Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154results about How to "Realize sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
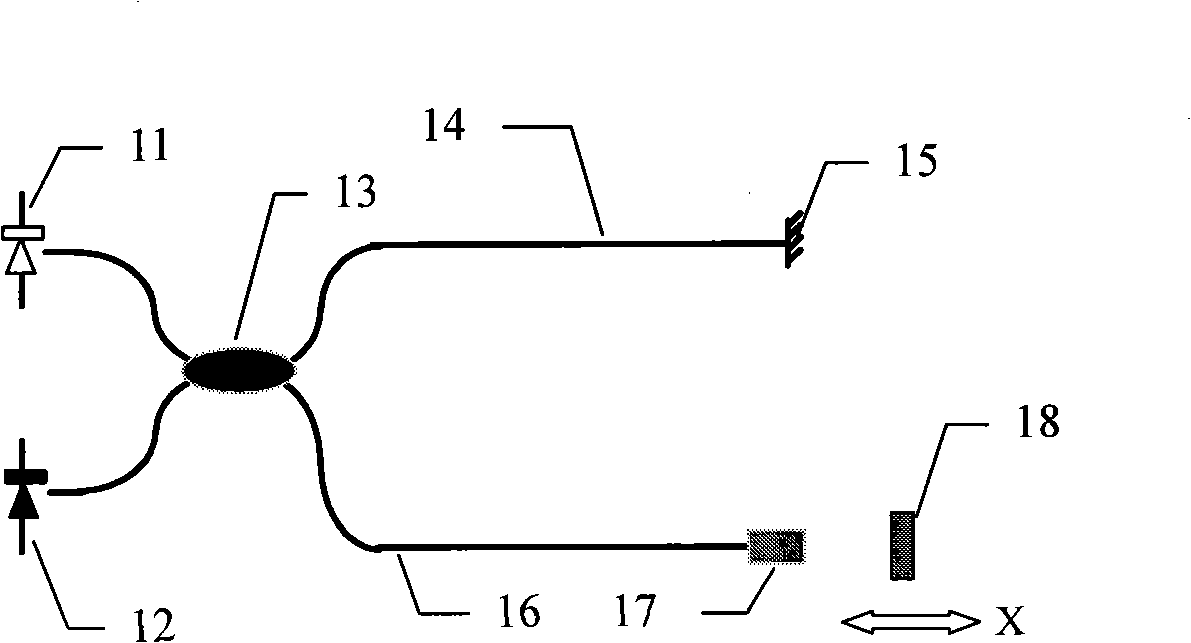
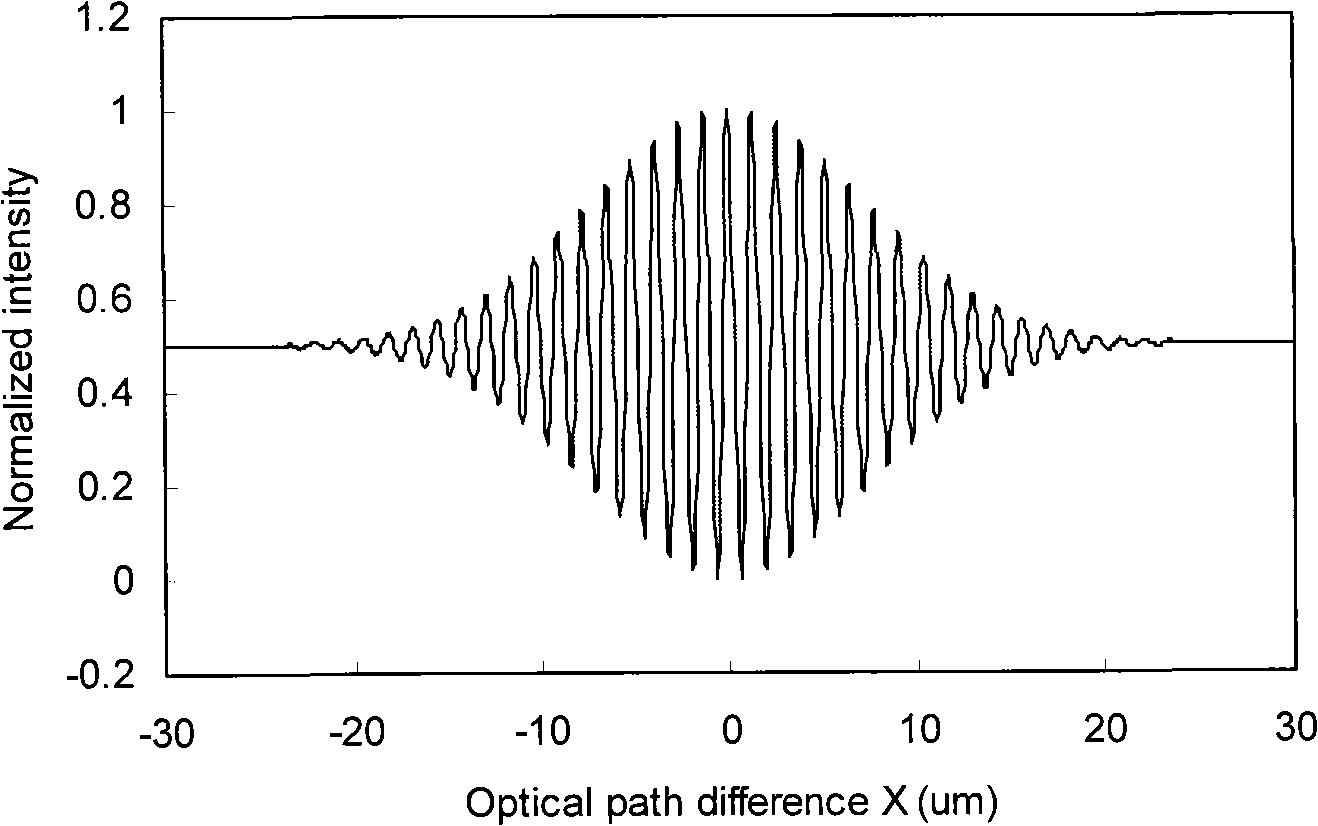
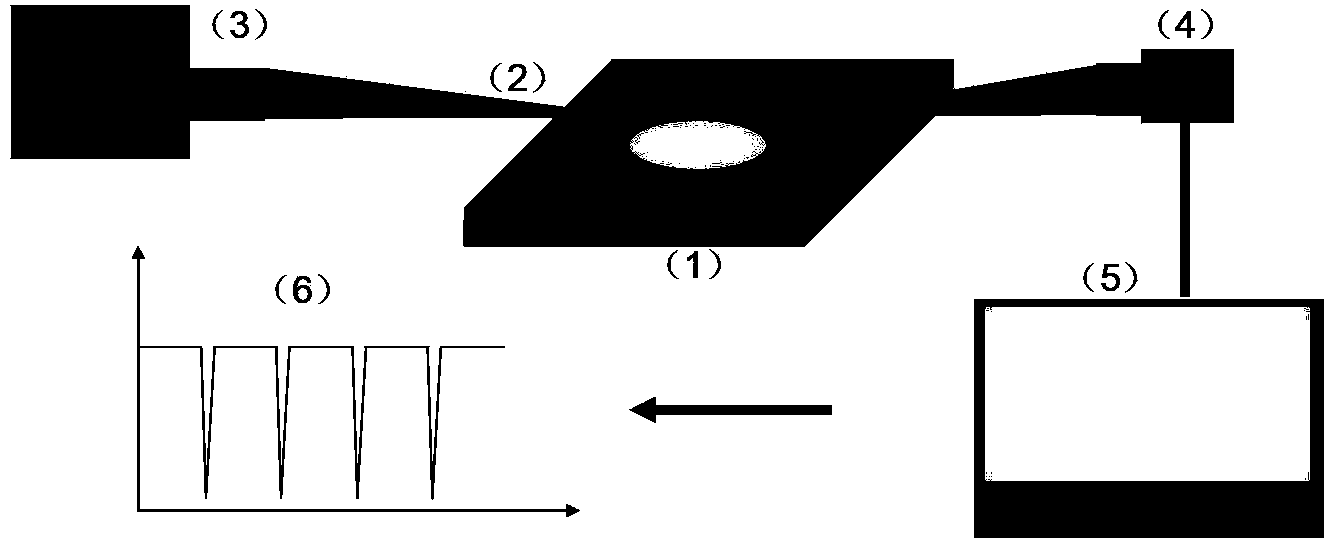
Space division multiplexing Mach-Zehnder cascade type optical fiber interferometer and measurement method thereof
InactiveCN101324443ARealize sensingRealize measurementCoupling light guidesConverting sensor output opticallySensor arrayPhotodetector
The invention provides a space division multiplexing Mach-Zehnder cascade fiber interferometer and a measurement method thereof. The space division multiplexing Mach-Zehnder cascade fiber interferometer is composed of a wide-spectrum light source, a photodetector, a coupler, a single-mode connection optical fiber, an optical fiber sensor, a continuous-variable optical delay device, and a reflector, wherein the optical fiber sensor is composed of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer and forms a cascade optical fiber sensor array or a network. The wide-spectrum light source and a photodetector are connected with the optical fiber sensor through the coupler to form a sensor network; and the sensor network is connected with the continuous-variable optical delay device and the reflector through the coupler and is used for enquiring and demodulating the optical fiber sensor. The space division multiplexing Mach-Zehnder cascade fiber interferometer solves the problem of breakage of the optical fiber sensor array, improves the anti-damage characteristics of the optical fiber sensor array and the network and solves the temperature compensation problem in the measurement process. The space division multiplexing Mach-Zehnder cascade fiber interferometer has the advantages of simple interferometer structure, easy implementation, improved measurement reliability and low cost, and better facilitates the technology generalization and popularization.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
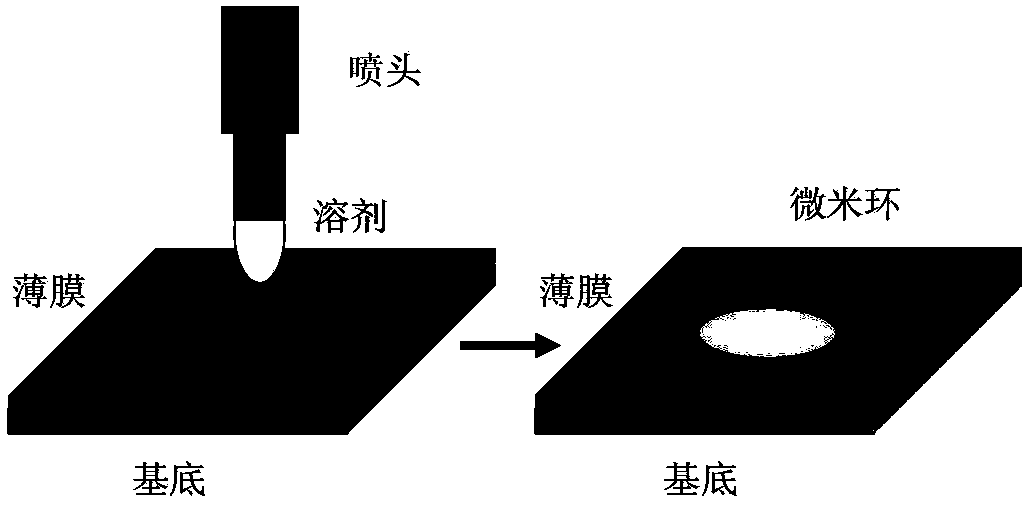
Whispering gallery mode photonic device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104253372ARealize the coupling effectSolve patterningOptical resonator shape and constructionWhispering galleryArray data structure
The invention provides a whispering gallery mode photonic device and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method of a micro ring array structure, solvent droplets are utilized to dissolve a polymer film, so that a "coffee ring effect" can be generated, and therefore, polymer can be accumulated at the periphery of liquid so as to form an annular structure of which the height is obviously different from the height of the film, and conduction and confinement of light in the polymer structure can be realized; and light signals are inputted to the micron ring structure through utilizing excitation, scattering or near field coupling modes, so that a resonance effect in a whispering gallery mode can be realized. The prepared micron ring structure can be adopted as a high-quality factor optical micro cavity, so that a modulation-mode spectrum can be obtained, the width of spectral lines of the spectrum being significantly narrowed; a whispering gallery-mode light amplification stimulated emission can be realized through optical gain; and in a multi-ring coupled array structure, light signal processing and high sensitive response to outside stimuli can be realized according to the wavelength change information of the modulated spectrum and laser modes.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
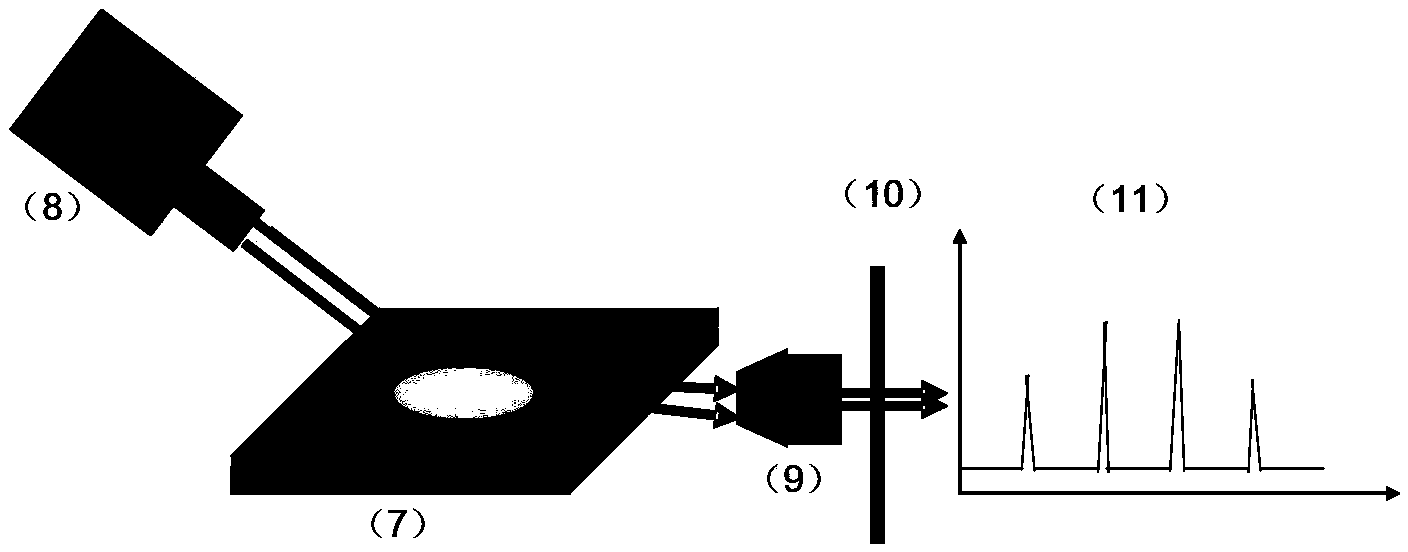
Fiber-integrated multi-helical-core optical fiber SPR sensing array chip
ActiveCN105954236AAchieving single-mode transmissionRealize sensingMaterial analysis by optical meansCore (optical fiber)Environmental monitoring
The invention relates to a fiber-integrated multi-helical-core optical fiber SPR sensing array chip and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber sensing, and particularly relates to the fiber-integrated multi-helical-core optical fiber SPR sensing array chip which can be widely used in the fields of bio-sensing, chemical analysis, medicine researching, food safety, environment monitoring, medical diagnosis and the like. The fiber-integrated multi-helical-core optical fiber SPR sensing array chip is composed of an optical fiber cladding (1), a double-core or multi-core optical fiber tapering coupled zone (2), a D-type polished surface (3), a gold nano film in certain thickness (4), a center fiber core (5) and an eccentric fiber core (6). The sensing units in the sensing chip have different SPR resonance angles, so that the chip can analyze and detect various different substances in a sample simultaneously in one time. The chip overcomes the defects of complex operations, low automation degree, low detection efficiency and the like in the prior art.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Thermal release electric infra-red ray human body detection device
InactiveCN101285710AFlexible mobile controlRealize sensingPyrometry using electric radation detectorsElectricityHuman body
The invention discloses a pyroelectric infrared human body detection device. The device comprises a pyroelectric infrared sensor, a Fresnel lens, an electronic circuit and a moving mechanism; the pyroelectricity infrared sensor is fixed on the moving mechanism which comprises drive equipment and a bracing frame driven by the drive equipment; and the pyroelectric infrared sensor is fixed on the bracing frame. A travel switch is arranged on the bracing frame; the electronic circuit comprises a control circuit of the travel switch; the control circuit of the travel switch receives a travel switch signal to control the operation of the drive equipment. The pyroelectric infrared human body detection device is provided with the moving structure to drive the pyroelectric infrared sensor to move in order that the static human body has movement relative to the pyroelectricity infrared sensor, thereby realizing the induction and the detection to the static human body.
Owner:SHENZHEN H&T INTELLIGENT CONTROL
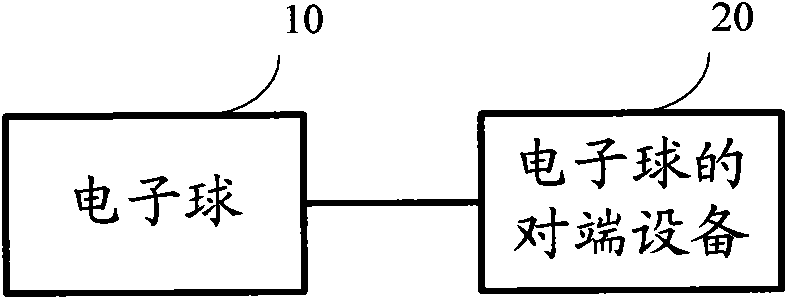
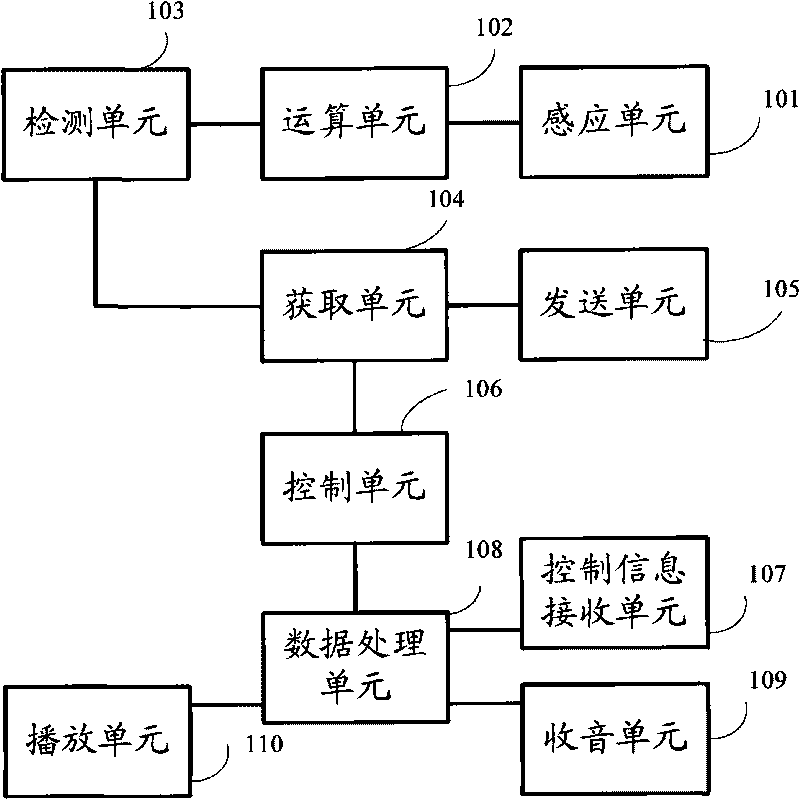
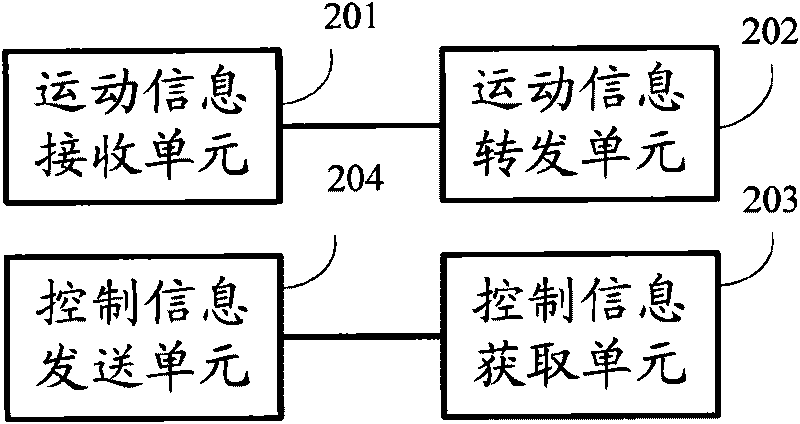
Sensing method of electronic ball, electronic ball and sensing system thereof
InactiveCN101701823ARealize sensingRealize interactive communicationTransmission systemsNavigation by terrestrial meansPeripheralSensing data
An embodiment of the invention provides a sensing method of an electronic ball, an electronic ball and a sensing system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sensing data of an electronic ball, wherein the sensing data comprises any one or more of acceleration sensing data, geomagnetic field sensing data and gyro sensing data; operating the obtained sensing data of the electronic ball so as to obtain the three-dimensional coordinate value and the direction value of the electronic ball; detecting whether the three-dimensional coordinate value and the direction value of the electronic ball are changed; when the detecting result is that the values are changed, obtaining the moving information of the electronic ball according to the three-dimensional coordinate value and the direction value of the electronic ball, wherein the moving information comprises any one or more of moving track information, moving identifying information and ball rotating information of the electronic ball; and transmitting the moving information of the electronic ball in wireless transmitting mode. The embodiment of the invention realizes interactive communication of sporting balls and external devices, and expands the space and interactivity of the using field of the sporting balls.
Owner:SHENZHEN HEZHI CHUANGYING ELECTRONICS
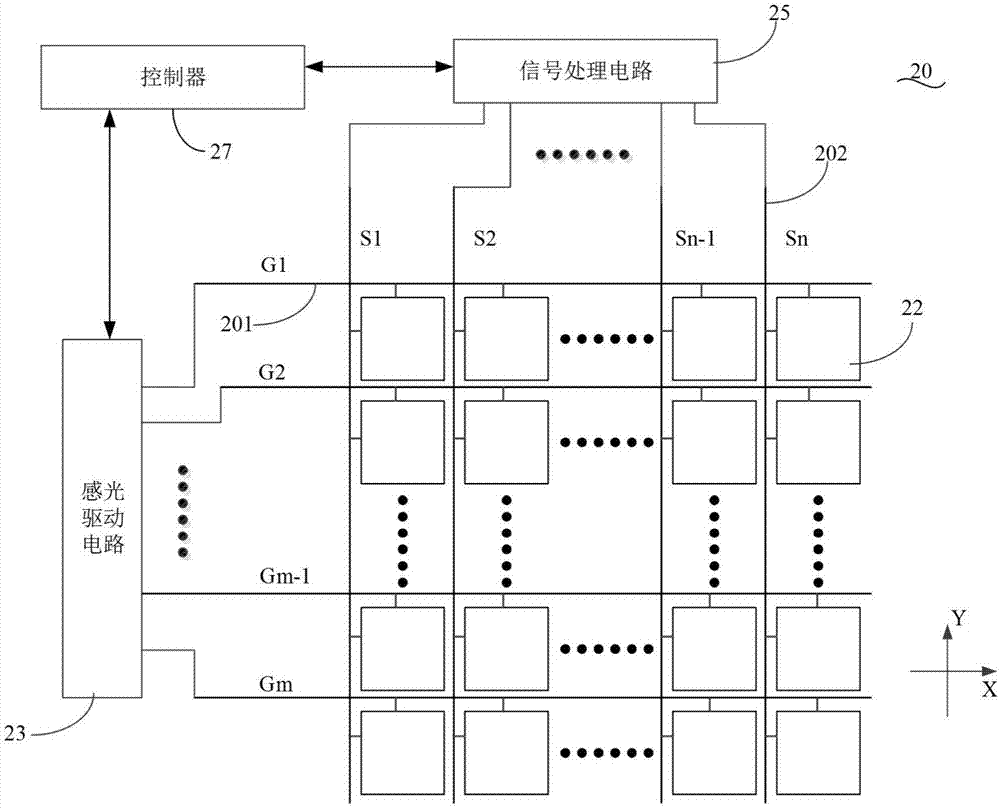
Display module and electronic device
ActiveCN107958193ASpeed up the processAvoid aliasingPrint image acquisitionInput/output processes for data processingTime-sharingDisplay device
The present invention discloses a display module and an electronic device. The display module comprises a display device, wherein the display device comprises a display panel for performing image display, and the display panel comprises a plurality of display pixels; and a photosensitive device, wherein the photosensitive device comprises a photosensitive panel, and the photosensitive panel and the display panel are arranged in a stacked manner for obtaining predetermined biometric information of a target object touching or approaching the display module by sensing an optical signal. The display device further comprises a display driving circuit, for driving the display pixels to be lit in a time-sharing manner when the photosensitive panel performs the biometric information sensing. The electronic device comprises the display module.
Owner:柳州梓博科技有限公司
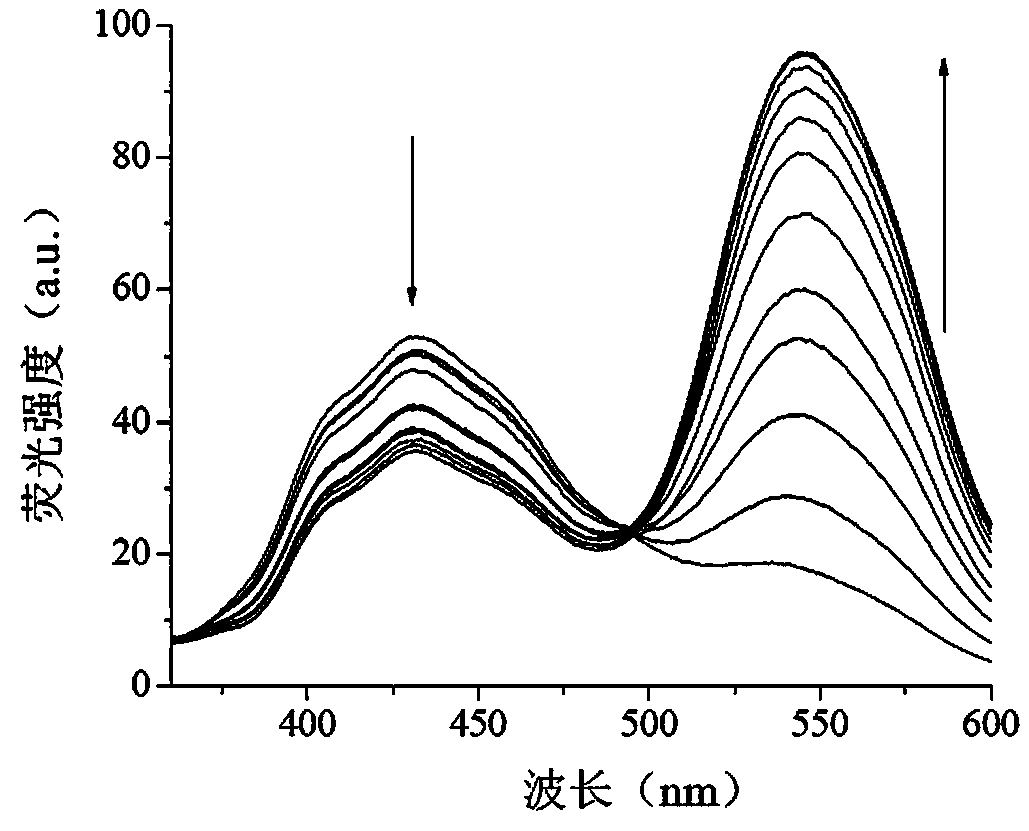
Ratiometric fluorescent probe for detecting hydrazine, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104109126AHigh sensitivityGood choiceOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescenceNaphthalene diimide
The invention discloses a ratiometric fluorescent probe for detecting hydrazine. The ratiometric fluorescent probe for detecting hydrazine is a derivative of 4-hydroxyl-N-butyl-1, 8-naphthalene diimide, with a structural formula of the derivative shown in the description and a molecular formula of C18H17NO4. The derivative of 4-hydroxyl-N-butyl-1, 8-naphthalene diimide is obtained by condensation of 4-hydroxyl-N-butyl-1, 8-naphthalene diimide and acetic anhydride. The fluorescent probe is used for realizing qualitative and quantitative detection and trace for hydrazine in a water environment system and a biological cell system, with high selectivity and high sensitivity, and has strong interference resistance.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Fiber bragg grating current transformer with automatic temperature tracking function and automatic temperature tracking method
InactiveCN102539874ARealize sensingRealize measurementCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationFiberGrating
The invention discloses a fiber bragg grating (FBG) current transformer with an automatic temperature tracking function and an automatic temperature tracking method, belonging to the field of photoelectricity. At present, since the technical scheme of arrangement of extra FBG is adopted for eliminating the influence of FBG drift with temperature, the system cost and the structural complexity are increased; through adoption of the FBG current transformer, the problems can be solved. The FBG current transformer comprises a distributed feedback (DFB) laser, a coupler, a photoelectric amplifier, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) acquisition and adjustment module, a digital-to-analog (D / A) converter and a laser temperature control circuit, wherein a laser beam emitted by the DFB laser enters the FBG through the coupler; a light beam reflected by the FBG is amplified by the photoelectric amplifier and converted into an electric signal which is transmitted to the FPGA acquisition and adjustment module; the FPGA acquisition and adjustment module performs proportion, integration and differentiation (PID) adjustment on the electric signal and outputs a voltage control command; and the laser temperature control circuit controls internal temperature of the DFB laser, so that the central wavelength of the DFB laser synchronously drifts with the wavelength of the FBG.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
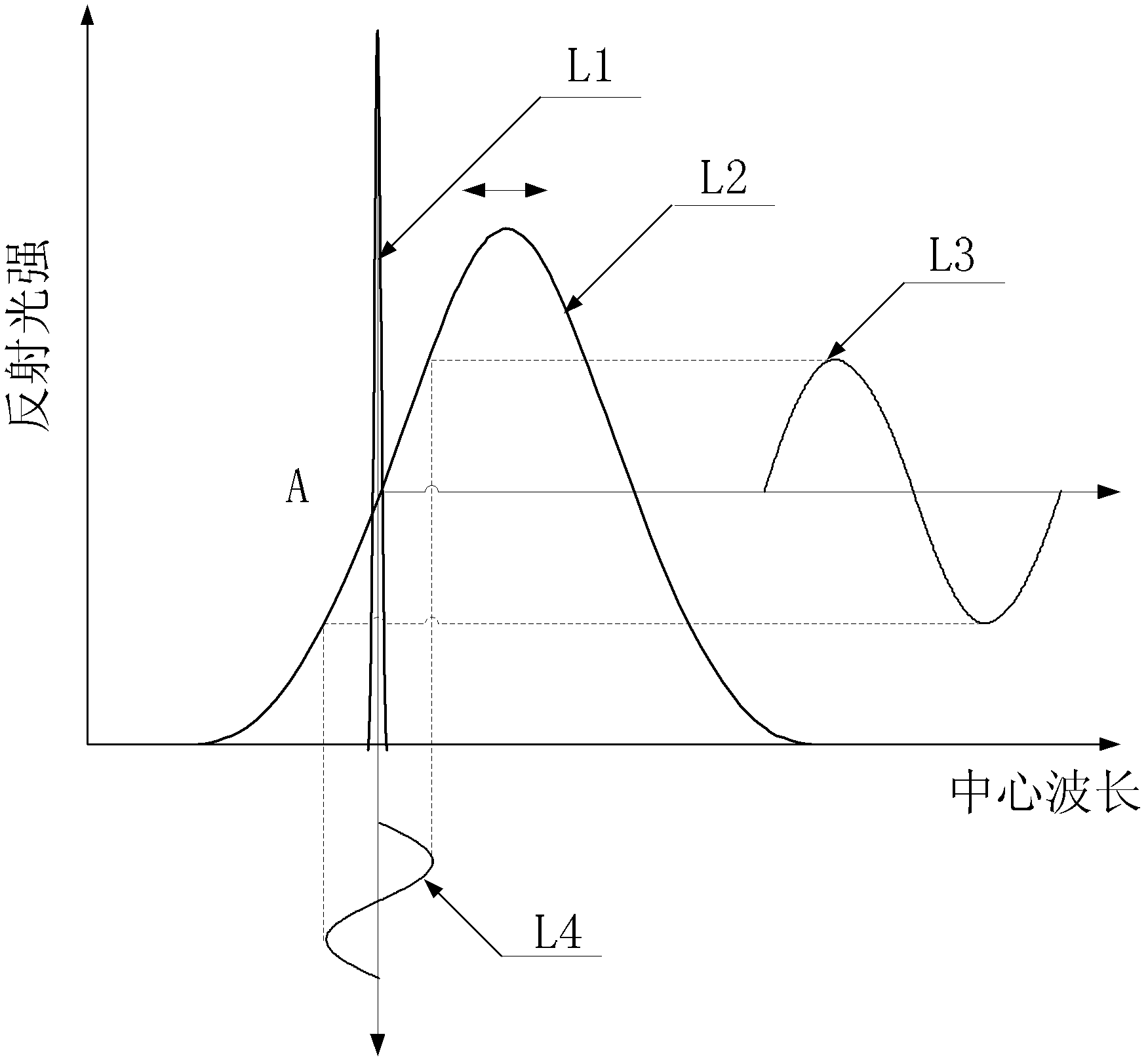
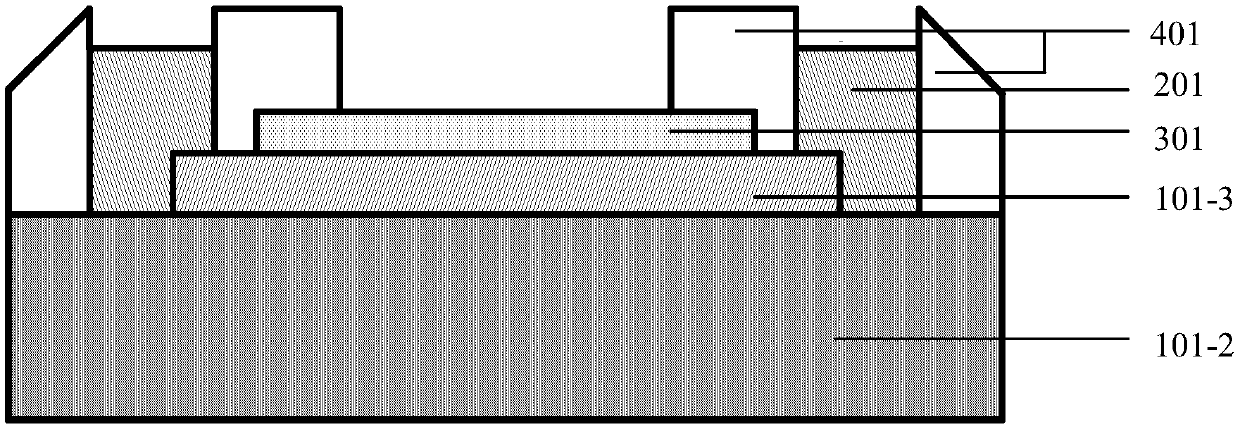
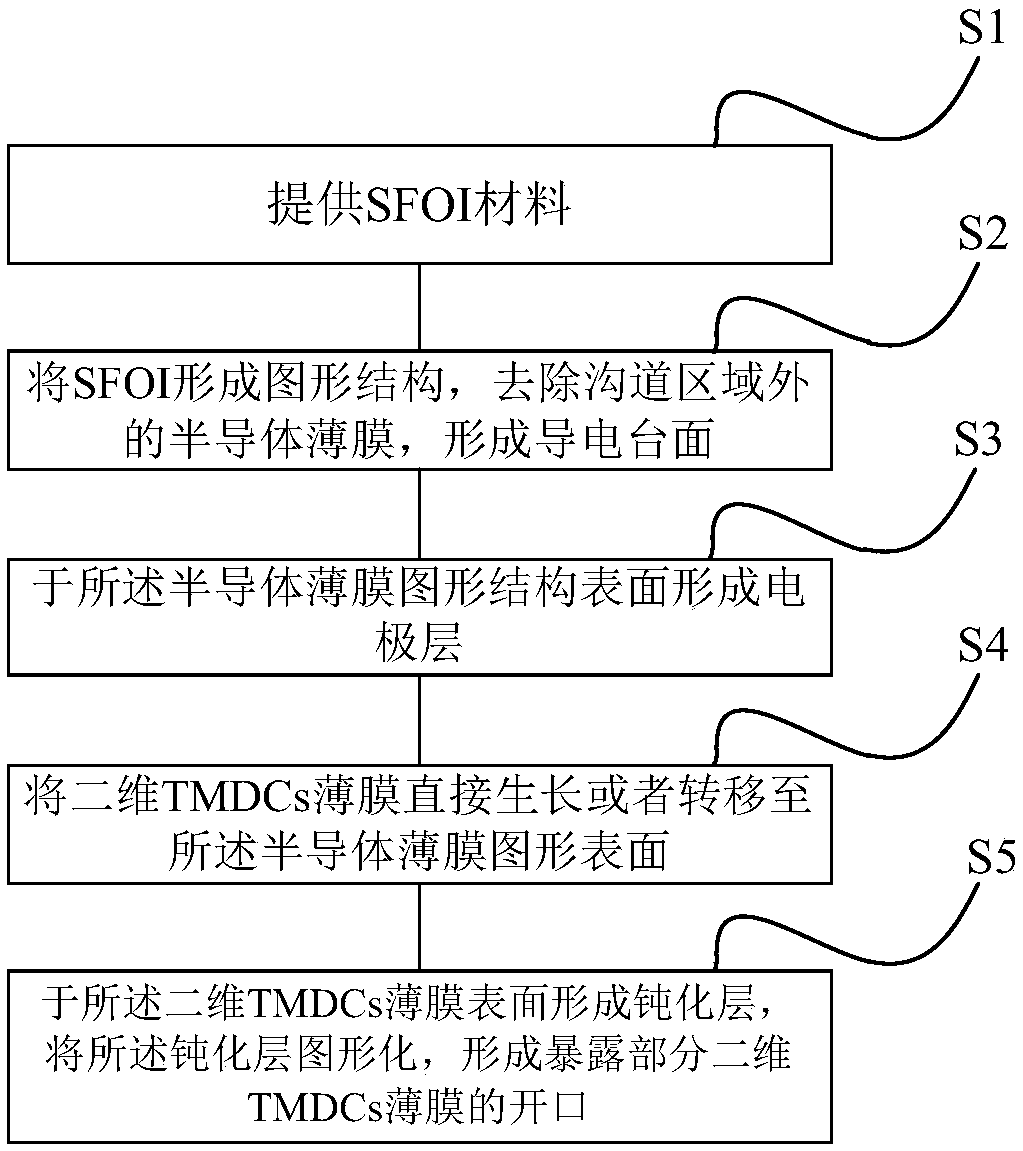
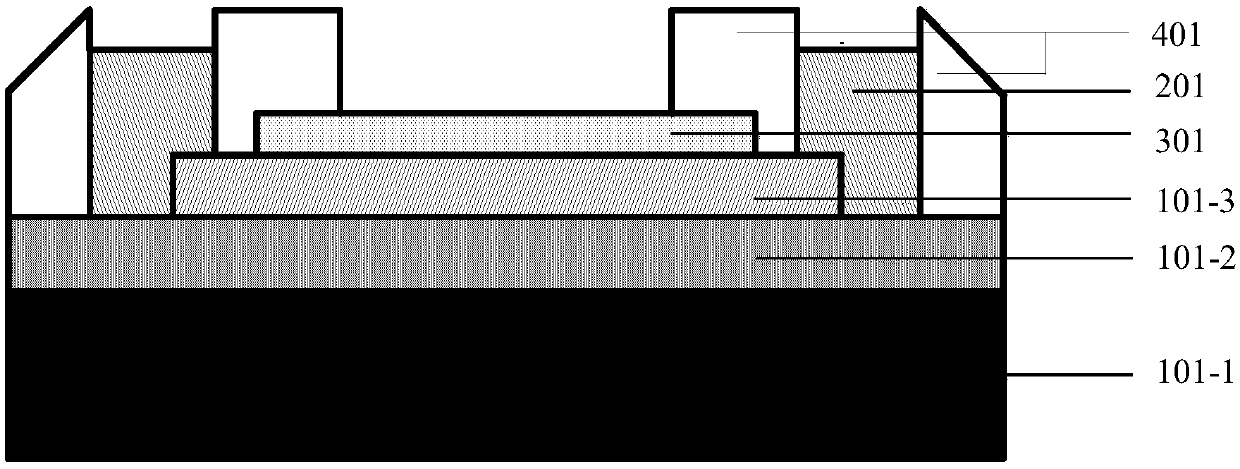
Gas sensor based on TMDCs-SFOI heterojunction and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a gas sensor based on TMDCs-SFOI heterojunction and a preparation method thereof. The gas sensor takes two-dimensional transition metal sulfide TMDCs as a gas sensitive layer and a semiconductor film on an insulator SFOI as a conductive channel; after TMDCs are contacted with SFOI, due to the Fermi level difference, electrons are transferred from the high Fermi level side tothe low Fermi level side, thereby generating space charge regions on both sides of the heterojunction and forming a p-n junction; when gas molecules to be detected are adsorbed on the surface of theTMDCs and charge transfer occurs between the gas molecules to be detected and the TMDCs, the concentration of carriers in the TMDCs is changed, a p-n junction potential barrier is changed, the width of the space charge region in the SFOI is changed, and finally the resistance of the conductive channel is changed, so that the gas to be detected is sensed. According to the gas sensor based on TMDCs-SFOI heterojunction and the preparation method thereof, the gas sensitive layer is separated from the conductive channel, meanwhile, the high sensitivity of the two-dimensional TMDCs to adsorbed gas molecules is utilized, and a gas detector is beneficial to achieving high sensitivity and high reliability and can be directly integrated on a semiconductor chip together with the mature traditional semiconductor device process.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Friction nanometer generator, preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN107612414ALight in massThe overall thickness is thinSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsMicro nanoEngineering
The invention relates to a friction nanometer generator, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The upper electrode and the lower electrode of the friction nanometer generator are made of conductive flexible materials, and a first insulating polymer, a first flexible material and a second insulating polymer, a second flexible material and a third insulating polymer are sequentially stacked up to form a film. According to the invention, the friction nanometer generator disclosed by the invention can be attached to an object with a small curvature radius and can reduce the requirements in the longitudinal space or in the transverse space. The limitation of a "heavy" substrate of the generator is avoided. The vertical and independent friction nanometer generator of the invention is ultra-thin in structure and light in weight. In addition, the friction nanometer generator can be attached to objects with complex shapes. Meanwhile, the energy collecting function and the sensing function are achieved. The damage of equipment is avoided. The generator is simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost and capable of being massively produced. The requirements of the currentmarket are met. The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-nano energy power generation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Transparent flexible sensor and preparation method thereof, electronic skin and wearable device
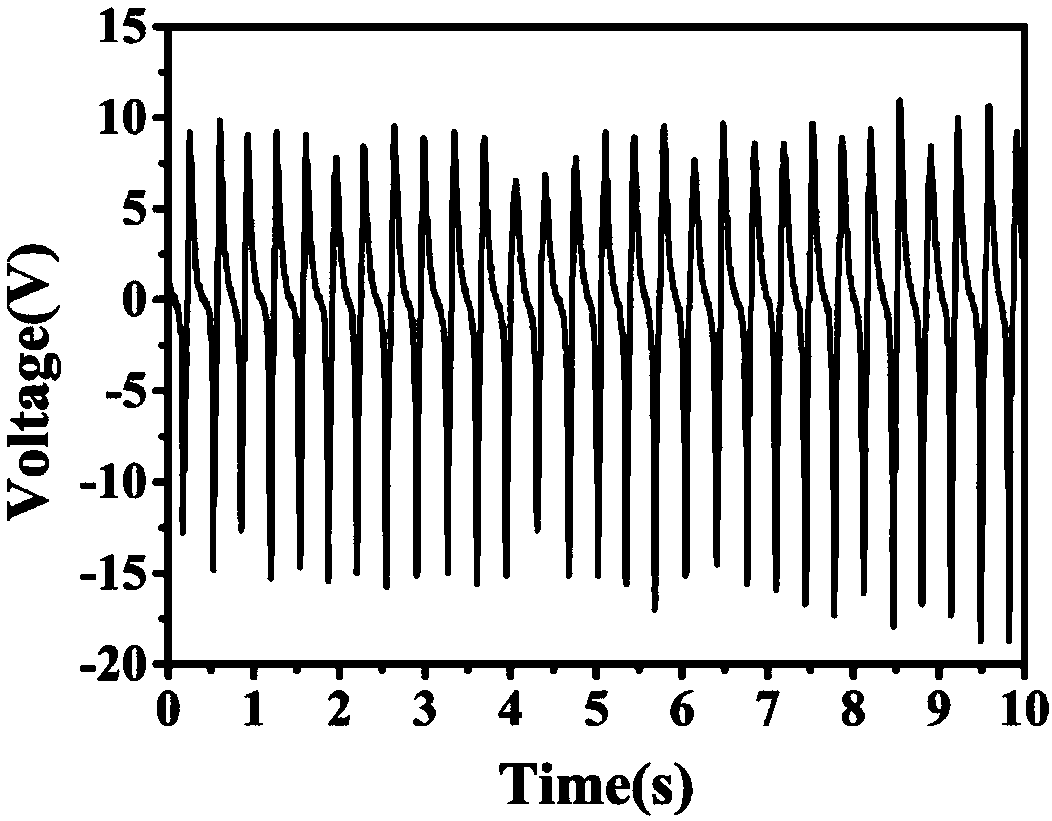
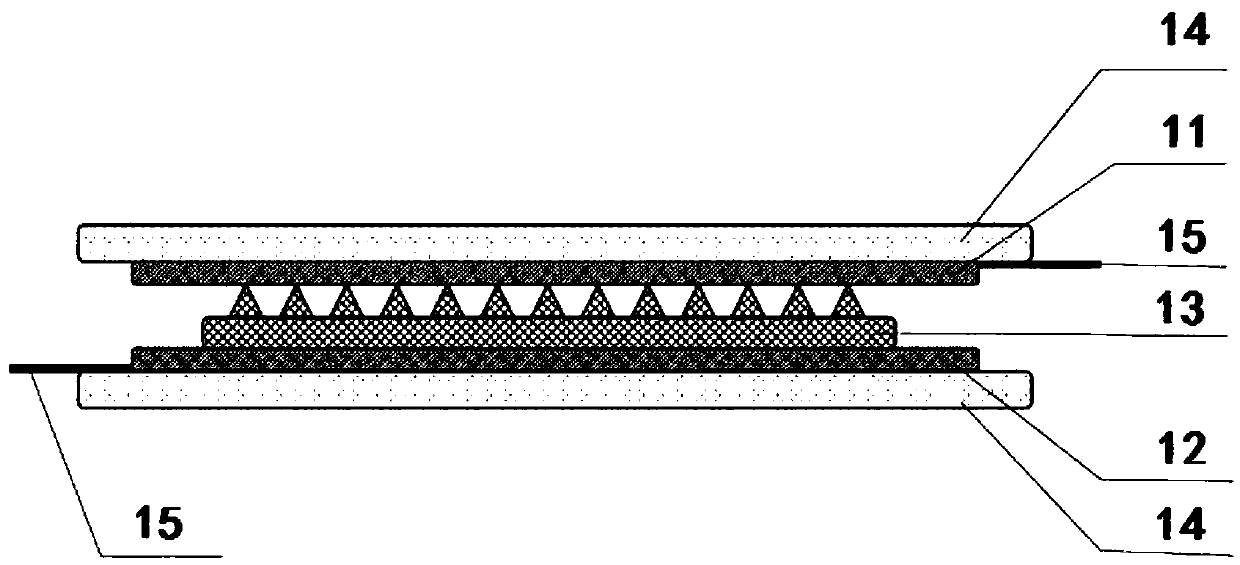
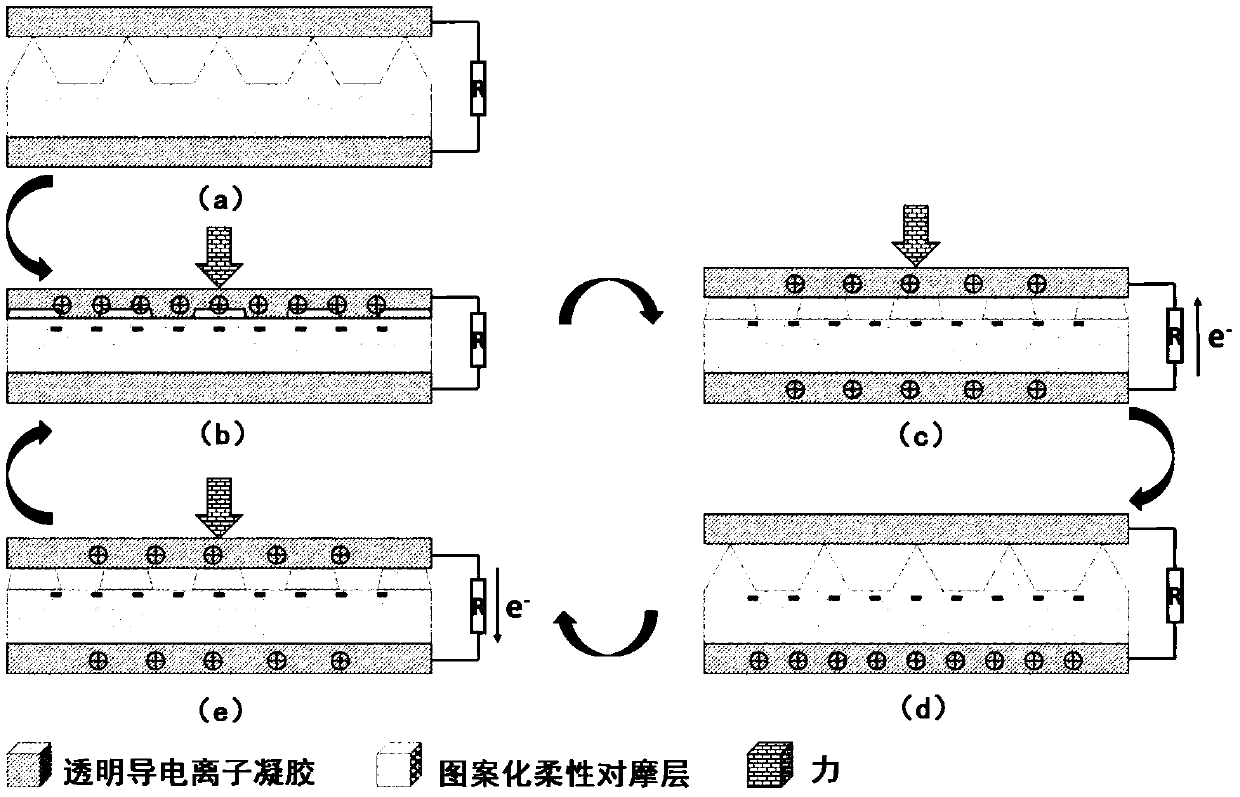
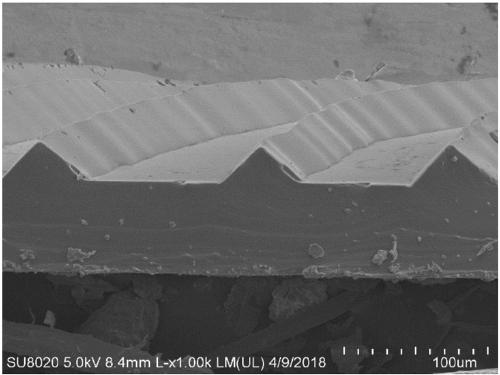
PendingCN111297321AGood flexibilityImprove portabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodySensing applications
The invention discloses a transparent flexible sensor and a preparation method thereof, electronic skin and a wearable device, and the transparent flexible sensor comprises a first electrode serving as a friction layer; a second electrode layer arranged opposite to the first electrode and friction layer; a patterned flexible antifriction layer located on the second electrode layer, wherein one surface, containing the pattern, of the patterned flexible antifriction layer is in contact with the first electrode and friction layer; flexible insulating layers respectively positioned on the outer sides of the first electrode and friction layer and the second electrode layer to realize packaging; wherein a conductive ion gel film is used as a first electrode and friction layer and a second electrode layer. The transparent flexible sensor has the advantages of good flexibility, portability, self-driven sensing, long service time and high detection sensitivity, is high in applicability, can beapplied to different body parts, realizes measurement of various forces and deformations, realizes sensing of various human activities, and is wide in application range.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
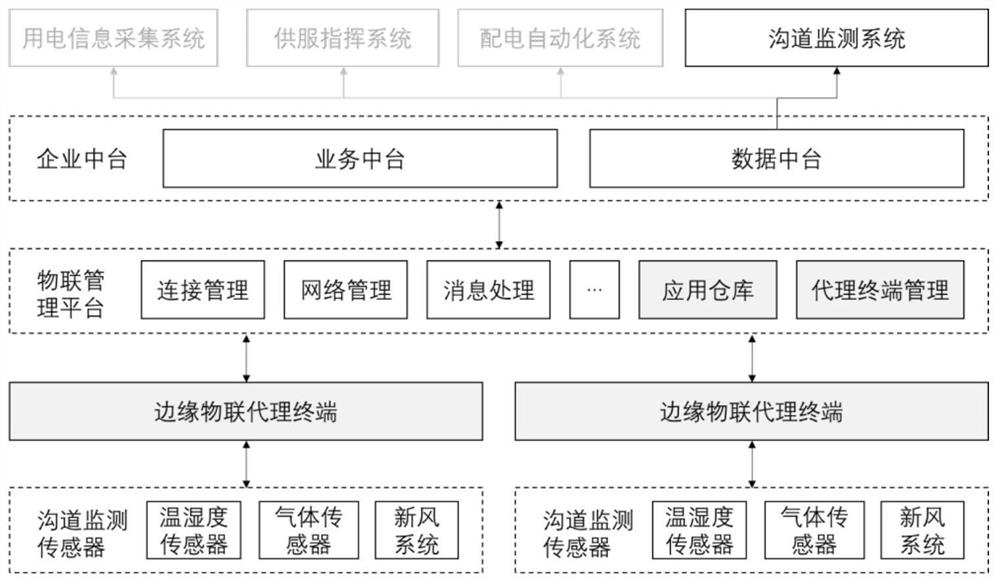
Cable channel comprehensive monitoring Internet of Things edge proxy device
PendingCN111726409ASolve real-timeFix security issuesData switching networksStatistical analysisThe Internet
The invention belongs to the technical field of urban construction, in particular to a cable channel comprehensive monitoring internet-of-things edge proxy device. The system consists of a sensing layer, a network layer, a platform layer and an application layer from bottom to top, the application layer comprises a data analysis unit, a service application display unit, a statistical analysis unitand a remote control unit; the platform layer is connected with a power optical fiber network on the network layer. The internet-of-things terminal on the sensing layer is arranged in the channel. According to the invention, the monitoring system is optimized based on the power distribution Internet of Things system architecture, edge computing and other technologies; an edge Internet of Things intelligent terminal is designed, the problems of real-time performance, safety and the like faced by on-site mass data acquisition and calculation are solved by means of an edge calculation technology, and the accuracy of equipment abnormal state monitoring and early warning is improved by fusing algorithms such as artificial intelligence and machine learning under an edge calculation framework.
Owner:国网陕西省电力公司信息通信公司
Method for preparing anionic colorimetric sensing cellulosic material
InactiveCN101871165AGood sensitivityGood choiceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorVegetal fibresIonSol-gel
The invention discloses a method for preparing an anionic colorimetric sensing cellulosic material. A titanium dioxide film is deposited on the surface of filter paper cellulose by taking natural cellulose fiber material as a matrix, and taking tetrabutyl titanate as a precursor by a surface sol-gel process; a fluoride ion colorimetric sensing cellulosic material is obtained by introducing a fluoride ion-sensitive ligand alizarin complexant molecule single layer in a self-assembly way; and fluoride ions in solution can be detected by infiltrating the material prepared by the invention in the aqueous solution of anions for a certain period of time simply, and observing the color change of the material. The anionic colorimetric sensing cellulosic material prepared by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and selectivity to the fluoride ions, abundant material sources, low cost, simple preparation method and simple, rapid and economic fluoride oil detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Surface friction-based several physical quantity detection device and detection method
ActiveCN107576610AHigh sensitivityImprove sensing efficiencySustainable transportationUsing mechanical meansResonanceSurface roughness
The invention relates to a surface friction-based several physical quantity detection device and detection method, and belongs to several physical quantity detection devices and detection methods. Thedevice comprises a high-frequency beam, a synchronous coupling beam, a low-frequency beam, a friction block, a supporting positioning structure, a piezoelectric exciting structure, a transverse piezoelectric large-displacement driving structure, a longitudinal piezoelectric large-displacement driving structure, an L-shaped supporting structure and the like, wherein the vibration pick-up structureof the low-frequency beam is used for picking up friction and vibration signals to detect the surface roughness and hardness; and a synchronized resonance structure is commonly formed by the low-frequency beam, the high-frequency beam and the synchronous coupling beam, and is used for detecting friction coefficients and multiplying output frequency to improve the sensitivity. The detection devicecan be used for detecting the kinetic friction coefficient, surface roughness and hardness by utilizing a relatively simple structure, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of surface detection and material identification.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
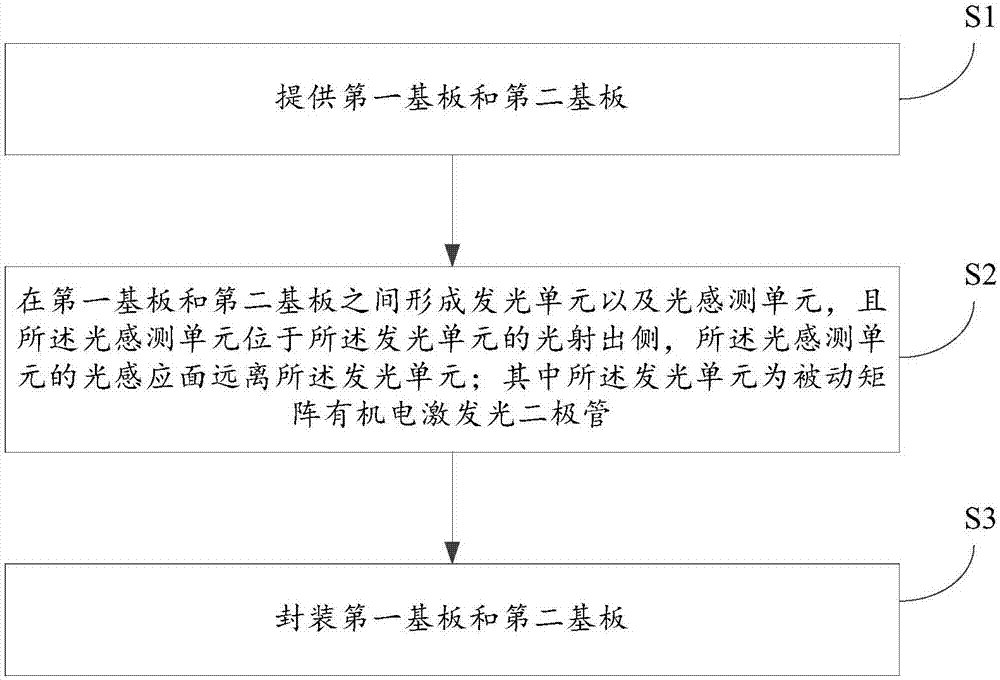
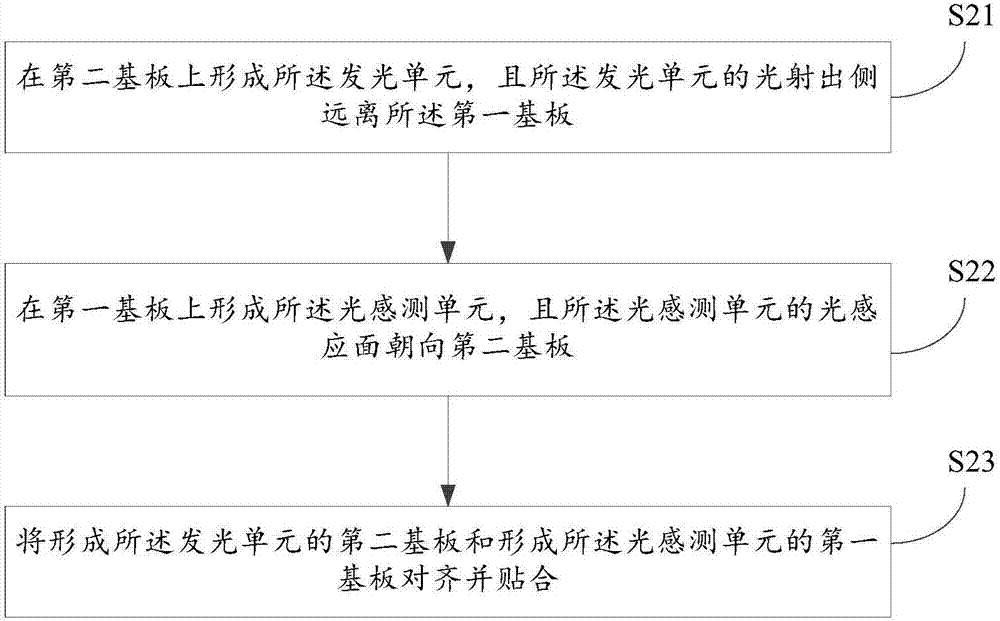
Photoelectric sensing module, preparation method thereof, and electronic device
ActiveCN107958178ASimple structureThe overall thickness is thinPrint image acquisitionOptical sensingOrganic electroluminescence
The invention discloses a photoelectric sensing module, a preparation method thereof, and an electronic device. The preparation method for the photoelectric sensing module comprises the following steps that: providing a first substrate and a second substrate; forming a light emitting unit and an optical sensing unit between the first substrate and the second substrate, enabling the optical sensingunit to be positioned on the light emission side of the light emitting unit, and enabling the light induction surface of the optical sensing unit to be far away from the light emitting unit, whereinthe light emitting unit is a passive matrix organic electroluminescence diode; and packaging the first substrate and the second substrate. The electronic device comprises the photoelectric sensing module prepared by the preparation method.
Owner:柳州梓博科技有限公司
Array resolution type ultrasonic focusing transducer
ActiveCN104122333ARealize sensingImprove points effectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectricityTransducer
The invention relates to an array resolution type ultrasonic focusing transducer which comprises a signal excitation / receiving source, a transducer housing, a commercial contact type ultrasonic probe, a quartz focusing lens and an array type acoustic space sensing area, wherein the array type acoustic space sensing area structurally comprises an array pattern type sensing bottom electrode, a PVDF piezoelectric film and a top protective electrode. The invention further discloses a structure principle, a manufacturing method and a use method of the array resolution type ultrasonic focusing transducer. The transducer is designed to sense a spatial sound field at multiple angles by arranging a piezoelectric sensing area spatially at multiple angles, so that the spatial distribution characteristics of the sound field can be known, and further the morphology information of the surface or the inner part of a reflection specimen is reflected.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
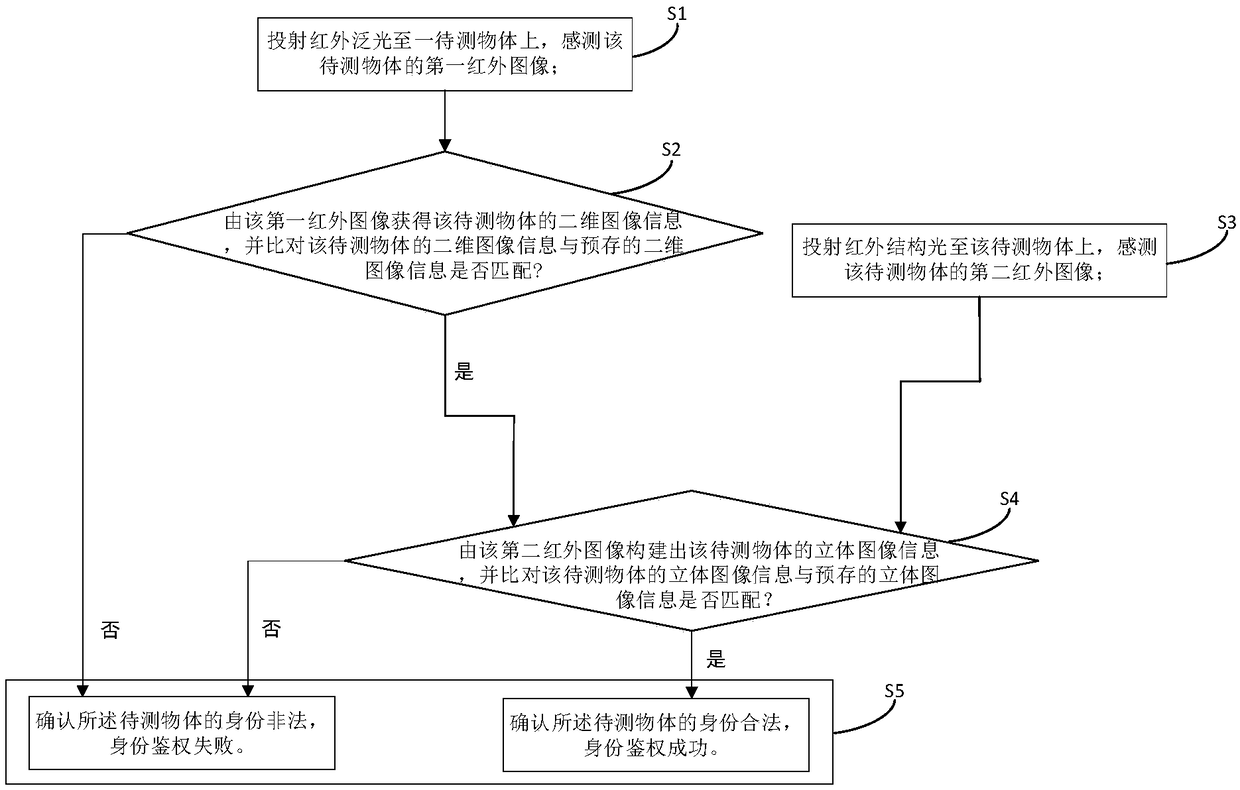
Authentication method, authentication device and electronic equipment
PendingCN108496182AFast sensing responseRealize sensingCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesComputer hardwareStereo image
The invention discloses an authentication method, an authentication device and electronic equipment. The authentication method comprises the steps: S1, infrared flood light is projected to a to-be-sensed object, a first infrared image of the to-be-sensed object is sensed; S2, according to the first infrared image, two-dimensional image information of the to-be-sensed object is acquired, and if thetwo-dimensional image information of the to-be-sensed object and pre-saved two-dimensional image information match is judged; S3, an infrared structured light is projected to the to-be-sensed object,and a second infrared image of the to-be-sensed object is sensed; S4, stereo image information of the to-be-sensed object is constructed from the second infrared image, and if the stereo image information of the to-be-sensed object and pre-saved stereo image information match is judged; and S5, according to the execution results of S2 and S4, if the identity of the to-be-sensed object is legal isdetermined. The authentication device runs the authentication method. The electronic equipment comprises the authentication device.
Owner:SHENZHEN FUSHI TECH CO LTD
D-shaped fiber-based cross-polarization beat laser and sensor
InactiveCN106356705AShorten cavity lengthGood laser coherenceActive medium shape and constructionWavelength-division multiplexingErbium doping
The invention provides a D-shaped fiber-based cross-polarization beat laser and a sensor. The laser comprises a pump laser, a wavelength division multiplexer connected with the pump laser, a first fiber Bragg grating, one end of which is connected with the wavelength division multiplexer, a second fiber Bragg grating, one end of which is connected with an output fiber, and an erbium-doped D-shaped fiber which is encapsulated between the other end of the first fiber Bragg grating and the other end of the second fiber Bragg grating, wherein the first fiber Bragg grating, the second fiber Bragg grating and the erbium-doped D-shaped fiber are integrated on one fiber. The distributed fiber grating is adopted as a reflector to form an ultrashort resonant cavity, and the cavity length can be effectively shortened, so that the laser can run in a single-longitudinal-mode state, and the generated laser has good coherence. The D-shaped fiber is used as the body of the resonant cavity, the constraining performance of the resonant cavity on light can be reduced, and part of the transmitted light is leaked from one side to form an evanescent field which is sensitive to external environment changes, so that induction of a specific parameter can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Biological recognition device and electronic device
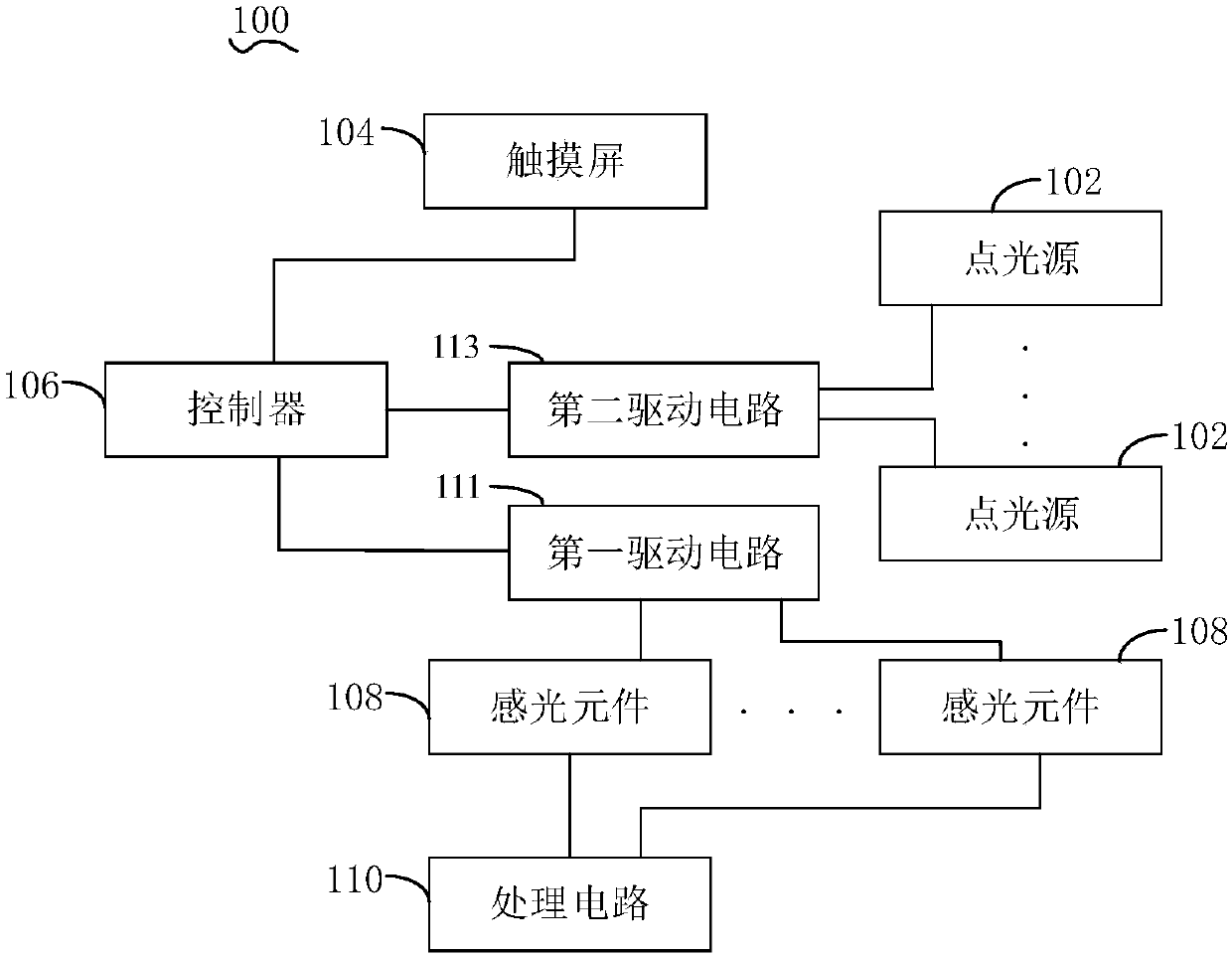
PendingCN108021854AThe overall thickness is thinSensing accuracy is smallBiometric pattern recognitionPrint image acquisitionPoint lightTime-sharing
The invention discloses a biological recognition device and an electronic device. The biological recognition device comprises multiple point light sources, a touch screen, a controller, multiple photosensitive elements and a processing circuit, wherein the touch screen is used for determining a contact area of a target object on the biological recognition device; the controller is used for controlling a plurality of point light sources corresponding to the contact area to be turned on in a time-sharing manner so as to transmit light signals to the target object; the multiple photosensitive elements are used for receiving the light signals reflected by the target object and converting the received light signals into corresponding electric signals; and the processing circuit is used for determining biological feature information of the target object according to the electric signals. The electronic device comprises the biological recognition device.
Owner:柳州梓博科技有限公司
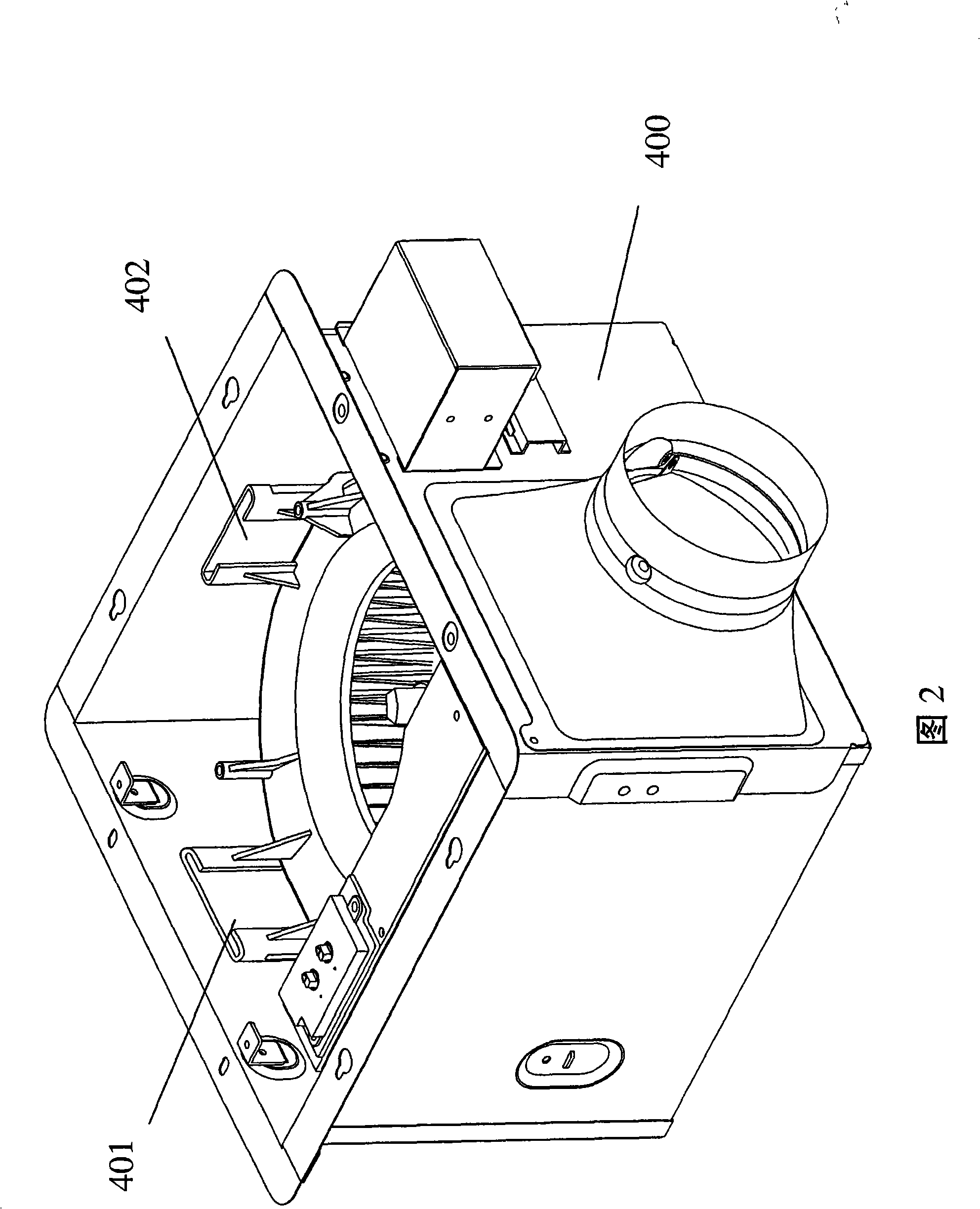
Ventilation fan with illumination instrument and human motion perception sensor
ActiveCN101294577AFlexible adjustmentAdjust the installation directionPump componentsSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsPattern perceptionHuman motion
The invention relates to a structure of a ventilator with an illuminating implement and a human-sensing sensor. The structure comprises a ventilator body and a mask; an exhaust inlet, a lamp as the illuminating implement and the human-sensing sensor are arranged on the mask; a lamp cover and the exhaust inlet are arranged on the middle part of the mask; the human-sensing sensor is arranged in the peripheral position of the mask, and the installation direction of the mask is changeable. The human-sensing sensor is arranged in the peripheral position of the mask so as to keep away from a lampshade and a wind inlet, thus ensuring that the human-sensing sensor is not affected by the heat emitted from the lampshade; furthermore, as the installation direction of the mask is changeable, the human-sensing sensor can be arranged in the position with best sensing effect.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Photoelectric sensing module and electronic device
PendingCN107958179ASimple structureThe overall thickness is thinPrint image acquisitionConverting sensor output opticallyEngineeringOptical sensing
The invention discloses a photoelectric sensing module and an electronic device. The photoelectric sensing module comprises a first substrate, a second substrate, a light emitting unit and an opticalsensing unit, wherein the first substrate and the second substrate are oppositely arranged; the first substrate comprises a first surface which faces the second substrate; the second substrate comprises a second surface which faces the first substrate; the light emitting unit is arranged between the first substrate and the second substrate, is a passive matrix organic electroluminescence diode andis used for emitting rays of light to reach a target object when the target object is positioned on the photoelectric sensing module; and the optical sensing unit is arranged on the first surface orthe second surface and is used for receiving an optical signal reflected by the target object and converting the received optical signal into a corresponding electric signal. The electronic device comprises the photoelectric sensing module.
Owner:柳州梓博科技有限公司
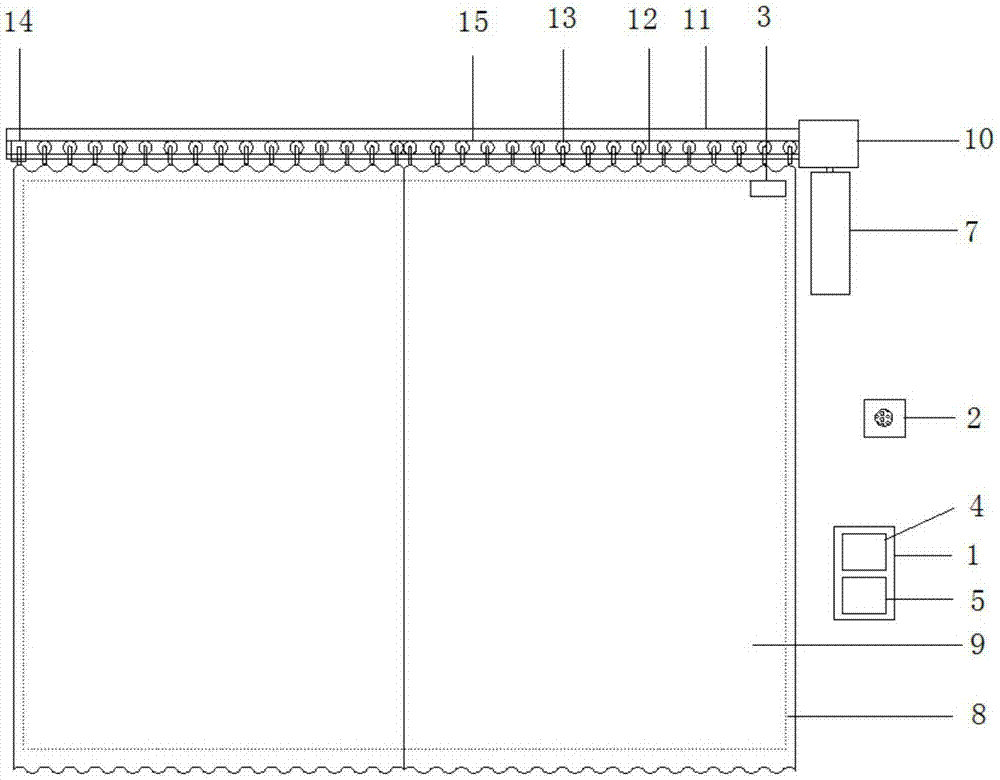
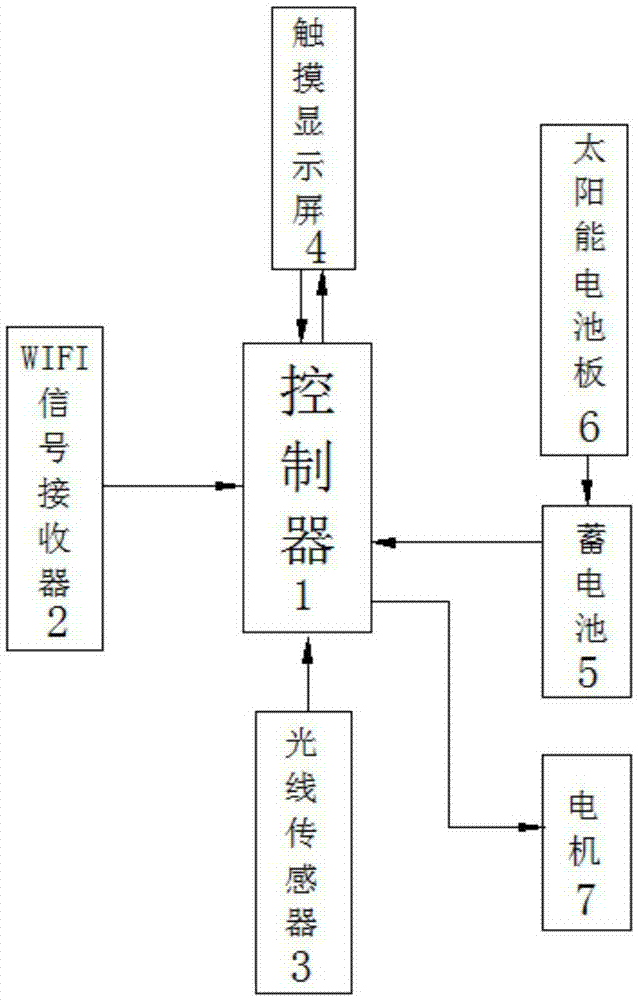
Intelligent curtain based on Internet-of-things
The invention discloses an intelligent curtain based on the Internet of Things, comprising a window frame, a track protection shell, a track, a roller, a curtain cloth, a transmission box, a slider, a belt, and a motor, and the rotating shaft of the motor is connected to the input shaft of the transmission box , the motor is electrically connected to the controller, the inside of the window frame is equipped with a light sensor, the light sensor is electrically connected to the controller, the controller is set on the window frame of the motor, the controller is electrically connected to the WIFI signal receiver, and the WIFI signal receiver passes the wireless signal The mobile terminal is connected, a touch display screen is provided on the controller shell and the touch display screen is electrically connected with the controller. With the help of the increasingly mature Internet of Things technology, the present invention realizes the intelligentization of curtains. The new curtains can realize the sensing, detection and collection of environmental data, and perform real-time data exchange, and adjust the opening and closing of curtains according to the intensity of outdoor light. Even the opening and closing size of the curtains realizes intelligent indoor lighting.
Owner:重庆潘多拉酒店有限责任公司
Extrinsic fabry-perot interferometer ultrasensitive gas sensor based on channel structure of tungsten selenide film
ActiveCN109164050ASmall sizeImprove thermal stabilityPhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMicro nanoElectricity
The invention belongs to the sensing field and in particular relates to an extrinsic fabry-perot interferometer ultrasensitive gas sensor based on a channel structure of a tungsten selenide film. A tungsten selenide-gold conductive structure is integrated on the end surface of a single mode fiber by adopting a mature and stable sensing principle and combining advanced processes in optics, metamaterial subjects and micro-nano machining. By means of physical absorption and electric adjustable characteristics of tungsten selenide, gas molecules are adsorbed and released by regulating a voltage applied to tungsten selenide. Response speed and sensitivity of the sensor are considered, and meanwhile, the apparatus is small in size, good in thermal stability and relatively small in power consumption of sensing. The response time of the sensor is only 0.01% of that of an electrochemical gas sensor, the sensitivity of the sensor can reach over 1000 times of that of a conventional optical gas sensor, and the power consumption of sensing is reduced to 100 nanowatt. The sensor can be directly integrated to a full optical system to achieve high speed information sensing of a full optical network.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Resonant membrane gas sensor and non-transitory machine-readable storage medium therefore
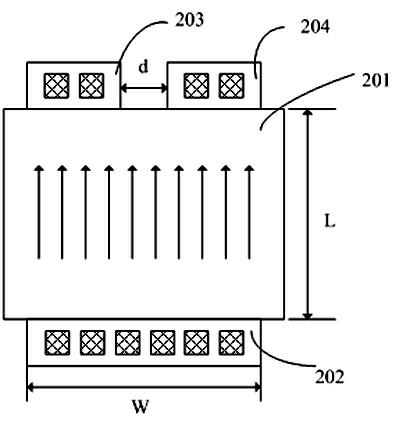
ActiveCN107076706ARealize sensingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsResonanceVolumetric Mass Density
A gas sensor (200) comprises a cavity (214) and is configured to sense at least one of a molar mass, a density and a viscosity of a gas mixture in the cavity (214). Moreover, various exemplary embodiments relate to a device to measure carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, including a first oscillator group (520) comprising a first sensor (250) to measure air pressure, where the first sensor (250) comprises a first sealed membrane (252), and where the first sealed membrane (252) overlays a sealed first cavity (258); a second oscillator group (522) including a second sensor (200) to measure the resonance frequency (f2) of a second unsealed oscillating membrane (210), and where the second unsealed membrane (210) overlays a second cavity (214) in contact with the air outside of the second sensor (200).
Owner:希奥检测有限公司
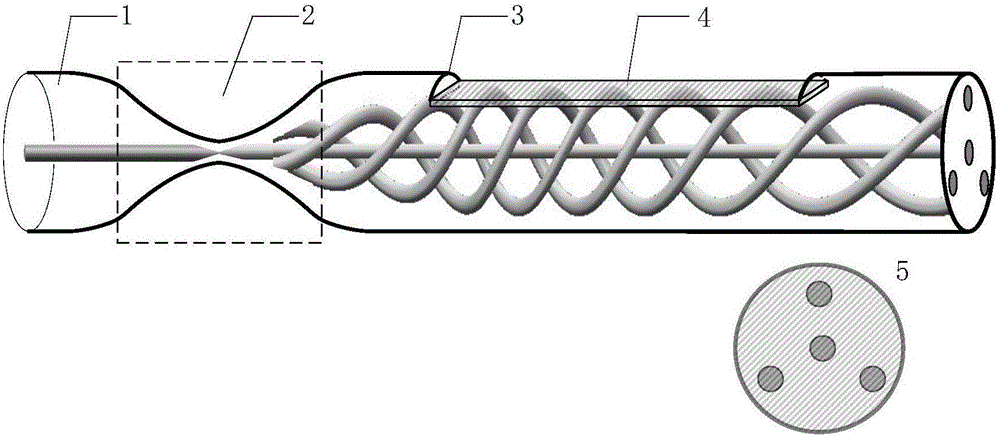
Micro optical fiber magnetic field sensor based on magnetostrictive material and preparation method
PendingCN114019430ARealize sensingImprove responsivenessCoupling light guidesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesResponse sensitivityPolymer thin films
The invention discloses a micro optical fiber magnetic field sensor based on a magnetostrictive material. The micro optical fiber magnetic field sensor comprises a single-mode optical fiber, a multimode optical fiber, a first thin film layer and a second thin film layer, the two ends of the multimode optical fiber are welded with the single-mode optical fiber, and the welded multimode optical fiber is tapered to obtain a micro optical fiber waist region; the first thin film layer covers the micro optical fiber waist region; the second thin film layer covers the first thin film layer; the first film layer is a polymer film; and the second thin film layer is a magnetostrictive thin film. Sensing of a magnetic field is realized through a method of coating after tapering, the diameter of the waist area is only about 10 microns, and the sensor can enter some relatively closed environments to carry out detection tasks; the polymer film is used as a stress conducting layer, so that light can still pass through the micro-optical fiber after the micro-optical fiber is plated with the metal film, and the response sensitivity of the optical fiber sensor to a magnetic field is improved by utilizing the characteristic of strong evanescent field of the micro-optical fiber.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
3D printing quality computer online monitoring method
ActiveCN111266577AReduce misjudgmentQuality improvementAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiency3d printEngineering
The invention discloses a 3D printing quality computer online monitoring method. In the multi-element powder different-barrel synchronous powder feeding laser 3D printing process, a CCD camera is adopted to collect temperature data of a laser molten pool in real time and update the temperature data to a computer, the collected temperature data are compared with standard temperature data prestoredin the computer, a working parameter is adjusted in real time, and the working parameter is at least one of the laser power, the scanning speed or the powder feeding speed; and the standard temperature data prestored in the computer are built according to a synchronous powder feeding laser 3D printing simulation experiment for premixed or pre-alloyed powder of which the element proportion is the same with that of multi-element powder conveyed by different barrels. According to the 3D printing quality computer online monitoring method, the relative ideal and stable simulation condition is adopted, thus, the standard data can meet the actual cladding requirements better, misjudgments and the overshoot proportion when real-time regulate and control are conducted on printing parameters are greatly reduced, sintering defects of cladding are decreased, and the quality of workpieces is improved.
Owner:山东水利职业学院
Monocrystalline silicon nano-film flexible transient electronic device, preparation method and application
ActiveCN108831952AAchieve self-destructRealize the function of "transient device"Final product manufactureNanosensorsMicro nanoInformation security
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-nano electronic devices, and specifically relates to a monocrystalline silicon nano-film flexible transient electronic device, a preparation method and an application. The invention adopts a preparation method of firstly preparing a device and then performing transfer, that is, a monocrystalline silicon nano-film electronic device / array prepared according to the standard semiconductor process is integrally transferred to a polyimide film flexible substrate with a transient functional layer. The preparation method has the advantages of compatibility with the current IC process, arbitrary adjustment of the structure scale and suitability for industrial large-scale production. According to the invention, the channel energy band is regulated and controlled through a gate, and the ratio of light current and dark current of the device can exceed 10<6>. The self-destructive transient process of a heating trigger device is realized throughadding the PAMS functional layer in the preparation process. The invention lays a foundation for obtaining high-sensitivity flexible photoelectric detectors and transient devices capable of adapting to a high temperature environment in a large scale in the fields such as on-chip integrated circuit protection, information security and sensing / control systems.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Double-drain type CMOS magnetic field induction transistor and fabricating method thereof
InactiveCN102683377ARealize sensingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon dioxideCondensed matter physics
The invention discloses a double-drain type CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) magnetic field induction transistor and a fabricating method thereof. The double-drain type CMOS magnetic field induction transistor comprises a P type substrate, two n+ drain doped region, an n+ source doped region, a p+ substrate contact doped region, a polycrystalline silicon gate and a silicon dioxide oxide layer. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, growing the silicon dioxide oxide layer and the polycrystalline silicon gate on the P type substrate; and secondly, generating a source n+ heavily doped region and a drain n+ heavily doped region and the p+ substrate contact doped region on the two sides of the polycrystalline silicon gate, wherein the drain n+ heavily doped region is divided into two same regions having a certain distance therebetween. The double-drain structure is capable of realizing induction to a magnetic field under the action of the magnetic field to current carriers in an inversion layer formed under the transistor and is completely compatible with standard CMOS process; and simultaneously, compared with a magnetic sensor of a hall disc structure, the double-drain type CMOS magnetic field induction transistor is lower in power consumption.
Owner:HUNAN SEEKSUNS OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Quantum magneto-optic sensor
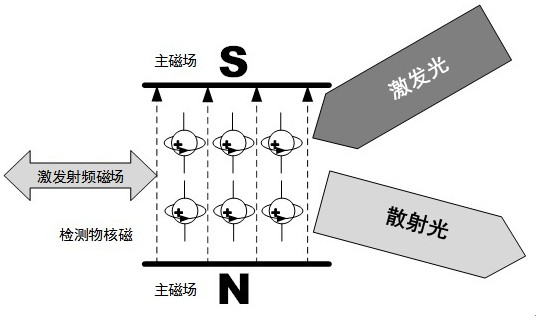
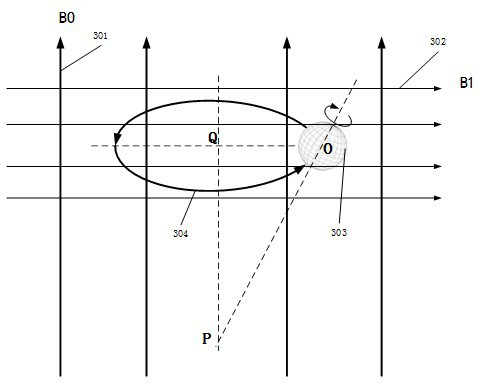
ActiveCN114441506BRealize associationRealize sensingRaman scatteringAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceParticle physicsMagnetic relaxation
Quantum magneto-optical sensors involve the field of sensors for quantum-level ultra-trace detection of nuclear magnetic resonance and Raman spectroscopy, specifically including the discovery of the electronic energy of specific protons in the detection object under the states of nuclear magnetic magnetization, nuclear magnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic relaxation and nuclear magnetic demagnetization. The difference in distribution probability of Raman scattered light in azimuth and direction caused by the order transition, and finding and adjusting the optimal magneto-optical angle between excitation light and Raman scattered light will obtain higher collection efficiency of Raman scattered light. The characteristic magnetic spectrum and the characteristic spectrum, according to the quantum correlation, can also find out more information from the quantum correlation. Specifically, the main magnetic field generator, the excitation induction coil, the control subsystem, the laser and the Raman probe constitute the quantum magneto-optical sensor. By adjusting the magneto-optical angle in an off-axis or coaxial way, the Raman spectrum collection efficiency can be improved, and at the same time, the correlation between the characteristic magnetic spectrum and the characteristic spectrum in multiple states can be realized, which provides a calculation basis for further analyzing the content of the detected molecules.
Owner:GREATER BAY AREA STAR BIOTECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank
InactiveCN108082797AConvenient classification deliveryRealize sensingWaste collection and transferRefuse receptaclesRefuse collectionWaste collection
The invention discloses an intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank which comprises a tank, a support and an electric appliance assembly. Harmful garbage release openings are formed in the tank, the tank is provided with maintenance and management doors, release openings for storing lamp sticks and annular fluorescent tubes are formed in the upper portion of the tank, and the fluorescent tubesare mounted on the support; a photovoltaic panel is mounted on the support of the tank and is connected with a photovoltaic interface of a photovoltaic panel controller, and a charge interface and a load interface of the photovoltaic panel controller are connected with a storage battery and the fluorescent tubes. The intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank has the advantages that the intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank has functions of harmful garbage collecting stations; fluorescent tube storage regions are arranged on the tank of the novel intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank, and the harmful garbage release openings are formed in the tank of the novel intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank; the intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank has functions of convenience service charge stations; the intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank further is a garbage classification propaganda station; infrared sensors are mounted on the novel intelligent harmful garbage collecting tank in the design, accordingly, users can be sensed by the sensors when the users enter the sensing ranges, garbage classification propaganda speech can be played, and the use and propaganda purposes can be achieved.
Owner:邓涛 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com