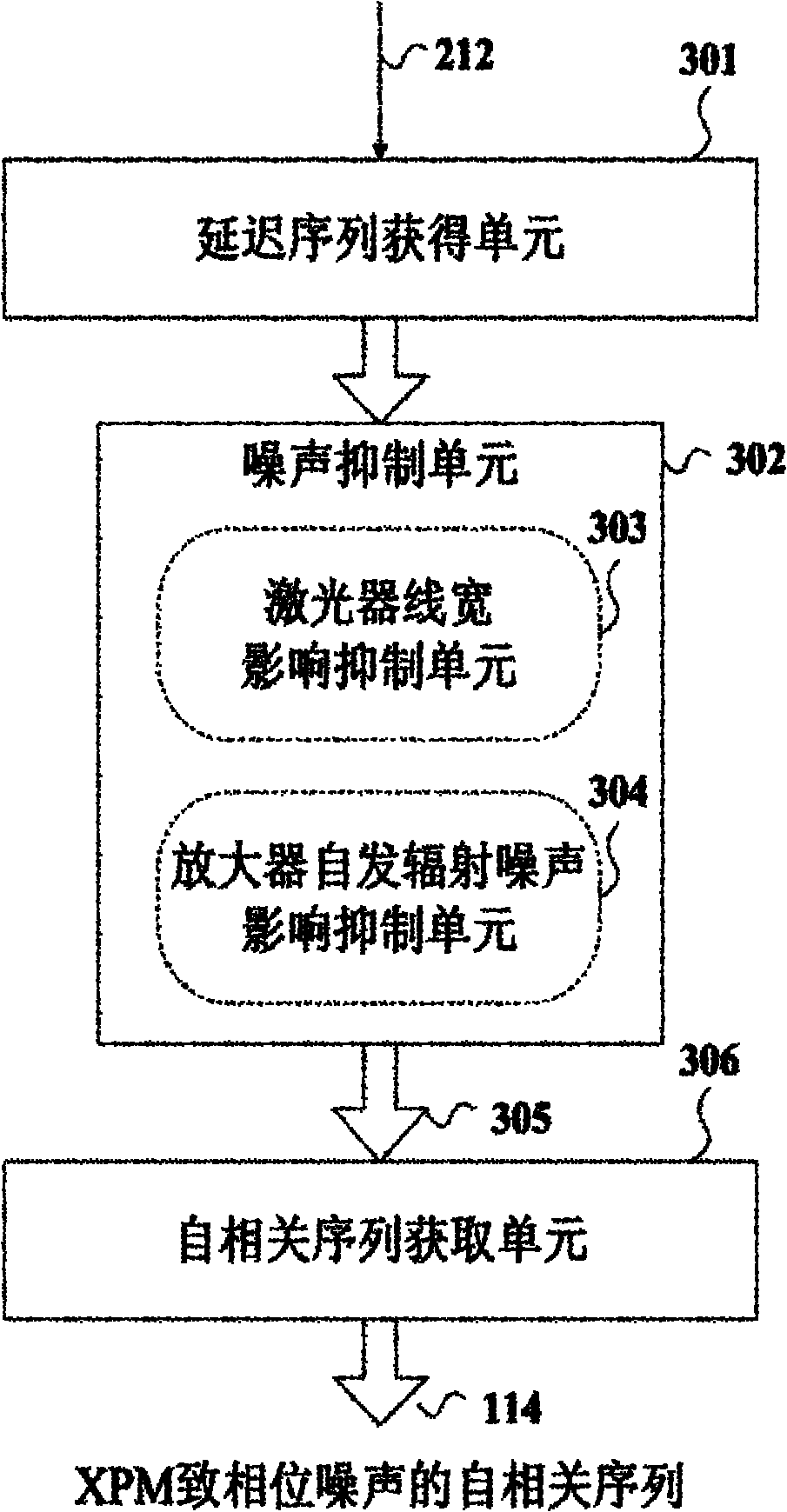
Apparatus and method for monitoring statistical characteristics of phase noises, and coherent optical communication receiver
ActiveCN102100024AWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversDifferential phasePhase noise
This invention relates to an apparatus and a method for monitoring statistical characteristics of phase noises, as well as to a coherent optical communication receiver. The apparatus for monitoring statistical characteristics of phase noises comprises an argument calculating unit (203), for obtaining an argument of a signal input thereto; an unwrapping unit (204), for unwrapping the argument obtained by the argument calculating unit (203) to obtain a phase signal (205); a delaying unit (207), for delaying the phase signal; a differentiating unit (209), for obtaining a difference between a phase 10 signal currently obtained by the unwrapping unit (204) and a phase signal delayed by the delaying unit (207); a modulus squaring unit (210), for obtaining a square of the modulus of the difference; and an averaging unit (211), for averaging squares of moduli of a plurality of differences obtained by the modulus squaring unit (210) to obtain a mean-squared differential phase 15 (MSDP) value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Estimation method of four-wheeled independent drive electric automobile road adhesion coefficient
The invention discloses an estimation method of a four-wheeled independent drive electric automobile road adhesion coefficient. The method includes the steps: calculating vertical tire force of four wheels under a current vehicle driving state; calculating longitudinal tire force of the corresponding wheels under different road adhesion coefficients of current slipping rate; calculating current longitudinal tire force of the wheels; calculating a road friction coefficient; performing subtracting on the longitudinal tire force of the corresponding wheels under the different road adhesion coefficients of the current slipping rate and the current longitudinal tire force of the wheels, and taking a square; taking a minimum value of the difference square, judging the road adhesion coefficient corresponding to the minimum value as a current road adhesion coefficient, comparing the current road adhesion coefficient with the road friction coefficient, and taking a maximum value between the current road adhesion coefficient with the road friction coefficient; updating an estimation value of the current road adhesion coefficient if the duration time of an estimation value of the changed roadadhesion coefficient is longer than 0.5 second; keeping invariability of an estimation value of the road adhesion coefficient of previous moment. The method can be used for adjustment of drive anti-skid strategies, and the driving performance of a vehicle is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Quadratic Performance, Infinite Steps, Set Point Model Tracking Controllers
InactiveUS20070112445A1Sampled-variable control systemsControllers with particular characteristicsControl systemLinear quadratic gaussian controller
Two linear quadratic tracking controllers and a minimal prototype controller are presented for the control of a discrete single input and single output (SISO) tracking control system. The minimal prototype controller is an unconstrained controller. Depending on the models of the set point and the plant transfer function, this controller might be desirable. But usually one would choose one of the two linear quadratic controllers which minimize the sum of squared errors between the output and the set point variables with a penalty on that of the input variable. The one degree of freedom (1-DOF) controller performs well, but for nonminimum phase systems the two and a half degrees of freedom (2.5-DOF) controller is the stronger one as it can suppress the inverse response of a non-minimum phase system. The 1-DOF controller gives the stochastic regulating controller counterpart known as the linear quadratic Gaussian controller. A digital control chip for implementation of the controllers is also disclosed.
Owner:AULAC TECH
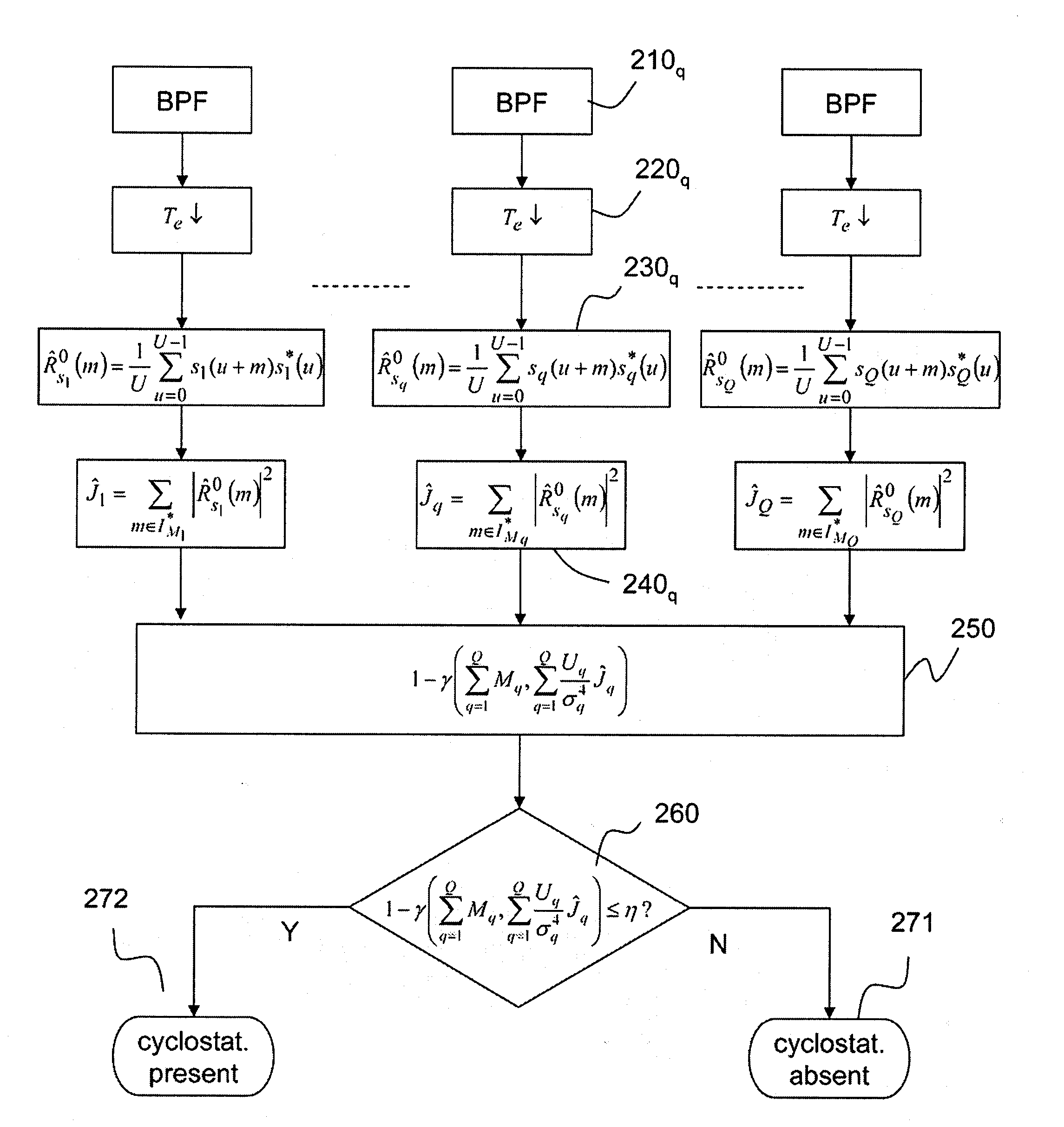
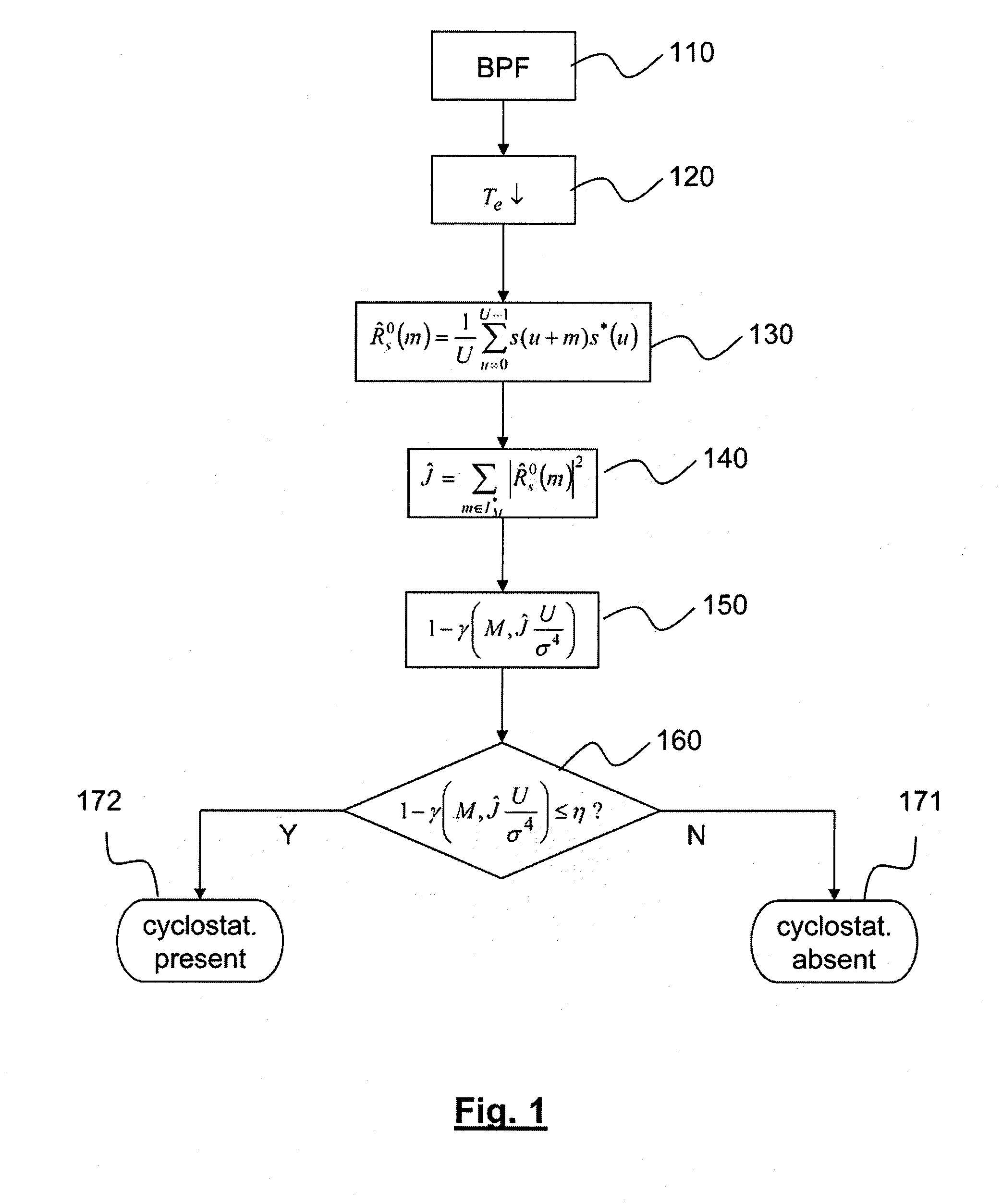
Method for detecting cyclostationary signals
ActiveUS20100195705A1Low signal-to-noise ratio conditionSpectral gaps assessmentAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTime shiftingComputer science
A method for detecting a cyclostationary signal in a signal to be analyzed, received from a transmitter by a receiver or read from a recording medium by a reader device. According to this method, the value of a discrimination function J is estimated, expressed as a quadratic form of the cyclic correlation coefficients of the signal to be analyzed for a set (I*M) of non-zero time shifts and a set (IK) of cyclic frequencies, and the value1-γ(v,Uσ4J)is compared with a wrong detection rate η in order to determine whether said cyclostationary signal is present in the signal to be analyzed, wherein γ(ν,x) is the normalized lower incomplete gamma function, ν is the product of the cardinal (M) of said set of non-zero time shifts and of the cardinal (K) of said set of cyclic frequencies, U is the width of the autocorrelation window on which the cyclic correlation coefficients are calculated, and σ4 is the square of the noise variance.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Kinematics-based five-axis numerical control machining tool attitude planning method
ActiveCN109375579AHigh precisionReduce distractionsNumerical controlNumerical controlUniversal structure
The invention discloses a kinematics-based five-axis numerical control machining tool attitude planning method, which comprises the steps of: defining a tool axis vector as a vector description of a tool axis direction in a workpiece coordinate system; adopting variations of a tool axis vector v at a tool location point P<L, i>, and tool axis vectors v<i-1> and v<i+1> at tool location points P<L, i-1> and P<L, i+1> adjacent to the tool location point P<L,i> on the same tool path as metrics of the vector description; specifically adopting a value obtained through extracting root of a sum ofsquares of included angles between the adjacent tool axis vectors as metric indexes; and establishing a tool axis vector integral smoothing model considering kinematics space mapping based on a universal structure machine tool kinematics model and tool axis vector smoothing metric indexes, and completing tool attitude planning method. The kinematics-based five-axis numerical control machining toolattitude planning method greatly improves the machining precision and machining efficiency of the multi-axis numerical control machine tool, reduces interference between the tool and the workpiece, and prevents the occurrence of accidents.
Owner:武汉武科伺服机电设备有限公司
Method for making micrometer scale speckle
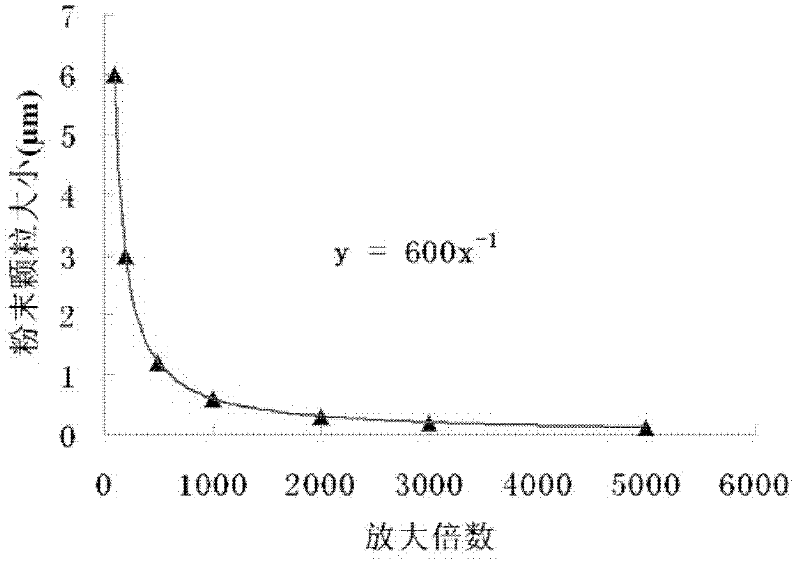
InactiveCN102506733AMeet deformation measurementRealize large-area micro-scale speckle productionLiquid surface applicatorsUsing optical meansEpoxyMicrometer scale
The invention relates to a method for making a micrometer scale speckle, belonging to the technical field of optical measurement mechanics. The method for making the micrometer scale speckle is technically characterized in that epoxy hardener and powder mixed solution are evenly coated on the surface of a test piece by using a photoresist spinner to complete the making of the micrometer scale speckle. The method is simple to operate. By changing the size of power particles, the volume mass ratio of the epoxy hardener and the power, centrifuge time and photoresist spinning speed parameter to control the density and the size of speckle particles, evaluating speckle grams obtained under different parameters through average grey scale gradient sum of squares and selecting a surface speckle gram with the largest average grey scale gradient sum of squares as the made micrometer scale speckle, the goal that the made speckle is suitable for the researches on micro deformation behaviors of different materials is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Color quantization based on desired upper bound for relative quantization step
InactiveUS20090096809A1Texturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerized systemBrightness perception
A computer system (710) receives a desired upper bound δSmax for a relative quantization step ∥S′−S″∥ / ∥S′∥ to be used when quantizing any color in some range of colors. Here S′ and S″ are adjacent colors in the set of colors to be made available for the quantized image, and ∥·∥ is a norm in a 70%-orthonormal linear color coordinate system, the norm being the square root of the sum of squares of the tristimulus values. The computer system determines (510) suitable quantization steps for the brightness coordinate (B) and the chromatic coordinates (e,f) in a non-linear color coordinate system, and quantizes (520) the brightness and chromatic coordinates accordingly.
Owner:KWE INT
Nonlinear process fault detection method based on differential locality preserving projection (DLPP)
InactiveCN106338977AGuaranteed internal structureKeep the original structure informationTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlHat matrixData set
The invention discloses a nonlinear process fault detection method based on differential locality preserving projection (DLPP) and relates to a nonlinear process fault detection method. Batch data acquired in a normal production process is taken as a training set of modeling data, three-dimensional data is expanded to be two-dimensional, a nearest neighbor of each sample in a data set is found, and differential operation is performed on the samples and their nearest neighbors; a locality preserving projection model is established, a projection matrix is found, and a control limit of a square prediction error (SPE) is calculated through kernel density estimation; for a batch sample of a new time point k, data is expanded to form a row of vectors; the data of the new time point is projected to a model of the DLPP, and an SPE statistical amount is calculated; according to whether the statistical amount exceeds the control limit of modeling, whether the data of the time point is normal is determined; if the statistical amount exceeds the control limit, there are faults in data samples of the time point; and otherwise, the data samples are normal. When a test indicates that the faults occur in a system, work personnel needs to examine conditions timely so as to eliminate dangers.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Out-of-focus low-sensitivity and process window enhancement light source-mask batch optimization method
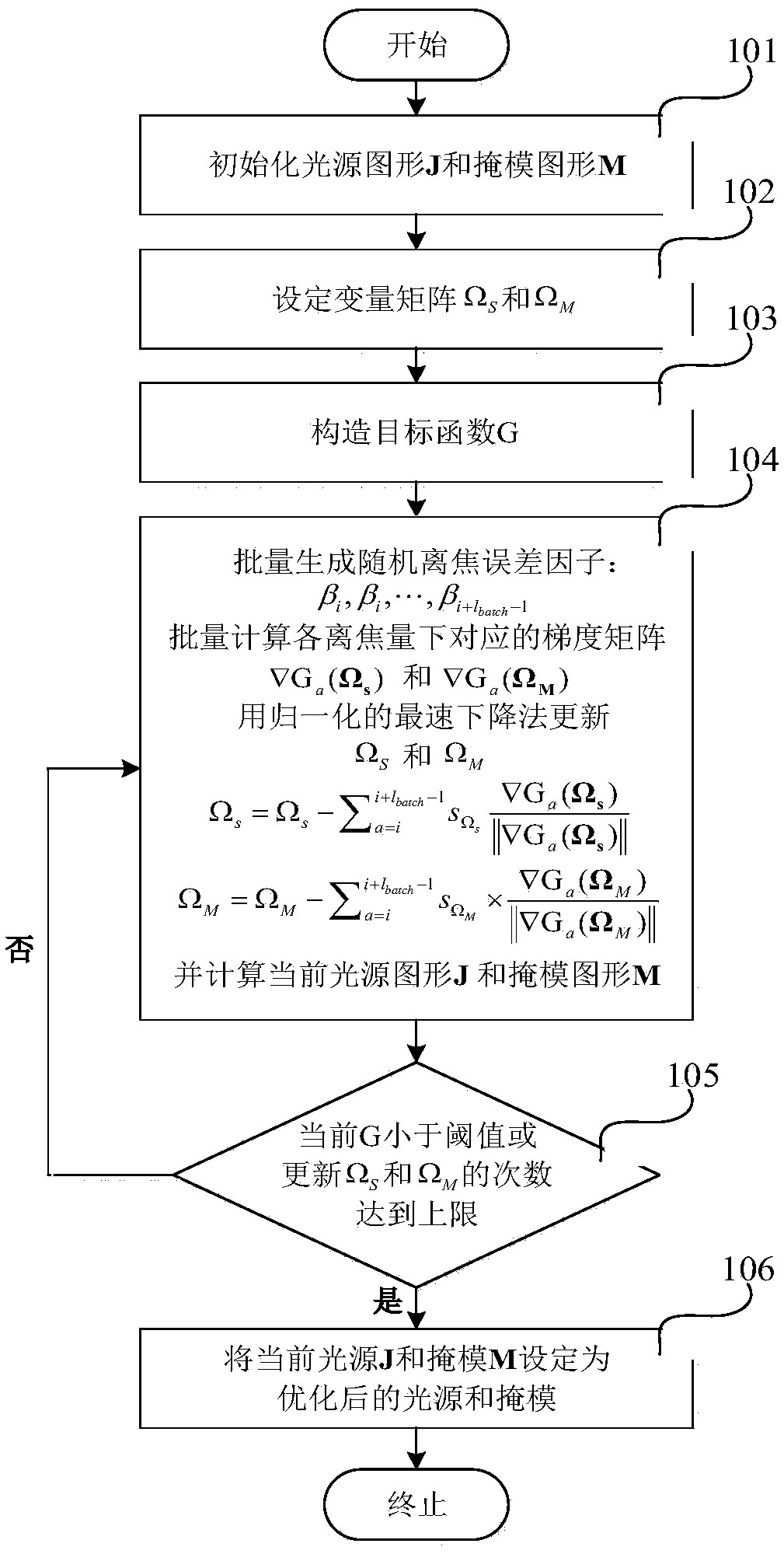
ActiveCN109634068AReduce uniformityDesensitizationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGraphicsSpatial image
The invention provides an out-of-focus low-sensitivity and process window enhancement light source-mask batch optimization method. The process comprises the following steps: selecting an initial lightsource and a mask graph; establishing an out-of-focus high-fidelity objective function as a square of an Euler distance between a target graph and an image in the photoresist corresponding to a current light source graph and the mask graph; constructing an out-of-focus low-sensitivity penalty function item (shown in the specification), wherein Idefox ((beta)i) is a spatial image calculated through a vector imaging model at the position of an out-of-focus error (beta)i, and (beta)I is a random out-of-focus variable obeying uniform distribution; respectively calculating weighted analysis gradients delta(G) of the objective function and a penalty function, namely delta(G) = F + Y; and updating and optimizing a light source and a mask through a small-batch gradient descent method. According to the system optimized through the method, the exposure graph which is more uniform and consistent is obtained within a certain defocusing error range, and the exposure graph is more uniform and consistent. Compared with a traditional light source-mask optimization method, the method has the advantages of higher defocusing robustness, larger focal depth and larger process window.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
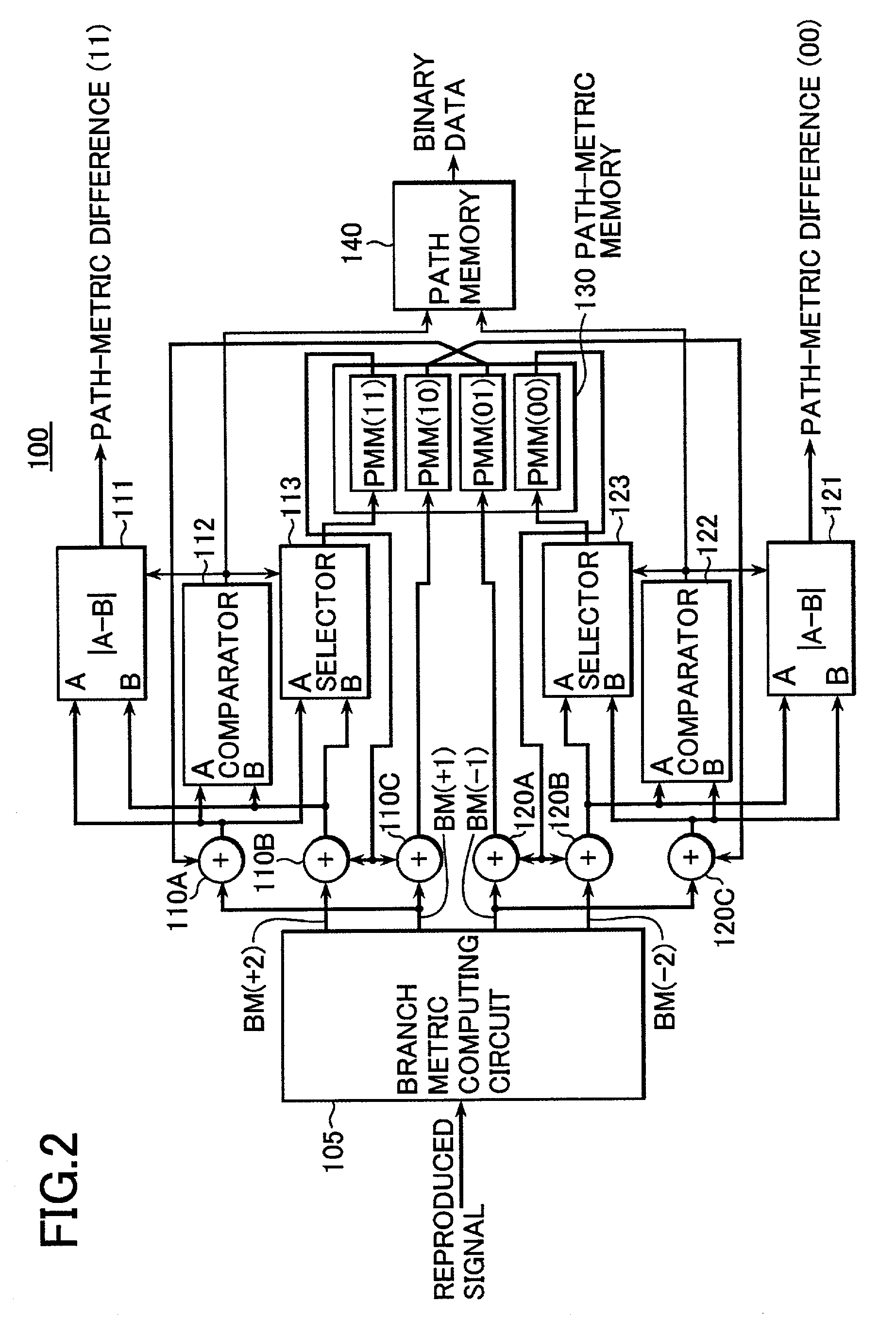
Reproduced signal evaluation apparatus and method, reproduction apparatus and method, and recording apparatus and method
InactiveUS20020114250A1Accurately carry-outHigh correlationTelevision system detailsOther decoding techniquesData valueComputer science
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for precisely and adequately evaluating actual quality of reproduced data whenever applying a maximum likelihood decoder for converting signal reproduced from a recording medium into binary signal. Based on data arrays of a pair of binary data outputted from a "Viterbi" decoder, SAM values are secured by selecting any of path-metric differential values (00) and (11) being the difference between a pair of values compared when renewing path-metric values PMM (00) and (11) outputted from the "Viterbi" decoder. The minimum SAM value for an ideally-reproduced signal is outputted from a constant generating circuit. If the SAM values are verified as valid, and yet, if the SAM values coincide with the equation "input SAM values"<="data value outputted from the constant generating circuit", then squared values outputted from a square circuit are averaged by an averaging circuit. Finally, the average value is outputted as the reproduced signal evaluation.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com