Excitation surge current fast identification method based on planar adjacent point distances formed by differential current adjacent order difference
A technology of exciting inrush current and differential current, applied in electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as uncertainty diversity, difficulty in judgment, and complexity of fault waveforms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Embodiment 1: A fast identification method for exciting inrush current based on the distance between adjacent points on the plane formed by the difference between adjacent orders of differential current. Get the three-phase differential current of the transformer, extract the three-phase differential current data recorded by the measurement unit, and obtain the first-order difference and second-order difference of each phase differential current through the three-phase differential current data; The first-order difference of the phase is divided into the vertical axis, and three planes are constructed; the sum of the squares of the distances of all adjacent points on the three constructed planes is calculated, and then the maximum value of the three sums of squares is calculated dist2 sum , and then find dist2 sum The standard deviation and average value of the squared distance between adjacent points of the corresponding phase; the obtained average value and standard d...
Embodiment 2
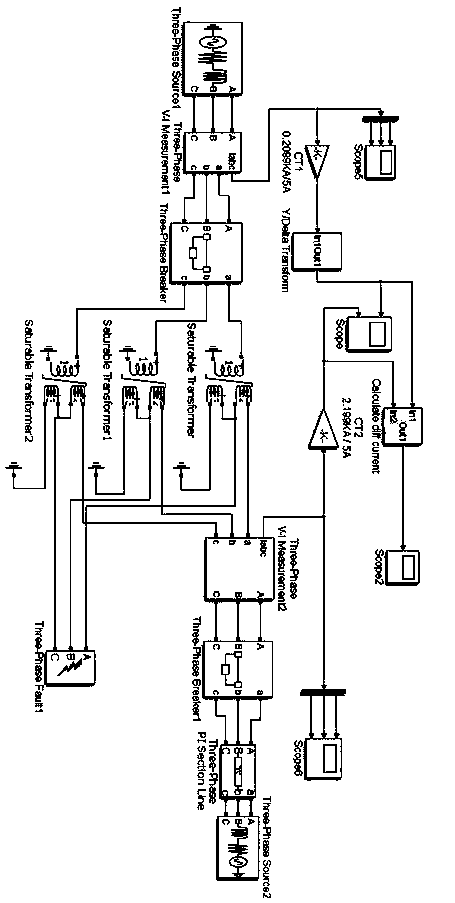
[0082] Example 2: Establish as figure 1 The simulation system model of transformer failure and excitation inrush current is shown, in which the transformers are three single-phase three-winding transformers, which adopt Yd11 connection method, connect its high-voltage windings to the 110kV system as the primary side of the transformer, and cascade the medium-voltage windings and low-voltage windings The secondary side of the transformer is formed, and the parameters of the equivalent double-winding transformer are as follows: rated capacity is 250MVA, rated transformation ratio is 110kV / 10.5kV, equivalent resistance is 0.002pu, and equivalent reactance is 0.08pu. Its magnetization parameters are shown in Table 1:
[0083]
[0084] Table 1
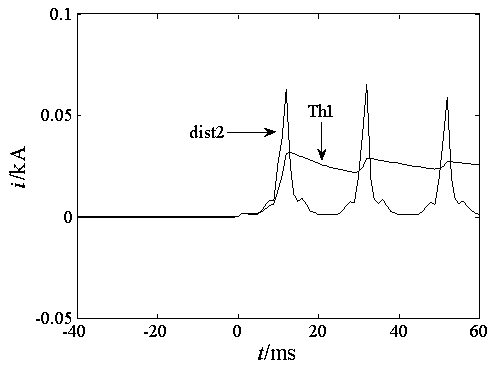
[0085] Assume that a 1.5% winding ground fault of phase A occurs on the low-voltage side of the transformer, and the sampling frequency is 1kHz. Under this model, dist2 A (n) and Th1 A The comparison diagram of (n) is as follows fig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com