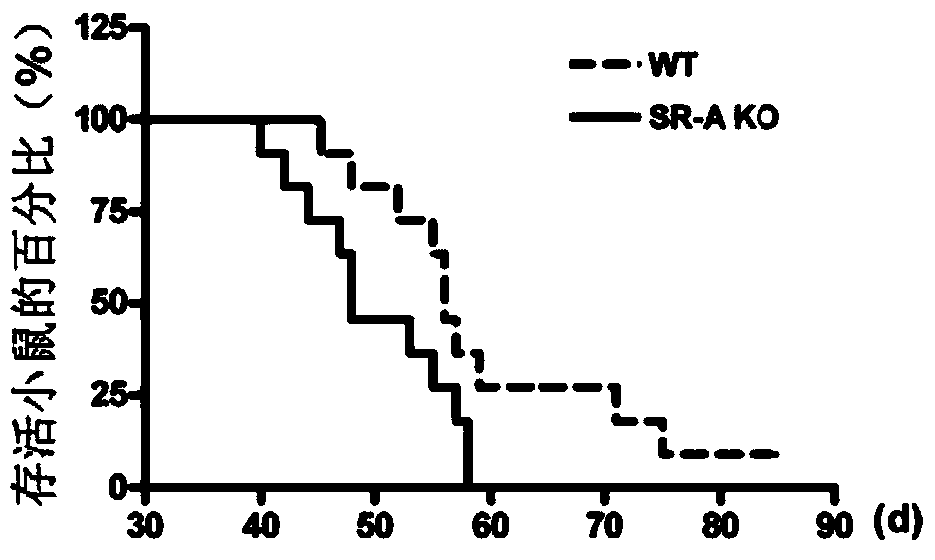
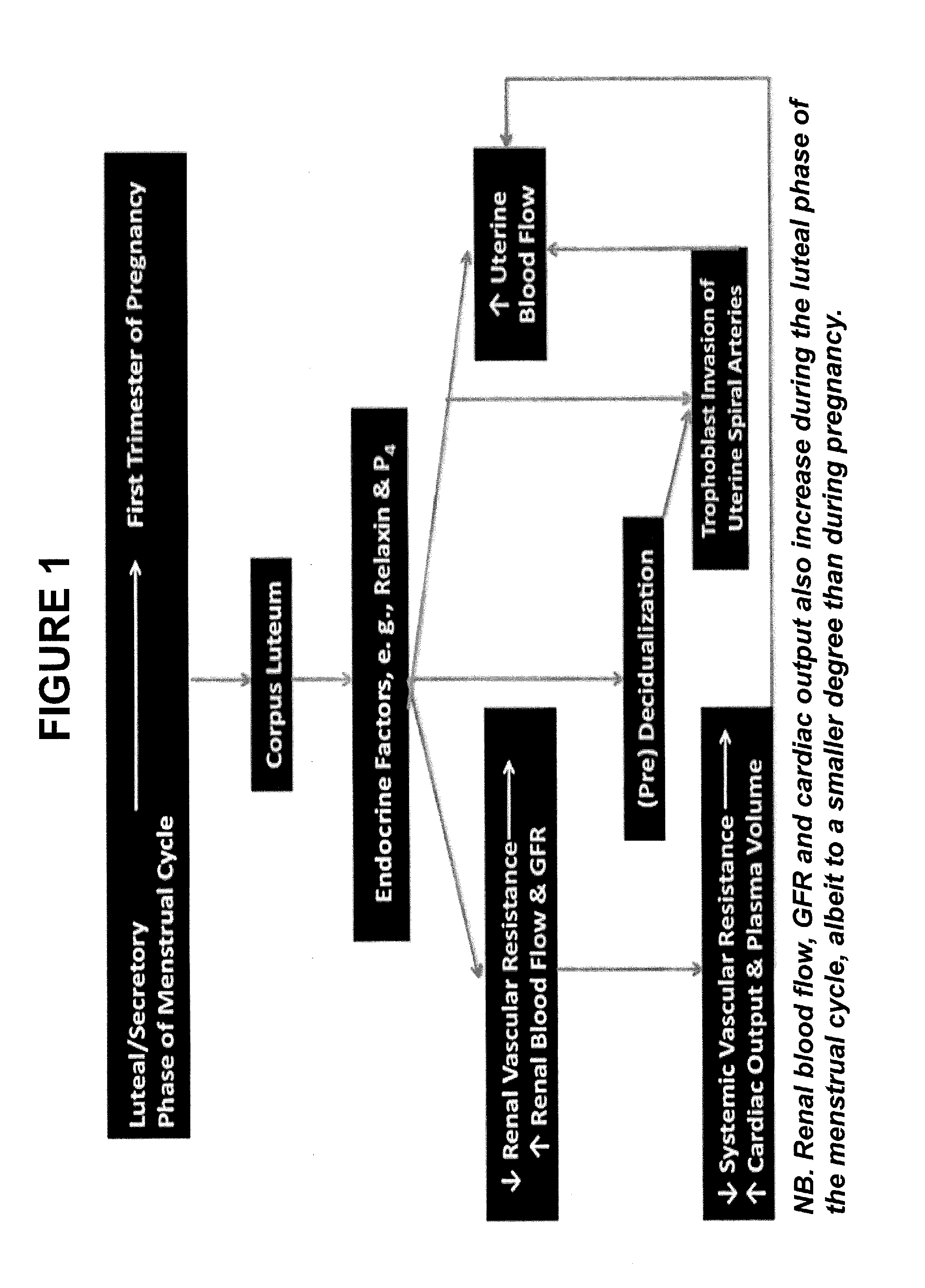
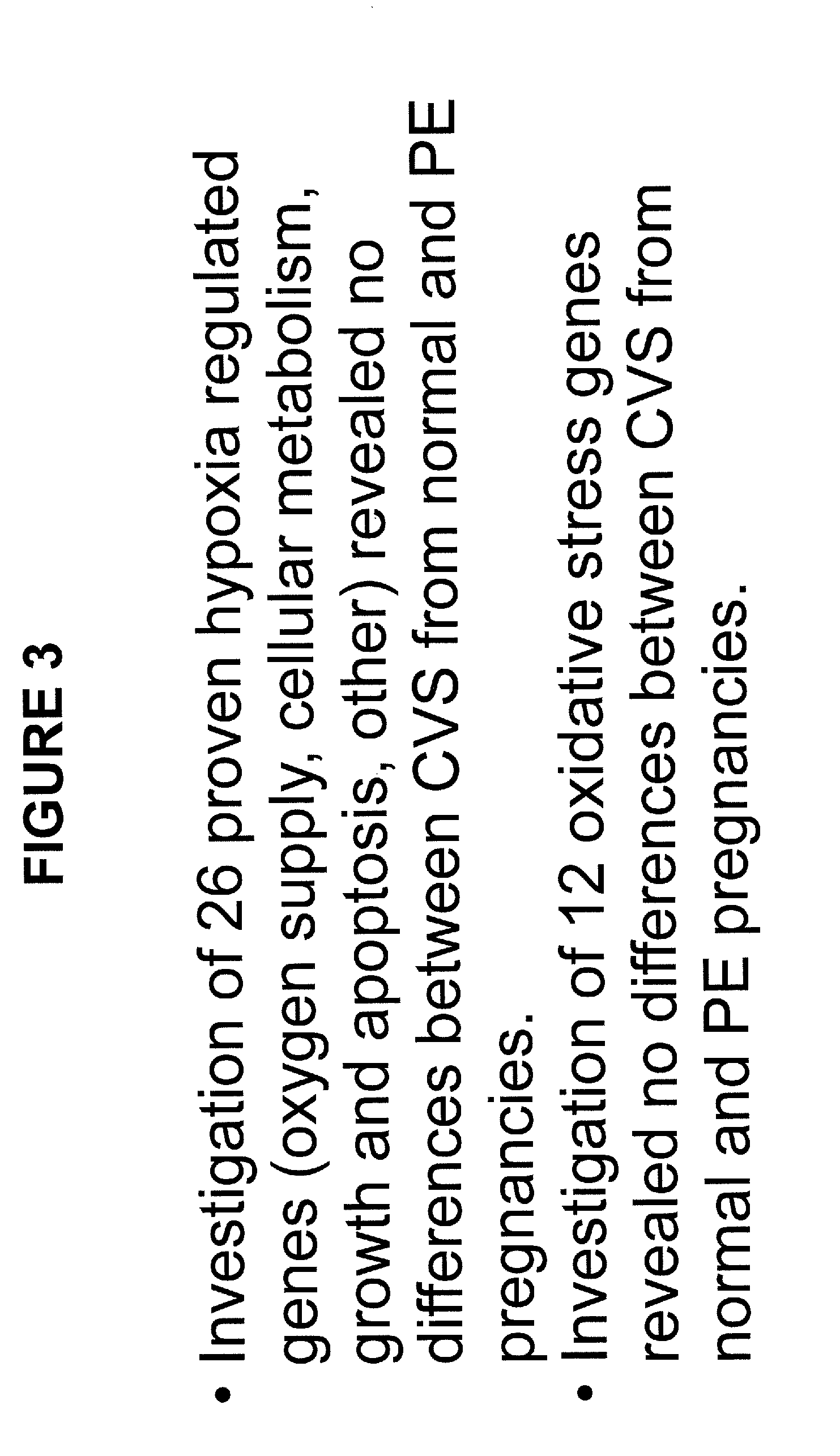
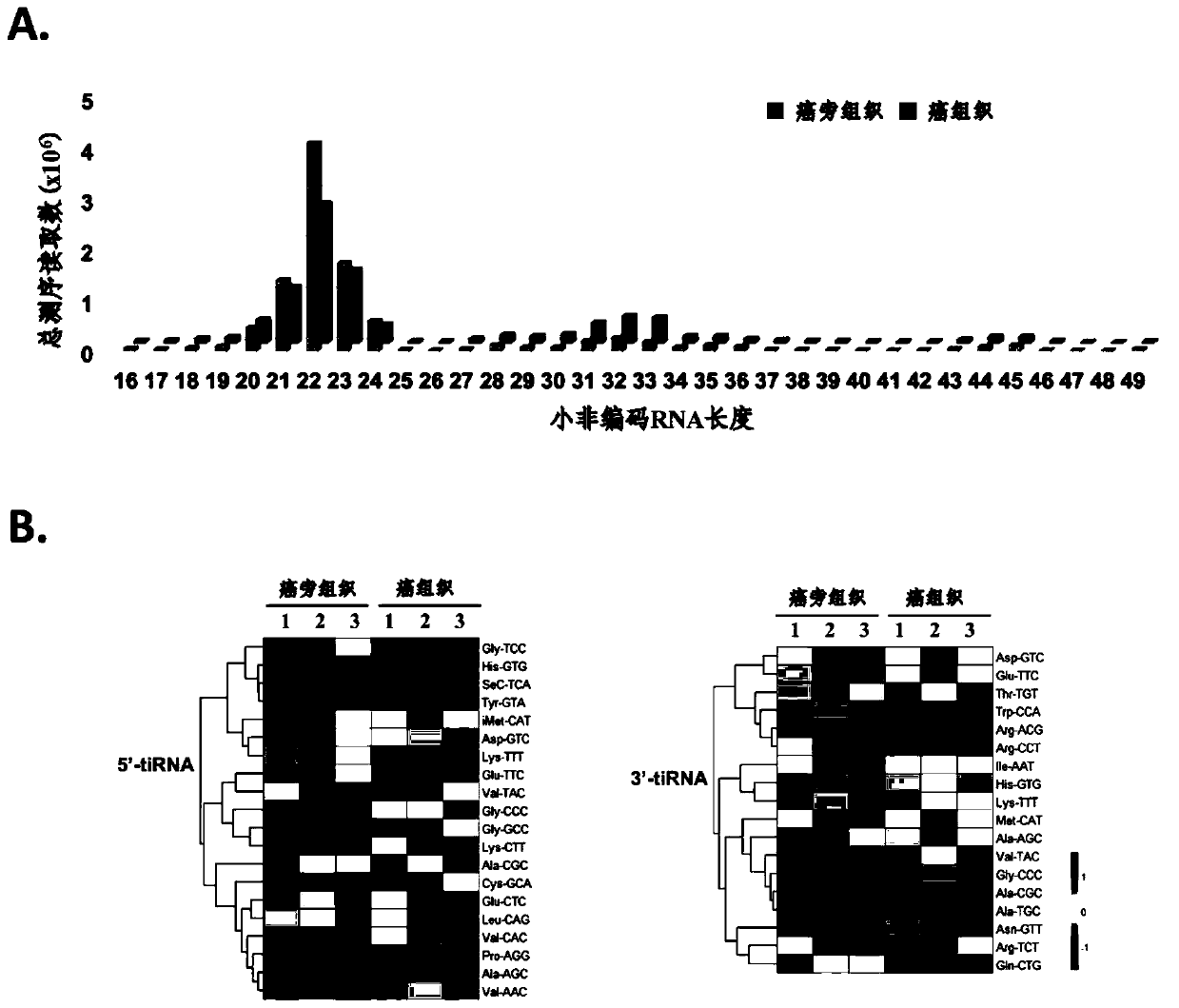
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110results about How to "Promote invasion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for culturing orchid special strain thereof
InactiveCN101338290ALoose textureImprove breathabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologySeedling
The invention discloses a method for culturing an orchid and a special bacterium thereof. The name of the bacterium of the invention is GDB181 the preservation number of which is CGMCCNo.2574. The method of the invention includes the steps for together culturing the bacterium of the invention and the orchid. The bacterium of the invention is applicable for the root culturing of an orchid bacteria and builds an epiphyte bacterium with excellent root which effectively coexists with the orchid. The method of the invention for culturing the orchid can better control the inoculation amount and can fix the inoculation position, thus fully ensuring the tissue culture seedling of the orchid to build the coexistence relation with the epiphyte bacterium with excellent root, simultaneously simplifying the inoculation steps and reducing the inoculation times. Permanent effect can be achieved by being inoculated for once, thus avoiding the dead seedling phenomenon caused by a plurality of manual inoculations, thereby improving the survival rate of transplanting and obtaining the root orchid seedling which grows strongly. Therefore, the method for culturing bacterium, the culture medium of the bacterium and the culture medium of the orchid of the invention has important economic values and is applicable for popularization and application.
Owner:金辉
Degradable temporary plugging agent for workover and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of workover operations, and particularly relates to a degradable temporary plugging agent for workover and a preparation method thereof. The degradable temporary plugging agent comprises the following components in parts by mass: 5-7% of acrylic acid, 15-21% of acrylamide, 5-15% of inorganic mineral soil, 0.002-0.005% of a polymerization inhibitor, 6-12% of a degradation promoter, 0.02-0.1% of a crosslinking agent, 0.6-1.0% of an initiator, 7-10% of corn flour and the balance of water. The degradable temporary plugging agent for workover disclosed by the invention has good degradation performance and does not need to add an additional degradation process; for high-water cut oil wells, water wells and the like, the degradable temporary plugging agent can be degraded by itself and resume operation and production only under the condition of a reservoir (under the condition of 90 DEG C, the 48-hour degradation rate can reach more than 90%).
Owner:DAGANG OIL FIELD GRP +1
Welding process method of brass H62
ActiveCN102699496AReduce evaporationImprove welding qualityArc welding apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSurface layerEngineering
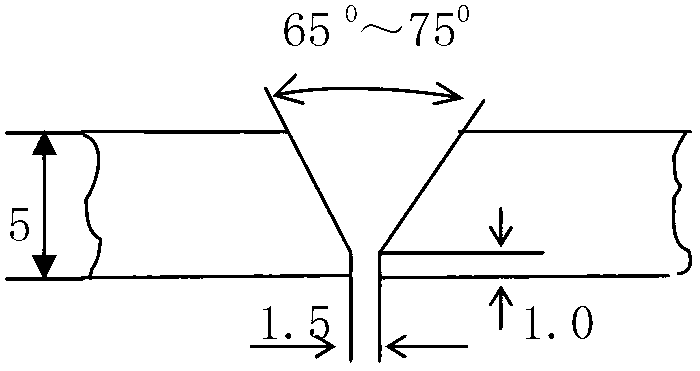
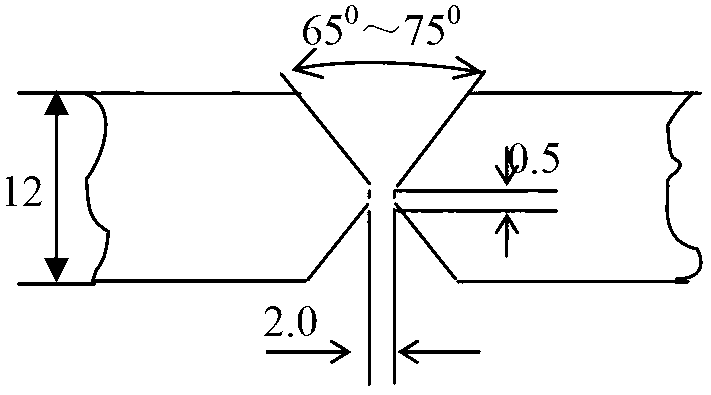
The invention discloses a welding process method of brass H62, which uses a welding wire Scu6810A and a soldering flux CJ301, and uses a manual argon tungsten-arc welding method. The welding process method of the brass H62 comprises the following steps of: firstly, machining a groove of a welding piece, wherein a groove angle is 32.5-37.5 degrees; controlling a truncated edge within a range of 0-1.5 mm; cleaning the welding surface of a welding piece and a welding wire; coating soldering flux paste of the soldering flux CJ301 on the groove of the clean welding piece and an area within a 30-mm range near the groove, as well as the surface of the welding wire; assembling the welding piece with an assembly clearance of 1.5-3.0 mm; pre-heating the welding piece to 200-300 DEG C before welding; welding a welding bead at a bottom layer by using a high-frequency arc striking technology; cleaning the surface of the welding bead at the bottom layer after the welding bead at the bottom layer is welded; coating the CJ301 soldering flux paste on the surface of the welding bead at the bottom layer; welding a filling layer, cleaning the surface of the filling layer after the filling layer is welded, and coating the CJ301 soldering flux paste after cleaning the surface of the filling layer; welding a cover surface layer; welding a weld joint and then pickling, and washing the weld joint with water; and drying with hot air.
Owner:CHINA NAT CHEM ENG THIRD CONSTR
Biomarker for forecasting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis
ActiveCN108315414AIncrease confidenceConfidenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLymphatic SpreadMetastasis
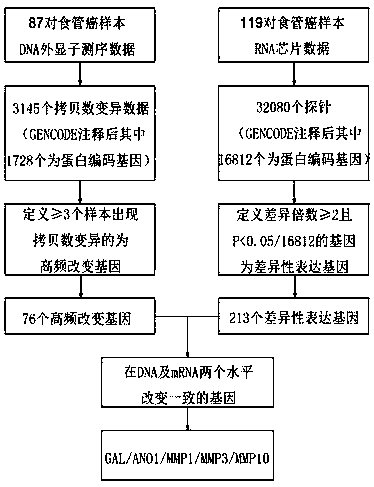
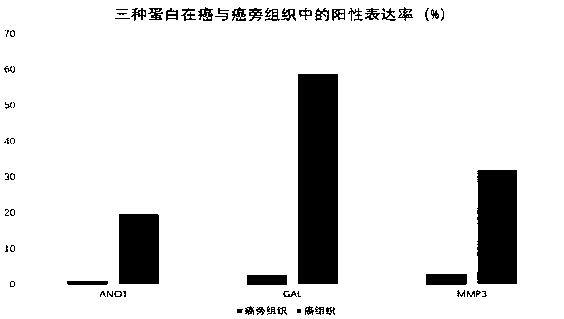
The invention discloses a biomarker for forecasting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis. A forecasting method comprises the following steps of screening of prognostic markers based on publiclarge data, verification of the prognostic markers and efficacy detection of the prognostic markers. The study discovers and verifies for the first time that an ANO1 binding MMP3 protein can be used as the biomarker for forecasting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis, the forecasting efficacy of the ANO1 binding MMP3 protein is equal to the forecasting efficacy of the eighth edition of TNM staging of clinically common prognosis forecasting by purely utilizing clinic information at present, and the accuracy of prognosis forecasting of a patient with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma can be remarkably improved with combination use of the two methods. At the same time, the study discovers that an ANO1 gene highly expresses in cancer tissues of the patient with the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, expression increase of the ANO1 gene can promote proliferation, invasion and metastasis of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and in vivo and in vitro progresses of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma can be remarkably inhibited by utilizing expression of an shRNA knockout ANO1 gene.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Inhibitors of protein tyrosine kinase activity
ActiveUS20090264440A1Promote motilityPromote invasionBiocideSenses disorderKinase activityProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
This invention relates to compounds that inhibit protein tyrosine kinase activity. In particular the invention relates to compounds that inhibit the protein tyrosine kinase activity of growth factor receptors, resulting in the inhibition of receptor signaling, for example, the inhibition of VEGF receptor signaling and HGF receptor signaling. More particularly, the invention relates to compounds, compositions and methods for the inhibition of VEGF receptor signaling and HGF receptor signaling. The invention also provides compositions and methods for treating cell proliferative diseases and conditions.
Owner:MIRATI THERAPEUTICS INC
System and method for providing computer network security
InactiveCN107517214AImprove network securityRemove threatTransmissionAnalysis centerNetwork security policy
The invention discloses a system for providing computer network security. The system comprises multiple intrusion detection modules, multiple management analyzers and a controller. The intrusion detection modules are used for collecting data transmitted on the target network segment, according to an intrusion rule preset by an administrator through a region management analysis center, executing the real-time tracking detection to an intrusion behavior from the inside and outside network. The management analyzers are used for managing a data detector, and executing the analysis of warning information. The controller is used for, through the guidance of a corresponding instruction of a security management center, configuring a network device, eliminating a threat, intercepting an intruder, sending a warning to an inside network user, and repairing bugs. The system is capable of improving the network security of the computer, convenient for detecting the intrusion and reminding the administrator.
Owner:合肥丹朋科技有限公司
Serratia marcescens and application thereof
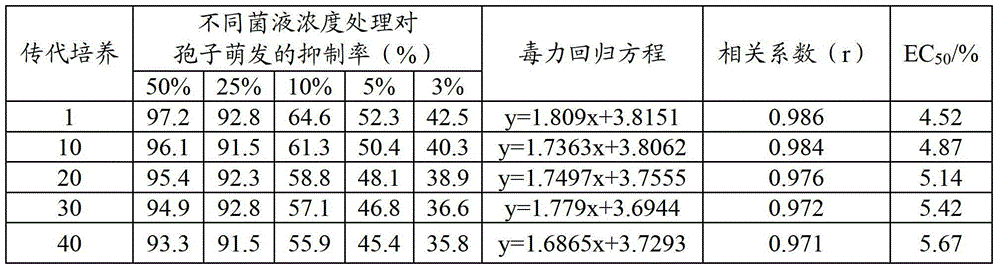
The invention relates to the field of microorganism, and in particular discloses a serratia marcescens and an application thereof. The serratia marcescens is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.7416. The serratia marcescens is transferred to the 40th generation and still has higher activity in inhibiting rubber powdery mildew and banana vascular wilt bacterial strain spores; the serratia marcescens has higher genetic stability, the rubber powdery mildew prevention effect of the serratia marcescens reaches a chemical prevention effect, and the serratia marcescens has an obvious prevention effect on banana vascular wilt; and moreover, the serratia marcescens cannot pollute the environment, is ecological and safe, and can be widely applied to prevent the rubber powdery mildew and the banana vascular wilt and prepare rubber powdery mildew and banana vascular wilt prevention preparations.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Inhibitors of serine protease activity of matriptase or MTSP1
InactiveUS6797504B1Elevated proteolyticPromote invasionBiocideOrganic chemistrySerine protease activityPeptide
The present invention provides compounds which inhibit serine protease activity of matriptase or MTSP1. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising those compounds and methods of using the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions to treat conditions ameliorated by inhibition of matriptase or MTSP1. The invention provides recombinant serine protease domains and methods of using peptides comprising a recombinant serine protease domain to screen for compounds that inhibit serine protease activity of matriptase or MTSP1.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
C9orf139 and MIR600HG as prognostic markers of pancreatic cancer and establishment method of markers
PendingCN109971862APrevent proliferationInhibit migrationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene technologyBiomarker (petroleum)
The invention belongs to the field of gene technology and medicine, in particular to C9orf139 and MIR600HG as prognostic markers of pancreatic cancer and an establishment method of the markers. The pancreatic cancer prognosis markers comprise C9orf139 and MIR600HG. By exploring the differentially-expressed mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA in pancreatic cancer, a ceRNA network is constructed to find new molecular screening biomarkers for pancreatic cancer and provide new analytical and molecular mechanisms for lncRNAs, miRNAs and pancreatic cancer mRNA. The invention determines two new biomarkers as potential pancreatic cancer prognosis indicators, and thus the prognosis of pancreatic cancer diseases is improved, and the accuracy of early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer is improved.
Owner:辽宁省肿瘤医院
Composite biological insecticide
InactiveCN101209058AGuaranteed After EffectsProlong the action timeBiocideAnimal repellantsForest industryBacillus thuringiensis
The invention discloses a compound living insecticide, including materials of the following volume portions of 10 to 20 portions of diflubenzuron; 0.01 to 0.1 portion of tryptophan; 1 to 2 portions of dispersant; 2 to 5 portions of glycerin; 72.9 to 86.99 portions of sterile water; the invention also includes clostera anachoreta granulosis virus, Bacillus thuringiensis fungus gemma and ENHANCIN increasing protein. The content of the clostera anachoreta granulosis virus is 0.5 to 2 billion per milliliter; the content of the Bacillus thuringiensis fungus gemma is 2 to 6 billion per milliliter; the content of the ENHANCIN increasing protein is 20 to 50 international units per milliliter. The compound living insecticide has the advantages of reasonable compatibility of medicines, convenient manufacture, broad desinsection spectrum and good desinsection effect. The invention overcomes the defects of wettable powder and emulsion; accessory ingredient is easy to disperse. The invention is more convenient to apply in fields and has no remnant and environment pollution, thus having remarkable superiority in actual application and being suitable for massive application on the forest industry.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
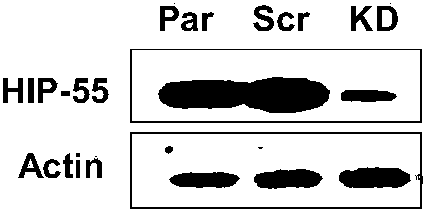
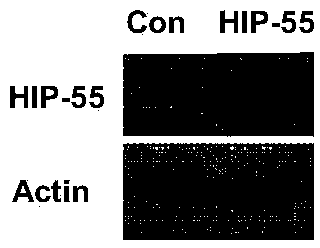
Application of HIP-55 protein to development of tumor inhibition drugs
InactiveCN103773802APromote migrationInhibit migrationGenetic material ingredientsBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthLung cancer
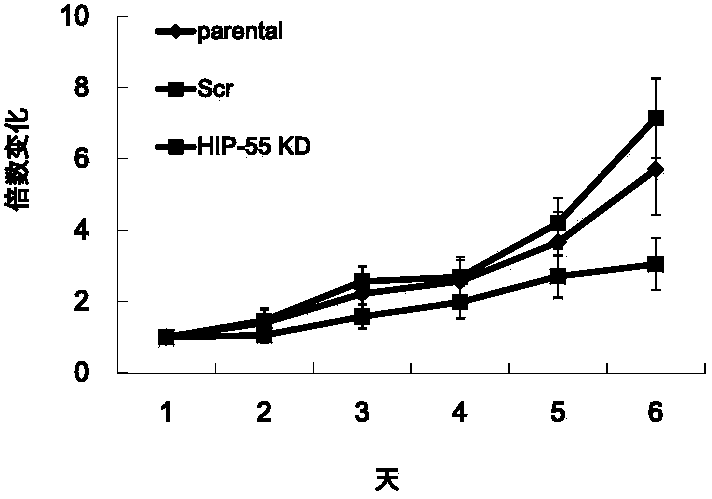
The invention discloses application of HIP-55 protein to development of tumor inhibition drugs. DNA molecules encoding and interfering HIP-55 protein from expressing siRNA are inserted into an expression vector to obtain a recombinant vector; the amino acid sequence of the HIP-55 protein is a sequence II in a sequence table; the invention also provides application of HIP-55 protein or the recombinant vector containing the HIP-55 protein coding gene to preparation of products having the following functions of (1) promoting tumor cell migration and / or (2) promoting tumor cell invasion. Experiments prove that the HIP-55 protein gene is overexpressed in lung cancer cells to promote tumor formation, lung cancer cell migration and lung cancer cell invasion; therefore, the HIP-55 provides a new target for clinical diagnosis, treatment and development of new drugs and can be used for screening, developing and / or designing products for prevention and / or treatment of tumors.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Human thymoma cell line and application thereof
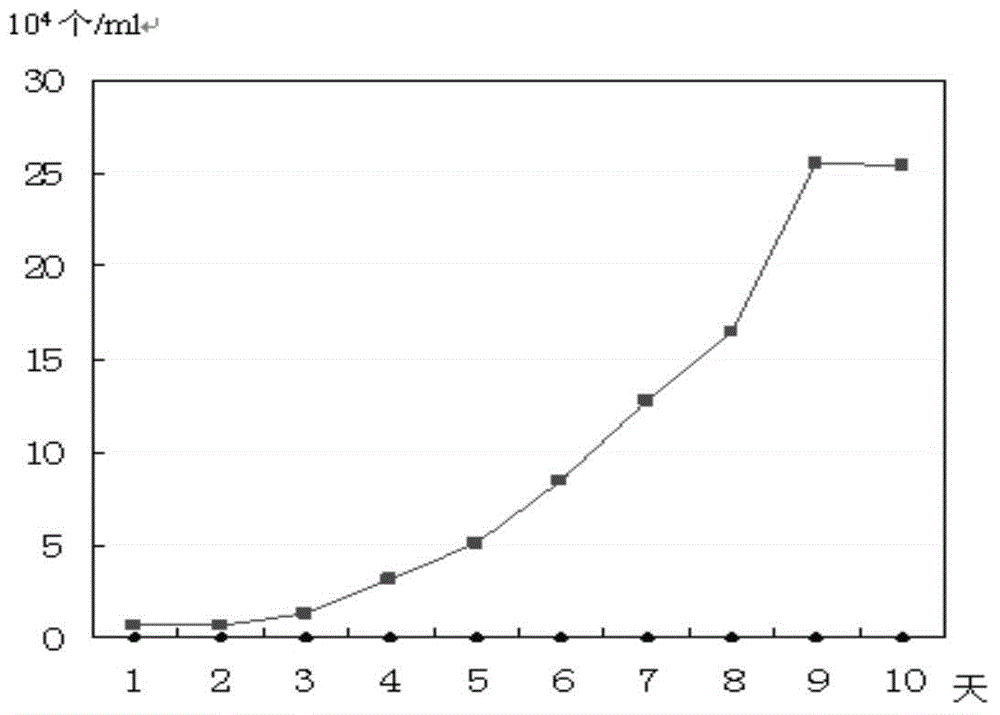
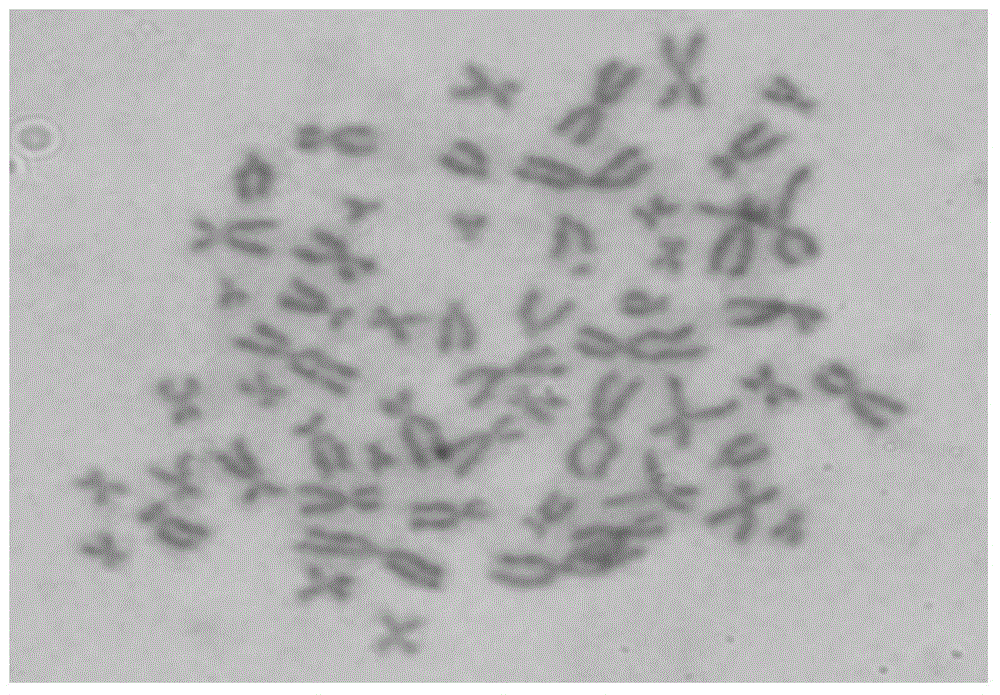
InactiveCN104087554AIn vitro tumorigenic abilityCharacteristics unchangedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses a human thymoma cell line and application thereof, belonging to the field of tumor biology. The human thymoma cell line is named Thy0517 and has a collection number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.9328. The human thymoma cell line Thy0517 has main advantages of having protein expression similar to primary tumor tissues, abnormal karyotype and characteristics of tumor cells with in-vitro tumor forming capability. After in-vitro continuous passage culture, the characteristics of thymoma cells keep unchanged, and therefore the human thymoma cell line can be used as a cell material for researching and developing thymoma-related drugs. EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) expression of the human thymoma cell line is positive, so that proliferation, angiogenesis, adhesion, invasion and metastasis of the tumor cells can be promoted; the cell line can be used as a powerful cell tool for researching EGFR-targeted drugs.
Owner:张鹏
Ca ix-specific inhibitors
InactiveUS20080095707A1Reduce adhesionIncreased invasion capacity of cellOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePyridinium
Therapeutic methods for inhibiting the growth of preneoplastic / neoplastic vertebrate cells that abnormally express MN protein are disclosed. Screening assays are provided for identifying compounds, preferably membrane-impermeant compounds, which inhibit the enzymatic activity of MN protein / polypeptides and that are useful for treating patients with preneoplastic / neoplastic disease. Further methods are disclosed for the preparation of positively-charged, membrane-impermeant heterocyclic sulfonamide CA inhibitors with high affinity for the membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase CA IX. Preferred CA IX-specific inhibitors are aromatic and heterocylic sulfonamides, preferably that are membrane-impermeant. Particularly preferred CA IX-specific inhibitors are pyridinium derivatives of such aromatic and heterocyclic sulfonamides. The CA IX-specific inhibitors of the invention can also be used diagnostically / prognostically for preneoplastic / neoplastic disease, and for imaging use, for example, to detect precancerous cells, tumors and / or metastases. The CA IX-specific inhibitors can be labelled or conjugated to radioisotopes for radiotherapy. The CA IX-specific inhibitors may be combined with conventional therapeutic anti-cancer drugs, with other different inhibitors of cancer-related pathways, with bioreductive drugs, or with radiotherapy to enhance the efficiency of each treatment. The CA IX-specific inhibitors may also be combined with CA IX-specific antibodies, preferably monoclonal antibodies or biologically active antibody fragments, more preferably humanized or fully human CA IX monoclonal antibodies or biologically active fragments or such monoclonal antibodies. Still further, the CA IX-specific inhibitors can be used for gene therapy coupled to vectors for targeted delivery to preneoplastic / neoplastic cells expressing CA IX on their surfaces.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
Application of serum amyloid protein A1
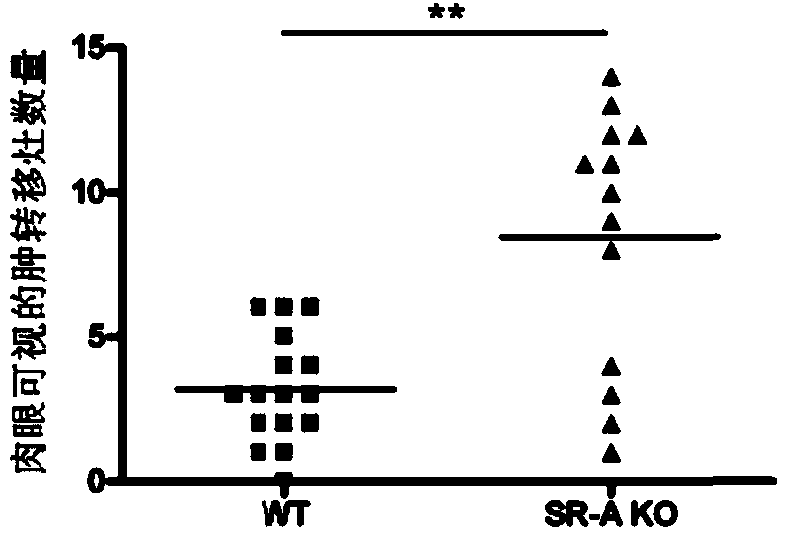
ActiveCN103908679APromote invasionGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsSerum igeSerum amyloid A1
The invention relates to an application of a serum amyloid protein A1. A kit comprises siRNAs shown in SEQ ID NO:1-4 or a polyclonal antibody of the serum amyloid protein A1 of a sequence shown in SEQIDNO:5. The serum amyloid protein A1 as a target of lung cancer metastasis effectively inhibits SAA1 to promote invasion of lung cancer cells by interfering cell SAA1 through siRNA.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Use of relaxin to treat placental syndromes
ActiveUS20150031616A1Facilitates treating womanReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementObstetricsPregnancy
The subject application relates to methods for treating a placental syndrome, wherein relaxin is administered during the late secretory / luteal (LS) phase of the menstrual cycle in women who have a propensity for developing the placental syndrome. In certain embodiments, administration of relaxin continues beyond the LS phase and into pregnancy.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Application of tiRNA as drug target in metastasis treatment of colorectal cancer
InactiveCN109999199AOvercoming non-selectivityImproved prognosisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical valueTreatment targets
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, relates to a novel target for colorectal cancer metastasis treatment, in particular to application of tiRNA as the target in the metastasis treatmentof the colorectal cancer, and also relates to the tiRNA and an antagonist siRNA and the application using the the tiRNA and the antagonist siRNA to prepare medicines for targeted treatment of colorectal cancer metastasis. The invention discloses the use of the tiRNA as the treatment target for the colorectal cancer metastasis or as a medicament for regulating and treating the colorectal cancer metastasis. The antagonist of 5'-tiRNA has a great clinical value in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions for treating the colorectal cancer, and provides novel drugs and methods for effectivetreatment of the colorectal cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
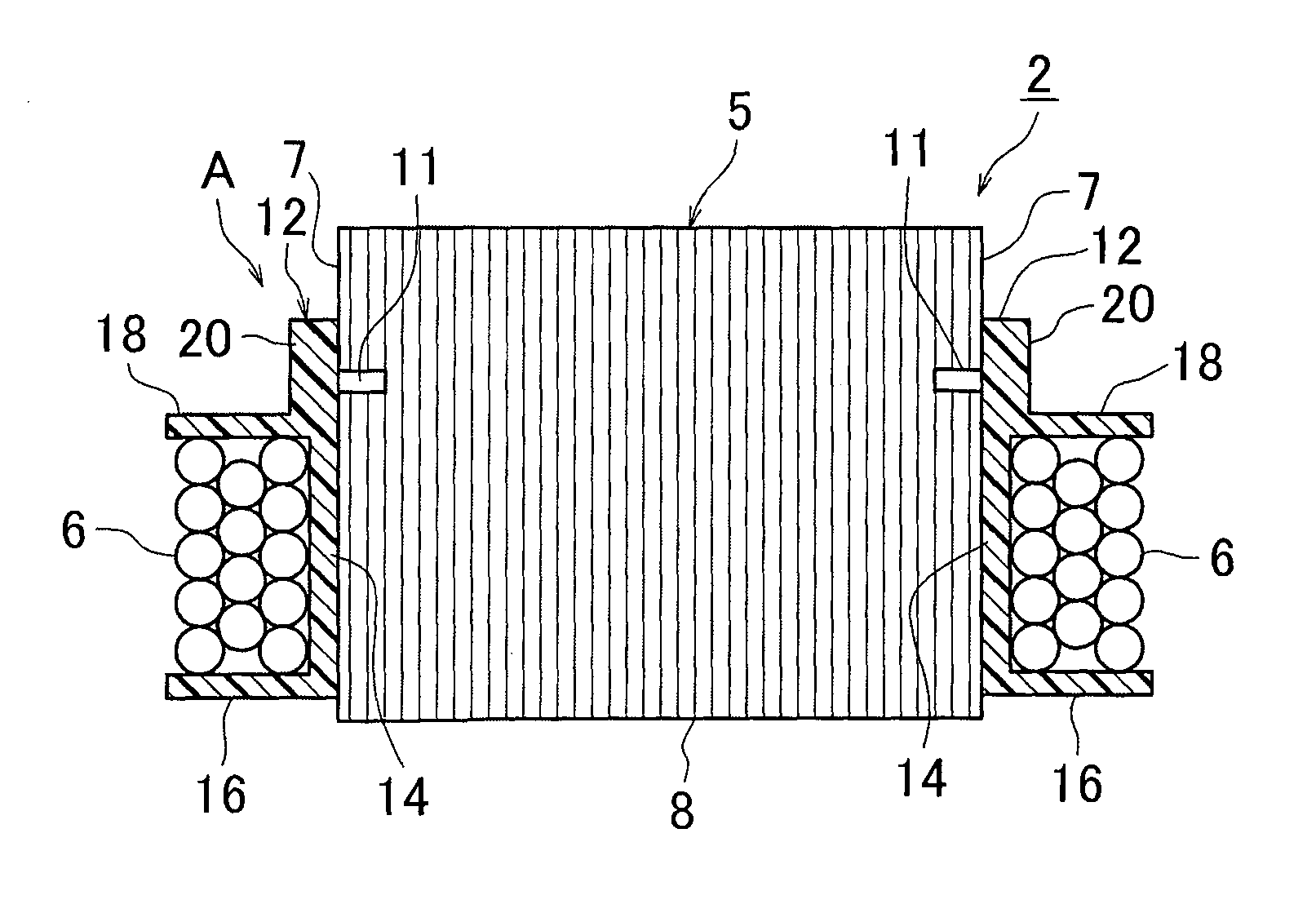
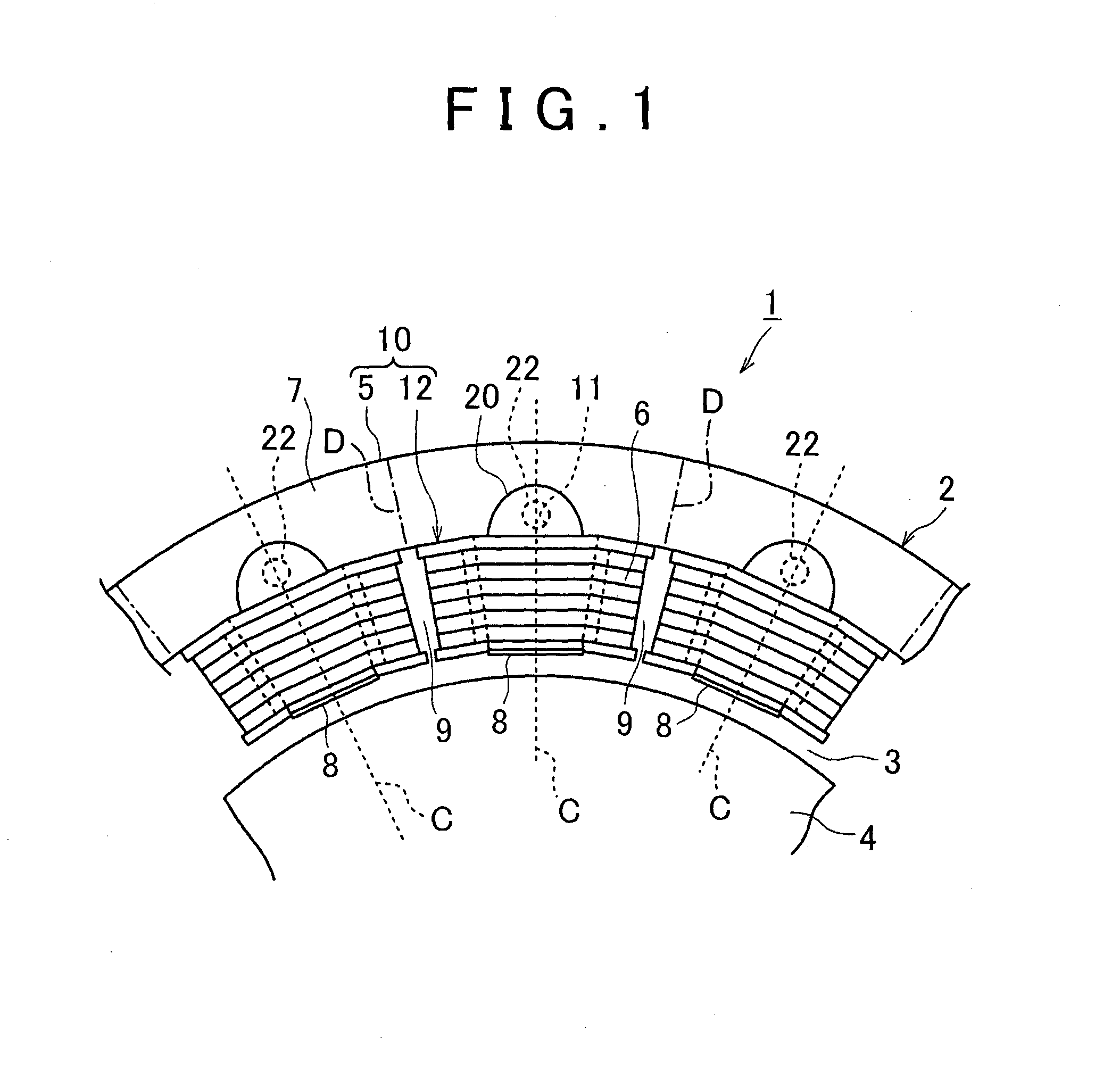
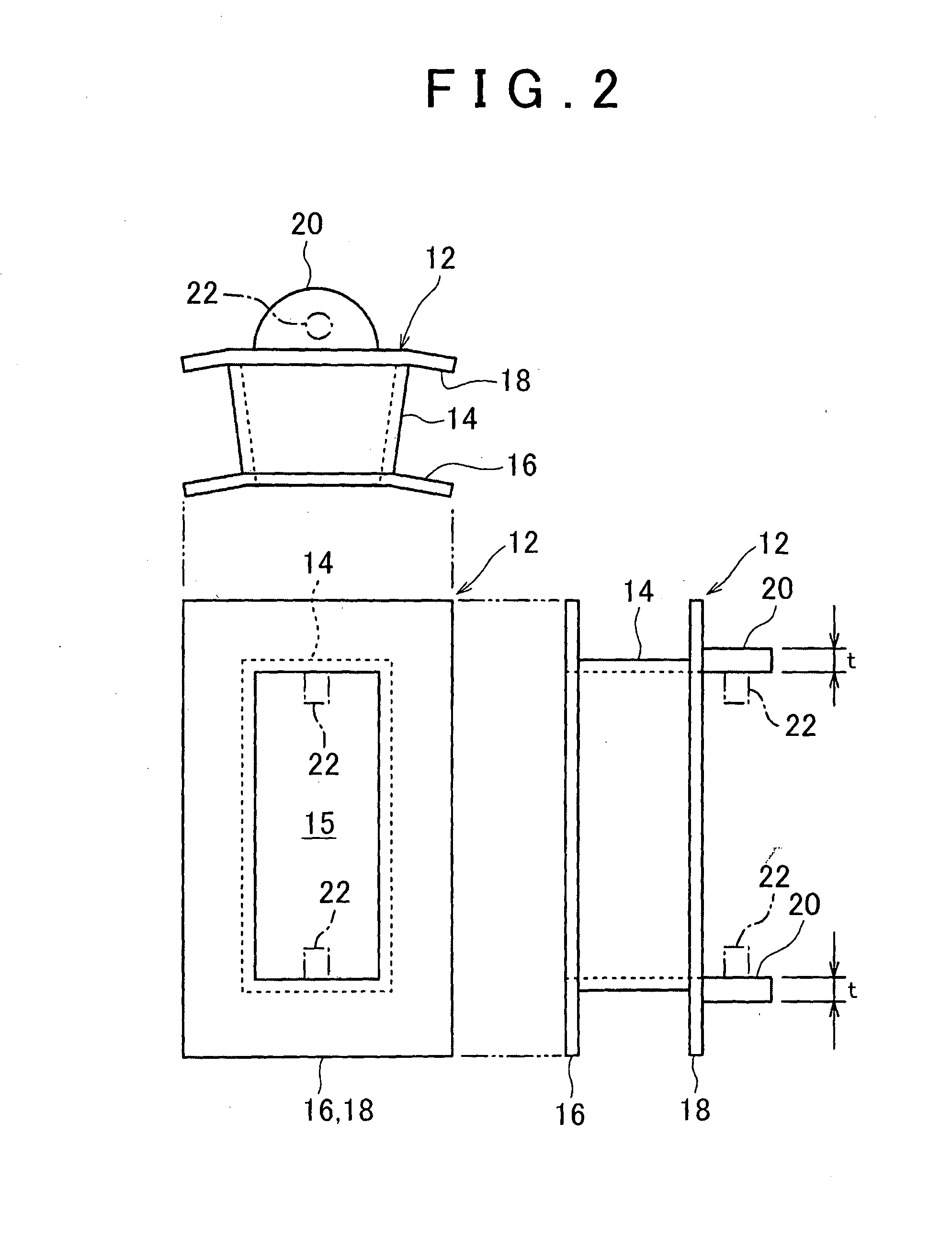
Fixing method and fixing structure for fixing a coil insulator, stator using the same and rotating electrical machine using the same
ActiveUS20160211733A1Stable fixing conditionStable conditionWindings insulation shape/form/constructionApplying solid insulationEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A fixing method for fixing a coil insulator which is provided between a stator core 5 including a back yoke 7 and a plurality of teeth 8 projecting in the radial direction from the back yoke 7, and a coil 6 wound around the stator core 5, to the stator core 5, includes preparing the stator core 5 in which a fixing hole 11 is formed corresponding to a respective one of the teeth 8, on an end face in the axial direction of the back yoke 7, and preparing a plurality of coil insulators 12 which include each a main body 14 composed of a heat-softenable insulating material and arranged on the circumference of a respective, one of the teeth 8, and a fixing portion 20 which is projected in the radial direction from the main body 14 and covers the fixing hole 11. Each coil insulator 12 is arranged on the circumference of a respective one of the teeth 8 by fitting thereto. By softening the fixing portion 20 by heating to bring part of the insulating material into the fixing hole 11 and then hardening the fixing portion 20, a projection 22 for fixing the coil insulator 12 to the stator core 5 is formed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
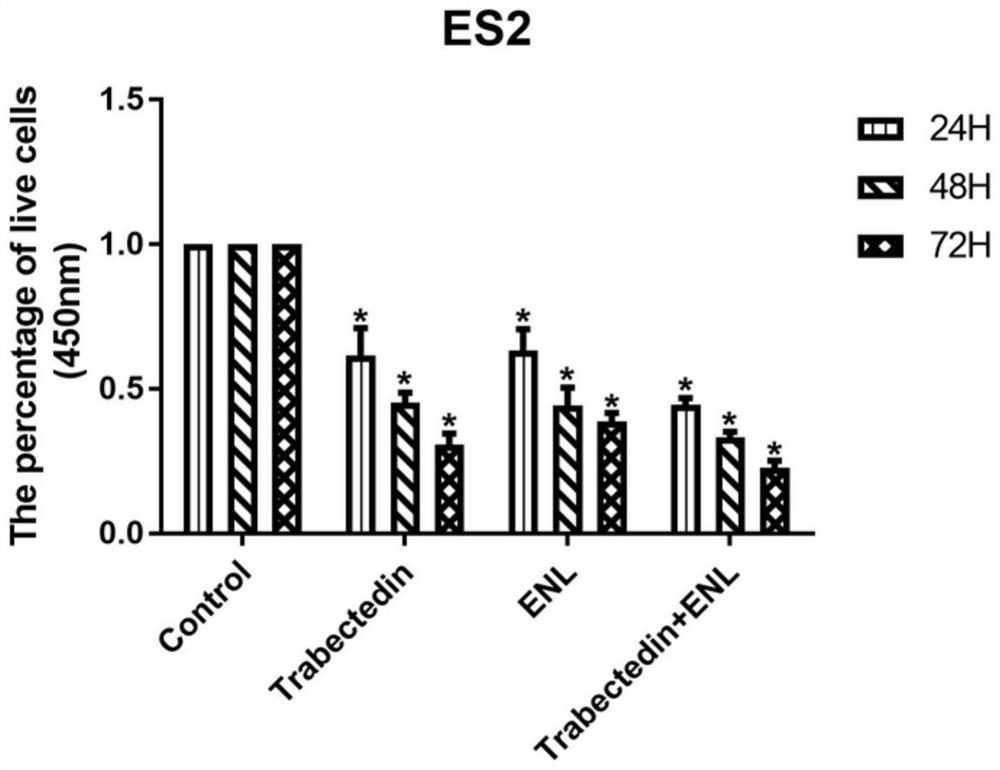
Anti-tumour combined pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveCN112386596APrevent proliferationInhibitory activityHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectLignan
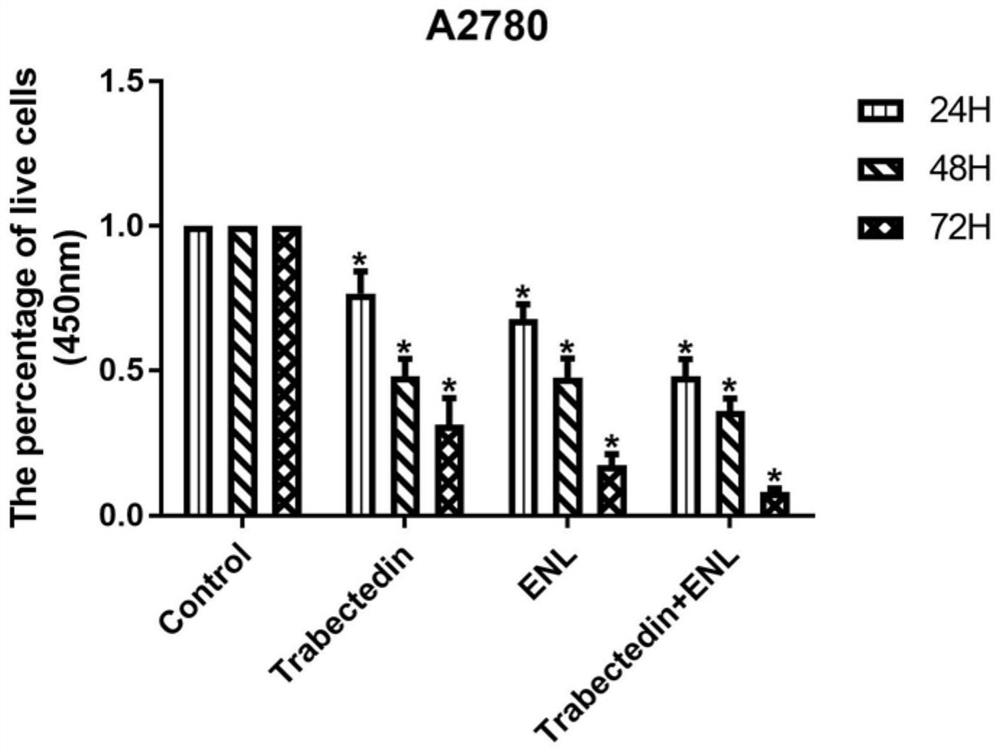
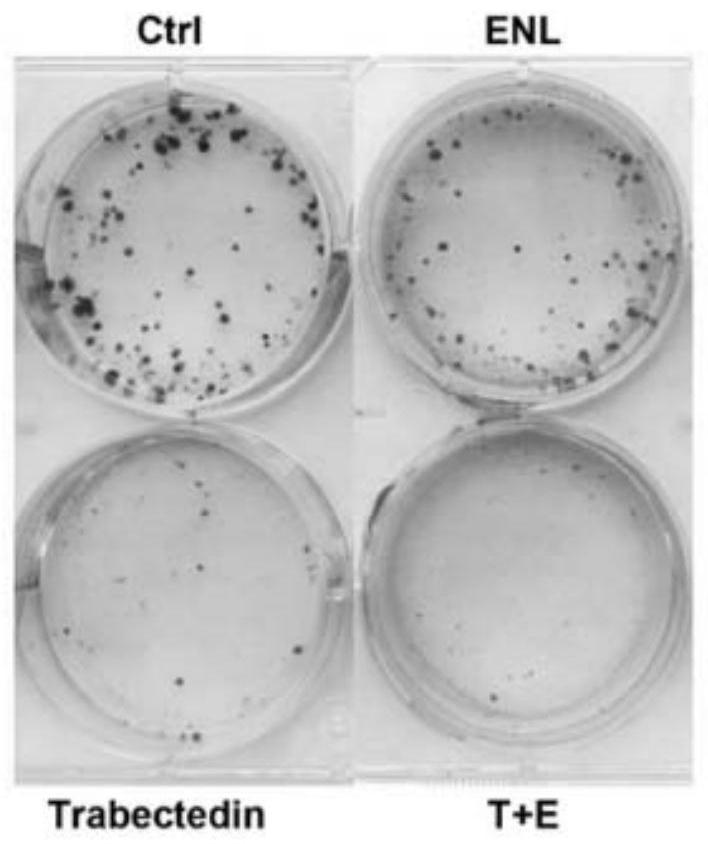
The invention relates to an anti-tumour combined pharmaceutical composition and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biological medicines. In order to further improve the cancer treatmenteffect and reduce the drug cost of applying trabectedin at the same time, the invention provides an anti-tumour combined pharmaceutical composition, which comprises an effective amount of enterolactone or a plant lignan precursor capable of being converted into enterolactone in a body, and further comprises an effective amount of trabectedin. According to the invention, experiments prove that combined application of trabectedin and enterolactone can inhibit proliferation, activity, metastasis, invasion and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer and promote tumour cell apoptosis; and, when the two drugs are combined for use, the inhibition effect on the ovarian cancer is stronger than that of a single drug after the dosage of the two drugs is halved. According to the invention, the administration amount of trabectedin is reduced by using the enterolactone with lower cost; the economic burden of a patient is reduced; and the enterolactone can also reduce the side effect of trabectedin. The combined pharmaceutical composition disclosed by the invention can improve the anti-tumour curative effect and promote clinical popularization of trabectedin.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Large-area welding method
ActiveCN102764922APromote invasionEasy to excludeSoldering apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingSolid phasesSurface type
The invention discloses a large-area welding method. The method comprises the following steps of: manufacturing a first welding film on the welding surface of a first welding part; manufacturing a second welding film on the welding surface of a second welding part, wherein the manufactured first welding film has a cylindrical microstructure, the melting point t of the material of the first welding film is higher than the melting point t1 of the material of the second welding film, and the materials of the first welding film and the second welding film form metallographic structures; and heating the second welding part to temperature t2 which is greater than t2 under the condition that the two welding films contact each other to ensure that loose structures of liquid-phase second welding film and solid-phase first welding film are infiltrated, and then cooling to finish welding. By the method, the problem that welding is failed because bubbles which are remained on a combination surface easily due to the welding surface types can be solved effectively.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
CA IX-specific inhibitors
InactiveUS7550424B2Reduce adhesionIncreased invasion capacity of cellBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
Therapeutic methods for inhibiting the growth of preneoplastic / neoplastic vertebrate cells that abnormally express MN protein are disclosed. Screening assays are provided for identifying compounds, preferably membrane-impermeant compounds, which inhibit the enzymatic activity of MN protein / polypeptides and that are useful for treating patients with preneoplastic / neoplastic disease. Further methods are disclosed for the preparation of positively-charged, membrane-impermeant heterocyclic sulfonamide CA inhibitors with high affinity for the membrane-bound carbonic anhydrase CA IX. Preferred CA IX-specific inhibitors are aromatic and heterocylic sulfonamides, preferably that are membrane-impermeant. Particularly preferred CA IX-specific inhibitors are pyridinium derivatives of such aromatic and heterocyclic sulfonamides. The CA IX-specific inhibitors of the invention can also be used diagnostically / prognostically for preneoplastic / neoplastic disease, and for imaging use, for example, to detect precancerous cells, tumors and / or metastases. The CA IX-specific inhibitors can be labelled or conjugated to radioisotopes for radiotherapy. The CA IX-specific inhibitors may be combined with conventional therapeutic anti-cancer drugs, with other different inhibitors of cancer-related pathways, with bioreductive drugs, or with radiotherapy to enhance the efficiency of each treatment. The CA IX-specific inhibitors may also be combined with CA IX-specific antibodies, preferably monoclonal antibodies or biologically active antibody fragments, more preferably humanized or fully human CA IX monoclonal antibodies or biologically active fragments or such monoclonal antibodies. Still further, the CA IX-specific inhibitors can be used for gene therapy coupled to vectors for targeted delivery to preneoplastic / neoplastic cells expressing CA IX on their surfaces.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
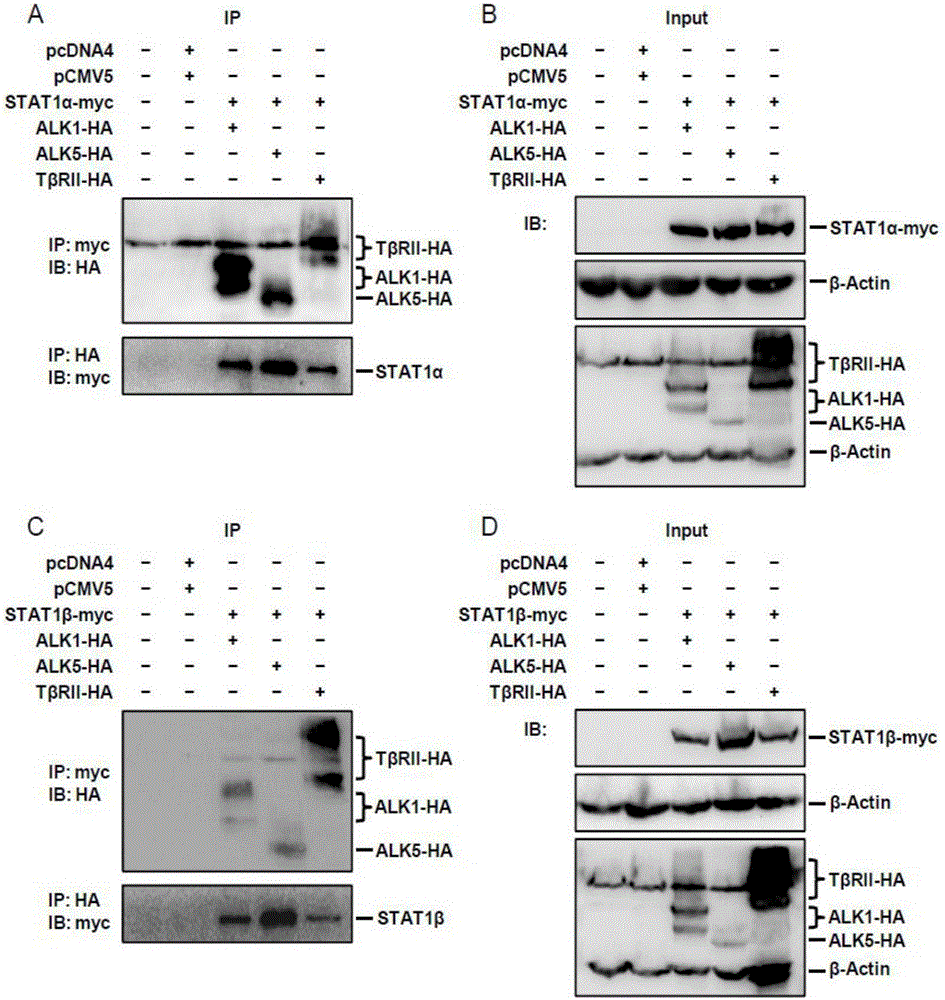
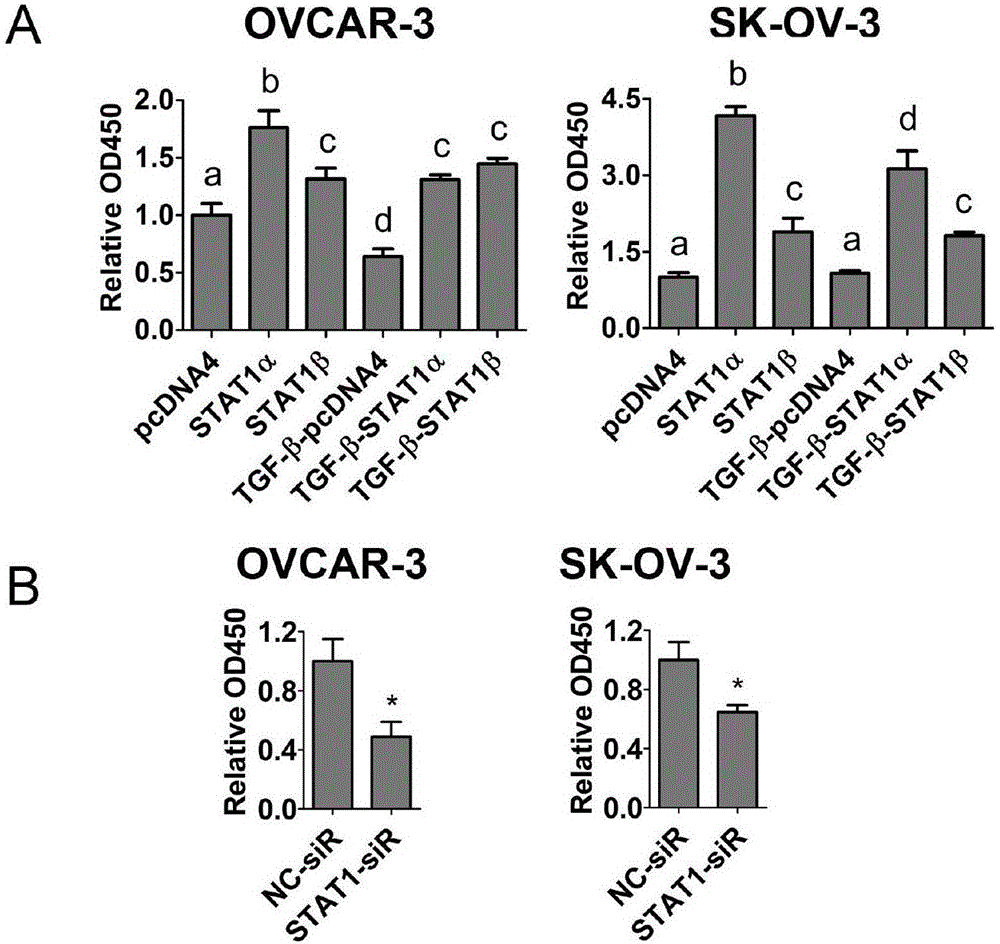
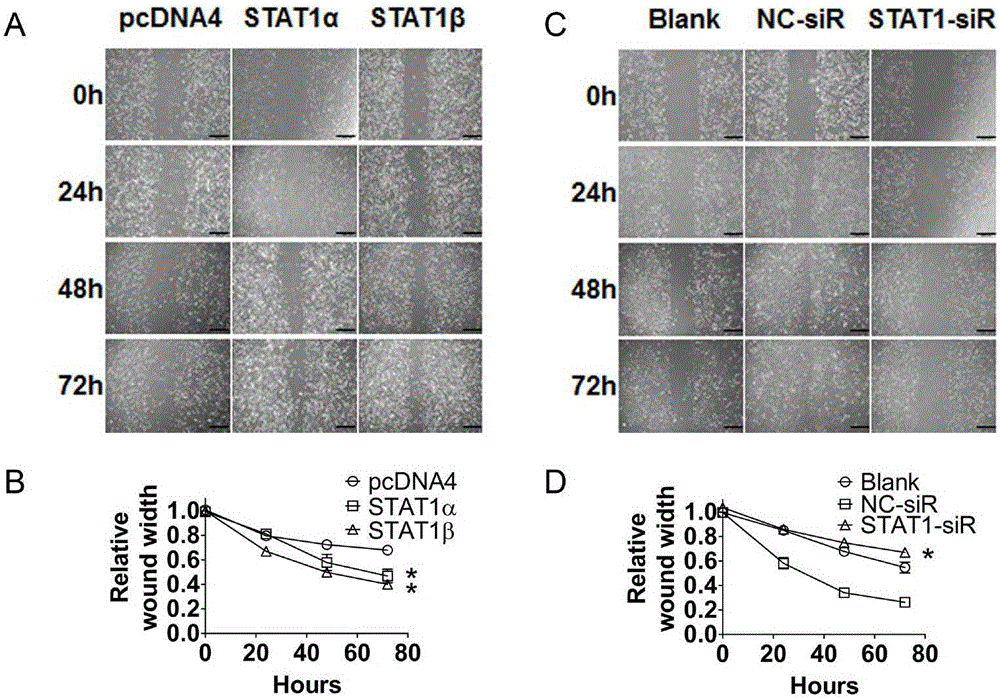
Application of STAT1 serving as ovarian cancer treatment target point
ActiveCN106334189APromote proliferationPromote migrationOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTreatment targetsTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to application of STAT1 serving as ovarian cancer treatment target point. Experiments prove that the STAT1 directly combines with a TGF-beta receptor (ALK1, ALK5 and TbetaRII), proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells can be promoted after STAT1overexpression, and proliferation, migration and invasion of the ovarian cancer cells can be inhibited after STAT1 knocking-down. Therefore, STAT1 reduction processing is conducted on patients with high ovarian cancer STAT1 expressions, a potential treatment effect exists. An STAT1 signal path mutually acts with a TGF-beta1 signal path to influence the proliferation, migration and invasion capability of ovarian cancers. The STAT1 is a potential novel ovarian cancer treatment target point and has a great clinical application value.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
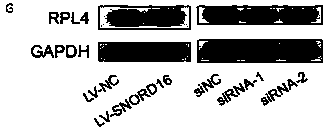
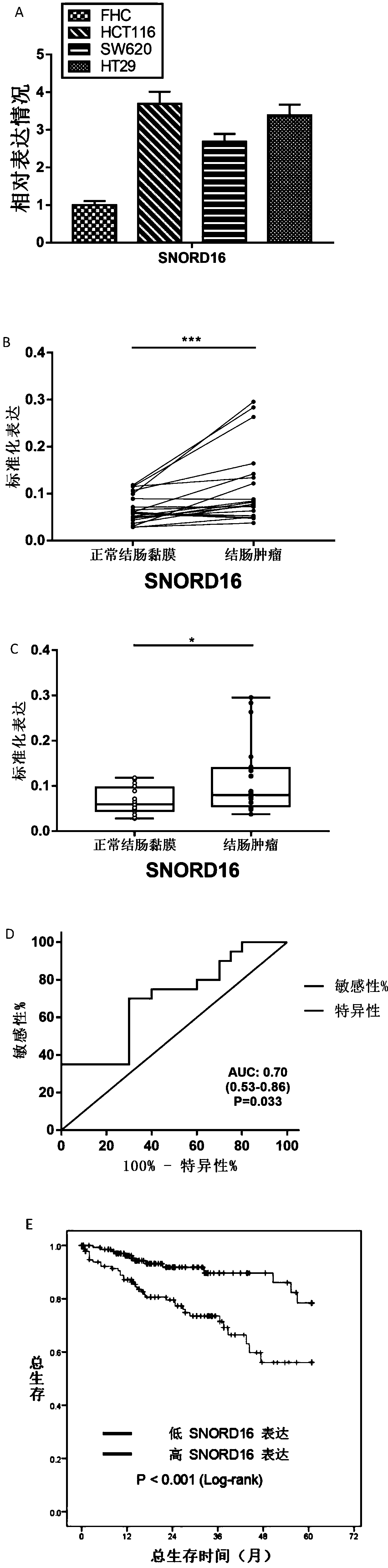
Application of SNORD16 gene in preparation of colon cancer detection kits and related kits
ActiveCN111118159APromote growthPromote proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCancers diagnosis
The invention provides an application of an SNORD16 gene in preparation of colon cancer detection kits and the related kits, and belongs to the technical field of biology. In order to mine prognosticbiomarkers for identifying high-risk patients and explore a novel molecular mechanism of colon cancer pathogenesis, the invention provides the application of the SNORD16 gene in the preparation of thecolon cancer detection kits, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the SNORD16 gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The kits are used for colon cancer diagnosis and / or prognosis assessment; compared with normal tissue adjacent to cancers, the SNORD16 gene is highly expressed in colon cancer cells or tissue. The invention also provides the related detection kits. In-vitro functional experiments show that the SNORD16 can promote growth, proliferation, migration and invasion of the colon cancer cells by inhibiting apoptosis, and indicate that the SNORD16 has carcinogenic effects in colon cancer and can beused as the novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for the colon cancer.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
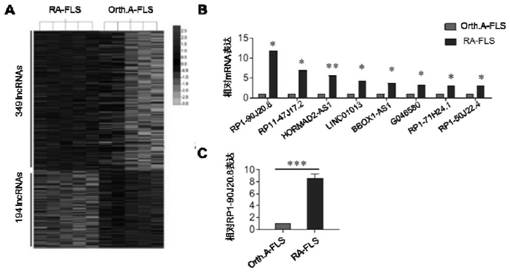
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and application thereof in diagnosis/treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
ActiveCN113278691APromote migrationPromote invasionOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticJoints inflammationDiagnosis treatment
The invention discloses a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and application thereof in diagnosis / treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The lncRNA is lncRNA RP1-90J20.8. The invention relates to application of the lncRNA in evaluation of the severity of RA joint inflammation and joint damage and target drug therapy. A reagent for detecting the lncRNA RP1-90J20.8 can assist in RA diagnosis, evaluation and joint erosion damage judgment; and a target silent lncRNA RP1-90J20.8 gene can be used for inhibiting joint damage and assisting in treatment of RA. According to the invention, the biological function and clinical significance of the lncRNA RP1-90J20.8 in RA are clarified; a sufficient theoretical basis is provided for taking the lncRNA RP1-90J20.8 as a marker for auxiliary diagnosis of RA and prediction of RA prognosis and a new therapeutic target; and the lncRNA RP1-90J20.8 has great significance and application prospects in development of auxiliary diagnosis, prognosis evaluation and therapeutic drugs for RA.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
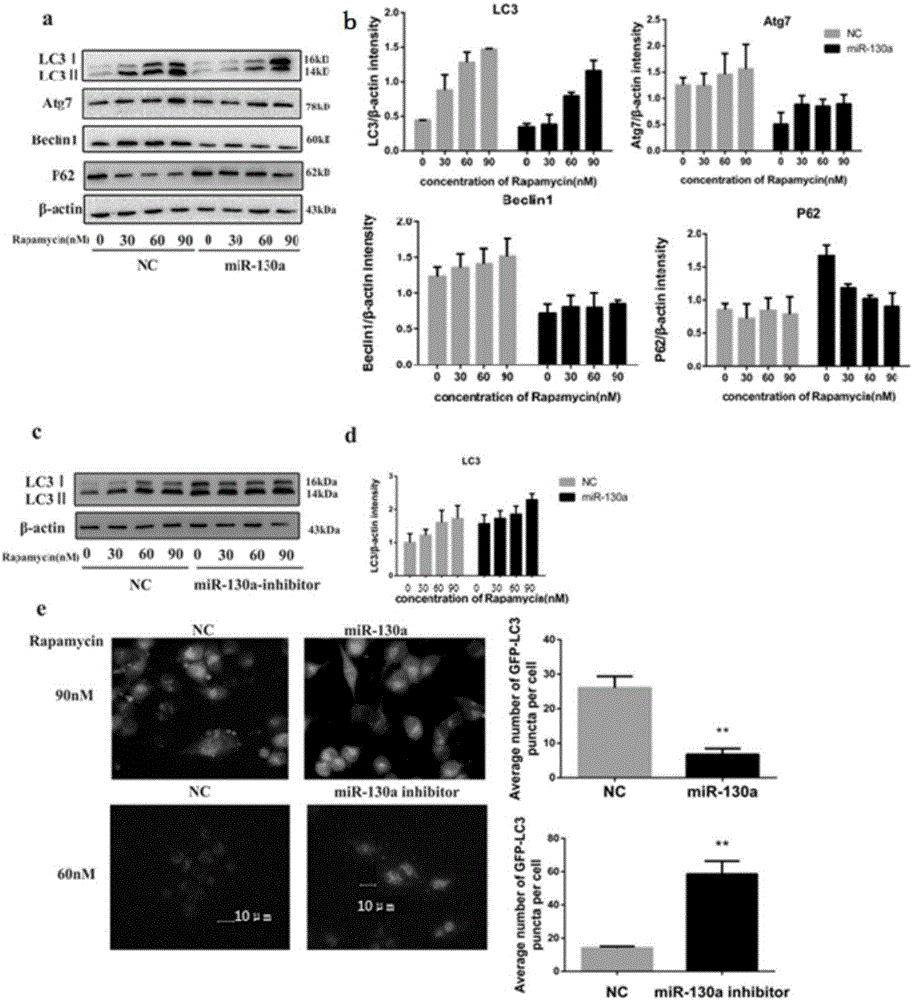
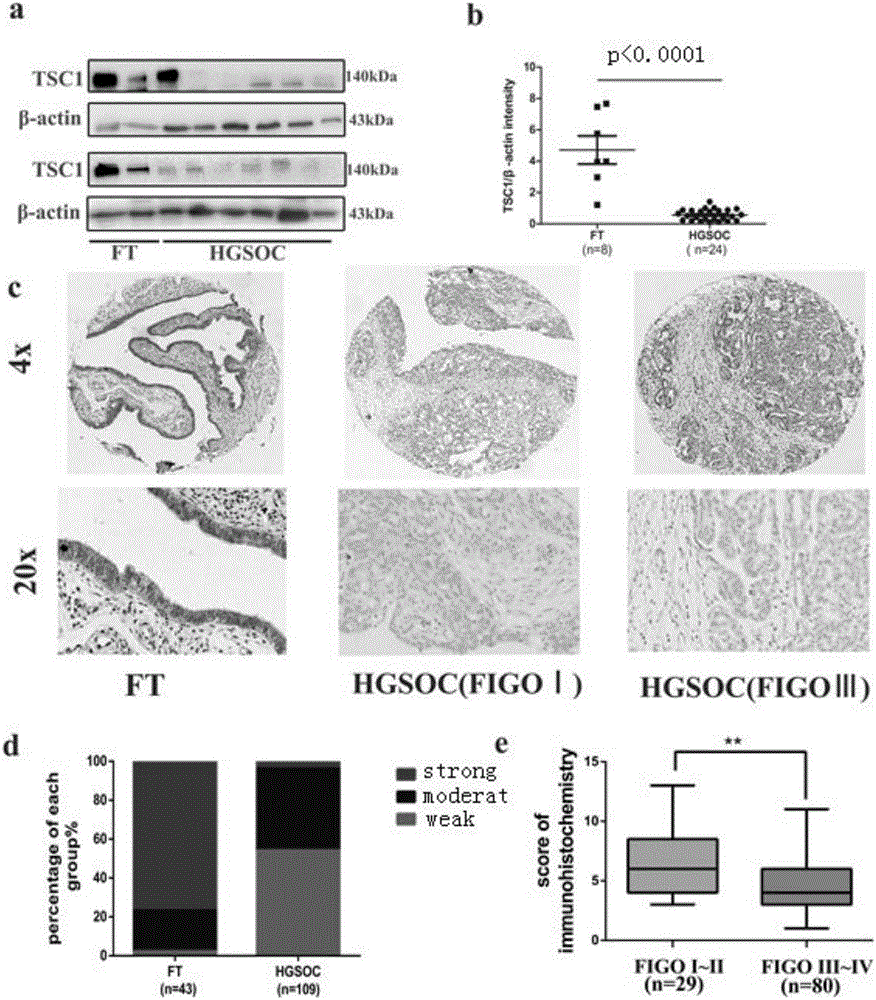
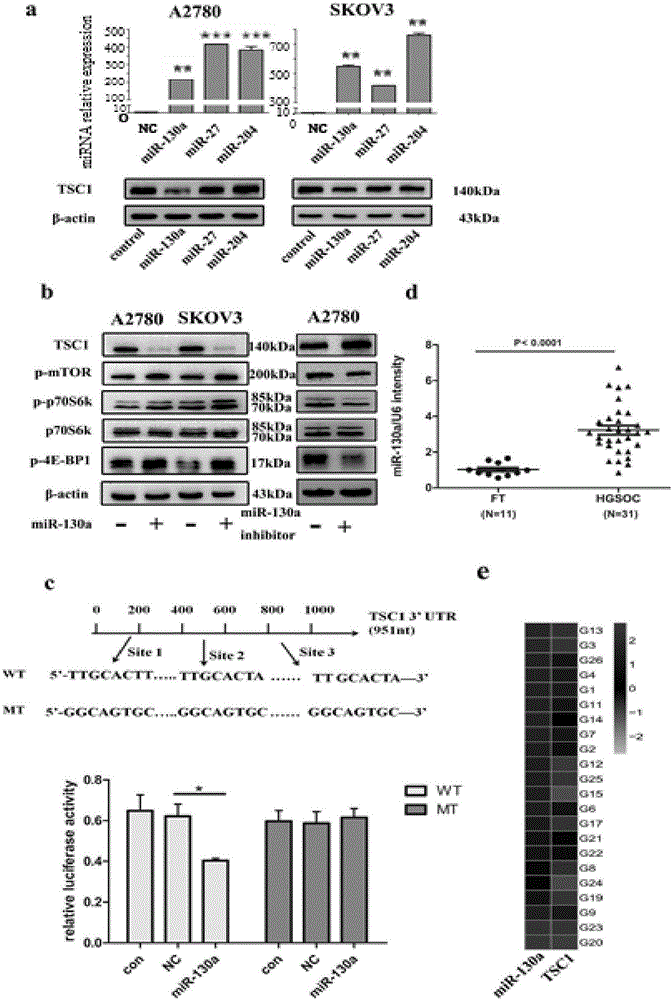
Application of miR-130a to diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer
ActiveCN106636368AObvious negative correlationPrevent invasionMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsAbnormal tissue growthGynecology
The invention discloses application of miR-130a to diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer. The miR-130a is defined, through in-vivo and in-vitro function test, that an mTOR (mammalian Target of Rapamycin) signal path is over-expressed through inhibiting translation of TSC1mRNA (Tuberous Sclerosis 1 Messenger RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)) by the miR-130a, so that proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells are promoted and autophagy of the cells is inhibited. The data testifies that the miR-130a with a reduced endogenous property can be used for inhibiting malignant biological behaviors including growth, invasion and the like of ovarian cancer tumors. Based on the characteristics, a specific miR-130a inhibitor can be designed, the content of TSC1 in a body is recovered and the mTOR signal path is inhibited, so that the aim of treating the ovarian cancer is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Tissue scaffold materials for tissue regeneration and methods of making
ActiveUS9968708B2High densityPromote invasionGranular deliveryTissue regenerationWound healingFibroblast
Disclosed herein are tissue scaffold materials with microspheres of one density embedded in hydrogel of a different density. The disclosed materials have improved ability to facilitate cellular invasion and vascularization for wound healing and tissue regeneration. The inventors have found that materials having components with different densities promotes invasion of cells, including desirable cells such as fibroblasts and endothelial precursor cells, into the scaffold.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Preparation process of carboxymethyl chitosan hemostatic sponge
PendingCN110559473AGood biocompatibilityPromote water swellingSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberMicroorganism
The invention discloses a preparation process of carboxymethyl chitosan hemostatic sponge and relates to the technical field of preparation of carboxymethyl chitosan hemostatic sponge. The carboxymethyl chitosan hemostatic sponge comprises components as follows: 1-10 parts of carboxymethyl chitosan, 1-10 parts of chitosan oligosaccharide, 1-10 parts of beta-chitosan, 1-10 parts of carboxymethyl chitosan fiber, 1-10 parts of collagen and 1-5 parts of glycerin, wherein the collagen is fish collagen. The carboxymethyl chitosan hemostatic sponge prepared by the preparation process has good biocompatibility, expands quickly after absorbing water, permeates quickly, has very high water absorption ratio, allows good gas exchange, has good liquid absorption performance, keeps wet healing environment for wounds and can isolate outer layer structures and prevent invasion of microorganisms so as to create an ideal healing environment for wounds.
Owner:孙与泽
HMBG (High Mobility Group Box) 1 modified bone tissue engineering bracket material and preparation method thereof
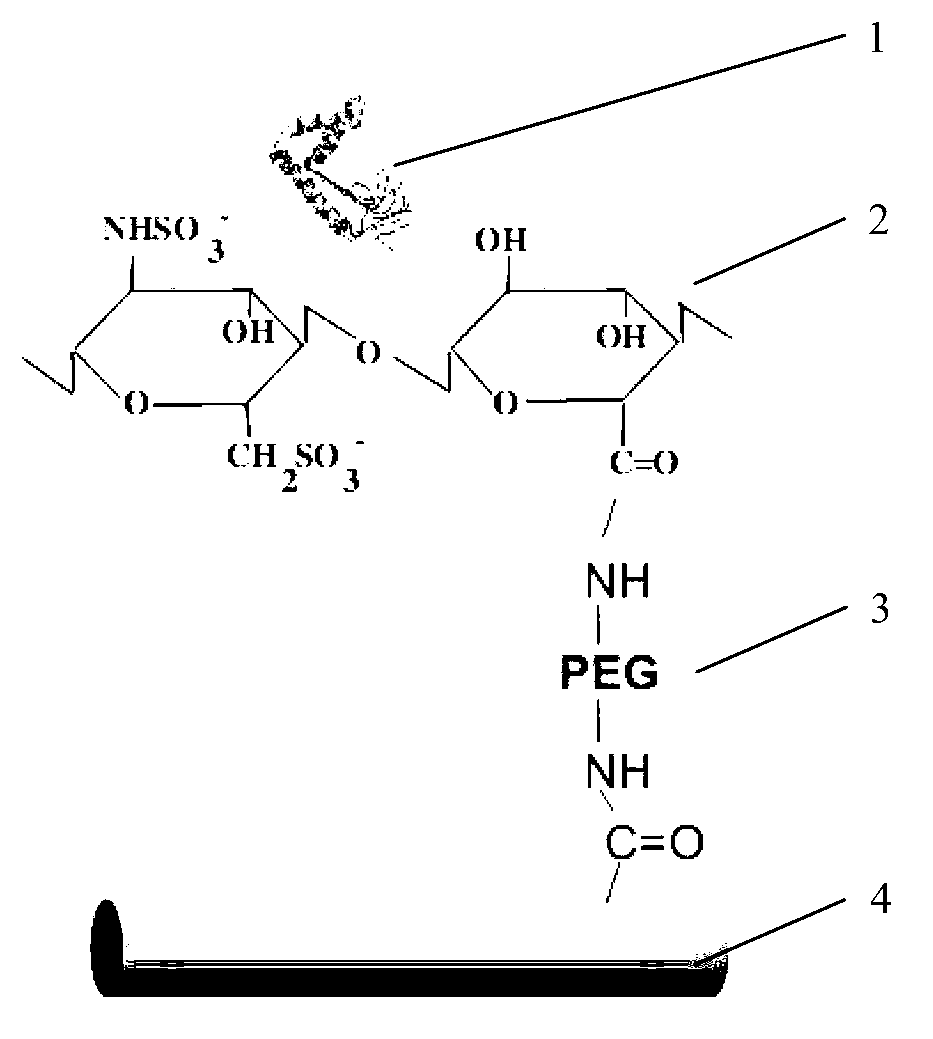
ActiveCN103316378AImprove repair speedImprove restoration qualityProsthesisFiberSignalling molecules
The invention discloses an HMBG (High Mobility Group Box) 1 modified bone tissue engineering bracket material and a preparation method thereof. The HMBG1 modified bone tissue engineering bracket material is prepared by crosslinking a signal molecule HMGB1 to a PLLA (Poly L Lactic Acid) nanofiber bracket by means of heparin (2) and a crosslinking molecule Di-NH2-PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) by using the PLLA nanofiber bracket manufactured by an electrostatic spinning technology as a matrix. According to the invention, various functions of recruitment, infiltration and mobility of cells are realized by the signal molecule, so that the material has good biocompatibility, and can be used to compose stem cells and further can be directly applied to bone tissue repair. The material is simple and accessible in process and good in repeatability.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
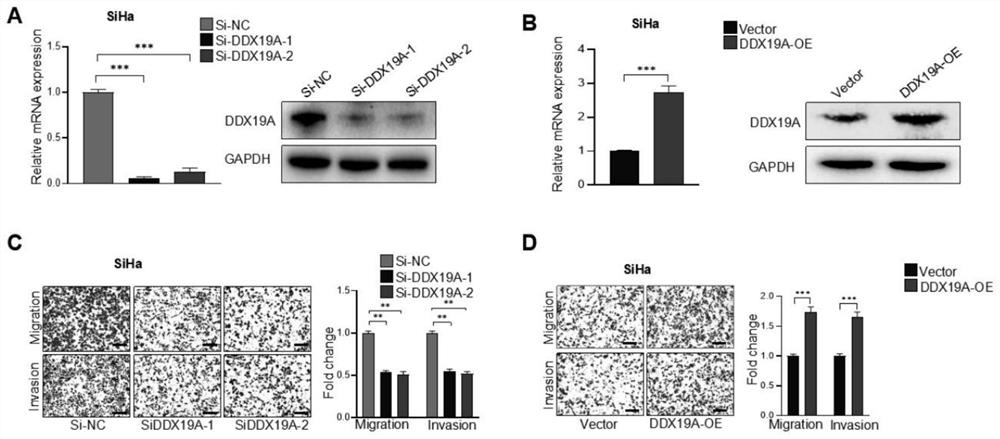
Application to promotion of cervical squamous cell carcinoma metastasis based on DDX19A
ActiveCN112813162AEasy transferPromote migrationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCell invasionSquamous Carcinomas
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical products, and discloses an application to promotion of squamous cell carcinoma metastasis based on DDX19A. In function, DDX19A is found to promote in-vitro migration and invasion of cervical squamous cell carcinoma cells and in-vivo lung metastasis. In terms of mechanism, overexpression of the DDX19A increases NOX1 expression, increases production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and induces migration and invasion of the cervical squamous cell carcinoma cells. Rescue experiments show that overexpression of NOX1 can retrieve and knock down cervical cancer squamous cell carcinoma cell invasion and migration and ROS generation caused by DDX19A, and the inventor further discovers that an ROS inhibitor N-acetylcysteine can inhibit DDX19A-induced cervical squamous cell carcinoma cell invasion and migration. Therefore, the DDX19A is proved to promote metastasis of the cervical squamous cell carcinoma by inducing NOX1 to mediate ROS production. Blocking of a DDX19A / NOX1 / ROS axis can be a potential therapeutic target for patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis diagnosis and/or prognosis evaluation
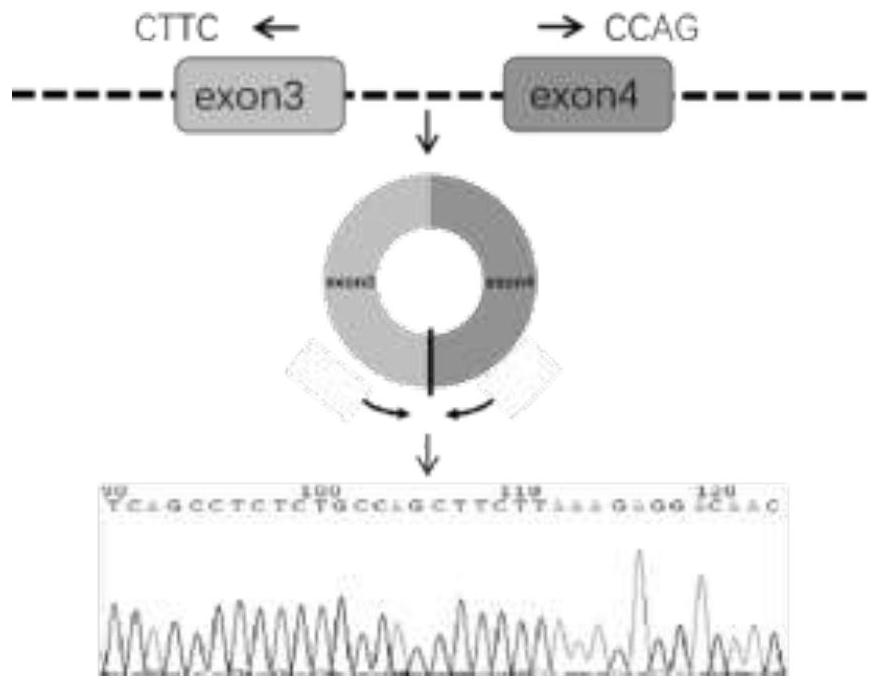
ActiveCN111718995APromote proliferationPromote migrationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsNasopharyngeal cancerTissue sample
The invention discloses a biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis diagnosis and / or prognosis evaluation. In the invention, we prove that circ-0046263 is highly expressed in a nasopharyngealcarcinoma cell line compared with a normal nasopharyngeal epithelial cell NP69. Clinical tissue sample detection results show that the expression of circ-0046263 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues isup-regulated and is in positive correlation with stages. In-vitro cell function experiments show that circ-0046263 can promote proliferation, migration and invasion of cells and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition of the cells. Therefore, circ-0046263 can be used as a biomarker to be applied to preparation of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis diagnosis and / or prognosis evaluation reagent, a kit or a detection device, and also can be used as a target spot to be applied to screening of medicines for treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma or nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis; and a reagent for inhibiting circ-0046263 expression can be used for preparing a medicine for treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma or nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis.
Owner:JIANGSU CANCER HOSPITAL
Bumped kinase inhibitor compositions and methods for treating cancer
ActiveUS20180271871A1Improve impactSpeed upOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryKinase inhibitionPharmacology
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com