Cellulosome enzymic preparation for catalyzing saccharification of lignocellulose
A technology of lignocellulose and cellulosomes, which is applied in the field of enzyme preparations and cellulosome enzyme preparations, can solve problems such as high cost and cumbersome process, and achieve the effects of improving synergy, reducing consumption, and achieving stability and activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Construction of Clostridium thermocellum expressing exocrine β-1,4 glucosidase
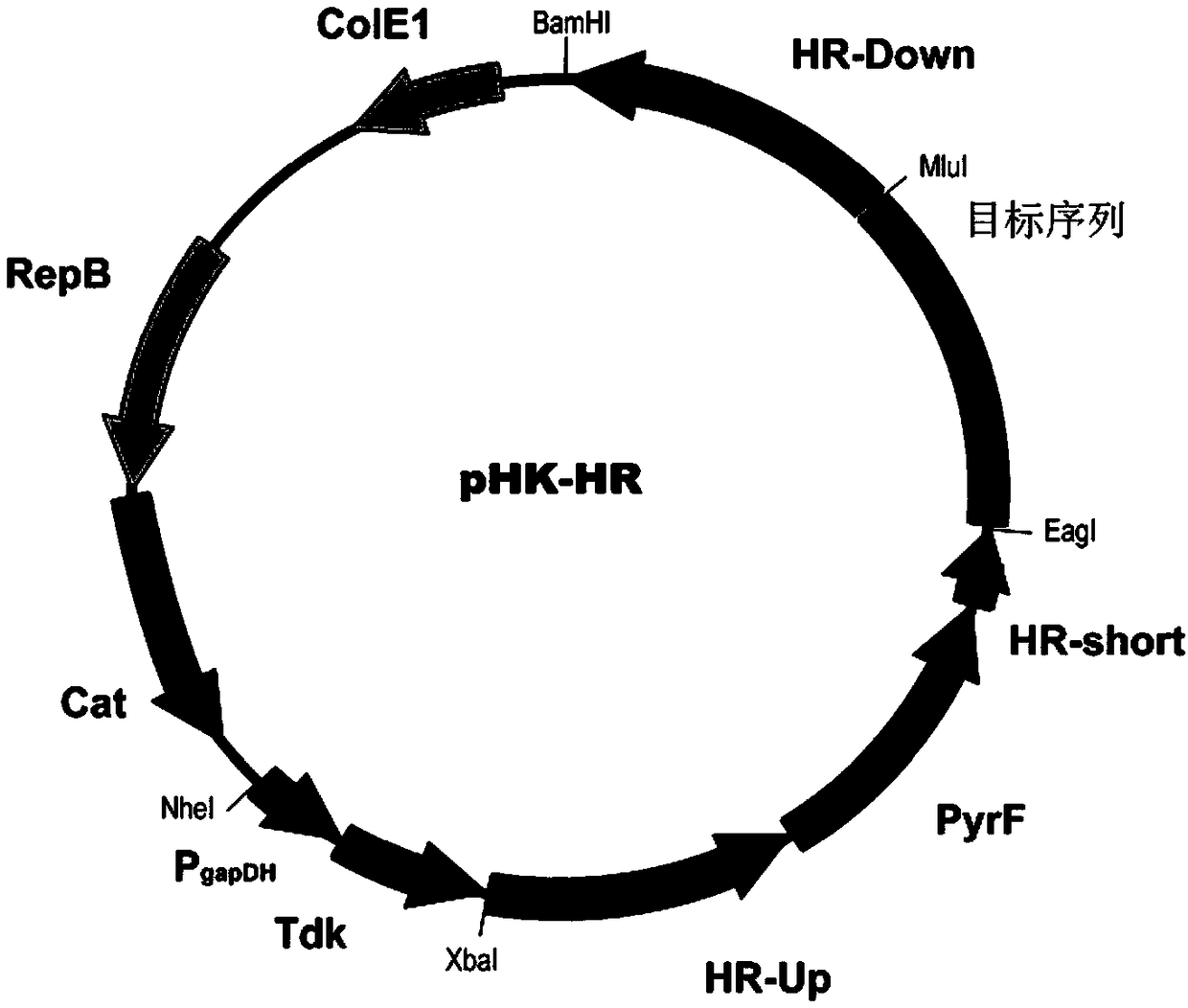
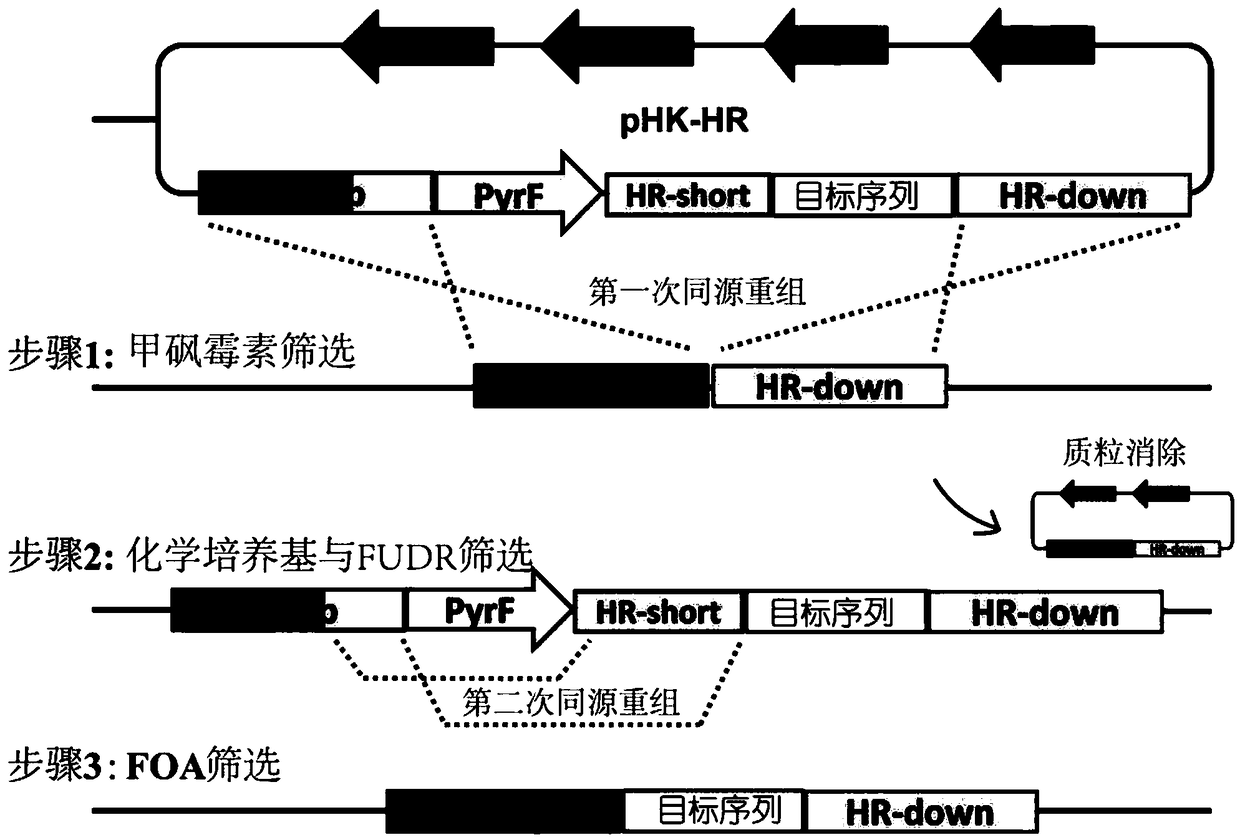
[0040] The cellulase Cel9K (exocellulase, encoded by the nucleic acid sequence 2113813 to 2111293 in the genome CP002416.1) in the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum and the docking module were selected as the targeted knock-in site point. First, the gene encoding β-1,4-glucosidase BglA (GENBANK sequence number is AFO70070.1) was used as the target sequence, and cloned into the homologous recombination plasmid pHK-HR( figure 2 ), construct the homologous recombination plasmid pHK-HR-BglA. The upstream homology arm HR-up sequence is the nucleic acid sequence from 2111347 to 2112870 in the Clostridium thermocellum DSM1313 genome (the sequence number in the NCBI database is CP002416.1), and the downstream homology arm HR-down is the 2109848 to 2111354 nucleic acid sequence in the DSM1313 genome, The middle homology arm HR-short is the nucleic acid sequence from 2111347 to 21...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: By the method of direct connection, construct the cellulosomal enzyme preparation based on Clostridium thermocellum cellulite
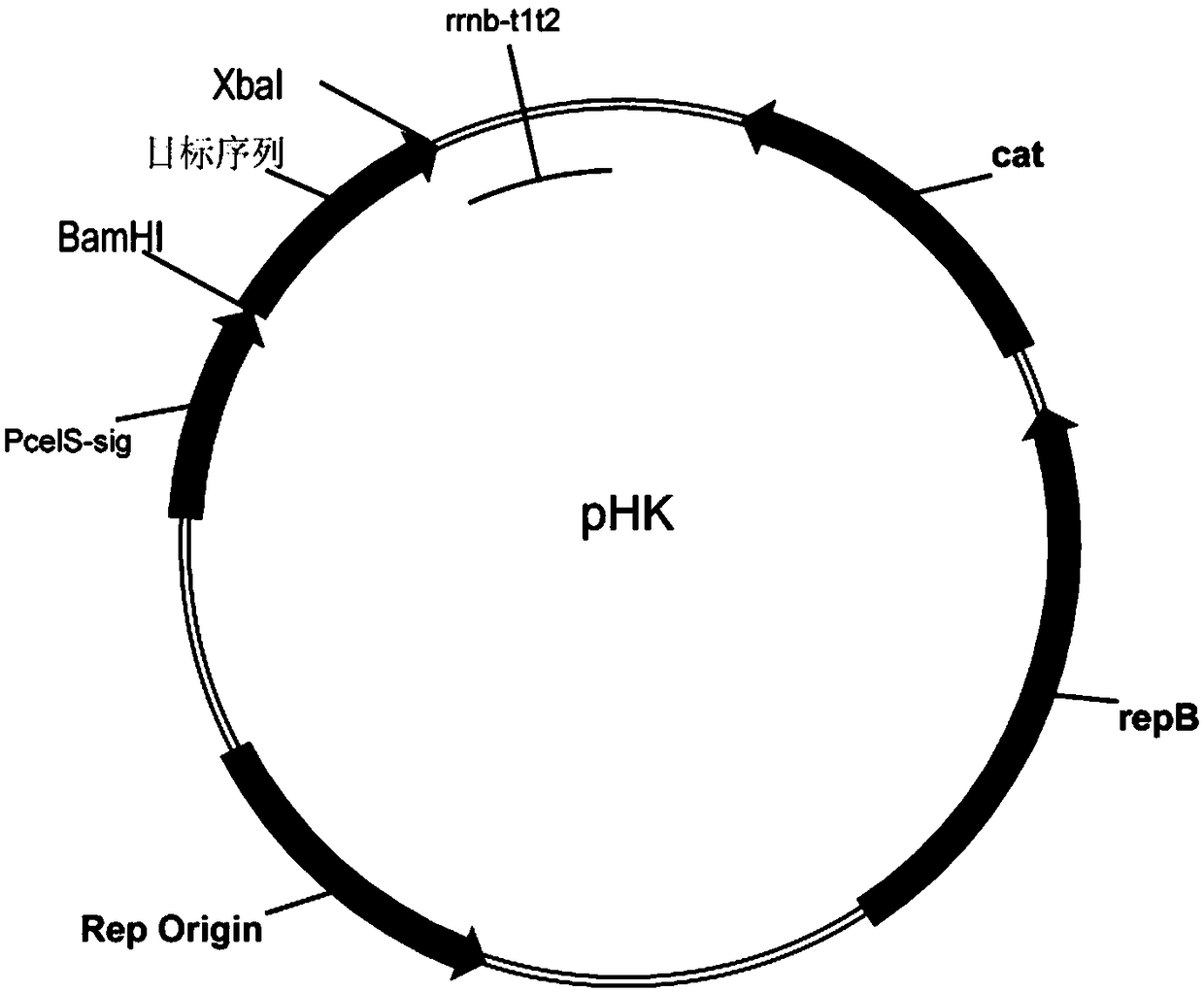
[0046] Using the method of overlap extension polymerase chain reaction, the sequence (SEQ ID NO: 10) of the type II adhesion module CohIIct of xylanase XynC (SEQ ID NO: 1) and Clostridium thermocellum or the type I docking module DocIct The sequence (SEQ ID NO: 9) is directly connected, wherein the sequence of CohIIct or DocIct is connected to the 3' end of the XynC sequence, thereby obtaining the XynC-CohIIct and XynC-DocIct sequences. Using BamHI and XbaI restriction sites again, the recombinant sequence connected together was cloned into the expression plasmid pHK( figure 1 )superior. Since pHK carries the promoter and signal peptide sequence (SEQ ID NO: 11) of the cellulase Cel48S derived from Clostridium thermocellum, the expressed target gene can be secreted to the extracellular space. The constructed plasmid was transform...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: By the method of direct connection, construct the cellulosomal enzyme preparation based on Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome
[0048] The gene encoding xylanase XynB (SEQ ID NO: 2) was used as the target sequence, and 5 of the cellulosic exonuclease Cel48S (encoded by the nucleic acid sequence from 3228088 to 3230229 in genome CP002416.1) of Clostridium thermocellum was selected. The 'end was used as the targeted knock-in site, and cloned into the homologous recombination plasmid pHK-HR( figure 2 ), construct the homologous recombination plasmid pHK-HR-xynB. The upstream homology arm HR-up is the nucleotide sequence from 3230200 to 3230700 in the genome of Clostridium thermocellum DSM1313 (the sequence number in the NCBI database is CP002416.1), the downstream homology arm HR-down is the nucleotide sequence from 3229699 to 3230199 in the DSM1313 genome, and the middle The homology arm HR-short is the nucleic acid sequence from 3230200 to 3230500 in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com