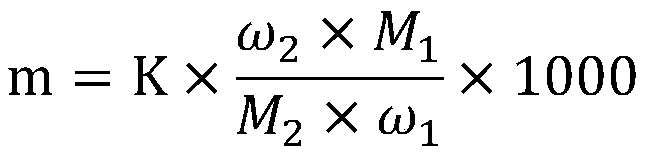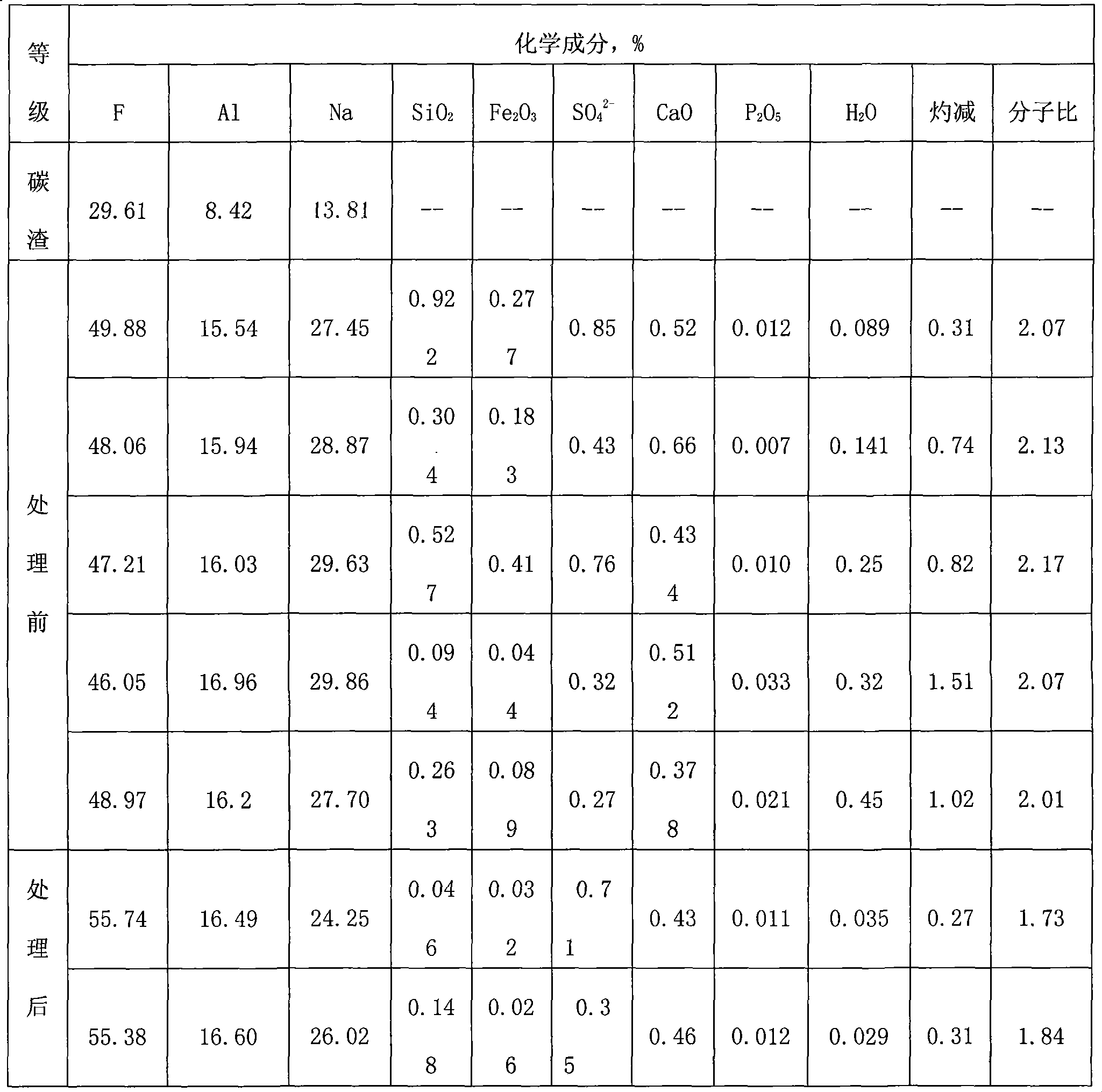Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Sodium bifluoride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
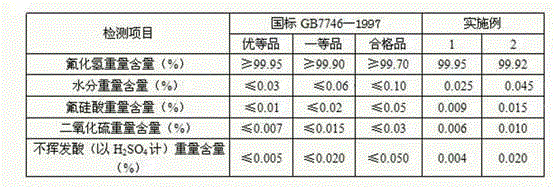
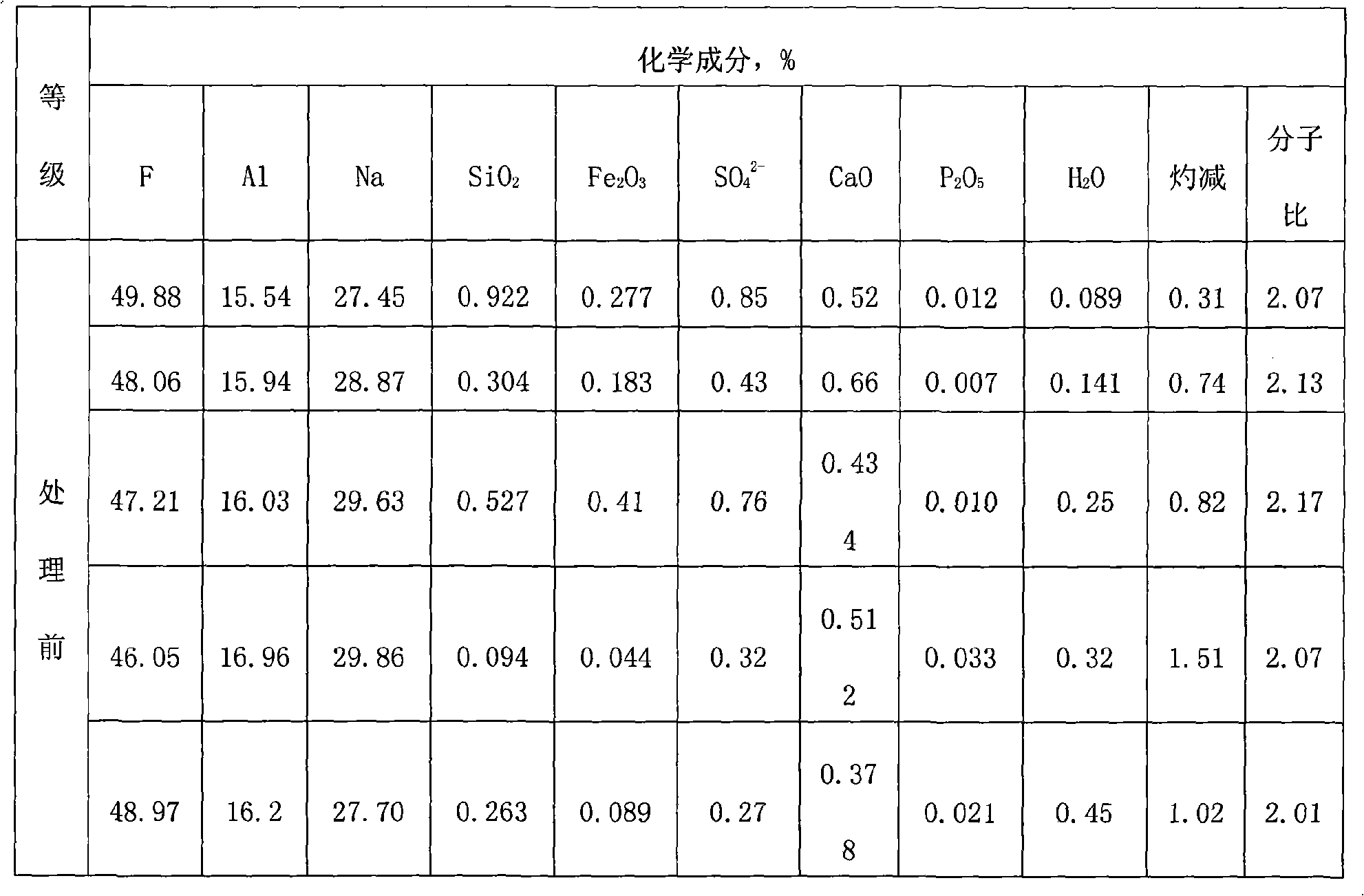
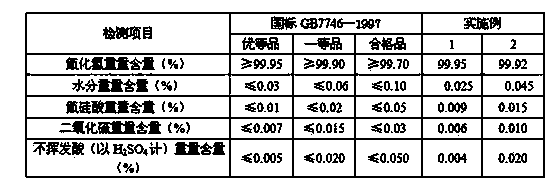
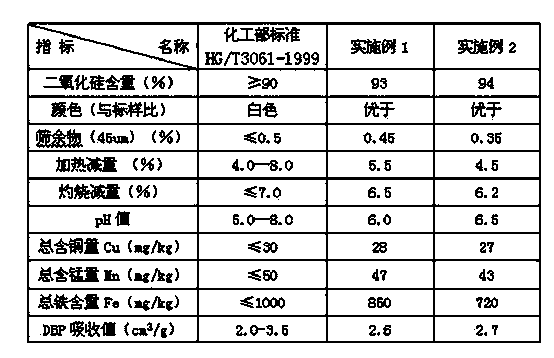
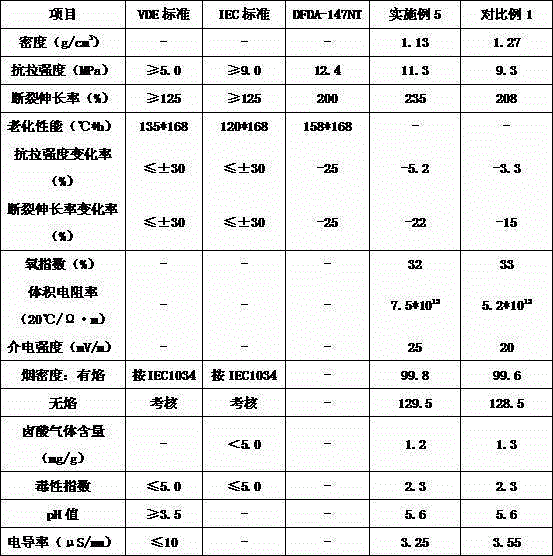
Sodium bifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula NaHF₂. It is a salt of sodium cation (Na⁺) and bifluoride anion (HF₂⁻). It is a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes upon heating . Sodium bifluoride is non-flammable, hygroscopic, and has a pungent smell. Sodium bifluoride has a number of applications in industry.
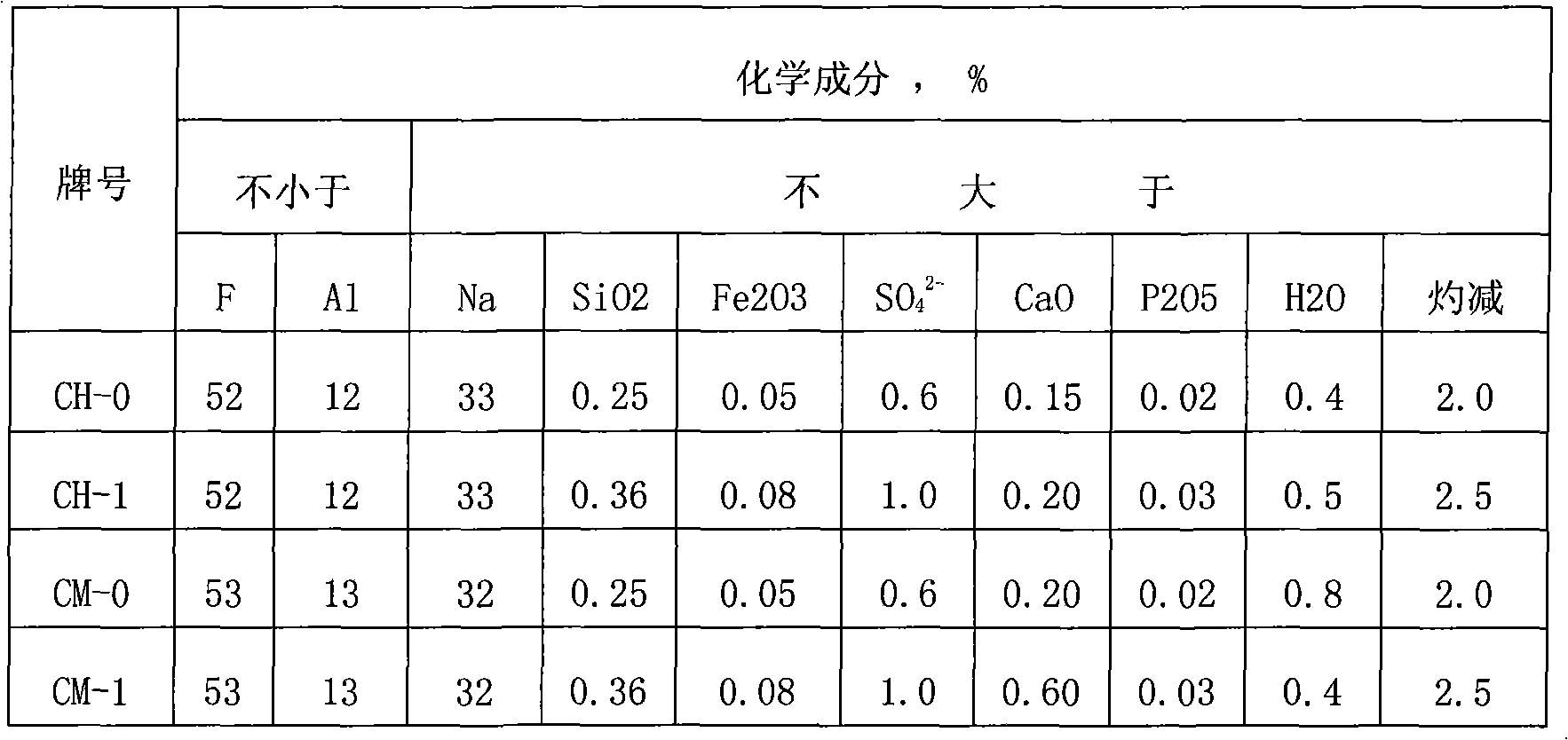
Metal surface conditioning agent and metal surface treatment technology
ActiveCN104131277ANo pollutionEasy to operateMetallic material coating processesEthylenediaminePhytic acid
The invention relates to a metal surface conditioning agent, which is composed of novel organic acidity, zinc nitrate, sodium molybdate, nicdel nitrate, sodium hydrogenfluoride, phytic acid, a nonionic surfactant and water; the novel organic acidity is the organic acidity obtained by respectively reacting ethene diamine or diethylenetriamine or triethylene tetramine or tetraethylenepentamine with citric acid. A metal surface treatment technology comprises the following steps: preparing the novel organic acidity, and using the novel organic acidity for complex formulation with zinc nitrate, sodium molybdate, nicdel nitrate, sodium hydrogenfluoride, phytic acid, the nonionic surfactant and water to obtain the metal surface conditioning agent. The concrete processing flow comprises the following steps: removing oil, washing, washing, pickling, neutralizing, conditioning surface, treating surface, performing post-treatment on surface or washing, performing air drying. The surface treatment technology can replace the current phosphatization technology, and has the technology advantages of environmental protection and simple operation, and is better than the phosphatization technology from the aspect of technology index.
Owner:DALIAN JIESHI CLEANING PRODS
Surface treatment process for radiator shell metal stamping piece
InactiveCN104451642AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesBenzoic acidPhytic acid
The invention discloses a surface treatment process for a radiator shell metal stamping piece. The surface treatment process comprises the following steps: 1) mixing 15 parts by mass of benzoic acid, 8 parts by mass of polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, 2 parts by mass of sodium molybdate, 4 parts by mass of nickel nitrate, 4 parts by mass of sodium hydrogenfluoride, 2 parts by mass of phytic acid and 3.6 parts by mass of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, and reacting for 3.5 hours at 110 DEG C to obtain a metal surface treatment agent; 2) mixing 13 parts by mass of metal surface treatment agent and 96 parts by mass of water to obtain a surface treatment working solution; and 3) heating the surface treatment working solution to 50 DEG C, and putting the metal stamping piece into the surface treatment working solution for 25 minutes. The surface treatment process for the radiator shell metal stamping piece can improve the oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance of the metal stamping piece.
Owner:常熟市宏福塑料金属制品有限公司
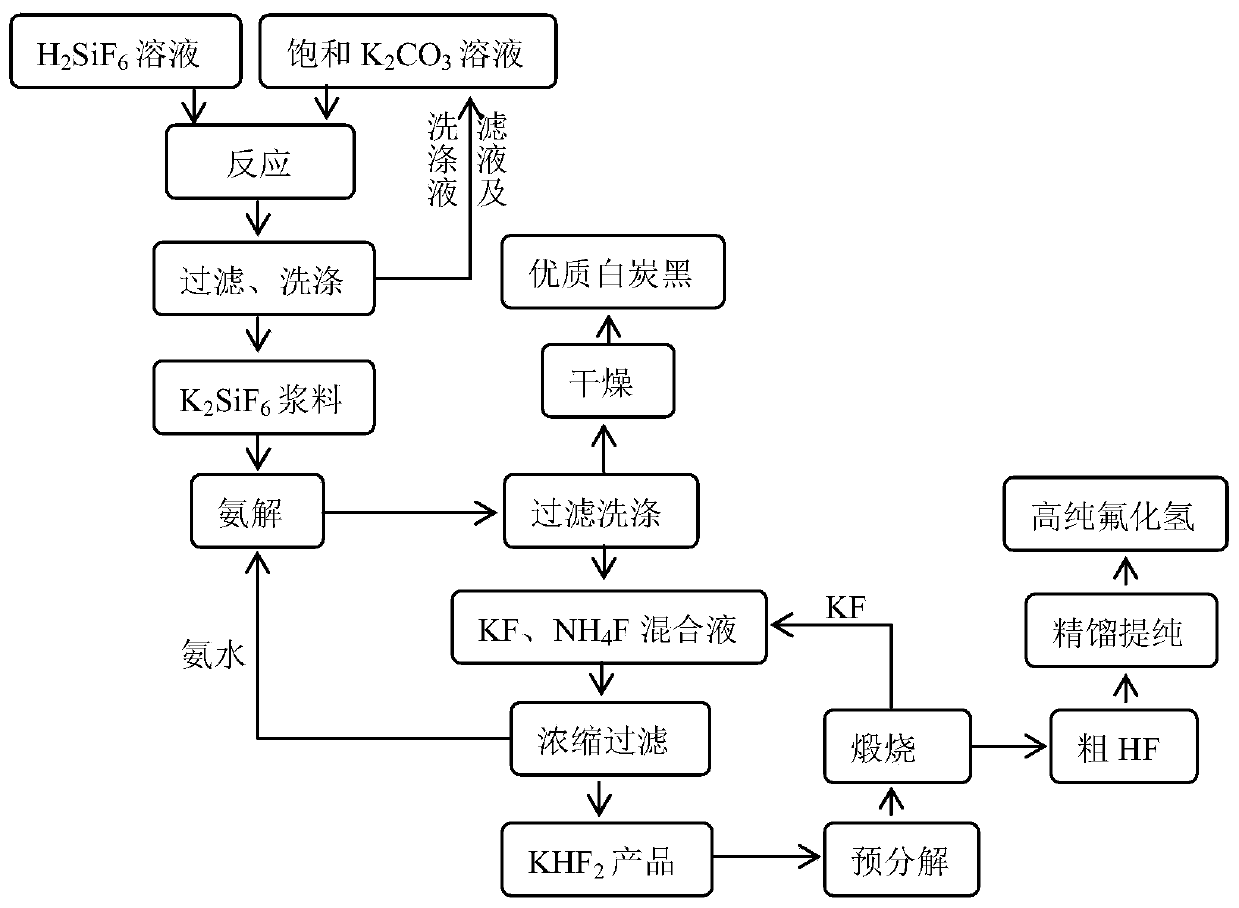
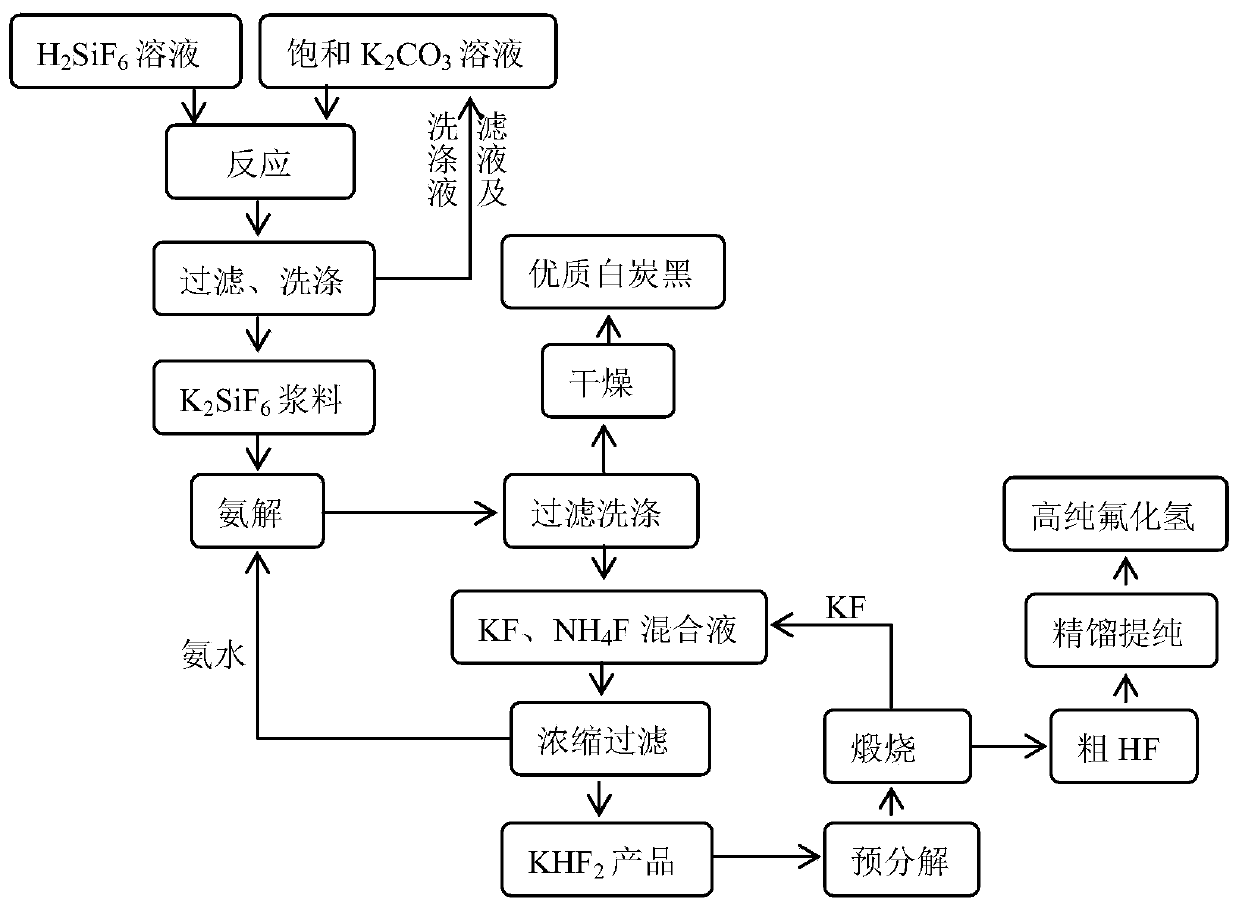
Method for producing anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and coproducing silica white from low-grade fluorine resources
ActiveCN102795601ALow impurity contentIncrease profitSilicaFluorine/hydrogen-fluorideSlurryHexafluorosilicic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and coproducing silica white from low-grade fluorine resources, which comprises the following steps: carrying out ammonolysis on a phosphate fertilizer byproduct fluosilicic acid solution to obtain an ammonium fluoride solution and silicon dioxide, washing the filter cake, and drying to obtain the silica white product, wherein the filtrate ammonium fluoride solution is used for the next production step; concentrating the ammonium fluoride solution, and carrying out pyrolysis to obtain an ammonium bifluoride solution and ammonia gas, wherein the ammonium bifluoride solution is used for the next production step, and the ammonia gas is used for ammonolysis of the fluosilicic acid solution; reacting the ammonium bifluoride solution and sodium fluoride to generate a sodium bifluoride slurry, and drying the filter cake to obtain sodium bifluoride, wherein the filtrate ammonium fluoride solution can be recycled; and carrying out pyrolysis on the sodium bifluoride to obtain crude anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and sodium fluoride, and purifying the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride to obtain the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride product, wherein the sodium fluoride can be recycled. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of accessible raw materials, low price, simple production technique and lower cost for the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride product, solves the bottleneck of environmental protection in the development of low-grade fluorine resource industry, and does not generate secondary pollution in the production process.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Surface treatment technique of CRT (cathode ray tube) lamp tube bracket metal stamping part
InactiveCN104404494AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesWorking fluidPhytic acid
The invention discloses a surface treatment technique of a CRT (cathode ray tube) lamp tube bracket stamping part, which comprises the following steps: 1) mixing 45 parts by mass of formic acid, 4 parts by mass of zinc nitrate, 4 parts by mass of sodium molybdate, 1.8 parts by mass of polyoxyethylene laurate, 3 parts by mass of sodium bifluoride, 4 parts by mass of phytic acid and 3 parts by mass of hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose, and reacting at 111 DEG C for 2 hours to obtain a metal surface treating agent; 2) mixing 8.9 parts by mass of metal surface treating agent with 93.5 parts by mass of water to obtain a surface treatment working fluid; and 3) heating the surface treatment working fluid to 53 DEG C, and immersing the metal stamping part in the surface treatment working fluid for 23 minutes. The surface treatment technique can enhance the oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance of the metal stamping part.
Owner:常熟市宏福塑料金属制品有限公司
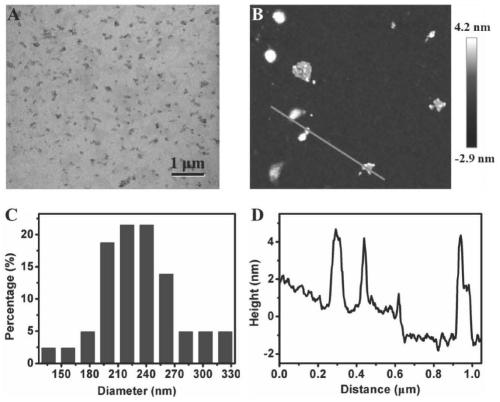
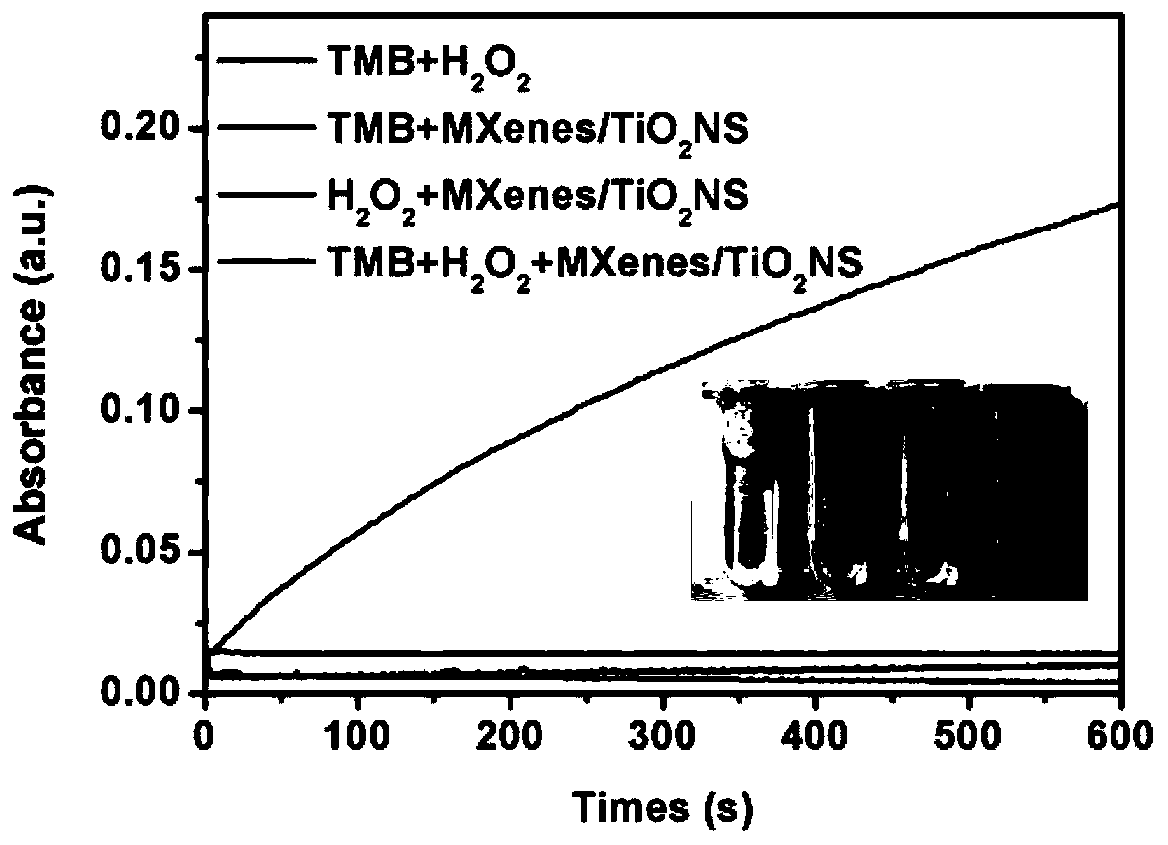
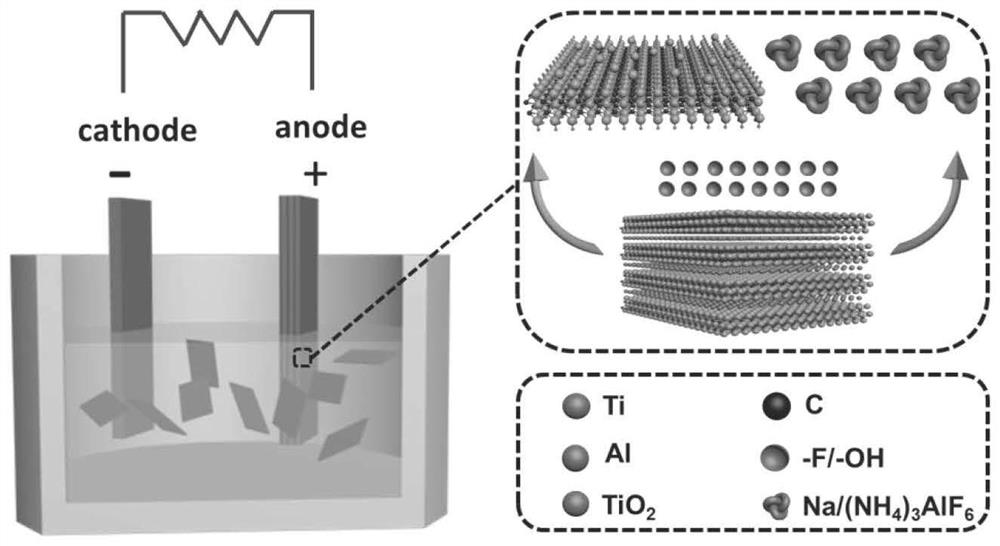
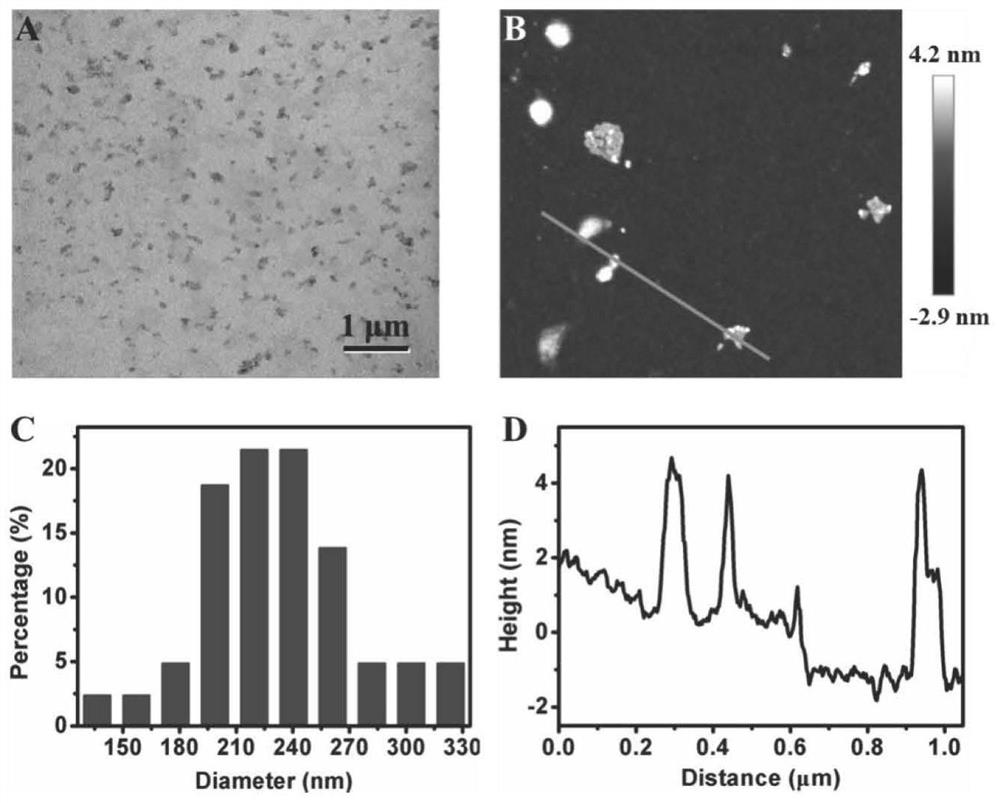
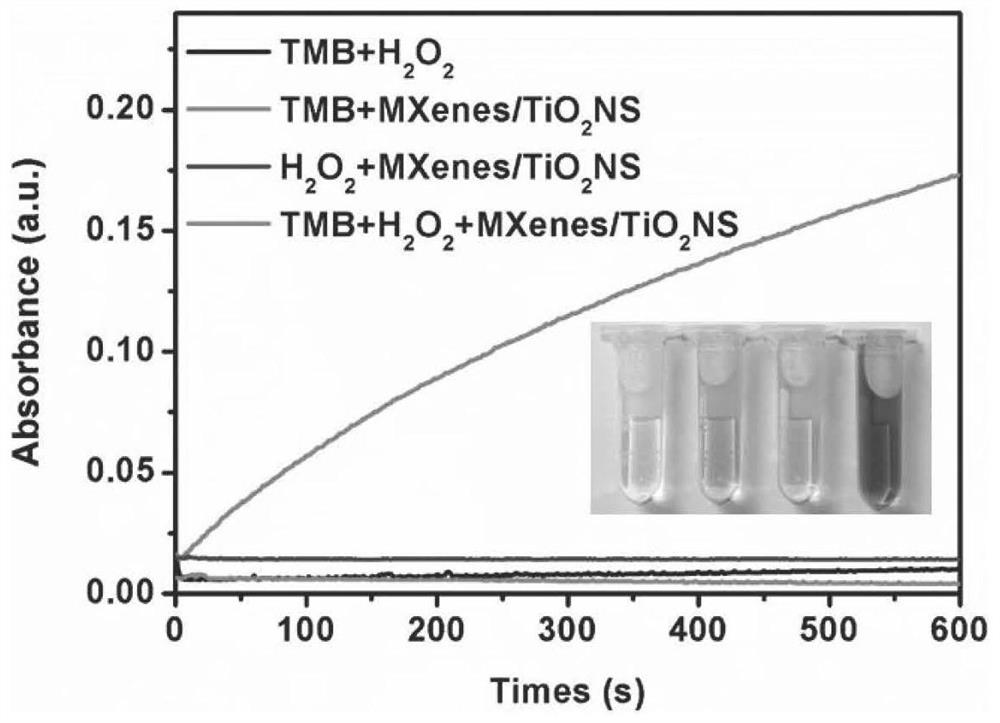
Method for preparing MXenes and derivative nanosheets by electrochemical process
ActiveCN109694074AGet quicklyHarm reductionMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisNon toxicity
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of MXenes and derivative nanosheets thereof, and relates to a method for preparing MXenes and derivative nanosheets by an electrochemical process. The method comprises the following steps: weighing 1.43 g of ammonium bifluoride powder, 0.93 g of ammonium fluoride powder and 1.55 g of sodium bifluoride powder, respectively placing above powders in a 50 mL beaker, taking and adding 50 mL of deionized water into the beaker containing the powders, placing the beaker on a magnetic stirrer, and completely dissolving the ammonium bifluoridepowder; fixing a large block of Ti3AlC2MAX to a clip electrode to form as an anode, using a Pt sheet electrode (with an area of above 1.0 cm<2>) as a cathode, applying a direct current constant voltage of 3 V, and performing a reaction for 6-24 h; and performing centrifugation to obtain the product. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of avoiding of a mixture of fluoride andhigh-concentration hydrofluoric acid or hydrochloric acid by using low-concentration ammonium bifluoride in the preparation process, non-toxicity, low hazards, elimination of potential hazardous processes, greenness and environmental protection; and electrolysis of the large block of MAX using the through electrochemical process shortens the reaction time and improves the peeling property.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Process for preparing kryocide
The invention relates to a method for producing cryolite, which takes electrolyte blocks of aluminum factories and sodium bifluoride as raw materials which are then reacted with each other in a solid phase. The method adopts a great deal of waste residue of the electrolytic aluminum factories - the electrolyte blocks as the raw materials, thereby the method increases a source of raw materials for producing villiaumite, relieves the dependency on fluorite, saves a large number of valuable resources, has low cost, greatly reduces the production cost, and relieves the ambient environmental pollution problem. Moreover, products generated during the reaction process of the method can be recycled, thereby the method greatly reduces the production cost to a certain degree, has good social benefit and economic benefit, and is easy to promote and apply.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Process for preparing kryocide
InactiveCN101318678AReduce manufacturing costSave resourcesAluminium fluoridesSocial benefitsElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for producing cryolite, which takes carbon residue of aluminum factories and sodium bifluoride as raw materials which are then reacted with each other in a solid phase. The raw materials of the method adopt a great deal of waste residue - the carbon residue of the electrolytic aluminum factories, and the cryolite product is prepared after flotation treatment and particularly refining treatment of products. The method increases a source of raw materials for producing villiaumite, relieves the dependency on fluorite, saves a large number of valuable resources, has low cost, greatly reduces the production cost, and relieves the ambient environmental pollution problem. Moreover, carbon powder containing about 10 percent of electrolyte obtained after flotationof the carbon residue can be dried and then used as auxiliary materials to be added when bottom paste is manufactured, and used for building a novel groove. Products generated during the reaction process of the method can be recycled, thereby the method greatly reduces the production cost to a certain degree, has good social benefit and economic benefit, and is easy to promote and apply.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
A brazing material outer coat and preparation method thereof, in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material, preparation method thereof, welding method and joint body
ActiveUS20200261995A1Improve wettabilityHigh activityWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesManganeseHigh activity
A brazing material outer coat and a method for preparing the same, an in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material and a method for preparing the same, a welding method and a joint body, wherein the in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material comprises a flux core and a brazing material outer coat wrapping the flux core, the brazing material outer coat comprises, in percentage by weight: silver Ag 20.0˜36.0%, copper Cu 35.0˜45.0%, zinc Zn 27.0˜37.0%, tin Sn 1.0˜3.0%, phosphorus P 0.1%˜0.5%, nickel Ni 0.5˜2.0%, germanium Ge 0.1˜0.3%, and lithium Li 0.1˜0.3%, the flux core comprises, in percentage by weight: elemental boron micropowder 5.0˜10.0%, sodium borohydride 5.0˜10.0%, potassium fluoroborate 15.0˜30.0%, boric anhydride 25.0˜40.0%, sodium fluoride 10.0˜30.0%, sodium bifluoride 2.0˜4.0%, and copper sulfate 1.0˜5.0%. The in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material in the present disclosure realizes self-reaction in a brazing process to coat a layer of copper film on a surface of a brazed metal, the core of the brazing material has good wettability, good flowability, self-brazing function, and zinc being hard to volatilize, the flux coat has high activity, low hygroscopicity, few carbon residues, good plasticity and toughness, etc. The present disclosure is particularly suitable for brazing pipeline components of stainless steel, manganese brass and so on.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
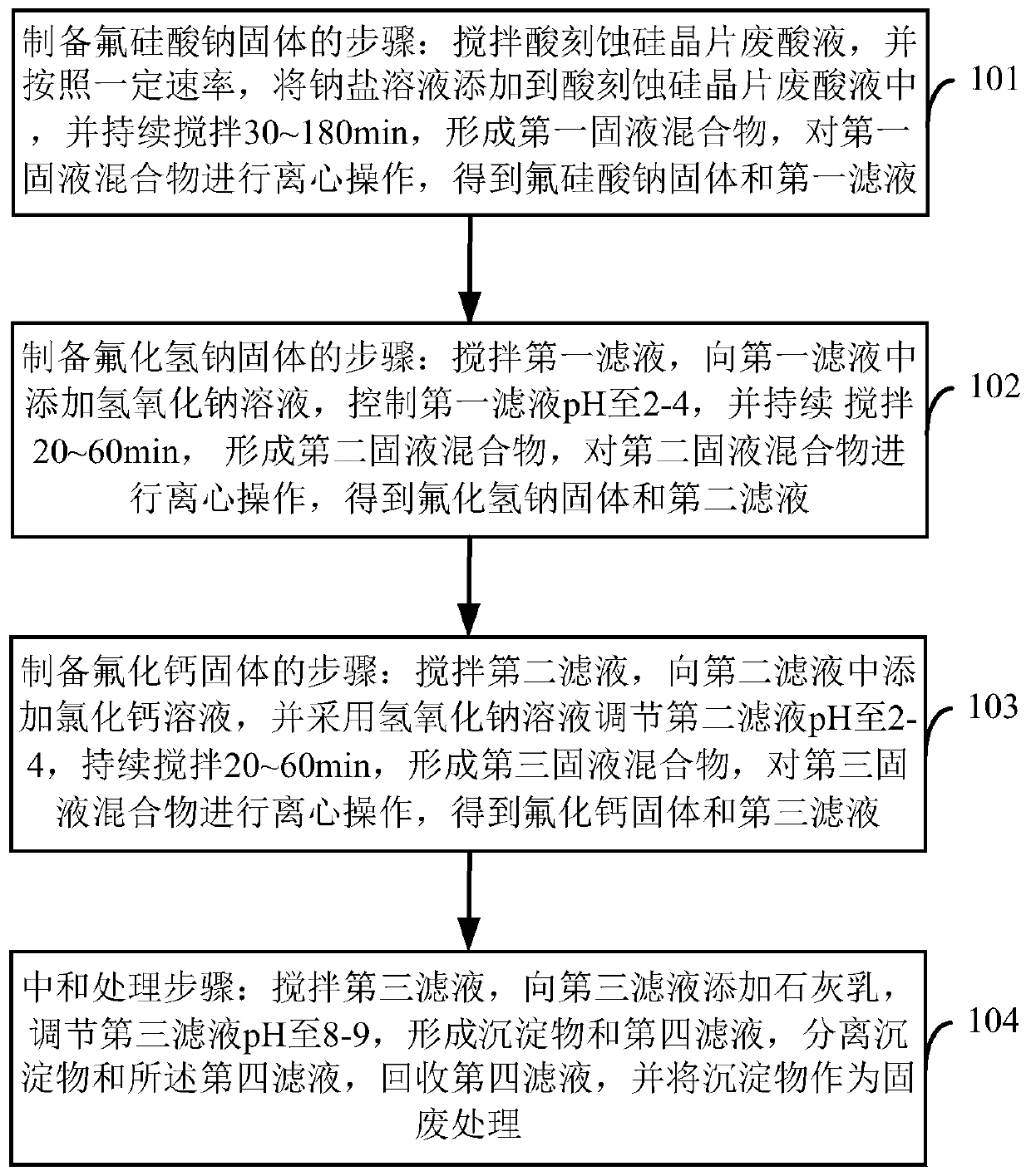
Acid etching silicon wafer waste acid liquid treatment method and system
InactiveCN110156062ARealize resource utilizationReduce productionCalcium/strontium/barium fluoridesAcid etchingHydrogen
The invention provides an acid etching silicon wafer waste acid liquid treatment method and system. The treatment method comprises the following steps: adding a sodium salt solution into an acid etching silicon wafer waste acid liquid, performing continuous stirring for 30-180 min to form a first solid-liquid mixture, and performing centrifugation to obtain a sodium fluorosilicate solid and a first filtrate; adding a sodium hydroxide solution into the first filtrate, controlling the pH to be 2-4, performing continuous stirring for 20-60 min to form a second solid-liquid mixture, and performingcentrifugation to obtain a sodium hydrogen difluoride solid and a second filtrate; adding a calcium chloride solution to the second filtrate, adjusting the pH to be 2-4, performing continuous stirring for 20-60 min to form a third solid-liquid mixture, and performing centrifugation to obtain a calcium fluoride solid and a third filtrate; and adding lime milk to the third filtrate, adjusting the pH to be 8-9, separating a precipitate and a fourth filtrate, recovering the fourth filtrate, and treating the precipitate as a solid waste. The provided scheme realizes the resource utilization of thewaste acid liquid.
Owner:北京环球中科水务科技股份有限公司
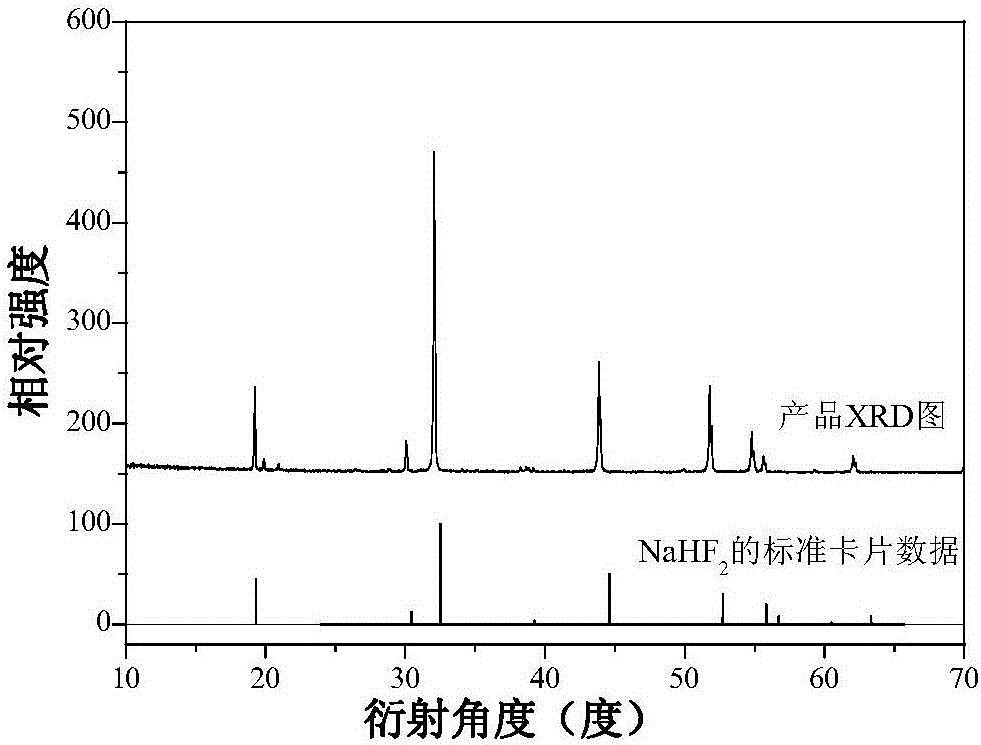
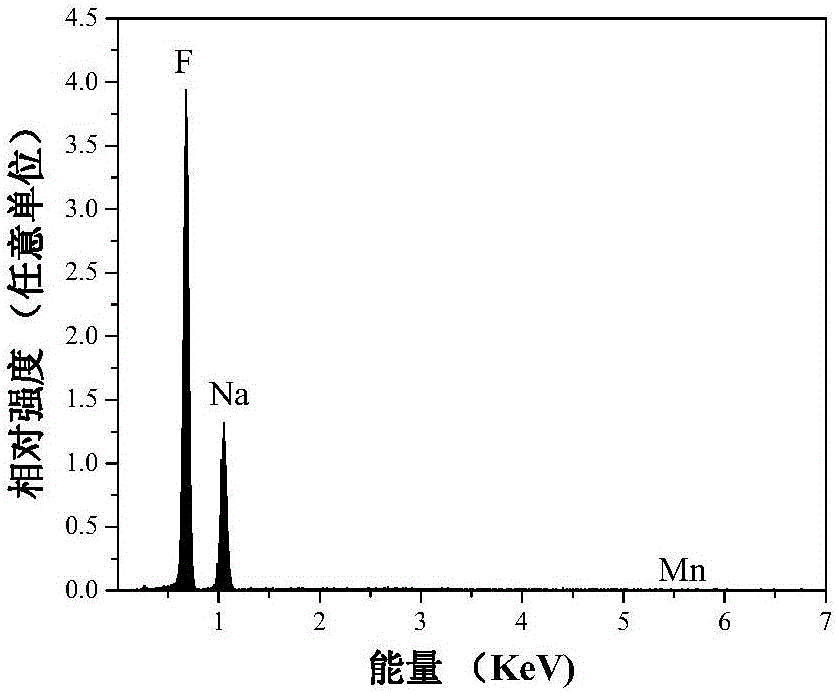
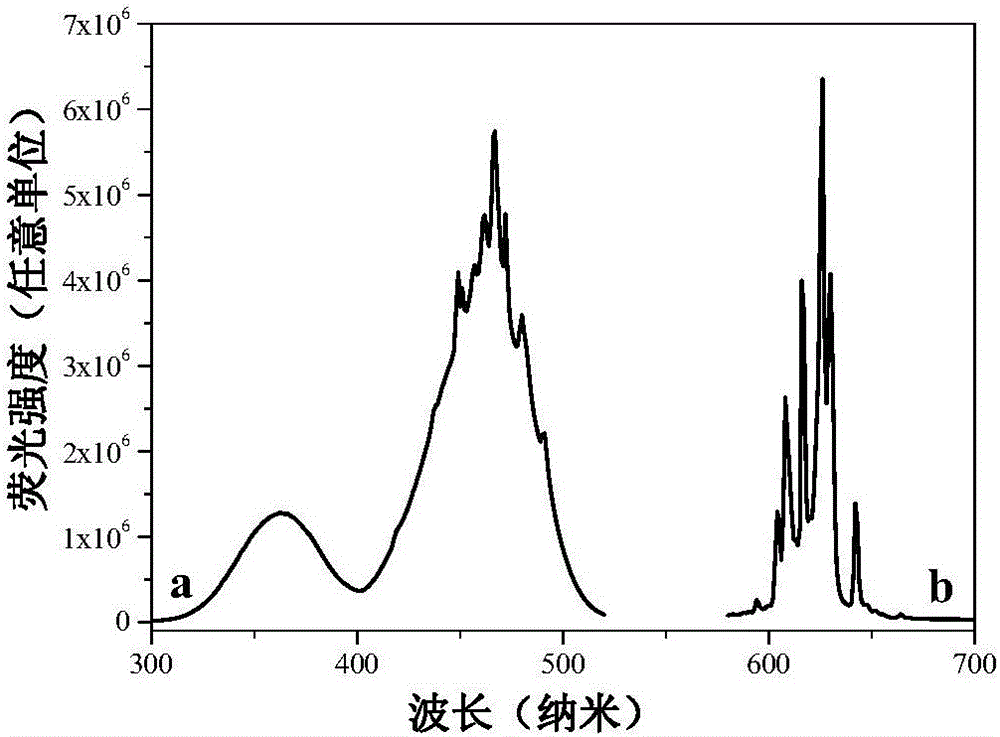
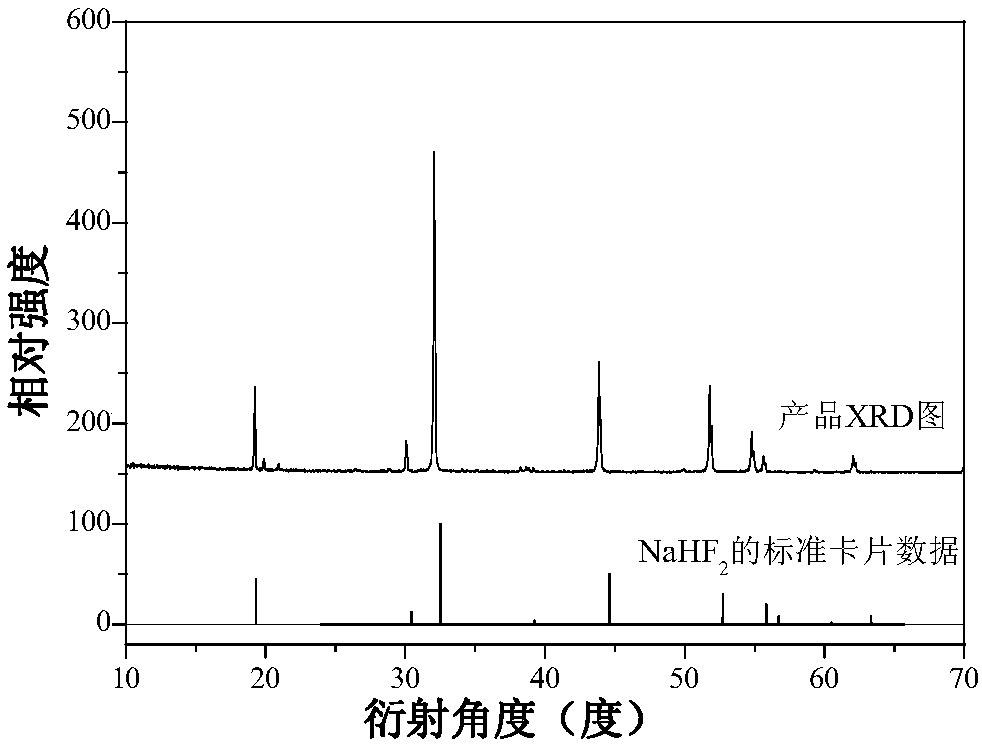
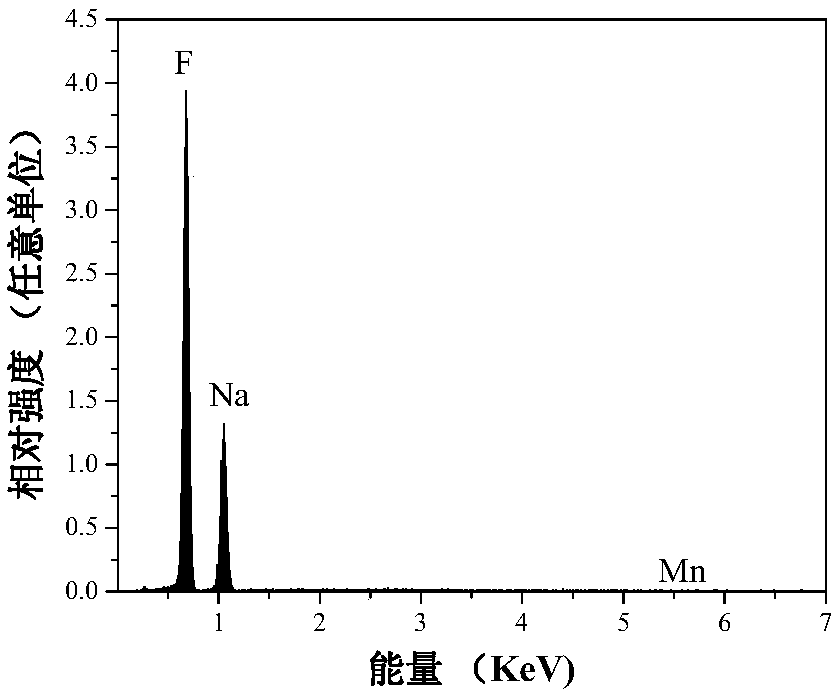
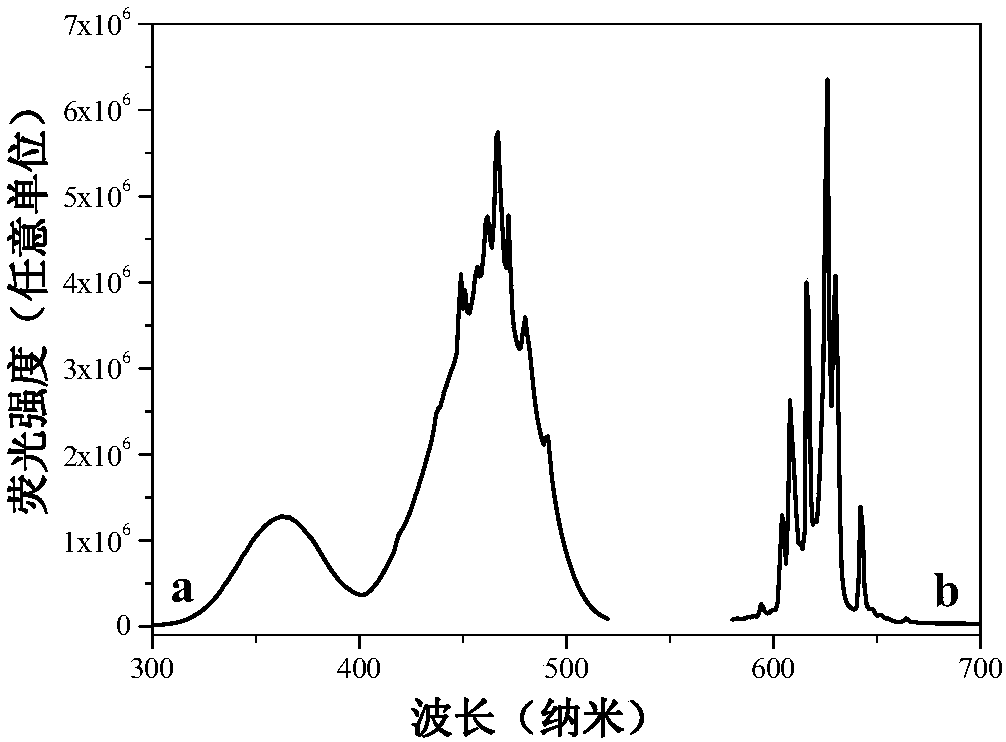
Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material and method for preparing same
ActiveCN106318381AEffective absorptionSimple ingredientsLuminescent compositionsFiltrationRare earth
The invention discloses a Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material and a method for preparing the same. Chemical composition of the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material is NaHF<2>:Mn<4+>. The Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material is made of raw materials including 15-30 mL of HF (with the concentration of wt 40%), 1*10<-4>-9*10<-4> mol of K<2>MnF<6> solid and 0.01-0.1 mol of NaF. The method includes adding the raw materials into deionized water to obtain liquid with the total volume of 40 mL; carrying out stirring reaction on the liquid at the normal temperature for 0.5-2 hours; carrying out suction filtration on reaction products; naturally drying the reaction products at the normal temperature to obtain white powder. The Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material and the method have the advantages that bright red light can be emitted by the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material under ultraviolet lamps, the maximum excitation bands of the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material can be completely matched with spectra of blue light emitted by blue light chips of white light LEDs, and an emission spectrum of the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material comprises seven red light emission peaks positioned at four locations of 595-643 nm; the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material can be possibly applied to a white light LED with two fundamental colors, so that color rendering indexes of the white light LED can be increased; the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material does not contain rare earth, the method is simple, and accordingly the Mn<4+>-doped sodium bifluoride red light material and the method are applicable to industrial production.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for producing anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and coproducing silica white from low-grade fluorine resources
ActiveCN102795601BLow impurity contentIncrease profitSilicaFluorine/hydrogen-fluorideHexafluorosilicic acidSlurry
The invention discloses a method for producing anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and coproducing silica white from low-grade fluorine resources, which comprises the following steps: carrying out ammonolysis on a phosphate fertilizer byproduct fluosilicic acid solution to obtain an ammonium fluoride solution and silicon dioxide, washing the filter cake, and drying to obtain the silica white product, wherein the filtrate ammonium fluoride solution is used for the next production step; concentrating the ammonium fluoride solution, and carrying out pyrolysis to obtain an ammonium bifluoride solution and ammonia gas, wherein the ammonium bifluoride solution is used for the next production step, and the ammonia gas is used for ammonolysis of the fluosilicic acid solution; reacting the ammonium bifluoride solution and sodium fluoride to generate a sodium bifluoride slurry, and drying the filter cake to obtain sodium bifluoride, wherein the filtrate ammonium fluoride solution can be recycled; and carrying out pyrolysis on the sodium bifluoride to obtain crude anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and sodium fluoride, and purifying the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride to obtain the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride product, wherein the sodium fluoride can be recycled. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of accessible raw materials, low price, simple production technique and lower cost for the anhydrous hydrogen fluoride product, solves the bottleneck of environmental protection in the development of low-grade fluorine resource industry, and does not generate secondary pollution in the production process.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Epoxy resin cable material and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105331051AReasonable formulaImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesEpoxyHydrogen fluoride
The invention discloses an epoxy resin cable material and a preparing method and application thereof. The epoxy resin cable material is prepared from, by weight, 68-75 parts of epoxy resin, 33-39 parts of trogopterus dung, 10-16 parts of bentonite, 5-10 parts of titanate coupling agents, 43-48 parts of polypropylene resin, 10-16 parts of talcum powder and 3-8 parts of sodium hydrogenfluoride. The preparing method includes the steps that the trogopterus dung is treated to obtain trogopterus dung extrct; the epoxy resin is put in ethyl alcohol to be treated, then the talcum powder is added, temperature is lowered, sodium hydrogenfluoride and the bentonite are added, the polypropylene resin and the titanate coupling agents are added, the trogopterus dung extrct is added after treatment is carried out, and the epoxy resin cable material is obtained after mixing and pelleting. The preparing method is simple and convenient to operate, the composition raw material formula is reasonable, and the prepared cable material has the advantages of being high in mechanical property, resistant to cold, high temperature and abrasion, high in flame retardant property and soft, has an electric insulation function and is low in fume and nontoxic when being combusted.
Owner:刘可
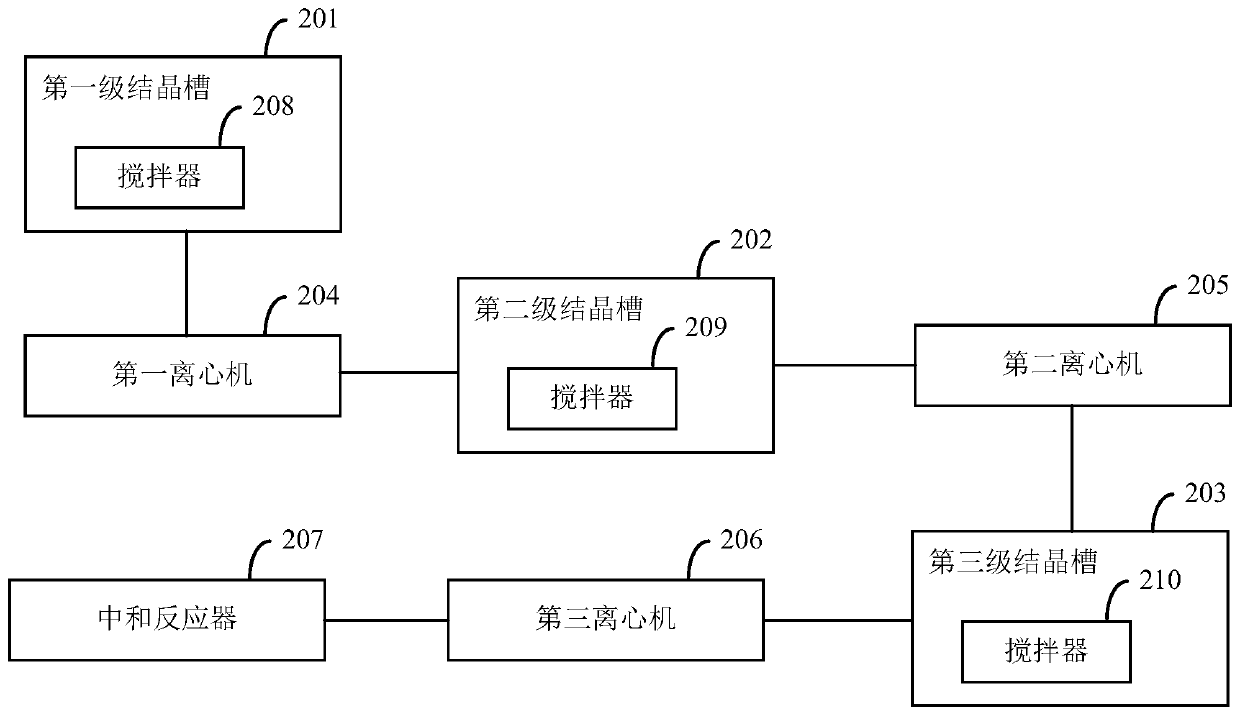
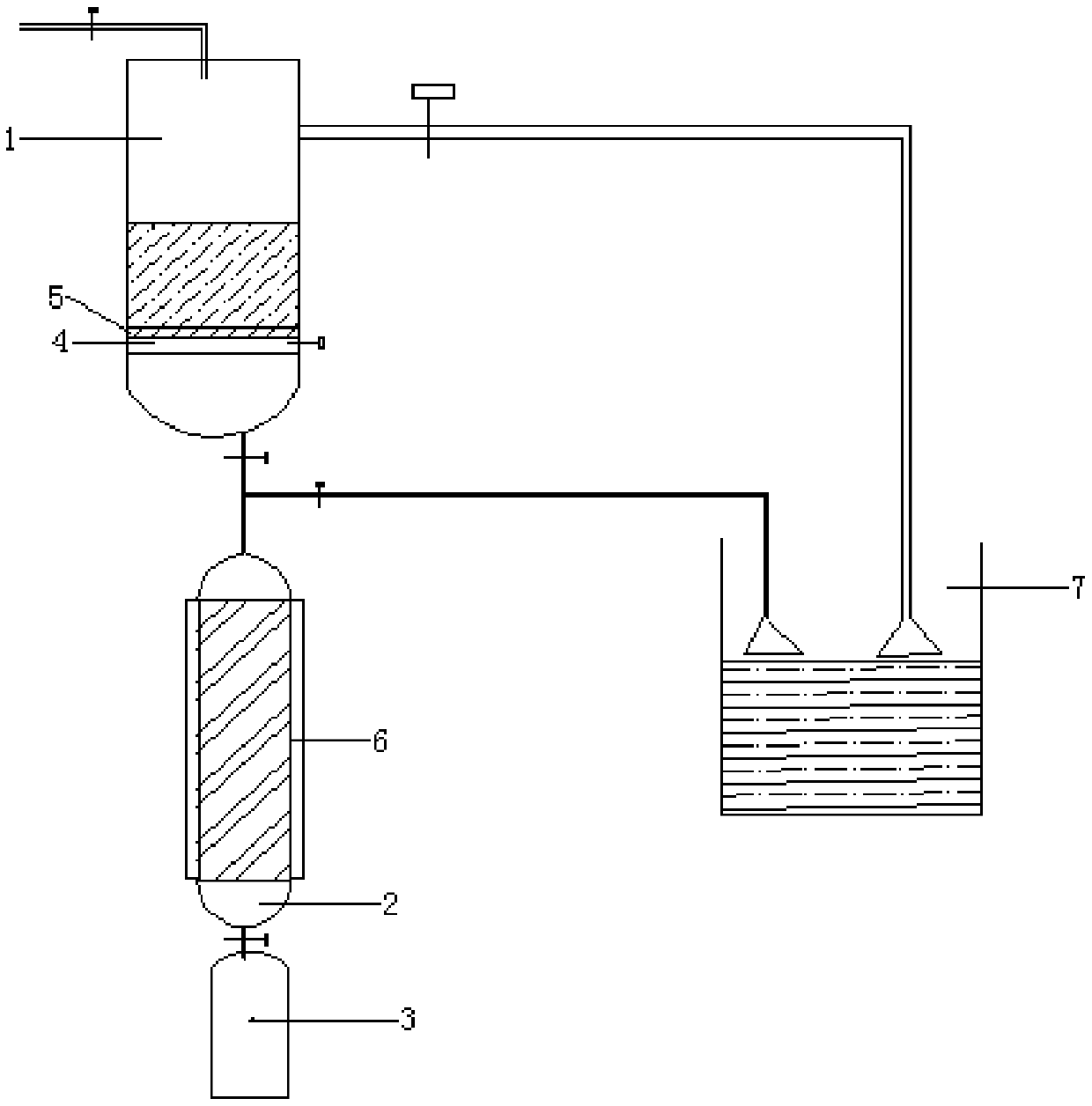
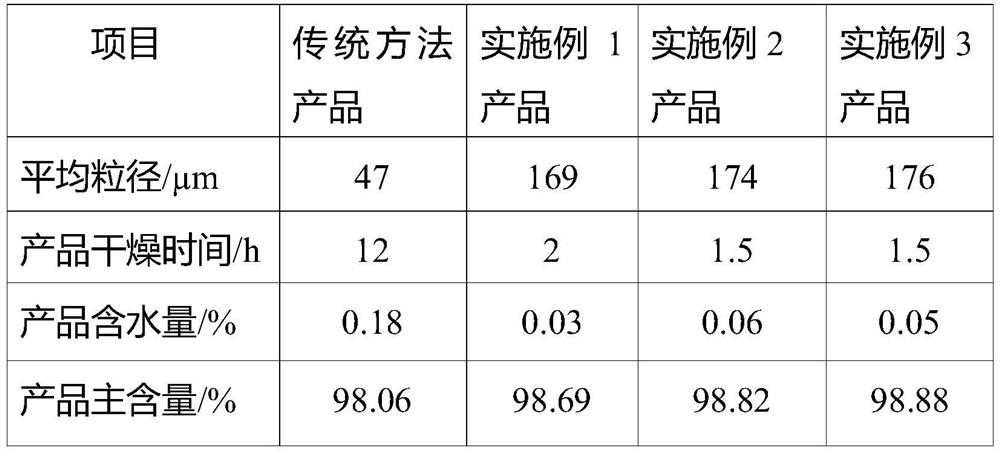
Preparation method of large-particle sodium bifluoride
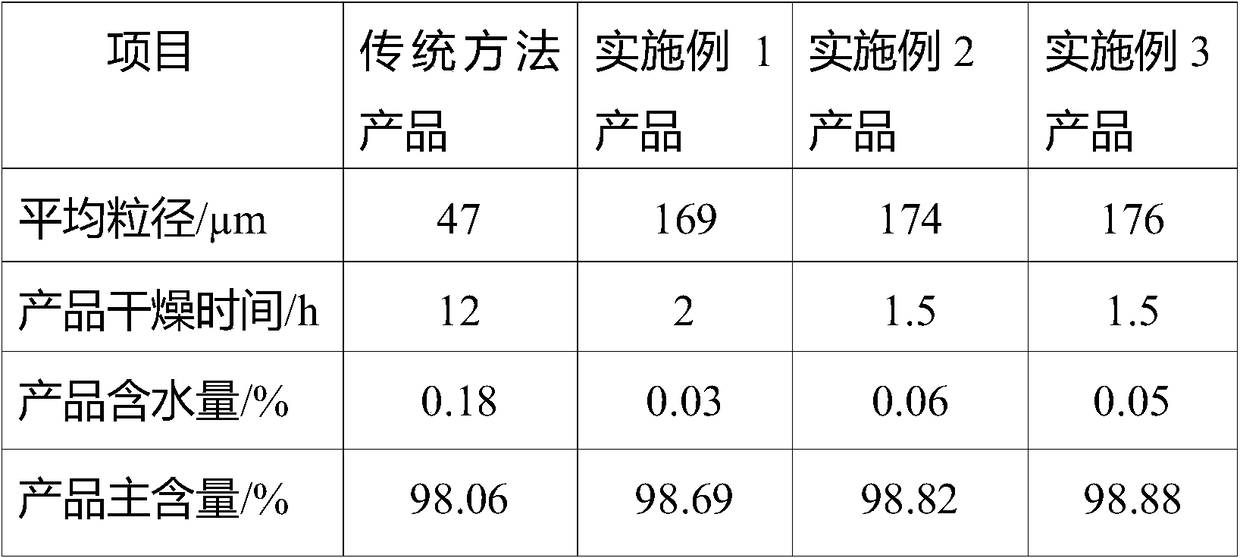
ActiveCN109019633ASolve the requestSolve corrosionAlkali metal fluoridesAlkali metal halide formation shapeHydrofluoric acidSeed crystal
The invention provides a preparation method of large-particle sodium bifluoride. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a sodium carbonate solution dissolving sodium carbonate in water to obtain the sodium carbonate solution; (2) carrying out a synthesis reaction on the sodium bifluoride: adding an appropriate amount of sodium bifluoride seed crystals into a reactor, adding the sodium carbonate solution, obtained in the step (1), and hydrofluoric acid into the reactor at the same time while stirring, and continuously stirring for carrying out a reaction after the end of feeding so as to obtain suspension; (3) filtering: filtering the suspension obtained in the step (2) so as to obtain a sodium bifluoride filter cake; (4) drying: drying the sodium bifluoride filter cake obtained in the step (3) so as to obtain the large-particle sodium bifluoride product. The method provided by the invention solves the problems that the sodium bifluoride product prepared by the traditional preparation method is fine in particles, high in drying difficulty and poor in operating environment.
Owner:福建省漳平市九鼎氟化工有限公司
Detergent for removing gypsum residues on dewaxing handicraft
ActiveCN104017677ALong-term maintenance and useEfficient removalSurface-active non-soap compounds and soap mixture detergentsCleansing AgentsFluoboric acid
The invention relates to a detergent for removing gypsum residues on a dewaxing handicraft. The stock solution is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 1-30 parts of penetrant, 5-50 parts of precipitant, 1-4.4 parts of pH regulator, 0.1-0.3 part of corrosion inhibitor, 0.1-1 part of surfactant and 30-92.7 parts of water. The penetrant is one or mixture of more of the following acids or salts capable of providing free fluorine ions: hydrofluoric acid, and sodium salt or potassium salt or ammonium salt thereof; fluoboric acid, and potassium salt or sodium salt or ammonium salt thereof; sodium bifluoride; potassium hydrogen fluoride; and ammonium acid fluoride. The detergent has favorable gypsum residue removal effect, does not generate the volatile toxic gas hydrofluoric acid, and has the characteristics of environmental protection, high economy and high efficiency.
Owner:深圳市汇利龙科技有限公司
Surface treatment process for framework stamping part of high-frequency tuner
The invention discloses a surface treatment process for a framework stamping part of a high-frequency tuner. The surface treatment process comprises the following steps: (1) in parts by mass, mixing 7.5 parts of zinc nitrate, 2.1 parts of polyoxyethylene laurate, 1.8 parts of sodium hydrogenfluoride, 3.4 parts of sodium molybdate, 2.6 parts of cocoanut fatty acid diethanolamide, 0.3 parts of phytic acid and 1.9 parts of polysiloxane polyether copolymer, and reacting at 105 DEG C for 125 minutes to obtain a metal surface treatment agent; (2) mixing 8.5 parts of the metal surface treatment agent with 32 parts of water to obtain a surface treatment working solution; (3) heating the surface treatment working solution to 65 DEG C, and putting the metal stamping part into the surface treatment working solution for 35 minutes. The surface treatment process can improve the oxidation resistance and the corrosion resistance of the metal stamping part.
Owner:江苏新华明机械制造实业有限公司
Lubricating treatment fluid for stainless steel subjected to oxalate treatment
InactiveCN104109576AGood effectImprove the lubrication effectLubricant compositionOxalateSulfite salt
The invention provides a lubricating treatment fluid for stainless steel subjected to oxalate treatment, relating to the technical field of lubricating treatment fluids. The lubricating treatment fluid is composed of oxalic acid, ammonium molybdate, sodium bifluoride, water, sodium sulfite, iron trisulfate and sodium bisulfate. When the treatment fluid is in use, the treatment temperature is kept at 90-95 DEG C, and the treatment time can not exceed 20 minutes and is preferably controlled within 15-20 minutes. The lubricating treatment fluid has obvious lubricating effect, can effectively enhance the yield and production efficiency of the product, and has more obvious effect on the stainless steel product subjected to oxalate treatment.
Owner:ANHUI CHENGYOU AUTO PARTS MFG
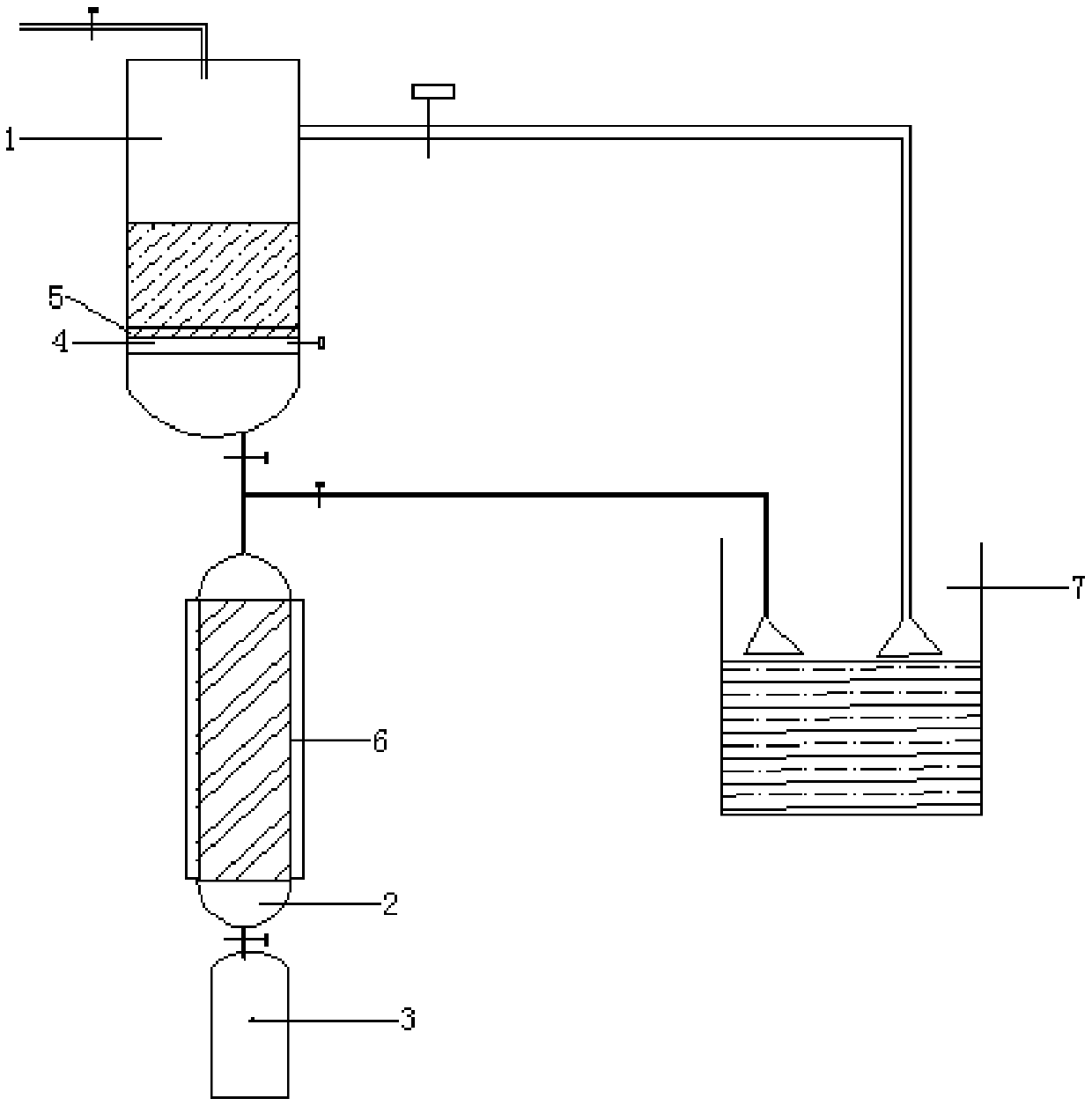
A kind of preparation method of hydrogen fluoride, the preparation method of hydrofluoric acid
The invention relates to a preparation method for hydrogen fluoride and a preparation method of hydrofluoric acid, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of hydrogen fluoride. The preparation method for hydrogen fluoride includes the following steps of: heating bifluoride solid to 150-450 DEG C so as to enable 10-40% of the bifluoride solid to be pre-decomposed and obtain paste; and then calcining the paste at 500-550 DEG C for decomposition so as to obtain fluoride and crude hydrogen fluoride gas, wherein the bifluoride is sodium bifluoride or potassium bifluoride. According to thepreparation method of hydrogen fluoride, incomplete decomposition caused by melting of the bifluoride can be reduced by heating the bifluoride solid for pre-decomposition and then performing high-temperature calcination, the rate of the decomposition reaction is accelerated, and the production efficiency is improved; meanwhile, by heating the bifluoride solid for pre-decomposition at a low temperature before high-temperature calcination, corrosion, which is caused by the hydrogen fluoride gas generated by the decomposition due to moisture or water absorption of the bifluoride solid, to equipment can be reduced when high-temperature calcination is performed.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Perfluoropolyether carboxylic acid with low HF content and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111116347AImprove work efficiencyGas treatmentPreparation from carboxylic acid halideChemical industryHydrogen fluoride
The invention belongs to the field of fluorine chemical industry. The invention relates to a preparation method of perfluoropolyether carboxylic acid with low HF content. The preparation method comprises the following steps that a saturated sodium fluoride aqueous solution is dropwise added into a reaction tank containing perfluoropolyether acyl fluoride at the speed of 1-10 ml / min, a product flows into an absorption tower containing a NaF recycling agent to absorb HF after the reaction is finished, and therefore perfluorocarboxylic acid with the HF content smaller than 0.1% is obtained. Perfluoropolyether acyl fluoride reacts with a saturated sodium fluoride aqueous solution to generate perfluoropolyether carboxylic acid and hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen fluoride and sodium fluoride generate sodium bifluoride which is less dissolved in water, sodium bifluoride is filtered, dried and heated (160 DEG C) to obtain sodium fluoride again, and sodium fluoride can be recycled.
Owner:TIANJIN CHANGLU CHEM NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Acid washing process for aluminum alloy profiles
InactiveCN110878417ANot easy to appear "hanging dust" phenomenonAvoid yellowingHydrogen fluorideAcid washing
The invention discloses an acid washing process for aluminum alloy profiles. The process includes the following steps: a, immersing the aluminum alloy profiles in an acid solution, and performing ultrasonic acid washing to obtain an A product, wherein the ultrasonic frequency is 50-60 kHz, and the acid washing time is 1-3 min; b, washing the A product by using a high-pressure water stream at a flow rate of 30-40 m / s to obtain a B product; and c, drying the B product to obtain a finished product, wherein in the step a, the acid solution is composed of the following materials in parts by weight:50-80 parts of dilute nitric acid, 10 parts of hydrogen peroxide and 1 part of sodium bifluoride, the concentration of the nitric acid solution is 3 mol / L, and the concentration of the hydrogen peroxide is 30%. The aluminum alloy profiles processed by the process have the advantage that a paint surface is not easy to peel off after paint spraying.
Owner:湖州织里宝丰铝业有限公司
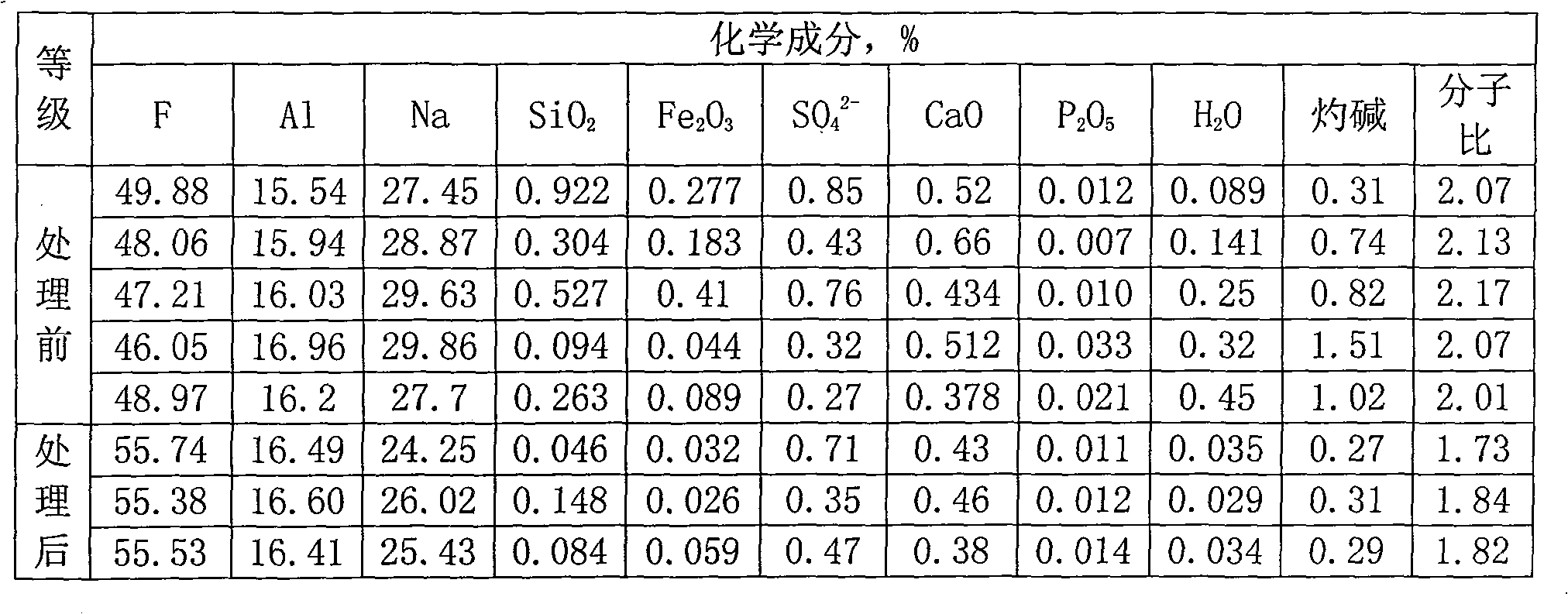
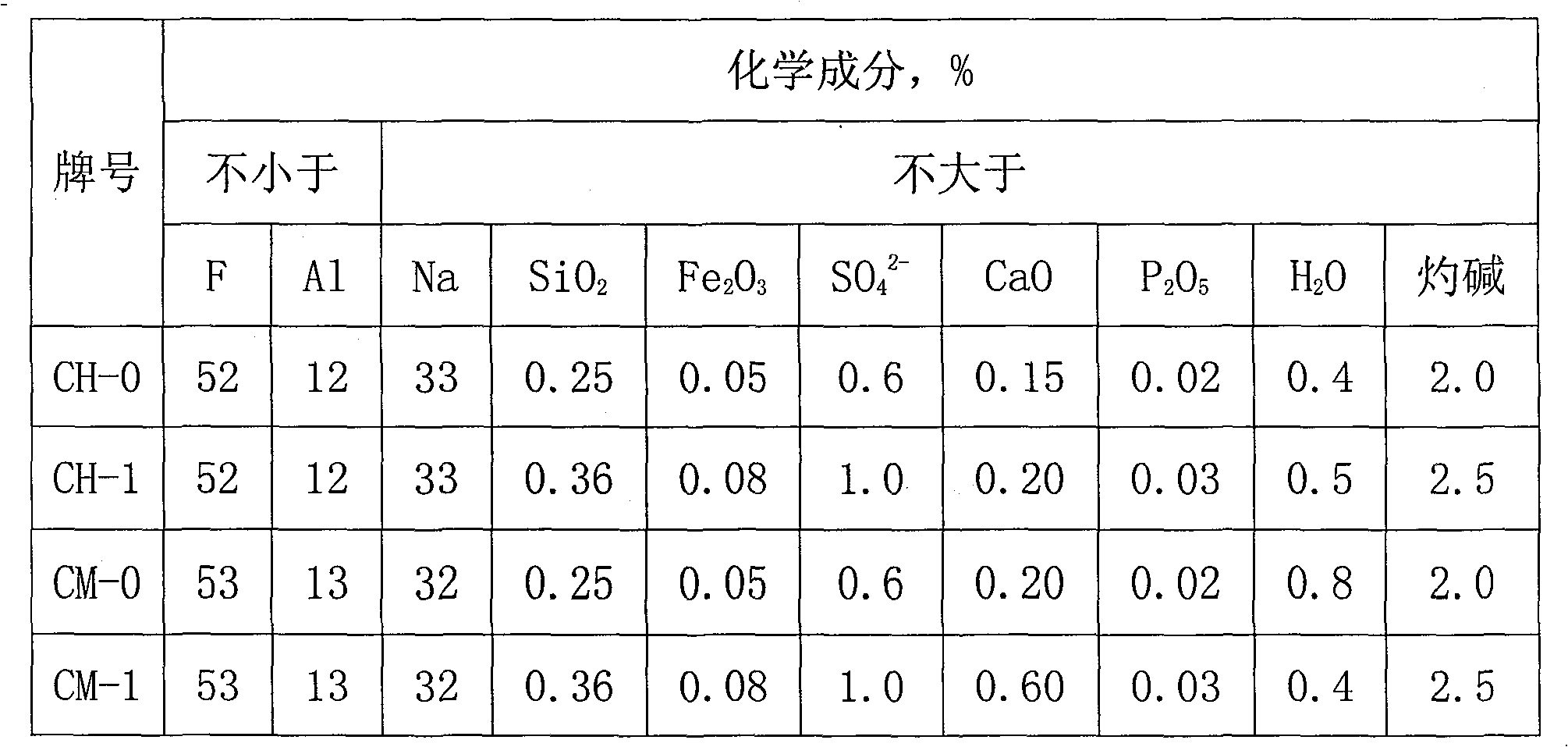
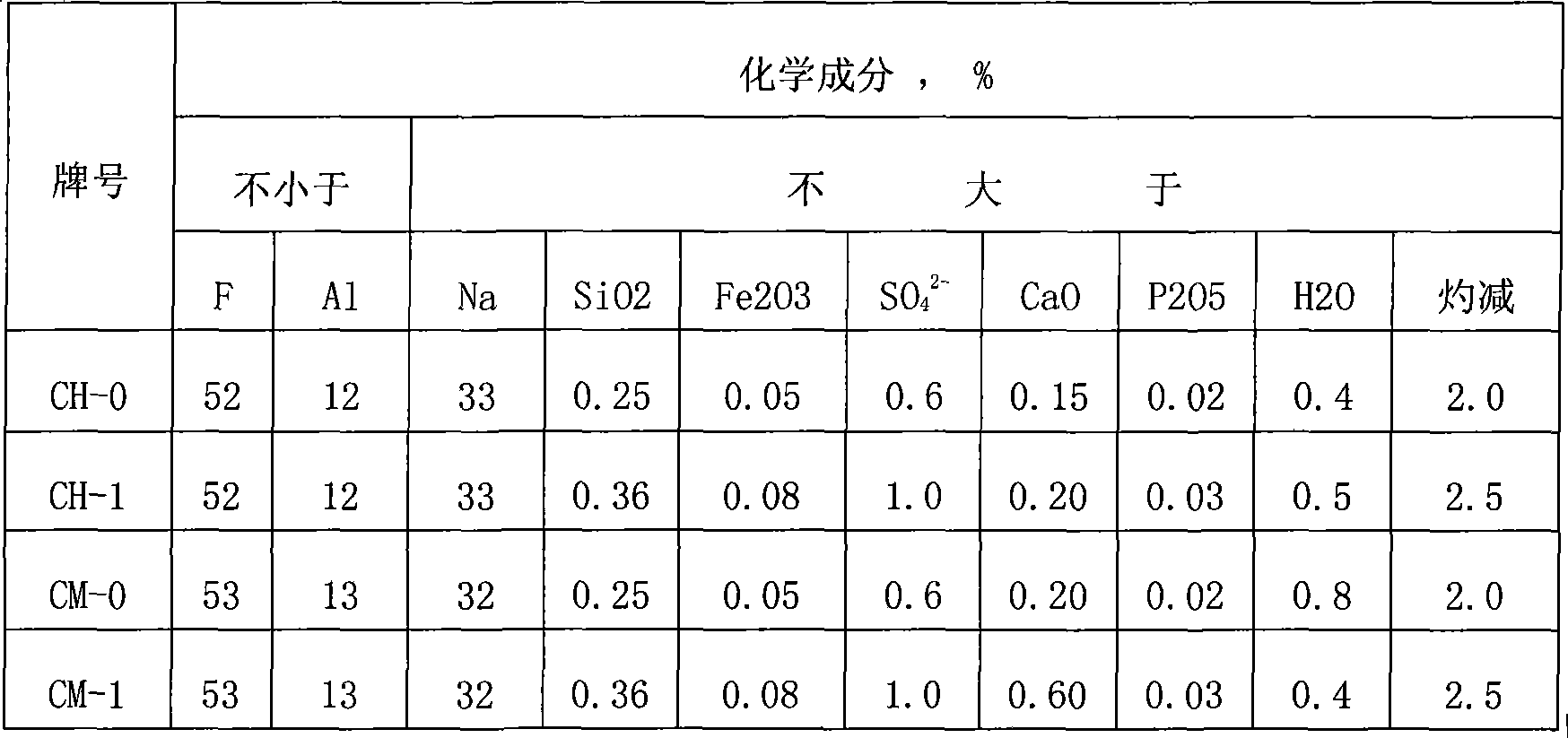
Technology of preparing sodium hydrogen fluoride by using fluosilicic acid, a by-product of phosphorus chemical industry
ActiveCN106241834BWide variety of sourcesLow costAlkali metal fluoridesChemical industryChemical reaction
The invention discloses a technique of preparing sodium bifluoride by using the phosphorus chemical industry byproduct fluorosilicic acid and belongs to the field of phosphorus chemical industry. The phosphorus chemical industry byproduct fluorosilicic acid is used as a raw material and prepared into the sodium bifluoride via the steps of (1), adding fluorosilicic acid solution into sodium fluoride solid, stirring, and press-filtering to obtain the filtrate low-concentration hydrofluoric acid and the filter cake sodium fluosilicate; (2), adding the sodium fluoride solid into the low-concentration hydrofluoric acid solution at a stoichiometric ratio, stirring well, charging into a concentrating system, cooling and crystallizing concentrate, drying obtained solid to obtain finished sodium bifluoride; (3), adding the sodium fluosilicate solid of step (1) into sodium carbonate solution for chemical reaction, standing for layering after reaction is over to obtain the upper layer silica gel suspension and the lower layer sodium fluoride solid, press-filtering the lower layer sodium fluoride to obtain sodium fluoride solid that is used as a raw material for the steps (1) and (2).
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
A kind of preparation method of large particle sodium bifluoride
ActiveCN109019633BAlkali metal fluoridesAlkali metal halide formation shapeHydrogen fluoridePhysical chemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of large-particle sodium bifluoride. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a sodium carbonate solution dissolving sodium carbonate in water to obtain the sodium carbonate solution; (2) carrying out a synthesis reaction on the sodium bifluoride: adding an appropriate amount of sodium bifluoride seed crystals into a reactor, adding the sodium carbonate solution, obtained in the step (1), and hydrofluoric acid into the reactor at the same time while stirring, and continuously stirring for carrying out a reaction after the end of feeding so as to obtain suspension; (3) filtering: filtering the suspension obtained in the step (2) so as to obtain a sodium bifluoride filter cake; (4) drying: drying the sodium bifluoride filter cake obtained in the step (3) so as to obtain the large-particle sodium bifluoride product. The method provided by the invention solves the problems that the sodium bifluoride product prepared by the traditional preparation method is fine in particles, high in drying difficulty and poor in operating environment.
Owner:福建省漳平市九鼎氟化工有限公司
Process for preparing kryocide
The invention relates to a method for producing cryolite, which takes electrolyte blocks of aluminum factories and sodium bifluoride as raw materials which are then reacted with each other in a solid phase. The method adopts a great deal of waste residue of the electrolytic aluminum factories - the electrolyte blocks as the raw materials, thereby the method increases a source of raw materials forproducing villiaumite, relieves the dependency on fluorite, saves a large number of valuable resources, has low cost, greatly reduces the production cost, and relieves the ambient environmental pollution problem. Moreover, products generated during the reaction process of the method can be recycled, thereby the method greatly reduces the production cost to a certain degree, has good social benefit and economic benefit, and is easy to promote and apply.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Preparation of racemic cis 8-benzyl-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane
ActiveCN112110916BHigh selectivityReduce dosageOrganic chemistryCatalyst protectionNonanePtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation process for racemic cis-8-benzyl-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane, which comprises the following steps: Step S1: preparing an attachment carrier: immersing a solid carrier into Prepare an attachment carrier in a roughening solution, the roughening solution is a sodium hydroxide solution or a sodium bifluoride solution; Step S2: Prepare a platinum dehydrogenation catalyst: use an impregnation method to support the precious metal platinum by impregnating it into an impregnation solution containing noble metal ions On the solid carrier, in parts by weight, the impregnation solution includes 30-40 parts of chloroplatinic acid and 1-5 parts of rice furoic acid; step S3: piperidine ring dehydrogenation reaction; step S4: high-pressure hydrogenation reaction. The invention provides a method for preparing racemic cis-8-benzyl-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane with high selectivity, high catalytic efficiency and high product purity.
Owner:SHAYANG QINJIANG CHEM
Brazing material outer coat and preparation method thereof, in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material, preparation method thereof, welding method and joint body
ActiveUS10987747B2Improve reliabilityImprove stabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesManganeseHigh activity
A brazing material outer coat and a method for preparing the same, an in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material and a method for preparing the same, a welding method and a joint body, wherein the in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material comprises a flux core and a brazing material outer coat wrapping the flux core, the brazing material outer coat comprises, in percentage by weight: silver Ag 20.0˜36.0%, copper Cu 35.0˜45.0%, zinc Zn 27.0˜37.0%, tin Sn 1.0˜3.0%, phosphorus P 0.1%˜0.5%, nickel Ni 0.5˜2.0%, germanium Ge 0.1˜0.3%, and lithium Li 0.1˜0.3%, the flux core comprises, in percentage by weight: elemental boron micropowder 5.0˜10.0%, sodium borohydride 5.0˜10.0%, potassium fluoroborate 15.0˜30.0%, boric anhydride 25.0˜40.0%, sodium fluoride 10.0˜30.0%, sodium bifluoride 2.0˜4.0%, and copper sulfate 1.0˜5.0%. The in-situ synthetic metal-coated flux-cored silver brazing material in the present disclosure realizes self-reaction in a brazing process to coat a layer of copper film on a surface of a brazed metal, the core of the brazing material has good wettability, good flowability, self-brazing function, and zinc being hard to volatilize, the flux coat has high activity, low hygroscopicity, few carbon residues, good plasticity and toughness, etc. The present disclosure is particularly suitable for brazing pipeline components of stainless steel, manganese brass and so on.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Method for preparing sodium hydrogen fluoride from phosphorus chemical byproduct fluosilicic acid
In order to overcome the defects in the prior art, the invention provides a method for preparing sodium hydrogen fluoride from a phosphorus chemical byproduct fluosilicic acid, which comprises the following steps of: S1, reacting the phosphorus chemical byproduct fluosilicic acid with ammonia water, and carrying out solid-liquid separation after the reaction is completed, thereby obtaining a solid-phase component A and a liquid-phase component A; S2, reacting the liquid-phase component A with slaked lime, and carrying out three-phase separation after the reaction is completed, so as to obtaina solid-phase component B, a liquid-phase component B and a gas-phase component A; S3, reacting the solid-phase component B with concentrated sulfuric acid, carrying out three-phase separation after the reaction is completed, so as to obtain a solid-phase component C, a liquid-phase component C and a gas-phase component B; S4, reacting the gas-phase component B with a saturated sodium carbonate solution, and carrying out three-phase separation after the reaction is completed to obtain a solid-phase component D, a liquid-phase component D and a gas-phase component C; and S5, sequentially dryingand crushing the solid-phase component D to obtain a sodium hydrogen fluoride product. Fluorosilicic acid can be prepared into sodium hydrogen fluoride, and the vacancy in the prior art is made up.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
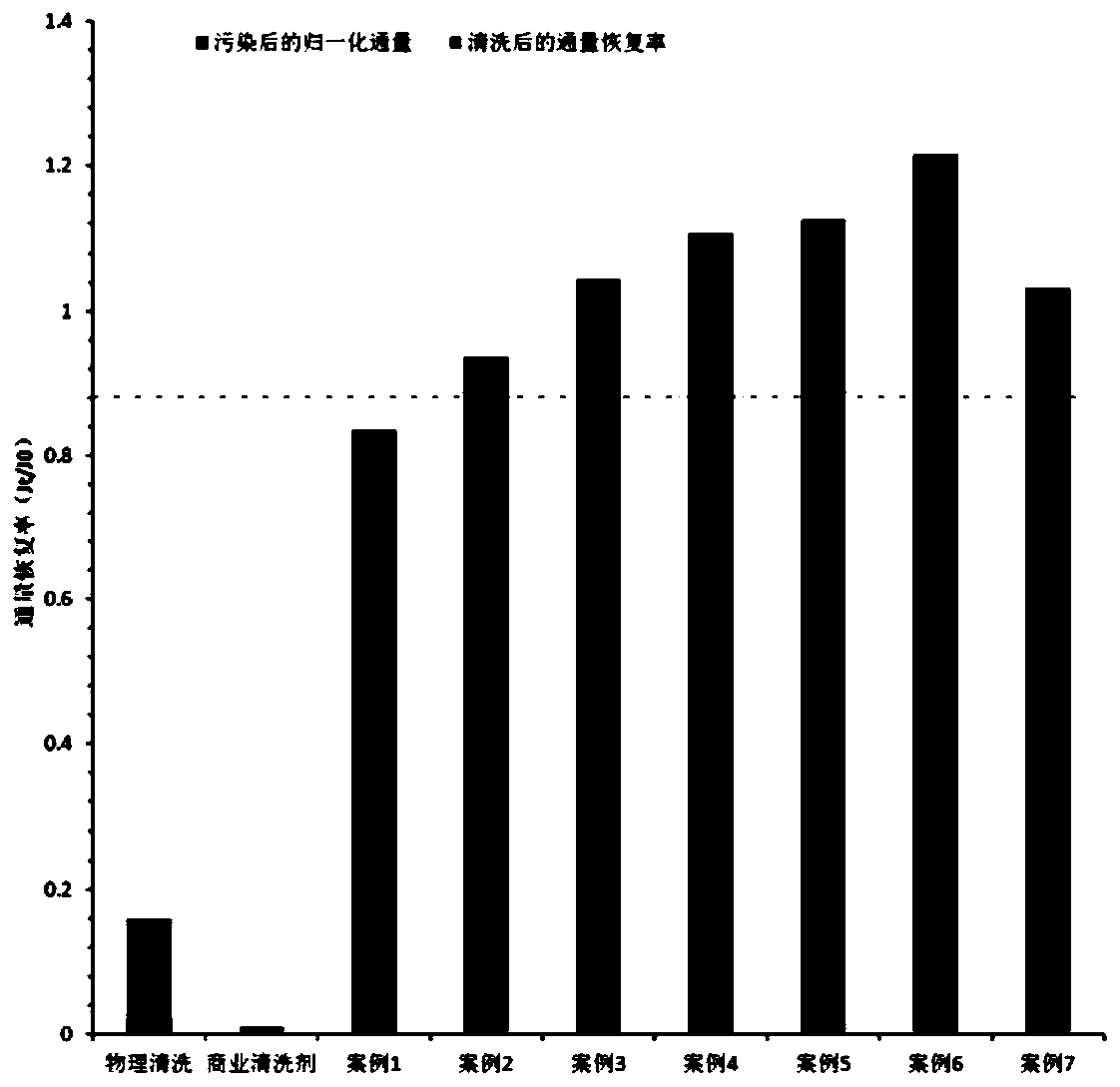
Ultrafiltration Membrane Cleaning Method in Membrane Polymer Flooding Oil Production Wastewater Treatment
ActiveCN106110895BEffective Cleaning TechnologyAchieving Pollution ControlWaste water treatment from quariesSemi-permeable membranesOrganosolvCleaning methods
The invention provides a cleaning method of an ultra-filtration membrane used in membrane-process polymer-flooding oilfield wastewater treatment. The cleaning method comprises the steps of (1) physical cleaning and chemical cleaning, wherein chemical cleaning comprises the following steps: (2) cleaning with a pickling solution; (3) cleaning with a sodium hydrogenfluoride and alkaline mixed solution, a sodium hydrogenfluoride and acid mixed solution or a sodium hydrogenfluoride and sodium fluoride mixed solution; (4) cleaning with an oxidizing agent lotion; (5) cleaning with a membrane cleaning additive; (6) cleaning with a surfactant or an organic solvent cleaning agent.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
A kind of mn4+ doped sodium hydrogen fluoride red light material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106318381BEffective absorptionSimple ingredientsLuminescent compositionsColor rendering indexUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a Mn4+ doped sodium hydrogen fluoride red light material and a preparation method thereof. The chemical composition of the material is NaHF2:Mn4+, with 15-30mL HF (concentration: wt 40%), 1×10‐4~9×10‐4mol K2MnF6 solid, 0.01~0.1mol NaF as raw materials, adding deionized water to make The total volume is 40 mL, stirred and reacted at room temperature for 0.5-2 hours, filtered with suction, and dried naturally at room temperature to obtain a white powder. The product emits bright red light under ultraviolet light, and its largest excitation band completely matches the blue light spectrum emitted by the white LED blue chip. Its emission spectrum consists of four red light emission peaks at 595-643nm. The material may be applied to dichroic white LEDs to improve their color rendering index. The product does not contain rare earth, has a simple preparation method and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIV
A method for electrochemically preparing nanosheets of mxenes and their derivatives
ActiveCN109694074BUniform particle sizeGet quicklyMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of MXenes and their derivatives nanosheets, and relates to a method for electrochemically preparing MXenes and their derivatives nanosheets. Put the sodium bifluoride powder into 50mL beakers respectively, add 50mL deionized water to the beaker containing the powder, put it on a magnetic stirrer to completely dissolve the ammonium bifluoride powder; 3 AlC 2 MAX is fixed to the clip electrode as anode, Pt sheet electrode (area > 1.0cm 2 ) as a negative electrode, and apply the direct current constant voltage of 3V, react 6-24 hours; At last centrifugation makes the product, the present invention is compared with the prior art, in the preparation process, the use of low-concentration ammonium bifluoride has avoided high-concentration hydrofluoric acid Or the mixture of hydrochloric acid and fluoride, which is non-toxic and low in hazard, eliminates the potentially dangerous process and is green and environmentally friendly; the electrolysis of the bulk MAX process by electrochemical methods shortens the reaction time and improves the peeling.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Process for preparing kryocide
InactiveCN101318678BReduce manufacturing costSave resourcesAluminium fluoridesSocial benefitsElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for producing cryolite, which takes carbon residue of aluminum factories and sodium bifluoride as raw materials which are then reacted with each other in a solid phase. The raw materials of the method adopt a great deal of waste residue - the carbon residue of the electrolytic aluminum factories, and the cryolite product is prepared after flotation treatment and particularly refining treatment of products. The method increases a source of raw materials for producing villiaumite, relieves the dependency on fluorite, saves a large number of valuable resources, has low cost, greatly reduces the production cost, and relieves the ambient environmental pollution problem. Moreover, carbon powder containing about 10 percent of electrolyte obtained after flotation of the carbon residue can be dried and then used as auxiliary materials to be added when bottom paste is manufactured, and used for building a novel groove. Products generated during the reaction process of the method can be recycled, thereby the method greatly reduces the production cost to a certain degree, has good social benefit and economic benefit, and is easy to promote and apply.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Method for preparing sodium hydrogen fluoride by using fluorosilicic acid, a by-product of phosphorus chemical industry
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com