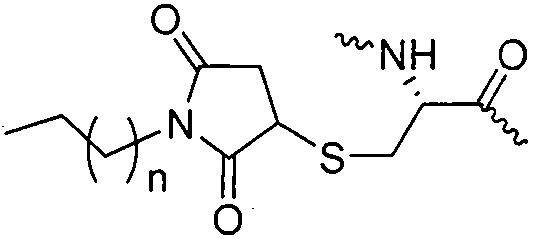
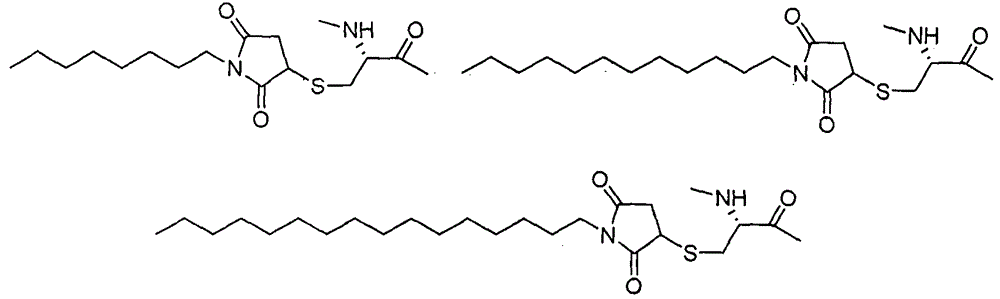
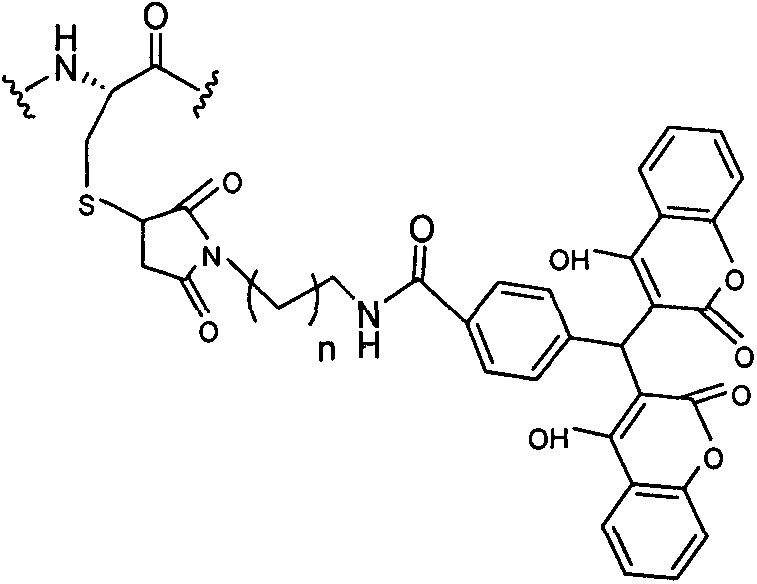
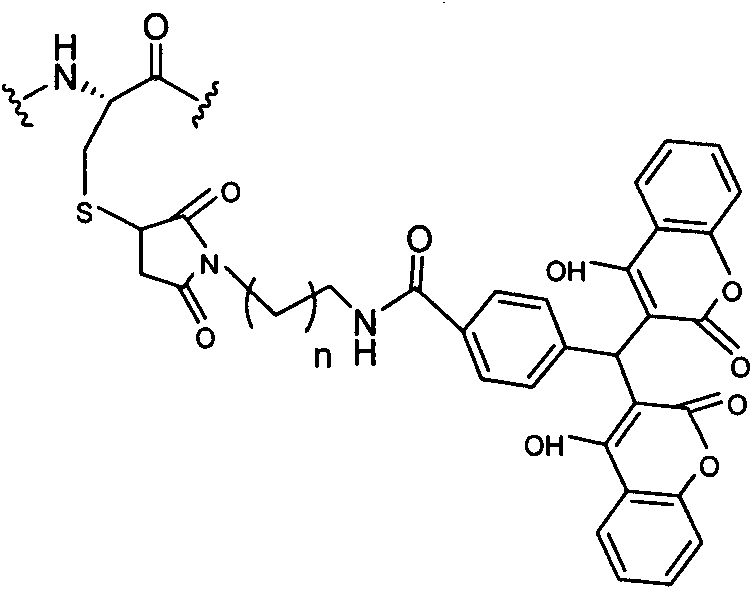
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
213results about How to "New structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Toy construction system
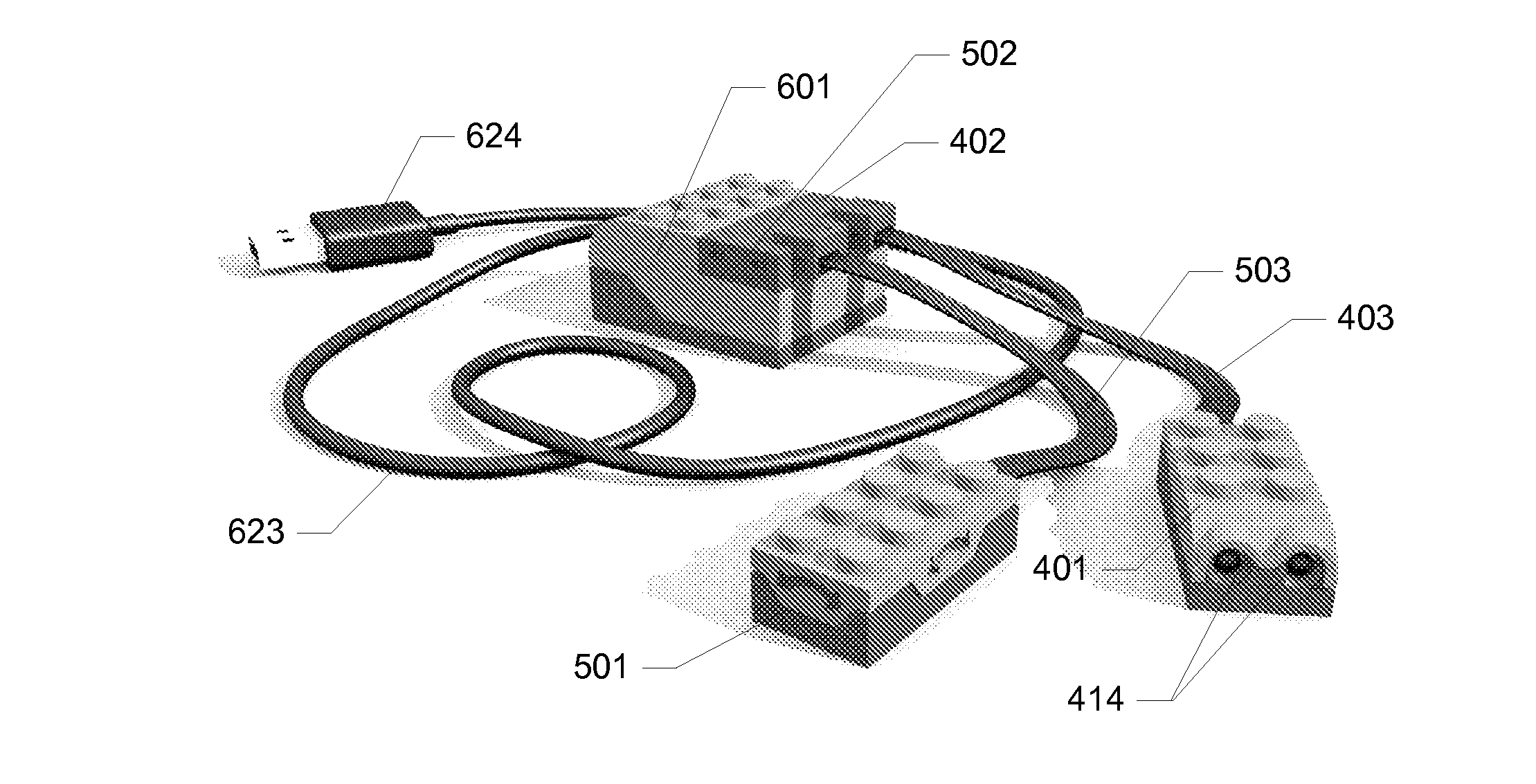
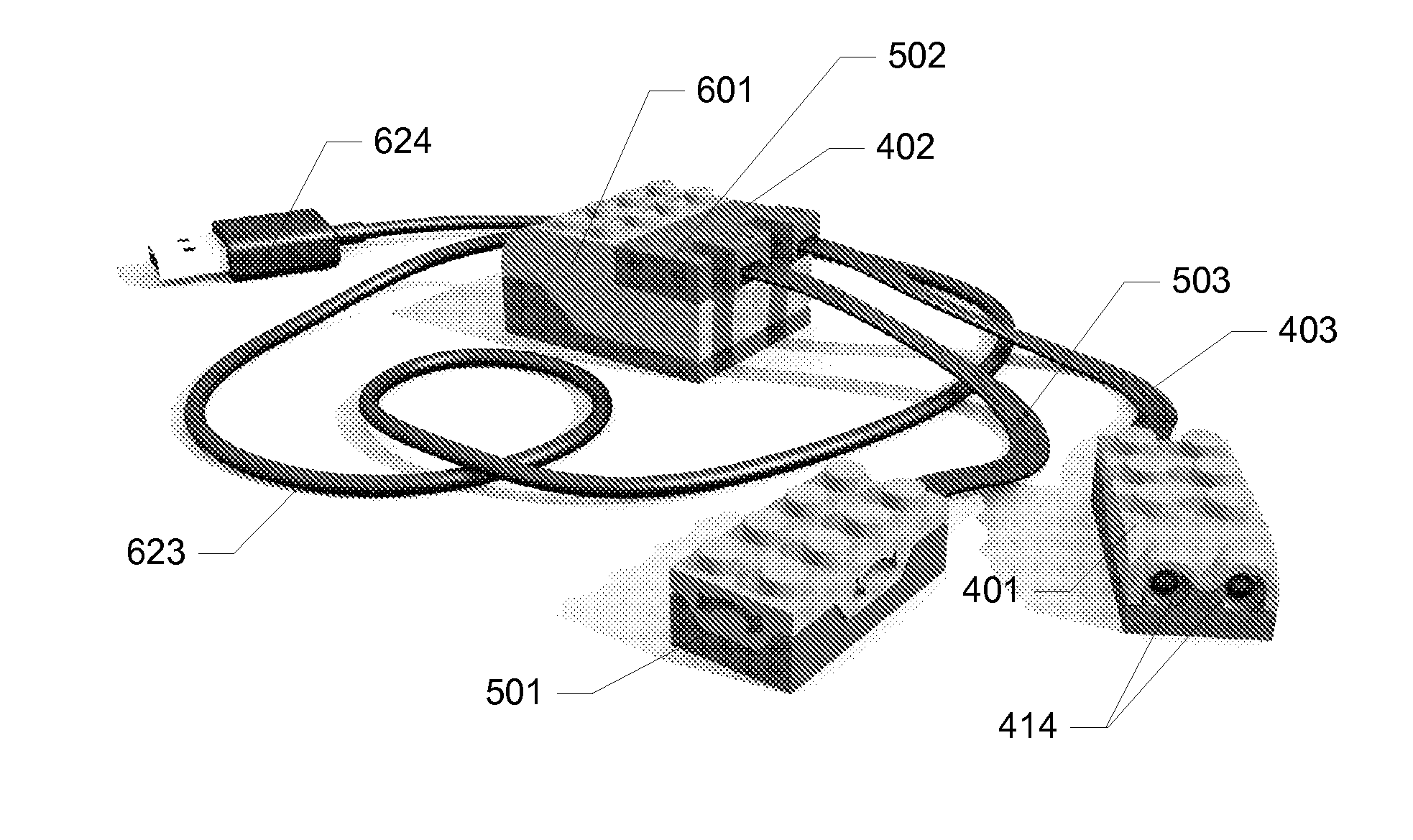
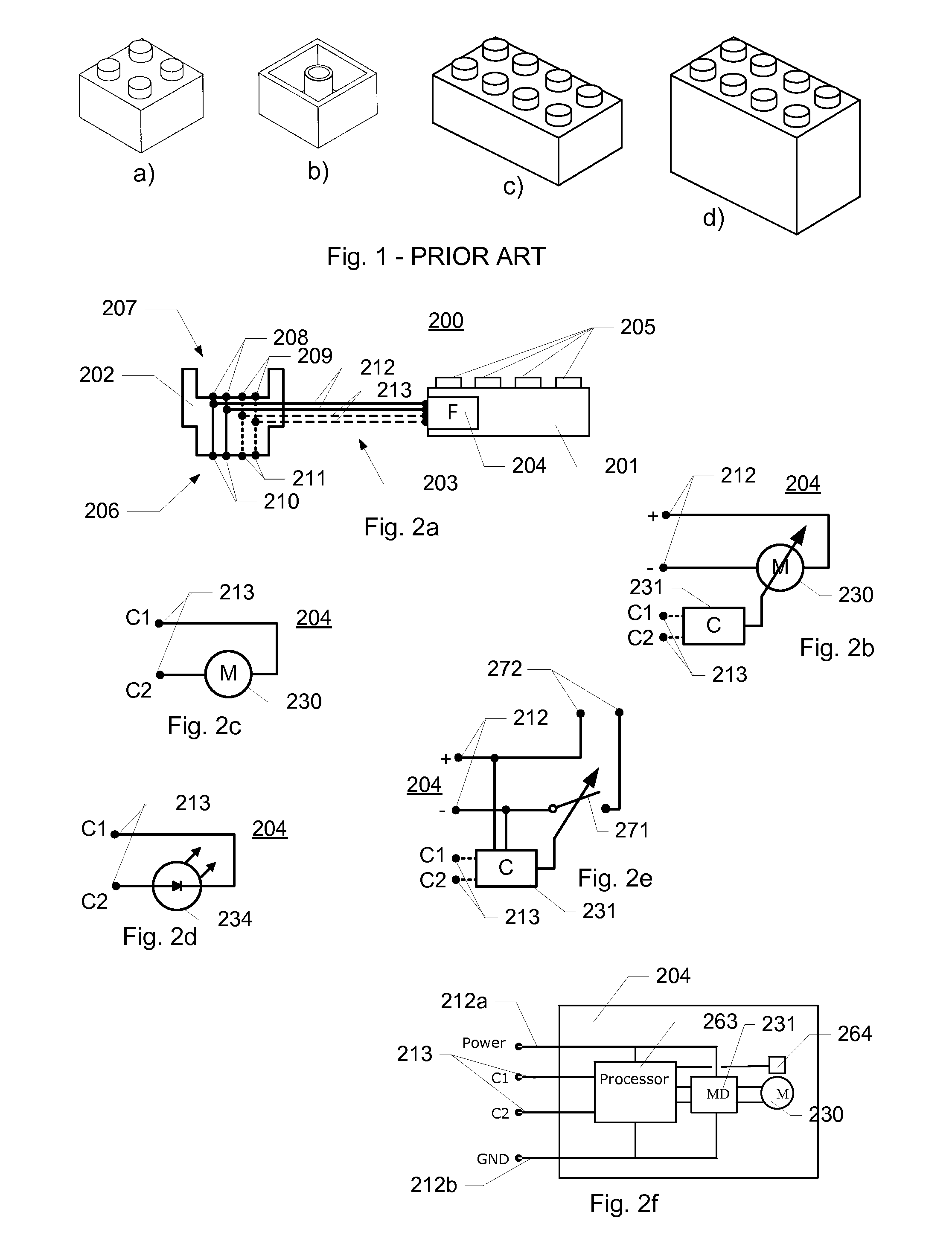
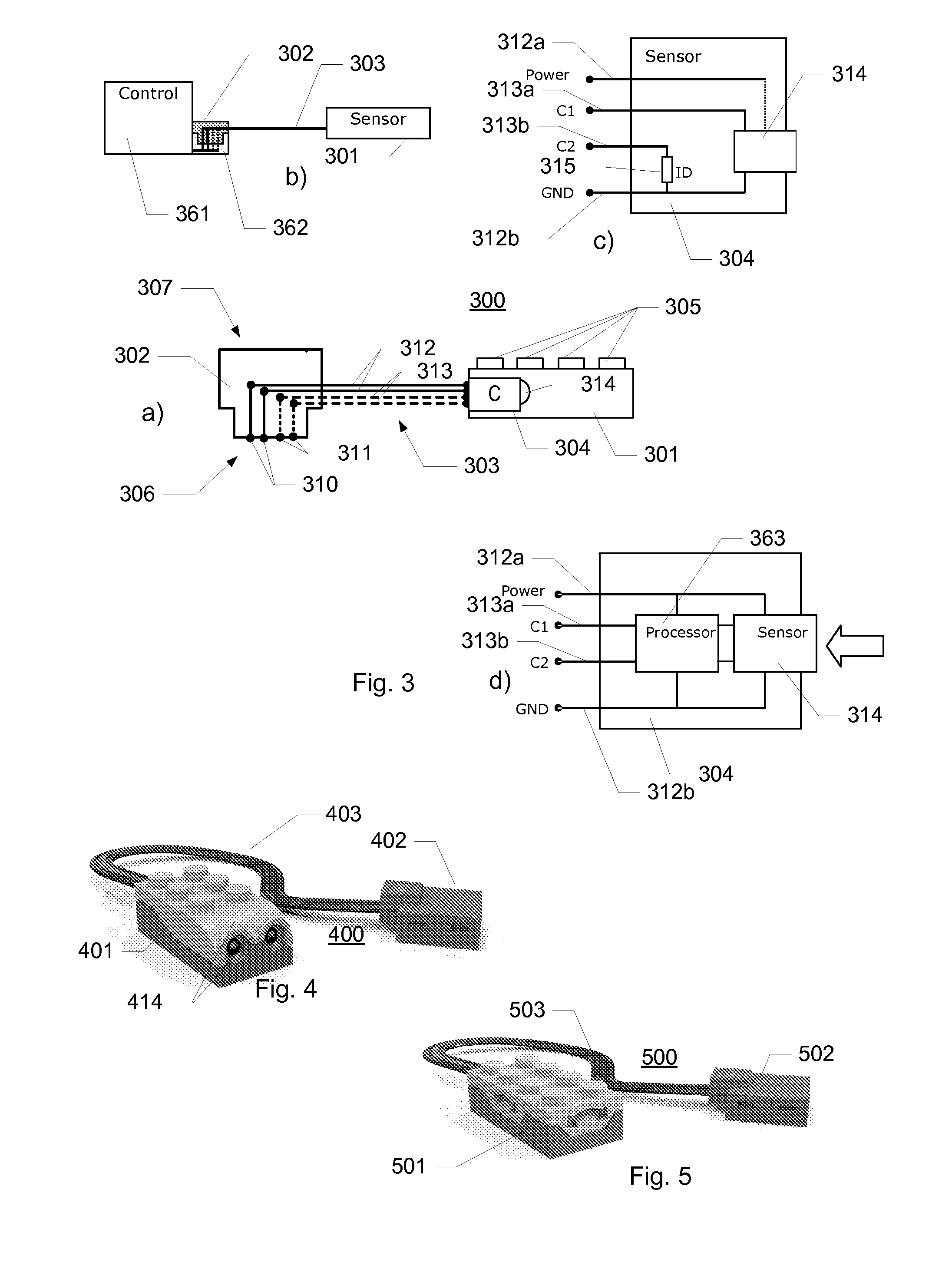
ActiveUS20100311300A1Low production costEnhanced play valueComputerized toysData processing systemControl signal
A toy construction system comprising a plurality of construction elements including one or more function construction elements for performing corresponding functions and including control connection means for communicating with one or more other construction elements; a data processing system providing a programming environment for generating one or more logic commands for controlling the one or more function elements; and an interface construction element comprising first connection means for providing a data-flow connection with the data processing system and for receiving said logic command from the data processing system, a processing unit adapted to convert said logic command into a control signal for controlling a function of said at least one function construction element, and second connection means for providing a control connection with the at least one function construction element via the control connection means of the function construction element, and for outputting the control signal.
Owner:LEGO AS
Toy construction system
ActiveUS8753164B2Easily learn how to control constructed structureNew structureComputerized toysData processing systemControl signal
Owner:LEGO AS
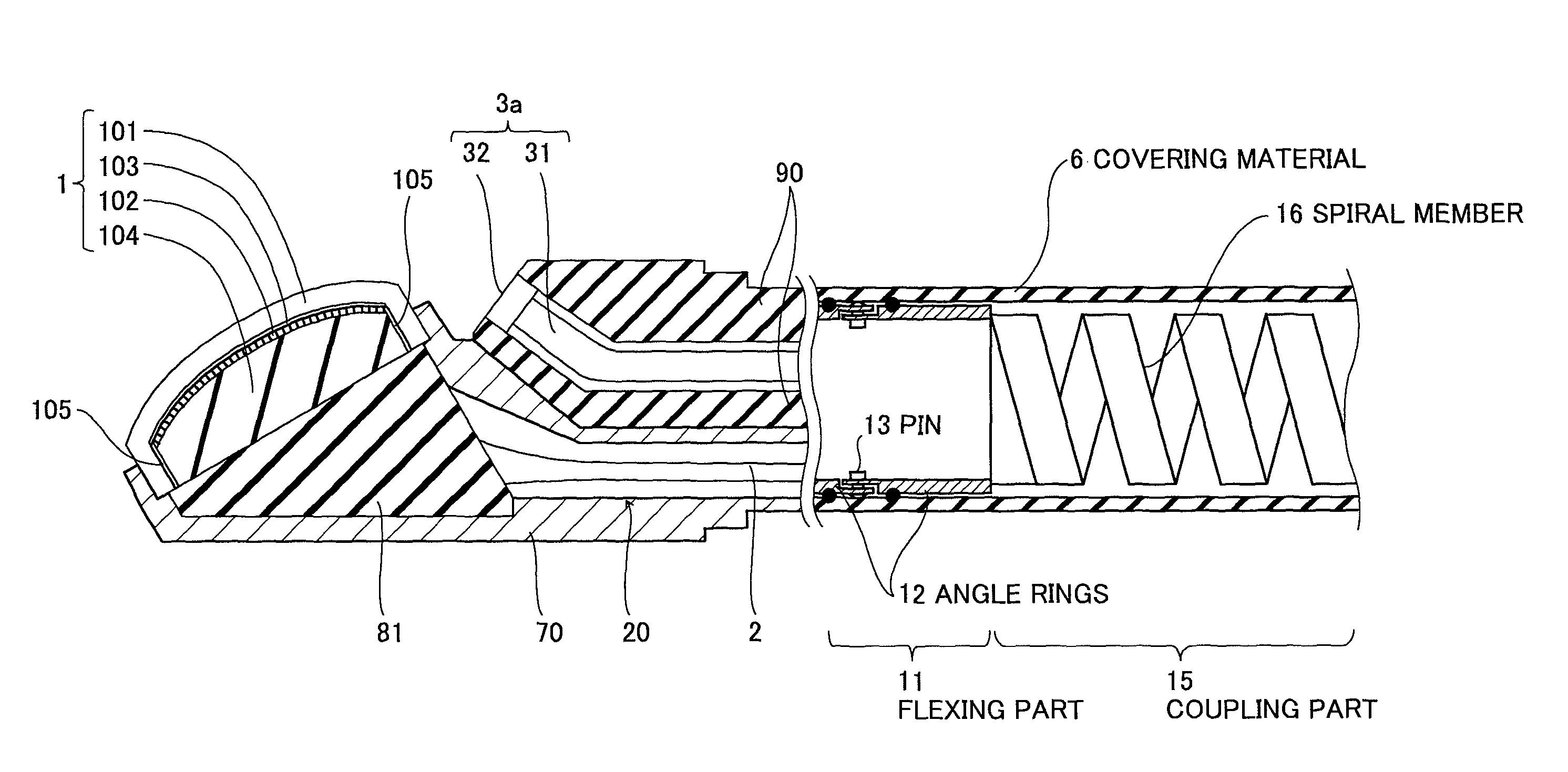
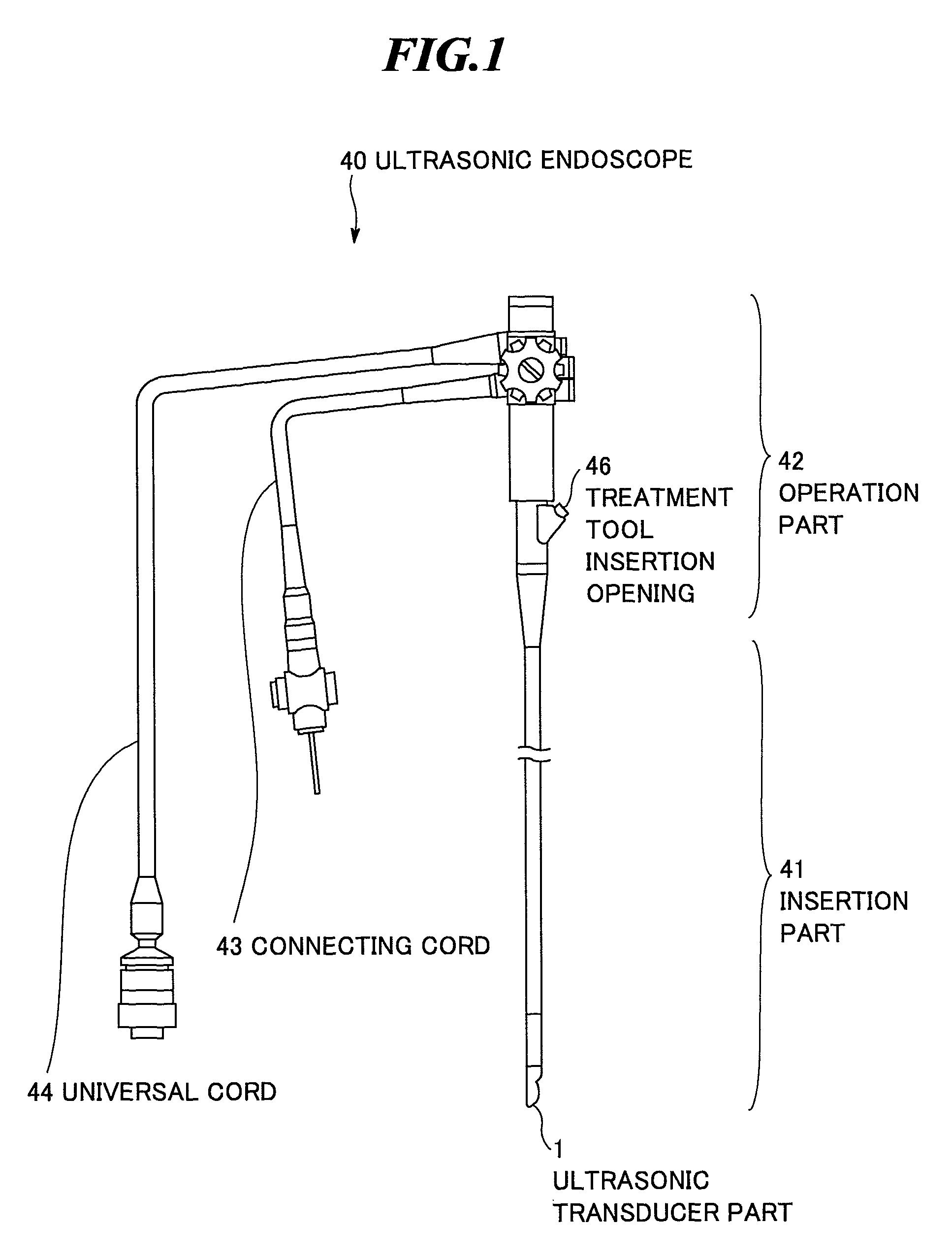
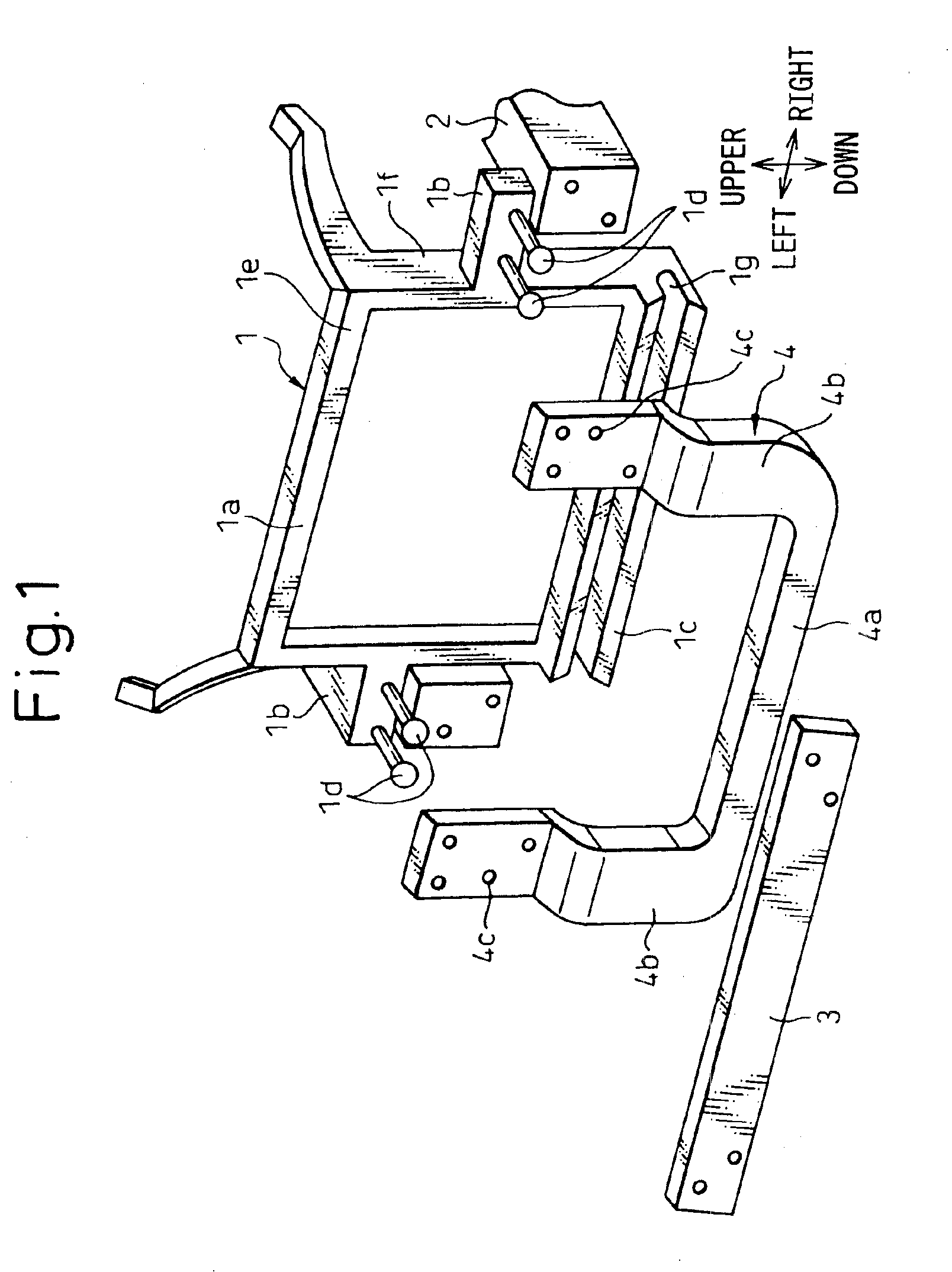
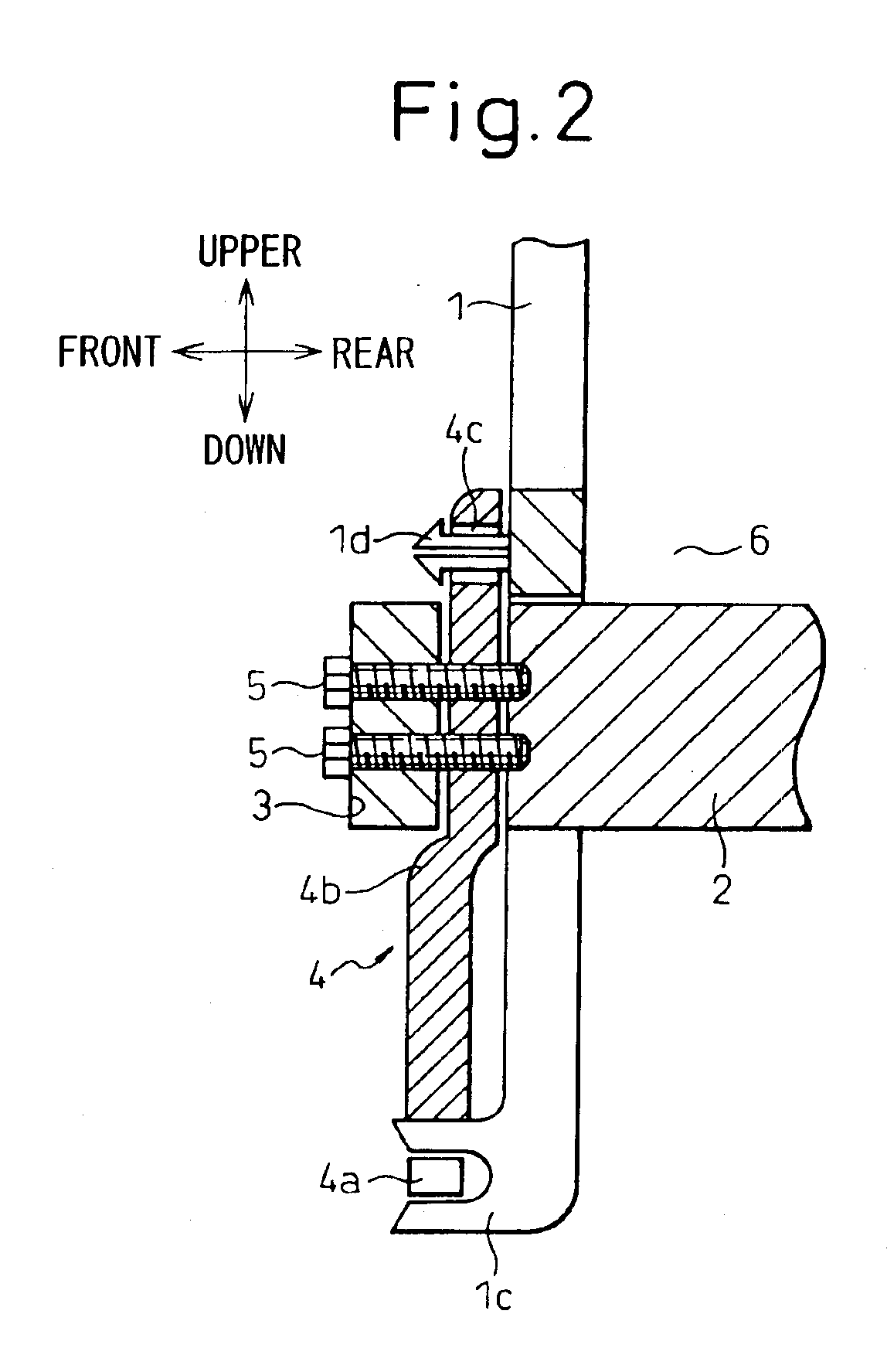
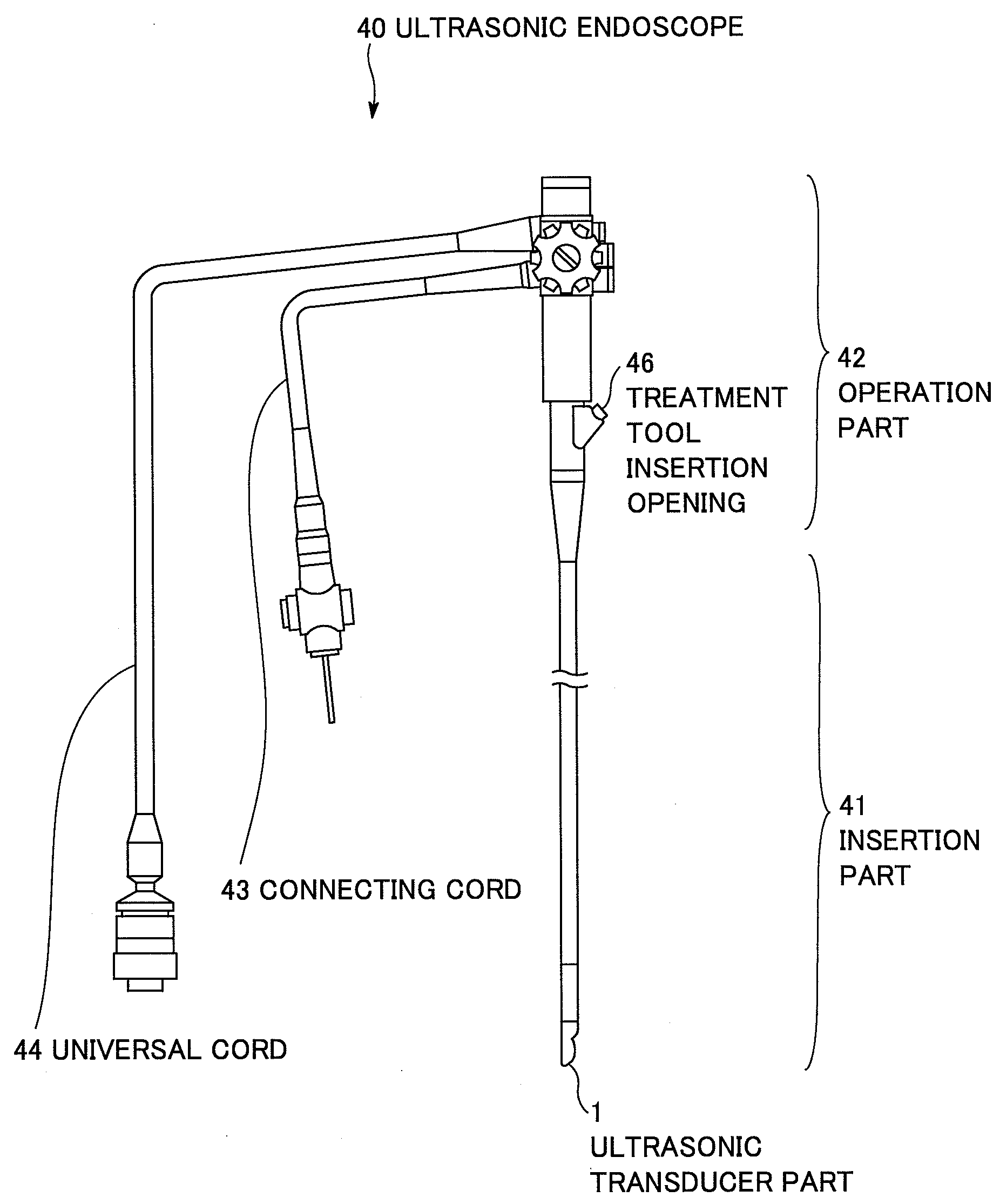
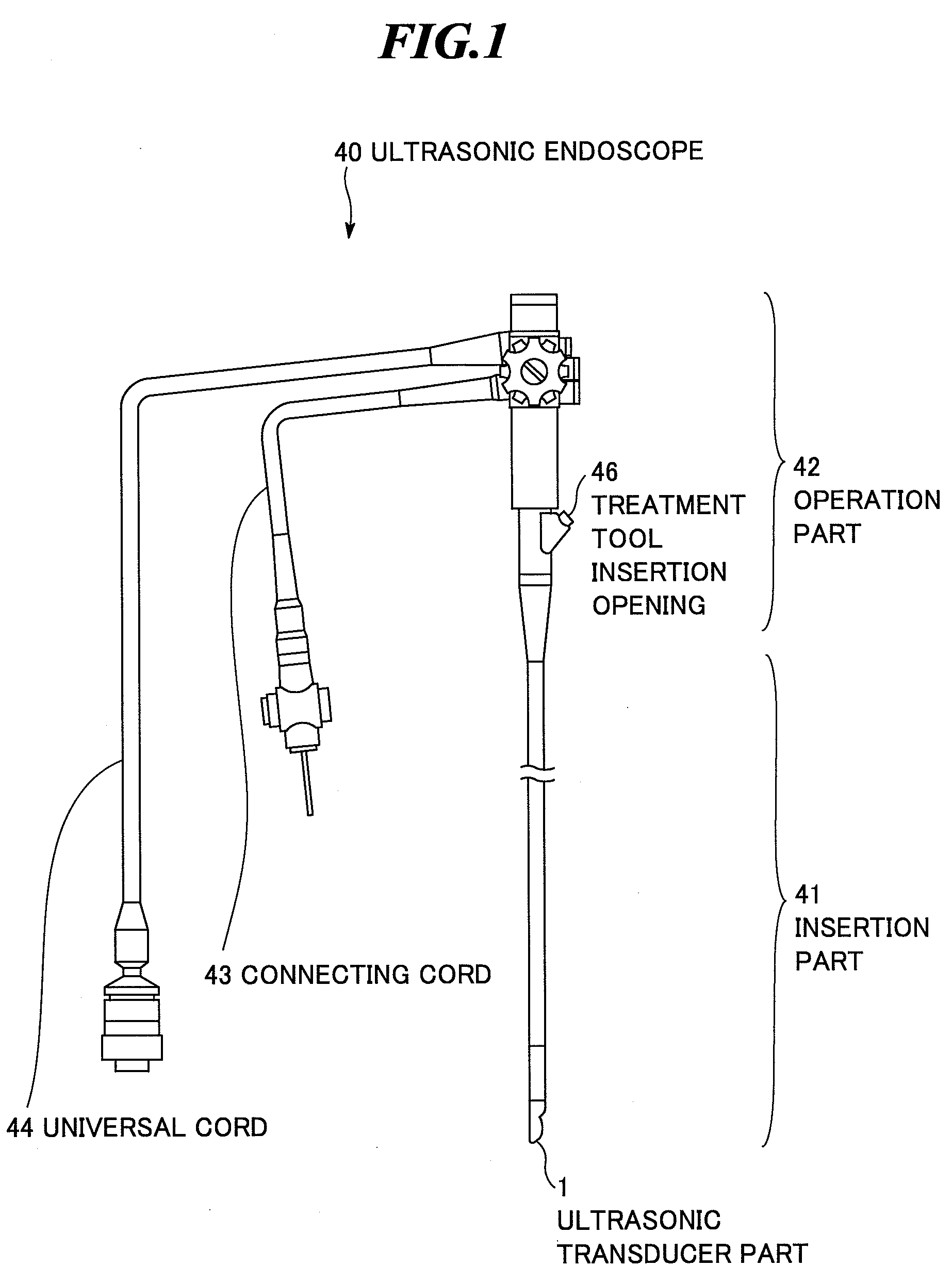
Ultrasonic endoscope
ActiveUS8382673B2New structureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHeat conductingUltrasonic Endoscopy
An ultrasonic endoscope in which the temperature rise can be suppressed with a reduced diameter. The ultrasonic endoscope includes: an ultrasonic transducer part including plural ultrasonic transducers; an exterior member for accommodating the ultrasonic transducer part; and a heat conducting part provided inside of the exterior member and respectively connected to the ultrasonic transducer part and an inner surface of the exterior member. It is preferable that the heat conducting part has a coefficient of thermal conductivity equal to or more than 10 W / (m·K). Further, it is preferable that one of the heat conducting member and the exterior member has an electric insulation property.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
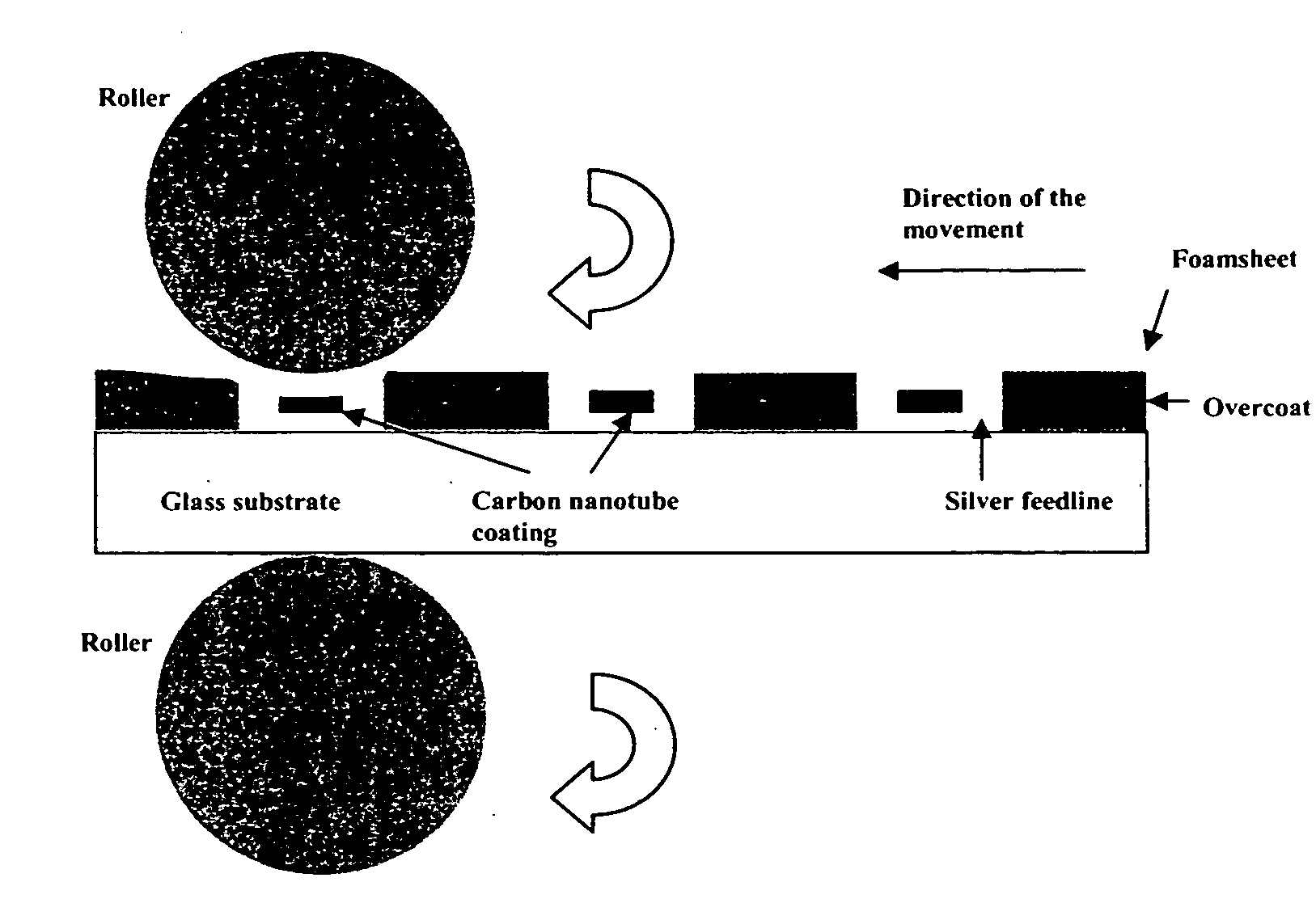
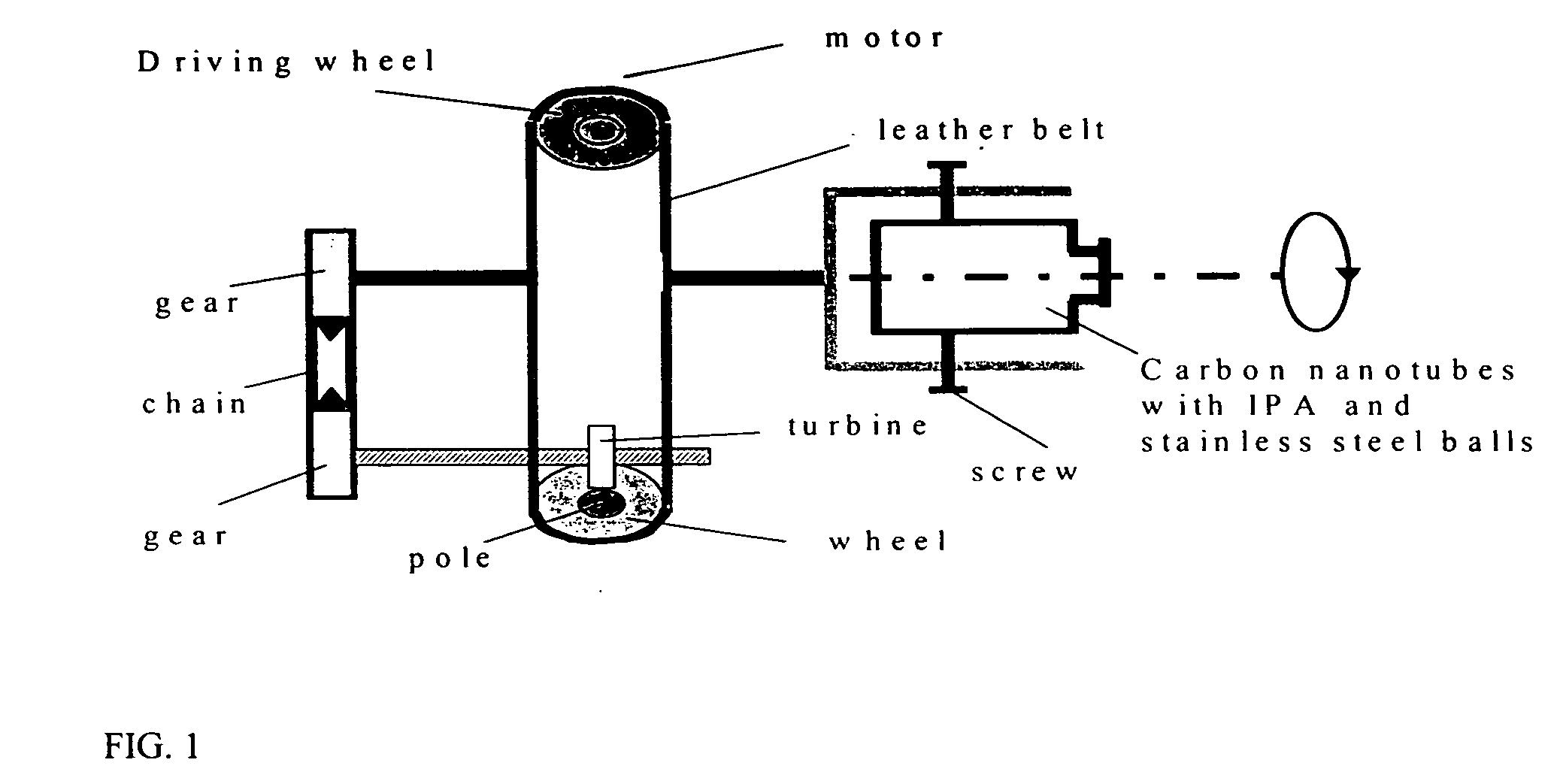
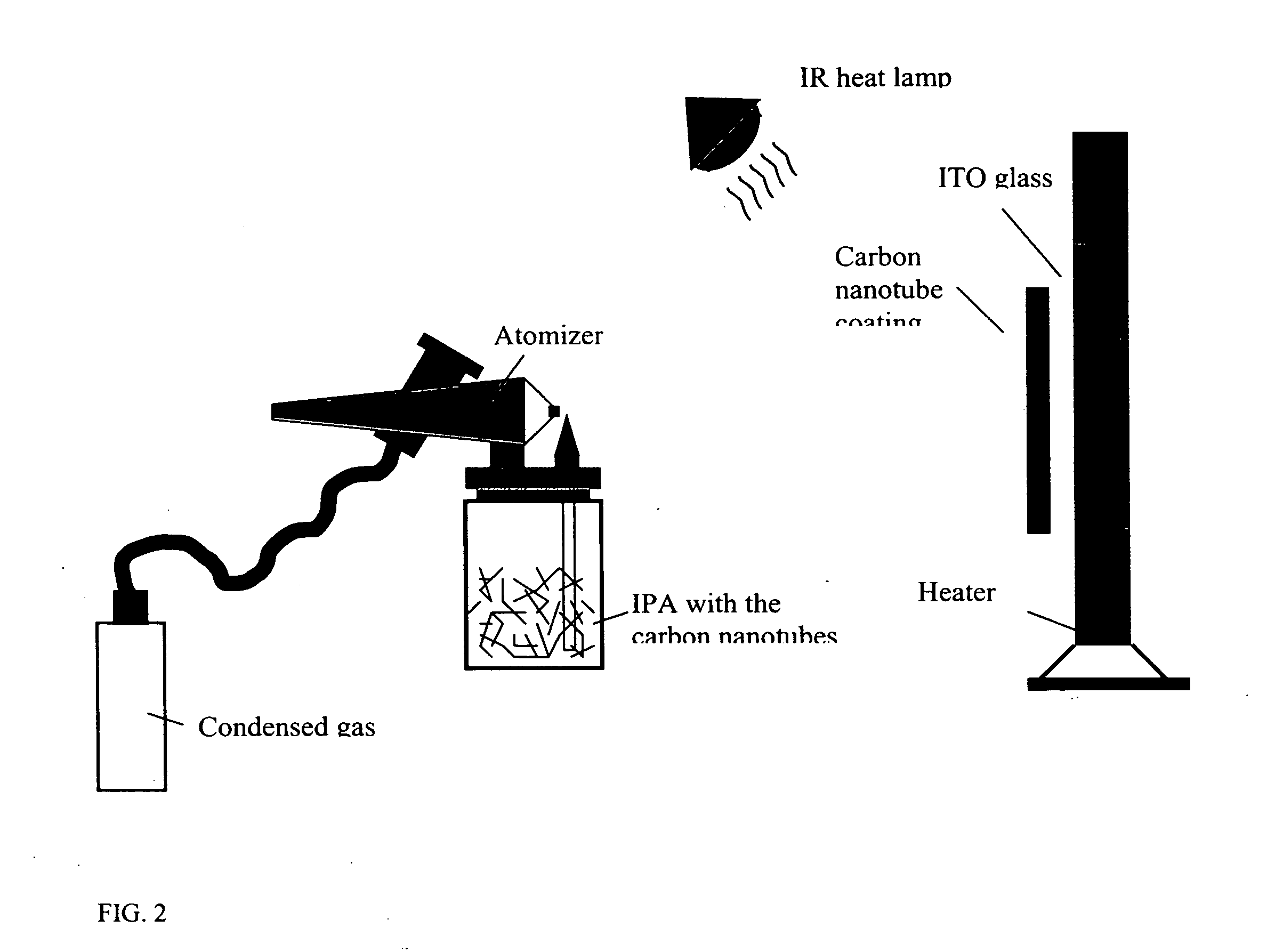
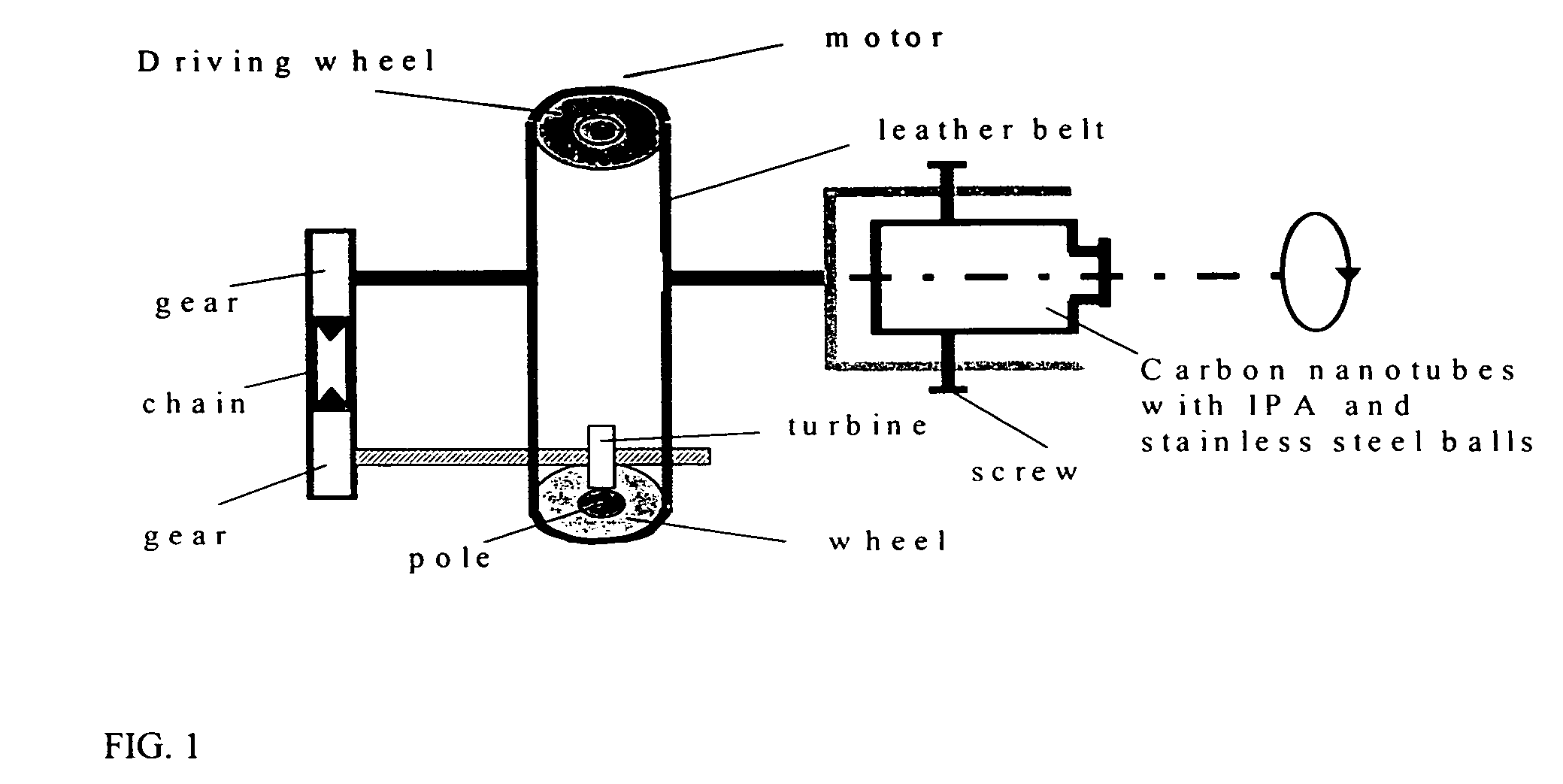
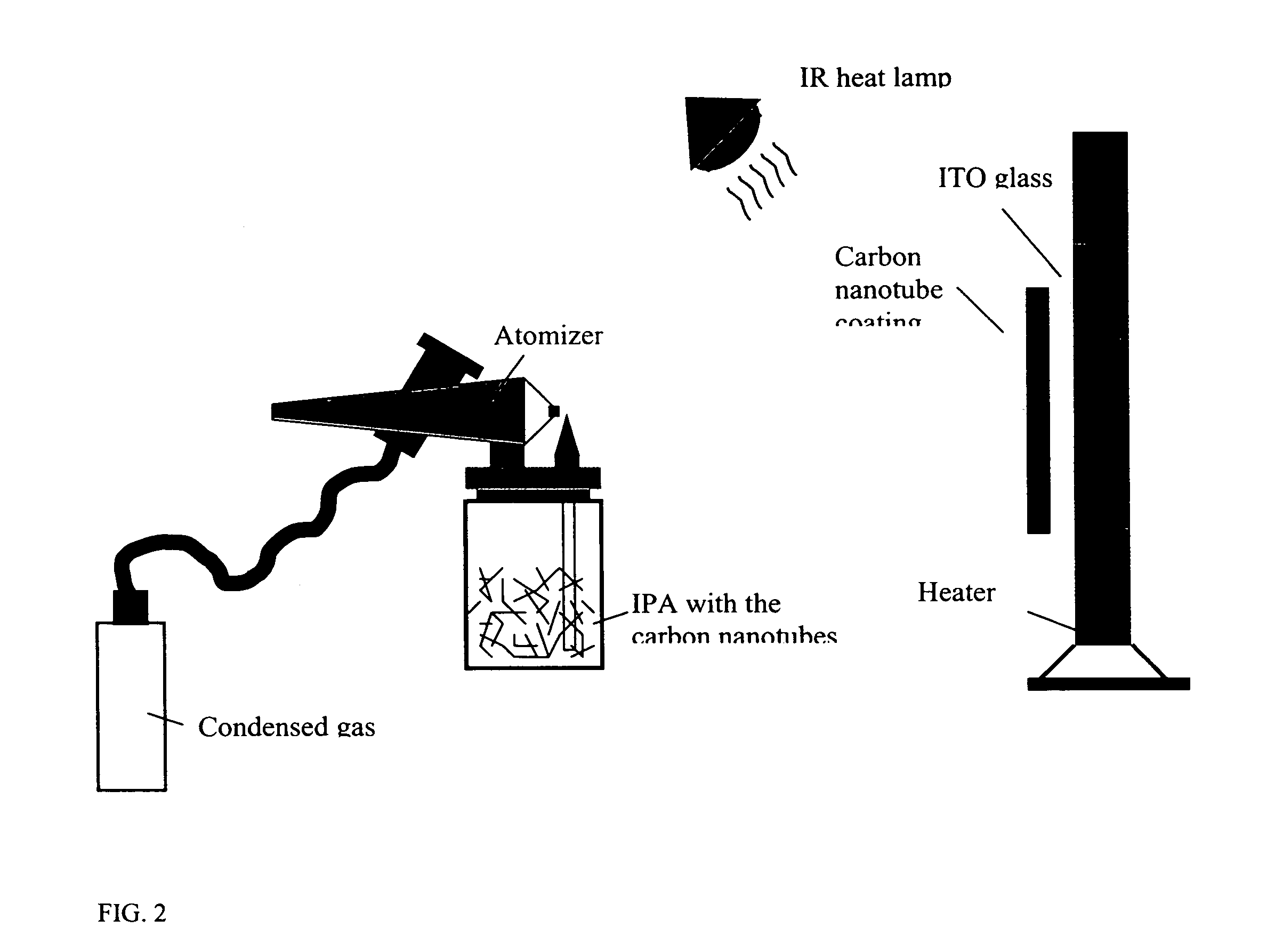
Activation of carbon nanotubes for field emission applications
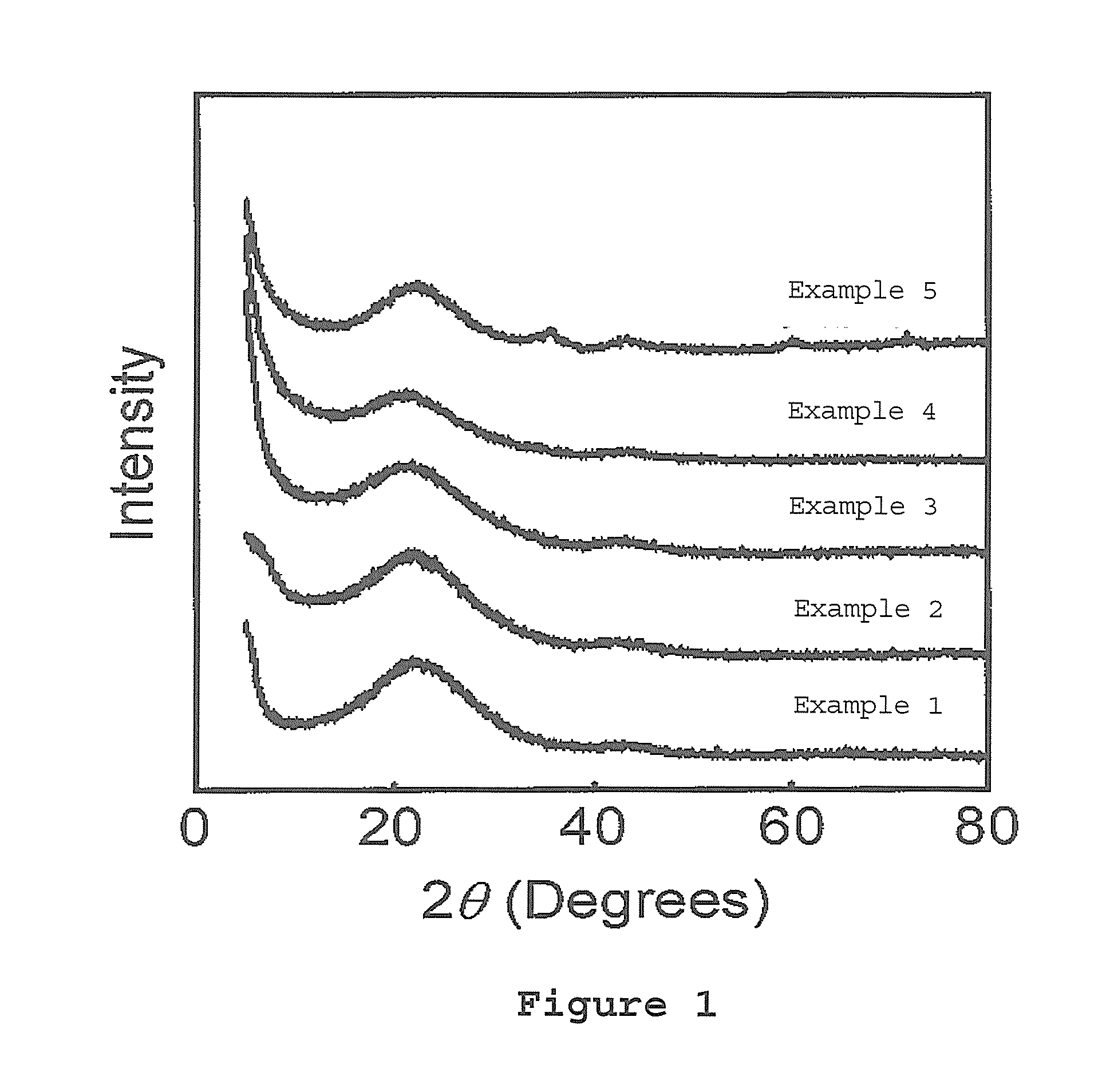
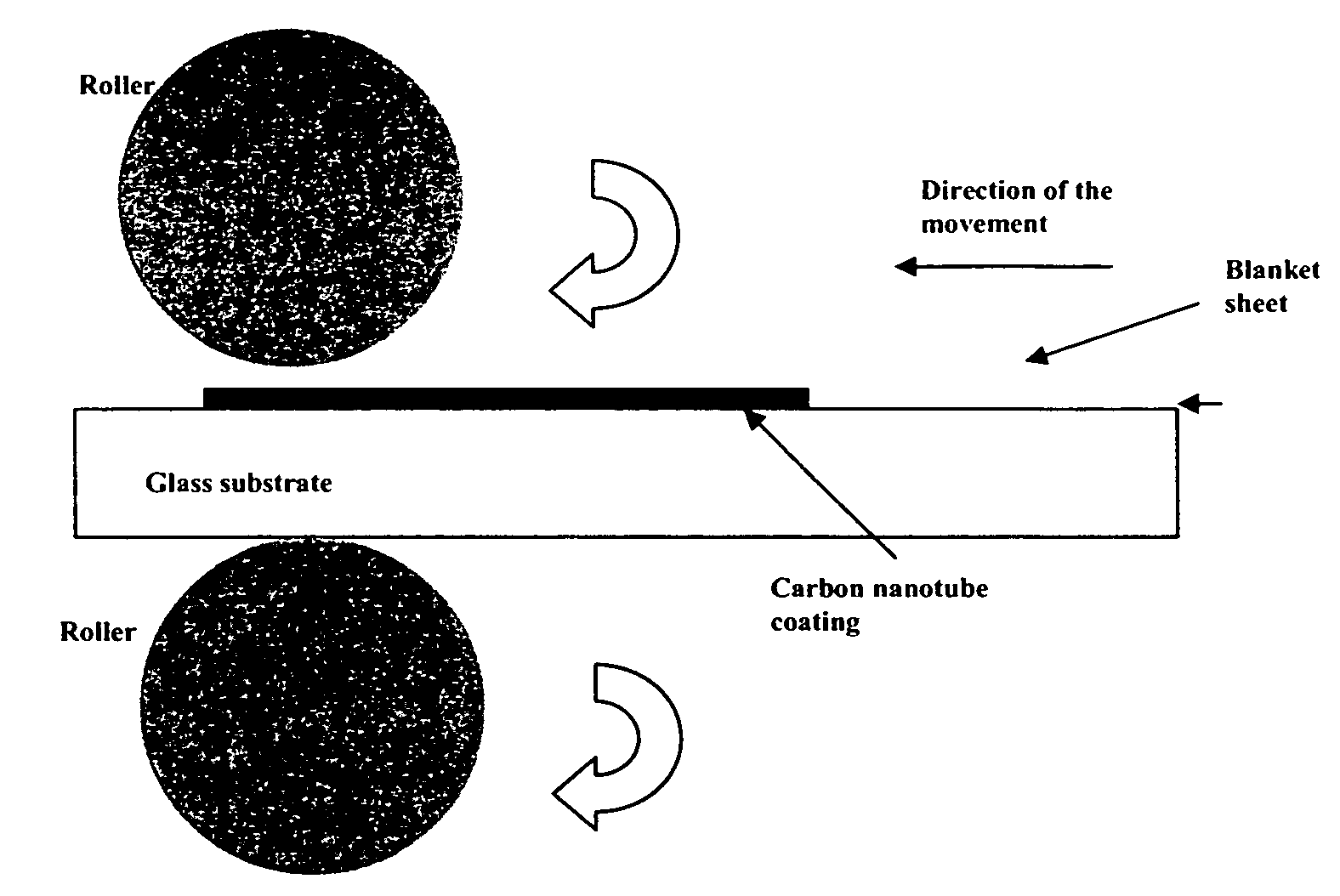
InactiveUS20050244991A1Field emission propertyNew structureCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeBiological activation
Substantially enhanced field emission properties are achieved by using a process of covering a non-adhesive material (for example, paper, foam sheet, or roller) over the surface of the CNTs, pressing the material using a certain force, and removing the material.
Owner:APPLIED NANOTECH HLDG
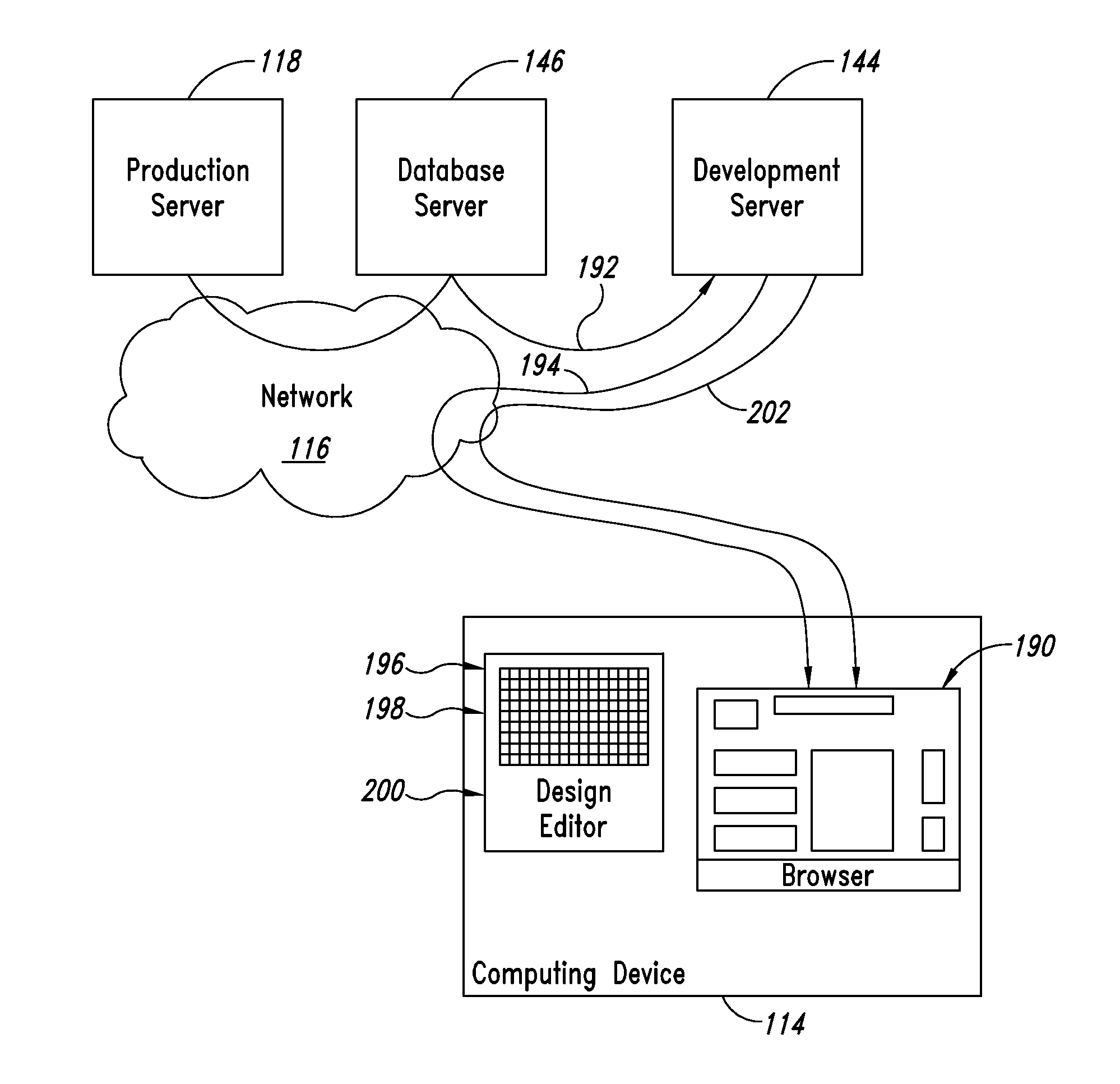
Website development tool
InactiveUS20140053060A1Improve efficiencyQuickly and efficiently be created and modifiedNatural language data processingWebsite content managementUser inputWeb page
A website is opened in a website development tool, and pages of the website are served with a web server. The web server accepts user input arranged to direct interactive execution the web page being served. A design editor is opened while the web pages continue to be served. The design editor presents a digital graph paper image configured to display one or more separately identifiable groups of one or more grid blocks of the digital graph paper image. Each of the separately identifiable groups represents a displayable object included in at least one web page. User input into the design editor is arranged to select a sector of grid blocks and modify a set of characteristics associated with the sector. A build process and a deployment process are executed in real time and the modified web page is served in real time.
Owner:WARHEAD
Structure of the stem of LED chip unit bulb
InactiveUS20050007010A1Facilitates efficient circulationProlong lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceAlloyNormal state
The present invention is related to a new structure of the stem of LED Chip Unit bulb, which comprises a cup disk, a chip, a stand, a molybdenum alloy wire and a stem. Essentially, the brace-end of the stem is connected to a supportive chip cup disk. The center of the disk is concave so as to form a holding chamber whose inner diameter is open, arc-shaped and circular. The molybdenum alloy wire is tapered off to a point and thus it takes a turn of 180°, hooking and pressing against the chip. Given the elastic coefficient of the barb-turning angle, the tip of the molybdenum alloy wire may point-press against the chip in a normal state in response to the temperature-dependent expansion-contraction feature of the chip. The gradient of the arc-shaped, circular wall of the disk enables the chip to generate light that refracts at different angles, giving rise to a wide-angle, open, homogeneous light source. The vacuum inside the bulb facilitates efficient circulation and therefore heat absorption. As a result, despite the heat dissipation of the chip, the temperature of the bulb does not increase, prolonging the life of the bulb. Hence, the new structure of the stem of LED chip unit bulb does have a practical utility.
Owner:LEE HAN MING
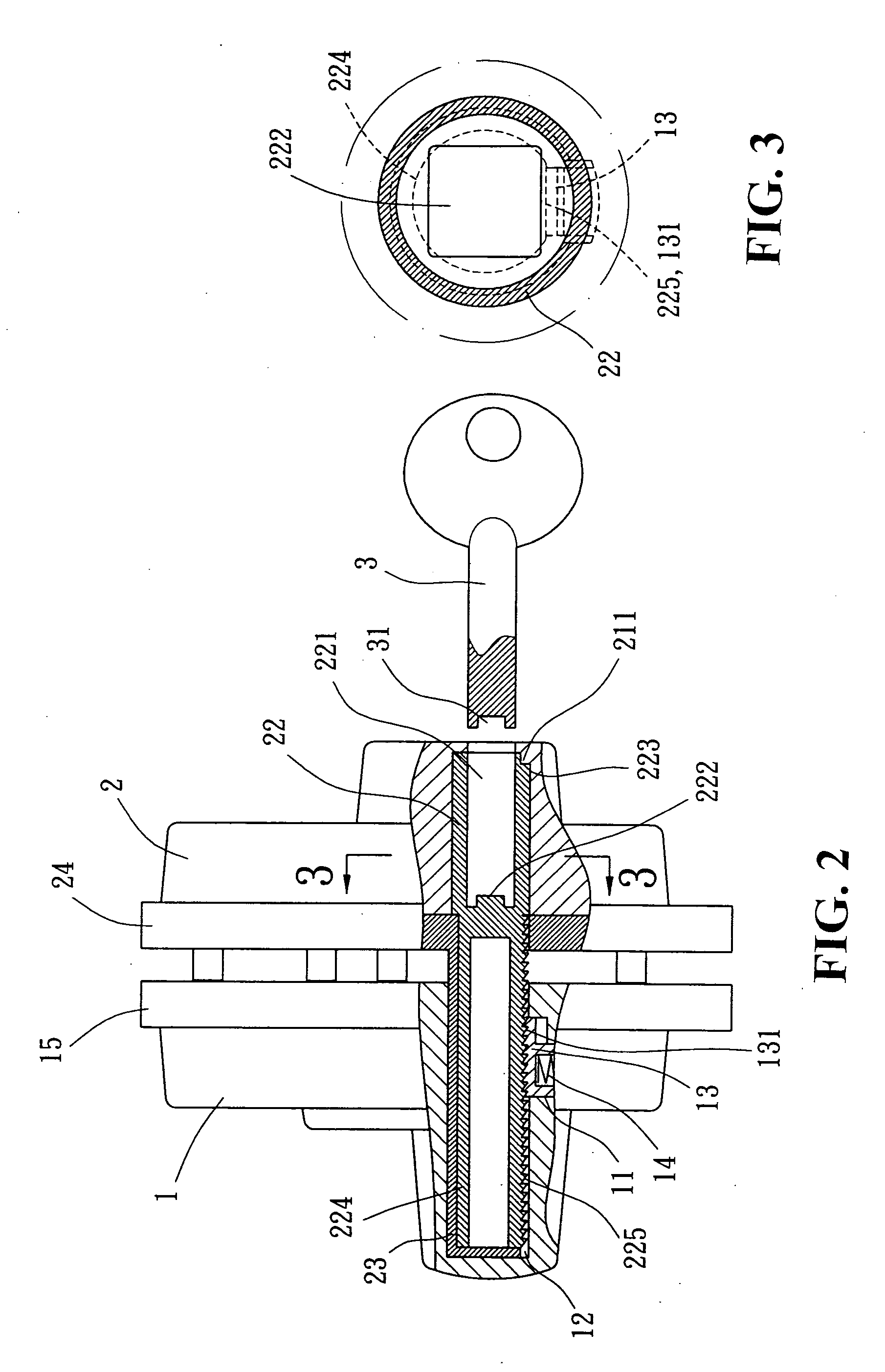
Core structure of a gun trigger lock
InactiveUS20060117633A1Easy and convenient to useEasy and convenient to and manageSafety arrangementEngineeringMechanical engineering
A core structure of gun trigger lock comprises two embedded parts. A first embedded part includes a pit and a straight hole; a lock piece and a spring are disposed in the pit; the lock piece, having parallel ratchets formed on one side, is pushed by the spring and moves upward constantly. A second embedded part includes a core rod hole, and a straight core rod is disposed therein; the straight core rod includes a long keyhole at the open end, and a aspheric bump is placed at the bottom of the keyhole; a gear shaft, having parallel ratchets on one side, extends from the straight core rod and can be inserted into the straight hole of the first embedded part. Moreover, a key is also included in the present invention, having an aspheric pit at the front end which matches with the shape of the aspheric bump at the bottom of the keyhole of the second embedded part. Thus, by turning the key to rotate the straight core rod together with the gear shaft, the first and second embedded parts can be combined together or released separately.
Owner:CHANG WEN KWEI
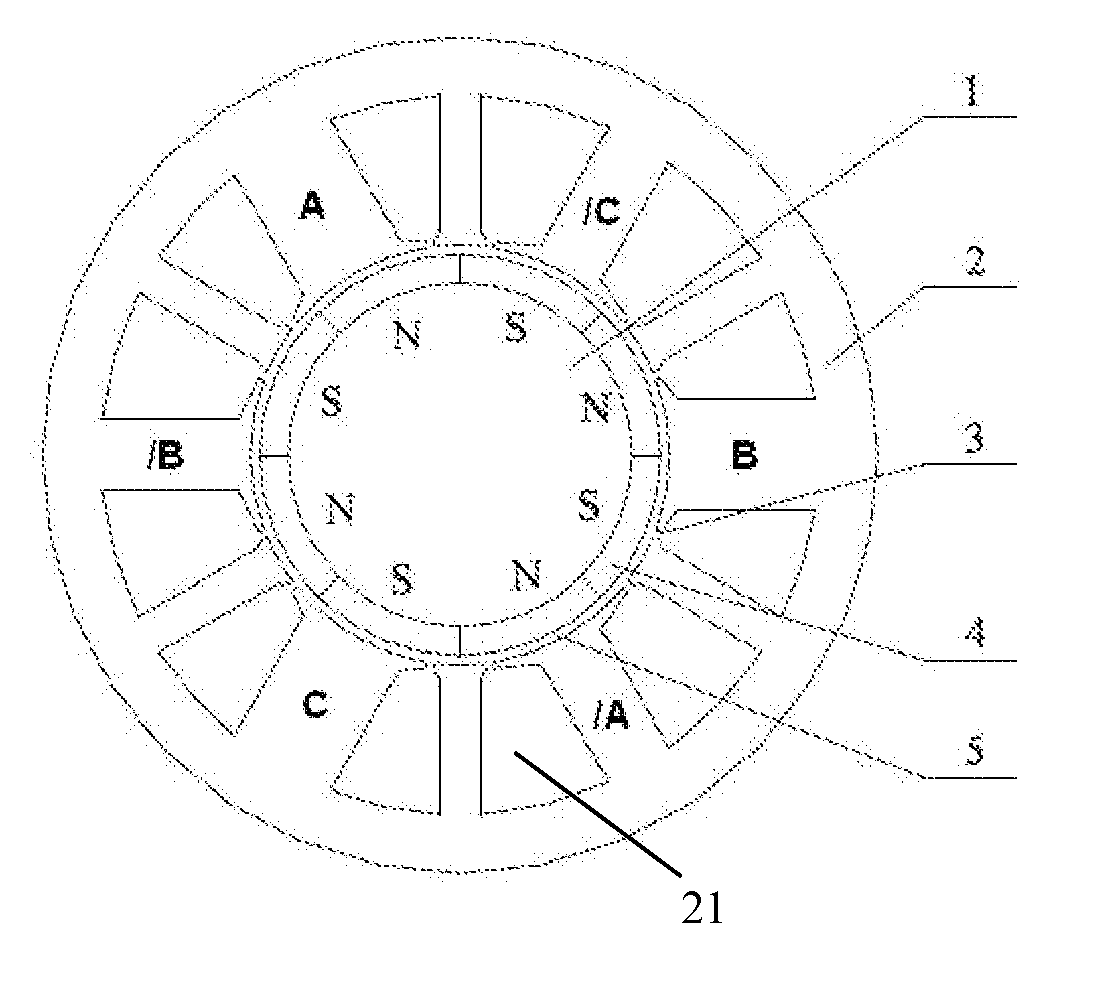
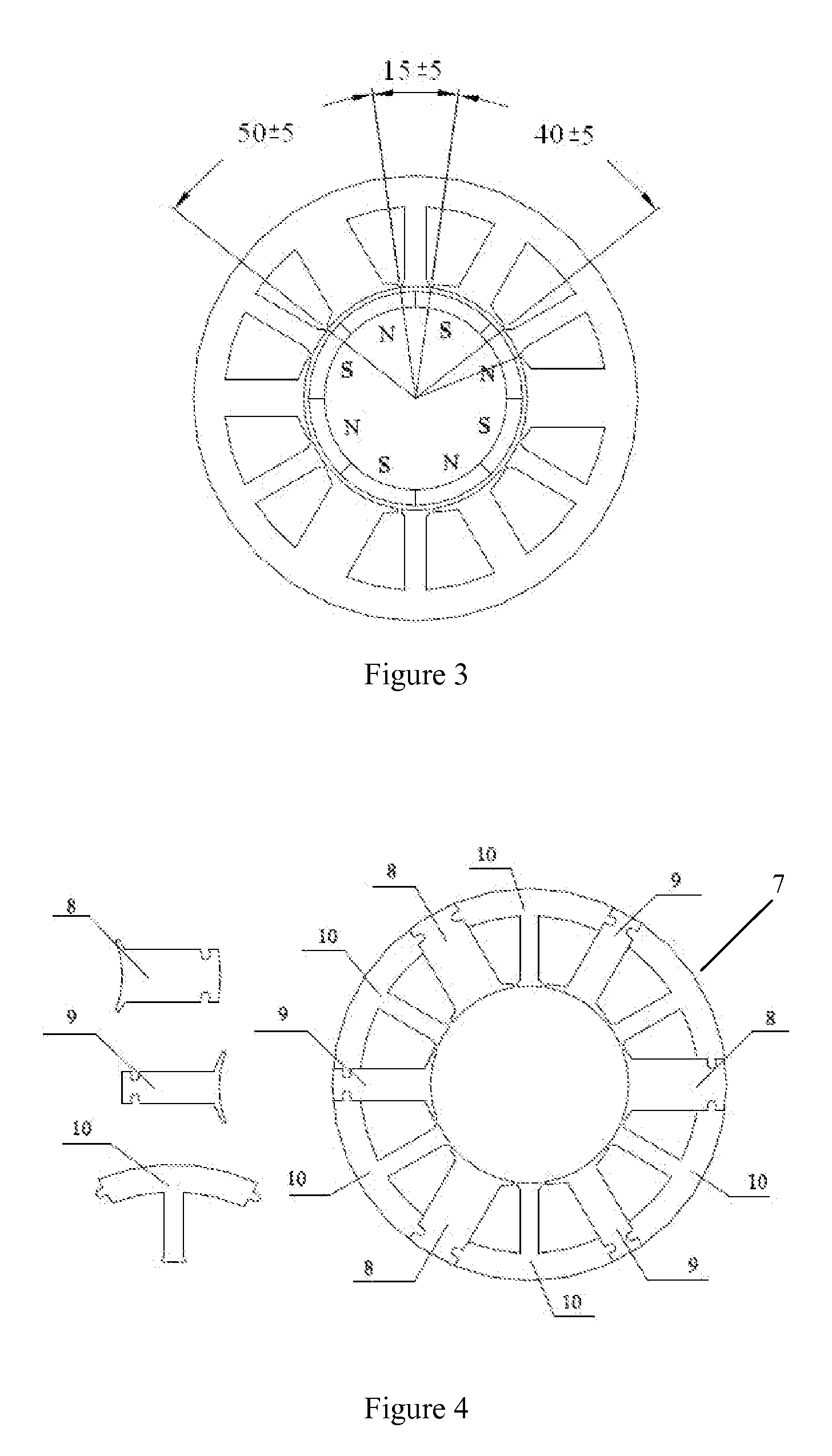
Three-Phase Square-Wave Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor
ActiveUS20090108699A1Improve performanceLow costWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic polesPermanent magnet motor
This invention relates to a three-phase square-wave permanent magnet brushless DC motor for solving problems of the existing square-wave permanent Magnet Motor and sine-wave permanent magnet motor. In this invention, the number 2P of magnetic poles on the said rotor core is 8; the slot number Z of the said stator core is 12, accordingly there are 12 teeth, including three big teeth, three medium teeth and six small teeth; the ratio of their mechanical angles is 50° (±5°) for big teeth: 40° (±5°) for medium teeth: 15° (±5°) for small teeth, and the sum of the mechanical angles of one big tooth, one medium tooth and two small teeth must be 120°. Three-phase concentrated windings are respectively wound on the big teeth and the medium teeth, in which there are only two concentrated windings for each phase, thus there are only 6 concentrated windings for the three-phase motor. With driven by three-phase square-wave current, the said motor can produce a smooth torque which ripple index corresponds to that of the sine-wave permanent magnet servo motor, at the same time, it also has a plurality of advantages including windings end minimization, air-gap minimization, material minimization, cogging torque minimization and loss minimization and so on.
Owner:SCBD (ANHUI) E TECH CO LTD
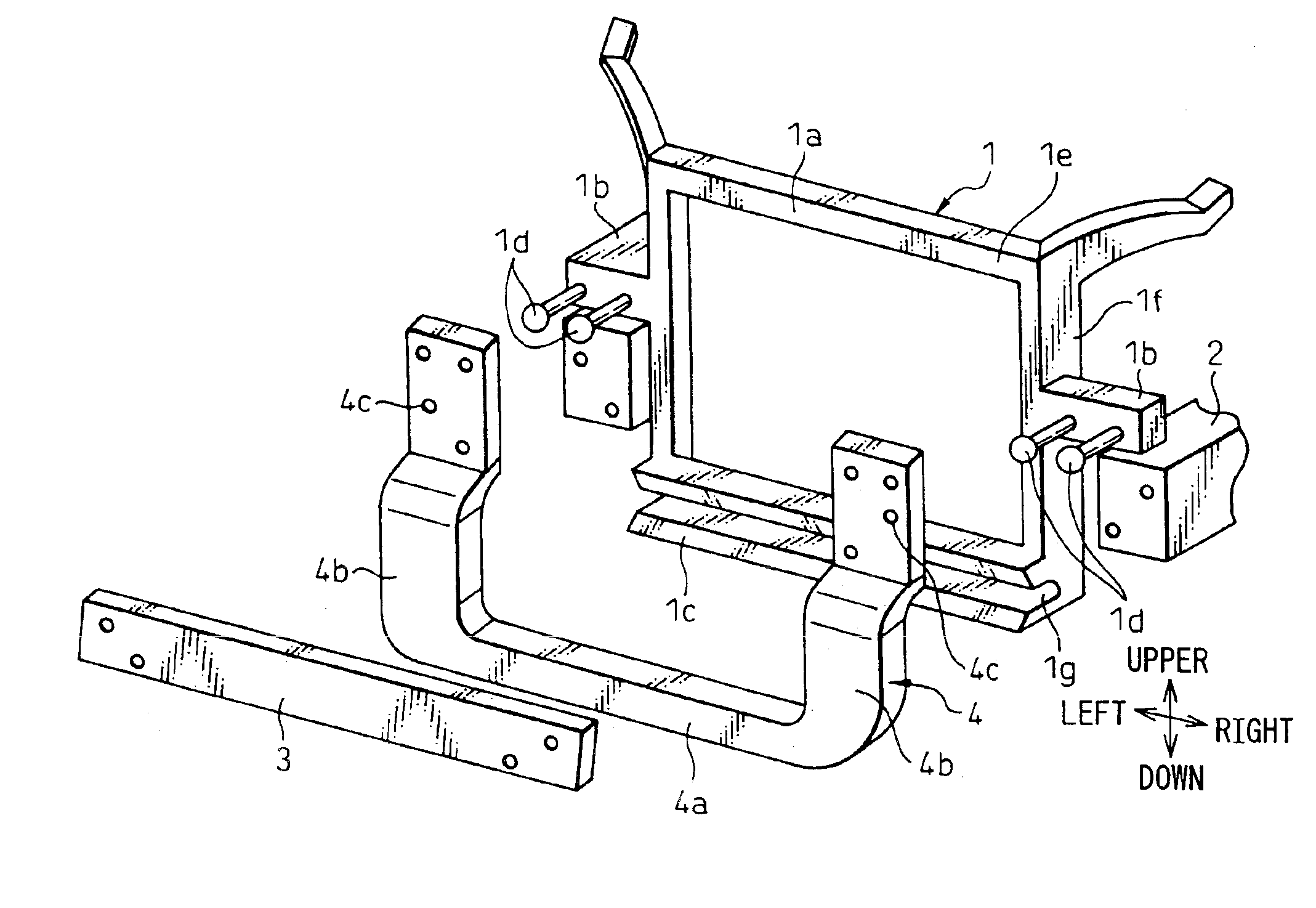
Vehicle front end structure
InactiveUS6869131B2Avoid breakingImprove rigidityVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A carrier (1) is secured to a vehicle front end portion via a bracket (4) secured to side members (2) and a bumper reinforcement (3). The connecting portions of the carrier (1) to the bracket (4) are deviated from the side members (2) when viewed from the front side of a vehicle. The bracket (4) is provided with a reinforcing member portion (4a) to connect the left and right side members (2). Accordingly, the action of a large impact force on the carrier (1) can be prevented because only a collision force from the bumper reinforcement (3) acts on the carrier (1) and no reaction force, from the side members, acts on the carrier, when a collision occurs. Therefore, the carrier (1) can be prevented from being broken when a light collision occurs because the attaching portions of the carrier (1) are seldom broken. The rigidity of a vehicle body can be increased by the reinforcing member portion (4a), and the necessary rigidity of the carrier (1) can be reduced. Thus, the weight of the carrier (1) can be reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Ultrasonic endoscope
ActiveUS20090088646A1New structureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHeat conductingEndoscope
An ultrasonic endoscope in which the temperature rise can be suppressed with a reduced diameter. The ultrasonic endoscope includes: an ultrasonic transducer part including plural ultrasonic transducers; an exterior member for accommodating the ultrasonic transducer part; and a heat conducting part provided inside of the exterior member and respectively connected to the ultrasonic transducer part and an inner surface of the exterior member. It is preferable that the heat conducting part has a coefficient of thermal conductivity equal to or more than 10 W / (m·K). Further, it is preferable that one of the heat conducting member and the exterior member has an electric insulation property.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Video processing circuit, video processing method, liquid crystal display device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20110205208A1Reducing reverse tilt domainDrawback can be solvedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayVideo processing
A video processing circuit used in a liquid crystal panel, includes: a first boundary detector that analyzes a video signal of a present frame to detect a boundary between a first pixel and a second pixel; a second boundary detector that analyzes a video signal of a frame one frame before the present frame to detect a boundary between the first pixel and the second pixel; a correction portion that corrects an applied voltage to a liquid crystal device corresponding to a second pixel which is adjacent to a portion of the boundary detected by the first boundary detector, which is changed from the boundary detected by the second boundary detector from the applied voltage specified by the video signal of the present frame to a voltage equal to or higher than the first voltage and lower than the second voltage.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
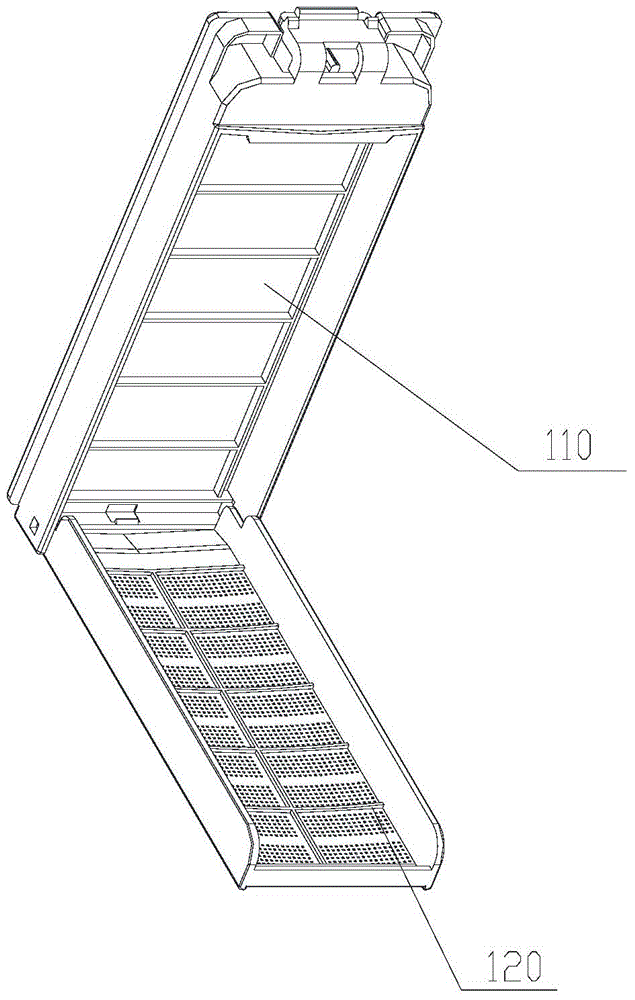
Panel construction system
InactiveUS20120240485A1Easy constructionNew structureRoof covering using slabs/sheetsSolar heating energyArchitectural engineeringSolar energy conversion
A panel construction system includes a plurality of rails and a plurality of panels. Each rail has a longitudinally-extending base with opposing longitudinally-extending L-shaped sides coupled to at least a portion of the base to thereby define a longitudinally-extending T-shaped channel. Each panel defines a longitudinally-extending T-shaped channel that is recessed within an outer surface of the panel at one end thereof and extends from the outer surface at an opposing end of the panel. One or more of the panels can incorporate at least one auxiliary-function feature such as solar energy conversion features.
Owner:AMARASINGHE DISAMODHA C
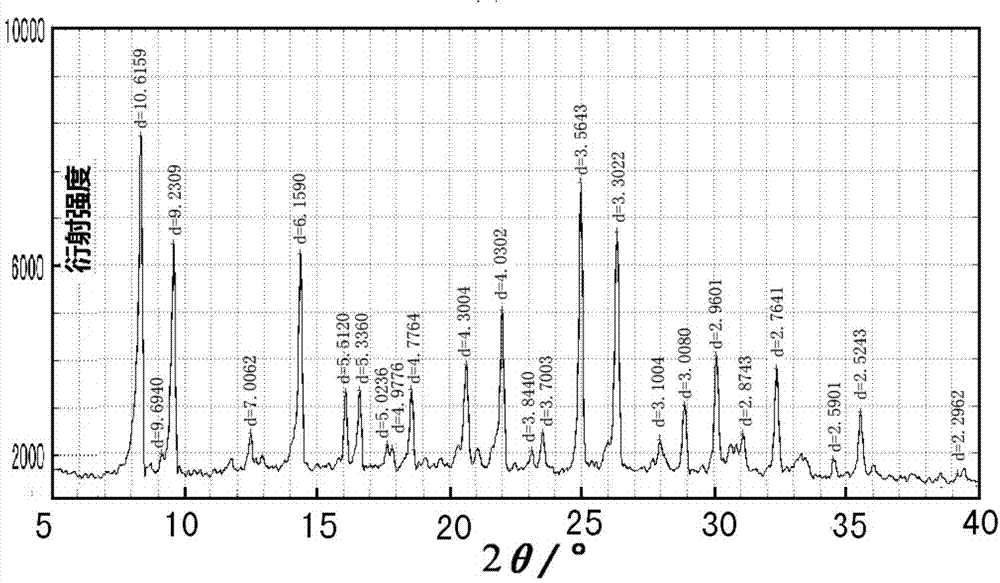
Nano-polycrystalline SAPO molecular sieve with high specific surface area, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104760975AImprove performanceNew structureMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesPhosphoric acidAluminium phosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of zeolite molecular sieve materials, and concretely relates to a nano-polycrystalline SAPO molecular sieve with a high specific surface area, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The nano-polycrystalline SAPO molecular sieve with a high specific surface area is a CHA structure type or RHO structure type or CHA structure and RHO structure eutectic silicoaluminophosphate (SAPO) molecular sieve, is synthesized through a gas and solid phase crystal transformation reaction of a amorphous silica alumina phosphorus oxide dry glue in steam of a water and diethylamine mixed template, and is especially suitable for catalyzing adsorbing separation of micro-molecular gases from low carbon olefins prepared from methanol.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUYU NEW MATERIAL TECH
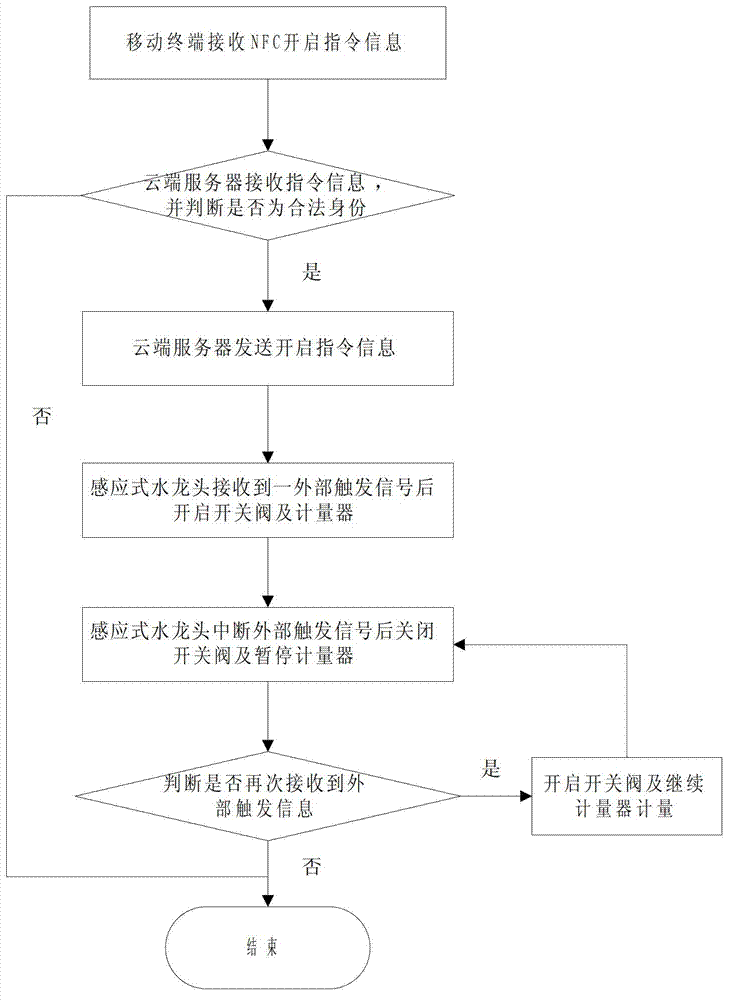
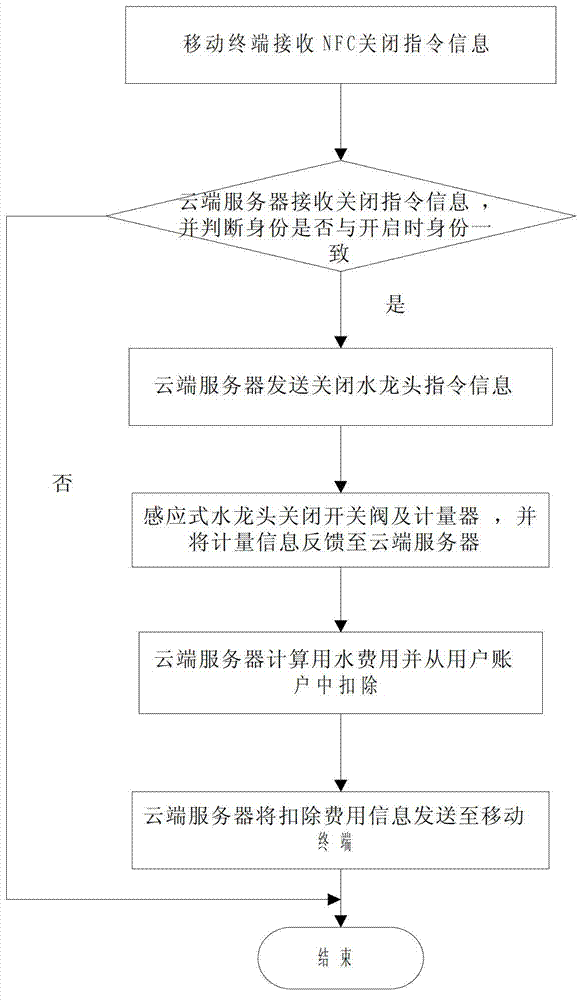
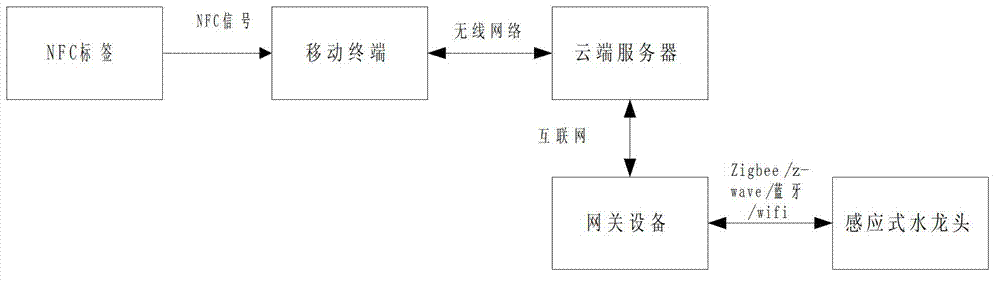
Use method and system for public water tap based on NFC (near field communications)
ActiveCN102829227ANew structureImprove performanceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesProcessing InstructionPublic place
The invention discloses a use method and a system of a public water tap based on NFC (near field communications), and the system comprises a NFC label, a mobile terminal, an inductive water tap and a cloud server. The NFC label is used to send the requests for turning on / turning off to the mobile terminal by means of NFC signals; the mobile terminal is used to receive the signals and send the control instruction to the cloud server according to the requests for turning on / turning off; the cloud server is used to receive the control instruction, process the instruction information, execute the instruction to turn on / turn off the inductive water tap and charge the water rate; the NFC label is corresponded with the inductive water tap. The conductive water tap, NFC communication technology and zigbee / z-wave / Bluetooth wireless technology are effectively combined in the system to realize the payment system of public water, and the waste problem of water resources in public place is effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING IOT SENSOR TECH
Deposition apparatus
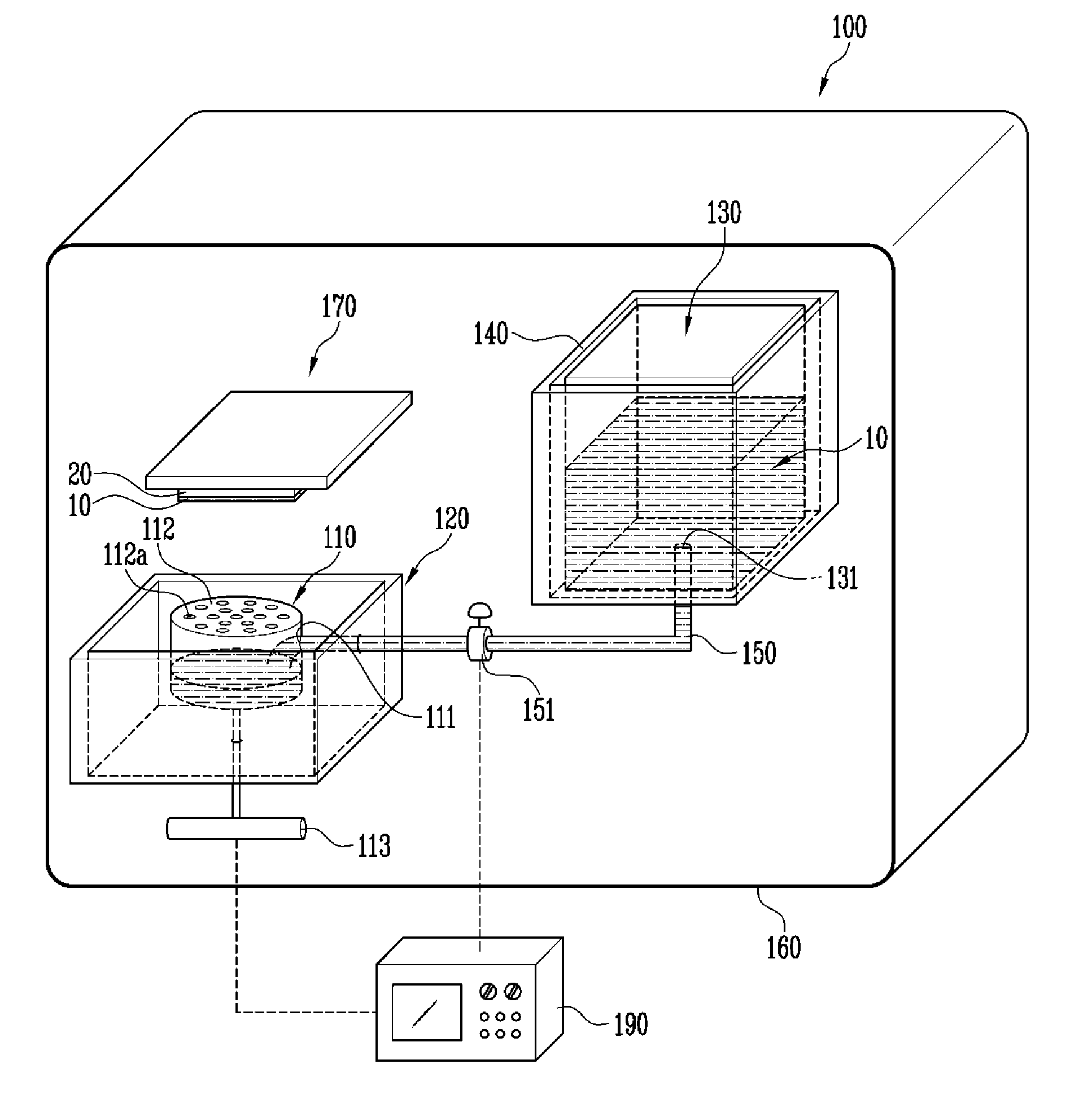
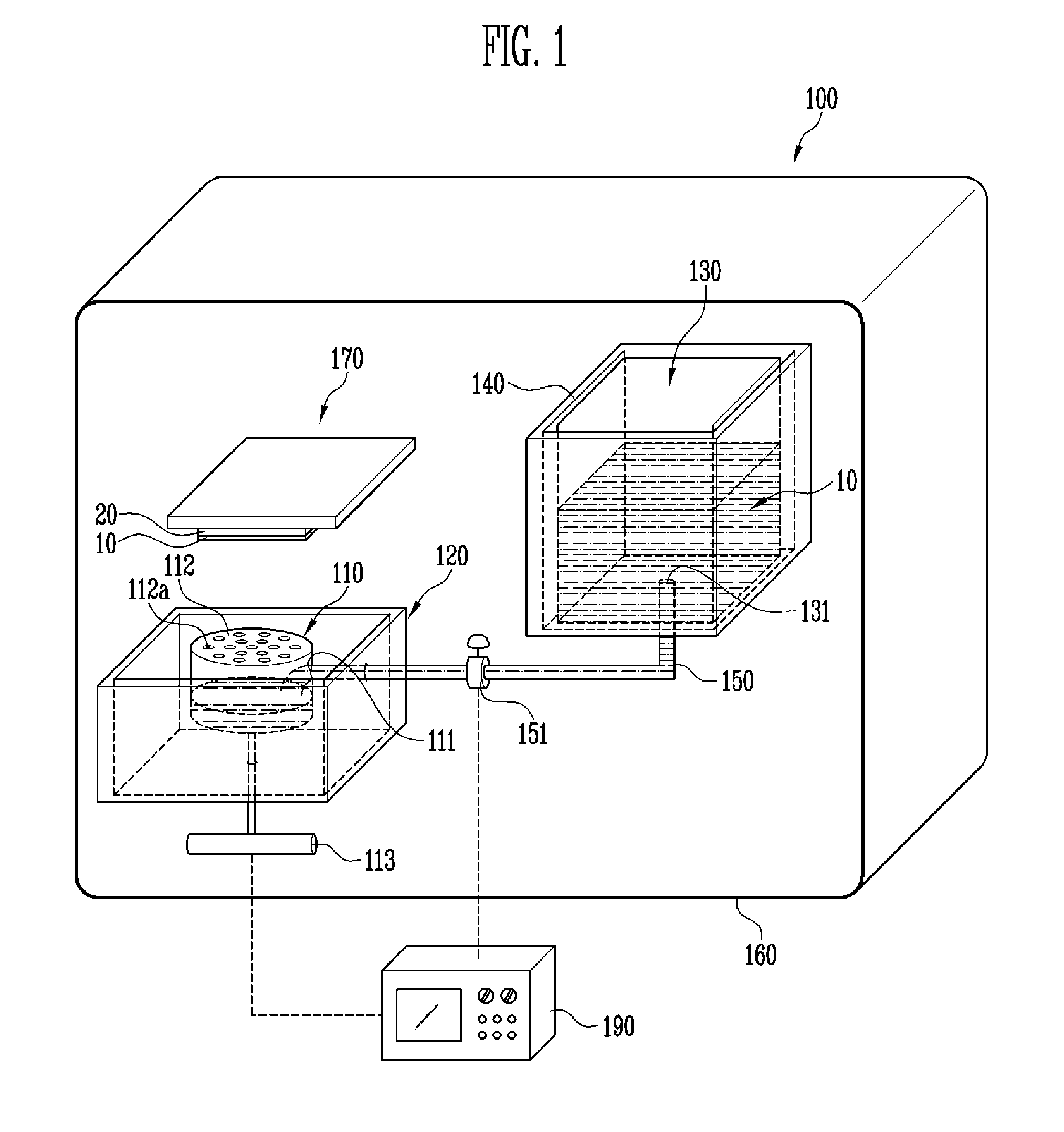
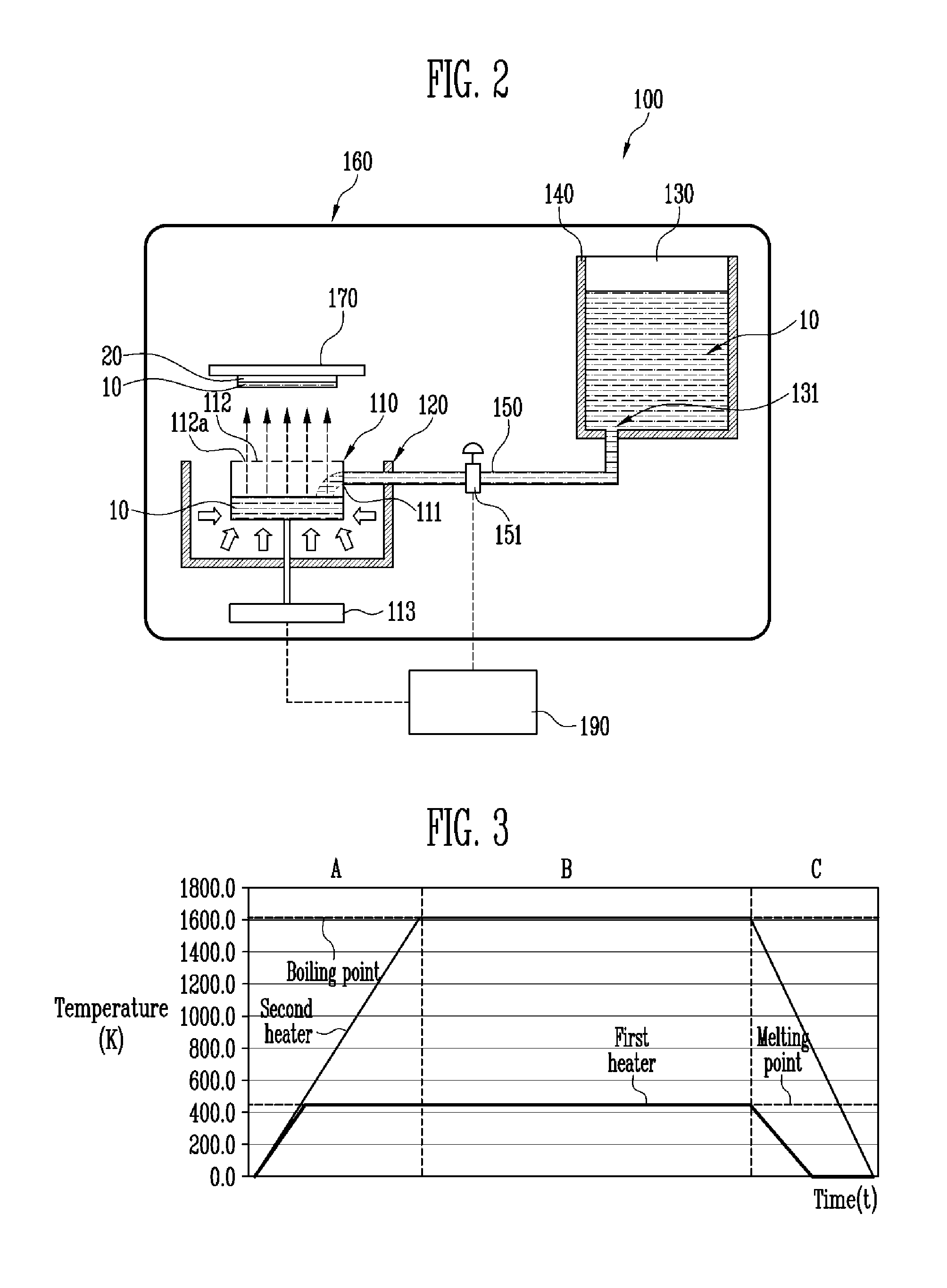
InactiveUS20130276706A1Guaranteed continuous performanceOverall size miniaturizationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEngineeringCrucible
A deposition apparatus includes a crucible having an inlet, a first heater heating the crucible, a tank supplying an object to be deposited to the crucible and having an outlet, a second heater heating the tank, and a transfer pipe connecting the outlet of the tank and the inlet of the crucible. The first heater has a first temperature range, and the second heater has a second temperature range lower than the first temperature range. The object to be deposited may be liquefied within the tank and transferred in the liquid state to the crucible via the transfer pipe. The amount of the object to be deposited within the crucible may be continuously maintained at an approximately constant value by regulation of the flow of the liquefied object to be deposited from the tank to the crucible based upon the weight of the object to be deposited within the crucible.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
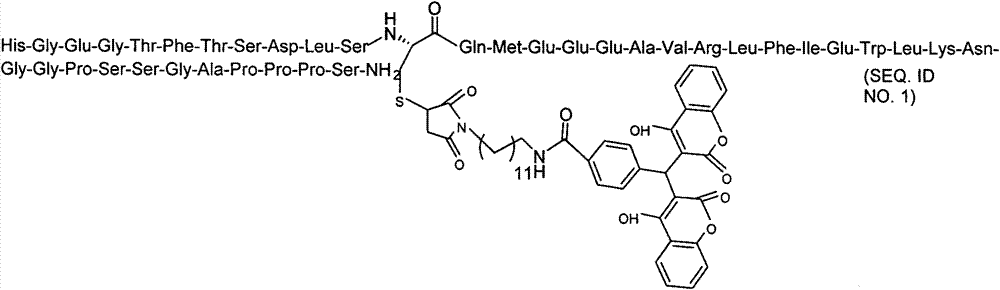
Long-acting Exendin-4 analogue and application thereof
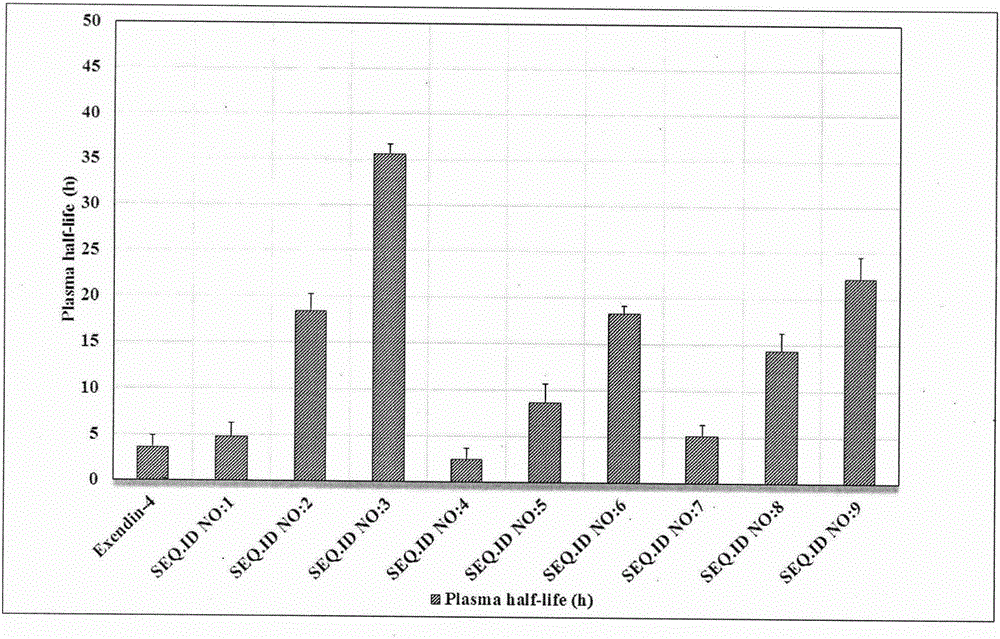
InactiveCN105936647AChemically stableProlonged plasma half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderLong actingPharmacological action
The invention relates to a long-acting Exendin-4 analogue and a synthesis method thereof. Exendin-4 is transformed to obtain the Exendin-4 analogue having longer pharmacological action time, synthesis of a target polypeptide is rapidly achieved by a microwave-promoted solid phase synthesis method, and a crude product is purified and freeze-dried to obtain the Exendin-4 analogue.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Long-effecting exenatide (Exendin-4) analogue and application thereof
ActiveCN107141348AGood hypoglycemic effectChemically stablePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSynthesis methodsPharmacologic action
The invention relates to a long-effecting exenatide (Exendin-4) analogue and a synthetic method thereof. The Exendin-4 is modified to obtain the Exendin-4 analogue with longer pharmacologic action time, the synthesis of target polypeptide is quickly realized through an orthogonally protection strategy solid-phase synthesis method, and a crude product is purified and freeze-dried to obtain the Exendin-4 analogue.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
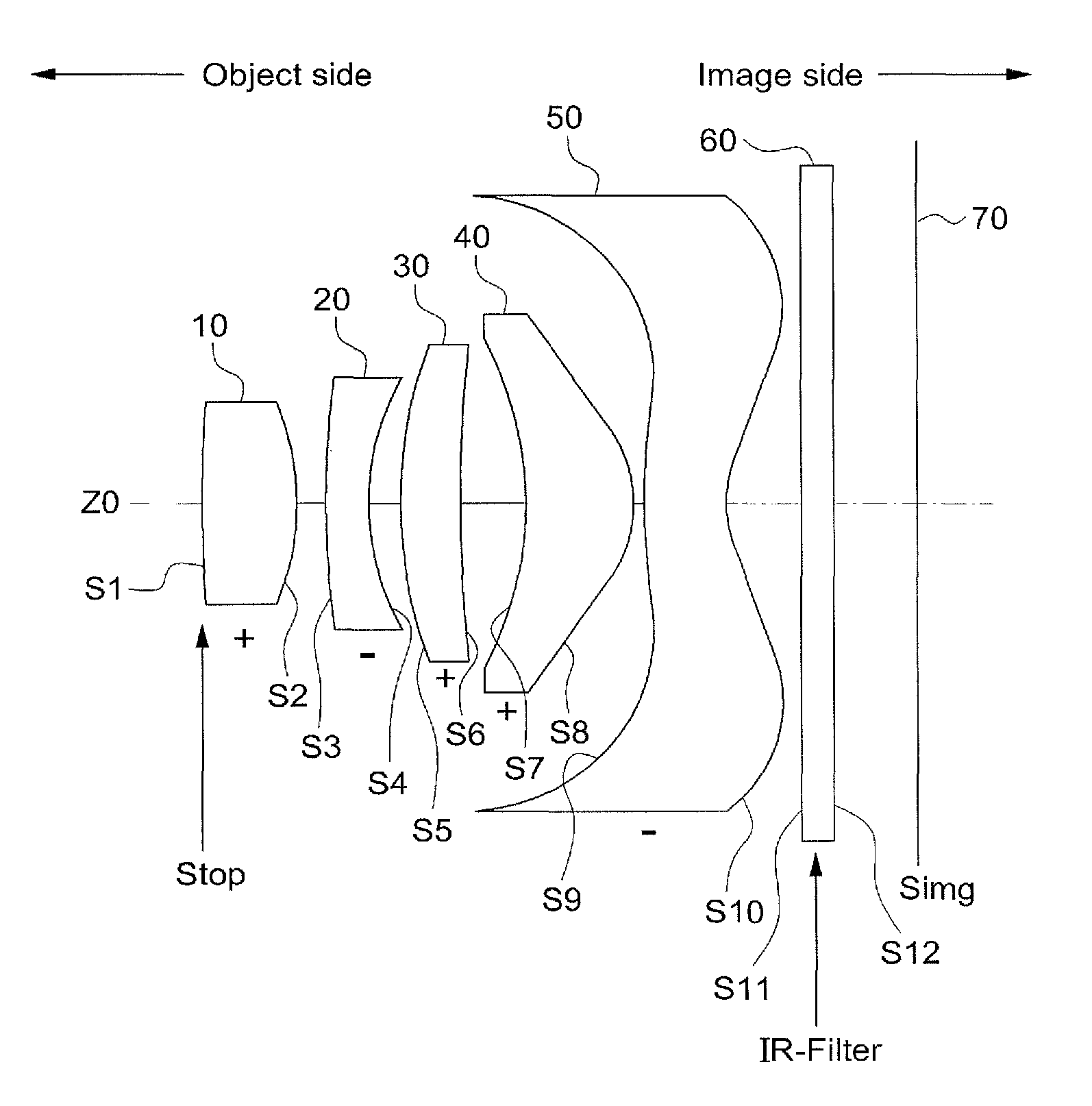
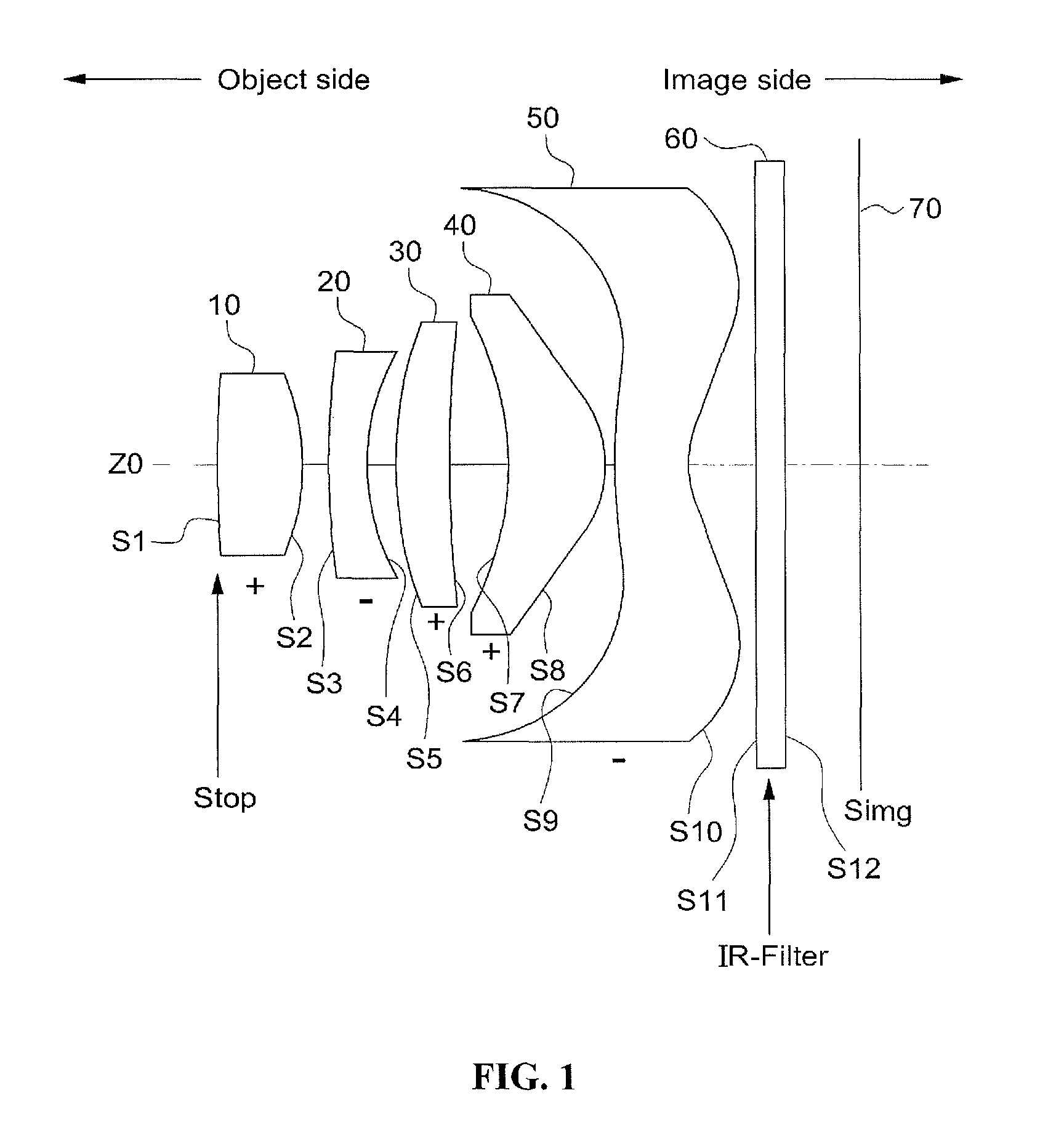
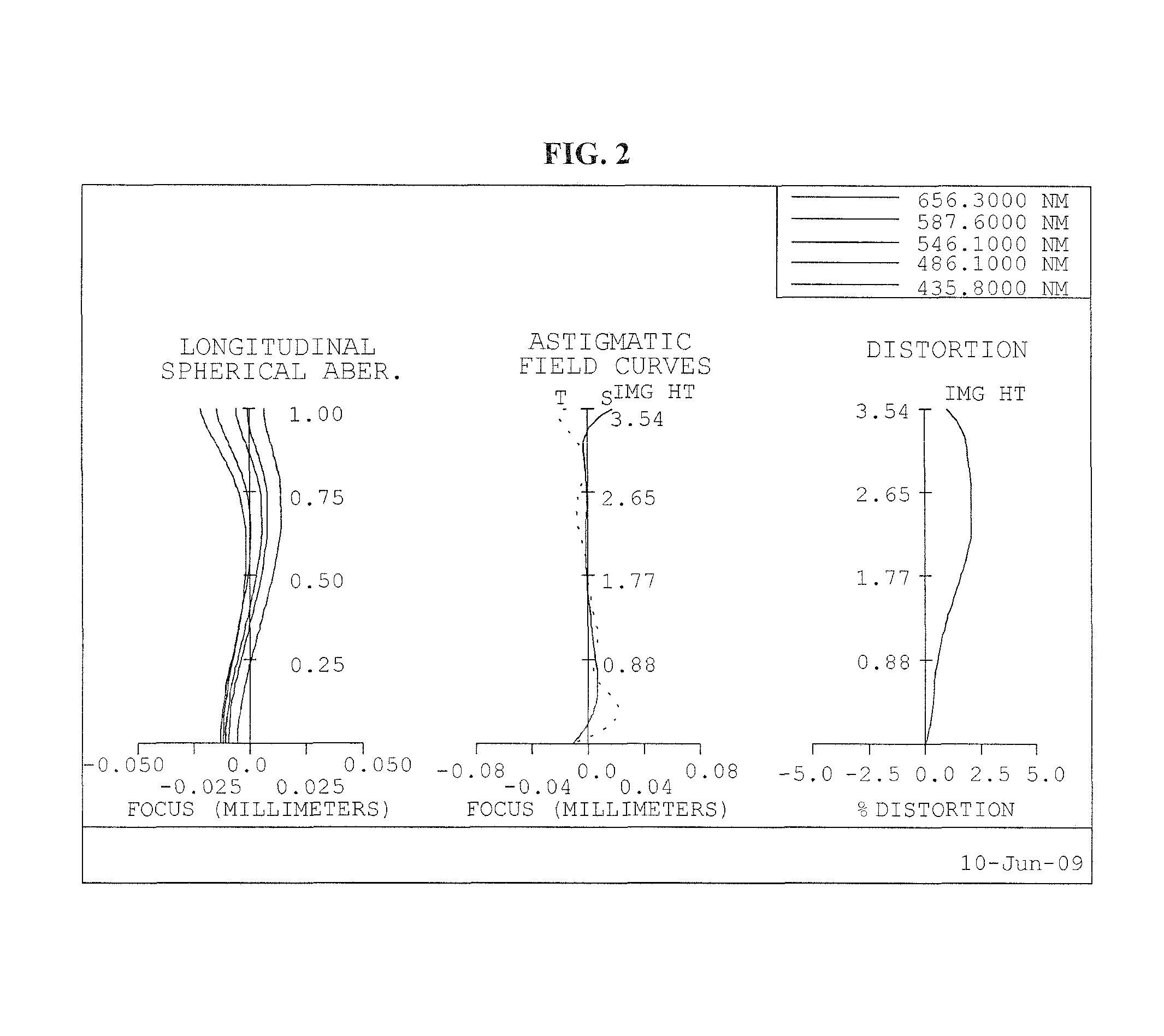
Imaging lens
Disclosed herein is an imaging lens suitable for a camera module using a high resolution imaging sensor, decreasing a flare phenomenon and reducing the sensitivity. The imaging lens comprises, in order from the object side, a first lens having positive (+) refractive force; a second lens having negative (−) refractive force; a third lens having positive (+) refractive force; a fourth lens having positive (+) refractive force; and a fifth lens having negative (−) refractive force, wherein an object side plane of the third lens is convexly formed.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Rotor for motor
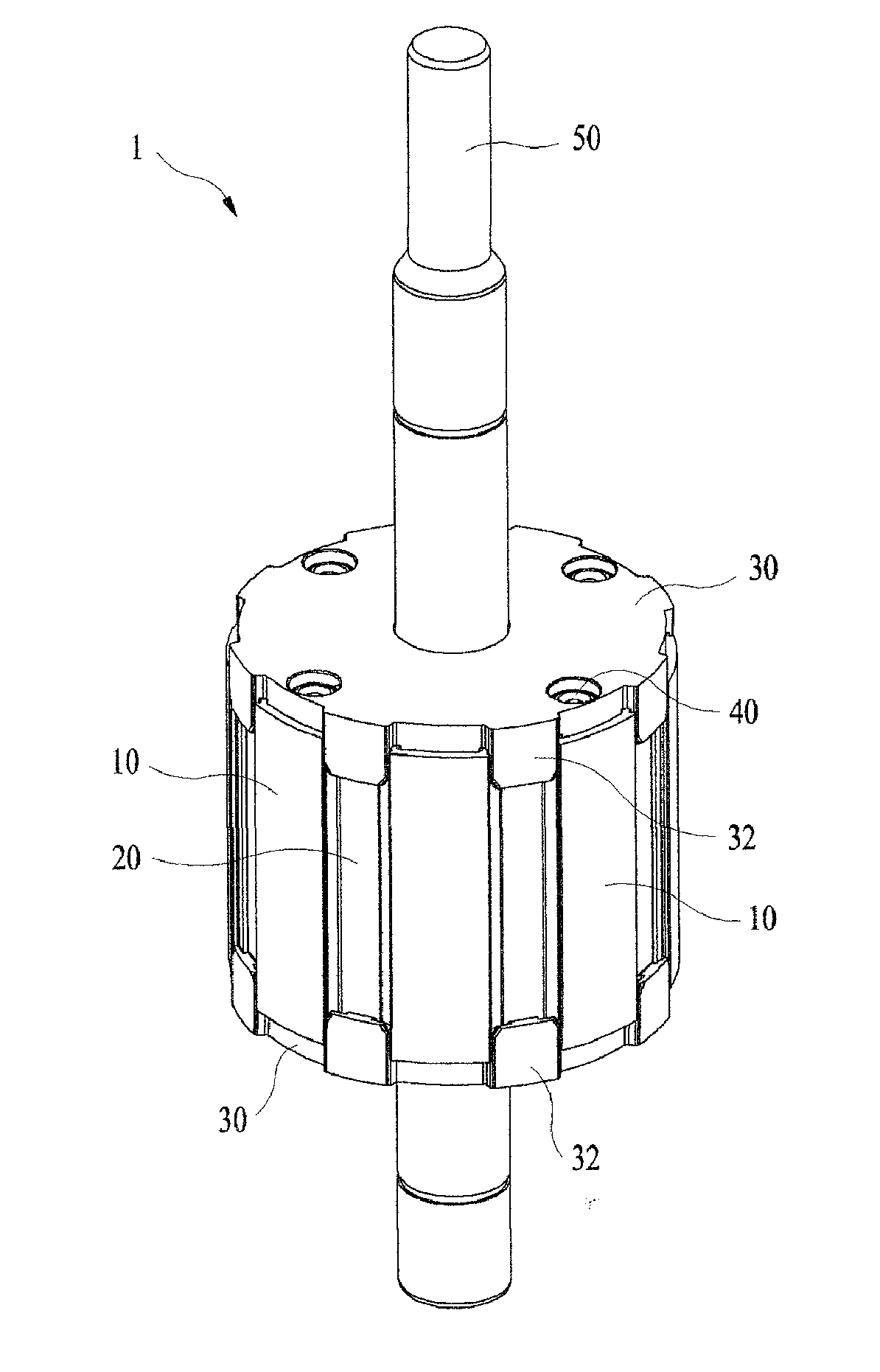
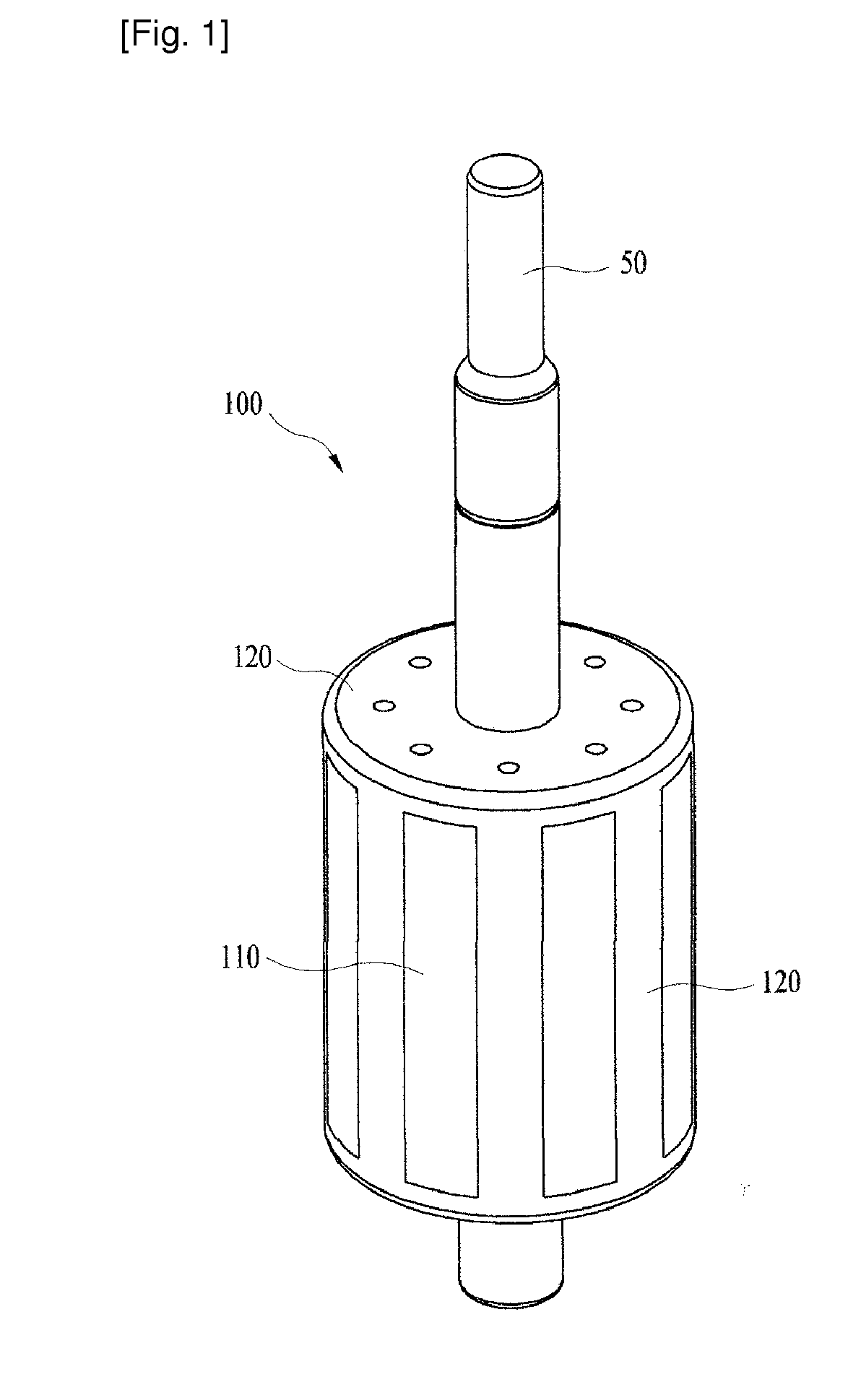
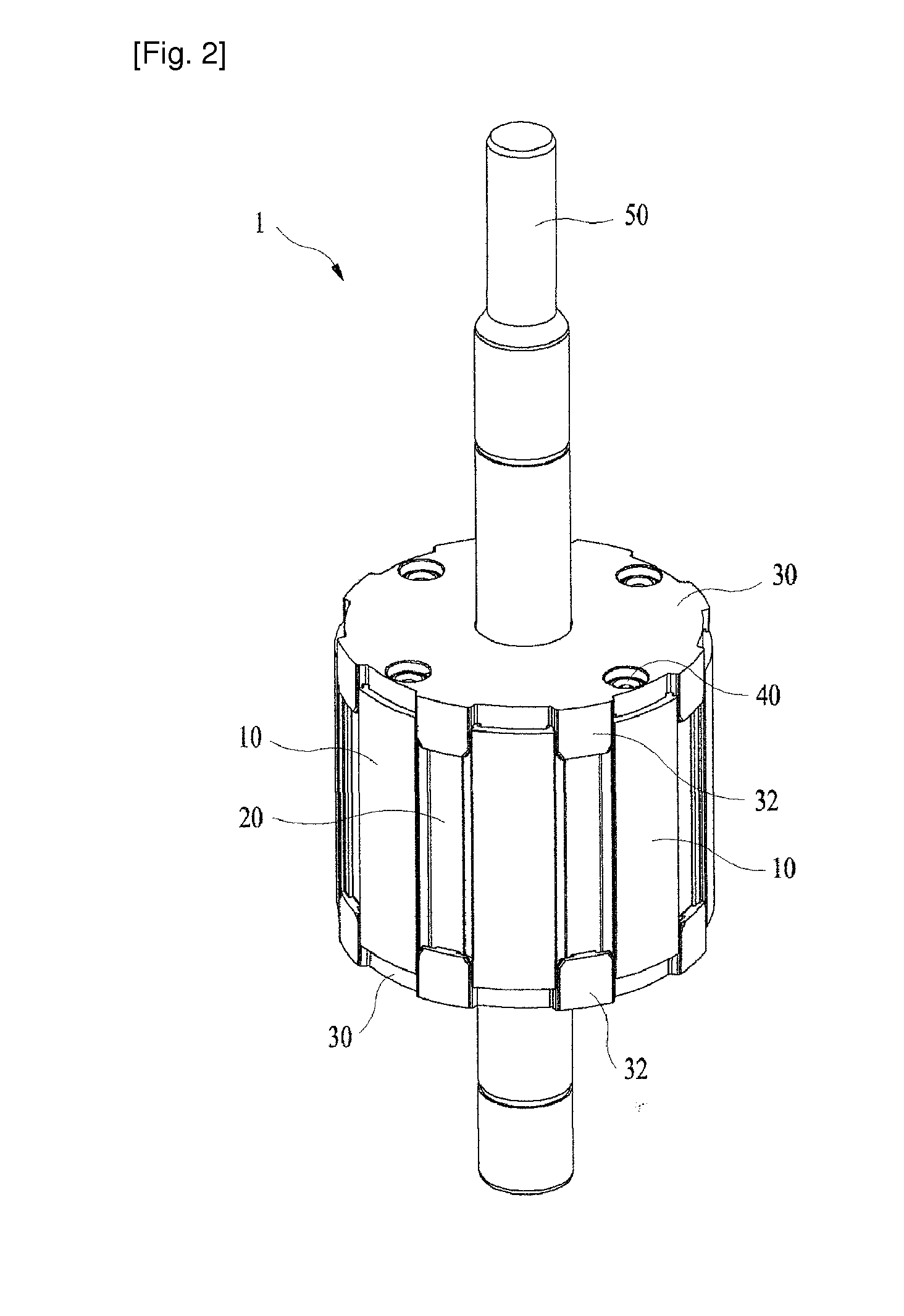
ActiveUS20140191608A1Simple manufacturing processReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnet
Disclosed therein is a rotor for a motor. The rotor includes: a rotor core including an annular ring having a shaft hole formed at a central portion thereof, a plurality of yokes formed around the annular ring, and magnet insertion holes formed between the neighboring yokes; magnets respectively inserted into the magnet insertion holes; and a pair of rotor covers each having a ring plate, which has a shaft insertion hole formed at a central portion thereof, and a plurality of stoppers protrudingly formed around the ring plate. A pair of the rotor covers are joined to an upper portion and a lower portion of the rotor core in such a fashion that the stoppers are respectively located at side portions of the magnet insertion holes.
Owner:NEW MOTECH
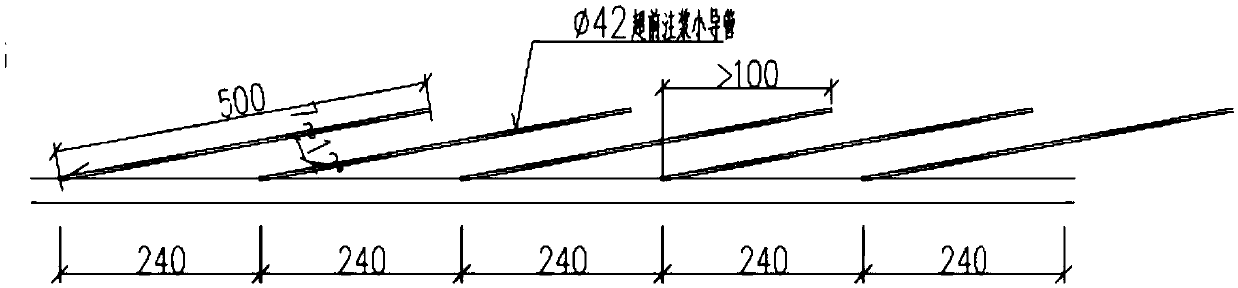
Sandy clay geological tunnel roof collapse treatment method
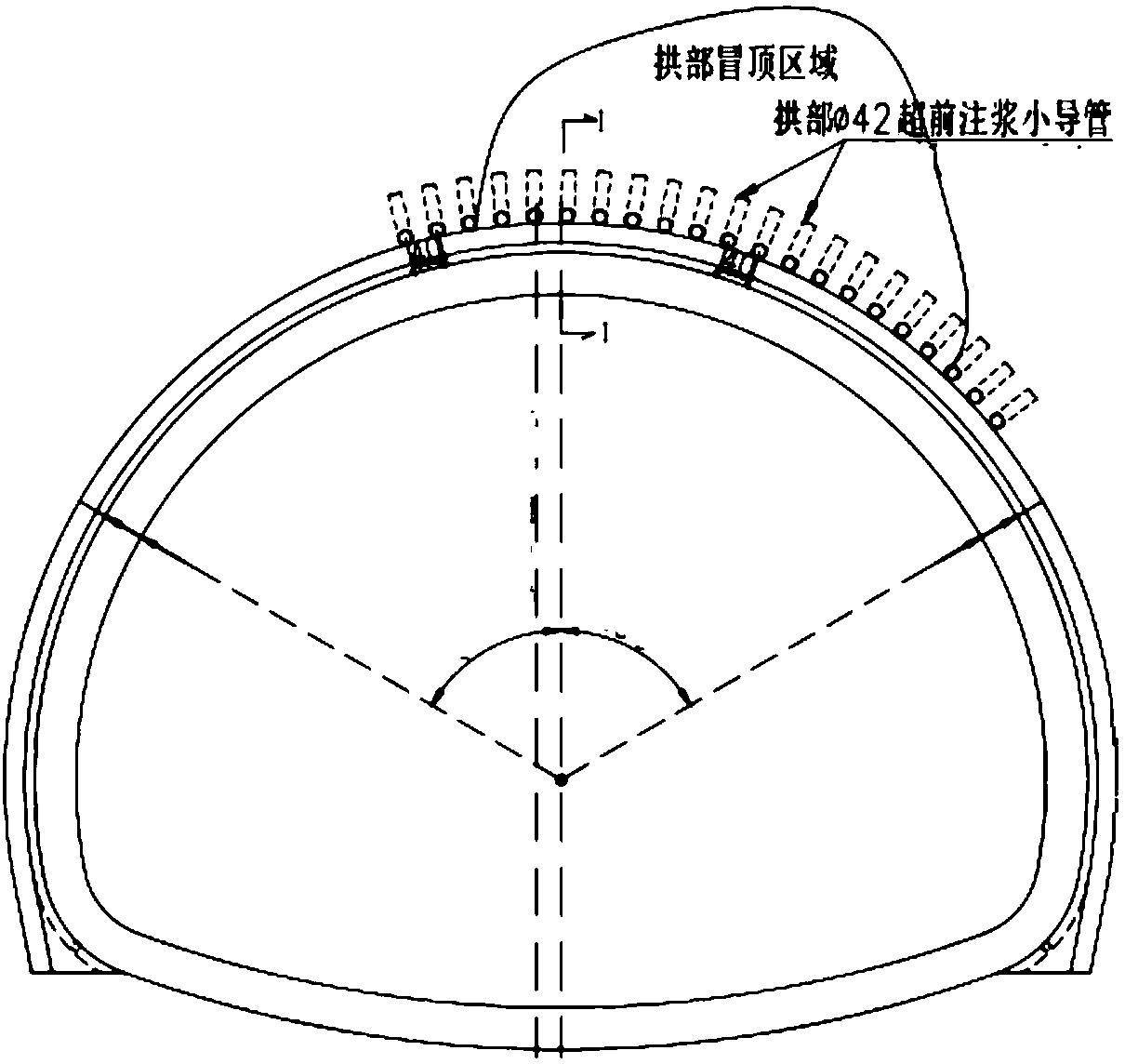
ActiveCN108678776AReduce construction riskEasy constructionMining devicesConstructionsEngineeringEarth surface
The invention discloses a sandy clay geological tunnel roof collapse treatment method. The method includes the steps of carrying out advanced geological forecasting, conducting roof collapse earth surface treatment, carrying out in-hole backpressure backfill, achieving advanced support through small conduits, adopting a follow-pipe drilling method based on alternate application of drilling tools for carrying out dual-layer pipe shed advanced pre-reinforcement treatment, conducting excavation, and continuing monitoring measurement after construction is finished. The sandy clay geological tunnelroof collapse treatment method is safe and reliable, the construction risks of tunnels can be reduced, the reinforcement effect is obvious, secondary collapse of a vault can be effectively controlled, construction is convenient, and the project quality can be ensured.
Owner:CHINA COMM NORTH ROAD & BRIDGE
Azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102093569ANew structureNon-linear opticsPolymer scienceAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
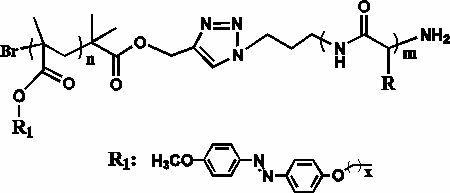
The invention discloses an azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. One block of the azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer is an azobenzene radical-containing polymer and one block of the azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer is a polypeptide shown as the formula, wherein the number of methylene in an azobenzene radical is x which is equal to 2 to 9. The preparation method of the azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer comprises the following steps of: preparing the azobenzene radical-containing polymer, namely a homopolymer, by an atom transfer radical polymerization method; preparing the polypeptide by homopolymerizing an amino acid or an amino acid derivative compound; and connecting the azobenzene radical-containing polymer and the polypeptide through a click chemistry process to form the azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer. The method has the advantage that the azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer with a novel structure is prepared by the preparation method which is simple and feasible and in which the advantages of the click chemistry are fully used; and the azobenzene polypeptide block copolymer can be applied in the fields of non-linear optical materials and special photoresponse and storage devices and has wide application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Display apparatus
ActiveUS20190129231A1Improve sound qualityFacilitates to output soundStatic indicating devicesElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersEngineeringMagnetic loop
A display apparatus includes a display panel configured to display an image; a supporting member on a rear surface of the display panel; a magnetic circuit unit in the supporting member, the magnetic circuit unit configured to generate a magnetic loop; and a coil unit on the rear surface of the display panel. The magnetic circuit unit and the coil unit are configured to vibrate the display panel to generate sound.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Anode active material for secondary battery and method for producing the same, anode and lithium ion battery using the same
InactiveUS20150214548A1New structureNon-metal conductorsConductive materialSmall-angle X-ray scatteringSilicon oxide
To form the silicon oxide-based composite material having new structure as directly obtained by pyrolyzing polysilsesquioxane having specific structure under an inert gas atmosphere, and the formed silicon oxide-based composite material having scattering recognized in a region: 0.02Å−1<q<0.21 Å−1 in a spectrum measured by a small-angle X-ray scattering method, having graphite carbon in which scattering is recognized at 1,590 cm−1 (G band / graphite structure) and 1,325 cm−1 (D band / amorphous carbon), and a peak intensity ratio (ID / IG ratio) of amorphous carbon to crystalline carbon being in a range of 2.0 to 5.0 in a spectrum measured by Raman spectroscopy, and being represented by a general formula SiOxCy (0.5<x<1.8, 1<y<5).
Owner:JNC CORP +1
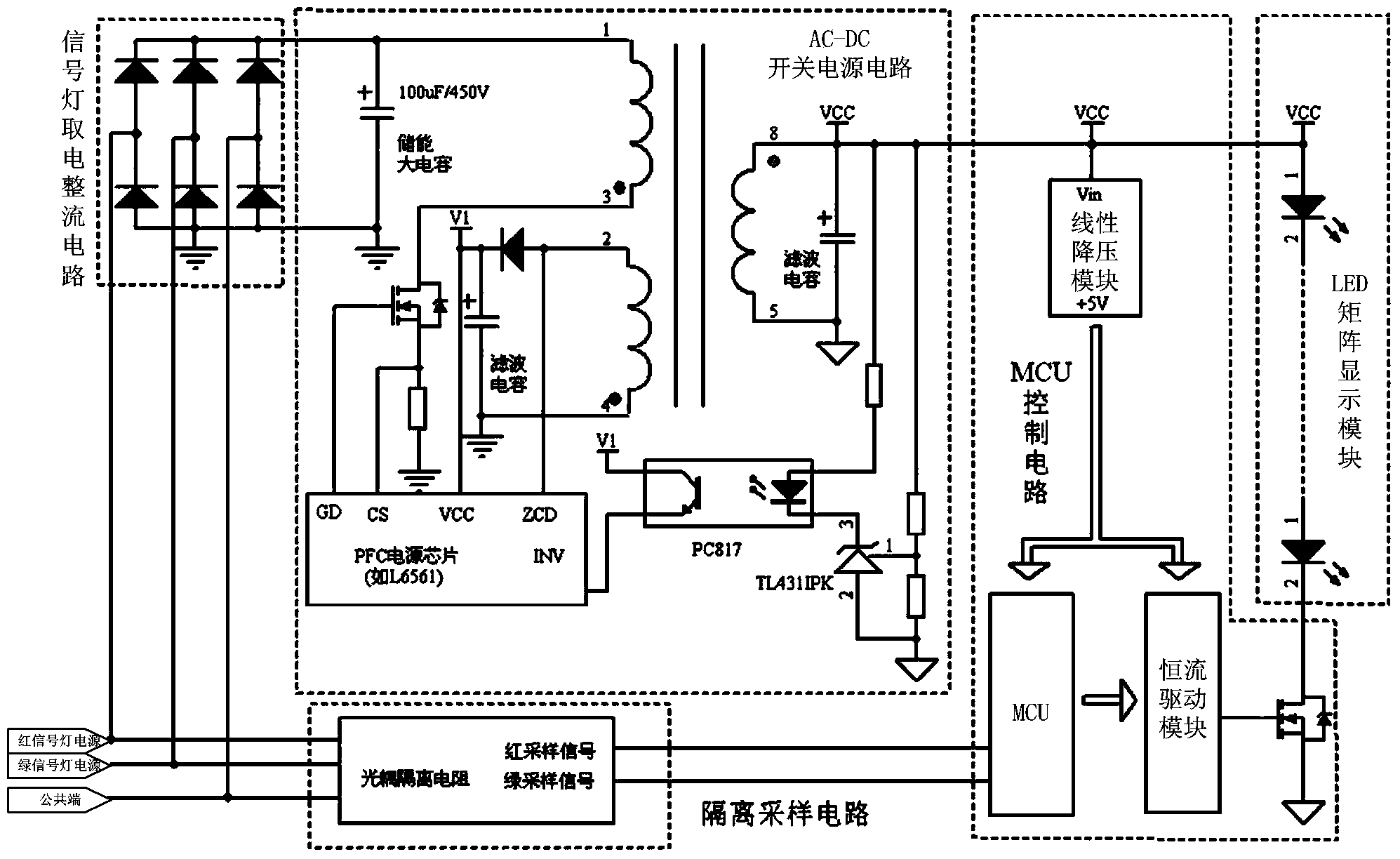
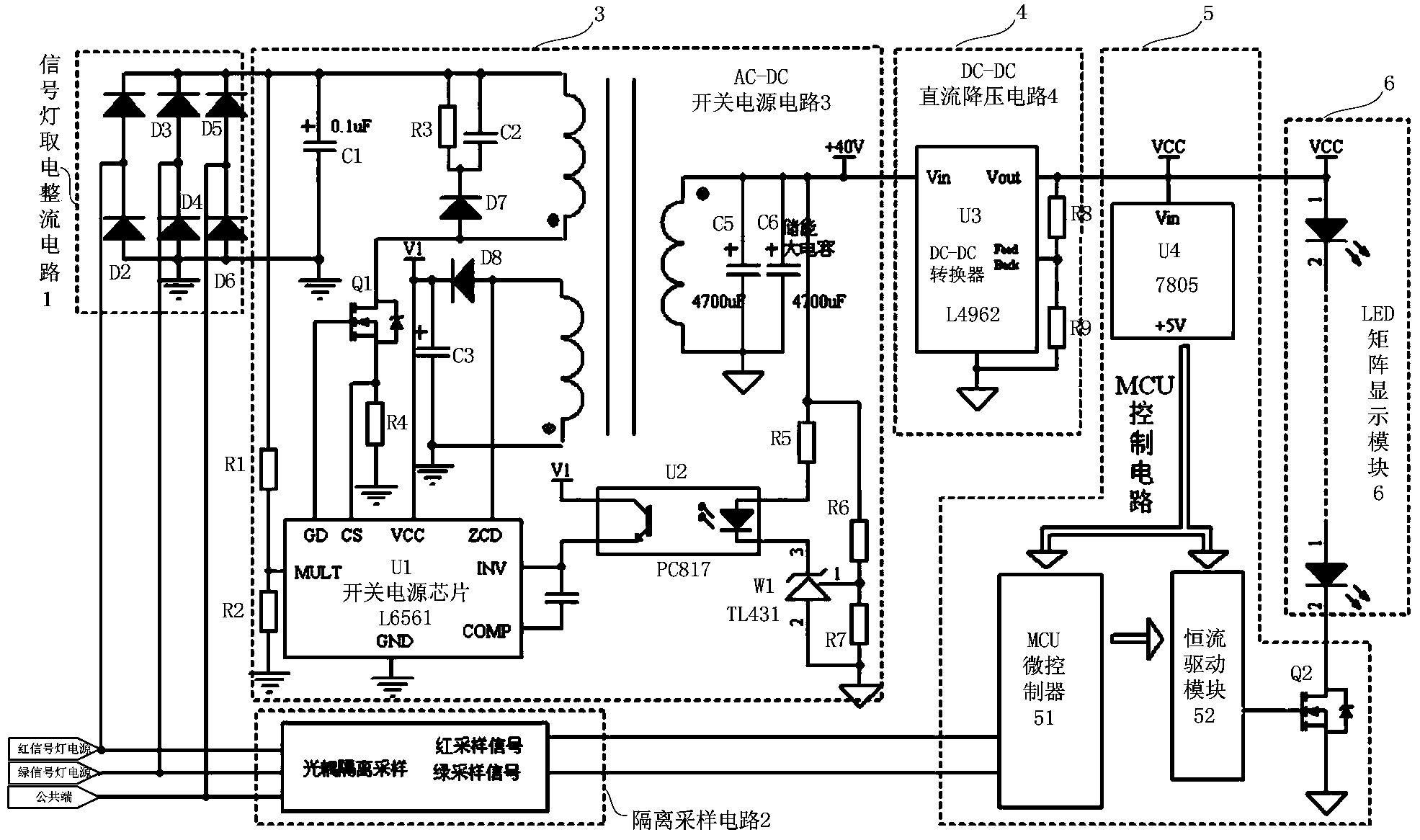
Low-impact-current high-power-factor energy storage type countdown display circuit
ActiveCN103680174ANew structureReduce the impact of starting currentRoad vehicles traffic controlCapacitanceDC - Direct current
The invention provides a low-impact-current high-power-factor energy storage type countdown display circuit which comprises a signal lamp electricity-taking rectifying circuit, an isolation sampling circuit, an AC-DC switching power supply circuit, a DC-DC direct current voltage-reducing circuit, a MCU control circuit and an LED matrix display module. The input end of the signal lamp electricity-taking rectifying circuit is connected with a red signal lamp power supply, a green signal lamp power supply and a common port, and the positive output end of the signal lamp electricity-taking rectifying circuit is connected with the input end of the AC-DC switching power supply circuit. An energy storage capacitor is connected between the output end of the AC-DC switching power supply circuit and the ground in parallel. The output end of the AC-DC switching power supply circuit is connected with the DC-DC direct current voltage-reducing circuit. The DC-DC direct current voltage-reducing circuit reduces direct-current voltage output by the AC-DC switching power supply circuit and supplies power for the MCU control circuit and the LED matrix display module. The MCU control circuit is connected with the red signal lamp power supply, the green signal lamp power supply and the common port through the isolation sampling circuit.
Owner:WUXI ANBANG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Activation of carbon nanotubes for field emission applications
InactiveUS7462498B2Field emission propertyNew structureCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeBiological activation
Substantially enhanced field emission properties are achieved by using a process of covering a non-adhesive material (for example, paper, foam sheet, or roller) over the surface of the CNTs, pressing the material using a certain force, and removing the material.
Owner:APPLIED NANOTECH HLDG
Fluff filter and washing machine with same
ActiveCN104975474AGood filtering effectNew structureOther washing machinesTextiles and paperImpellerPulp and paper industry
The invention provides a fluff filter. The fluff filter is installed on an inner drum, the side, facing the inner side of the inner wall of the inner drum, of the fluff filter is closed, and a filtering part is arranged on the side, facing the outer side of the inner wall of the inner drum, of the fluff filter. Through the fluff filter, washing water inside the inner drum is filtered, and then drained out of the inner drum. The fluff filter filters the washing water inside the inner drum, then the washing water is drained out of the inner drum, an existing fluff filtering mode is changed, and therefore the fluff filter is suitable for an existing impeller type washing machine and achieves a good filtering effect when applied to a twin power washing machine and other novel washing machines.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER WASHING MASCH CO LTD
Device and method of household appliance intelligent control
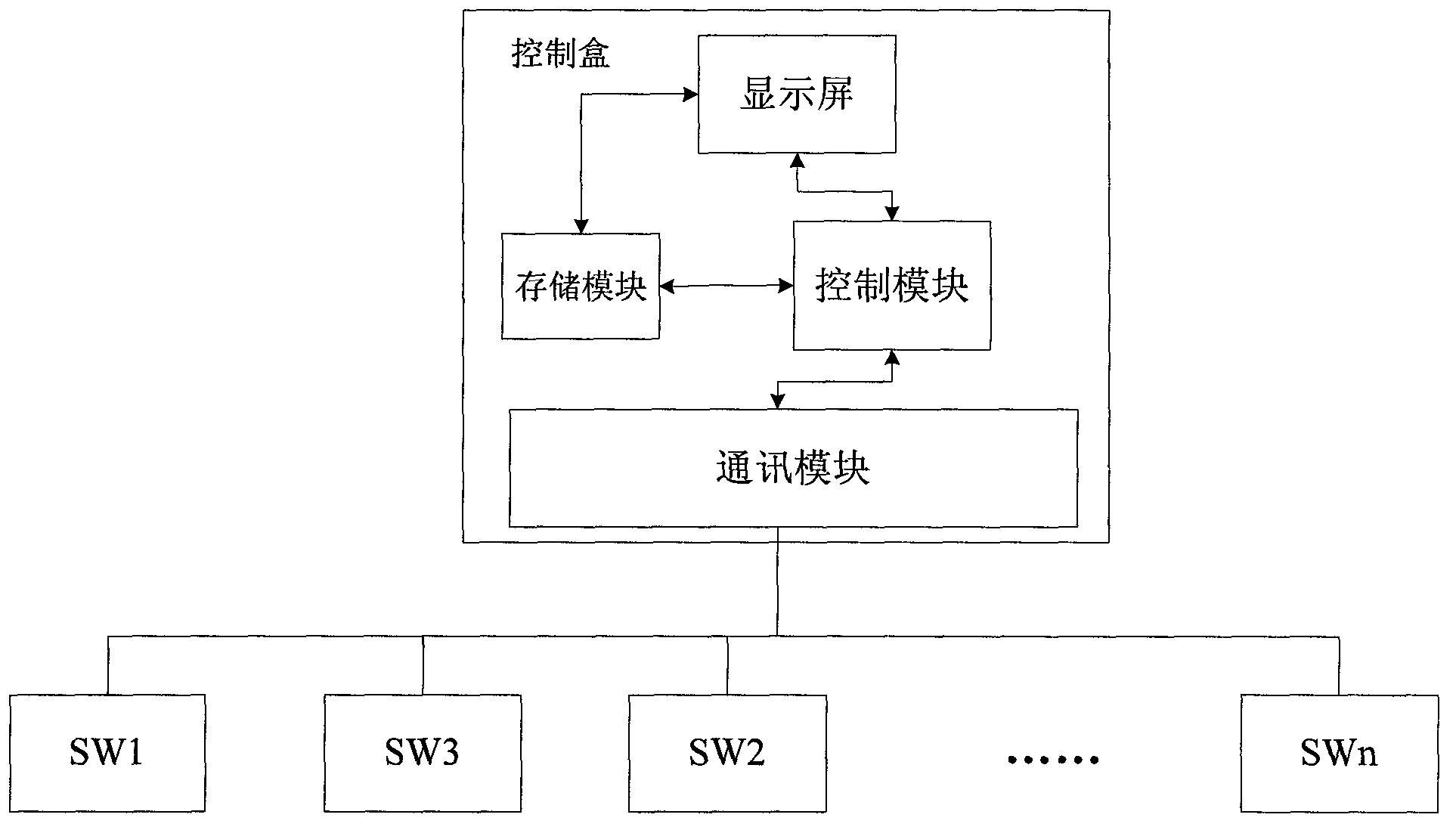
InactiveCN103257600AEasy to openEasy to closeProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersIntelligent controlControl function
The invention relates to a device of household appliance intelligent control. The device of the household appliance intelligent control comprises a plurality of switch controllers and a control box, wherein the switch controllers are respectively connected with different household appliances and used for controlling working states of the household appliances. The switch controllers have same structures. The switch controllers are connected with one another through a CAN bus. The switch controllers are connected with the control box. The control box is used for executing collection and configuration of the working states of the household appliances and operation of master control. Compared with the prior art, the device of the household appliance intelligent control has the advantages that the control box can be used for carrying out 'one key' fast control on all working states of the household appliances. When the control box is broken down, any switch controller can serve as a temporary control box for use, therefore, even the control box is broken down, and any switch controller can further carry out a uniform and fast control function on other household appliances.
Owner:BEIHAI HESI TECH
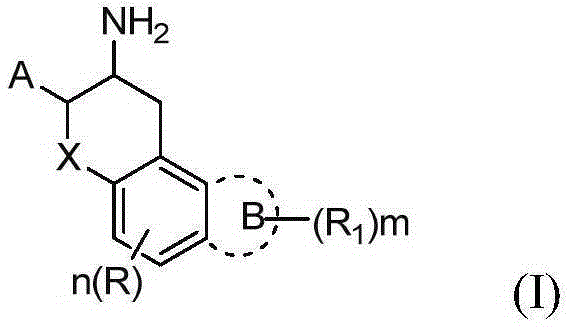
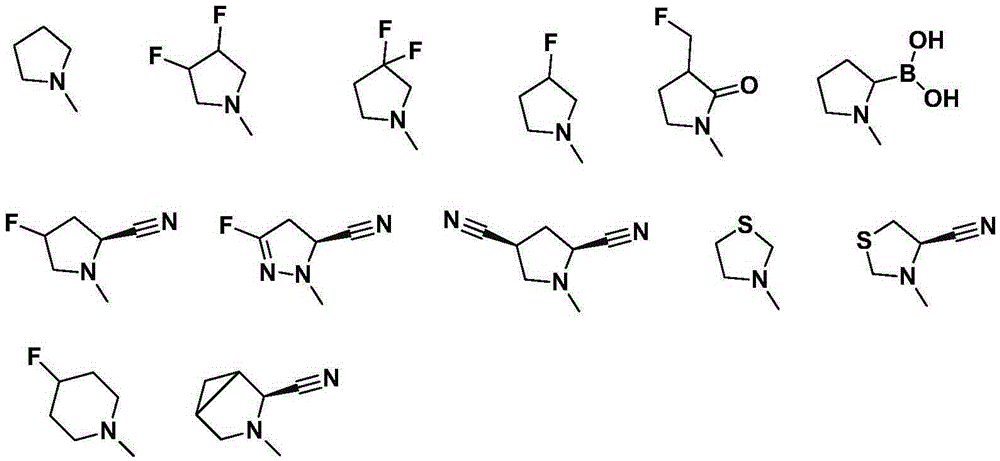
Benzo-hexatomic ring derivative used as DPP-4 inhibitor and application of benzo-hexatomic ring derivative
ActiveCN105566276ANew structureStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryMedicinal chemistryDPP-4 Inhibitors
The invention relates to a benzo-hexatomic ring derivative used as a DPP-4 inhibitor and application of the benzo-hexatomic ring derivative, in particular to compounds shown as in formula I, medicine compositions with the compounds shown as in the formula I and application of the compounds in preparing medicines for treating diseases related to DPP-4 or inhibiting the DPP-4.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Class of long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog and application thereof
ActiveCN107056928AGood hypoglycemic effectChemically stablePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSynthesis methodsGlucagon-like peptide-1
The invention relates to a class of long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog and a synthesis method thereof. The GLP-1 analogue with longer pharmacological action time is obtained by modifying GLP-1. The synthesis of target polypeptide is quickly achieved by a orthogonal protection strategy solid phase synthesis method. The crude product is purified and lyophilized to obtain the GLP-1 analog.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
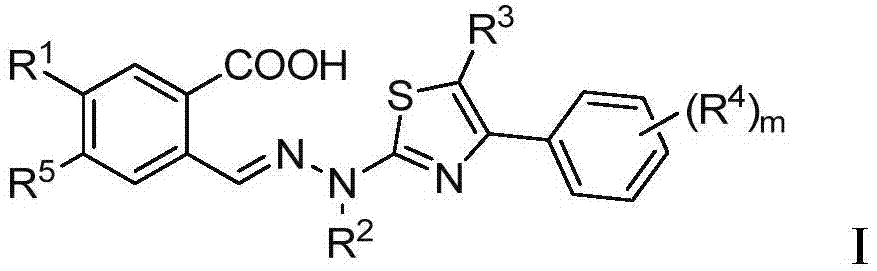
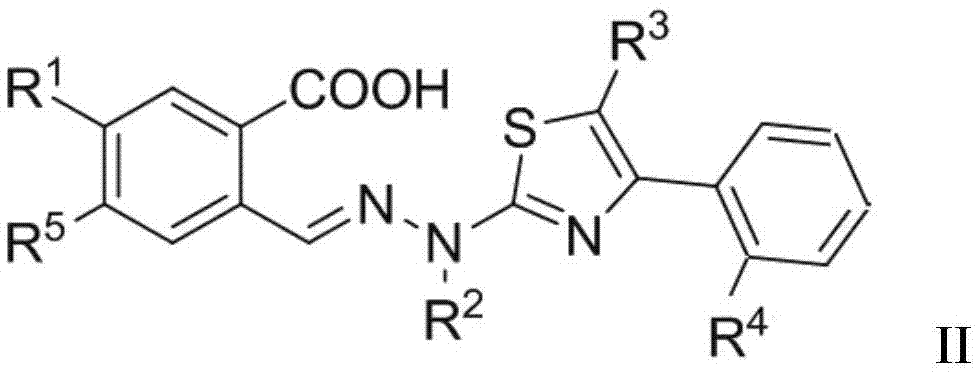
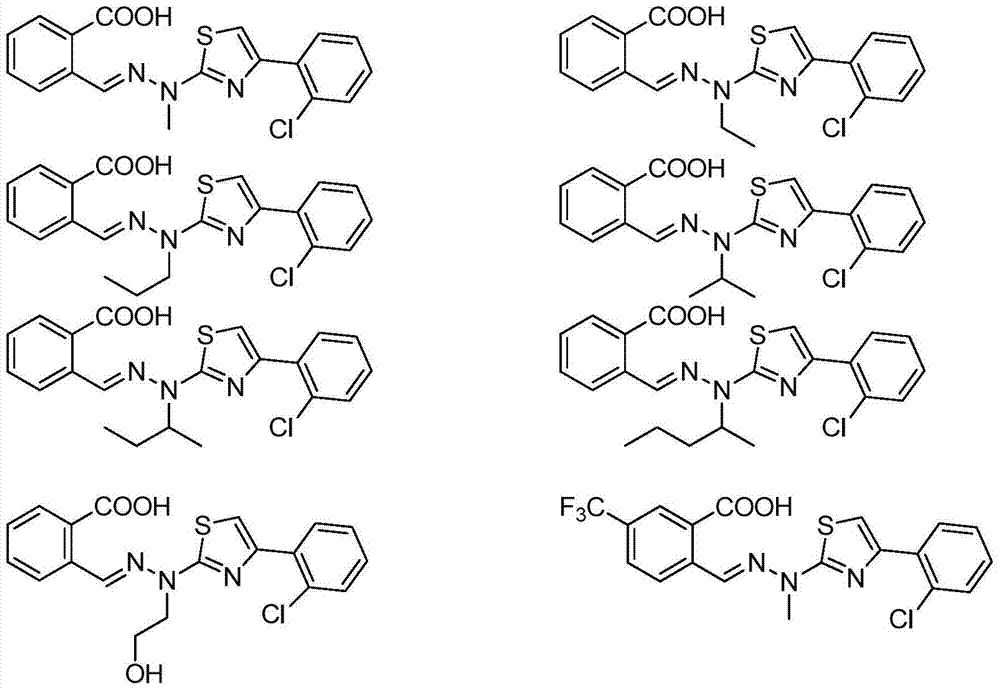
Thiazole derivative and application thereof in restraining dihydroorate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a thiazole derivative used as a DHODH restrainer and an application thereof. Specifically, the invention relates to a compound shown as formula I, a drug compound containing the compound shown as formula I and the application of the compound in preparing the drug for treating DHODH mediated diseases or restraining DHODH.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com