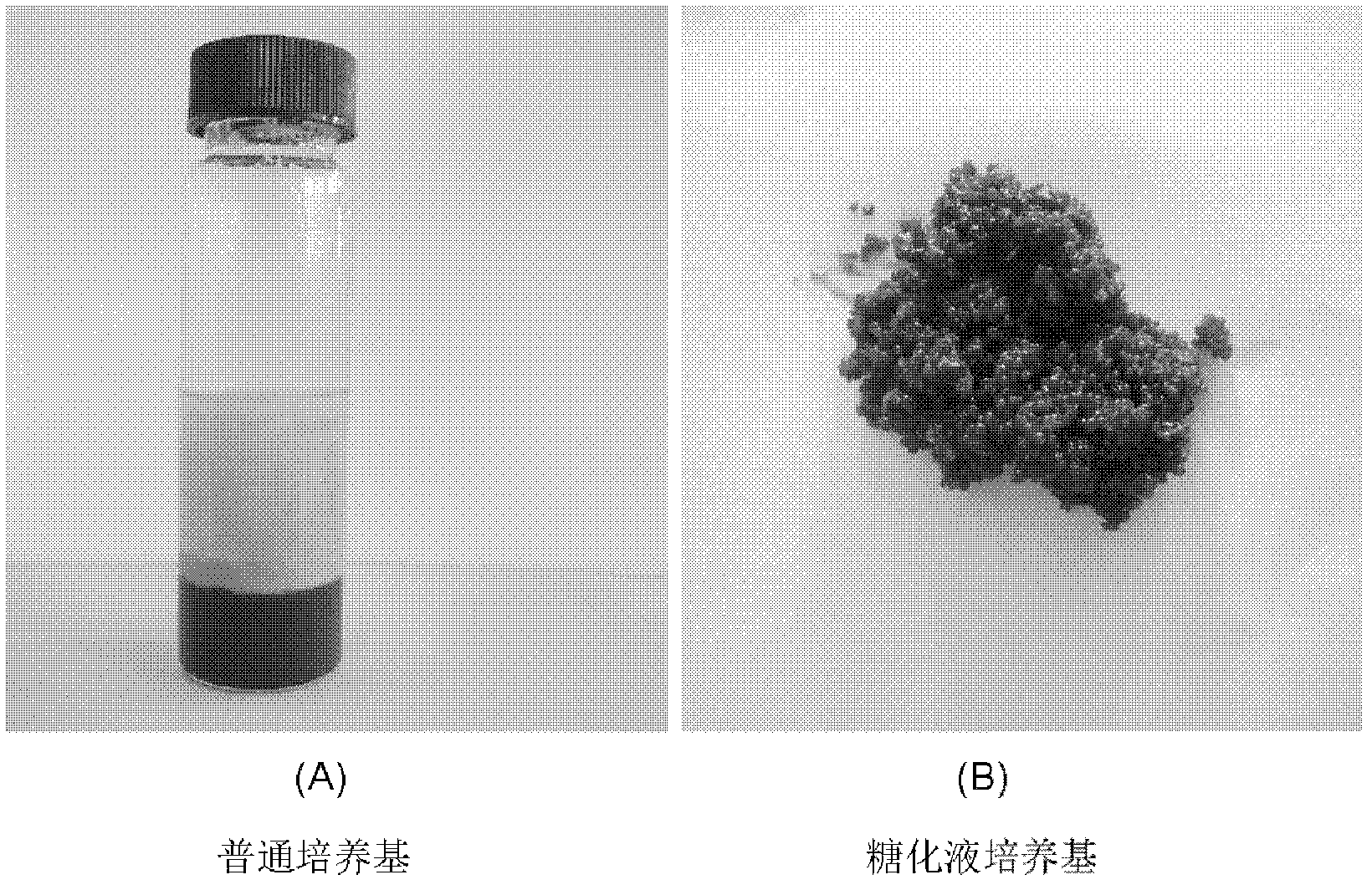
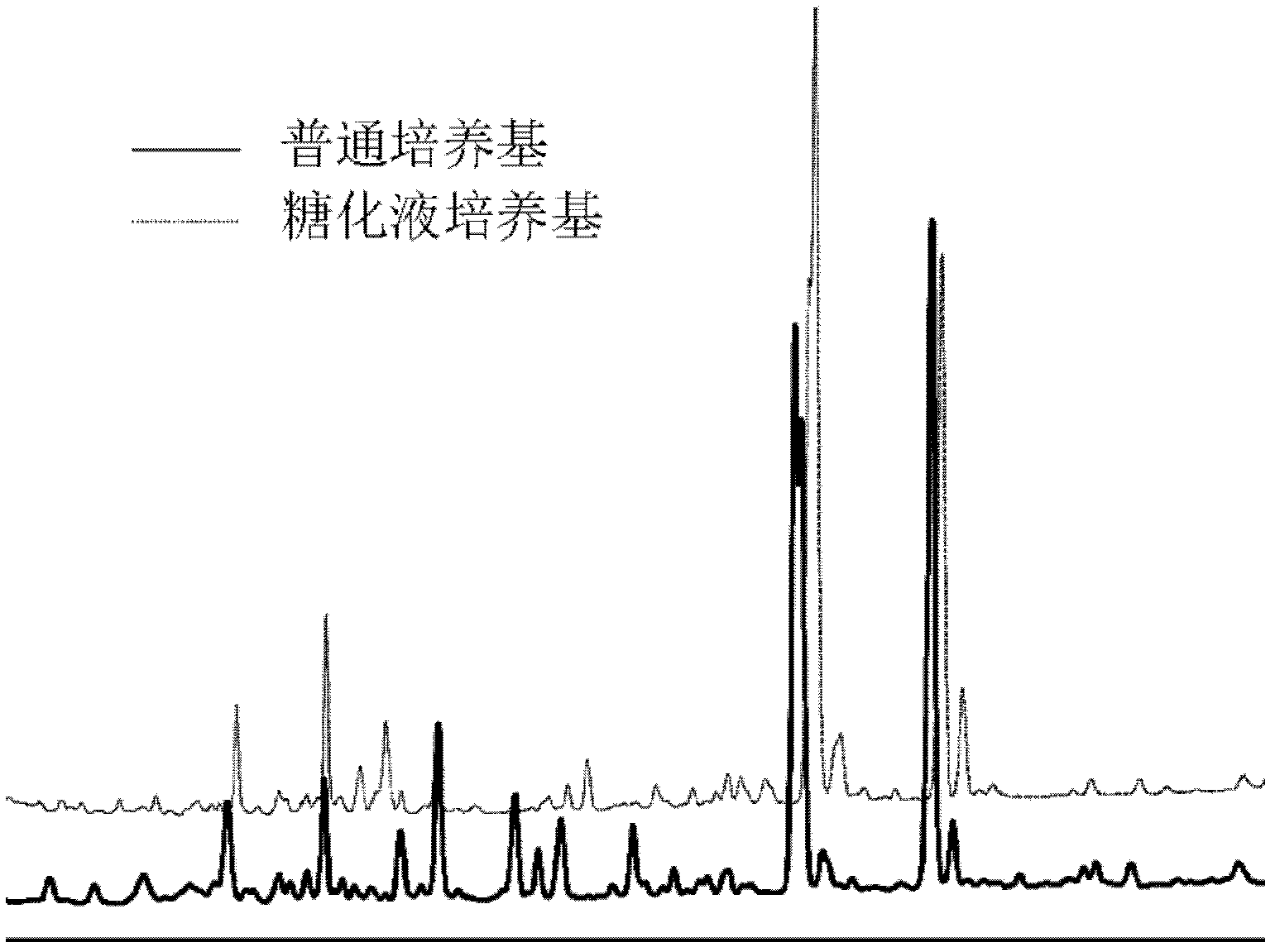
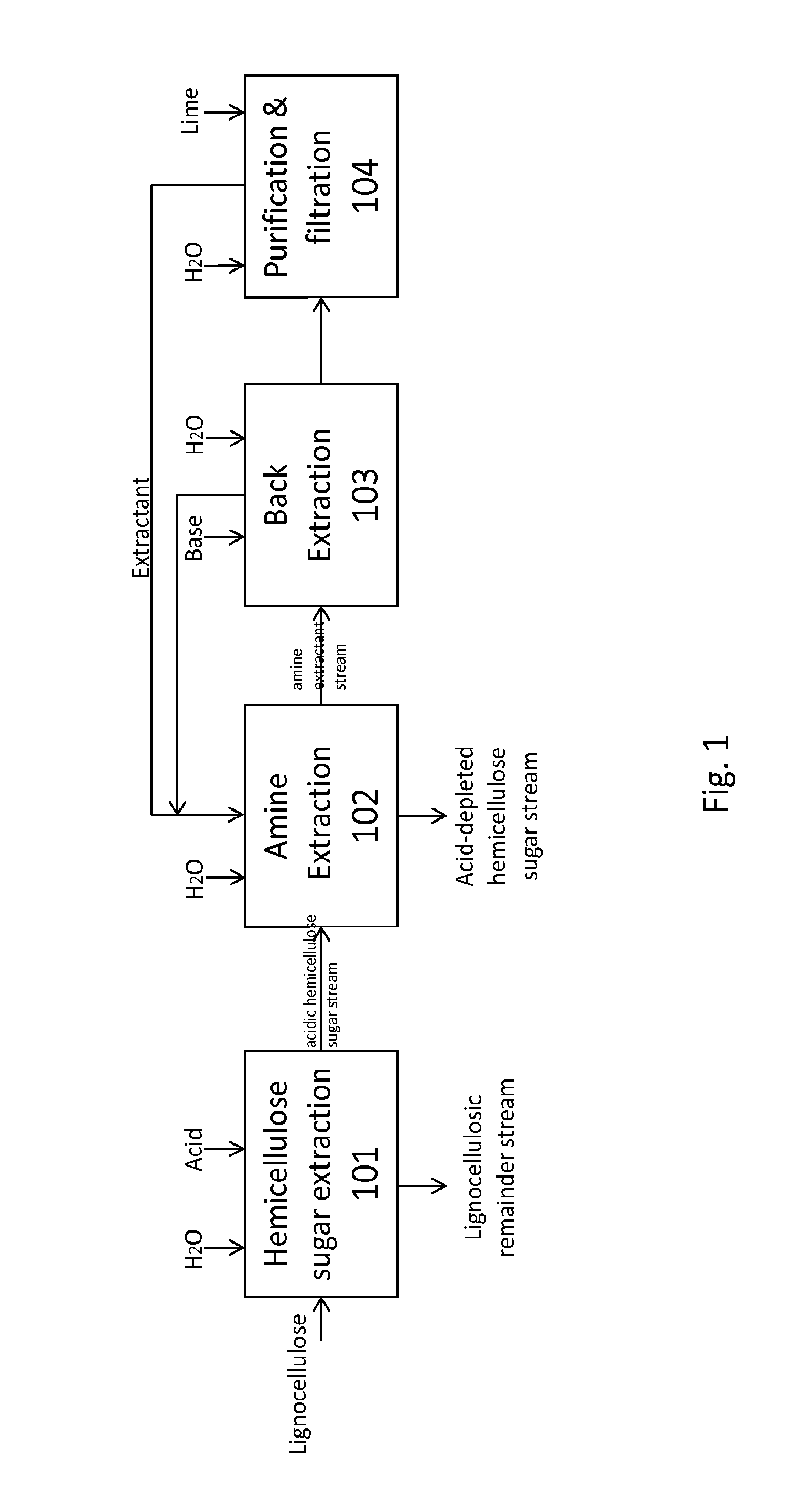
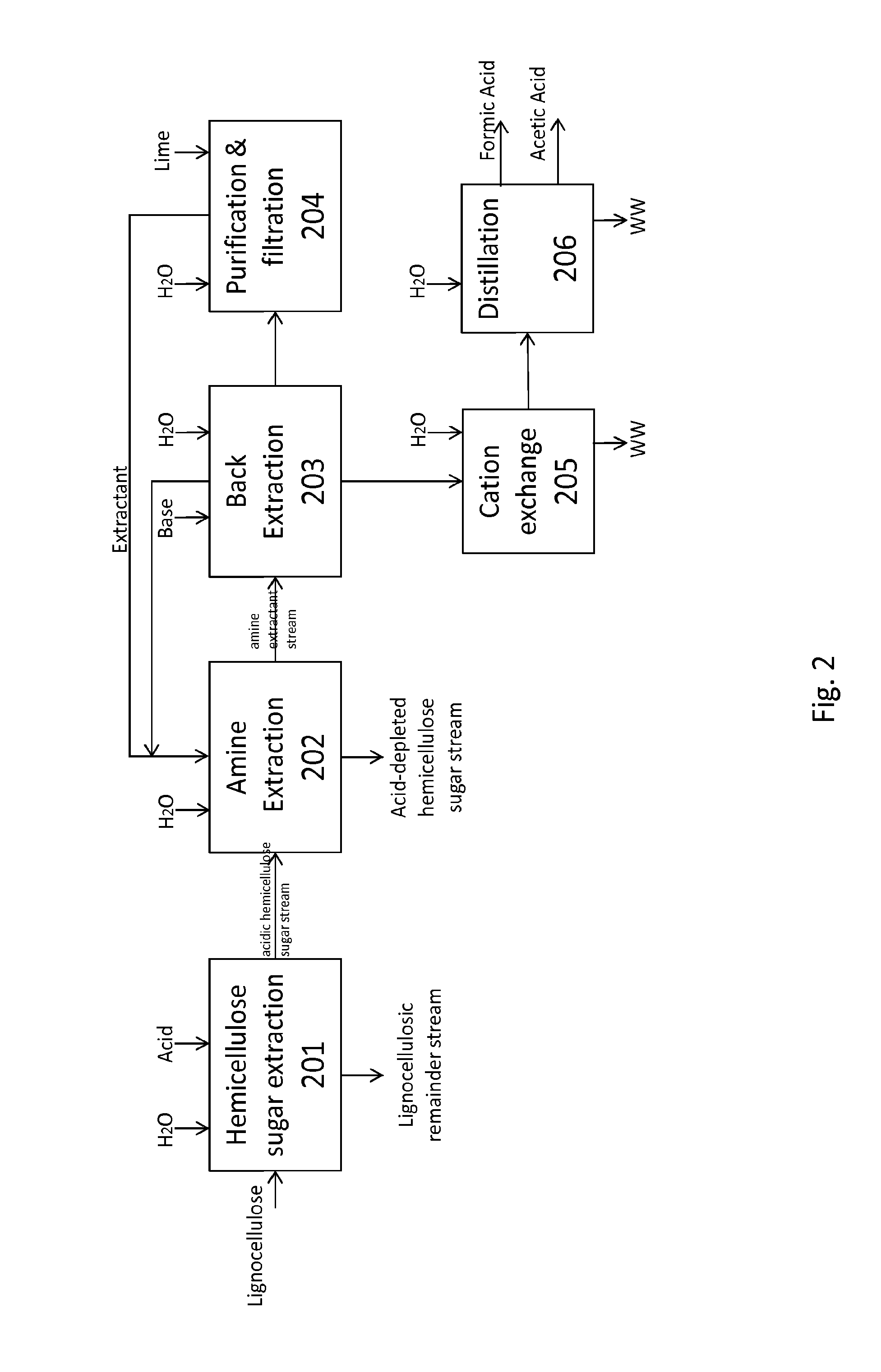
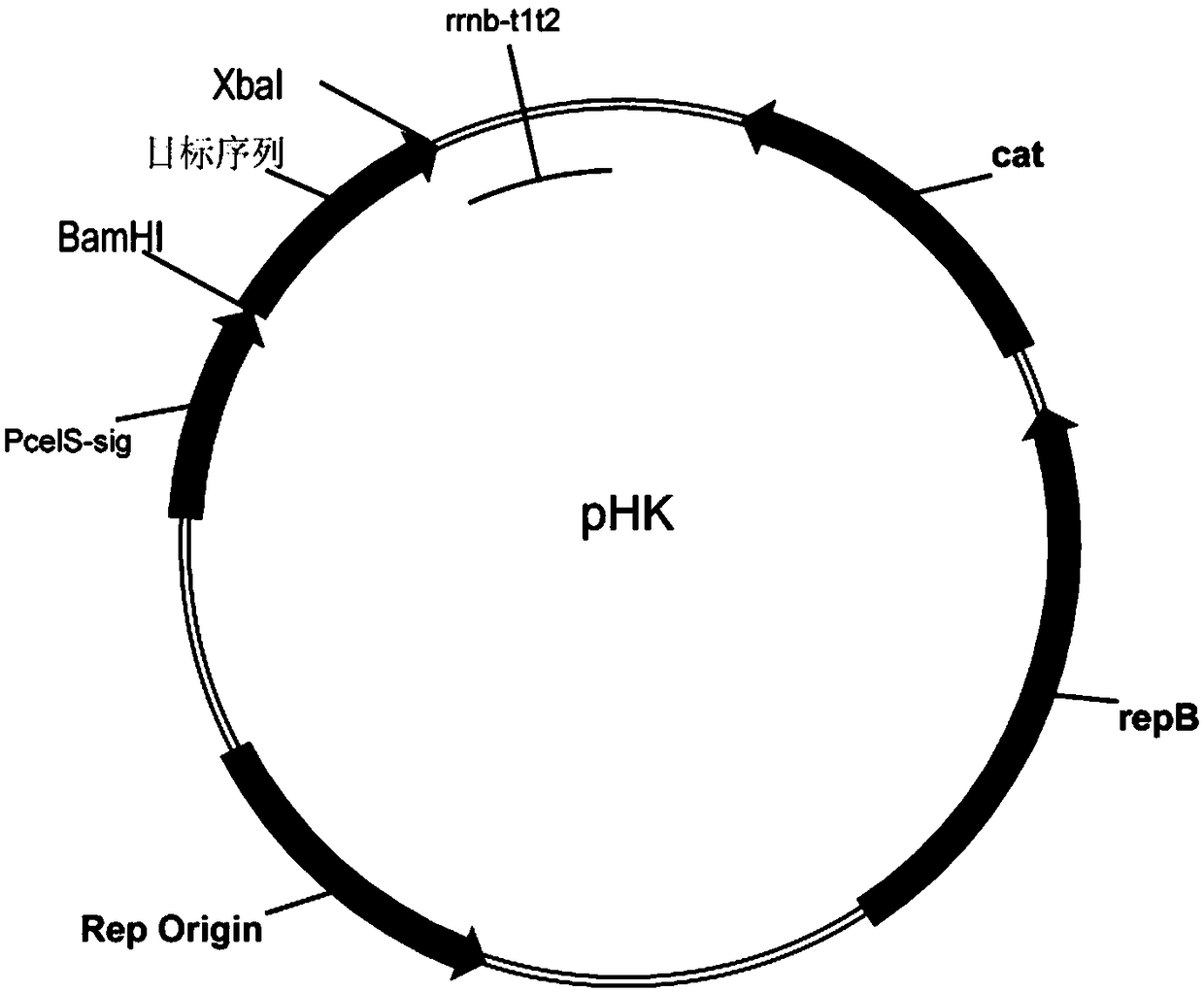
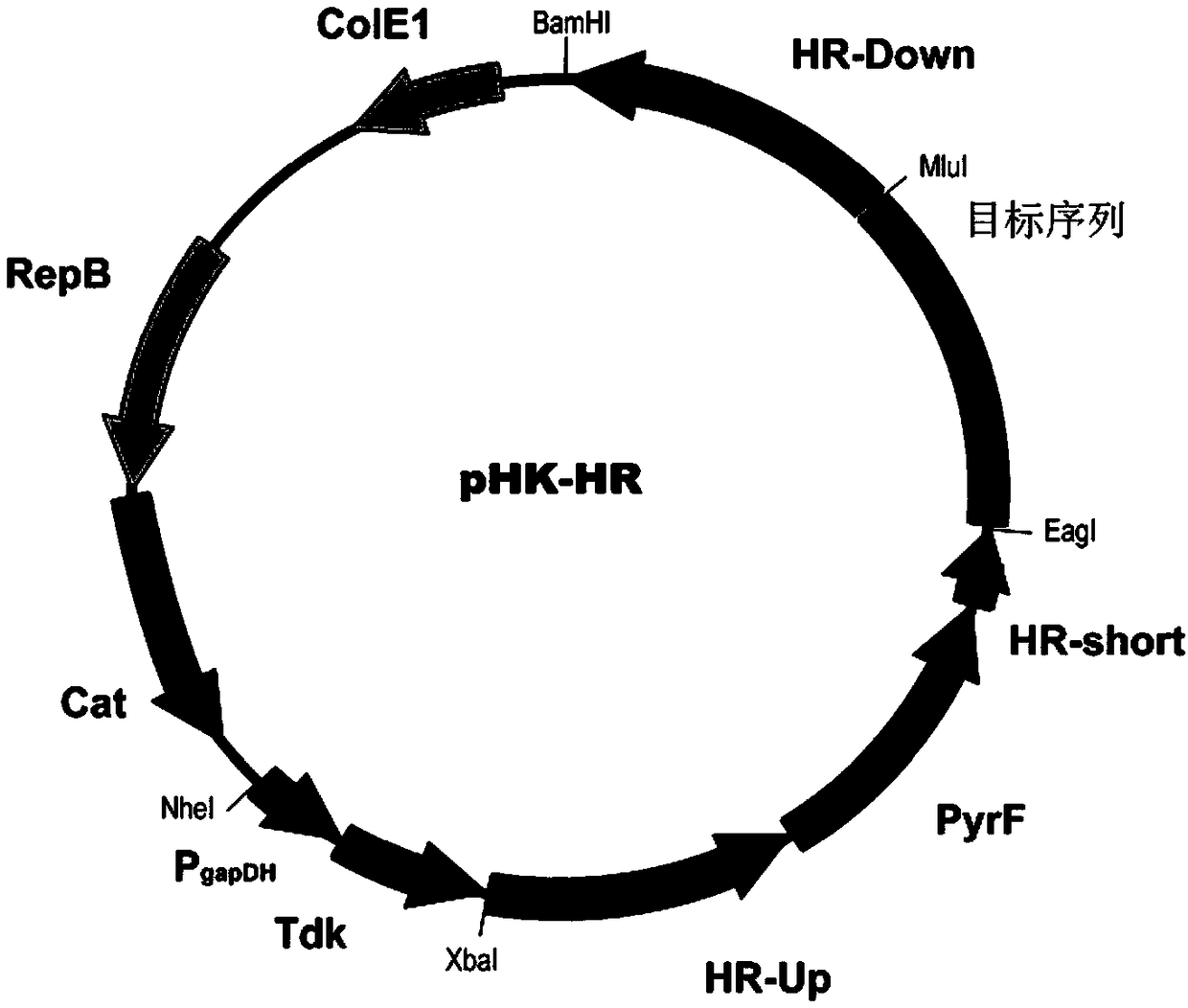
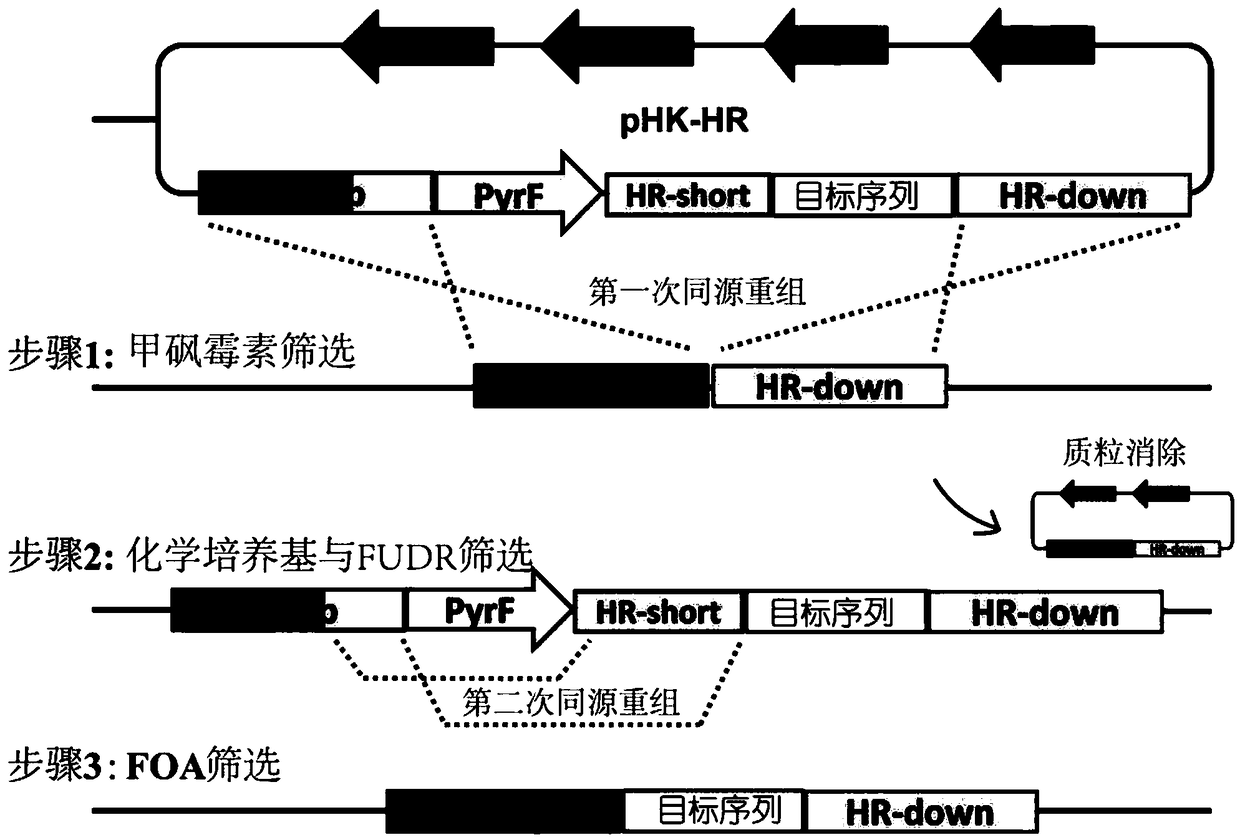
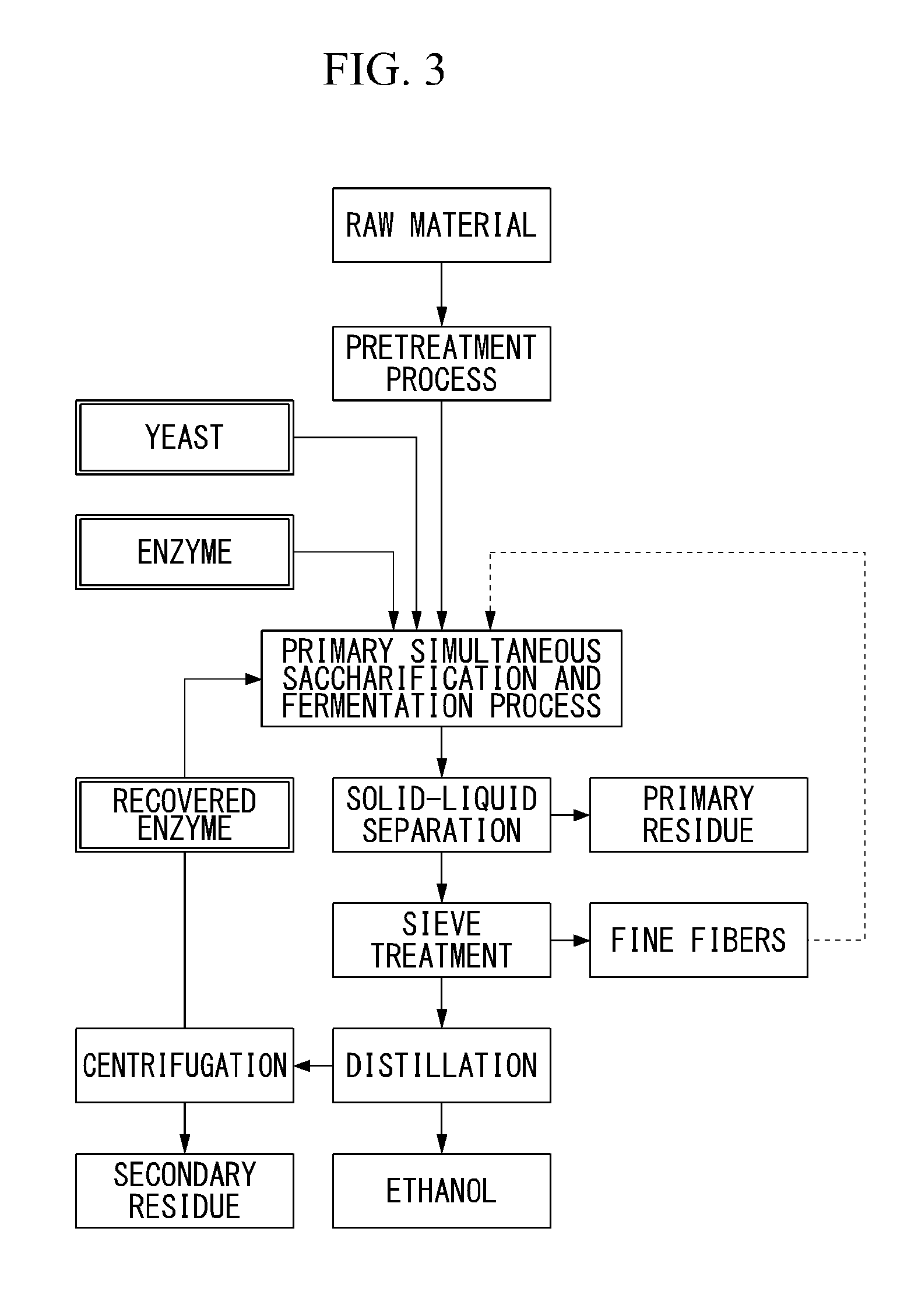
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Cellulosic sugars" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
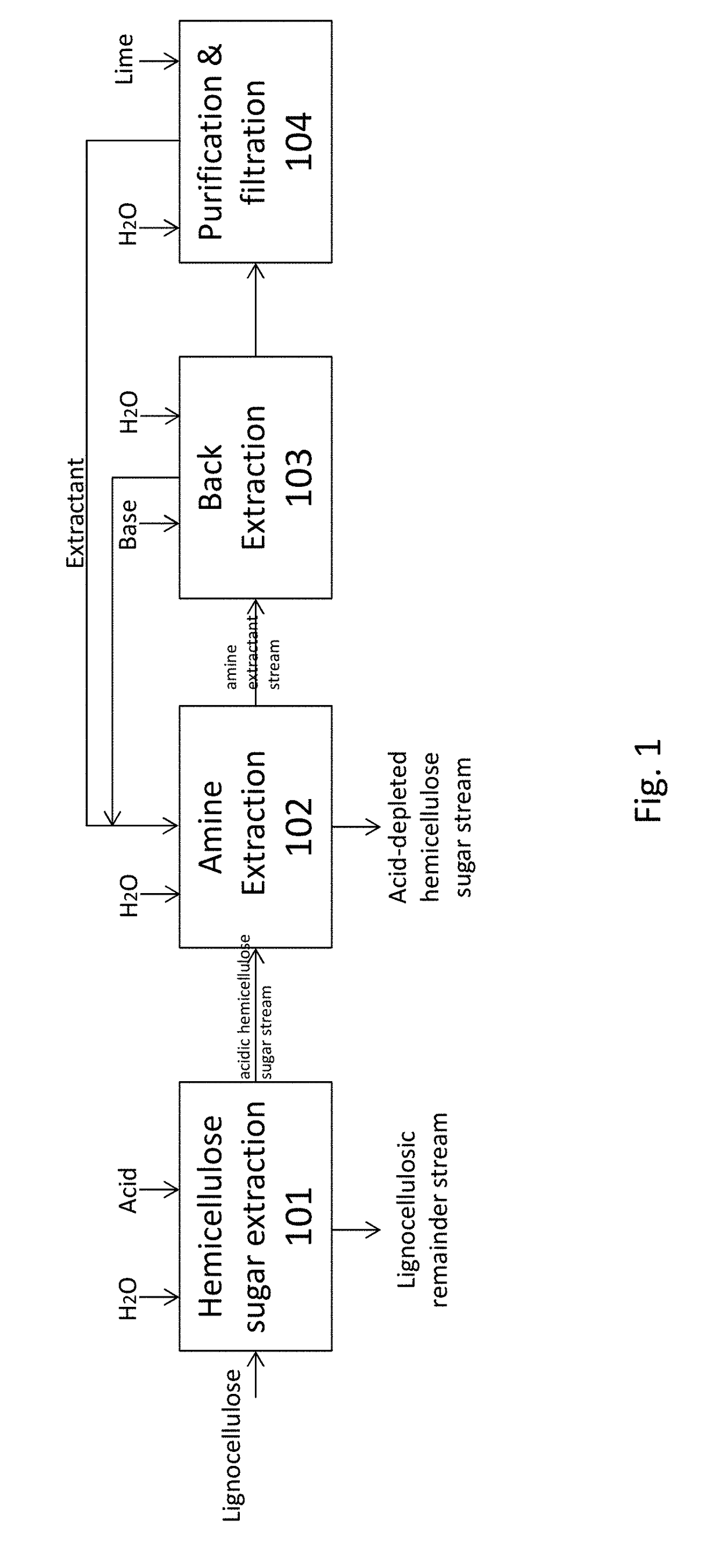
Cellulosic sugars are derived from non-food biomass (e.g. wood, agricultural residues, municipal solid waste). The biomass is primarily composed of carbohydrate polymers cellulose, hemicellulose, and an aromatic polymer (lignin). The hemicellulose is a polymer of mainly five-carbon sugars C₅H₁₀O₅ (xylose). and the cellulose is a polymer of six-carbon sugar C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose). Cellulose fibers are considered to be a plant’s structural building blocks and are tightly bound to lignin, but the biomass can be deconstructed using Acid hydrolysis, enzymatic hydrolysis, organosolv dissolution, autohydrolysis or supercritical hydrolysis.
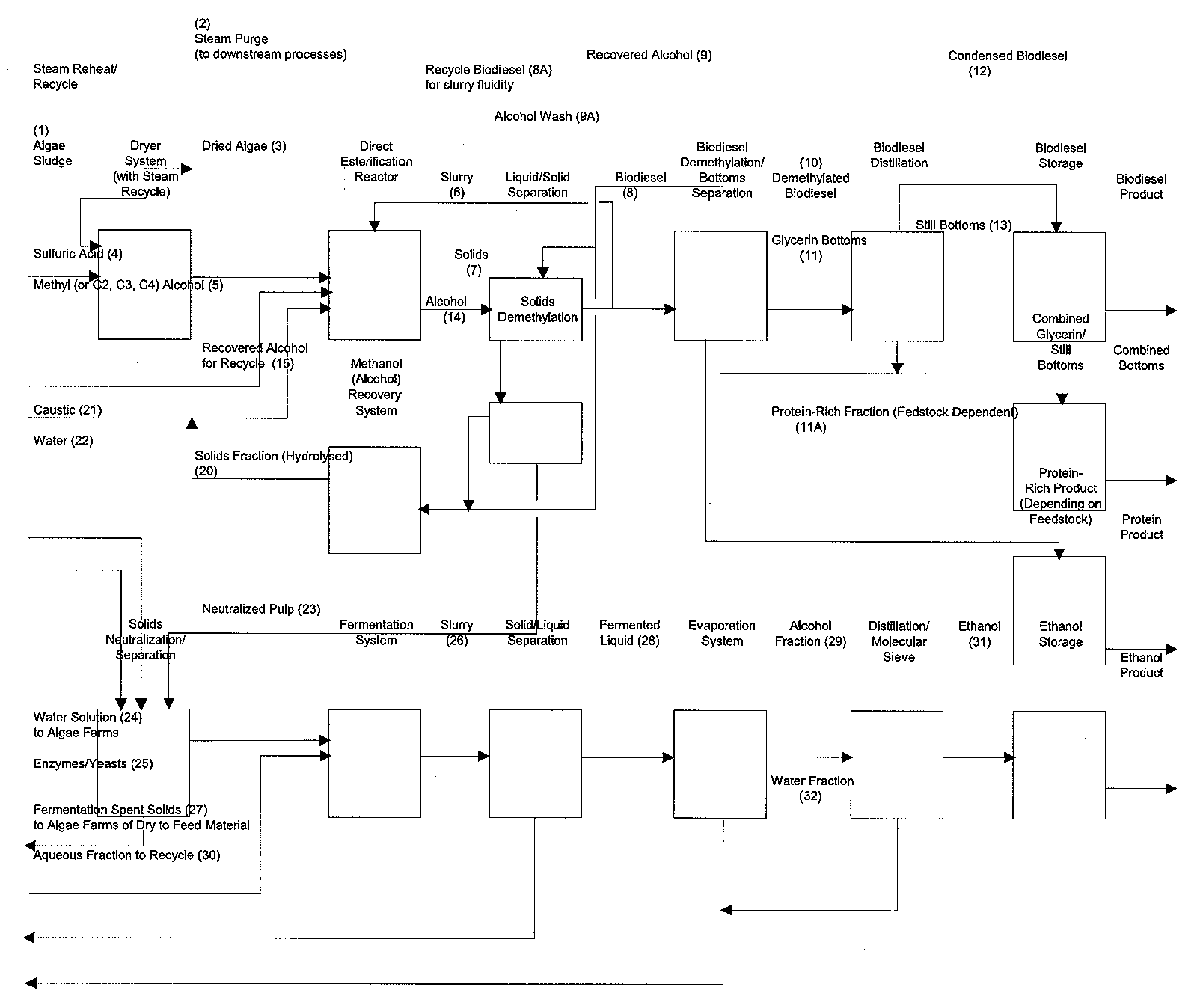
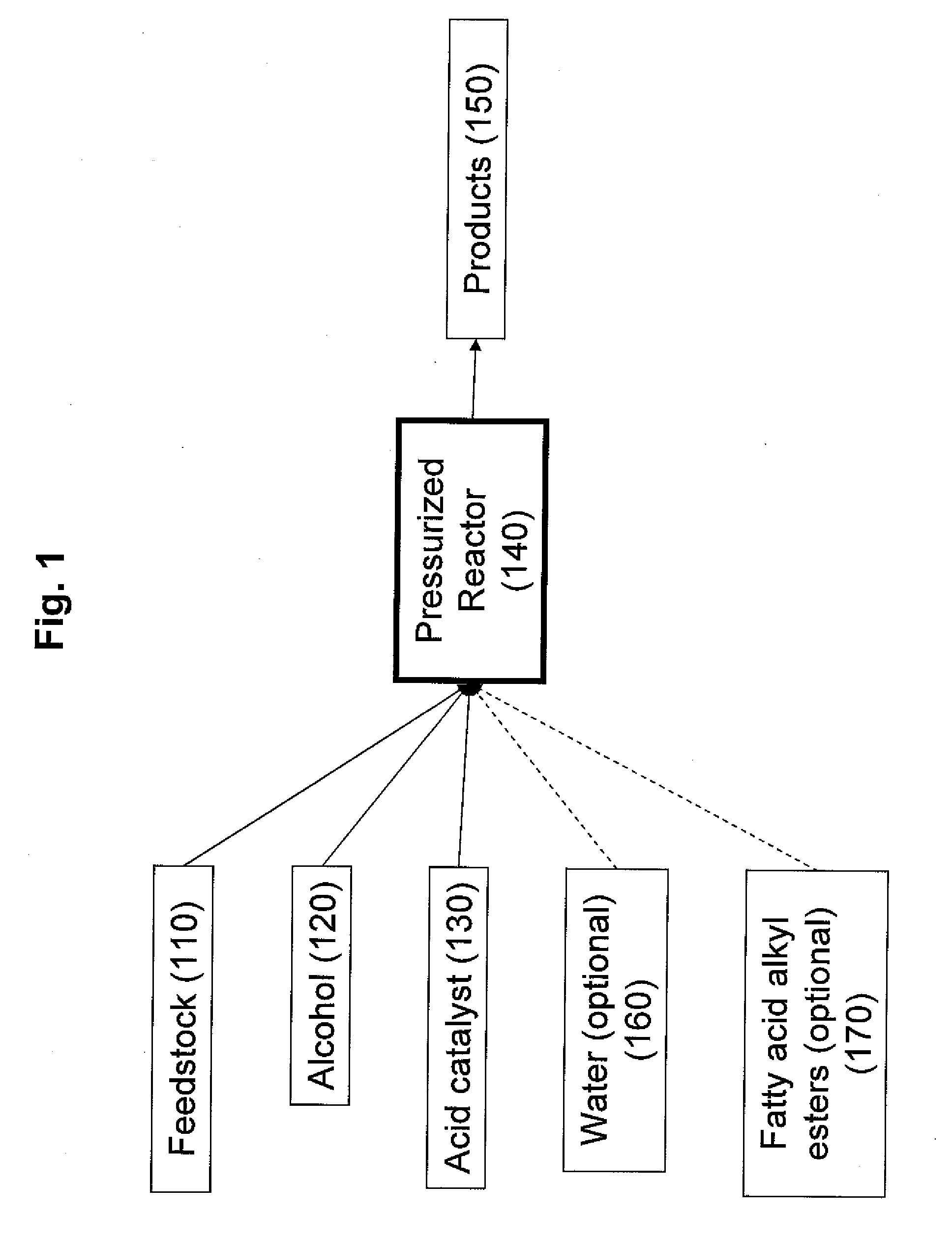
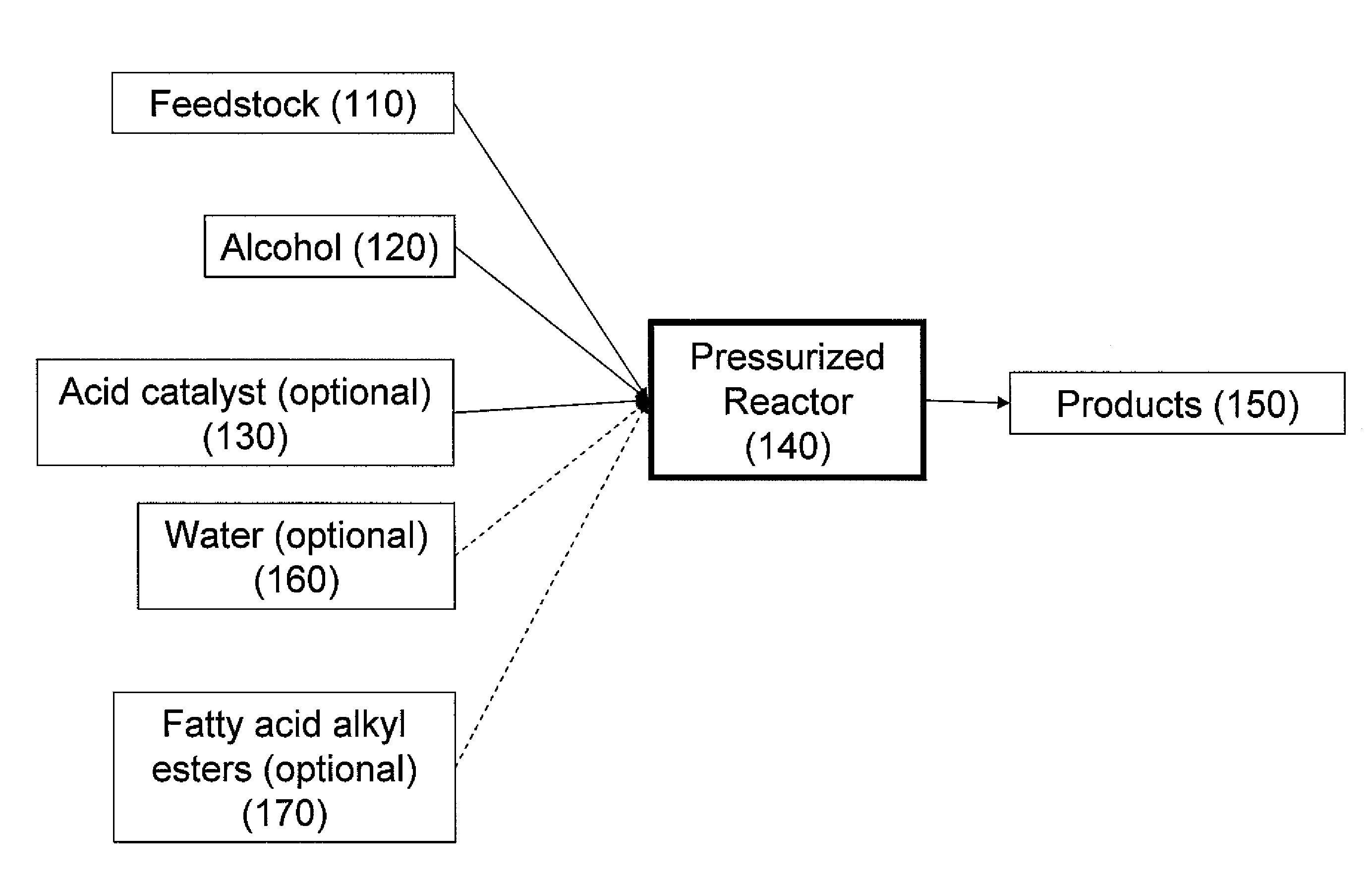
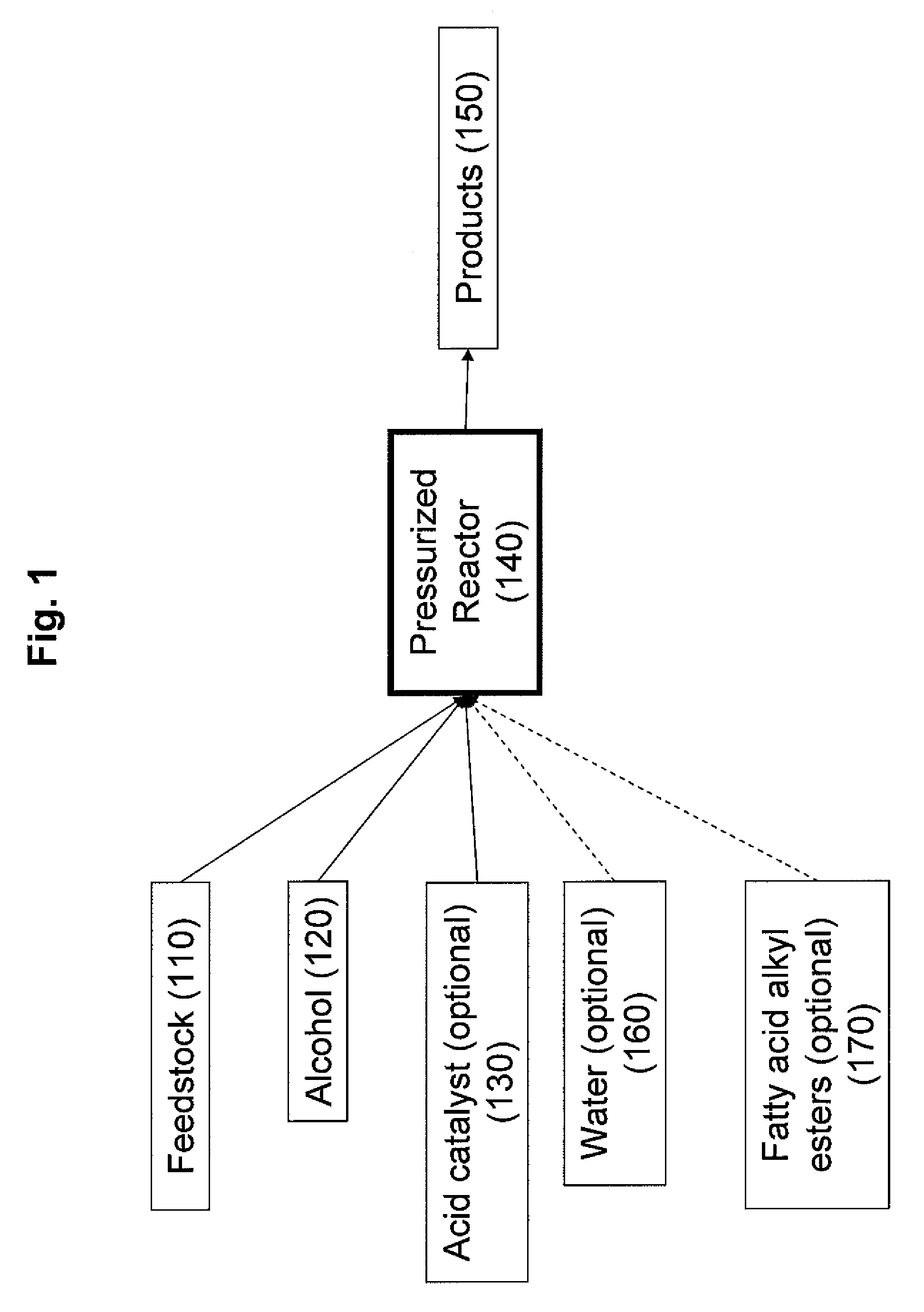
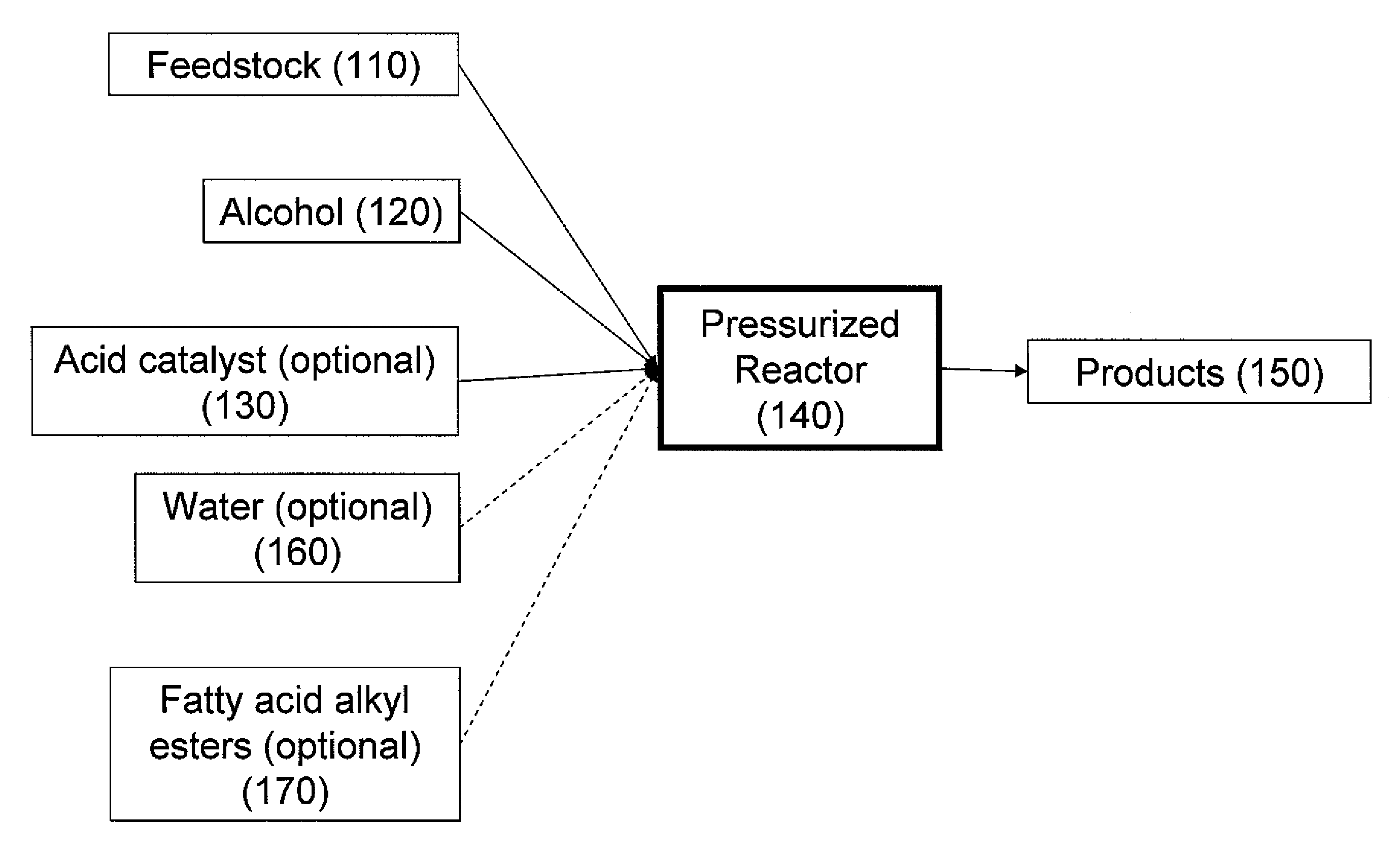
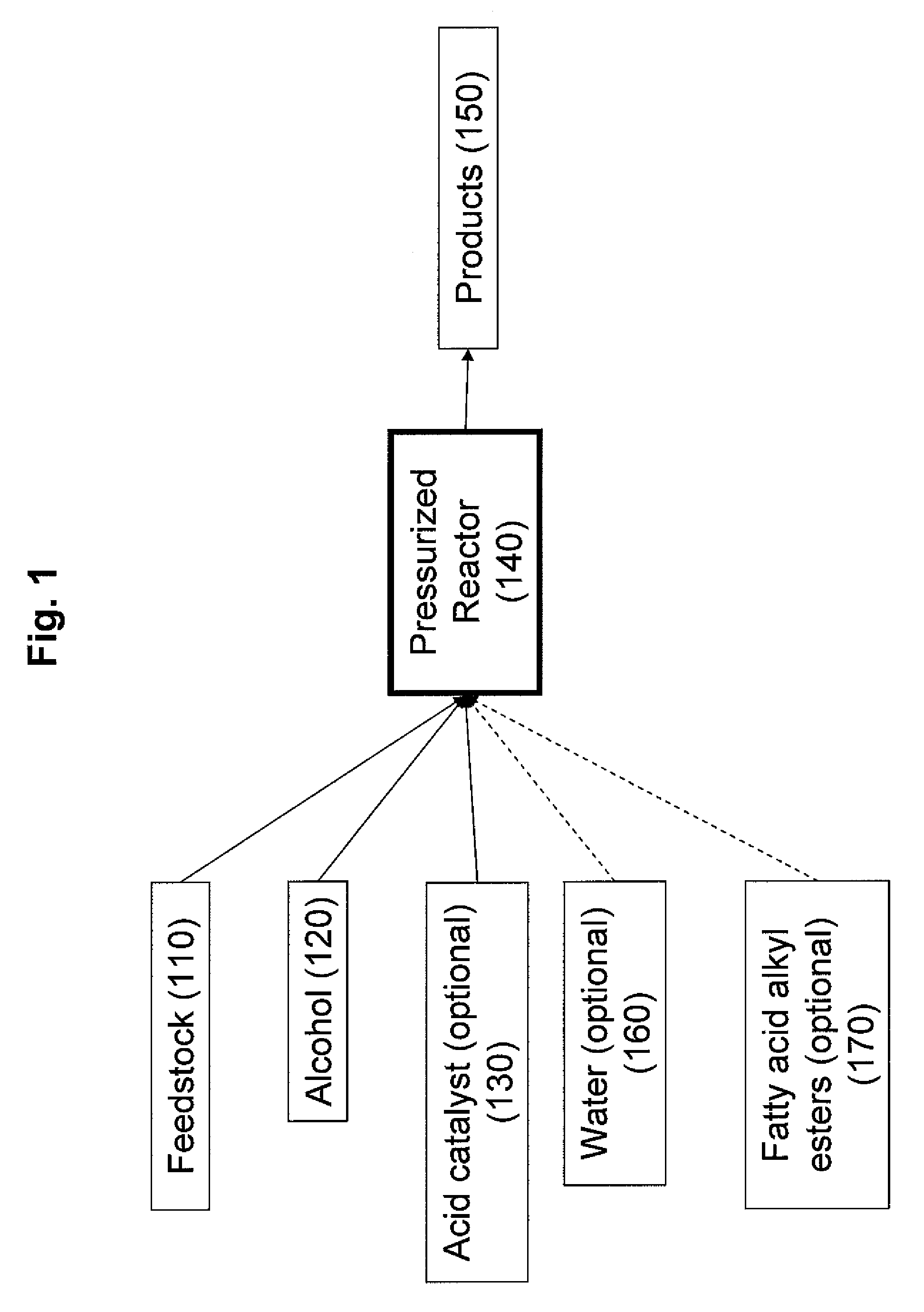
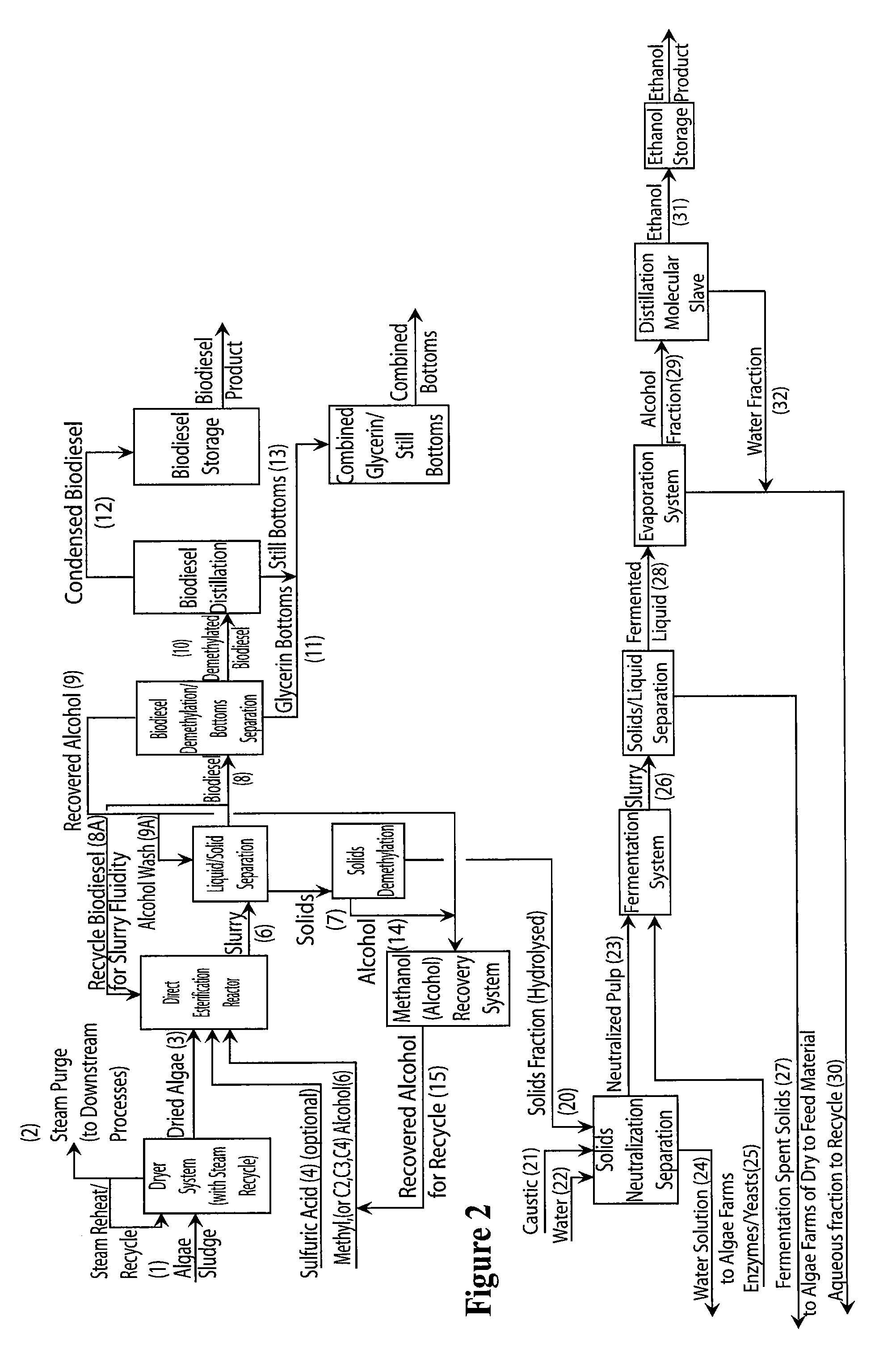
Production of biodiesel, cellulosic sugars, and peptides from the simultaneous esterification and alcoholysis/hydrolysis of oil-containing materials with cellulosic and peptidic content
The present invention relates to a method for producing fatty acid alkyl esters as well as cellulosic simplified sugars, shortened protein polymers, amino acids, or combination thereof resulting from the simultaneous esterification and hydrolysis, alcoholysis, or both of algae and other oil containing materials containing free fatty acids (FFA), glycerides, or combination thereof as well as polysaccharides, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignocellulose, protein polymers, or combination thereof in presences of an alcohol and an acid catalyst.
Owner:INVENTURE RENEWABLES INC
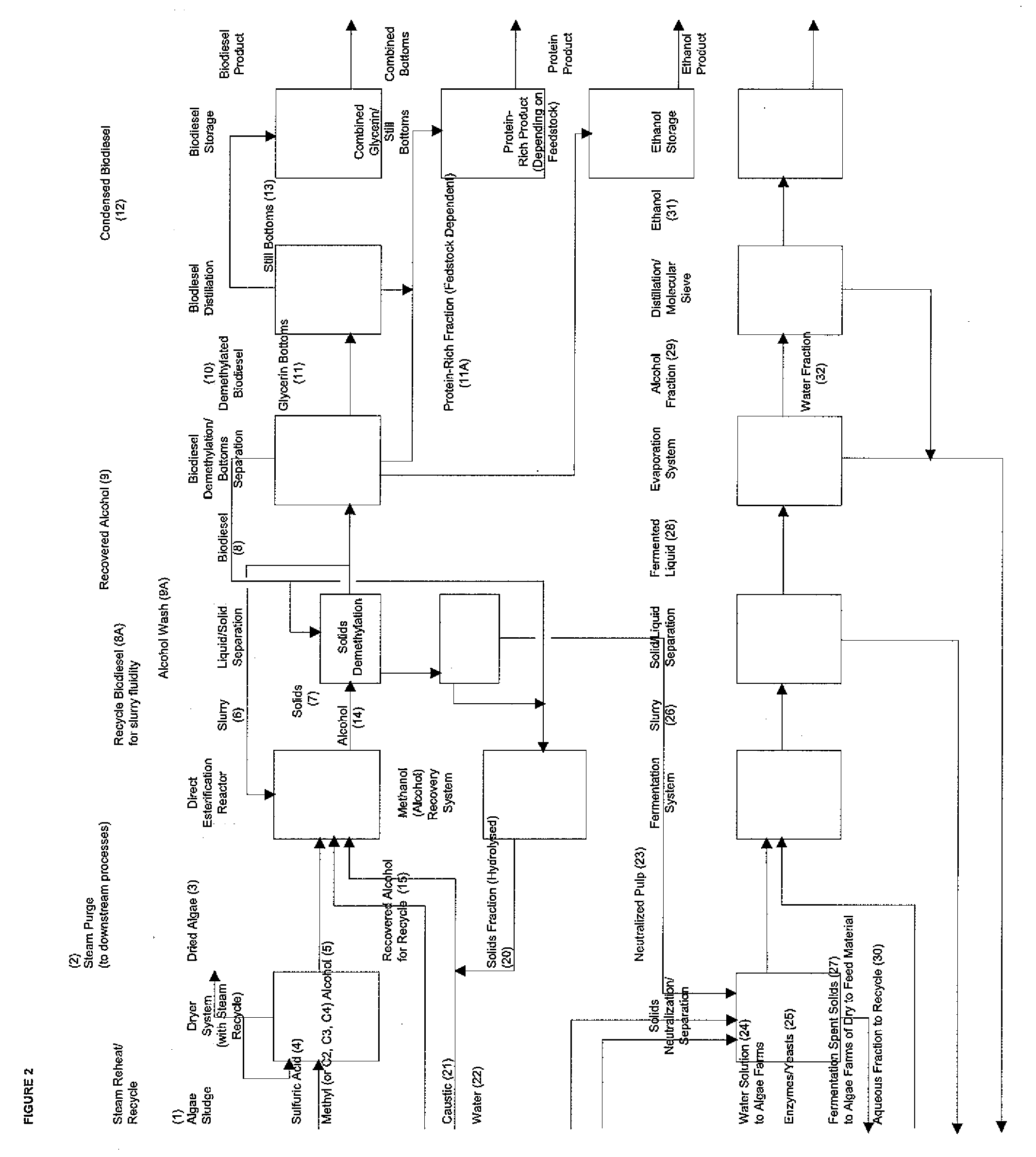
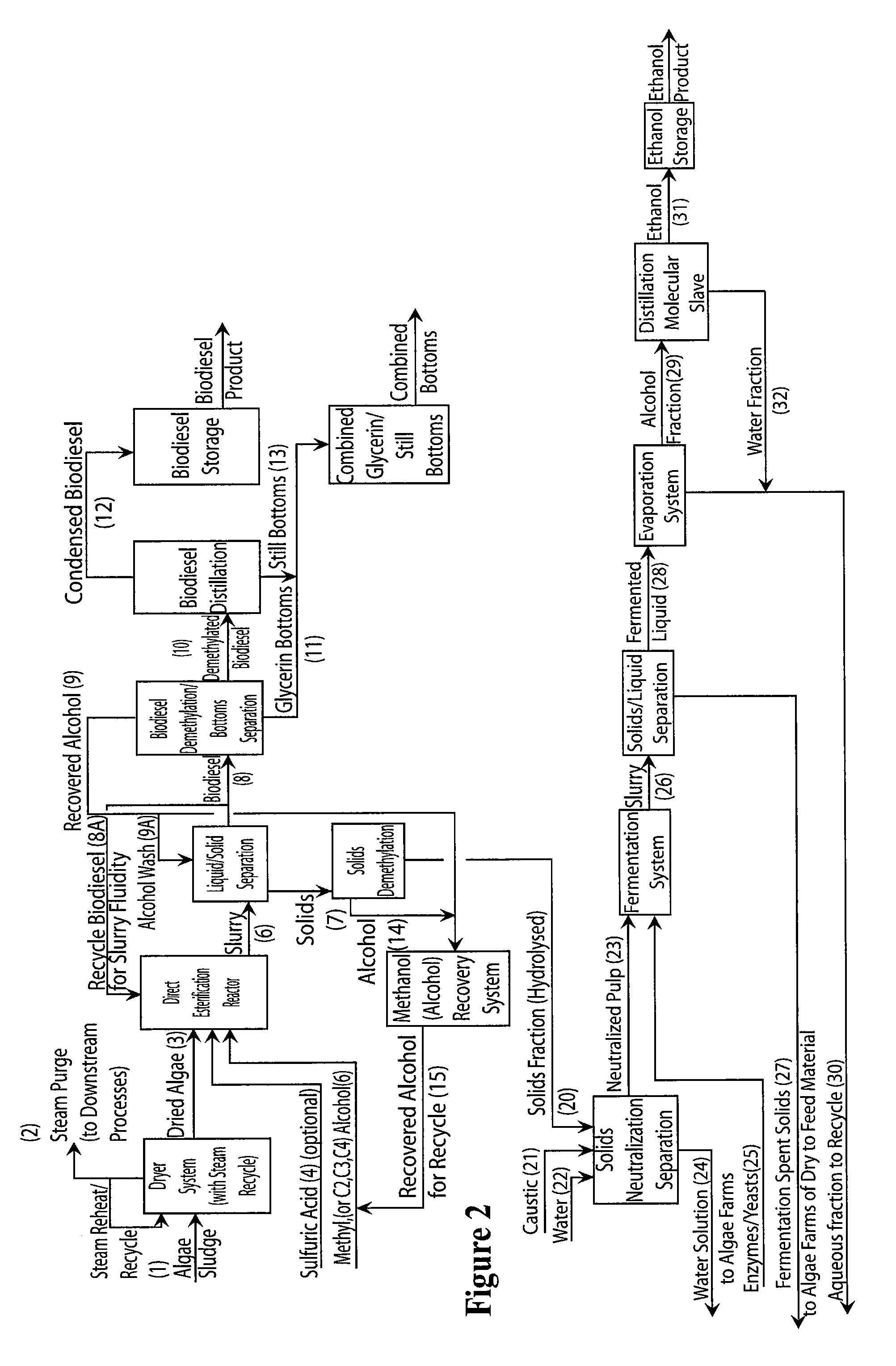
Production of biodiesel, cellulosic sugars, and peptides from the simultaneous esterification and alcoholysis/hydrolysis of materials with oil-containing substituents including phospholipids and peptidic content
InactiveUS7943792B2Avoid boilingFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselPhospholipid
The present invention relates to a method for producing fatty acid alkyl esters as well as cellulosic simplified sugars, shortened protein polymers, amino acids, or combination thereof resulting from the simultaneous esterification and hydrolysis, alcoholysis, or both of algae and other oil containing materials containing phospholipids, free fatty acids (FFA), glycerides, or combination thereof as well as polysaccharides, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignocellulose, protein polymers, or combination thereof in the presence of an alcohol and an optional acid catalyst.
Owner:INVENTURE RENEWABLES INC
Method for increasing lignocellulose saccharification yield through multi-step enzymolysis
InactiveCN102191299AHigh yield of enzymatic hydrolysisReduce generationFermentationHydrolysateCellobiose
The invention relates to a method for increasing the lignocellulose saccharification yield through multi-step enzymolysis. The method comprises the following main steps: 1) pretreating wood fiber raw material; 2) adding one or more of bio-degrading enzymes in the pretreated wood fiber stepwise or simultaneously, removing the extract component or lignin in the raw material to change the fiber structure of the raw material; 3) adding one or more of hemicellulose degrading enzymes in the lignocellulose which is removed extract or lignin through enzymolysis stepwise or simultaneously, extracting pentose in the raw material; and 4) filtering fiber residue obtained in the step 3) through the enzymolysis, and adding cellulase and / or cellobiase to hydrolyze continuously and obtain glucose hydrolysate. By adopting the method, each component can be recycled and the total reducing sugar yield can be increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
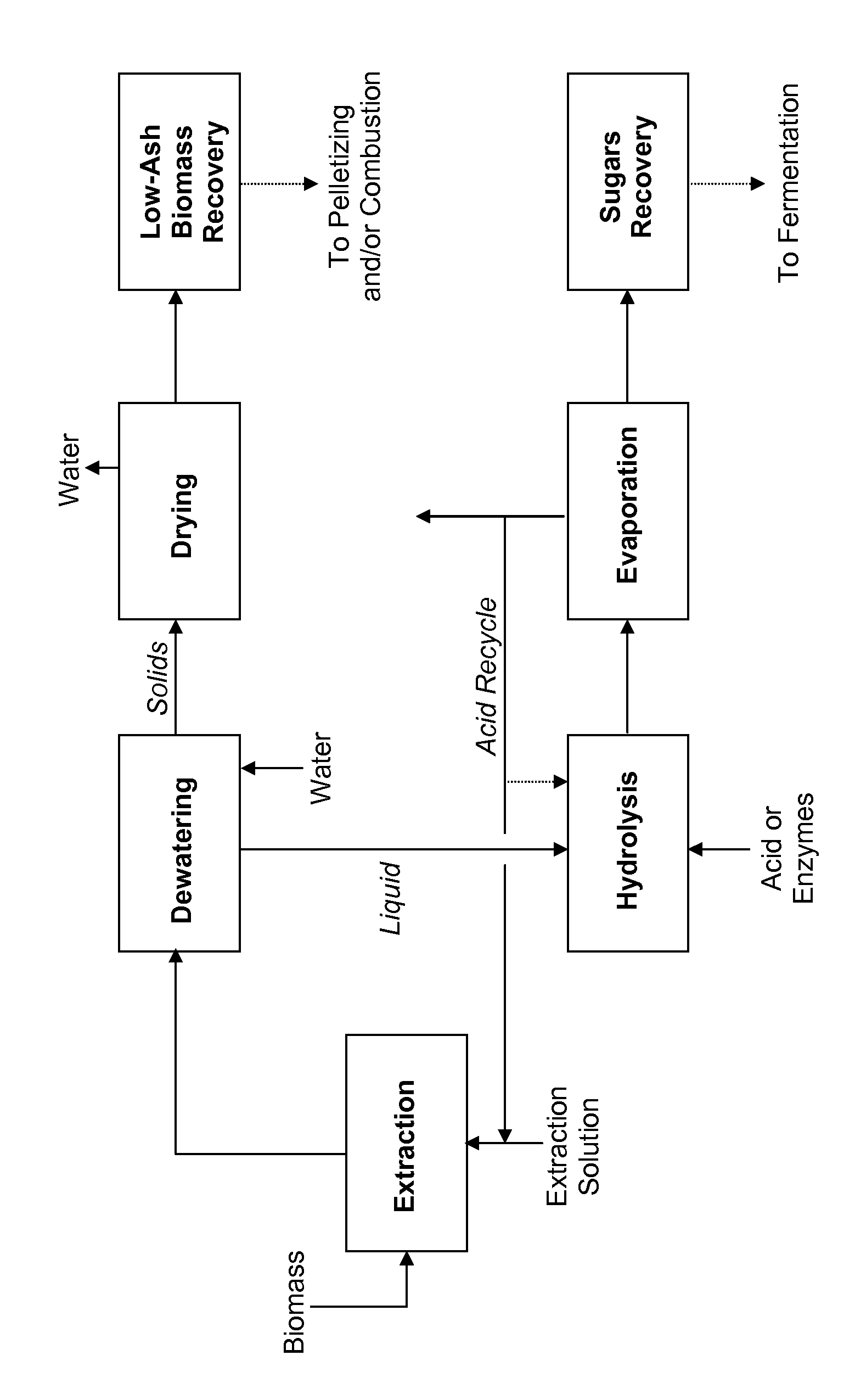
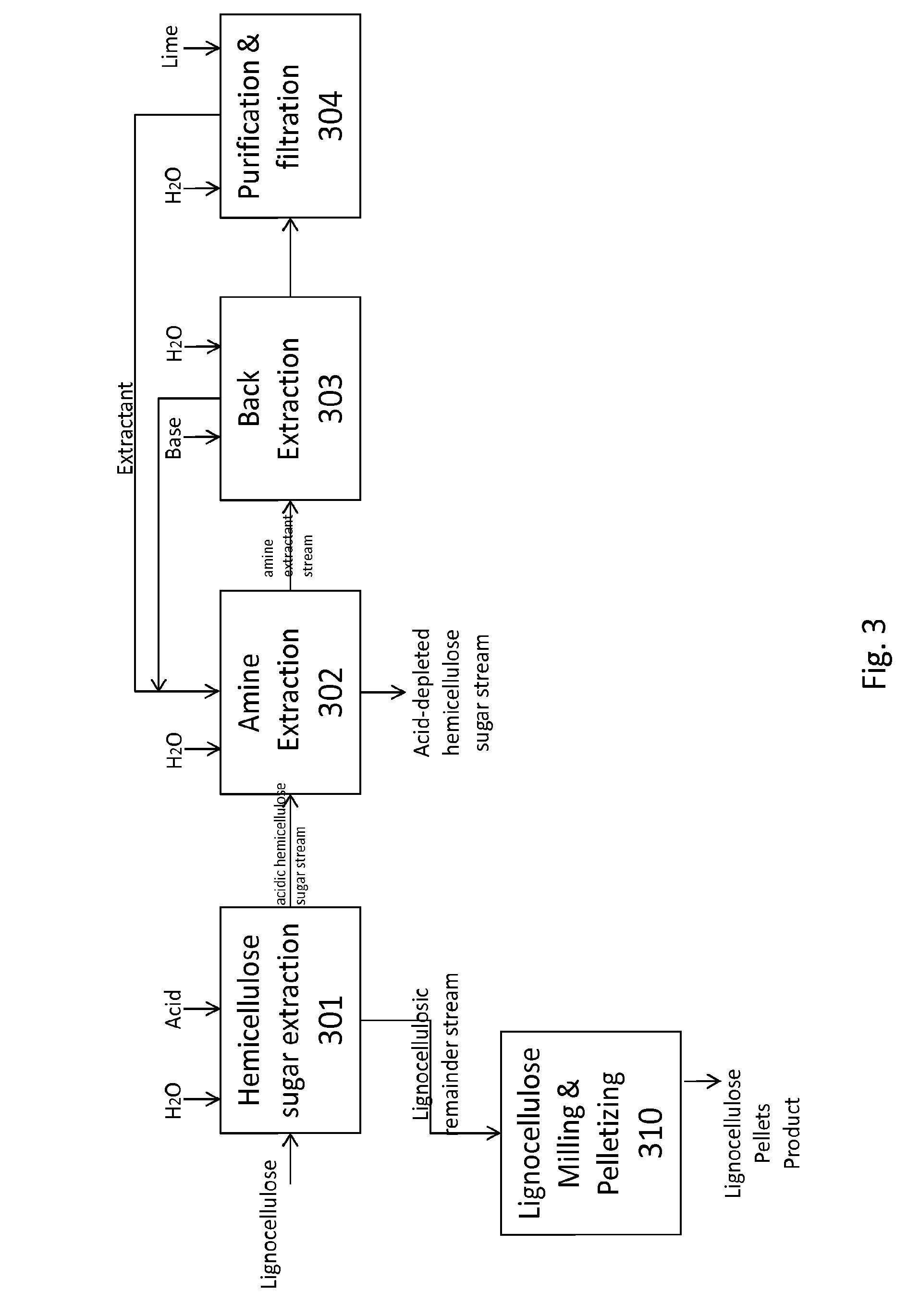
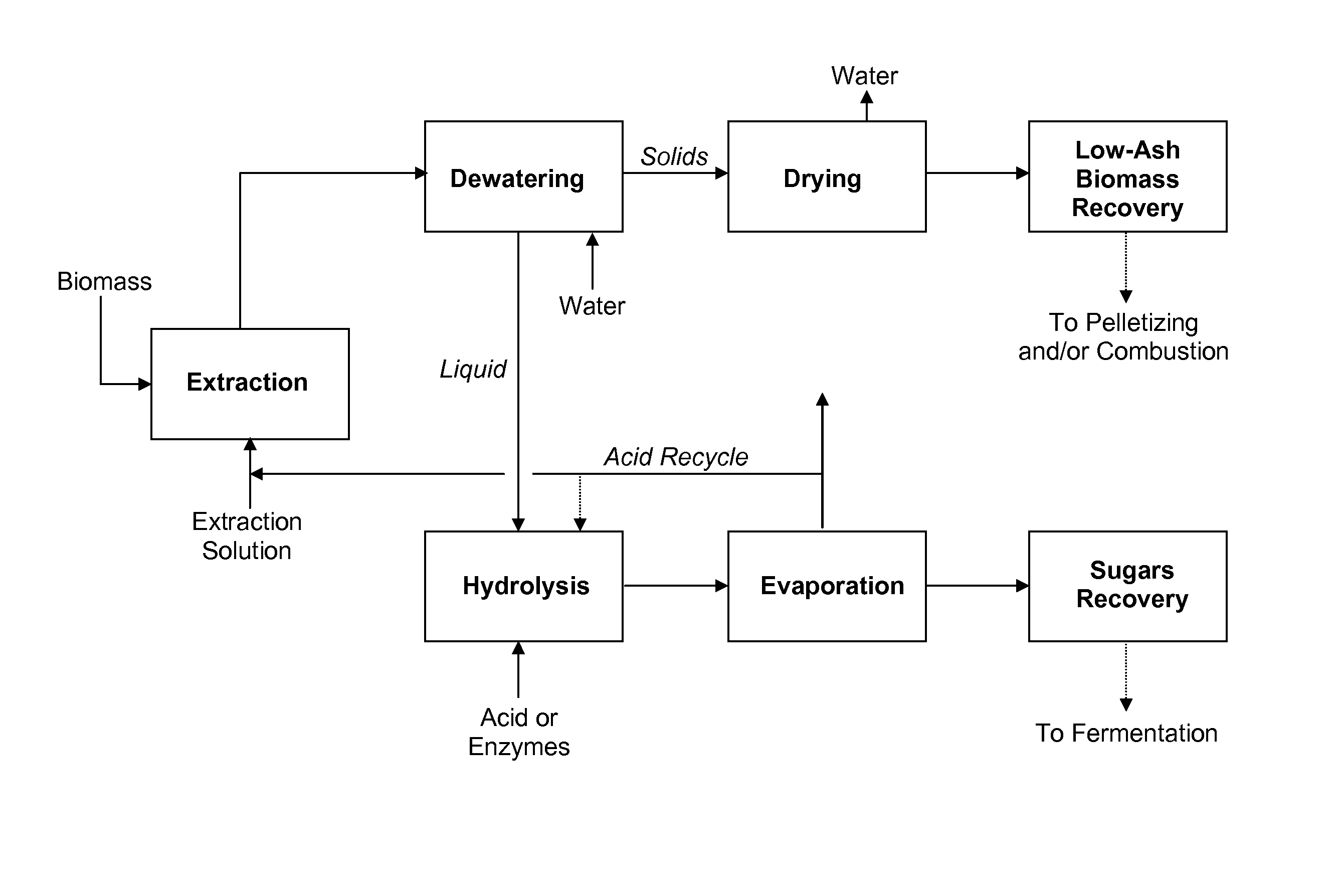
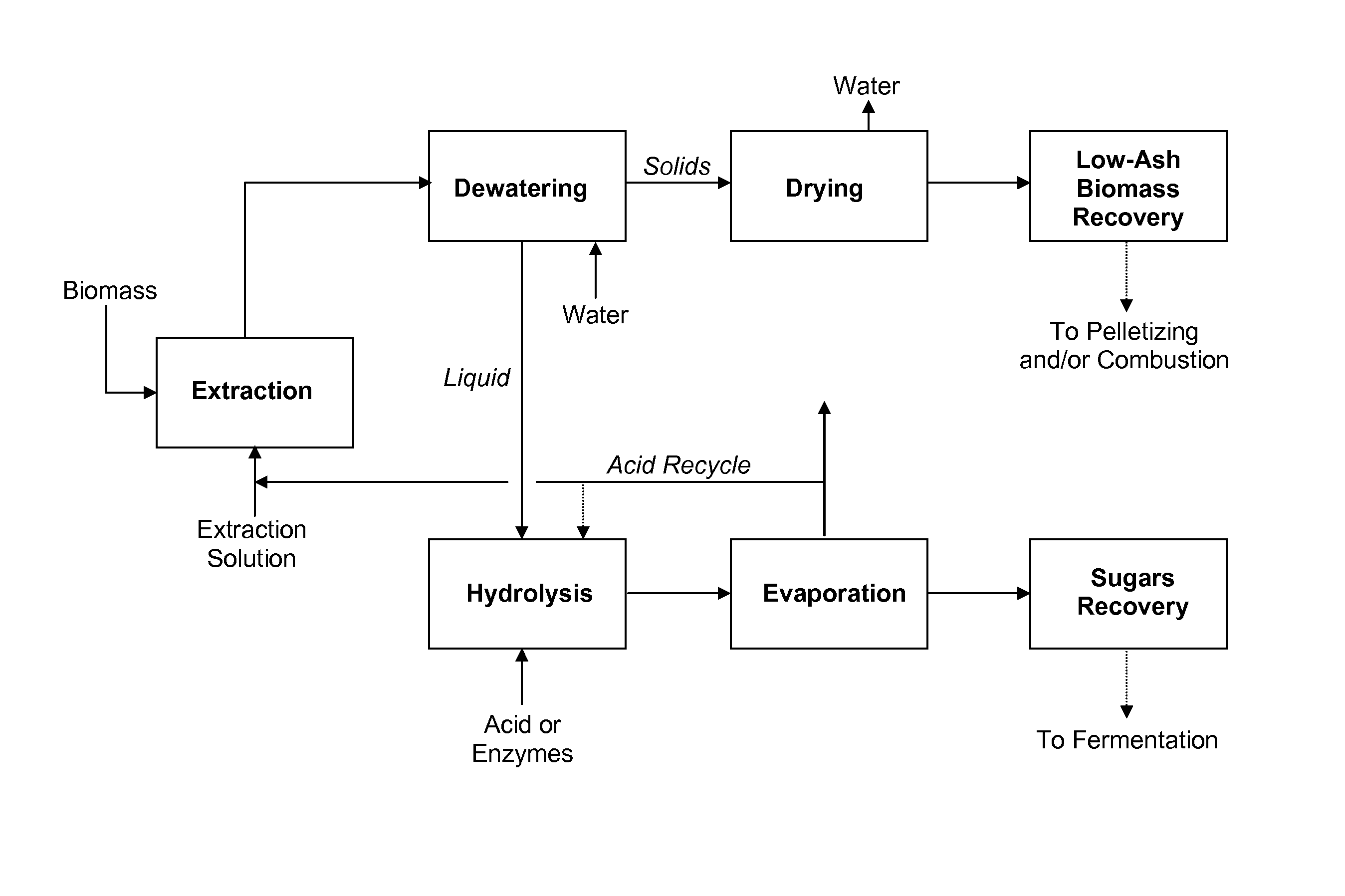
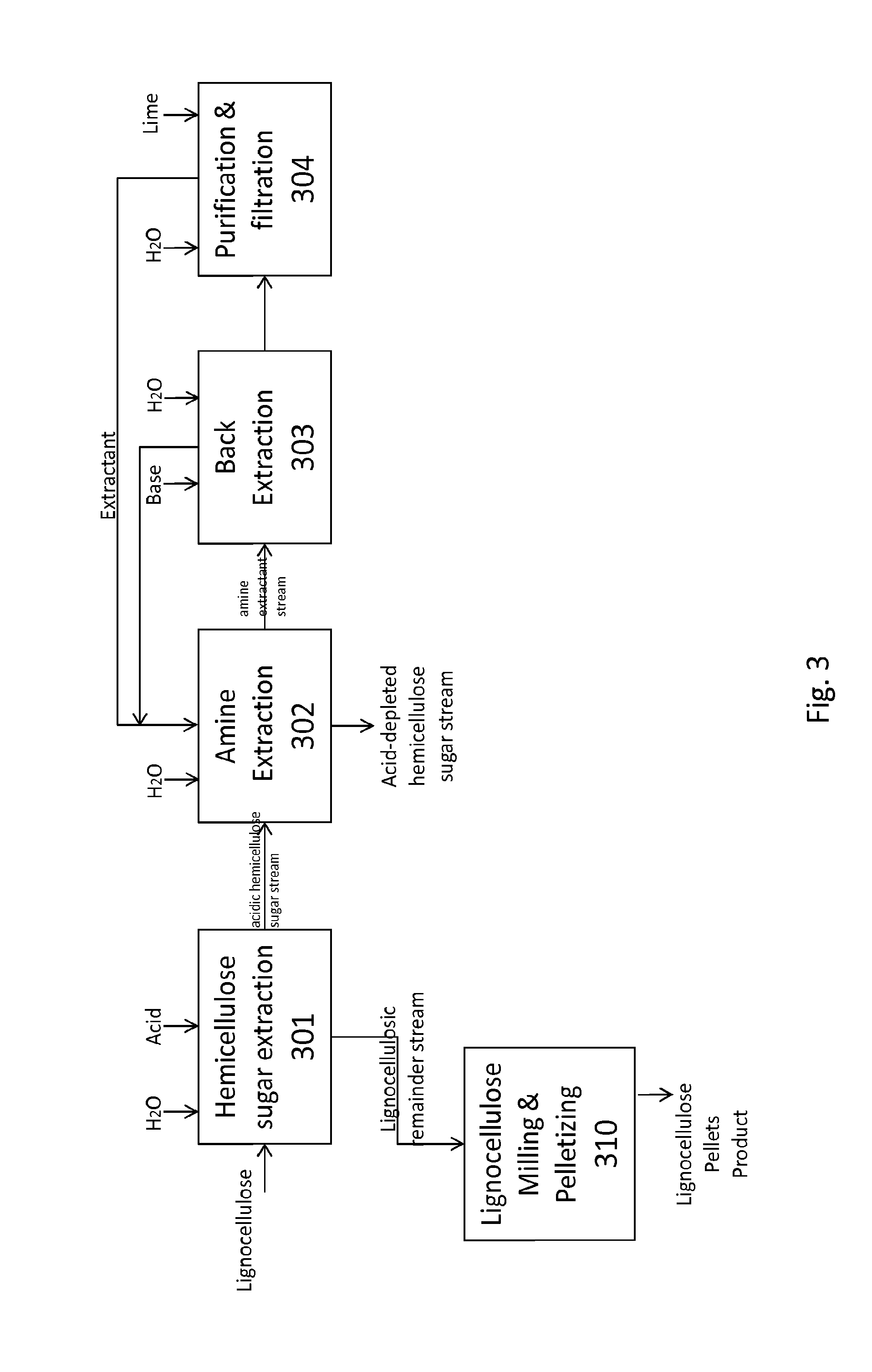
Processes for producing fermentable sugars and low-ash biomass for combustion or pellets
This invention provides processes and apparatus to convert biomass, including wood and agricultural residues, into low-ash biomass pellets for combustion, alone or in combination with another solid fuel. Some embodiments provide processes for producing hemicellulosic sugars and low-ash biomass from cellulosic biomass, comprising providing an aqueous extraction solution with acetic acid; extracting the feedstock to produce an extract liquor containing soluble ash, hemicellulosic oligomers, acetic acid, dissolved lignin, and cellulose-rich solids; dewatering and drying the cellulose-rich, lignin-rich solids to produce a low-ash biomass; hydrolyzing the hemicellulosic oligomers to produce fermentable hemicellulosic sugars, wherein additional acetic acid is generated; removing a vapor stream comprising vaporized acetic acid from the extract; recycling the vapor or its condensate to provide some starting acetic acid for the extraction solution; and recovering fermentable hemicellulosic sugars. The disclosed processes can produce clean power from biomass. Co-products include fermentation products such as ethanol, fertilizers, and lignin.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Precision polishing technique for stainless steel printed circuit board
the invention discloses a precise polishing technology of stainless steel printing circuit, which comprises the following steps: electrolyzing to remove oil; cleaning working piece; removing burr through electrolyzing; polishing; inactivating; cleaning; drying. the electrolyte at electrolyzing disposal contains 1.62-1.65% sulfuric acid, 0.56-0.60% phosphoric acid and 97.76-97.80% water. the electrolyte at electrolyzing precise polishing contains 24-28% sulfuric acid, 47-51% phosphoric acid, 0.02-0.04% ammonia sulfate, 0.01-0.03% ammonium phosphate, 0.03-0.04% cellulose, 0.005-0.007% saccharin and 21.1-28.9% water.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for saccharification of lignocellulose by ultrasonic synergistic catalysis of modified cellulose
InactiveCN1970781AIncrease concentrationImprove adaptabilityEnzymesFermentationMonomethoxypolyethylene glycolBeta-Glucosidases
The invention discloses a saccharifying method of xylon cellulose through ultrasonic coordinated modified cellulose enzyme, which comprises the following steps: grinding and predisposoing xylon in the raw material through alkaline; reacting activated methoxy carbowax and cellulose enzyme in the citrate-sodium citrate buffer solution to obtain modified cellulose enzyme; blending modified cellulose enzyme, beta-glucosidase, amylase and pectase to obtain composite liquid; adding composite enzyme into predisposed raw material according to corresponding proportion; proceeding enzyme catalytic reaction through ultrasound; filtering; decompressing; evaporating; obtaining condensed sugar liquid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
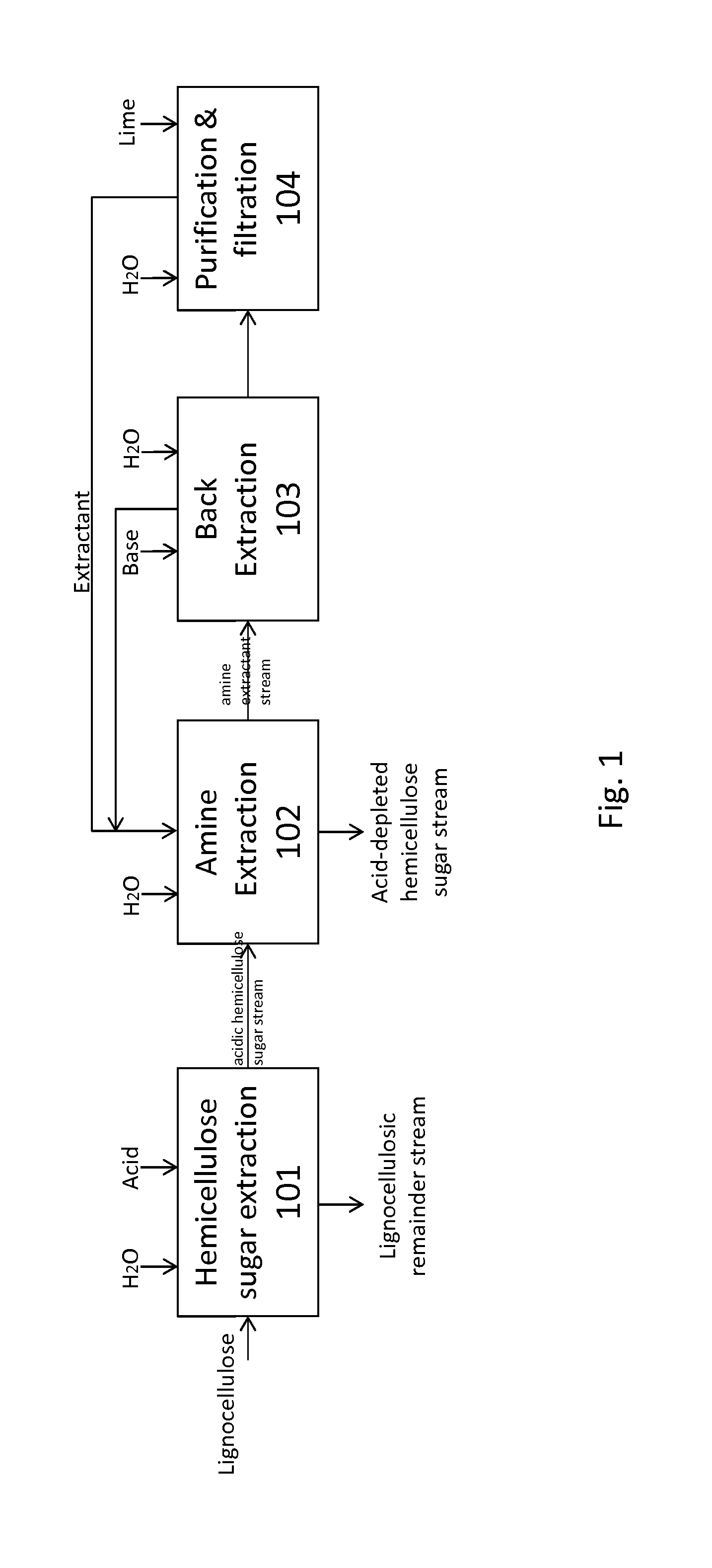
Methods for treating lignocellulosic materials
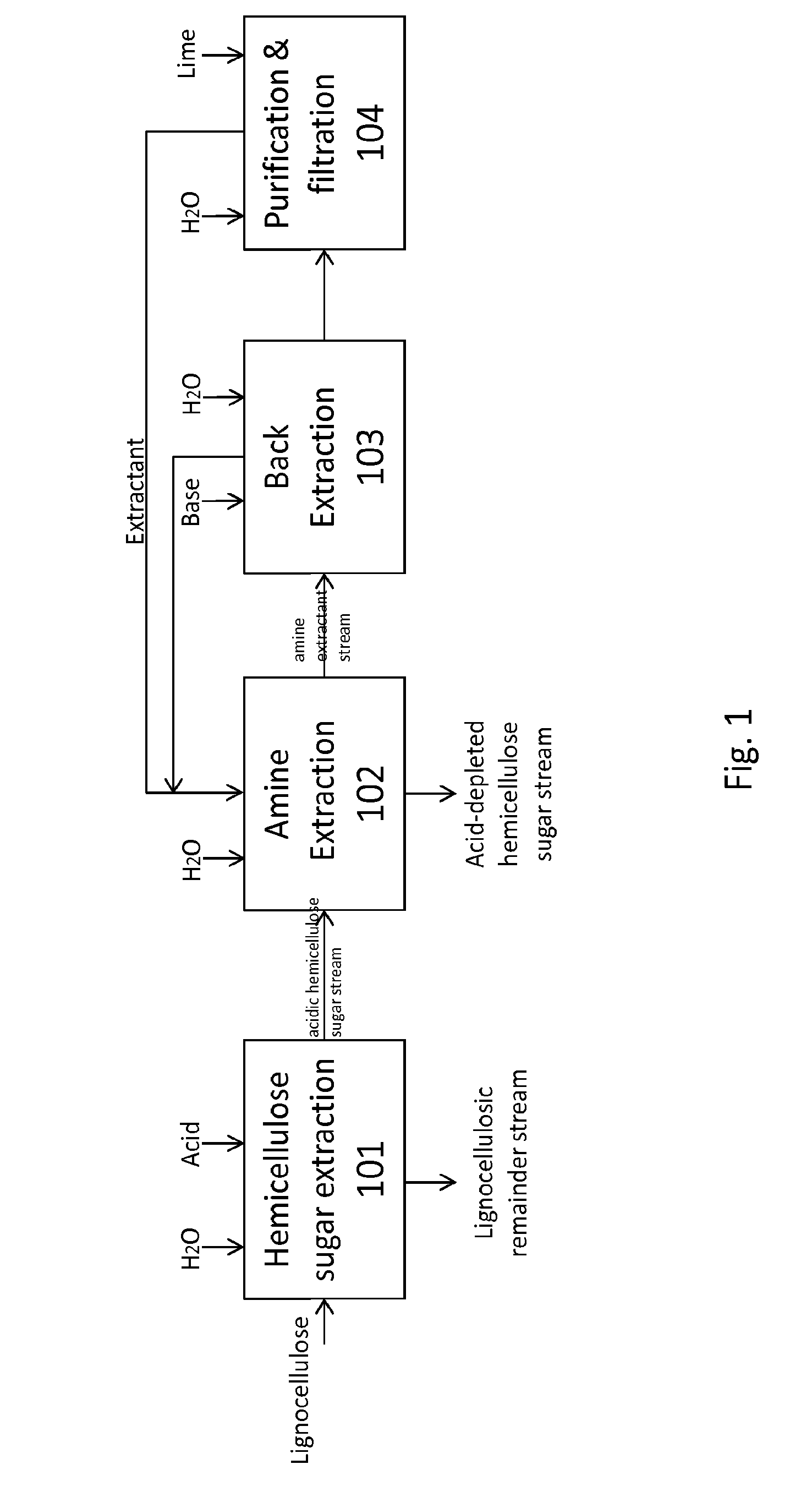
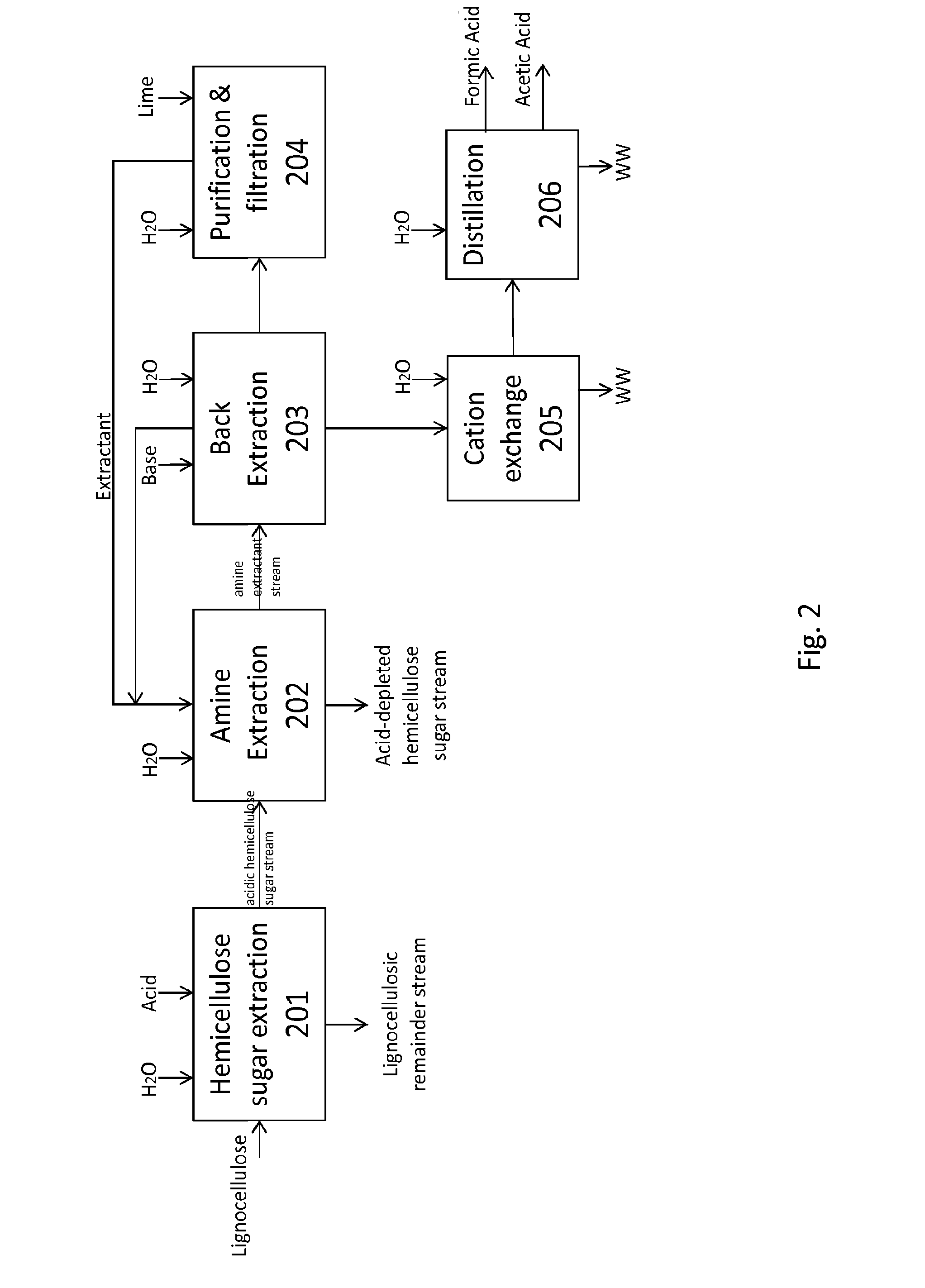
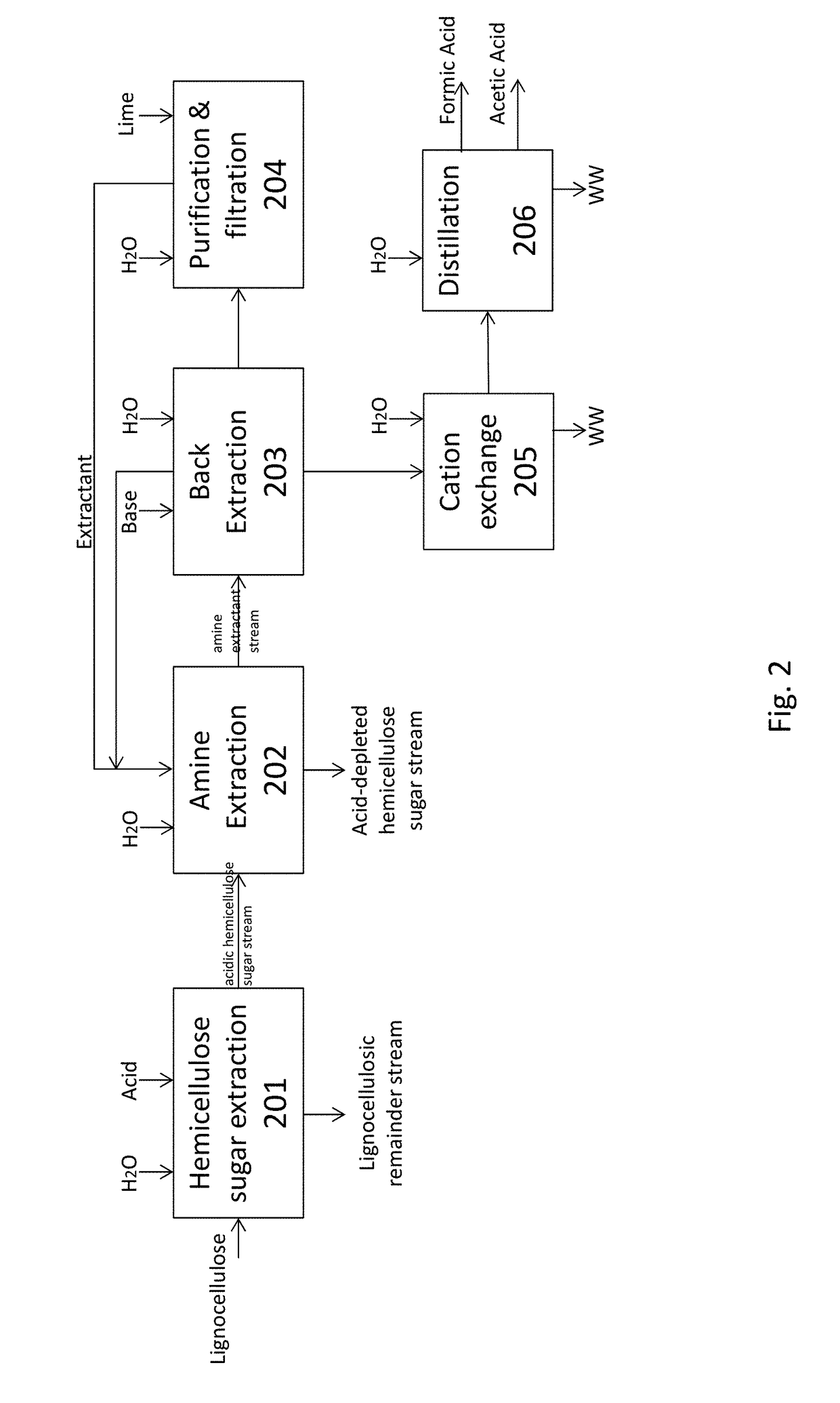
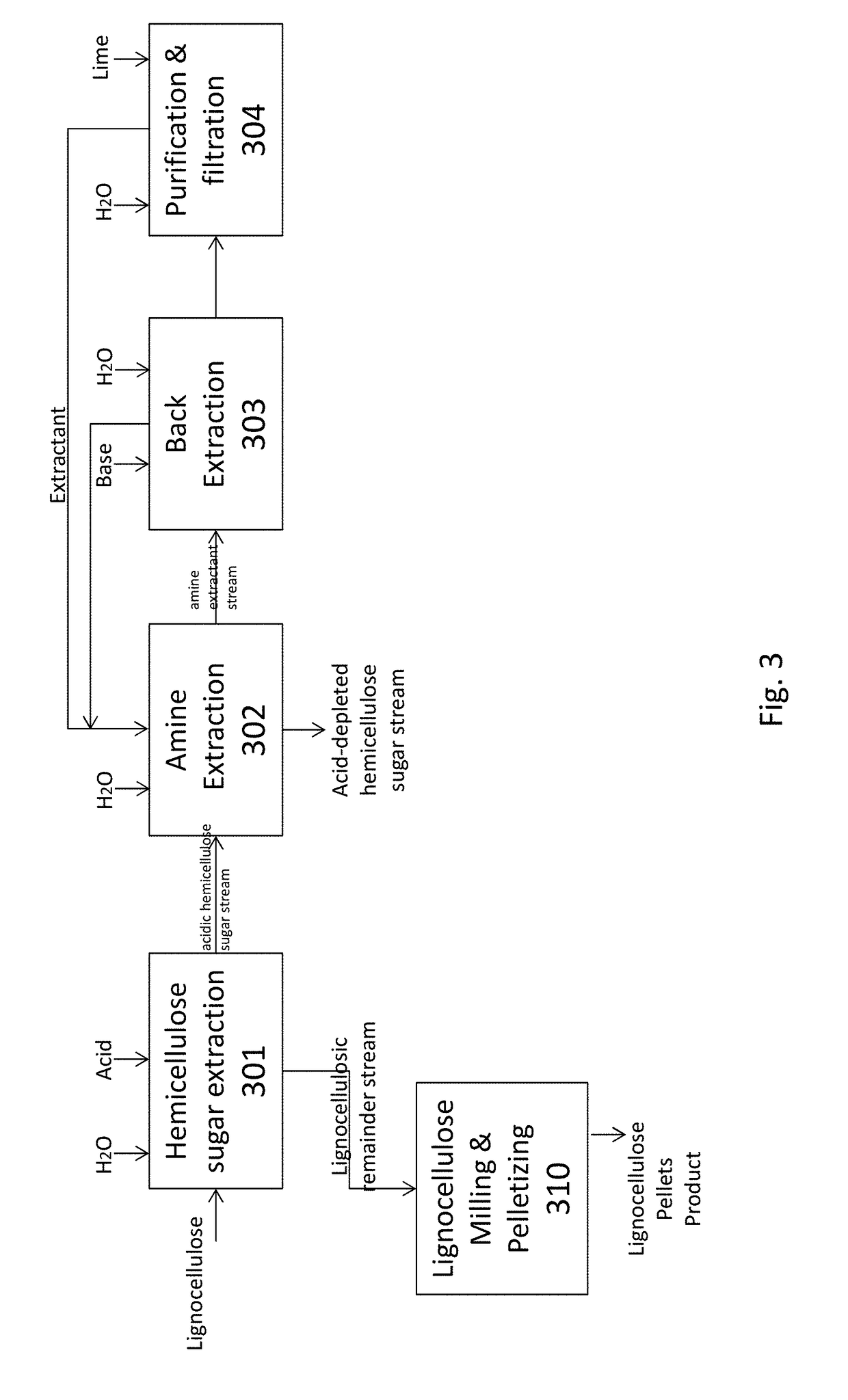
The present invention relates to methods of processing lignocellulosic material to obtain hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose and other high-value products. Also provided are hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose, and other high-value products.
Owner:VIRIDA
Method for promoting hydrolysis of lignocellulose
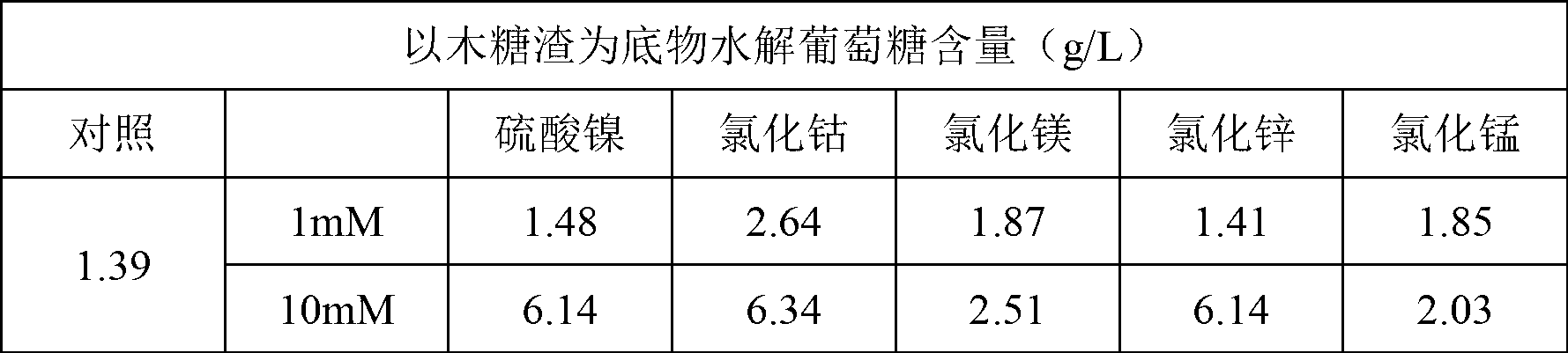
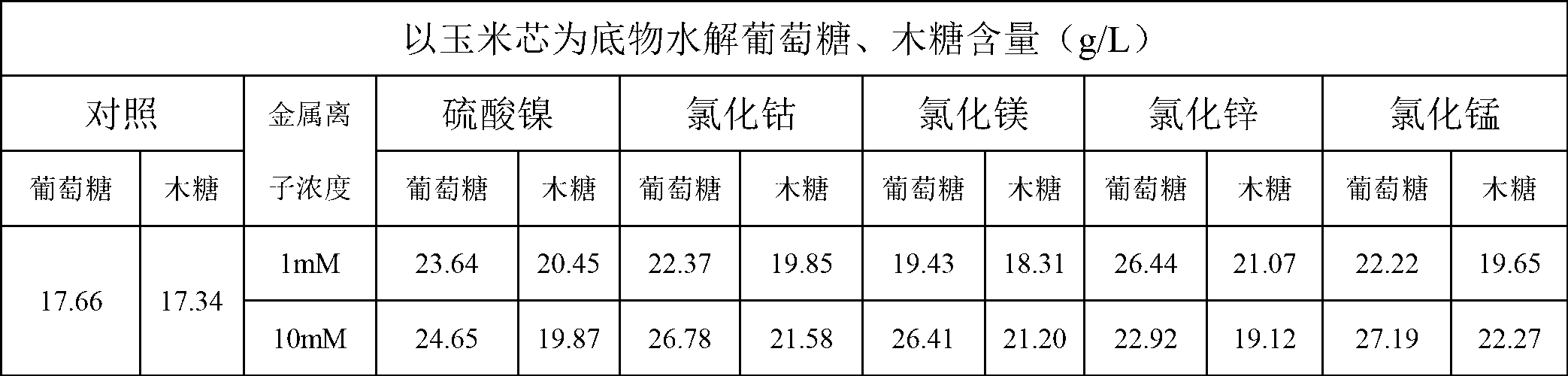
The invention discloses a method for promoting hydrolysis of lignocelluloses. According to the method, metal ions such as nickel, cobalt, magnesium, zinc, manganese and the like are added in the processes of saccharifying and hydrolyzing the lignocelluloses so as to improve the enzyme activity of the ligno-cellulase and hemicellulase, thereby further improving the hydrolysis efficiency of the ligno-cellulase. Proved by experiments, the hydrolysis efficiency of glucan can be improved by 4.5 times by adding the metal ions. According to the method, the operation is simple, the metal ions can be recycled, the investment cost is low, the usage range is wide, the pollution does not exist, the hydrolysis efficiency of the cellulose is obviously improved, and the method can be widely applied in the process of hydrolyzing the lignocelluloses and in the fields of manufacturing and developing biomass energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Method for producing glucose and cellobiose using cellulose complex enzyme
InactiveCN101603065AIncrease saccharification rateSatisfy productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberConcentrations glucose
A method for producing glucose and cellobiose using cellulose complex enzyme is the technology using the cellulose complex enzyme as a catalyst and realizing the high saccharification rate conversion of cellulose by adding cellulose enzyme activator at the optimized stirring speed. Glucose concentration can reach 150g / L after using cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis, and the method is a cellulose saccharification production technology with economic feasibility. With the technology used, low cost, low usage of enzyme and high saccharification rate can be realized, and the productions of cellulose alcohol and biochemical products (lactic acid, succinic acid and the like) are satisfied. In the whole technology, no beta-glucosaccharase is added additionally, no sugar concentrating device is added, and the technology is simple, the equipment cost is low and the industrialized prospect is good.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Method for culturing microalgae by adopting lignocellulose
ActiveCN108977401AExtensive sources of raw materialsInexpensive sources of raw materialsBacteriaUnicellular algaePre treatmentCarbon source
The invention provides a technology taking lignocellulose type agricultural and forest wastes as raw materials, aiming at the problem in the prior art that the cost of a carbon source in a microalgaeheterotrophic fermentation process. The technology comprises the steps of pre-treating lignocellulose raw materials, saccharifying, carrying out microalgae heterotrophic fermentation, carrying out post-treatment and the like. The technology adopts a strategy combining biological saccharifying of lignocellulose and the microalgae heterotrophic fermentation, so that the production cost of the microalgae heterotrophic fermentation is remarkably reduced, and the comprehensive utilization problem of the agricultural and forest wastes is also solved. Meanwhile, a cellulose preparation for catalyzingthe lignocellulose to be saccharified is adopted, so that the enzyme utilization cost of a saccharifying phase is remarkably reduced. Furthermore, a culture medium at a lignocellulose saccharifying phase and a fermentation culture medium in the technology can be circularly utilized, so that water can be remarkably reduced and the dosage of chemicals also can be remarkably reduced; the technologyhas great significance on industrialization.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods for treating lignocellulosic materials
The present invention relates to methods of processing lignocellulosic material to obtain hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose and other high-value products. Also provided are hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose, and other high-value products.
Owner:VIRDIA
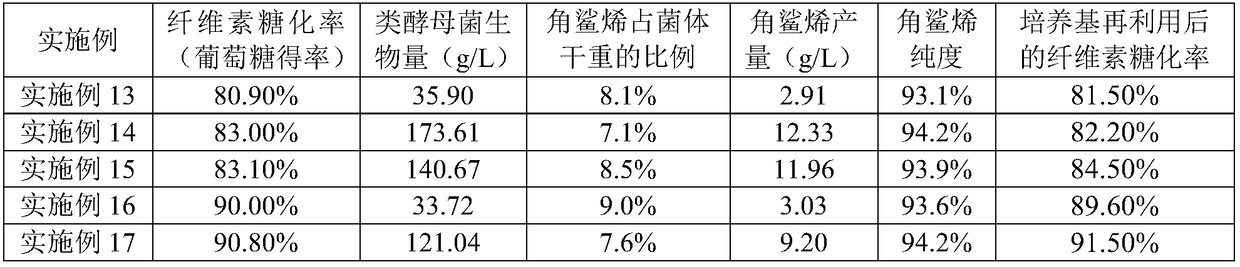
Method for preparing squalene by adopting lignocellulose
ActiveCN108866112ASolve market needsReduce manufacturing costDistillation purification/separationWaste based fuelCelluloseDry weight
The invention provides a process for preparing squalene by taking lignocellulosic agricultural and forestry wastes as raw materials, which aims at problems in the aspect of the production of squaleneby microbial fermentation in the prior art. The process comprises the steps of pre-treatment, saccharification, yeast-like fungi fermentation and squalene extraction and the like. According to the process provided by the invention, lignocellulose biological saccharification is combined with yeast-like fungi high-density fermentation; by adopting lignocellulose biomass as raw material, on the one hand, the cost of enzyme usage and the production cost of squalene microbial fermentation in a saccharification stage are significantly reduced; on the other hand, the problem of comprehensive utilization of the agricultural and forestry wastes is solved. In addition, medium and fermentation medium in the lignocellulose saccharification stage can be recycled, water can be saved and usage of chemicals can be reduced, and has significant effect on reducing the discharge of wastewater and reducing the cost. In the process provided by the invention, the squalene yield can reach 13 g / L, accounting for 5% of the dry weight of thallus, and the purity of refined squalene is higher than 93%.
Owner:青岛中科潮生生物技术有限公司
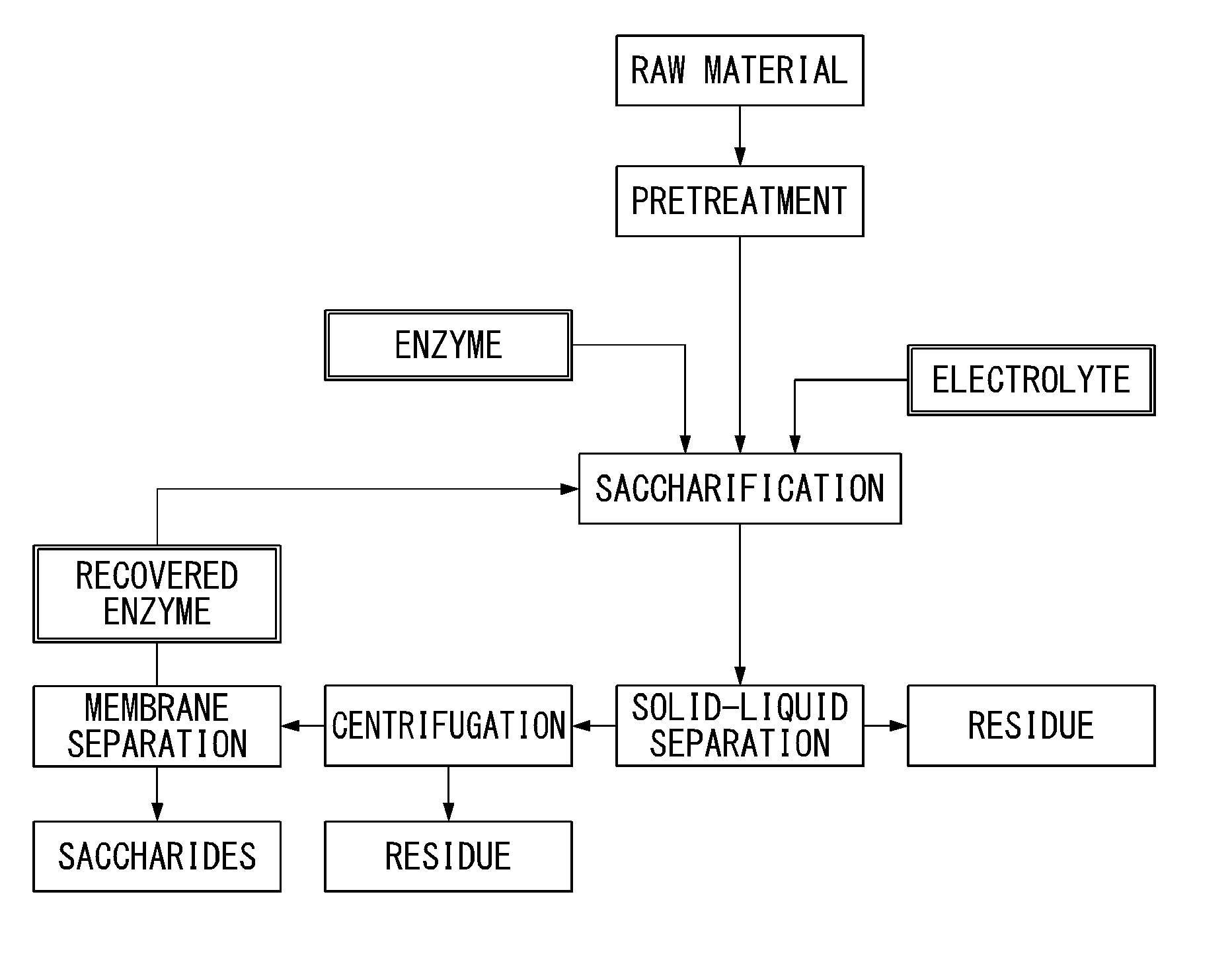
Method for enzymatic saccharification treatment of lignocellulose-containing biomass, and method for producing ethanol from lignocellulose-containing biomass
ActiveUS8728770B2Inhibition of adsorptionFacilitated separation and recoverySolid waste disposalBiofuelsCelluloseWater soluble
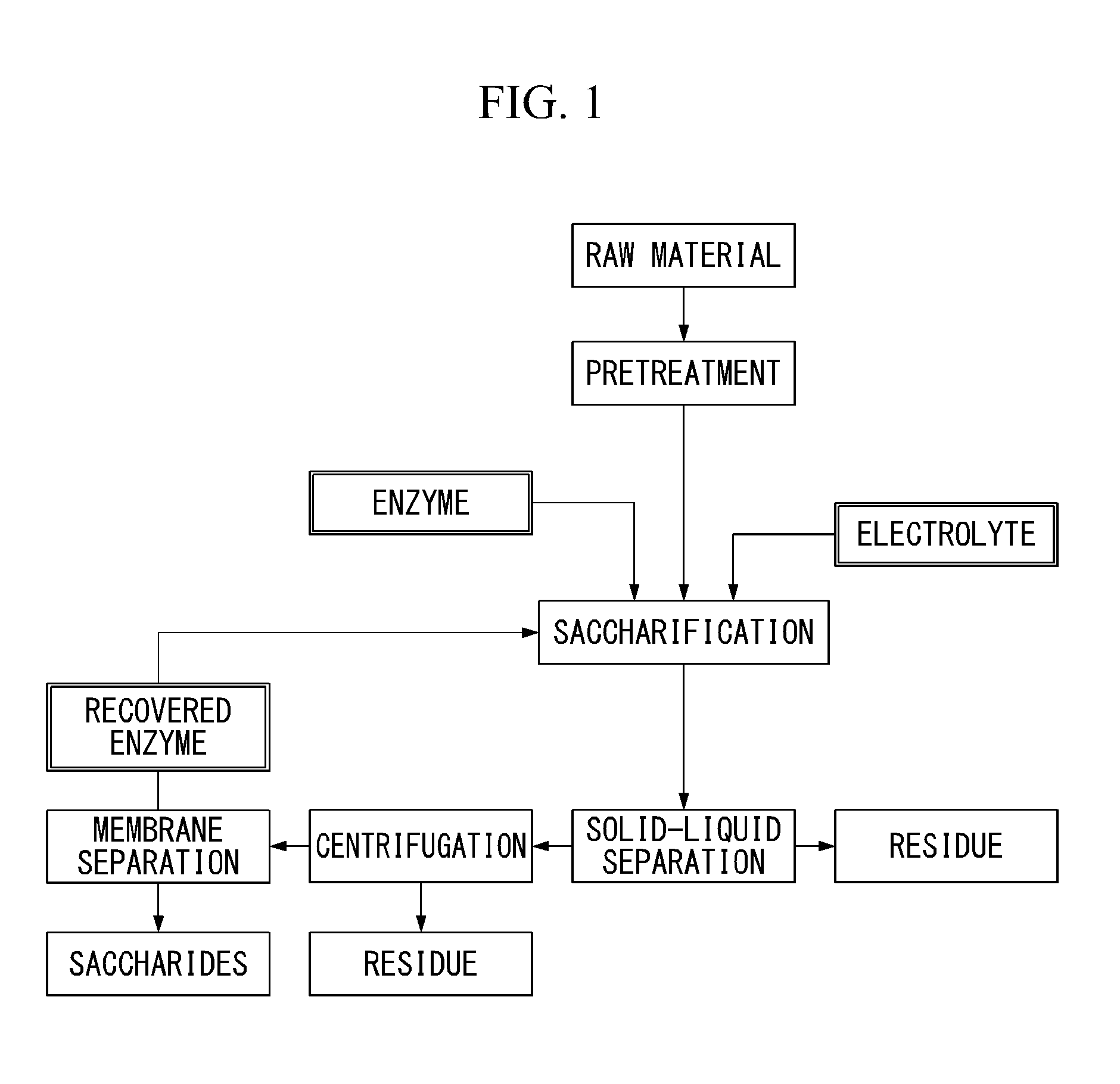
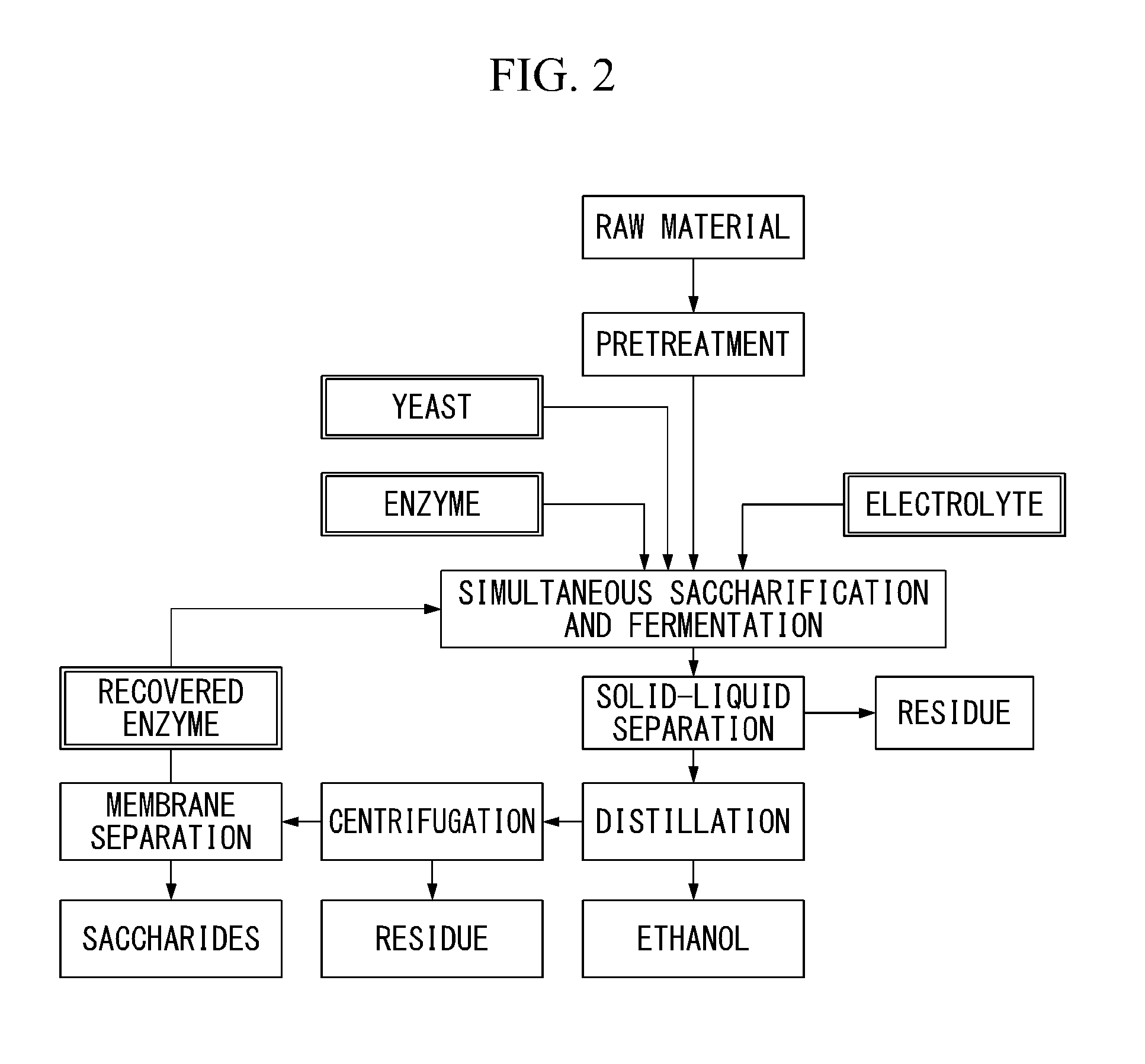
A method for the enzymatic saccharification of a lignocellulosic raw material, including adding a pretreated lignocellulosic raw material as a material suitable for an enzymatic saccharification reaction, together with an electrolyte containing a water-soluble salt, to water that contains a celluolose saccharification enzyme; saccharifying the raw material by an enzymatic saccharification reaction, as a suspension of the raw material having an electrical conductivity adjusted to 5-25 mS / cm; separating and recovering a reaction product and an enzyme-containing solution from the enzymatically saccharified treatment suspension; and recycling the recovered enzyme-containing solution as the enzyme for the enzymatic saccharification step.
Owner:OJI HLDG CORP
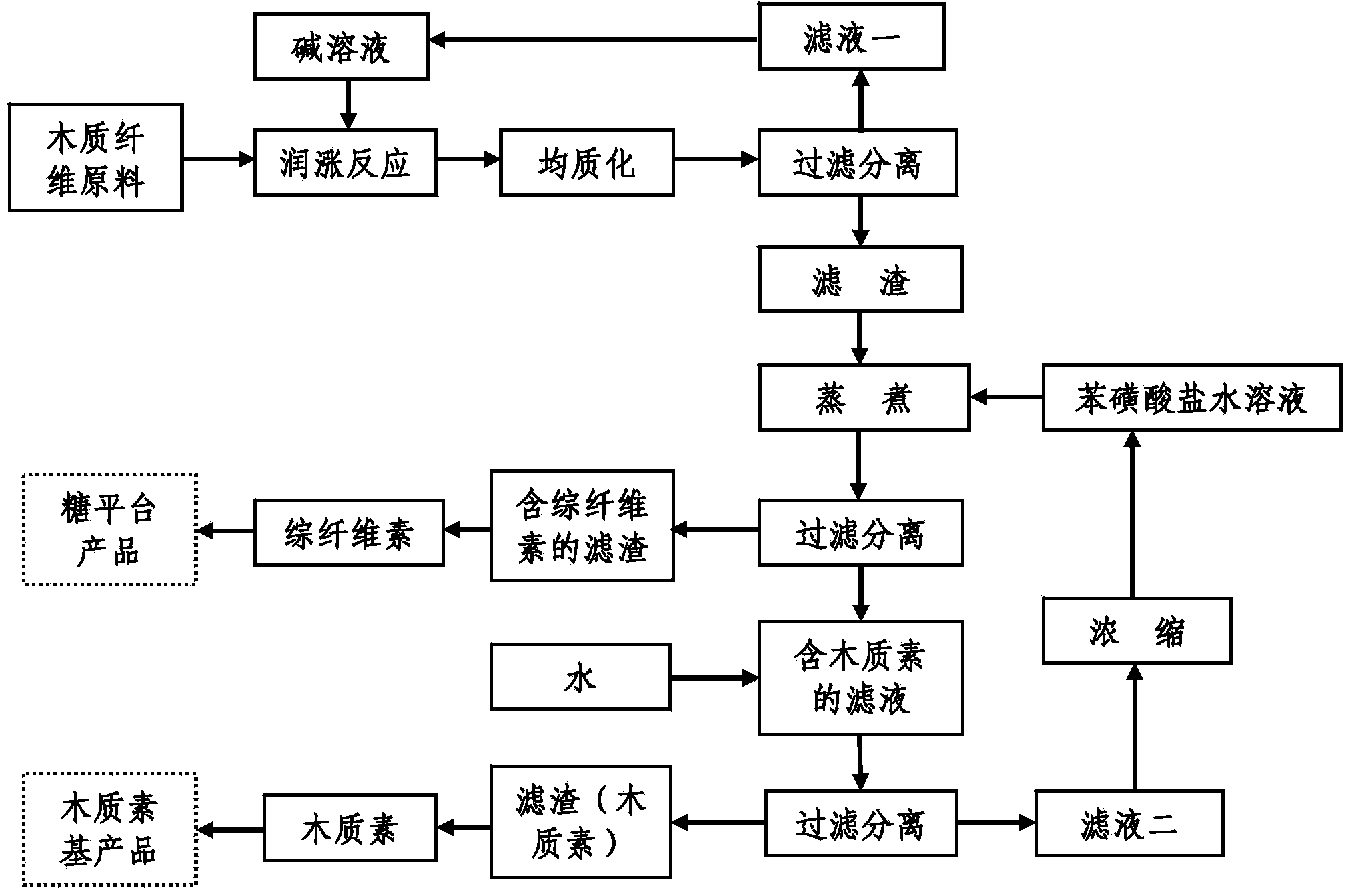
Method for separating lignin and holocellulose from wood fiber raw materials and application thereof
InactiveCN104389216AHigh extraction yieldImprove saccharification efficiencyPaper material treatmentCelluloseFiber
The invention relates to utilization and technology of agriculture and forestry biological data, in particular to a method for separating lignin and holocellulose from wood fiber raw materials. The method comprises the following steps: a, wood fiber raw materials are mixed with an alkali liquor and then soaked and moistened; b, the soaked and moistened wood fiber raw materials are homogenized and then filtered and separated to obtain solid residues and a filtrate I; c, the solid residues which are washed with water are added into a benzene sulfonate water solution for digestion, and the digested solid residues are filtered and separated to obtain residues containing holocellulose and a filtrate containing lignin; d, the residues containing holocellulose are washed to obtain holocellulose; e, water is added into the filtrate containing lignin to separate lignin, filtering is performed to obtain lignin residues and a filtrate II, and the lignin residues are washed and dried to obtain lignin. The method provided by the invention is simple and feasible in process, environment-friendly, and low in toxicity, the lignin extraction yield is high, and the saccharification efficiency of holocellulose obtained through separation is also high.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
Processes and apparatus for producing fermentable sugars and low-ash biomass for combustion at reduced emissions
This invention provides processes and apparatus to convert biomass, including wood and agricultural residues, into low-ash biomass pellets for combustion, alone or in combination with another solid fuel. Some embodiments provide processes for producing hemicellulosic sugars and low-ash biomass from cellulosic biomass, comprising providing an aqueous extraction solution with acetic acid; extracting the feedstock to produce an extract liquor containing soluble ash, hemicellulosic oligomers, acetic acid, dissolved lignin, and cellulose-rich solids; dewatering and drying the cellulose-rich, lignin-rich solids to produce a low-ash biomass; hydrolyzing the hemicellulosic oligomers to produce fermentable hemicellulosic sugars, wherein additional acetic acid is generated; removing a vapor stream comprising vaporized acetic acid from the extract; recycling the vapor or its condensate to provide some starting acetic acid for the extraction solution; and recovering fermentable hemicellulosic sugars. The disclosed processes can produce clean power from biomass. Co-products include fermentation products such as ethanol, fertilizers, and lignin.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
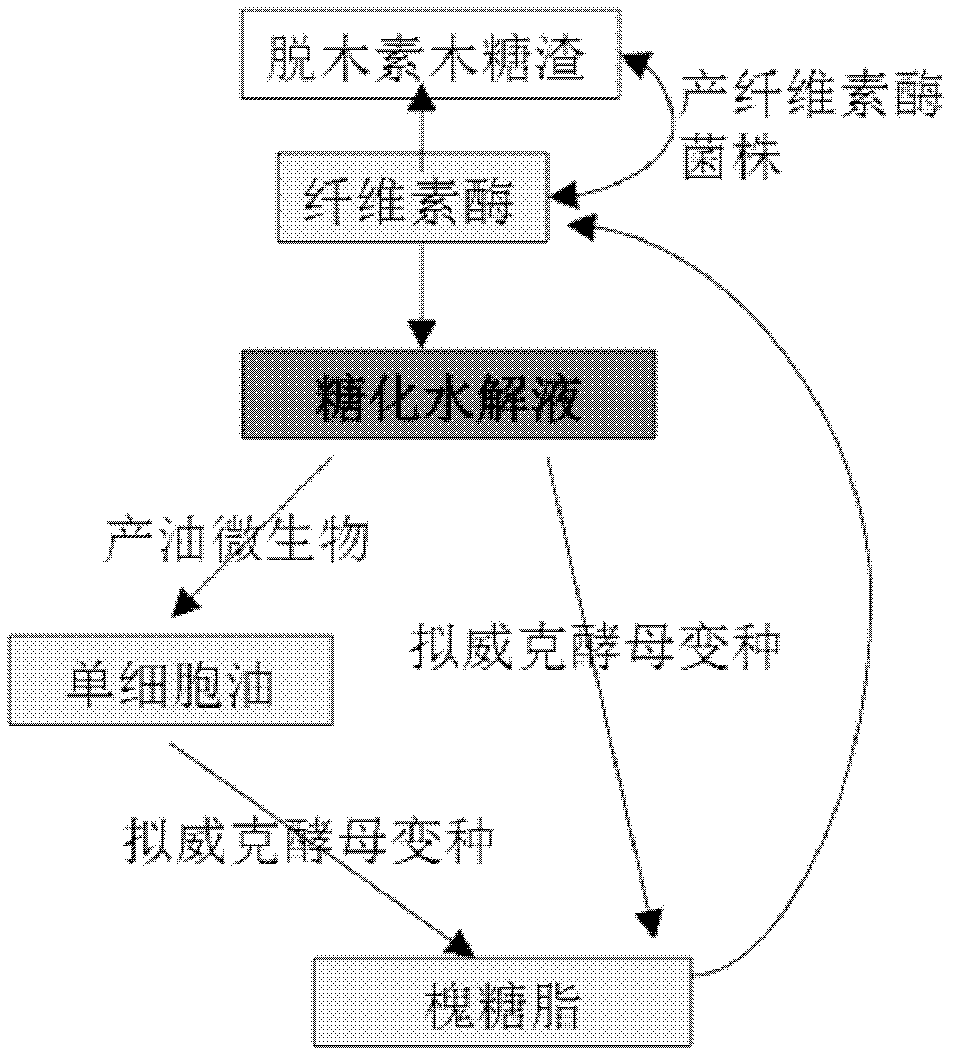
Method for producing sophorolipid through fermentation of lignocellulose material
InactiveCN102492753AEasy to separateIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseHydrolysate
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods for treating lignocellulosic materials
ActiveUS20150136121A1Increase acid concentrationChromatographic cation exchangersPurification using adsorption agentsSugarHemicellulose
The present invention relates to methods of processing lignocellulosic material to obtain hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose and other high-value products. Also provided are hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose, and other high-value products.
Owner:VIRDIA
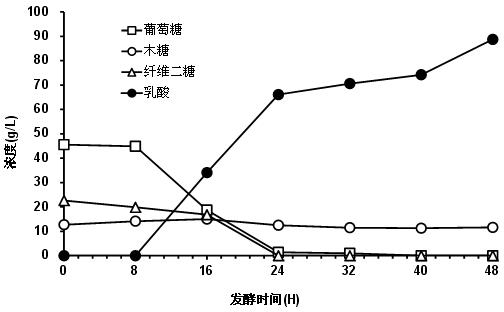
Preparation method of lactic acid by saccharifying and fermenting lignocellulose
The invention discloses a preparation method of lactic acid, which takes lignocellulose as raw material, and is low in cost and high in efficiency, wherein the preparation method specifically comprises the following steps of: separating from lignocellulose to store pediococcus acidilactici, carrying out liquid culture on the pediococcus acidilactici to obtain cell bacteria taken as seeds, inoculating into a reactor with high lignocellulose content, adding cellulase, and synchronously carrying out saccharification and high-temperature fermentation to generate the lactic acid; or firstly saccharifying the cellulase of the lignocellulose to obtain sugar-containing hydrolysate, then carrying out high-temperature lactic acid fermentation by the hydrolysate to obtain the lactic acid; or uniformly blending the pediococcus acidilactici and the lignocellulose raw material, carrying out solid state cultivation, adding the pediococcus acidilactici-containing lignocellulose raw material into a fermentation tank, adding the cellulase, and synchronously carrying out saccharification and high-temperature fermentation to prepare the lactic acid. By adopting unique fermentation technology and microorganism, the preparation method is high in product concentration, simple in process, and low in cost; and particularly by taking the lignocellulose as raw material, the preparation method is wide in production space and development prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Production of biodiesel, cellulosic sugars, and peptides from the simultaneous esterification and alcoholysis/hydrolysis of materials with oil-containing substituents including phospholipids and peptidic content
InactiveUS20090198077A1Avoid boilingFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationCellulosePolymer science
The present invention relates to a method for producing fatty acid alkyl esters as well as cellulosic simplified sugars, shortened protein polymers, amino acids, or combination thereof resulting from the simultaneous esterification and hydrolysis, alcoholysis, or both of algae and other oil containing materials containing phospholipids, free fatty acids (FFA), glycerides, or combination thereof as well as polysaccharides, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignocellulose, protein polymers, or combination thereof in the presence of an alcohol and an optional acid catalyst.
Owner:INVENTURE RENEWABLES
Pre-treating method for improving sugar conversion rate of lignocellulose
InactiveCN104404108AHigh removal rateImprove sugar conversion rateFermentationCellulosePretreatment method
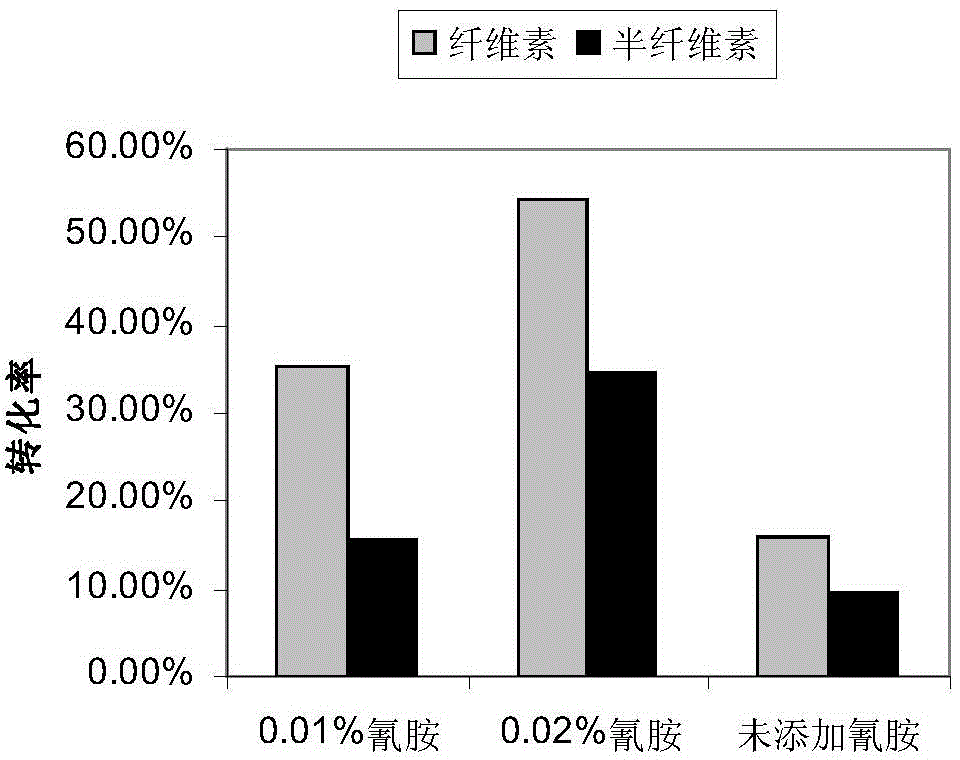
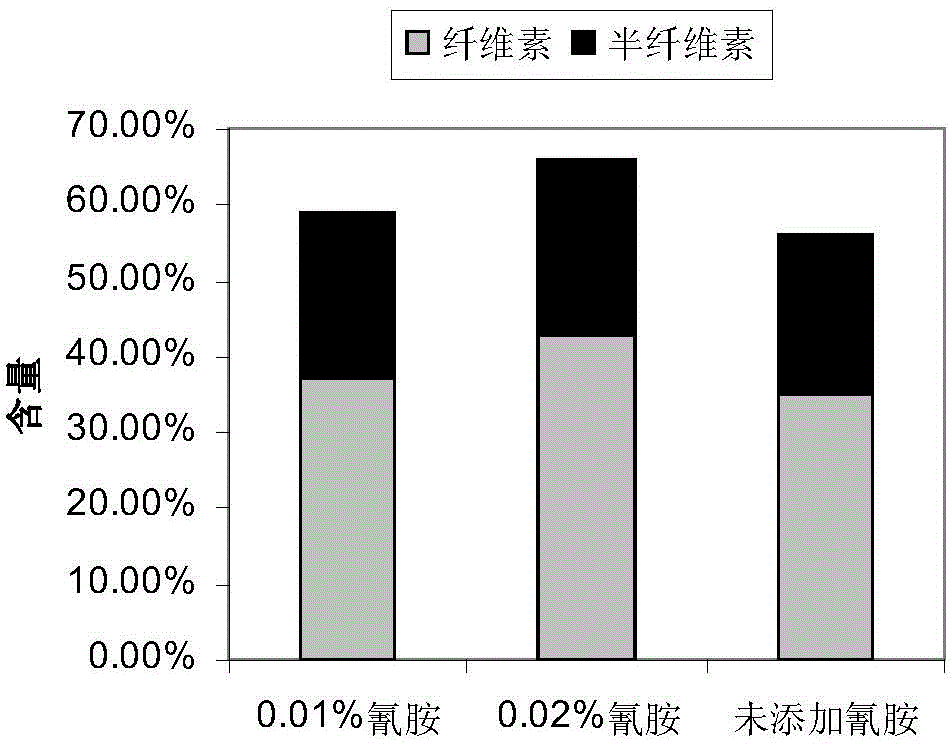
The invention relates to a pre-treating method for improving the sugar conversion rate of lignocellulose. The pre-treating method comprises the following steps: (1) removing impurities in a lignocellulose raw material, and carrying out air drying, smashing and sieving on the lignocellulose to prepare a cellulose raw material; (2) adding the cellulose raw material into a NaOH solution, uniformly stirring, then sequentially adding in H2O2 and cyanogen amine adopted as an activator, uniformly stirring again to prepare a mixed reaction liquid, and reacting by stirring to prepare the pre-treated lignocellulose. The pre-treating method adopts the method of combining low-concentration NaOH and H2O2 with the activator to treat the cellulose raw material, the pre-treating process is simple and feasible, intractable wastewater is prevented from generating, and the sugar conversion rate of the lignocellulose is remarkably improved.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing sodium gluconate from lignocellulose
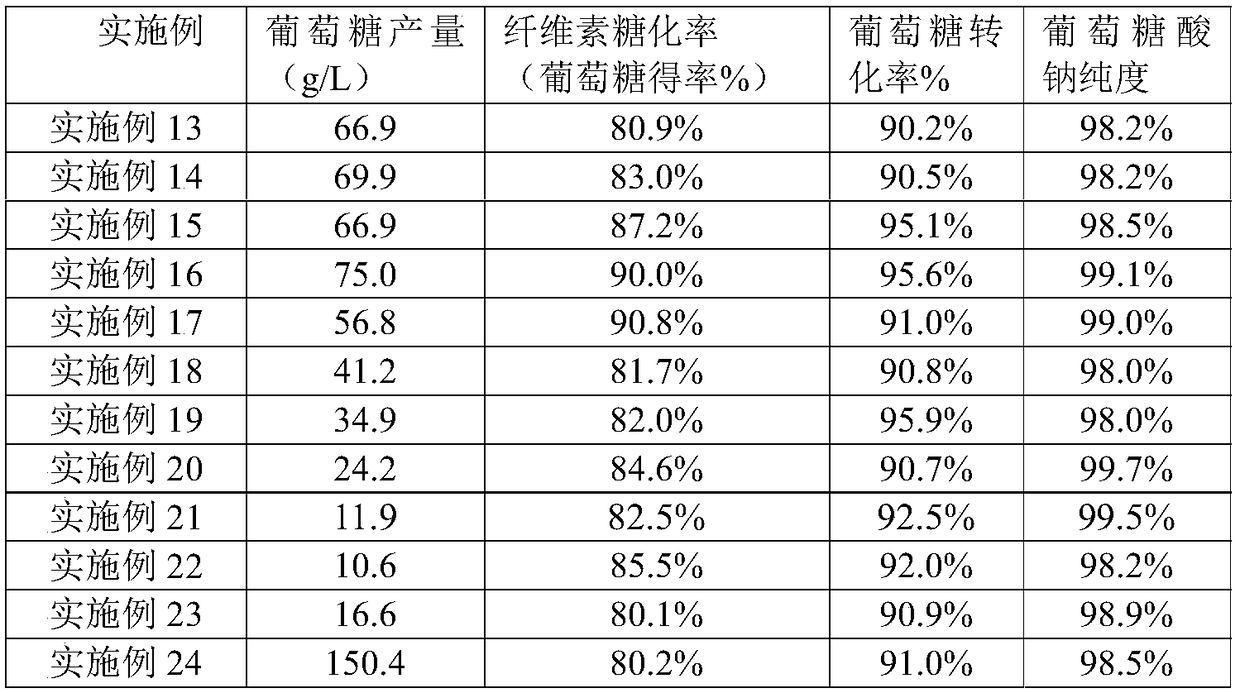
ActiveCN109022506ARaw materials are widely sourced and cheapSolve market needsFermentationConcentrations glucoseFixed bed
The invention provides a method for producing sodium gluconate from lignocellulose agriculture and forestry wastes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing: preprocessing a lignocellulose raw material to obtain a lignocellulose substrate; (2) saccharifying: transferring the lignocellulose substrate to a medium in an anaerobic fermentation tank, adding a cellulase preparation, and carrying out a hydrolysis reaction to obtain a glucose-containing sugar solution; (3) roughly preparing: allowing the sugar solution to enter a fixed bed reactor with glucose oxidase and catalase after the concentration of glucose in the sugar solution reaches 10-100 g / L, introducing air at 35-55 DEG C until dissolved oxygen saturation in order to oxidize glucose into gluconic acid, and controlling the pH value to 5.5-8.0 to convert gluconic acid into sodium gluconate; and (4) refining: refining the sodium gluconate obtained in step (3) in order to obtain the finished sodium gluconate. Themethod adopts a cellulase preparation for catalyzing the saccharification of lignocellulose, so the problems limited sodium gluconate raw material, complicated process and low yield are solved.
Owner:青岛中科潮生生物技术有限公司
Cellulose-solvent-based lignocellulose fractionation with modest reaction conditions and reagent cycling
ActiveUS20140190471A1Readily converted into glucoseLow costPressurized chemical processBiofuelsAcetic acidSugar
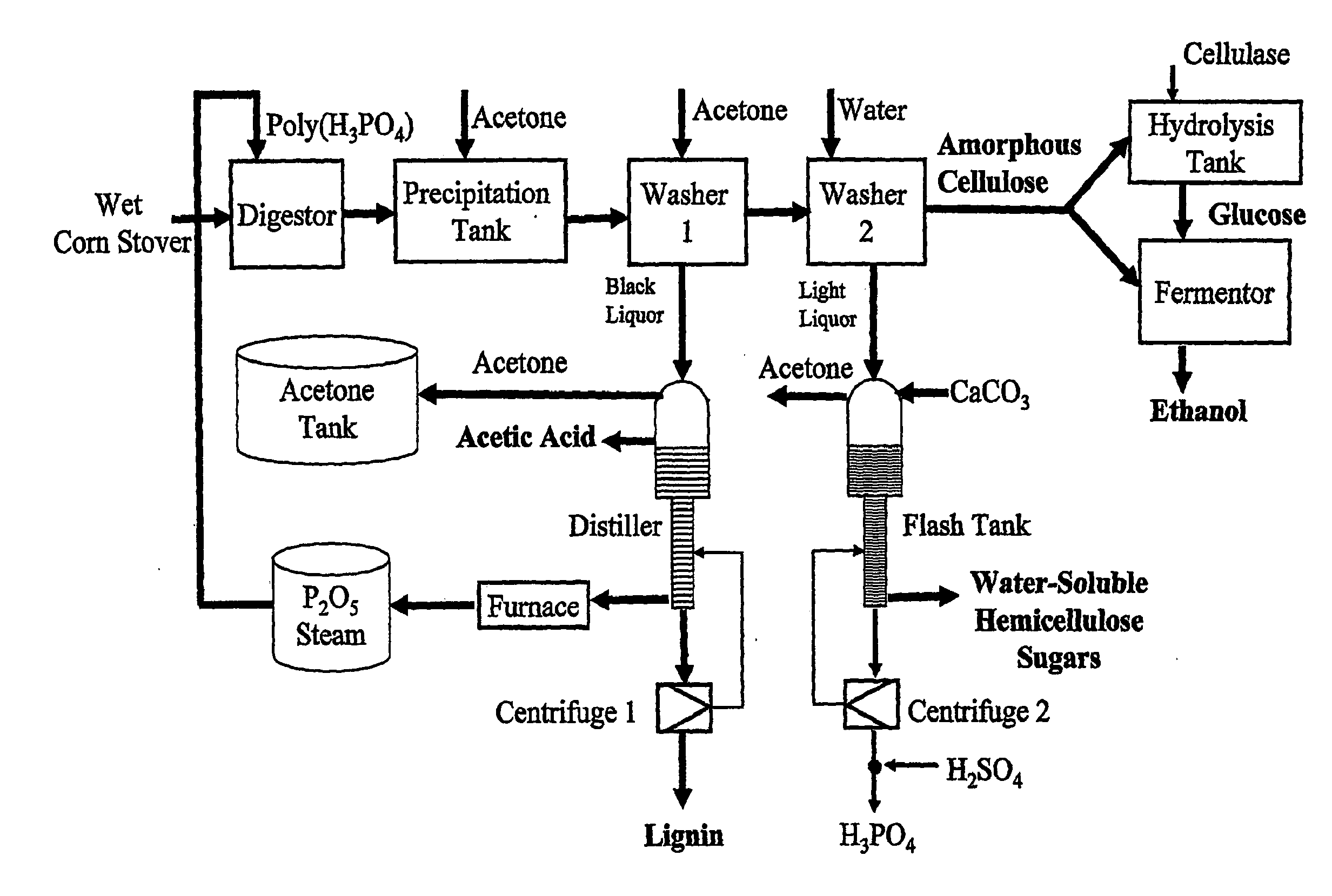
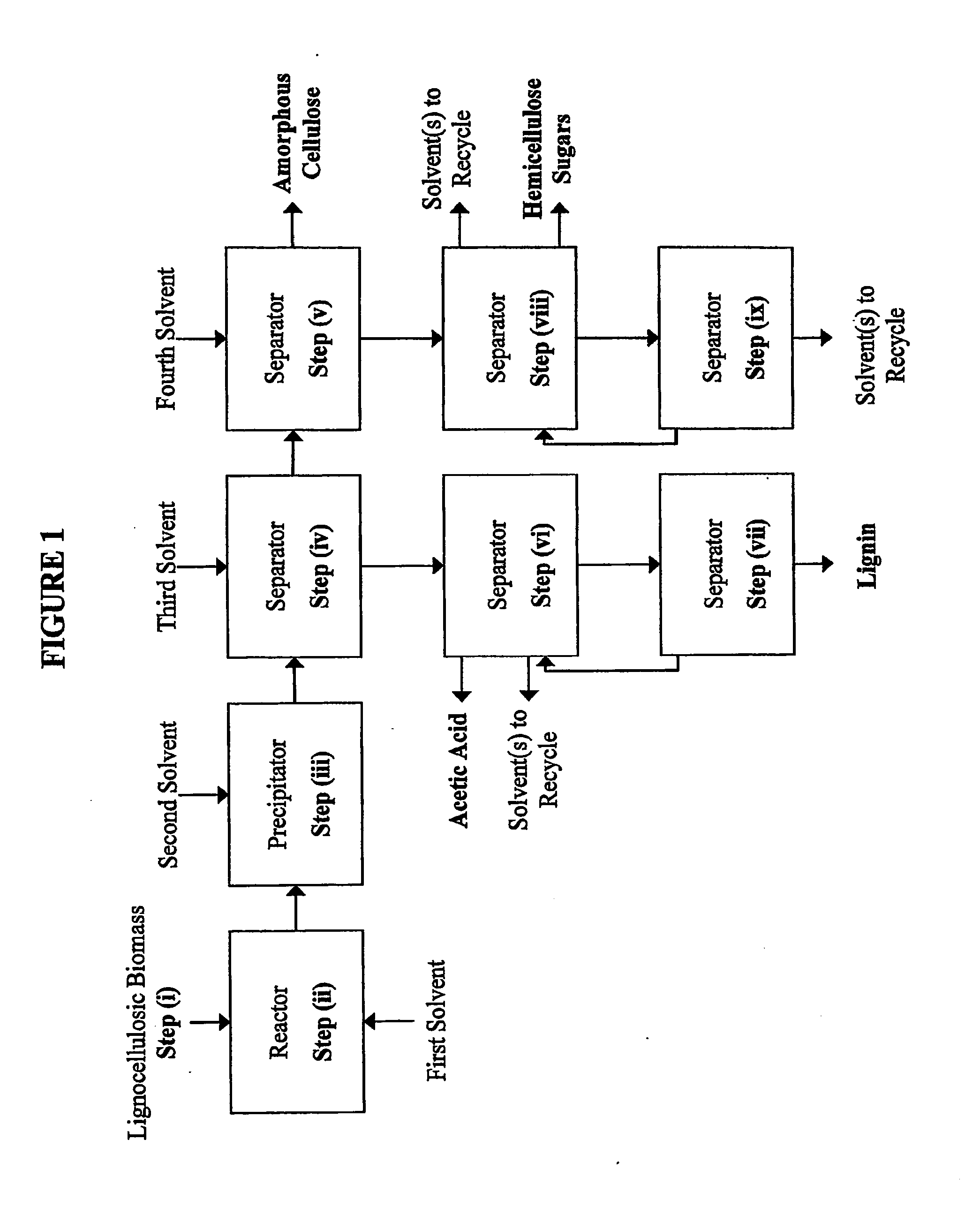
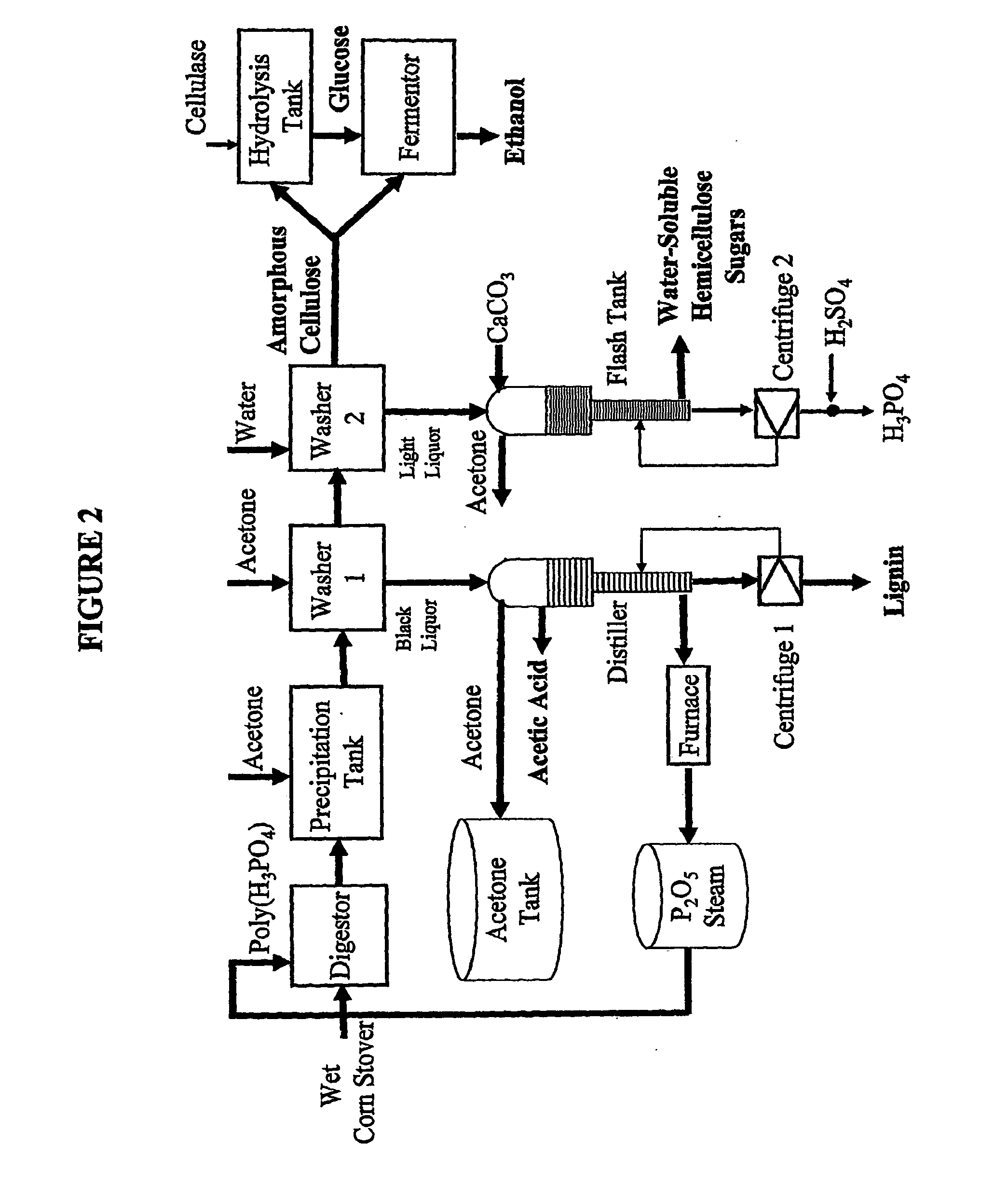
Embodiments of the present invention overcome the well-known recalcitrance of lignocellulosic biomass in an economically viable manner. A process and system are provided for the efficient fractionation of lignocellulosic biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose sugars, lignin, and acetic acid. The cellulose thus obtained is highly amorphous and can be readily converted into glucose using known methods. Fermentable hemicellulose sugars, low-molecular-weight lignin, and purified acetic acid are also major products of the process and system. The modest process conditions and low solvent / solid ratios of some embodiments of the invention imply relatively low capital and processing costs.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method of using lignocellulose for preparing DHA
ActiveCN108893501AWide range of sources and cheapSolve market needsMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseHigh density
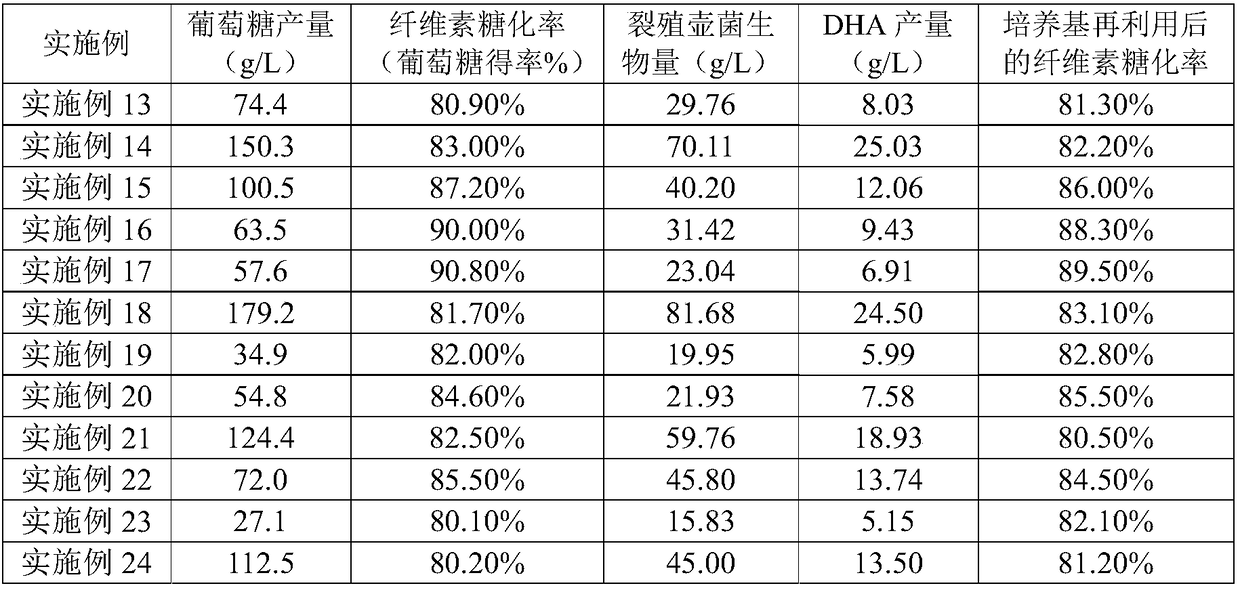
The invention provides a process for producing DHA with lignocellulosic agricultural and forestry waste as a raw material in order to solve problems of industrial production of DHA in the prior art. The process includes the steps of pretreatment, saccharification, fermentation of schizochytrium limacinum, extraction of DHA and the like. The process adopts a combination of lignocellulosic biosaccharification and high-density schizochytrium limacinum fermentation; by adopting lignocellulosic biomass as the raw material, on the one hand, the production cost of DHA is significantly reduced; on theother hand, the problem of comprehensive utilization of the agricultural and forestry waste is also solved. In the process, a lignocellulose saccharification stage culture medium and a fermentation medium can be recycled so that water can be significantly saved, and the use of chemicals is reduced. In addition, the cellulose saccharification efficiency is 80-90%, the biomass of schizochytrium limacinum can reach 15-80g / L, and the production of DHA is 5-25g / L. Compared with the prior art, the process has the advantage that the production and yield of DHA are higher.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cellulosome enzymic preparation for catalyzing saccharification of lignocellulose
ActiveCN108976302AReduce consumptionGood synergyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFermentationState of artFiber
The invention provides a cellulosome enzymic preparation for catalyzing saccharification of lignocellulose aiming at the problem of cellulosome in lignocellulosic saccharification in the prior art. The cellulosome enzymic preparation for catalyzing the saccharification of lignocellulose is a protein complex obtained by binding non-cellulosome proteins in cellulosome through the mutual action of non-cellulosome proteins and components in the cellulosome; then the protein complex is used for saccharifying, namely, bacterial cells are not involved in the saccharification process. The cellulosomeenzymic preparation provided by the invention not only achieves the maintenance of stability and activity, but also greatly enhances the synergistic effect with other enzymes in the system, thereby reducing the enzyme consumption, and reducing the production cost and the trivialness of the process.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
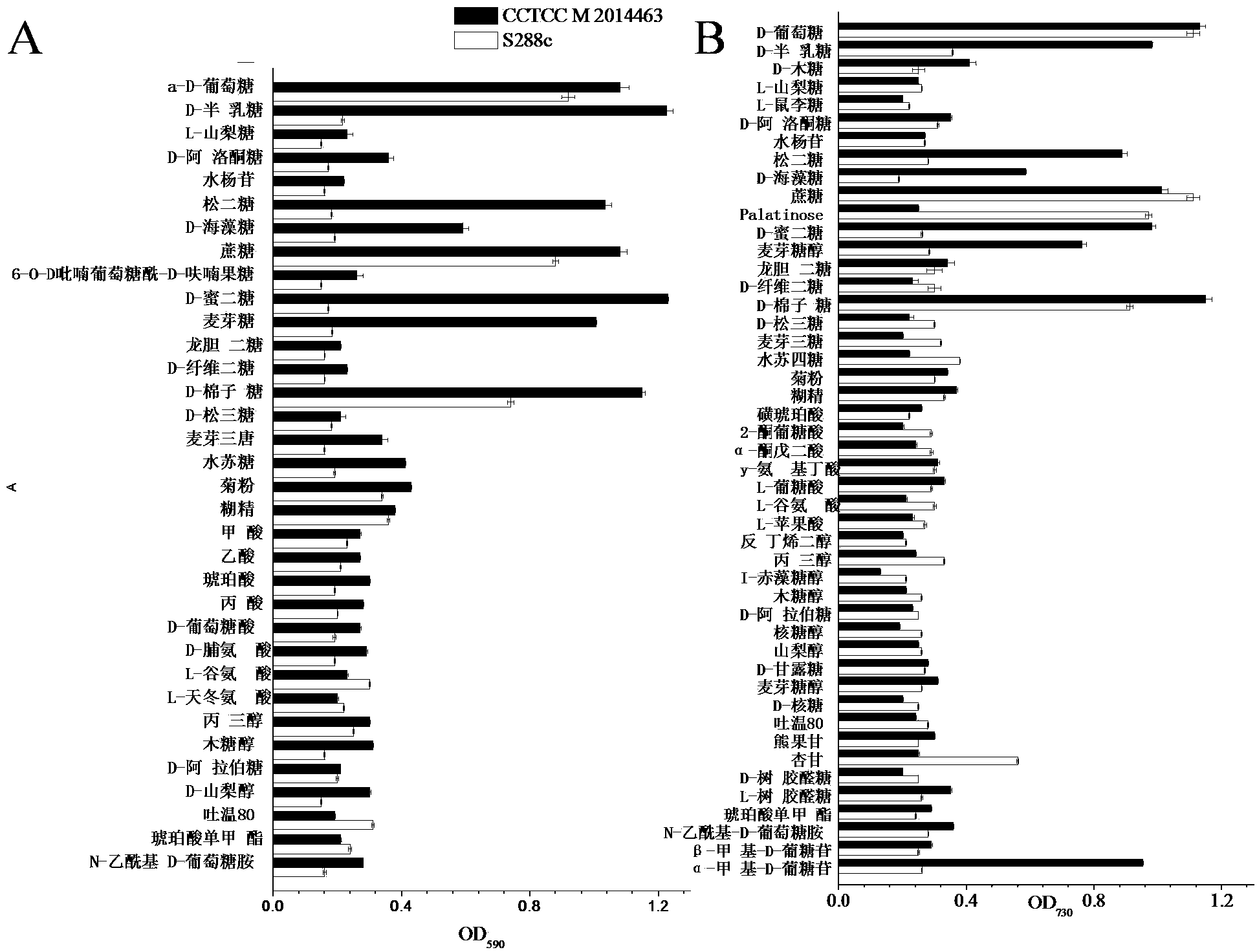
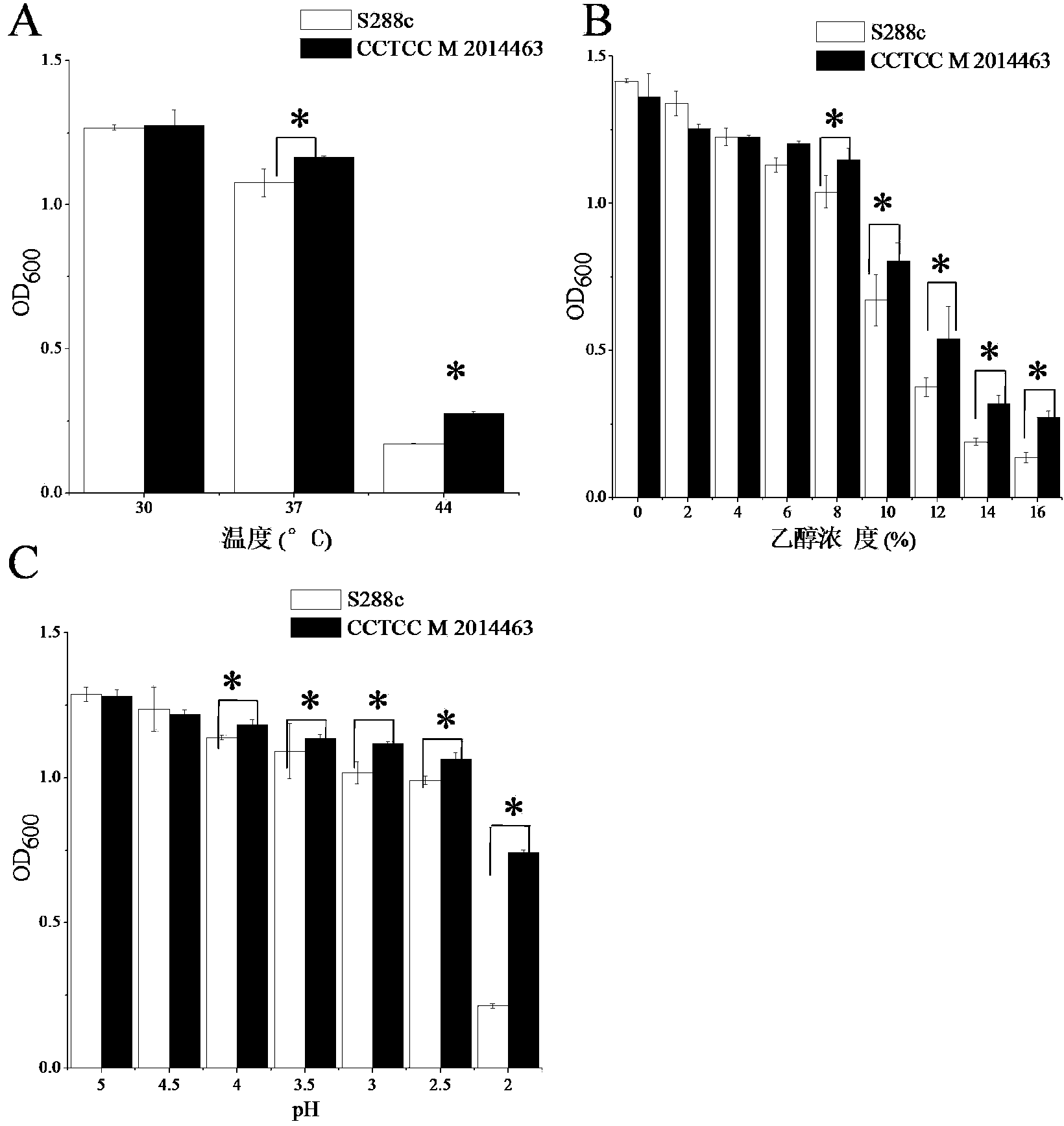
Saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of being co-fermented by a plurality of carbon sources and application thereof
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of being co-fermented by a plurality of carbon sources and an application thereof, belonging to the technical fields of microbes and fermentation engineering. The saccharomyces cerevisiae namely a CCTCC M 2014463 strain is separated from Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor wine brewing fermented grains. The strain can adopt glucose, galactose, xylose, allulose, cane sugar, maltose, melibiose, turanose, mycose and melitose, and can adopt glucose and other sugars synchronously. Meanwhile, the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be used for resisting high temperature, high ethanol and high acid, and also can be used for producing acids, alcohols, esters and various flavor substances such as benzeneacetaldehyde, acetophenone 4-vinyl guaiacol and the like. The saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention can be directly applied to the production of beverage wines, the reinforcement of wine brewing fermented grains in beverage wine production, and the production of fuel ethanol which is used as a carbon source substrate after starch and cellulose saccharification, thereby significantly improving the carbon source utilization rate and the ethanol yield.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Industry glycerol normal pressure pretreatment method of eco-efficient conversion of agricultural straw cellosugar
InactiveCN101323871AConducive to high-value utilizationImprove enzymatic attackFermentationFiberCellulose
The invention relates to an economical preprocessing method for efficiently transforming crop straw cellulose sugar, with technical glycerin under normal temperature. Straw which is sufficiently soaked in water can be rapidly heated up under normal pressure after the addition of the technical glycerin so as to realize pre-treatment to straws by high temperature steaming. Water insoluble fiber section obtained by the pre-treatment can be transformed efficiently into glucose by direct enzymolysis without airing or baking. By the pre-treatment method, under the condition that the temperature is between 180 DEG C and 250 DEG C, and the dosage of the technical glycerin is equal to 10 times to 25 times of the weight of the straw, the pre-treatment is carried out for 1hour to 6 hours to obtain the crop straw fiber section, the weight of which accounts for 48 percent to 78 percent of the net weight of the straw; after the pre-treatment for 24 hours, the transformation rate of the cellulose sugar of the straw fiber section is 62 percent to 95 percent, and after the pre-treatment for 48 hours, the transformation rate of the cellulose sugar reaches 71 percent to 98 percent. The method is economical, high efficient, safe to be operated, easy and convenient, environment friendly and convenient to popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for treating lignocellulosic materials
ActiveUS20170313826A1Improve propertiesStability against oxidationNon-fibrous pulp additionBiofuelsSugarHemicellulose
The present invention relates to methods of processing lignocellulosic material to obtain hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose and other high-value products such as asphalt and bio oils. Also provided are hemicellulose sugars, cellulose sugars, lignin, cellulose, and other high-value products such as asphalt and bio oils.
Owner:VIRDIA
Cellulase preparation and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and in particular relates to a cellulase preparation for catalyzing lignocellulose saccharification, and application of the cellulase preparation. The cellulase preparation provided by the invention contains a cellulosome complex and beta-1, 4-glucosidase at the same time, wherein the beta-1, 4-glucosidase is compounded in the cellulosome complex in a way of interaction of covalent or non-covalent proteins or fusion expression with the cellulosome complex. The cellulase preparation not only can realize high-efficiency hydrolysis of a lignocellulose substrate and has high fermentable sugar yield and saccharification rate, but also has the advantages of being low in production cost, and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for enzymatic saccharification treatment of lignocellulose-containing biomass, and method for producing ethanol from lignocellulose-containing biomass
ActiveUS20130157318A1Highly economicalInhibition of adsorptionSolid waste disposalBiofuelsCelluloseWater soluble
A method for the enzymatic saccharification of a lignocellulosic raw material, including adding a pretreated lignocellulosic raw material as a material suitable for an enzymatic saccharification reaction, together with an electrolyte containing a water-soluble salt, to water that contains a celluolose saccharification enzyme; saccharifying the raw material by an enzymatic saccharification reaction, as a suspension of the raw material having an electrical conductivity adjusted to 5-25 mS / cm; separating and recovering a reaction product and an enzyme-containing solution from the enzymatically saccharified treatment suspension; and recycling the recovered enzyme-containing solution as the enzyme for the enzymatic saccharification step.
Owner:OJI HLDG CORP
Hydrolysis method of wood fiber raw material
ActiveCN105330869AHigh utilization rate of raw materialsAvoid long time-consuming hydrolysisAdhesivesFiberEvaporation
The invention provides a hydrolysis method of a wood fiber raw material. The hydrolysis method comprises the following steps: (1) adding an alkaline water solution of hydrogen peroxide into the wood fiber raw material to react; after the reaction is finished, filtering and separating to obtain filter residues (containing rich holocellulose) and filtrate; (2) after washing the filter residues with water, adding the filter residues into a high-pressure reaction kettle; adding an organic solvent, a catalyst and a catalyst auxiliary agent into the high-pressure reaction kettle to carry out a hydrolysis reaction; after the reaction is finished, filtering, wherein the filtrate contains reduced monosaccharide; (3) adding absolute ethyl alcohol into the filtrate of the step (1) and adjusting the pH value to be 5 to 6 by organic acid; after standing, filtering and separating to obtain filter residues and another kind of filtrate, wherein the filter residues are hemicellulose; taking the filtrate and carrying out rotary evaporation to remove ethanol; then adjusting the pH value to be 1 to 2; standing and then centrifuging, and separating to obtain solids, namely lignin. The wood fiber raw material, provided by the invention, has a simple and feasible process, is environmentally friendly, and has low toxin and high lignin removing and recycling rate; the separated holocellulose has high saccharifying efficiency; the industrialization is easy to realize and the hydrolysis method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com