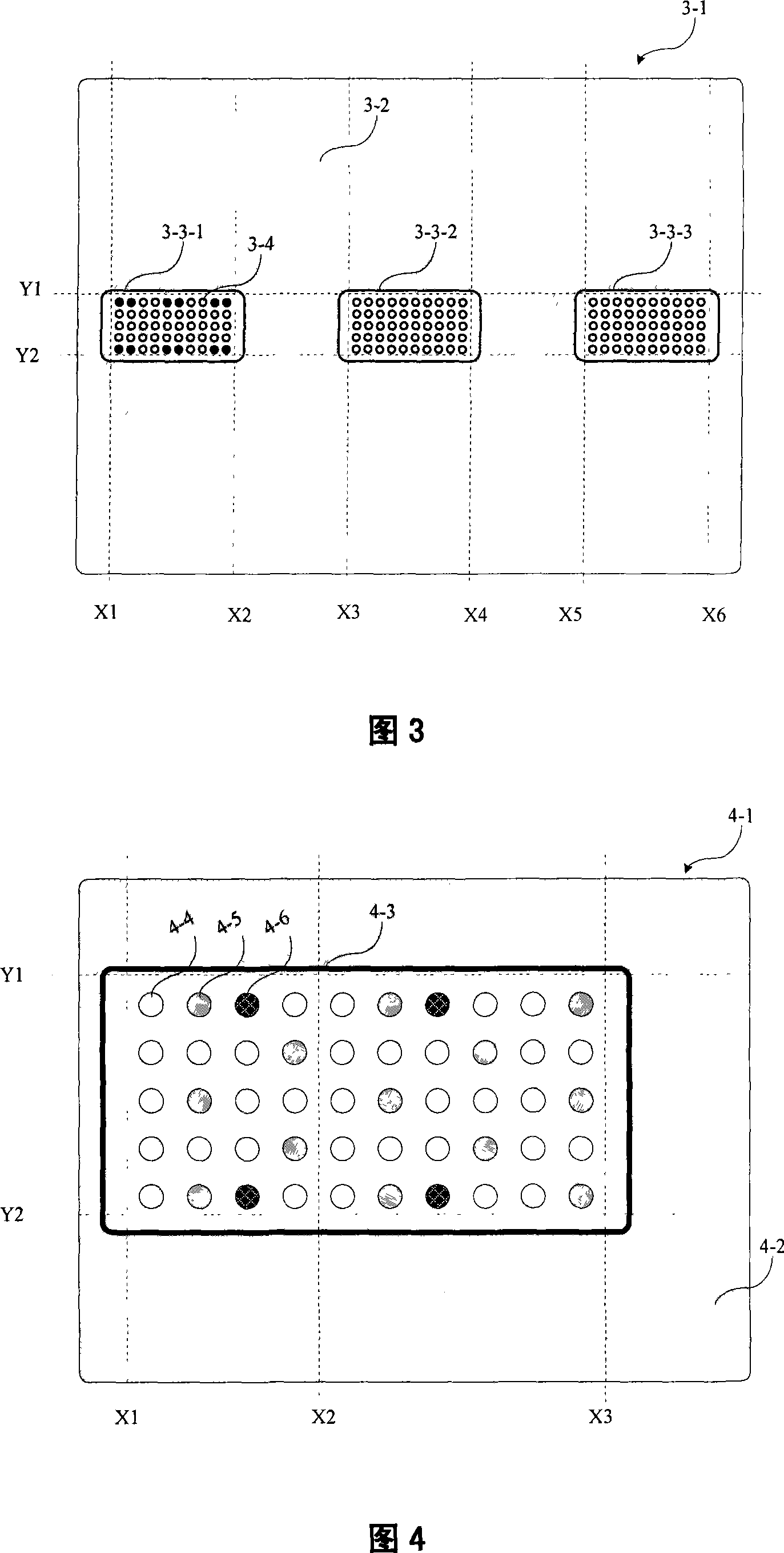
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
309 results about "Space-division multiple access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
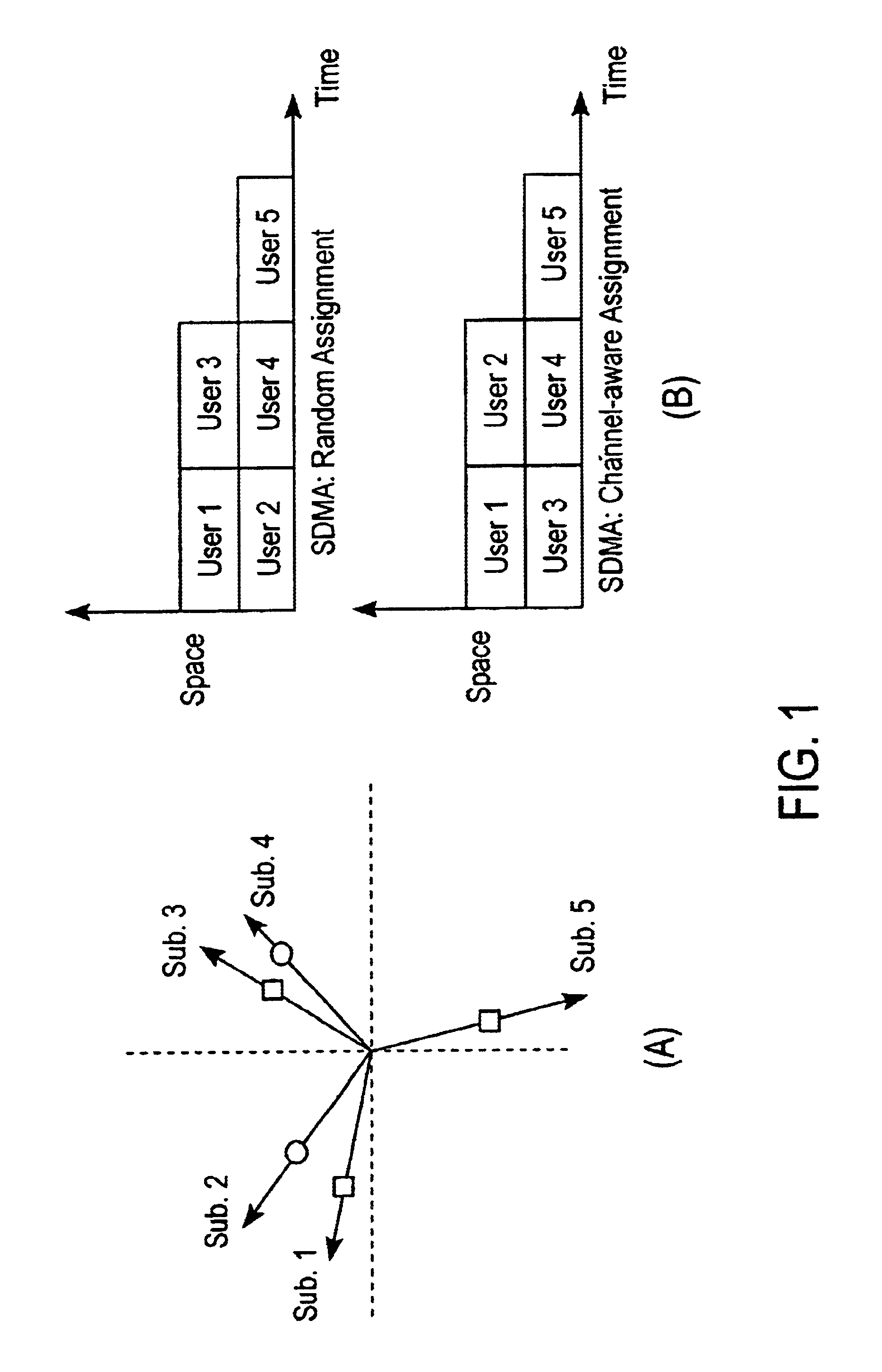
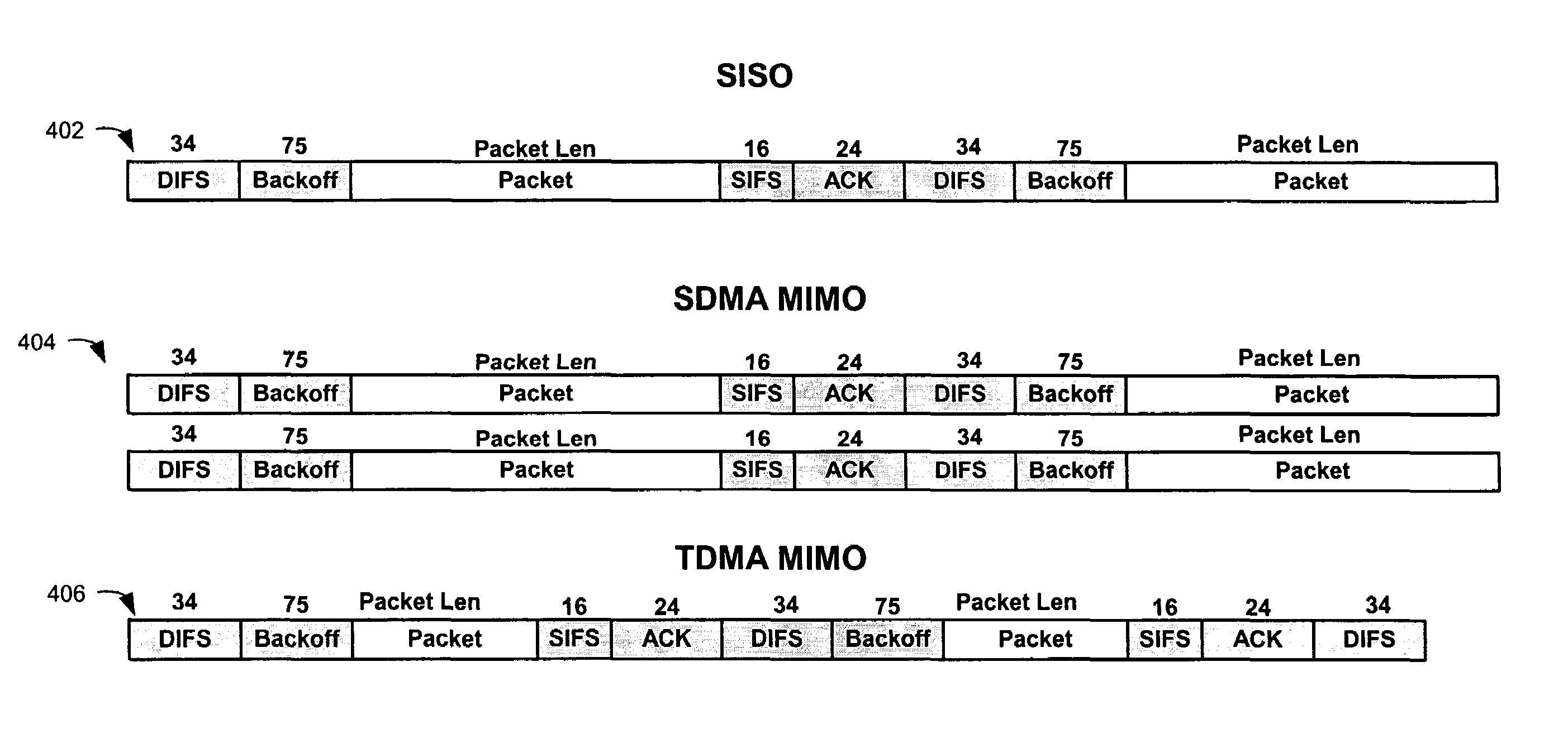
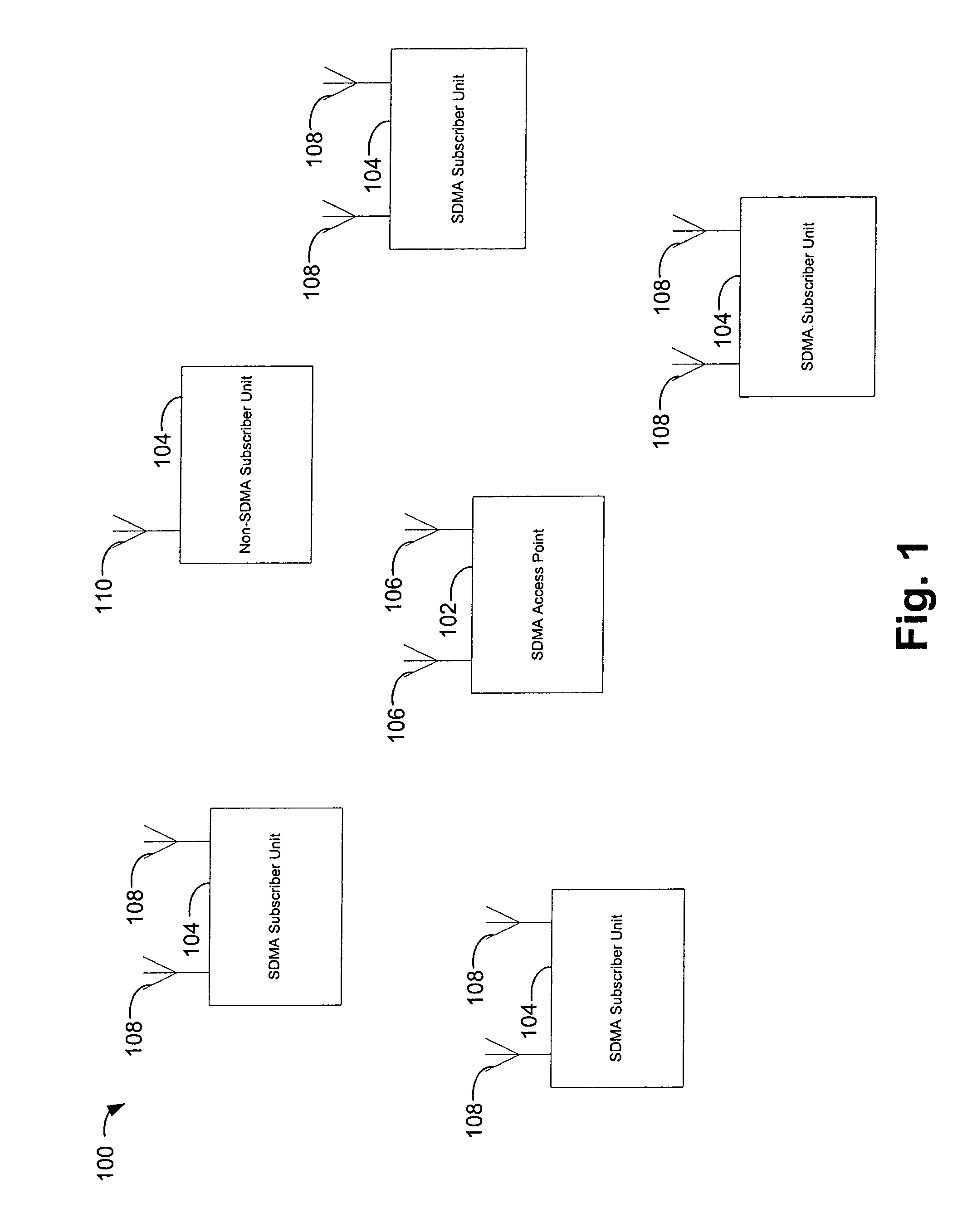
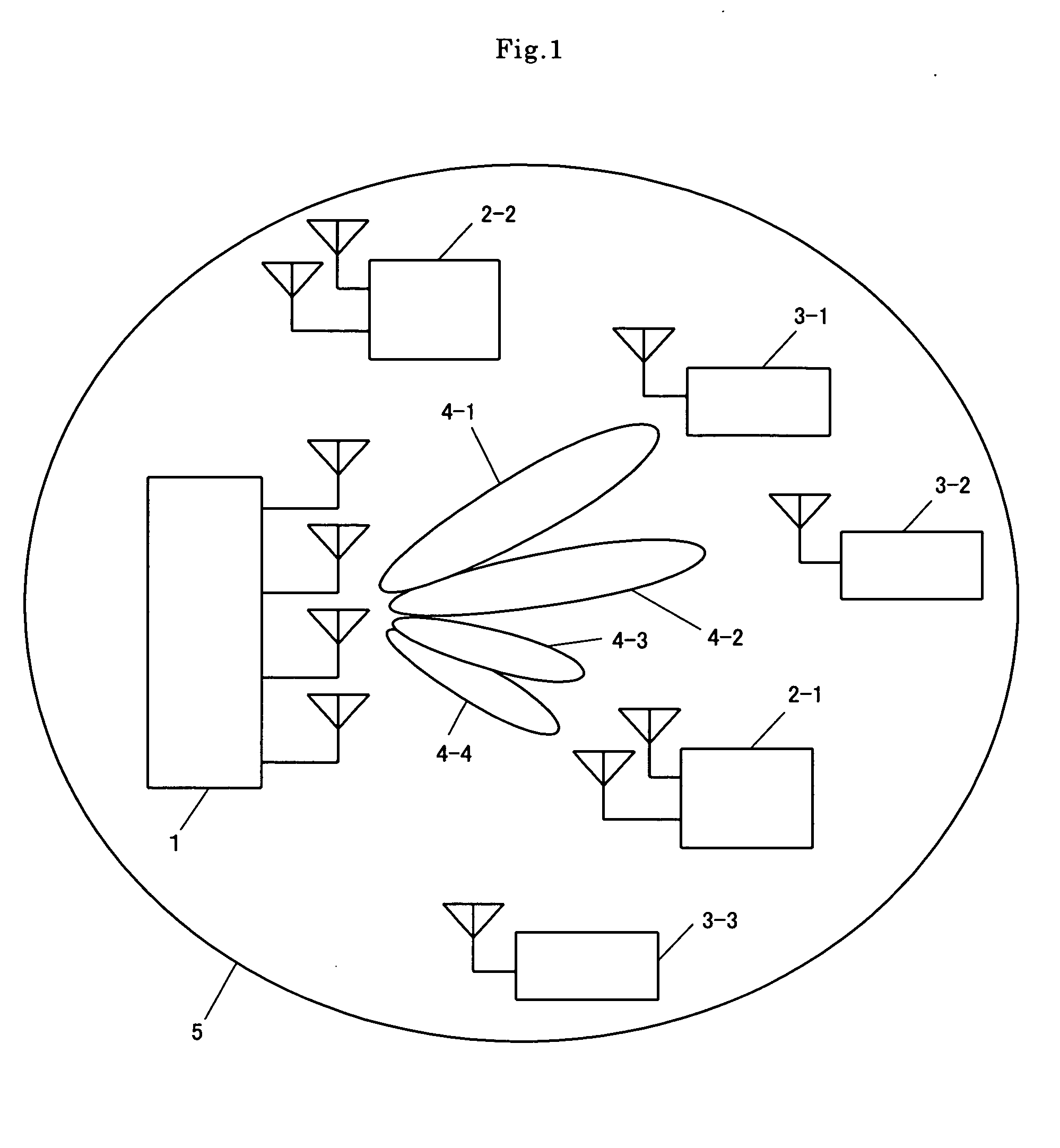
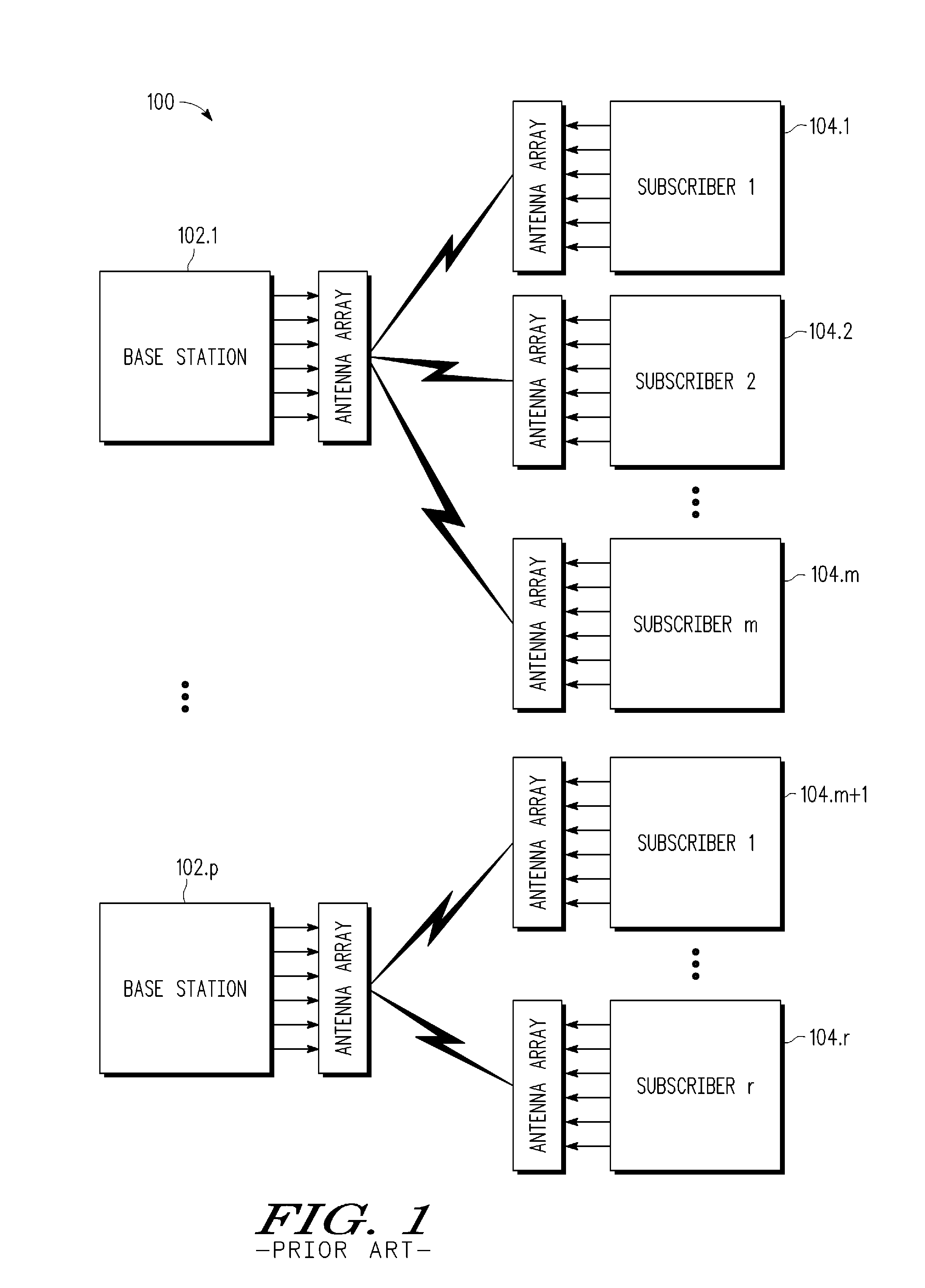
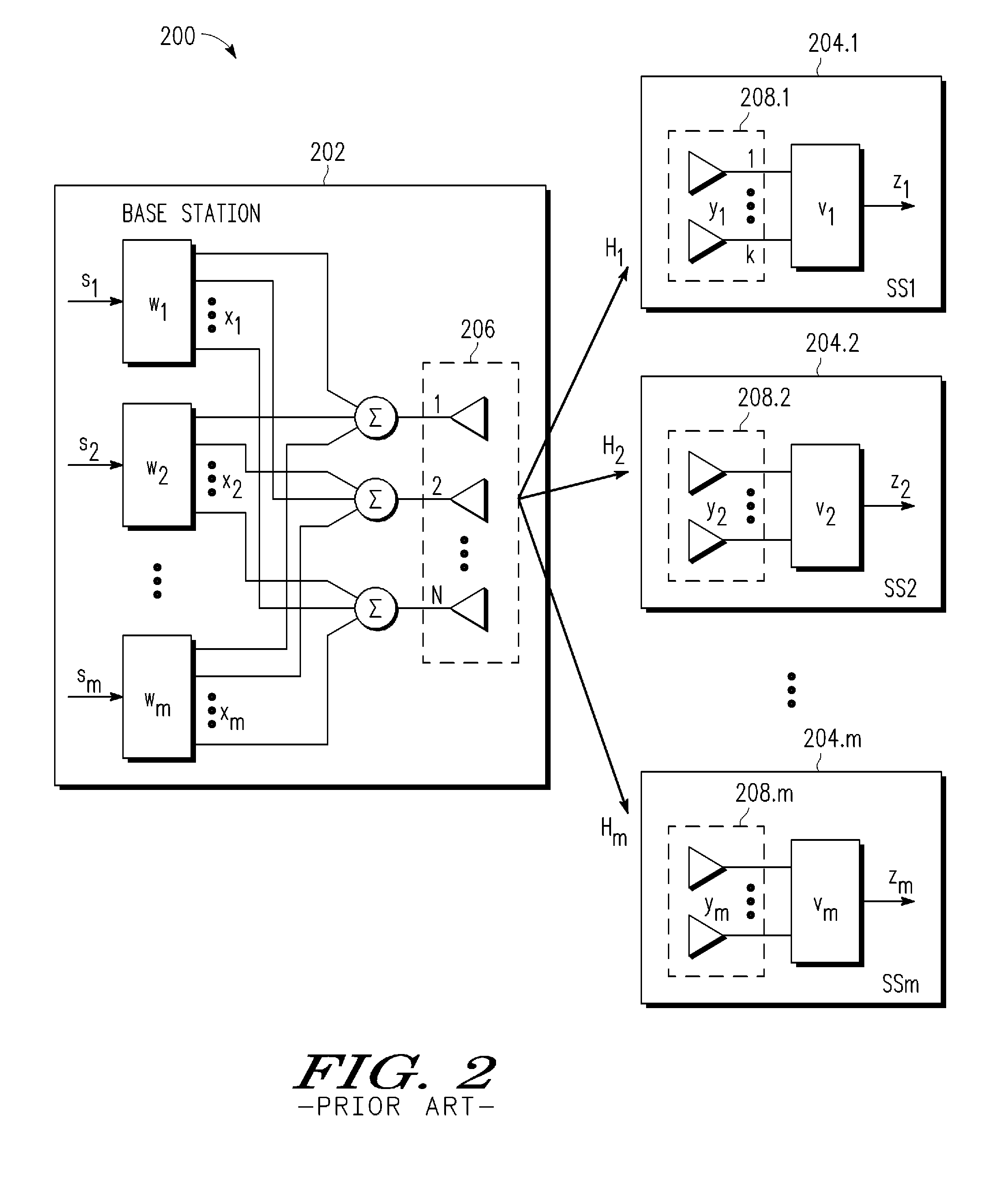
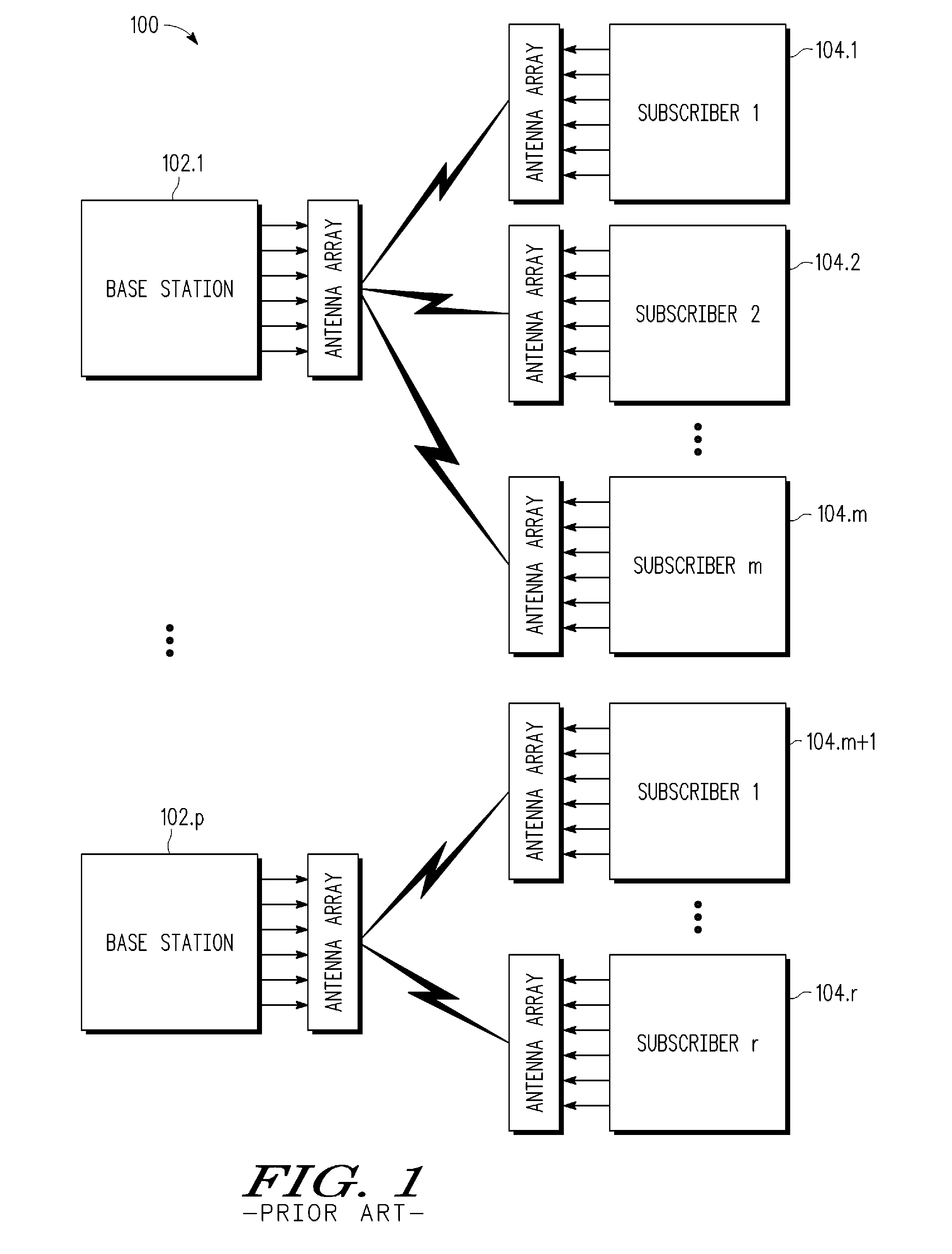
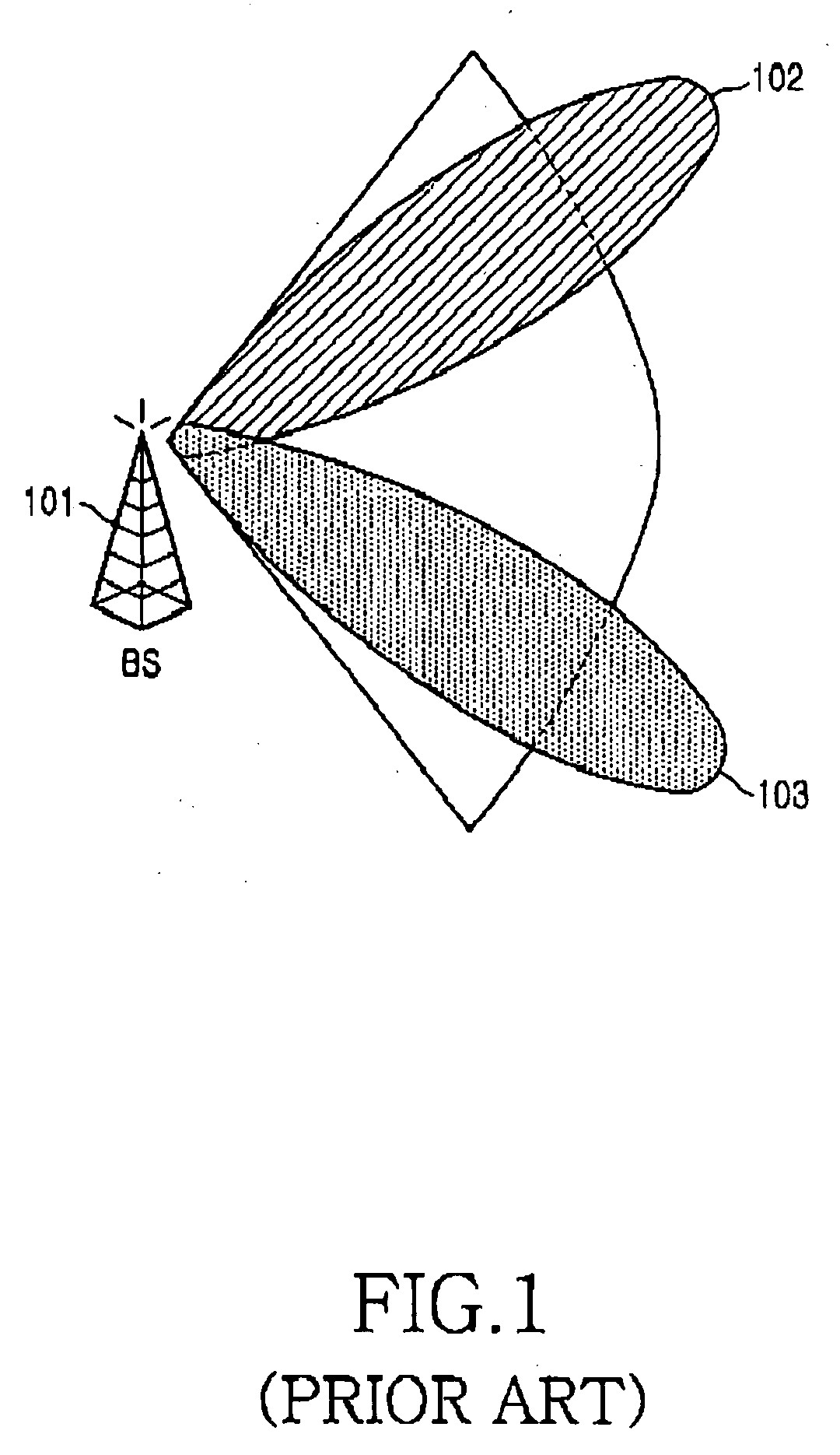
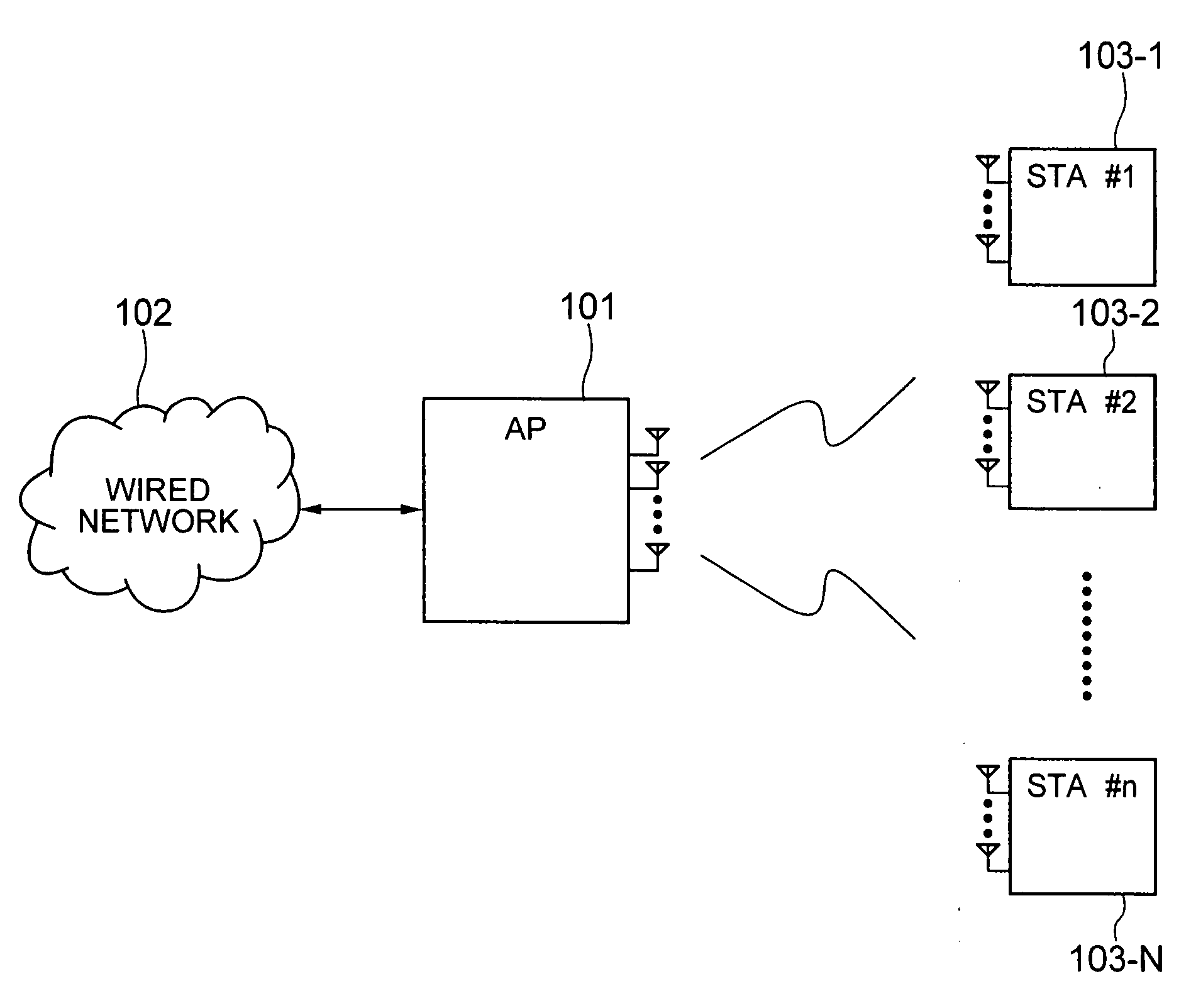
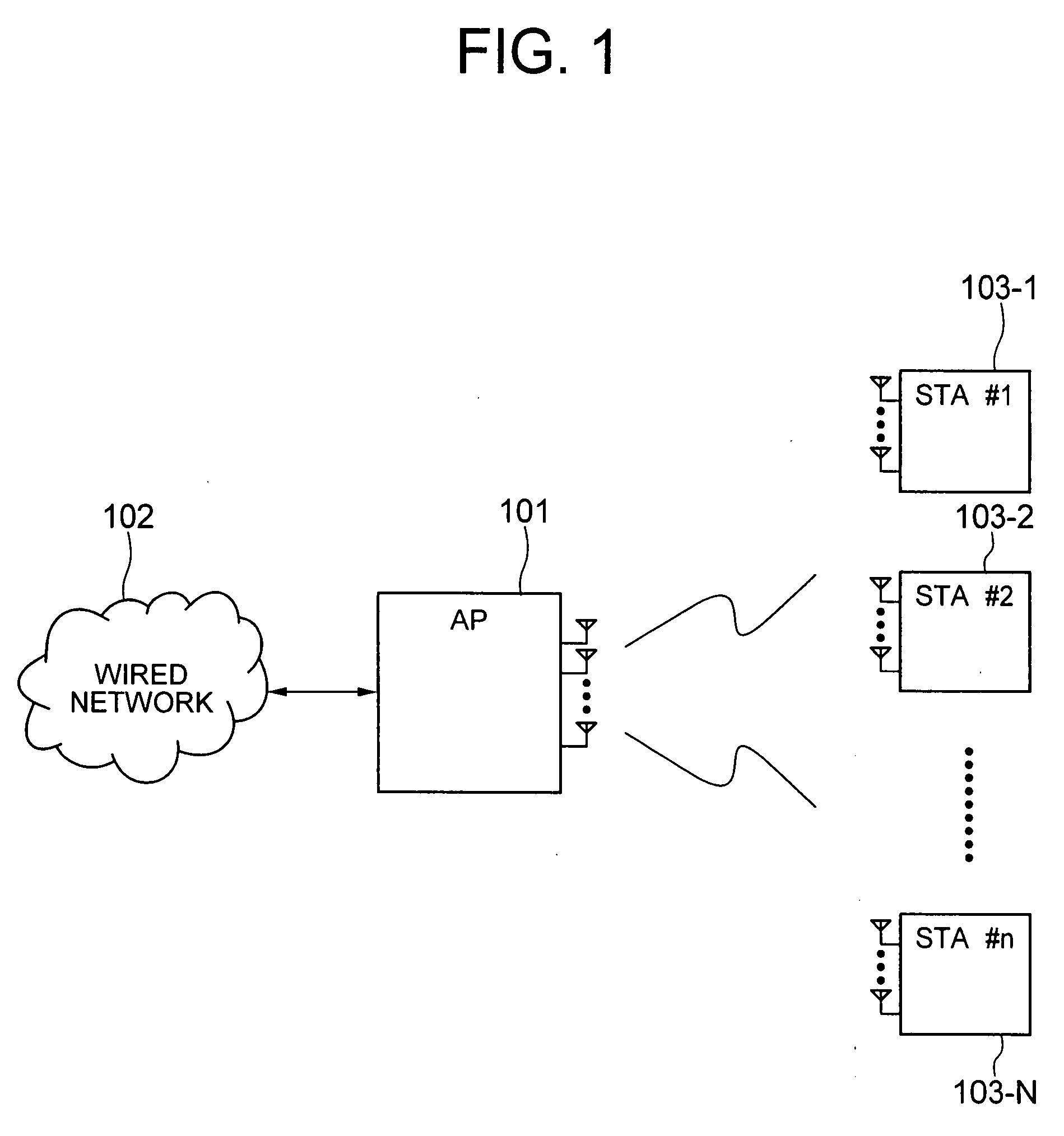
Space-division multiple access (SDMA) is a channel access method based on creating parallel spatial pipes next to higher capacity pipes through spatial multiplexing and/or diversity, by which it is able to offer superior performance in radio multiple access communication systems. In traditional mobile cellular network systems, the base station has no information on the position of the mobile units within the cell and radiates the signal in all directions within the cell in order to provide radio coverage. This method results in wasting power on transmissions when there are no mobile units to reach, in addition to causing interference for adjacent cells using the same frequency, so called co-channel cells. Likewise, in reception, the antenna receives signals coming from all directions including noise and interference signals. By using smart antenna technology and differing spatial locations of mobile units within the cell, space-division multiple access techniques offer attractive performance enhancements. The radiation pattern of the base station, both in transmission and reception, is adapted to each user to obtain highest gain in the direction of that user. This is often done using phased array techniques.
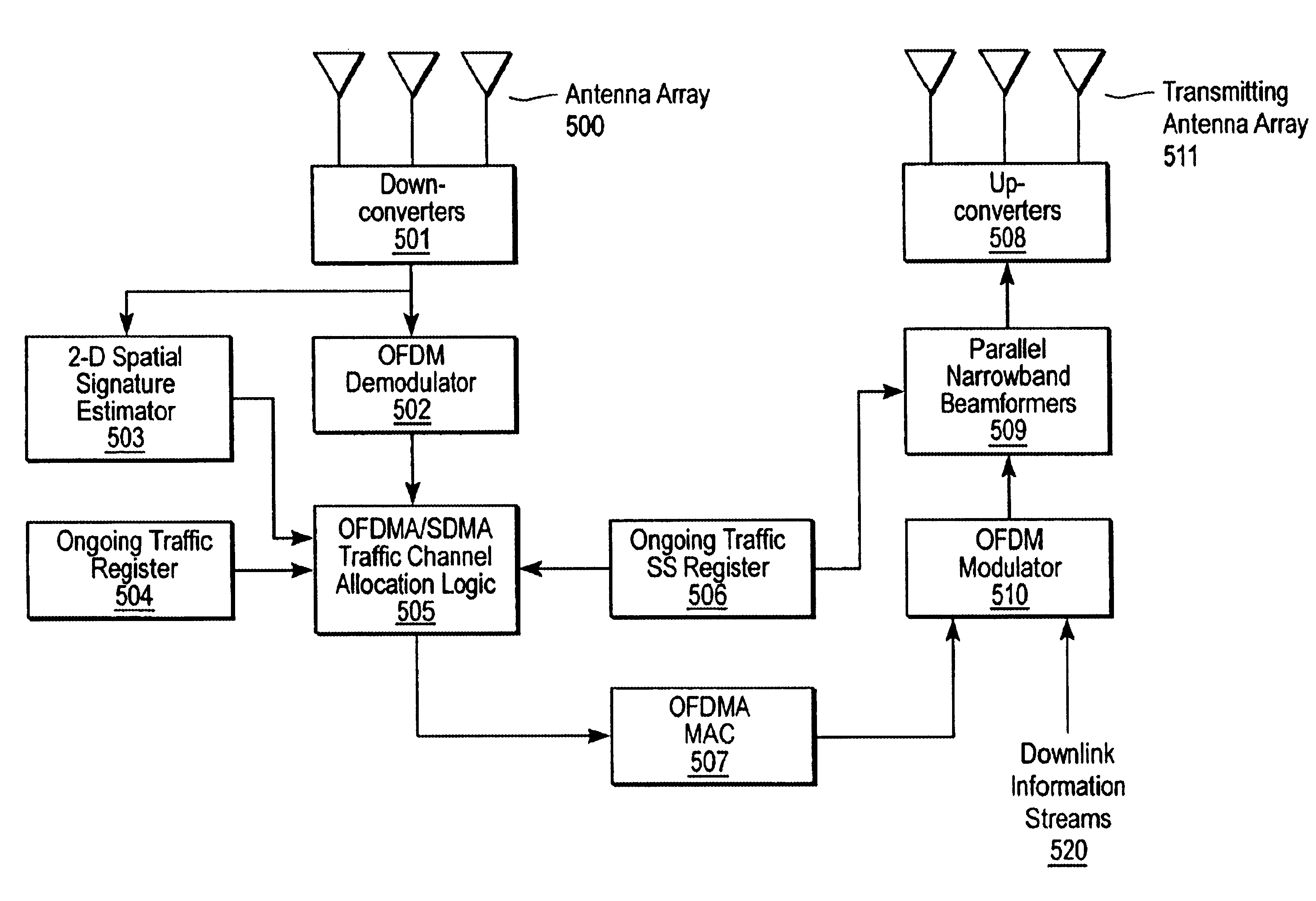
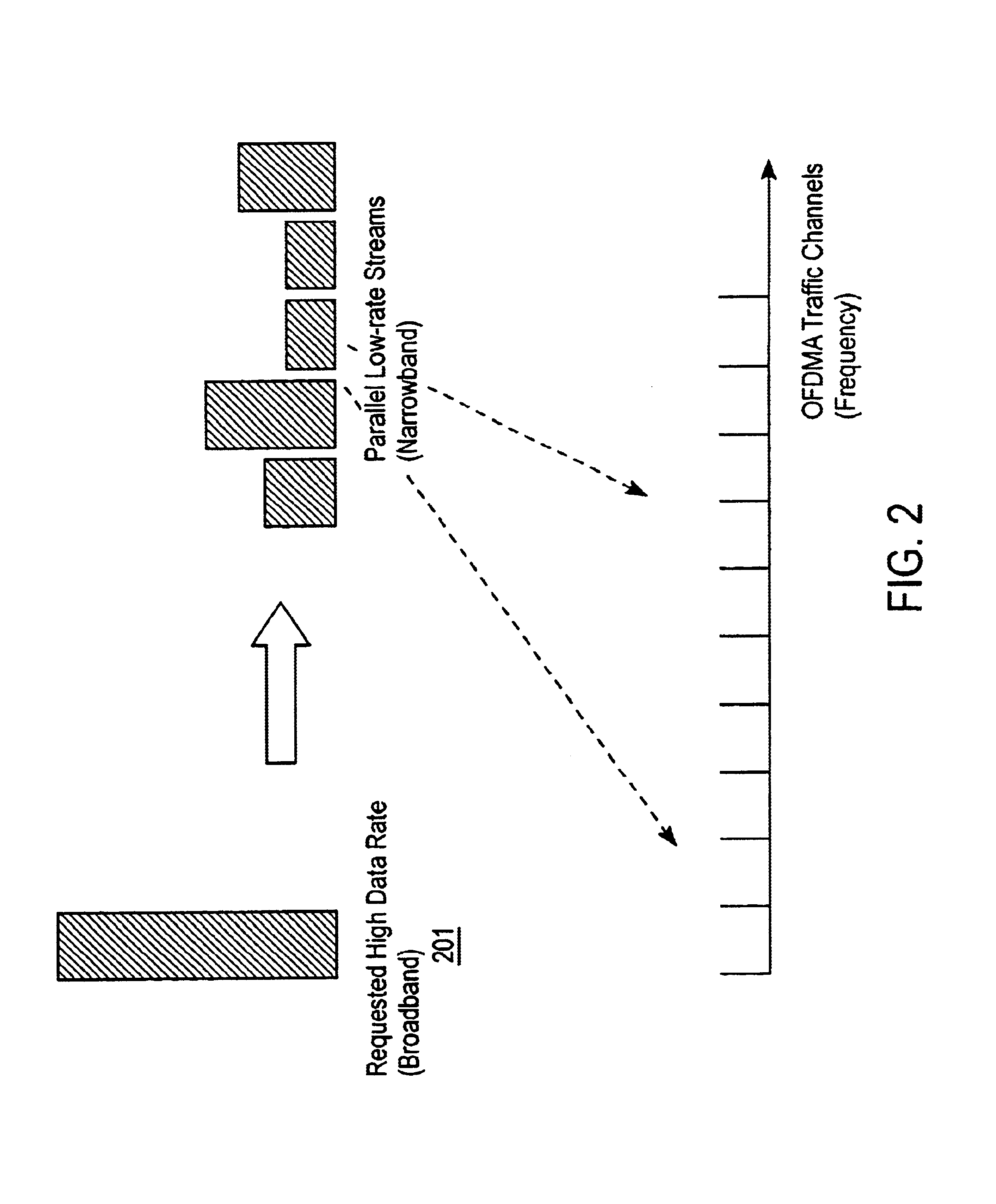
Channel allocation in broadband orthogonal frequency-division multiple-access/space-division multiple-access networks
A network is described. In one embodiment, the network comprises multiple subscriber units to communicate with the base station using an orthogonal frequency-division multiple-access (OFDMA) protocol, and a base station. The base-station includes a memory unit to store broadband spatial signature vectors associated with each subscriber and traffic channel allocation logic. The vectors are a function of frequency. The traffic channel allocation logic allocates OFDMA channels using the broadband spatial signature vectors of the subscribers.
Owner:ADAPTIX +1
Spatial division multiple access for wireless networks
ActiveUS7352718B1Doubling and of network throughputIncrease system capacityPower managementPolarisation/directional diversityWireless mesh networkSystem capacity
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology in conjunction with the IEEE 802.11 standard enables simultaneous communication of data packets to or from multiple users in the same frequency. Spatial divisional multiple access (SDMA) is thus provided. In this way, system capacity can be increased to an extent that depends on available antenna resources and the multipath characteristics of the communication channel. Doubling or quadrupling of network throughput can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Providing space division multiple access in a wireless network
To provide space division multiple access in a wireless network, plural beams are transmitted within a cell segment. Different information sets are sent in the corresponding plural beams, where one or more of the information sets are detectable by a mobile station depending upon a location of the mobile station in the cell segment. An indication responsive to which of the different information sets is detected by the mobile station is received, and beam selection from among the plural beams is performed according to the received indication.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Radio communication system, radio communication method, and radio communication device
ActiveUS20050265470A1Efficient use ofFacilitate communicationSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemEngineering
In the environment of a communication area including a SDM-compatible mobile station for space division multiplex transmission and a SDM-uncompatible mobile station not compatible with space division multiplex transmission, a base station having a plurality of antennas and capable of adaptively changing directivity performs allocation of a mobile station which simultaneously performs space division multiplex transmission (SDM) and space division multiplex access (SDMA) by using a predetermined space division multiplex transmission evaluation criterion and a space division multi access evaluation criterion. By using this radio communication method, it is possible to use the spatial degree of freedom at its maximum and provide a radio communication system having an improved communication capacity.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Methods for opportunistic multi-user beamforming in collaborative MIMO-SDMA
InactiveUS20080075058A1Network topologiesRadio transmissionCommunications systemCooperative beamforming
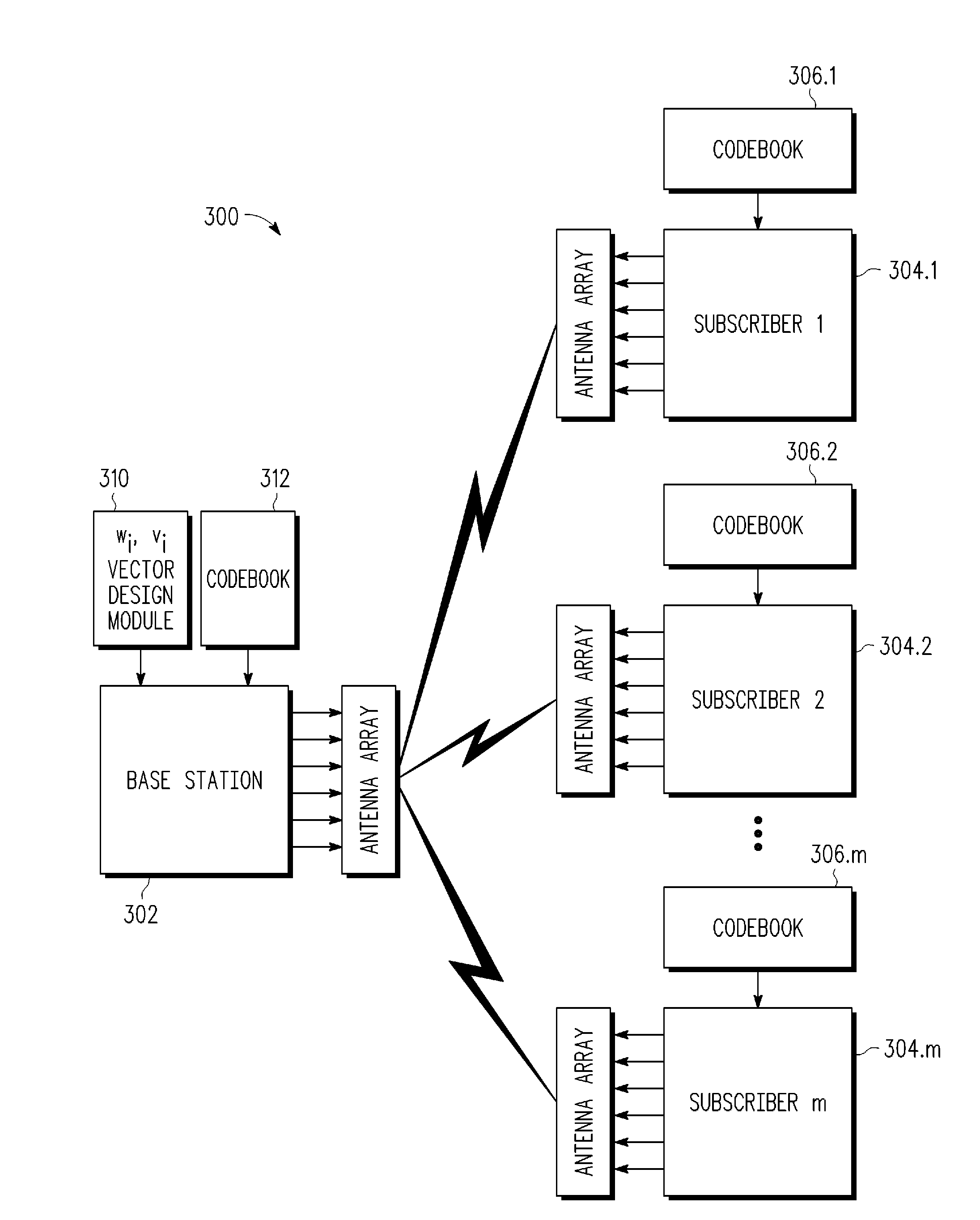
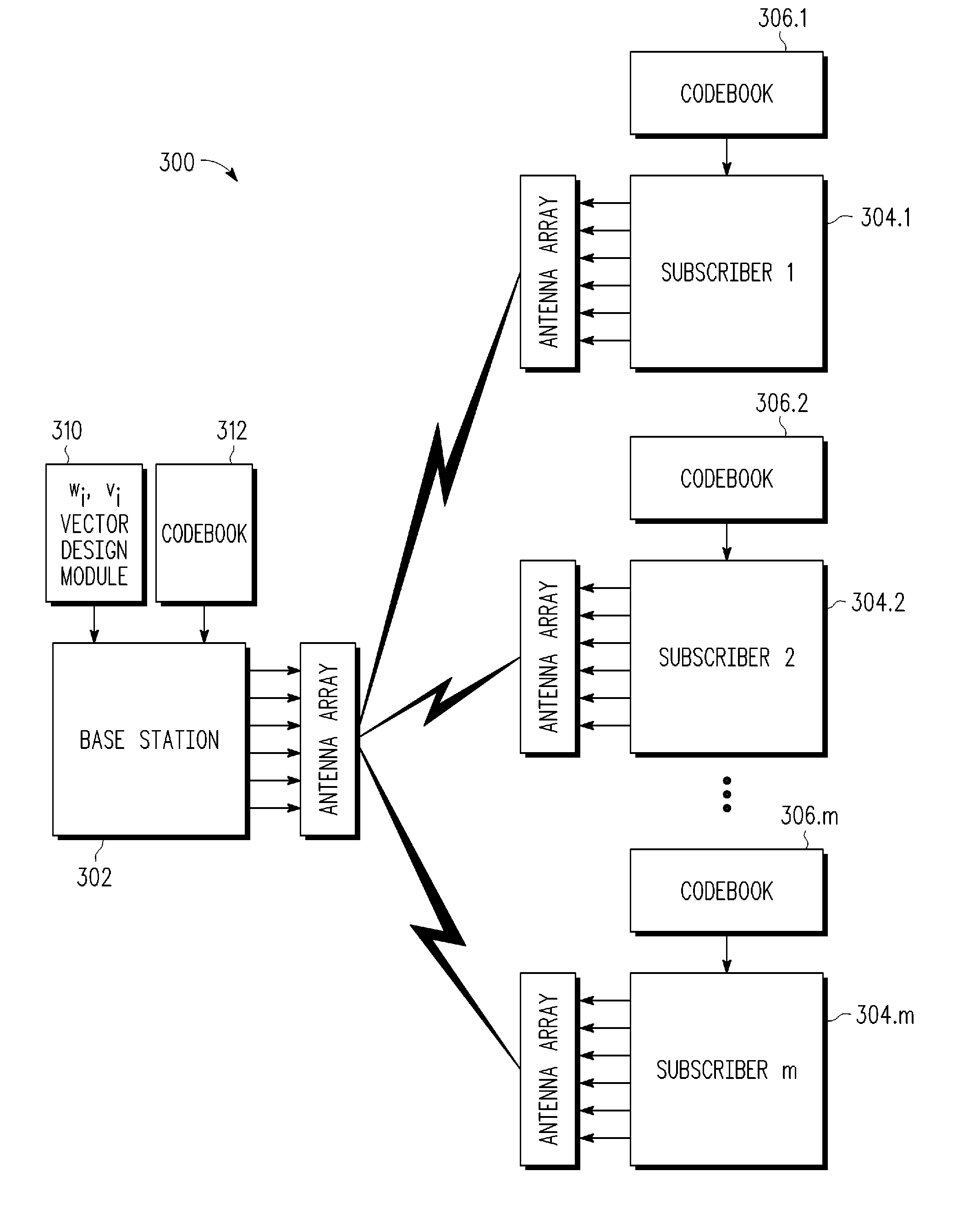
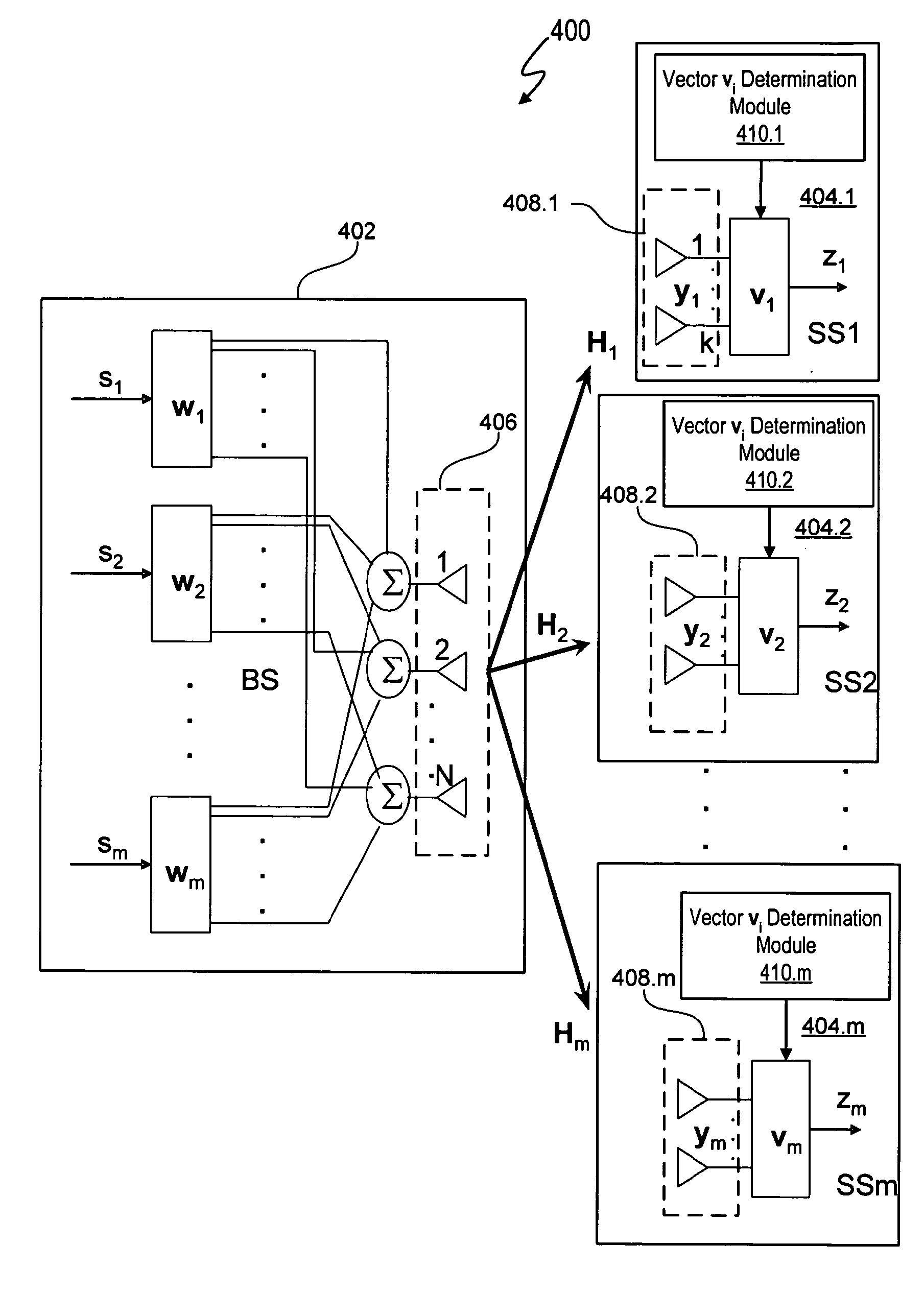
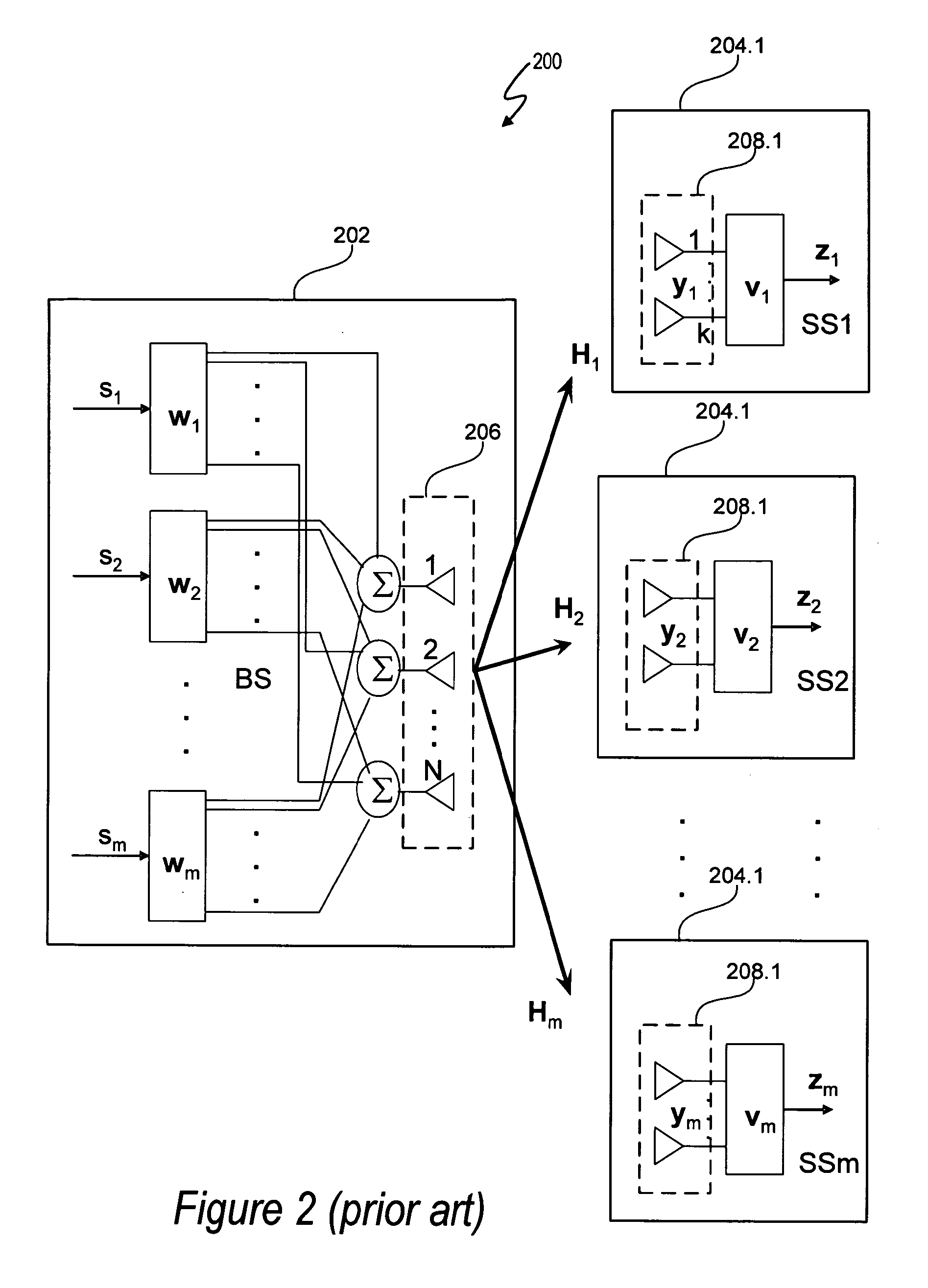
A system and method for opportunistically designing collaborative beamforming vectors is disclosed for a wireless multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) communication system by sequentially designing beamforming vectors for ranked channels in order to exploit the instantaneous channel conditions to improve per user average SNR performance. Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine beamforming vectors for each subscriber station by ranking the subscriber stations by channel strength. Using sequential nullspace methods, the ranked channel matrices are then used to select the channel matrix Hi for the best subscriber station, to design the wi, vi for the best subscriber station as the left and right singular vectors of the MIMO channel matrix Hi, to transform the remaining channels and to continue the process until beamforming vectors are designed for all channels.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods for optimal collaborative MIMO-SDMA
ActiveUS20080076370A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemTrade offs
A system and method for collaboratively designing optimized beamforming vectors is disclosed for a wireless multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) communication system to optimize an aggregate SNR performance metric across the different users, thereby permitting the flexibility to trade off computational requirements and size of control information exchanged with performance. Using adaptive vector space search methods, the space of all receive beamformers is searched to find the set which maximizes either the sum or product of SNRs of the users.
Owner:APPLE INC
Communicating data between an access point and multiple wireless devices over a link
ActiveUS7512096B2Transmission control/equlisationError preventionTransmission protocolTelecommunications
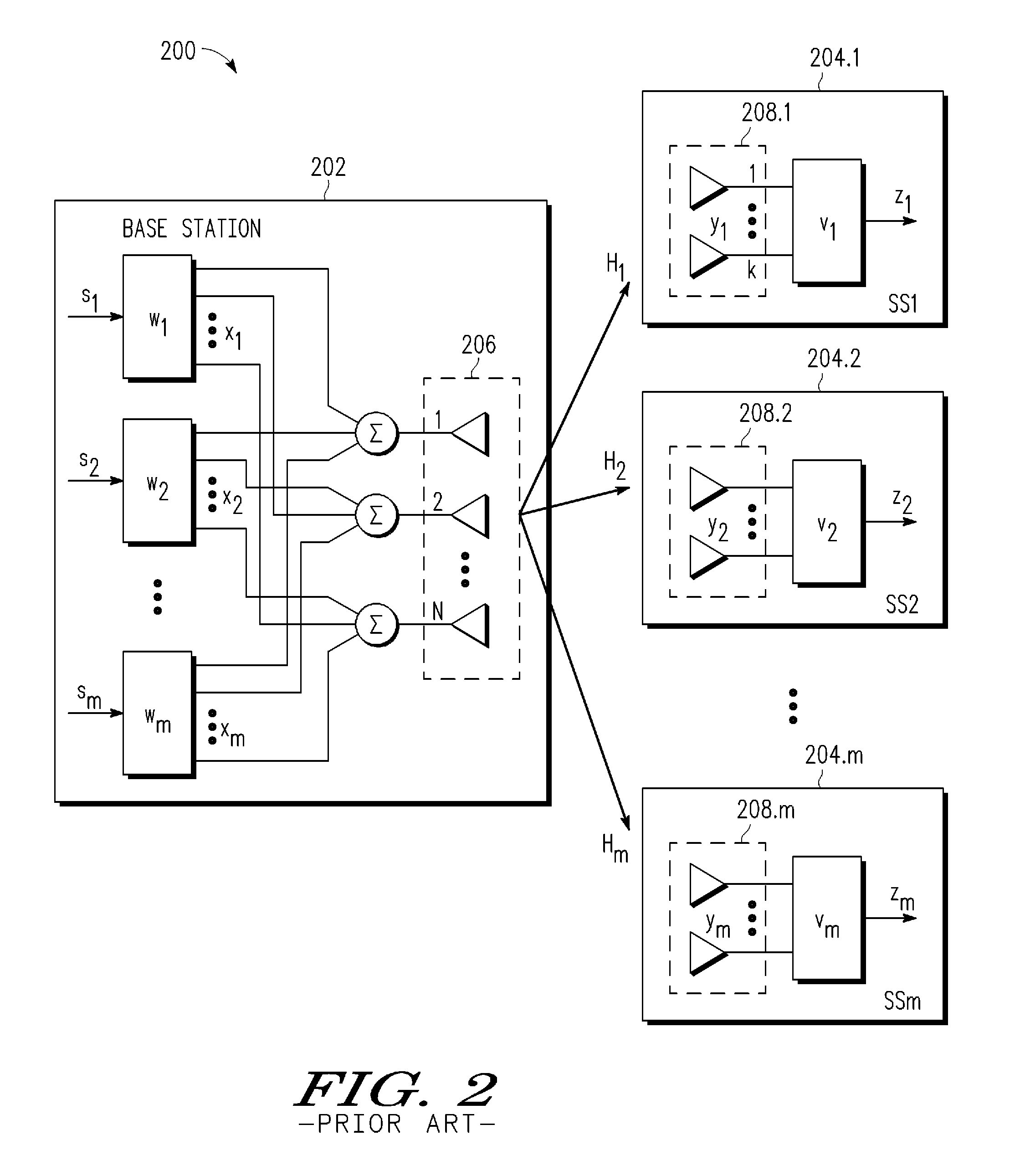
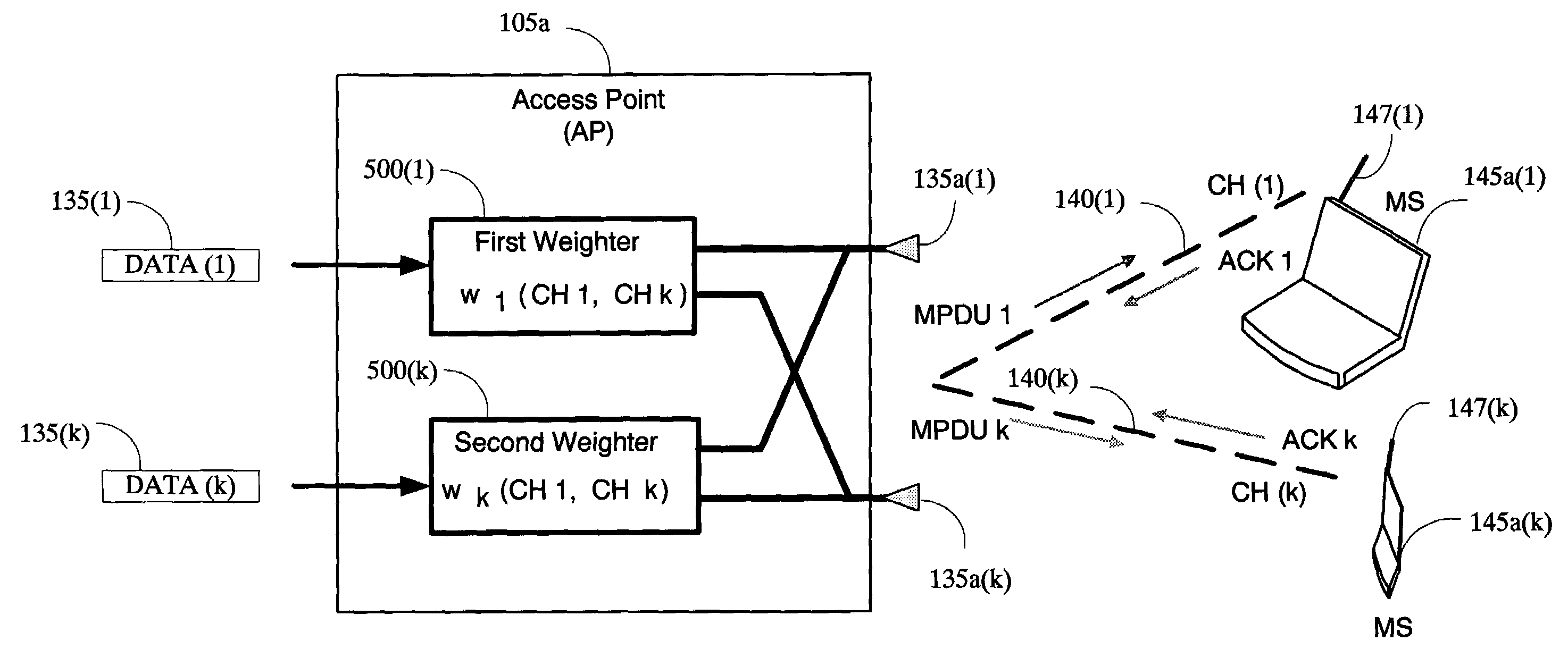
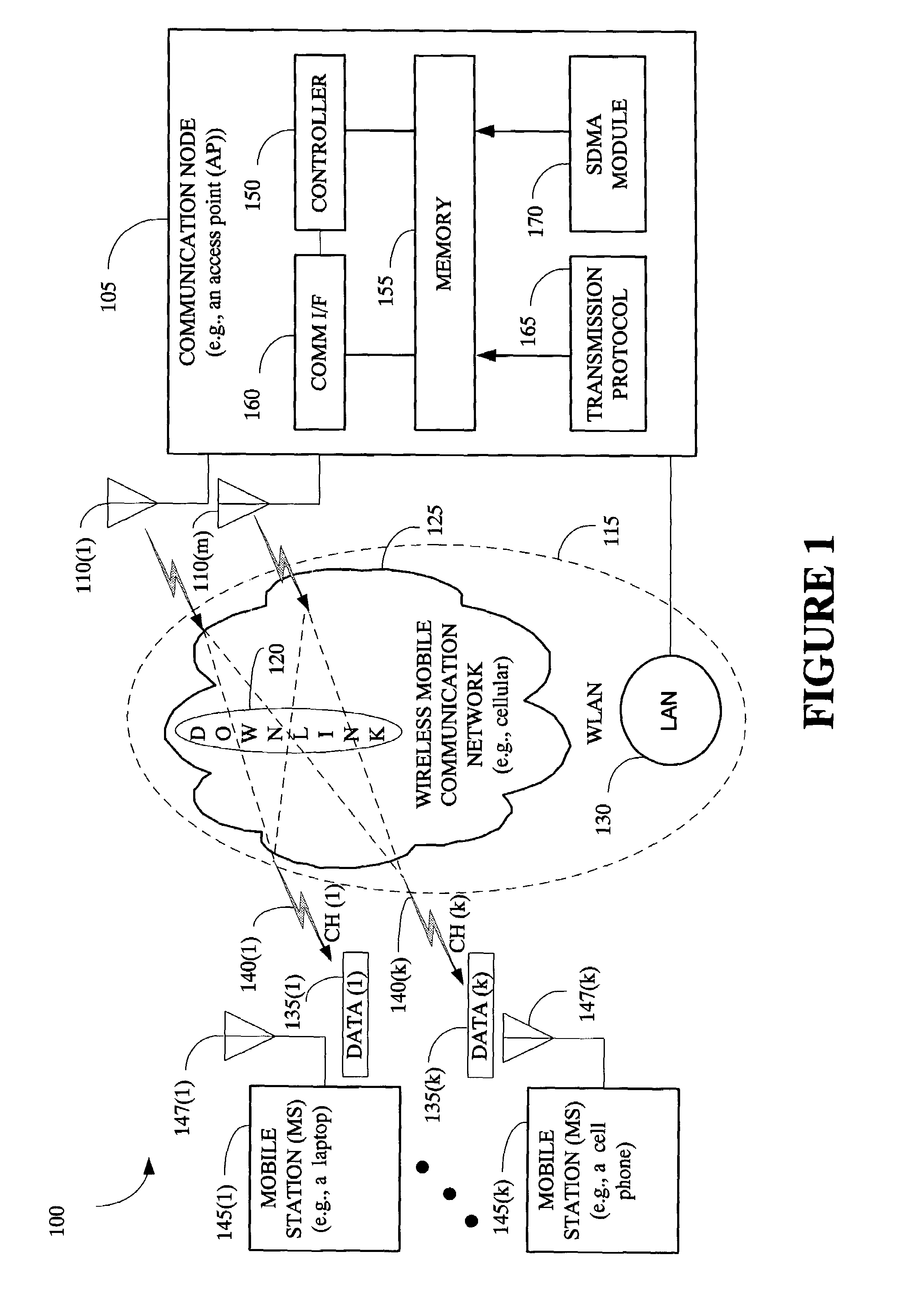
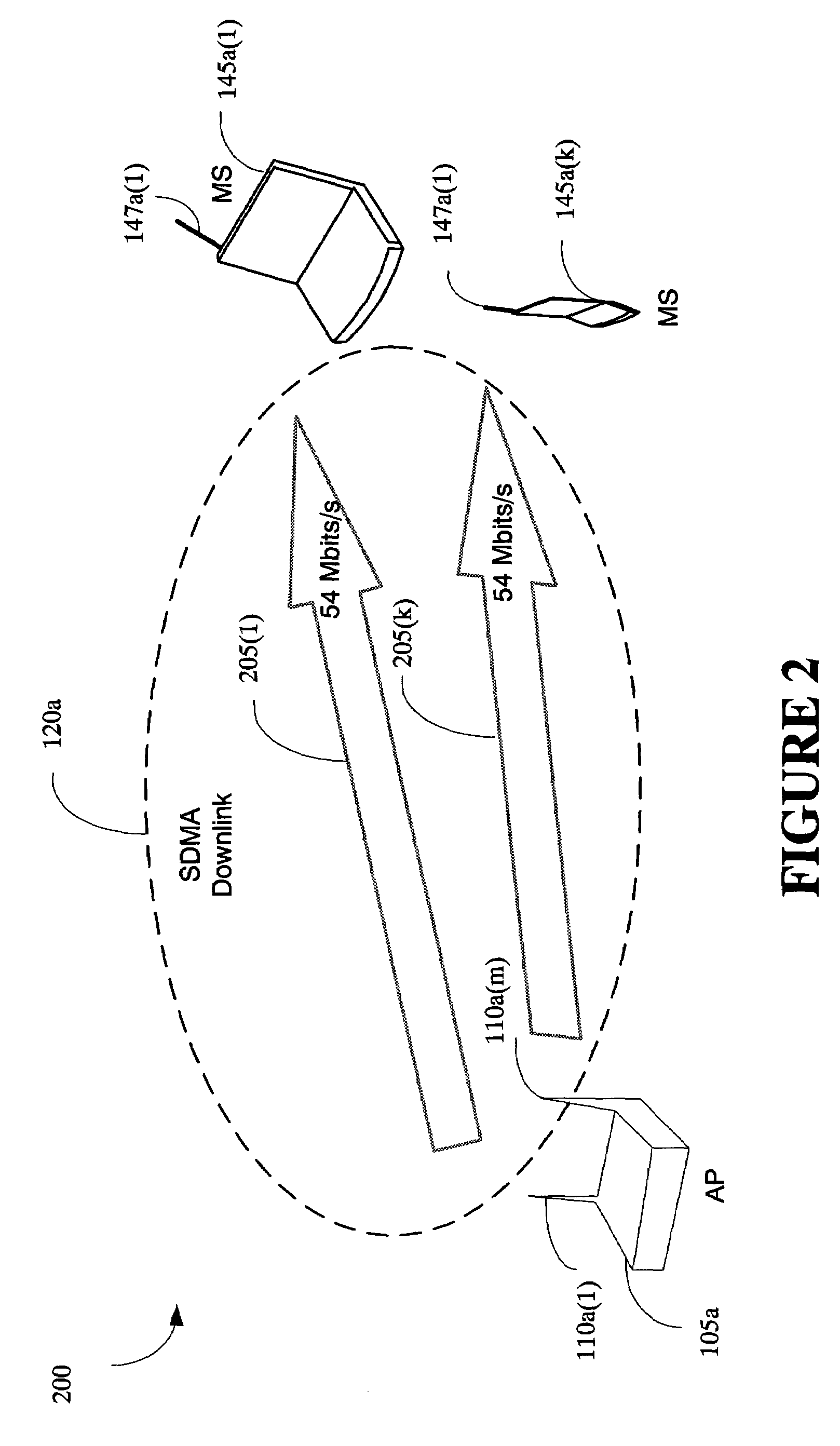
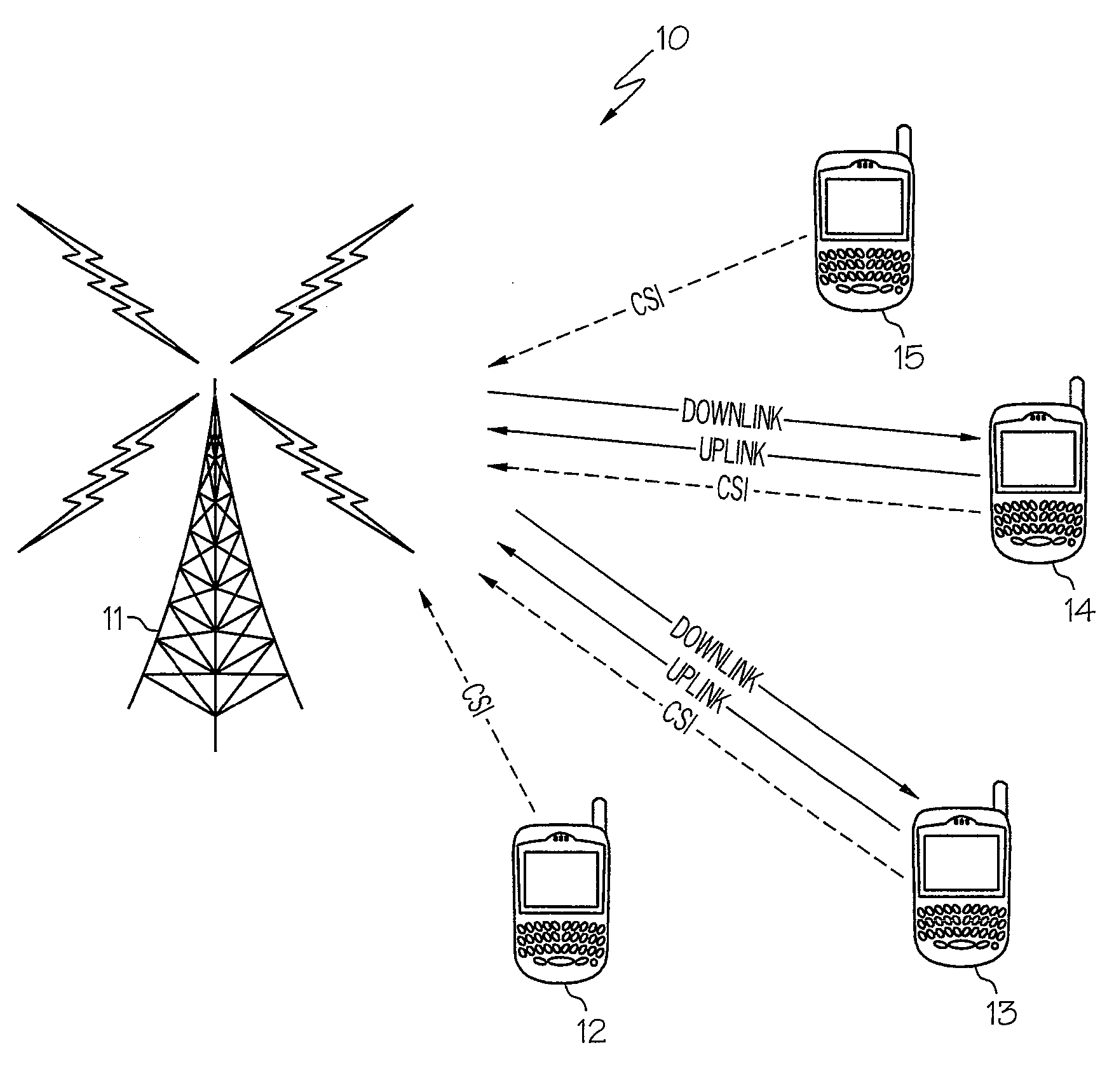
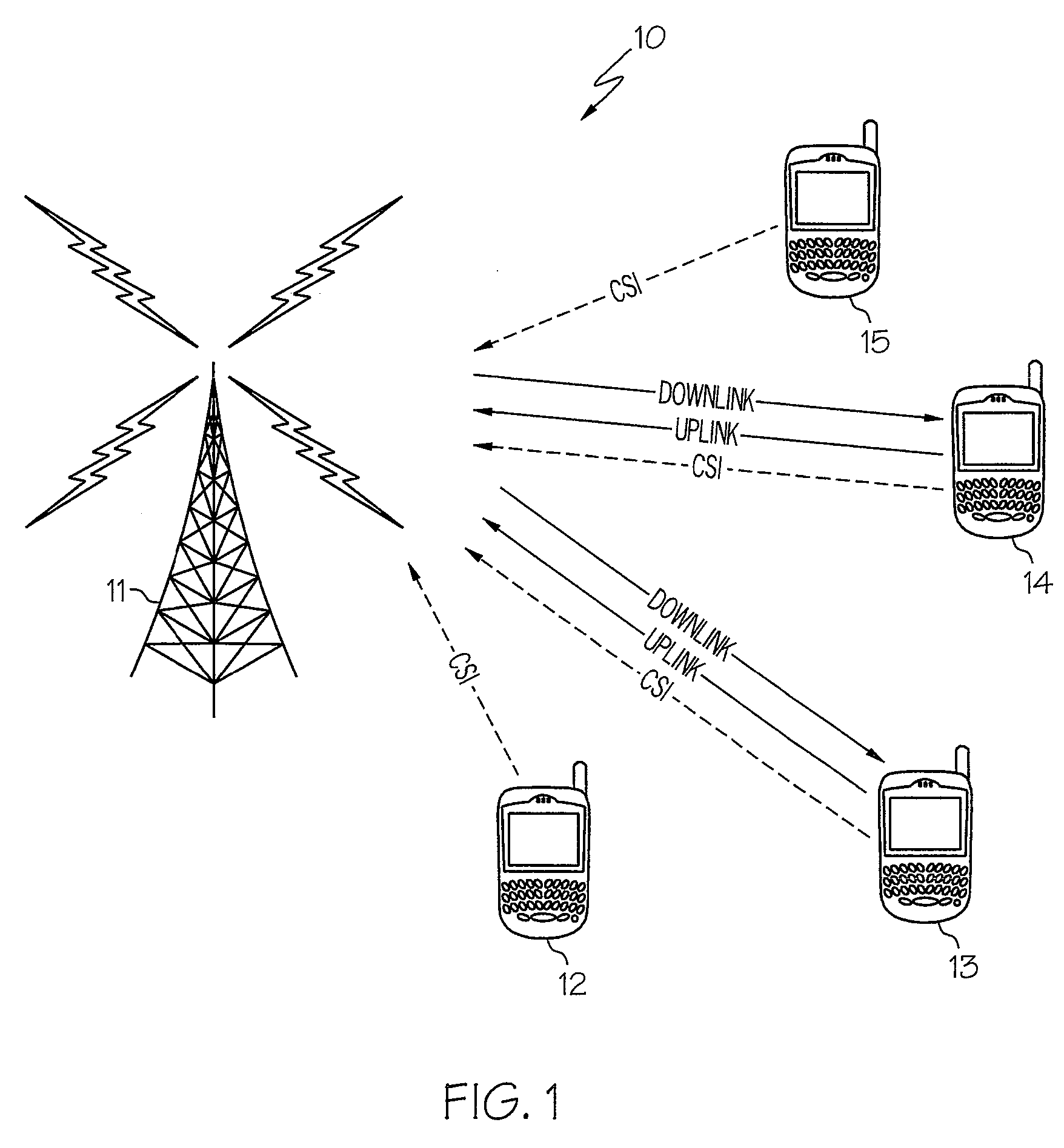
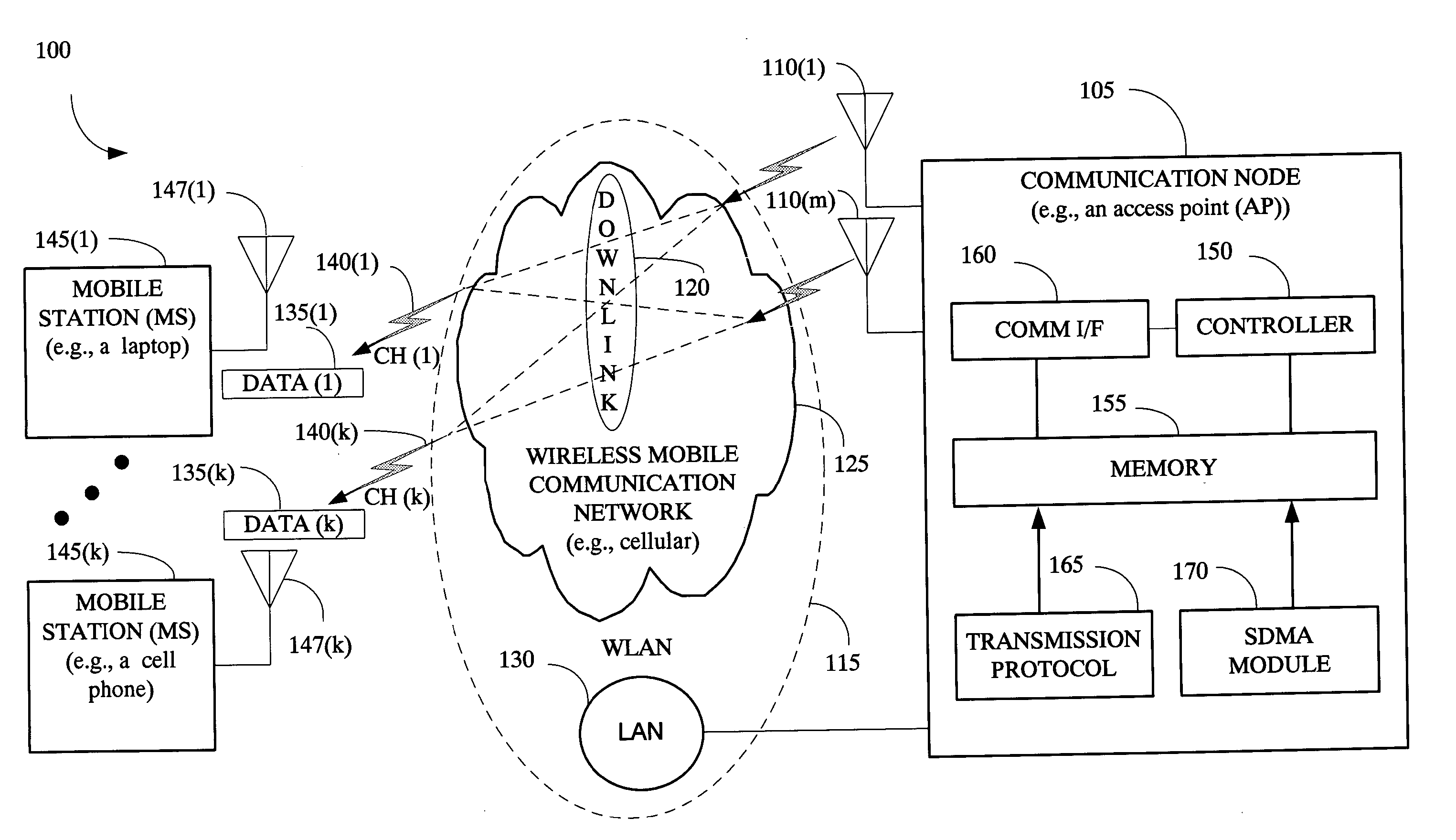
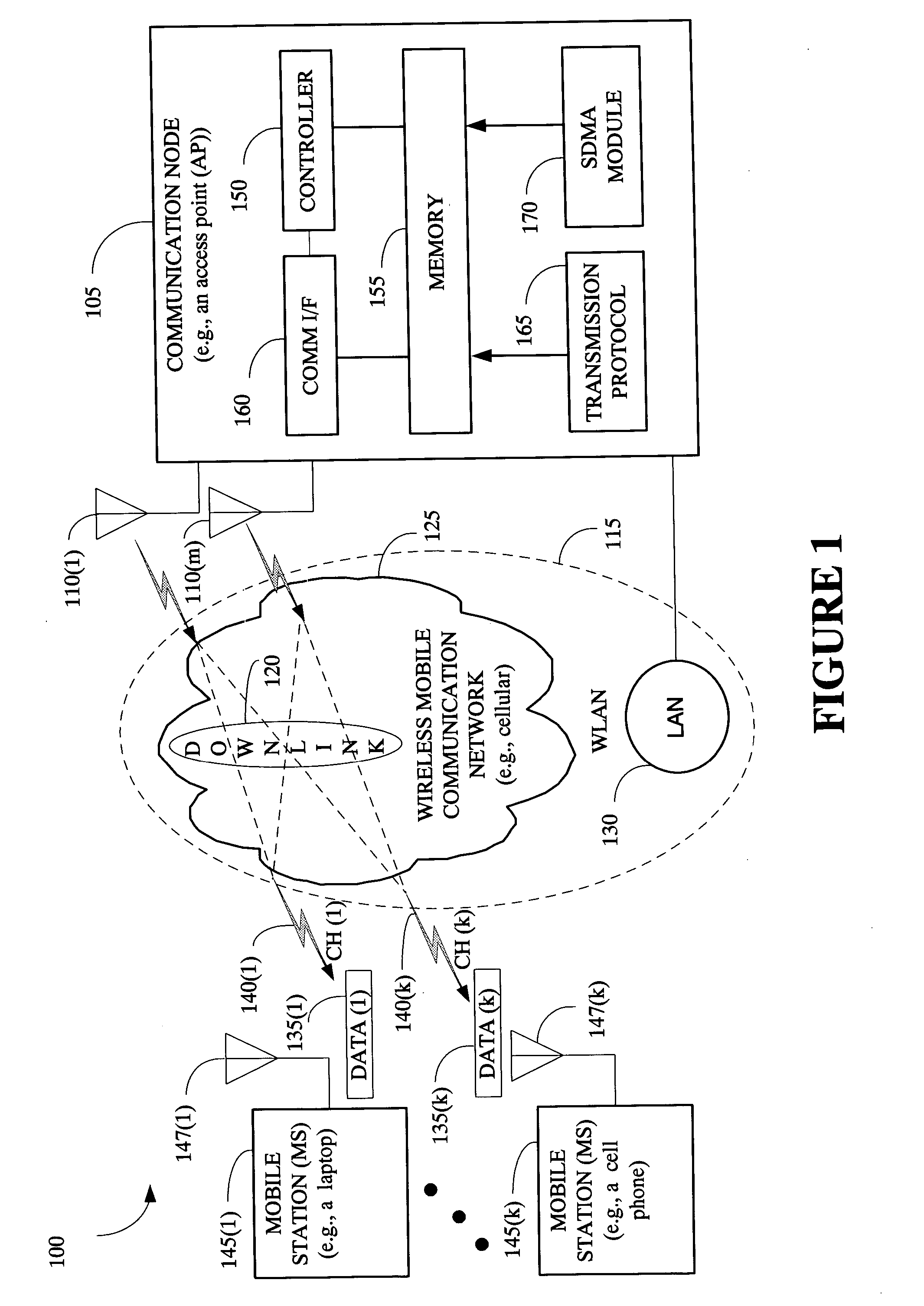
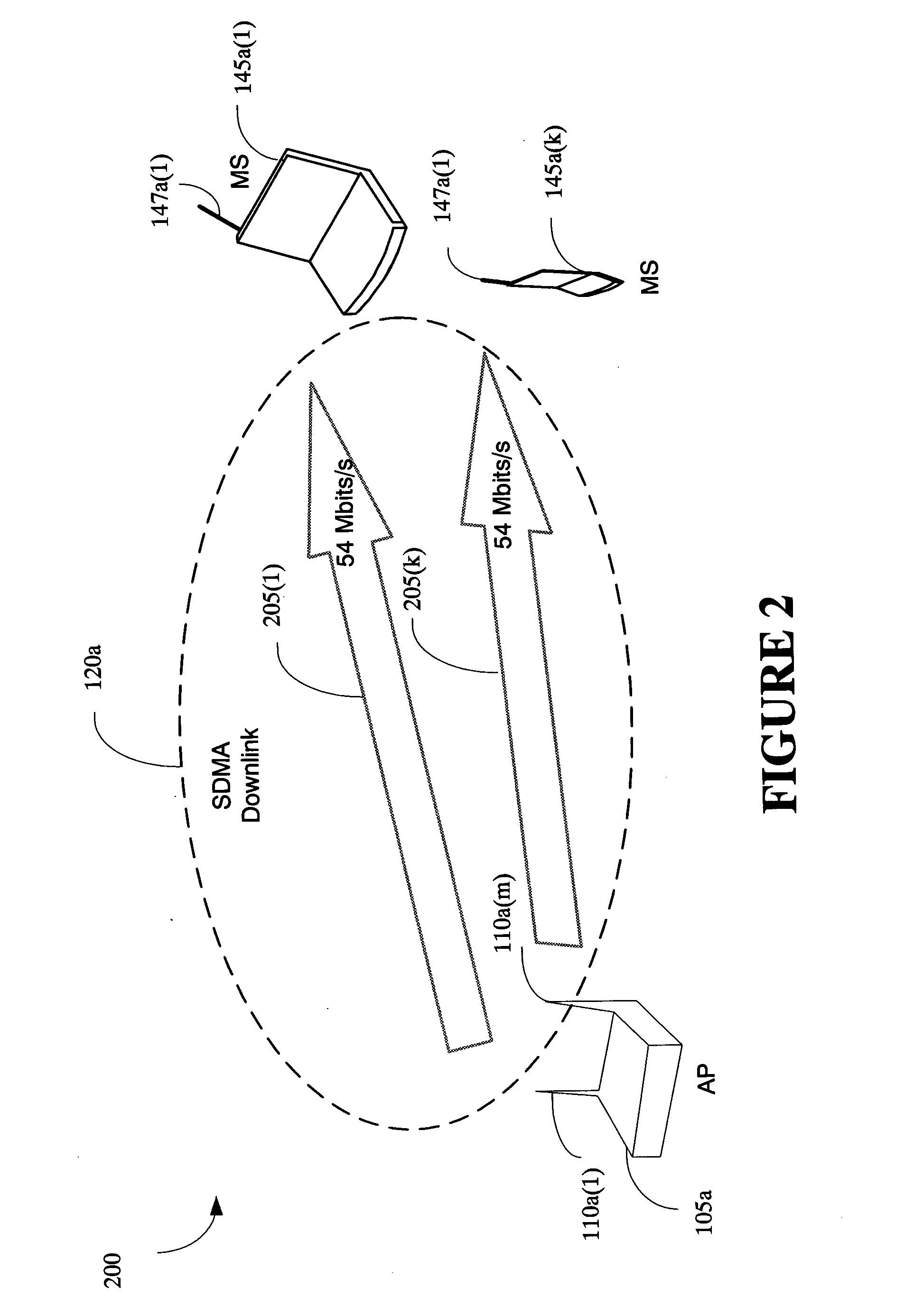
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for communicating data over a network between a communication node, for example, an access point having a first and a second antenna and a first and a second mobile station. The method comprises weighting a first data at the access point to transmit the first data using the first and second antennas so that the first mobile station only receives the first data and weighting a second data at the access point to transmit the second data using the first and second antennas so that the second mobile station only receives the second data. A space division multiple access (SDMA) module may cause a transmission protocol to transmit the first data to the first mobile station on the downlink and transmit the second data to the second mobile station in parallel to the transmission of the first data on the downlink. In a telecommunication system, this substantially simultaneous transmission of the first and second data using a similar carrier frequency in a radio frequency communication over a wireless local area network (WLAN) may increase throughput of a downlink, for example, by a factor nominally equal to the number of antennas at an access point.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
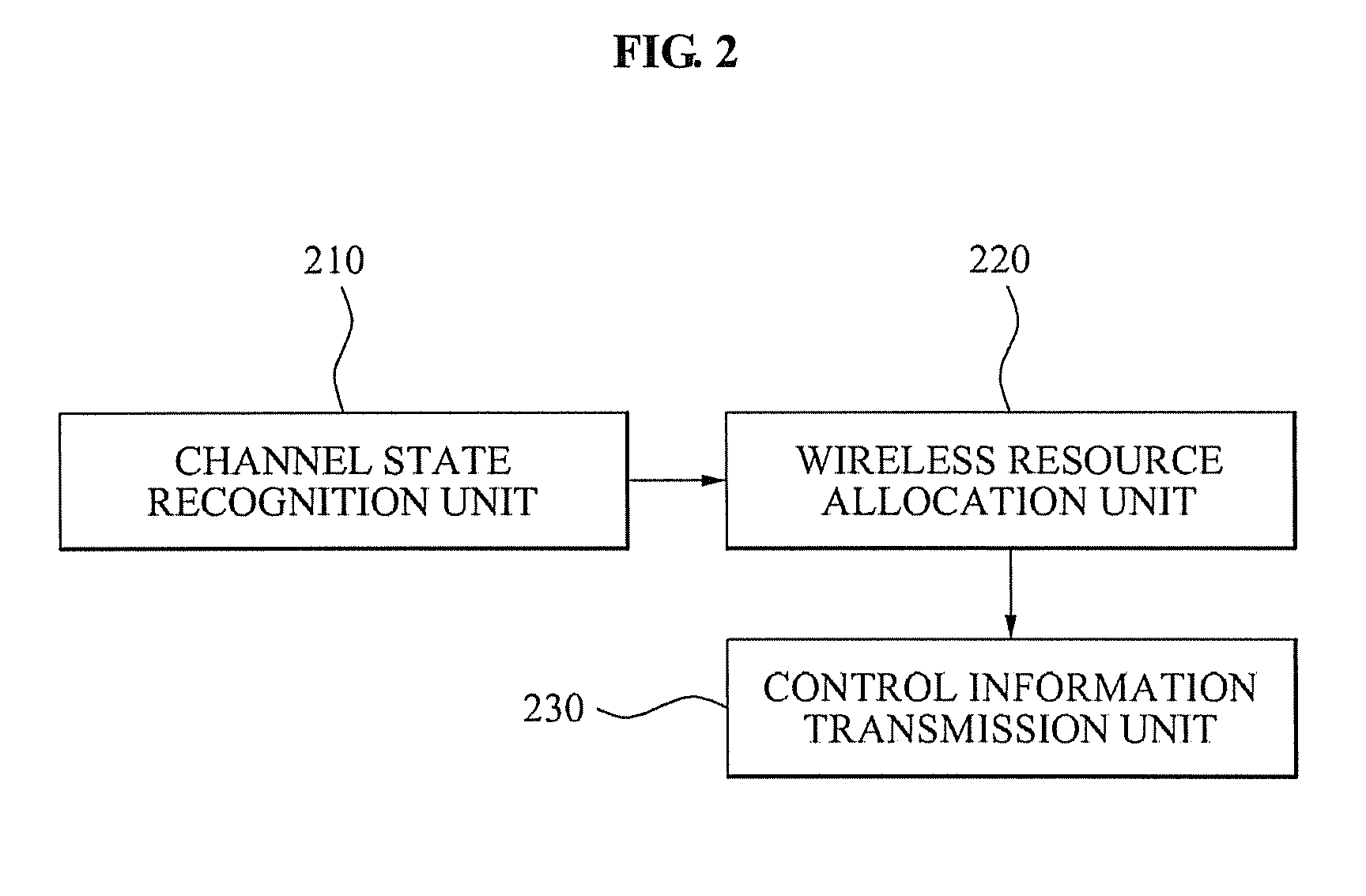
Method of allocating wireless resource for space division multiple access communication and wireless resource allocation system of enabling the method
ActiveUS20090010215A1Increase data rateRaise the ratioFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesChannel state informationTelecommunications
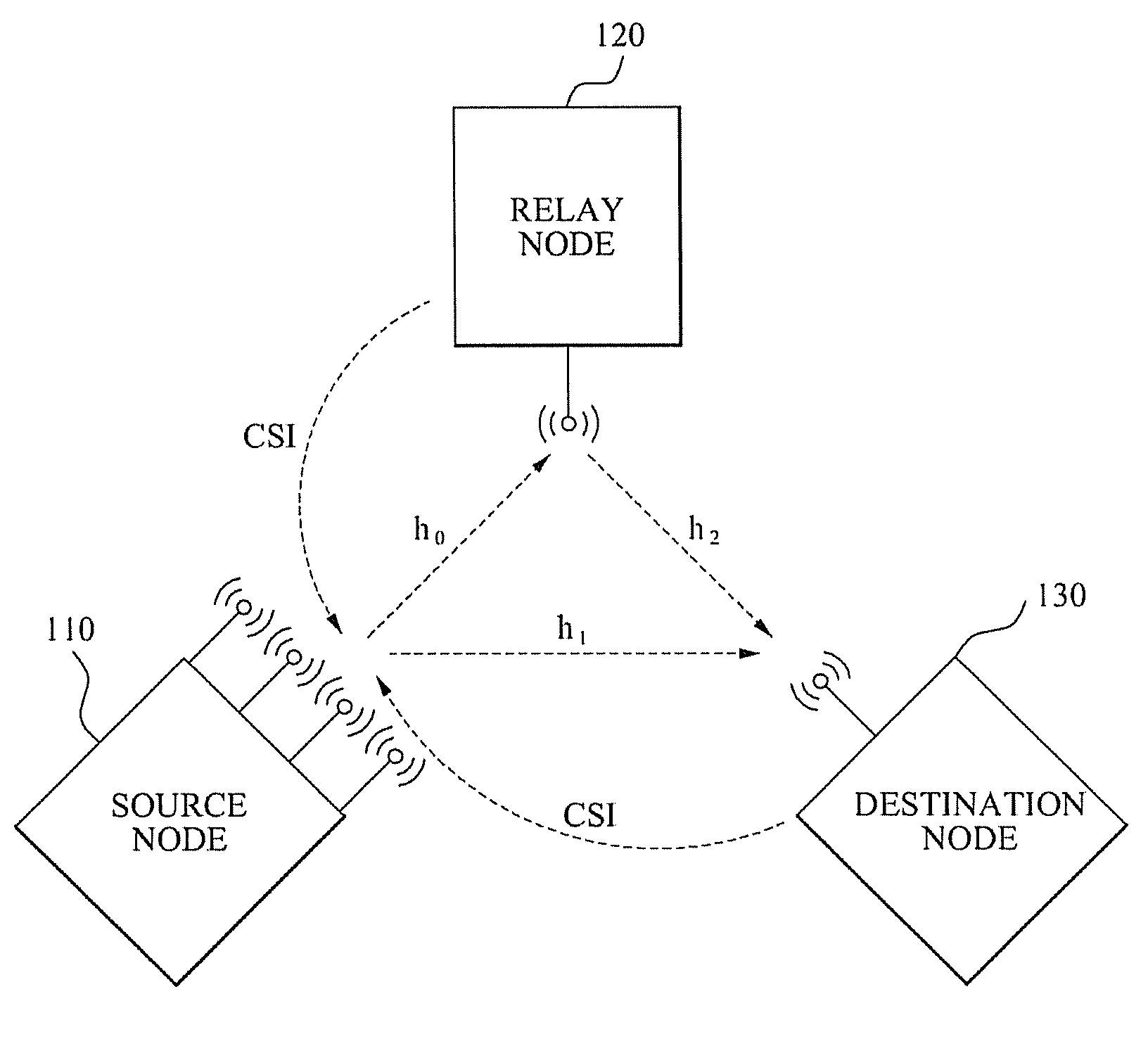
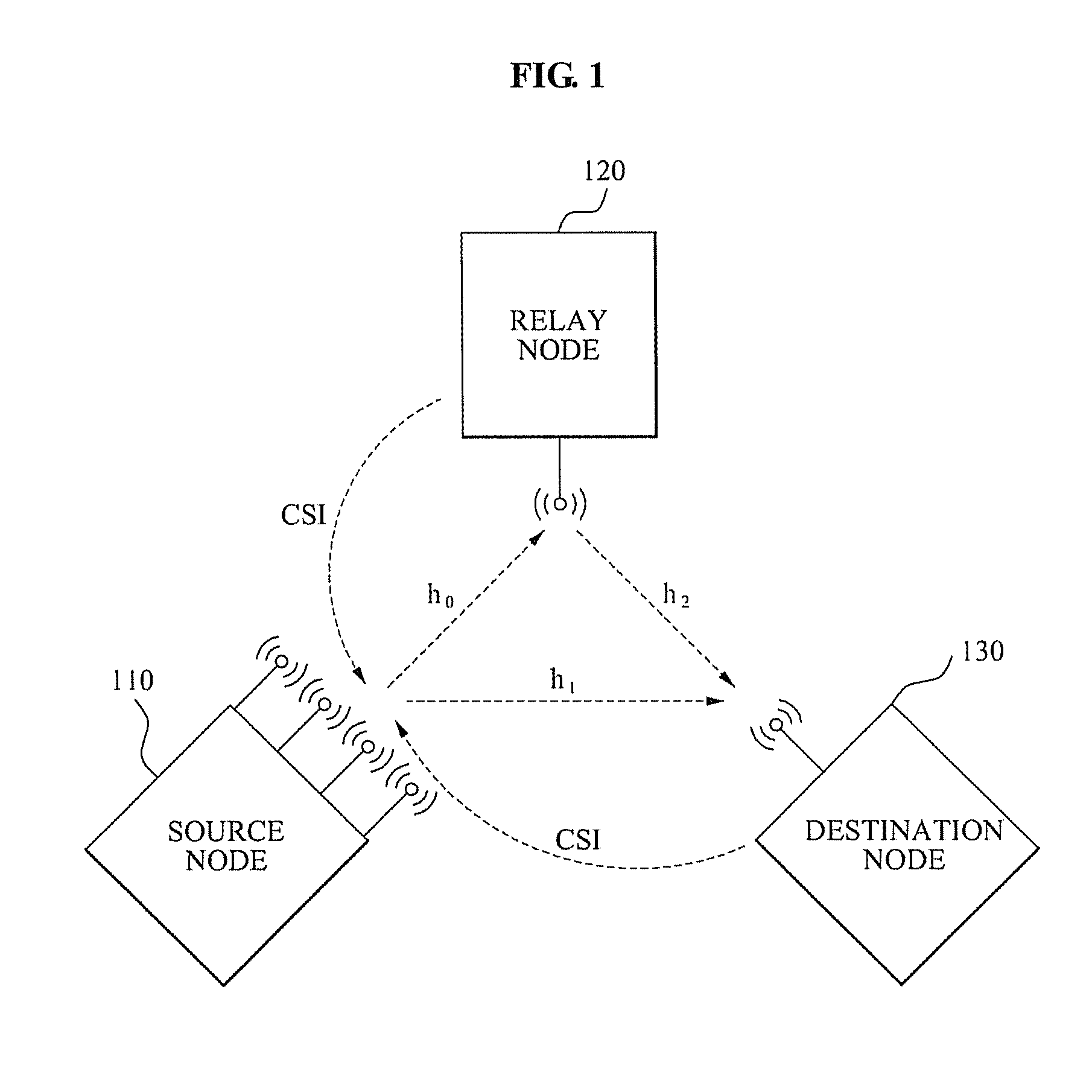
A system for allocating a wireless resource for a Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) communication is provided. The system for allocating the wireless resource for the SDMA communication includes: a channel state recognition unit to recognize a channel state of wireless channels generated among adjacent nodes including a source node, a relay node, and a destination node; and a wireless resource allocation unit to control at least one of an amount of channel state information fed back from the destination node to the source node, and a relay level of a relay signal, the relay signal being generated by relaying a source signal transmitted from the source node, according to the channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
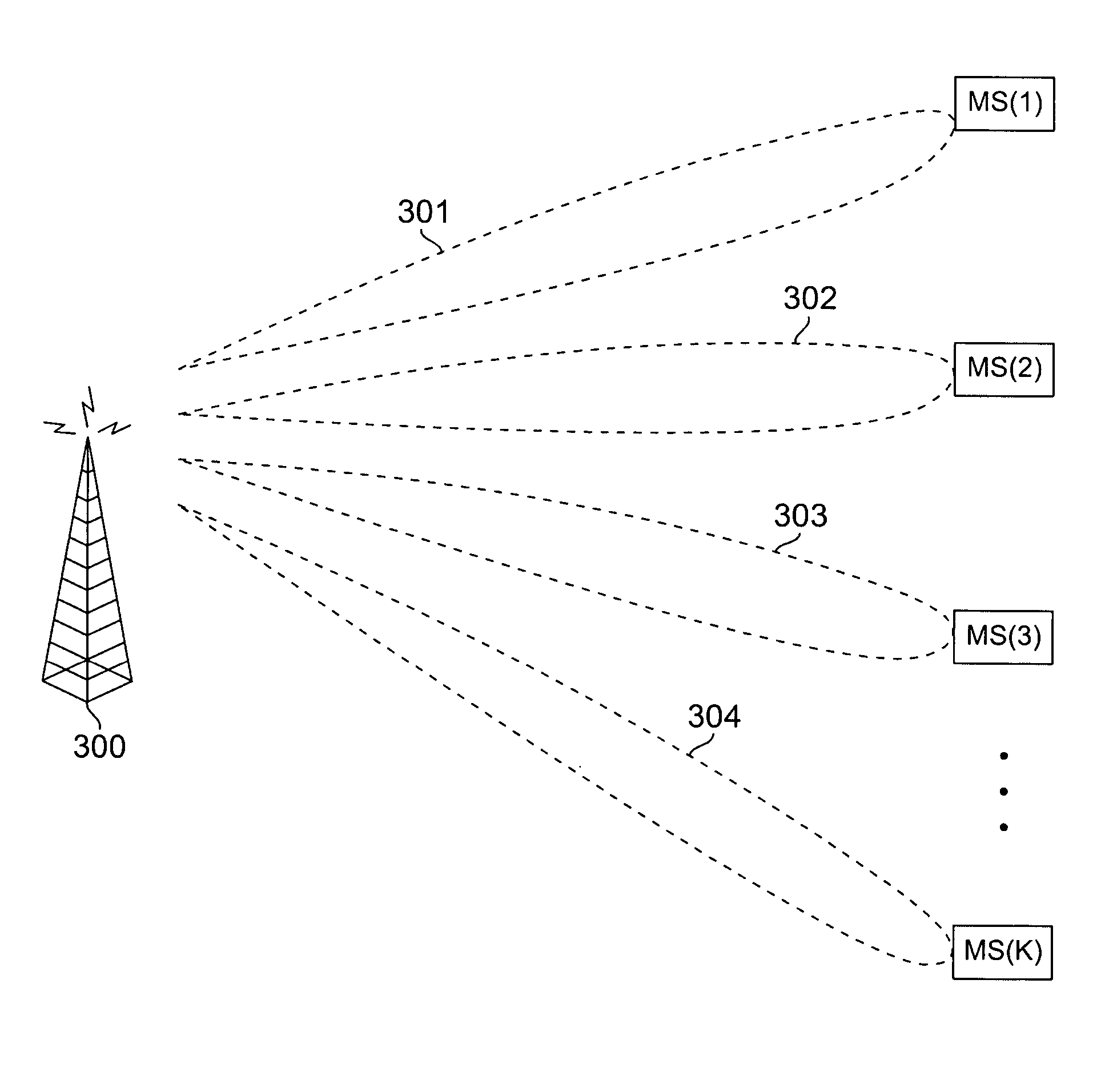
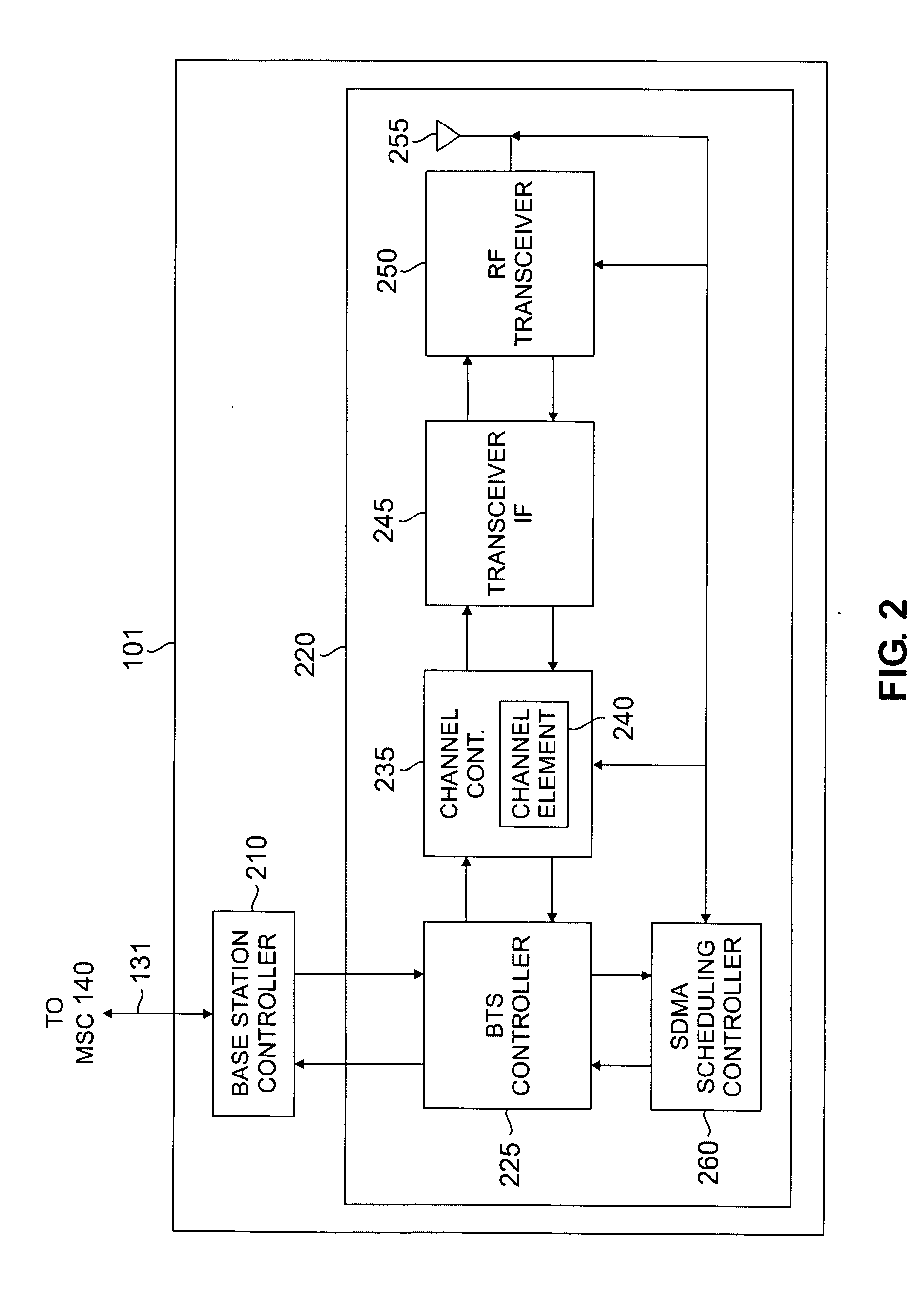
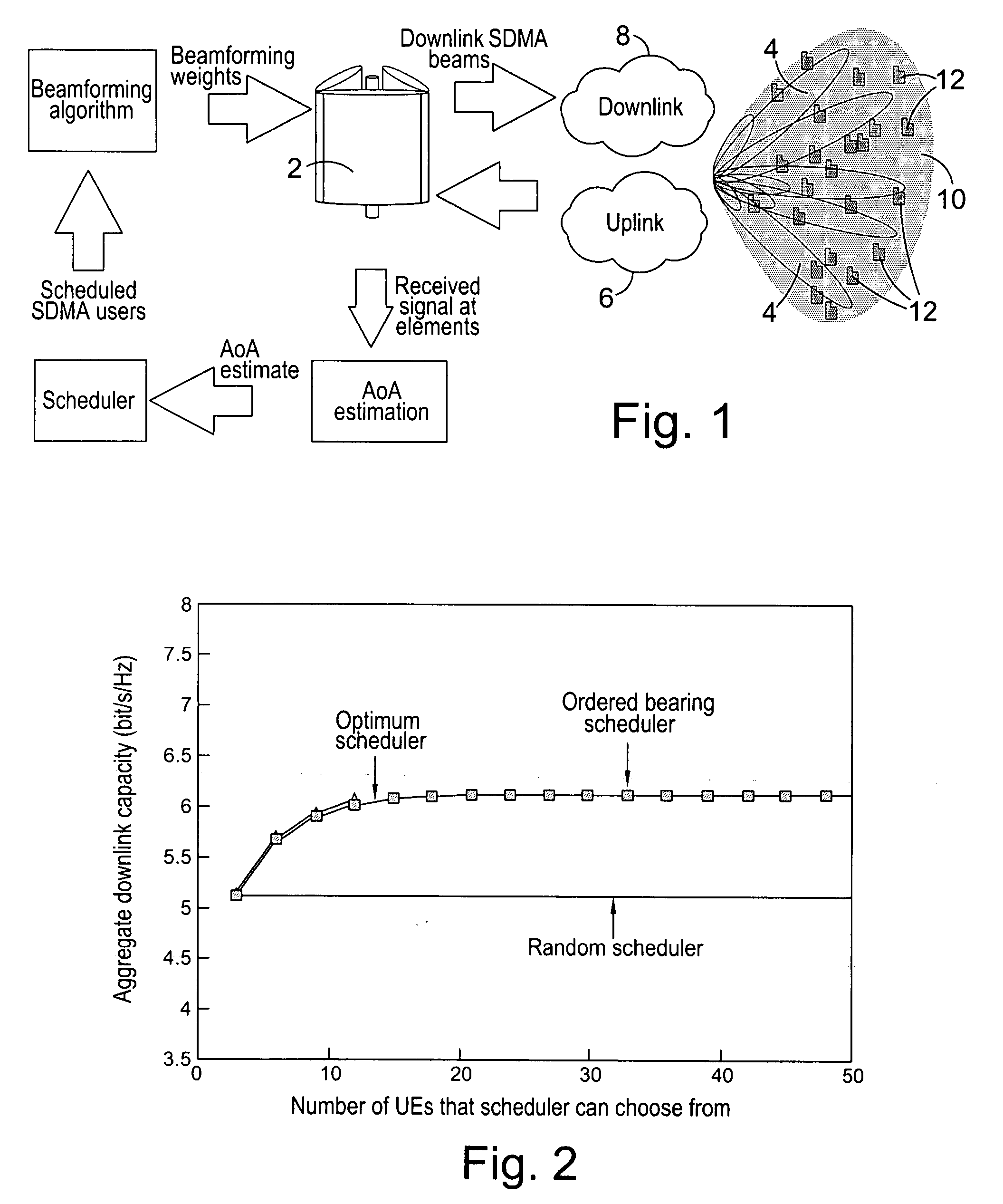
Apparatus and method for downlink spatial division multiple access scheduling in a wireless network
A base station for communicating with mobile stations in a coverage area of the wireless network. The base station comprises: 1) a transceiver for transmitting downlink OFDMA signals to each mobile station; 2) an antenna array for transmitting the downlink OFDMA signals to the mobile stations using spatially directed beams; and 3) an SDMA scheduling controller for scheduling downlink transmissions to the mobile stations. The SDMA scheduling controller determines a first mobile station having a highest priority and schedules the first mobile station for downlink transmission in a particular time-frequency slot. The SDMA scheduling controller then determines additional mobile stations that are spatially uncorrelated with the first mobile station, as well as each other, and schedules the additional mobile stations for downlink transmission in that particular time-frequency slot according to priority.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method, apparatus and system of spatial division multiple access communication in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20070153760A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsSpace-division multiple access
Some demonstrative embodiments of the invention include a method, apparatus, and system of performing simultaneous downlink transmission over a wireless medium to a plurality of wireless stations, using Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). In one demonstrative embodiment of the invention, the method may include synchronizing transmission of first and second data frames to be received by first and second wireless stations, respectively, such that the transmissions of the first and second data frames end substantially simultaneously. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:CELENO COMMUNICATIONS (ISRAEL) LTD
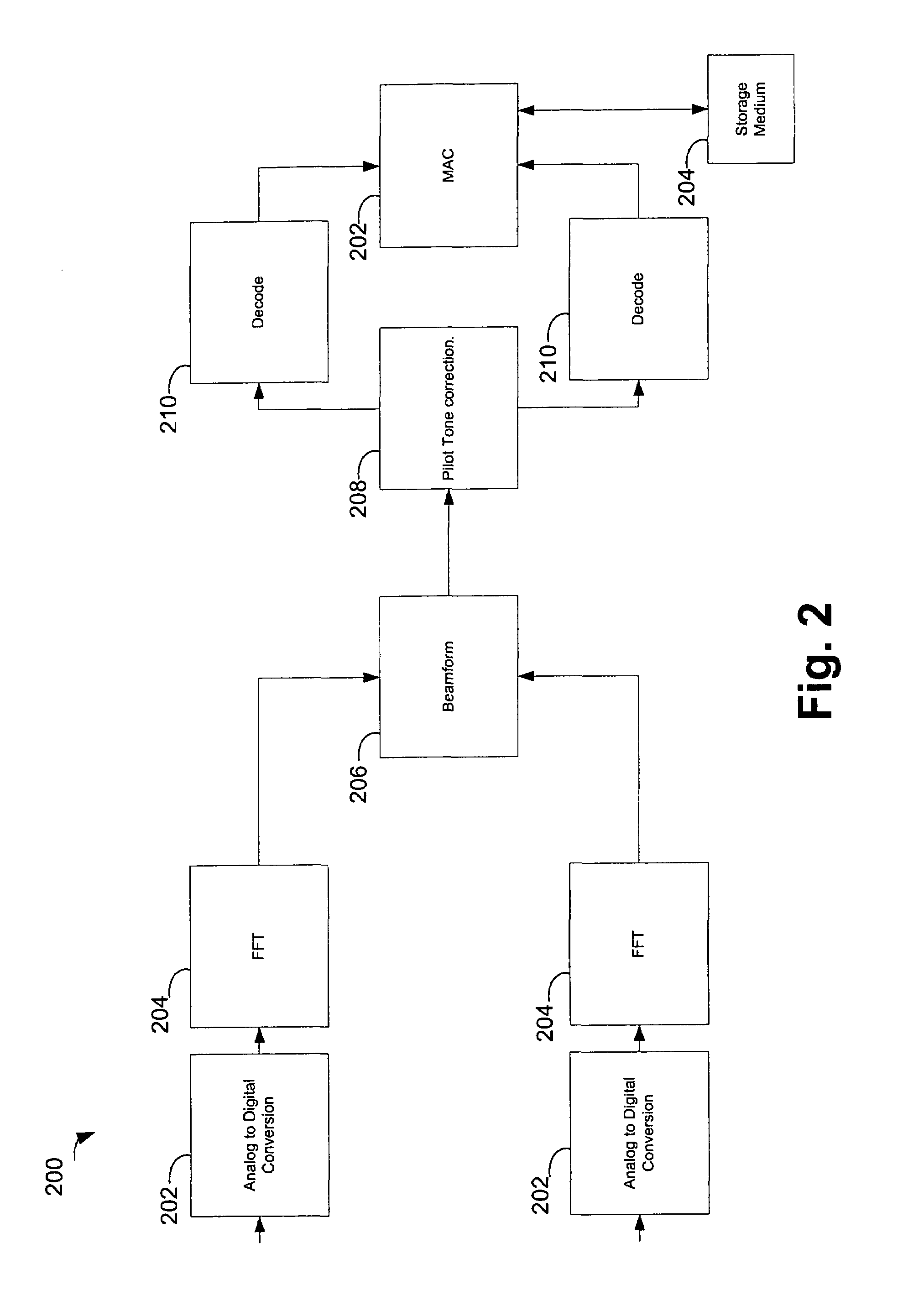
Method and apparatus for performing space division multiple access in a wireless communication network
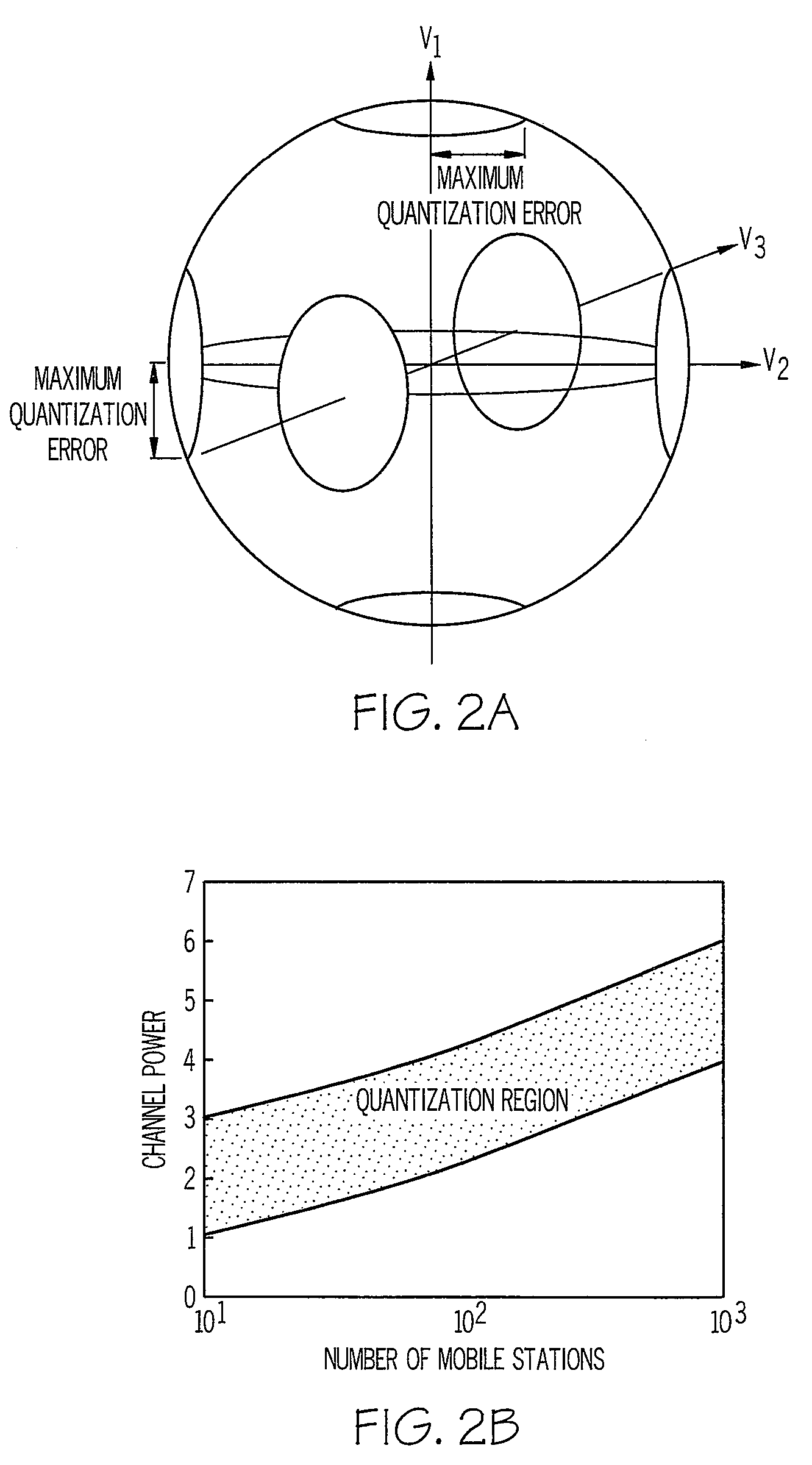
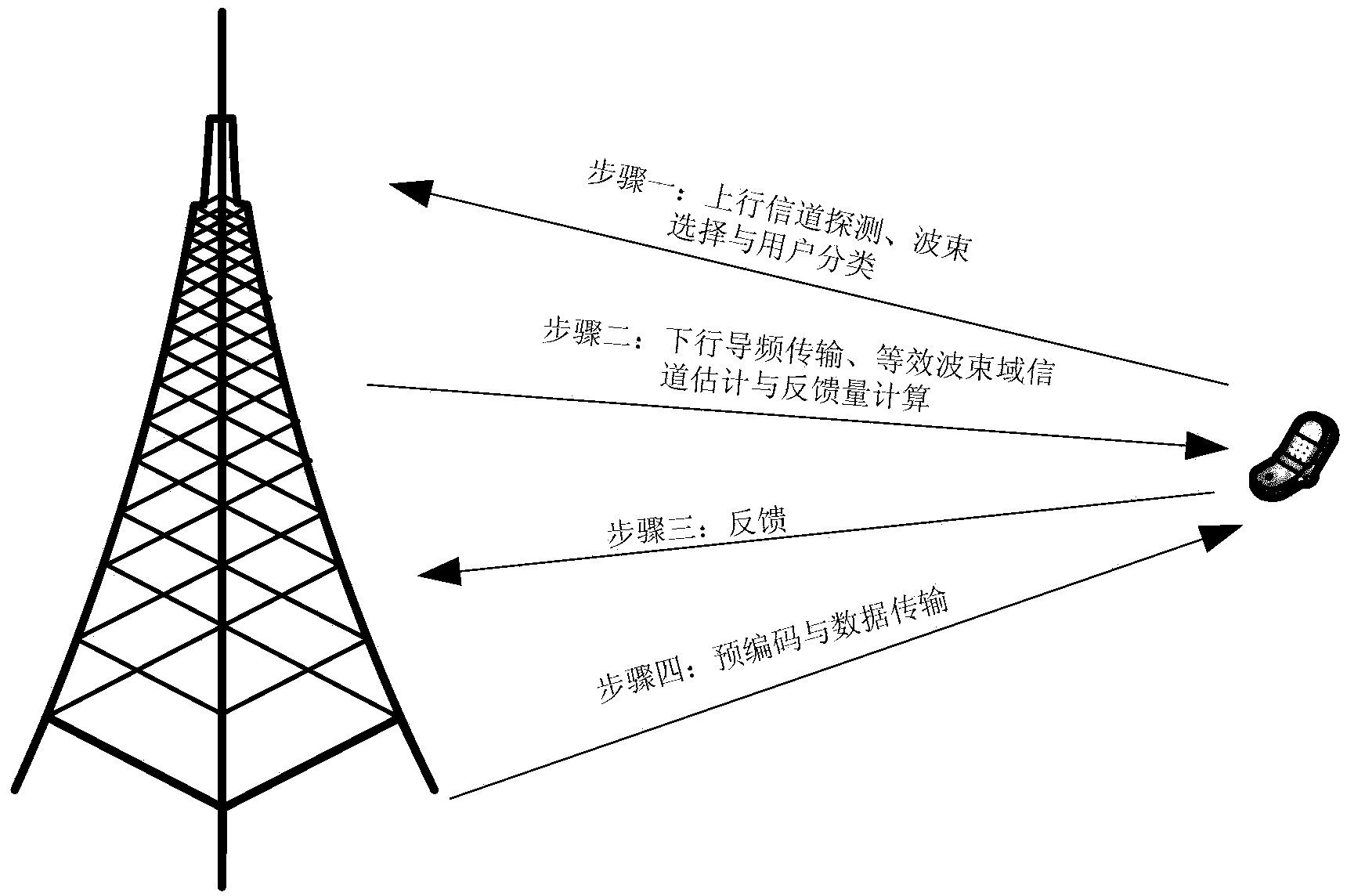
A method and apparatus for performing space division multiple access in wireless communications are disclosed. After the receipt of a set of training data from a base station, an estimated channel state information (CSI) is then generated by a mobile station. The CSI is subsequently quantized. The mobile station then determines whether or not the quantized CSI falls within a set of thresholds. If the quantized CSI falls within the set of thresholds, the mobile then sends feedback information to the base station to allow the base station to consider the mobile station as one of the mobile station candidates available for data communications. Otherwise, if the quantized CSI falls outside the set of thresholds, the mobile station then discards the quantized CSI.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Communicating data between an access point and multiple wireless devices over a link
ActiveUS20060109814A1Transmission control/equlisationError preventionTransmission protocolTelecommunications
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for communicating data over a network between a communication node, for example, an access point having a first and a second antenna and a first and a second mobile station. The method comprises weighting a first data at the access point to transmit the first data using the first and second antennas so that the first mobile station only receives the first data and weighting a second data at the access point to transmit the second data using the first and second antennas so that the second mobile station only receives the second data. A space division multiple access (SDMA) module may cause a transmission protocol to transmit the first data to the first mobile station on the downlink and transmit the second data to the second mobile station in parallel to the transmission of the first data on the downlink. In a telecommunication system, this substantially simultaneous transmission of the first and second data using a similar carrier frequency in a radio frequency communication over a wireless local area network (WLAN) may increase throughput of a downlink, for example, by a factor nominally equal to the number of antennas at an access point.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for generating preamble sequence for adaptive antenna system in orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
ActiveUS20050243940A1Network traffic/resource managementCode division multiplexTelecommunicationsCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for generating a preamble sequence for an adaptive antenna system supporting a space division multiple access in an OFDMA communication system. Particularly, disclosed is a method for forming a preamble sequence identifying each of a plurality of mobile subscriber stations located within a cell or a sector of a communication system which includes a plurality of sub-channels assigned to the mobile subscriber stations, each of the sub-channels including a plurality of bins each of which includes n number of contiguous subcarriers in a frequency domain, the preamble sequence being transmitted before each of the sub-channels is transmitted, the method including the step of generating a preamble sequence by phase-shifting a predetermined sequence according to a predetermined phase shift sequence in the frequency domain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
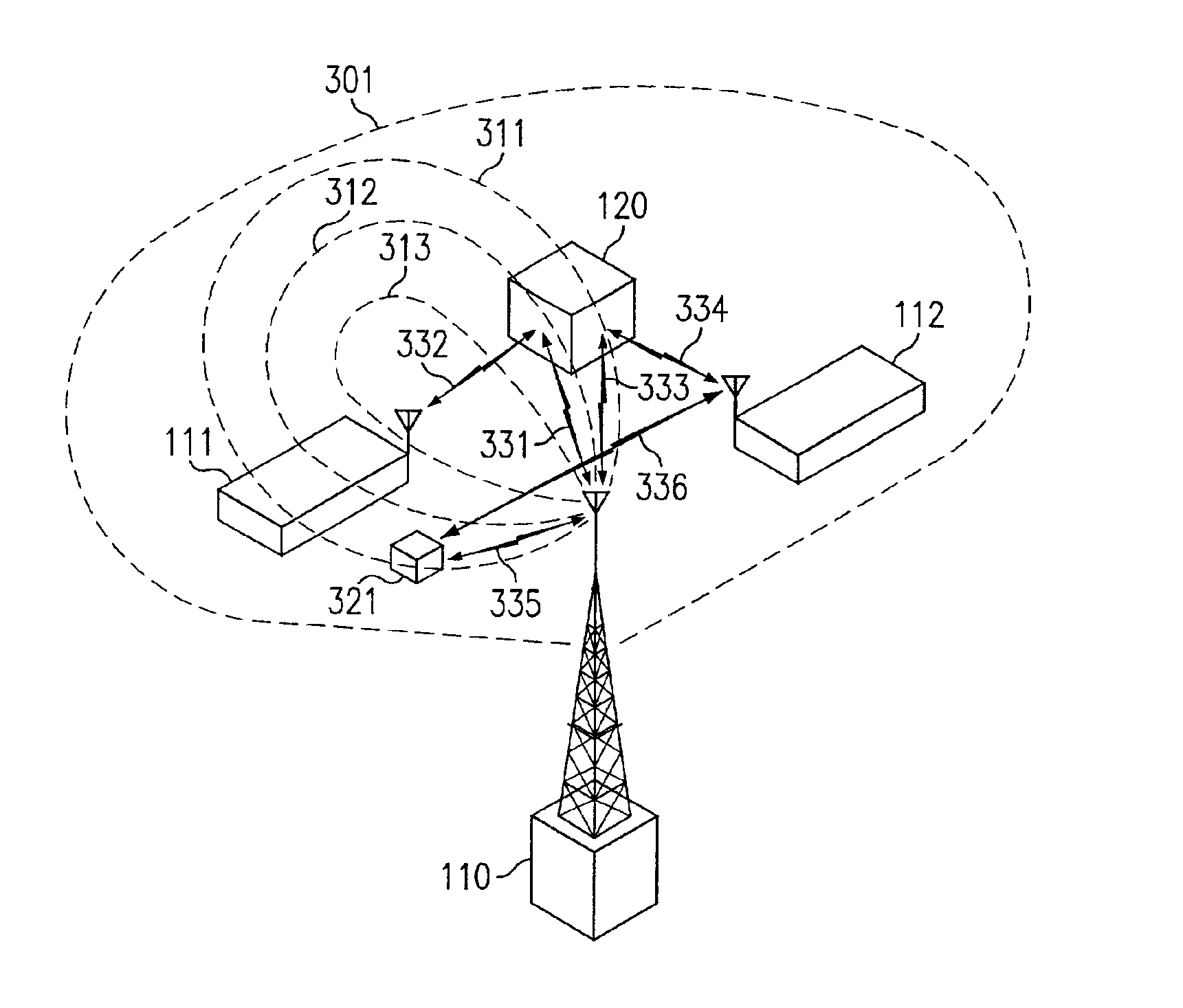
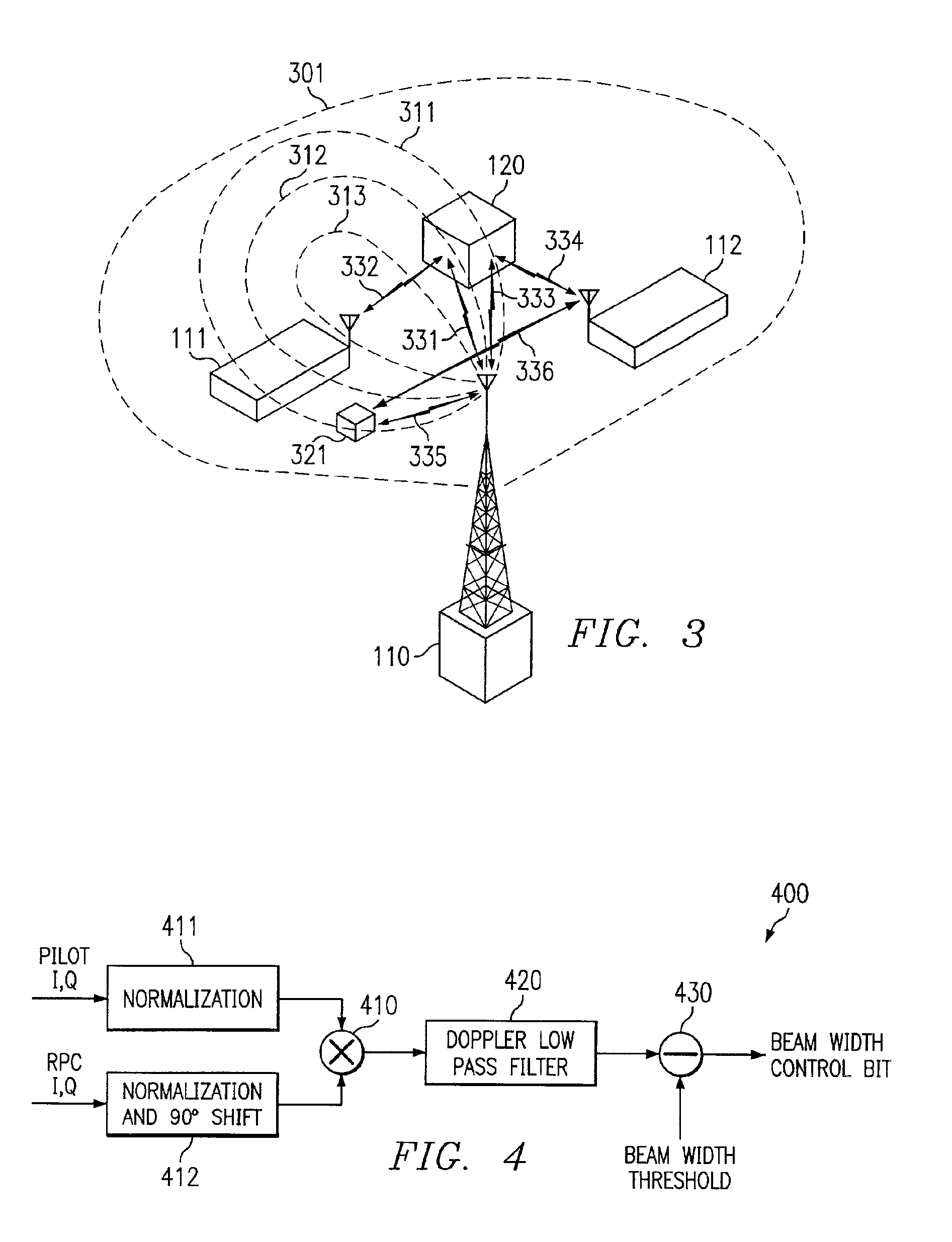
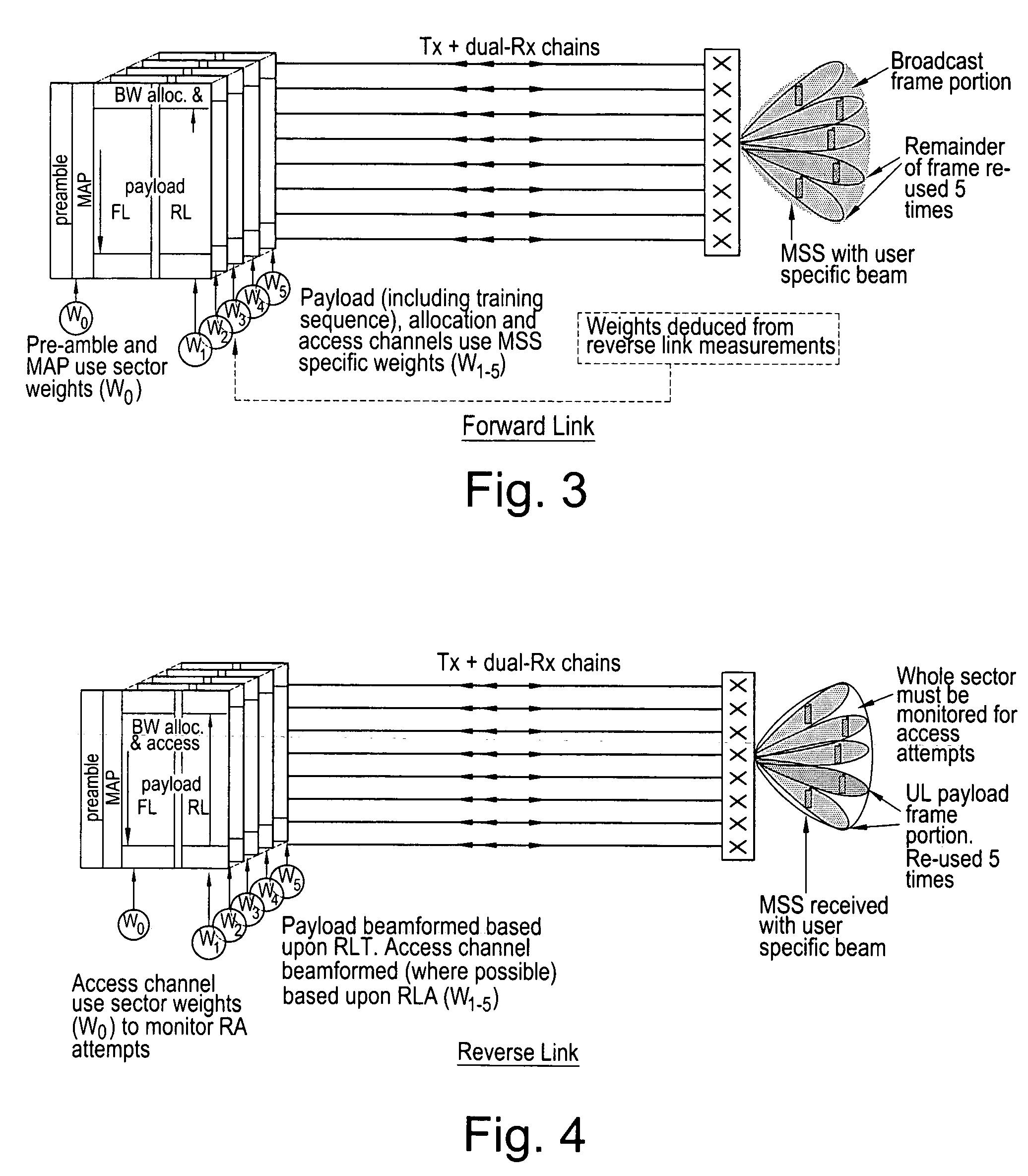
Space division multiple access strategy for data service
InactiveUS6895258B1Facilitate communicationEnsure isolationSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentQuality of serviceEngineering
Disclosed are systems and methods which select multiple communication beams for simultaneous use such that potential scatters (e.g. reflectors) are not illuminated by simultaneous transmissions. Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide for maximizing aggregate throughput by continuously selecting the best subscriber station combination to be serviced simultaneously, such as based upon their spatial status and Quality of Service (QOS) metrics. Additionally or alternatively, embodiments of the present invention may facilitate demodulation reference using a system common pilot, training sequence, or other system signal.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
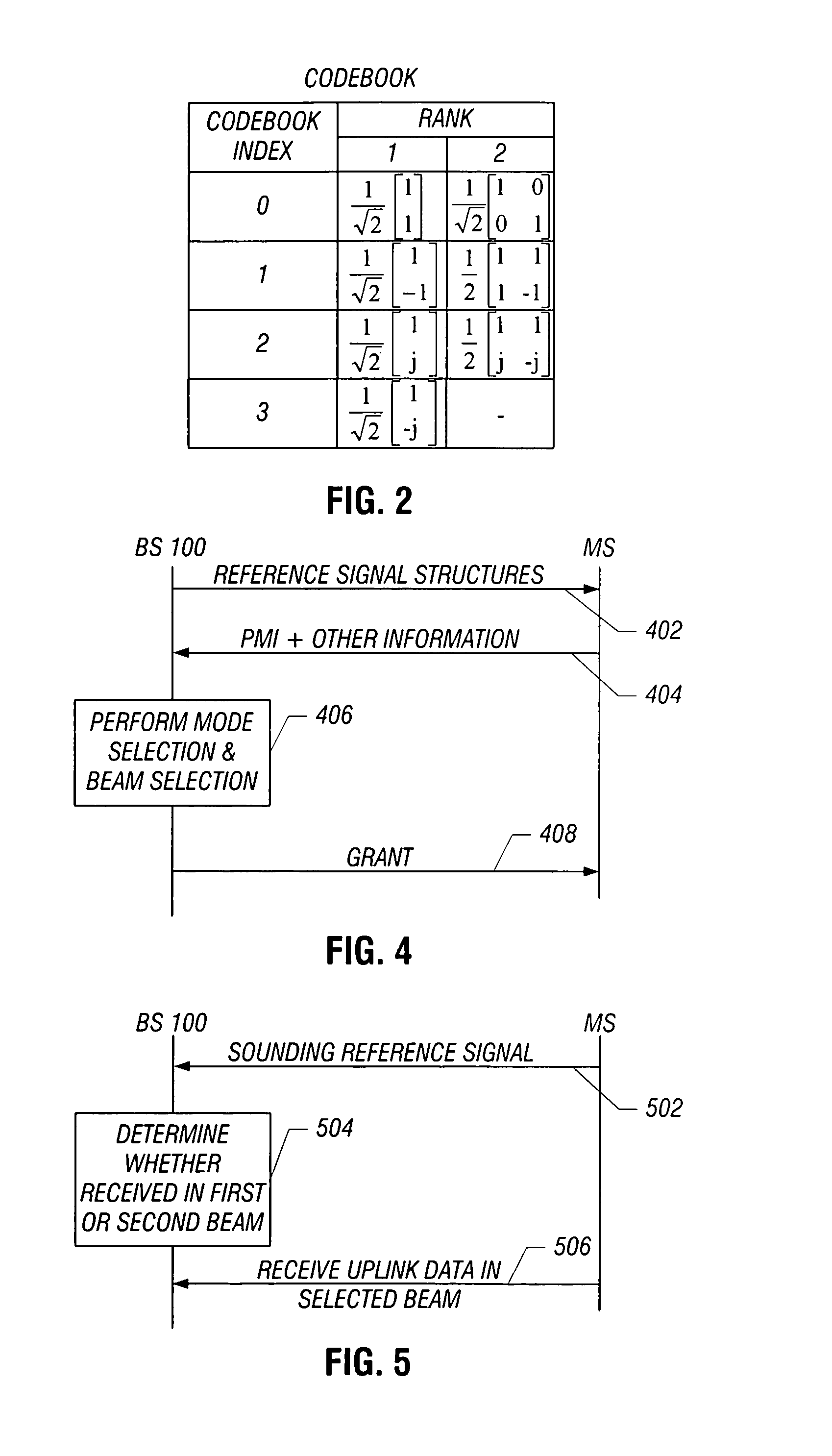
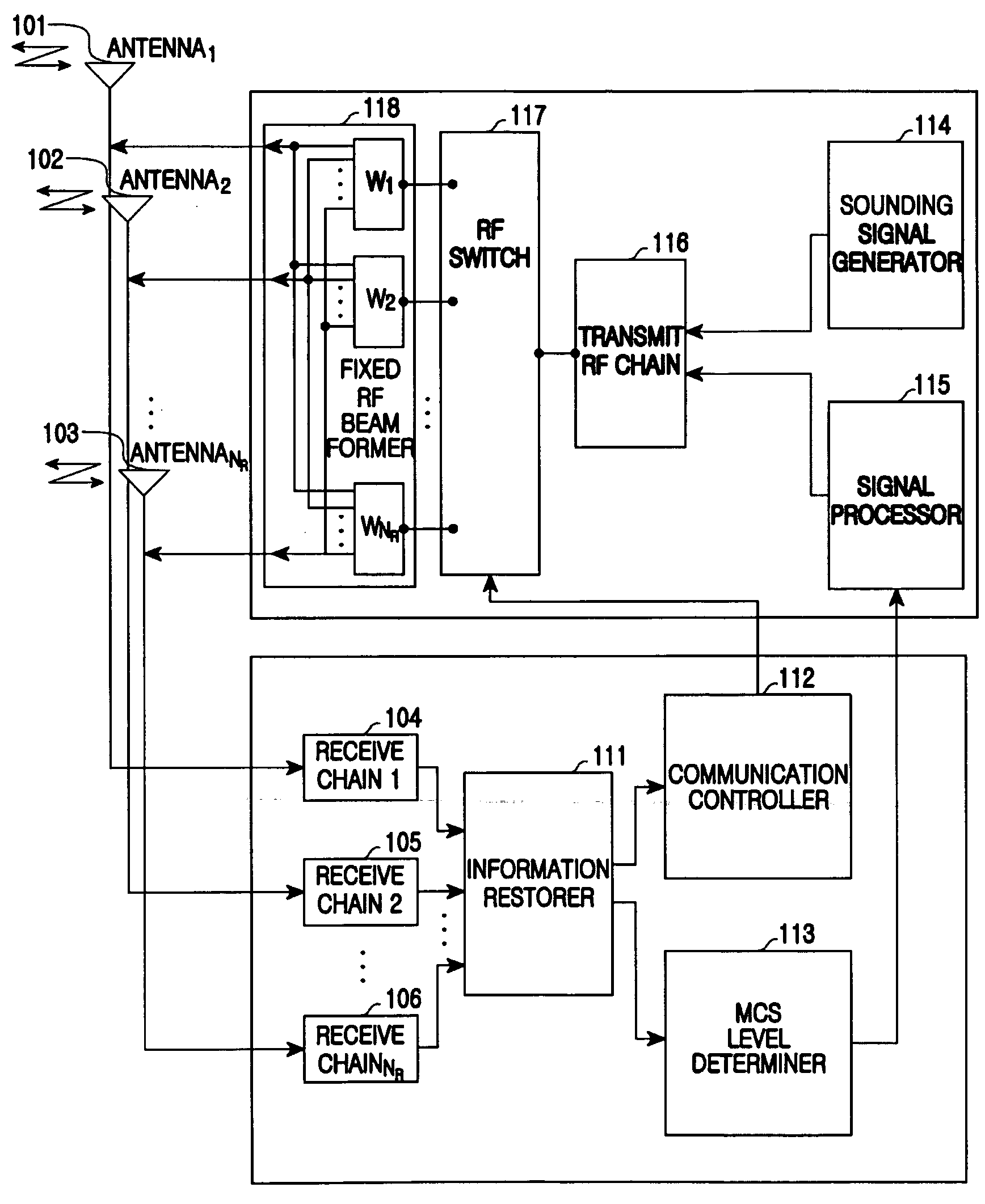
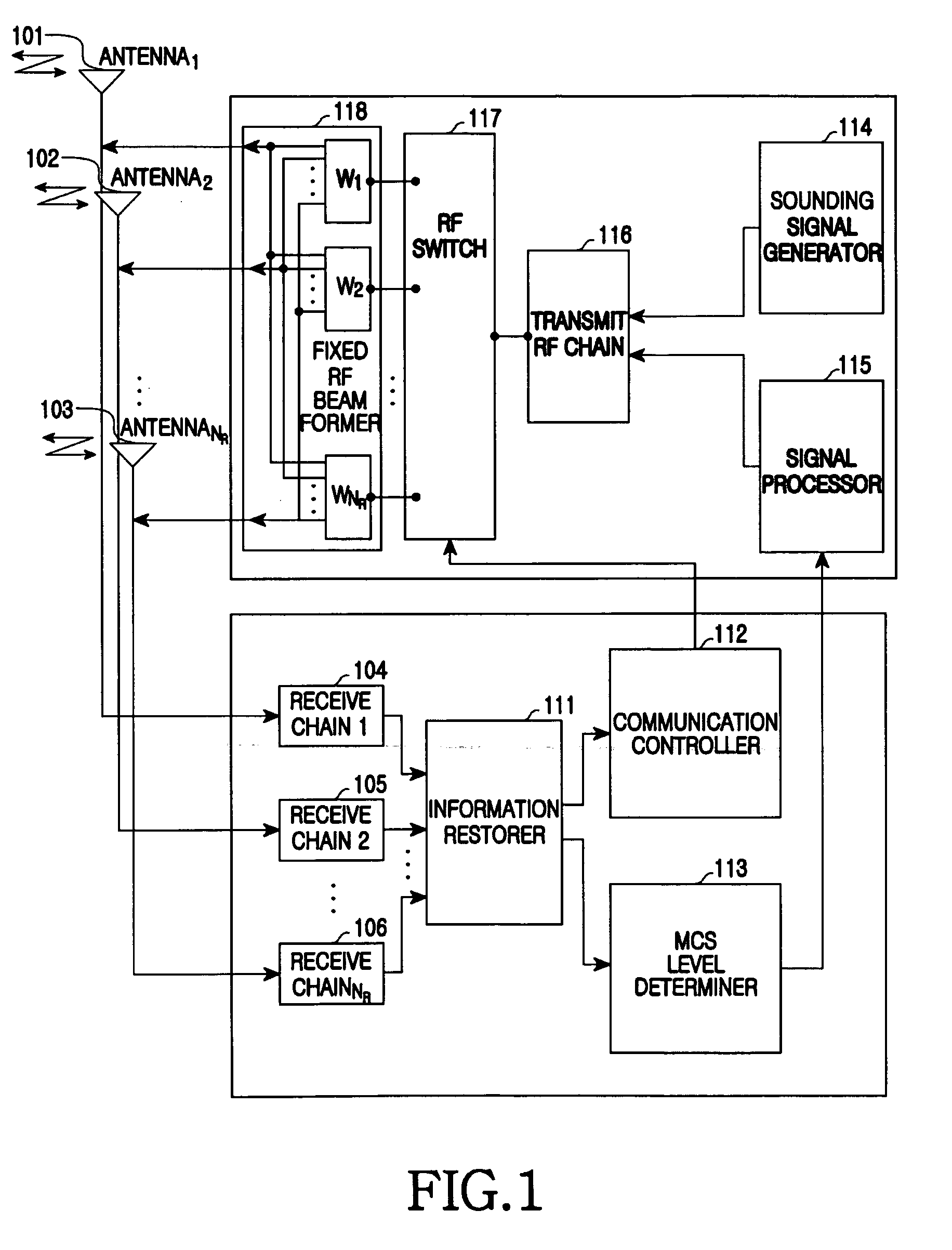
Apparatus and method for uplink beamforming and space-division multiple access (SDMA) in multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communication systems
ActiveUS20090239565A1Maximizing signal transmission capacityMaximize capacityModulated-carrier systemsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemCode division multiple access
An apparatus and method for beamforming of a terminal in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication system are provided. The method includes transmitting sounding signals beamformed through a plurality of beamforming weight vectors in sequence, receiving control information indicative of an uplink weight vector determined by a base station and a maximum channel quality value using the sounding signals and transmitting a transmit signal beamformed with the uplink weight vector via a plurality of antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Beamforming for non-collaborative, space division multiple access systems
ActiveUS20070092019A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A wireless communication system noncollaborative, multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) system determines subscriber station combining and weighting vectors that yield a high average signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR). Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine a weight vector wi for each subscriber station using the determined combining vector of the subscriber station. The ith combining vector corresponds to a right singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between a base station and the ith subscriber station. Each subscriber station transmits signals using a weight vector vi, which corresponds to a left singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between the ith subscriber station and the base station. The base station uses the weight vector wi to determine the signal transmitted by the ith subscriber station.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods for wireless communication
InactiveUS20070274256A1Improve wireless resource utilization efficiencyImprove communication stabilityNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplex communicationQuality of serviceCommunications system
In a wireless communication system for communicating with a plurality of stations at the same point of time with the same frequency using a Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA), wireless resources are allocated by a first decision unit which evaluates performance of each station obtained when the SDMA is used and which determines periods of time to be allocated to groups of stations formed according to the SDMA technique. Using a first evaluation unit and a second evaluation unit to evaluate performance required by each station and each application, the first decision unit allocates the wireless resources to the stations. It is therefore possible that the wireless resources are efficiently allocated to the stations while preventing an event in which the wireless resources are excessive or insufficient for required quality of service.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
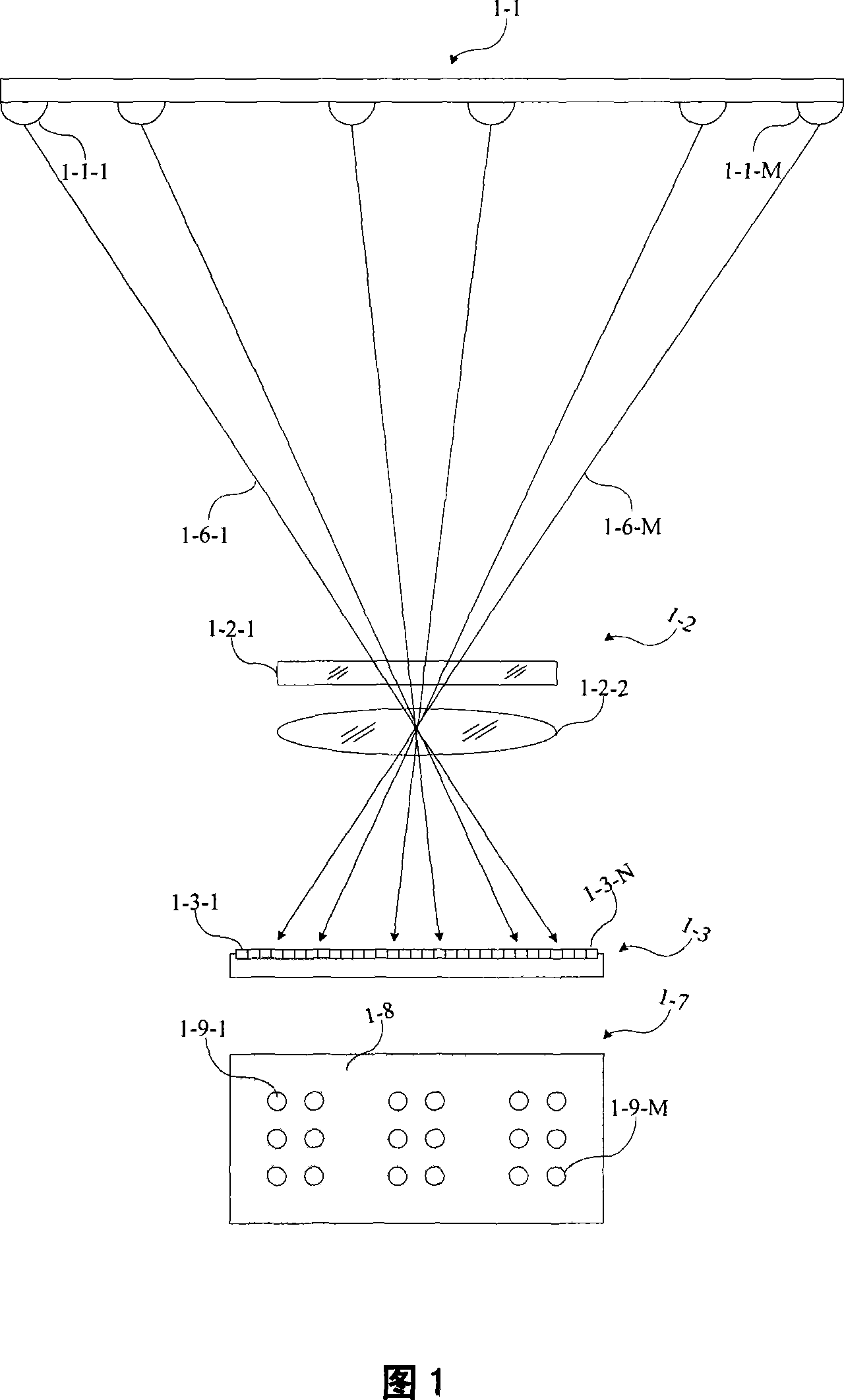
Visible light space division multiple access multichannel communication system
The invention relates to a realization proposal of a visible light space division multi-access multi-channel communication system. A visible light LED array at a sending end sends multiple channels of coded light signals, a light receiver forms the space separated LED image spots on a planar array photodetector by an imaging optical system thereof, the different receivers select their own outputs according to the different positions of image spots and the different response signals of the image elements which are covered by the image spots, thus realizing the tracking of light spots during the space diversity and the movement.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Space division multiple access for wireless lan, and channel estimation for the same
ActiveUS20110243025A1Easy to useReduce overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime division multiple accessUplink transmission
Provided are space division multiple access for wireless local area network (WLAN), and channel estimation for the same. A frequency division multiple access technique and a space division multiple access technique based on competition are used together for channel access. The channel access method includes: a competition period for estimating channel characteristics for a plurality of stations and transmitting, to the plurality of stations, downlink schedule information or uplink schedule information based on the estimated channel characteristics; and a data transmission period for performing downlink transmission or uplink transmission with all or some of the plurality of stations in accordance with the downlink schedule information or the uplink schedule information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
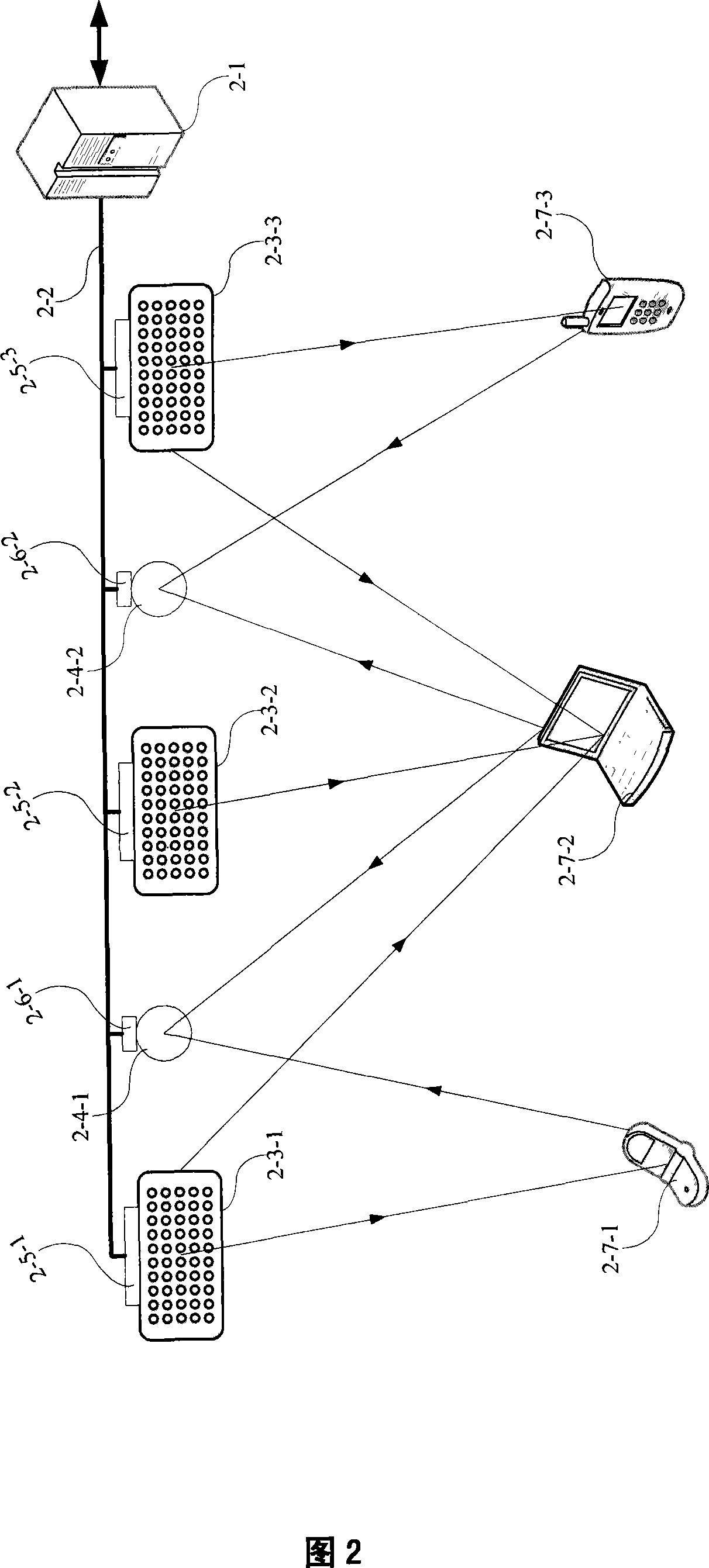
Method and device for implementing the multi-wave bundle intelligent antenna with the directional antenna
InactiveCN101056451AEasy to control and useSimple structureSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityDirectional antennaSmart antenna
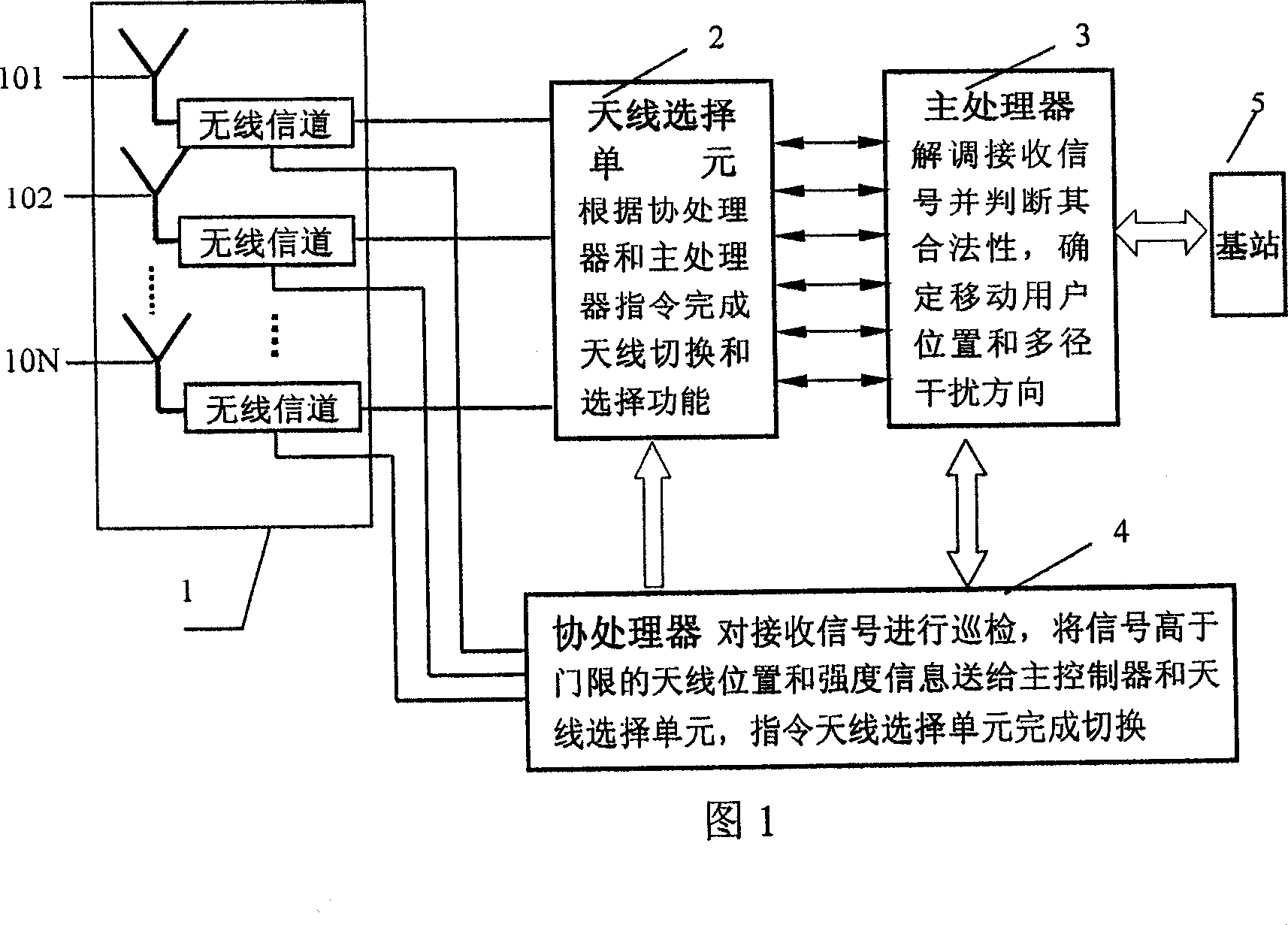
A method and an apparatus for realizing a multibeam smart antenna by directional antennas in a mobile communication system, are provided. The method comprises performing space division on a base station service region by N directional antennas independent with one another to divide the base station service region into N cells, each cell satisfying a perdetermined electromagnetic radialization request; composing a delamination multibeam array by the N directional antennas based on the region to be covered by the base station, the directional antenna adjusting direction of the beam in advance to realize space division multiple access, the antenna for performing transmission and receiving of signals are controlled by a main processor unit, auxiliary processors and an antenna selection unit to position and track a mobile user. The apparatus includes a delamination antenna array composed of N directional antennas independent with one another, the antenna selection unit, auxiliary processors, a main processor; wherein the N directional antennas are connected with input ends of the auxiliary processors respectively, the auxiliary processors are connected with the antenna selection unit and the main processor respectively, the main processor is connected with the antenna selection unit and the base station. The invention has a high communication capacity and immunity.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIV ELECTRONICS TECH DEV APPL RES INST
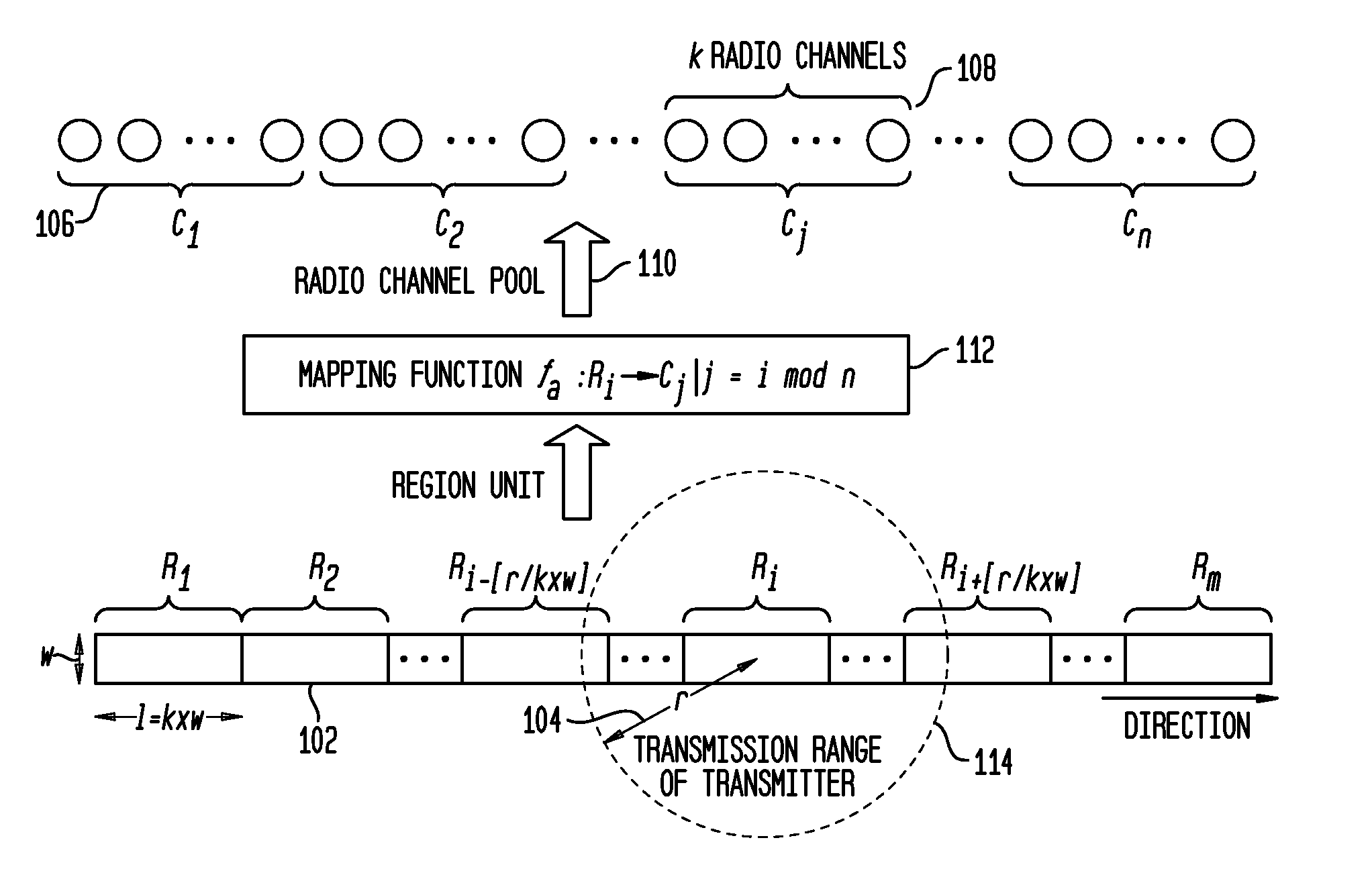
Region-based clustering mechanism for channel access in vehicular ad hoc networks
ActiveUS20120120883A1High data transmission data throughputLower latencyNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesTime division multiple accessTelecommunications
In a Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET) a hybrid method combines SDMA (Space Division Multiple Access) and dynamic TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) that divides the roadway into regions (whose size is larger than the SDMA unit) where each region is allocated a pool of radio channels based on SDMA and may contain a limited number of vehicles. Vehicles within the same region compete for and access the channels using dynamic TDMA. A channel allocation scheme that maps the pool of channels to the regions such that when a vehicle acquires multiple channels (time slots) in a region, the intervals among the channels are as uniform as possible, thus minimizing the waiting time of the messages to be broadcast by the vehicle, which is critical for safety related applications. This solution is referred to as R-SDMA (Region based SDMA).
Owner:TELCORDIA APPLIED RES CENT TAIWAN
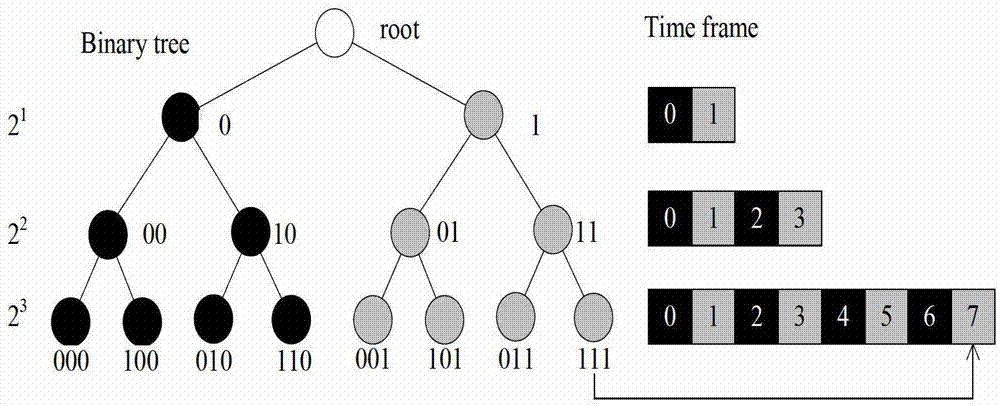
Vehicle-mounted ad hoc network self-adaptive time slot distributing method based on a time division multiple address (TDMA)
InactiveCN103096327AReduce access conflictsReduce the chance of merge conflictsRadio transmission for post communicationNetwork planningTime division multiple accessCode division multiple access
The invention relates to a vehicle-mounted ad hoc network self-adaptive time slot distributing method based on a time division multiple address (TDMA), the vehicle-mounted ad hoc network self-adaptive time slot distributing method divides a time frame into a left time slot set and a right time slot set, nodes are divided into a left node set and a right node set based on the moving direction of the nodes, and the nodes in the left / right node sets choose competition time slots in the left / right time slot set based on the current geographical location information and according to certain rules. The vehicle-mounted ad hoc network self-adaptive time slot distributing method based on the TDMA reduces the ratio of a connect-in confliction and an amalgamation confliction occurred by the nodes to a large degree; and based on density changes of the nodes sensed by the nodes, the lengths of frames are dynamically adjusted, so that the demand that the nodes swiftly connect-in channels is satisfied; low time delay of the vehicle-mounted ad hoc network self-adaptive time slot distributing method based on the TDMA is authenticated by both theoretical analysis and simulating experiments. Compared with the prior art, the vehicle-mounted ad hoc network self-adaptive time slot distributing method based on the TDMA has the advantages of having less quantities of confliction nodes, higher utilizing ratio of the channels and good expansibility.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
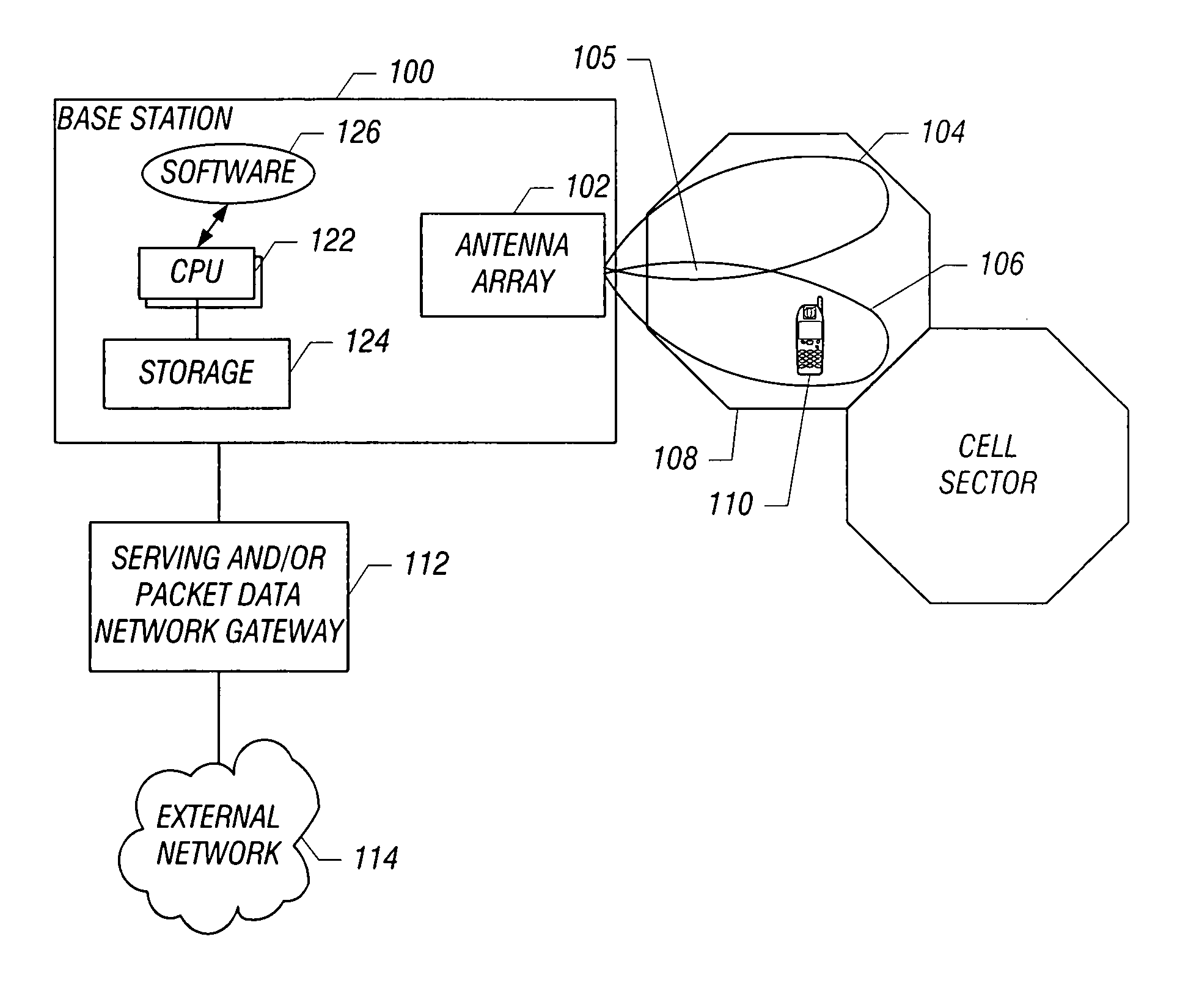
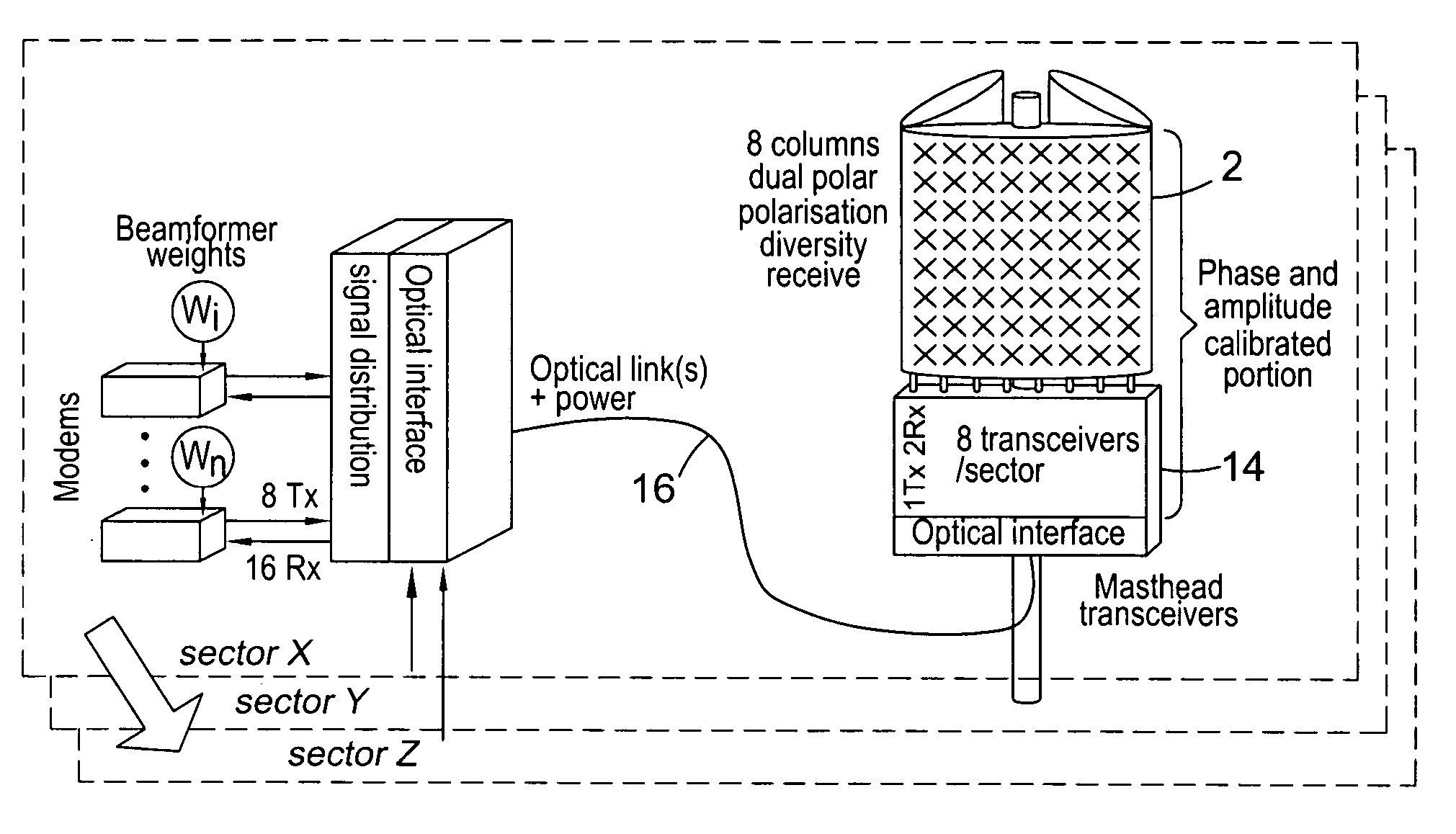
Downlink beamforming for broadband wireless networks
ActiveUS20060281494A1Multiplicative spectral efficiency gainHigh trafficSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionDownlink beamformingFrequency spectrum
Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) offers multiplicative spectral efficiency gains in wireless networks. An adaptive SDMA beamforming technique is capable of increasing the traffic throughput of a sector, as compared to a conventional tri-cellular arrangement, by between 4 and 7 times, depending on the environment. This system uses an averaged covariance matrix of the uplink signals received at the antenna array to deduce the downlink beamforming solution, and is equally applicable to Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD) systems. A scheduling algorithm enhances the SDMA system performance by advantageously selecting the users to be co-scheduled.
Owner:APPLE INC
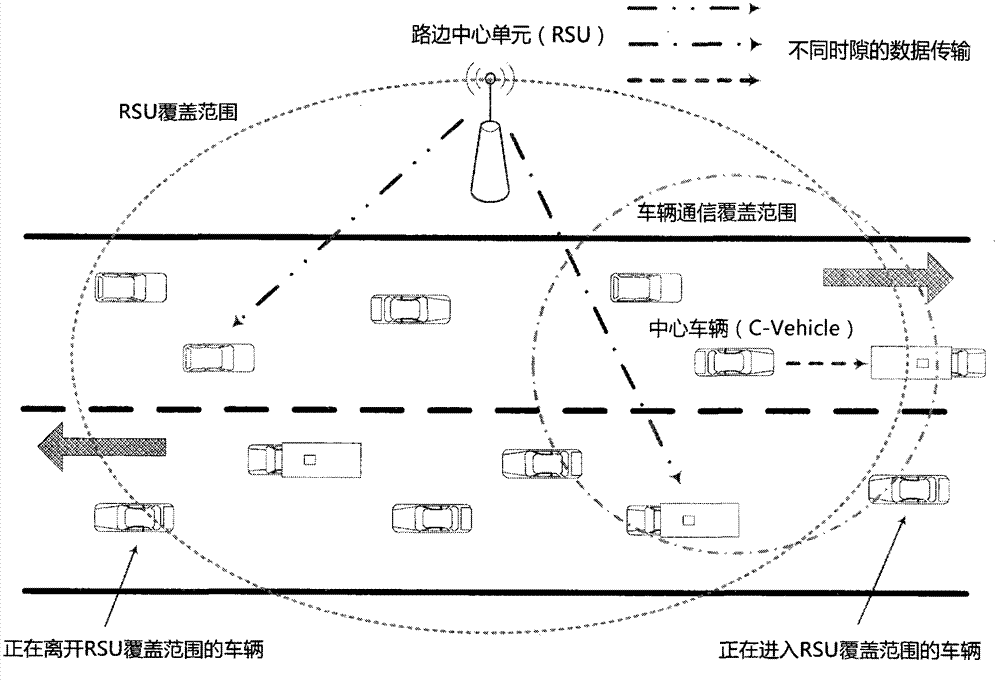
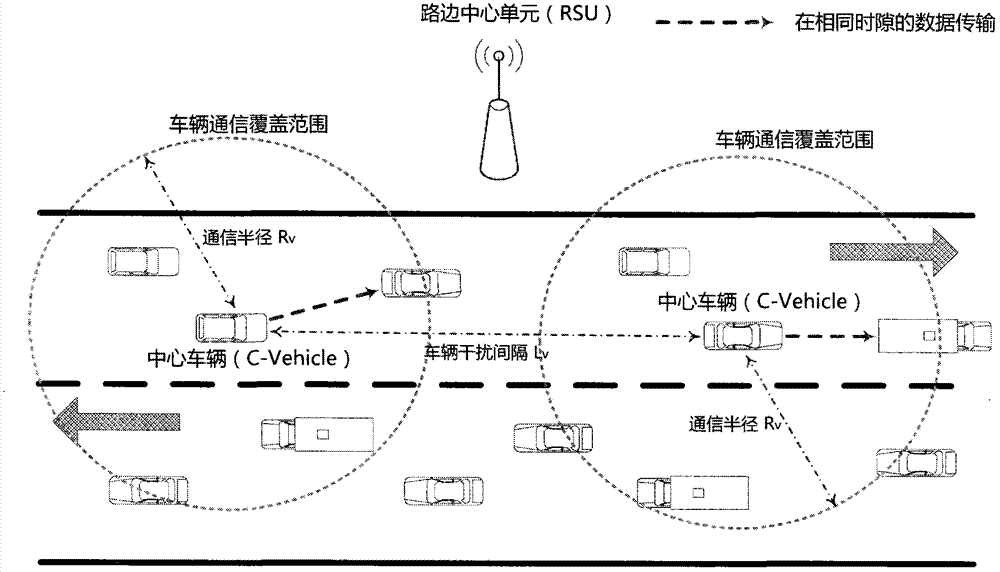
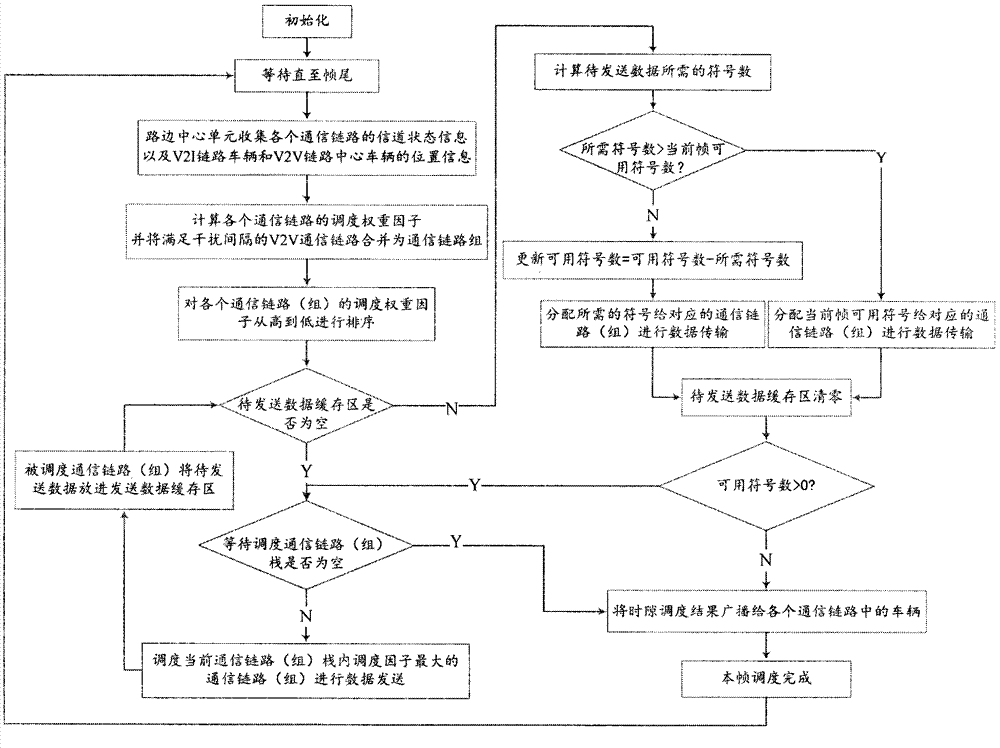
Time division multiple access-based resource scheduling scheme for Internet of vehicles
The invention discloses a time division multiple access technology-based resource scheduling method for the Internet of vehicles. The method mainly comprises the following steps of implementing the resource scheduling of vehicle-to-infrastructure and vehicle-to-vehicle communication links under the control and strategies of a roadside center unit; calculating a scheduling weight factor of each communication link according to information such as channel states, positions and movement speed cyclically fed back by vehicles, and preferentially scheduling timeslot resources to communication links (groups) with higher scheduling weight factors for data transmission by using the roadside center unit, wherein a plurality of vehicle-to-vehicle communication links can be combined into a communication link group if a distance between every two center vehicles serving as data transmitting terminals is longer than a preset interference interval, and a scheduling weight factor of each communication link group is the summation of the scheduling weight factors of all the communication links in the group; the same timeslot resource can be shared by each communication link in the same communication link group for data transmission; the sharing of the timeslot resources between different vehicle-to-infrastructure communication links and between the vehicle-to-infrastructure communication links and the vehicle-to-vehicle communication links for data transmission is not allowed. According to the resource scheduling method, the network throughput and the spectral efficiency of the Internet of vehicles can be effectively improved, and high network throughput performance can still be maintained particularly under the condition of high network load.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Millimeter wave large-scale MIMO system multi-user transmission method based on space division multiple access and interference suppression
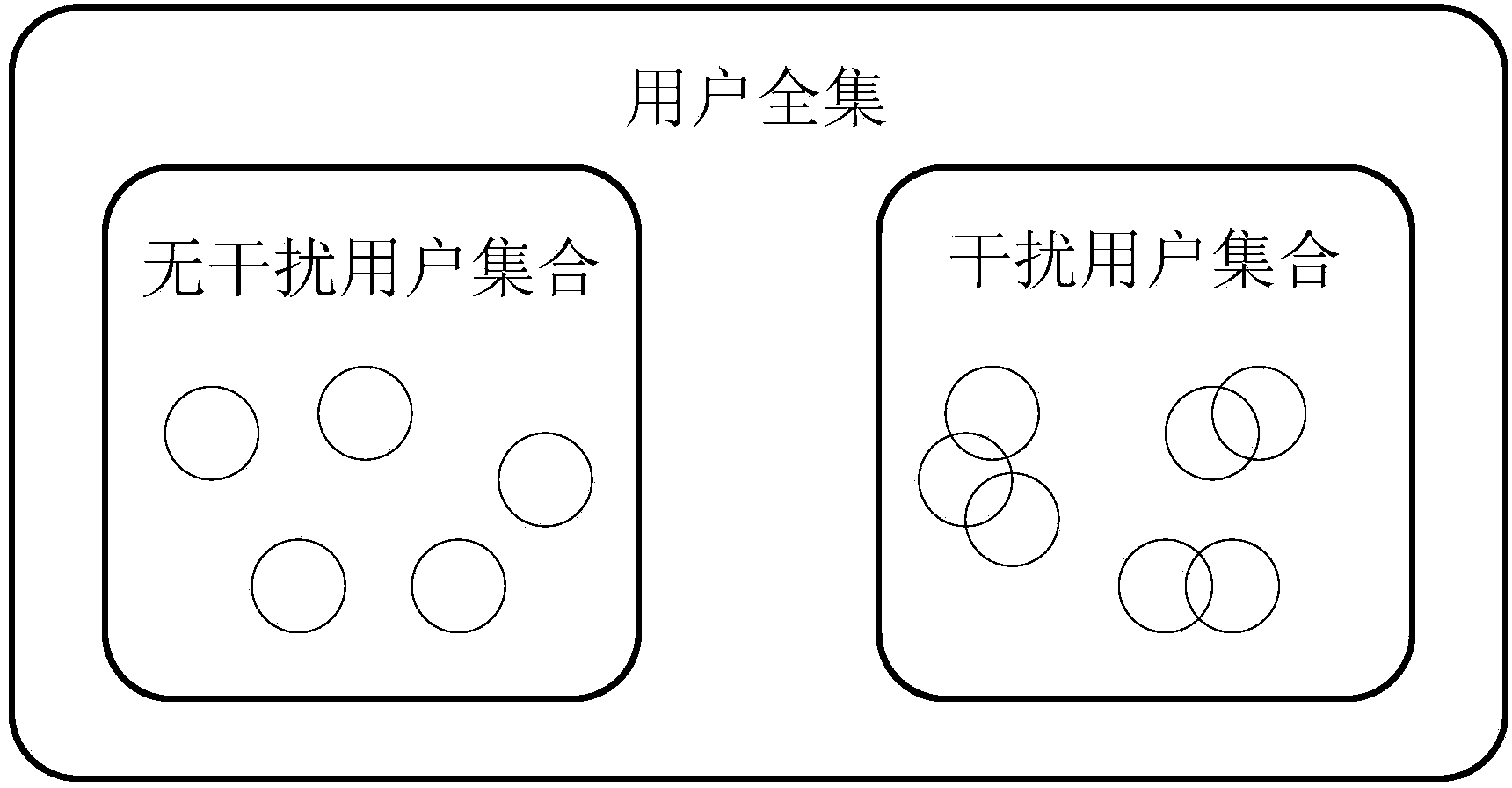
ActiveCN104052535AReduce computational complexitySolve the feedback problemSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsPrecodingComputation complexity
The invention discloses a millimeter wave large-scale MIMO system multi-user transmission method based on space division multiple access and interference suppression. A base station is provided with a millimeter wave large-scale uniform panel antenna array; a plurality of single-antenna users receive service from the base station on the same time-frequency resource; according to information of wave beam clusters selected by the users, a universal user set is divided into an interference-free user subset and an interference user subset; the space division multiple access transmission method based on double-layer pre-coded codes is adopted to the interference-free user subset, and the transmission method based on interference suppression is adopted to the interference user subset. According to the method, the advantages of two traditional multi-user transmission methods based on space division multiple access and interference suppression respectively are combined, and the bottleneck that in an FDD transmission mode, downlink channel information of a large-scale MIMO system is difficult to obtain is broken through; meanwhile, the computation complexity problem is solved, it is guaranteed that all the users can receive the service from the base station simultaneously, and considerable system performance and speed performance are achieved at limited feedback quantity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Beamforming for non-collaborative, space division multiple access systems
ActiveUS7602837B2Diversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A wireless communication system noncollaborative, multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) system determines subscriber station combining and weighting vectors that yield a high average signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR). Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine a weight vector wi for each subscriber station using the determined combining vector of the subscriber station. The ith combining vector corresponds to a right singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between a base station and the ith subscriber station. Each subscriber station transmits signals using a weight vector vi, which corresponds to a left singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between the ith subscriber station and the base station. The base station uses the weight vector wi to determine the signal transmitted by the ith subscriber station.
Owner:APPLE INC
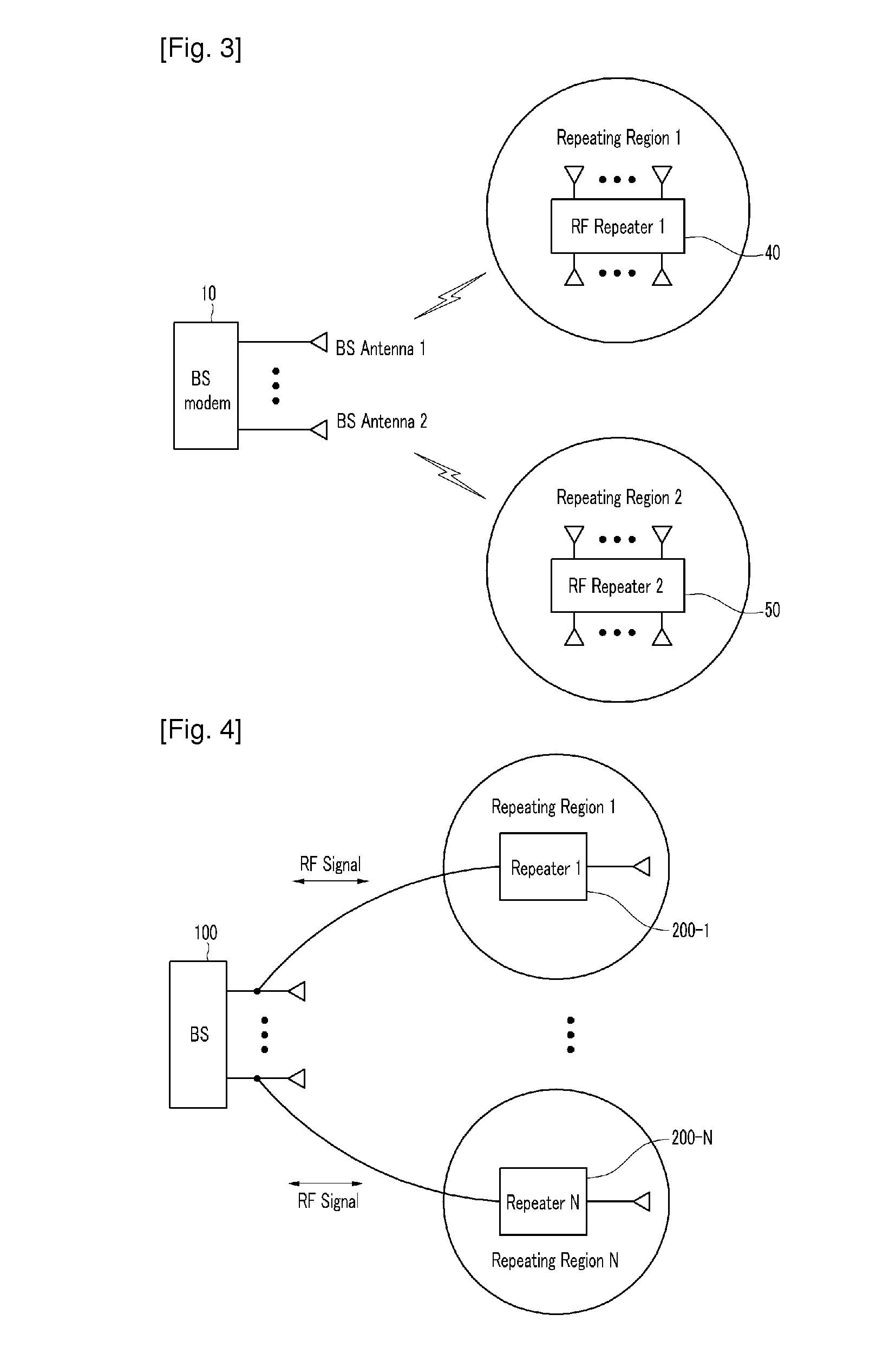
Method for connecting base station and repeater for spatial division multiple access and repeating method thereof
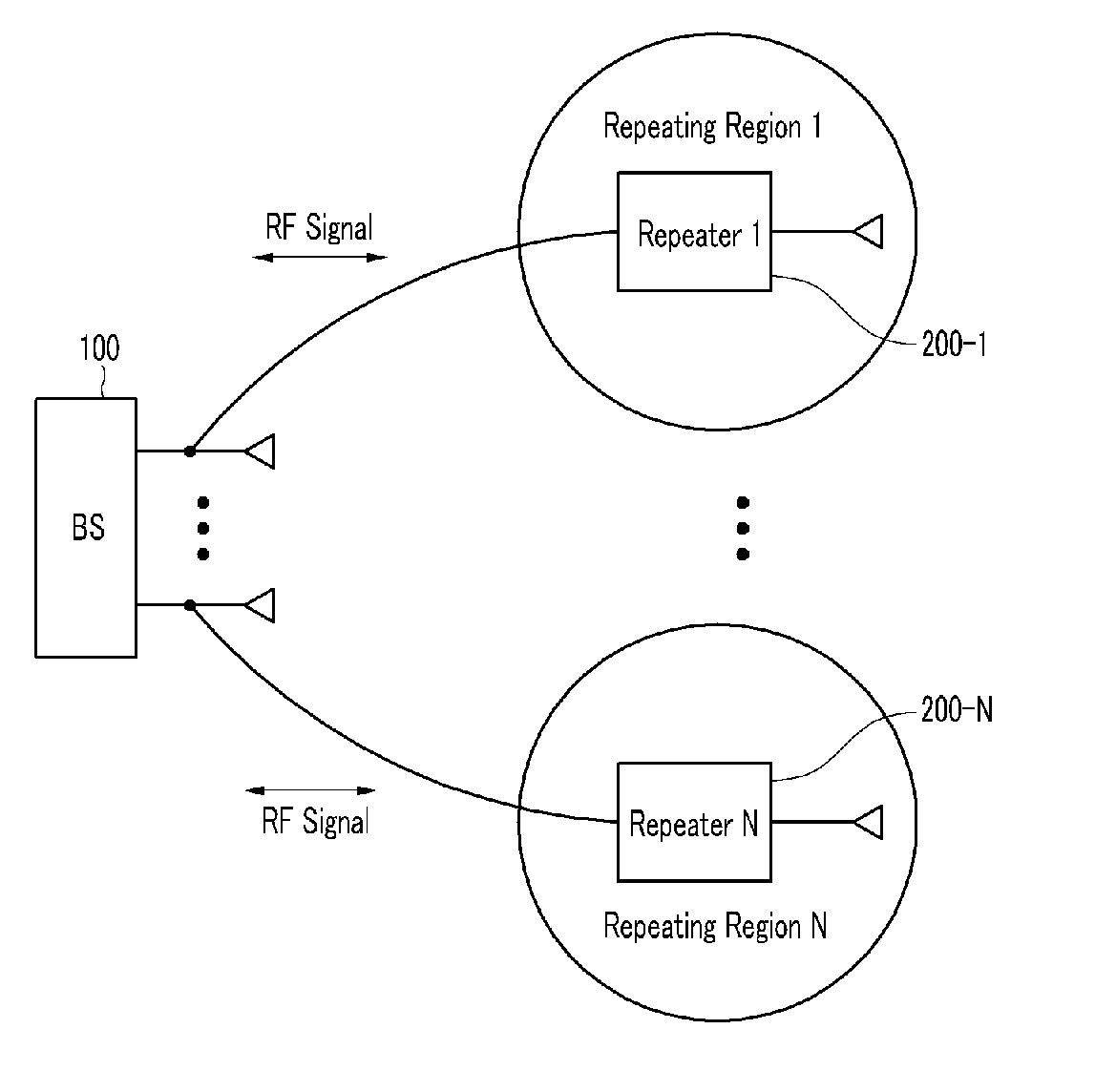
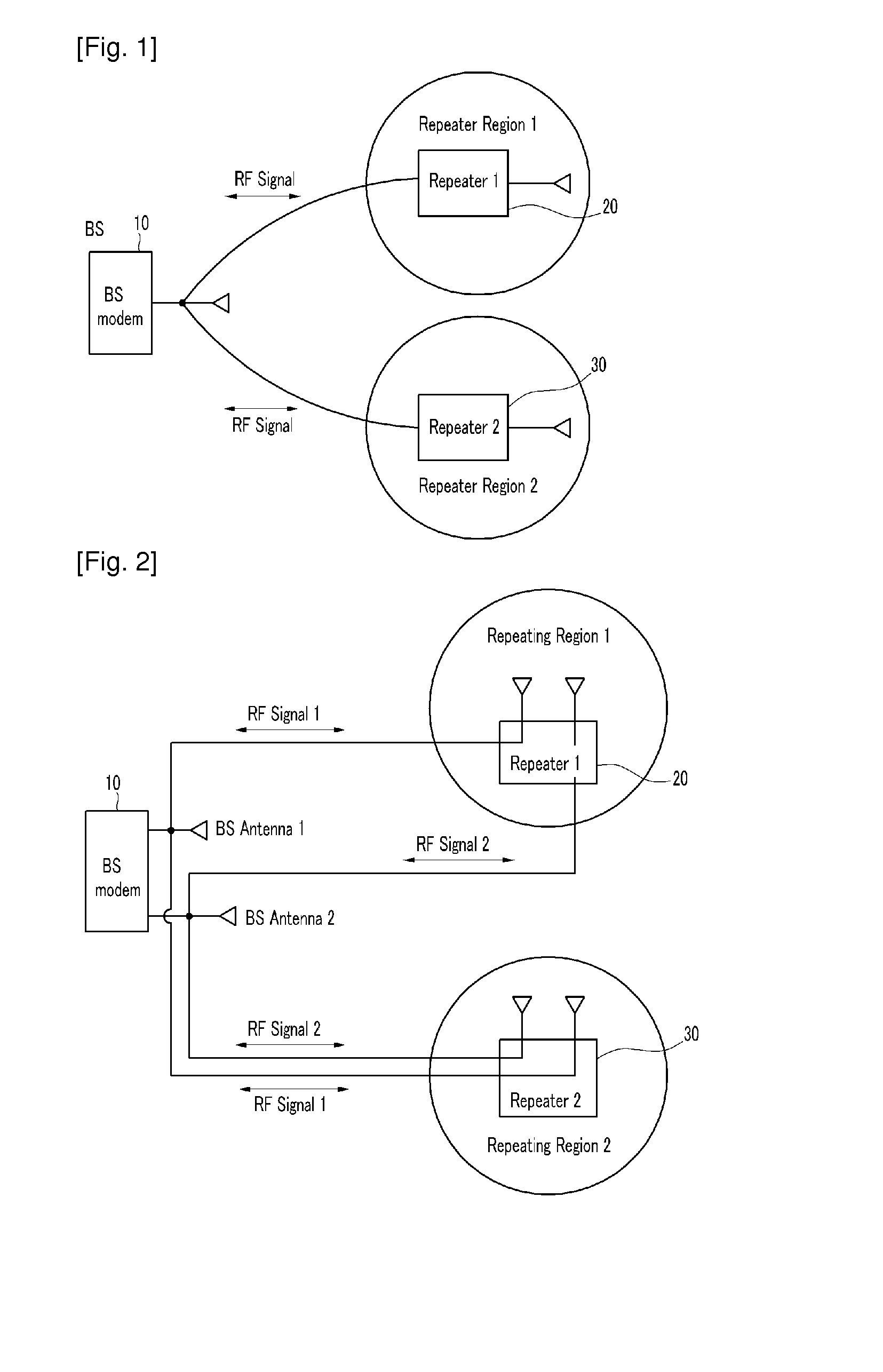
InactiveUS20100208776A1Increase capacityEasily transmitted/receivedRepeater/relay circuitsActive radio relay systemsData streamSpatial partition
The present invention relates to a method for connecting a base station and a repeater for a spatial division multiple access, and a repeating method thereof. In order to provide efficient spatial division by using a repeater, data streams are repeated by using a repeating system including at least one repeater for performing wireless communication with a terminal located in a repeating region controlled by using at least one repeating antenna and a base station including a plurality of base station antennas corresponding to the repeating antenna. In this instance, the terminal detects location information on the repeating region to which the terminal belongs by using the pilot signal transmitted by the base station or repeated by the repeater. Location information detected by the terminal is fed back to the base station so that the base station may use it for the spatial division multiple access for simultaneous transmission to many terminals. Therefore, the spatial division multiple access for increasing sector capacity by efficiently combining the base station including multiple antennas and the repeater is available.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Beamforming for Non-Collaborative, Space Division Multiple Access Systems
ActiveUS20090190688A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A wireless communication system noncollaborative, multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) system determines subscriber station combining and weighting vectors that yield a high average signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR). Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine a weight vector wi for each subscriber station using the determined combining vector of the subscriber station. The ith combining vector corresponds to a right singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between a base station and the ith subscriber station. Each subscriber station transmits signals using a weight vector vi, which corresponds to a left singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between the ith subscriber station and the base station. The base station uses the weight vector wi to determine the signal transmitted by the ith subscriber station.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for generating preamble sequence for adaptive antenna system in orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
ActiveUS7567639B2Network traffic/resource managementAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationPhase shiftedCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for generating a preamble sequence for an adaptive antenna system supporting a space division multiple access in an OFDMA communication system. Particularly, disclosed is a method for forming a preamble sequence identifying each of a plurality of mobile subscriber stations located within a cell or a sector of a communication system which includes a plurality of sub-channels assigned to the mobile subscriber stations, each of the sub-channels including a plurality of bins each of which includes n number of contiguous subcarriers in a frequency domain, the preamble sequence being transmitted before each of the sub-channels is transmitted, the method including the step of generating a preamble sequence by phase-shifting a predetermined sequence according to a predetermined phase shift sequence in the frequency domain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication apparatus and method, computer program, and communication system
ActiveUS20120099530A1Facilitate communicationIncrease volumeSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesStart timeCommunications system
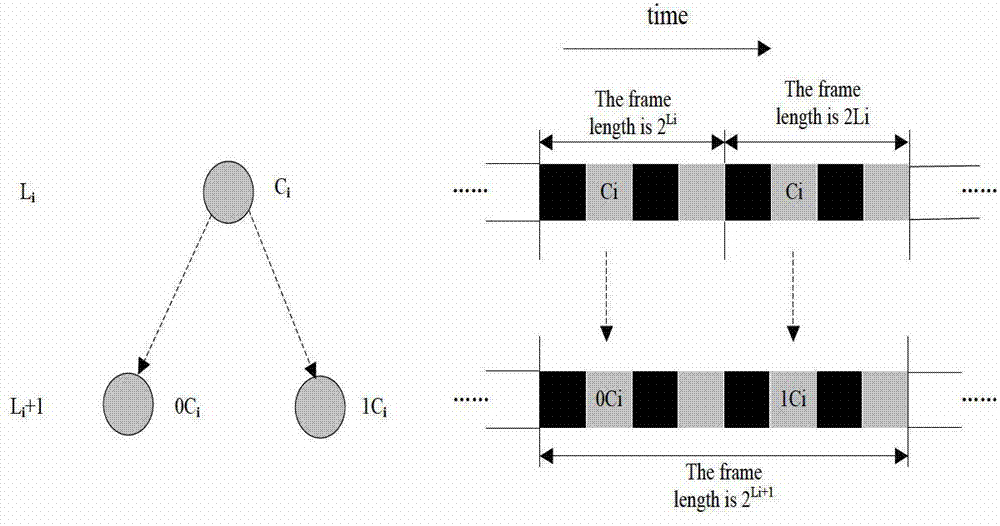
Communication operations are optimally conducted by applying space-division multiple access in which wireless resources on a spatial axis are shared among a plurality of users.By applying an RD protocol to a communication system that conducts space-division multiple access, spatially multiplexed frames in a TXOP are made more efficient. By specifying a frame length for reverse direction frames with reverse direction permission information and having respective transmitters of reverse direction frames make their frame lengths uniform while respecting the specification, AGC operation stabilizes. Also, a transmit start time for reverse direction frames can be specified by reverse direction permission information, and respective transmitters of reverse direction frames can transmit frames at the same time while respecting the specification.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com