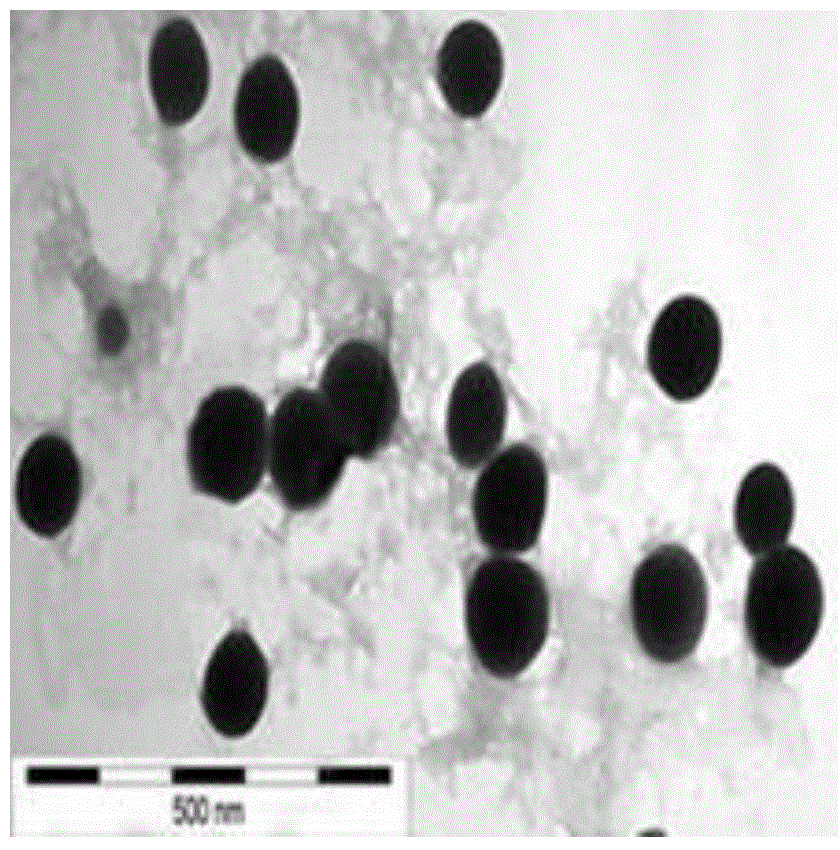
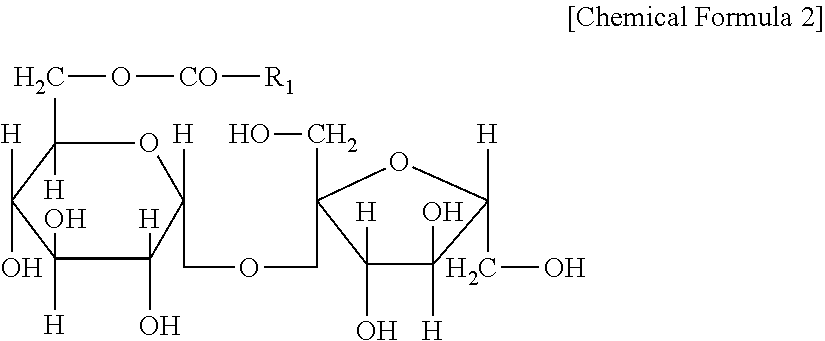
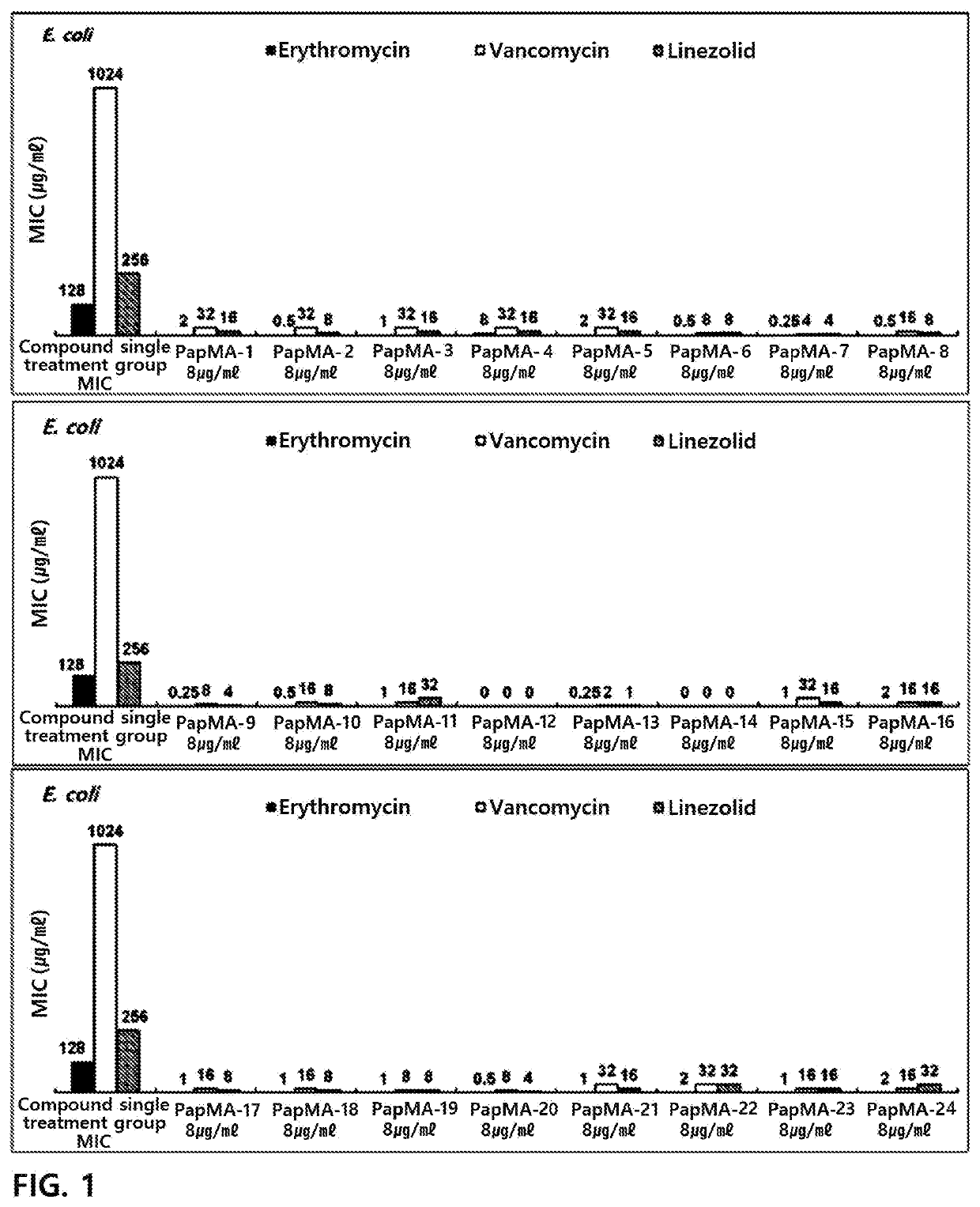
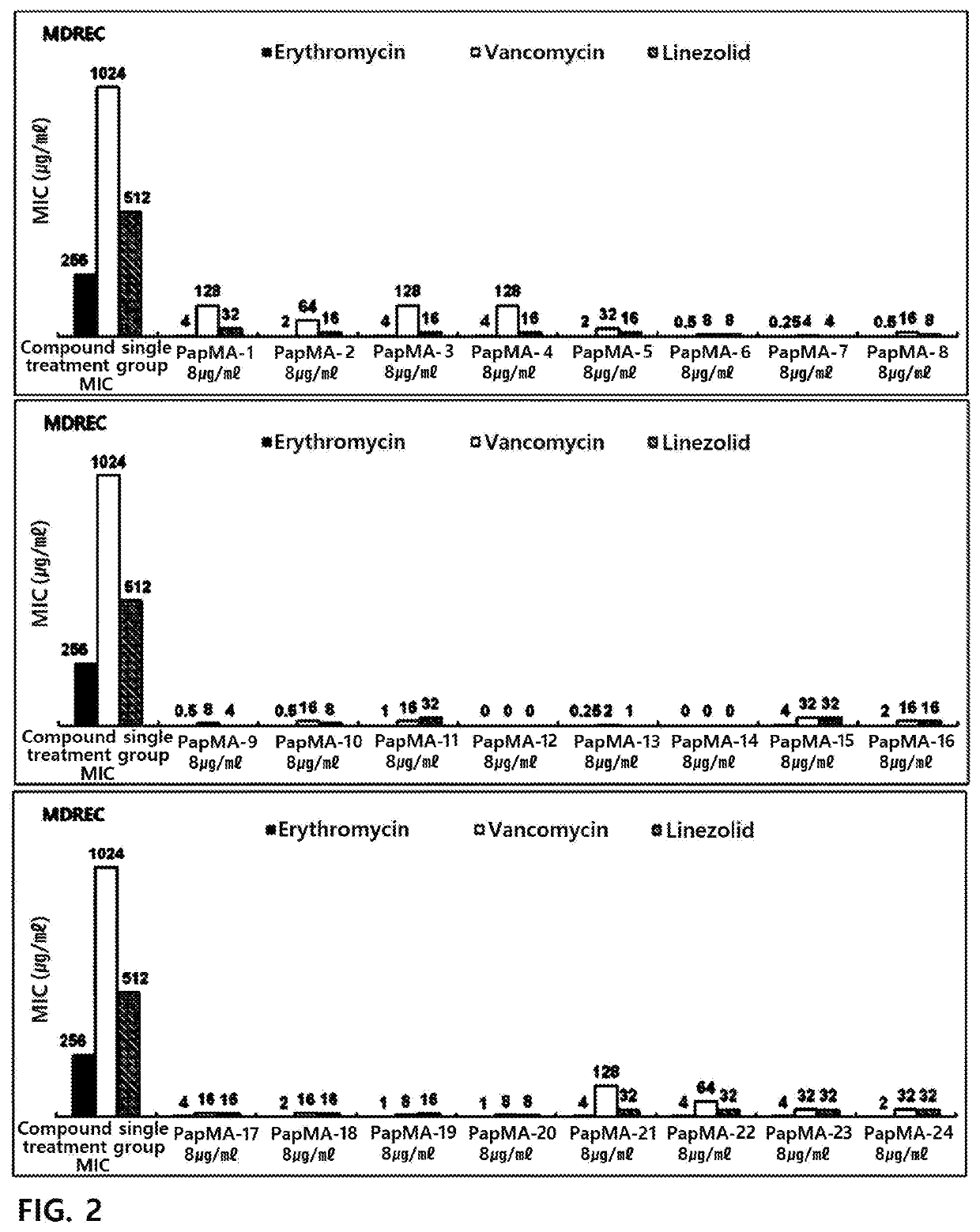
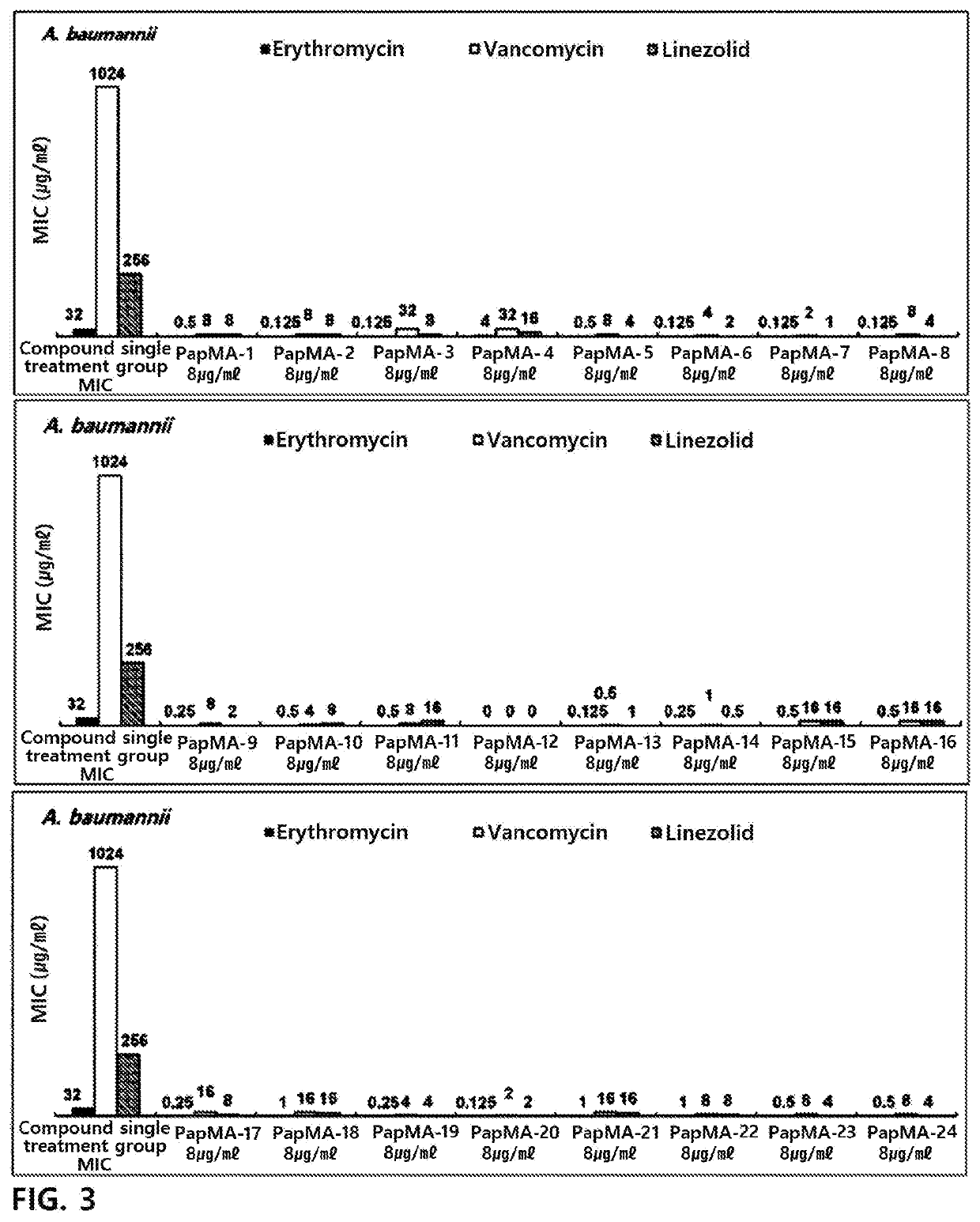
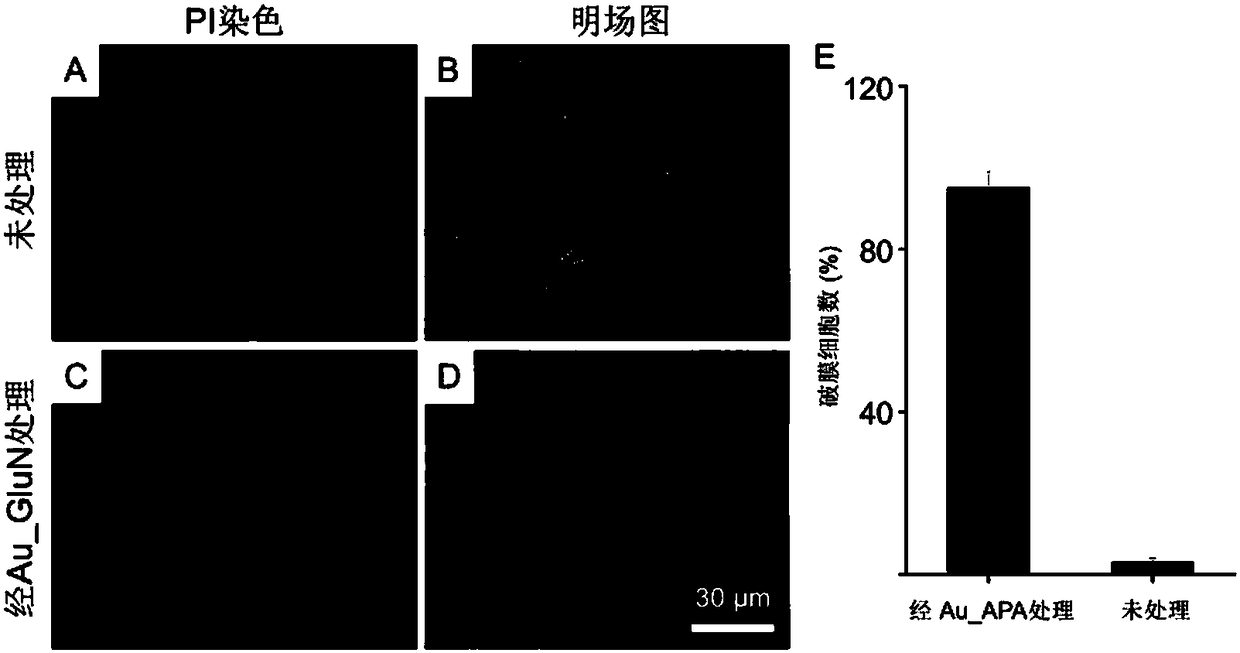
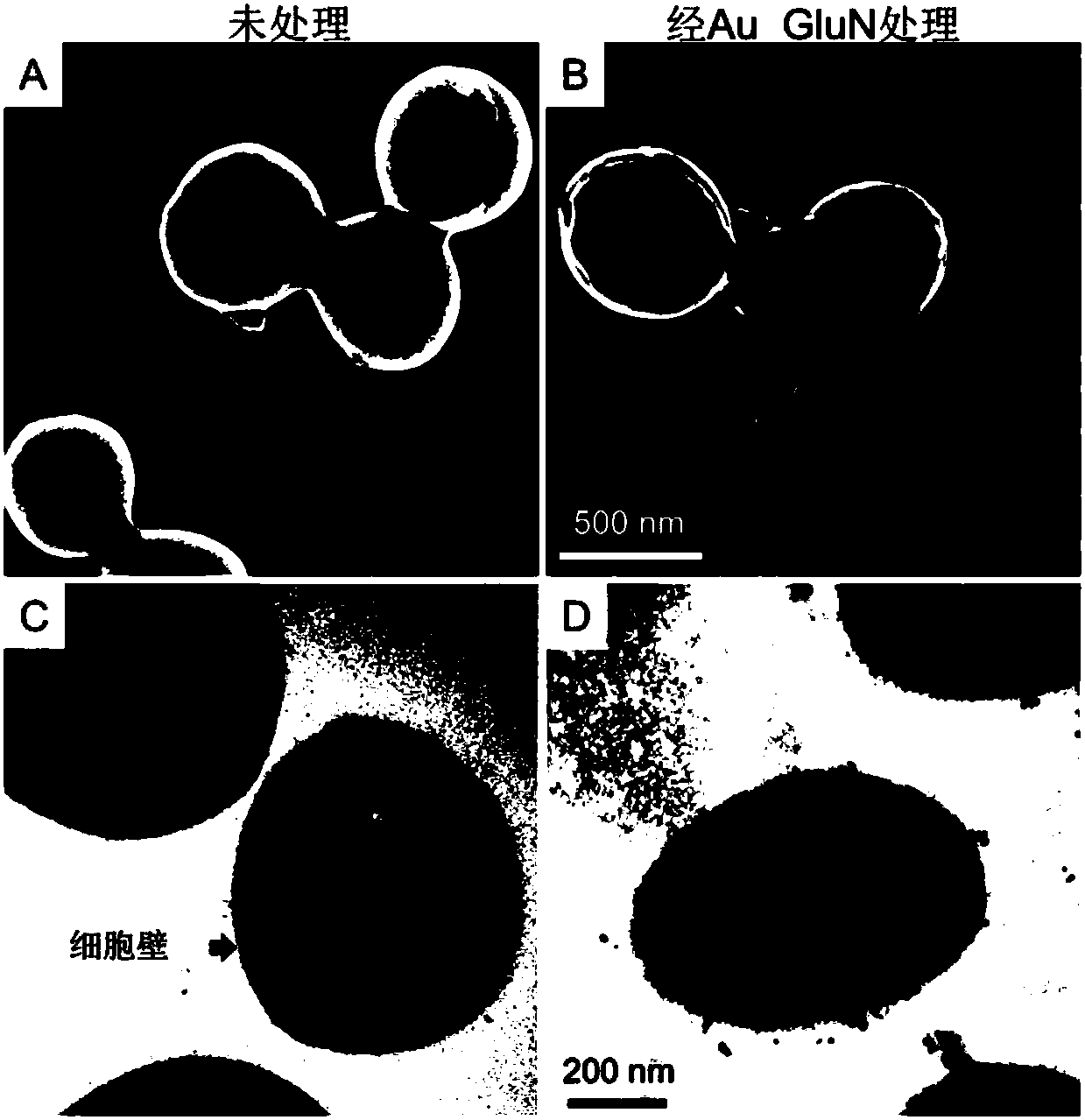
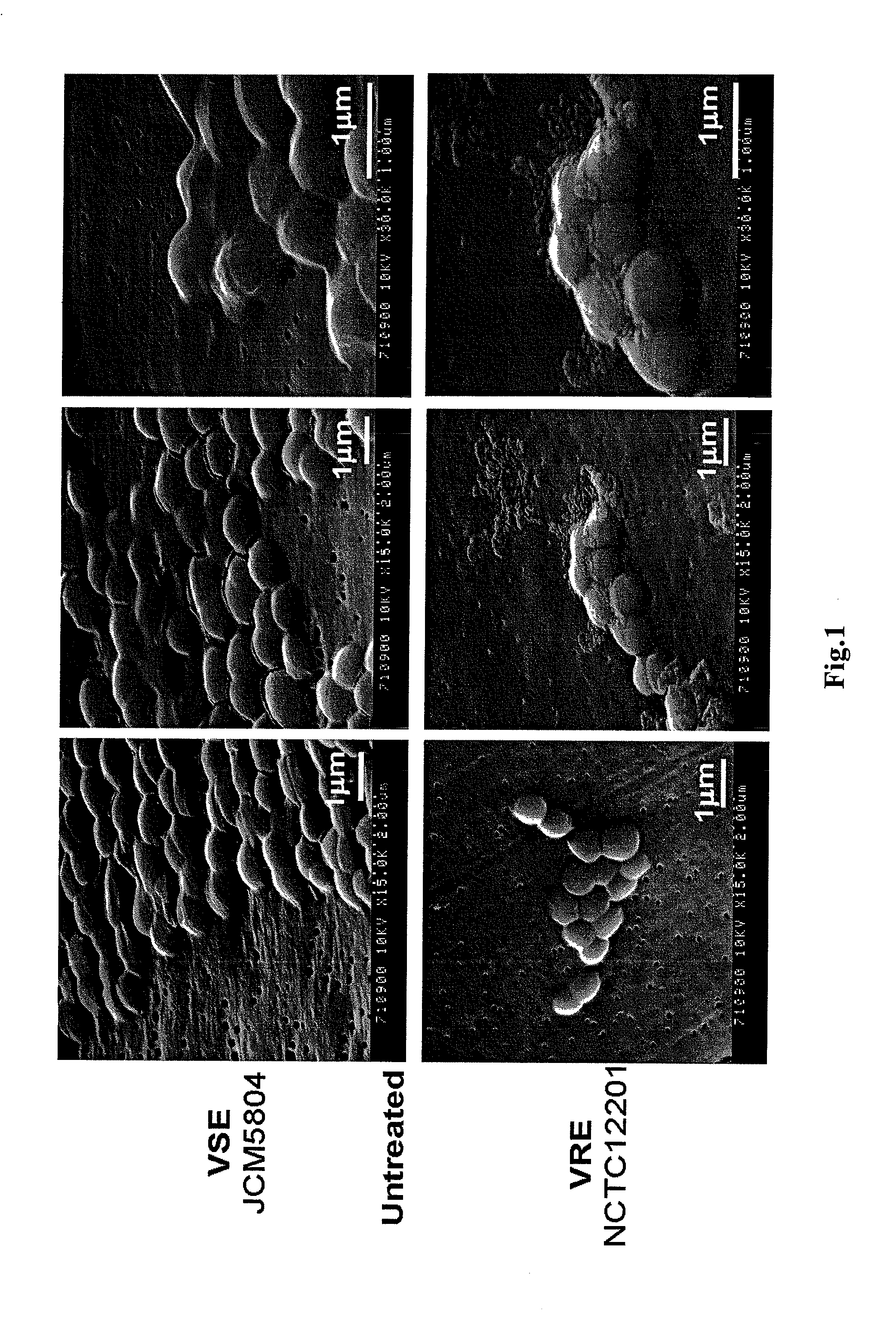
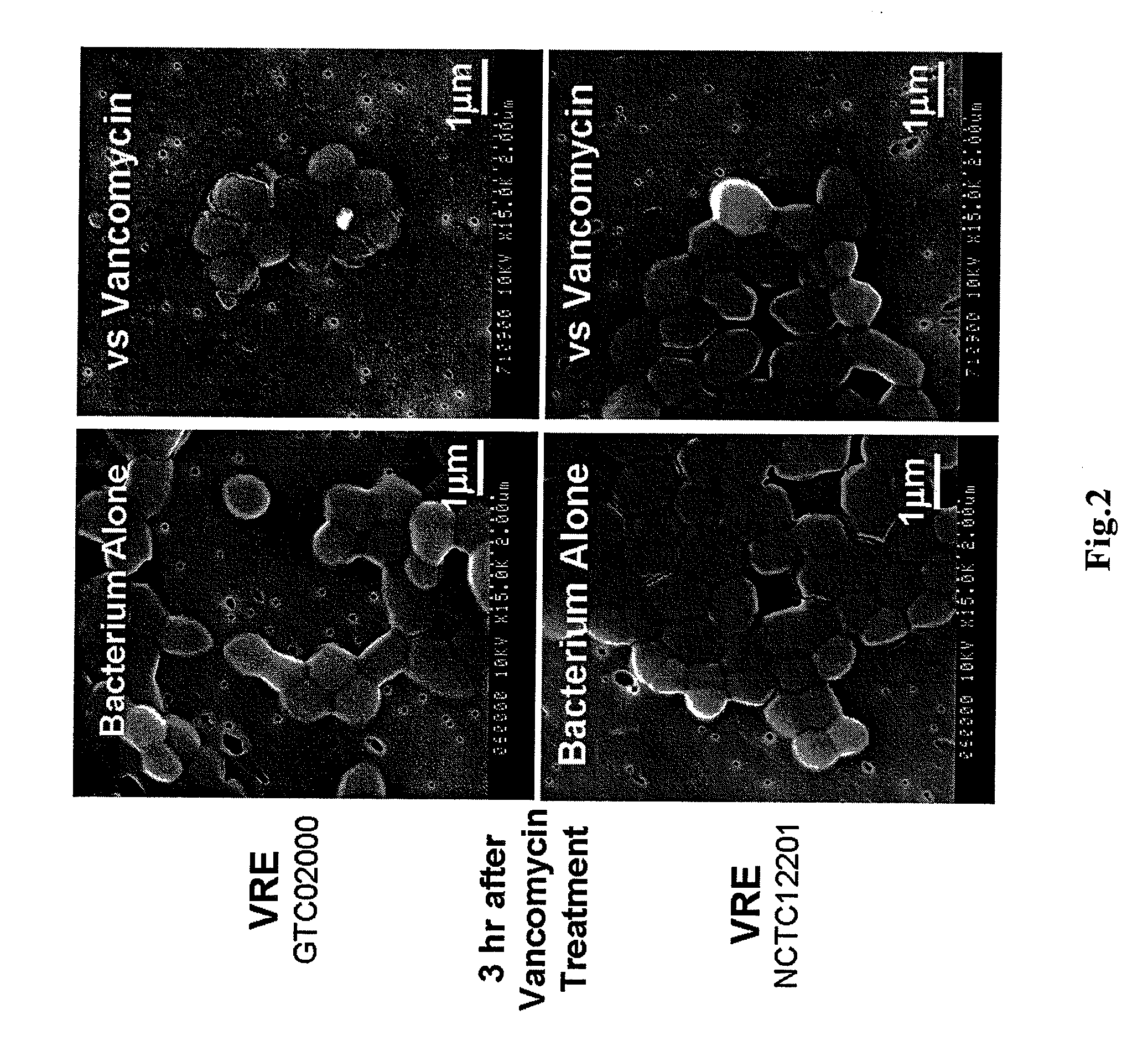
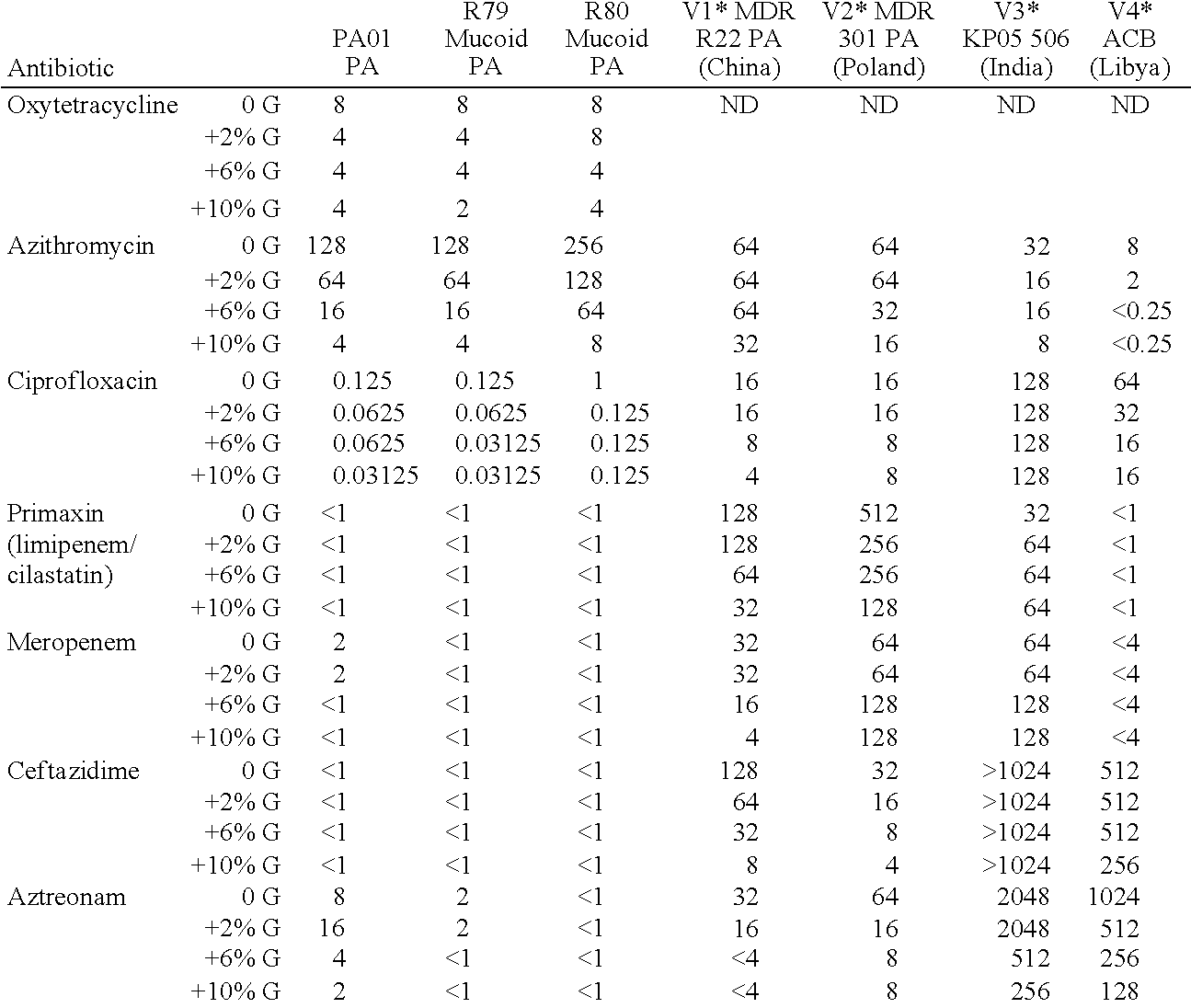
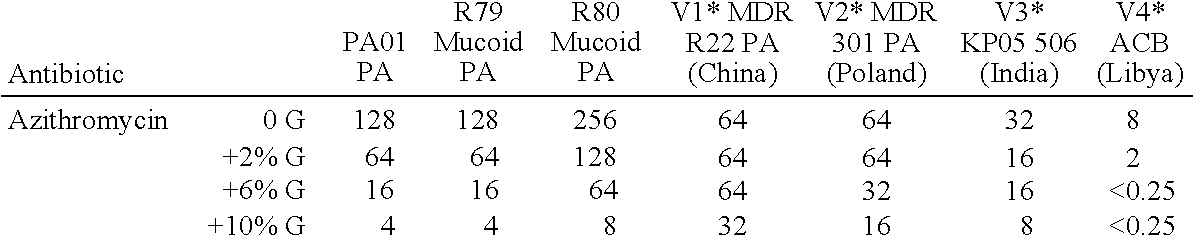
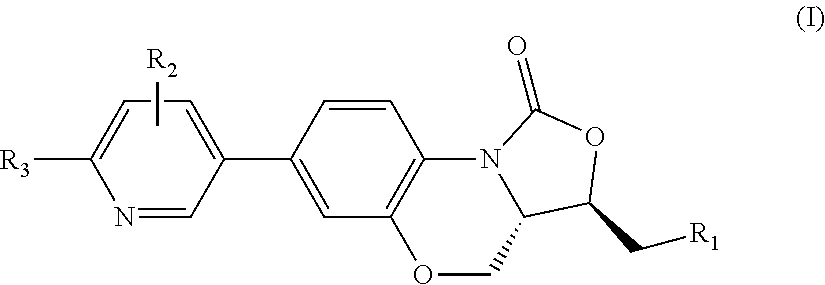
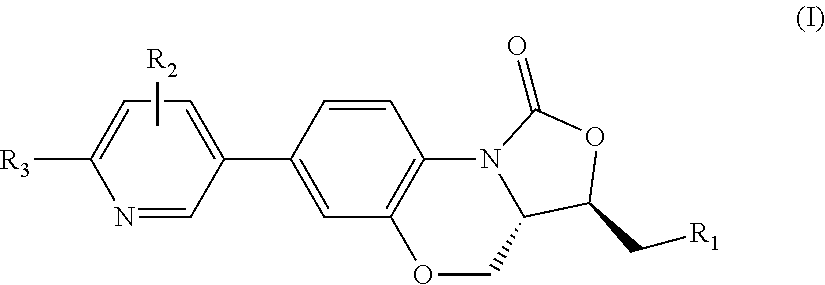
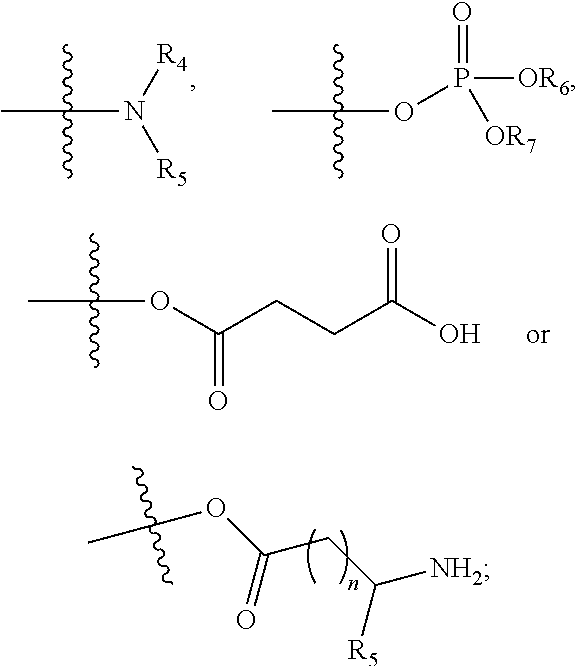
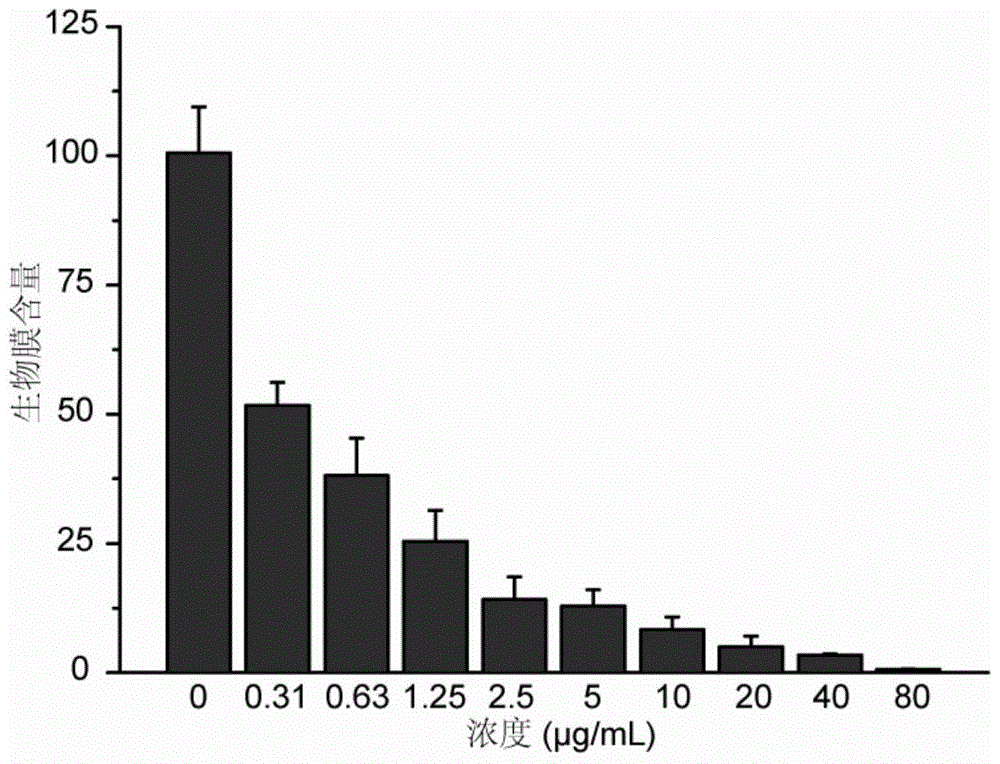
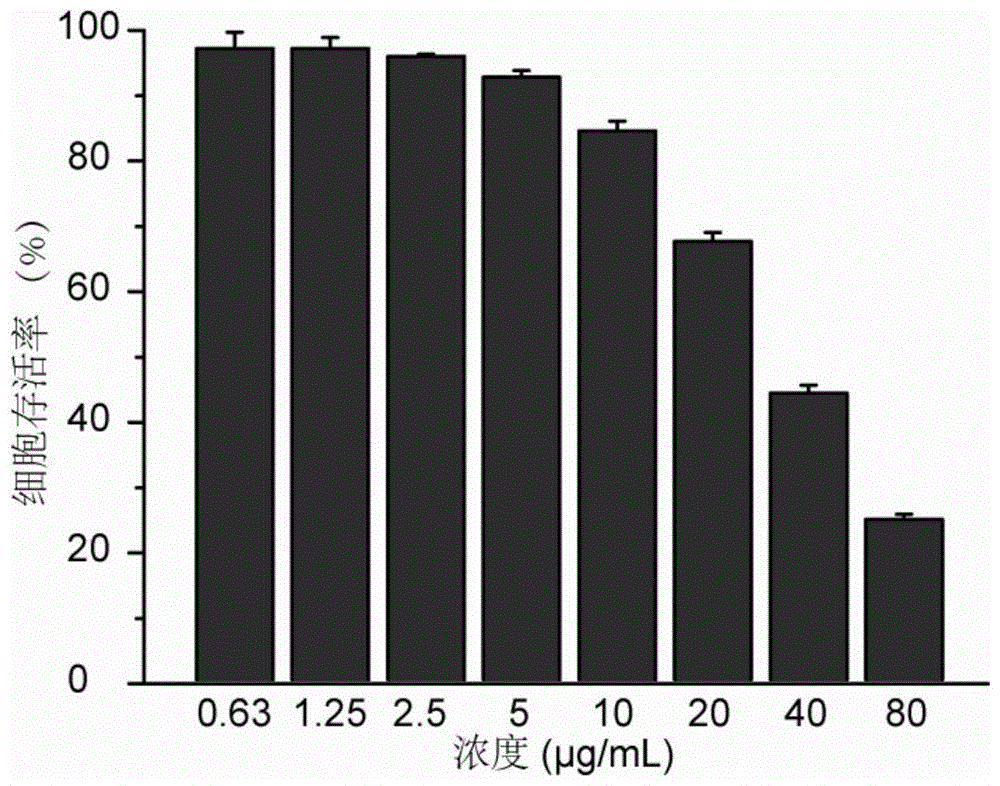
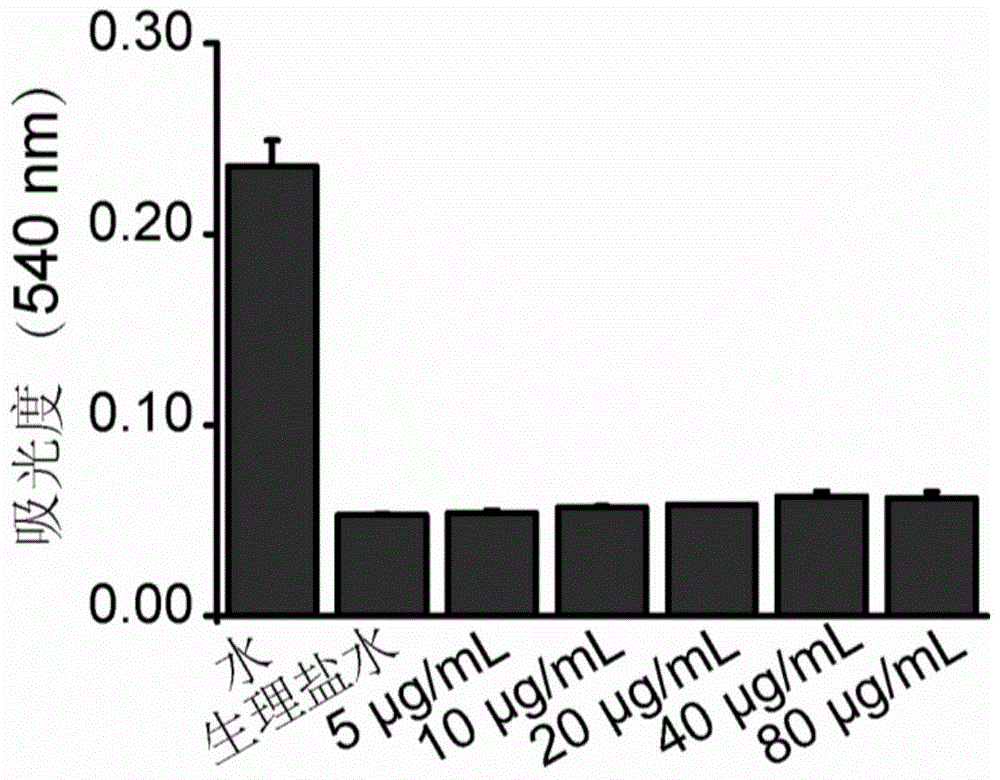
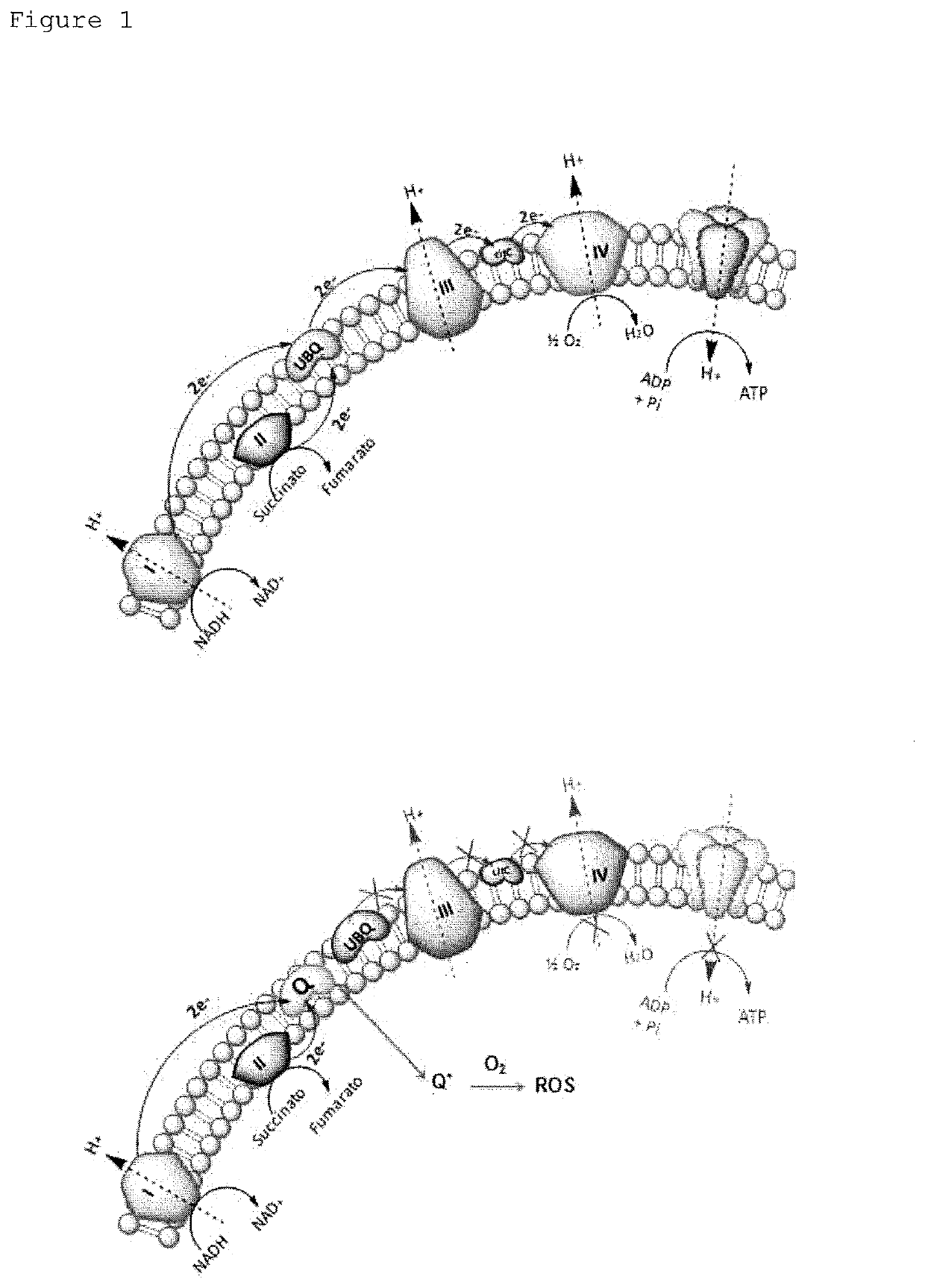
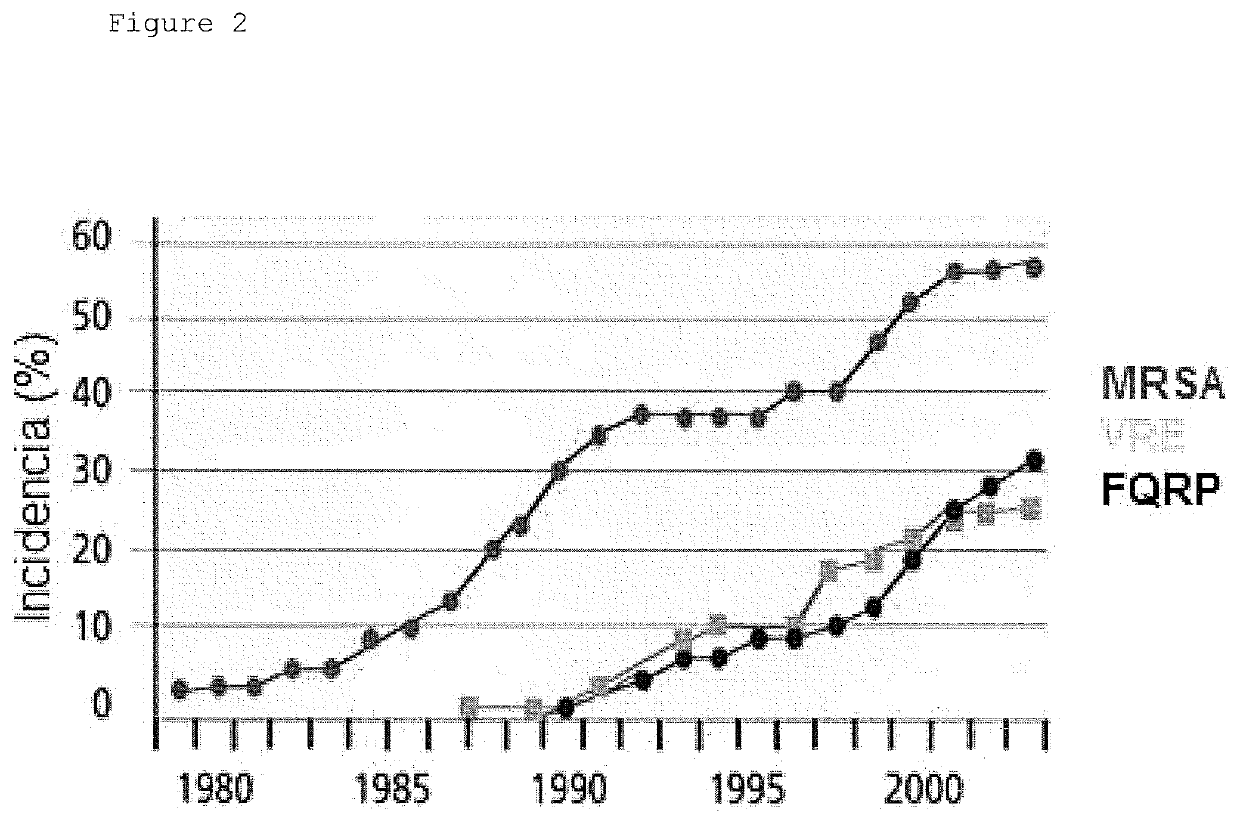
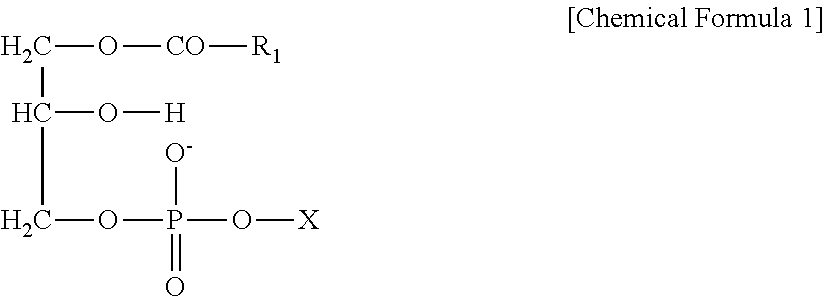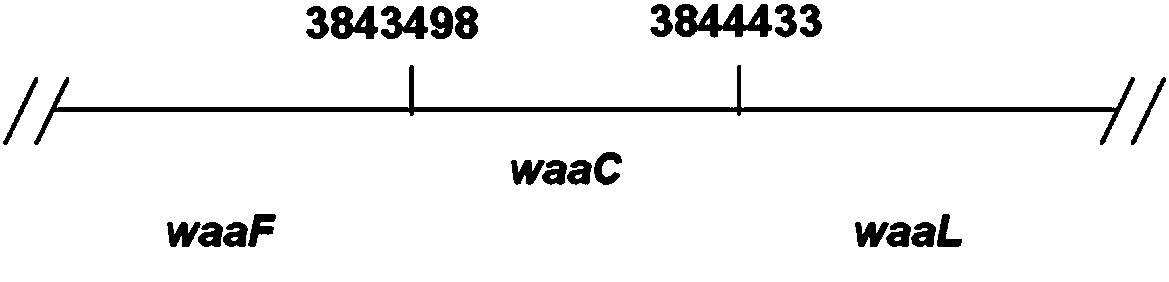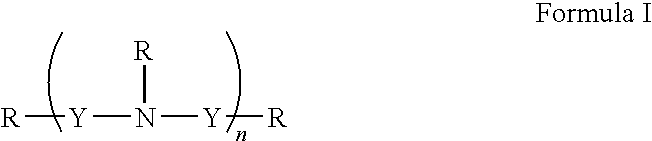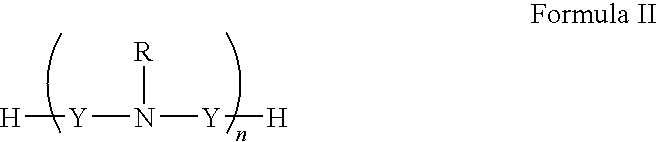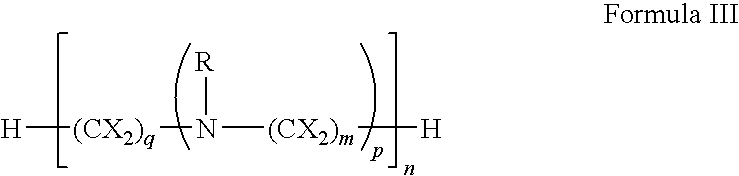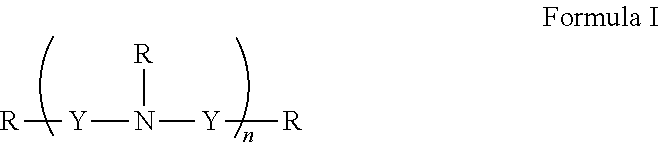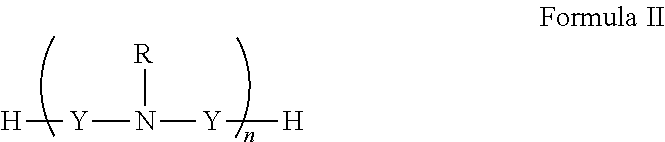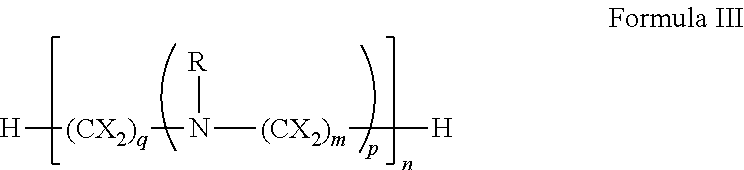Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
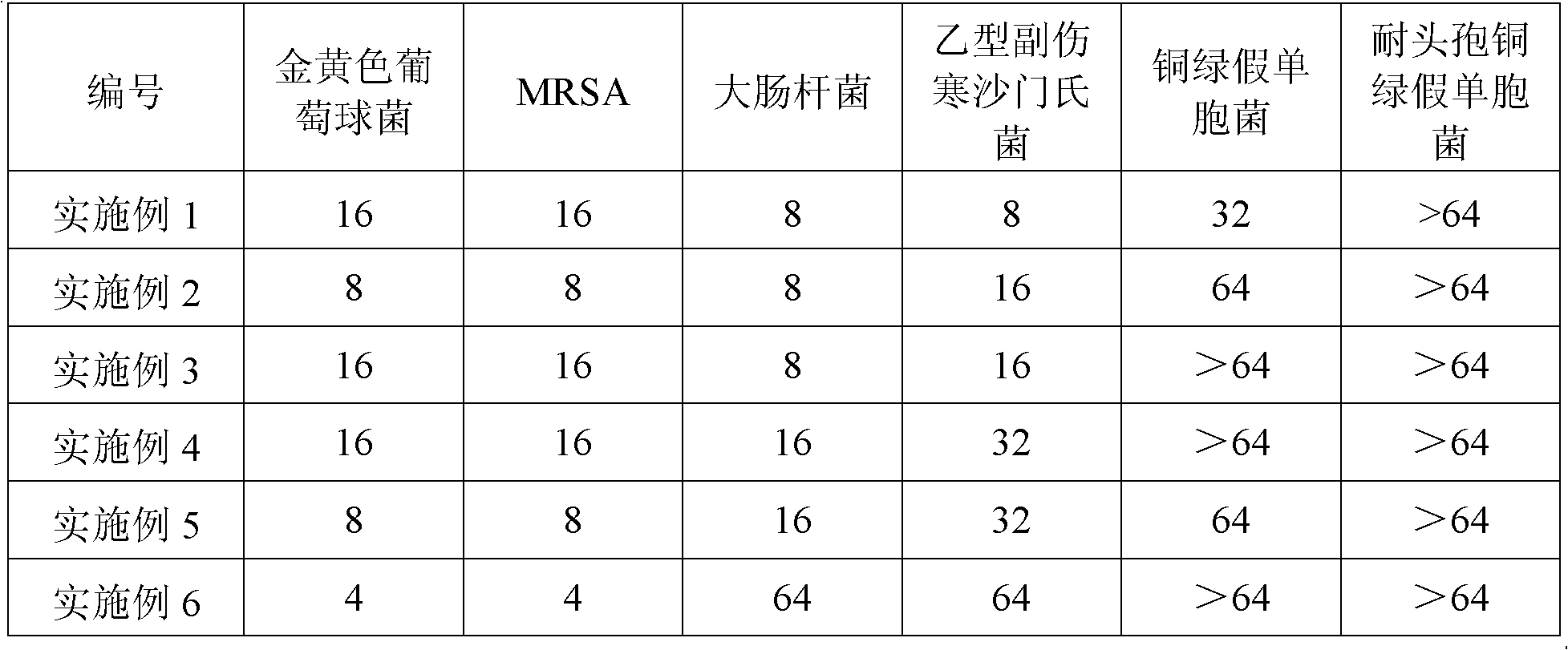
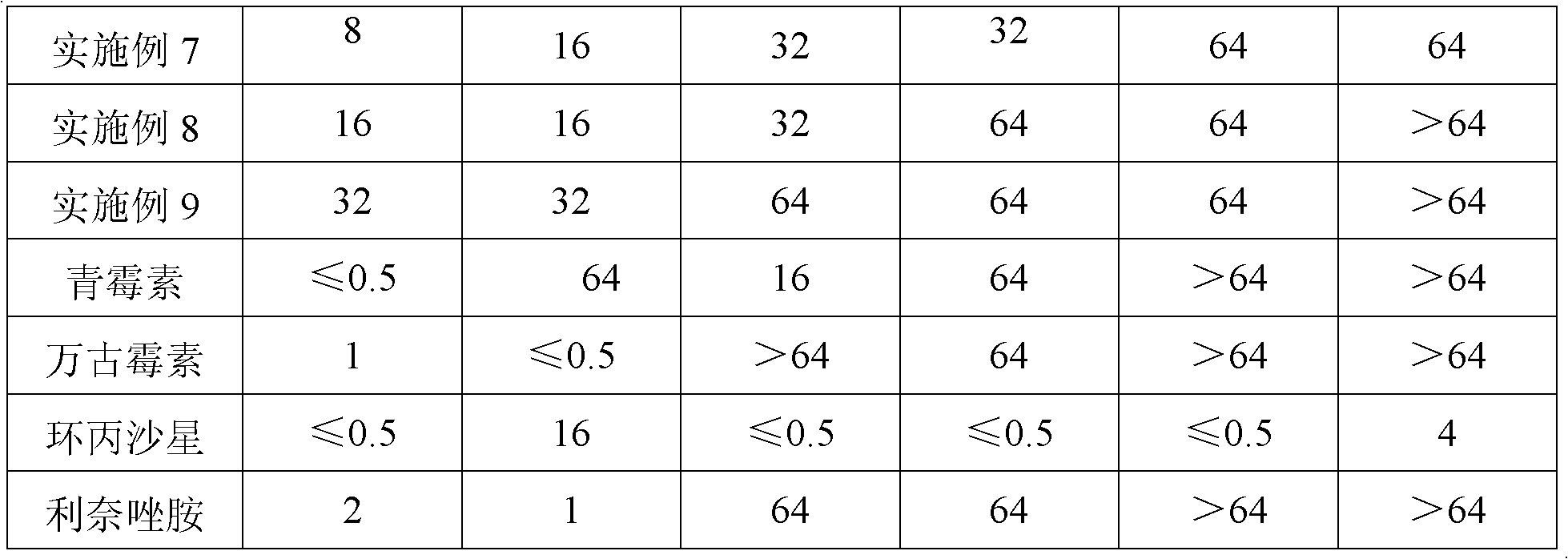
34 results about "Multidrug resistant bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Also known as: TB, multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB), or extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB), Mycobacterium tuberculosis ( M. tuberculosis) About: TB is caused by the bacteria M. tuberculosis, and is among the most common infectious diseases and a frequent cause of death worldwide.
Methods and Kits for Direct Detection and Susceptibility Profiling of Beta-Lactam Resistant Bacteria
InactiveUS20110245105A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBacteroidesBeta lactam resistant bacteria
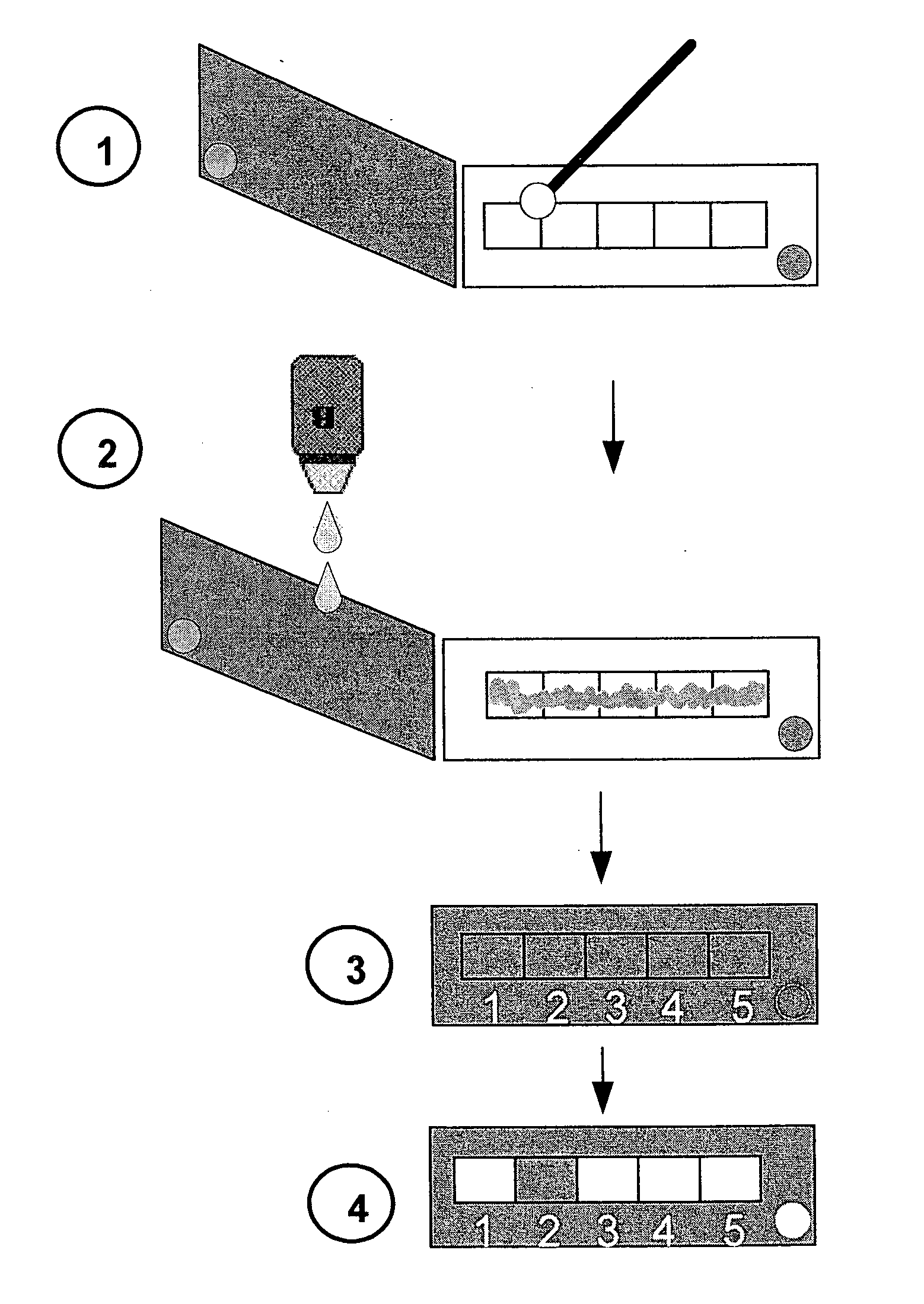
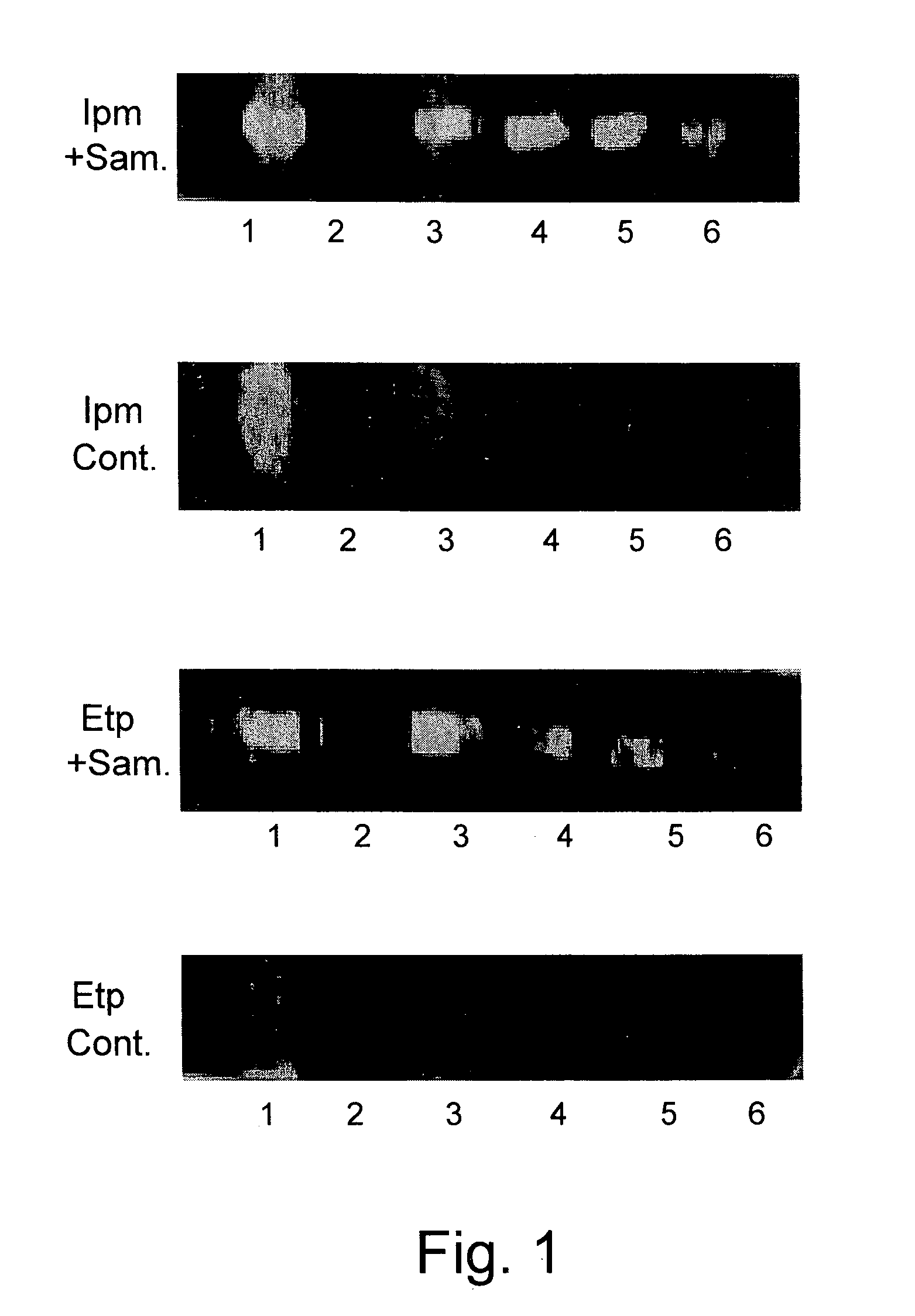
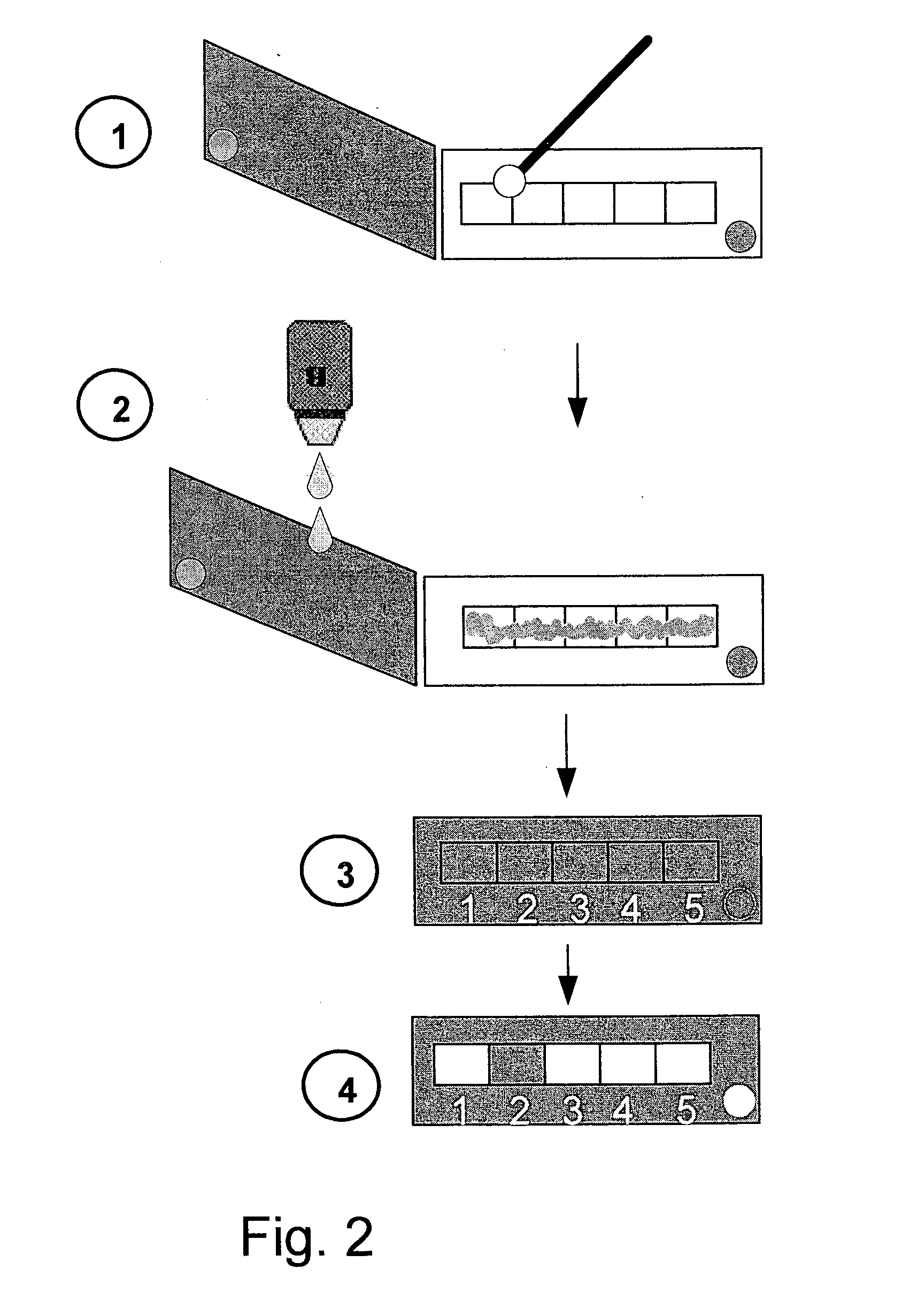
The present invention relates to a convenient, flexible and cost-efficient technology for detection and resistance-profiling of bacteria, enabling effective, evidence-based treatment of infections. The invention provides methods and modular kits for the rapid and direct detection of beta-lactam resistant bacteria in a test sample, and optionally for susceptibility profiling of the bacteria, by directly determining hydrolysis product / s of beta-lactam antibiotic substrates in the tested sample. The invention also provides methods and modular kits for the rapid and direct detection of the presence of multidrug resistant bacteria in a test sample.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
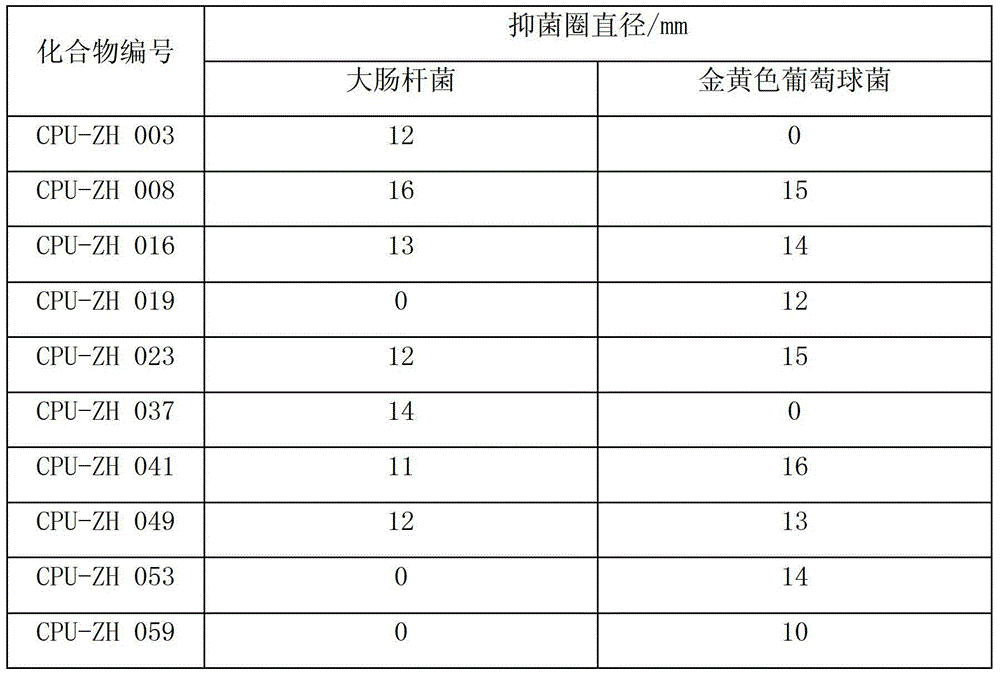
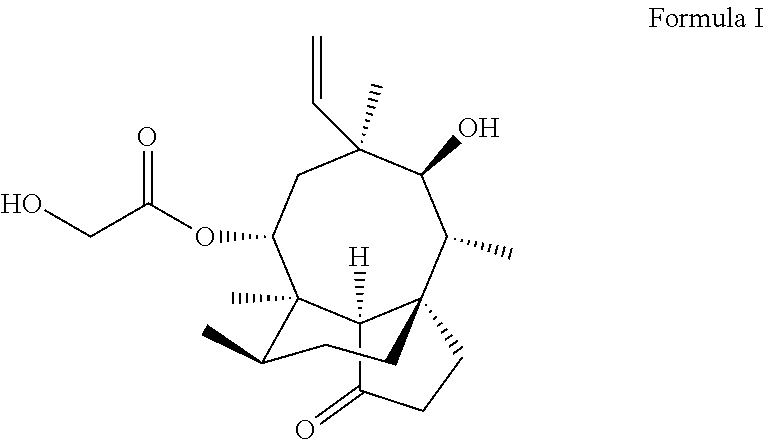
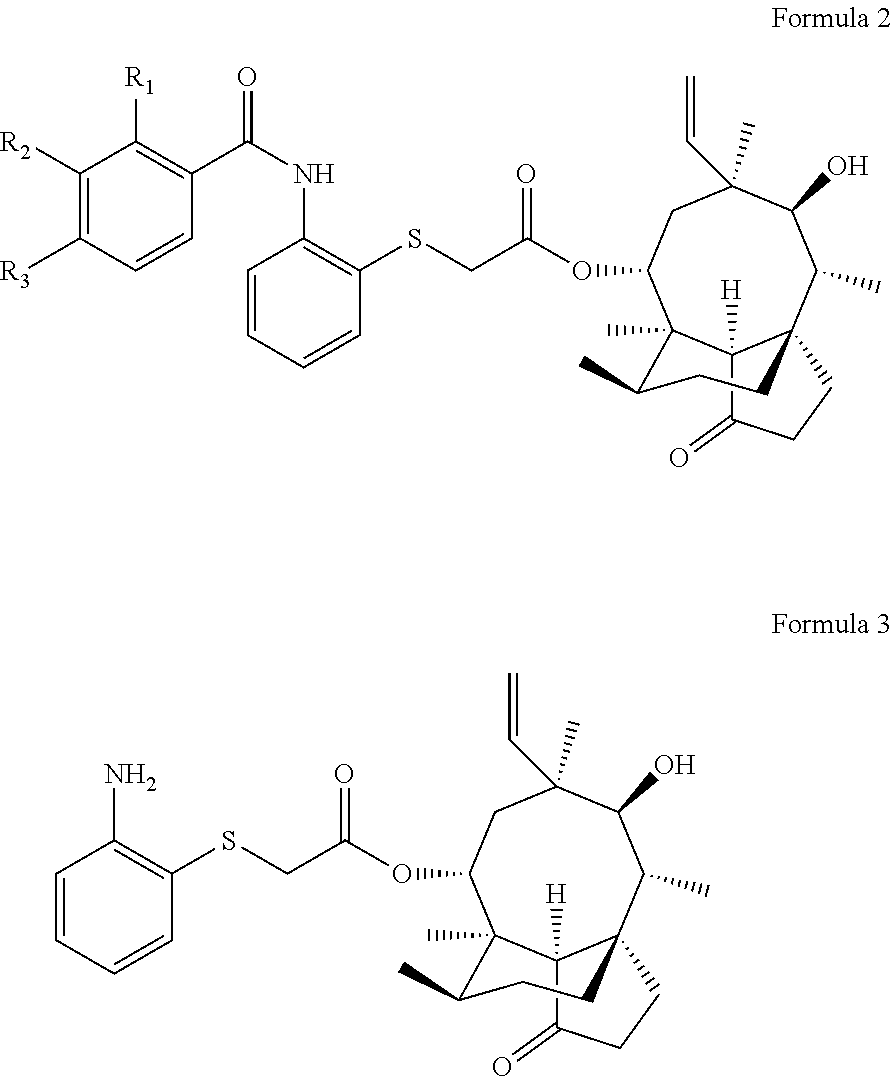
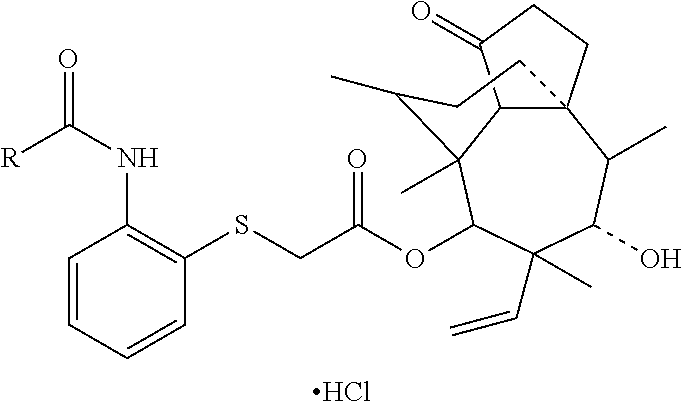
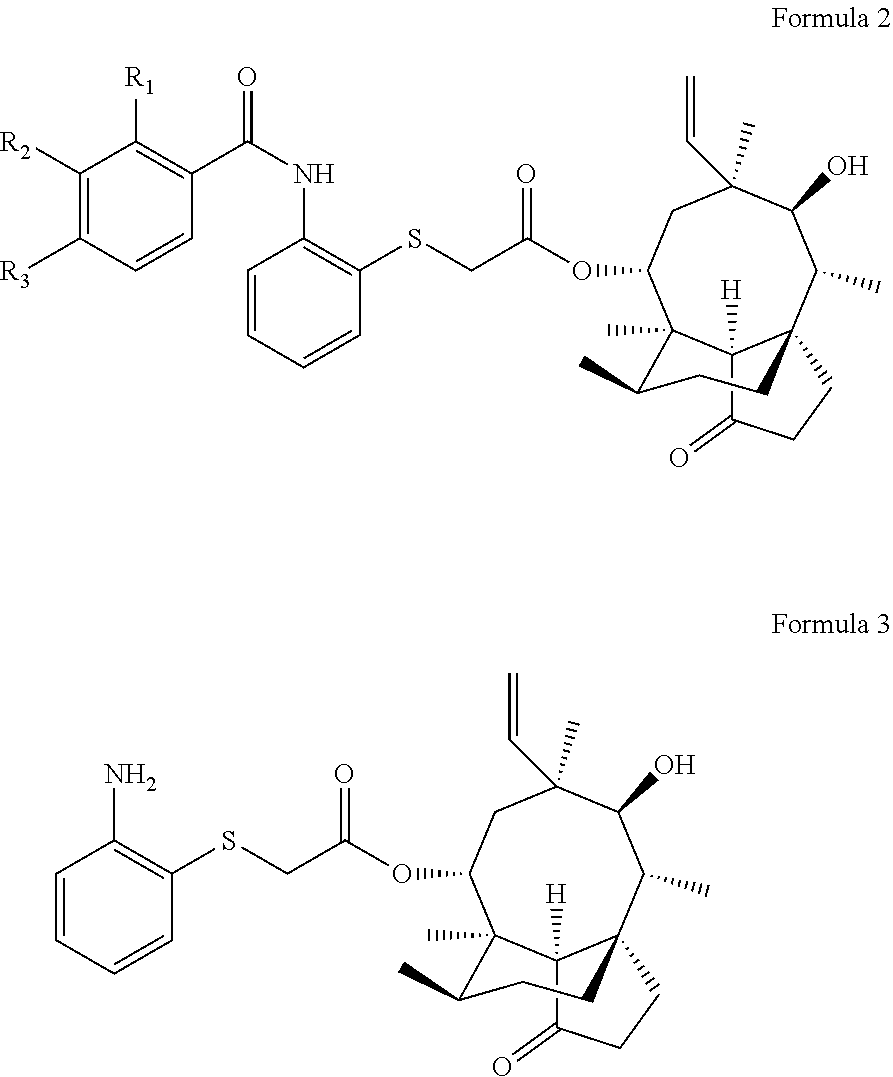
Pleuromutilin derivative with 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain and preparing method and application of pleuromutilin derivative
InactiveCN106565564AGood in vitro antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsSulfonic acid esters preparationSide chainStaphylococcus aureus
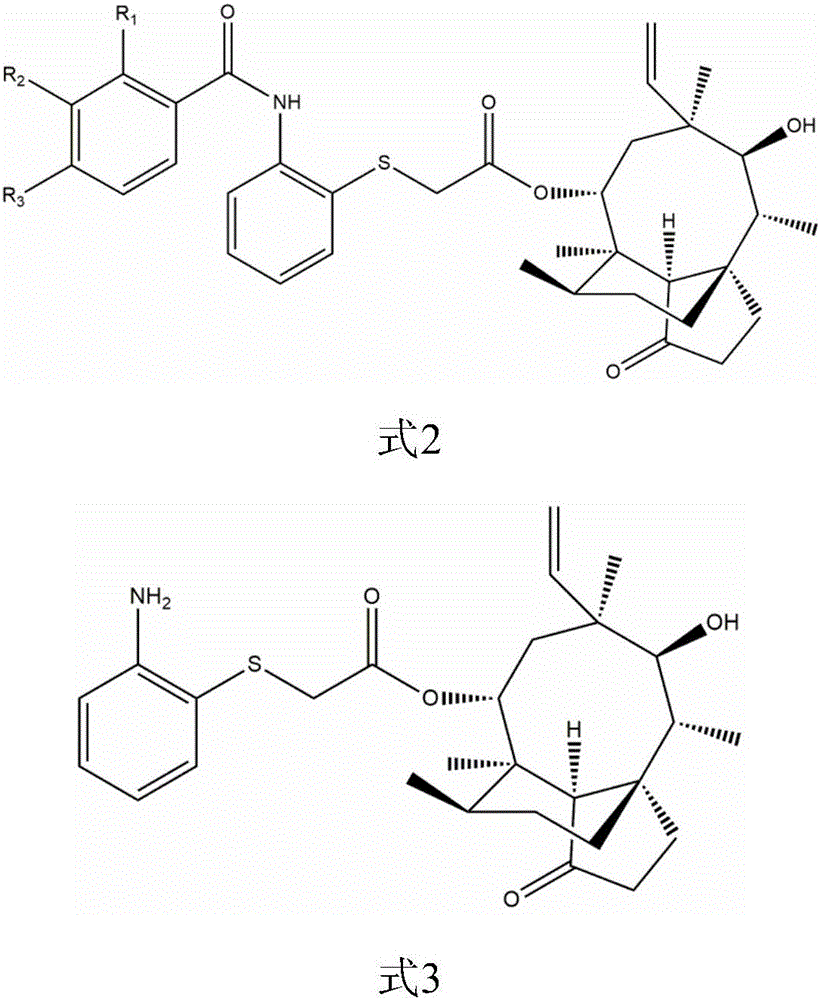
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry and discloses a pleuromutilin derivative with a 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain and a preparing method and application of the pleuromutilin derivative. The compound has the structures shown in formula 2 and formula 3, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are respectively and independently selected from the hydrogen atom, the hydroxyl, the amino, the sulfydryl, the hydroxymethyl, the amine methyl, the nitro, the halogen, the trihalogenated methyl, the methyl, the natural amino acid acylamino and the C1-6 alkoxy. The pleuromutilin derivative with the 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain has good activity for inhibiting the drug resistant staphylococcus aureus and the mycoplasma and is particularly suitable for serving as a novel antibacterial medicine for preventing infectious diseases caused by the human or animal mycoplasma or drug resistant staphylococcus aureus or multidrug resistant bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antisense peptide nucleic acid of cell penetrating peptide-mediated antibacterial RNA polymerase sigma 70 factor gene rpoD
InactiveCN101891804AGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesDisease
The invention provides a group of peptide nucleic acid-cell penetrating peptide antisense antibacterial sequences taking bacterial gene rpoD as a target. The cell penetrating peptide-mediated antibacterial RNA polymerase sigma 70 factor gene rpoD which is antisense nucleic acid of a specificity target can selectively inhibit the expression of in-vivo ropD genes of Gram-negative bacterium (containing sensitive and multidrug resisting clinical pathogenicity Escherichia coli, salmonellatyphimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae and pseudomonas aeruginosa) or gram-positive bacterium (containing sensitiveand multidrug resisting staphylococcus aureus) and further inhibit bacteria growth and reproduction, thus having the advantages of good antibacterial effect, low toxicity, good stability and better tolerance. The invention also discloses a chemical preparation method of a peptide nucleic acid-cell penetrating peptide solid phase. The antibacterial peptide synthesized in the invention can be used for preparing multidrug-resistant bacteria infection proofing antisense drugs and has the potency of being developed into a broad-spectrum antisense antibacterial agent which is expressed by efficiently transferred and peculiarly blocked bacterium disease-causing genes.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
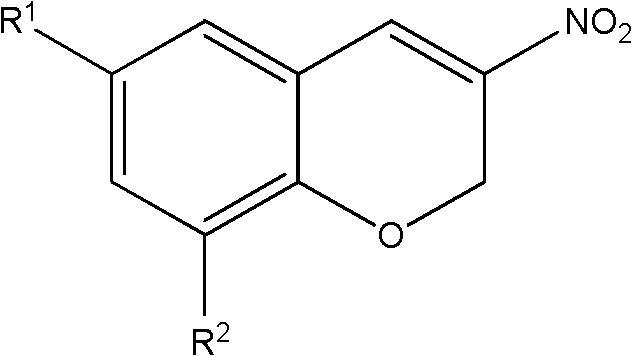
3-nitro-2h-chromene compounds with antibacterial activity and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102153533ANew structureAvoid the conundrum of easy aggregationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySalicylaldehydeAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses 3-nitro-2H-chromene compounds, a preparation method and application thereof. The 3-nitro-2H-chromene compounds have a novel antimicrobial parent nucleus structure, are prepared by reacting salicylaldehyde or substituted salicylaldehyde, n-Bu2NH, phthalic anhydride and 2-nitroethanol, and can be used for preparing medicaments for treating infectious diseases, particularly can be used for preparing medicaments for treating infectious diseases caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Antibacterial Macrolactin A that bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 produced in
InactiveCN101636501AShow broad-spectrum antimicrobial activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryMicroorganismAntibiotic Y
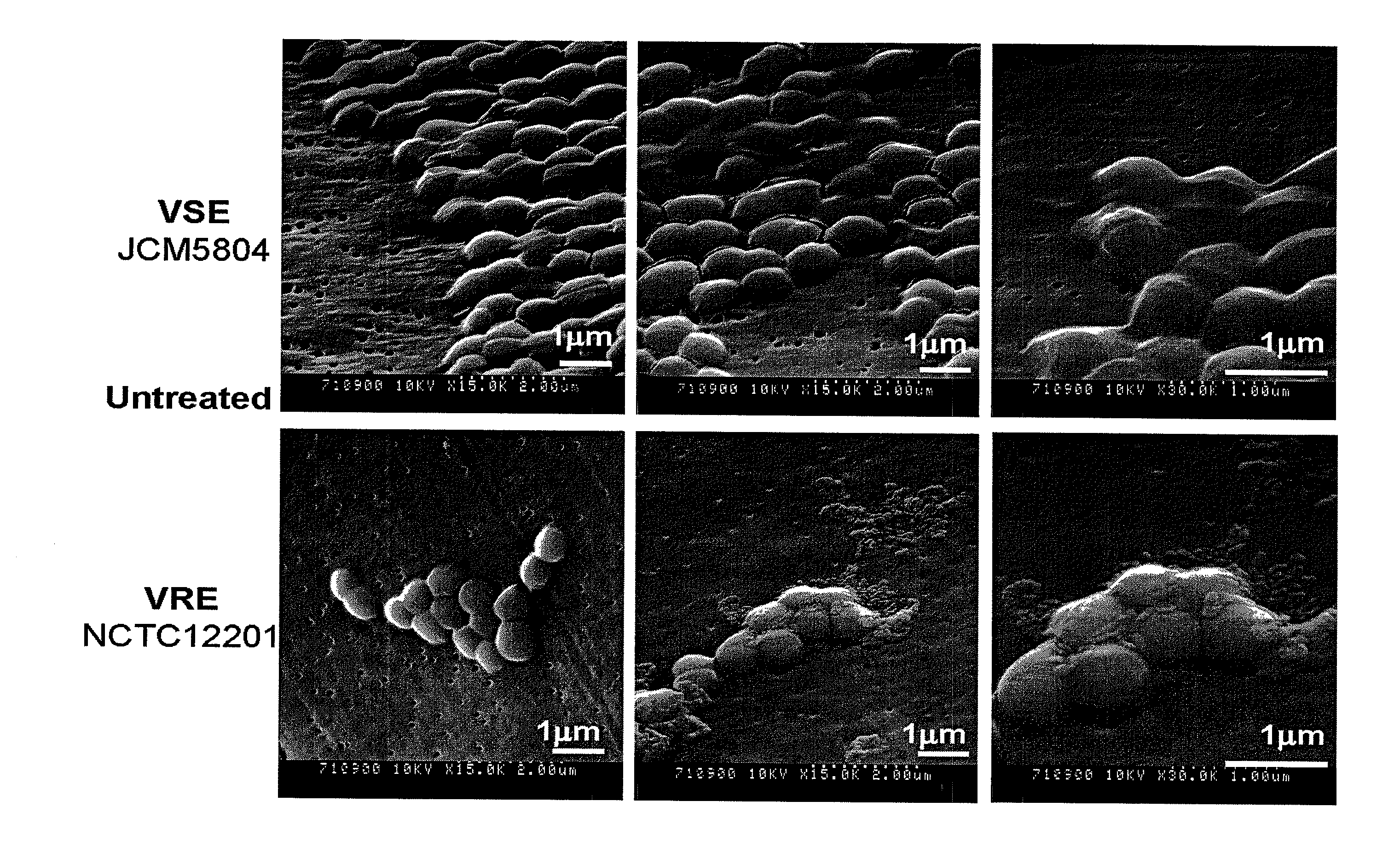
The present invention relates to uses of Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 (KCCM 10769P), which is a new bacillus strain, as an antibiotic. Macrolactin A of the present invention, which is produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, shows a broad spectrum of antibiotic activity against a variety of microorganisms and fungi, and is proved to be very efficient for the inhibition of particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) that are multidrug-resistant bacteria. The antibiotic Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, can be used as an excellent antibiotic against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), and thus the present invention is a very useful invention for medical industry.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Functional nano-selenium and preparation thereof as well as application of functional nano-selenium in preparation of anti-bacteria and sterilization drugs
InactiveCN104447660APromote growthImprove biological activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell membraneAcetylcholine Chloride
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of nano-selenium, and discloses functional nano-selenium and preparation method thereof as well as application of functional nano-selenium in preparation of anti-bacteria and sterilization drugs. The functional nano-selenium is at least one of nano-selenium modified by quercetin, nano-selenium modified by acetylcholine chloride and nano-selenium modified by quercetin-acetylcholine chloride. The functional nano-selenium has the activity for killing bacteria and multidrug resistant bacteria, also has the biological activity for inhibiting the growth of bacteria and multidrug resistant bacteria, and is suitable for preparing drugs for inhibiting the growth of bacteria and multidrug resistant bacteria and sterilization drugs. The functional nano-selenium is simple in preparation method, can be obtained through in-situ reduction modification, and can be directly stored and used. The functional nano-selenium is modified through various functions, so that the targeting property of the functional nano-selenium is improved, the transportation and transmembrane absorption of the functional nano-selenium in a bacteria cell membrane are improved, the medicine intake of bacteria can be increased, and the discharge is reduced, so that the fact that drugs in bacteria cells are kept at a higher level is ensured.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Positive Bacteria Antibacterial Agent and Topical Agent
InactiveUS20160303148A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesGram-positive bacterium
To provide a multidrug-resistant Gram positive bacteria antibacterial agent containing as an active ingredient a novel component to which multidrug-resistant bacteria are not resistant, and an external agent containing the same. The multidrug resistant Gram-positive bacteria antibacterial agent according to the present invention contains an amphipathic compound having an HLB value of greater than 9.5 and 20 or less and an acyl group as an active ingredient. The external agent according to the present invention contains the multidrug resistant Gram-positive bacteria antibacterial agent.
Owner:Q P CORP
Antimicrobial peptide having synergistic antibacterial effect with antibiotics on multidrug resistant bacteria, and use thereof
ActiveUS20200040035A1High antibacterial activityImprove antibacterial propertiesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyMulti resistant bacteria
The present invention relates to an antimicrobial peptide having an improved antibacterial effect through glutamic acid substitution and, more specifically, to a use of the antimicrobial peptide as an active ingredient in an antibacterial pharmaceutical composition, a food additive, a feed additive, an antiseptic composition, and an antibacterial quasi-drug composition. Not only does the antimicrobial peptide of the present invention exhibit significant antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria, but it also exhibits a significant synergistic effect when combinedly treated with antibiotics which have strong antibacterial activity only against gram-positive bacteria and has no or low antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria, thereby exhibiting excellent antibacterial effects on gram-positive bacteria, E. coli and Acinetobacter bacteria among gram-negative bacteria, and antibiotic-resistant strains thereof.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV IND COOP CORP
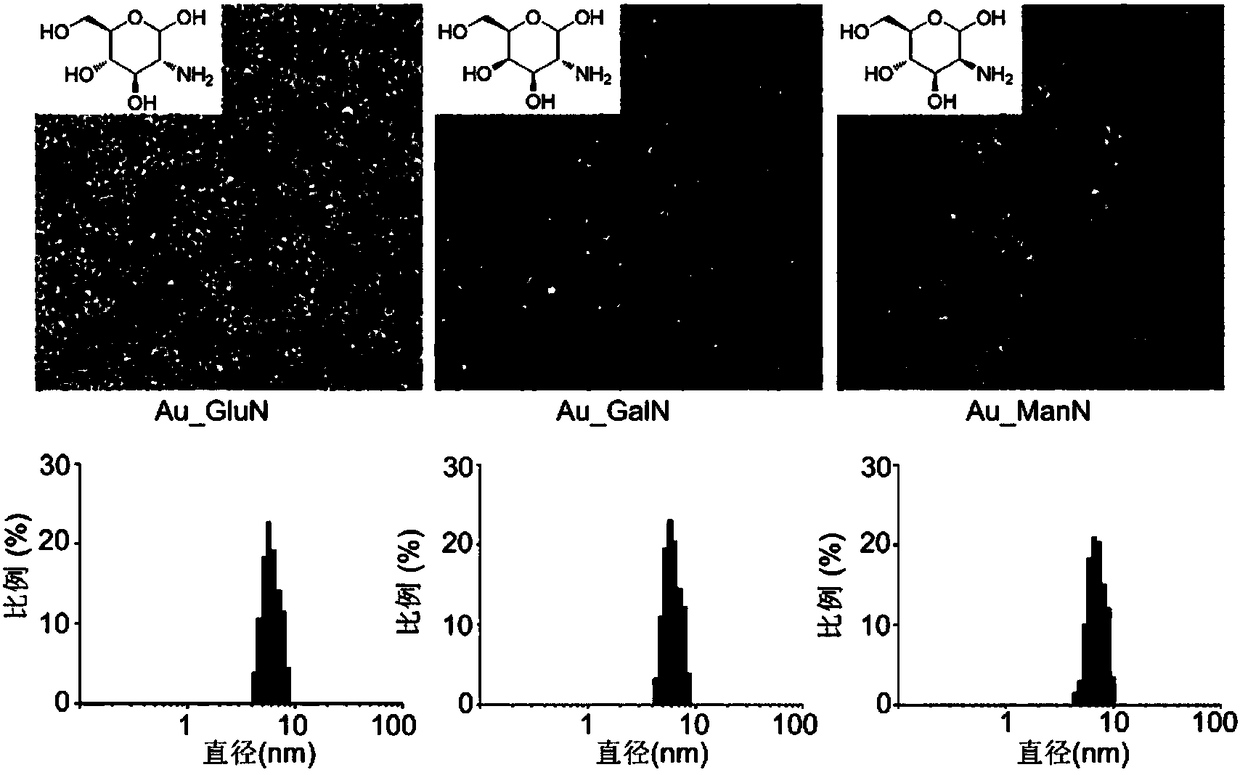
Amino sugar modified antibacterial gold nanoparticle and preparation method thereof, and applications
ActiveCN109108275AImprove antibacterial propertiesGood biocompatibilityAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsMedicineNanoparticle
The invention provides an amino sugar modified antibacterial gold nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof, and applications. The prepared antibacterial gold nanoparticle has an excellent antibacterial property, and can resist multidrug resistant bacteria; and the antibacterial gold nanoparticle is good in biocompatibility and low in toxicity to body cells. The antibacterial gold nanoparticlecan be used for clinical wound management, operations to prevent organs from adhering, beauty treatment, and various wound infections such as burn, scald and bedsore infections, so that the antibacterial gold nanoparticle is an extremely excellent medical antibacterial material.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
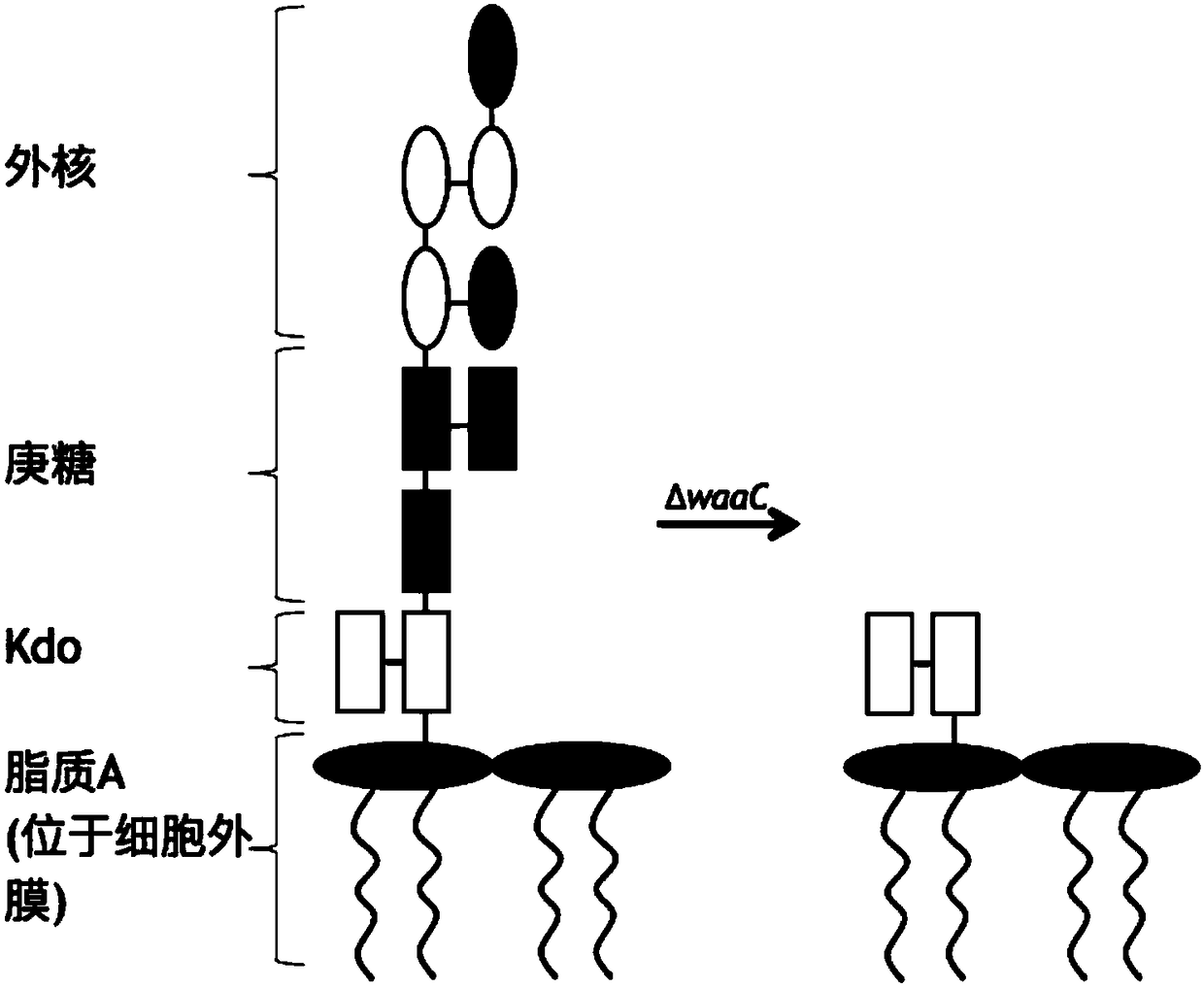
Method for evolving host specificity of bacteriophage
InactiveCN108265035AGrowth inhibitionComplementAntibacterial agentsBacteriaSynthetic biologyAntibiotic Y
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnologies, and provides a method for evolving the host specificity of a bacteriophage by the aid of a springboard host, the obtained springboard host and the obtained bacteriophage. The method, the springboard host and the bacteriophage have the advantages that lipopolysaccharide structures in bacteriophage hosts start to be transformed from known bacteriophages with clear genetic backgrounds by the aid of ideas and means of evolutionary biology and synthetic biology to obtain the springboard host, the springboard host can be infected by bacteriophages to obtain bacteriophages with variant receptor binding proteins, and the host specificity of the bacteriophages is changed, so that new host bacteria can be recognized and infected by the bacteriophages; as shown by experiments, the obtained bacteriophage can resist Gram-negative bacteria and multidrug-resistant bacteria, plaque can be generated, growth can be inhibited, and the bacteriophage has the potential of supplement and reinforcement effects for bacteria infection treatment by the aid of antibiotics.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
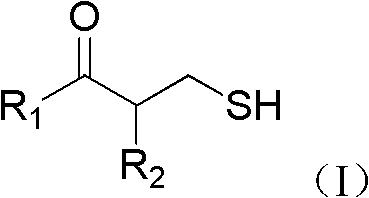
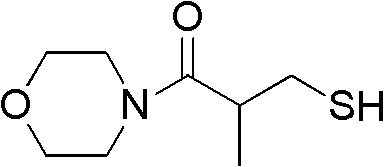
Application of 3-mercaptopropionic acid amide compounds
InactiveCN103156856AReduce or even eliminate hydrolysisGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsAmide active ingredientsMultidrug resistant bacteria3-Mercaptopropionic Acid
The invention provides application of 3-mercaptopropionic acid amide compounds with the following general formula (I) in medicine which restrains the activity of multidrug-resistant bacteria through restraining the activity of NDM-1, wherein R1 is selected from a formula and R2 is selected from a C1-C4 alkyl group.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Antimicrobial agent for gram-positive bacteria
InactiveUS20100285140A1Safety for human healthPrevent bacterial growthAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBacteroidesAdditive ingredient
A novel antibacterial agent for Gram-positive bacteria which disregards the drug-resistant mechanisms of bacteria is disclosed. The antibacterial agent contains as an effective ingredient particles having a particle diameter of not more than 5 μm, which particles are adhesive to cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria and not adhesive to mammalian cell membrane and substantially do not contain an active antibacterial ingredient effective against Gram-positive bacteria. By the antibacterial agent according to the present invention, the growth of the multidrug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria such as MRSA and VRE can be inhibited, as well as the occurrence of novel multidrug-resistant bacteria, which is a big problem in use of antibiotics, can be avoided.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV
Substituted polyamines as inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps
Disclosed are methods of treating bacterial infections including those caused by multidrug resistant bacteria using polyamine efflux pump inhibiting compounds, including for example N-benzylated polyazaalkanes, N-benzylated polyaminoalkanes, or mixed N-benzylated poly(aza / amino)alkanes, optionally in combination with other drugs such as antibiotics, as well as pharmaceutical compositions thereof.
Owner:PARATEK PHARM INC
Antibacterial macrolactin a that bacillus polyfermenticus kjs-2 produced in
InactiveUS20100087516A1Broad spectrum of antibiotic activityExcessive activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismEnterococcus avium
The present invention relates to uses of Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 (KCCM 10769P), which is a new bacillus strain, as an antibiotic. Macrolactin A of the present invention, which is produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, shows a broad spectrum of antibiotic activity against a variety of microorganisms and fungi, and is proved to be very efficient for the inhibition of particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) that are multidrug-resistant bacteria. The antibiotic Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, can be used as an excellent antibiotic against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), and thus the present invention is a very useful invention for medical industry.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Alginate oligomers for use in overcoming multidrug resistance in bacteria
ActiveUS20150238520A1Effective approachOvercoming antibiotic resistanceBiocideSenses disorderBacteroidesOligomer
The invention provides a method of overcoming resistance to at least one antibiotic in a multidrug resistant bacterium, said method comprising contacting said bacterium with an alginate oligomer together with the antibiotic. The multidrug resistant bacterium may be on an animate or inanimate surface and both medical and non-medical uses and methods are provided. In one aspect the invention provides an alginate oligomer for use together with at least one antibiotic in treating a subject infected, suspected to be infected, or at risk of infection, with a multidrug resistant bacterium to overcome resistance to the antibiotic in said multidrug resistant bacterium. In another aspect the method can be used to combat contamination of a site with multidrug resistant bacteria, e.g. for disinfection and cleaning purposes.
Owner:ALGIFARMA IPR AS
Substituted polyamines as inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps
InactiveUS20110218168A1High activityImprove drug activityBiocideSugar derivativesAntibiotic YPolyamine
Disclosed are methods of treating bacterial infections including those caused by multidrug resistant bacteria using polyamine efflux pump inhibiting compounds, including for example N-benzylated polyazaalkanes, N-benzylated polyaminoalkanes, or mixed N-benzylated poly(aza / amino)alkanes, optionally in combination with other drugs such as antibiotics, as well as pharmaceutical compositions thereof.
Owner:PARATEK PHARM INC
Multifunctional cloth
InactiveCN102061612AImprove the air environmentImprove odorCurtain accessoriesFibre treatmentStaphylococcus aureusBacilli
The invention provides a multifunctional cloth. By using the ionization effect of low-level microscale radiation which is not apparently different from that from natural ores in BG, that is, the radiation harmless to the human, under the condition of needing no artificial energy, light sources, etc., the multifunctional cloth has the effective antibacterial effect and the deodorizing effect constantly in 24 hours, is suitable for indoor application, and in excellent is infection prevention and deodorization. Ceramics containing uranium-series nuclides or thorium-series nuclides are fixed on a grey cloth to form the multifunctional cloth with excellent infection prevention and deodorization. The multifunctional cloth is characterized in that, by the ionization effect of the ceramics, when bacteria evaluated by the JIS-L-I902 bacteria transferring method is reduced, the multidrug resistant bacteria MRSA, the pneumobacillus and the staphylococcus aureus are all more than 0.0, and the deodorization efficiency of ammonium odour obtained by the deodorization experiment according to the JIS-L-2017-103 method is higher than 90%.
Owner:E G CYCLE LAB +1
Disubstituted bicyclic derivative and application thereof as efflux pump inhibitor to anti-microbial
InactiveCN106008373AHas antibacterial synergistic effectAntibacterial synergistic effect is obviousAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationAntibiotic YStructural formula
The invention discloses a disubstituted bicyclic derivative and application thereof as an efflux pump inhibitor to anti-microbial. It is proved by experiments that the disubstituted bicyclic derivative has a good inhibition function on multidrug-resistant bacteria carrying an AcrB efflux pump and can effectively recover or enhance antibacterial efficiency of existing antibiotics. The chemical structural formula of the disubstituted bicyclic derivative is as shown in a formula (I) (the formula can be seen in specification), and R1, R2, X, Y, Z and W are as defined in the specification.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Experiment method for multidrug resistant bacterial infection of burn wounds
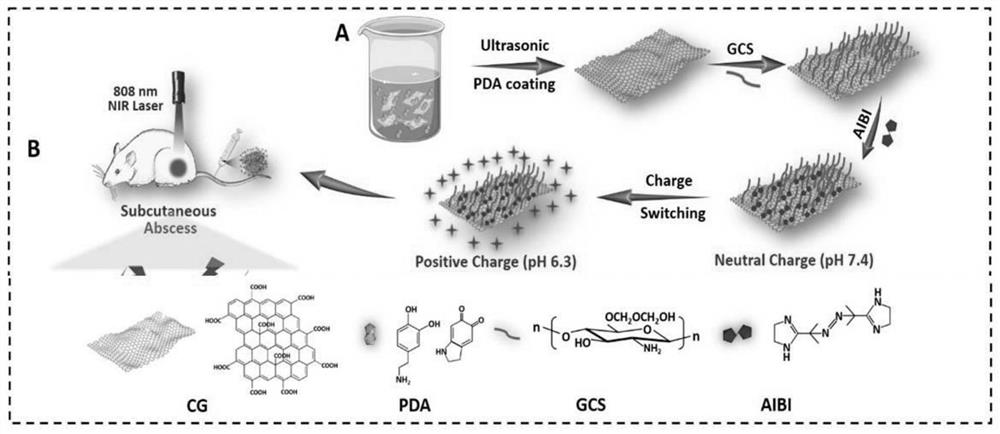
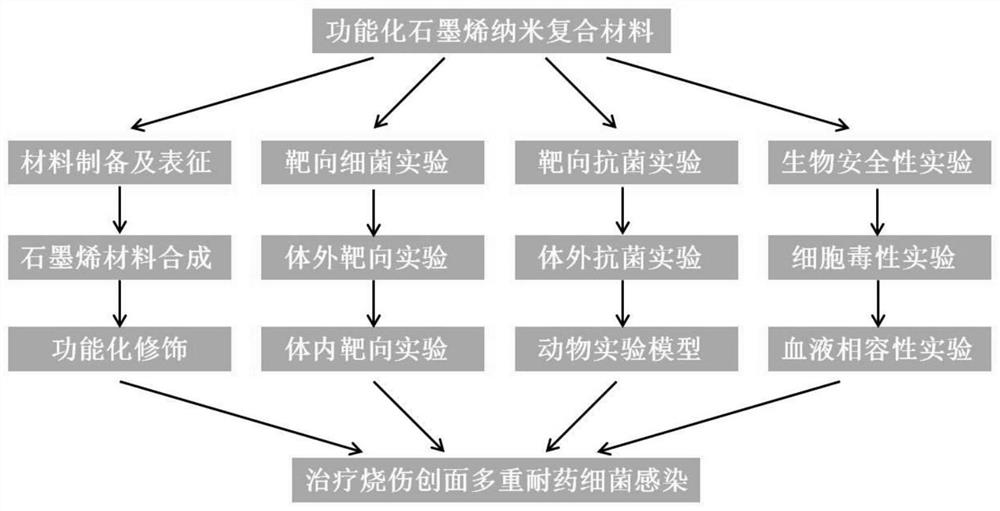
PendingCN111676267AEasy to exploreCompounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementAntimicrobial actionIn vivo
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, in particular to an experiment method for multidrug resistant bacterial infection of burn wounds. The experiment method comprises the following steps of A, performing target bacteria action research on a functional graphene nanometer composite modified with a free radical initiating agent under in vivo and in vitro conditions; B, under thein vivo and in vitro conditions, performing photo-irradiation induced target antibiotic action research on the functional graphene nanometer composite modified with the free radical initiating agentunder in vivo and in vitro conditions; C, performing research of influence of the functional graphene nanometer composite modified with the free radical initiating agent on multidrug resistant bacterial infection wound healing and an action mechanism of the functional graphene nanometer composite modified with the free radical initiating agent; and D, performing research on the biological safety of the functional graphene nanometer composite modified with the free radical initiating agent. Under complex conditions, the invention provides more selections for an application of photodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy under complex conditions, provides a new treatment direction and strategy for multidrug resistant bacterial infection of burn wounds, and is favorable for further exploration of a new multi-functional nanometer platform for multidrug resistant bacteria treatment.
Owner:中国人民解放军32298部队
Antimicrobial agent for gram-positive bacteria
InactiveCN101959523ABroaden access to treatmentAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBacteroidesCell membrane
Disclosed is a novel antimicrobial agent for Gram-positive bacteria extending beyond the mechanism of bacterial drug resistance. The antimicrobial agent contains, as active ingredients, particles which adhere to a Gram-positive bacterial cell wall and do not adhere to a mammalian cell membrane, have a particle diameter of 5 [mu]m or less, and practically do not contain an antimicrobially active component against Gram-positive bacteria. According to the antimicrobial agent of the invention, antimicrobial effect also on Gram-positive bacteria showing multidrug resistance typified by MRSA and VRE can be achieved. Further, the emergence of new multidrug resistant bacteria which becomes a major problem in the use of an antibiotic can be avoided.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV
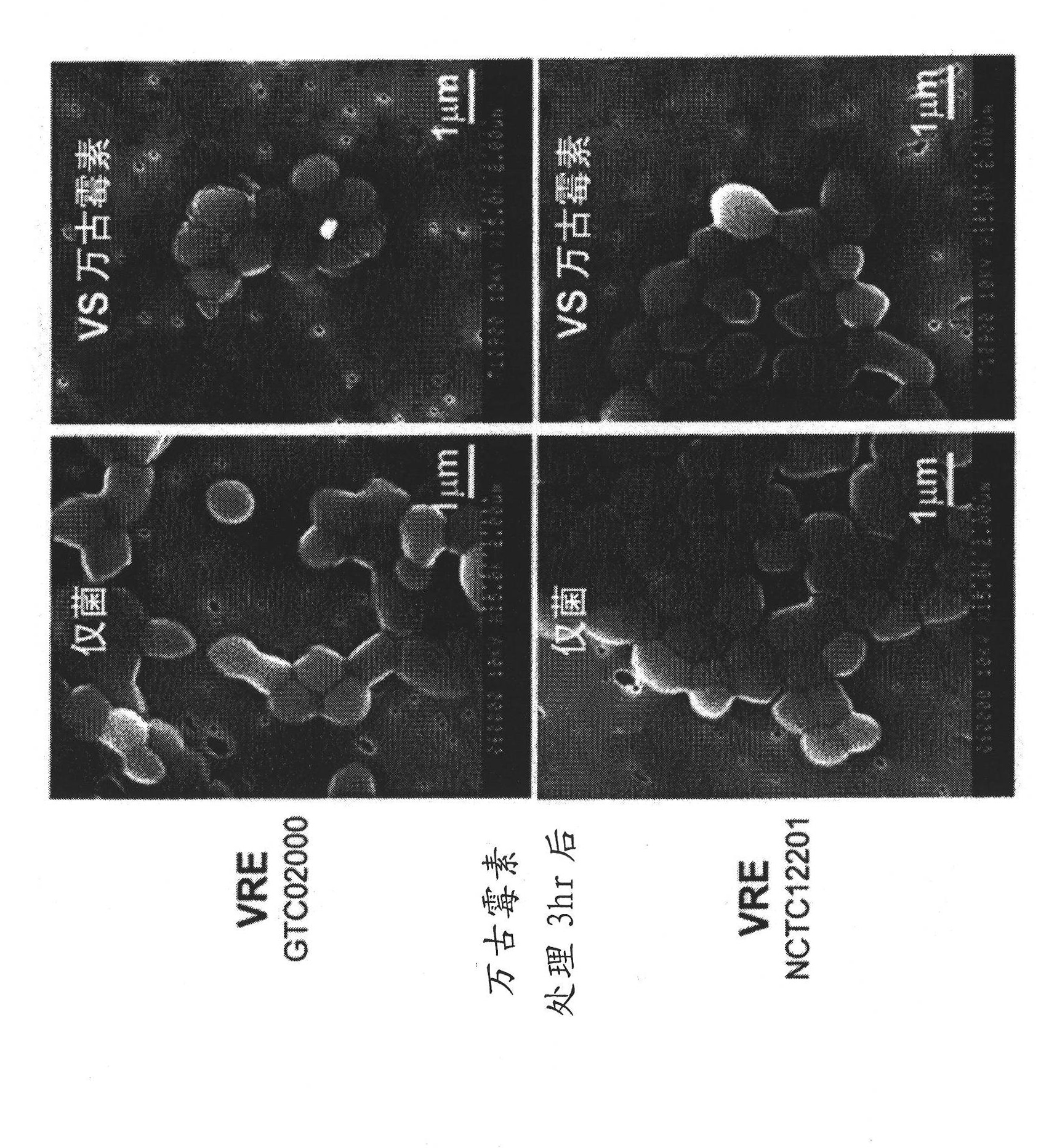
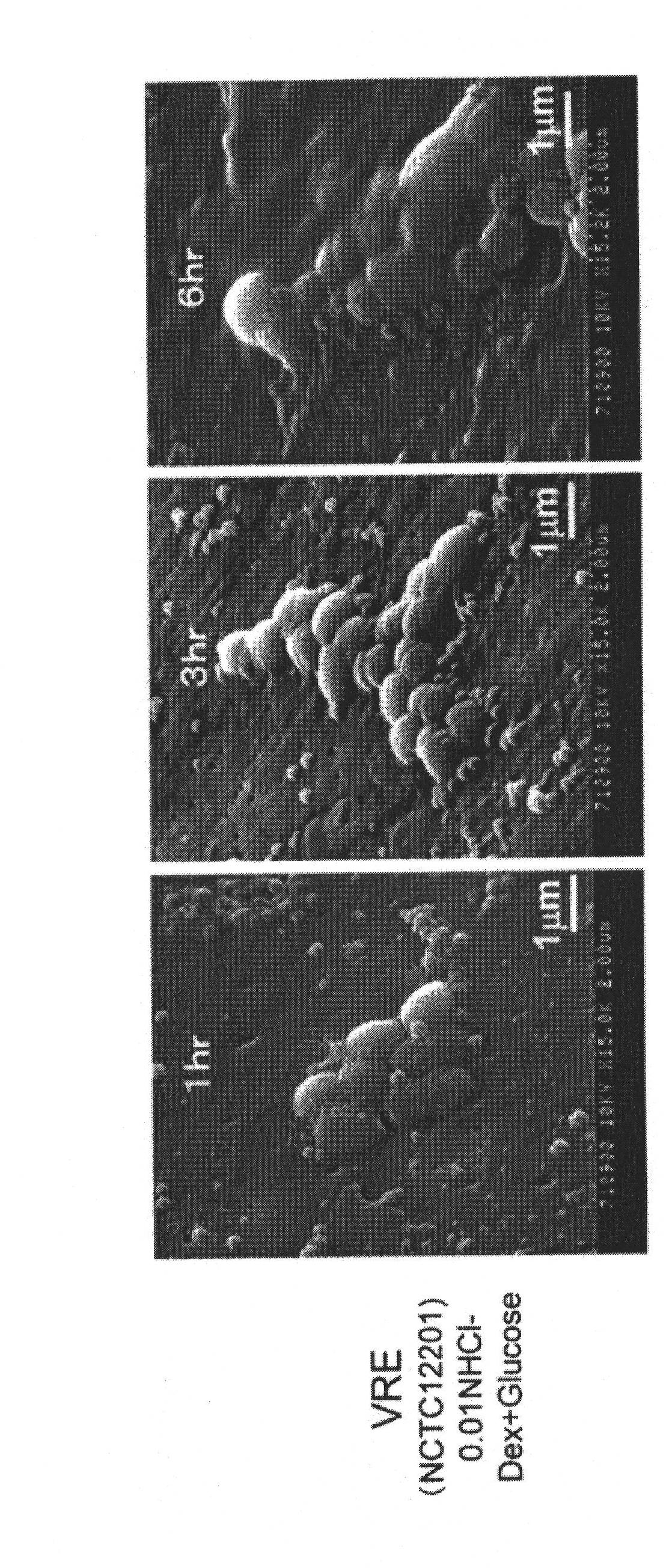
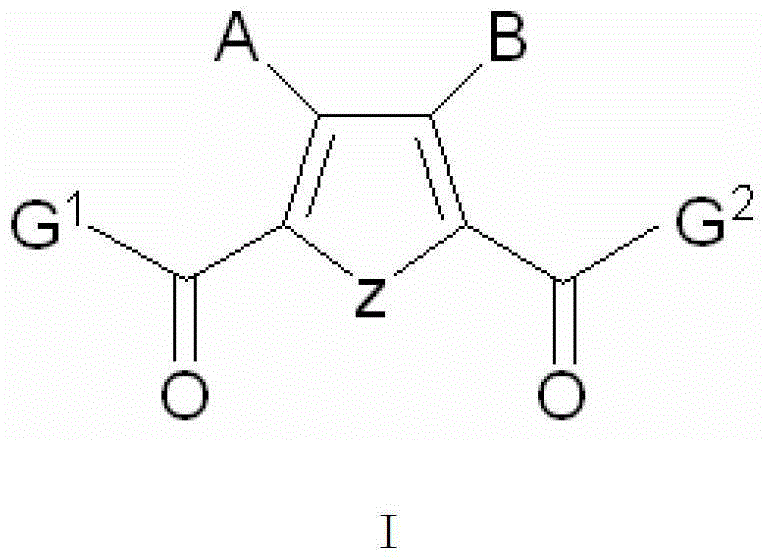
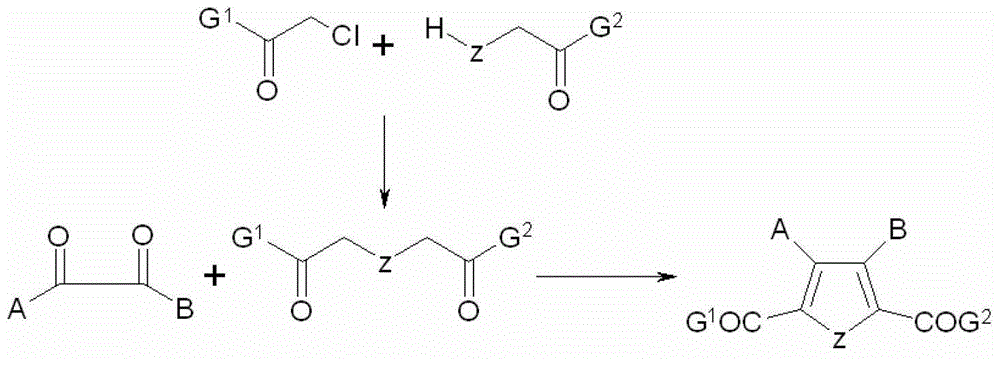
Five-membered heterocyclic dicarbonyl derivative and applications thereof for resisting multidrug-resistant bacteria
The invention relates to the field of medicinal chemistry, and particularly relates to a five-membered heterocyclic dicarbonyl derivative (I) and applications thereof for resisting multidrug-resistant bacteria. Proved by pharmacological tests, the compound is jointly combined with antibiotics, thus having better inhibition effect on the multidrug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Pleuromutilin derivative having 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS10421715B2High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsSulfonic acid esters preparationSide chainStaphylococcus aureus
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Alginate oligomers for use in overcoming multidrug resistance in bacteria
The invention provides a method of overcoming resistance to at least one antibiotic in a multidrug resistant bacterium, said method comprising contacting said bacterium with an alginate oligomer together with the antibiotic. The multidrug resistant bacterium may be on an animate or inanimate surface and both medical and non-medical uses and methods are provided. In one aspect the invention provides an alginate oligomer for use together with at least one antibiotic in treating a subject infected, suspected to be infected, or at risk of infection, with a multidrug resistant bacterium to overcome resistance to the antibiotic in said multidrug resistant bacterium. In another aspect the method can be used to combat contamination of a site with multidrug resistant bacteria, e.g. for disinfection and cleaning purposes.
Owner:ALGIFARMA IPR AS
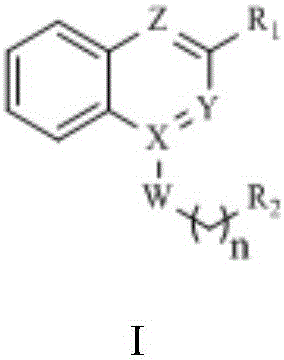
Benzoxazine oxazolidinone compound, preparation method and application thereof
Disclosed are a benzoxazine oxazolidinone compound shown by a general formula (I), an optical isomer thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof in preparing a drug for treating an infectious disease and in particular, an infectious disease caused by multidrug resistant bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of a tetraphenylethylene derivative in the preparation of antibacterial drugs
ActiveCN104224776BGood treatment effectGood resistance to planktonic bacteriaAntibacterial agentsDipeptide ingredientsHemolysisSide effect
The invention relates to an application of a tetraphenyl ethylene derivative in preparation of an antibacterial agent. The tetraphenyl ethylene derivative has a tetraphenyl ethylene structure with a substituent group on at least one benzene ring, can resist multidrug-resistant bacteria, especially can also resist planktonic bacteria and biofilm bacteria, can be used for effectively eliminating a biofilm, is low in cytotoxicity, has no hemolysis side effect, can be used for curing an animal model infected by common bacteria and multidrug-resistant bacteria and has a broad application prospect in the field of preparation of antibacterial agents.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Pyrimido-isoquinolin-quinone derivative compounds, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, isomers and tautomers thereof; pharmaceutical composition; preparation method; and use thereof in the treatment of diseases caused by bacteria and multidrug-resistant bacteria
The present invention provides pyrimidine-isoquinolin-quinone derivatives of formula I, their salts, isomers, pharmaceutically acceptable tautomers; pharmaceutical composition; preparation procedure; and their use in the treatment of bacterial and resistant bacterial diseases, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), intermediate vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VISA), vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus spp. (VRE), Enterococcus faecalis, Emerging Staphylococcus aureus with resistance to linezolid and / or bacterial strains not susceptible to daptomycin.Where the radicals R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are as defined in the work specifications of the present invention.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
Inhibitor of metallo-beta-lactamase produced by multi-drug resistant bacteria and preparation method thereof
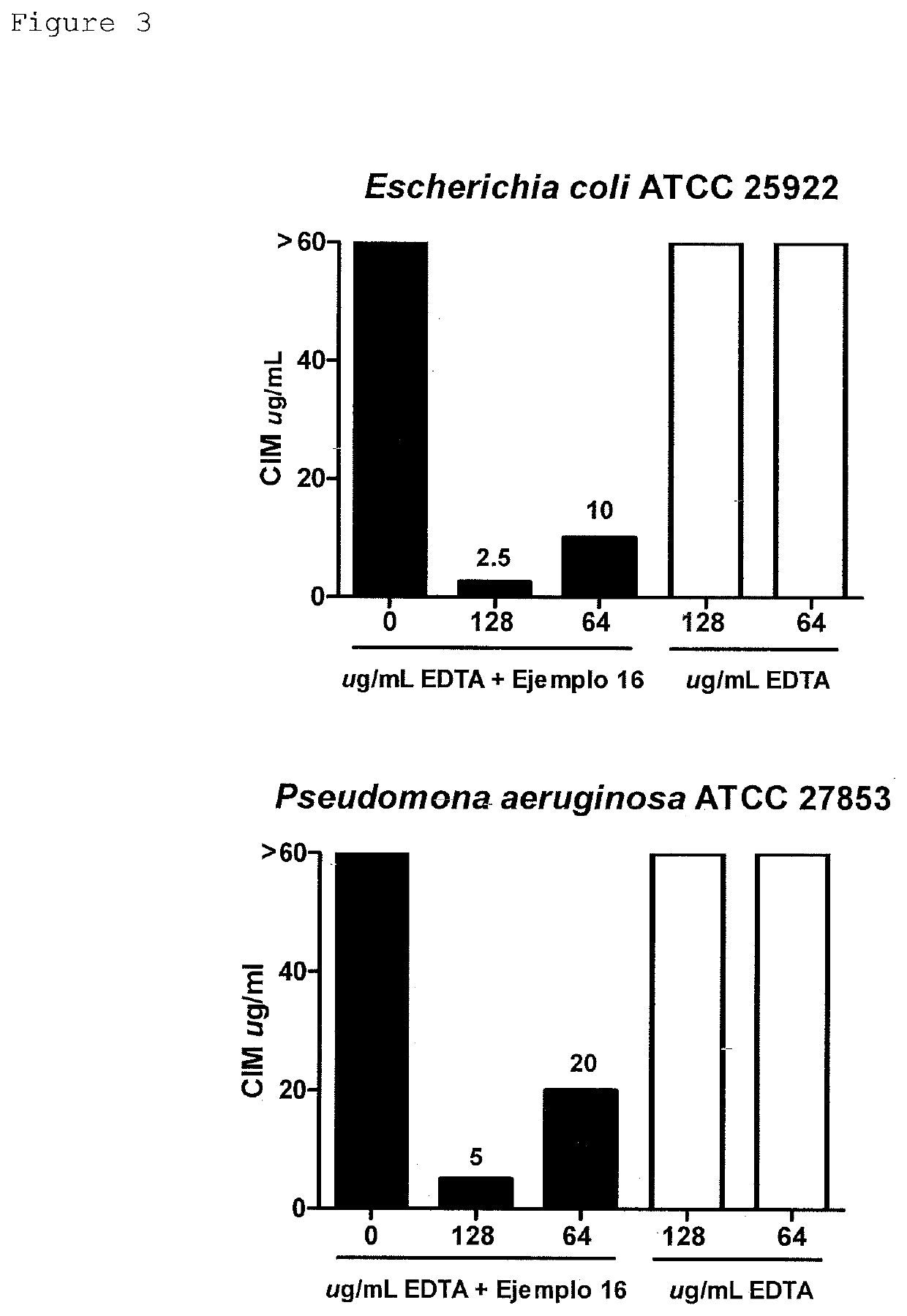
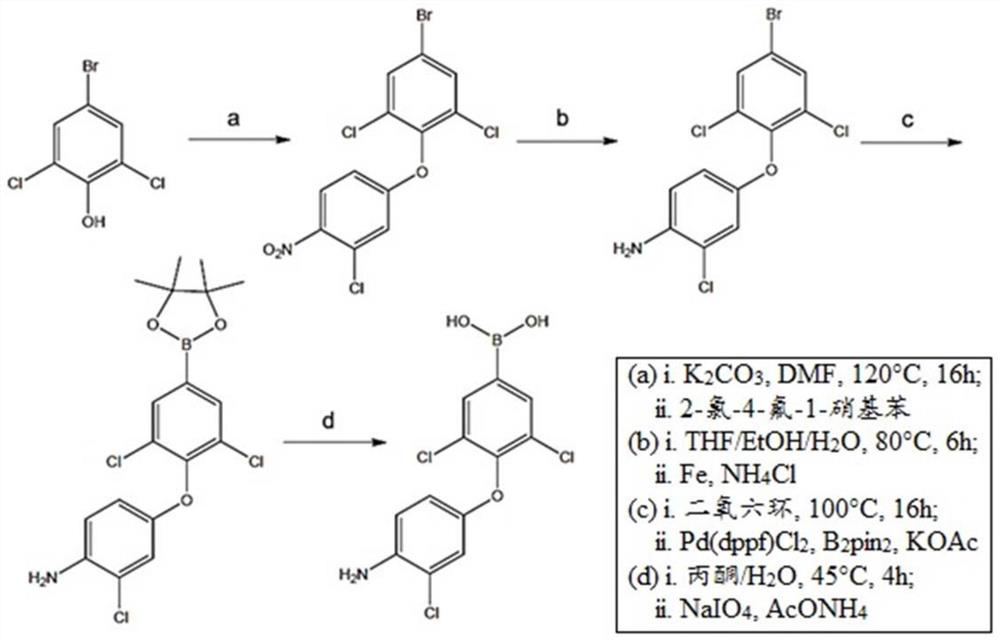
PendingCN113195505AFree from degradationAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsBoron compound active ingredientsChlorobenzeneBoronic acid
The present invention relates to a novel metallo-beta-lactamase (MBL) inhibitor of formula I and an antibacterial composition comprising the same for use in the treatment of multidrug resistant bacteria. In particular, the present invention relates to 3, 5-dichlorophenylboronic acid, (4-(4-amino-3-chlorophenoxy)-3, 5-dichlorophenylboronic acid, and (3, 5-dichloro-4-(2-hydroxyethoxy) phenyl) boronic acid. The compounds of formula I according to the present invention have inhibitory activity against broad spectrum metallo-beta-lactamase. By administering the MBL inhibitor of the present invention together with a beta-lactam antibiotic agent, it is possible to protect the antibiotic agent from degradation by MBL produced by microorganisms. Therefore, the time and range of the antibacterial agent activity can be extended or expanded. Some bacteria that are resistant to antibacterial agents due to the presence of MBL can be controlled by the composition of the invention. Therefore, the invention can be used for treating or preventing infection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND
Antibacterial agent against multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacteria and external agent
ActiveUS20180289726A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGram-positive bacteriumBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:Q P CORP
Functionalized nano-selenium and its preparation and application in the preparation of bacteriostatic and bactericidal drugs
InactiveCN104447660BBiologically activeGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell membraneAnti bacteria
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of nano-selenium, and discloses functional nano-selenium and preparation method thereof as well as application of functional nano-selenium in preparation of anti-bacteria and sterilization drugs. The functional nano-selenium is at least one of nano-selenium modified by quercetin, nano-selenium modified by acetylcholine chloride and nano-selenium modified by quercetin-acetylcholine chloride. The functional nano-selenium has the activity for killing bacteria and multidrug resistant bacteria, also has the biological activity for inhibiting the growth of bacteria and multidrug resistant bacteria, and is suitable for preparing drugs for inhibiting the growth of bacteria and multidrug resistant bacteria and sterilization drugs. The functional nano-selenium is simple in preparation method, can be obtained through in-situ reduction modification, and can be directly stored and used. The functional nano-selenium is modified through various functions, so that the targeting property of the functional nano-selenium is improved, the transportation and transmembrane absorption of the functional nano-selenium in a bacteria cell membrane are improved, the medicine intake of bacteria can be increased, and the discharge is reduced, so that the fact that drugs in bacteria cells are kept at a higher level is ensured.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Pleuromutilin derivative having 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS20190135742A1High antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsSulfonic acid esters preparationHydrogen atomHalogen
A pleuromutilin derivative having a 2-amino phenyl mercaptan side chain as well as a preparation method and application thereof are provided. The derivative has a structure represented by formula 2 or formula 3, wherein, R1, R2 and R3 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom, hydroxyl, amino, sulfydryl, hydroxymethyl, amine methyl, nitro, halogen, trihalogenated methyl, methyl, natural amino acid acylamino and C1-6 alkoxy. The plueuromutilin derivative in the disclosure has good activity of inhibiting drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus and mycoplasma, and is especially suitable for preventing and treating infectious diseases caused by human or animal mycoplasma or drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus or multidrug resistant bacteria as a novel antibacterial drug.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com