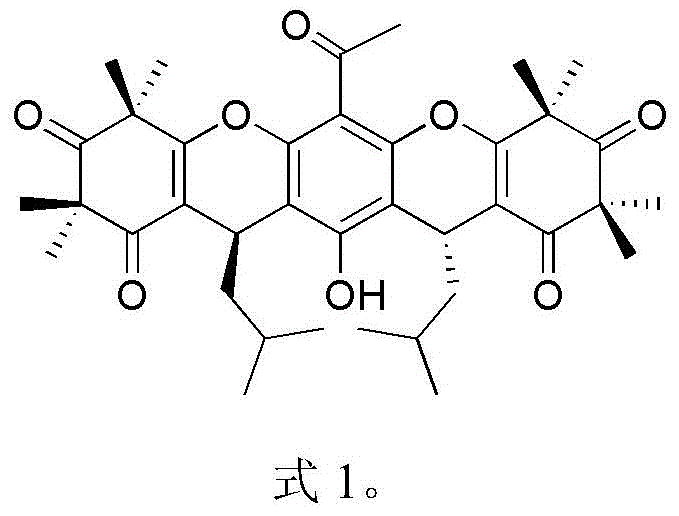
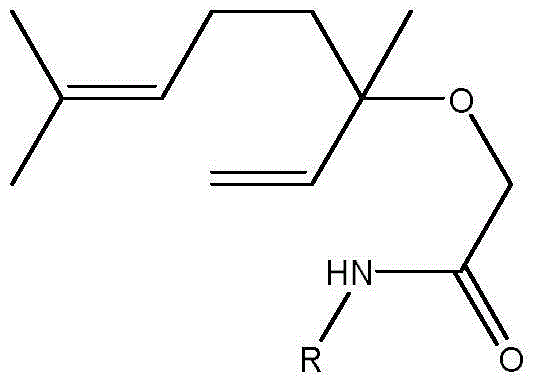
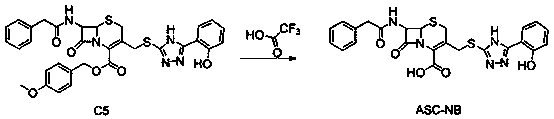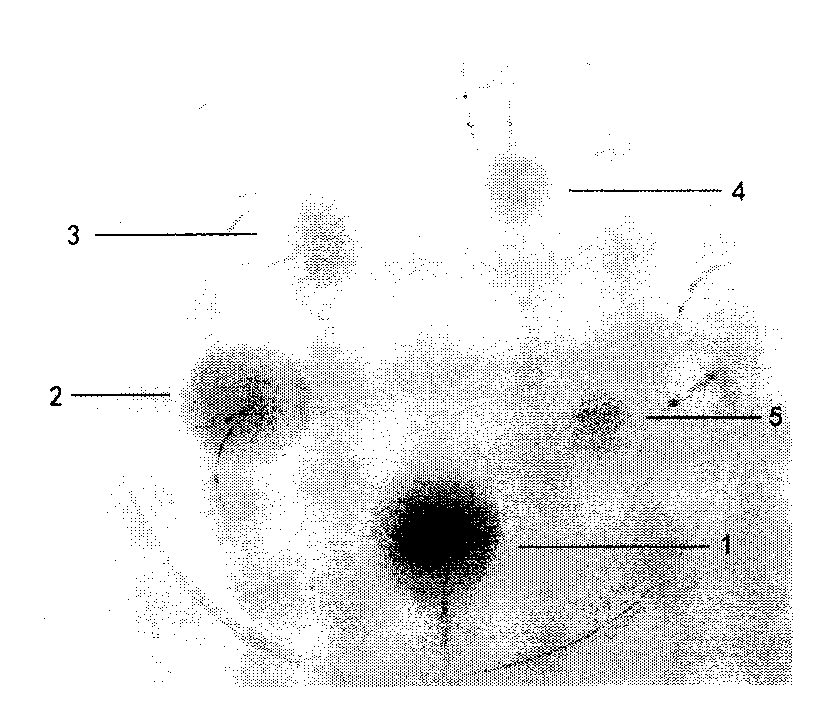Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Antileishmanial agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
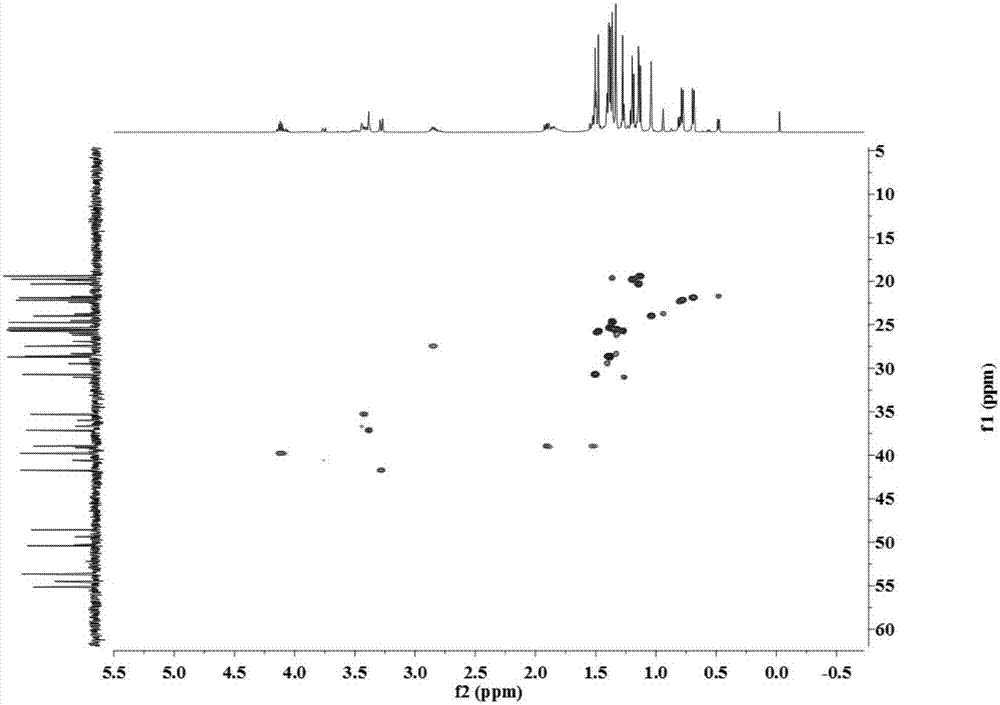
In order to develop potential antileishmanial agents, glycosyl and galactosyl dihydropyridine analogs have been synthesized (86,87) and accessed for their antileishmanial activity in terms of inhibiting effects offered by the compounds on the pteridine reductase enzyme of parasite, which has been reckoned as relevant target.
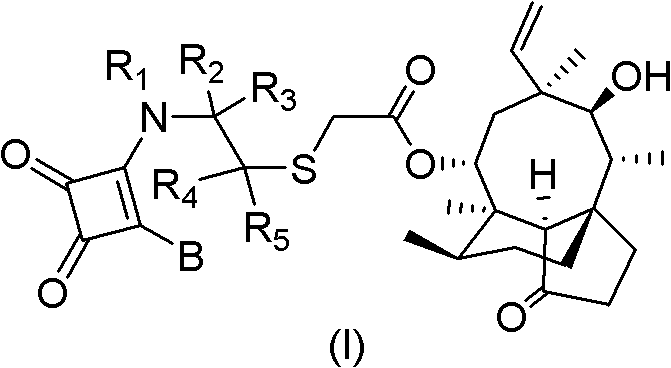
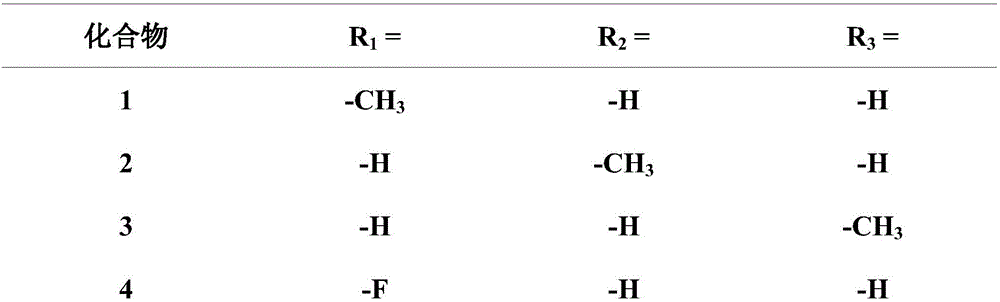
Mulin acetate containing substituted squaric acid and application thereof
The invention relates to Mulin acetate containing substituted squaric acid and an application thereof which belong to the technical field of medicines, specifically to substituted squaric acid containing Mulin acetate as shown in a general formula (I), pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a hydrate and an isomer thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and B are defined in the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of these compounds, a pharmaceutical composition containing these compounds and an application of these compounds in the preparation of drugs for treating or preventing bacteria and virus. As for staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus equin MIC value, the compounds have an antibacterial effect 15-20 times higher than a control commercially-available antibiotic tiamulin in the test. And the compounds provided by the invention are effective antimicrobial agents. And the compounds provided by the invention are effective antimicrobial agents.
Owner:BEIJING ABLEPHARMTECH CO LTD
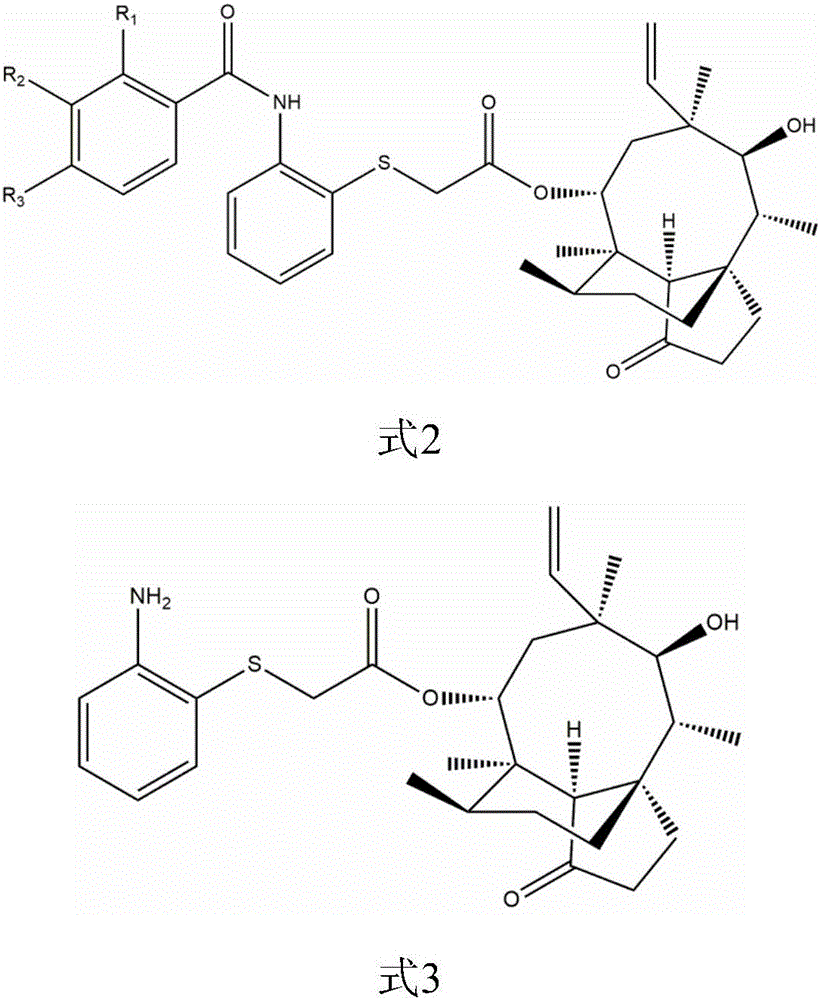
Pleuromutilin derivative with 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain and preparing method and application of pleuromutilin derivative
InactiveCN106565564AGood in vitro antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsSulfonic acid esters preparationSide chainStaphylococcus aureus
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry and discloses a pleuromutilin derivative with a 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain and a preparing method and application of the pleuromutilin derivative. The compound has the structures shown in formula 2 and formula 3, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are respectively and independently selected from the hydrogen atom, the hydroxyl, the amino, the sulfydryl, the hydroxymethyl, the amine methyl, the nitro, the halogen, the trihalogenated methyl, the methyl, the natural amino acid acylamino and the C1-6 alkoxy. The pleuromutilin derivative with the 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain has good activity for inhibiting the drug resistant staphylococcus aureus and the mycoplasma and is particularly suitable for serving as a novel antibacterial medicine for preventing infectious diseases caused by the human or animal mycoplasma or drug resistant staphylococcus aureus or multidrug resistant bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fenneropenaeus chinensiss anti-lipopolysaccharide factor as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN103724412AGrowth inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliPichia pastoris
The invention relates to genetic engineering and particularly to a fenneropenaeus chinensiss anti-lipopolysaccharide factor as well as preparation and an application thereof. A gene of the FcALF (fenneropenaeus chinensiss anti-lipopolysaccharide factor) is (a) protein represented by an amino acid sequence in SEQ ID NO.1 or (b) protein which is derived from (a) through substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence limited by (a) and has the anti-lipopolysaccharide factor activity. According to the factor, pichia pastoris is used as a eukaryon expression system, and recombinant expression is performed on the FcALF. In addition, the antibacterial activity of the FcALF is analyzed, so that guidance is provided for screening of antibacterial agents and immunopotentiators . Specifically, recombinant protein of the FcALF has obvious growth-inhibition and bactericidal effects on Gram-negative bacterium escherichia coli.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antibacterial drug for targeted therapy of staphylococcal infection by synergizing with antibiotic as well as synthesis method and application of antibacterial drug
InactiveCN108794508AIncrease vitalityExcellent synergistic antibacterial efficacyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibacterial agentTarget therapy
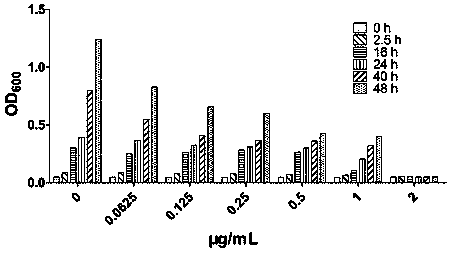
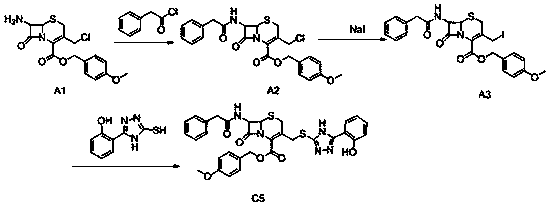
The invention designs and synthesizes a novel antibacterial drug ASC for staphylococcus aureus based on a beta-lactam ring of a parent nucleus structure of beta-lactam antibiotic molecules, wherein the ASC is an antibacterial reagent and is also a broad-spectrum inhibitor of beta-lactam antibiotic drug-resistant target protein metal beta-lactamase; the ASC can synergize with three kinds of 7 to 8antibiotics such as beta-lactams, aminoglycosides and tetracyclines to carry out targeted therapy on the staphylococcal infection. The vitality of the antibiotics is increased by 4 to 128 times by combining with 1 [mu]g / ml dosage of ASC.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Antibiotic Lobophorin E and F, preparation methods and applications thereof in preparing antibacterial and antitumor drugs
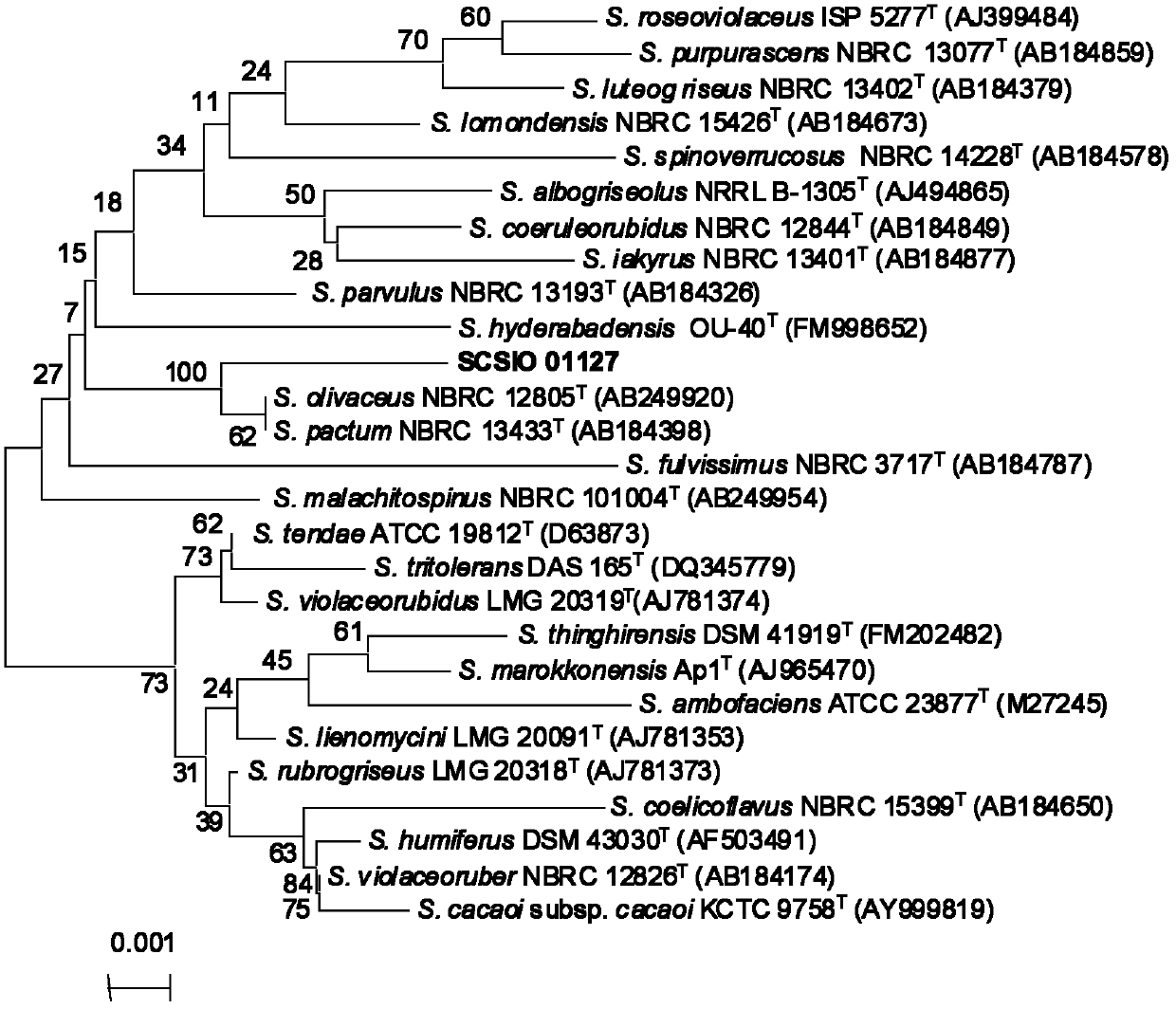
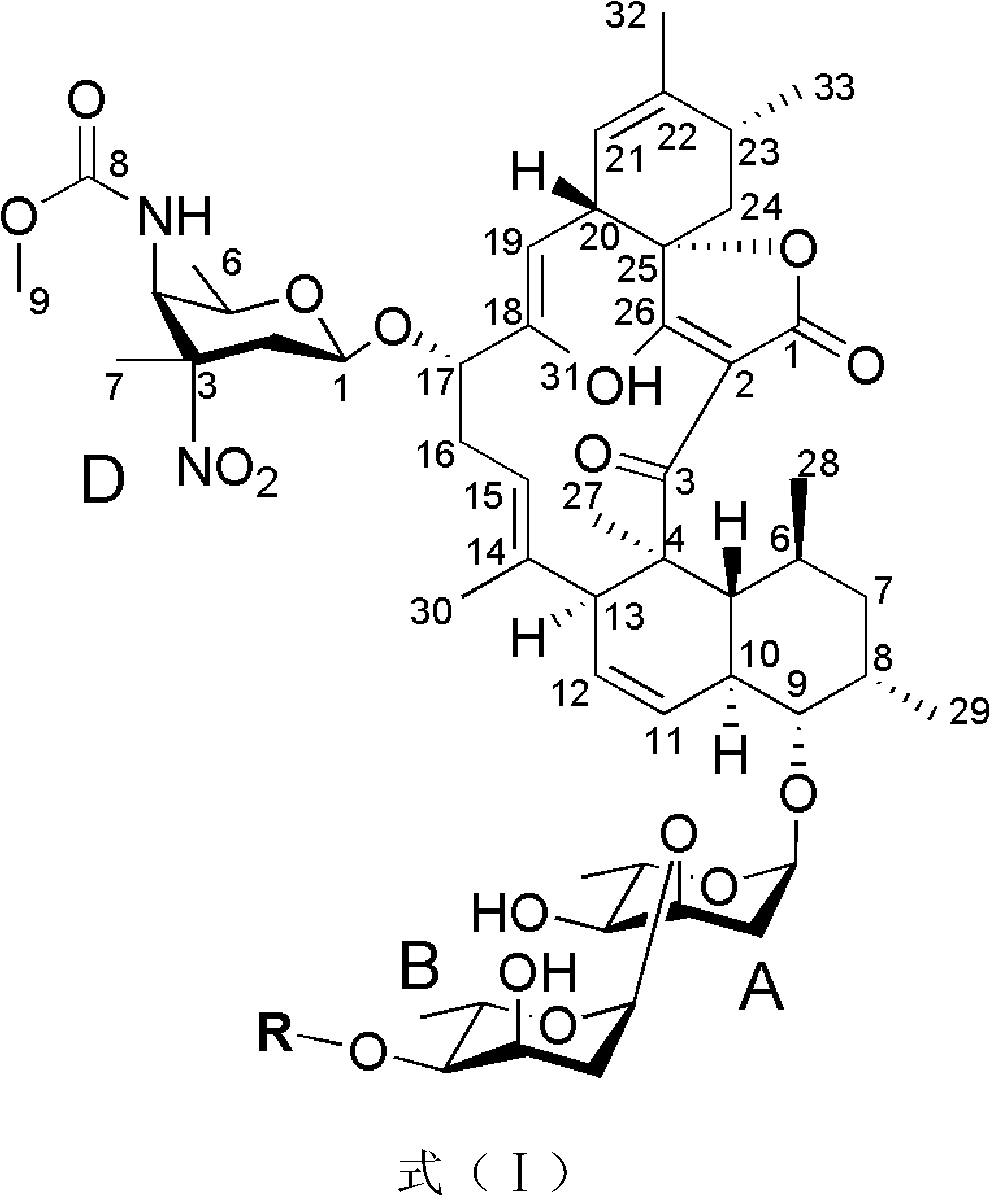
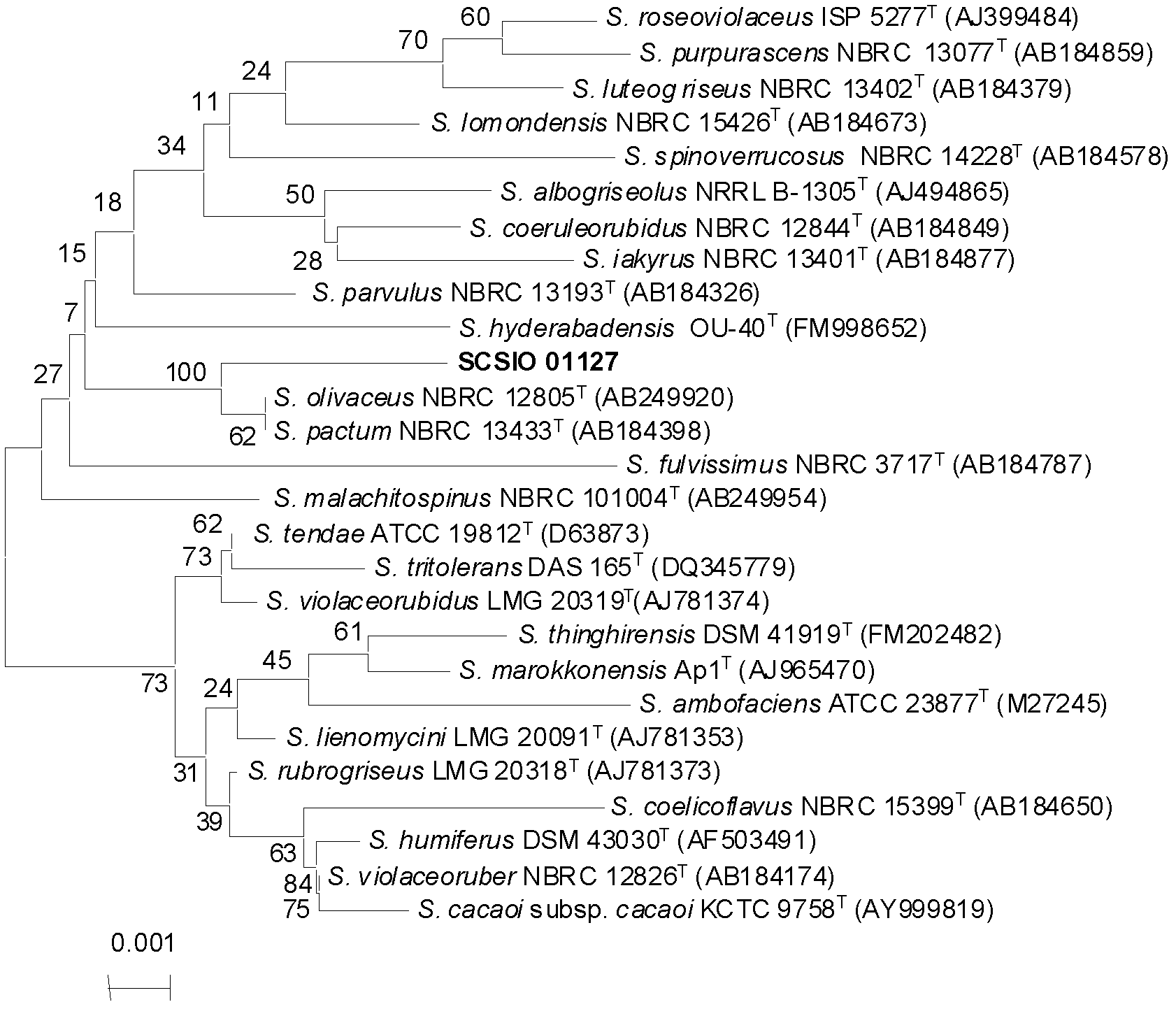
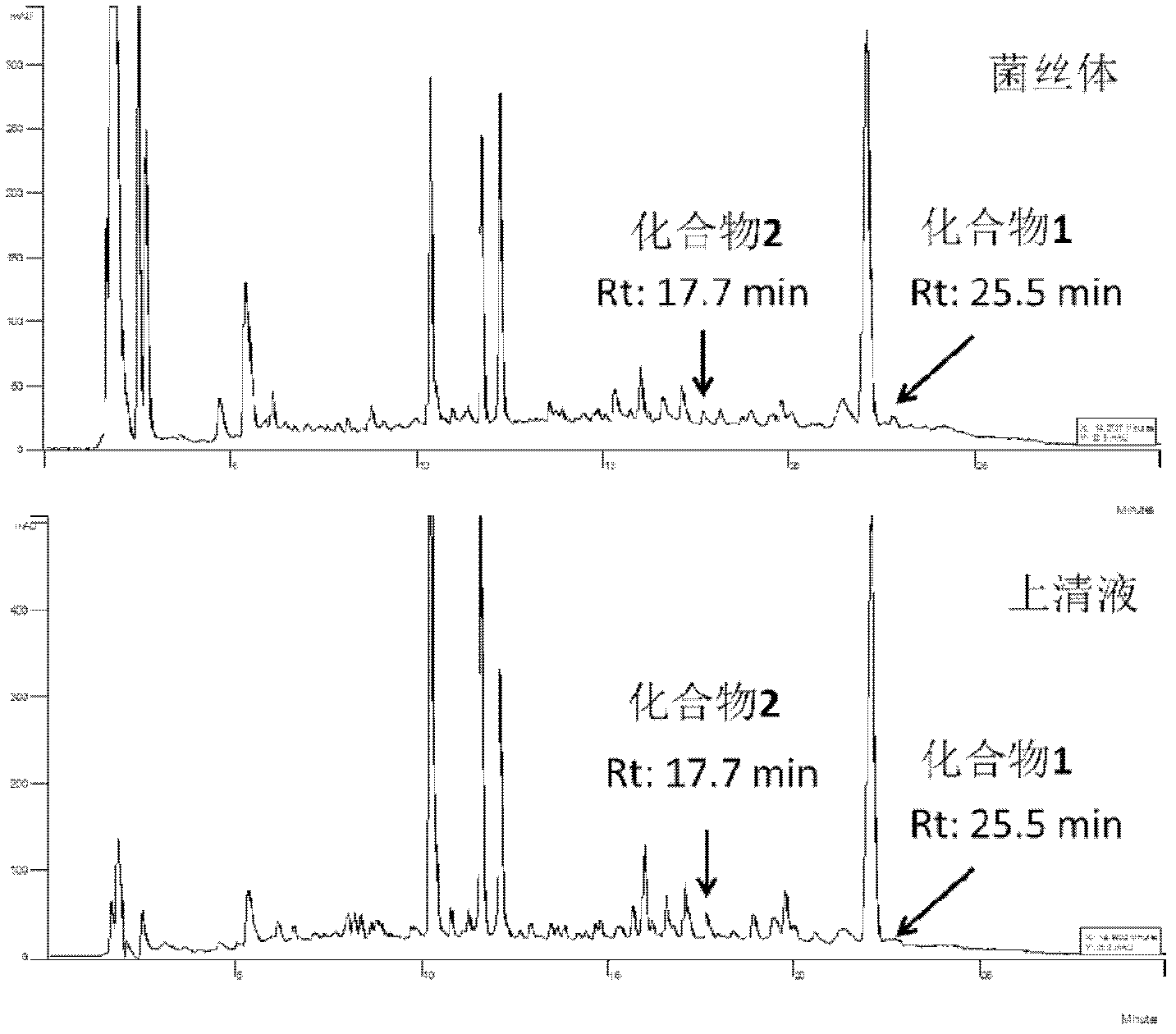
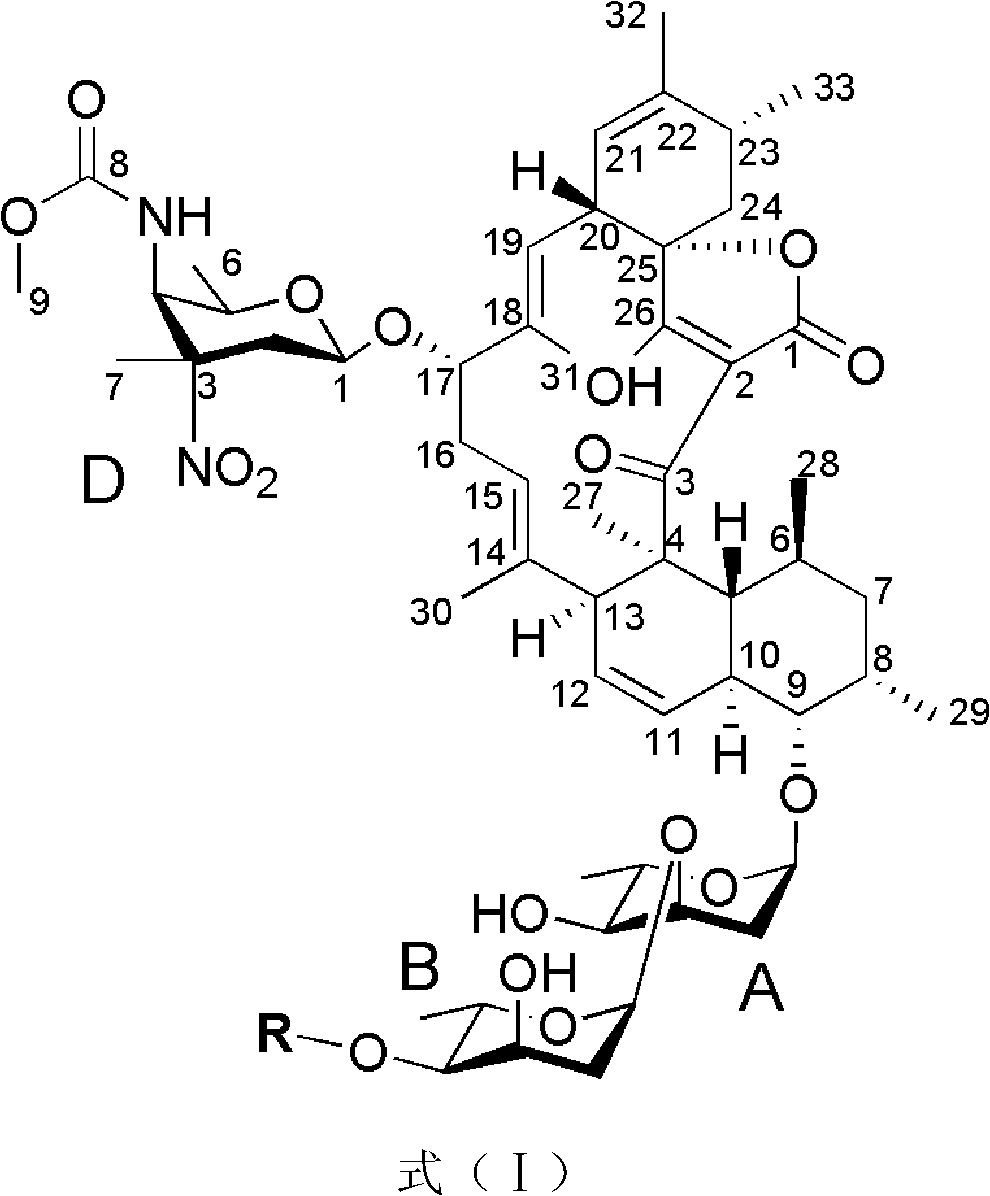
The invention discloses antibiotic Lobophorin E and F, preparation methods and applications thereof in preparing antibacterial and antitumor drugs. The Lobophorin E and F are obtained by separating from fermentation cultures of streptomyces SCSIO 1127; the Lobophorin E and F have antibacterial activities and can be used for preparing antibacterial drugs; the Lobophorin F has an antitumor activity and can be used for preparing antitumor drugs; and the structures of the antibiotic Lobophorin E and F are showed as a formula (I), wherein R is as the following for the lobophorin E, and R equals to H for the lobophorin F.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
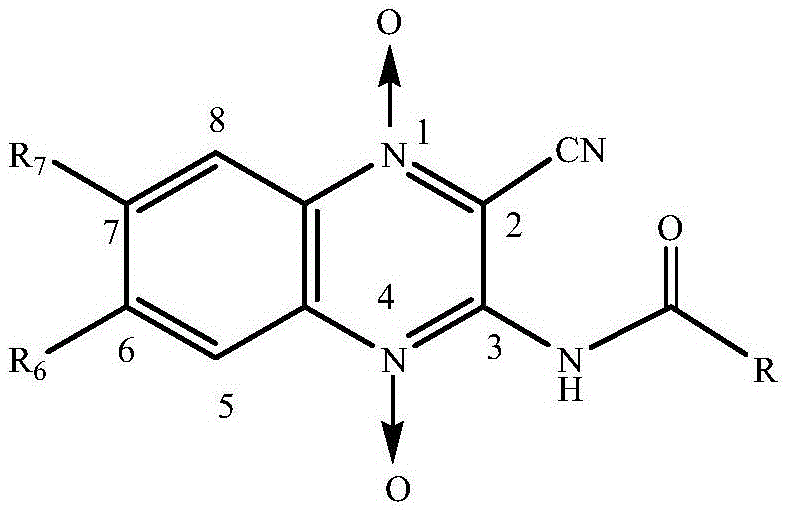
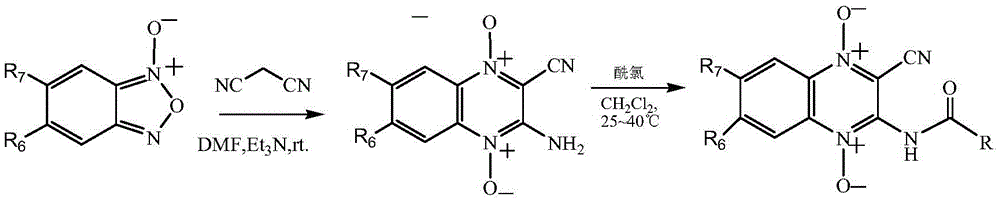
Quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivatives with antimicrobial activity
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical chemosynthesis, and particularly relates to quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivatives with antimicrobial activity. The invention also relates to preparation of the derivatives and antimicrobial activity testing of the derivatives. The new synthetic compounds are prepared by the following steps: carrying out Beirut reaction on the raw material N-benzofuroxan oxide and malononitrile under alkaline conditions to obtain 3-amino-2-cyano-quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide, and reacting with appropriate acyl chloride to obtain a series of 2-cyano-amidoquinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxides. The in-vitro antibacterial activity test result indicates that the quinoxaline-N1,N4-dioxide derivatives have favorable antibacterial activity for mycobacterium hominis and mycobacterium bovis and also have antibacterial activity for Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Pasteurella. The invention also discloses a structural formula of the compounds used as a target antibacterial drug.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
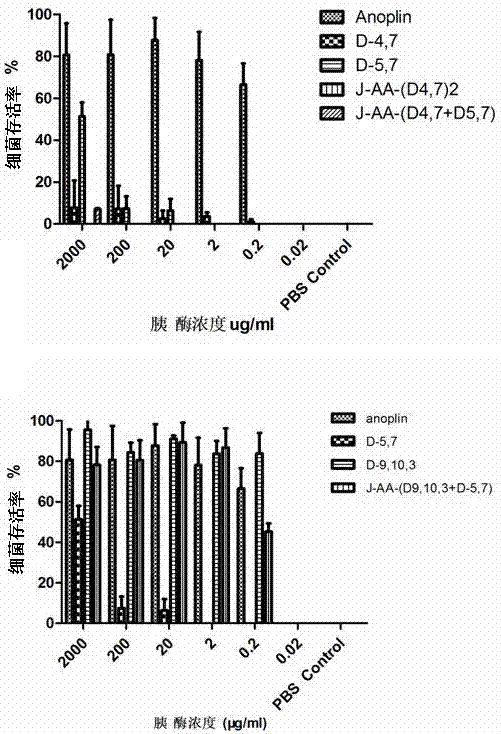
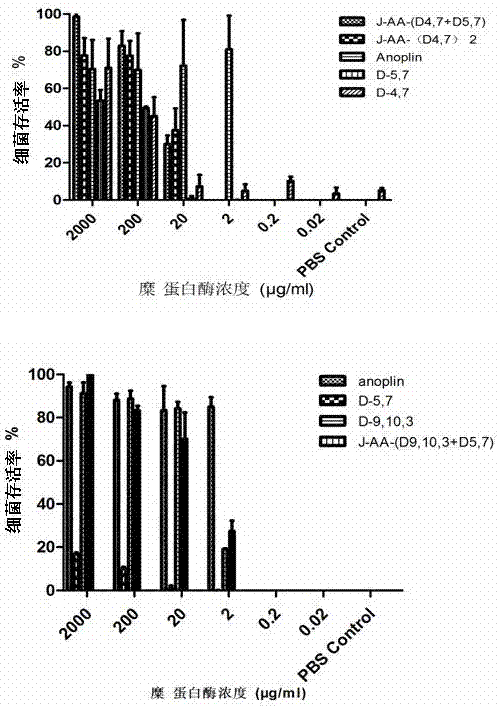
Antibacterial peptide dimer analogues containing D type amino acids as well as synthesis and application of dimer analogues
ActiveCN107129520ADose dependentAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMinimum inhibitory concentrationSide chain
The invention discloses antibacterial peptide dimer analogues containing D type amino acids. The dimer analogues are prepared by respectively performing N-terminal side chain polymerization on D type amino acid-containing precursor peptides of a naturally antibacterial peptide Anoplin. According to determination of the lowest minimum inhibitory concentration of common standard microorganisms, a biofilm formation test is inhibited. An enzymatic stability test shows that the antibacterial activities of the antibacterial peptide dimer analogues containing D type amino acids synthesized according to the invention are enhanced by 4-16 times compared with those of parent peptides, and the dimer analogues have strong abilities of inhibiting bacterial biofilm formation. In addition, the stabilities of the antibacterial peptide dimer analogues containing D type amino acids synthesized according to the invention are obviously improved. Compared with the parent peptide Anoplin, the tolerance to trypsin enzymolysis is improved by 104-105 times, and the tolerance to chymotrypsin is improved by 102 times. Therefore, the antibacterial peptide dimer analogues containing D type amino acids have excellent application prospects in preparation of long-lasting clinical antibacterial drugs.
Owner:倪京满
Gorgonian-originated fungus secondary metabolite derivatives and application of same as antiseptics
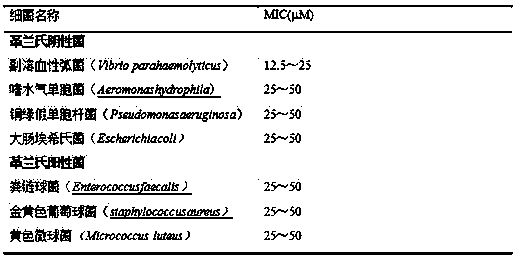
The invention specifically relates to gorgonian-originated fungus secondary metabolite derivatives and application of the same as antiseptics, belonging to the field of medicine. The derivatives provided by the invention exert strong inhibitory effect on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE) and certain inhibitory effect on Gram-negative bacteria; and the minimal inhibition concentrations MIC of the derivatives are all less than 12.5 mu M, which proves that the derivatives can be developed into potential antibacterial drugs.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
glmm gene knock-out bacterial strain as well as preparation method and application in sieving mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase inhibitors
InactiveCN101928691AIntegrity breachImprove efficacyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention discloses a glmM gene knock-out bacterial strain ML2009 (mycobacterium smegmatis), CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 3418, which is constructed by using phosphoglucomutase participating in the biosynthesis of key components in a mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall. The bacterial strain ML2009 can be used as a cell model for sieving phosphoglucomutase inhibitors with high flux, be used for sieving effective phosphoglucomutase inhibitors from a combined compound library, traditional Chinese medicine and natural products to prepare tuberculosis-resisting medicaments with high medicine effects; and in addition, in the cells of a human body, the synthesis approach of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-acetyl glucosamine is different from that of mycobacterium tuberculosis, no phosphoglucomutase exists in the UDP-acetyl glucosamine, therefore, the reaction catalyzed by the mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase does not exist in the cells of the human body so that the tuberculosis-resisting medicaments developed by using the phosphoglucomutase as a target enzyme are harmless to the human body, and the defect that the traditional antibacterial medicament also kill normal cells is overcome.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Phloroglucinol derivatives and application of same in preparation of antibacterial drugs
ActiveCN107417697ANovel structureNovel skeleton structureAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsVancomycin intermediateAntibacterial agent
The invention discloses phloroglucinol derivatives and an application of same in preparation of antibacterial drugs. The phloroglucinol derivatives are (+ / -) Myrtucyclitone C and (+ / -) Myrtucyclitone D, wherein the structures are represented as the formula (I). The (+ / -) Myrtucyclitone C and the (+ / -) Myrtucyclitone D are cyclopolyketone-phloroglucinol-cyclopolyketone trimers, which are composed of 38 carbon atoms, wherein one cyclopolyketone fragment is subjected to rearrangement. The phloroglucinol derivatives are chemical entities having novel framework structures. The compounds show significant antibacterial activity to staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin intermediate-resistant staphylococcus aureus even in low concentration and meanwhile have very low toxicity to eukaryotic cells.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Litopenaeus vannamei antibacterial peptide gene Lv-BigPEN and recombinant protein and application thereof
ActiveCN108396030ABiologically activeBroad-spectrum antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliBacteroides
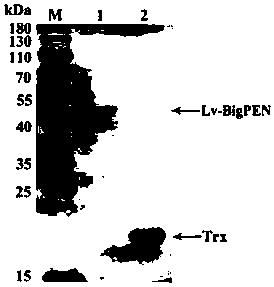
The invention discloses a litopenaeus vannamei antibacterial peptide gene Lv-BigPEN and a recombinant protein and application thereof. The Lv-BigPEN is a litopenaeus vannamei Penaeidin (PEN) antibacterial peptide family gene, the length of a nucleotide sequence of the gene is 810 bp, the open reading frame encodes 269 amino acids, and the speculated protein molecular weight is 29.2 kDa. An expression vector Pet32a(+) and an expression strain of escherichia coli Transetta (DE3) are used for performing the prokaryotic recombinant expression, recombinant protein with bioactivity is obtained. Therecombinant protein has the broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, and is capable of generating the inhibiting effect to multiple bacteria and WSSV viruses. The recombinant protein can be used for producing livestock and aquatic product antibacterial agents, vaccines or feed additives, and has the larger application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Synthesis and use of 9-O-aryl substituted berberine derivatives
ActiveCN109232557AWide range of efficacyStrong antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryProtonationStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a novel method for synthesizing a 9-O-aryl substituted berberine derivative 5 and a 9-O-phenyl bridged berberine dimer 7. The method comprises the steps: removing methyl of a site 9 from berberine 1, which serves as a raw material, so as to obtain berberrubine 2, and subjecting the berberrubine 2 to protonation and reduction, so as to prepare tetrahydro berberrubine 3; subjecting the tetrahydro berberrubine 3 and iodo aromatic hydrocarbon to a C-O cross-coupling reaction under nitrogen protection so as to obtain a product 4, and then, carrying out oxidation, so as to obtain the target 9-O-aryl substituted berberine derivative 5; coupling the tetrahydro berberrubine 3 and 4o, and carrying out oxidation, thereby obtaining the berberine dimer 7. The berberine derivatives synthesized by the method have the advantages of good fat solubility, simple preparation method, high yield and the like. Discovered by in-vitro experiments, this kind of berberine derivatives havea relatively good inhibiting action on staphylococcus aureus, thereby having a potential application value in the field of antibacterial drugs.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Small peptide C with antibacterial and antitumor functions and applications thereof
InactiveCN101648991ANo toxicityEasy to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsSmall peptideNormal growth
The invention discloses small peptide C with antibacterial and antitumor activities. The peptide C has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, has a peptide sequence with antitumor and antibacterial activities at low concentrations and has no effect on normal growth of cells of humans at corresponding concentrations. The invention also discloses applications of the small peptide in preparingantitumor and antibacterial drugs, in preparing genetically modified organisms and in preparing additives for feed, food and cosmetics.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
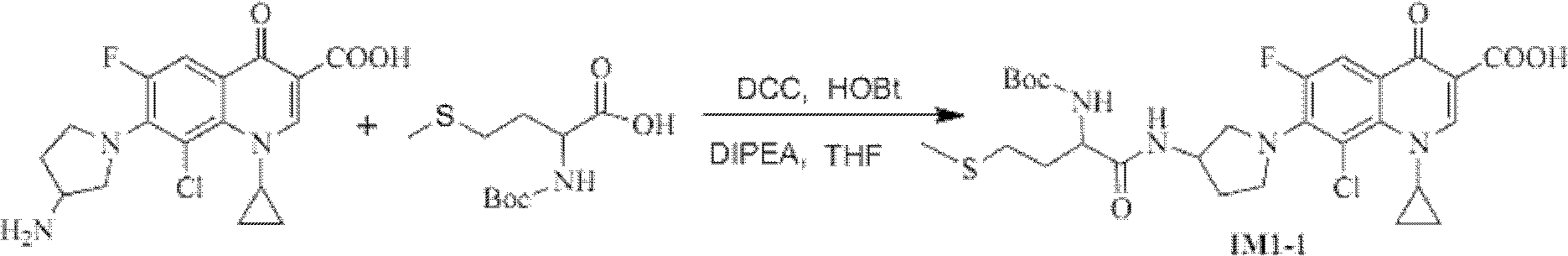
Methionine or oxidized methionine modified Clinafloxacin and application thereof
InactiveCN102633774AMeet various needsGood chemical stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
The invention discloses methionine or oxidized methionine modified Clinafloxacin, which refers to compounds shown in a formula I, wherein X is SO or SO2; Y is tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) or H.HZ, and HZ is HCl or trifluoroacetic acid (TFA); or X is S and Y is H.HCl. The compounds have certain bacteriostasis activity to gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, and gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli, saimonella, and pseudomonas aeruginosa. The bacteriostasis activity to Staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa and saimonella of the compounds TM2-1 (X is S and Y is H.HCl) and TM2-3 (X is SO2 and Y is H.HCl) is approximate to that of Clinafloxacin, and is superior to that of the known compound TM1-1 (X is S and Y is H.TFA). In the compound TM2-3 structure, S is in a maximum oxidation state, so that the compound TM2-3 is high in chemical stability. The Clinafloxacin derivatives can be used for preparing antibacterial medicaments, can provide more efficient and safe candidate medicaments for clinical treatment of infectious diseases, and meets various demands of clinical treatment.
Owner:金河牧星(重庆)生物科技有限公司 +1
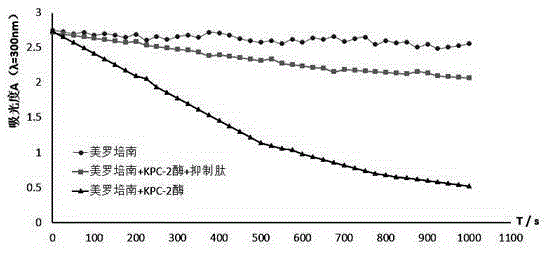
KPC (Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase) inhibition peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN105254711AStrong inhibitory activityImprove securityAntibacterial agentsTetrapeptide ingredientsBeta lactam antibioticAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a KPC (Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase) inhibition peptide and an application thereof and belongs to the field of biological medicines. The amino acid sequence of the KPC inhibition peptide is Pro-Asn-Gln-Trp, and the KPC inhibition peptide can be prepared with a solid-phase synthesis method and has a remarkable inhibiting effect on KPC. Through combined utilization of the inhibition peptide and beta-lactam antibiotics, the antibiotics can be prevented from being hydrolyzed and damaged by the KPC and losing efficacy, and the inhibition peptide can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by drug-resistant bacteria infection and / or antibacterial agents. The KPC inhibition peptide has higher enzyme inhibitory activity and low hemolytic activity, realizes artificial synthesis conveniently, is suitable for industrialization, provides a new choice for development of new antibacterial agents and compound preparations and has the good development prospect in the field of treatment of the drug-resistant bacteria infection.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Xanthenone dimer compound IUE-1799a use
ActiveCN105497004AGrowth inhibitionNo apparent cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCytotoxicityXanthone
The present invention discloses xanthone dimer compouns IUE-1799a use, specifically antibacterial use such as use to inhibit growth of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, and xanthone dimer compouns IUE-1799a has no significant cytotoxicity to a variety of cell lines, and can be used for the preparation of antibacterial agents.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
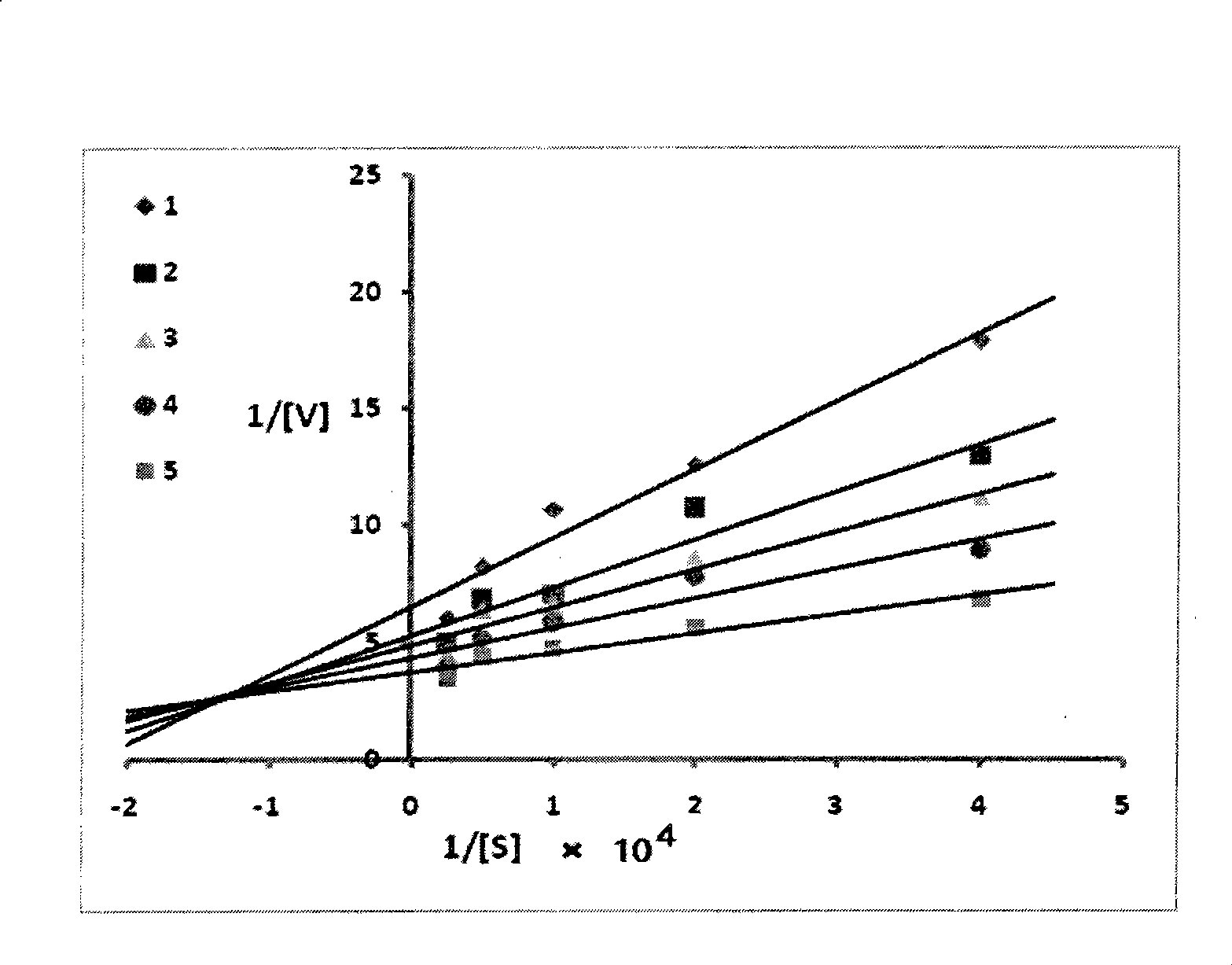
Application of rosmarinic acid in bacillus coli L-asparaginase activator
InactiveCN101423827AHigh activityQuick responseHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacterium L
The invention relates to application of rosmarinic acid in an escherichia coli L-asparaginase enzyme activator, which belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The application comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing an L-asparaginase enzyme extract from escherichia coli; secondly, adding the rosmarinic acid and an L-asparaginase which have different concentrations into an enzyme activity measuring system of the L-asparaginase respectively; thirdly, measuring the reaction speed of each reaction system, calculating the michaelis constant under the concentration of each rosmarinic acid, and judging the activation of the michaelis constant on the L-asparaginase enzyme. The rosmarinic acid can significantly improve the degradation activity of the L-asparaginase enzyme to catalyze the L-asparagine when the concentration of the rosmarinic acid is between 0.375 x 10<-4> and 3.0 x 10<-4> g / L. The application can reduce the dosage of the L-asparaginase enzyme in the process of tumor therapy clinically, and reduce side effects caused by immunogenicity of the L-asparaginase enzyme, or a rosmarinic acid derivative is designed aiming at a target point of the bacterium L-asparaginase enzyme and is used as a new antibacterial drug.
Owner:邵楠 +1
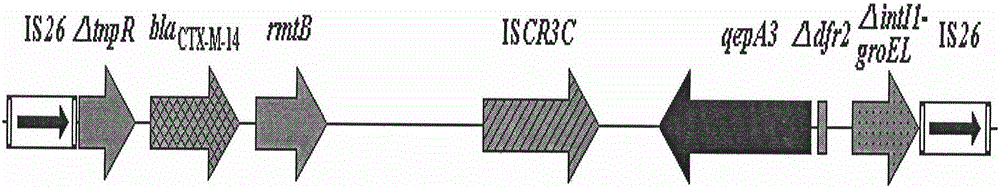
Plasmid fragment carrying novel gene qepA3
InactiveCN105039357AReduce usagePrevent outbreakBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliResistant bacteria
The invention discloses a plasmid fragment carrying novel gene qepA3. Sequences of the plasmid fragment are shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The plasmid fragment is found in a genome of Escherichia coli EC3157. Discovery of the plasmid fragment, on the one hand, is of important theoretical and practical significance to genetic level study on molecular mechanisms of resistance transfer in bacteria; on the other hand, has certain guidance on clinical medication and is helpful for clinical reduction in usage of certain antibacterial agents, reduction in selective pressure of resistance gene transfer of this agents, and prevention of explosive epidemic of drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:王冬国
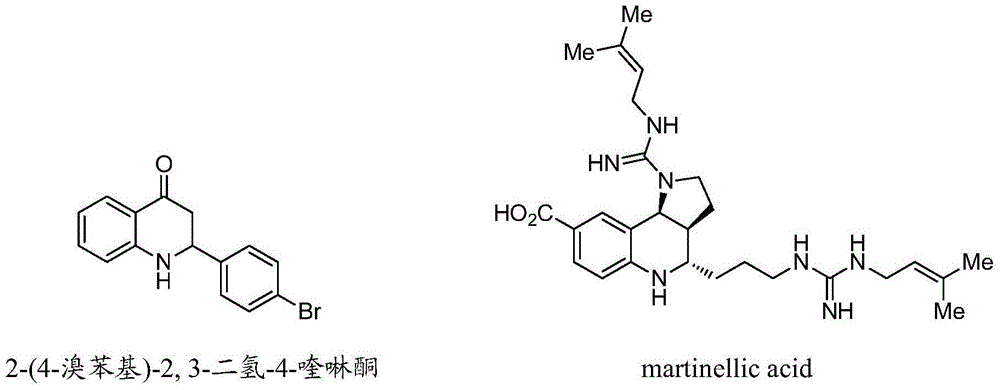
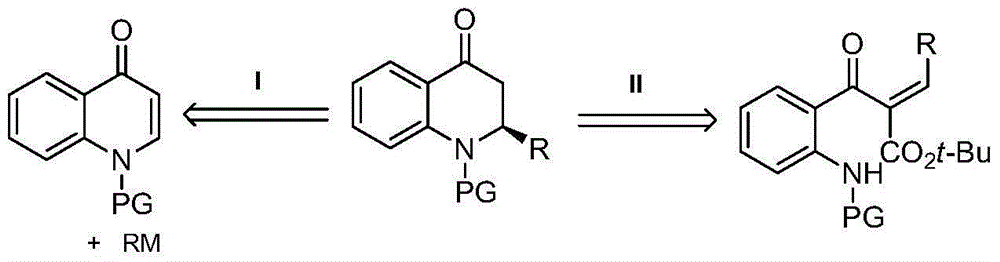
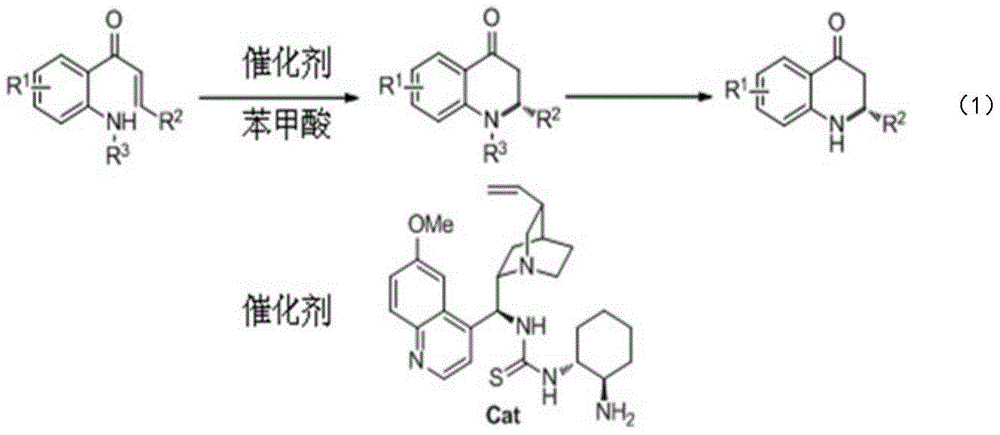
Synthetic method for high-enantioselectivity N-acetyl-2-substitued-2, 3-dihydro-4-quinolinone compounds
ActiveCN103601676AHigh enantioselectivityEasy to makeAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryCompound organicThiourea
A synthetic method for high-enantioselectivity N-acetyl-2-substitued-2, 3-dihydro-4-quinolinone compounds is disclosed. A raw material 1-aryl-3-aryl (or alkyl)-2, 3-unsaturated ketone is subjected to an intramolecular 6-endo-trig aza-Michael addition reaction for 4 days under the effect of 0. 2 equivalent of a quinine-derived thiourea compound organic micromolecule catalyst, then separation purification is carried out for obtaining of the N-acetyl-2-substitued-2, 3-dihydro-4-quinolinone compounds. The quinine-derived thiourea compound organic micromolecule catalyst has a structure shown in the specification, wherein R1 represents a bromine atom or a hydrogen atom, R2 represents aryl or alkyl, and R3 represents tosyl (Ts) or acetyl (Ac). Compared with conventional preparation methods, the preparation method provided by the invention employs the simply prepared raw material, the obtained products are substantially high in enantioselectivity, and the products have extremely good application to antitumor drugs and antibacterial medicaments.
Owner:南京方生和医药科技有限公司
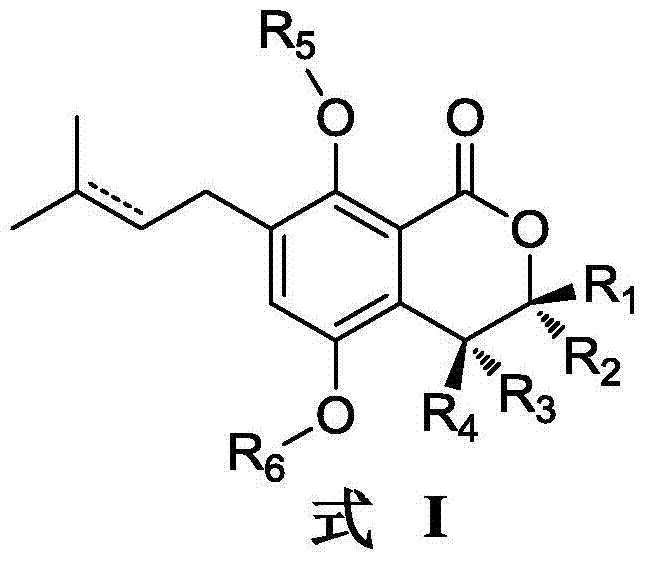
Myrtleone compound and its application in the preparation of antibacterial drugs
ActiveCN104761565BHigh antibacterial activityStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryChemical compoundAntibacterial activity
Owner:GUANGZHOU LEADER BIO TECH
Amide derivatives of linalool, preparation method of amide derivatives and application of amide derivatives in bacteria prevention
ActiveCN104892446AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationLinaloolPerylene derivatives
Owner:JIANGSU NAIQUE BIOLOGICAL ENG
Application of PA4608 protein as target in preparing antibacterial drugs
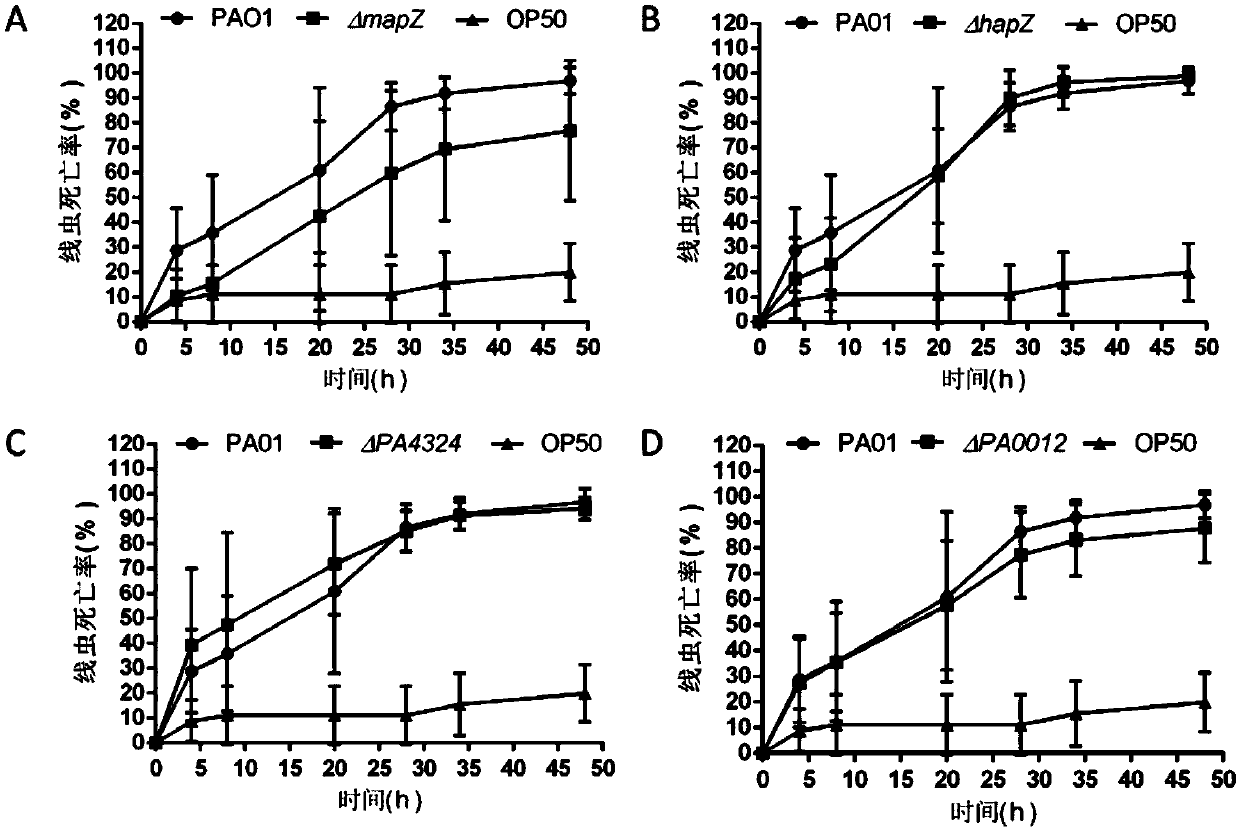
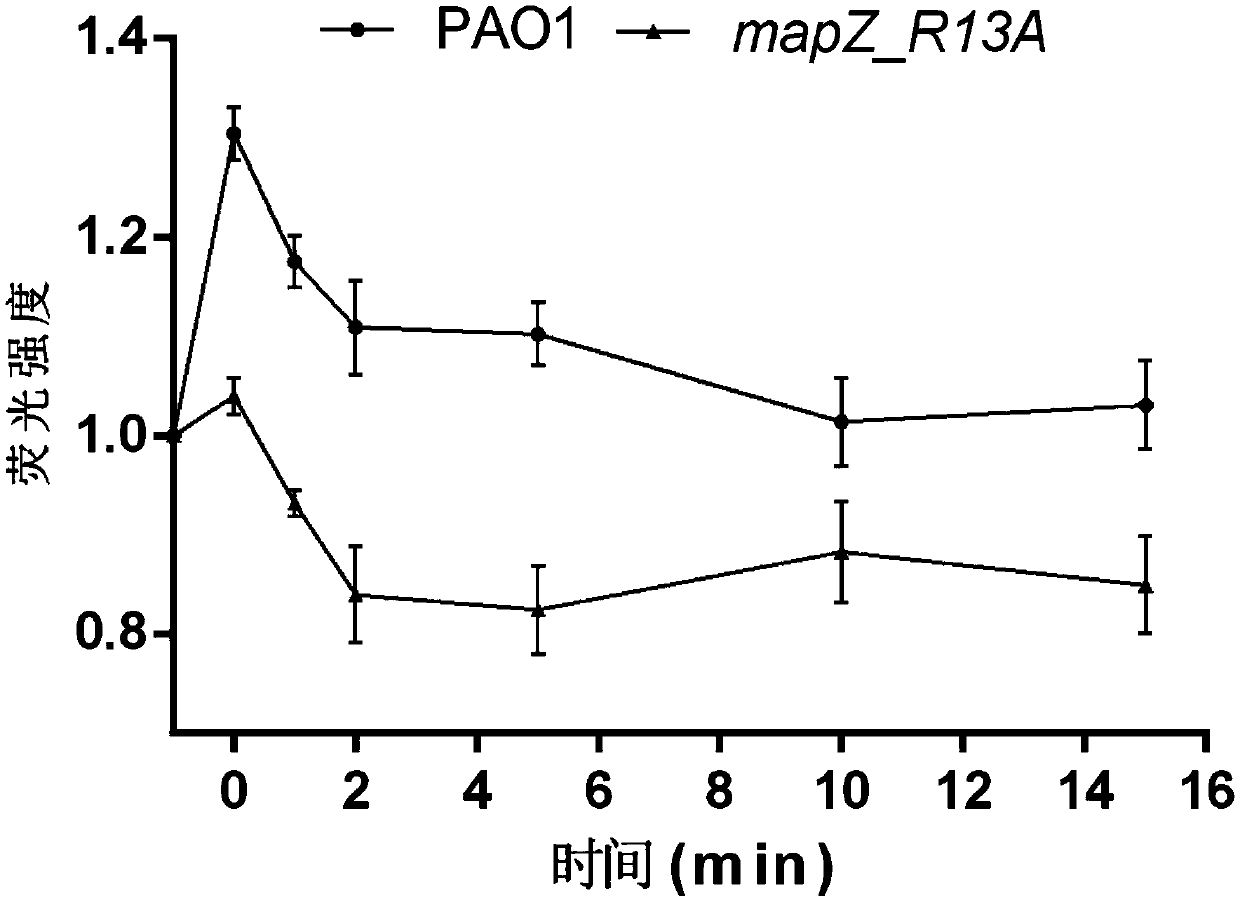
The invention discloses an application of PA4608 protein as a target in preparing antibacterial drugs. By constructing a PA4608 (mapZ) site mutant strain mapz_R13A and a mapZ whole gene knockout mutant and by utilizing a nematode-quick killing infection model, a scratch cell model and a mouse abdominal infection model for study, the invention first puts forwards that the c-di-GMP binding site of PA4608 protein plays an important regulatory role in pseudomonas aeruginosa infection process, puts forwards that the site is a key site for the pathogenicity of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, and furtherputs forwards a new target, namely a c-di-GMP receptor PA4608 used for preventing and / or treating the pseudomonas aeruginosa. The invention provides an important theoretical basis for the developmentof new antibacterial drugs, especially for the design of new antibacterial drugs based on c-di-GMP receptor induction mechanism, provides an important theoretical reference for the prevention and clinical treatment of pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, and has important practical significance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antibiotic Lobophorin E and F, preparation methods and applications thereof in preparing antibacterial and antitumor drugs
The invention discloses antibiotic Lobophorin E and F, preparation methods and applications thereof in preparing antibacterial and antitumor drugs. The Lobophorin E and F are obtained by separating from fermentation cultures of streptomyces SCSIO 1127; the Lobophorin E and F have antibacterial activities and can be used for preparing antibacterial drugs; the Lobophorin F has an antitumor activity and can be used for preparing antitumor drugs; and the structures of the antibiotic Lobophorin E and F are showed as a formula (I), wherein R is as the following for the lobophorin E, and R equals to H for the lobophorin F.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of screening for antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS20050202522A1Microbiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesChemical compoundMicrobial agent
[Object] To identify FFRPs which are prospective targets of antimicrobial agents, and by using the FFRPs, to provide a pharmaceutical agent and a novel method for screening for a pharmaceutical agent, in particular, an agent that acts against P. aeruginosa. [Solving Means] Using the genomic sequence of a bacterium, FFRPs coded therein are identified on the basis of correlation between FFRPs summarized in a multiple alignment shown in FIG. 1. By specifying chemical compounds that can specifically interact with the identified FFRPs or their assemblies, thereby changing their 3D structures, candidates for antimicrobial agents are screened.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
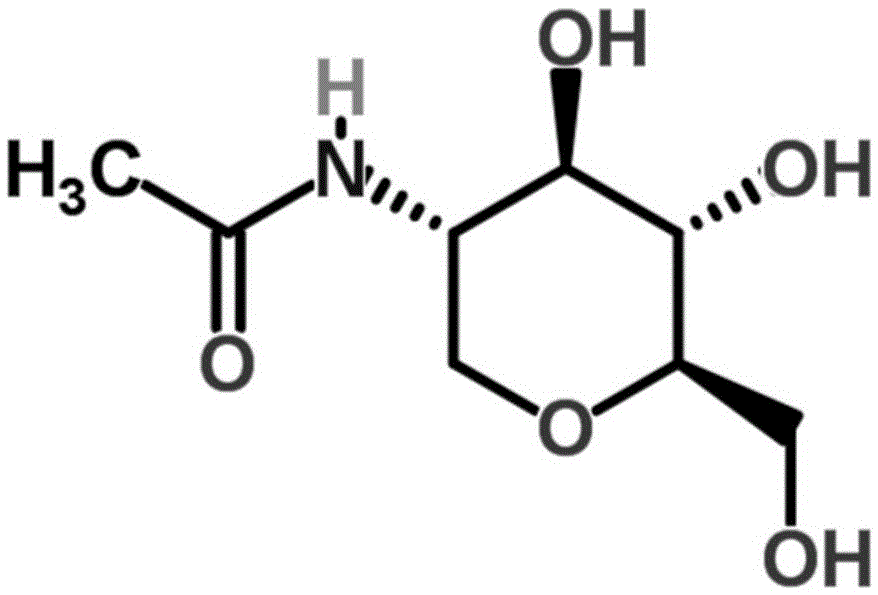
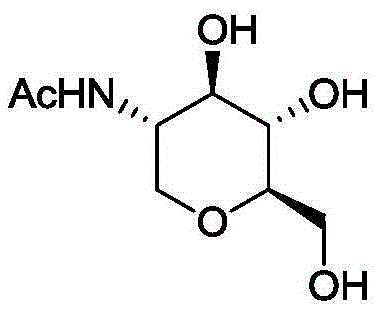
Application of 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol to preparation of anti-rice-leaf-blight-bacterial-activity medicine
InactiveCN105454235AStrong antagonistic effectHas activity against rice bacterial blightBiocideFungicidesMinimum inhibitory concentrationMicrobiology
The invention discloses application of 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol to preparation of an anti-rice-leaf-blight-bacterial-activity medicine. It is found for the first time that 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol has anti-rice-leaf-blight-bacterial-activity. After 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol is prepared into antibacterial medicine, it is found that rice leaf blight bacterial antimicrobial activity of 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol is specific, antagonistic ability is strong, the minimal inhibitory concentration of 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol is only 23.90 ug / ml, and 2-acetamido-1,5,-dehydrated-2-deoxy-D-glucitol has no inhibition activity on various common pathogenic bacteria and pathogenic fungi. Therefore, the technical scheme provides a new choice for preparation of a novel preparation preventing rice leaf blight.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +2
Phenylurea-substituted n-thioacylhomoserine lactone compounds, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107098874BHigh activityGood application effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHomoserineAcyl-Homoserine Lactones
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry and discloses an N-thioacyl homoserine lactone compound containing phenylurea substitution and having bacterial quorum-sensing inhibitory activity, and a synthetic method and application thereof. The preparation method is simple, and has mild conditions and high yield. In-vitro activity test results indicate that the N-thioacyl homoserine lactone compound containing phenylurea substitution exhibits significant inhibitor effect to both Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and pqs systems, and is applicable to the preparation of bacterial quorum sensing resistant antibacterial synergists and antibacterial drugs. The N-thioacyl homoserine lactone compound containing phenylurea substitution has a chemical structural general formula shown in the description.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
A kind of spirocyclic indole diketopiperazine alkaloid and its synthesis method and application
ActiveCN103435622BReduce dosageSave the reaction substrateAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsSchotten–Baumann reactionSynthesis methods
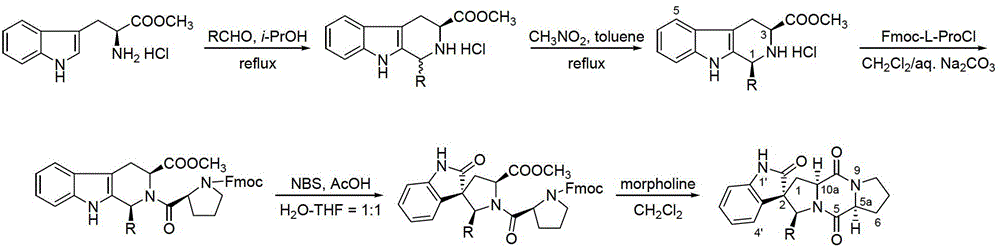
The invention relates to spiro indole diketopiperazine alkaloid, and a synthesis method and an application of the spiro indole diketopiperazine alkaloid. The synthesis method comprises the steps that L-tryptophan methyl ester hydrochloride and fatty aldehyde perform Pictet-Spengler reaction to form enantiomeric hydrochloride, an inducer for inducing asymmetric conversion through crystallization induces the asymmetric conversion to form a single-configuration product, the single-configuration product performs Schotten-Baumann reaction to form an amido bond, then a spiral structure is obtained by NBS (N-bromosuccinimide) rearrangement, a protecting group is removed from the spiral structure under base catalysis, and the spiral structure is subjected to ring closing to form the spiro indole diketopiperazine alkaloid. The method has the advantages that the method is low in cost, simple and convenient in path, high in yield and easy to process, an end product and a natural product are the same in configuration, etc. The prepared spiro indole diketopiperazine alkaloid can be further applied to preparation of antibiotics.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
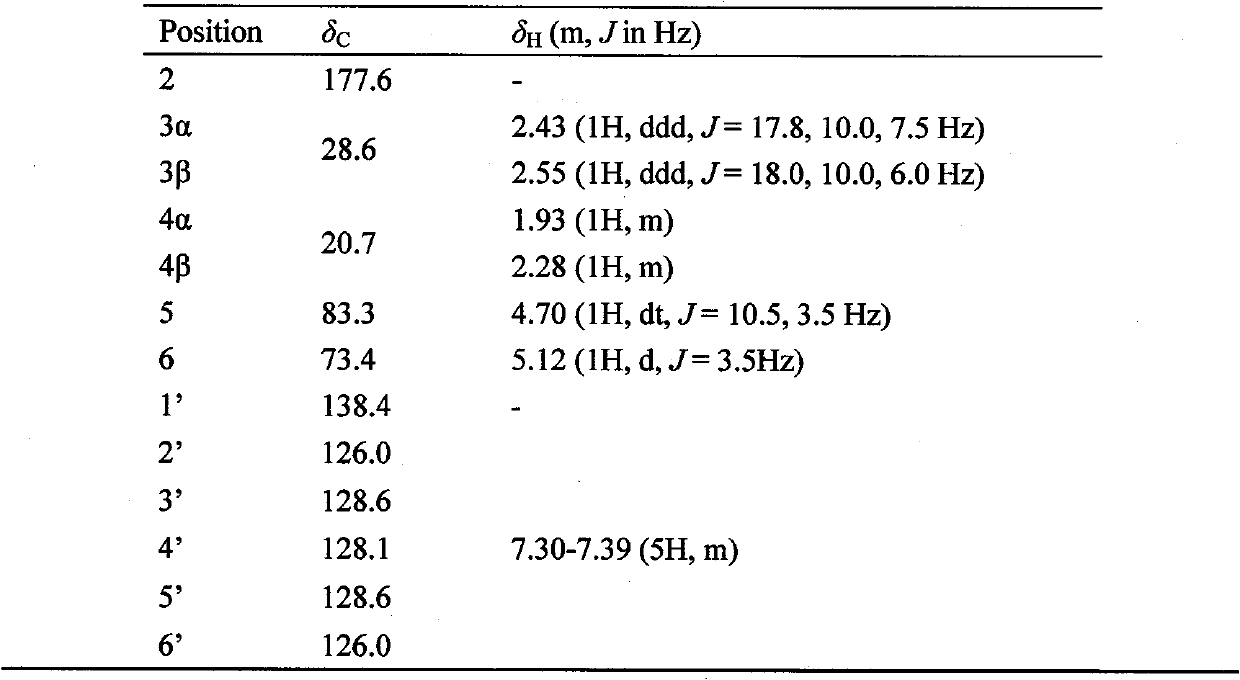
Furanone compound Cytosporanone A having antibacterial activity
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine, in particular to furanone compound Cytosporanone A which is separated from plant endophytic fungi Cytospora sp. leavening, has antibacterial activity and has the systematic name of (R)-5-((S)-hydroxy (phenyl)-methyl) dihydrofuran-2 (3H)-one, and the furanone compound Cytosporanone A has the chemical structural formula as follows. The in vitro antibacterial experiment proves that the compound Cytosporanone A has obvious bacteriostatic effect for botrytis cinerea, septoria musiva leaf blight fungi and bacillus megaterium, thus being used for preparing antibacterial medicines. The invention provides a lead compound for developing new antibacterial medicines, and has important valve for developing endophytic fungi medical resources of China.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Purpose of benzo indolium containing compound LTH02 in treating multi-drug resistant bacterial infection diseases
InactiveCN103224463AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliChemical structure
The invention belongs to a field of pharmacy, and relates to a purpose of benzo indolium containing compound LTH02 in treating multi-drug resistant bacterial infection diseases. The benzo indolium containing compound LTH02 has relatively strong inhibition effect on clinically separated multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli, and can be used for researching novel and effective antibiosis medicament and treating the multi-drug resistant bacterial infection diseases. The antibiosis medicament can be prepared into tablet, pill, capsule, suspending agent, emulsion, injection or dries pulvis. The benzo indolium containing compound LTH02 has a chemical structure as shown in a formula I.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
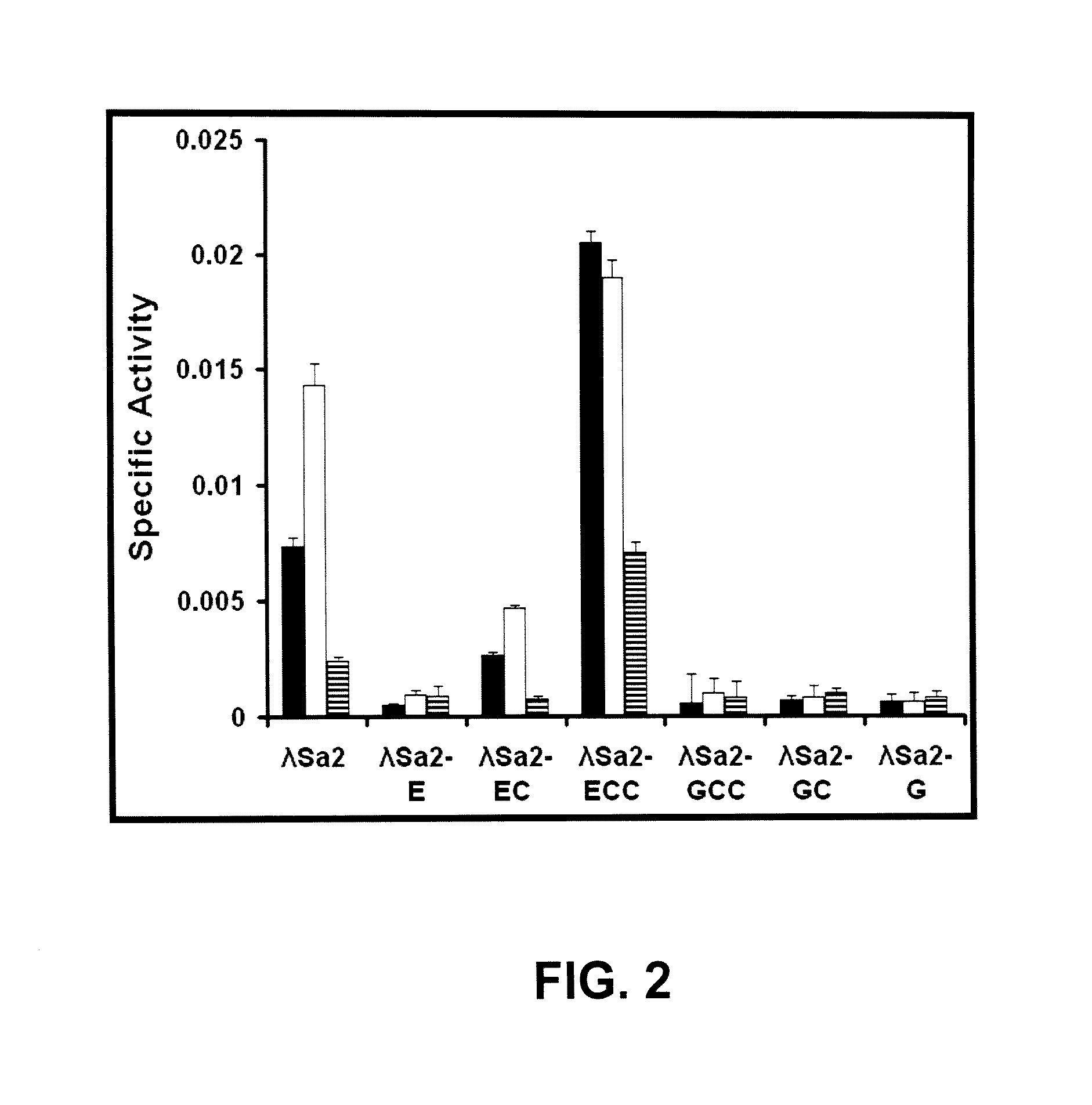
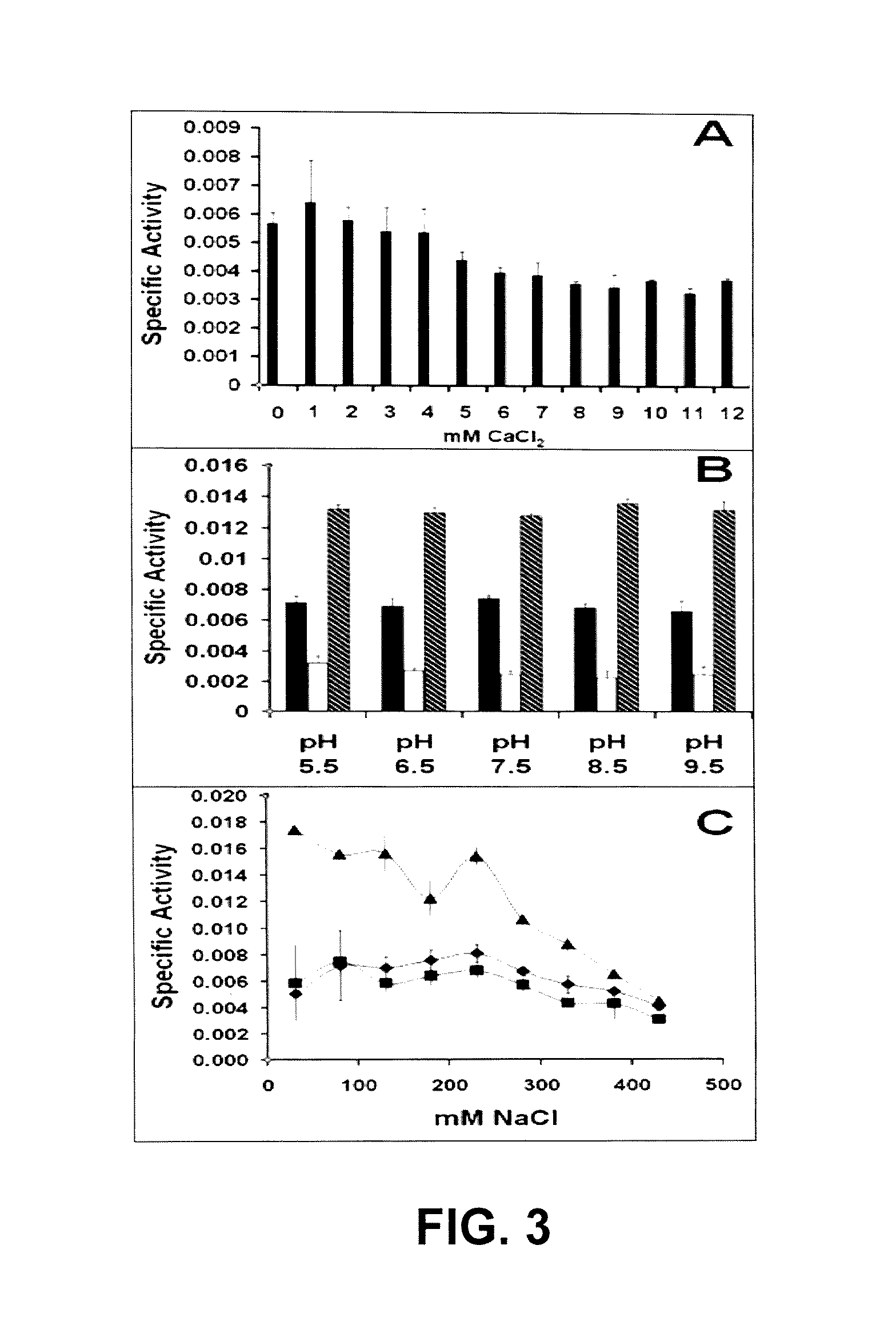
Isolated recombinant cDNA
InactiveUS9545431B1Enhancing exolysisImprove targetingPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymesADAMTS ProteinsStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
The routine use of antibiotics to battle Streptococcal pathogens has produced a new class of superbug—multi-drug resistant streptococci resulting in a need for new antimicrobials. The LambdaSa2 prophage endolysin gene harbors an amidase-5 (endopeptidase), an amidase-4 (glycosidase) domain and two Cpl-7 cell wall-binding domains. This endolysin can digest the cell walls of Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. Turbidity reduction and plate lysis assays indicate that this peptidoglycan hydrolase also shows strong lytic activity toward Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus equi, GES, and GGS. Deletion analysis on the His-tagged version of this gene further indicates that the N-terminal endopeptidase domain is minimally active in the absence of a Cpl-7 domain when lysing cells from without; however, with both Cpl-7 domains, it achieves a higher specific activity than the full length protein (on some strains) and shows weak activity against two Coagulase Negative Staphylococci, Staphylococcus hyicus and Staphylococcus xyloses.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com