Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Quantum size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
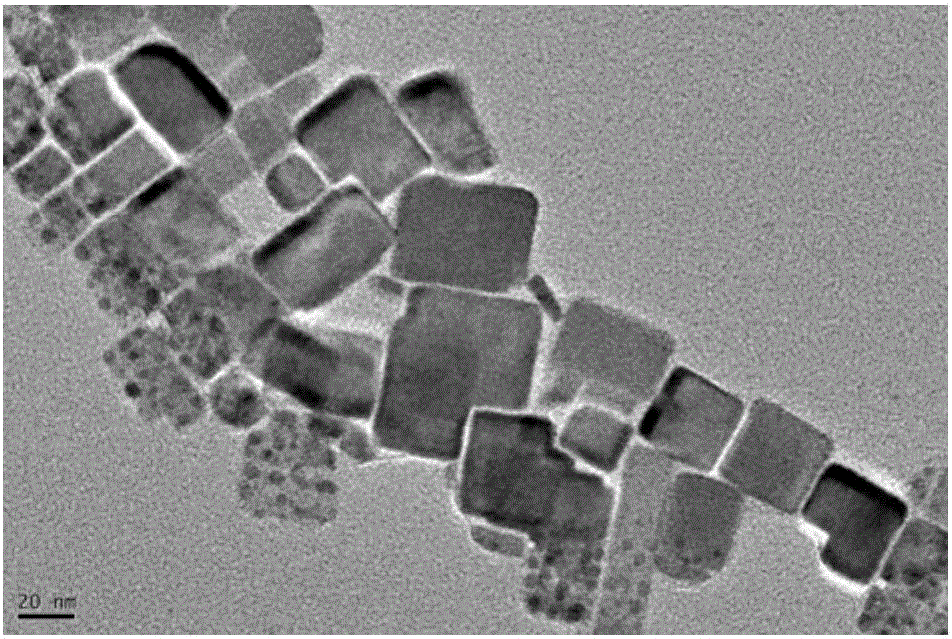
Small quantum dots, such as colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals, can be as small as 2 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to 10 to 50 atoms in diameter and a total of 100 to 100,000 atoms within the quantum dot volume. Self-assembled quantum dots are typically between 10 and 50 nm in size.
Nanostructured bulk thermoelectric material
ActiveUS20060118158A1High quality factorImprove mechanical propertiesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsNanowire
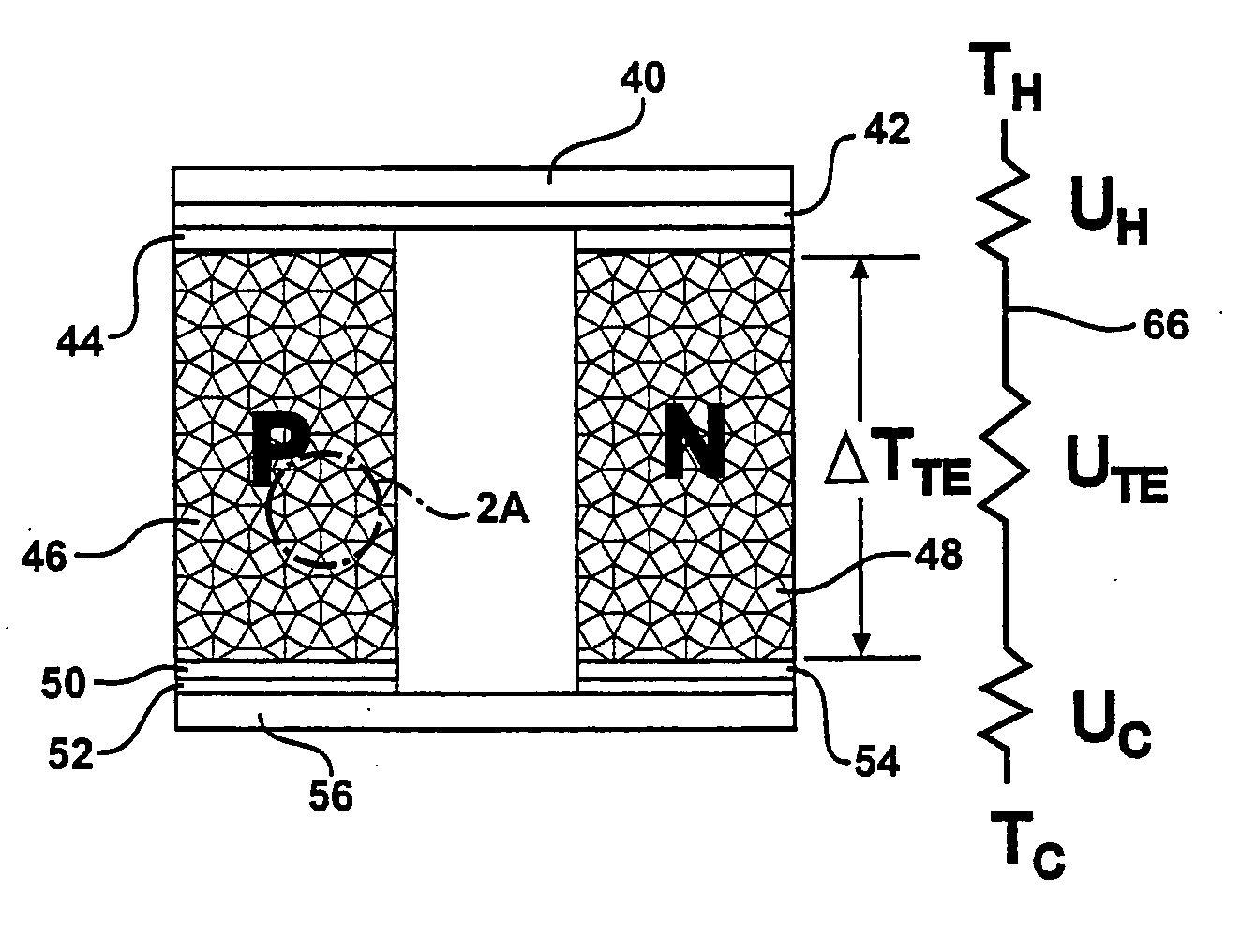
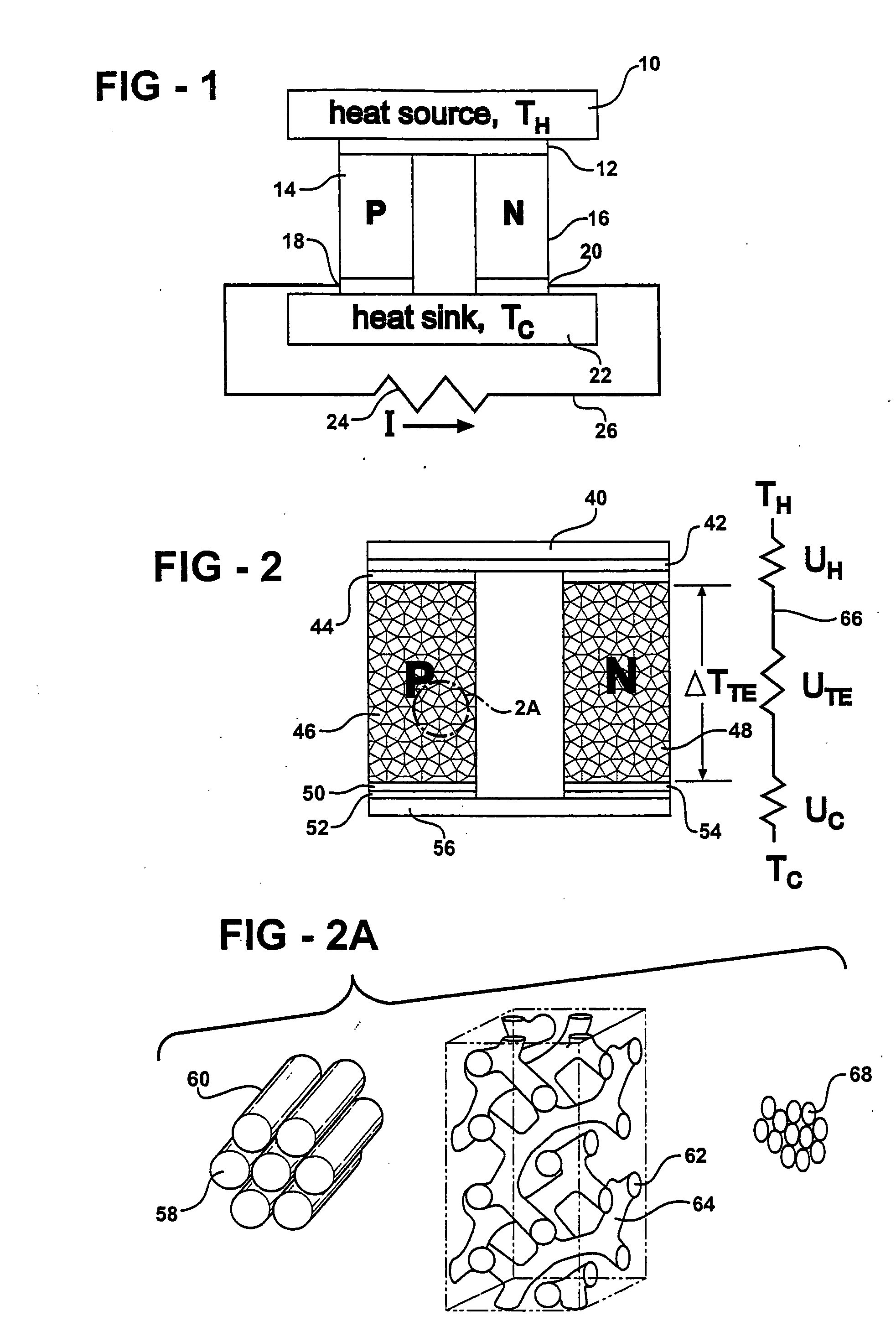
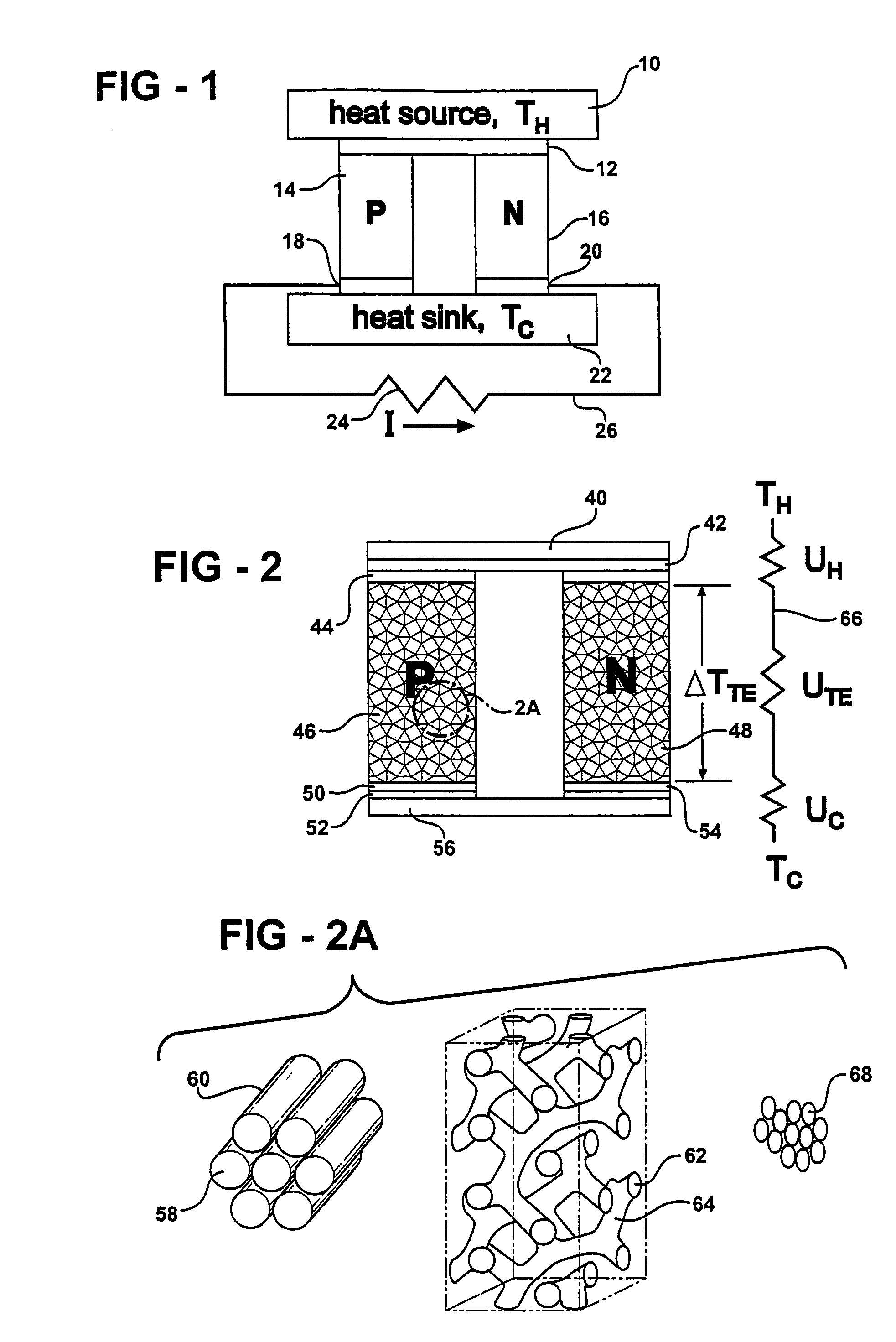
A thermoelectric material comprises two or more components, at least one of which is a thermoelectric material. The first component is nanostructured, for example as an electrically conducting nanostructured network, and can include nanowires, nanoparticles, or other nanostructures of the first component. The second component may comprise an electrical insulator, such as an inorganic oxide, other electrical insulator, other low thermal conductivity material, voids, air-filled gaps, and the like. Additional components may be included, for example to improve mechanical properties. Quantum size effects within the nanostructured first component can advantageously modify the thermoelectric properties of the first component. In other examples, the second component may be a thermoelectric material, and additional components may be included.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Nanostructured bulk thermoelectric material
ActiveUS7309830B2High quality factorImprove mechanical propertiesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsNanowire
A thermoelectric material comprises two or more components, at least one of which is a thermoelectric material. The first component is nanostructured, for example as an electrically conducting nanostructured network, and can include nanowires, nanoparticles, or other nanostructures of the first component. The second component may comprise an electrical insulator, such as an inorganic oxide, other electrical insulator, other low thermal conductivity material, voids, air-filled gaps, and the like. Additional components may be included, for example to improve mechanical properties. Quantum size effects within the nanostructured first component can advantageously modify the thermoelectric properties of the first component. In other examples, the second component may be a thermoelectric material, and additional components may be included.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Surface modification of nanocrystals using multidentate polymer ligands
InactiveUS20060088713A1Colloidal stabilityStabilizing quantum size-dependent propertyMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSolventComputational chemistry
The present invention provides a method of surface passivation of colloidal nanocrystalline materials using a ligand exchange process in which quantum nanoparticles of pre-selected size and shape has polymer multidentate ligands bound at the surface of the nanocrystals for stabilizing quantum size-dependent properties of nanocrystals and providing colloidal stability of the nanoparticles in solvents. The method includes preparing a colloidal dispersion of nanoparticles, preparing a suitable polymer multidentate ligand and dissolving said suitable polymer multidentate ligand in a fluid, the polymer multidentate ligand having first portions which can bind to a surface of the nanoparticles and a second portion which does not bind to the surface of the nanoparticles, and mixing the fluid containing the suitable polymer with the colloidal dispersion of nanoparticles under conditions suitable to induce binding of at least some of the first portions of the polymer multidentate ligand onto the surface of the nanoparticles, the suitable polymer multidentate ligand being selected so that the at least some of the first portions which bind to the surface to stabilize quantum size-dependent properties of the nanocrystals, and the second portion which does not bind to the surface provides colloidal stability of the nanoparticles in a desired fluid.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO +6
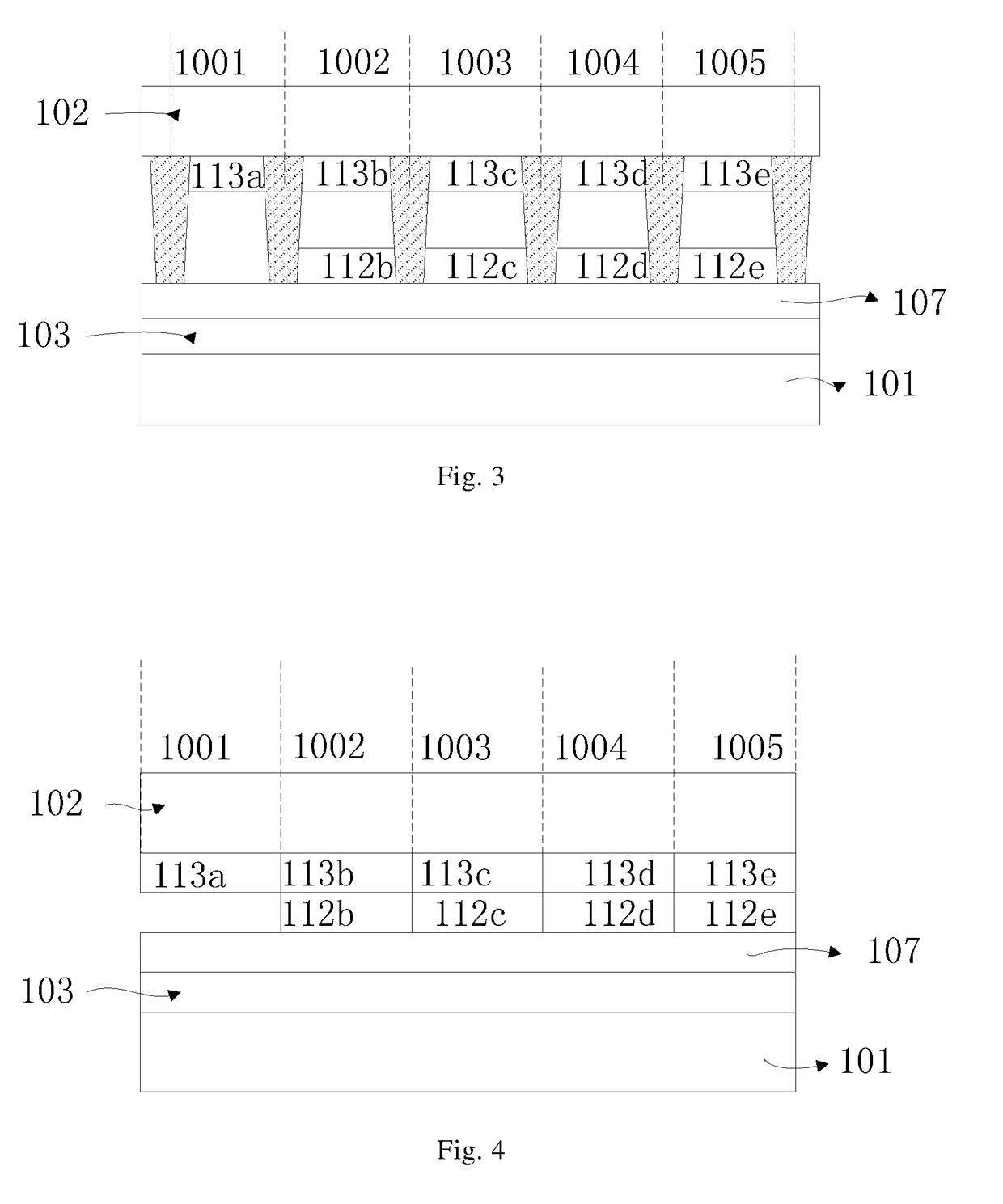
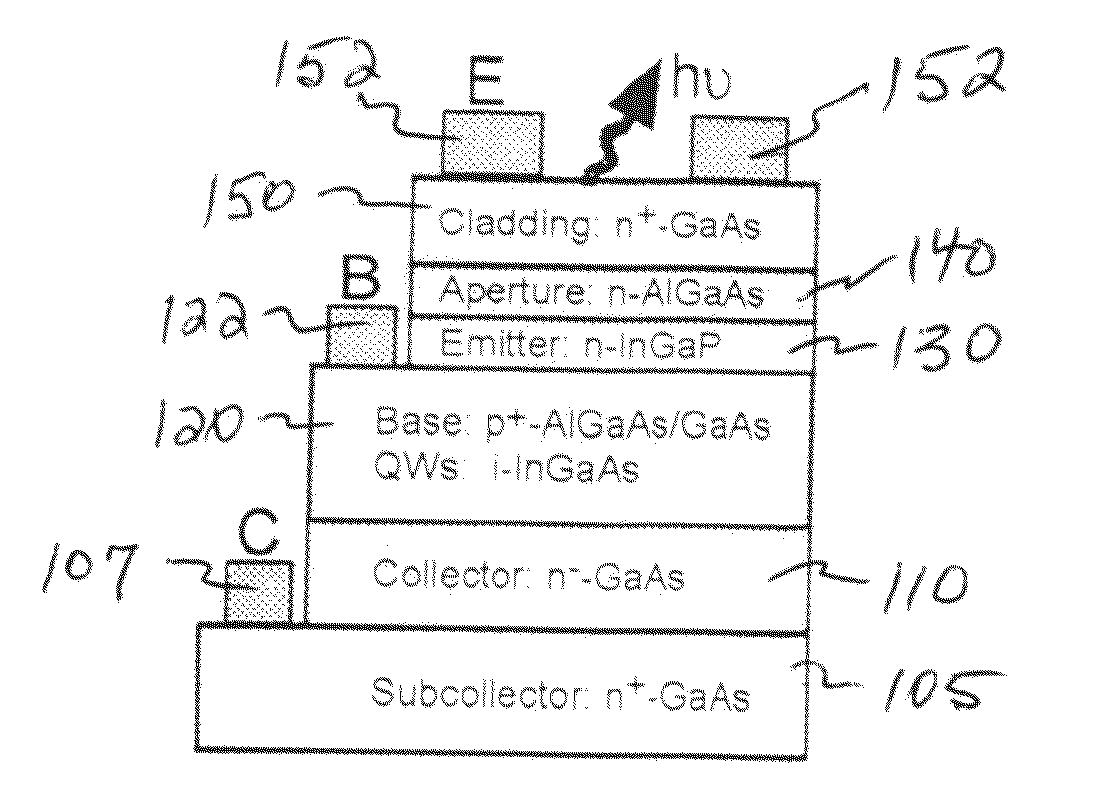
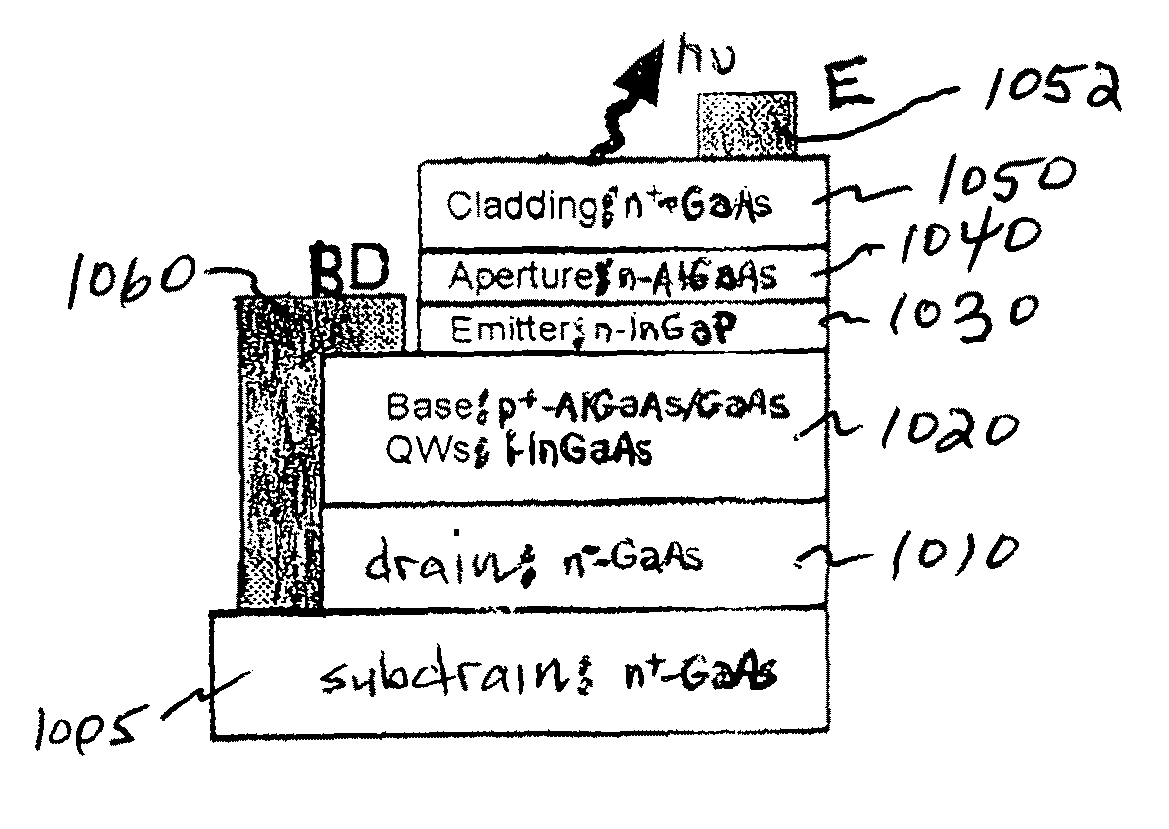
Light emitting and lasing semiconductor devices and methods
ActiveUS20100034228A1Inhibit injectionAvoid transportLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersElectron flowQuantum size effect
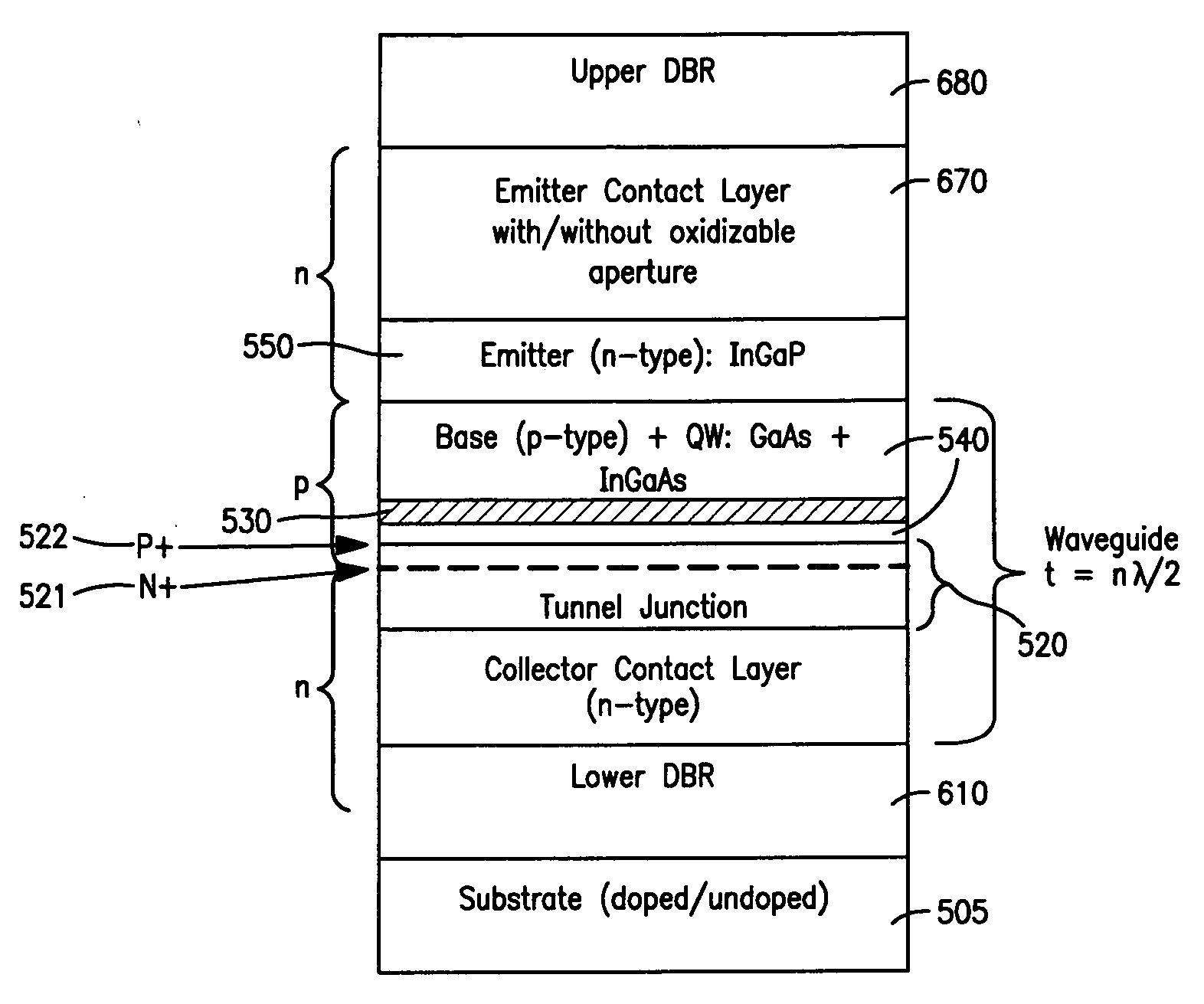
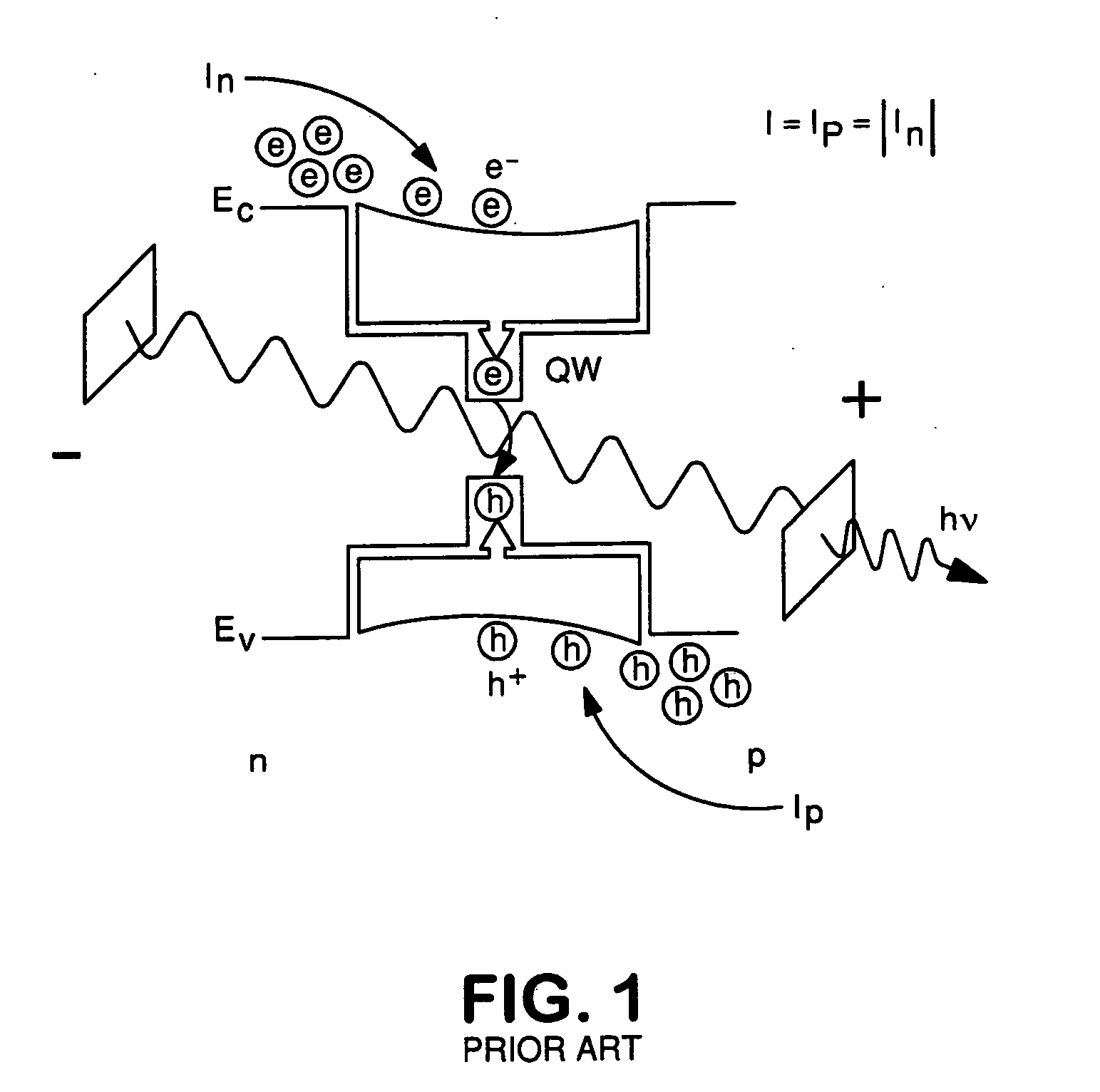
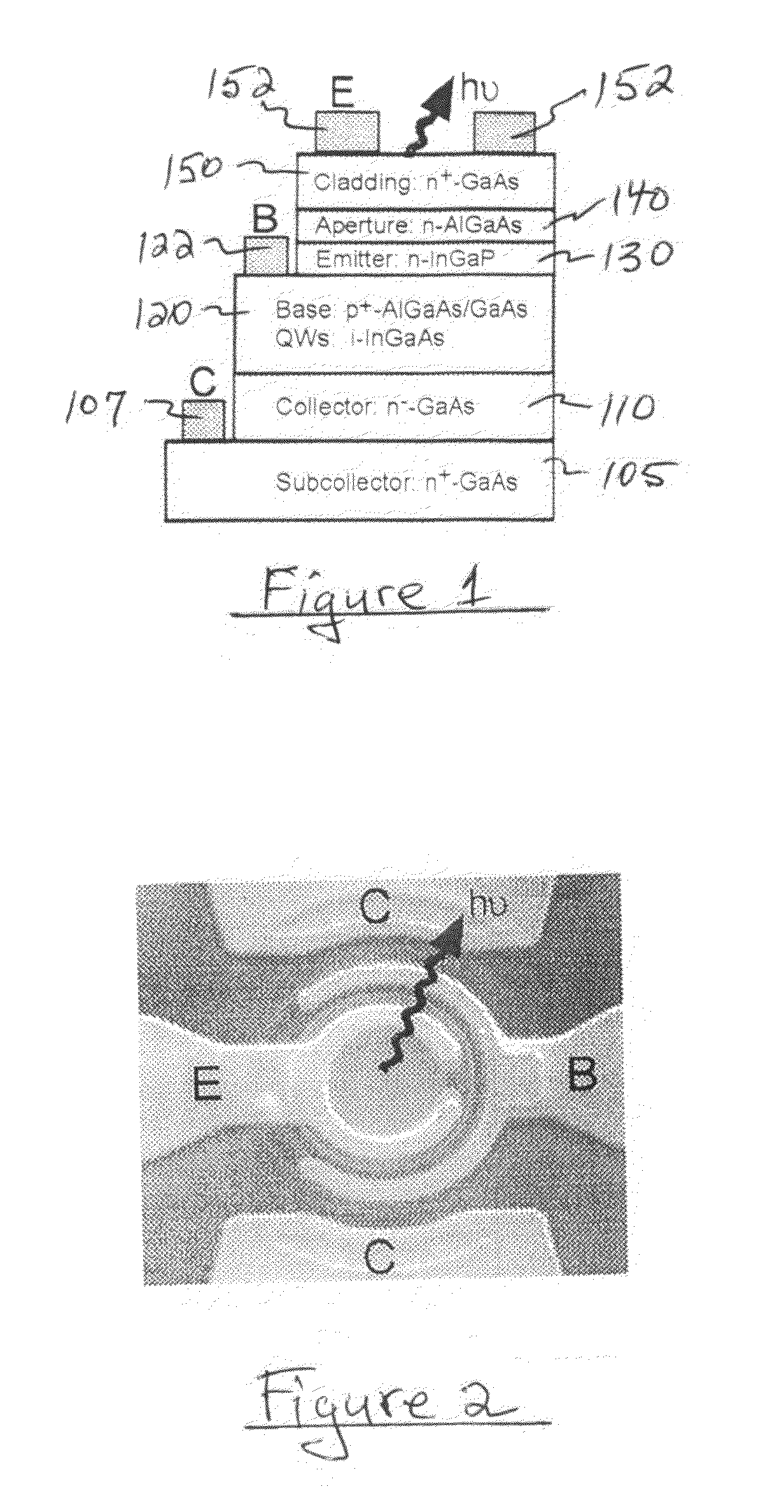
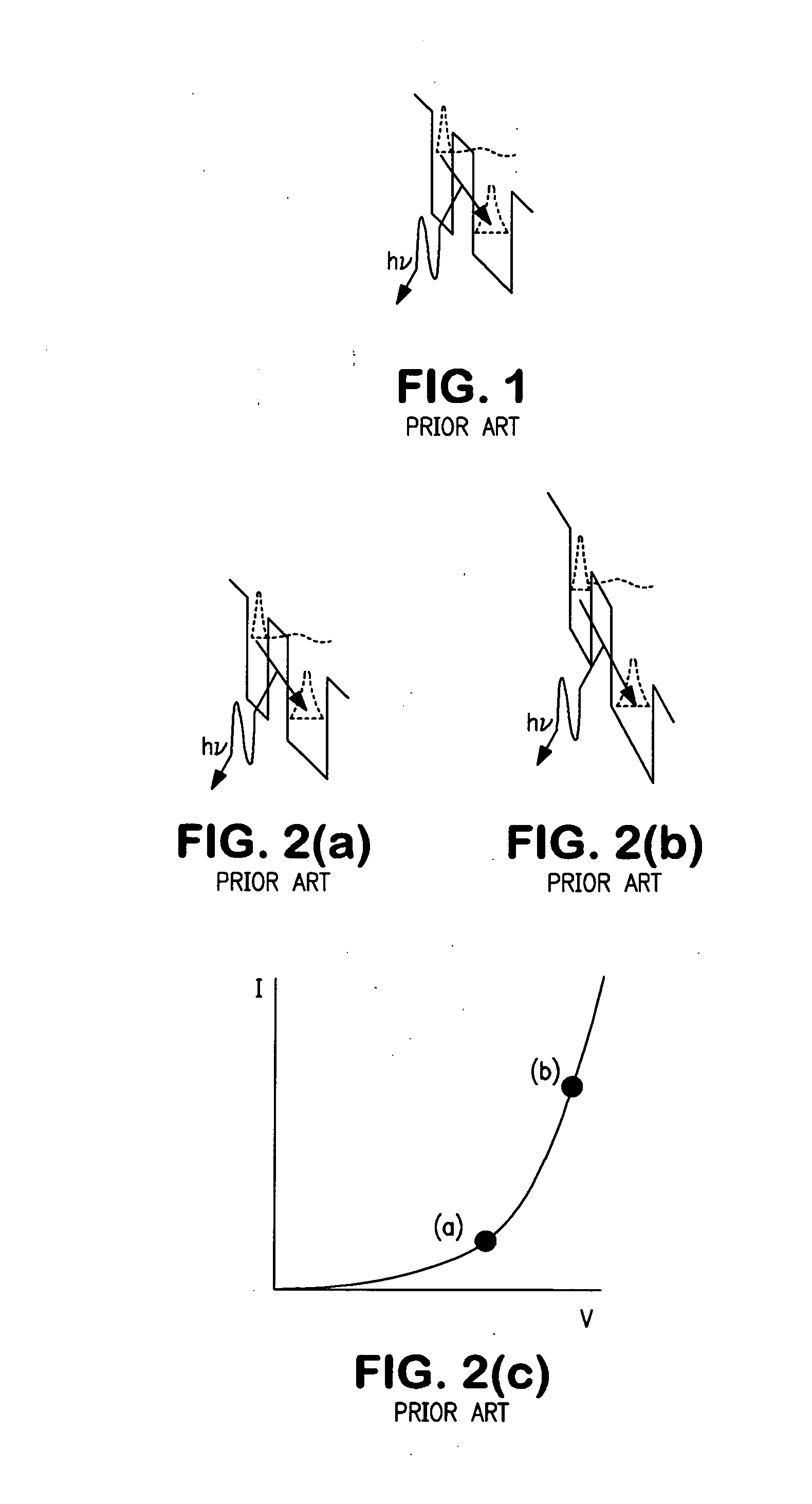
A two terminal semiconductor device for producing light emission in response to electrical signals, includes: a terminal-less semiconductor base region disposed between a semiconductor emitter region and a semiconductor collector region having a tunnel junction adjacent the base region; the base region having a region therein exhibiting quantum size effects; an emitter terminal and a collector terminal respectively coupled with the emitter region and the collector region; whereby application of the electrical signals with respect to the emitter and collector terminals, causes light emission from the base region. Application of the electrical signals is operative to reverse bias the tunnel junction. Holes generated at the tunnel junction recombine in the base region with electrons flowing into the base region, resulting in the light emission. The region exhibiting quantum size effects is operative to aid recombination.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
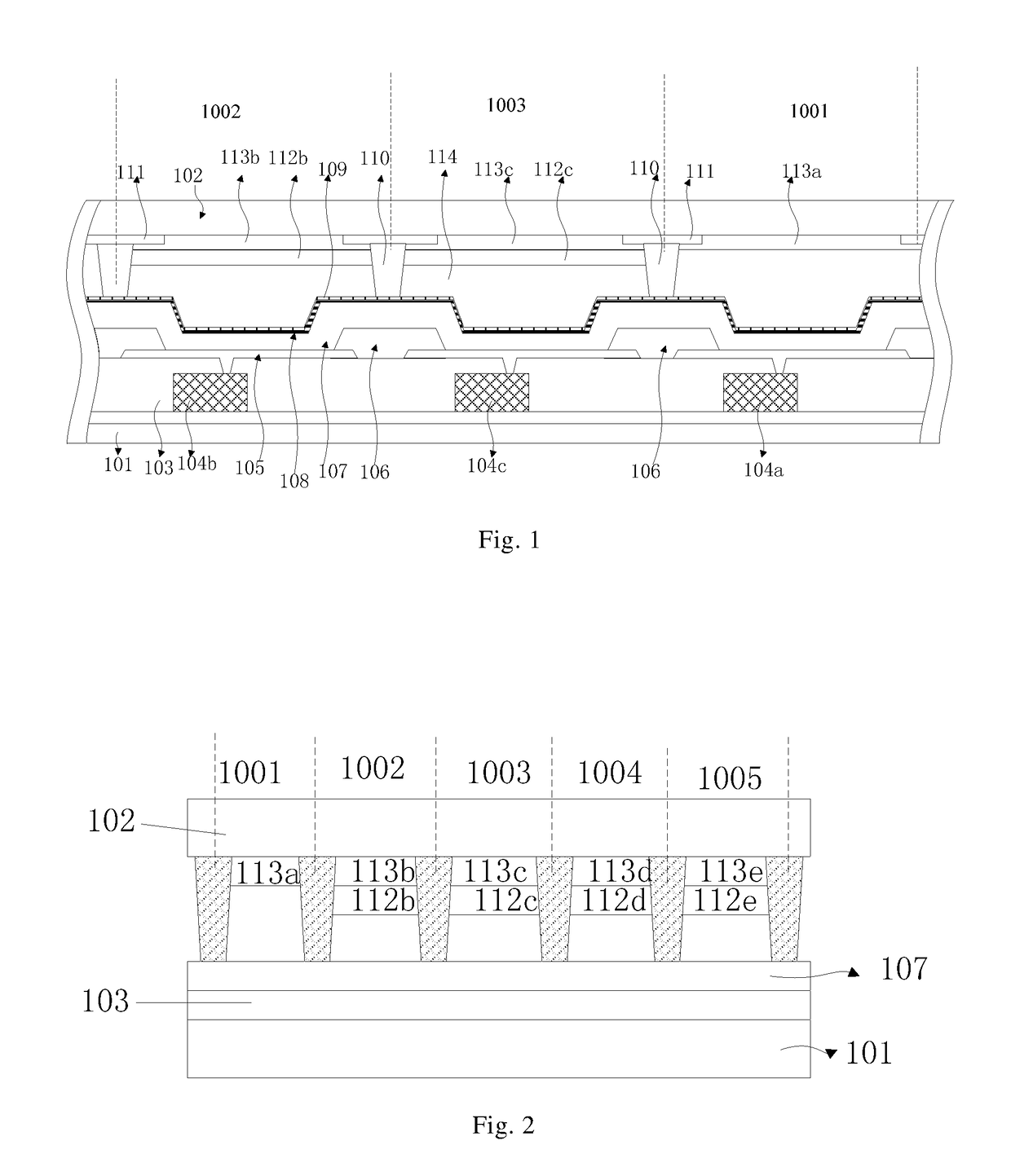
Organic light emitting display panel and manufacturing method thereof, and display device
ActiveUS20170179438A1Increase profitIncrease brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceQuantum size effect
The invention provides an organic light emitting display panel and a manufacturing method thereof, and a display device. In the organic light emitting display panel and the manufacturing method thereof, and the display device of the invention, since a quantum material layer exhibiting quantum size effects is arranged on a side of a color filter substrate close to an array substrate or on a side of an array substrate close to a color filter substrate, and can convert a part of light emitted thereinto from the organic light emitting unit into light with a same color as that of a corresponding sub-pixel, the utilization rate of light emitted from the organic light emitting unit is increased, brightness is improved, and power consumption is reduced.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
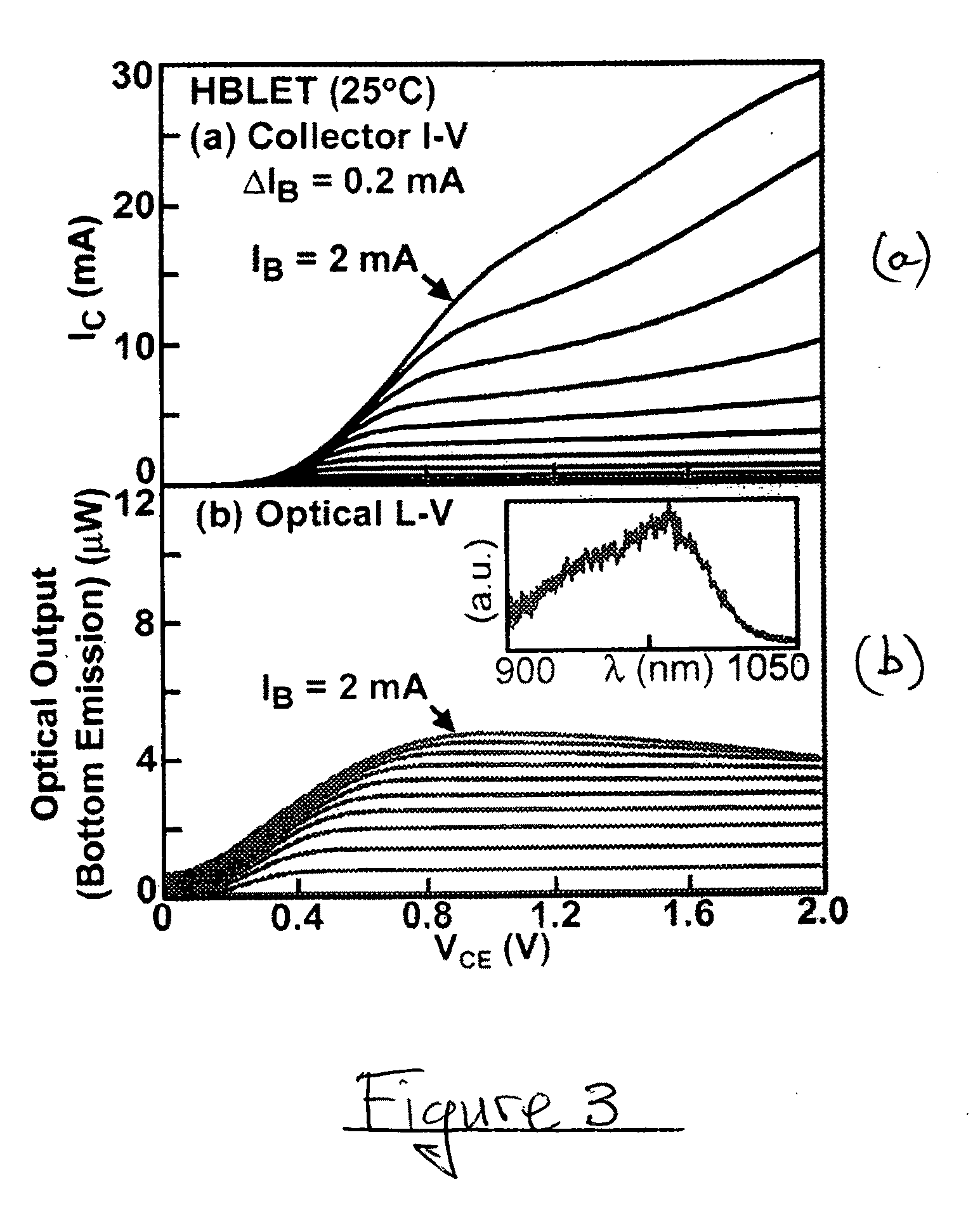
High speed light emitting semiconductor methods and devices
ActiveUS20100272140A1Improve featuresHigh yieldLaser detailsElectric lighting sourcesOptical cavityQuantum size effect
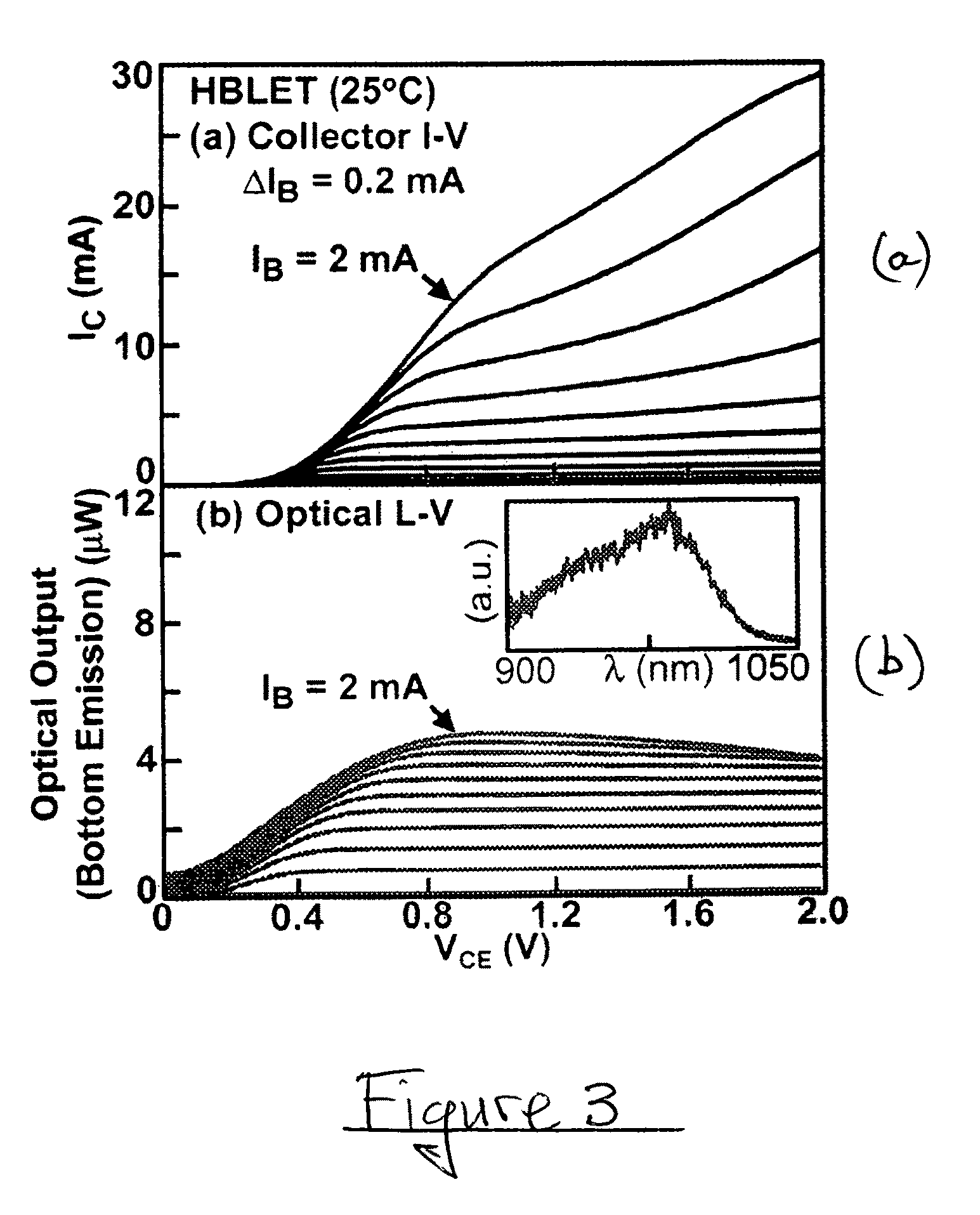
A method for producing a high frequency optical signal component representative of a high frequency electrical input signal component, includes the following steps: providing a semiconductor transistor structure that includes a base region of a first semiconductor type between semiconductor emitter and collector regions of a second semiconductor type; providing, in the base region, at least one region exhibiting quantum size effects; providing emitter, base, and collector electrodes respectively coupled with the emitter, base, and collector regions; applying electrical signals, including the high frequency electrical signal component, with respect to the emitter, base, and collector electrodes to produce output spontaneous light emission from the base region, aided by the quantum size region, the output spontaneous light emission including the high frequency optical signal component representative of the high frequency electrical signal component; providing an optical cavity for the light emission in the region between the base and emitter electrodes; and scaling the lateral dimensions of the optical cavity to control the speed of light emission response to the high frequency electrical signal component.
Owner:QUANTUM ELECTO OPTO SYST +1
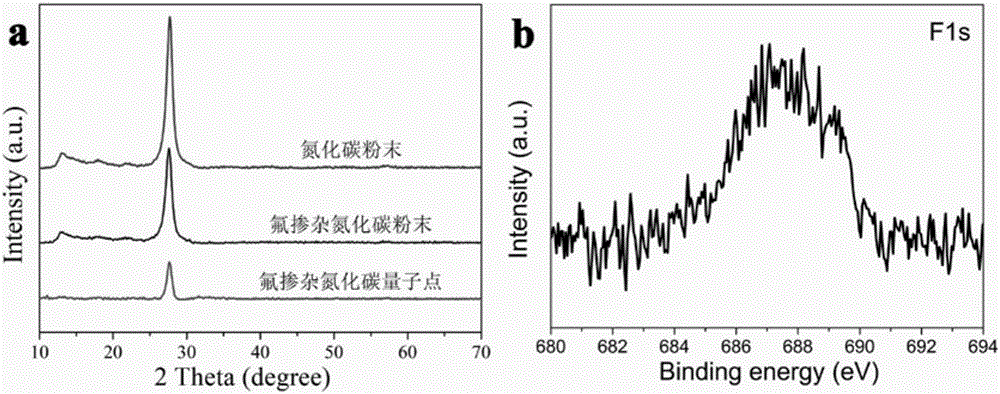
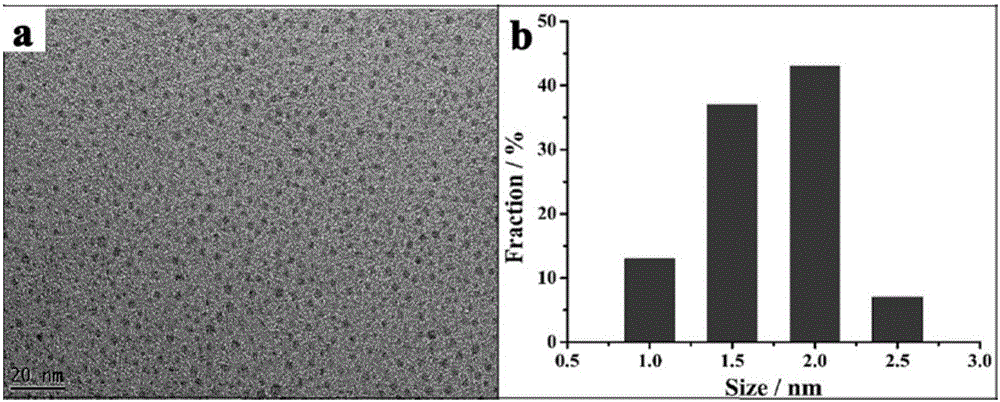
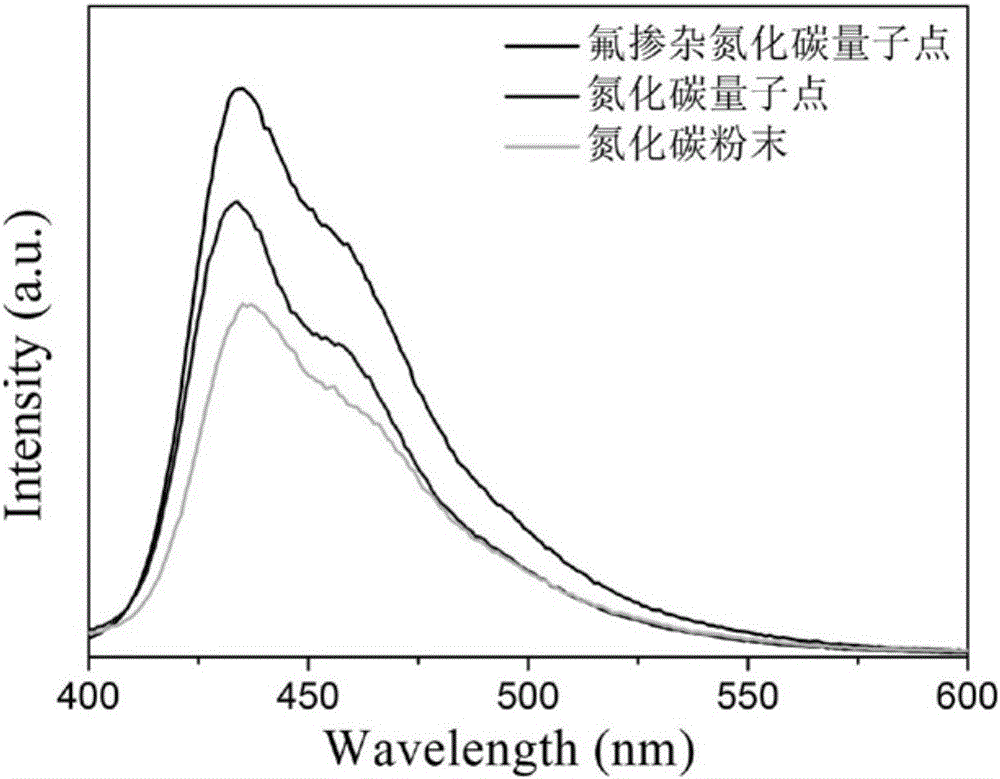
Preparation method of doped carbon nitride fluorescent quantum dots
InactiveCN105670620AEffective regulatory structureEffective control of fluorescence propertiesNanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsSolubilityChemical reaction
The invention relates to a preparation method of doped carbon nitride fluorescent quantum dots.According to the preparation method, melamine and compounds corresponding to doped atoms serve as raw materials, while melamine molecules are roasted to form a carbon nitride structure, the doped atoms enter the carbon nitride structure through a chemical reaction, a doped carbon nitride block material is formed, and the block material is subjected to ultrasound crushing in an alcohol solvent to prepare the doped carbon nitride fluorescent quantum dots which are uniform in quantum size and grain size.The dried quantum dots are good in water solubility and dispersibility and have high fluorescent quantum dot yield.The method can be used for preparing the doped carbon nitride quantum dots in batches, the synthesis method is simple, and repeatability is good.The synthesized quantum dots have wide application prospects in the fields of fluorescence detection, light-emitting devices, biological marking and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Two terminal light emitting and lasing devices and methods
InactiveUS20100202483A1Cheap manufacturingCheap to packageLaser detailsLaser active region structureElectrical conductorSemiconductor structure
A method for producing light emission from a semiconductor structure, including the following steps: providing a semiconductor structure that includes a first semiconductor junction between an emitter region of a first conductivity type and a base region of a second conductivity type opposite to that of the first conductivity type, and a second semiconductor junction between the base region and a drain region; providing, within the base region, a region exhibiting quantum size effects; providing an emitter electrode coupled with the emitter region; providing a base / drain electrode coupled with the base region and the drain region; and applying signals with respect to the emitter and base / drain electrodes to obtain light emission from the semiconductor structure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Light emitting and lasing semiconductor devices and methods
ActiveUS20100202484A1Minimize non-radiative recombination componentReduced quantum efficiencyLaser detailsLaser active region structureHeterojunctionLight emitting device
A semiconductor light emitting device, including: a heterojunction bipolar light-emitting transistor having a base region between emitter and collector regions; emitter, base, and collector electrodes for coupling electrical signals with the emitter, base, and collector regions, respectively; and a quantum size region in the base region; the base region including a first base sub-region on the emitter side of the quantum size region, and a second base sub-region on the collector side of the quantum size region; and the first and second base sub-regions having asymmetrical band structures.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
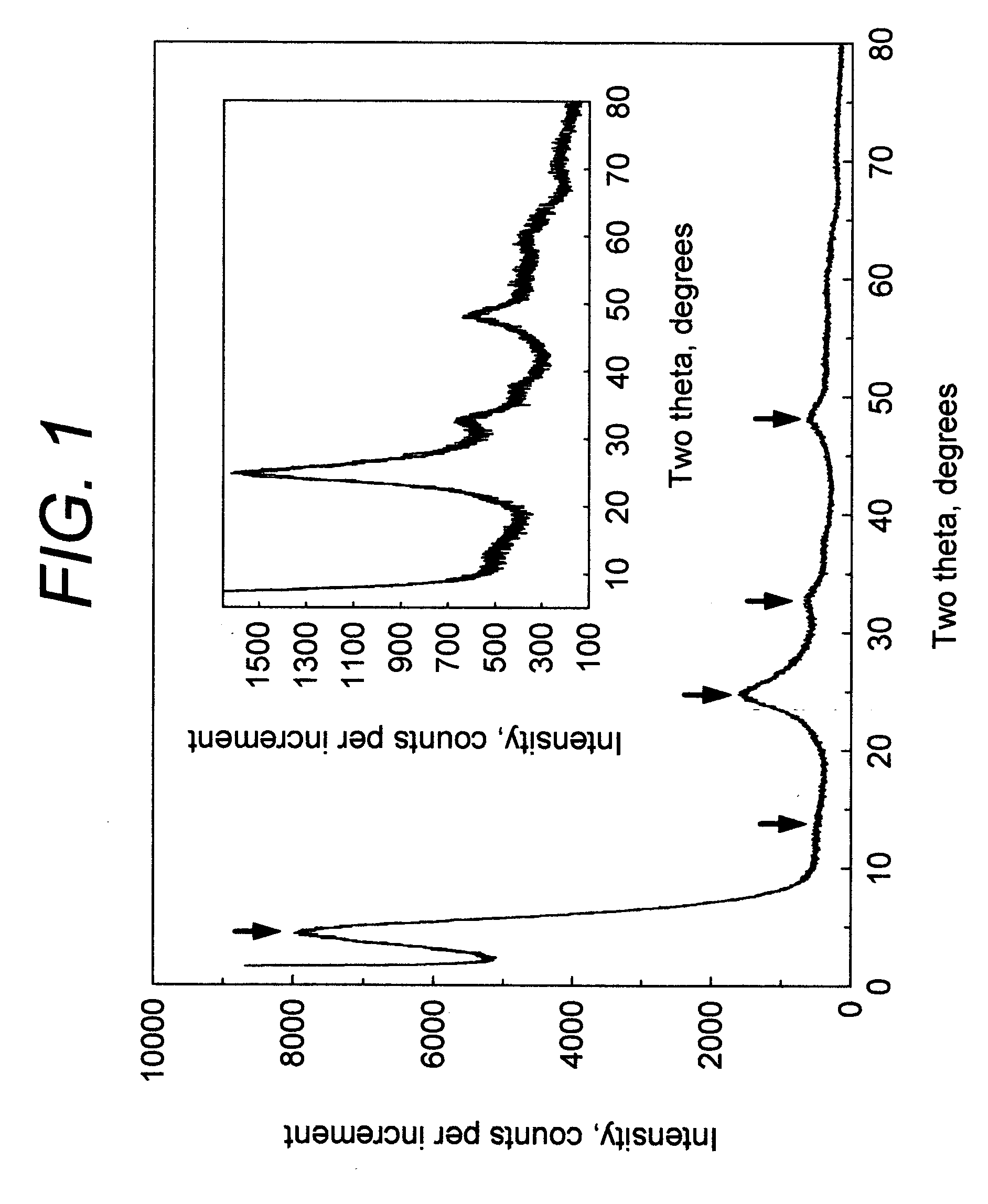
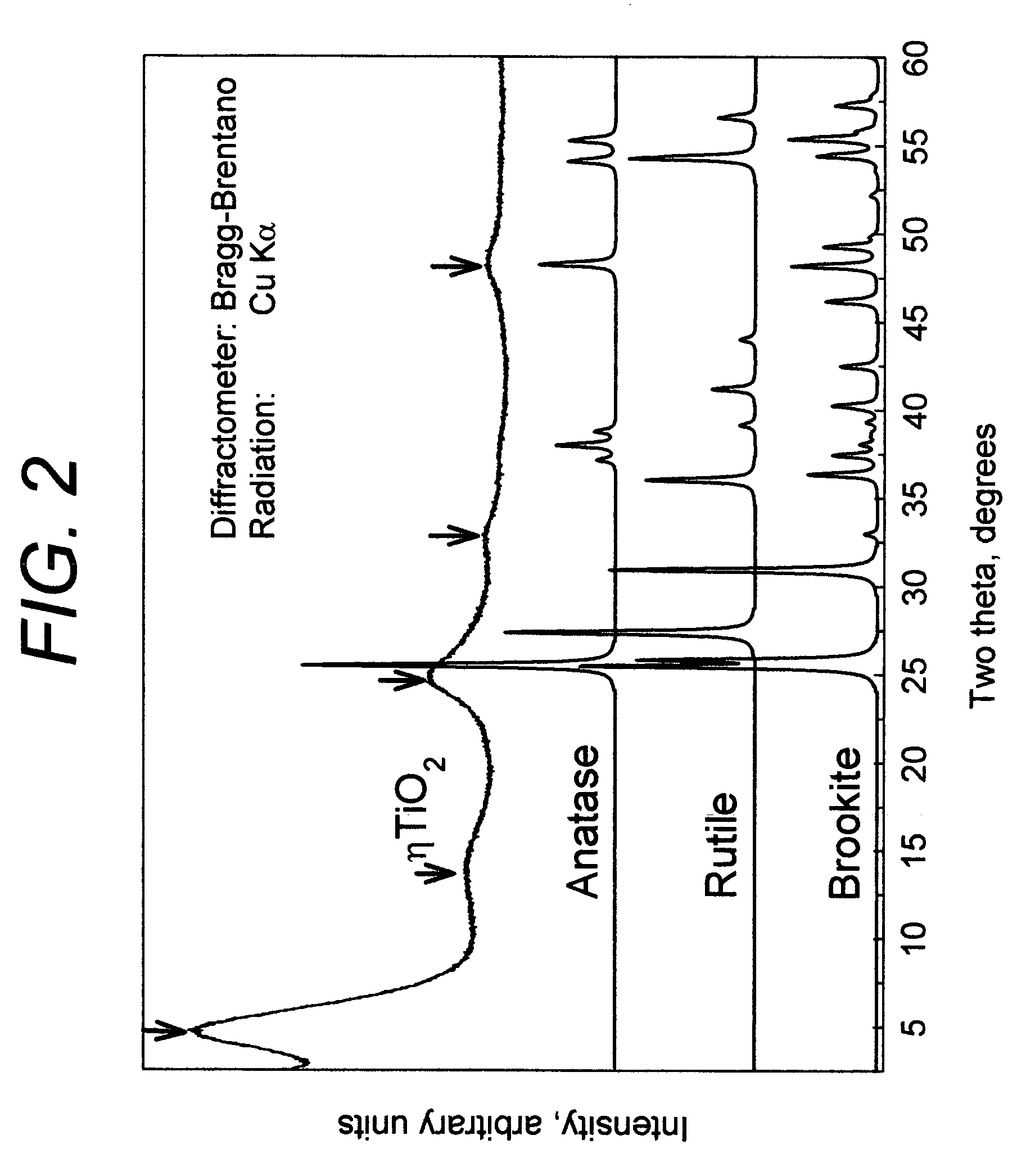
Novel titanium dioxide, process of making and method of using same
InactiveUS20060171877A1Inhibition formationQuantity minimizationPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesSorbentRutile
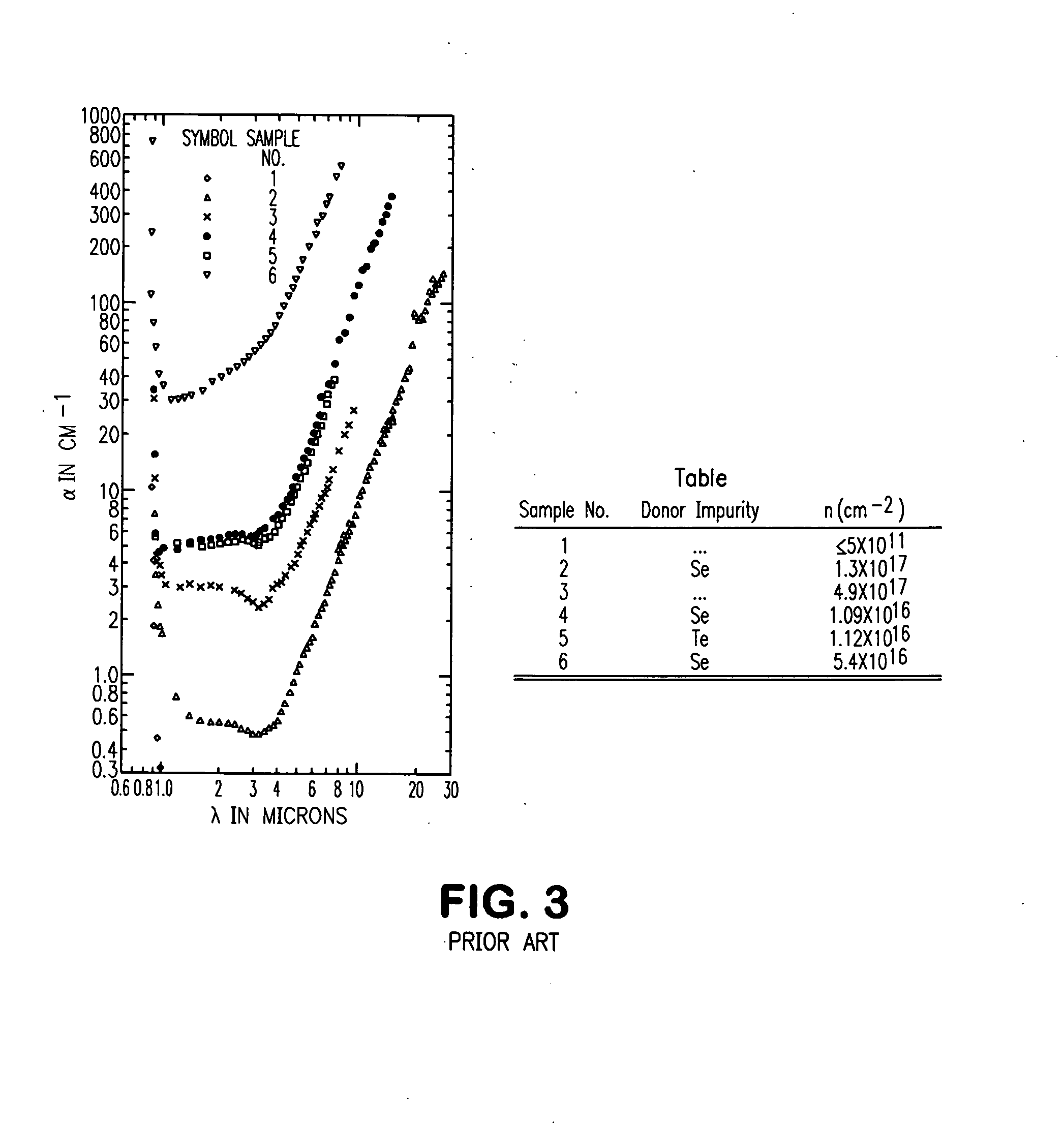
Adsorbents and Methods used for effective removal or concentration or retention and recovery of harmful or valuable dissolved ions and compounds from aqueous systems using quantum size effect on large band gap semiconductors are provided. Invention provides methods for creating surface hydroxyl groups on surfaces of anatase, brookite and rutile which comprise methods of reducing dimensions of individual crystals to the sizes where surface hydroxyl groups are self generated via quantum size effects when they contacted with electrolytes. This invention also provides methods of preparation of quantum sized anatase, brookite and rutile. The invention also provides methods using quantum size effected anatase, brookite and rutile products for treatment of water, comprising rapid and high capacity adsorption of dissolved molecules and ions to the surface of said crystals via surface reaction process between said effect created hydroxyl groups with molecules and ions.
Owner:DADACHOV MAZAKHIR
Method for preparing CsPbBr3 nanosheets with quantum size effects
InactiveCN106809872APreserve quantum size effectsAchieving controllable equipmentMaterial nanotechnologyLead compoundsOleic Acid TriglycerideQuantum size
The invention discloses a method for preparing CsPbBr3 nanosheets with quantum size effects. The method includes dissolving cesium carbonate in oleic acid under argon filling conditions, and stirring the cesium carbonate and the oleic acid under heating conditions until the cesium carbonate is dissolved to obtain cesium oleate precursors; adding lead bromide, long-chain ligands and short-chain ligands into octadecene under argon filling conditions, carrying out reaction at the temperature of 100-150 DEG C until the lead bromide is dissolved, heating first reaction products until the temperature of the first reaction products reaches 120-150 DEG C, then injecting the cesium oleate precursors into the first reaction products, carrying out reaction for 5-15 s, then continuing to carry out reaction at the temperature of 100-130 DEG C for 1-5 min to obtain second reaction products and centrifuging the second reaction products. The method has the advantages that the transverse sizes of the CsPbBr3 nanosheets can be assuredly regulated and controlled in the range from 100 nm to 1 micrometer while the thicknesses which are equal to the thicknesses of a few atomic layers can be guaranteed; the thicknesses which are lower than the diameters of Bohr excitons can be kept, and accordingly the quantum size effects of the CsPbBr3 nanosheets can be reserved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Light emitting and lasing semiconductor methods and devices
InactiveUS20120068151A1Easy to useSmaller (Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor structure
The invention is applicable for use in conjunction with a light-emitting semiconductor structure that includes a semiconductor active region of a first conductivity type containing a quantum size region and having a first surface adjacent a semiconductor input region of a second conductivity type that is operative, upon application of electrical potentials with respect to the active and input regions, to produce light emission from the active region. A method is provided that includes the following steps: providing a semiconductor output region that includes a semiconductor auxiliary layer of the first conductivity type adjacent a second surface, which opposes the first surface of the active region, and providing the auxiliary layer as a semiconductor material having a diffusion length for minority carriers of the first conductivity type material that is substantially shorter than the diffusion length for minority carriers of the semiconductor material of the active region.
Owner:QUANTUM ELECTRO OPTO SYST
High speed light emitting semiconductor methods and devices
ActiveUS8179937B2Improve featuresRecombine rapidlyLaser detailsElectric lighting sourcesElectricityOptical cavity
A method for producing a high frequency optical signal component representative of a high frequency electrical input signal component, includes the following steps: providing a semiconductor transistor structure that includes a base region of a first semiconductor type between semiconductor emitter and collector regions of a second semiconductor type; providing, in the base region, at least one region exhibiting quantum size effects; providing emitter, base, and collector electrodes respectively coupled with the emitter, base, and collector regions; applying electrical signals, including the high frequency electrical signal component, with respect to the emitter, base, and collector electrodes to produce output spontaneous light emission from the base region, aided by the quantum size region, the output spontaneous light emission including the high frequency optical signal component representative of the high frequency electrical signal component; providing an optical cavity for the light emission in the region between the base and emitter electrodes; and scaling the lateral dimensions of the optical cavity to control the speed of light emission response to the high frequency electrical signal component.
Owner:QUANTUM ELECTO OPTO SYST +1
Perovskite type solar energy battery with quantum dot size performing gradient change and preparation method
ActiveCN105576150AImprove absorption efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionPhotocathode
The invention discloses a perovskite type solar energy battery with a quantum dot size performing gradient change and a preparation method. The perovskite type solar energy battery consists of a transparent conductive substrate, a compact electronic transmission layer, a composite light-absorption layer and a metal electrode layer; the composite light-absorption layer consists of n layers of perovskite-wrapping P type semiconductor quantum dot core shell structures, the sizes of which can perform V type gradient changing. Because the light-absorption layer of the perovskite type solar energy battery adopts multiple layers of perovskite-wrapping P type semiconductor quantum point core shell structures with the quantum sizes performing V type gradient change, the invention can realize the fact that the composite material presents gradient distribution of the forbidden bandwidth on the vertical gradient through designing the quantum dot size V type form distribution, and expands the spectrum scope of the absorption layer. Besides, the invention can improve the interface electric field on the photocathode interface, promotes the separation of the photo-induced carrier under the electric field and improves the conversion efficiency of the photoelectron.
Owner:ANHUI HUASUN ENERGY CO LTD
Quantum-size electronic devices and operating conditions thereof
Quantum-size electronic devices comprise electrodes and at least one cluster separated from the said electrodes by a tunnelly transparent gap. The characteristic dimensions for elements of quantum-size devices are determined by the formula in the range 1x4 r0, wherein r0 = h / (me alpha <2>c), wherein h is the Planck's constant, me is the electron mass, alpha = 1 / 137,036 is the fine structure constant, c is the light speed. The cluster may be made of a semiconductor material, conductor, superconductor, high-molecular substance or a sheath with a tunnelly transparent dielectric. The matured theory provides possibilities for designing logical devices operating in the mode of transfer and / or storing of several electrons at normal conditions and high temperatures. The operating regimes of the devices are determined. The invention provides basic condition for constructing of high-temperature superconducting elements and devices based thereon.
Owner:QUATRAN HK LTD
High Speed Optical Tilted Charge Devices And Methods
ActiveUS20130126825A1Reduce heatReduce surface recombinationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureQuantum size effect
A method for producing optical signals with improved efficiency, including the following steps: providing a layered semiconductor structure that includes a substrate, a semiconductor collector region of a first conductivity type, a semiconductor base region of a second conductivity type disposed on the collector region, and a semiconductor emitter region of the first semiconductor type disposed as a mesa over a portion of a surface of the base region; providing, in the base region, at least one region exhibiting quantum size effects; providing collector, base, and emitter electrodes, respectively coupled with the collector, base and emitter regions; providing a tunnel barrier layer over at least the exposed portion of the surface of the base region; and applying signals with respect to the collector, base, and emitter electrodes to produce optical signals from the base region.
Owner:QUANTUM ELECTRO OPTO SYST
Semiconductor Device And Method For Producing Light And Laser Emission
ActiveUS20140050241A1Easy to switchEasily modulatedLaser detailsLaser active region structureHigh energyLight emission
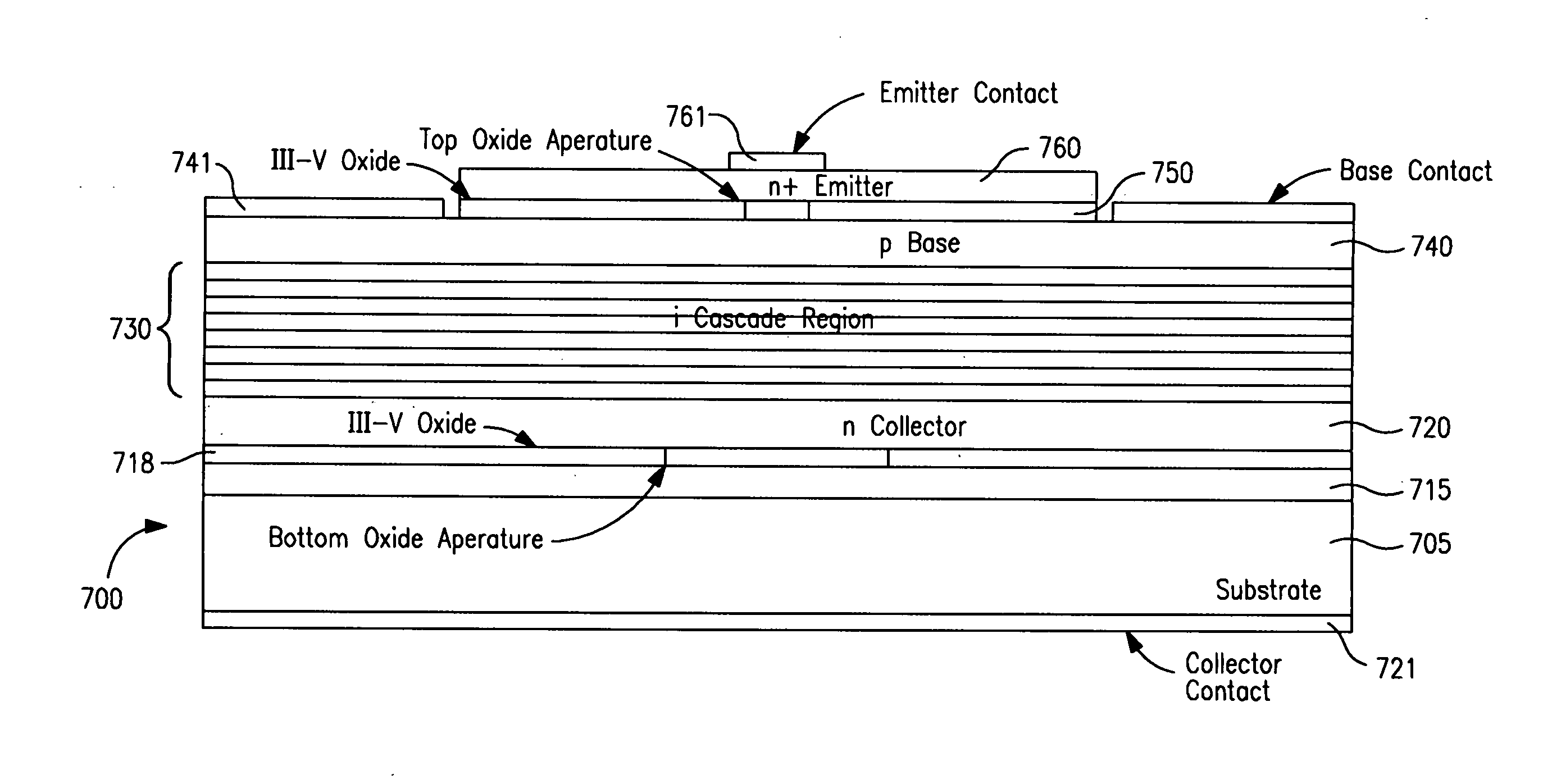
A method for producing light emission, including the following steps: providing a transistor structure that includes a semiconductor base region disposed between a semiconductor emitter region and a semiconductor collector region; providing a cascade region between the base region and the collector region, the cascade region having a plurality of sequences of quantum size regions, the quantum size regions of the sequences varying, in the direction toward the collector region, from a relatively higher energy state to a relatively lower energy state; providing emitter, base and collector electrodes respectively coupled with the emitter, base, and collector regions; and applying electrical signals with respect to the emitter, base, and collector electrodes to cause and control light emission from the cascade region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Light emitting and lasing semiconductor devices and methods
ActiveUS7953133B2Avoid injection and transportMaximize the stimulated recombination (emissionLaser active region structureLaser cooling arrangementsElectron flowQuantum size effect
A two terminal semiconductor device for producing light emission in response to electrical signals, includes: a terminal-less semiconductor base region disposed between a semiconductor emitter region and a semiconductor collector region having a tunnel junction adjacent the base region; the base region having a region therein exhibiting quantum size effects; an emitter terminal and a collector terminal respectively coupled with the emitter region and the collector region; whereby application of the electrical signals with respect to the emitter and collector terminals, causes light emission from the base region. Application of the electrical signals is operative to reverse bias the tunnel junction. Holes generated at the tunnel junction recombine in the base region with electrons flowing into the base region, resulting in the light emission. The region exhibiting quantum size effects is operative to aid recombination.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Aggregate of Semicnductor micro-needles and method of manufacturing the same, and semiconductor apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20030057451A1Easy to manufactureEnhancing quantum size effectElectrophonic musical instrumentsFinal product manufactureInformation processingQuantum size effect
On a silicon substrate is formed a silicon dioxide film and then hemispherical grains made of silicon, each having an extremely small diameter, are deposited thereon by LPCVD. After annealing the hemispherical grains, the silicon dioxide film is etched using the hemispherical grains as a first dotted mask, thereby forming a second dotted mask composed of the silicon dioxide film. The resulting second dotted mask is used to etch the silicon substrate to a specified depth from the surface thereof, thereby forming an aggregate of semiconductor micro-needles. Since the diameter of each of the semiconductor micro-needles is sufficiently small to cause the quantum size effects as well as has only small size variations, remarkable quantum size effects can be obtained. Therefore, it becomes possible to constitute a semiconductor apparatus with a high information-processing function by using the aggregate of semiconductor micro-needles (quantized region).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
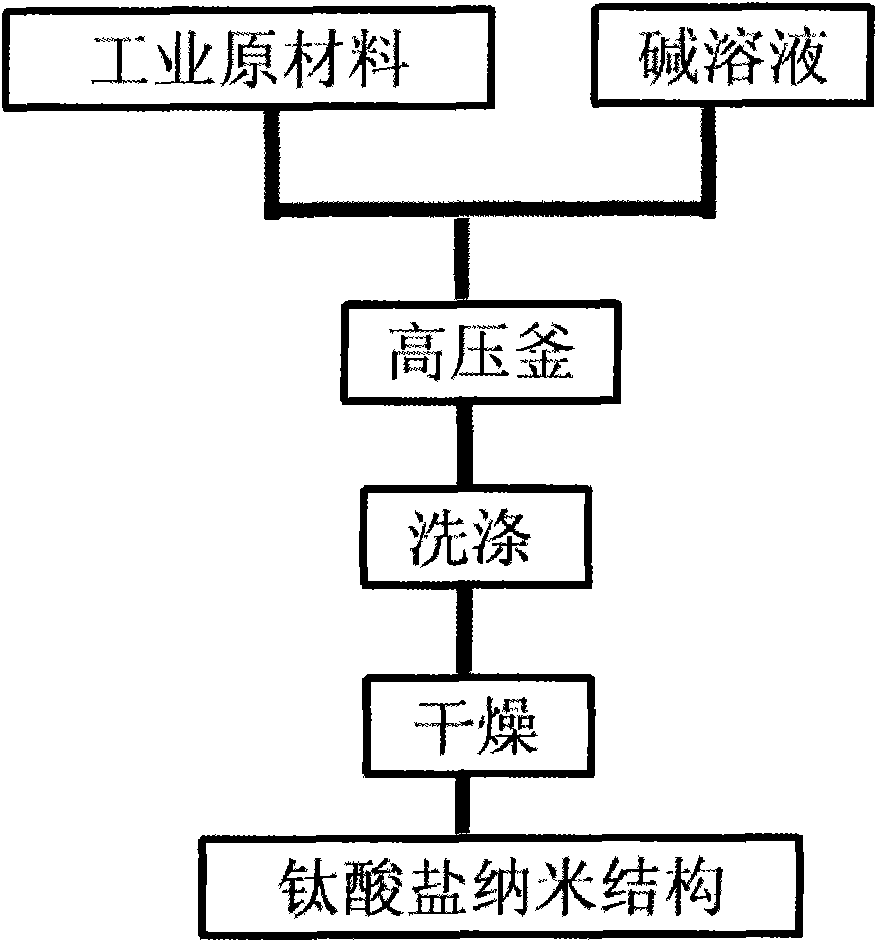
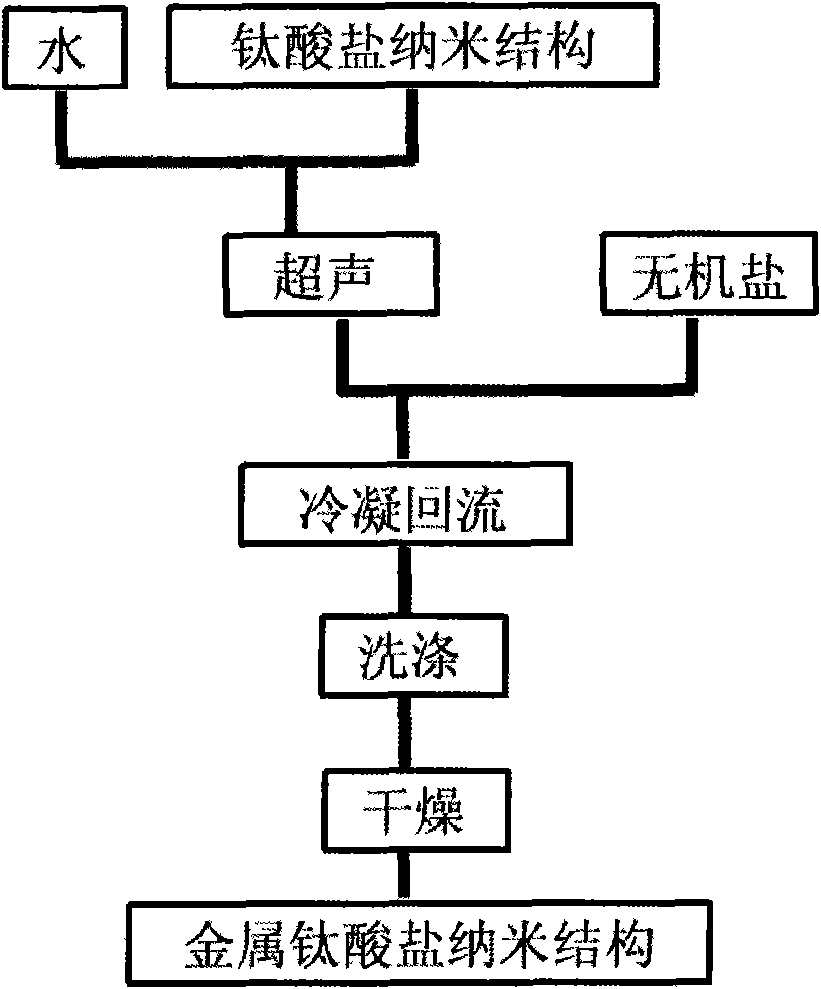
Method for preparing nanometer titanate with controllable appearances by utilizing industrial raw materials
InactiveCN101643240ALow costExcellent physical and chemical propertiesTitanium compoundsMicro nanoSulfate
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantum size zinc oxide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102161499AQuantum sizeStable structureZinc oxides/hydroxidesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansZno nanoparticlesCrystallinity
The invention provides quantum size zinc oxide, a preparation method thereof and application of the quantum size zinc oxide used as a gas-sensitive material. The method comprises the following steps of: performing an ethanol heat reaction of solution of zinc salt and solution of sodium hydroxide, and successfully preparing a zinc oxide quantum dot material with high crystallinity by adding a surface modification agent and controlling reaction conditions. The dimensions of quantum dots of the zinc oxide are 1 to 10nm. Compared with the conventional method for preparing the quantum dots of the zinc oxide, the method has the advantages of low cost, low energy consumption, high product crystallinity and the like and is easy to operate. A prepared nanometer zinc oxide material has excellent gas sensitivity to nitrogen dioxide gas, and is a good gas-sensitive material.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Optical Tilted Charge Devices And Methods
InactiveUS20130126826A1Improve internal quantum efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureLattice constant
A method for making an optical tilted-charge device that is substantially matched to GaAs lattice constant, including the following steps: providing a layered semiconductor structure that includes: a GaAs substrate; a semiconductor collector region; a semiconductor base region that includes a doped GaAs second base sub-region, an InGaAsN quantum size region, and a doped GaAs first base sub-region; and a semiconductor emitter region; and providing collector, base, and emitter electrodes respectively coupled with the collector region, the base region, and the emitter region. Electrical signals, applied with respect to the collector, base, and emitter electrodes, produces light emission from the base region.
Owner:MELAKA MEDIA HOUSE
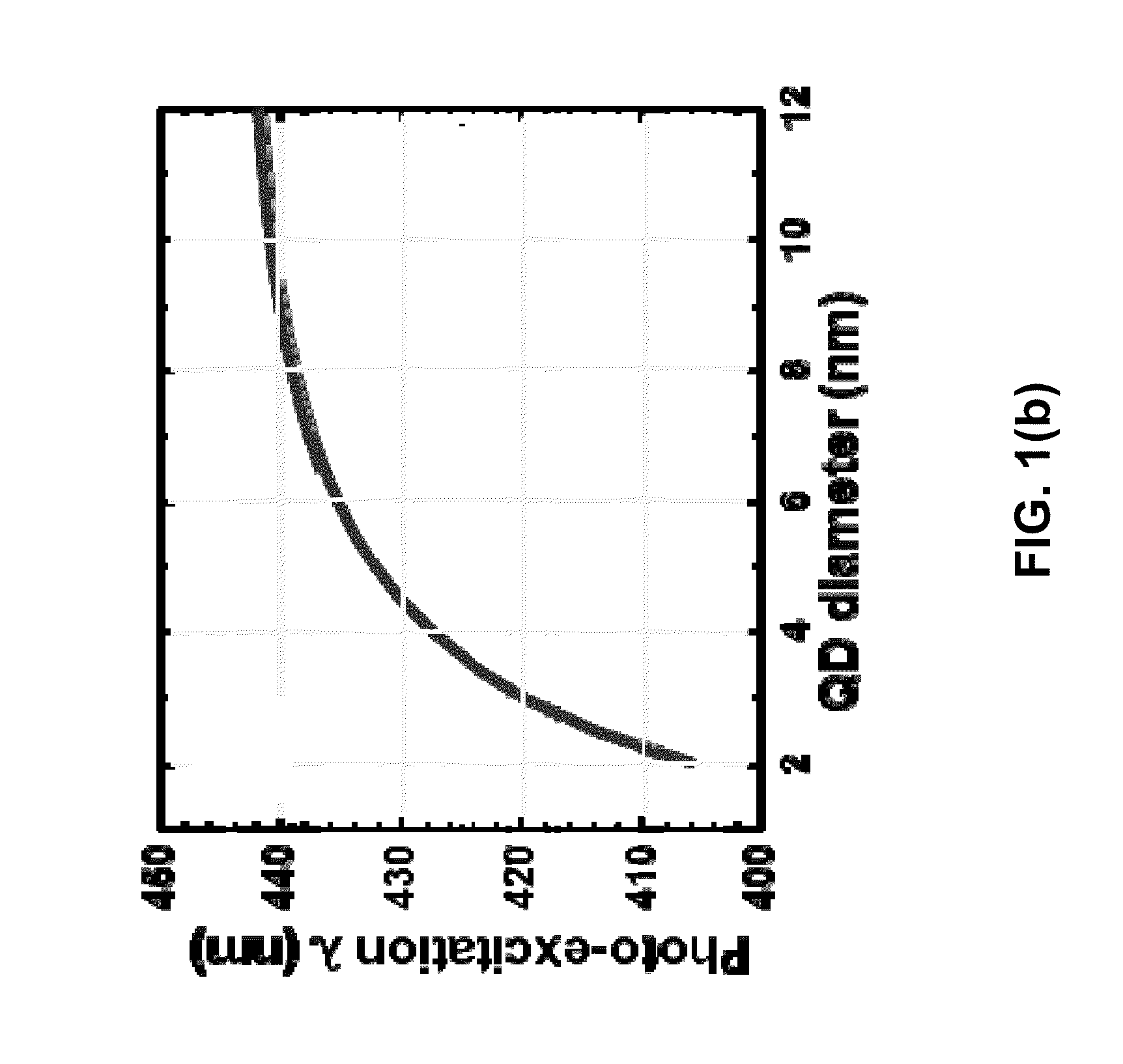
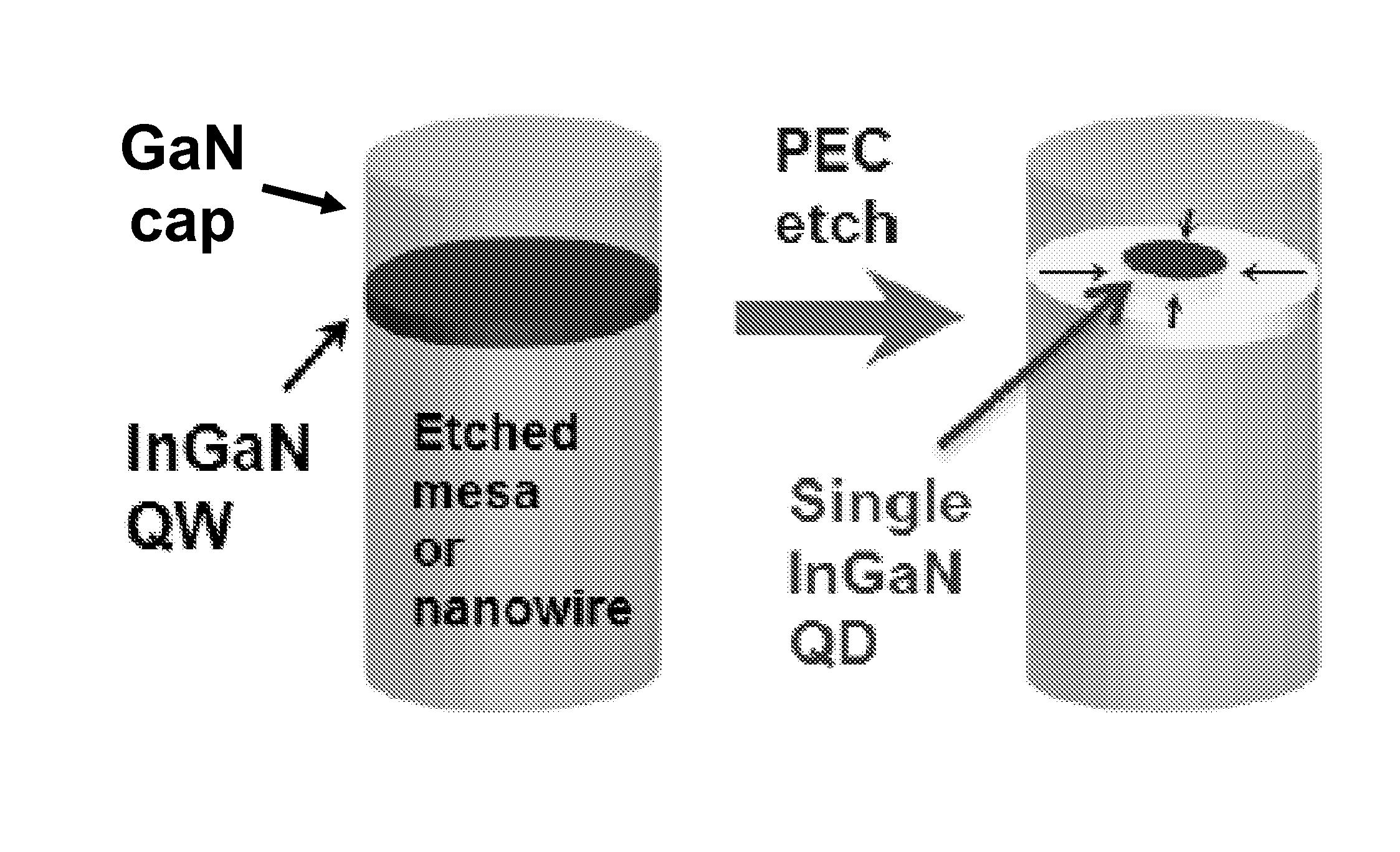
Quantum-size-controlled photoelectrochemical etching of semiconductor nanostructures
ActiveUS9276382B2Increase etch rateIncrease of bandgapsLaser detailsIndividual molecule manipulationPhotoelectrochemical etchingPhotoluminescence
Quantum-size-controlled photoelectrochemical (QSC-PEC) etching provides a new route to the precision fabrication of epitaxial semiconductor nanostructures in the sub-10-nm size regime. For example, quantum dots (QDs) can be QSC-PEC-etched from epitaxial InGaN thin films using narrowband laser photoexcitation, and the QD sizes (and hence bandgaps and photoluminescence wavelengths) are determined by the photoexcitation wavelength.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Quantum-Size-Controlled Photoelectrochemical Etching of Semiconductor Nanostructures
ActiveUS20150270136A1Increase etch rateLower the volumeLaser detailsIndividual molecule manipulationPhotoelectrochemical etchingPhotoluminescence
Quantum-size-controlled photoelectrochemical (QSC-PEC) etching provides a new route to the precision fabrication of epitaxial semiconductor nanostructures in the sub-10-nm size regime. For example, quantum dots (QDs) can be QSC-PEC-etched from epitaxial InGaN thin films using narrowband laser photoexcitation, and the QD sizes (and hence bandgaps and photoluminescence wavelengths) are determined by the photoexcitation wavelength.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Zinc sulfide-benzoic acid nano composite photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103191783ASmall sizeGood electron transport propertiesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsZinc hydroxideBenzoic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nano composite materials and specifically relates to a zinc sulfide-benzoic acid nano composite photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. The zinc sulfide-benzoic acid nano composite photocatalytic material is obtained by taking zinc salt and a benzoate as raw materials, obtaining a benzoate intercalated layered zinc hydroxide nano composite material in a water phase solution through the coordination of zinc ions and benzoate carboxyl functional group and then reacting the benzoate intercalated layered zinc hydroxide nano composite material with H2S gas. Compared with the prior art, the zinc sulfide-benzoic acid nano composite photocatalytic material provided by the invention realizes even dispersion of zinc sulfide nano-particles of quantum size in benzoic acid array, and is capable of effectively inhibiting compounding of electrons with holes and improving the photocatalytic efficiency of zinc sulfide nano-particles; besides, the method is simple in preparation process, rich in raw material source and easy to expand in production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Optical Tilted Charge Devices And Techniques
A method for producing light emission, including the following steps: providing a layered semiconductor structure that includes a collector region, a first base region, a first emitter region, a coupling region, a second base region, and a second emitter region; providing a quantum size region within the second base region; and applying electrical signals with respect to the second emitter region, the first base region and the collector region, to produce light emission from the second base region.
Owner:QUANTUM ELECTRO OPTO SYST
Nickel-titanium dioxide-carbon trinary nano composite catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104826631AEffective size controlEffective control over dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationNickel saltP-Aminophenol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nickel-titanium dioxide-carbon trinary nano composite catalyst. In the provided preparation method, nickel salts, titanium salts and salicylate are taken as the primary raw materials; nickel ions, titanium ions and salicyl-carboxyl functional groups can self-assemble in an aqueous solution through the coordination interaction so as to obtain a three-dimensional flower-shaped structure, namely a salicyl-intercalated layered nickel-titanium hydroxide nano composite material, and finally burning the composite material in an atmosphere of inert gas through utilizing the self-reductive property of carbon so as to obtain the catalyst. Through the preparation method, carbon-coated nickel nano particles with a quantum size can be evenly dispersed among the titanium dioxide carrier, and thus the catalytic activity and stability of the catalyst are both improved. In the liquid-phase hydrogenation reactions of nitro-phenol, the provided catalyst can convert nitro-phenol into p-aminophenol within three minutes, the catalyst efficiency of the provided catalyst is 7 times faster than that of Pt@C catalyst, after the catalyst is repeatedly used for 10 times, the conversion rate of the provided catalyst can still reach 90% or more, and the catalyst can be recovered magnetically.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing metal oxide nanosheet with quantum size by taking biomass as template
ActiveCN109879314ALow costSolve the contradiction of low separation efficiencyCatalyst activation/preparationNanotechnologyPorosityMetal oxide nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for preparing a metal oxide nanosheet with a quantum size by taking biomass as a template. The method comprises the following steps that carbonized biomass obtained through high-temperature calcination is used as a template, oxygen-containing functional groups exposed out of the surface of a hierarchical structure of the carbonized biomass are used as bridging points, and a metal oxide precursor is anchored to the hierarchical structure through the coupling effect; then high-temperature annealing is carried out in an N2 atmosphere for forming metal oxide nanoparticles, and calcination is carried out to remove a carbon frame structure, so that a lamellar structure composed of the quantum-size metal oxide nanoparticles is formed. Raw materials related in theinvention are low in price, the preparation process is simple and controllable, no organic solvent is contained, no harmful gas is generated, and environmental friendliness is achieved. The nanosheetprepared by the method has the characteristics of large size, adjustable particle size, porosity and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Biosensor and manufacturing method for same
InactiveCN103926295AHigh sensitivityImprove compatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetal oxide nanoparticlesComposite film
The invention discloses a biosensor and a manufacturing method for the same, and belongs to the technical field of sensor detection. The biosensor comprises an electrode, wherein a composite film is arranged on the surface of the electrode, and comprises a biomolecular probe and conductive metal doped metal oxide nanoparticles; metal oxide has semiconductor properties; the molar ratio of conductive metal to the metal oxide is 0.5 to 10 percent. According to the biosensor and the manufacturing method for the same, the surface of the electrode is wrapped with the composite film comprising the conductive metal doped metal oxide nanoparticles and the biomolecular probe, the nanoparticles are introduced into the construction of a biosensitive interface by utilizing the characteristics of surface effects, quantum size effects, dielectric confinement effects and the like of the nanoparticles, and the conductive metal is doped into the metal oxide nanoparticles, so that the electron transfer efficiency of the composite film is improved, an oxidation-reduction electrochemical signal is enhanced, the sensitivity of the sensor is improved, and the limit of detection is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG TESTING INST OF PROD QUALITY SUPERVISION +2
Preparation method for semiconductor nanowire orderly distributed in array mode
InactiveCN104051576AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyReduce power generation costsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnode oxidationAluminium
A preparation method for semiconductor nanowires orderly distributed in an array mode includes the first step of washing a substrate to obtain a polished substrate without organisms or heavy metal or oxidation layers, the second step of arranging a thickness-adjustable aluminum layer on the substrate through evaporation, the third step of oxidizing the aluminum layer to obtain a porous anode alumina template according to an anode oxidation method, the fourth step of pouring precursor liquid in holes of the porous anode alumina template according to an electroplating method and achieving metal lattice array sedimentation in the holes of the porous anode alumina template by controlling the electroplating time, the fifth step of etching the porous anode alumina template in a wet mode through a solution to obtain a metal lattice array which is highly orderly distributed on the surface of the substrate and is uniform in quantum size, the sixth step of growing a required semiconductor nanowire array according to a gas-liquid-solid method with the metal lattice array as a catalyst, and the seventh step of removing the metal lattice array at the top end of the semiconductor nanowire array to complete preparation.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com