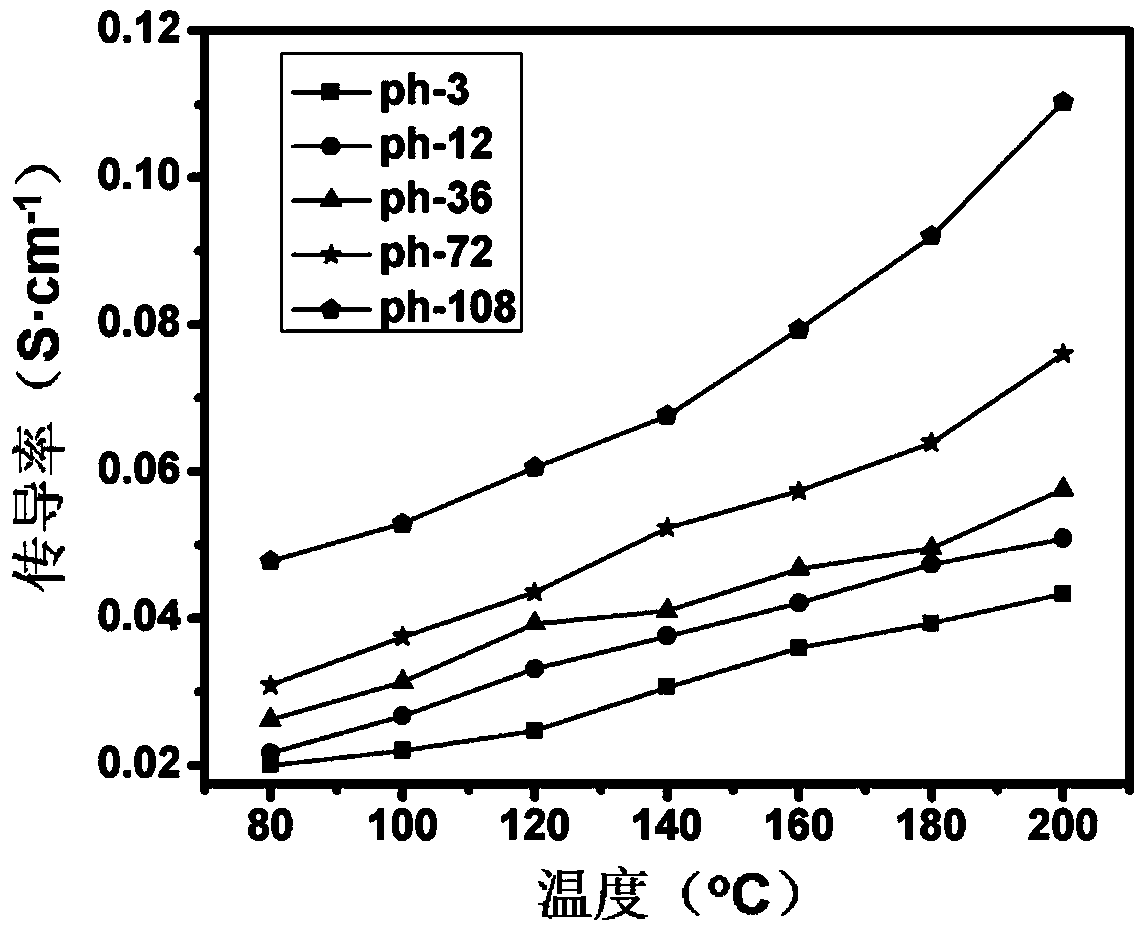
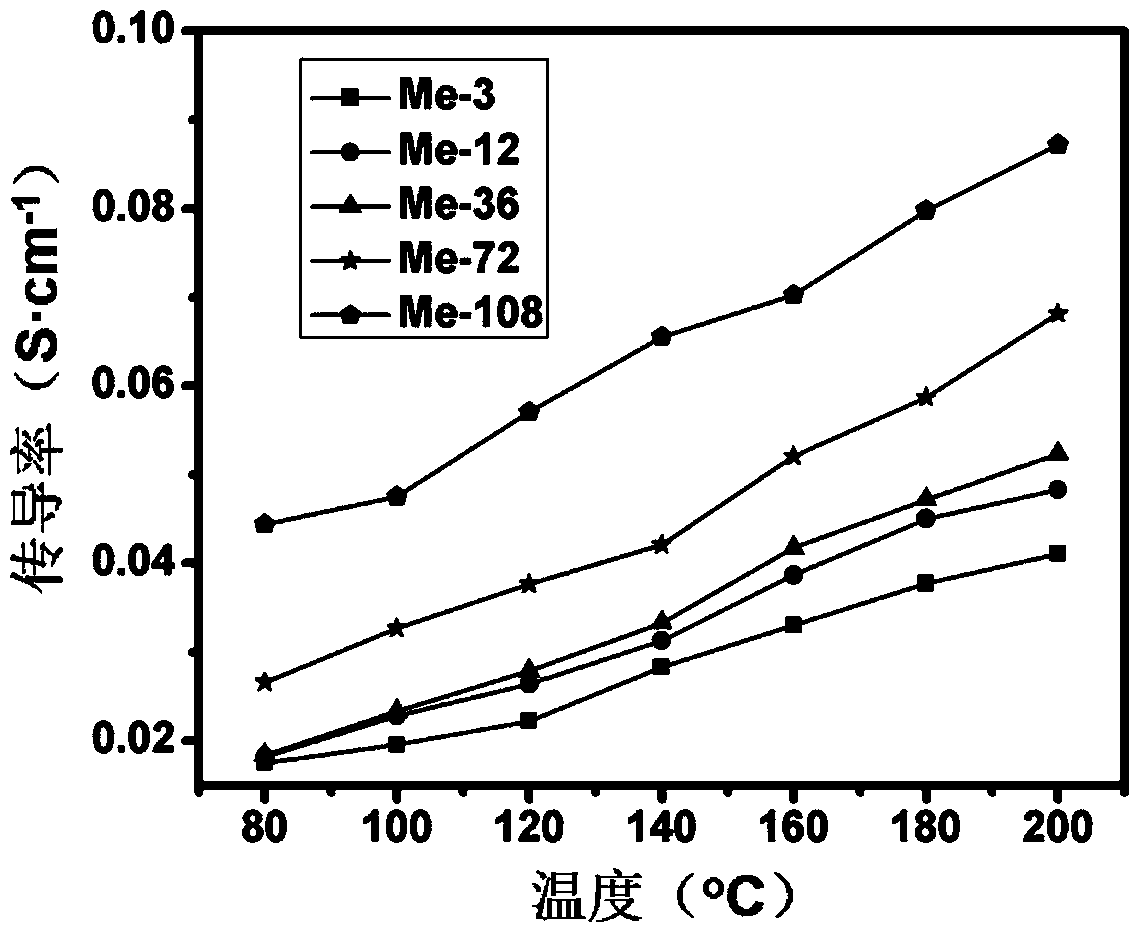
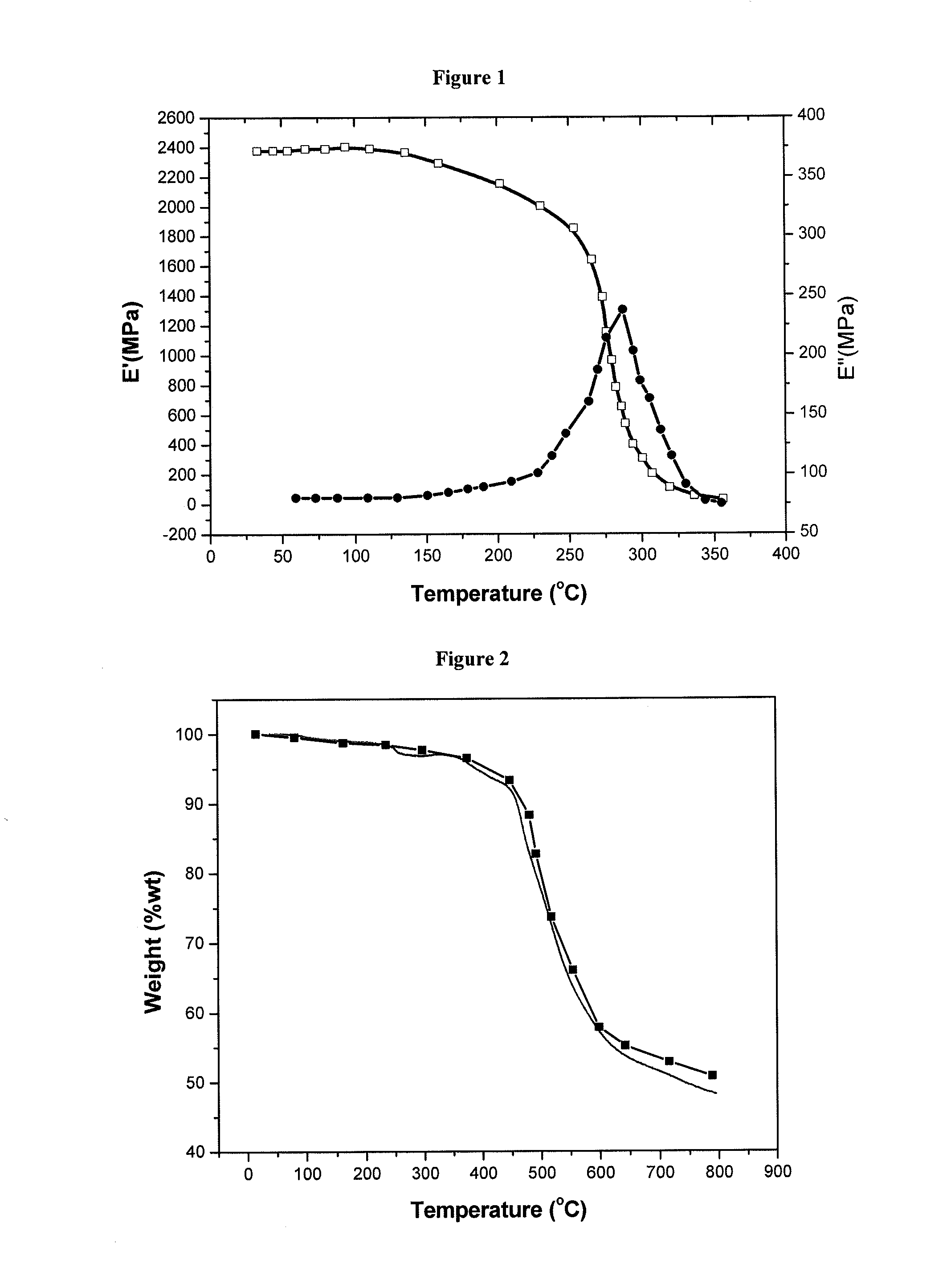
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Raise the level of doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
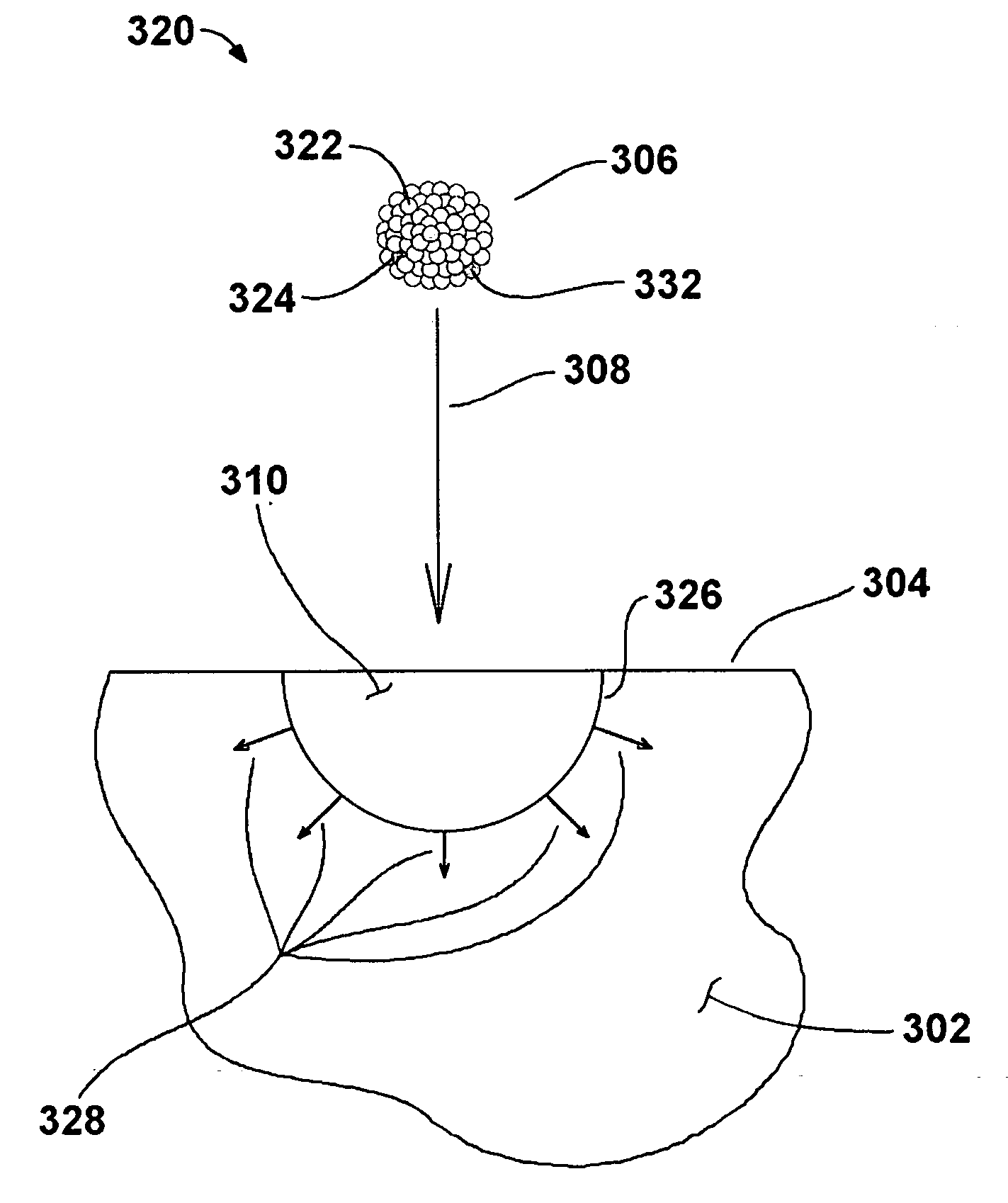
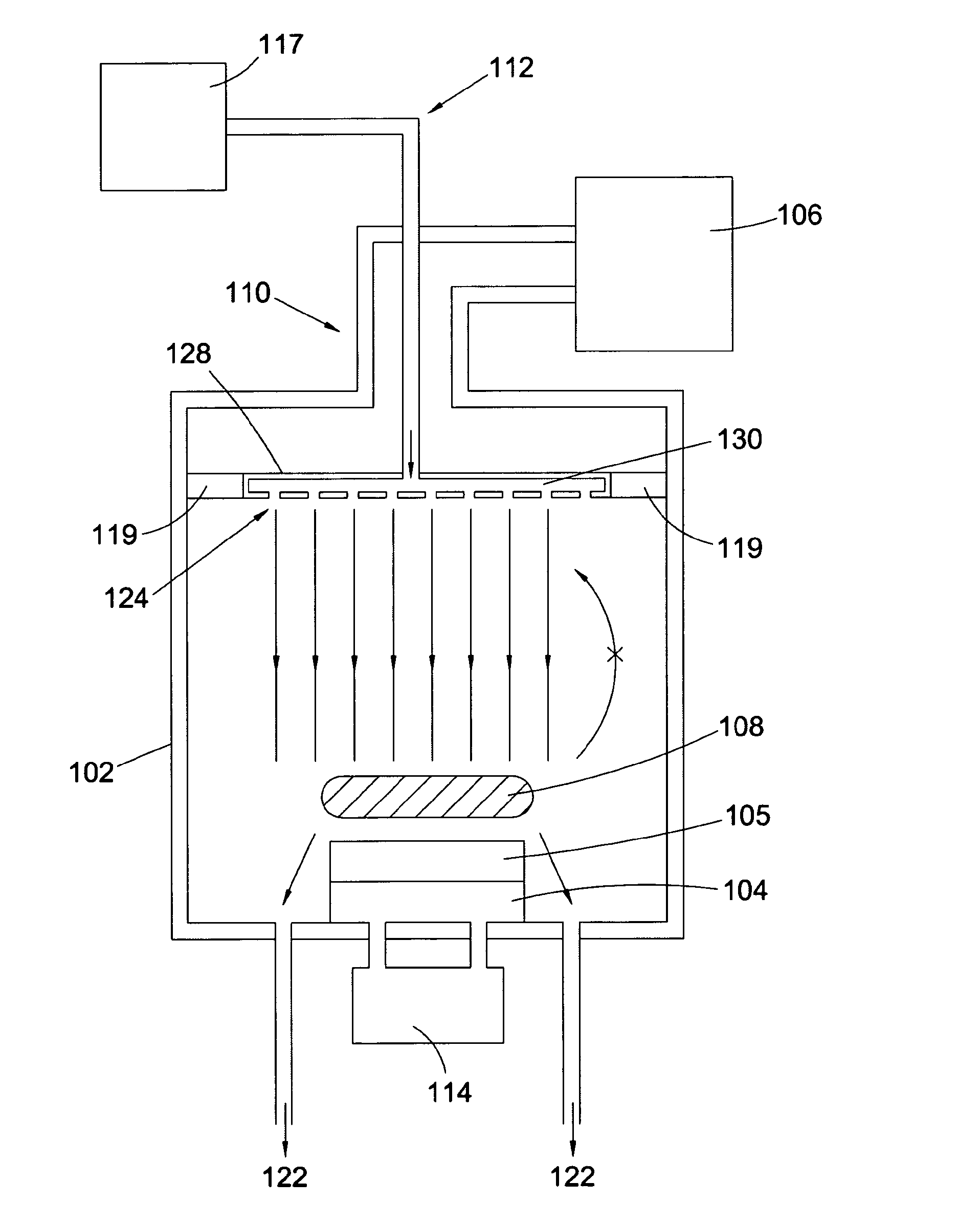
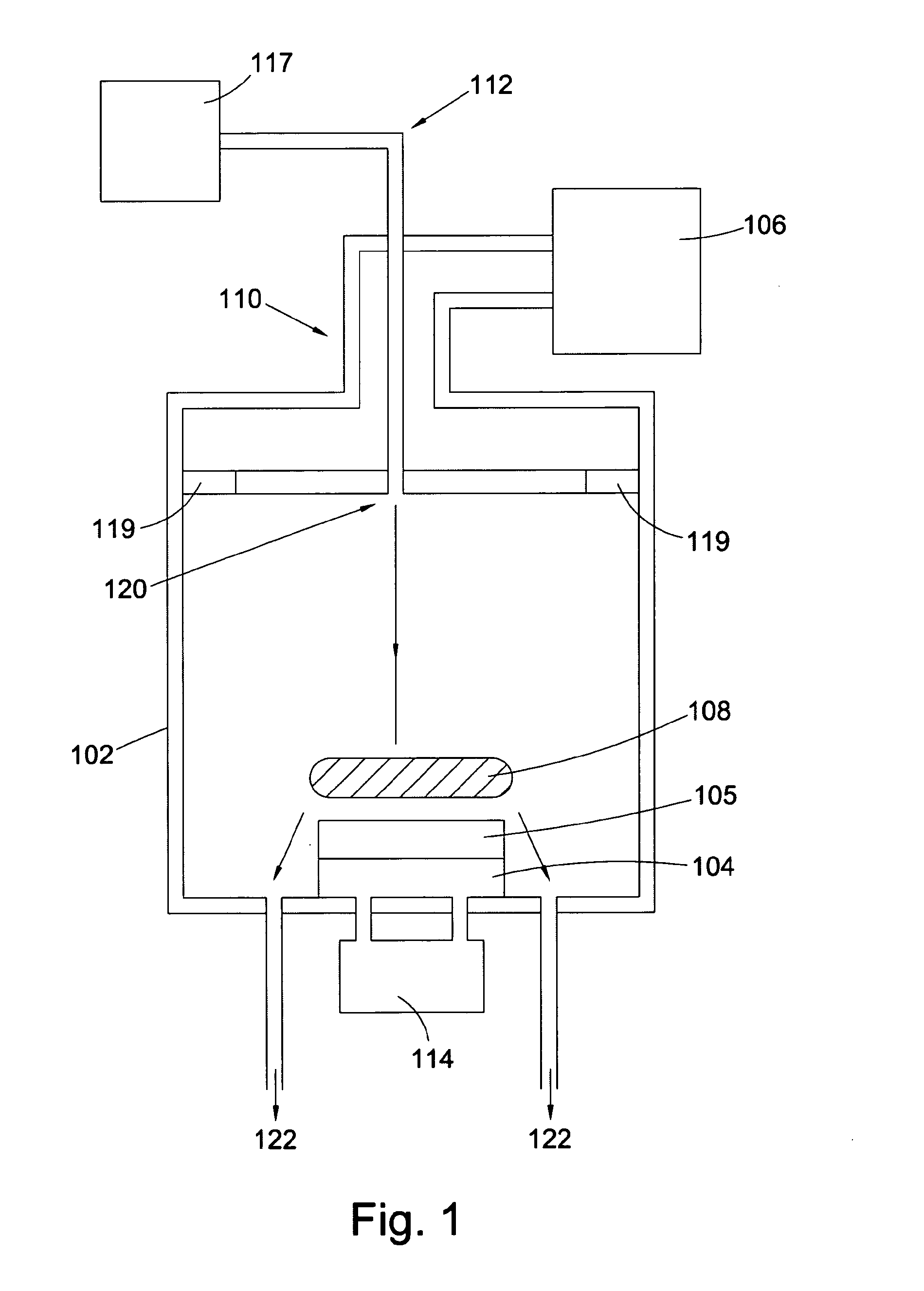
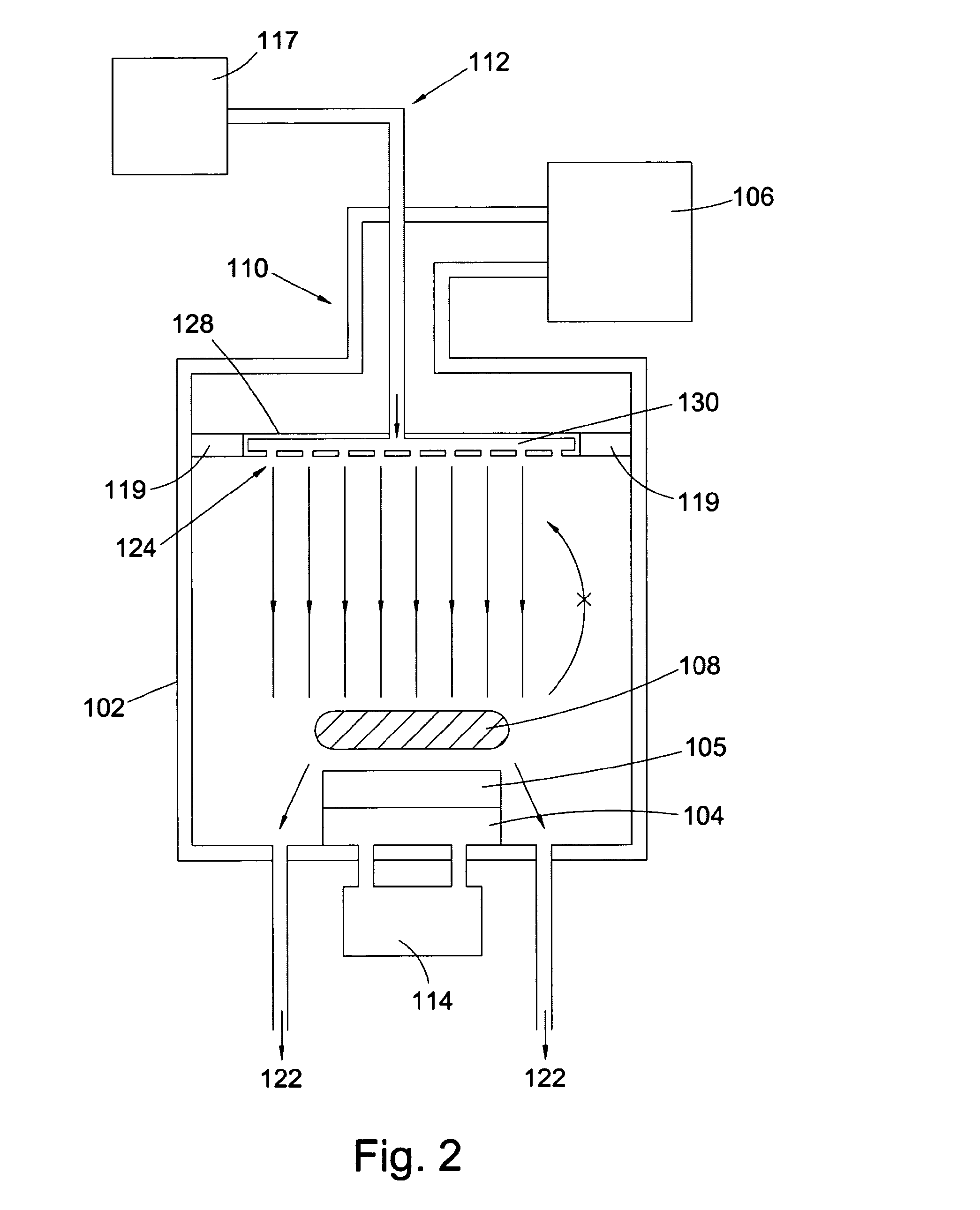
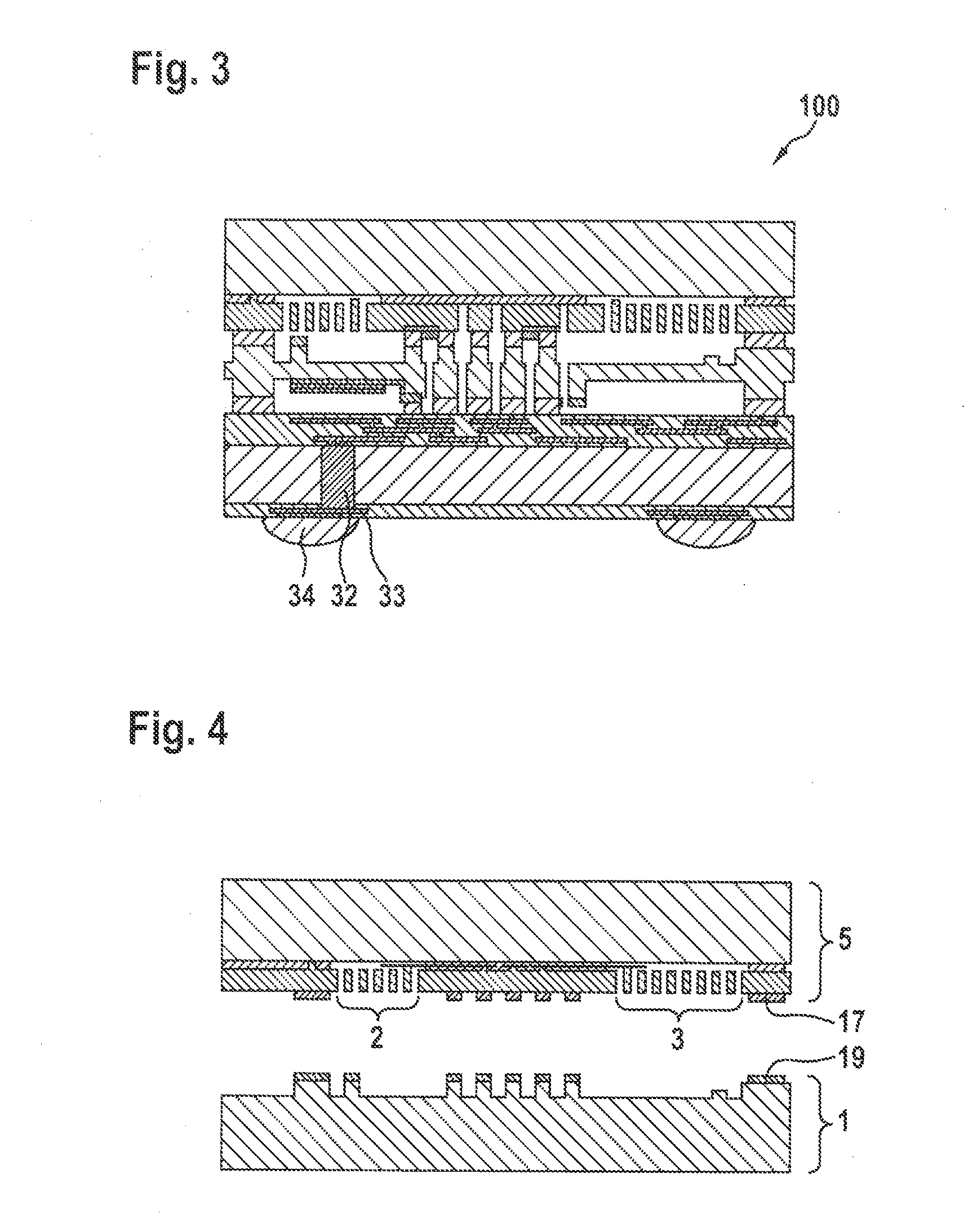
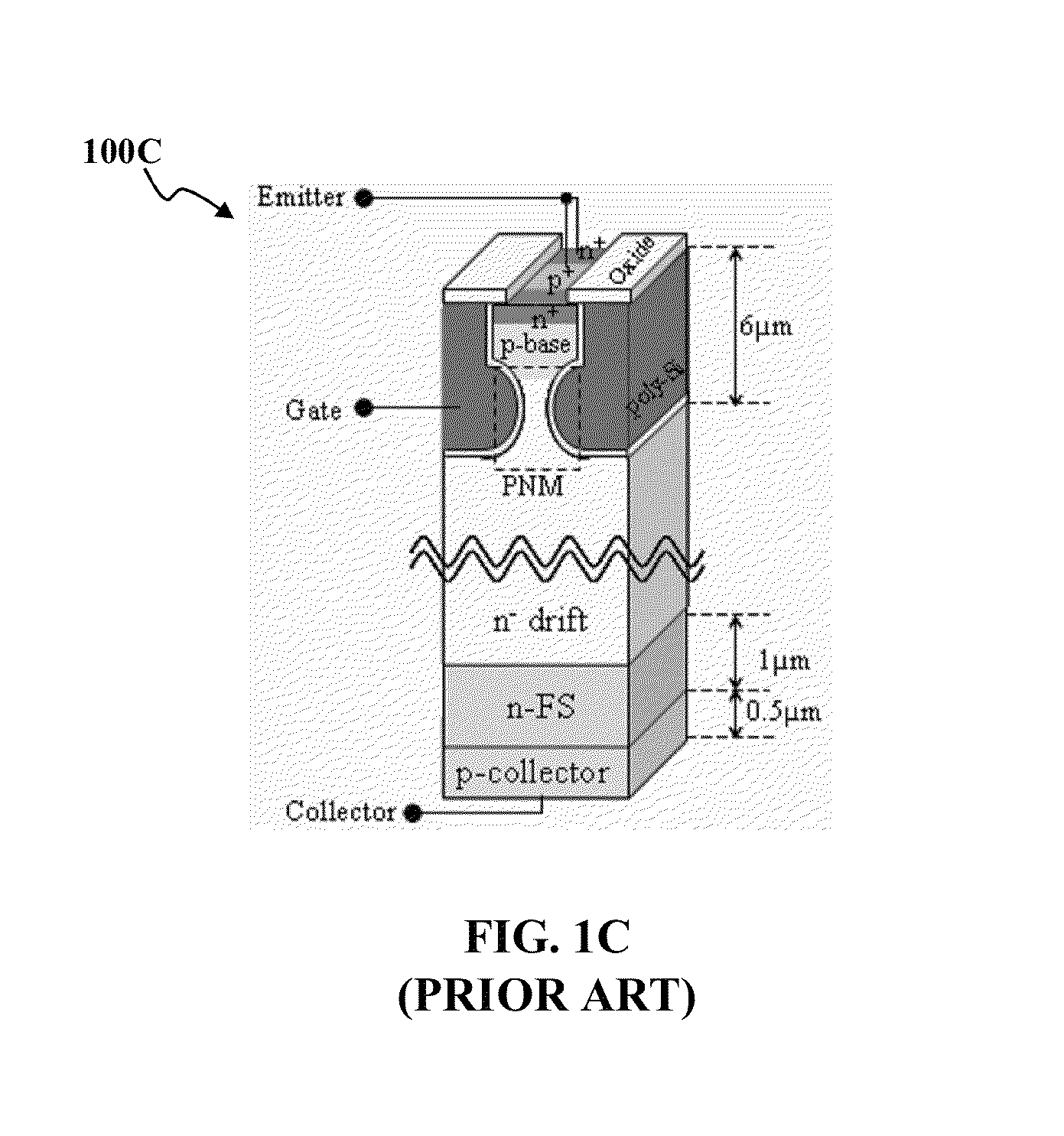
Formation of doped regions and/or ultra-shallow junctions in semiconductor materials by gas-cluster ion irradiation
ActiveUS20050277246A1Improve solid solubilityImprove efficiencyElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor materialsGas cluster ion beam
Method of forming one or more doped regions in a semiconductor substrate and semiconductor junctions formed thereby, using gas cluster ion beams.
Owner:TEL EPION
Detectable micro to nano sized structures, methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20040171076A1InexpensivelyEasy to mass producePeptide librariesNucleotide librariesAnalyteRare earth
Homogeneously mixed rare-earth doped particles and methods of using such particles include nano to microsized particles having a concentration of at least about 0.0005 mole percent of a Rare-Earth Oxide (Re2O3). The particles can be used for detecting the presence of an analyte in a sample and for detecting interactions of biomolecules.
Owner:CORNING INC
Formation of ultra-shallow junctions by gas-cluster ion irradiation
ActiveUS20050202657A1Improve solid solubilityImprove efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas cluster ion beamIrradiation
Method of forming one or more doped regions in a semiconductor substrate and semiconductor junctions formed thereby, using gas cluster ion beams.
Owner:TEL EPION
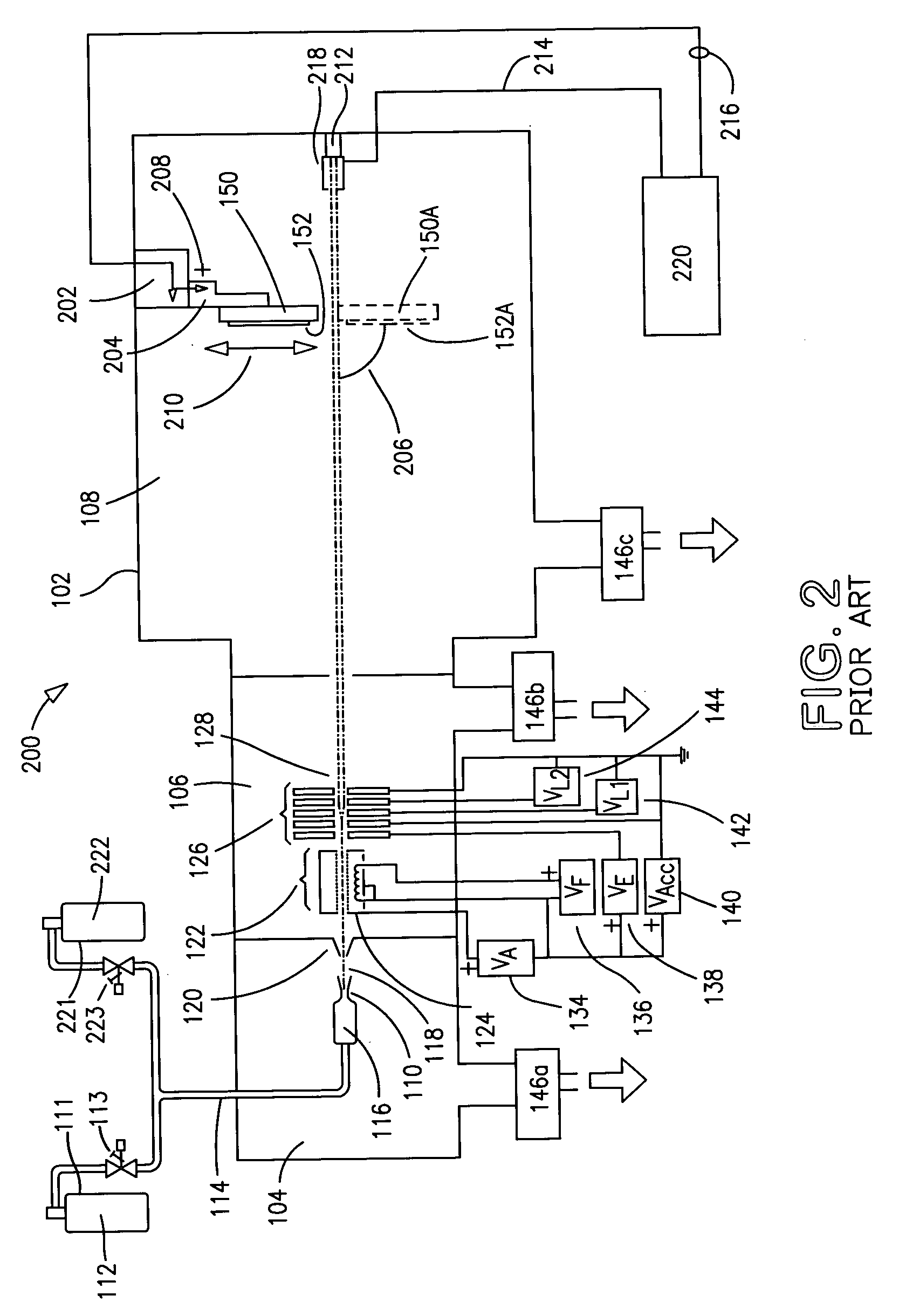
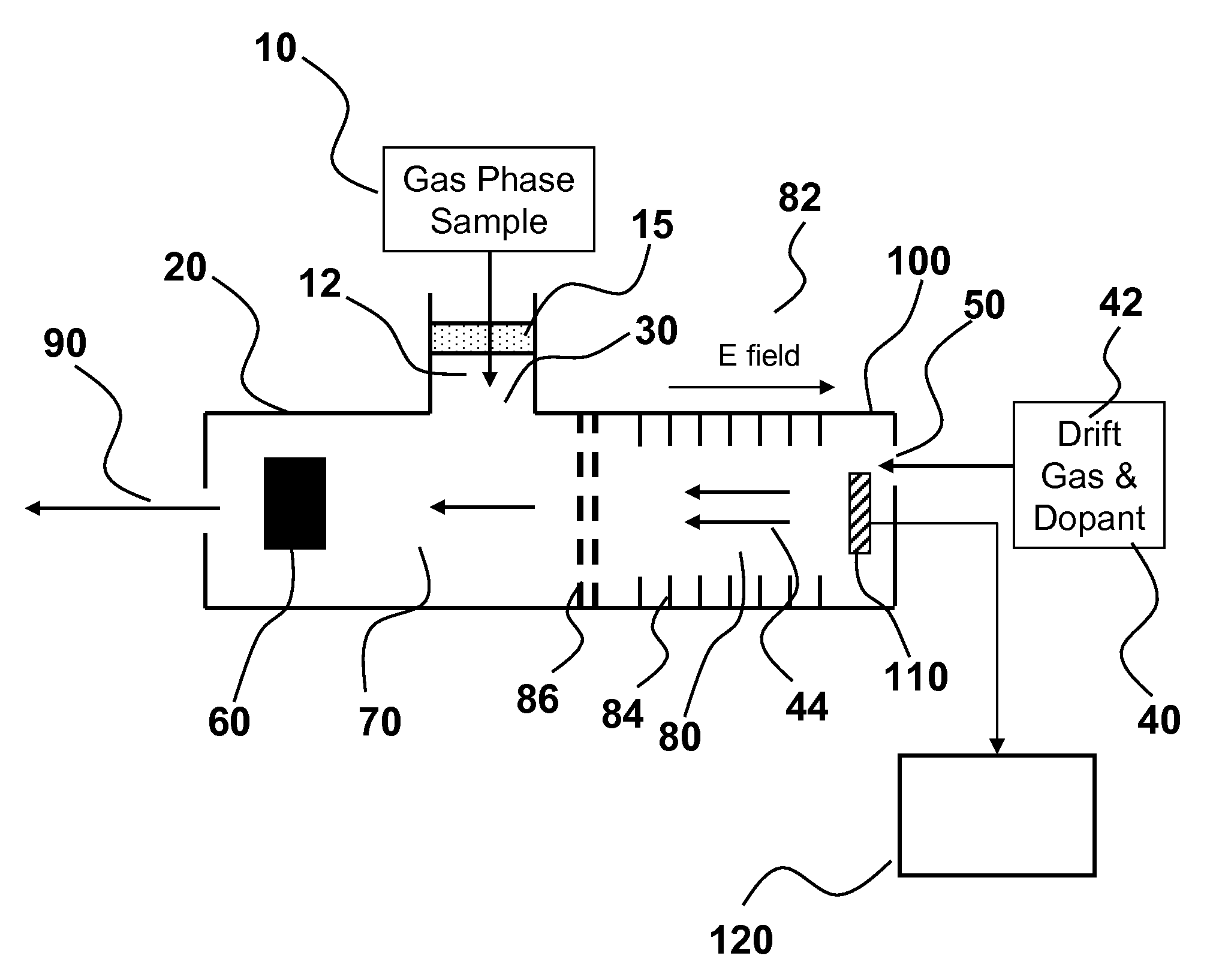
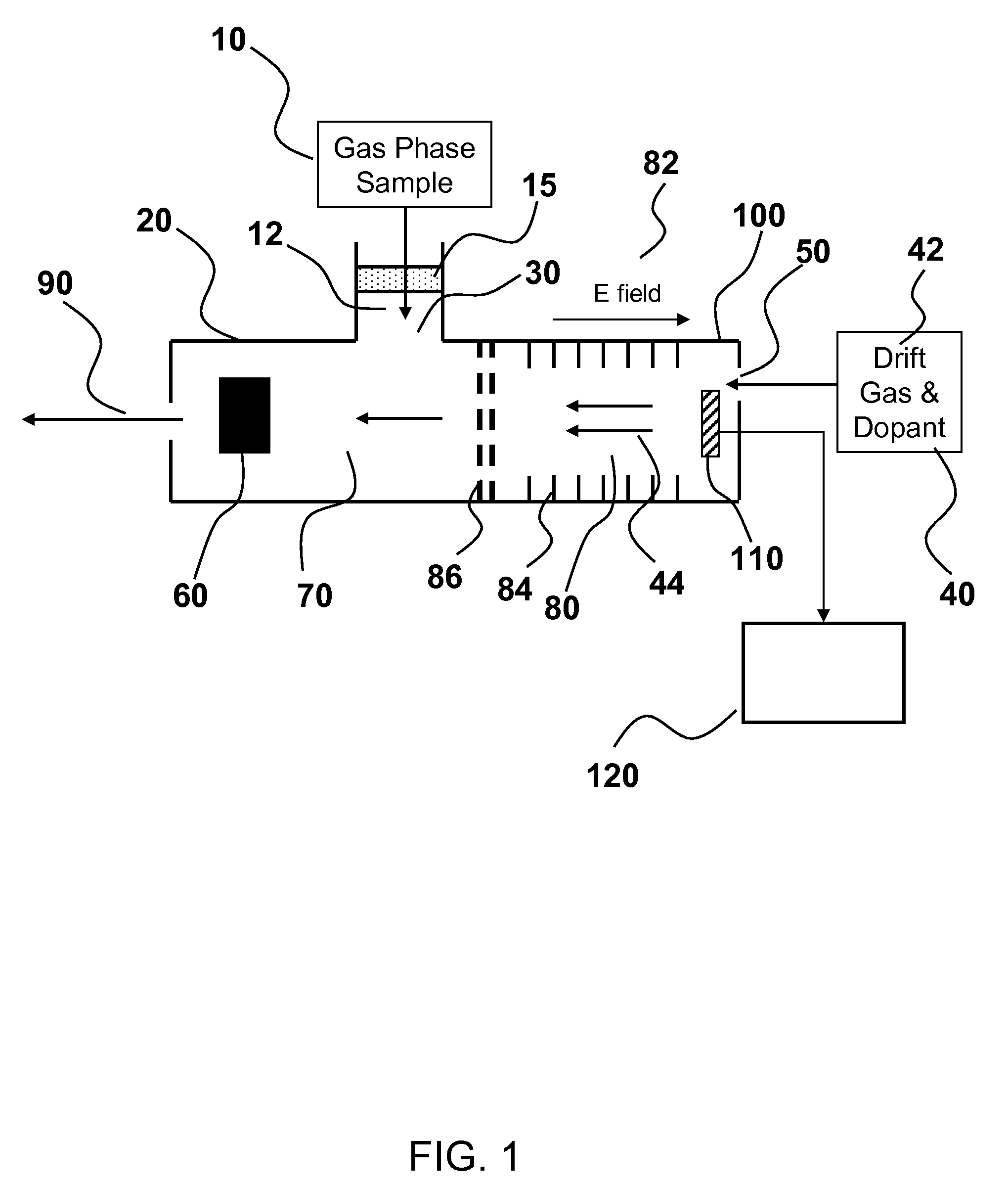
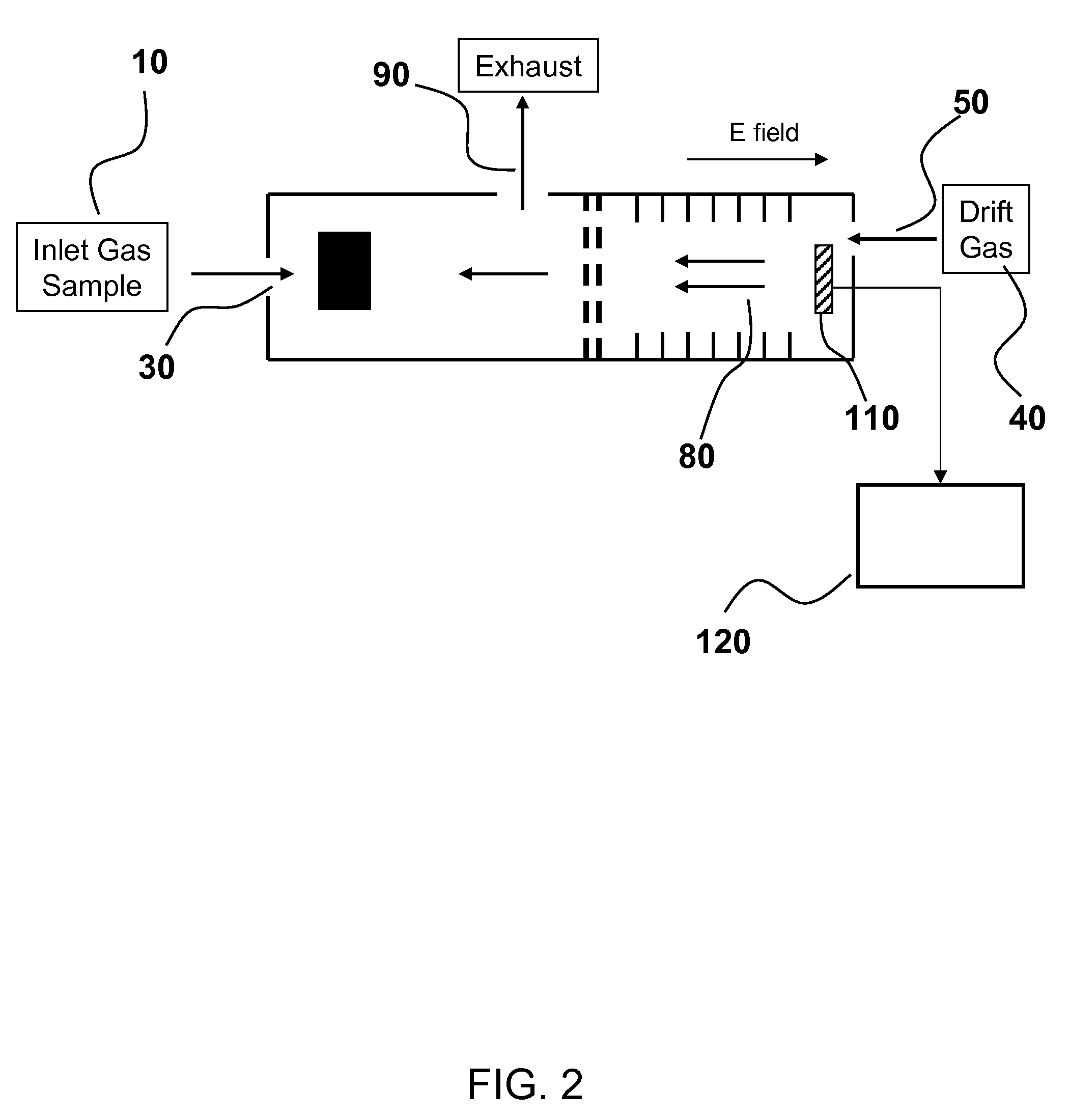
Detection of analytes using ion mobility spectrometry
ActiveUS7985949B2High sensitivityAccurate detectionTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiffusionDopant
Methods and systems are provided for detecting analytes in a gas phase sample. An ion mobility spectrometer is provided for detecting analytes having an excess amount of dopant in its separation region. In an embodiment, the dopant is added directly to the separation region, such as with a drift gas or by diffusion, thereby providing excess dopant that dominates subsequent cluster formation and maintenance. Excess dopant in the separation region minimizes or reduces interfering signals associated with unwanted substances, such as water vapor, that are introduced to the IMS. In an aspect, the invention provides IMS systems and methods having increased sensitivity and reliability for analyte detection.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Detectable labels, methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20030119207A1Good adhesionAbsorption cross sectionPeptide librariesNanosensorsAnalyteReady to use
Owner:CORNING INC
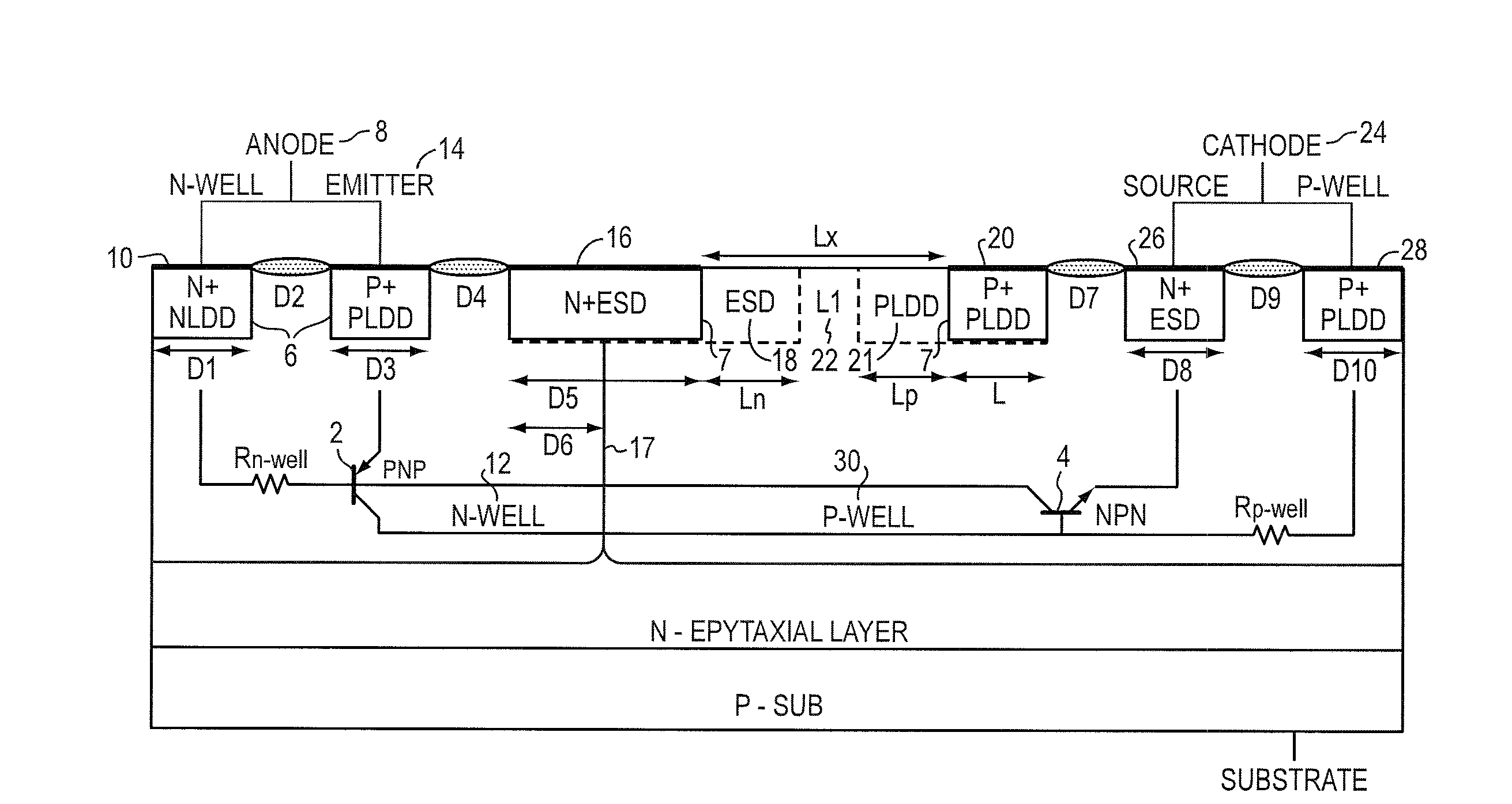
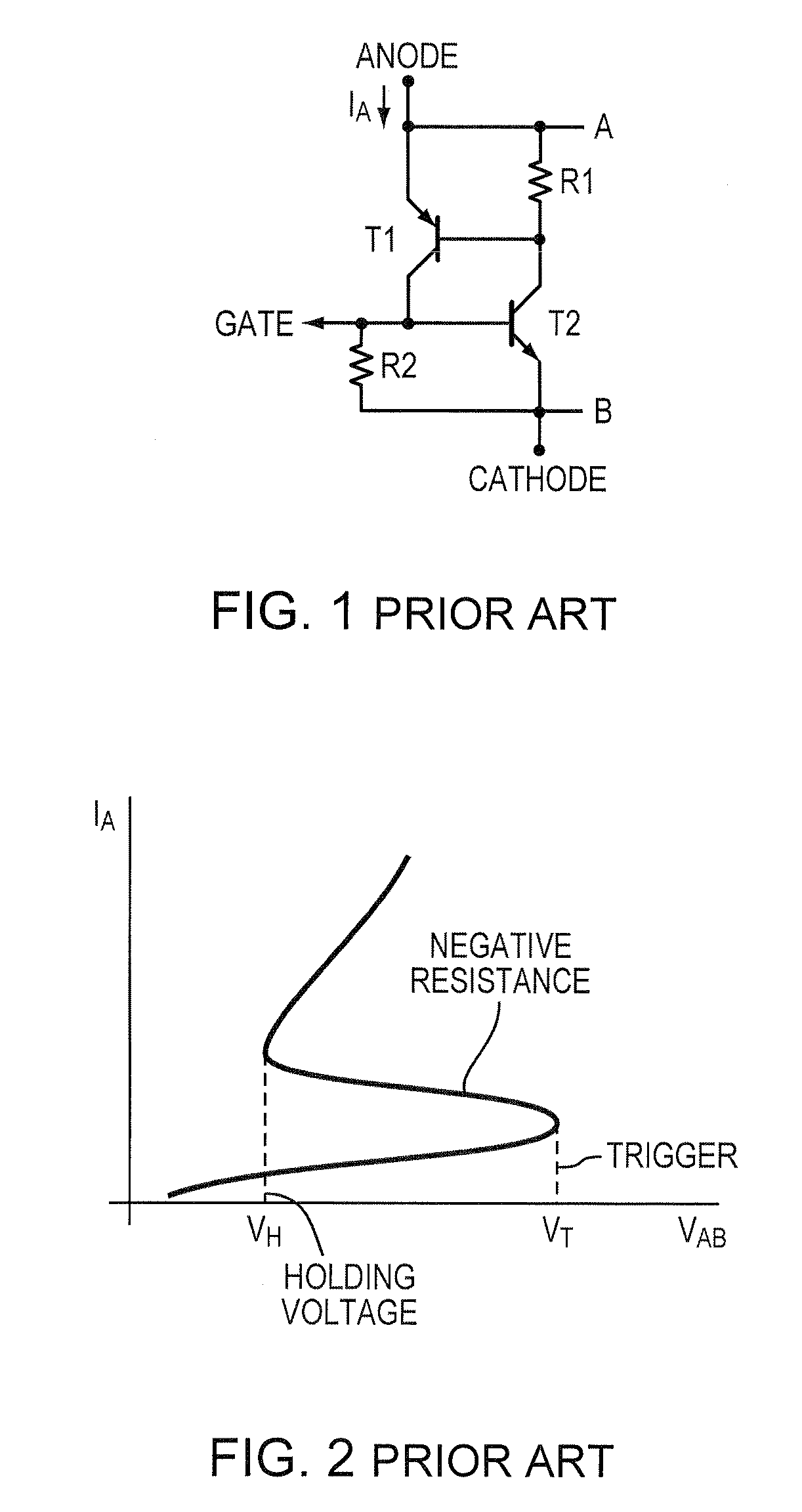
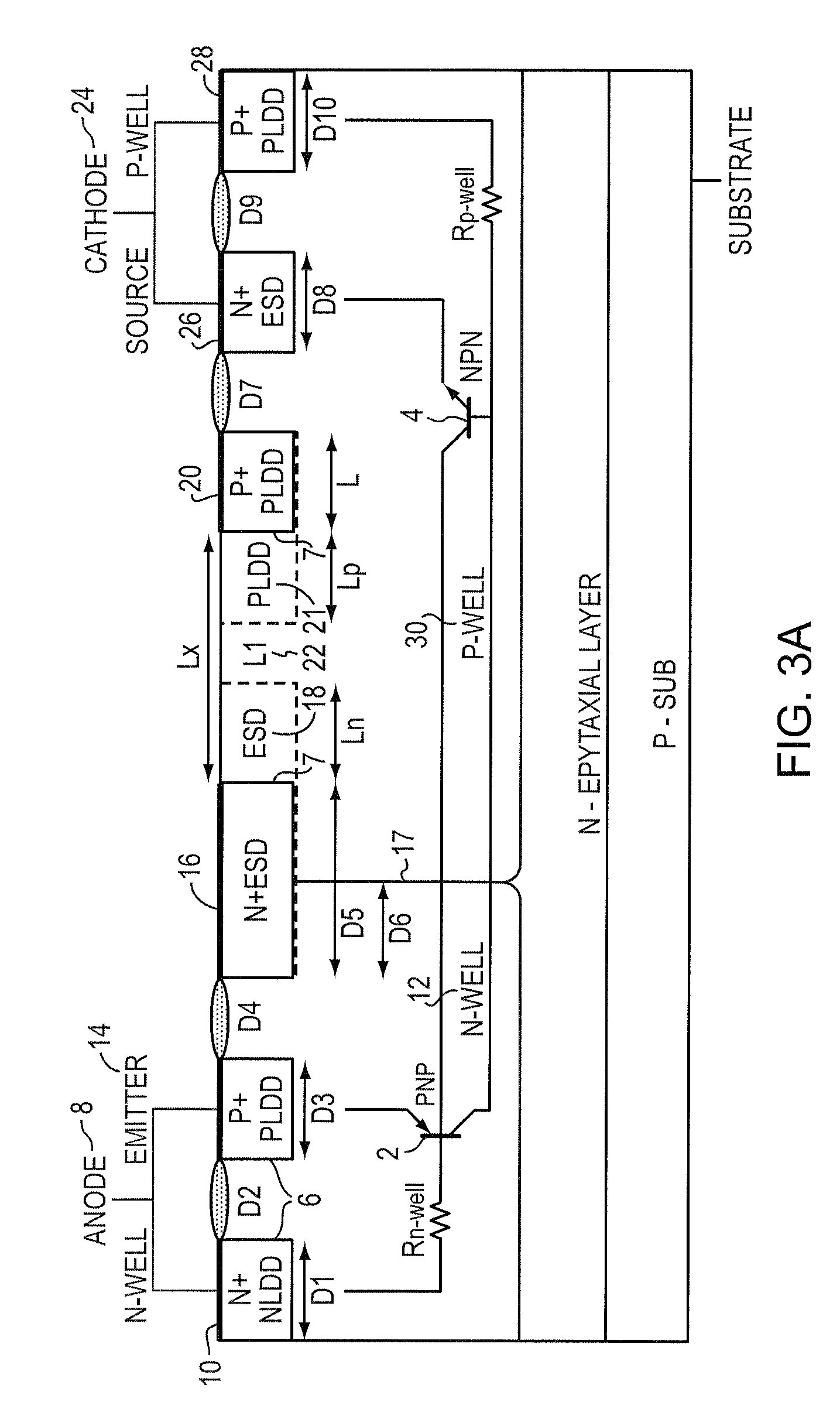
Un-assisted, low-trigger and high-holding voltage SCR
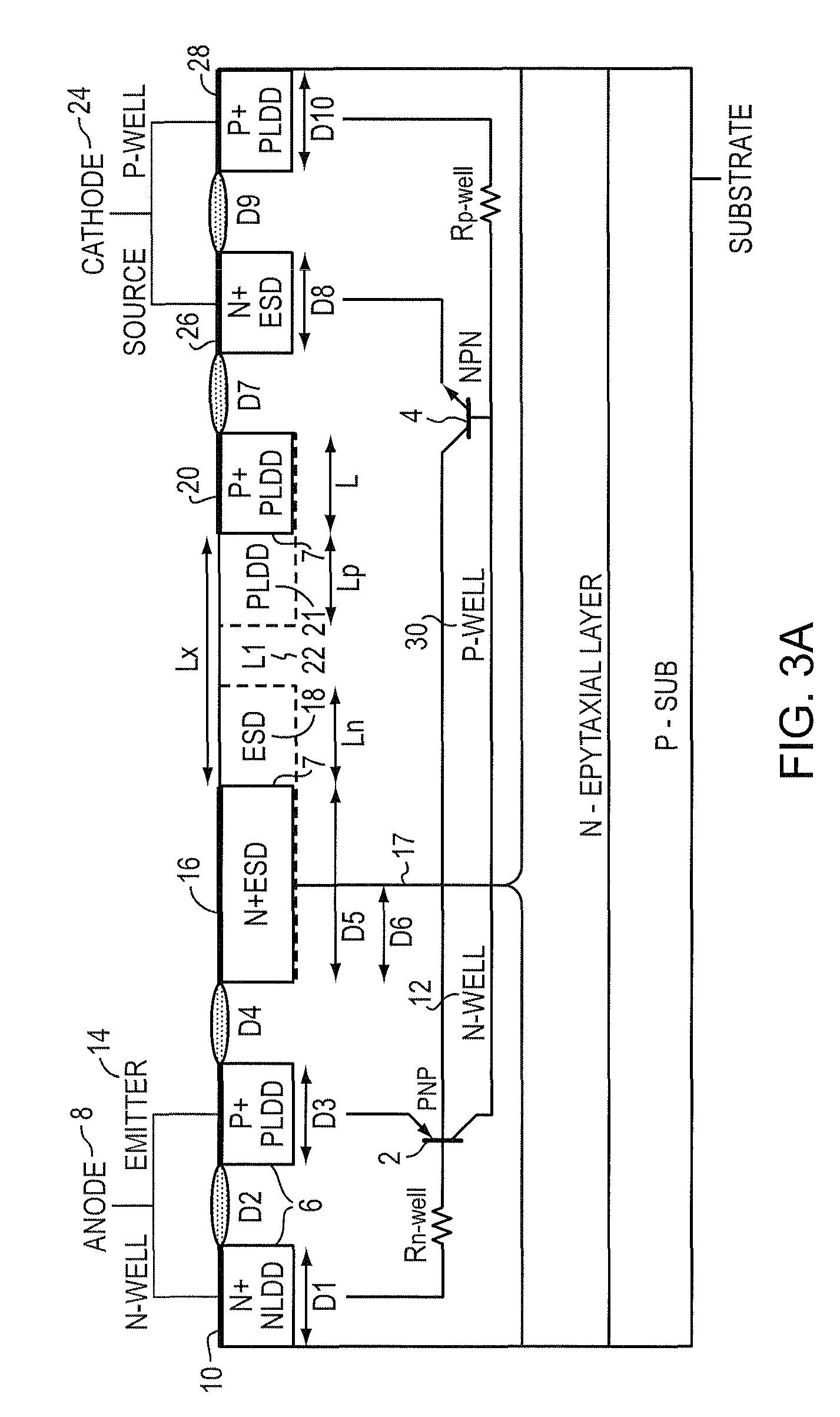
ActiveUS7719026B2Sacrificing ESD protection robustnessHigh n-type doping densityTransistorThyristorEngineeringExternal circuit
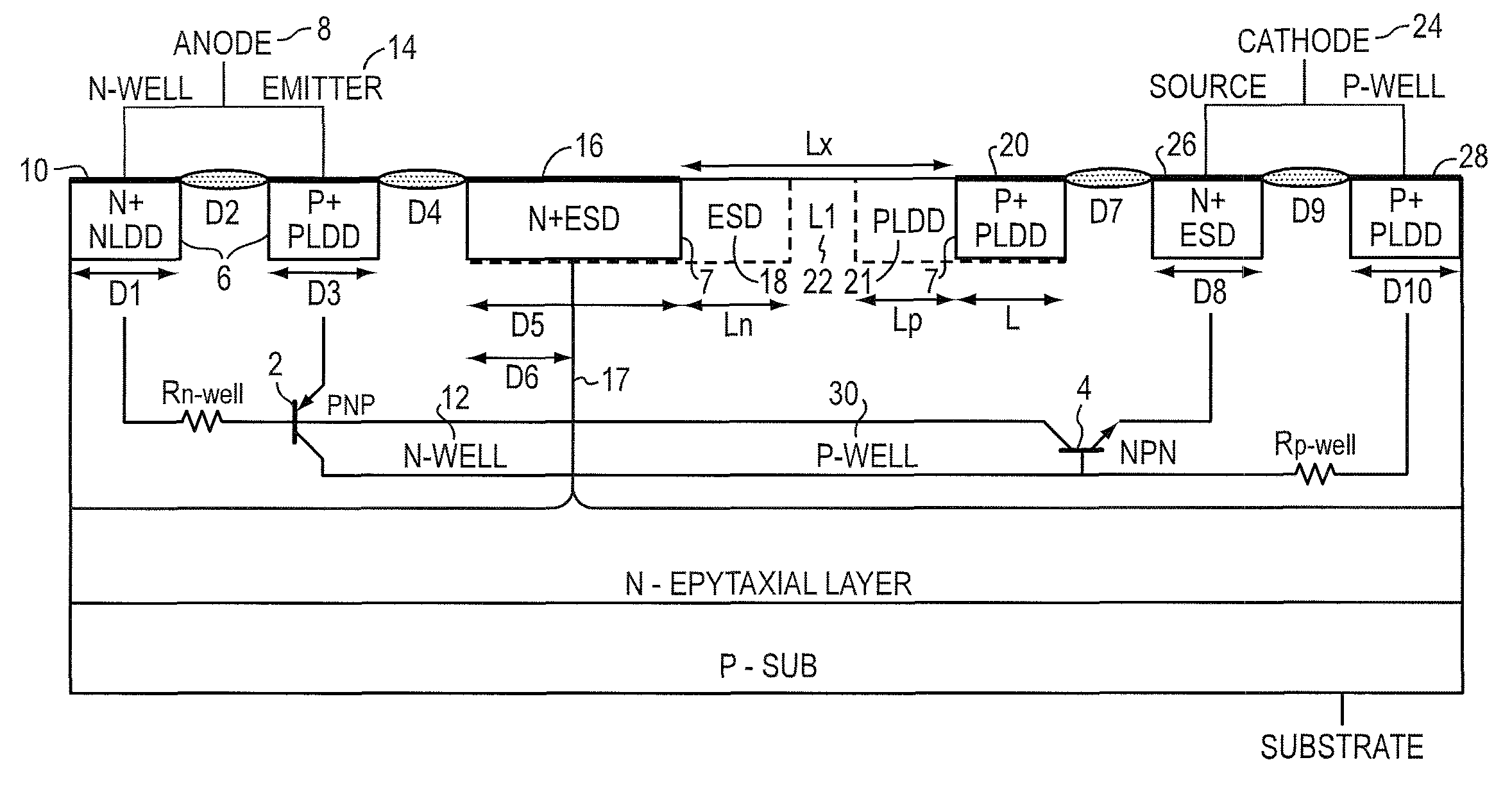
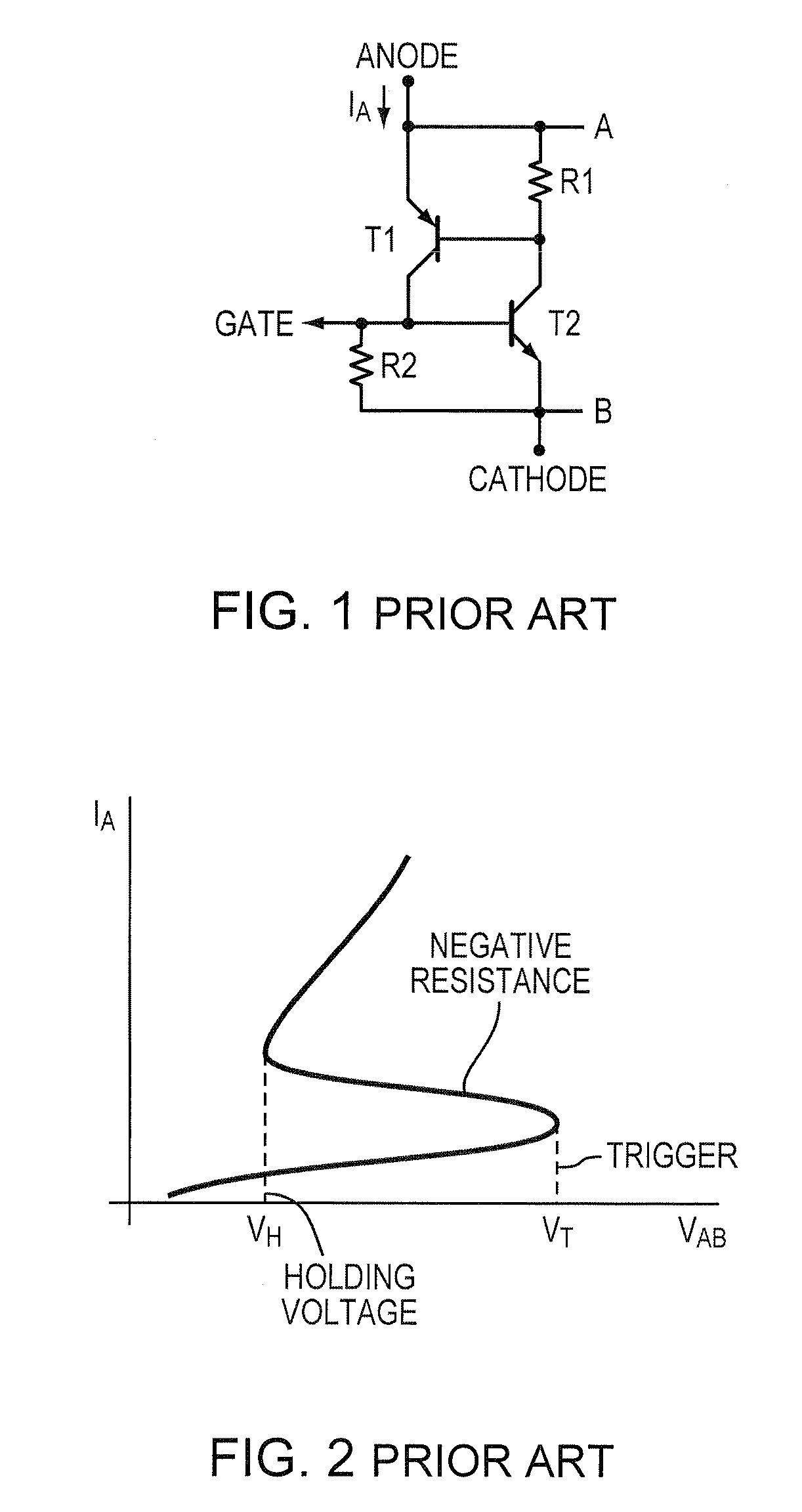
A protective SCR integrated circuit device is disclosed built on adjacent N and P wells and defining an anode and a cathode. In addition to the anode and cathode contact structures, the device has an n-type stack (N+ / ESD) structure bridging the N-Well and the P-Well, and a p-type stack (P+ / PLDD) structure in the P-Well. The separation of the n-type stack structure and the p-type stack structure provides a low triggering voltage without involving any external circuitry or terminal, that together with other physical dimensions and processing parameters also provide a relatively high holding voltage without sacrificing the ESD protection robustness. In an embodiment, the triggering voltage may be about 8V while exhibiting a holding voltage, that may be controlled by the lateral dimension of the n-type stack of about 5-7 V.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
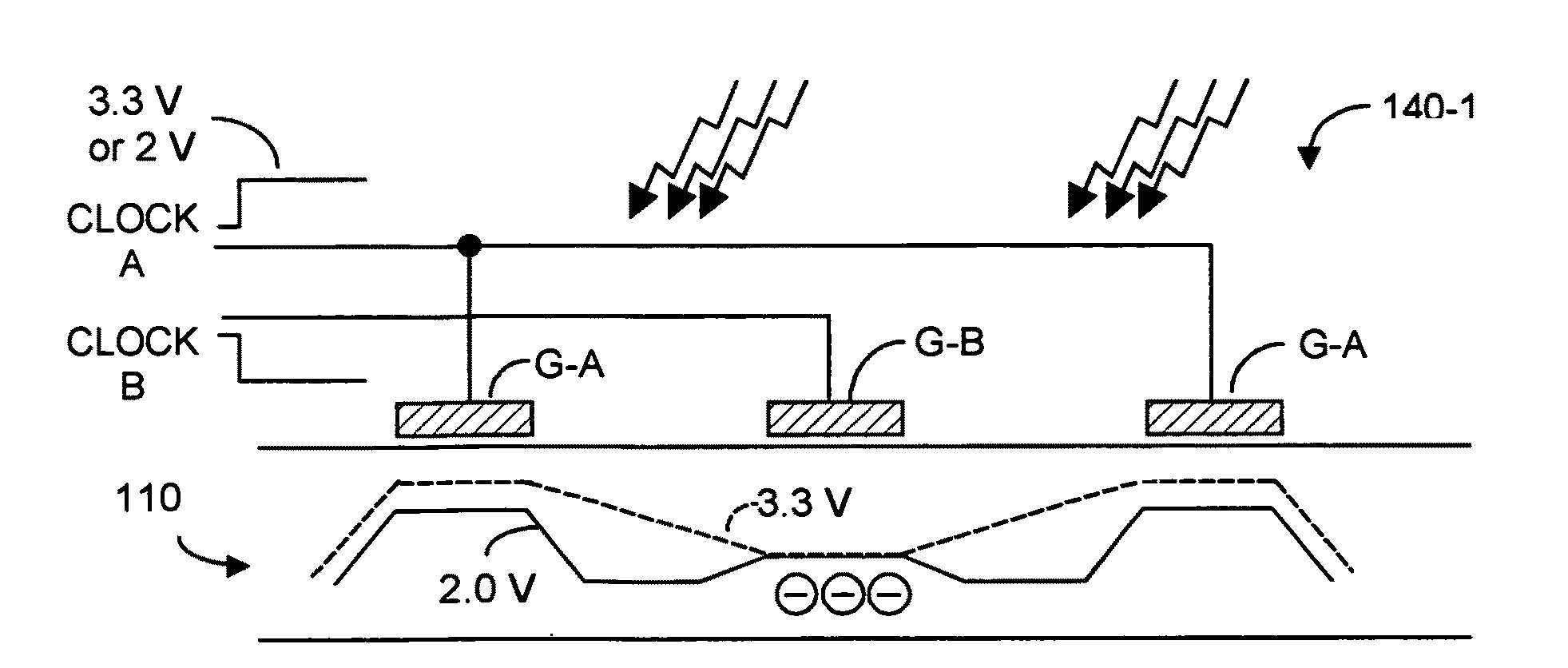
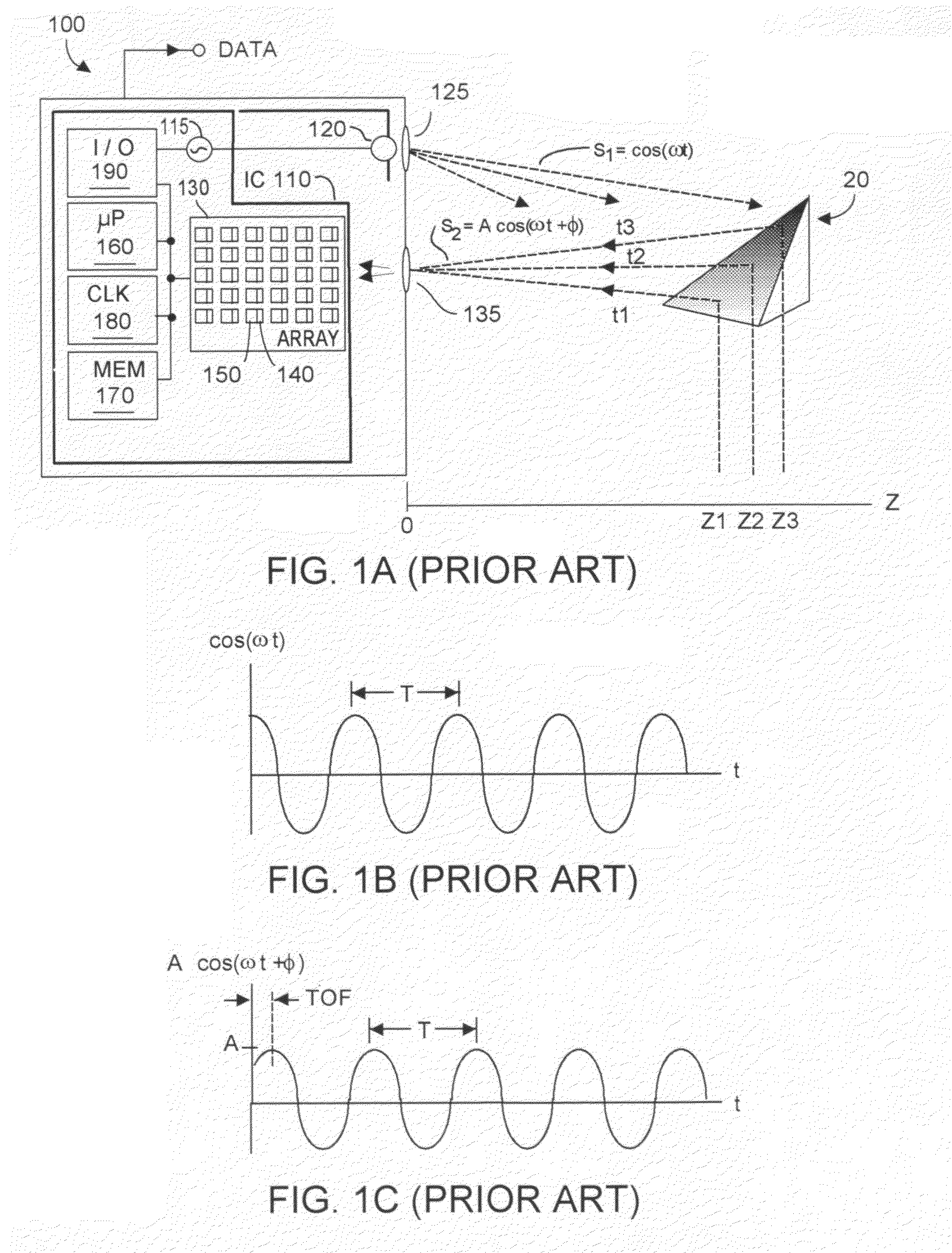
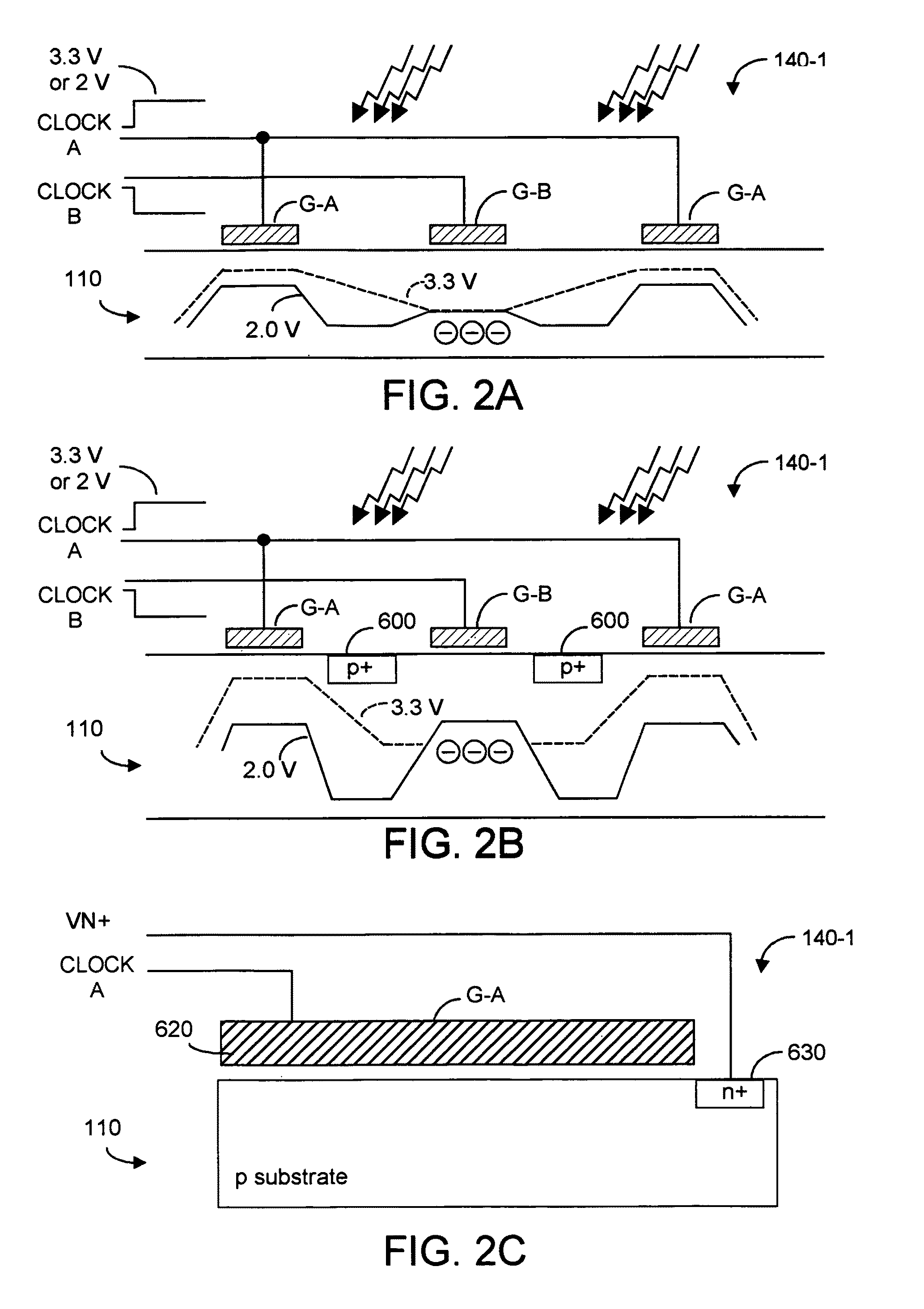
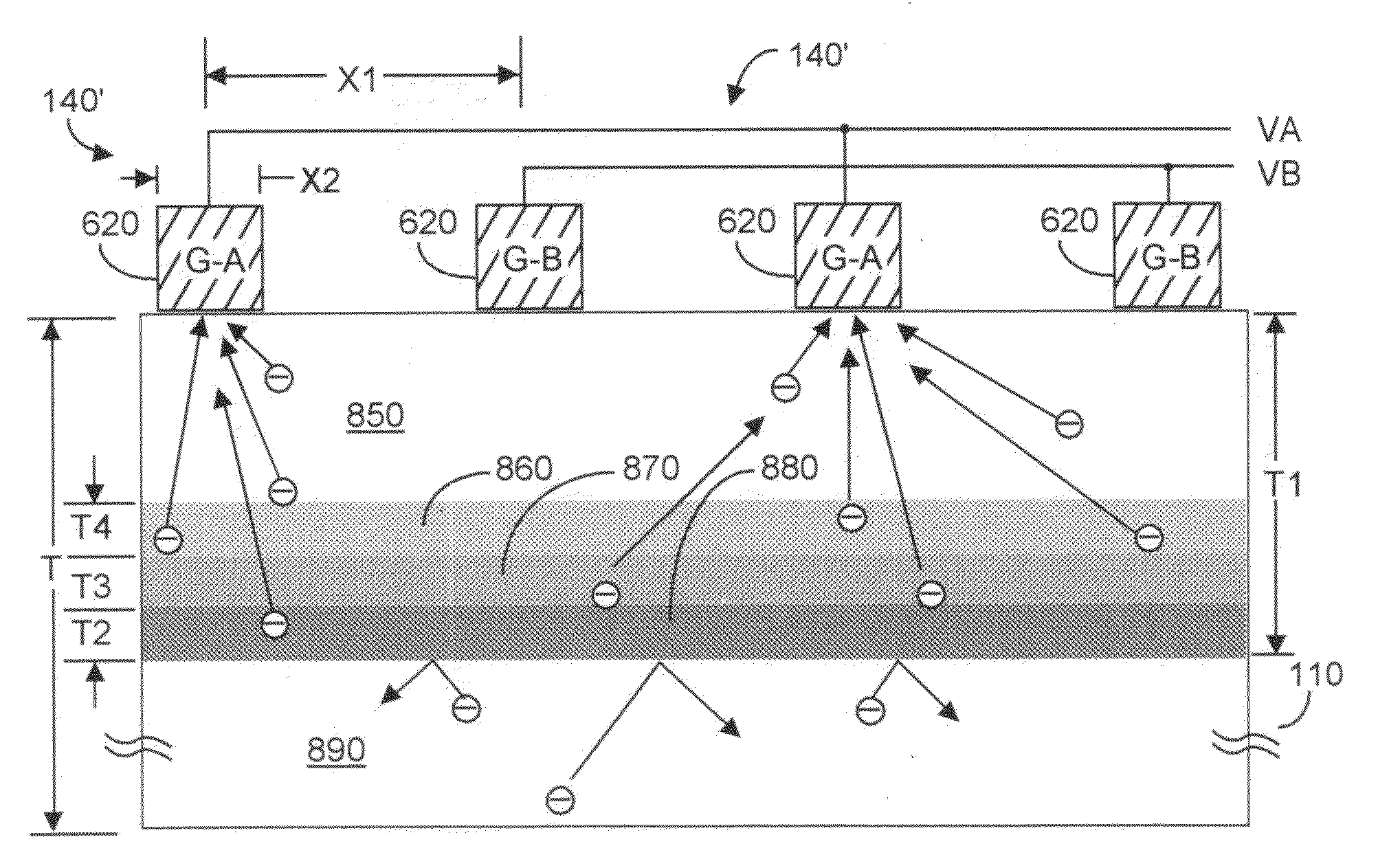
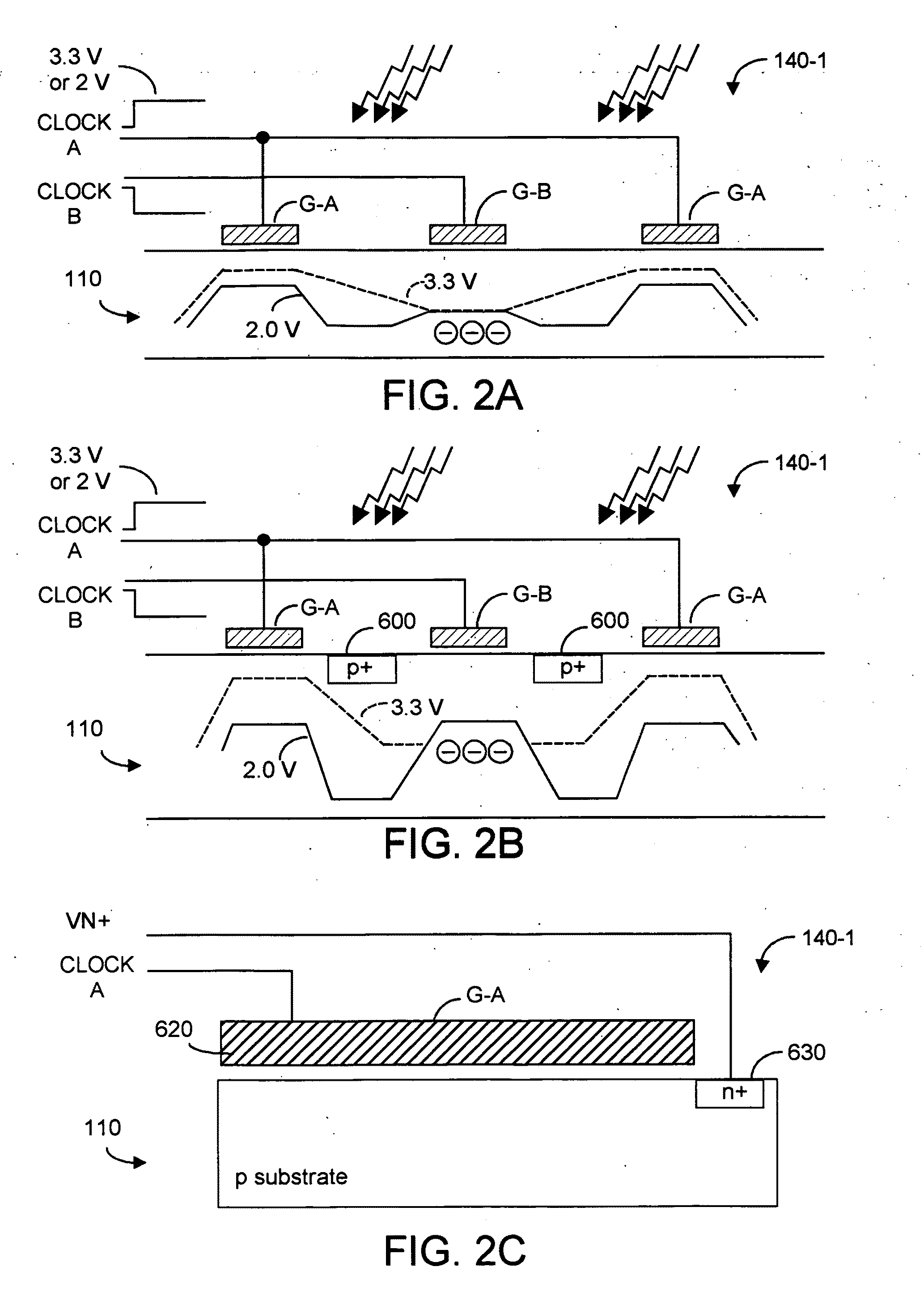
CMOS three-dimensional image sensor detectors with assured non collection of late arriving charge, more rapid collection of other charge, and with improved modulation contrast
InactiveUS8314924B2Maximize collectionMinimize collectionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSContrast ratio
A CMOS-implementable TOF detector promptly collects charge whose creation time can be precisely known, while rejecting collection of potentially late arriving charge whose creation time may not be precisely known. Charges created in upper regions of the detector structure are ensured to be rapidly collected, while charges created in the lower regions of the detector structure, potentially late arriving charges, are inhibiting from being collected.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Controlling doping of synthetic diamond material
ActiveUS20140150713A1Reliably and consistently processedQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge tubesPlasma reactorPlasma chamber
A method of manufacturing synthetic CVD diamond material, the method comprising: providing a microwave plasma reactor comprising: a plasma chamber; one or more substrates disposed in the plasma chamber providing a growth surface area over which the synthetic CVD diamond material is to be deposited in use; a microwave coupling configuration for feeding microwaves from a microwave generator into the plasma chamber; and a gas flow system for feeding process gases into the plasma chamber and removing them therefrom, injecting process gases into the plasma chamber; feeding microwaves from the microwave generator into the plasma chamber through the microwave coupling configuration to form a plasma above the growth surface area; and growing synthetic CVD diamond material over the growth surface area, wherein the process gases comprise at least one dopant in gaseous form, selected from a one or more of boron, silicon, sulphur, phosphorous, lithium and beryllium at a concentration equal to or greater than 0.01 ppm and / or nitrogen at a concentration equal to or greater than 0.3 ppm, wherein the gas flow system includes a gas inlet comprising one or more gas inlet nozzles disposed opposite the growth surface area and configured to inject process gases towards the growth surface area, and wherein the process gases are injected towards the growth surface area at a total gas flow rate equal to or greater than 500 standard cm3 per minute and / or wherein the process gases are injected into the plasma chamber through the or each gas inlet nozzle with a Reynolds number a Reynolds number in a range 1 to 100.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
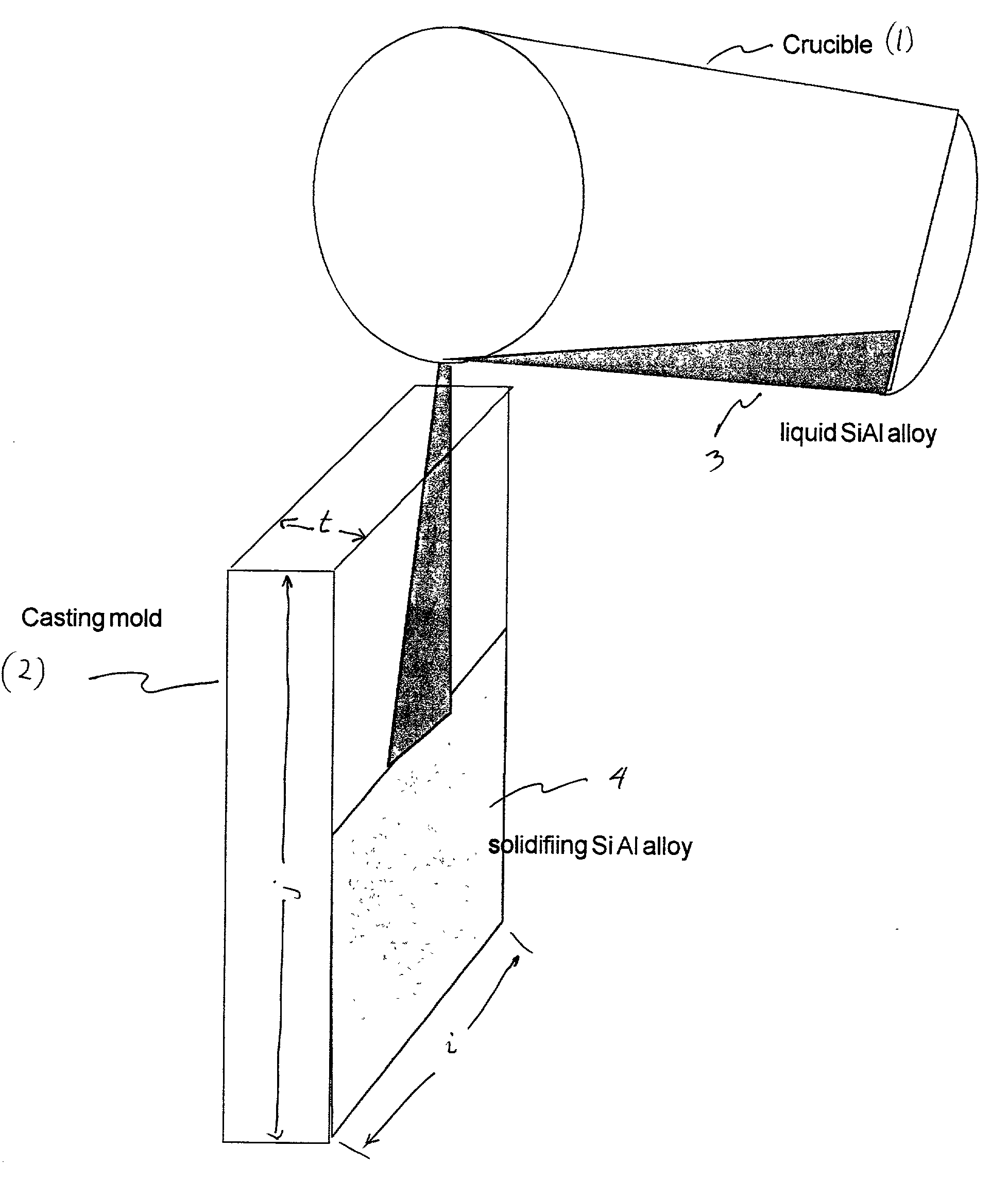
Sputtering target for depositing silicon layers in their nitride or oxide form and a process for its preparation
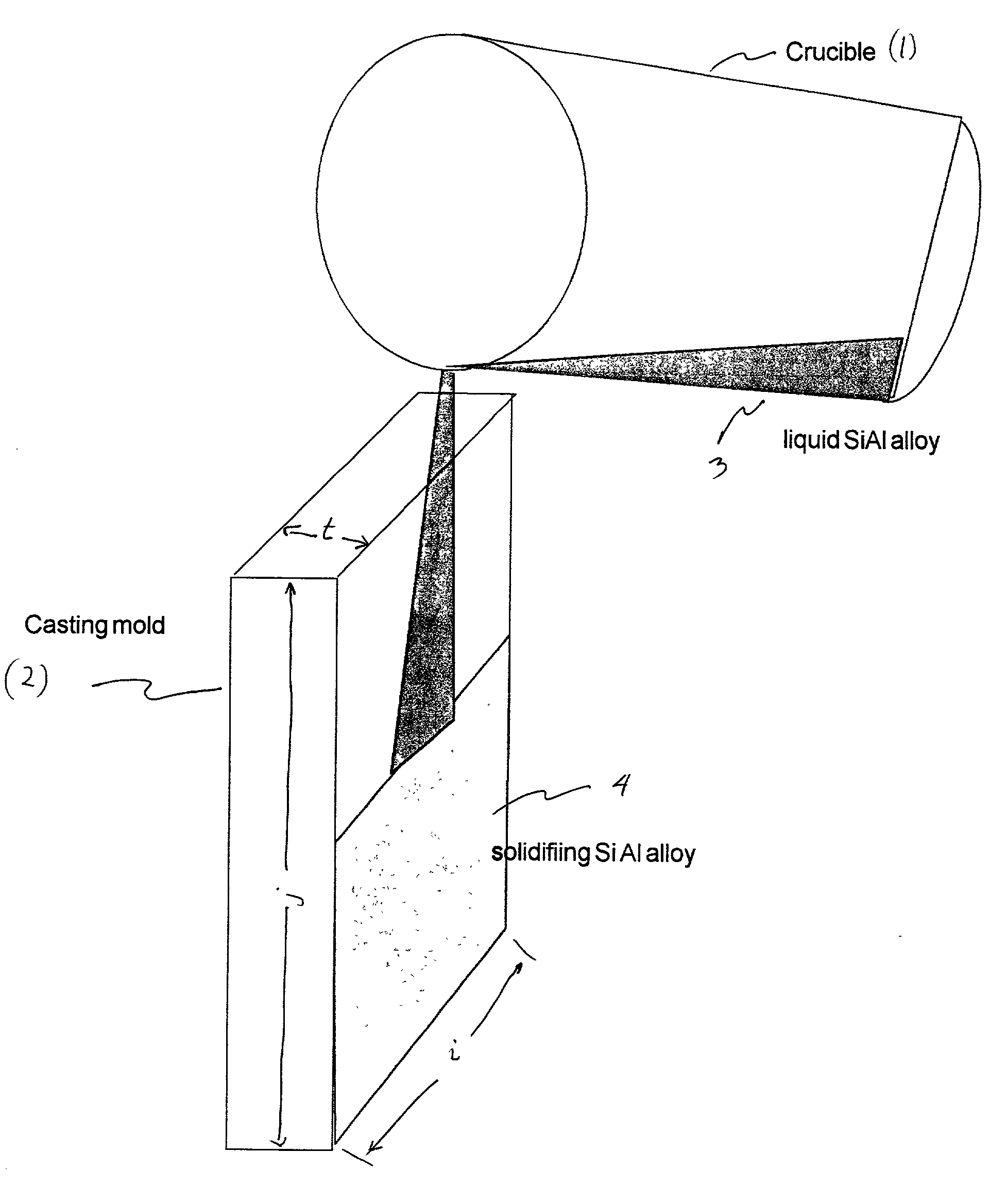
InactiveUS20020008021A1Low costRaise the level of dopingCellsVacuum evaporation coatingDopantCasting mold
The target material for a sputtering target for depositing silicon layers in their nitride or oxide form by means of reactive cathode atomization, such as e.g. Si3N4 or SiO2 in the form of optical functional layers or in the form of thermal protective layers on glass substrates, is a cast silicon element, that has been solidified from the melt condition and which forms a parallelepiped, with a dopant, that has been mixed in with the melt, whereby the dopant is 1 wt % to 15 wt % aluminum, and whereby the casting mold preferably has a cavity which forms a parallelepiped.
Owner:HERAEUS MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY GMBH & CO KG
Planar split-gate high-performance MOSFET structure and manufacturing method
ActiveUS7504676B2Stable and precisely controllable gate threshold voltageRaise the level of dopingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantMOSFET
This invention discloses an improved semiconductor power device includes a plurality of power transistor cells wherein each cell further includes a planar gate padded by a gate oxide layer disposed on top of a drift layer constituting an upper layer of a semiconductor substrate wherein the planar gate further constituting a split gate including a gap opened in a gate layer whereby the a total surface area of the gate is reduced. The transistor cell further includes a JFET (junction field effect transistor) diffusion region disposed in the drift layer below the gap of the gate layer wherein the JFET diffusion region having a higher dopant concentration than the drift region for reducing a channel resistance of the semiconductor power device. The transistor cell further includes a shallow surface doped regions disposed near a top surface of the drift layer under the gate adjacent to the JFET diffusion region wherein the shallow surface doped region having a dopant concentration lower than the JFET diffusion region and higher than the drift layer.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
CMOS three-dimensional image sensor detectors with assured non collection of late arriving charge, more rapid collection of other charge, and with improved modulation contrast
InactiveUS20110291164A1Maximize collectionMinimize collectionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSContrast ratio
A CMOS-implementable TOF detector promptly collects charge whose creation time can be precisely known, while rejecting collection of potentially late arriving charge whose creation time may not be precisely known. Charges created in upper regions of the detector structure are ensured to be rapidly collected, while charges created in the lower regions of the detector structure, potentially late arriving charges, are inhibiting from being collected.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Un-assisted, low-trigger and high-holding voltage scr
ActiveUS20080253046A1Sacrificing ESD protection robustnessHigh n-type doping densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A protective SCR integrated circuit device is disclosed built on adjacent N and P wells and defining an anode and a cathode. In addition to the anode and cathode contact structures, the device has an n-type stack (N+ / ESD) structure bridging the N-Well and the P-Well, and a p-type stack (P+ / PLDD) structure in the P-Well. The separation of the n-type stack structure and the p-type stack structure provides a low triggering voltage, that together with other physical dimensions and processing parameters also provide a relatively high holding voltage. In an embodiment, the triggering voltage may be about 8V while exhibiting a holding voltage, that may be controlled by the lateral dimension of the n-type stack of about 5-7 V.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Process for fabricating a semiconductor structure having a self-aligned spacer
InactiveUS6090722ARaise the level of dopingImprove throughputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantDielectric
A self-aligned dielectric spacer is etched by providing capped gate structure along a second layer of dielectric material located above the gate cap material. Dopant material at an increased doping level is provided in the second layer of dielectric material where the self-aligned spacer is to be located. The second layer of dielectric material is then etched selective to the dopant to define the self-aligned dielectric spacer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Alumina Dry-Coated Cathode Material Precursors
ActiveUS20130209885A1Improve securityLarge particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureParticulatesCrystal structure
A particulate precursor compound for manufacturing an aluminum doped lithium transition metal (M)-oxide powder usable as an active positive electrode material in lithium-ion batteries includes a transition metal (M)-hydroxide or (M)-oxy-hydroxide core and a non-amorphous aluminum oxide coating layer covering the core. By providing an aluminum thy-coating process where the particulate precursor core compound is mixed with alumina powder in one or more procedures, higher doping levels of aluminum compared to the known prior art may be achieved. The crystal structure of the alumina is maintained during the coating procedures and the core of each mixed transition metal precursor particle is surrounded by a coating layer containing crystalline alumina nano particles. The aluminum concentration in the particulate precursor decreases as the size of the core increases.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
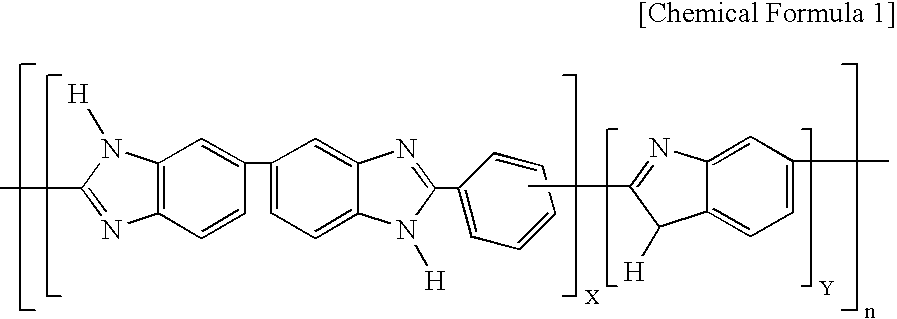
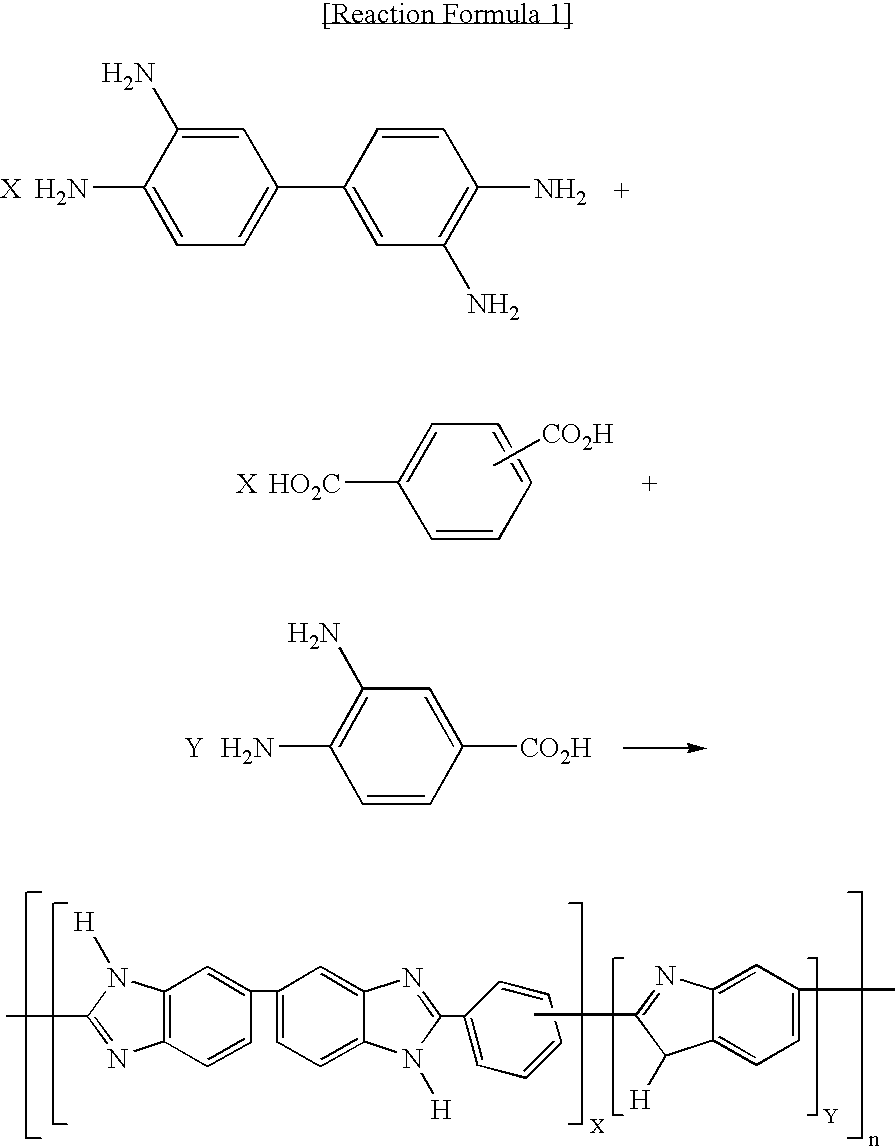
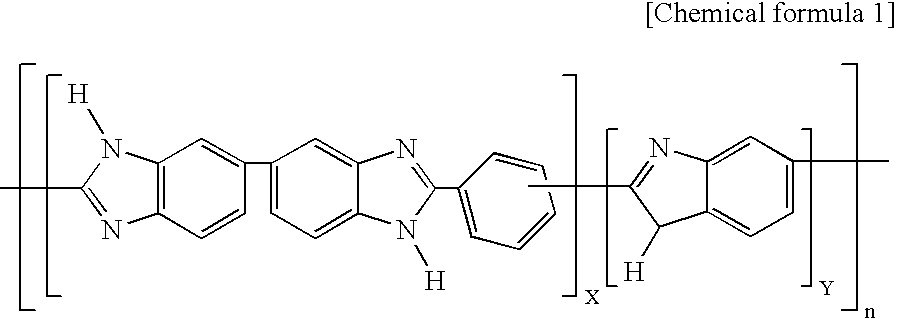
Polybenzimidazole based polymer and method for preparing the same
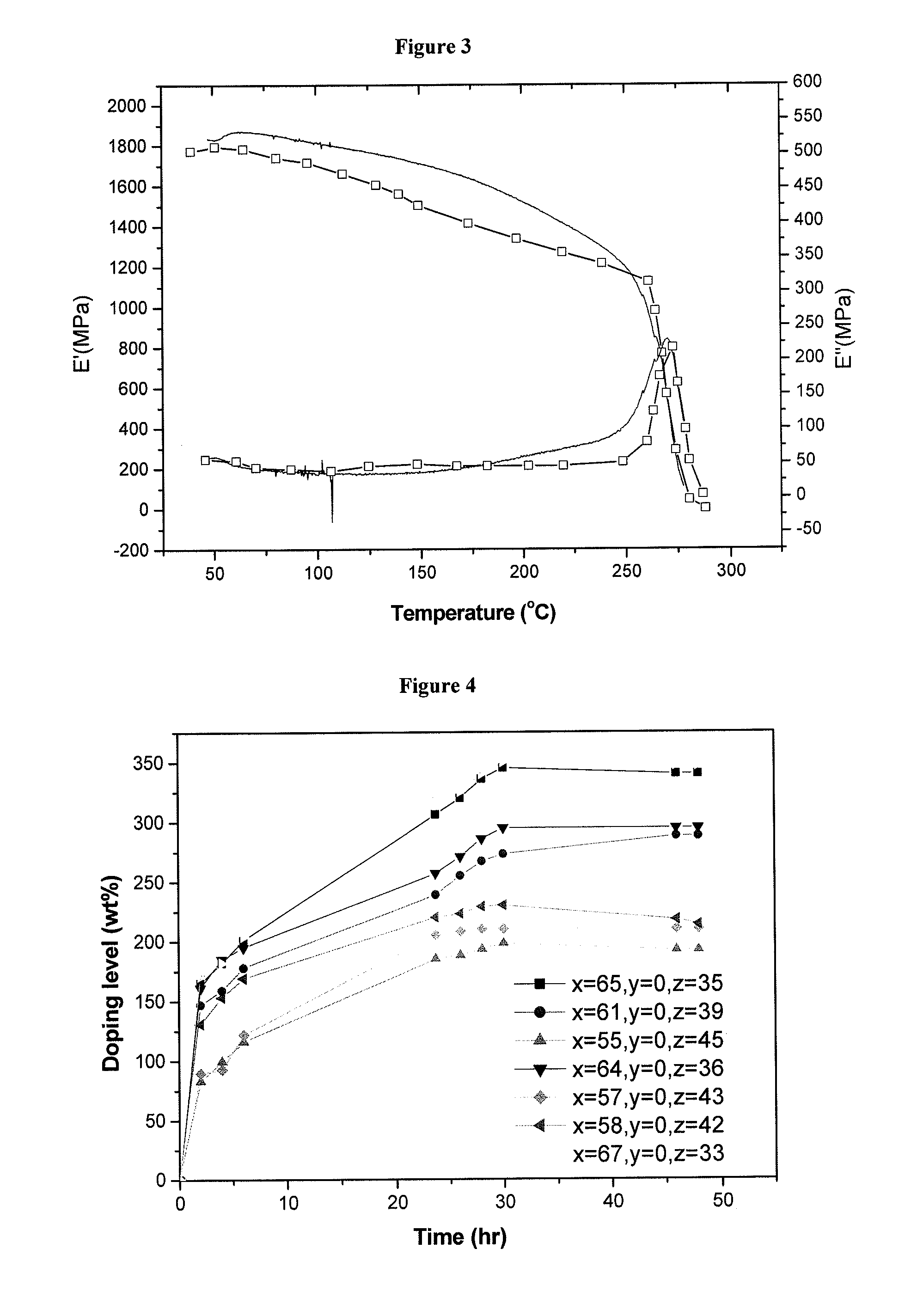
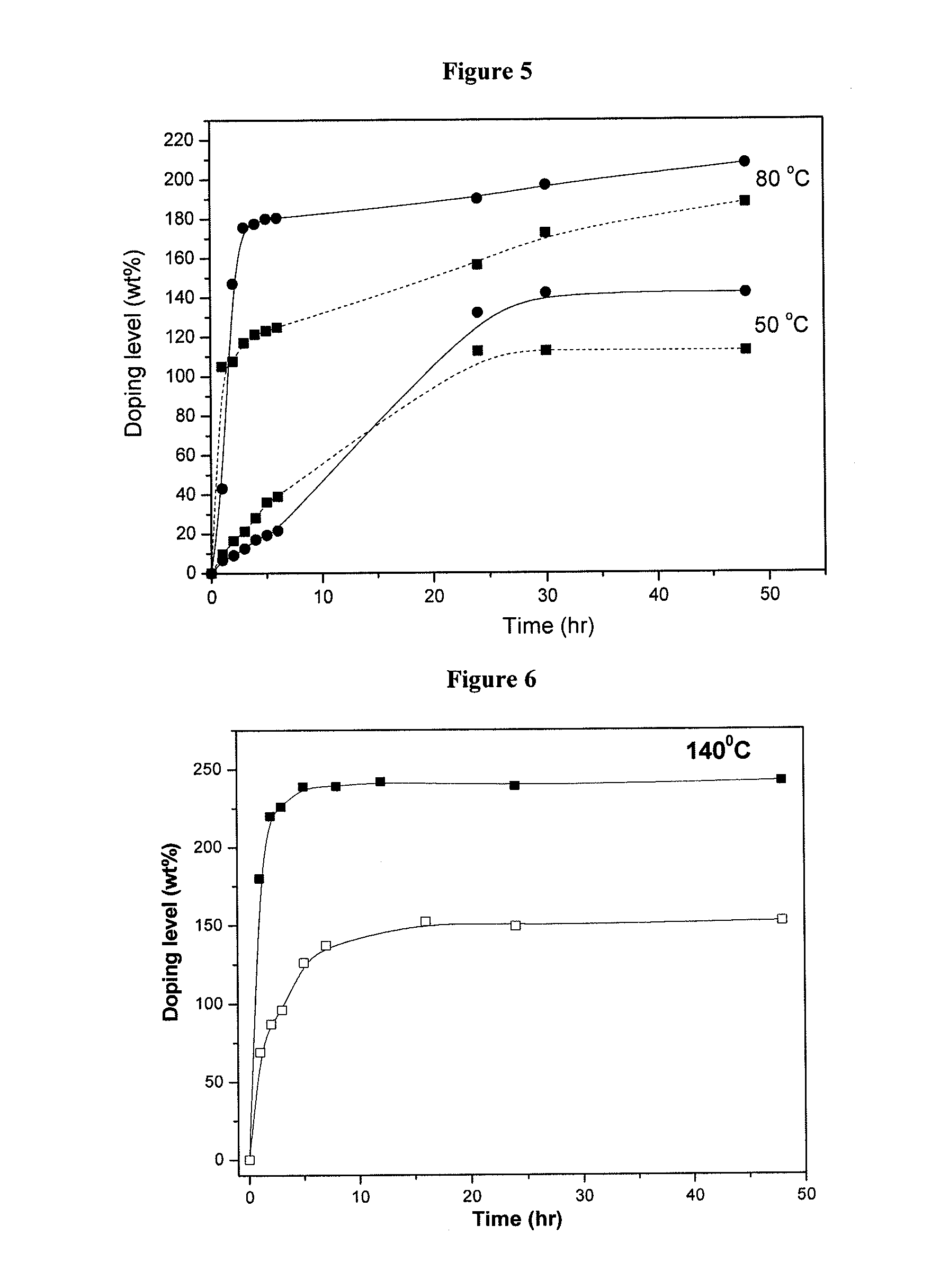
InactiveUS20060211844A1Good mechanical propertiesHigh doping levelSolid electrolytesSubstation equipmentPoly(benzimidazole)Membrane configuration
Disclosed is a polybenzimidazole based polymer, which can be used at high temperature under no-humidification conditions for preparing a fuel cell, in particular, a fuel cell membrane instead of the existing Nafion type perfluorosulfonated polymers, with which it is easy to increase a doping level, and also, which exhibits an excellent mechanical strength, further, which is inexpensive. Further, disclosed is a method for preparing the polybenzimidazole based polymer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Sputtering target for depositing silicon layers in their nitride or oxide form and a process for its preparation
The target material for a sputtering target for depositing silicon layers in their nitride or oxide form by means of reactive cathode atomization, such as e.g. Si3N4 or SiO2 in the form of optical functional layers or in the form of thermal protective layers on glass substrates, is a cast silicon element, that has been solidified from the melt condition and which forms a parallelepiped, with a dopant, that has been mixed in with the melt, whereby the dopant is 1 wt % to 15 wt % aluminum, and whereby the casting mold preferably has a cavity which forms a parallelepiped.
Owner:HERAEUS MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY GMBH & CO KG
Application of polybenzimidazole polymer containing side group in proton exchange membrane
InactiveCN104341607AHigh doping levelImprove stabilitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cell detailsPhosphoric acidPoly(benzimidazole)
The invention discloses an application of a polybenzimidazole polymer containing a side group in a proton exchange membrane, belonging to the technical field of proton exchange membranes for high-temperature fuel cells. The polybenzimidazole polymer containing the side group is characterized in that the side group is introduced on a PBI molecular chain, and preferably, the polymer is polybenzimidazole containing meta-benzyl or polybenzimidazole containing a benzene side group. A preparation method of the proton exchange membrane comprises the following steps: dissolving the polybenzimidazole polymer containing the side group into DMSO, baking on a glass plate to form a thin film, and then soaking into phosphoric acid for 3-108 hours to prepare a proton exchange membrane of phosphoric acid doped polybenzimidazole containing the side group. The proton exchange membrane of phosphoric acid doped polybenzimidazole containing the side group disclosed by the invention has higher phosphoric acid doping level and conduction rate on the basis of keeping relatively good mechanical performance and chemical stability.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Crosslinked or non-crosslinked aromatic (CO)polymers as proton conductors for use in high temperature PEM fuel cells
InactiveUS20120202129A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove stabilityCell electrodesFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesPolymer science
A polymer electrolyte comprising at least one aromatic polyether copolymer with main chain pyridine groups and side chain carboxylic acid or carboxylic ester or toluene or methoxy phenyl or hydroxyl phenyl or propenyl or styrene groups and / or pyridine groups, which have the ability to be covalently cross-linked.
Owner:ADVENT TECH
High-temperature-resistant composite proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
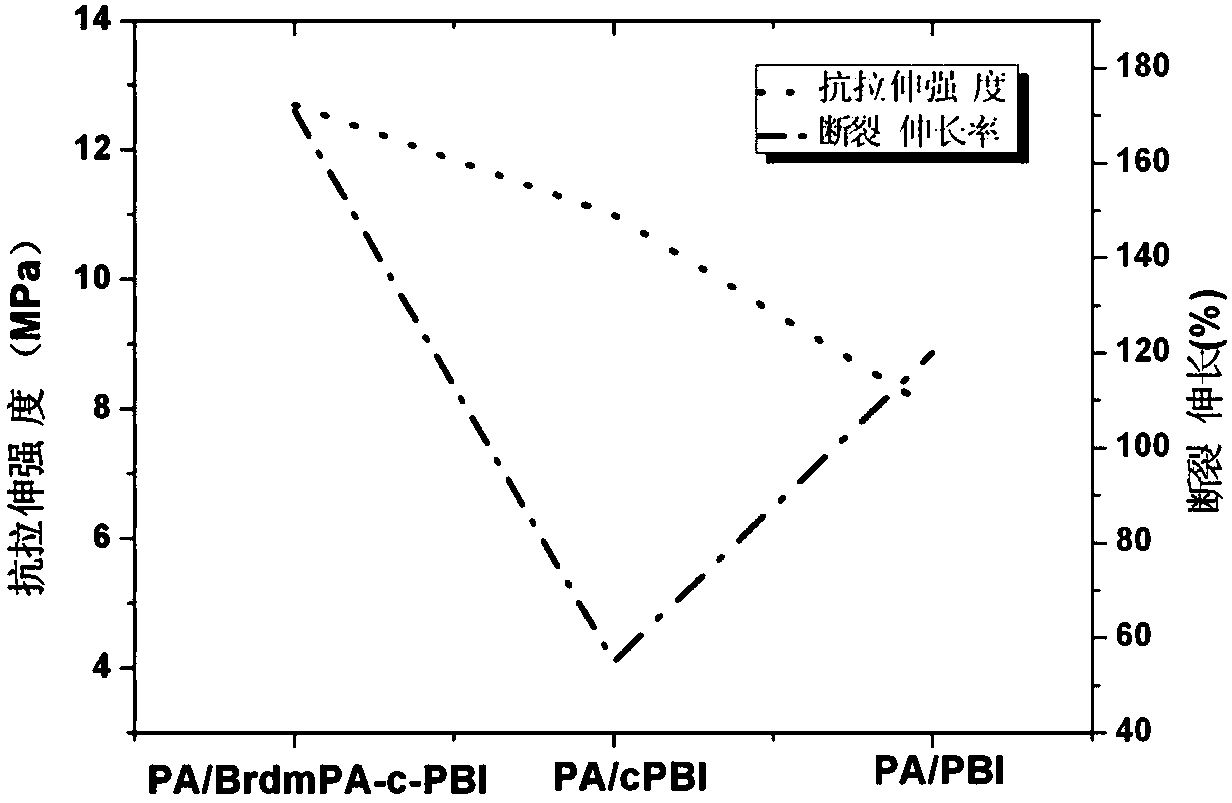
InactiveCN109962274AHigh glass transition temperatureGuaranteed stabilityFinal product manufactureFuel cellsBenzoyl bromideSide chain
A high-temperature-resistant composite proton exchange membrane is formed by compositing polybenzimidazole and an aromatic polymer with benzyl halide in side chains to form a composite cross-linking membrane and impregnating the composite cross-linking membrane in phosphoric acid. The mass fraction of the heterocyclic aromatic polymer containing benzyl halide in the composite cross-linking membrane is 0.01-99.99wt%. The mass fraction of the phosphoric acid doped in the composite proton exchange membrane is 1-99%. Compared with the existing phosphoric acid doped high-temperature proton exchangemembrane, the high-temperature-resistant composite proton exchange membrane of the invention has the advantages as follows: the glass transition temperature of the aromatic polymer with benzyl halidein side chains is high, which ensures the stability of the composite proton exchange membrane at high temperature; and each molecular chain contains multiple benzyl bromide groups and forms a covalent bond with multiple polybenzimidazole molecular chains, which improves the dimensional stability of the composite membrane; the composite proton exchange membrane has a high phosphoric acid doping level and good mechanical performance, and is a high-temperature proton exchange membrane with excellent comprehensive performance; and the preparation method is simple, and the composite proton exchange membrane has wide applications and is convenient for large-scale production.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
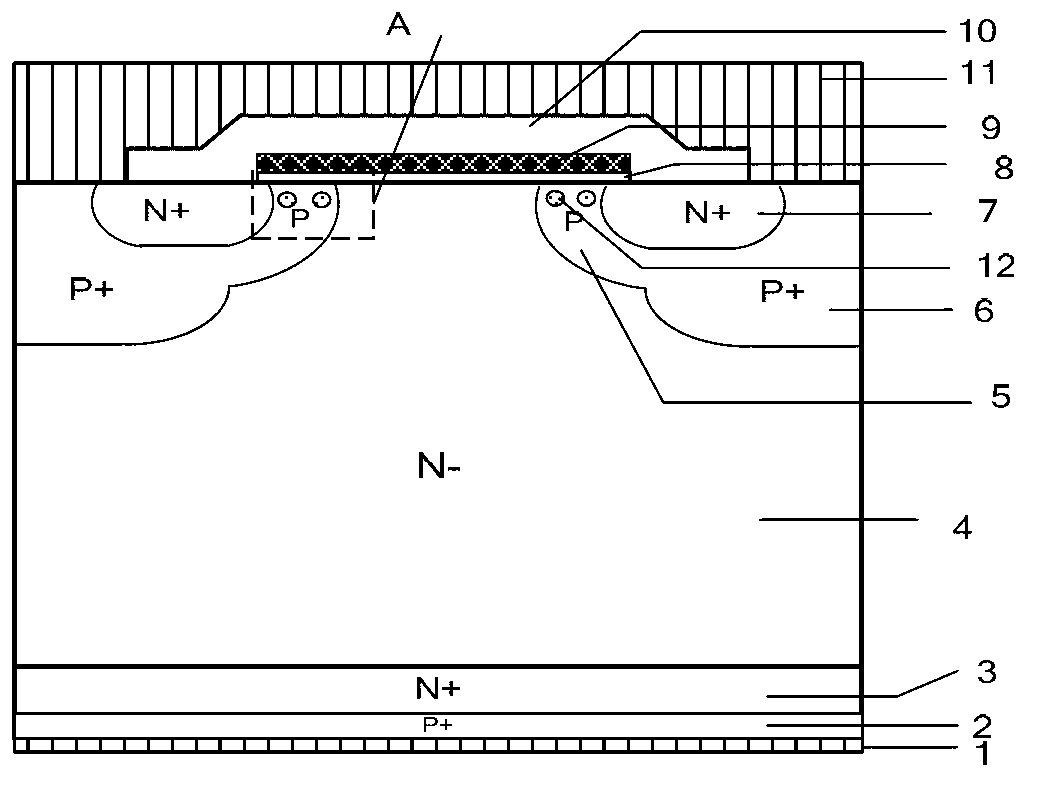
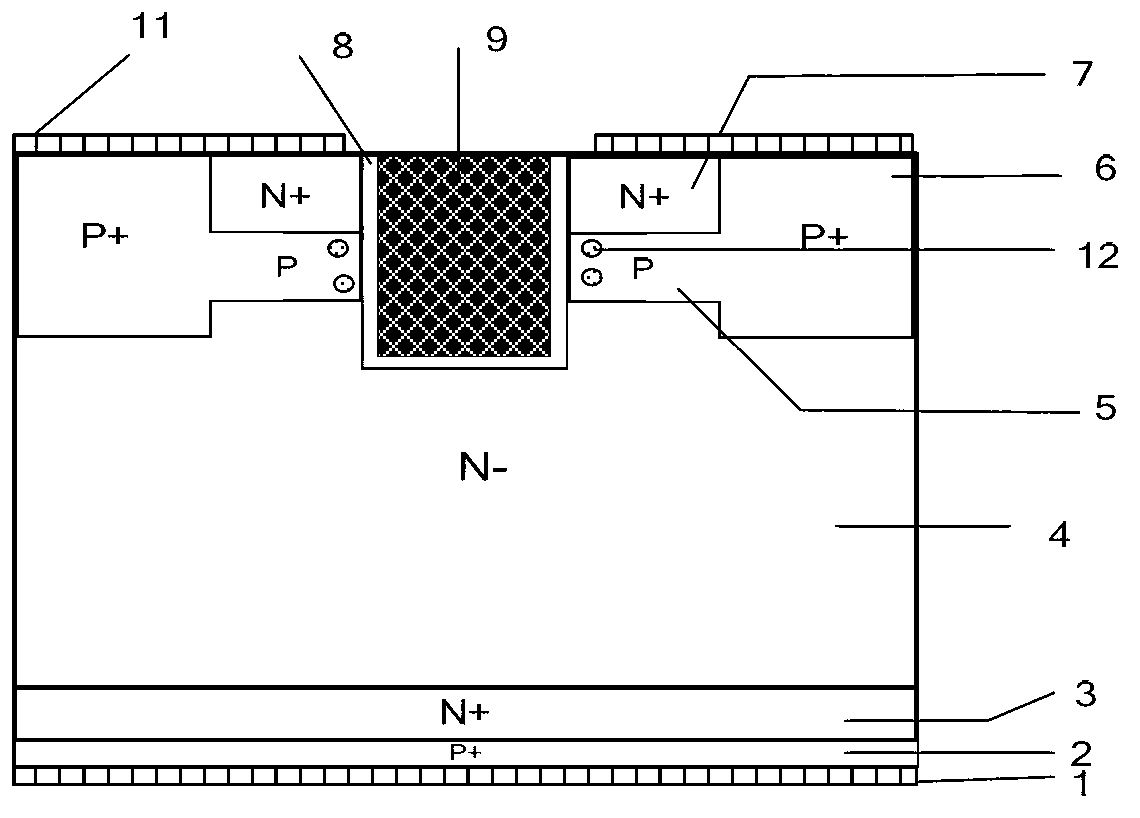
IGBT (insulated gate bipolar translator) device with high-temperature self-protection function
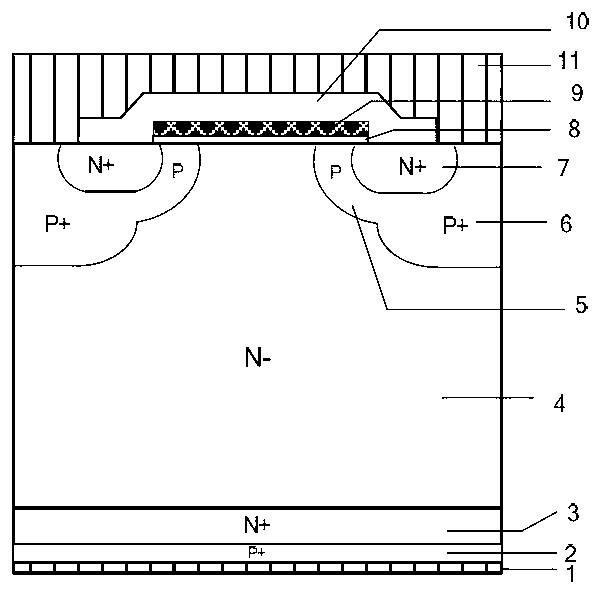
InactiveCN102800697AIncrease ionization rateRaise the level of dopingSemiconductor devicesPolysilicon gateImpurity
The invention discloses an IGBT (insulated gate bipolar translator) device with a high-temperature self-protection function, belonging to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. According to the invention, deep-energy-level impurities (12) with an acceptor energy level are introduced in a channel region (A) close to a polysilicon gate electrode (9) in the P-type base region (5) of the traditional IGBT device, and the deep-energy-level impurities (12) have a low ionization rate at a normal temperature, and little influence on the threshold voltage of the device. In the case that the device works under a large current, the temperature of the device rises, the ionization rate of the deep-energy-level impurities (12) is greatly increased, that is, the effective doping level of the P-type base region (5) is increased, so that the threshold voltage of the device is greatly increased, the saturation current value of the IGBT device and the negative temperature coefficient of the forward voltage drop of the device are decreased, and a purposes of further optimizing the negative temperature coefficient of the forward voltage drop of the IGBT device is achieved under the action of the dual mechanisms. The failure of the device due to the too high temperature caused by the own generated heat loss is avoided, so that the device has a high-temperature self-protection function.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
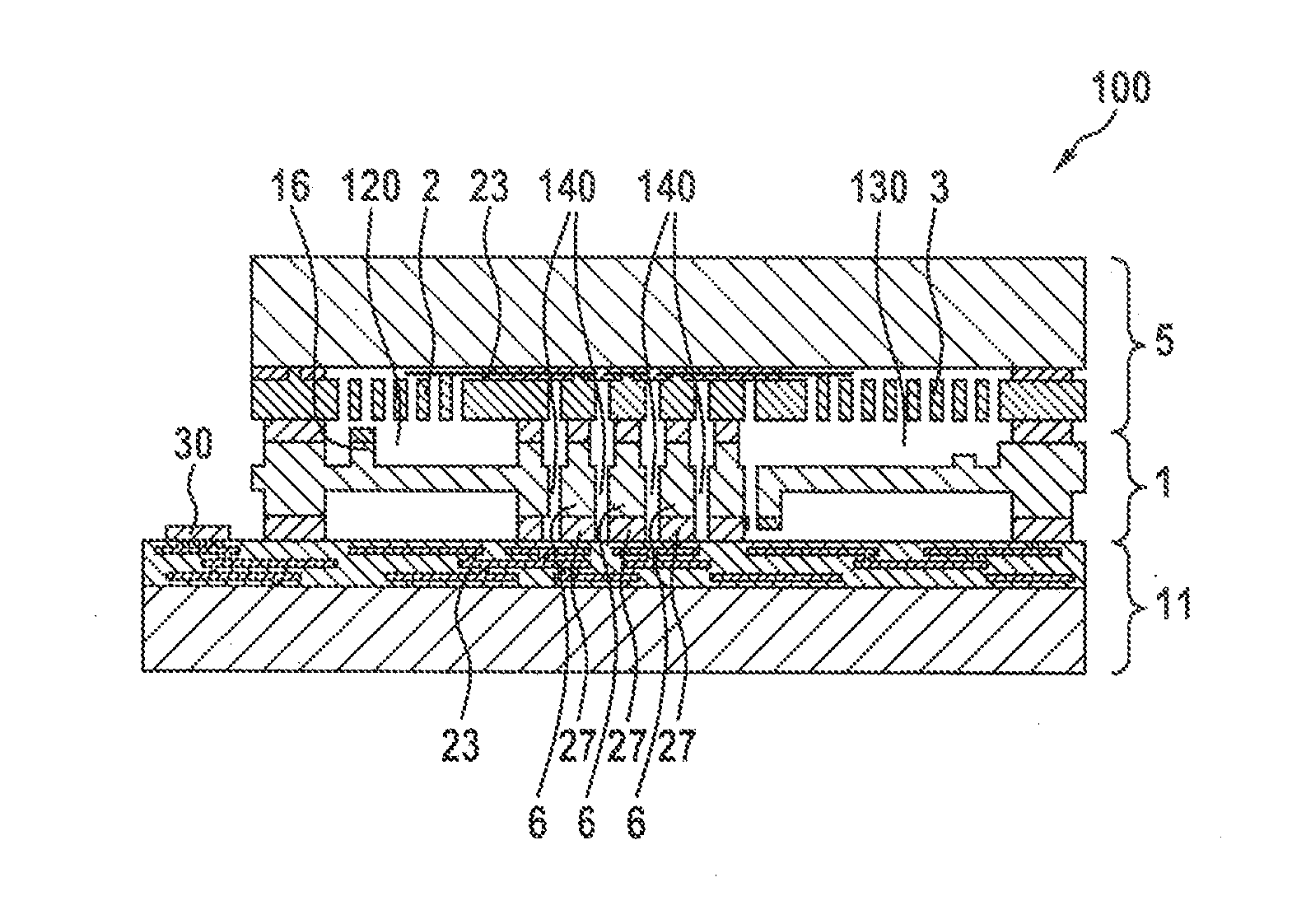
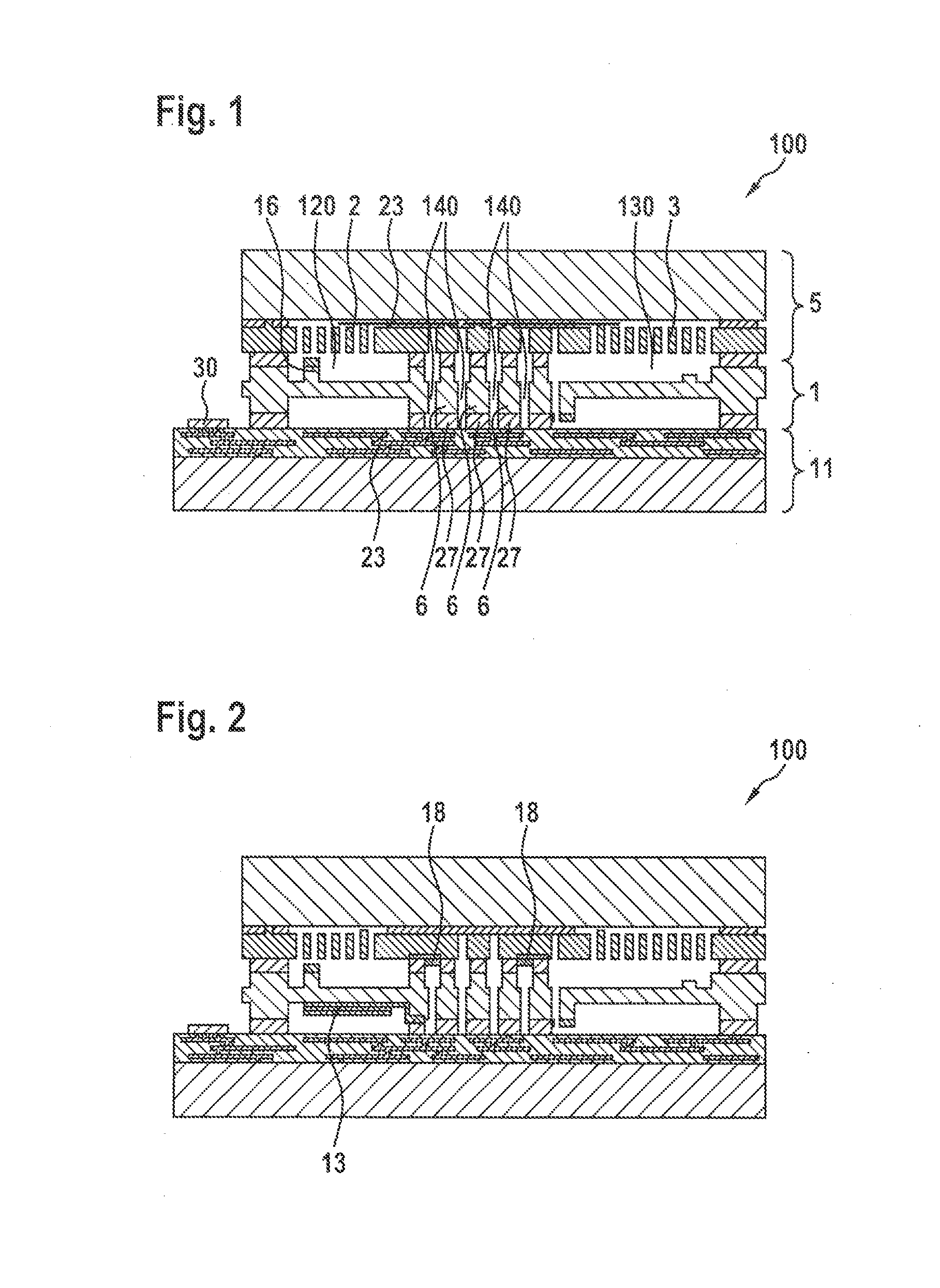
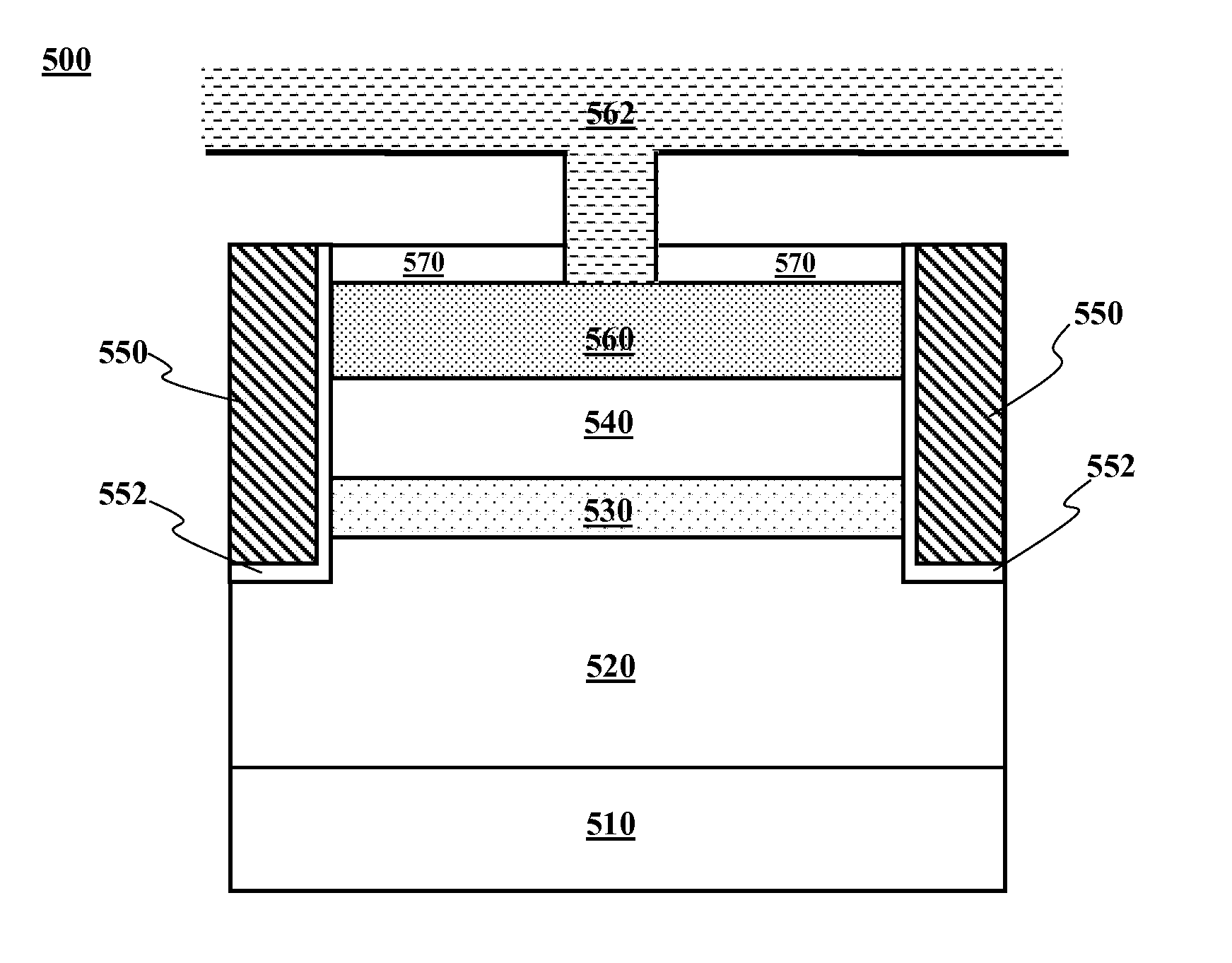
Integrated rotation rate and acceleration sensor and method for manufacturing an integrated rotation rate and acceleration sensor
InactiveUS20160084865A1Improved connection propertyHigh melting temperatureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsApplication-specific integrated circuitIntegrated circuit
A micromechanical device having a main plane of extension includes a sensor wafer, an evaluation wafer, and an intermediate wafer situated between the sensor wafer and the evaluation wafer, the evaluation wafer having at least one application-specific integrated circuit. The sensor wafer and / or the intermediate wafer includes a first sensor element and a second sensor element spatially separated from the first sensor element, the first and second sensor elements being respectively located in a first cavity and a second cavity each formed by the intermediate wafer and the sensor wafer, a first gas pressure in the first cavity differing from a second gas pressure in the second cavity, and the intermediate wafer having an opening at a point in a direction perpendicular to the main plane of extension.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
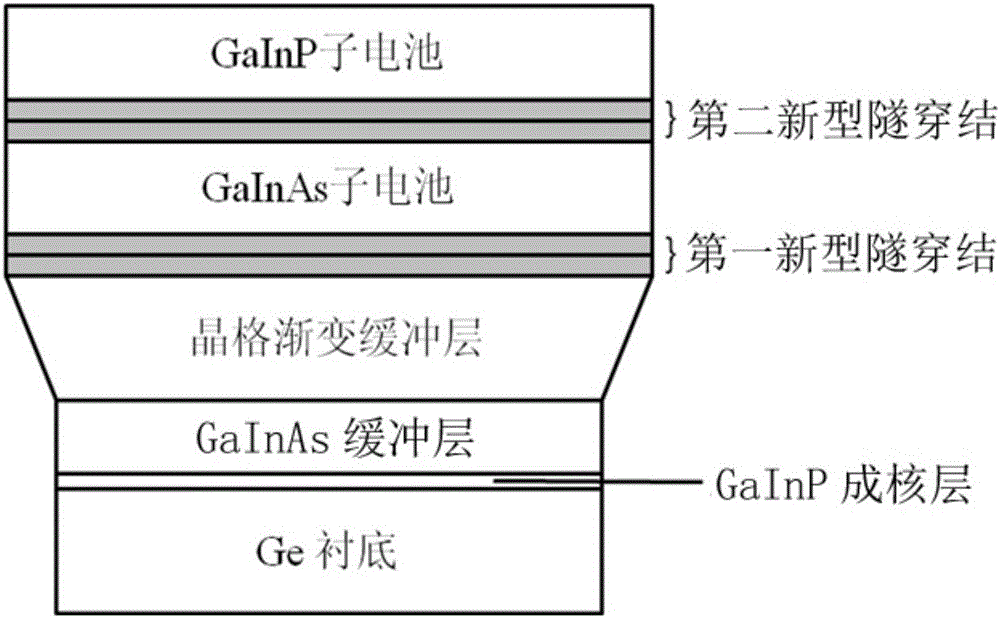
Lattice mismatch solar cell containing novel tunneling junction and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106024924AImprove crystal qualityActs as a dislocation barrierFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumLattice mismatch
The invention discloses a lattice mismatch solar cell containing a novel tunneling junction and a preparation method thereof. A Ge monocrystal is used as a substrate, and a GaInP nucleation layer, a GaInAs buffer layer, a lattice gradient buffer layer, a first novel tunneling junction, a GaInAs sub cell, a second novel tunneling junction and a GaInP sub cell are grown on the surface of the substrate sequentially from bottom to top. The first novel tunneling junction and the second novel tunneling junction include a layer of degenerate p-type gallium indium nitrogen arsenide (Ga<1-y>In<y>N<x>As<1-x>) and a layer of degenerate n-type gallium indium arsenide (Ga<1-z>In<z>As), the lattice constants of the two layers of materials are respectively consistent with the materials of the adjacent semiconductor layers or the mismatching degree is less than 3%, and the thickness of each layer is 5-100nm. The novel tunneling junction adopted in the invention has better conductivity and light transmission than general tunneling junctions. More importantly, as a rigid material, the novel tunneling junction can filter a lot of threading dislocation and mismatch dislocation, reduce non-radiative recombination, prolong the service life of minority carriers and improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN DEHUA CHIP TECH CO LTD
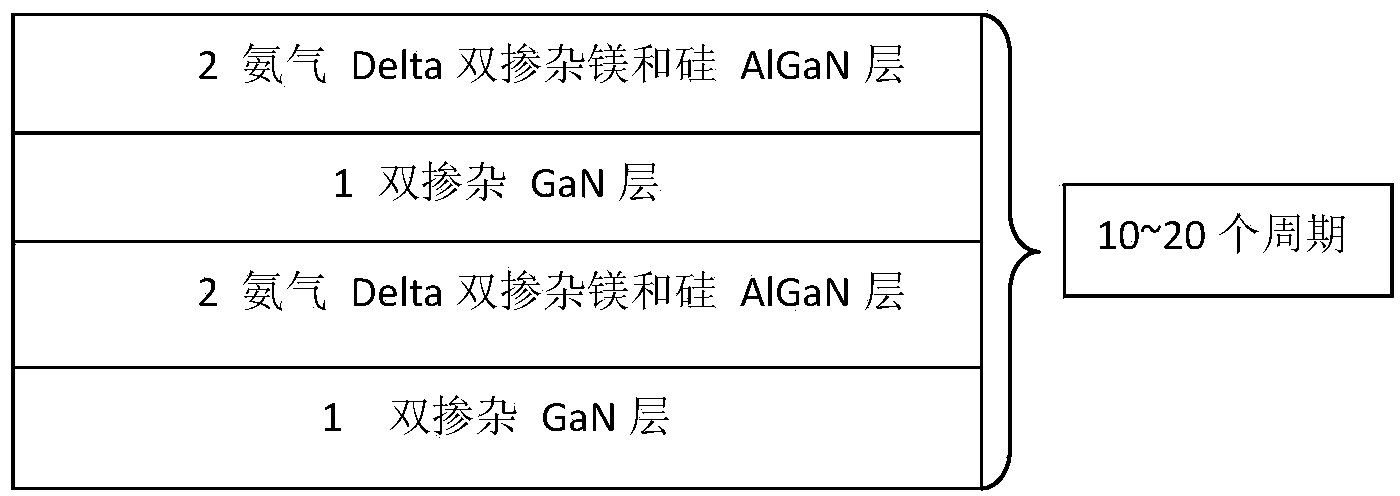
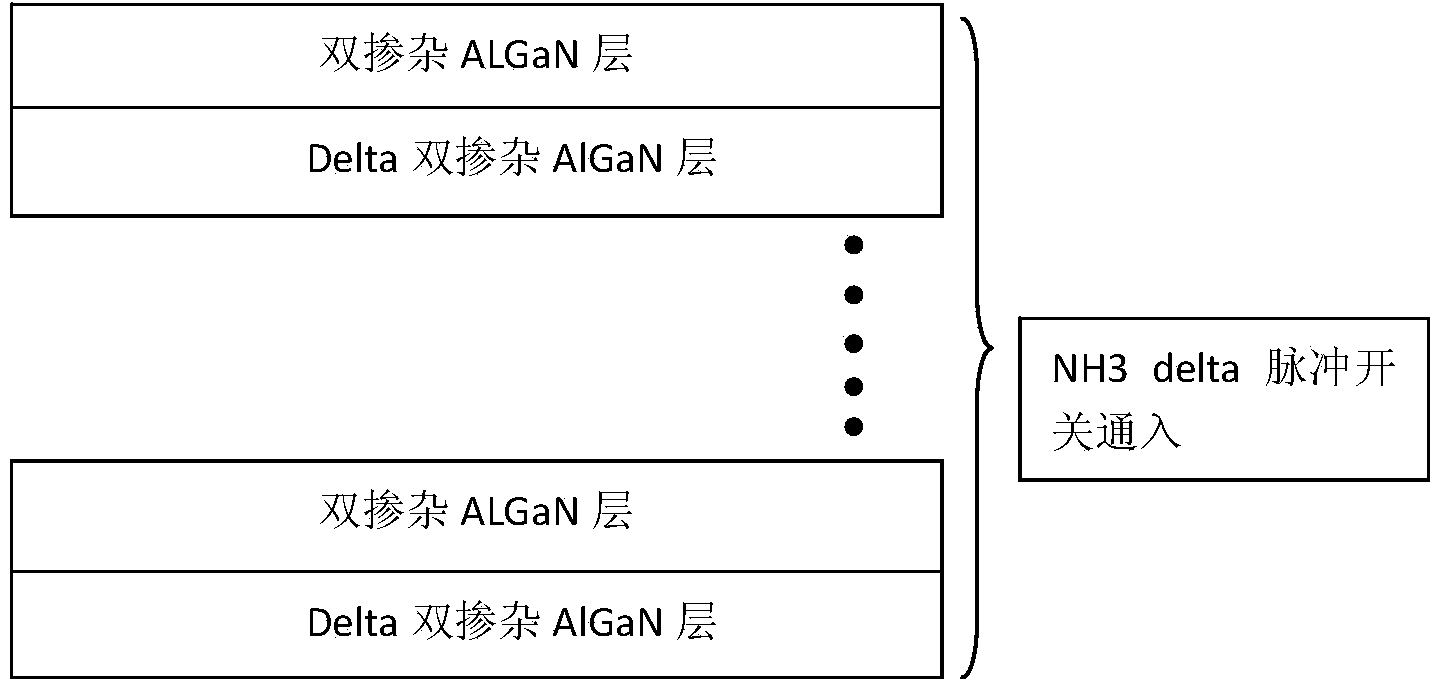
Epitaxial growth method with p-layer special doped structure
InactiveCN103854976AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilanesSelf compensation
The invention discloses an epitaxial growth method with a p-layer special doped structure. According to the method, when a p-type layer of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) is grown, double-element doping of a GaN / AlGaN superlattice structure is adopted, that is, a small amount of silane is doped when doping magnesium. The silane is doped as a donor, however, due to the small amount of the doped silane, the lattice imperfection caused by the doped magnesium can be remarkably improved, a self-compensation effect is reduced, the crystal quality is improved, non-composite imperfection centers are reduced, a small number of scattering centers are caused, the carrier mobility and the ionization efficiency of an accepter are improved, and in addition, as the growing temperature of AlGaN is high, such doping is beneficial for improving the doping concentration of magnesium, the doping effect of the p-layer is improved, and the overall lighting efficiency of the LED is greatly improved. Due to improvement of the crystal quality and the improvement of barrier layer conductivity, the current expansion capability is improved, and the reliability of the LED device is also improved.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
Method of fabrication SiGe heterojuction bipolar transistor
InactiveCN100521113CPrevent oxidationAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringNitride
The present invention provides for a method of fabricating a semiconductor device comprising a non-selectively grown SiGe(C) heterojunction bipolar transistor including the steps of forming an insulating layer ( 12, 40 ) on a substrate and providing a layer structure including a conductive layer ( 14, 42 ) on the insulating layer ( 12, 40 ), etching a transistor area opening ( 12, 44 ) through the conductive layer ( 14, 42 ), depositing a SiGe base layer ( 24, 46 ) on the inner wall of the transistor area opening ( 22, 44 ) and forming an insulator ( 32, 52 ) on an upper surface so as to fill the transistor area opening wherein prior to the filling step, a nitride layer ( 30, 50 ) is formed as an inner layer of the transistor area opening ( 22, 44 ).
Owner:NXP BV
Multilayer light-emitting electrochemical cell device structures
InactiveUS20150123096A1Improve recombination efficiencyOptimize lifetimeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionEngineering
Novel structures and compositions for multilayer light-emitting electrochemical cell devices are described, particularly those that are adapted to work with stable and printable electrode metals, that optimize recombination efficiency, lifetime and turn-on kinetics. In particular, embodiments of the present invention provide improved performance and extended lifetime for doped electronic devices, where ionic doping levels, ionic support materials content, and electronic transport content are advantageously structured within the device. The doping profile of mobile or semi-mobile ionic dopants is intentionally made to be non-uniform to enhance doping in the interface regions of a device where the active layer interfaces with the electrode.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Polymer electrolyte membrane for a fuel cell, method for manufacturing same, and fuel cell comprising same
InactiveUS20160254558A1Raise the level of dopingReducing BOPFinal product manufactureFuel cell detailsPolymer electrolytesO-Phosphoric Acid
The present disclosure relates to a polymer electrolyte membrane containing polybenzimidazole for a fuel cell and to a method for manufacturing the same. In the polymer electrolyte membrane containing polybenzimidazole for a fuel cell according to the present disclosure, carbon black or a metal-grafted porous filler based on carbon black or carbon black and silica is efficiently dispersed in polybenzimidazole, and physically and chemically bound with polybenzimidazole, and thus the polymer electrolyte membrane has excellent mechanical and thermal properties, can improve impregnating efficiency of phosphoric acid to exhibit high proton conductivity, and can reduce deterioration in ion conductivity of the electrolyte membrane due to the leakage of phosphoric acid.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
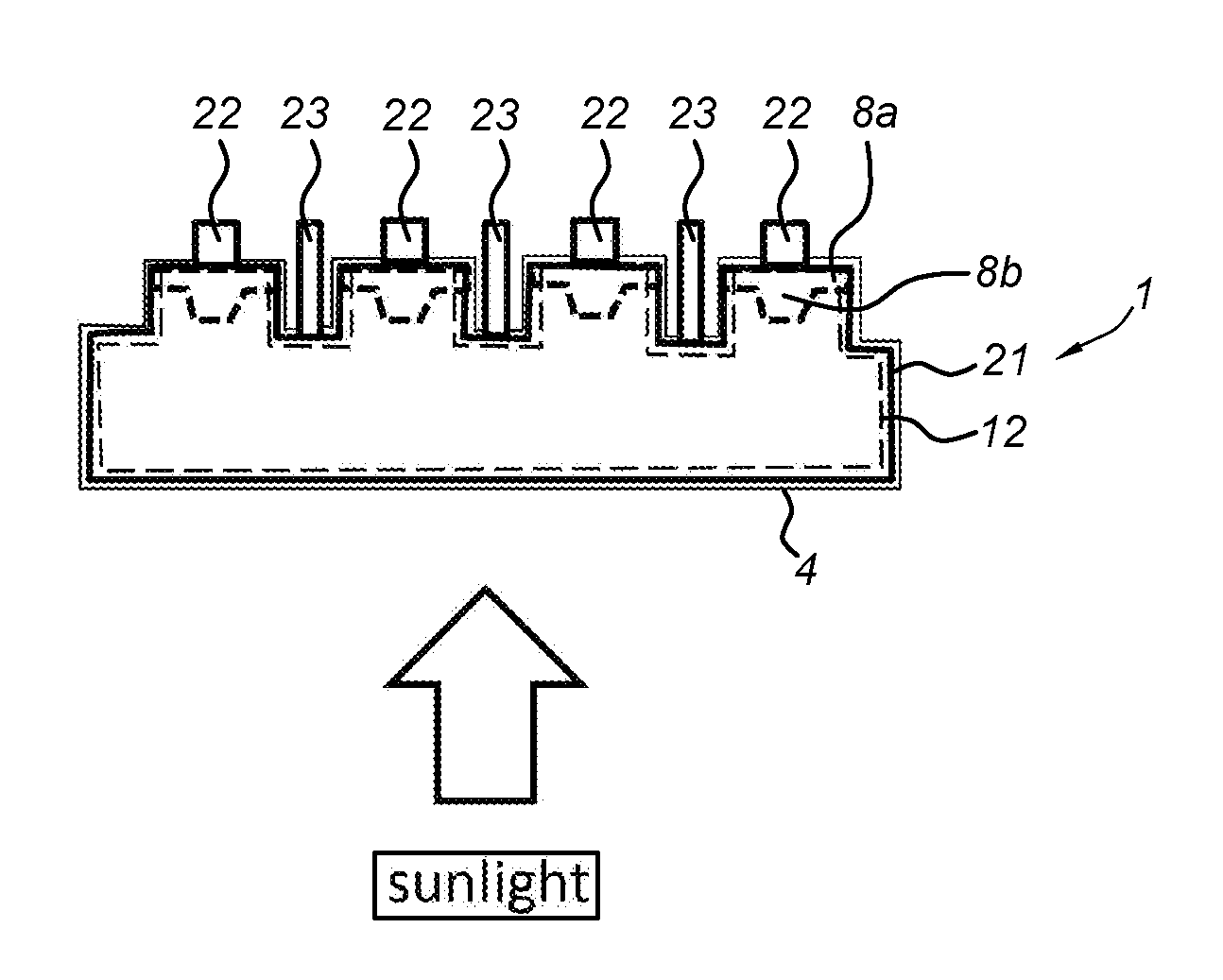
Method of providing a boron doped region in a substrate and a solar cell using such a substrate
ActiveUS20150357499A1Enlarge regionImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideSolar cell
Method of providing a boron doped region (8, 8a, 8b) in a silicon substrate (1), includes the steps of: (a) depositing a boron doping source (6) over a first surface (2) of the substrate (1); (b) annealing the substrate (1) for diffusing boron from the boron doping source (6) into the first surface (2), thereby yielding a boron doped region; (c) removing the boron doping source (6) from at least part of the first surface (2); (d) depositing undoped silicon oxide (10) over the first surface (2); and (e) annealing the substrate (1) for lowering a peak concentration of boron in the boron doped region (8, 8a) through boron absorption by the undoped silicon oxide. The silicon oxide (10) acts as a boron absorber to obtain the desired concentration of the boron doped region (8).
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Charge reservoir IGBT top structure
ActiveUS20150137175A1Lower breakdown voltageEnlarge regionTransistorThyristorSubject matterBody region
An IGBT device includes one or more trench gates disposed over a semiconductor substrate and a floating body region of the first conductivity type disposed between two neighboring trench gates and between a semiconductor substrate and a heavily doped top region of the second conductivity type. A body region of the first conductivity type disposed over the top region has a doping concentration higher than that of the floating body region of the first conductivity type. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Charge reservoir IGBT top structure
An IGBT device includes one or more trench gates disposed over a semiconductor substrate and a floating body region of the first conductivity type disposed between two neighboring trench gates and between a semiconductor substrate and a heavily doped top region of the second conductivity type. A body region of the first conductivity type disposed over the top region has a doping concentration higher than that of the floating body region of the first conductivity type. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Methods of manufacturing synthetic diamond material by microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition from a microwave generator and gas inlet(s) disposed opposite the growth surface area
ActiveUS9637838B2Raise the level of dopingPromote growth ratePolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge tubesMicrowaveGas phase
Disclosed herein are methods of manufacturing synthetic CVD diamond material including orienting and controlling process gas flow in a microwave plasma reactor to improve performance. The microwave plasma reactor includes a gas flow system with a gas inlet comprising one or more gas inlet nozzles disposed opposite the growth surface area and configured to inject process gases towards the growth surface area. The method comprises injecting process gases towards the growth surface area at a total gas flow rate equal to or greater than 500 standard cm3 per minute wherein the process gases are injected into the plasma chamber through the one or more gas inlet nozzles with a Reynolds number in a range 1 to 100.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com