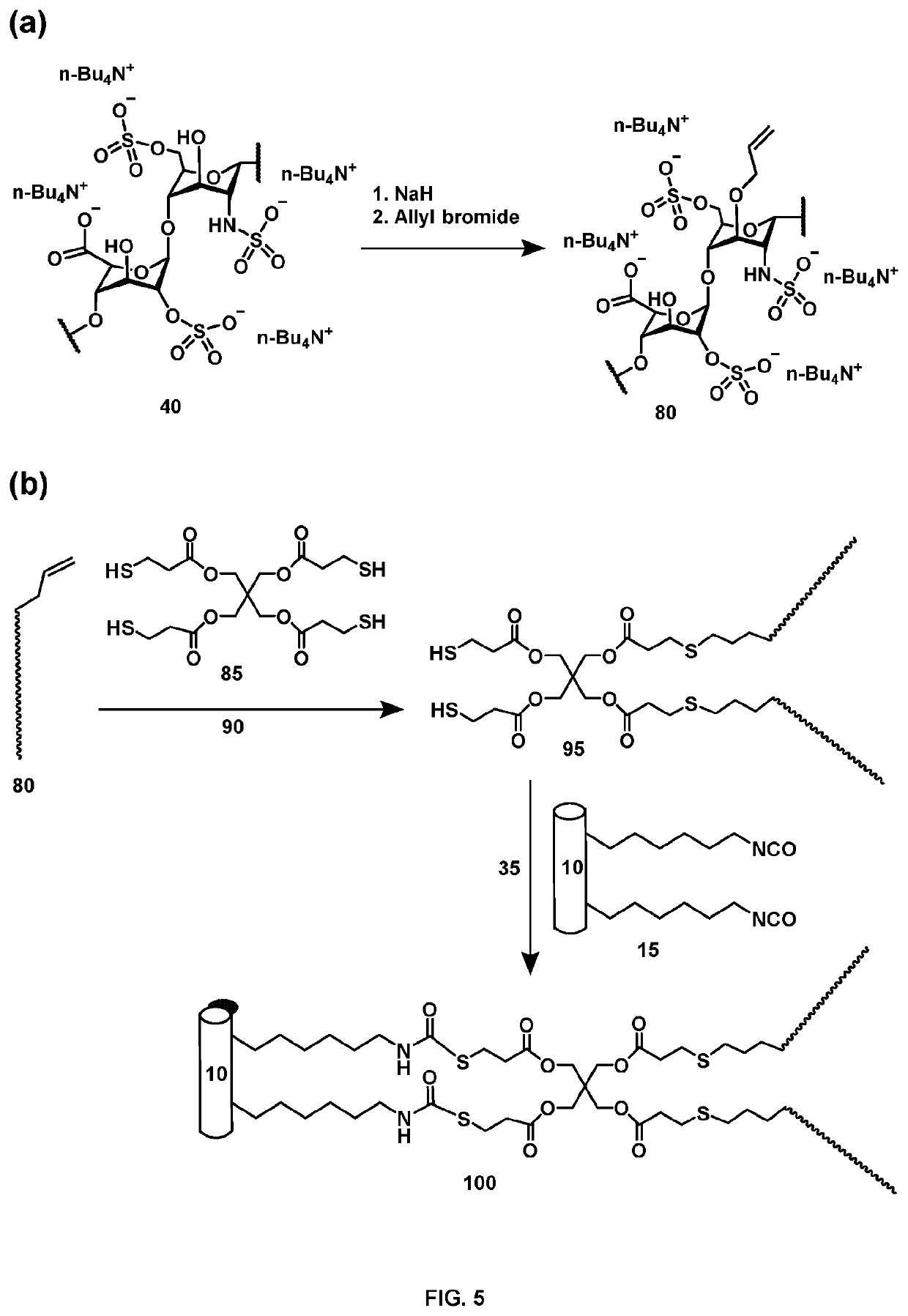
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Blood compatible" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Kidney donors must have a compatible blood type with the recipient. In living donation, the following blood types are compatible: Donors with blood type A... can donate to recipients with blood types A and AB Donors with blood type B... can donate to recipients with blood types B and AB Donors with blood type AB...
Wound healing polymer compositions and methods for use thereof
The present invention provides bioactive polymer compositions that can be formulated to release a wound healing agent at a controlled rate by adjusting the various components of the composition. The composition can be used in an external wound dressing, as a polymer implant for delivery of the wound healing agent to an internal body site, or as a coating on the surface of an implantable surgical device to deliver wound healing agents that are covalently attached to a biocompatible, biodegradable polymer and / or embedded within a hydrogel. Methods of using the invention bioactive polymer compositions to promote natural healing of wounds, especially chronic wounds, are also provided. Examples of biodegradable copolymer polyesters useful in forming the blood-compatible, hydrophilic layer or coating include copolyester amides, copolyester urethanes, glycolide-lactide copolymers, glycolide-caprolactone copolymers, poly-3-hydroxy butyrate-valerate copolymers, and copolymers of the cyclic diester monomer, 3-(S)[(alkyloxycarbonyl)methyl]-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione, with L-lactide. The glycolide-lactide copolymers include poly(glycolide-L-lactide) copolymers formed utilizing a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 5:95 to 95:5 and preferably a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 45:65 to 95:5. The glycolide-caprolactone copolymers include glycolide and ε-caprolactone block copolymer, e.g., Monocryl or Poliglecaprone.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
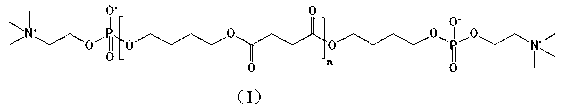
Blood compatible biological material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1799649AHigh mechanical strengthIncreased mechanical toughnessPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingAnticoagulantMolecular materials
A biological material of blood compatiblility and the preparing method, relating to a biological material of blood compatible used externally or be implanted into body and the preparing method. Dissolving the medical high molecular material of high mechanical property and anticoagulant material with two different solvent and mixing them, fixing the anticoagulant material in the high molecular material uniformly, and preparing the restoring material for tissue organs used externally or be implanted into body with normal process, the invention overcomes the shortcomings existing in traditional technique of not obvious effect or for a short time of the anticoagulant modifying caused by only adsorbing, coating or grafting on the product surface, and makes the material possesses good anticoagulant property and prolongs the anticoagulant durability, and can meet demands of good anticoagulant, biological compatibility, strong mechanical strength and toughness needed by the restoring material for tissue organs used externally or be implanted into body.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
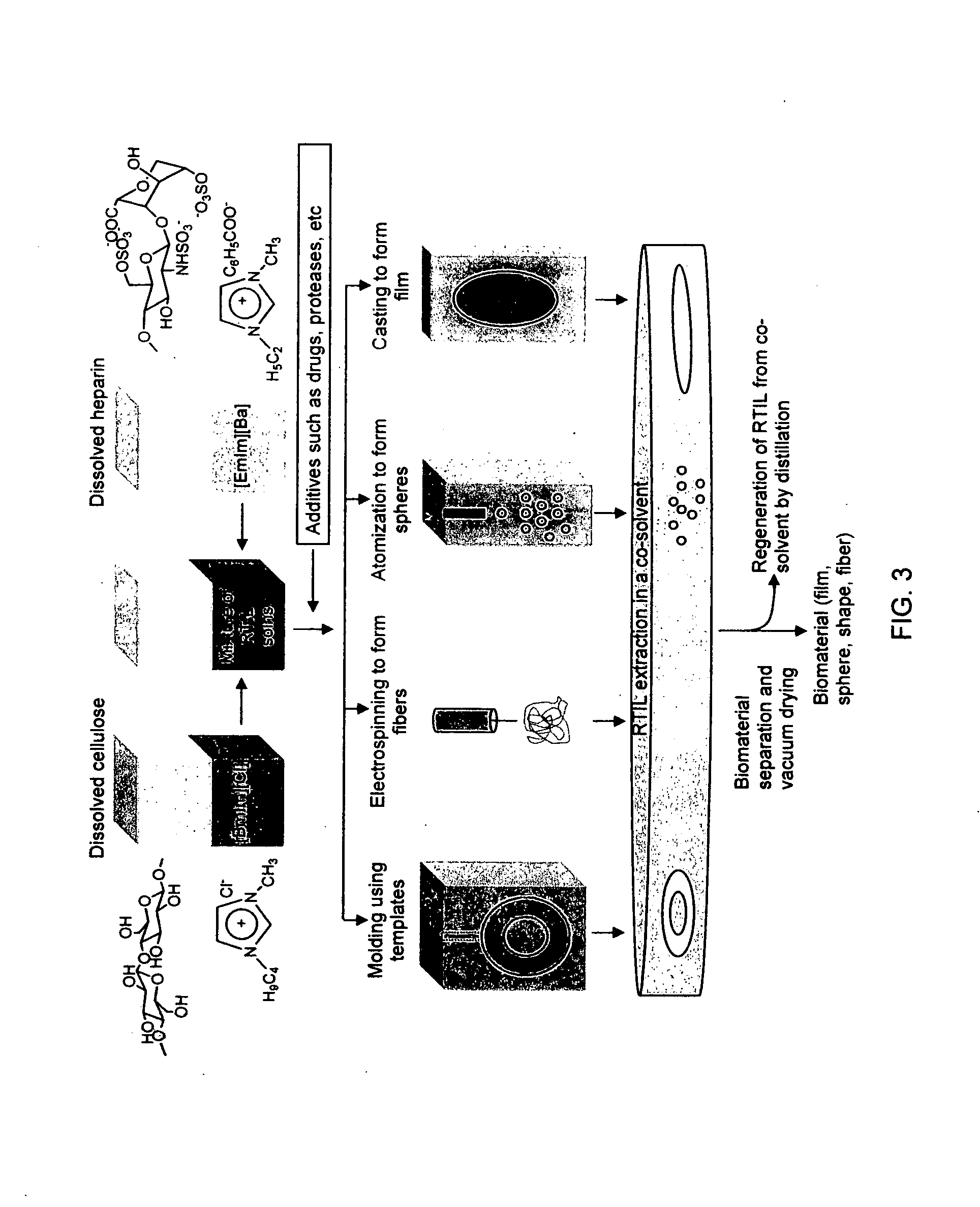
Blood compatible nanomaterials and methods of making and using the same
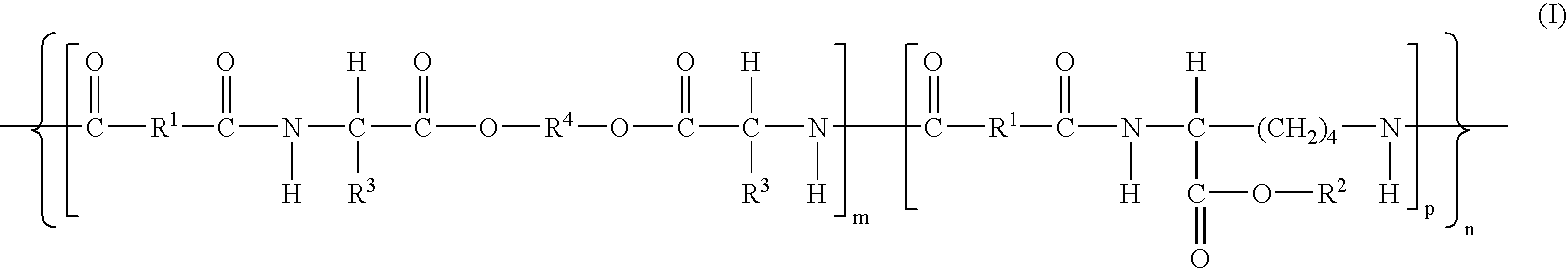
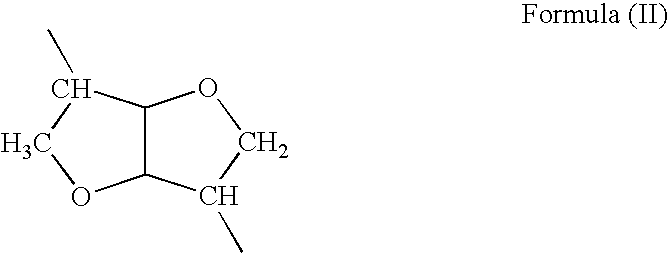
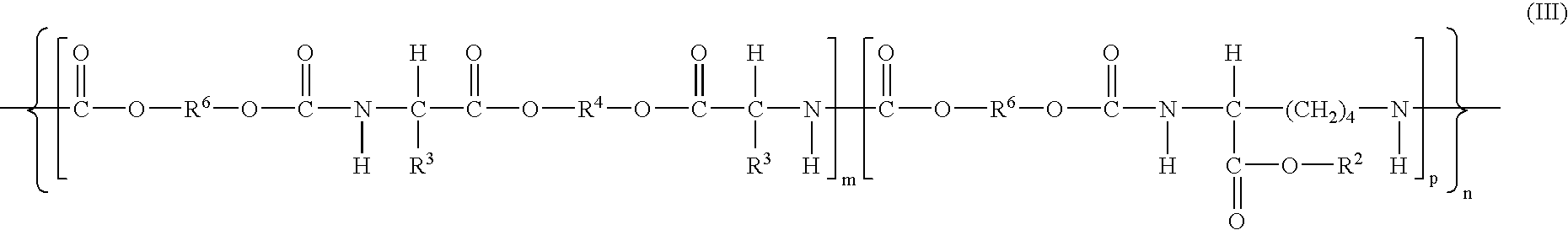
The invention provides blood compatible nanomaterials, biomaterials prepared therewith and blood compatible medical devices fabricated using the biomaterials of the invention. The invention further provides methods of making and using the nanomaterials, biomaterials and medical devices of the invention for the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of medical conditions. The invention further provides methods of using room temperature ionic liquids to make blood compatible nanomaterials.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
POSS (Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane) fluorosilicone acrylate-polyurethane blood compatible coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103468120AImprove hydrophobicityGood film formingPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyvinyl chlorideEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a POSS (Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane) fluorosilicone acrylate-polyurethane blood compatible coating and a preparation method thereof. The coating is formed on a medical polyvinyl chloride sheet by using a (methyl)acryloxy oligo-POSS fluorosilicone acrylate copolymer and one or two curing agents selected from hexamethylene diisocyanate and isophorone diisocyanate. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the POSS fluorosilicone acrylate copolymer into a mixed solution of dichloromethane or ethyl acetate and n-hexane; spraying the solution on the surface of medical polyvinyl chloride through a spray gun to form the coating with good blood compatibility. The POSS fluorosilicone acrylate-polyurethane blood compatible coating and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the preparation method is simple in process, easy to obtain raw materials and easy to realize industrial and large-scale production; the prepared blood compatible coating has good film forming property and hydrophobicity, favorable blood compatibility and relatively high practical values.
Owner:天津渤化讯创科技有限公司
Cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103382252ARegulating Molecular WeightStrong specificityBulk chemical productionPolyesterHemocompatible Materials
The invention discloses cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester and a preparation method thereof. The cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester is prepared through combination of ring opening polymerization and click chemical reaction. The preparation method comprises the following steps of adopting small-molecule alcohol containing acetylene alkynyl as an initiator to initiate ring opening polymerization of a cyclic ester monomer so as to prepare single-end alkynylation biodegradation aliphatic polyester; enabling the single-end alkynylation biodegradation aliphatic polyester and acid halide and sodium azide to perform reaction sequentially to prepare linear biodegradation aliphatic polyester containing the acetylene alkynyl and azide group; and finally, preparing the cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester through the click chemical reaction. The ring size of the cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester is controllable, reaction conditions are moderate, and reaction products are pure. In addition, the cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester has a topological structure and performance which are different from a structure and the performance of corresponding linear biodegradation aliphatic polyester and can be well applied in the aspects of sustained or controlled release of drug carriers, scaffolds for tissue engineering, blood compatible materials and the like.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Latent reactive blood compatible agents
A reagent and related method for use in passivating a biomaterial surface, the reagent including a latent reactive group and a bifunctional aliphatic acid (e.g., fatty acid), in combination with a spacer group linking the latent reactive group to the aliphatic acid in a manner that preserves the desired function of each group. Once bound to the surface, via the latent reactive group, the reagent presents the aliphatic acid to the physiological environment, in vivo, in a manner (e.g., concentration and orientation) sufficient to hold and orient albumin.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Latent reactive blood compatible agents
InactiveUS7071235B2Organic active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationCombinatorial chemistryBlood compatible
A reagent and related method for use in passivating a biomaterial surface, the reagent including a latent reactive group and a bifunctional aliphatic acid (e.g., fatty acid), in combination with a spacer group linking the latent reactive group to the aliphatic acid in a manner that preserves the desired function of each group. Once bound to the surface, via the latent reactive group, the reagent presents the aliphatic acid to the physiological environment, in vivo, in a manner (e.g., concentration and orientation) sufficient to hold and orient albumin.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
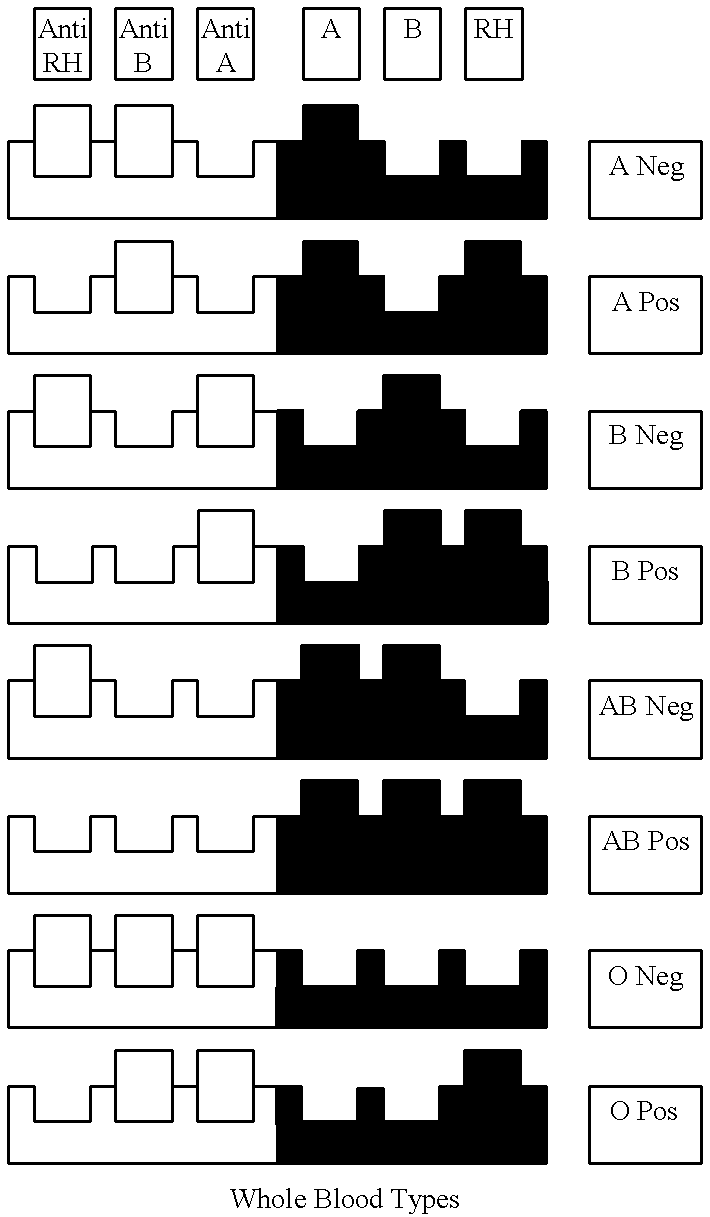
Blood type-specific safety labeling system for patients and blood products
A labeling system to ensure that blood products are compatible with a patient's blood type. A blood product housing, which is attached to a blood product, comprises a plurality of block-like projections and recesses corresponding to the antigens / antibody characteristics of a blood product. A patient housing, secured to the patient, comprises a plurality of mirror image three-dimensional block-like projections and recesses corresponding to the antigen / antibody characteristics of the patient's blood. If the blocks and recesses of the housings mate and seat to one another this confirms the blood product is compatible with the blood of the patient. If the blocks and recesses of the housings do not mate and seat to one another this confirms the blood product is not compatible with the blood of the patient.
Owner:KEENE DOUGLAS
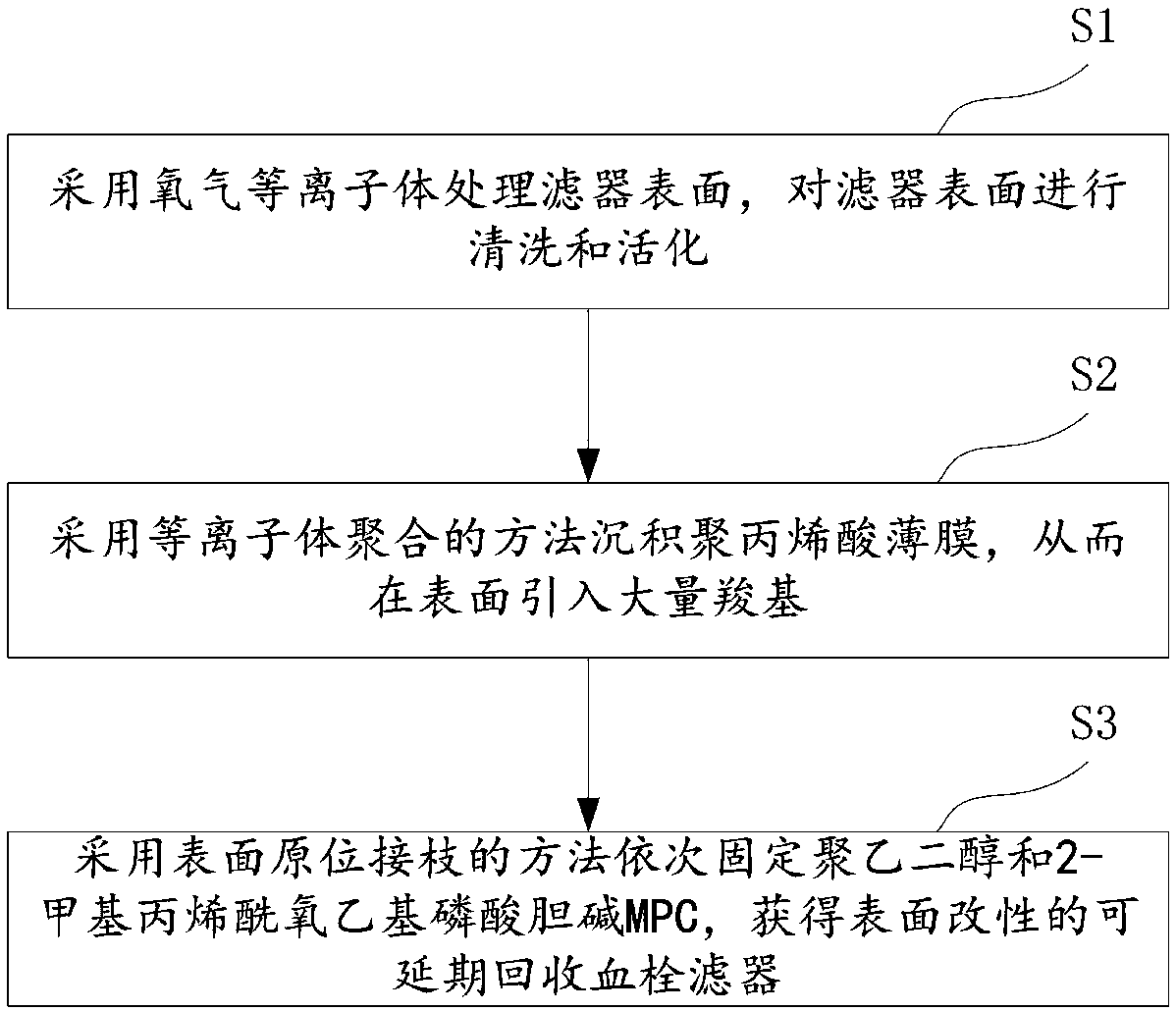
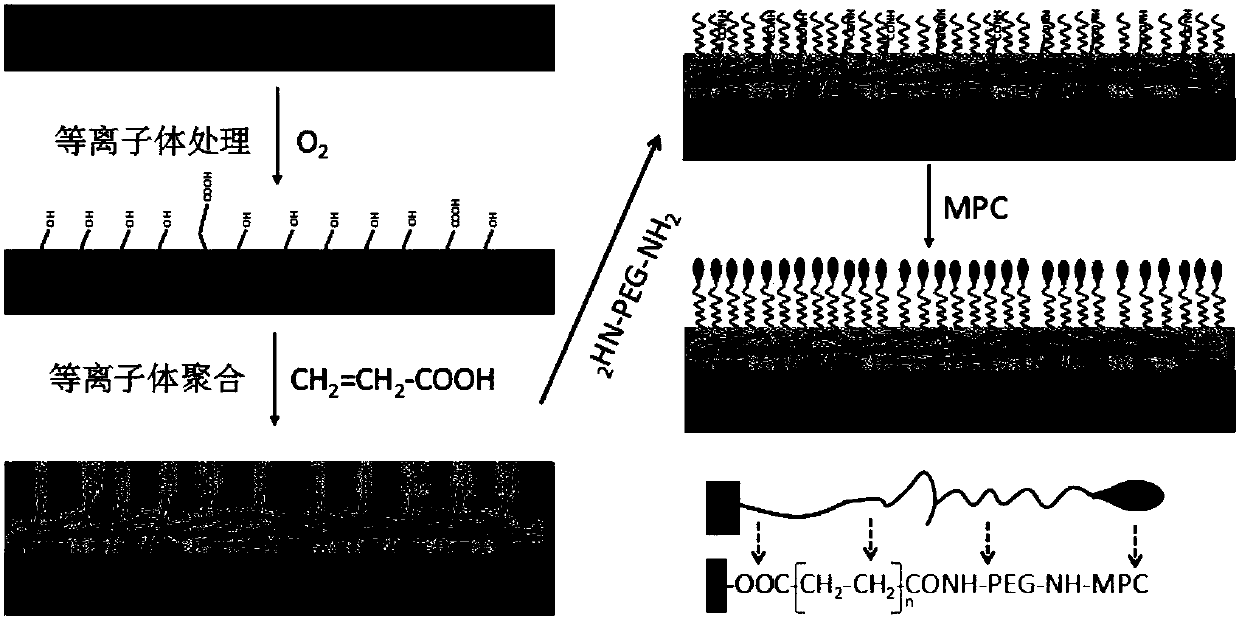
Thrombus filter capable of realizing delayed recovery and preparation method of thrombus filter
ActiveCN107823725AAdjustable thicknessInhibit growthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatings2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholinePhosphorylcholine
The invention discloses a thrombus filter capable of realizing delayed recovery and a preparation method of the thrombus filter and particularly discloses a blood compatible coating. The blood compatible coating comprises a polyacrylic acid layer and a polyethylene glycol layer, and 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine is covalently linked with the surface of the polyethylene glycol layer. Theinvention further discloses medical apparatus such as the thrombus filter coated with the blood compatible coating. According to the technical scheme, thrombogenesis and endothelial tissue growth canbe better inhibited. The whole surface coating is adjustable in thickness and surface grafting amount and can well bear stress and strain actions in apparatus assembly and release processes, molecules are firmly combined without falling off, and mechanical properties of the apparatus are not affected.
Owner:SHANGHAI JUNLIAN MEDICAL EQUIP
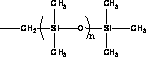
Polysiloxane-polyarylester block copolymer, preparation thereof and applications thereof
ActiveCN103524749ALower surface energyImprove hydrophobicityPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingHemocompatible MaterialsPolymer science
The invention discloses a polysiloxane-polyarylester block copolymer, preparation thereof and applications thereof. The polysiloxane-polyarylester block copolymer is showed in the following formula. The polysiloxane-polyarylester block copolymer has low surface energy, strong hydrophobicity and an obvious microphase separation structure, and has great application value in the field of blood compatible materials. According to a preparation process of the block copolymer, a fluorine-containing / fluorine-free polyarylester having terminal alkenes, and a fluorine-containing / fluorine-free polysiloxanes having terminal hydrogens are used as raw materials, one or over two types of tetrahydrofuran, isopropanol, tolune and benzotrifluoride are used as solvent; and the block polymer is synthesized by hydrosilylation under the catalytic action of a catalyst 1,3-divinyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane platinum (0) or chloroplatinic acid. The synthetic method is simple with mild and controllable reaction conditions, and is prone to industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Hemoglobin microcapsule blood substitute and its preparation method
ActiveCN102871985AAdjustable sizeChange the size arbitrarilyRespiratorsPeptide/protein ingredientsNon toxicityStructure and function
The invention discloses a hemoglobin microcapsule and its preparation method. The hemoglobin microcapsule is a biocompatible and blood-compatible hemoglobin microcapsule blood substitute prepared through Schiff base bond layer-by-layer assembling, the capsule wall components used by the hemoglobin microcapsule comprise a biocompatible and biodegradable polysaccharide derivative and hemoglobin, Schiff base bonds are formed between the components of the capsule wall, and a toxic crosslinking agent is not used in the invention. The hemoglobin microcapsule blood substitute obtained in the invention has the advantages of good stability, biological compatibility, blood compatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, no use of the crosslinking agent, and adjustable dimension, structure and functions.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
POSS (Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane) fluorine-silicon acrylate block copolymer as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103467679AIncrease roughnessHigh hardnessCoatingsHemocompatible MaterialsFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a POSS (Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane) fluorine-silicon acrylate block copolymer as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The copolymer is composed of a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) block and an FAC (Fluorinated Acrylate) block and has a structural formula shown in the specification. According to the preparation method, free-radical polymerization is carried out on acrylate monomers, hydroxyl-containing acrylic functional monomers, fluorinated functional acrylic monomers and (methyl) propylene acyloxy oligomeric silsesquioxane by utilizing a polydimethyl siloxane macromolecular initiator to obtain the POSS fluorine-silicon acrylate block copolymer. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the raw materials are easily available and the experimental conditions are gentle; the surface of the block copolymer has a micro-phase separating structure, so that the block copolymer has the characteristics of low surface energy, strong base material adhesive force and the like after being formed into a film, has certain crudeness and hardness, and is applied to a blood compatible material.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Blood compatibility testing method and device
InactiveUS20050148033A1Microbiological testing/measurementMedical devicesWhole blood productHemocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a method and device for testing a blood product and a patient's blood immediately prior to transfusing the blood product to the patient. The device comprises a testing chamber within which the blood product and the patient blood are drawn and tested for compatibility. A first end of the testing chamber is coupled with an infusion needle in communication with the patient. A second end of the testing chamber is in fluid communication with the container housing the blood product. In an embodiment, blood product and patient blood are drawn into the testing chamber. One of a number of tests for determining blood compatibility is performed in the testing chamber. If the blood product and patient blood are compatible, blood product is delivered to the patient through a transfusion line bypassing the testing chamber.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Preparation method of blood-compatible polypropylene non-woven fabric
ActiveCN109252364AGood mechanical propertiesImprove machinabilityPhysical treatmentFibre typesPolymer scienceAnti platelet
The invention discloses a preparation method of a blood-compatible polypropylene non-woven fabric, the preparation method comprises the following operation steps: (1) dimethylamine and glycidyl etherare subjected to addition reaction, and then the mixture is purified to obtain a component A; (2) N-[2] [bis (carboxymethyl)) amino ] ethyl ]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)) glycinate trisodium is subjected to self-polymerization reaction to obtain a component B; (3) a polypropylene non-woven fabric is cleaned, then is modified liquid by a modification liquid; and (4) the component A and the component B are loaded on the surface of the modified polypropylene non-woven fabric so as to obtain the blood-compatible polypropylene non-woven fabric. The blood-compatible polypropylene non-woven fabric prepared bythe method disclosed by the invention is excellent in mechanical property and high in machinability, the prepared blood-compatible polypropylene non-woven fabric is non-toxic, environment-friendly, high in biochemical stability and long in service life, especially is strong in surface polarity, high in surface energy and remarkable in hydrophilicity, and has extremely excellent anti-protein adsorption capacity and anti-platelet adhesion capability.
Owner:福建金成纤维制品有限公司
Blood type-specific safety labeling system for patients and blood products
A labeling system to ensure that blood products are compatible with a patient's blood type. A blood product housing, which is attached to a blood product, comprises a plurality of block-like projections and recesses corresponding to the antigens / antibody characteristics of a blood product. A patient housing, secured to the patient, comprises a plurality of mirror image three-dimensional block-like projections and recesses corresponding to the antigen / antibody characteristics of the patient's blood. If the blocks and recesses of the housings mate and seat to one another this confirms the blood product is compatible with the blood of the patient. If the blocks and recesses of the housings do not mate and seat to one another this confirms the blood product is not compatible with the blood of the patient.
Owner:KEENE DOUGLAS
Blood compatible surfaces
InactiveUS20150093543A1Limit intrinsic coagulation activityIncrease the curvatureDiagnosticsSurgeryRough surfaceBlood compatible
The disclosure features blood compatible articles and methods of making the articles. The methods include providing a substrate and forming a rough surface on the substrate. The rough surface includes a plurality of three-dimensionally curved features each having a radius of curvature of less than about 50 nm. The surface includes a sufficient concentration of features per unit area to limit blood coagulation activity on the substrate and to limit the number of platelets that adhere to the surface when the substrate is exposed to blood.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD +1
Medical device comprising covalently bonded heparin coating
Disclosed herein is a medical device, comprising a covalently-bonded heparin coating on a substrate, where the covalently bonded heparin coating is the reaction product of (a) an isocyanate-bearing material on or covalently bonded to the substrate and (b) a heparin molecule selected from one of the formulae in the claims. The current invention also relates to a method of forming the medical device, which may be useful as heart stent or intravascular stent that is hemocompatible for preventing the formation of blood clots.
Owner:JMEDTECH XIAMEN COATING TECH CO LTD +1
Biomolecule-functionalised PVC and production method thereof
ActiveUS20200062872A1Improve hydrophilicityIncrease flexibilityCatheterAntithrombogenic treatmentPolymer scienceBio molecules
The present invention relates to the medical industry. In particular, it is related to a polyvinyl chloride polymer (PVC) functionalized for medical use, which is flexible and compatible with blood. Specifically, this invention is related to a biomolecule-functionalized PVC and its production method, in order to produce a flexible and blood-compatible polymer for medical use.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
A kind of blood compatible polymer layer and preparation method thereof
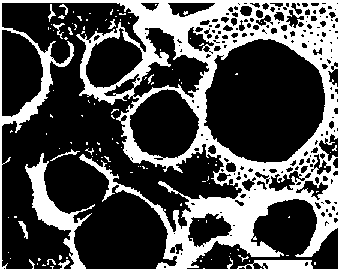
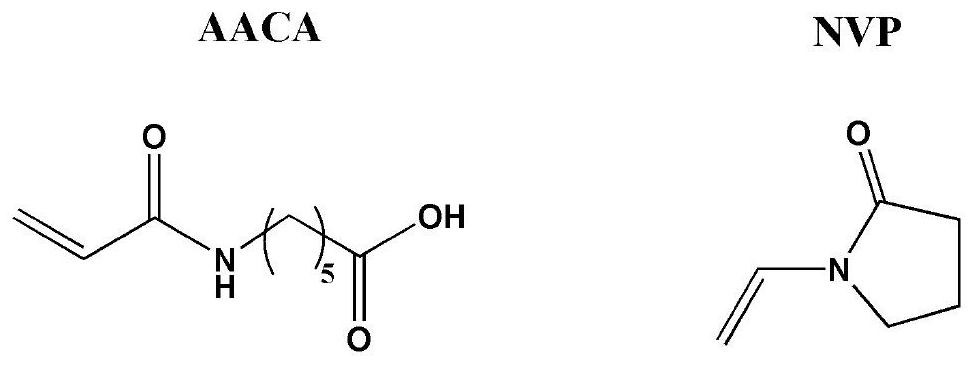
ActiveCN112592441BExperimental conditions are easy to controlNo pollution in the processSurgeryCoatingsUltraviolet lightsAnti platelet
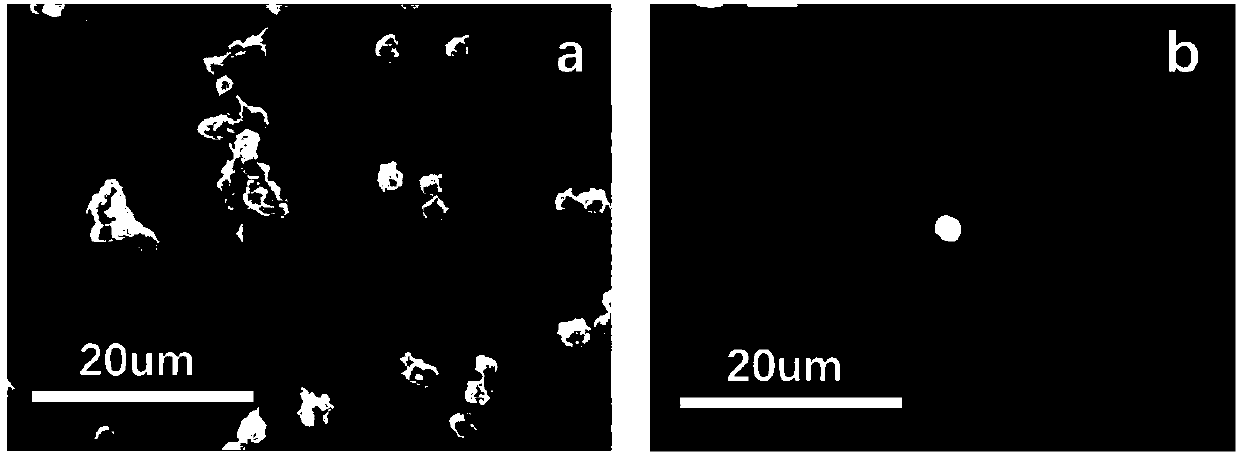
The invention relates to a blood-compatible polymer layer and a preparation method thereof. Under the condition of ultraviolet light irradiation, a copolymerization reaction of 6-acrylamidocaproic acid and N-vinylpyrrolidone is initiated on the surface of a silanized substrate to obtain the preparation method. The blood-compatible polymer layer; the water contact angle of the prepared blood-compatible polymer layer is 40 to 45°; after the blood-compatible polymer layer is grafted on the surface of the silanized substrate, the BSA and Fib proteins are adsorbed The amount was reduced by 75-80% and 60-68% respectively. Using laser confocal microscope test, no obvious adhesion phenomenon was observed on the red blood cell adhesion test picture and the platelet adhesion test picture. The invention utilizes ultraviolet light to initiate the copolymerization of AACA and NVP monomers, and introduces a blood-compatible polymer layer with hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance ability on the surface of the substrate, the operation is simple, the reaction process is controllable, clean and pollution-free, and large-scale production is possible; The blood-compatible polymer layer has excellent anti-protein adsorption properties, anti-erythrocyte adhesion properties and anti-platelet adhesion properties.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Device for removal of noxious agents from blood, extracorporeal perfusion system comprising such device and method for producing such device
PendingCN110180046ACombine won'tGood blood compatibilityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibreFiber
The invention relates to a device (4) in an extracorporeal perfusion system (2), the invention relates to a device for removing, in particular negatively charged harmful substances (38), the method comprises the following steps: removing blood (44) containing plasma (46) and a cell component (48); the filter comprises a shell (12) and a plurality of hollow fibers (14) arranged in the shell (12), the hollow fibers are configured to allow blood (44) to flow through. Wherein the hollow fibers (14) each have a plurality of pores (34), the hole is arranged to be a hole, wherein the hollow fibers (14) are arranged in such a way that plasma (46) of blood (44) can flow through the holes (34) from the inside of the hollow fibers (14) to the outside of the hollow fibers (14), at the same time, the hollow fibres (14) are subjected to, in particular chemical, modification or pre-treatment, such that they have a functional surface (36) that can bind to and remove the harmful substances (38) from the blood (44). The inner side surface (40) of the hollow fiber (14) is also provided with, in particular, a blood-compatible, anticoagulant, coating (50), which is designed to prevent damage to the cellular components (48) of the blood (44) when the blood (44) flows through the hollow fiber (14). The invention also relates to an extracorporeal perfusion system (2) comprising said device (4) and toa method for producing said device (4).
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
Biomolecule-functionalised PVC and production method thereof
ActiveUS10882930B2Increase flexibilityReducing and avoiding useCatheterAntithrombogenic treatmentPolymer scienceBio molecules
The present invention relates to the medical industry. In particular, it is related to a polyvinyl chloride polymer (PVC) functionalized for medical use, which is flexible and compatible with blood. Specifically, this invention is related to a biomolecule-functionalized PVC and its production method, in order to produce a flexible and blood-compatible polymer for medical use.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
Method for constructing blood-compatible coating with degradable polyester
The invention discloses a method for constructing a blood-compatible coating with degradable polyester. The method comprises the following steps of: coating a solution of polybutylenes succinate (PBS-PC) of which the terminal is provided with a phosphorylcholine group onto the surfaces of glass, metal and a high-polymer material to form a coating; and heating in water and performing thermal treatment in vacuum to obtain coatings of different shapes, structures and properties on the surface of a polymer. A simple and practicable method is provided for preparing a blood-compatible coating. The coating with high blood compatibility has research values and wide application prospects in the fields of medicament controlled release, in-vivo short-term implants, medical packing materials such as intravascular stents and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Blood compatible polymer layer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112592441AExperimental conditions are easy to controlNo pollution in the processSurgeryCoatingsUltraviolet lightsPyrrolidinones
The invention relates to a blood compatible polymer layer and a preparation method thereof. Under the condition of ultraviolet irradiation, 6-acrylamide aminocaproic acid and N-vinyl pyrrolidone are initiated to be subjected to a copolymerization reaction on the surface of a silanized substrate, and the blood compatible polymer layer is prepared; and the water contact angle of the prepared blood compatible polymer layer is 40-45 degrees. After the surface of the silanized substrate is grafted with the blood compatible polymer layer, the BSA and Fib protein adsorption amounts are respectively reduced by 75-80% and 60-68%, and no obvious adhesion phenomenon is observed on an erythrocyte adhesion test picture and a platelet adhesion test picture by adopting a laser confocal microscopy test. According to the invention, ultraviolet light is utilized to initiate copolymerization of AACA and NVP monomers, the blood compatible polymer layer with hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance capability is introduced to the surface of the substrate, the operation is simple, the reaction process is controllable, the method is clean and pollution-free, and large-scale production can be realized; and the prepared blood compatible polymer layer has excellent protein adsorption resistance, erythrocyte adhesion resistance and platelet adhesion resistance.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Oriented polymer/liquid-crystal composite membrane blood compatibility biological material and production thereof
InactiveCN100349626CLow viscosityImprove liquiditySurgeryPharmaceutical containersPolyvinyl chlorideSolvent
A blood compatible oriented polymer-liquid crystal film is prepared from the polymer (medical polyether-type polyurethane and medical polyvinyl chloride) and the liquid crystal compound (cholesterin-type liquid crystal) through dissolving them is solvent, pouring the solution in a lower copper plate frame connected to an electric pole, putting another copper plate connected another electric pole on it, applying a voltage to generate an electric field for volatalizing the solvent to obtain a film, and vacuum drying. Its advantages are anticoagulation performance able to meet the requirement of human organs, and high biologic compatibility to human body.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Medical device comprising covalently bonded heparin coating
Disclosed herein is a medical device, comprising a covalently-bonded heparin coating on a substrate, where the covalently bonded heparin coating is the reaction product of (a) an isocyanate-bearing material on or covalently bonded to the substrate and (b) a heparin molecule selected from one of the formulae in the claims. The current invention also relates to a method of forming the medical device, which may be useful as heart stent or intravascular stent that is hemocompatible for preventing the formation of blood clots.
Owner:JMEDTECH COATING TECH PTE LTD
Chitosan-polylactic acid graft copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101628947BEasy to separateGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Double-layer hollow membrane for bio-reactor applications
InactiveUS7485249B2Easy to manufactureImprove compatibilitySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPolymer scienceBlood compatible
In a method of manufacturing a double-layer membrane of different polymers or polymer mixtures with opposite blood-compatible and tissue-compatible surfaces, a first polymer solution of a blood-compatible polymer and a second solution of a tissue-compatible polymer are extruded concurrently in layered form through a nozzle into a coagulation bath so as to form a double layer membrane.
Owner:GKSS FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM GEESTHACHT GMBH
Preparation method of polyimide novel material with anticoagulant function
InactiveCN109232898AHas anticoagulant functionImprove solubilityPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingHemocompatible MaterialsSolubility
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polyimide novel material with an anticoagulant function. The method first adopts 4,4-(4,4-Isopropylidenediphenoxy)bis(phthalic anhydride) to react with polyether amine and then adopts 3,3-iminobis(N,N-dimethylpropylamine) for blocking ends, thereby preparing powder containing cerium polyimide resin; then polyethylene glycol and a sulfonic lactone compound are used for preparing sulfonated polyethylene glycol, which is then grafted to the molecule of polyimide resin for preparing the polyimide novel material with the anticoagulant function. Thematerial has excellent solubility and good thermal stability, effectively improves the blood compatibility, greatly prolongs the coagulation time in vitro and the recalcification coagulation time anddoes not have any hemolytic action, thereby being a promising blood compatible material.
Owner:张玲
Cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103382252BRegulating Molecular WeightStrong specificityBulk chemical productionPolyesterHemocompatible Materials
The invention discloses cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester and a preparation method thereof. The cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester is prepared through combination of ring opening polymerization and click chemical reaction. The preparation method comprises the following steps of adopting small-molecule alcohol containing acetylene alkynyl as an initiator to initiate ring opening polymerization of a cyclic ester monomer so as to prepare single-end alkynylation biodegradation aliphatic polyester; enabling the single-end alkynylation biodegradation aliphatic polyester and acid halide and sodium azide to perform reaction sequentially to prepare linear biodegradation aliphatic polyester containing the acetylene alkynyl and azide group; and finally, preparing the cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester through the click chemical reaction. The ring size of the cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester is controllable, reaction conditions are moderate, and reaction products are pure. In addition, the cyclic biodegradation aliphatic polyester has a topological structure and performance which are different from a structure and the performance of corresponding linear biodegradation aliphatic polyester and can be well applied in the aspects of sustained or controlled release of drug carriers, scaffolds for tissue engineering, blood compatible materials and the like.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Coating
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com