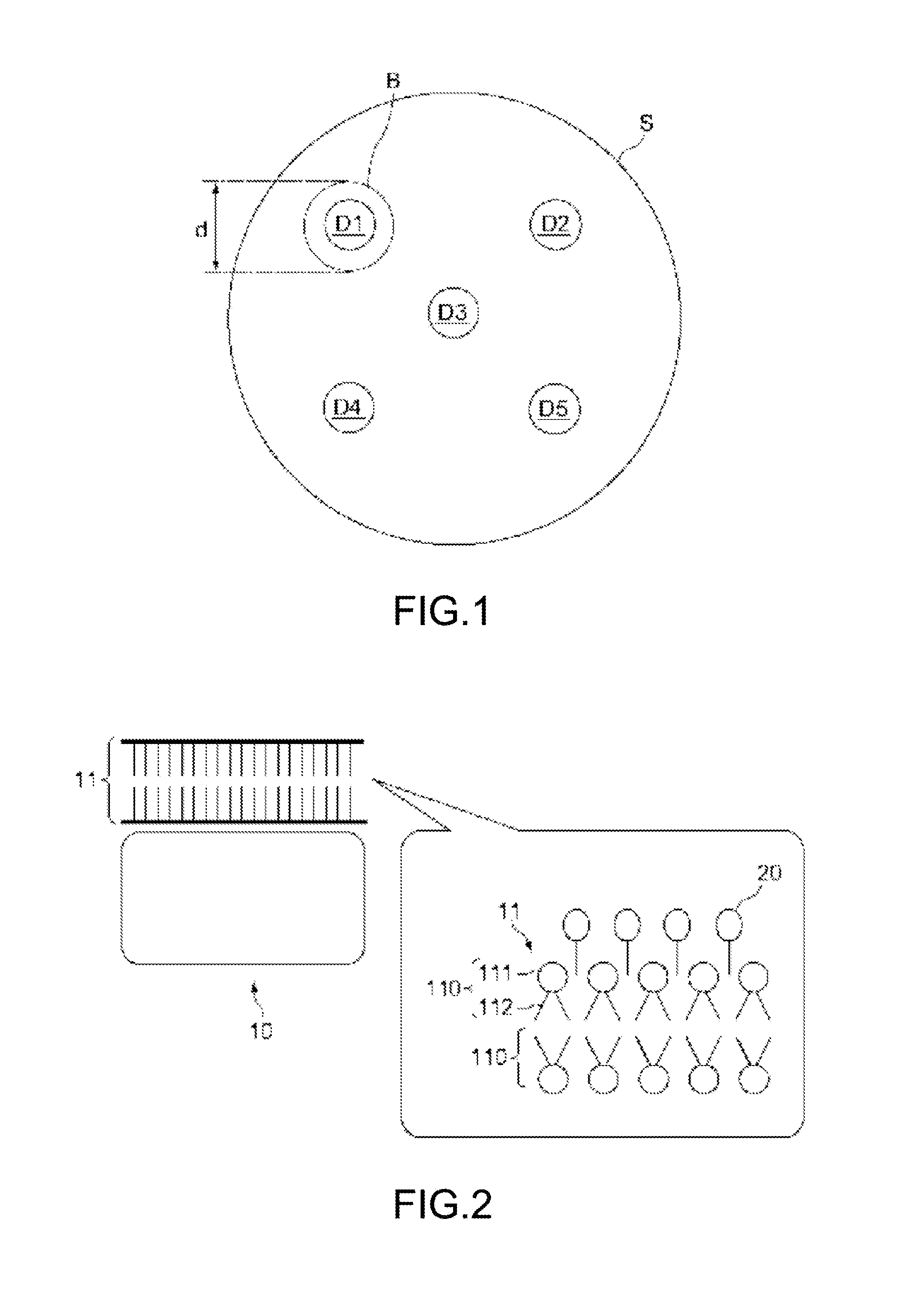
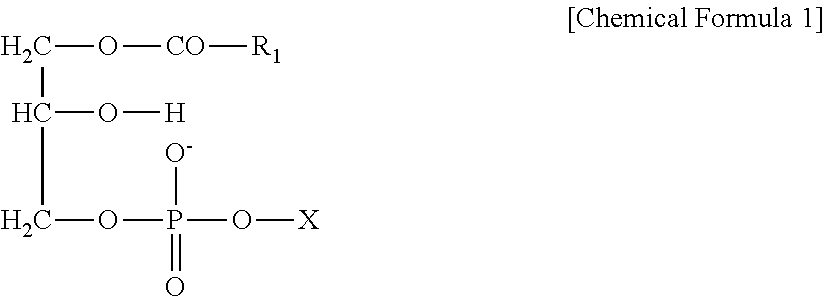Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Positive Bacteria Antibacterial Agent and Topical Agent
a multi-drug-resistant, topical technology, applied in the direction of antibacterial agents, drug compositions, aerosol delivery, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the difficulty of countermeasures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
Example 1
[0075]Firstly, an antibacterial agent in Example 1 was prepared. In Example 1, as the amphiphilic compound, which is the active ingredient of the antibacterial agent, lyso phosphatidylcholine derived from egg yolk (manufactured by Kewpie Corporation, egg yolk lysolecithin LPC-1) was used. The lyso phosphatidylcholine in Example 1 had the HLB value of 14 and the iodine value of 9. Table 2 shows substance names, derived sources, and HLB values in Examples and Comparative Examples, respectively.
TABLE 2Ingredient ofDerivedHLBantibacterial agentfromvalueEx. 1lysoegg yolk14phosphatidylcholineEx. 2lysophospholipidssoybeans11 to 20Ex. 3sucrose fatty acidsynthesized15esterEx. 4sucrose fatty acidsynthesized19esterComp. Ex. 1lyso phosphatidylsoybeans22glycerolComp. Ex. 2sucrose fatty acidsynthesized1esterComp. Ex. 3glycerin fatty acidsynthesized4.3esterComp. Ex. 4sucrose fatty acidsynthesized6esterComp. Ex. 5glycerin fatty acidsynthesized7esterComp. Ex. 6sucrose fatty acidsynthesized9...
example 2
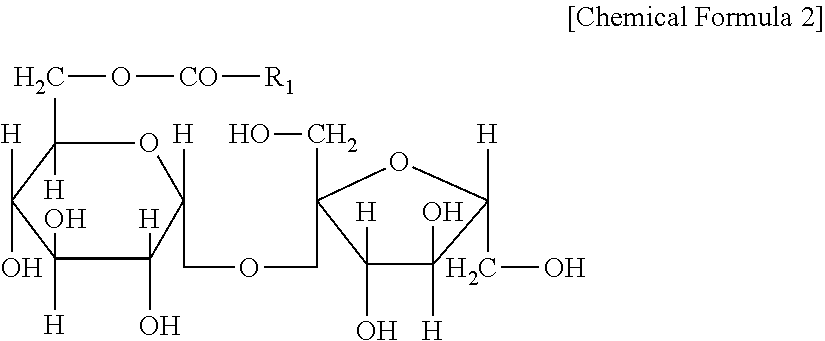
[0078]In Example 2, as the amphiphilic compound, hydrogenated soybean lysophospholipid (manufactured by Nikko Chemicals Co., Lecinol LL-20) was used. It is conceivable that a plurality of phospholipids may be mixed to provide the soybean lysophospholipid in Example 2, and it confirms that the soybean lysophospholipid had an HLB value of 11 to 20. The iodine value was 20 or less. The soybean lysophospholipid is represented by the above formula 1. The soybean lysophospholipid was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, and the test solution having a concentration of 5000 ppm (5000 μg / mL), 1250 ppm (1250 μg / mL), or 313 ppm (313 μg / mL) was prepared. When the soybean lysophospholipid was not easily dissolved in purified water, it was heated to about 70° C.
example 3
[0097]In Example 3, as the amphiphilic compound, sucrose fatty acid ester (manufactured by Dai-ichi Kogyo Seiyaku Co., Ltd., DK ester F-160) was used (see Table 2). The sucrose fatty acid ester in Example 3 had the HLB value of 15. The sucrose fatty acid ester was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, and the test solution having a concentration of 5000 ppm (5000 μg / mL), 1250 ppm (1250 μg / mL), or 313 ppm (313 μg / mL) was prepared. When the sucrose fatty acid ester was not easily dissolved in purified water, it was heated to about 70° C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| iodine value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com