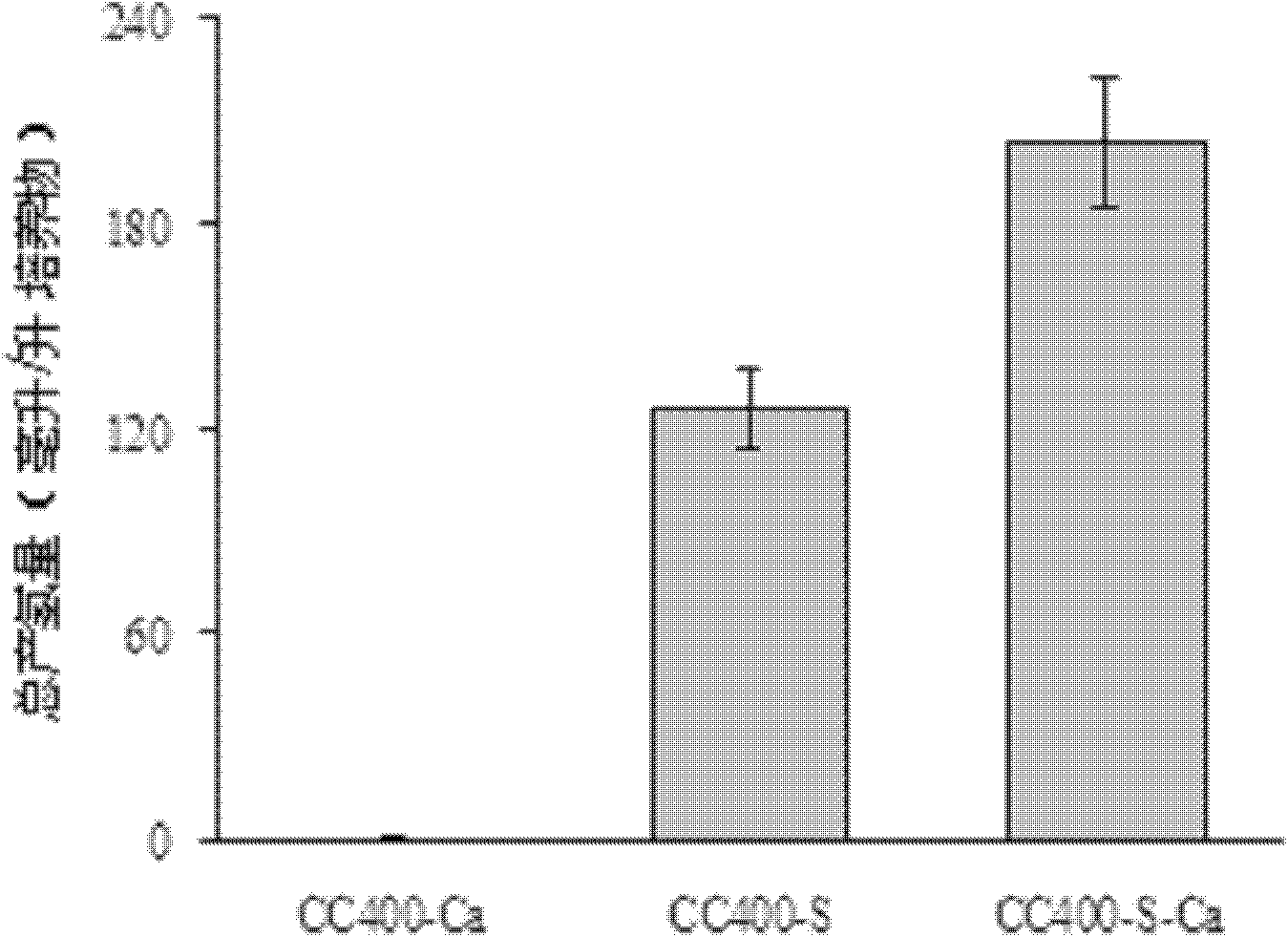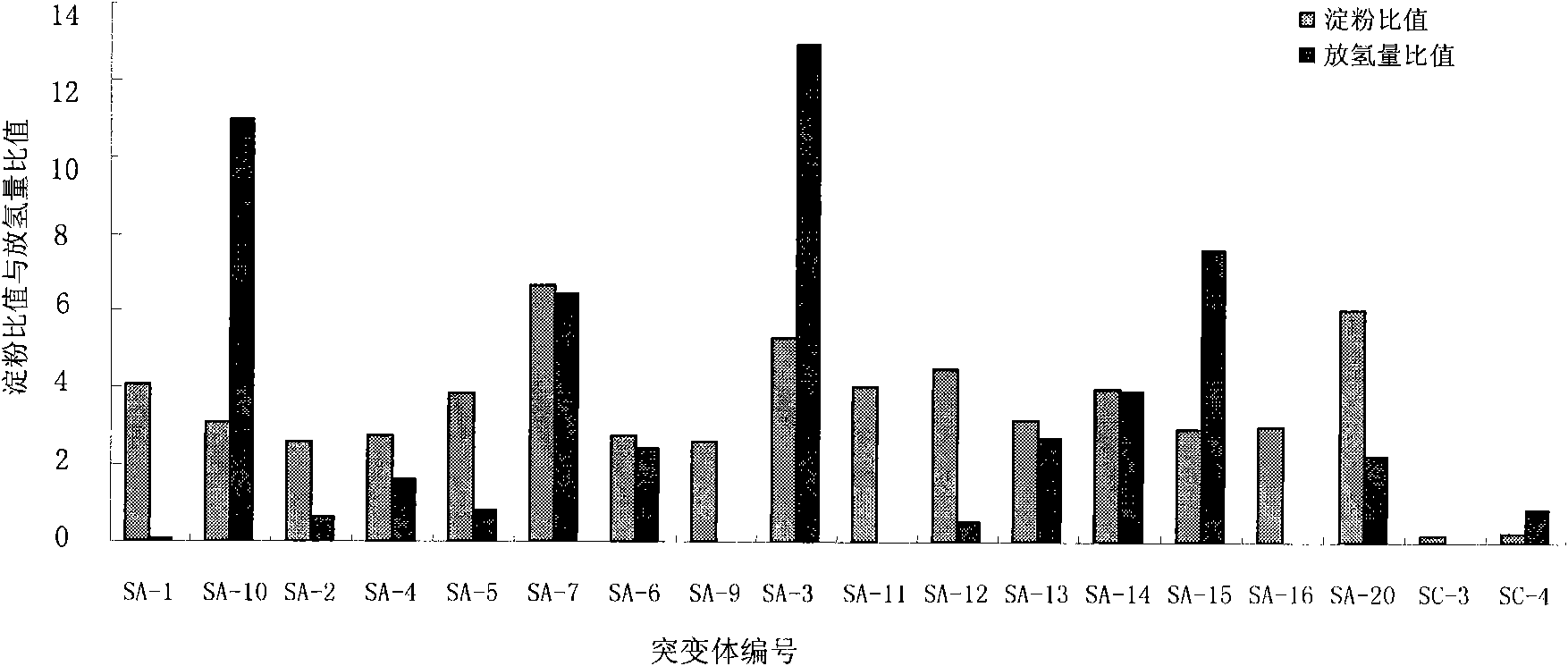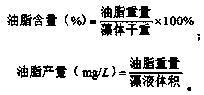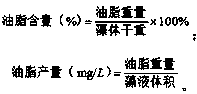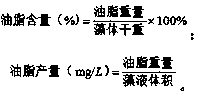Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Chlamydomonas sajao" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Salt algae NADP glyceral dehyde-3-phosdehydrogenase gene clone and protein expression method
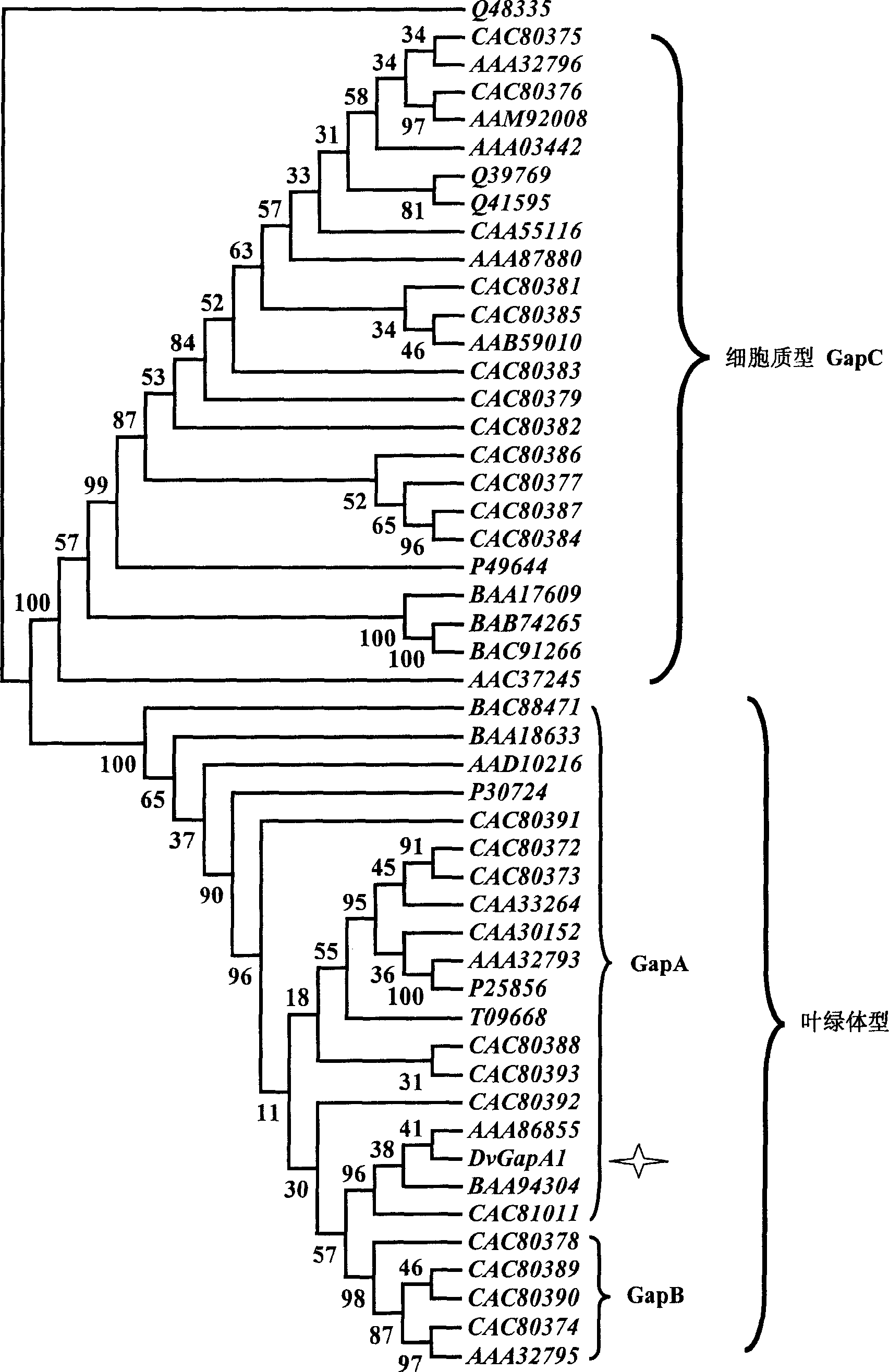
The present invention relates to a kind of saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, coded protein and its clone and protein expression method. The invented saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene has the base sequence showed by SEQ NO 5, and its coded protein has the amino acid sequence showed by SEQ NO 6. Said invention uses homologous fragment of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene originated from chlamydomonas as probe and firstly clones a glyceraldehydes-3 phosphate dehydrogenase specialized by saline alga. Besides, said invention makes primary analysis for its sequence and coded protein sequence, at the same time makes primary function analysis for said gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Hydrogen production chlamydomonas chloroplast separation method
ActiveCN104277974AThe method steps are simpleShorten the timeUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesLysisGreen band
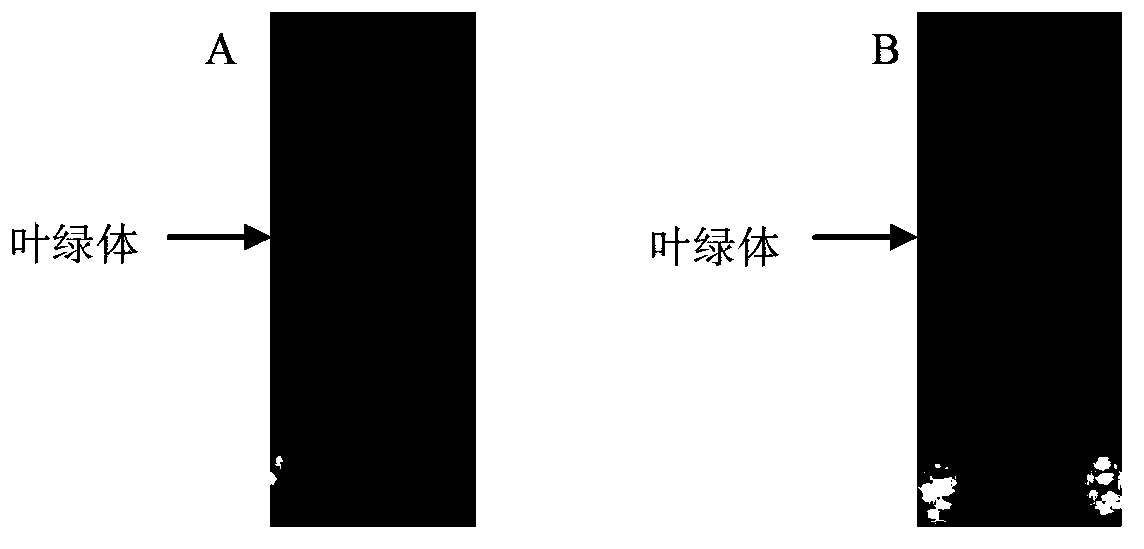
The invention discloses a hydrogen production chlamydomonas chloroplast separation method which comprises the following steps: 1) hanging Chlamydomonas in a lysate, adding saponin until the final concentration is 0.25g / 100mL; 2) putting the step 1) solution on the ice for 1-2min for chlamydomonas cell lysis; 3) centrifuging the step 2) solution for 1min at 2300g at 4 DEG C; 4) using the lysate for rinsing steps 3) precipitate, centrifuging for 1min at 1000-2300g at 4 DEG C to obtain crude chloroplast extract; 5) hanging the crude chloroplast extract in a lysate; 6) adding 75% by volume of Percoll on the centrifugal pipe bottom, adding 45% by volume of Percoll into the upper layer, adding the step 5) solution into the uppermost layer to the form the gradient, centrifuging for 20min at 4600g at 4 DEG C to form dark green bands between two different volume fractions of Percoll; and 7) taking the dark green bands out, using the lysate to dilute, centrifuging for 2min at 890-1000g at 4 DEG C, and collecting precipitate to obtain chlamydomonas chloroplast. The experiment proves that the method has the advantages of simple operation, high chlamydomonas chloroplast yield and shorter time.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Culture medium for improving hydrogen production amount of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and its preparation method
ActiveCN102925490AReduce compositionEasy to removeMicroorganism based processesFermentationAcetic acidChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a culture medium for improving the hydrogen production amount of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and its preparation method. The culture medium provided by the invention is composed of NH4Cl, MgCl2.6H2O, K2HPO4, KH2PO4, a Tris base, H3BO4, ZnCl2, MnCl2.4H2O, CoCl2.6H2O, CuCl2.2H2O, (NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O, FeCl2.4H2O and glacial acetic acid. Experiments in the invention prove that the hydrogen production amount of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in the sulfur-lack and calcium-lack TAP culture solution is about 2 / 3 higher than the hydrogen production amount of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in present sulfur-lack systems after optimizing the formulas of present hydrogen desorption culture mediums (sulfur-lack TAP culture solutions), and a culture medium component is omitted, so the cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
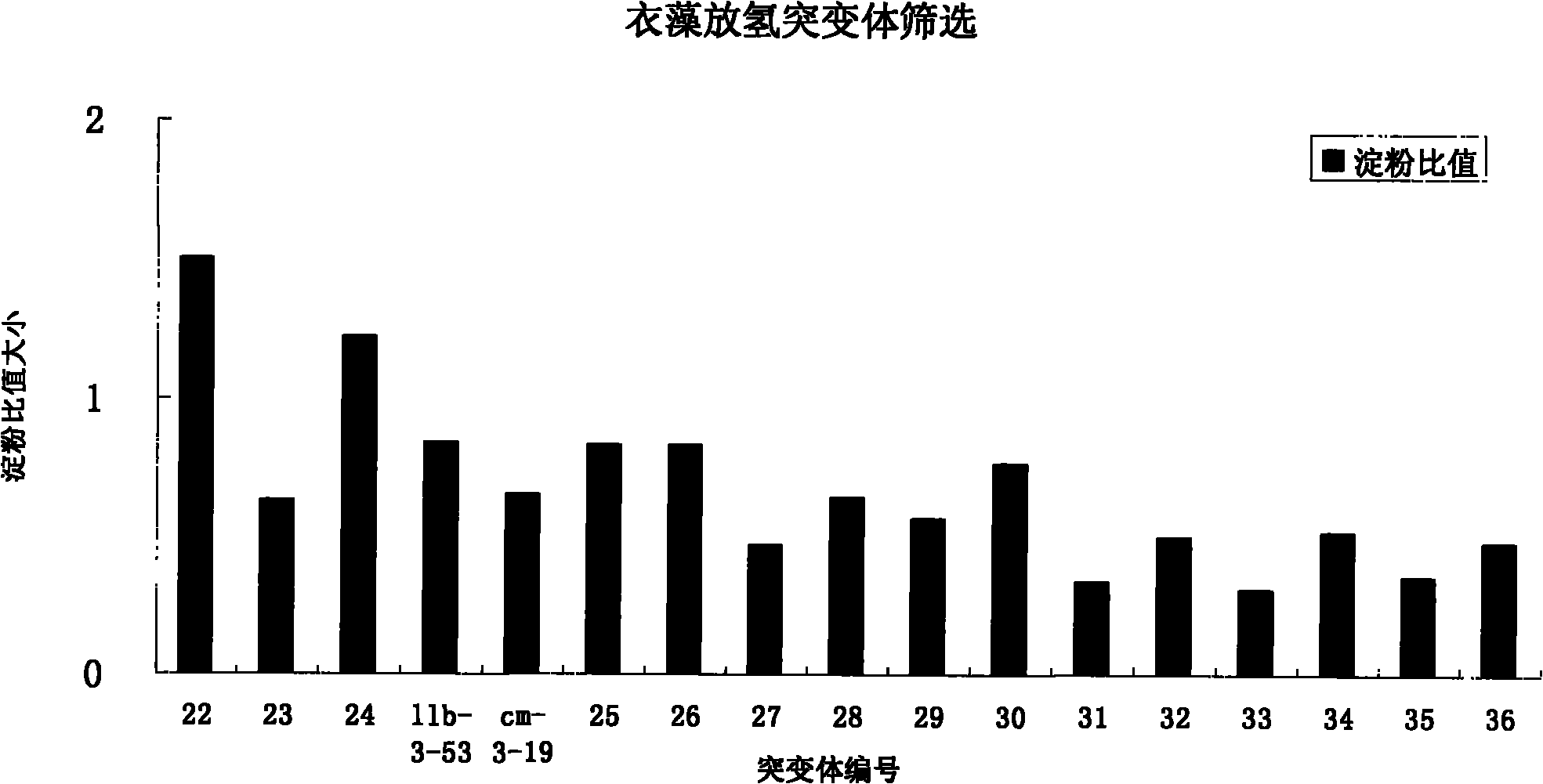
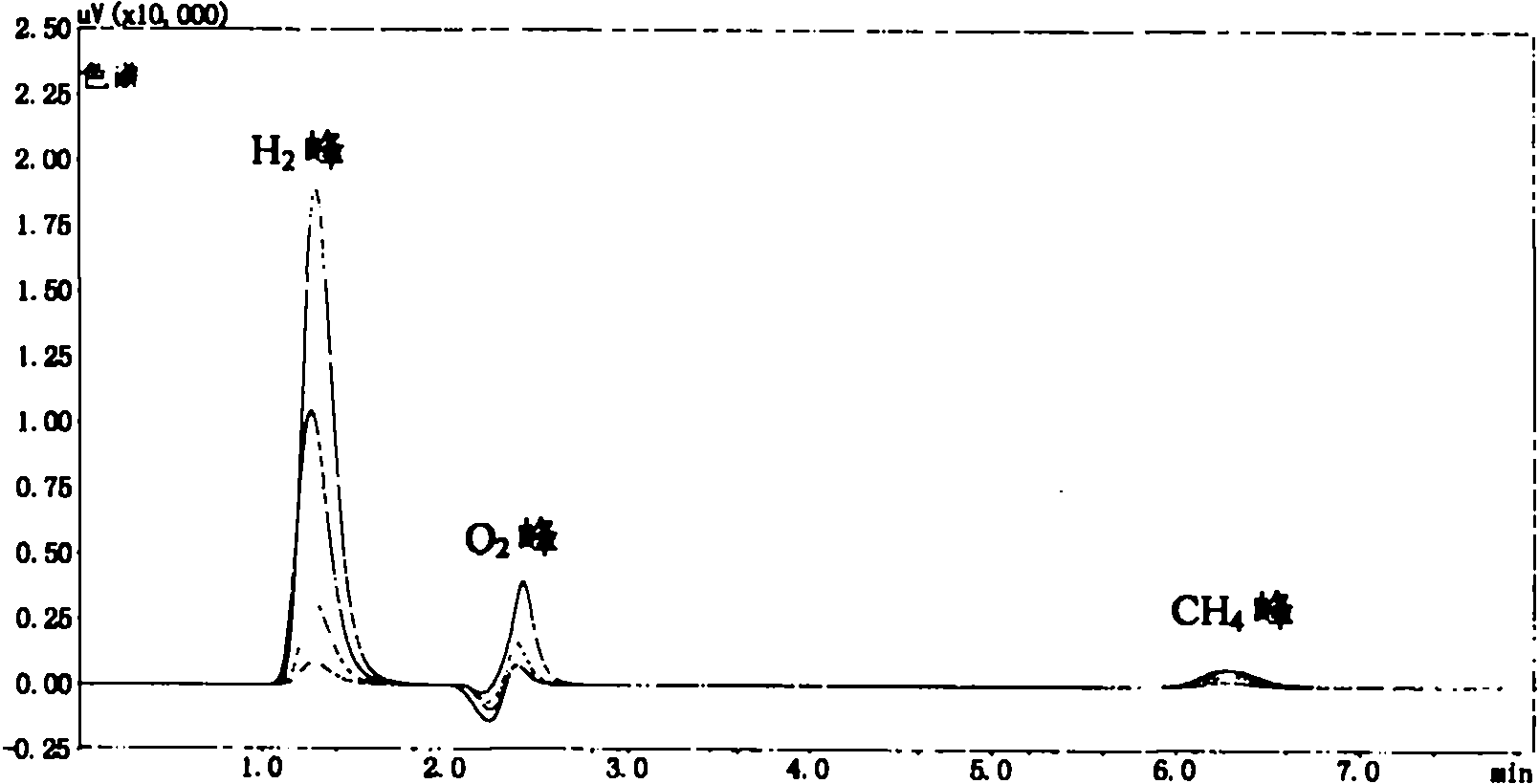
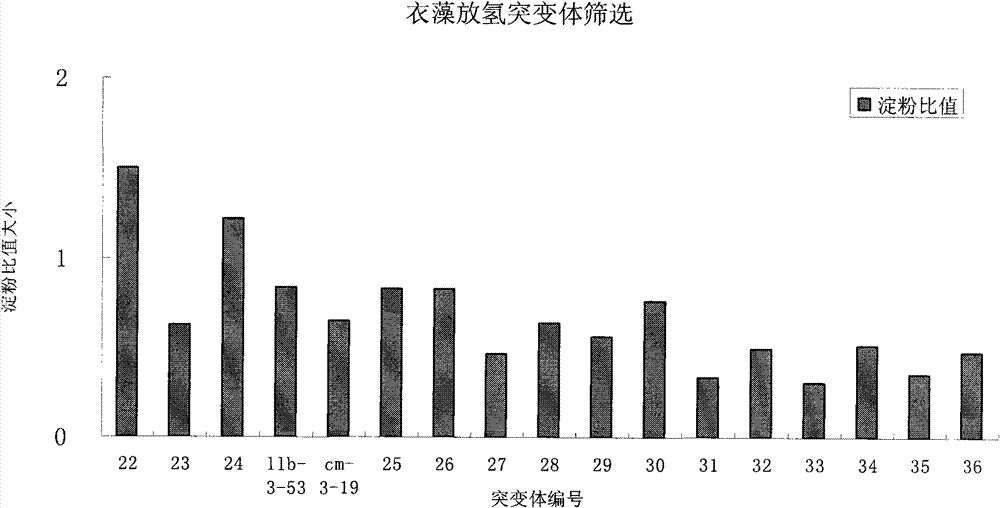
Method for effectively screening out chlamydomonas hydrogen desorption mutant
InactiveCN102337216AEfficient conversionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas sajao
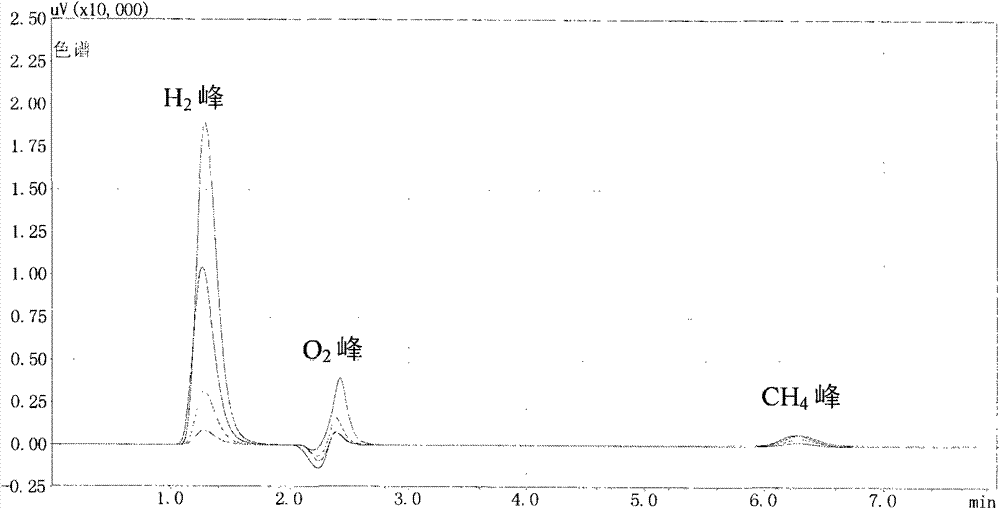
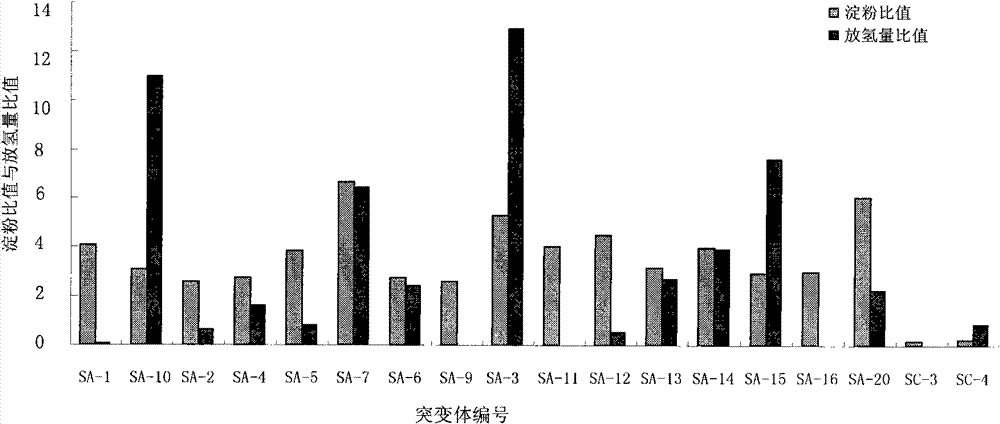
The invention discloses a method for effectively screening out a chlamydomonas hydrogen desorption mutant, which comprises the following steps of: (1) introducing pJD67 plasmid to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CC425, culturing transformants on a culture medium without arginine, and screening out the transformants which can grow, i.e., the mutant embedded with the pJD67 plasmid; and (2) screening out in the mutant embedded with pJD67plasmid to obtain a transgenic chlamydomonas mutant with increased hydrogen desorption quantity. According to the invention, the workload of directly measuring the hydrogen generation quantity is reduced; the efficiency of screening out the chlamydomonas hydrogen desorption mutant is increased; an important foundation for study on a mechanism of increasing the hydrogen generation quantity by microalgae photosynthesis is established; and meanwhile, the basis of improving a large-scale hydrogen generation technique in the future is provided.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of composition with skin tightening effect
ActiveCN104323976AGood effectImprove coexistenceCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFreeze-dryingMethacrylate methyl
The invention relates to a preparation method of a composition with skin tightening effect. The preparation method comprises the following steps of A: weighing a klamath blue-green algae extractive, a chlamydomonas nivalis extractive, ethanol, a wild soybean seed extractive, a methyl methacrylate / ethylene glycol dmethylacrglate cross-linked polymer or a allyl methacrylate cross-linked polymer, uniformly mixing, and then heating to obtain a-phase liquid; B: weighing a cell enabling compound, an undaria pinnatifida extractive, trehalose and deionized water, and uniformly stirring to obtain b-phase liquid; C: mixing the a-phase liquid and the b-phase liquid to obtain a mixed solution c; D: weighing a padina pavonica thallus extractive and the mixed solution c, uniformly mixing and stirring to obtain a mixed solution d; and E: loading the mixed solution d into a freeze-drying glass bottle, carrying out freeze-drying to obtain freeze-dried powder, sealing in a vacuum environment to obtain the freeze-dried powder of the composition with the skin tightening effect. The composition prepared through the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of obvious effect, good coexistence among active matters, stable quality and long retention period.
Owner:PROYA COSMETICS
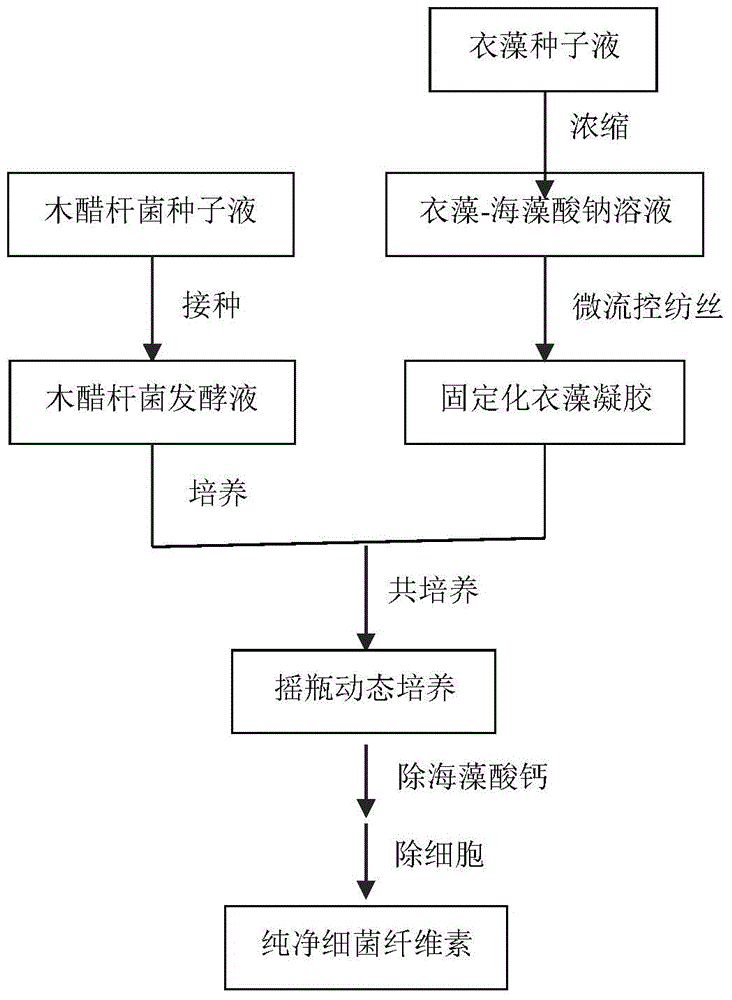
Method for constructing microorganism co-culture system for producing bacterial cellulose
ActiveCN105671115ASolve the dissolved oxygen problemRealize mutual benefit and symbiosisMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismAcetic acid
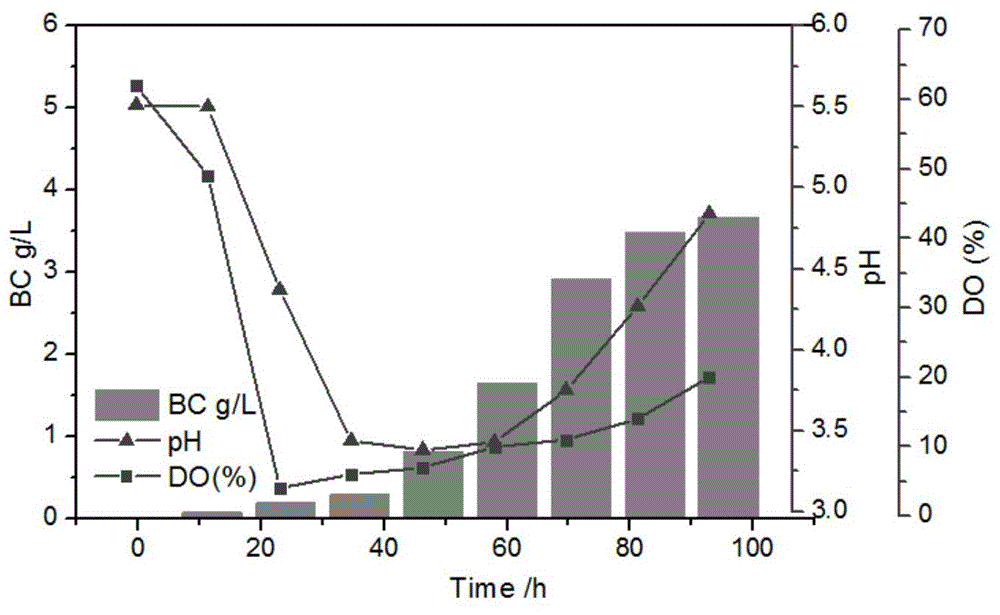
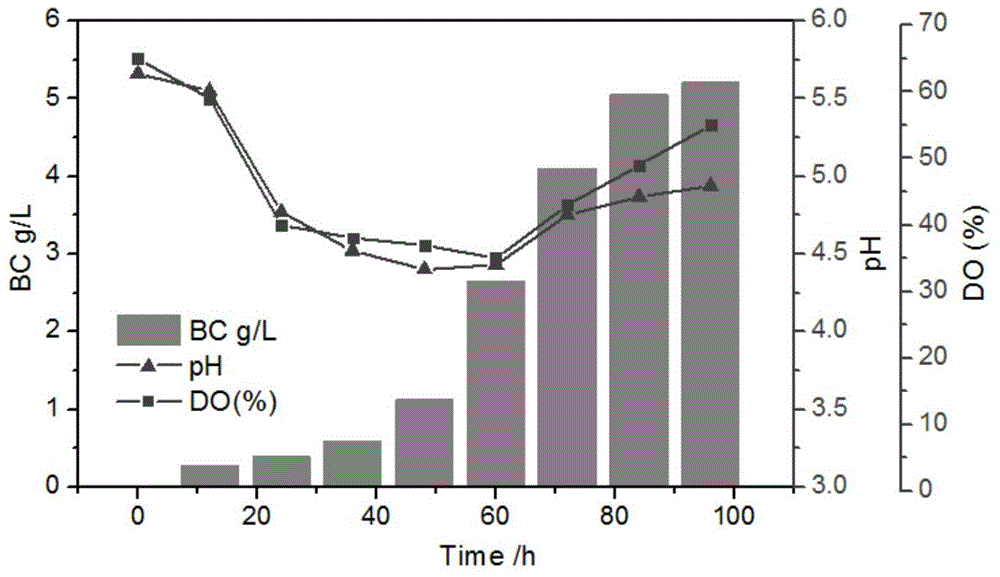
The invention discloses a method for constructing a microorganism co-culture system for producing bacterial cellulose. The method comprises the following steps: conducting seed amplification culture on acetobacter xylinum NUST4.2 and chlamydomonas in a separated mode, immobilizing chlamydomonas cells in calcium alginate by virtue of a micro-fluidic technique, and then conducting co-culture; and after culture, removing acetobacter xylinum cells and the chlamydomonas, so that pure bacterial cellulose is obtained. The chlamydomonas, as an oxygen producing microorganism adopted by the invention, can provide oxygen to the production of the bacterial cellulose in the later fermentation period, so that the problem of dissolving of oxygen caused by viscosity is solved. In addition, the acetobacter xylinum can secrete acetic acid during fermenting, and the chlamydomonas, which is a microorganism taking the acetic acid as a carbon source, can consume the acetic acid in a fermentation broth, so that ambient pH value is kept at an appropriate level. According to the scheme, a feasible solution is provided for solving the problem of dissolving of oxygen caused by excessive viscosity in the later fermentation period and for keeping the pH value stable during fermenting is provided, and a method for constructing a microorganism co-culture system for producing bacterial cellulose is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetic engineering chlamydomonas having increased hydrogen producing capacity and application thereof
InactiveCN102181369AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesGas phaseWild type
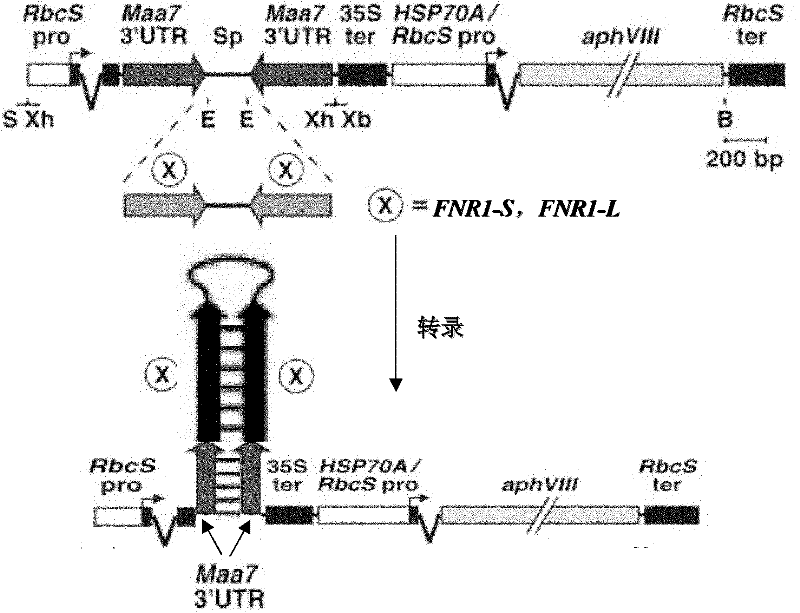
The invention discloses a genetic engineering chlamydomonas having increased hydrogen producing capacity and application thereof. The genetic engineering chlamydomonas provided by the invention is a genetic engineering chlamydomonas which is obtained by inhibiting an expression level of ferredoxin-NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) reductase coding genes in a starting chlamydomonas. It is determined by gas chromatography that the hydrogen producing capacity of the genetic engineering chlamydomonas is increased by 6-10 times compared with a wild strain after phosphorus deficiency treatment is carried out for 48 hours. The mutant strain is obtained to lay the basis for industrialization of a microalgal photosynthetic hydrogen production technology.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder and application thereof in flour and rice food
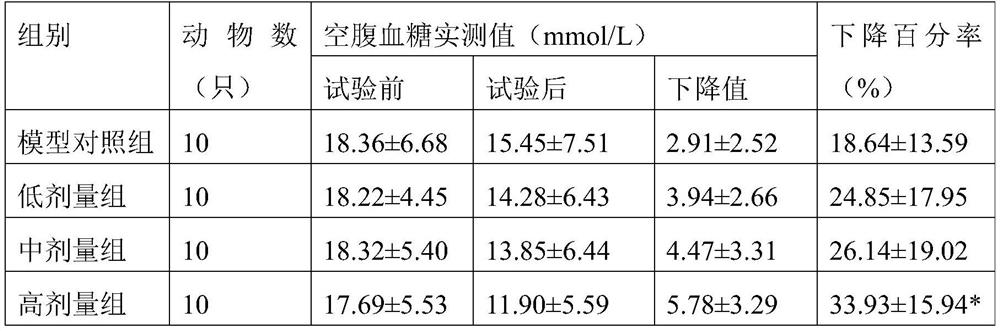
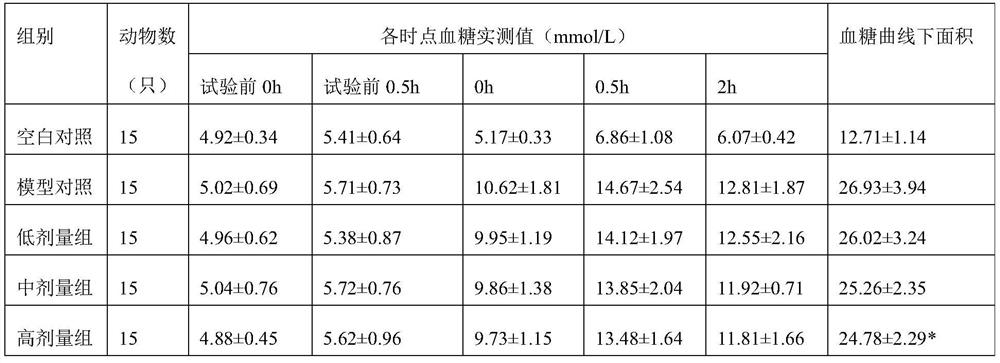
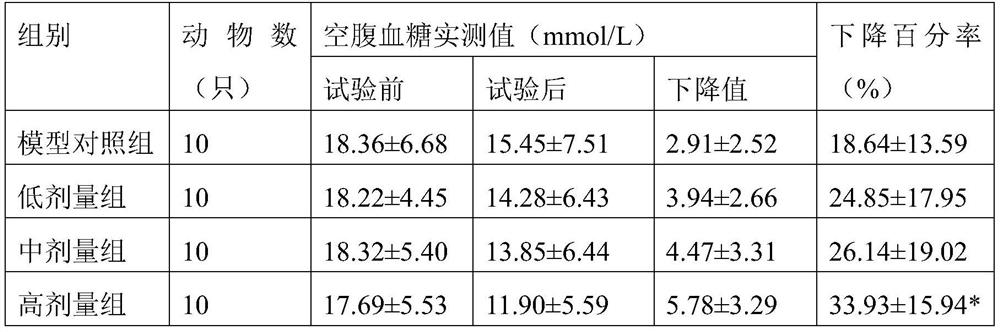
PendingCN112501026AImprove securityGood hypoglycemic effectUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention provides chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder and application thereof in flour and rice food. A preparation method of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder comprises the following steps: (a)inoculating chlamydomonas reinhardtii seeds into a seed tank for heterotrophic culture, and after the culture, inoculating the chlamydomonas reinhardtii seeds with the inoculation quantity of 1-10vol%into a fermentation tank for heterotrophic fermentation; (b) after the fermentation is finished, carrying out membrane separation on the obtained fermentation liquid to obtain a chlamydomonas reinhardtii solid product; and (c) carrying out spray drying or vacuum freeze drying on the obtained product to obtain the chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder. The chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder disclosed bythe invention can be added when staple foods such as steamed buns, noodles, rice and rice noodles are made in daily life, has the effect of assisting in reducing blood sugar, and can enhance the nutrition and immunity of diabetic patients.
Owner:山西透云生物科技有限公司
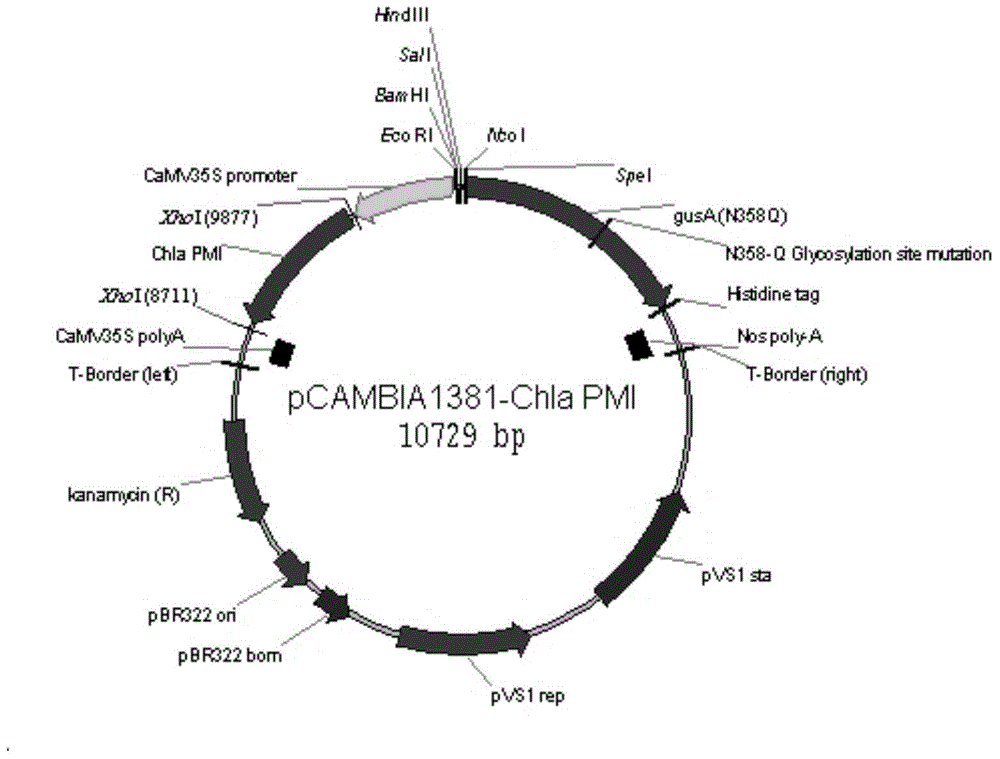
Phosphomannose isomerase gene with plant origin and application of phosphomannose isomerase gene
InactiveCN104531657ANo potential hazardOxidoreductasesIsomerasesEscherichia coliChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention provides a phosphomannose isomerase gene ChlaPMI with the plant origin. The nucleotide sequence of the phosphomannose isomerase gene ChlaPMI is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention further provides a prokaryotic expression vector with ChlaPMI, and the prokaryotic expression vector can be used for identifying the ChlaPMI proteometabolism mannose activity. Based on the prokaryotic expression vector, the ChlaPMI proteometabolism mannose activity is identified so that it can be identified that the prokaryotic expression vector can carry out metabolism on the mannose. The invention provides an expression box with the ChlaPMI, a plant expression vector and application of expression box and expression vector in the plant genetic transformation application. The plant expression vector established through the ChlaPMI gene is utilized, the mannose serves as the screening reagent, and rice cells are successfully converted. The phosphomannose isomerase gene with the plant origin is successfully separated and cloned, and due to the fact that the phosphomannose isomerase gene comes from the plant (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), the phosphomannose isomerase gene is an environmentally-friendly natural substance, and potential danger cannot be caused to the human beings. The phosphomannose isomerase gene can be used for replacing phosphomannose isomerase from the Escherichia coli.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
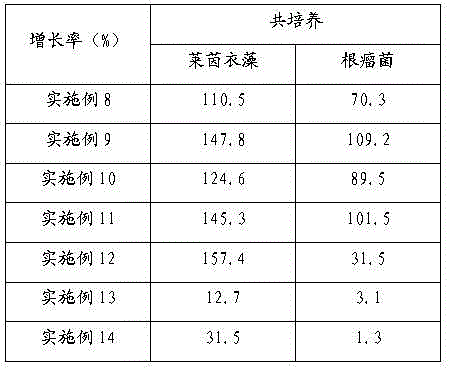
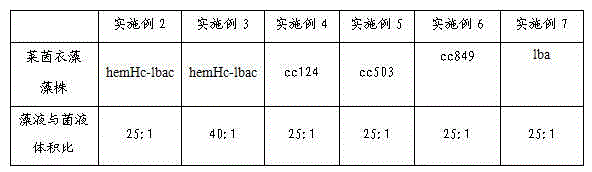
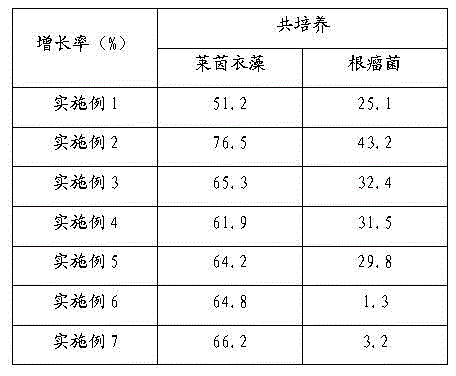
Method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN104017763AIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeChlamydomonas reinhardtiiEcological environment
The invention relates to the technical field of biological hydrogen production and particularly relates to a method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.. The method comprises the following steps: respectively co-culturing Bradyrhizobium japonicum (hereinafter referred to as rhizobia) and another three strains, namely Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain cc124 (hereinafter referred to as 124), algal strains cc503 (hereinafter referred to as 503) and transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hemHc-lbac (hereinafter referred to as hemHc-lbac) in a normal culture medium and a sulfur-deficient culture medium, the results show that the growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Bradyrhizobium japonicum can be promoted and the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gathers around the Chlamydomonas cell and grows prior to the hydrogen production decrescence, which indicates that a phenomenon of a periodical reciprocal symbiosis exists between Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and rhizobia. The method disclosed by the invention provides an experimental basis and a new idea for further broadening the host range of rhizobia, promoting the biomass accumulation of large-scale cultivation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, producing a renewable biological energy source and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
A Chlamydomonas strain and its application in biogas slurry purification
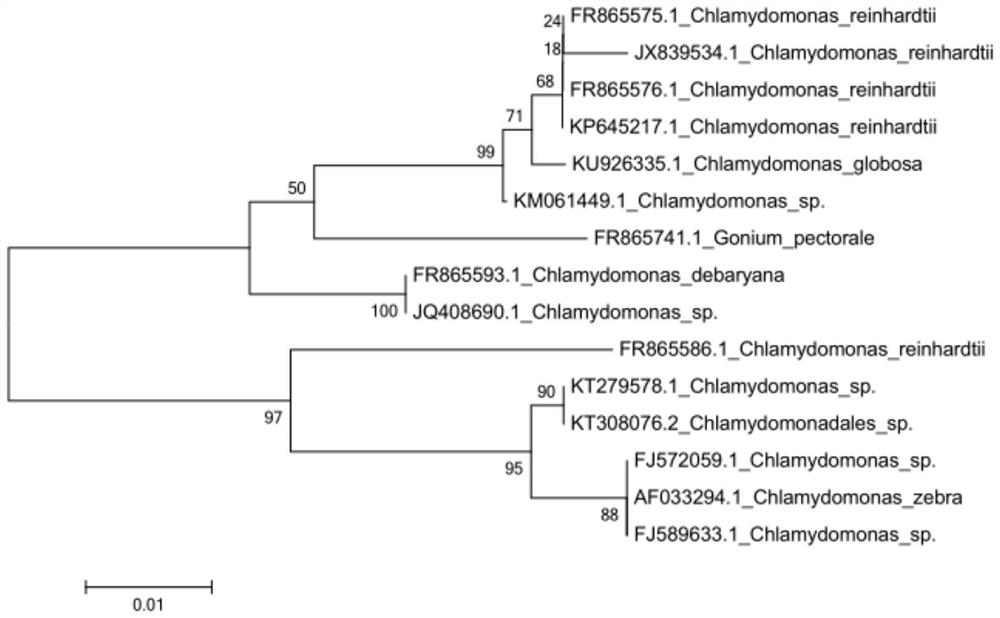
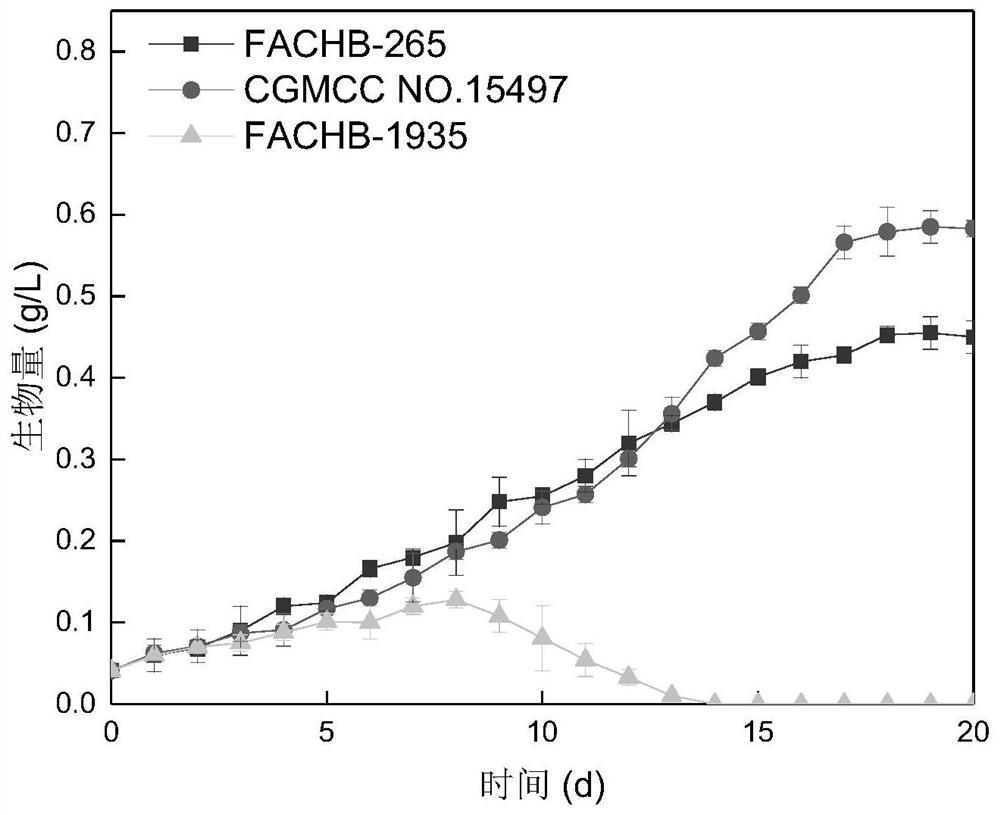
ActiveCN109251866BPlay a role in the purification of nitrogen and phosphorus removalAdvantages of Nitrogen and Phosphorus RemovalUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas sajaoAmmoniacal nitrogen
The present invention proposes a strain of Chlamydomonas algae, the preservation number of which is: CGMCC NO.15497. The invention also proposes the application of the Chlamydomonas strain in biogas slurry purification. The Chlamydomonas whose preservation number is CGMCC NO.15497 proposed by the present invention can grow in pig manure biogas slurry under suitable culture conditions, using the pollutant ammonia nitrogen in pig manure biogas slurry as its own growth nitrogen source, and using pig manure The pollutant total phosphorus in the biogas slurry is used as a source of phosphorus for its own growth, and it plays a role in denitrification and phosphorus purification of pig manure biogas slurry. Compared with the Chlamydomonas strains purchased from other commercial algae species banks, the Chlamydomonas with the preservation number CGMCC NO.15497 of the present invention is no matter in the accumulation of biomass or in the effect of denitrification and phosphorus removal of swine manure and biogas slurry. have obvious advantages.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Biological crust restoration material for promoting ecological restoration of ionic rare earth tailing area, application and restoration method
ActiveCN113857235APromote the leaching of ammonia nitrogenIncrease contentClimate change adaptationContaminated soil reclamationChlamydomonas sajaoAmmoniacal nitrogen
The invention belongs to the technical field of ecological restoration of mines, and relates to a biological crust restoration material for promoting the ecological restoration of an ionic rare earth tailing area, application and a restoration method. The biological crust restoration material for promoting the ecological restoration of the ionic rare earth tailing area provided by the invention comprises broadleaf algae and / or indigenous soil algae; the types of the indigenous soil algae comprise cyanobacteria sphingothrix and / or chlorophyta chlamydomonas; the variety of the broadleaf algae comprises nostoc nitrogen fixing and / or microcoleus vaginatus. According to the restoration material, the culture solution of the broadleaf algae and the indigenous soil algae is applied to the soil of an ion type rare earth tailing area to be repaired, the content of organic matter in the tailing soil can be remarkably increased, the ammonia nitrogen content is reduced, the crust area of a tailing surface layer is increased, an exposed surface layer is greatly reduced, the extremely degraded ecological environment of the ionic rare earth abandoned mining area caused by abandoned tailings can be quickly improved, and the soil degradation and environmental pollution of the mining area caused by the mining of the rare earth mine can be improved.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF ECO-ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & PLANNING
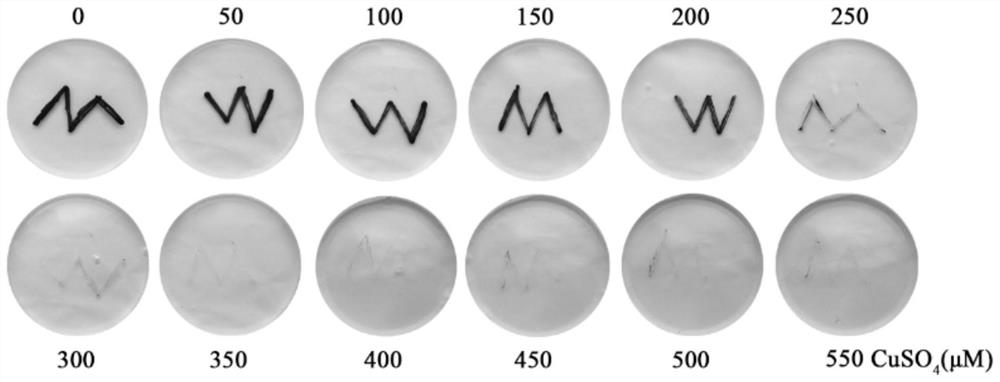
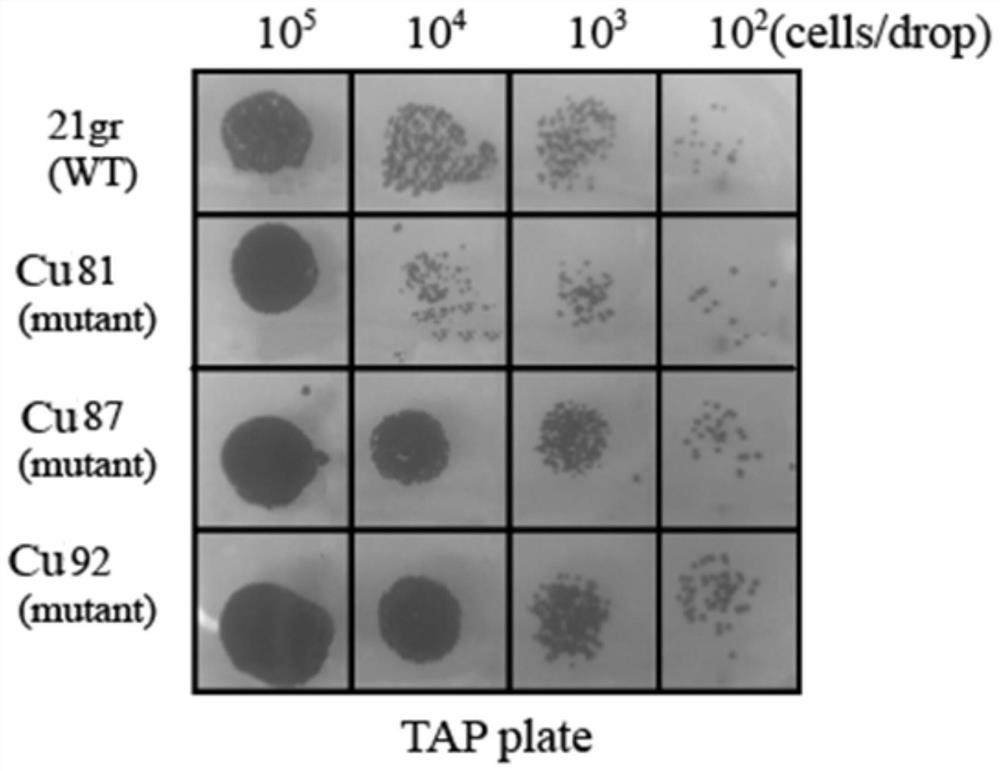
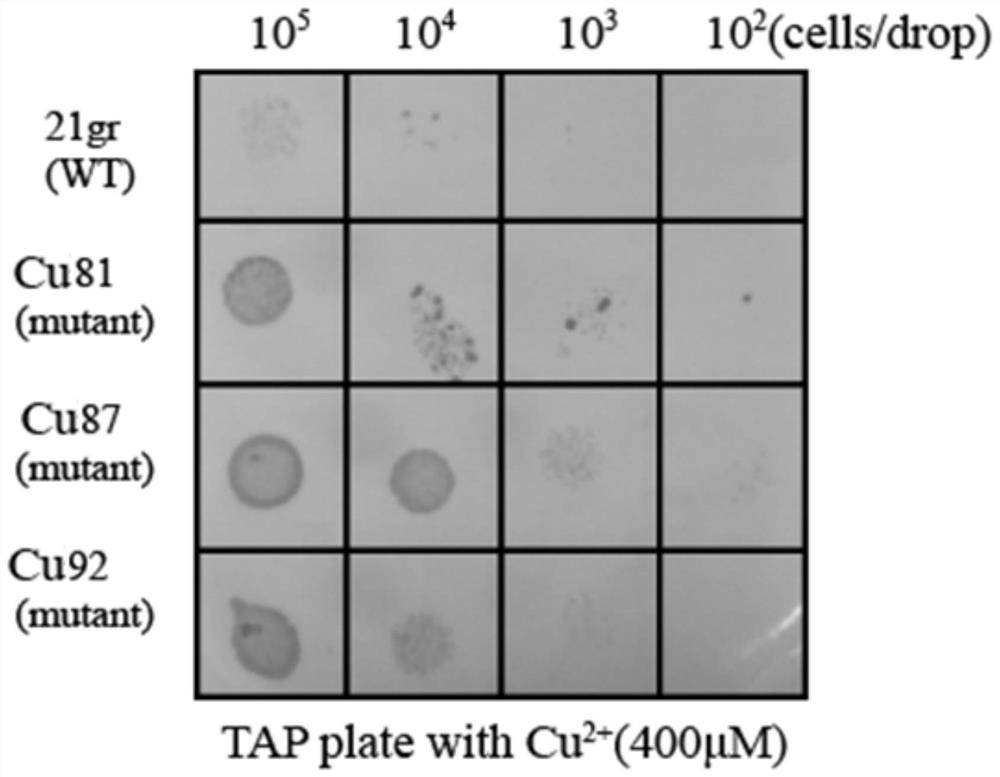
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains capable of efficiently adsorbing copper ions
ActiveCN113913299AImprove adsorption capacityImprove adsorption efficiencyUnicellular algaeTransferasesChlamydomonas sajaoChlamydomonas reinhardtii
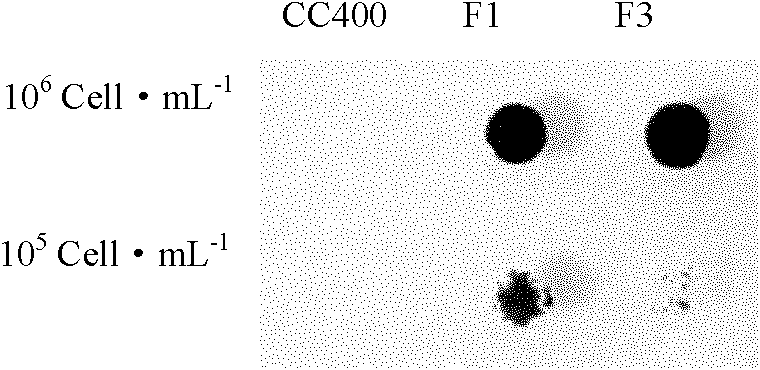
The invention provides chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains capable of efficiently adsorbing copper ions. The three strains are respectively named Chlamydomonasreinhardtii Cu81, Cu87 and Cu92, and the preservation numbers are respectively CGMCC No. 21484, CGMCC No. 21485 and CGMCC No. 21486. According to the invention, a chlamydomonas mutant library (resistance gene fragment aphVIII is randomly integrated into a chlamydomonas genome to cause random insertion mutation) is constructed, and a corresponding screening method is established to screen potential chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains capable of adsorbing metal copper, so that in subsequent research, mutant genes can be conveniently searched through the known sequence of the aphVIII fragment, the potential molecular mechanism of the strains in the aspects of heavy metal metabolism, resistance gene function and the like can be deeply researched, and a solid foundation is laid for further excavating the potential of the heavy metal adsorption strains in genetic engineering improvement.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii instability domain gene, protein expression regulation method based on instability domain and application of chlamydomonas reinhardtii instability domain gene
ActiveCN111153970AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsUnicellular algaeChlamydomonas reinhardtiiRapamycin-Binding Proteins
The invention provides a chlamydomonas reinhardtii instability domain gene, a protein expression regulation method based on an instability domain and application of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii instability domain gene. The chlamydomonas reinhardtii instability domain gene includes a mutant rapamycin binding protein gene and chlamydomonas reinhardtii RBCS2 intron 1; and the instability domain geneincludes a nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Expression product instability domain protein of the instability domain gene constructed by binding the mutant rapamycin binding protein gene and the chlamydomonas reinhardtii RBCS2 intron 1 in chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells is extremely unstable and can be rapidly degraded by intracellular proteases to enable fusion protein containing an instability domain to be degraded; and the stability of the instability domain can be improved by small molecule inducer Shield-1, so that the fusion protein is stably and continuously expressed, and the purpose of regulating protein expression in chlamydomonas reinhardtii is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
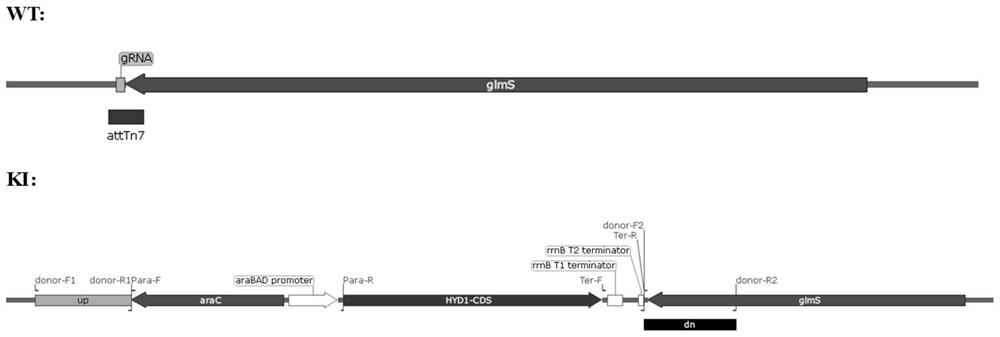
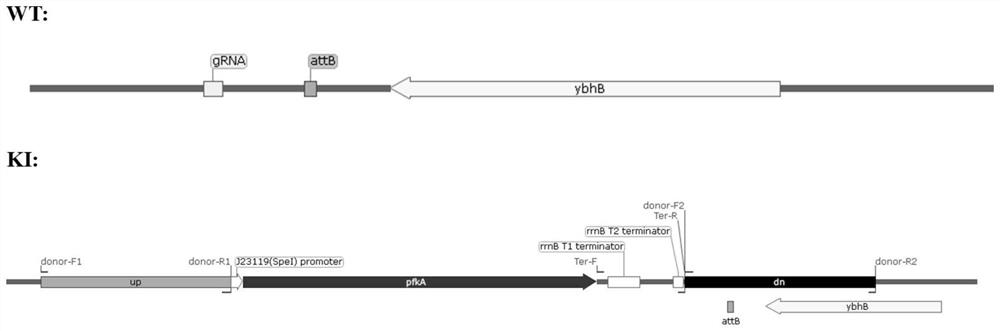
Recombinant escherichia coli and hydrogen production application
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli and a hydrogen production application thereof. The recombinant escherichia coli is obtained by transferring a [FeFe]-hydrogenase gene hyd1, which is derived from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and a phosphofructokinase isoenzyme I gene pfkA, which is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, into a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) chromosome of the escherichia coli. The hydrogen-producing recombinant escherichia coli screened by the invention can efficiently produce hydrogen in cells, and takes glucose, fructose, cane sugar, starch and glycerol as substrates. The recombinant Escherichia coli strain for screening hydrogen production has the advantages that inducers such as IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) are not added, interference of high-concentration glucose can be overcome, cost reduction is brought to green hydrogen preparation, and the recombinant Escherichia coli strain is environment-friendly, has practical value and can realize'safe, clean, economical and continuous' large-scale production of green energy.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing Porcine circovirus type 2 antigen with chloroplast and its product
InactiveCN102311972ASmall molecular weightSimple structureViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenChloroplast
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Porcine circovirus type 2 antigen with chloroplast and its product. The preparation method comprises the steps of: (1) constructing a Chlamydomonas chloroplast expression vector of a Porcine circovirus type 2 antigen gene; (2) conversing the Chlamydomonas chloroplast expression vector into Chlamydomonas, and conducting screening so as to obtain transgenic Chlamydomonas; (3) culturing the transgenic Chlamydomonas, and collecting expressed recombinant protein, thus obtaining the antigen. The method of the invention employs a Chlamydomonas chloroplast expression system to produce the Porcine circovirus type 2 antigen in a Chlamydomonas bioreactor, and the expressed recombinant protein has high specificity, good immune effect and generate no non-purposive immune reaction. The preparation method provided in the invention can greatly reduce the production cost of the Porcine circovirus type 2 antigen, and has many advantages like safety, high efficiency, less energy consumption and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHANCE HEQISHI BIO SCI& TECH CO LTD
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder heterotrophic fermentation preparation method and application
ActiveCN112430546AEliminate potential safety hazardsHigh quality proteinUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas sajao
The invention provides chlamydomonas reinhardtii and a chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder heterotrophic fermentation preparation method and application.The preparation method of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder comprises the following steps that (a) chlamydomonas reinhardtii seeds are inoculated into a seed tank for heterotrophic culture, and after culture is completed, the chlamydomonas reinhardtii seeds are inoculated into a fermentation tank for heterotrophic fermentation, wherein the culture temperature of the seed tank and the culture temperature of the fermentation tank are 15-38 DEG C, the pressure is 0.03-0.08 MPa, the pH value is 5.0-8.0, the dissolved oxygen is 10-100%, and the stirring rotating speed is 0-700 revolutions per minute; (b) after the fermentation is finished, membrane separation is performed on the obtained fermentation liquid to obtain a chlamydomonas reinhardtii solid product; and (c) spray drying is performed on the obtained product to obtain the chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder. The chlamydomonas reinhardtii powder prepared by the method has high-quality nutrient substances such as protein, polysaccharide, unsaturated fatty acid and vitamin, is high insafety and has a remarkable blood sugar reducing effect.
Owner:山西透云生物科技有限公司
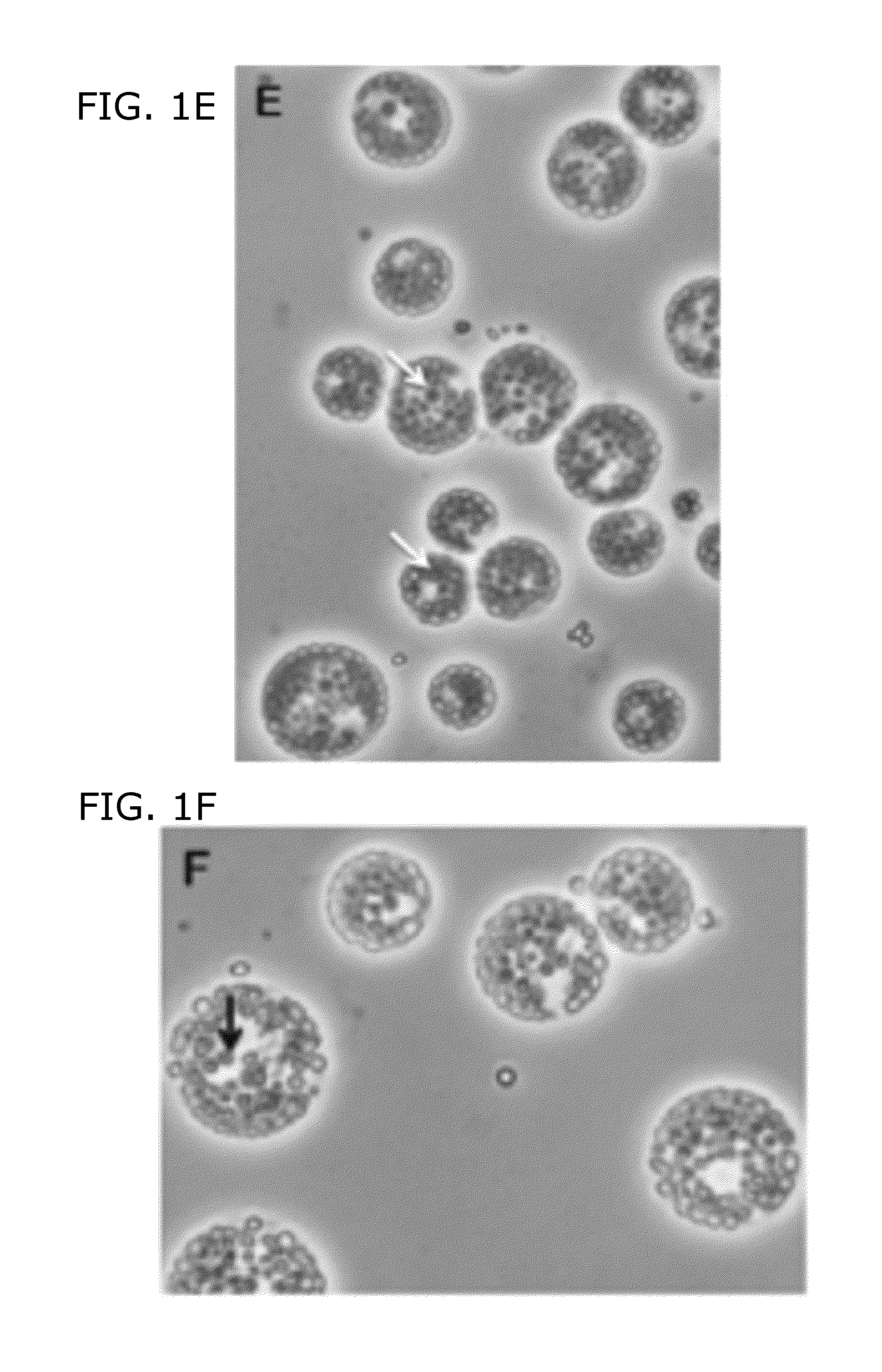
Buoyant triacylglycerol-filled green algae and methods therefor
Cultures of Chlamydomonas are disclosed comprising greater than 340 mg / l triacylglycerols (TAG). The cultures can include buoyant Chlamydomonas. Methods of forming the cultures are also disclosed. In some embodiments, these methods comprise providing Chlamydomonas growing in log phase in a first culture medium comprising a nitrogen source and acetate, replacing the first culture medium with a second medium comprising acetate but no nitrogen source, and subsequently supplementing the second medium with additional acetate. In some embodiments, a culture can comprise at least 1,300 mg / l triacyglycerols. In some embodiments, cultures can be used to produce a biofuel such as biodiesel.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
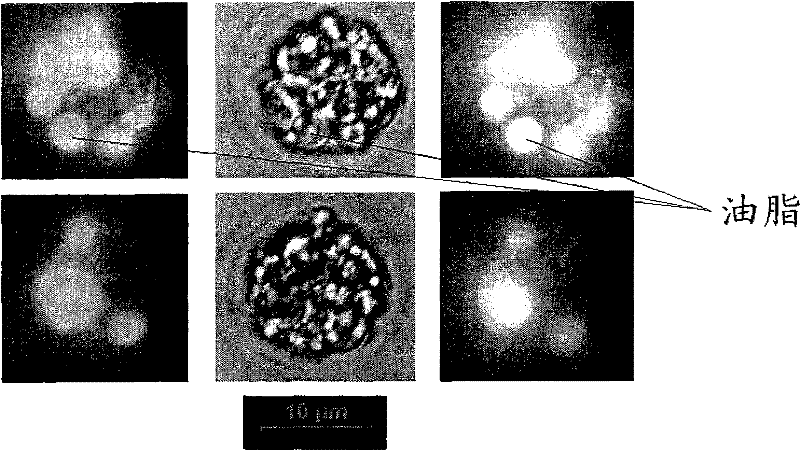
Method for extracting grease from chlamydomonas
InactiveCN110903897AImprove qualityGood market application valueUnicellular algaeBiofuelsChlamydomonas sajaoBiodiesel
The invention discloses a method for extracting grease from chlamydomonas. The method comprises the following steps: culturing the chlamydomonas, preparing dry microalga powder and extracting the grease. The accumulation of grease in the chlamydomonas is remarkably improved under the interaction of red light and blue light, the higher the blue light proportion is, the more the grease is accumulated, and the accumulation amount of the grease under the red light and blue light (1:2) reaches the highest value. The grease can be used for preparing biodiesel with good quality, and has good market application values.
Owner:沈兰兰
Green alga strain and application thereof in rare earth ammonia nitrogen wastewater treatment
ActiveCN114606131AStable and efficient denitrification processSolve the problem of ammonia nitrogen pollutionUnicellular algaeWater contaminantsChlamydomonas sajaoAmmoniacal nitrogen
The invention discloses a green alga strain and application thereof in rare earth ammonia nitrogen wastewater treatment, the green alga strain is classified and named as Chlamydomonas YC, the chemical name is Chlamydomonas sp.YC, the green alga strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan on May 13, 2021, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2021529. The green algae strain can be used for treating high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater.
Owner:福州文泽生物科技有限公司
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112662697AConducive to research structureGood for studying interactionsHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionHygromycin BChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid comprises a hygromycin B screening gene, an endogenous promoter for expressing a TCTN1 gene, TCTN1 gDNA, a 3 * HA tag at the 3'terminal and a terminator rbcS2 for terminating TCTN1 transcription; The construction method comprises the following steps: cloning a chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 gene segment; constructing a T vector plasmid containing a TCTN1 fragment; obtaining a terminal phosphorylated TCTN1 fragment; preparing a pHyg-3HA vector; and constructing and verifying the plasmid of the pHyg-TCTN1-3HA. According to the expression plasmid of the chlamydomonas TCTN1, algal strains capable of stably expressing the TCTN1-HA fusion protein can be efficiently screened, so that a chlamydomonas cilia transition region is marked, and the structure of the transition region and the function of a complex are known.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
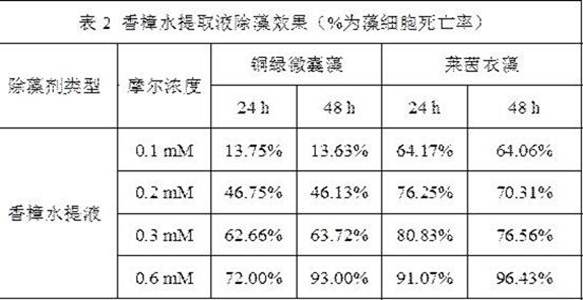
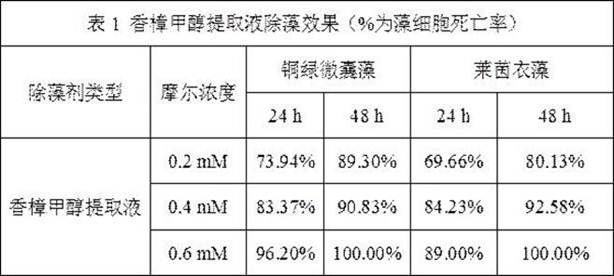
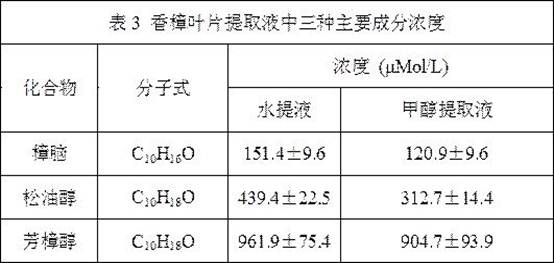
Camphor-based biological algicide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108605996BExcellent killing effectGood killing effectBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyChlamydomonas sajao
The biological algicide based on Cinnamomum camphora and preparation method thereof disclosed by the present invention provide three different preparation methods of the algicide, and respectively obtain Cinnamomum camphora methanol extract and Cinnamomum camphora water extract obtained by extracting Cinnamomum camphora leaves and The mixed algaecide solution compounded by camphor, terpineol and linalool has different characteristics of the algaecide prepared by the method of the present invention; the camphor methanol extract has outstanding killing effect on Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii The effect of camphor water extract is slightly weaker than that of methanol extract, but the cost is lower; the raw material procurement of mixed algae removal solution is simple, the preparation process is quick, and it is convenient to store, and it can be prepared in an emergency, and at a higher molar concentration, it has no effect on aeruginosa. Both Microcystis and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii can produce efficient killing effect. In addition, the active ingredients of the algaecide of the present invention are all derived from plants themselves, can be naturally degraded, and belong to an eco-friendly algaecide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
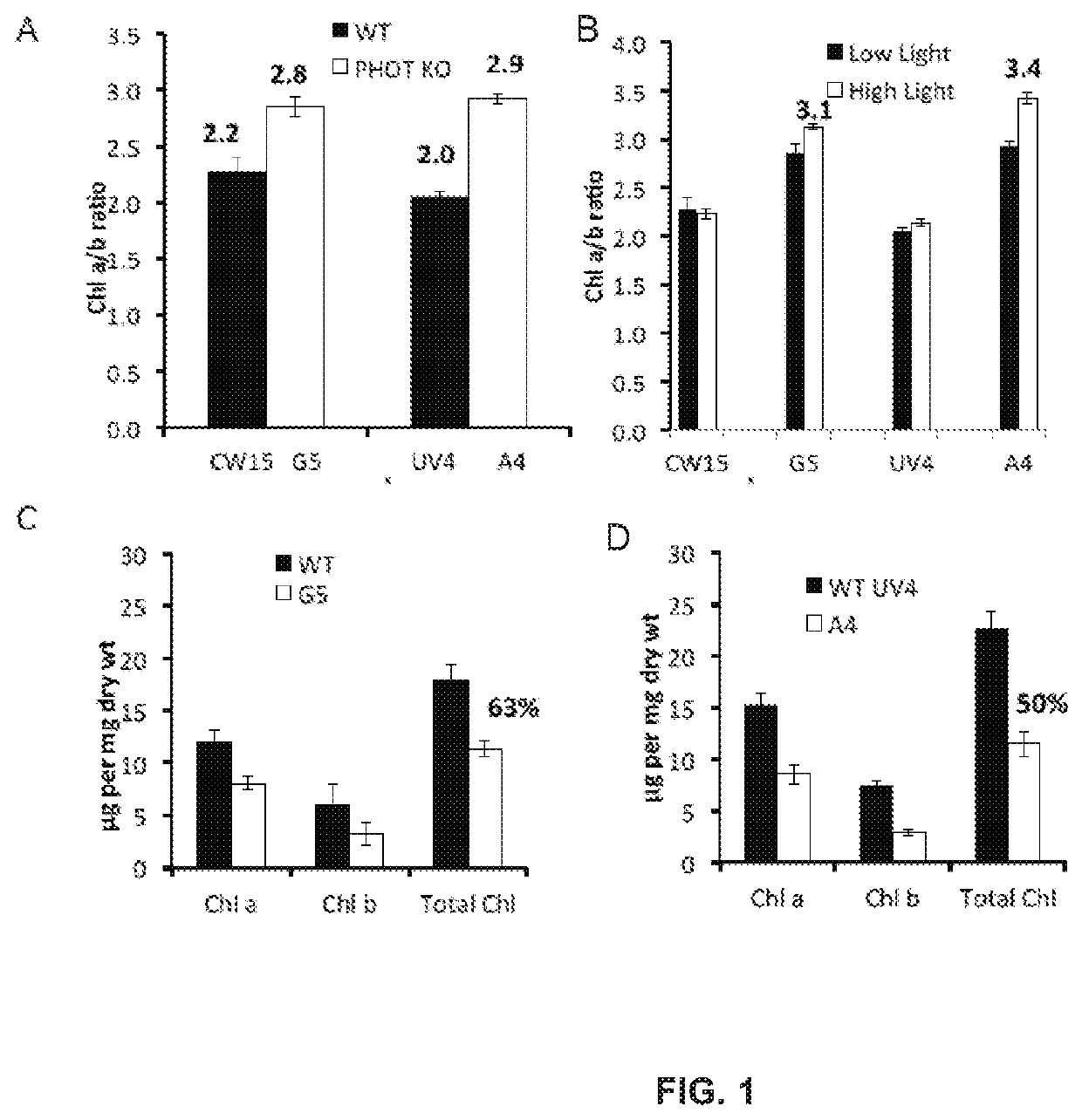
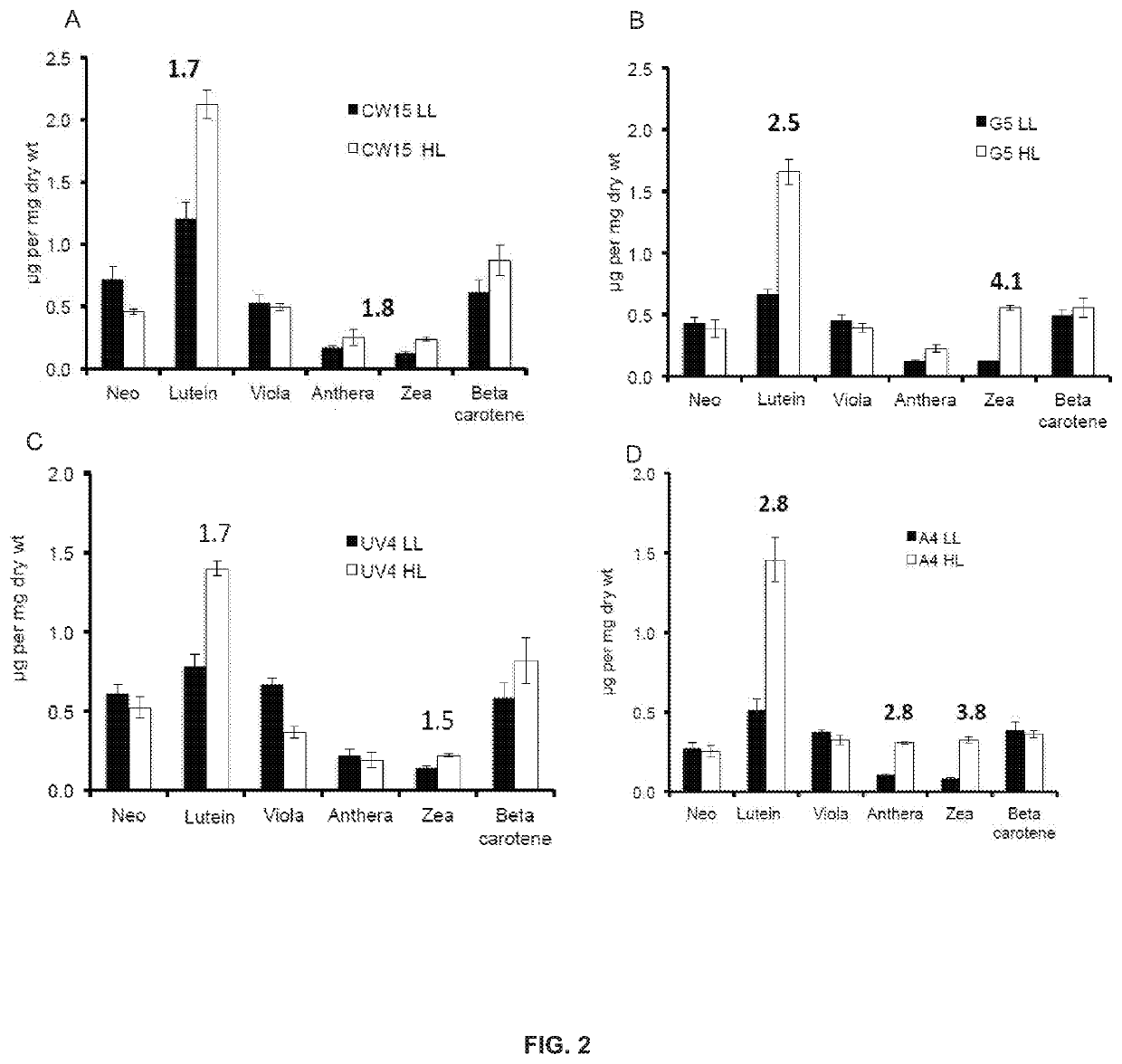
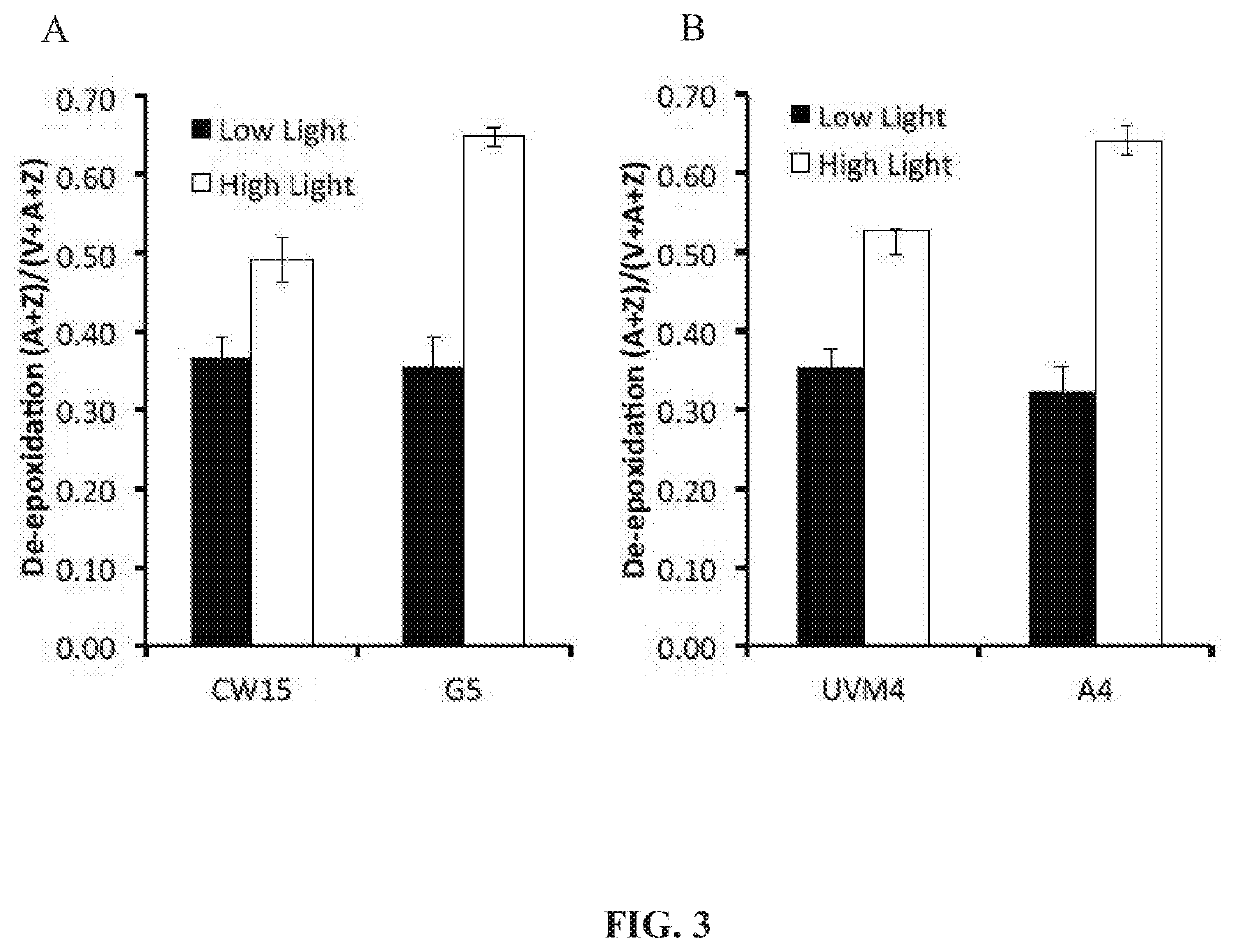
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
InactiveUS20200208125A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityUnicellular algaeTransferasesElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Chlamydomonas strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101892159BImprove liquidityImprove qualityFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeChlamydomonas sajaoMicrobiology
The invention provides a chlamydomonas strain. Through authentication, the chlamydomonas strain is a novel strain, and the collection number of the chlamydomonas strain is CGMCC No.3577. The chlamydomonas strain has higher grease content and can be applied to preparing biodiesel, feed or edible oil.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
A kind of collembola implantation culture solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106721677BImprove the ability to resist environmental interferenceImprove domestication success rateAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyDipotassium hydrogen phosphate
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
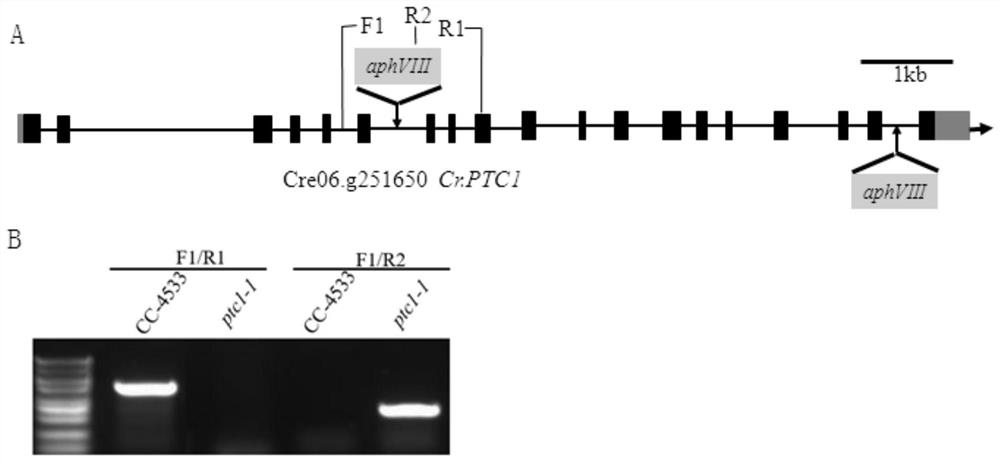
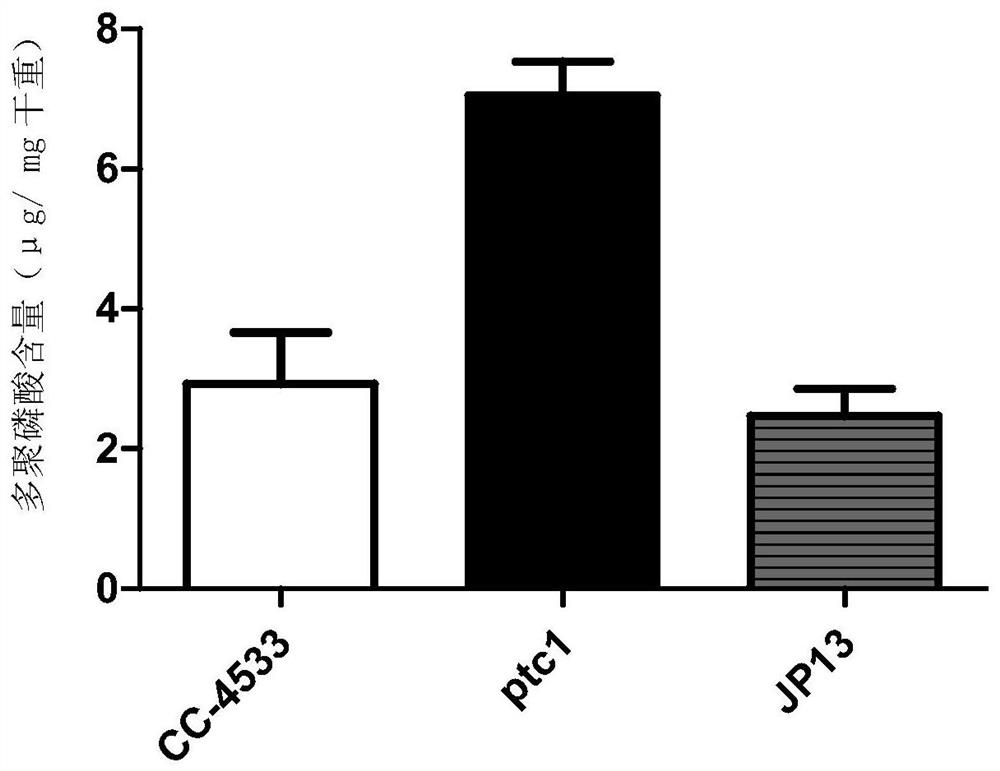
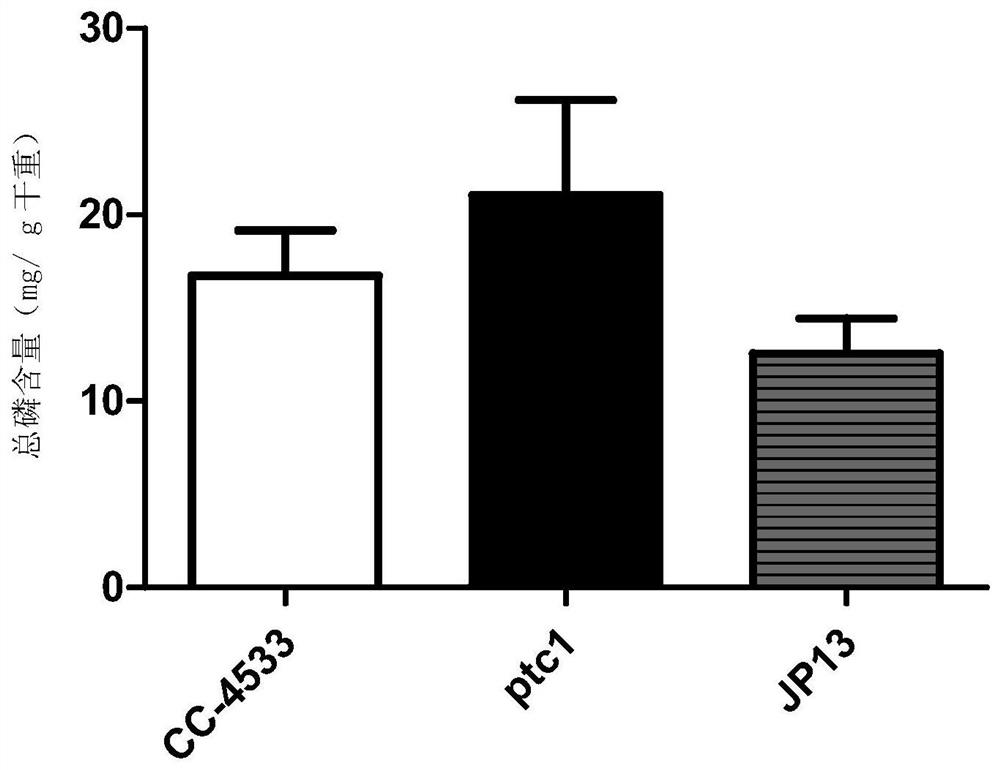
A method and application of increasing algae total phosphorus and polyphosphoric acid content through ptc gene manipulation
The invention discloses a method for increasing algal total phosphorus and polyphosphoric acid content through PTC gene operation and application. Provided protein is named as ptc1 protein and shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table. Nucleic acid molecule coding the protein also belongs to the protection range of the invention. The invention further discloses recombinant microalgae which is obtained by inhibiting expression of gene coding the protein in starting microalgae. The invention further discloses application of the recombinant microalgae in water phosphorus removal or in fertilizerpreparation. The inventor finds a protein related to polyphosphoric acid balance in chlamydomonas, polyphosphoric acid accumulation and total phosphorus content increase are caused after gene coding the protein in chlamydomonas is silenced, and alkaline phosphatase can be efficiently secreted, so that effect of chlamydomonas on purifying phosphorus in water can be promoted, and high-phosphorus chlamydomonas is a great microalgae fertilizer raw material.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for effectively screening out chlamydomonas hydrogen desorption mutant
The invention discloses a method for effectively screening out a chlamydomonas hydrogen desorption mutant, which comprises the following steps of: (1) introducing pJD67 plasmid to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CC425, culturing transformants on a culture medium without arginine, and screening out the transformants which can grow, i.e., the mutant embedded with the pJD67 plasmid; and (2) screening out in the mutant embedded with pJD67plasmid to obtain a transgenic chlamydomonas mutant with increased hydrogen desorption quantity. According to the invention, the workload of directly measuring the hydrogen generation quantity is reduced; the efficiency of screening out the chlamydomonas hydrogen desorption mutant is increased; an important foundation for study on a mechanism of increasing the hydrogen generation quantity by microalgae photosynthesis is established; and meanwhile, the basis of improving a large-scale hydrogen generation technique in the future is provided.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hemolytic phosphatidic acid acyltransferase and its gene and application
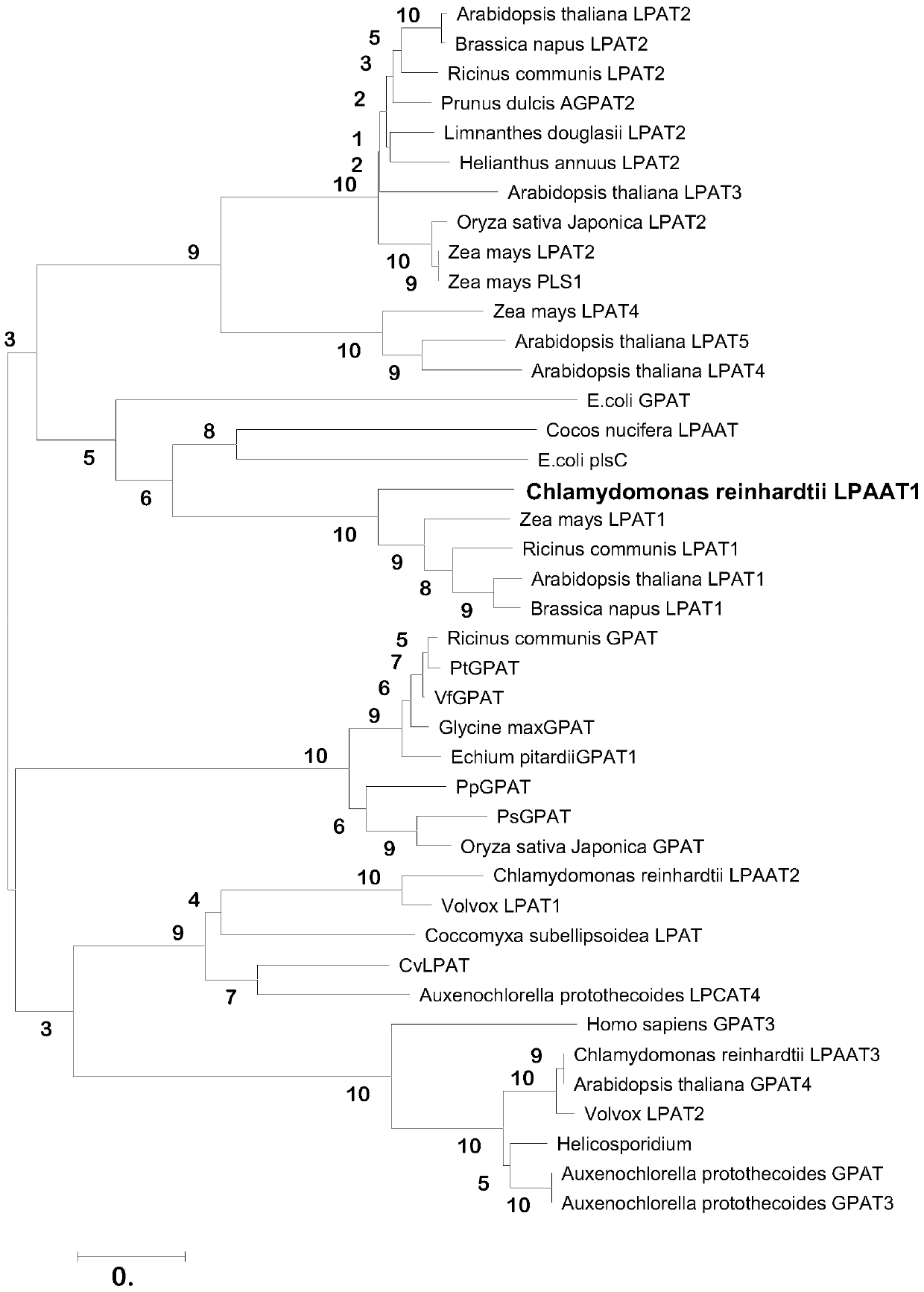
ActiveCN106916798BRaise the ratioHigh selectivityFungiUnicellular algaeChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBiodiesel
The invention discloses Chlamydomonas reinhardti lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, and a gene and application thereof. The Chlamydomonas reinhardti lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase is 1) a protein composed of amino acids as shown in SEQ ID No. 1; or 2) a protein derived from the protein 1) by subjecting the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 to substitution, deletion or addition of one or plural amino acids and having same activity as the protein 1). Research results show that the Chlamydomonas reinhardti lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase has intense selectivity on 16:0-CoA. Through excess expression of the gene, a ratio of C16:0 aliphatic acid in biological cells to total aliphatic acid can be substantially increased; and thus, the gene can be applied to production of high-quality biodiesel (with low burning point and low viscosity and other related products.
Owner:GUOTOU BIO TECH INVESTMENT CO LTD +1
Biostable solvent for determining low-temperature fluorescence spectrum of chlamydomonas
InactiveCN111624178AAvoid Poor Permeability ConsequencesStrong fluorescent signalFluorescence/phosphorescenceChlamydomonas sajaoGlycine
The invention relates to a biological buffer reagent for determining fluorescence spectrum of chlamydomonas. The biological buffer reagent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1-2 parts of N-(hydroxymethyl) methylglycine, 0.5-1.5 parts of trihydroxymethyl aminomethane, 40-60 parts of glycerol, 0.5-1 part of sodium hydroxide and 40-50 parts of water. The chlamydomonas cell morphology can be kept, the physiological state of chlamydomonas is kept unchanged, the consequence of poor permeability of a sample caused by low-temperature freezing solidification expansion of achlamydomonas culture solution is avoided, and a fluorescence signal is strong.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
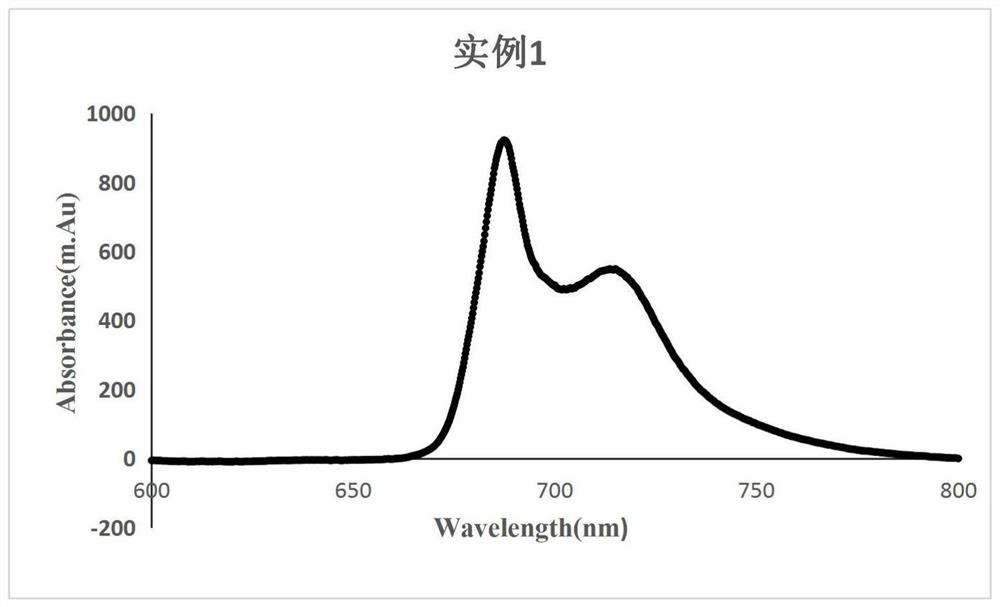
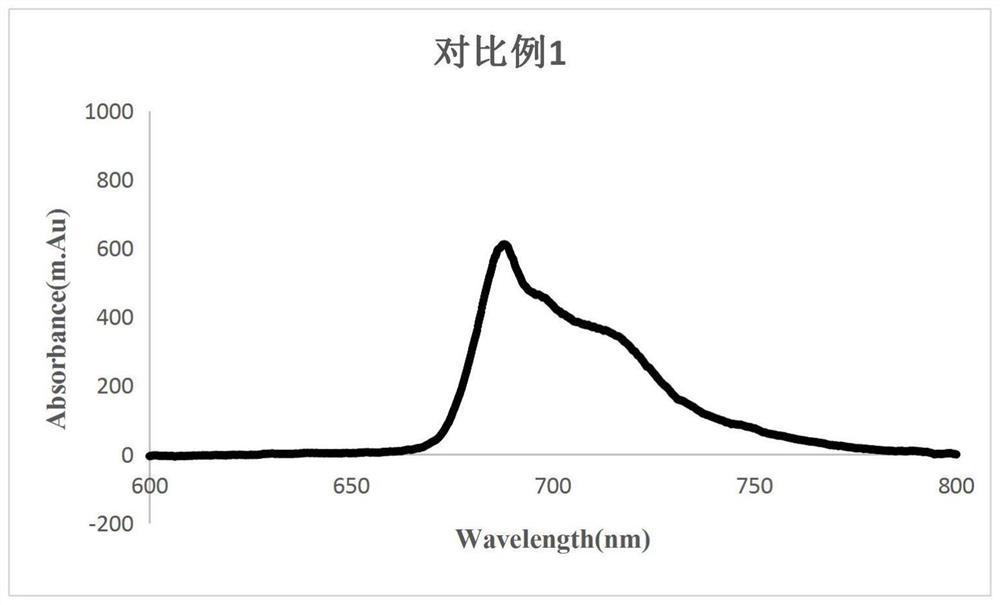
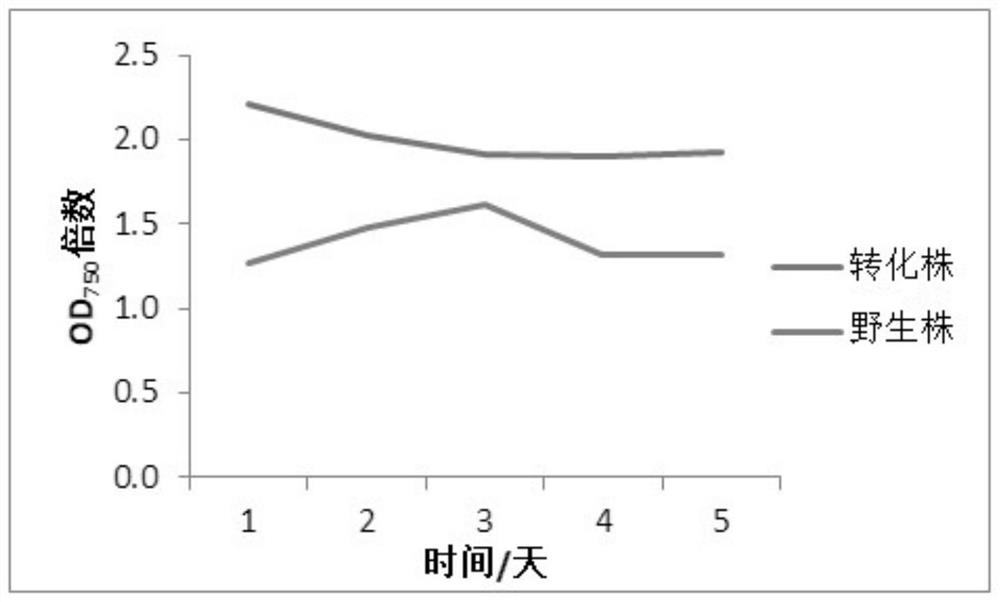
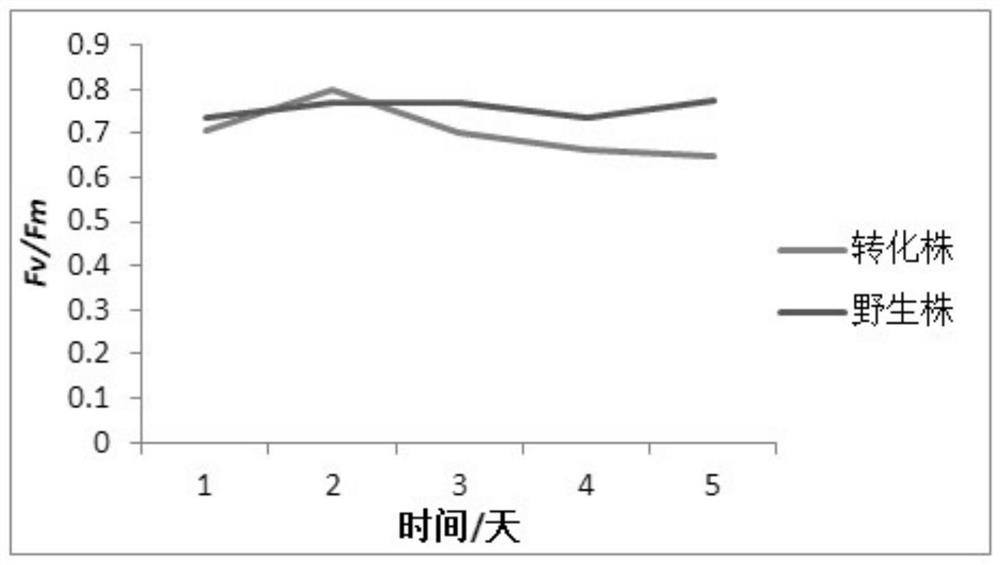
A method for improving carbon fixation efficiency of microalgae and transgenic Chlamydomonas and application
ActiveCN109825441BDoes not affect normal growthIncrease growth rateUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method for improving the carbon fixation efficiency of microalgae. Chlamydomonas chloroplast-type glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene was overexpressed to enhance the ability of Chlamydomonas photosynthetic carbon fixation. It specifically includes the construction of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene recombinant expression vector, and transforming the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene recombinant expression vector into Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells by electric shock transformation, and screening to obtain glyceraldehyde-3 ‑Phosphate dehydrogenase enhanced expression in transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Microalgae can synthesize biomass such as oil, protein, starch, and carotenoids through photosynthetic carbon fixation, and accelerating the production efficiency of microalgal biomass plays an important role in downstream industries. The invention transfers the target gene into Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, accelerates the carbon fixation efficiency and increases its growth rate, and has significant application prospects in the field of microalgae bioengineering.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com