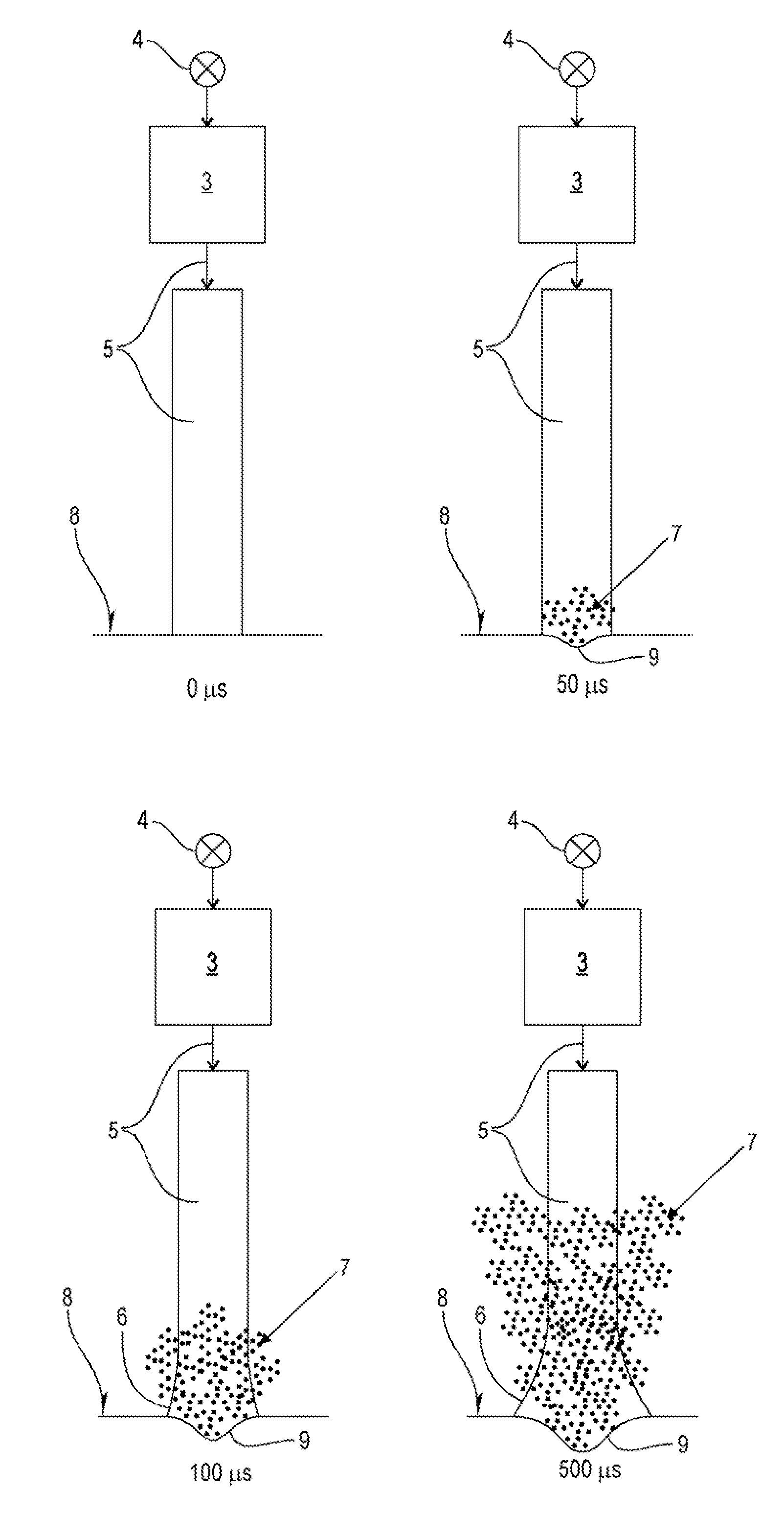
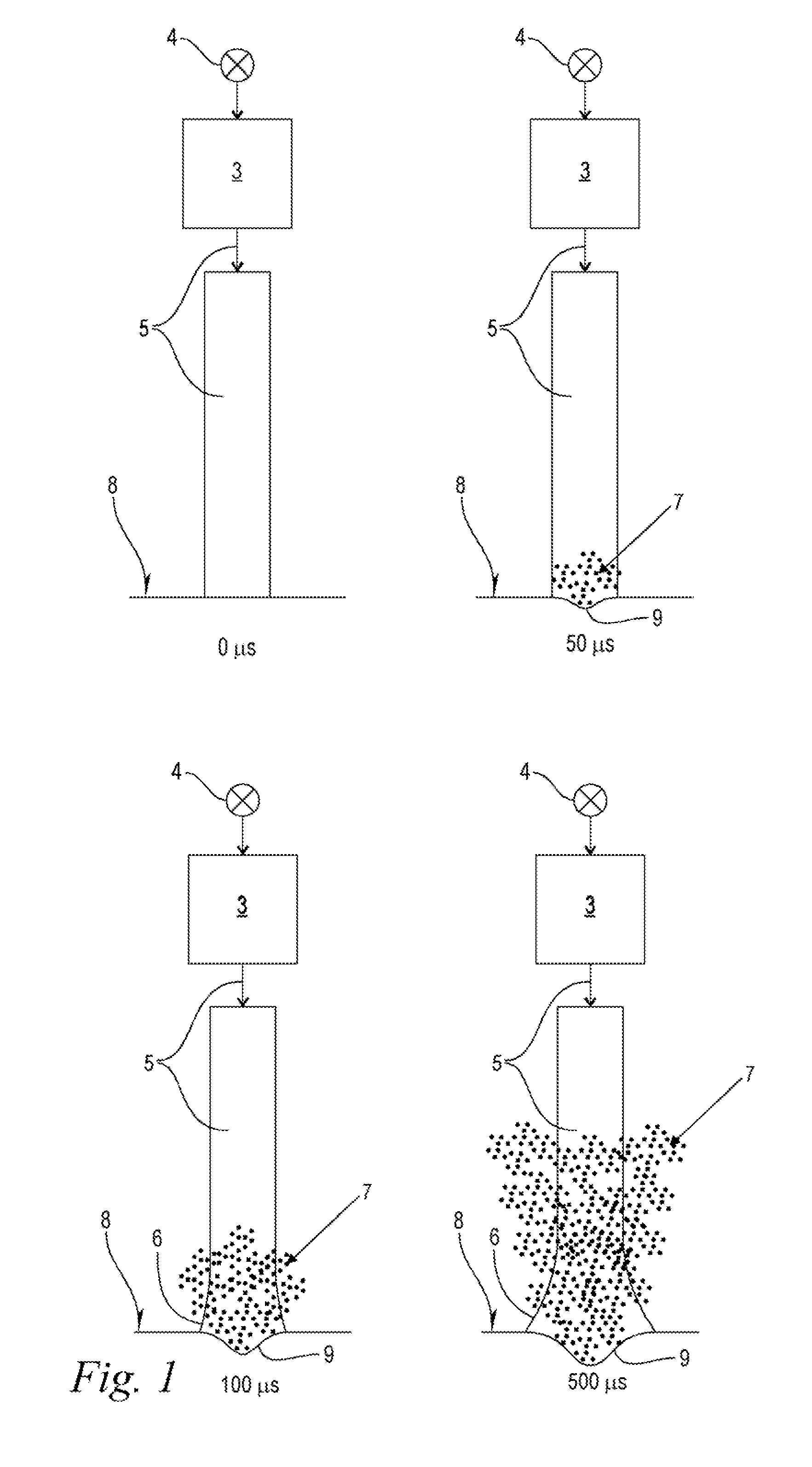
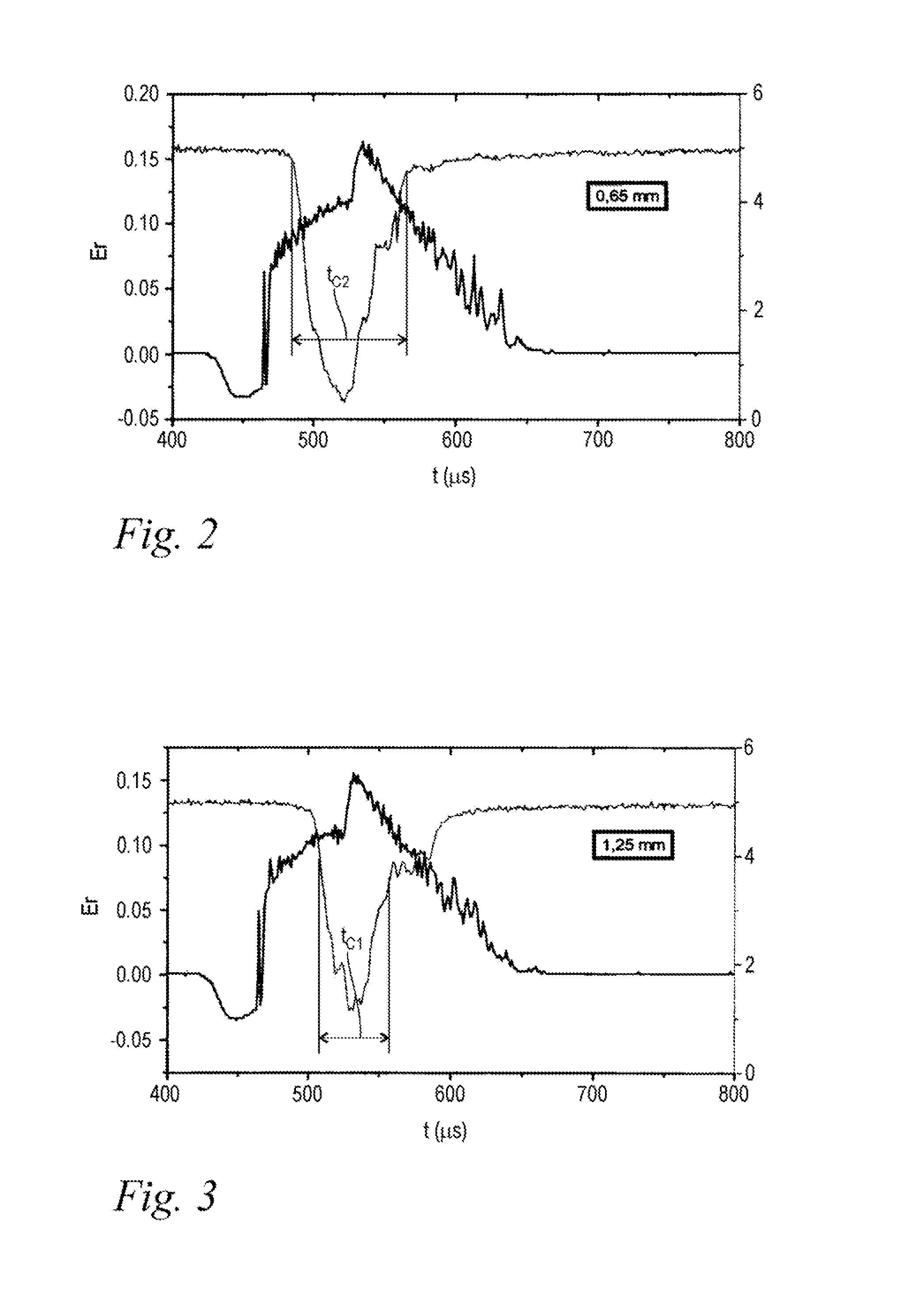
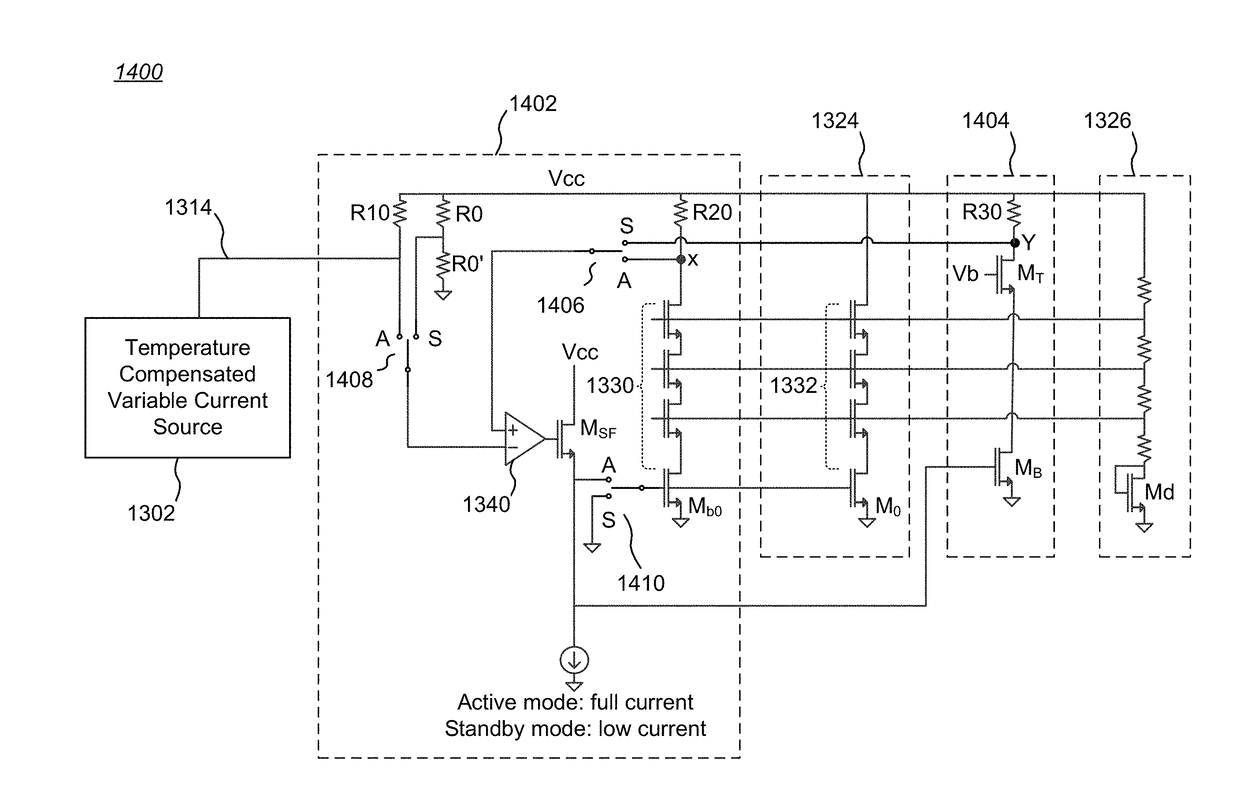
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
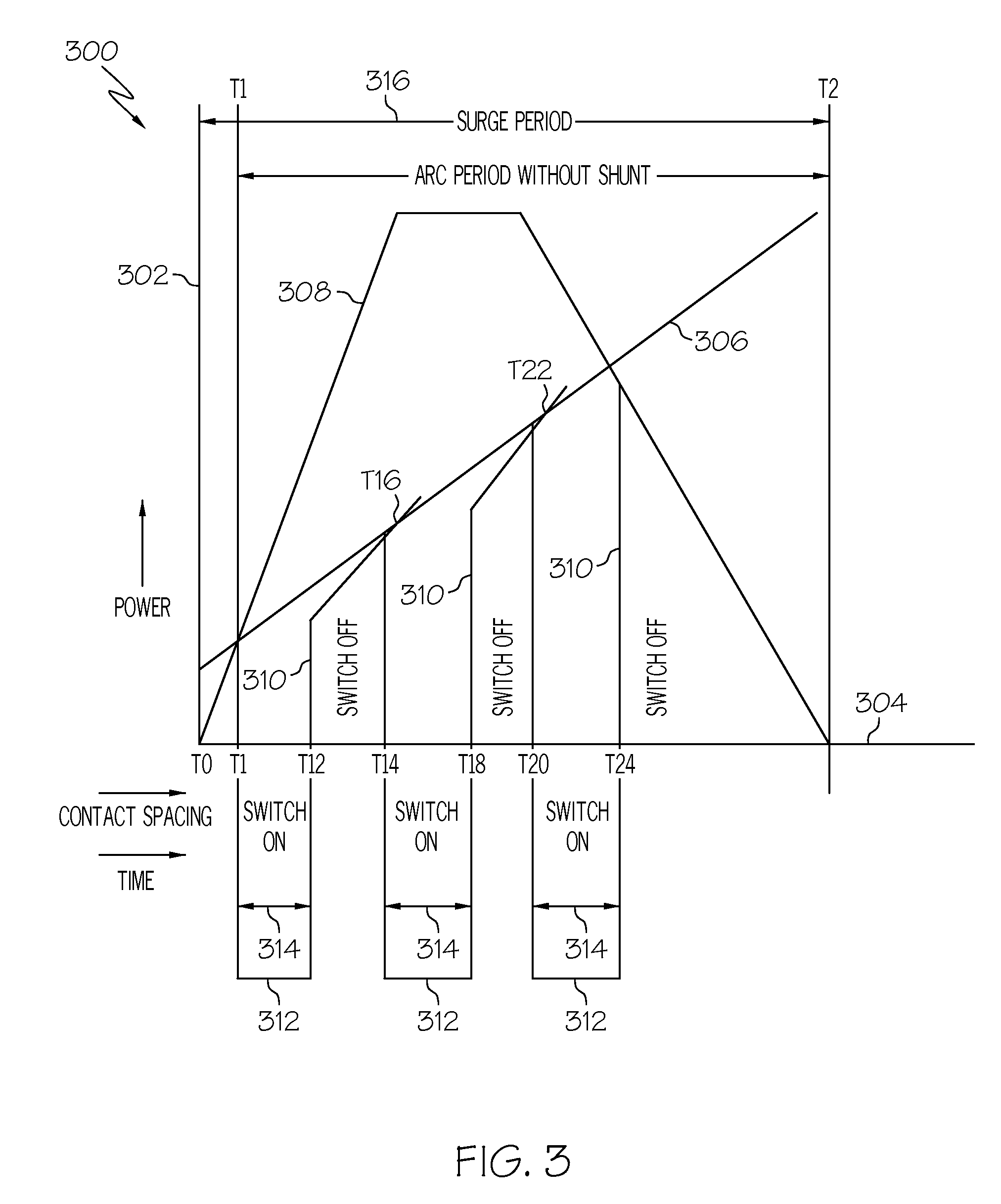
182 results about "Pulse operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
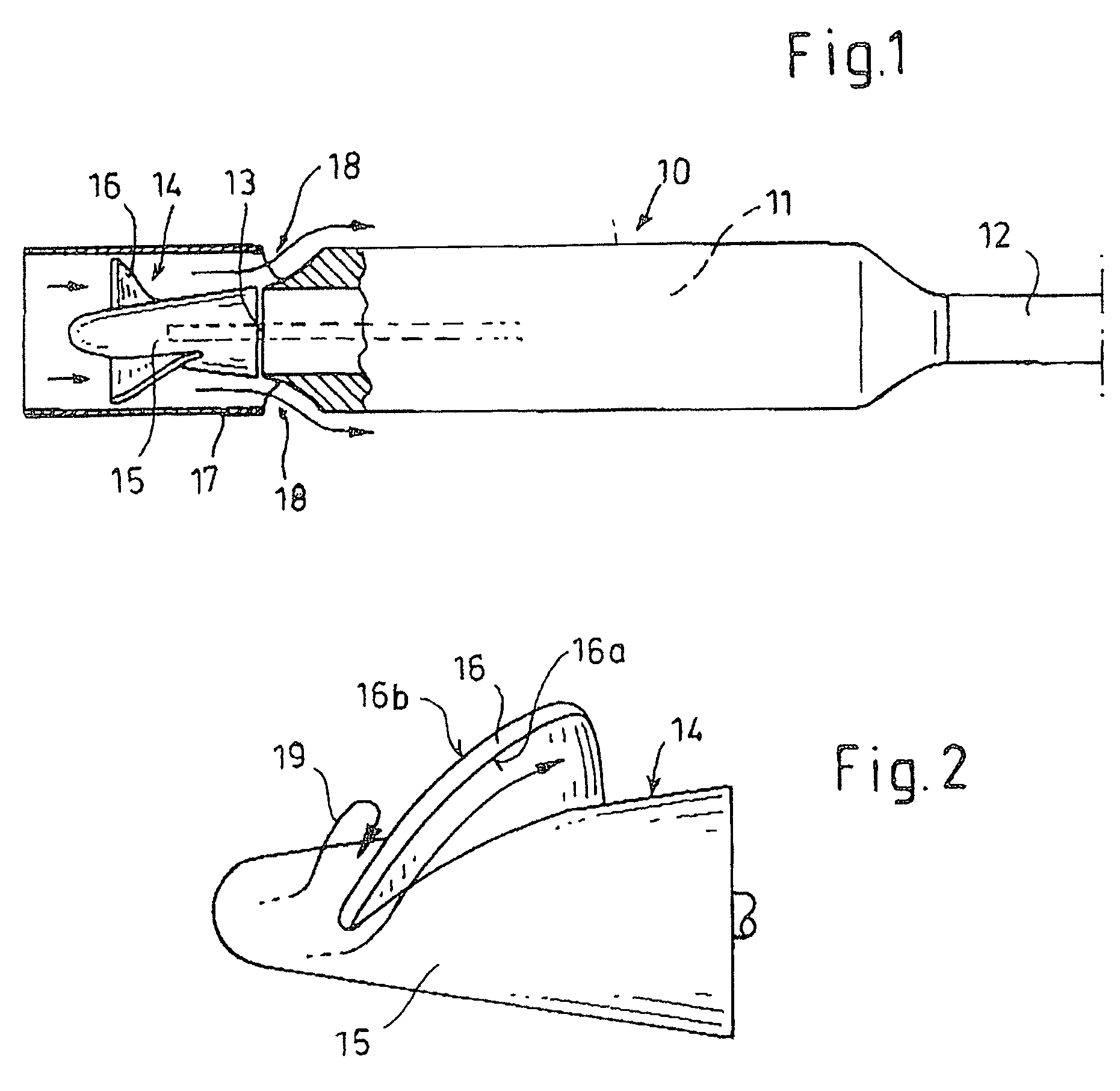
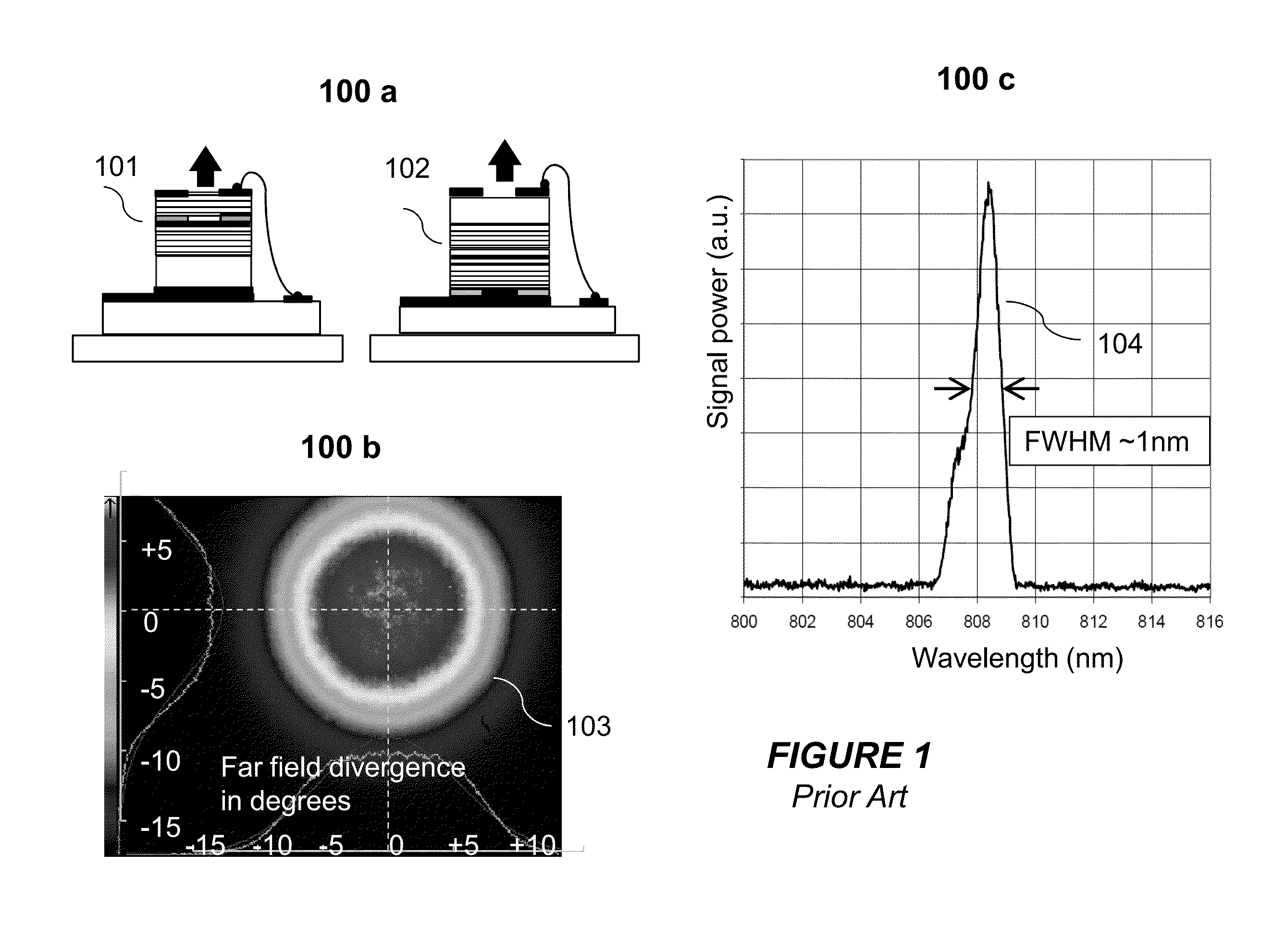
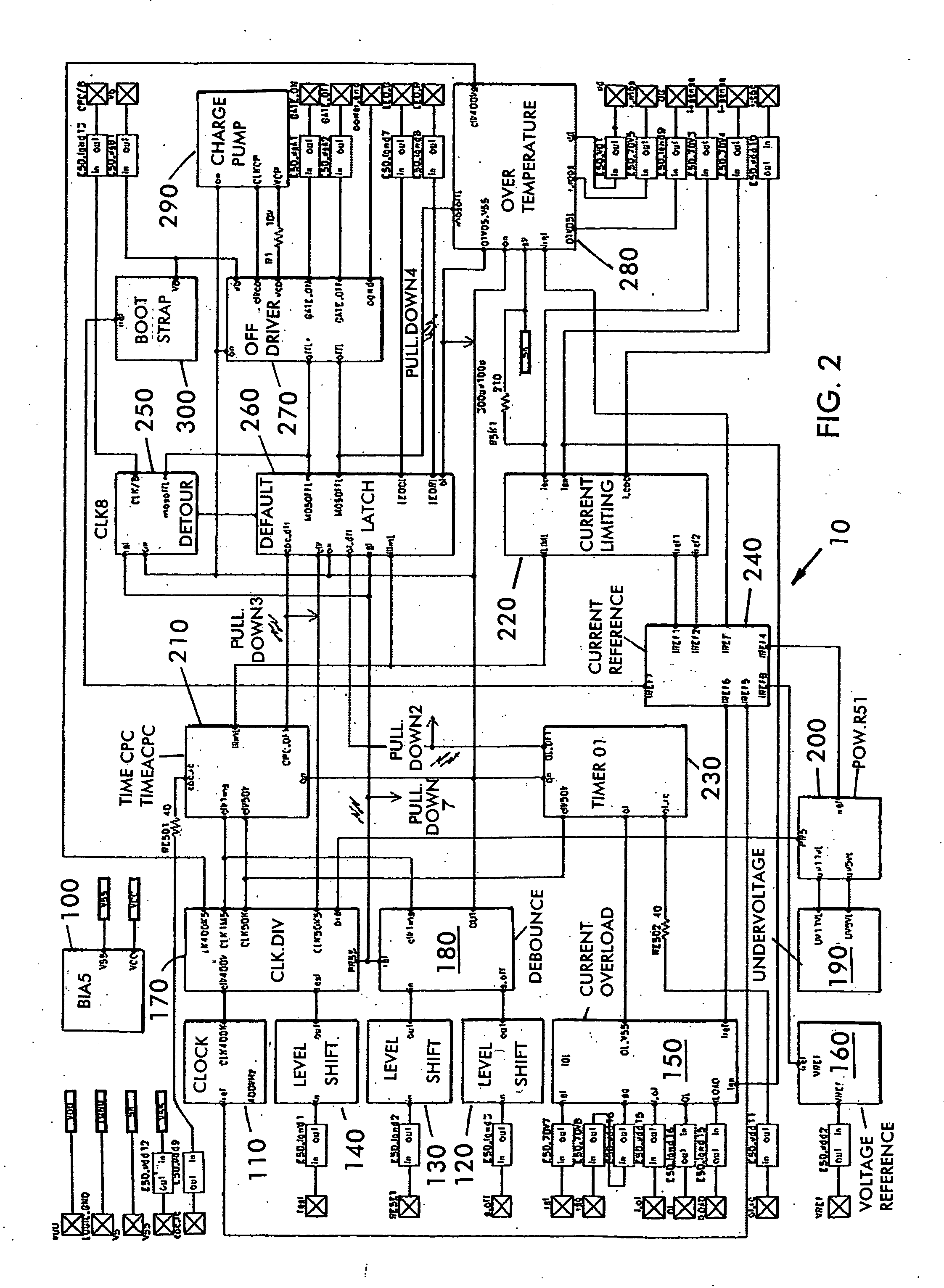
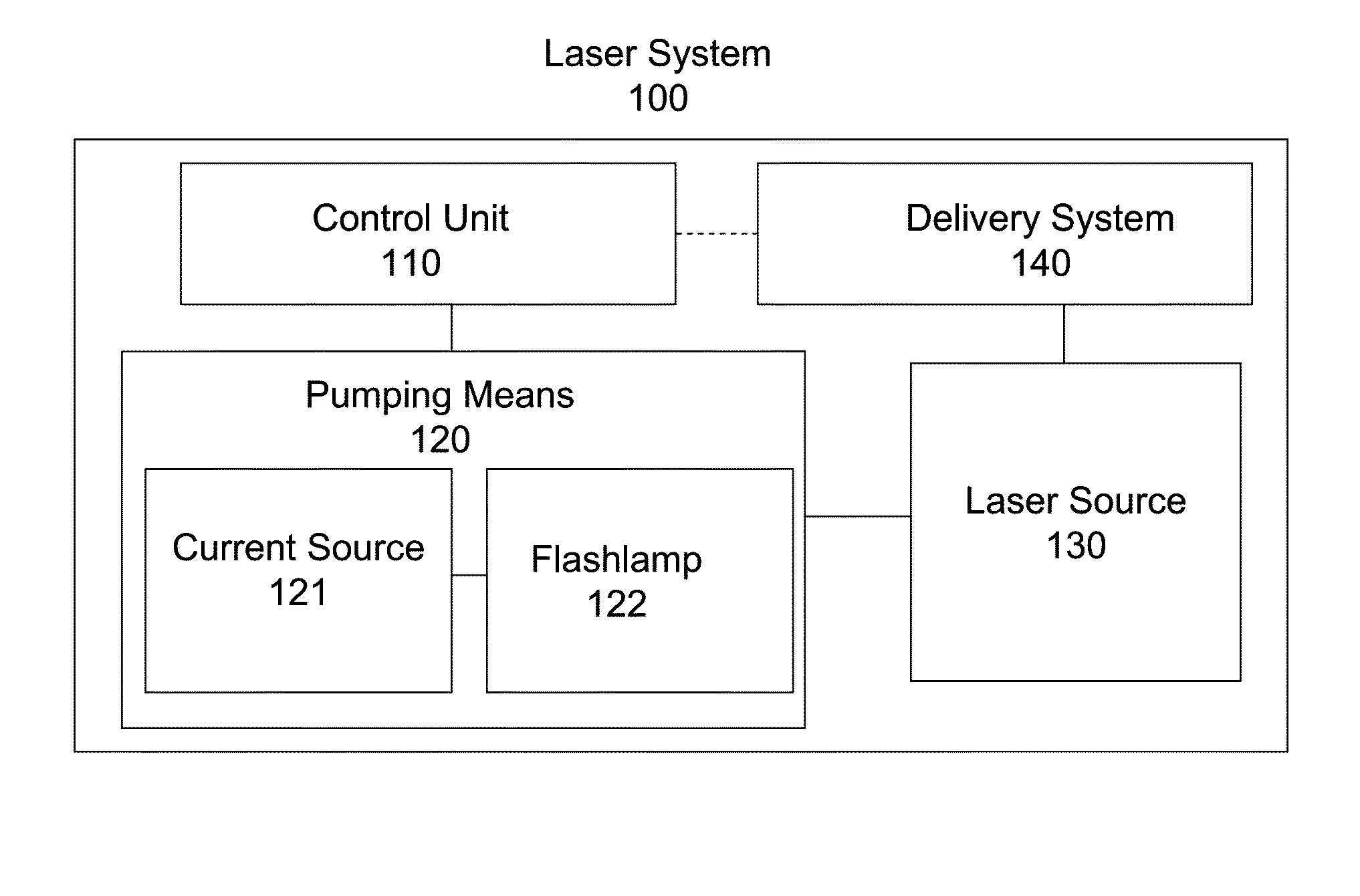
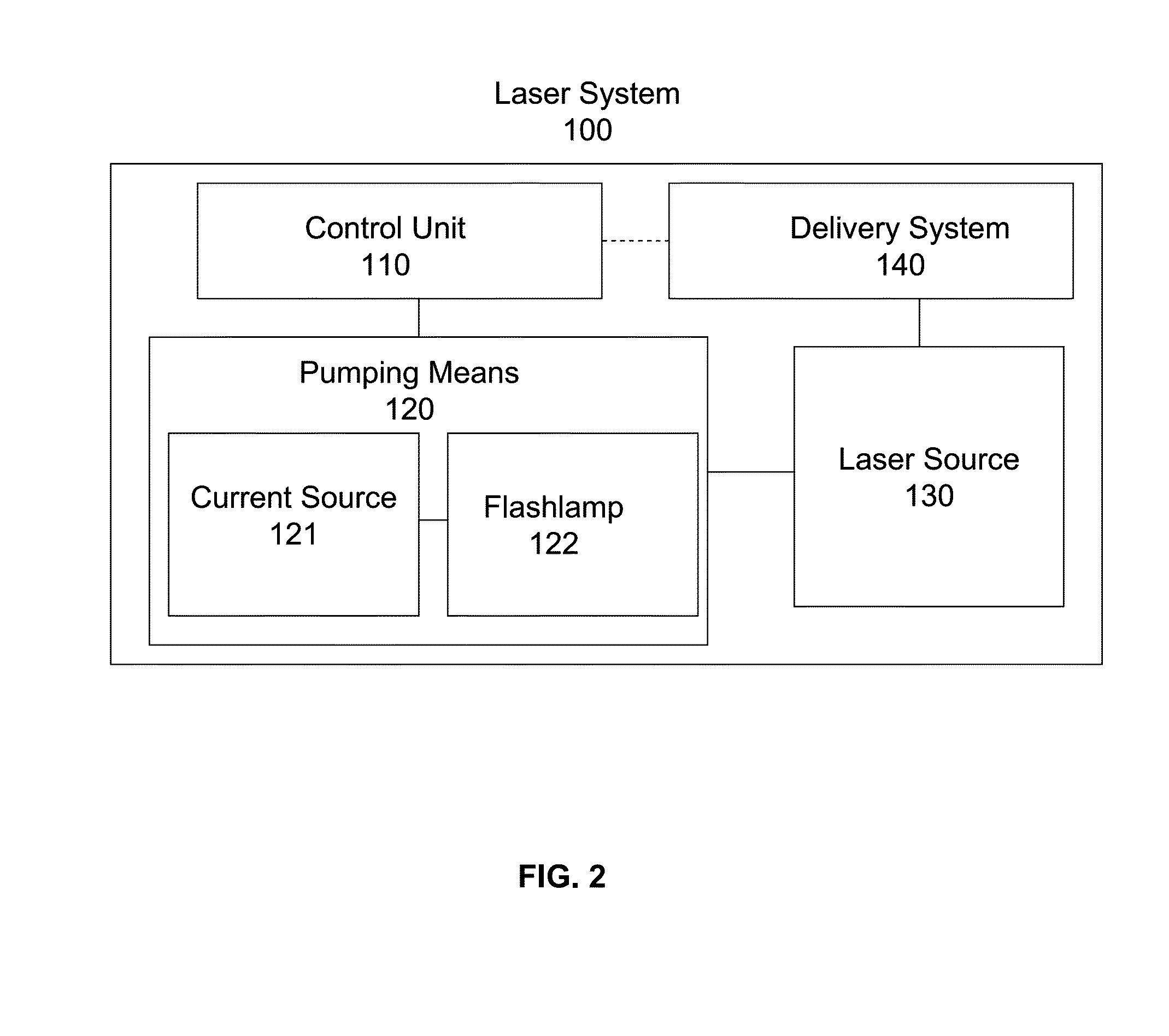
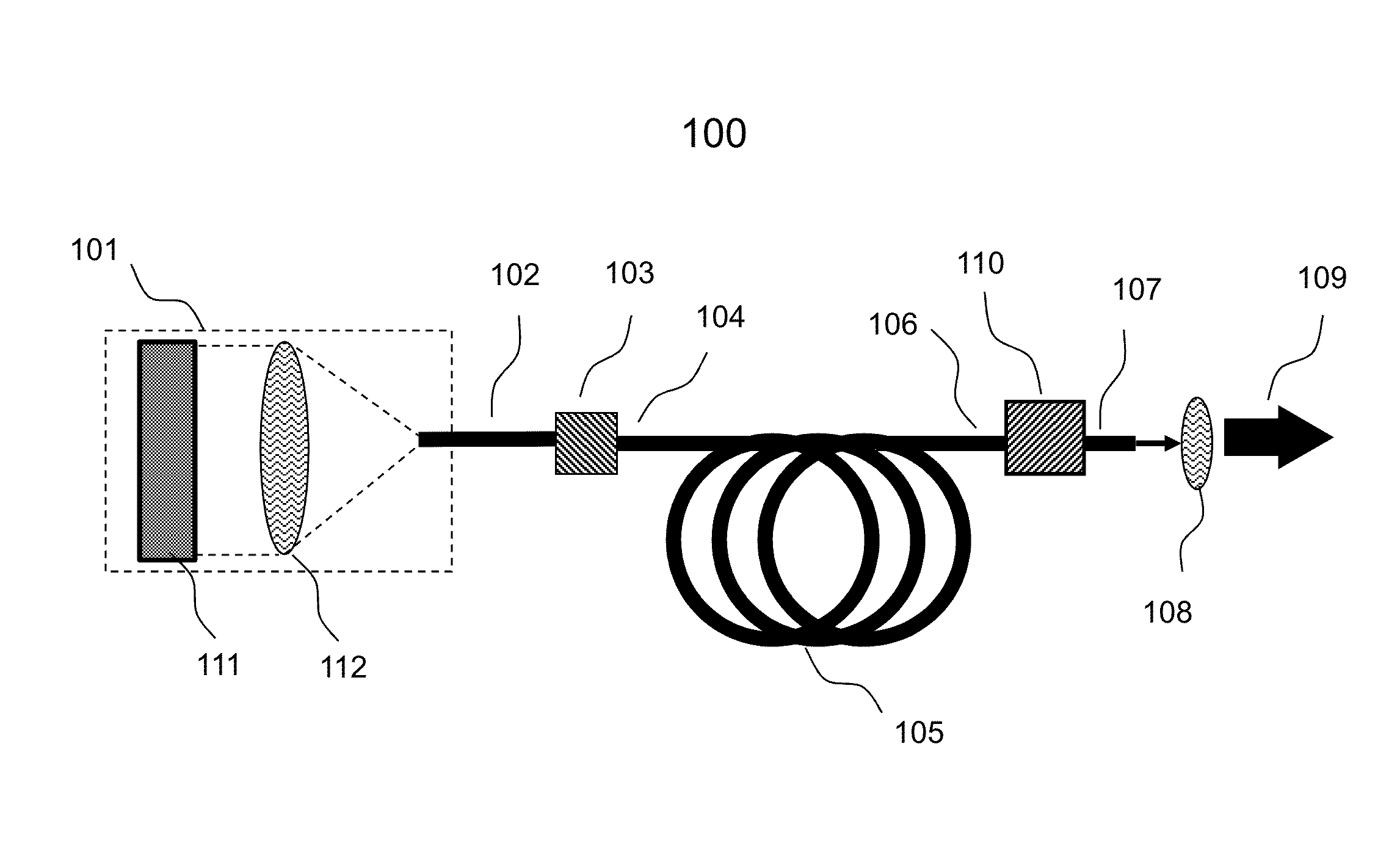
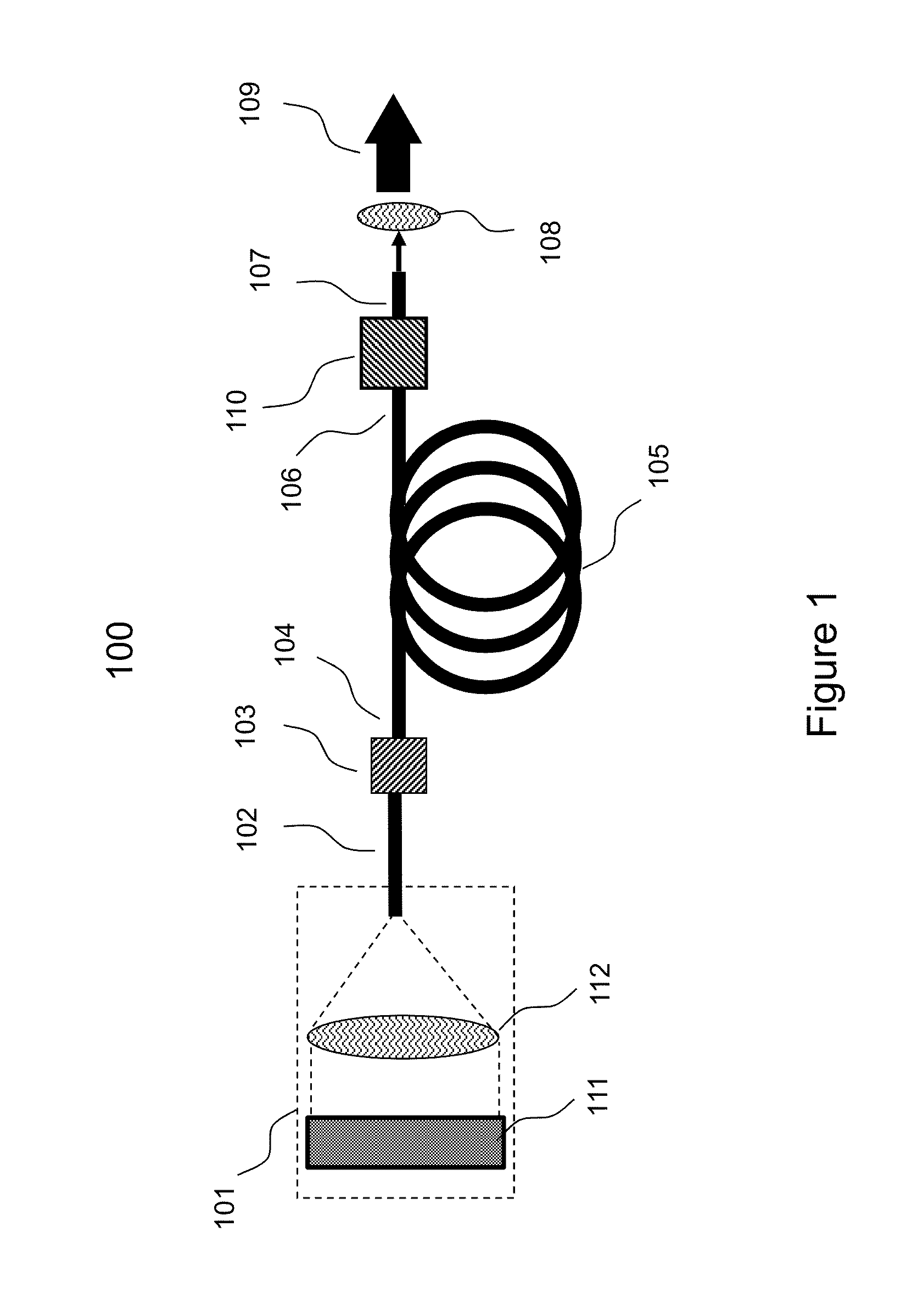
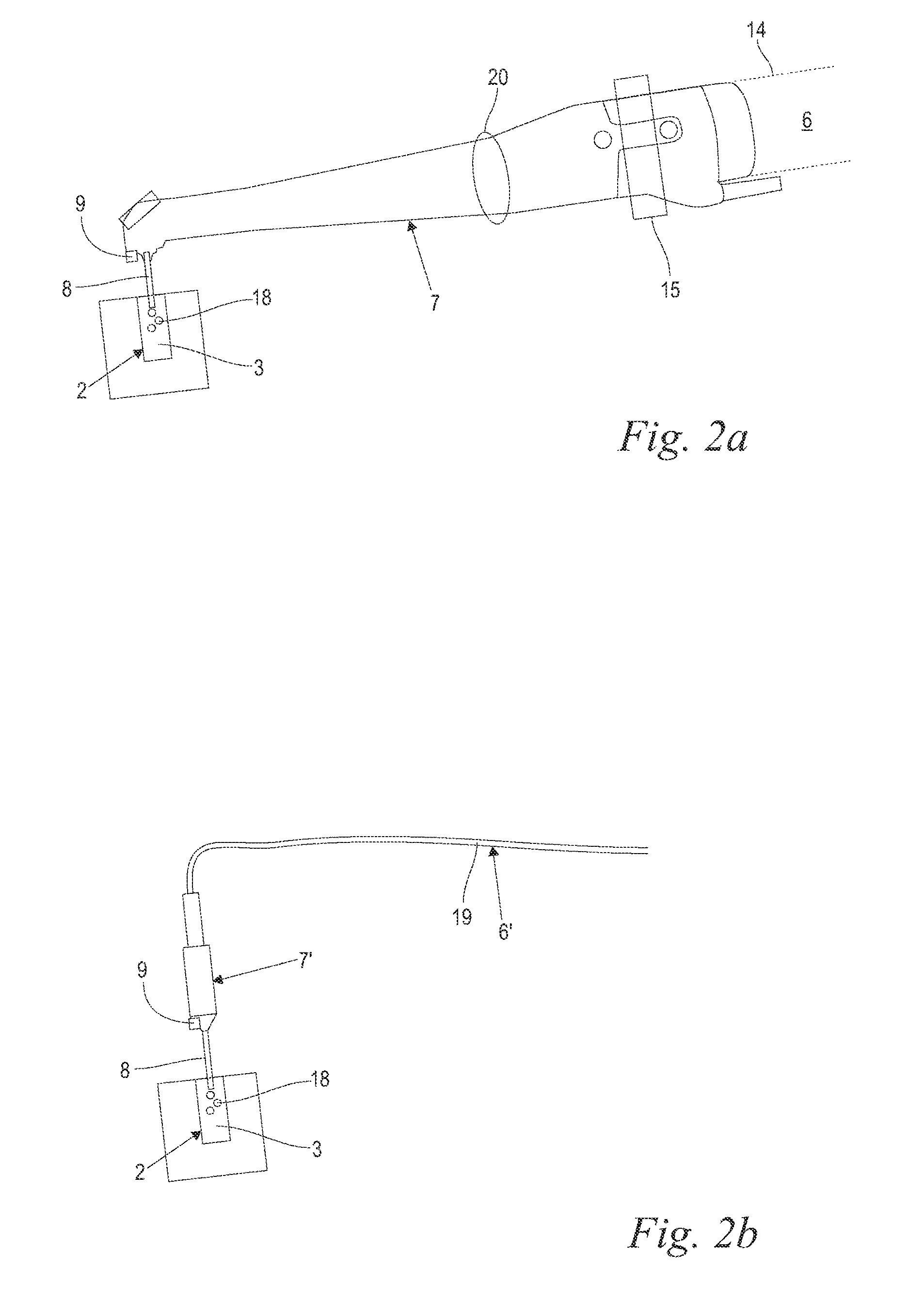
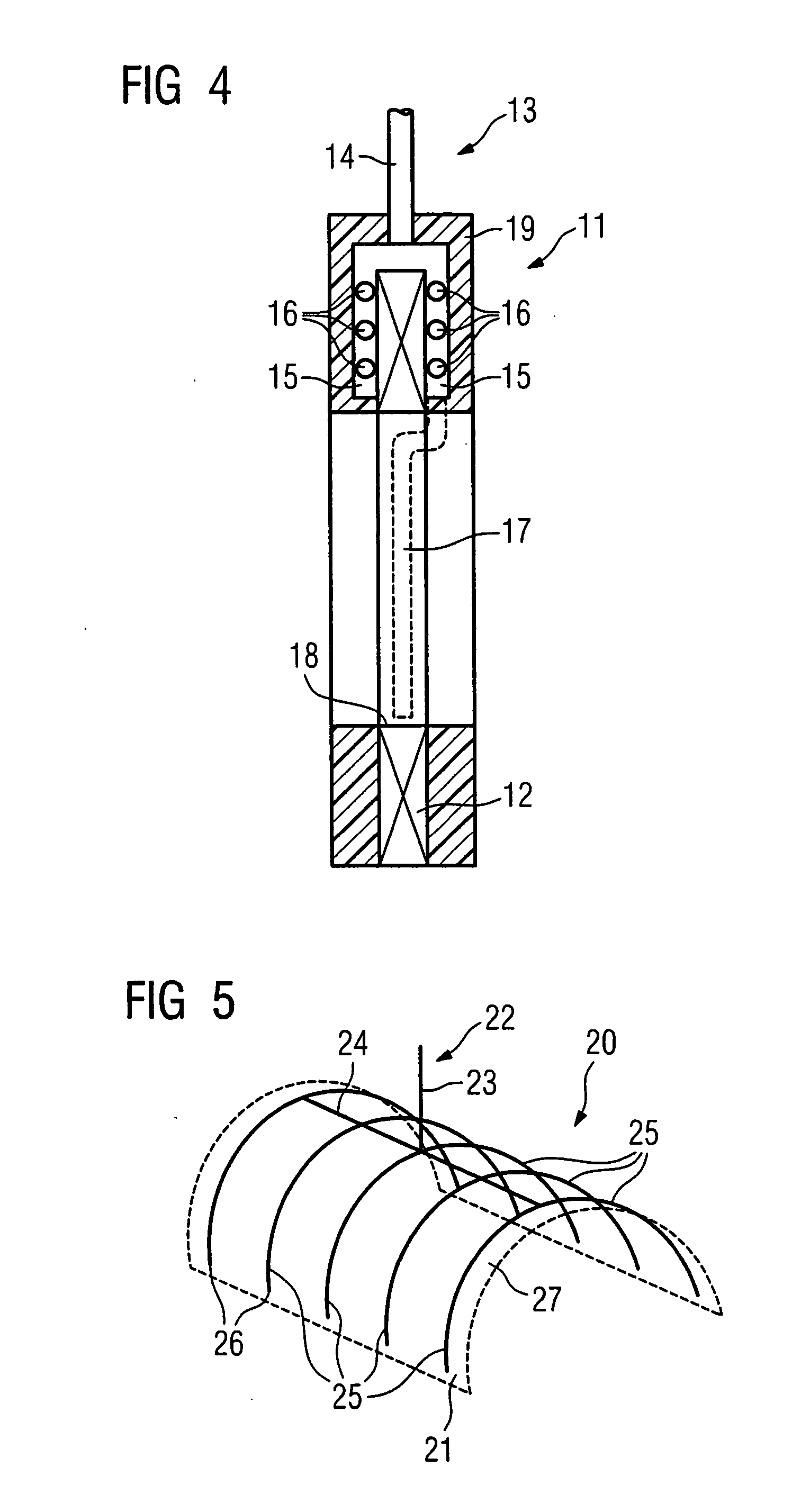
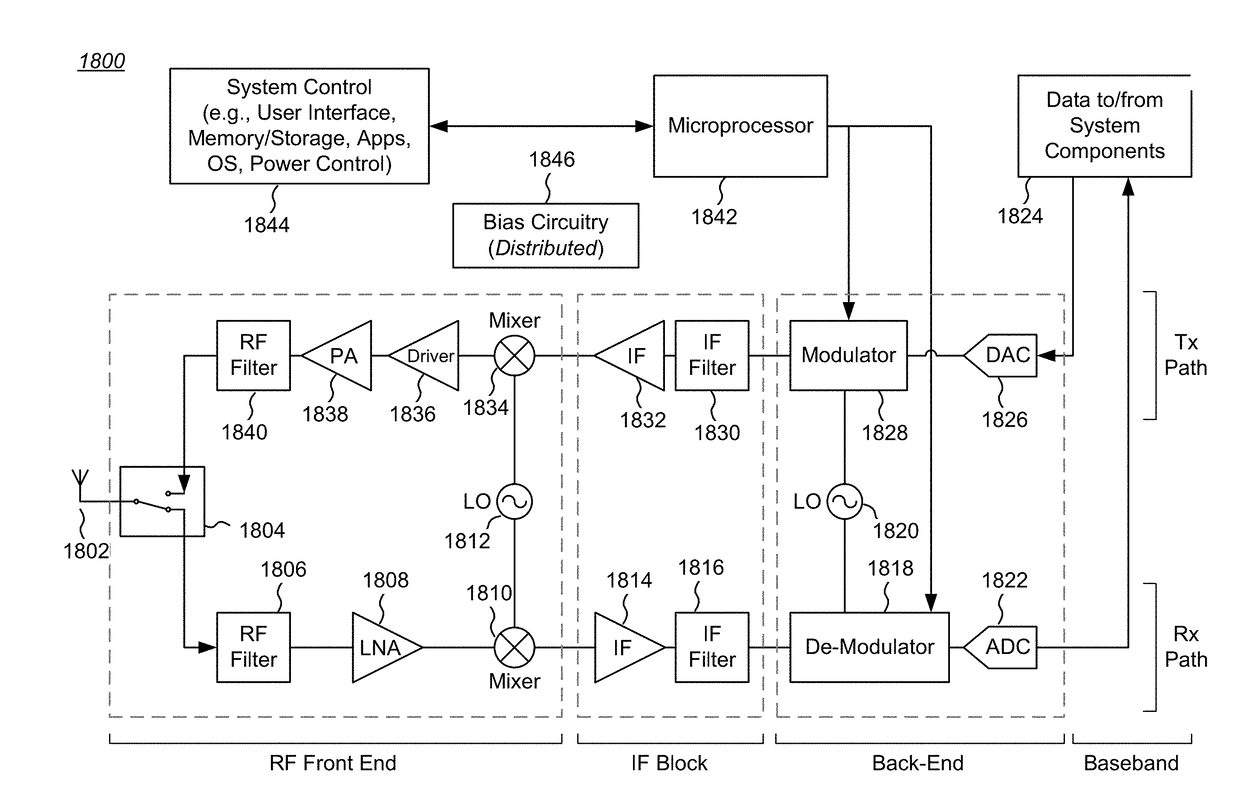
Laser Illuminator System
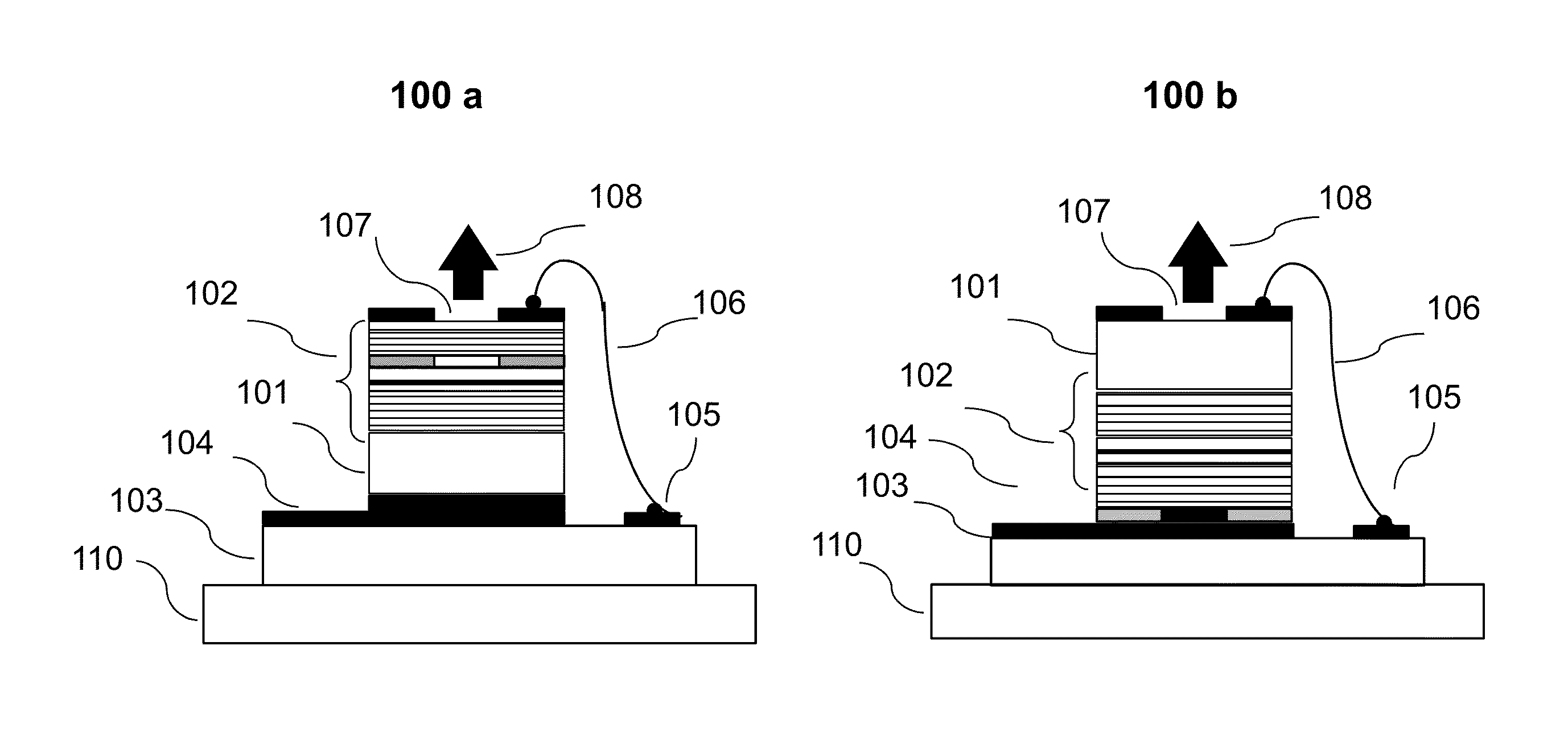
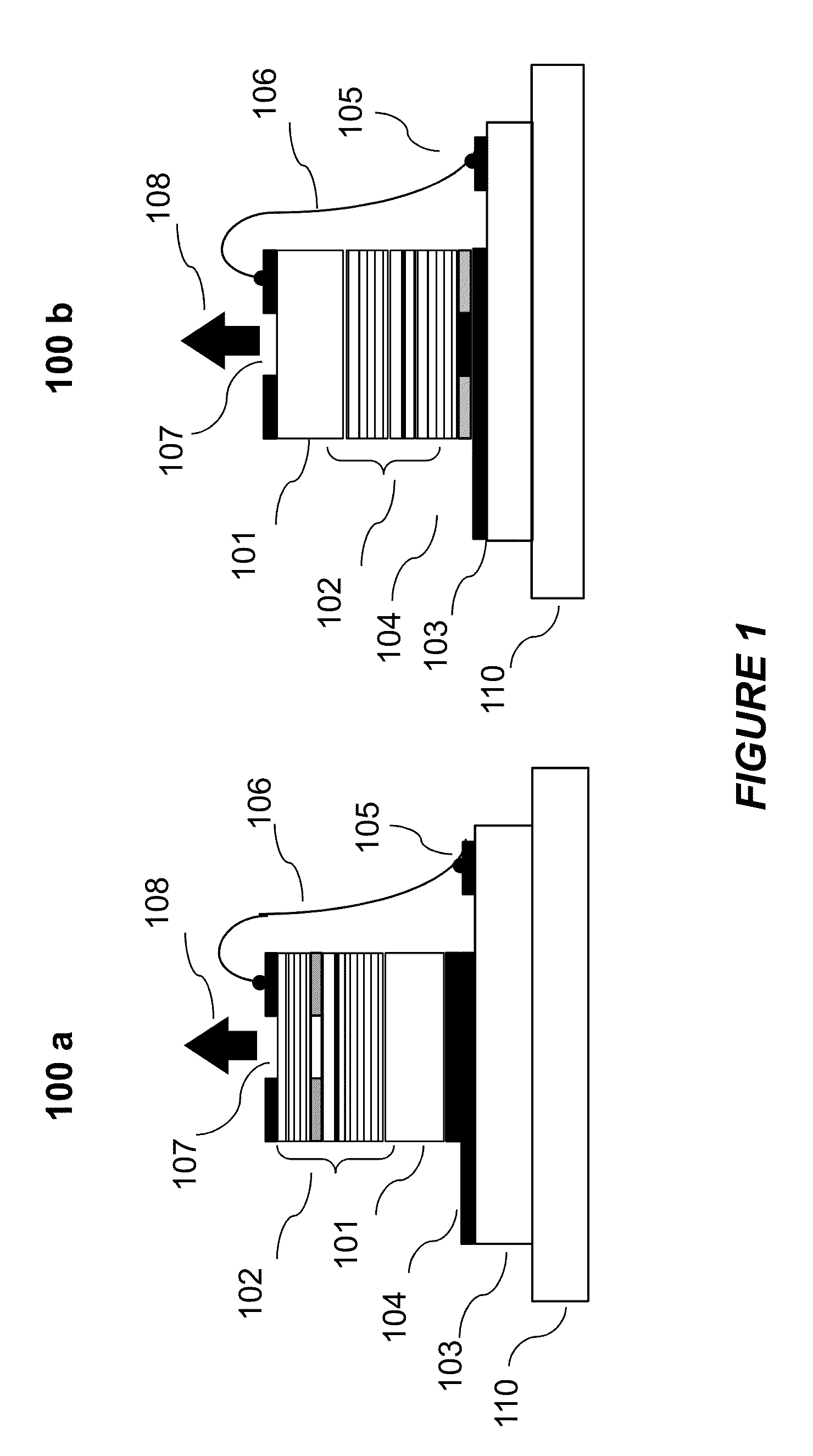
InactiveUS20130163627A1Improve thermal conductivityHeat dissipation fastSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLow inductance
An optical illuminator using Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is disclosed. Optical modules configured using single VCSEL and VCSEL arrays bonded to a thermal submount to conduct heat away from the VCSEL array, are suited for high power and high speed operation. High speed optical modules are configured using single VCSEL or VCSEL arrays connected to a high speed electronic module on a common thermal submount or on a common Printed Circuit Board (PCB) platform including transmission lines. The electronic module provides low inductance current drive and control functions to operate the VCSEL and VCSEL array. VCSEL apertures are designed for a desired beam shape. Additional beam shaping elements are provided for VCSELs or VCSEL arrays, for desired output beam shapes and / or emission patterns. VCSEL arrays may be operated in continuous wave (CW) or pulse operation modes in a programmable fashion using a built-in or an external controller.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
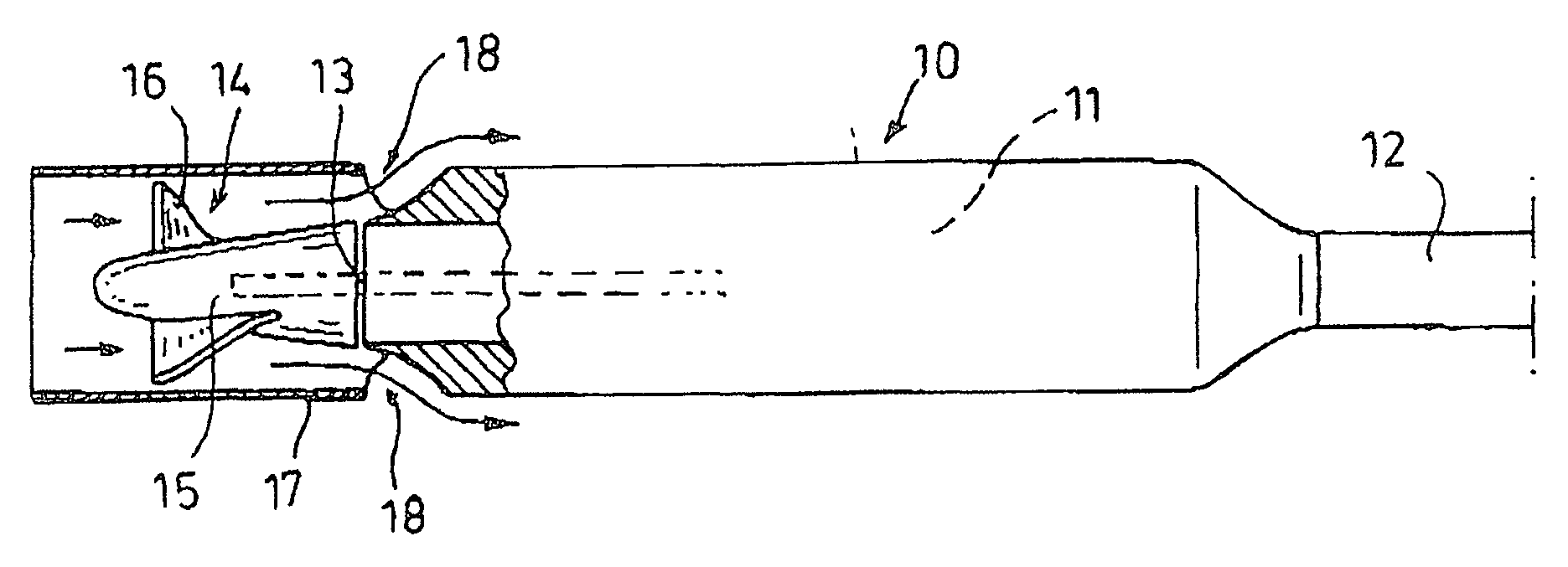
Method for controlling a blood pump
A blood pump is temporarily operated at a low rotational speed lying below a design rotational speed. This involves a risk of thrombogenesis since flow detachments may occur at blades of an impeller of the rotary blood pump. For eliminating deposits at said impeller, the rotational speed of said pump is temporarily increased to the design rotational speed. Alternatively, said pump alternately operates at said design rotational speed and a low rotational speed, and this pulsed operation is synchronized with the heart rate.
Owner:ABIOMED EURO
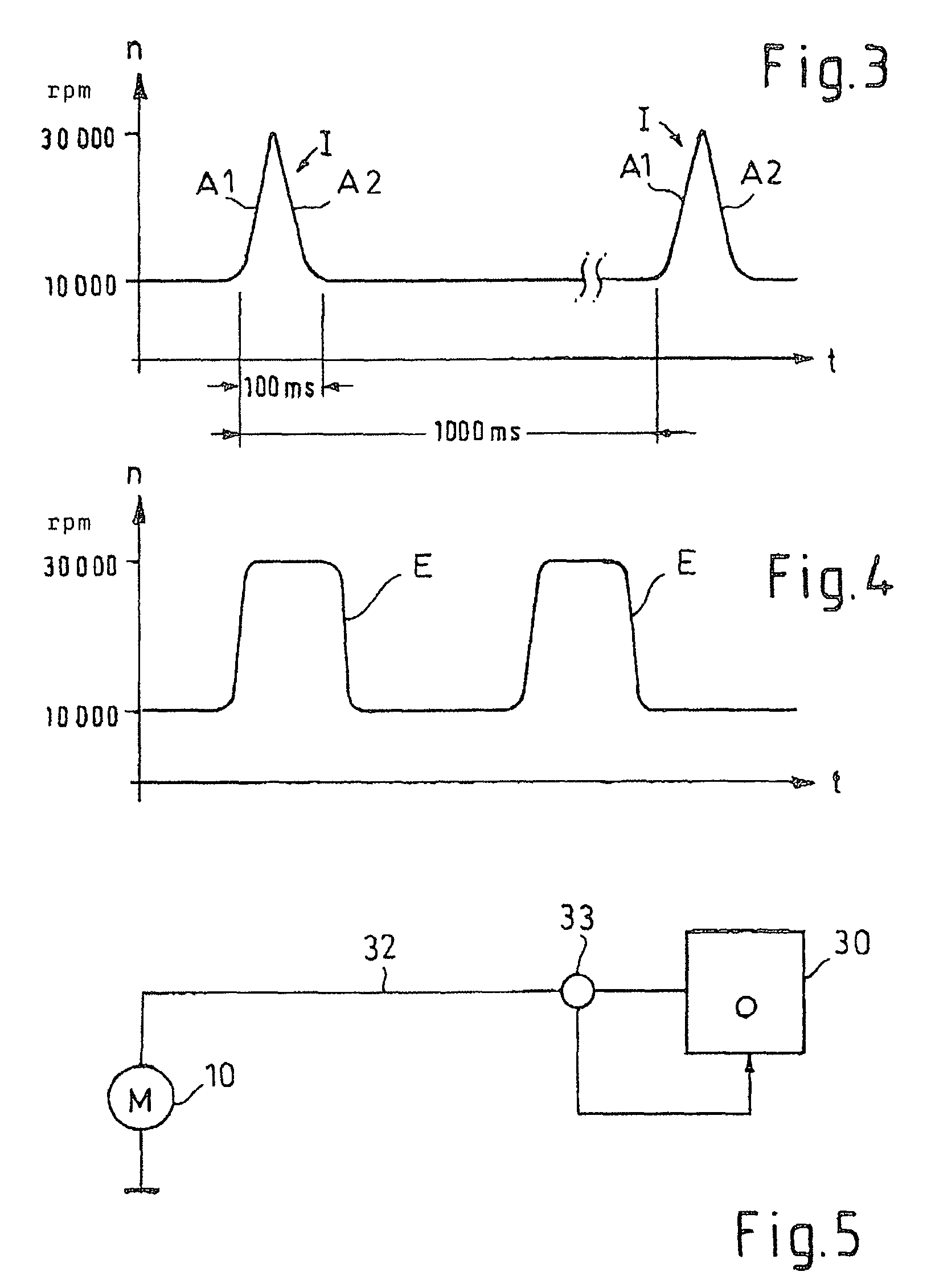
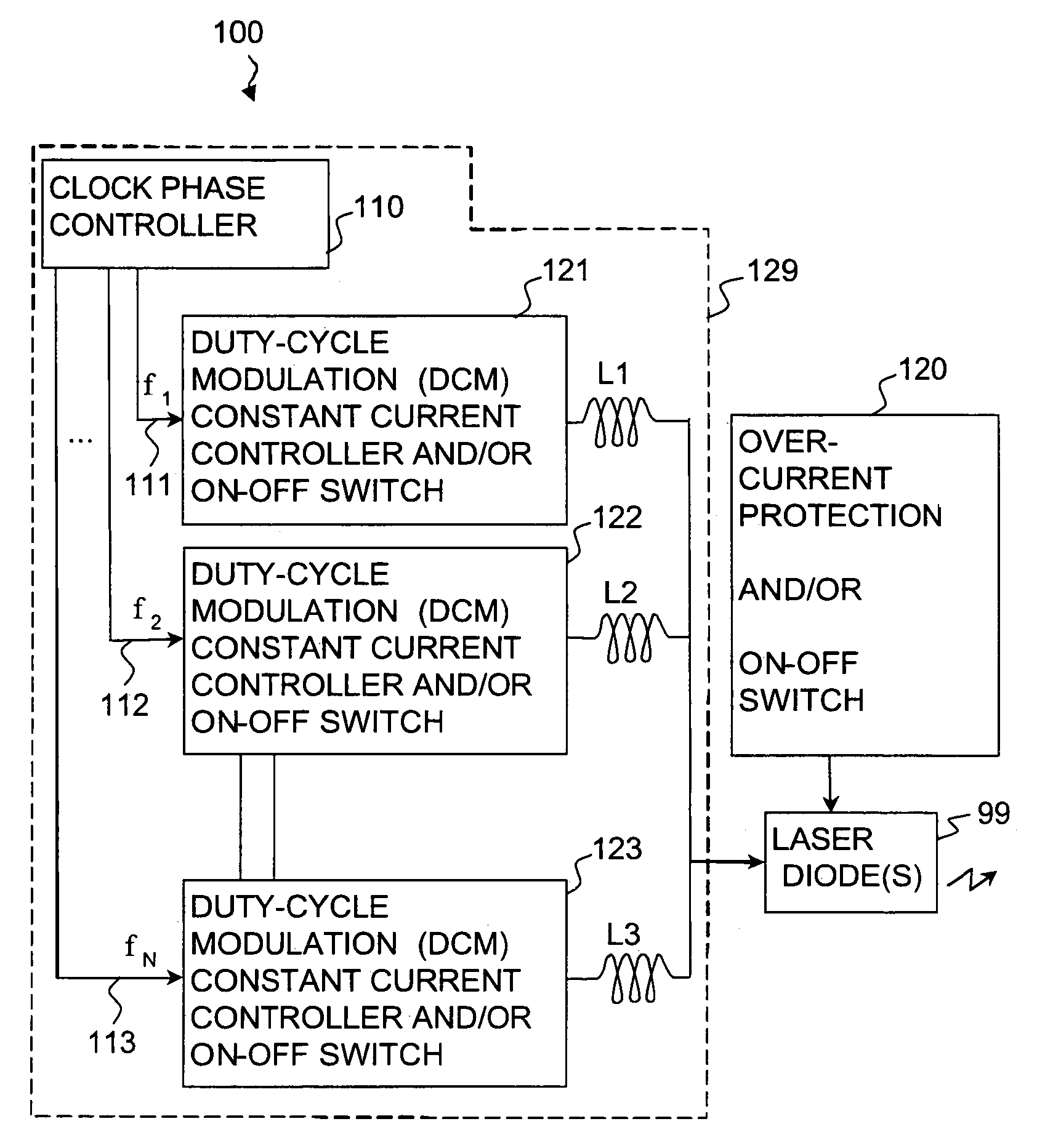
Apparatus and method for driving laser diodes
InactiveUS20060291512A1Fast rise timeImprove efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCapacitanceMode control
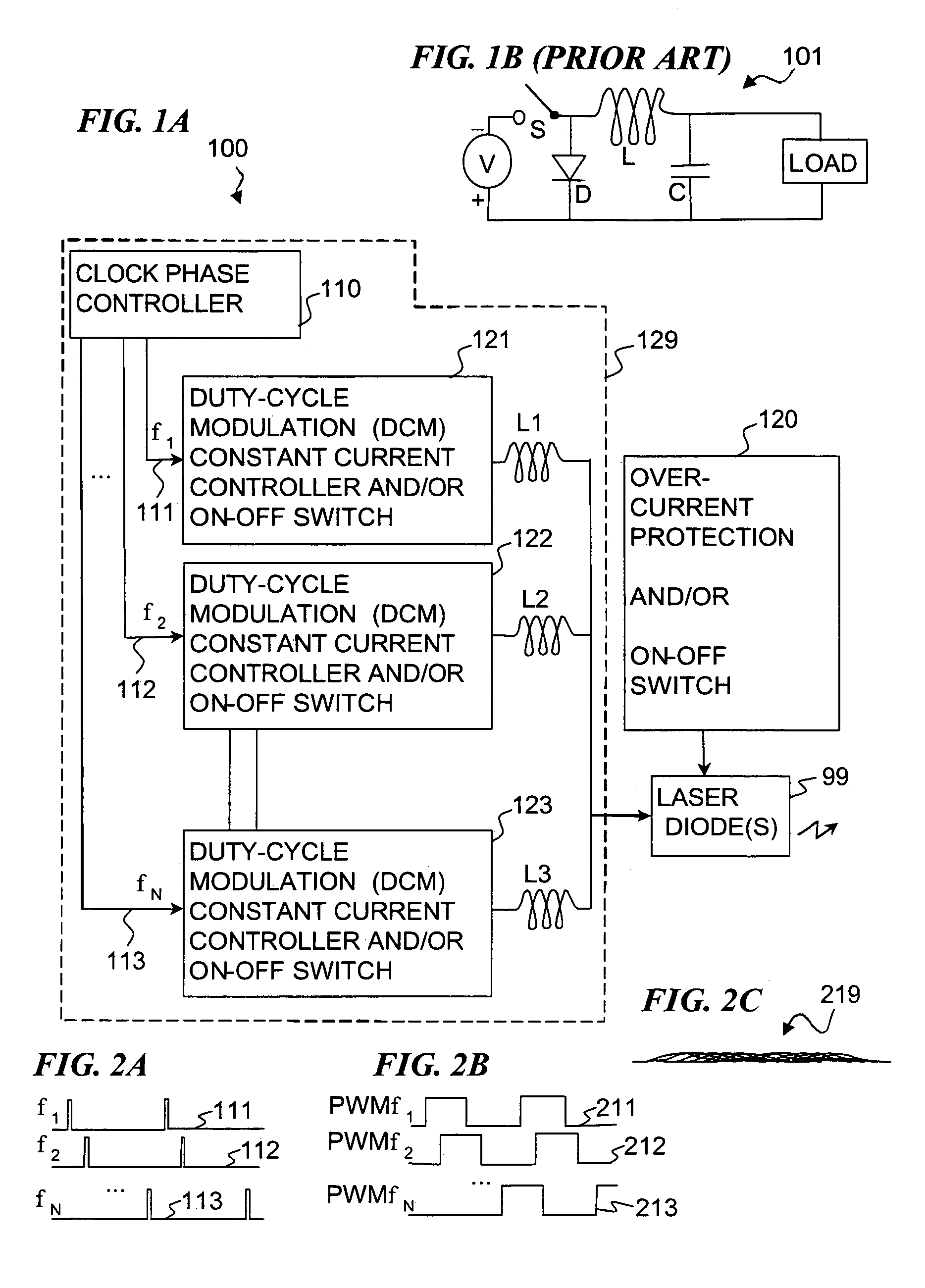
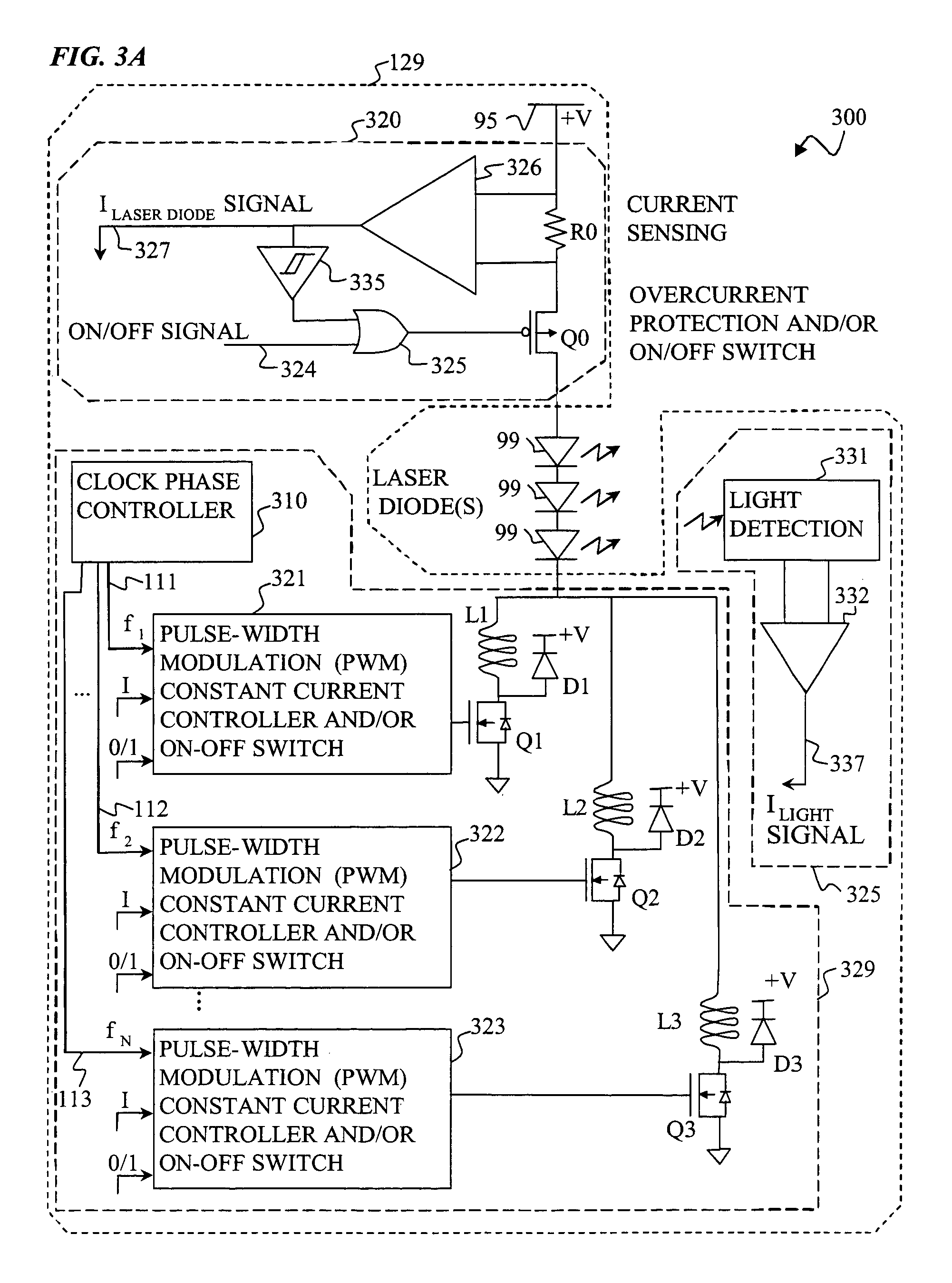
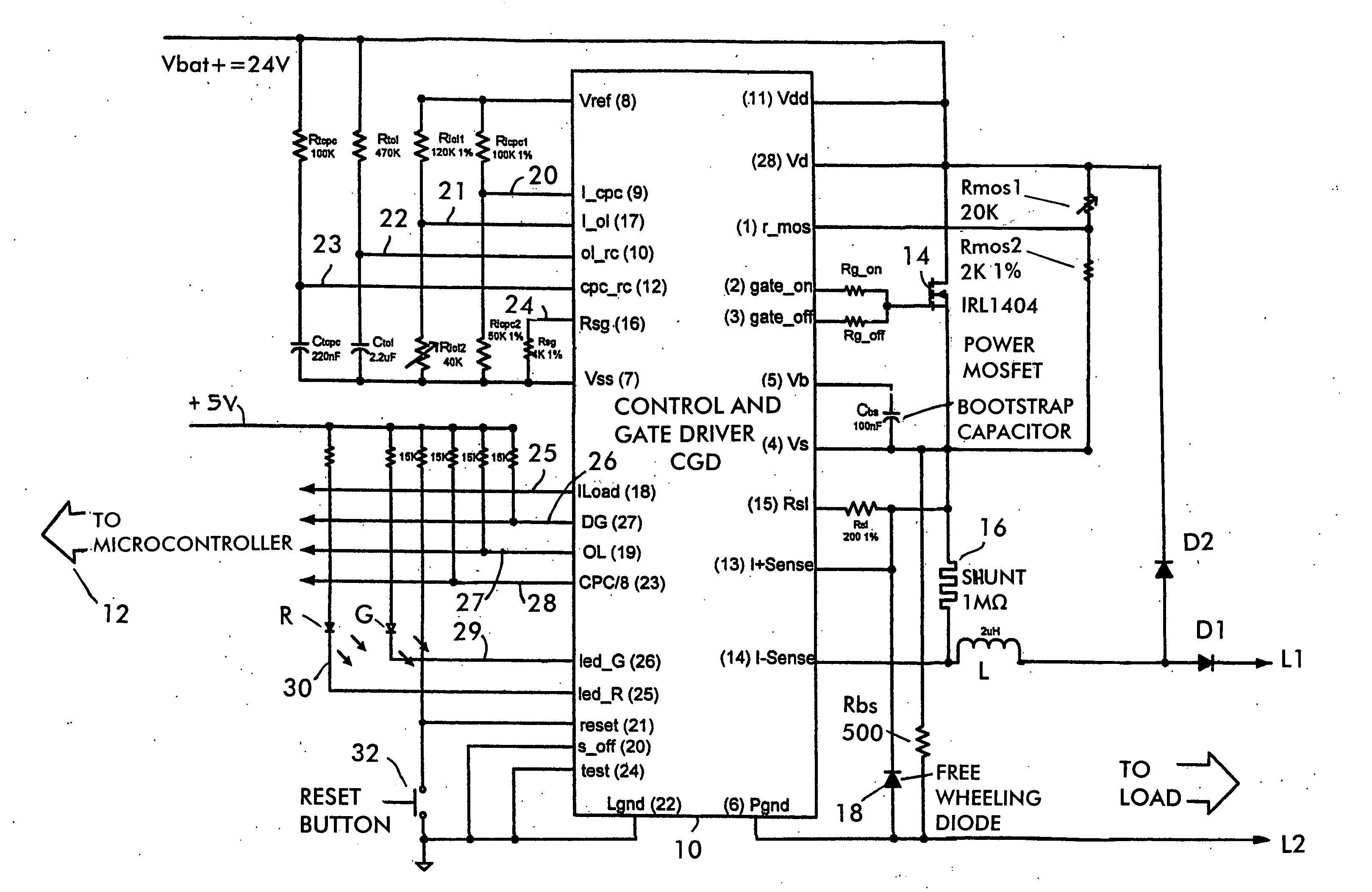
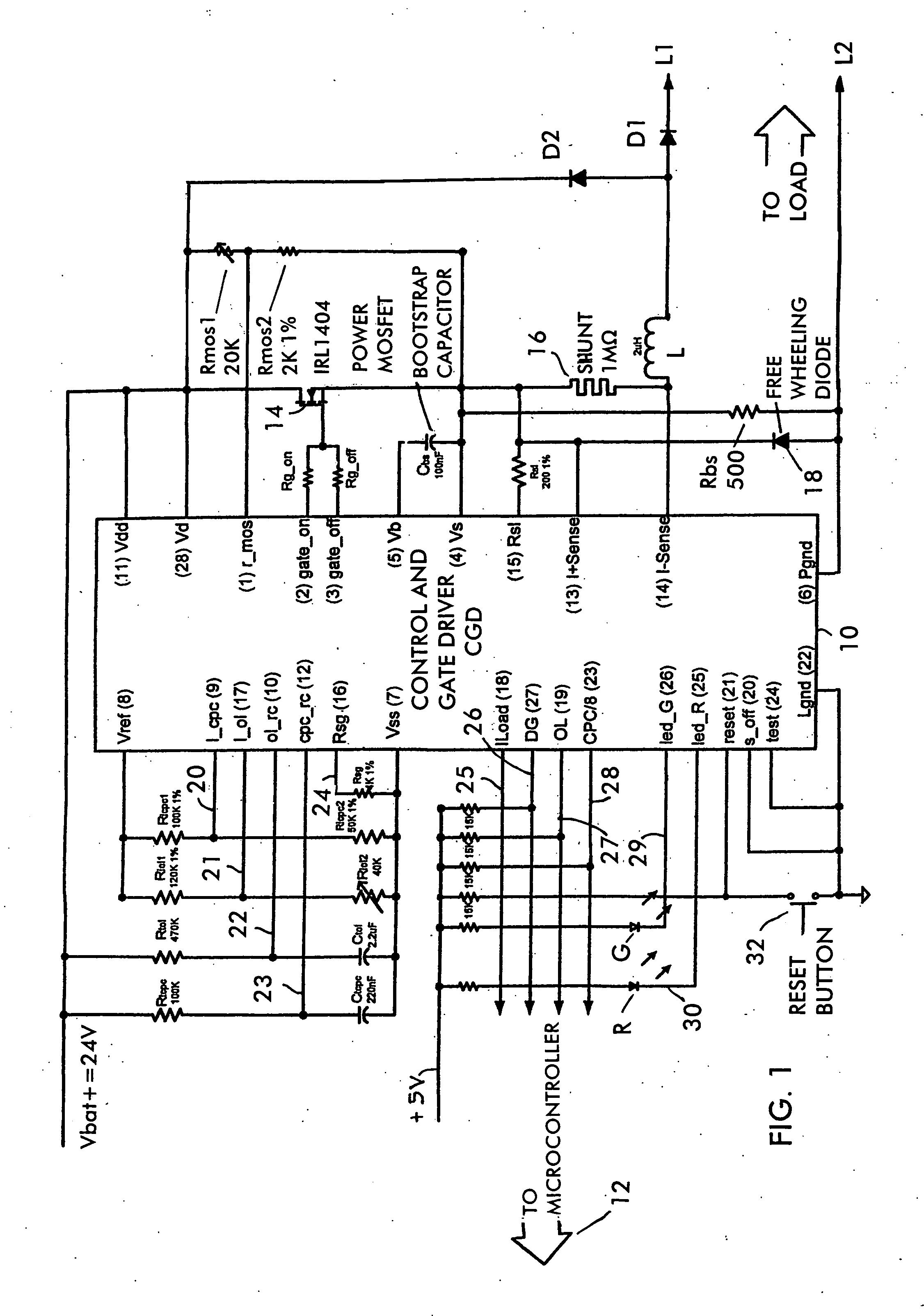
Apparatus and method for driving laser diodes with electrical power in pulsed operation. Pulsed power, for example using pulse-width modulation, is applied through an inductor in one or more parallel regulator circuits having little or no output capacitance to provide a high-efficiency laser-diode-driver power supply. Some embodiments that use two or more parallel regulator circuits in the laser-diode driver, drive each from a different phase of a clock signal. Some embodiments provide a first DC-to-DC converter has a relatively high-voltage input (e.g., about 275 volts, 0.75 amps) and an intermediate output of e.g., 11 to 15 volts, 15 to 11 amps used to charge a storage capacitor, and a second DC-to-DC converter diode driver having one or more parallel circuits (each having, e.g., a PWM switching-mode controller and its respective switch, inductor, and diode) to turn on, regulate, and turn off a constant laser-diode current through one or more laser diodes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
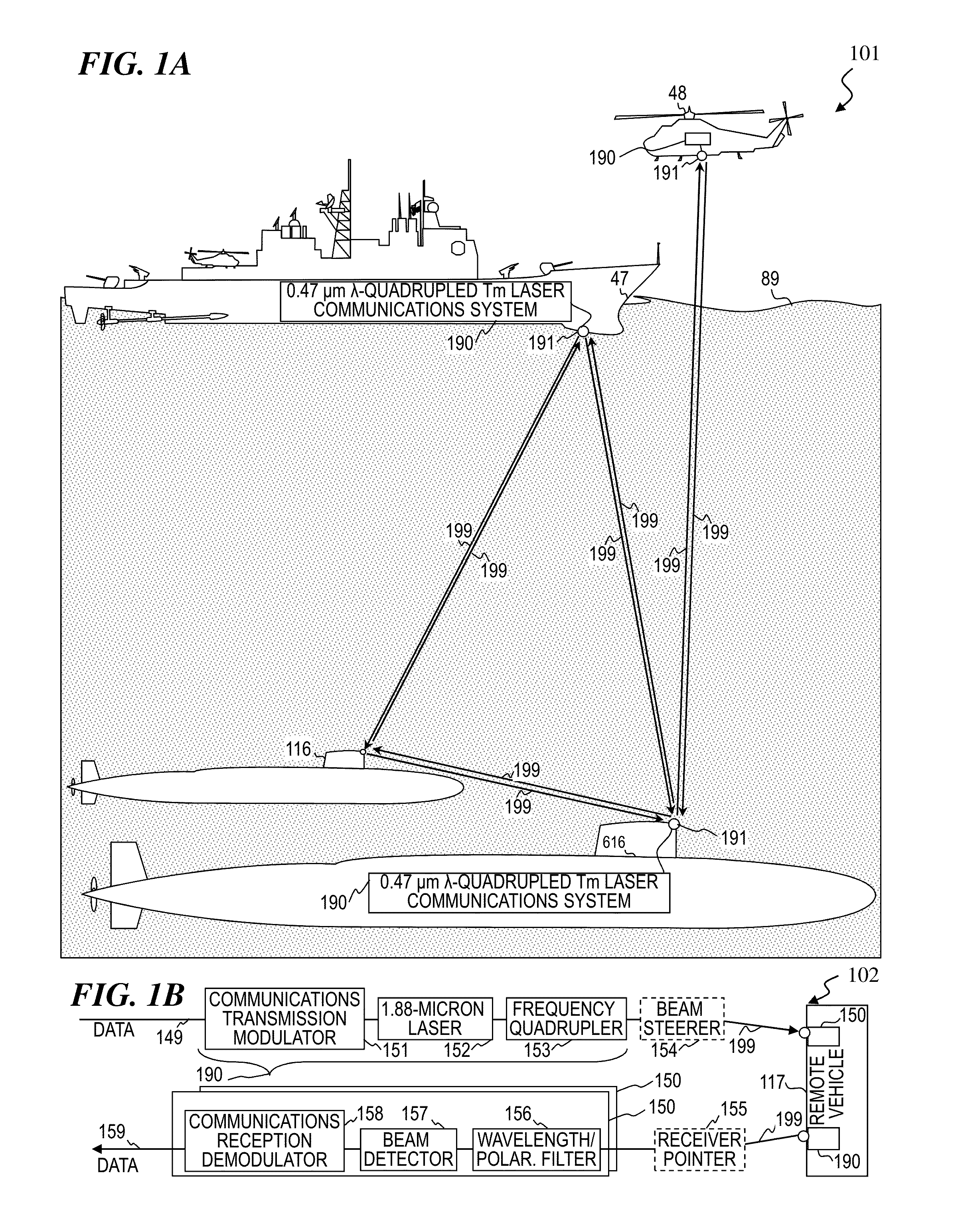
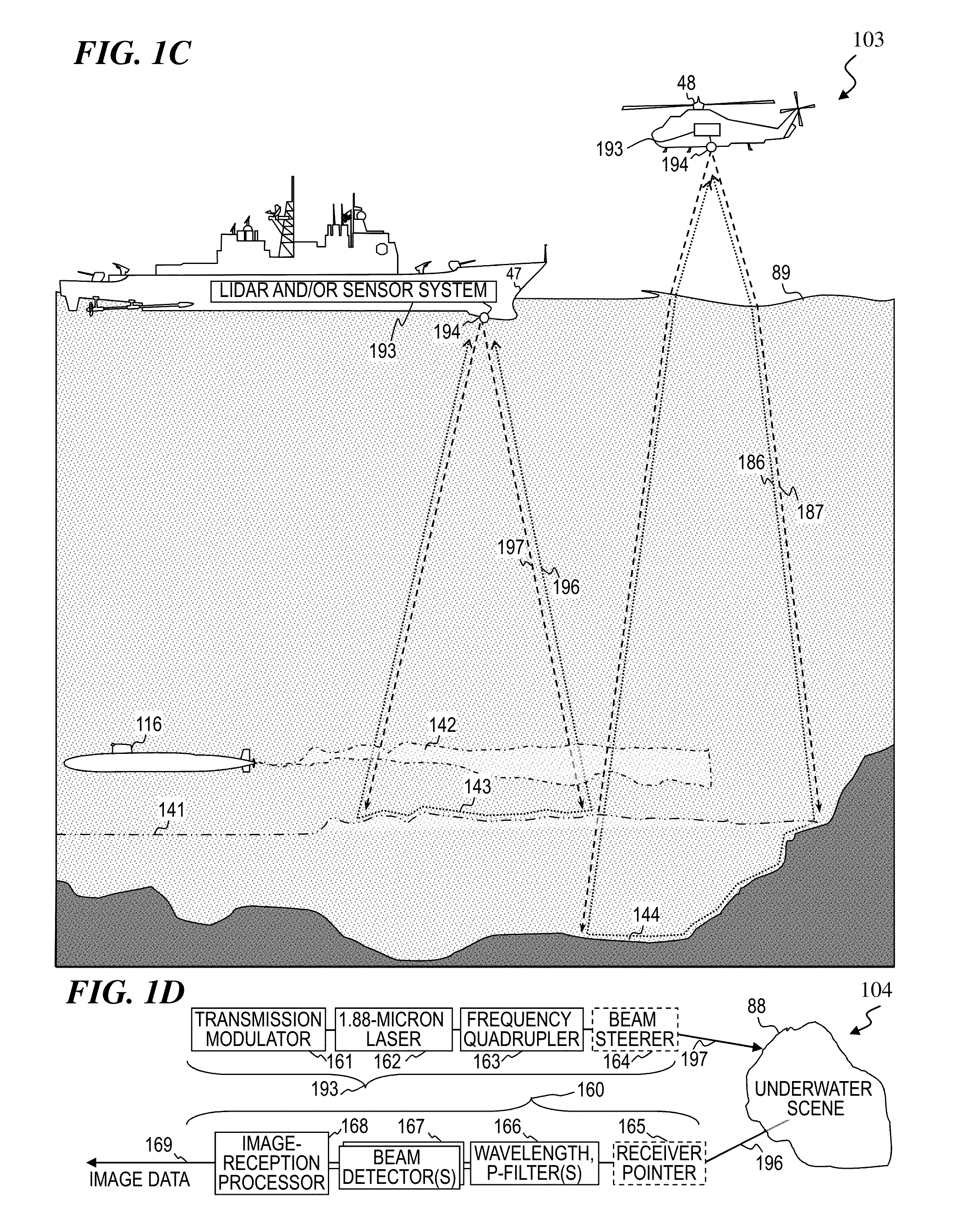
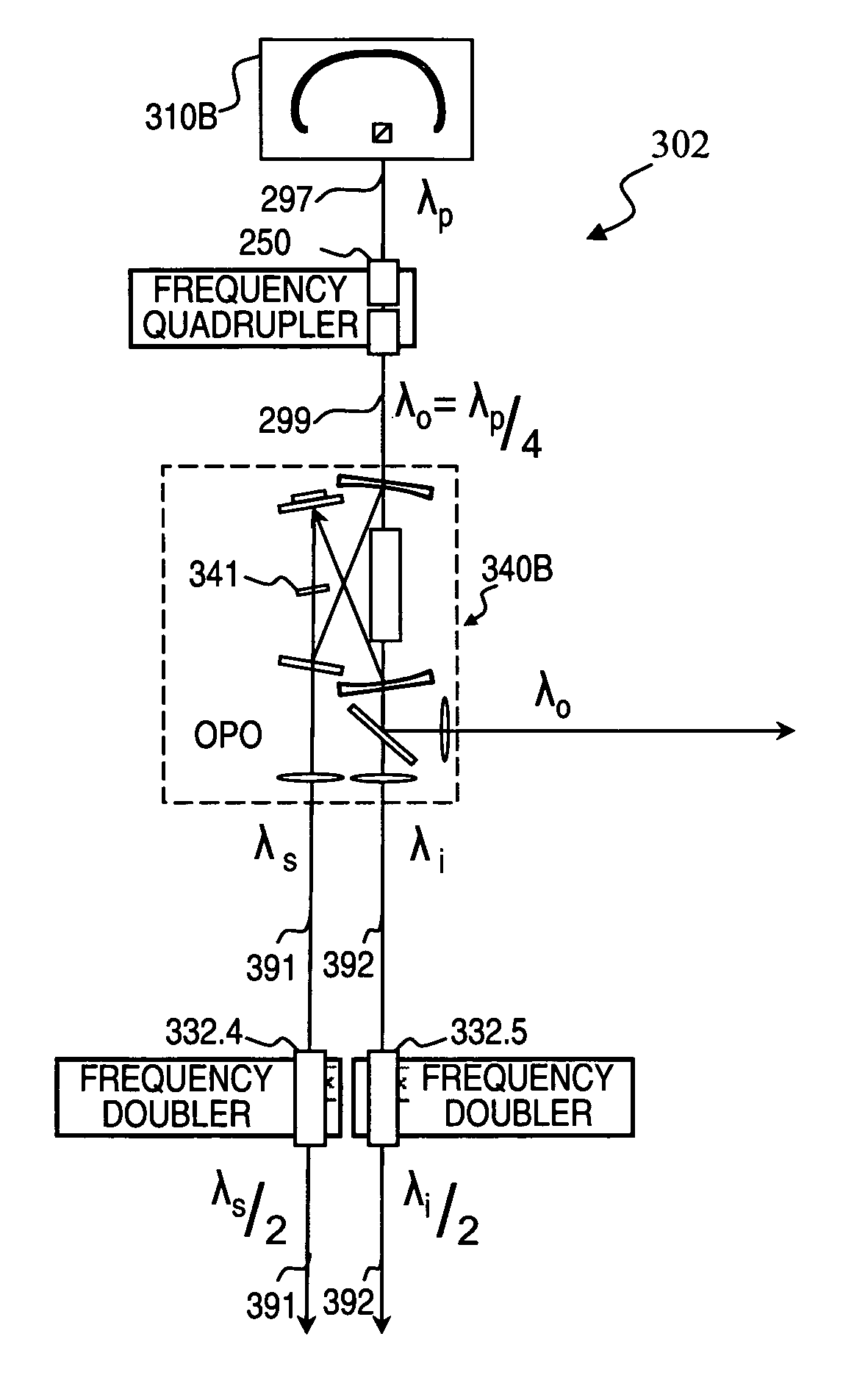
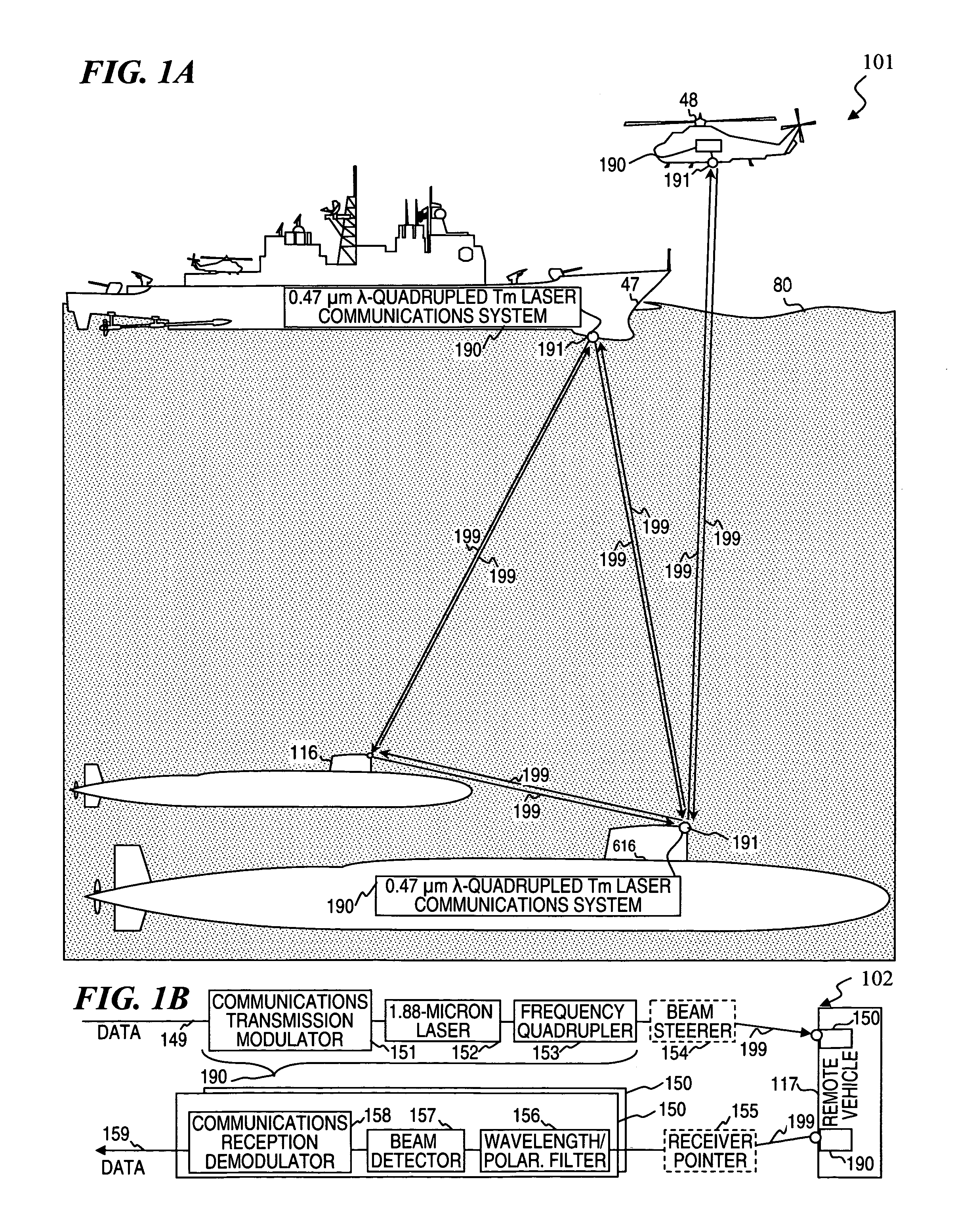
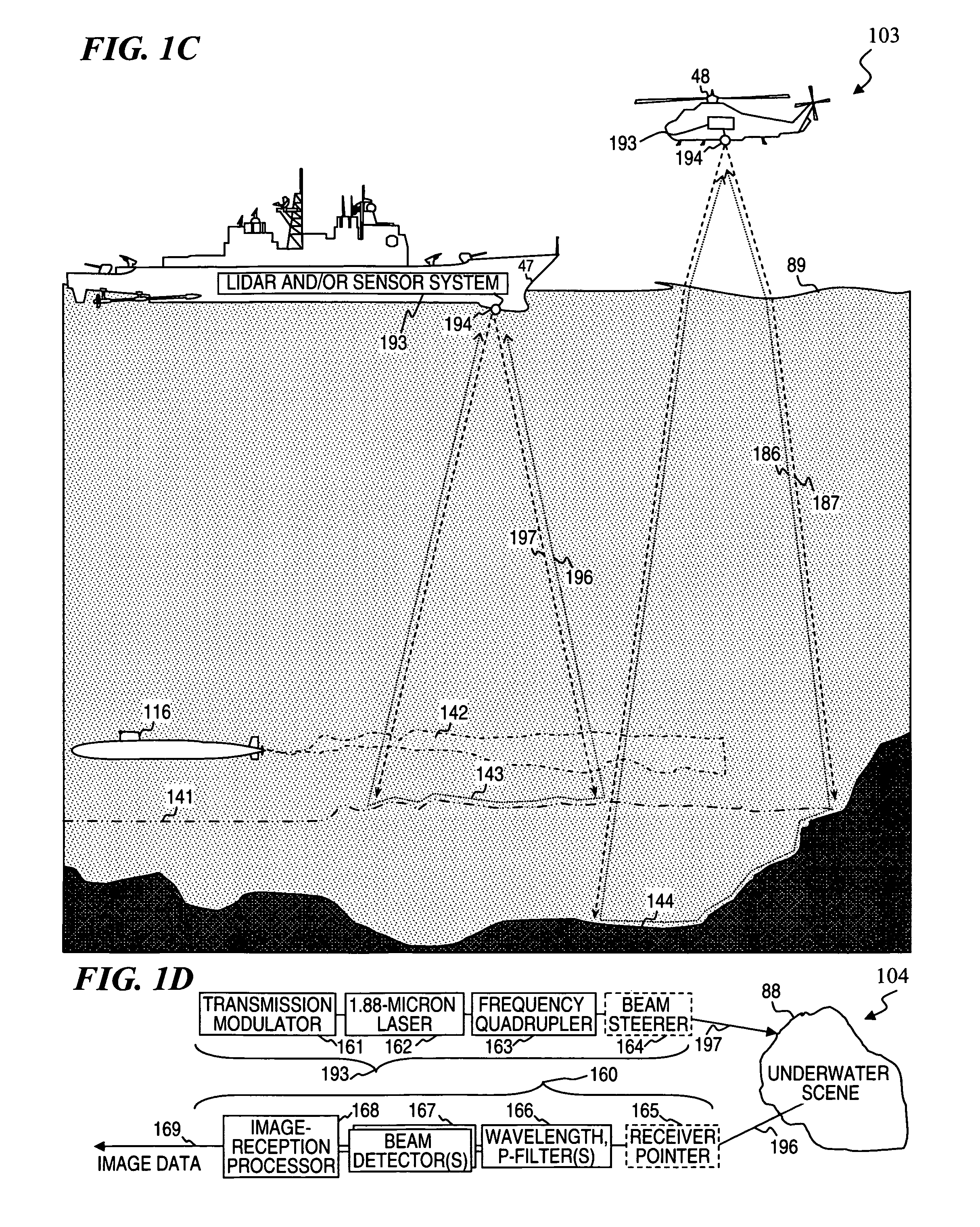
Frequency quadrupled laser using thulium-doped fiber amplifier and method
ActiveUS20150219765A1Minimizes effectsMinimize fractionLaser detailsOptical rangefindersGratingRing fibers
An apparatus, method and associated fiber-laser architectures for high-power pulsed operation and pumping wavelength-conversion devices. Some embodiments generate blue laser light by frequency quadrupling infrared (IR) light from Tm-doped gain fiber using non-linear wavelength conversion. Some embodiments use a fiber MOPA configuration to amplify a seed signal from a semiconductor laser or ring fiber laser. Some embodiments use the frequency-quadrupled blue light for underwater communications, imaging, and / or object and anomaly detection. Some embodiments amplitude modulate the IR seed signal to encode communication data sent to or from a submarine once the modulated light has its wavelength quartered. Other embodiments transmit blue-light pulses in a scanned pattern and detect scattered light to measure distances to objects in a raster-scanned underwater volume, which in turn are used to generate a data structure representing a three-dimensional rendition of the underwater scene being imaged for viewing by a person or for other software analysis.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Picosecond laser apparatus and methods for its operation and use
ActiveUS7929579B2Apparatuses may be further simplifiedSimple componentsLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsPicosecond laserHigh energy
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for applying laser energy having desired pulse characteristics, including a sufficiently short duration and / or a sufficiently high energy for the photomechanical treatment of skin pigmentations and pigmented lesions, both naturally-occurring (e.g., birthmarks), as well as artificial (e.g., tattoos). The laser energy may be generated with an apparatus having a resonator with the capability of switching between a modelocked pulse operating mode and an amplification operating mode. The operating modes are carried out through the application of a time-dependent bias voltage, having waveforms as described herein, to an electro-optical device positioned along the optical axis of the resonator.
Owner:CYNOSURE
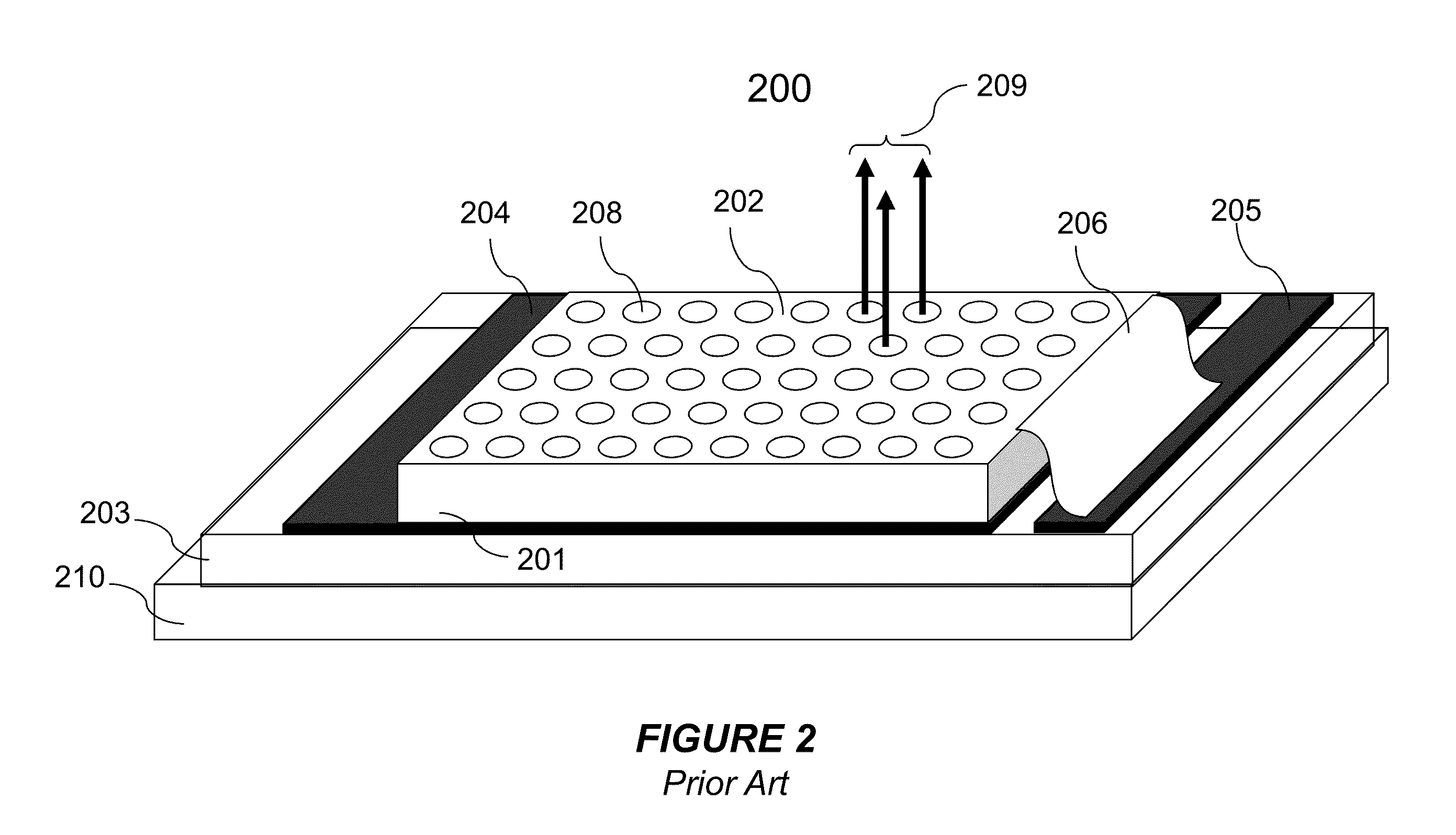
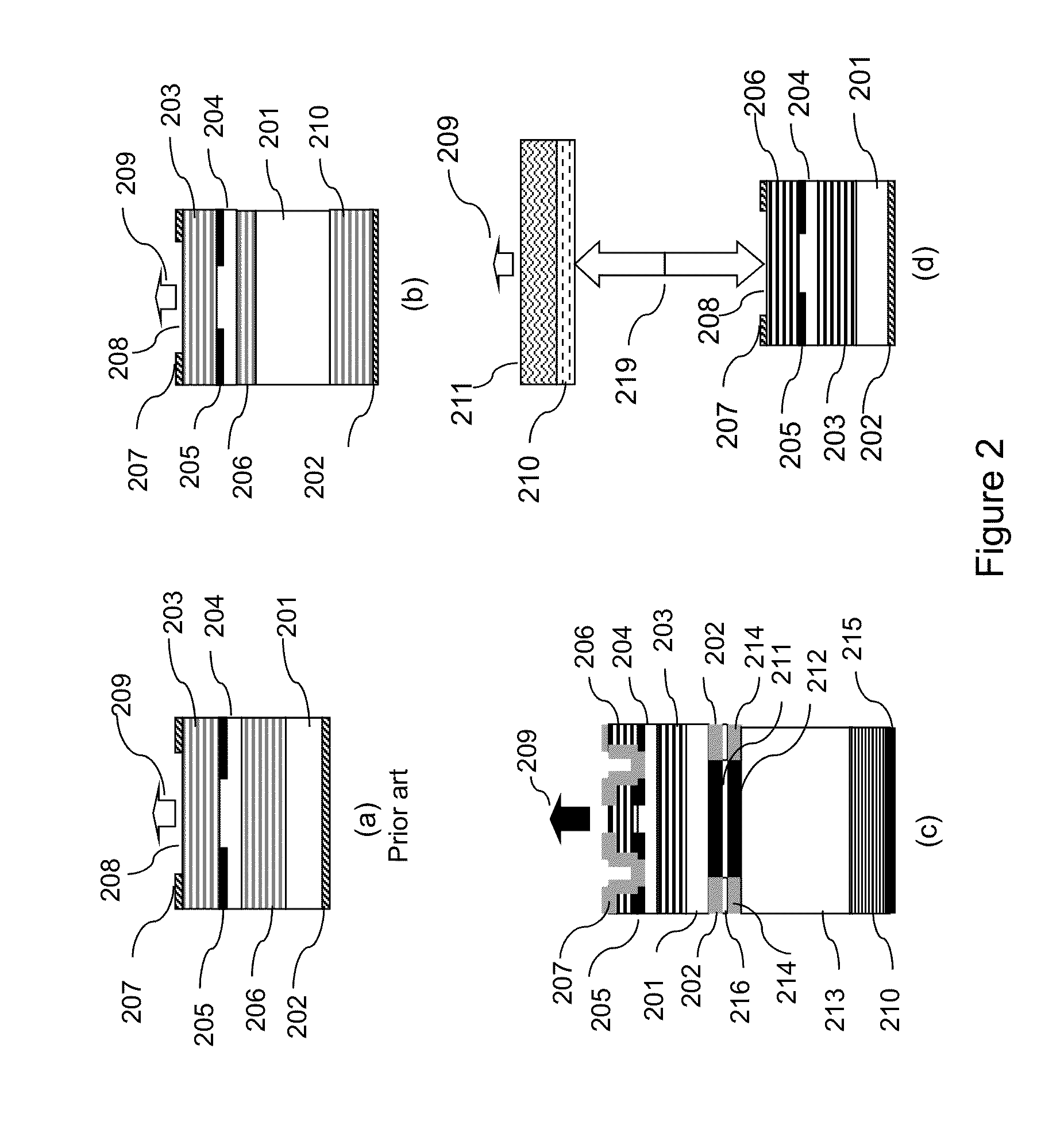
Collector mirror for plasma-based, short-wavelength radiation sources
ActiveUS20060227826A1High-performance thermal connectionGreat expenditureMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingTransport mediumThermostat
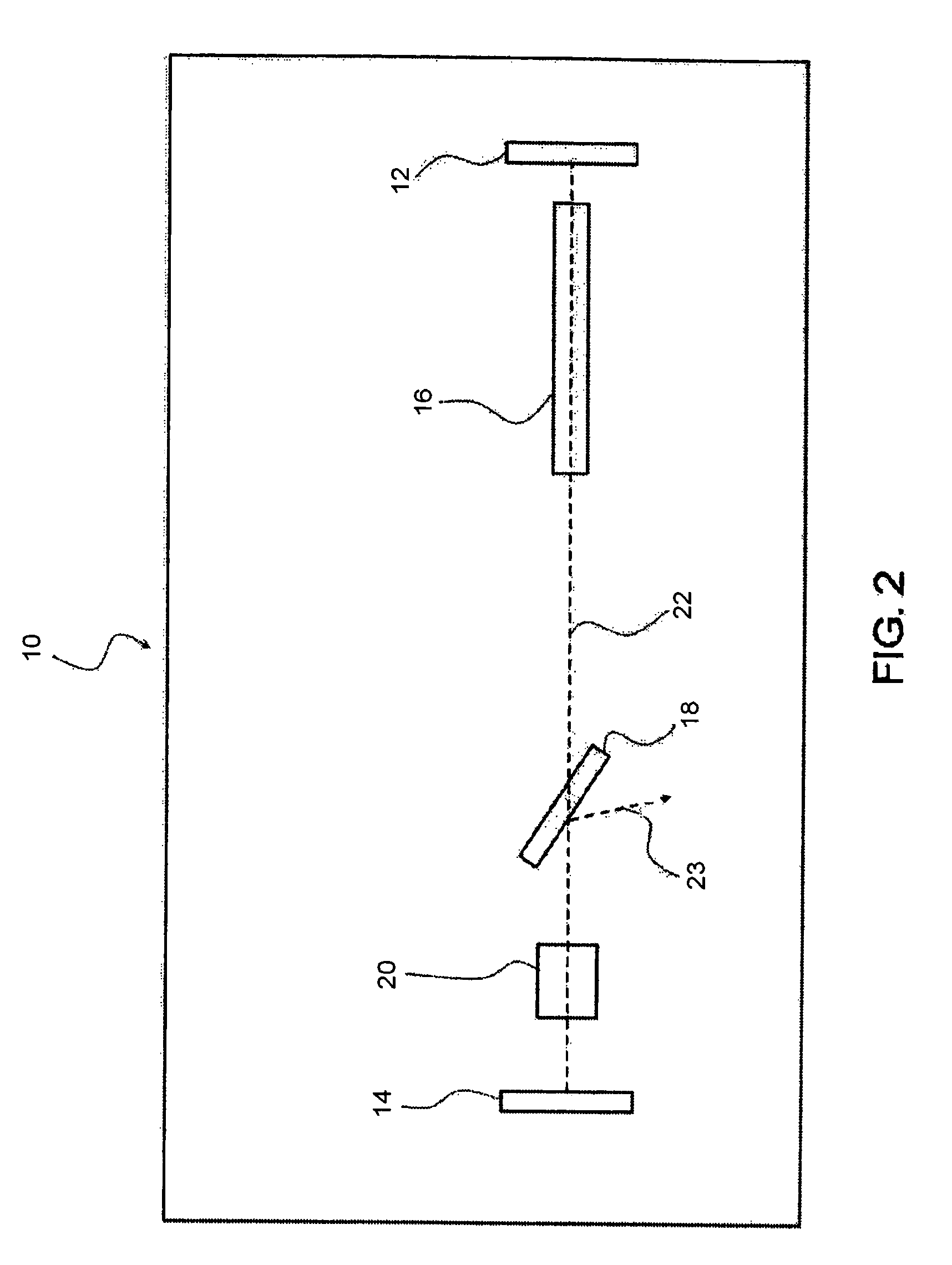
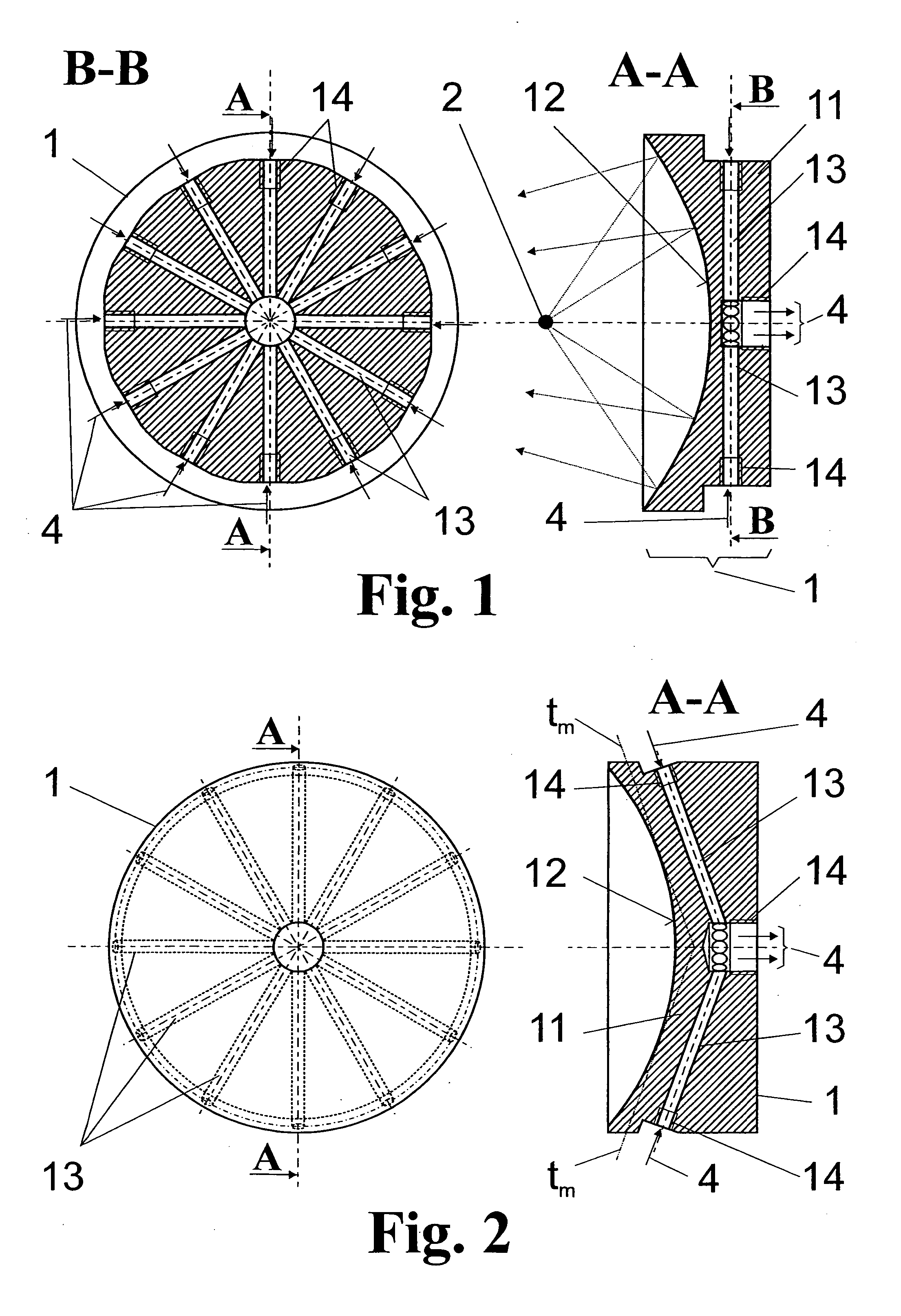
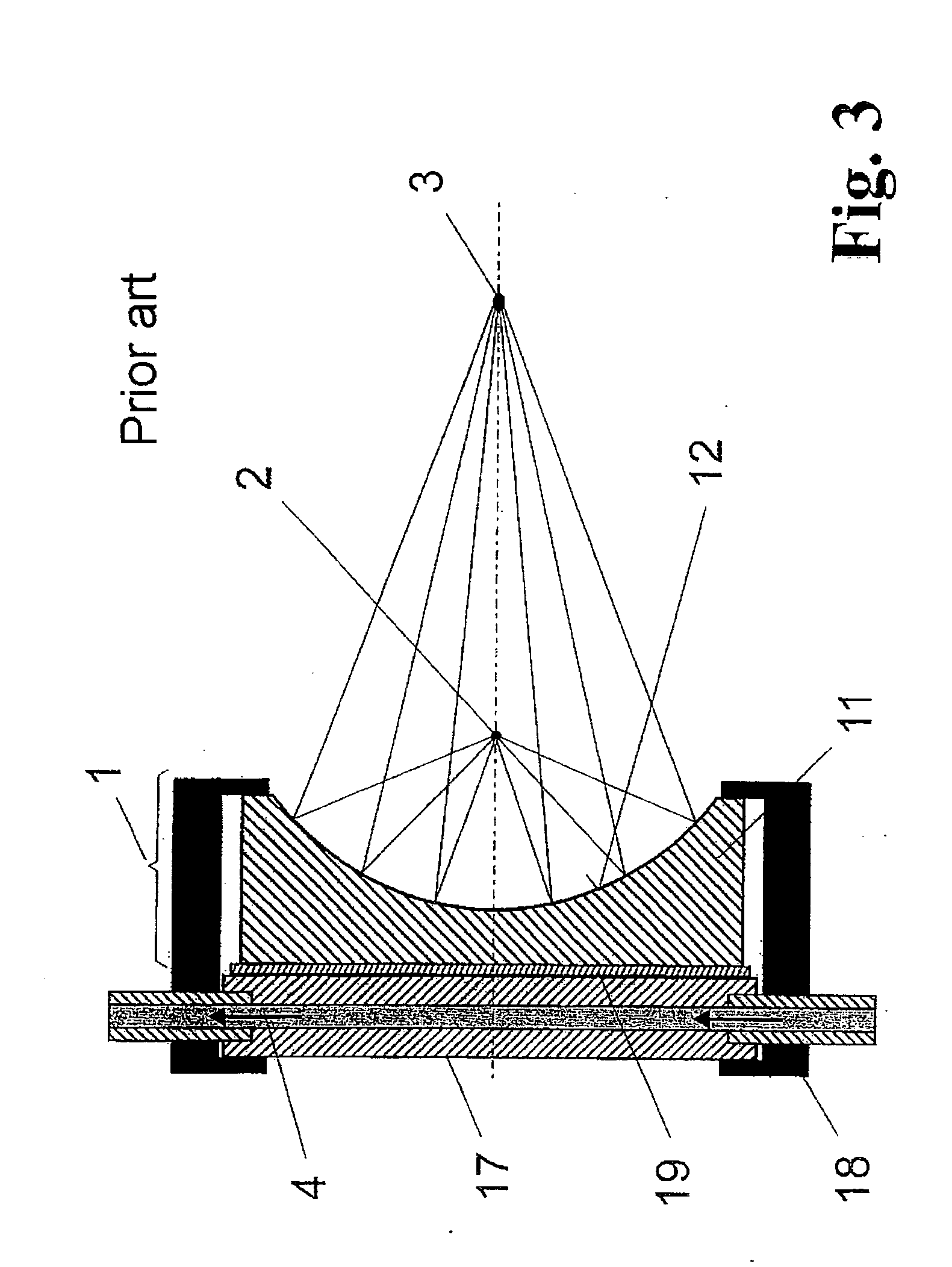
The invention is directed to a collector mirror for short-wavelength radiation based on a plasma. It is the object of the invention to find a novel possibility for managing the temperature of a collector mirror for focusing short-wavelength radiation generated from a plasma which allows an efficient thermal connection to be produced between the optically active mirror surface and a thermostat system without the disadvantages relating to space requirements or high-precision manufacture of the collector mirror. This object is met, according to the invention, in that the collector mirror has a solid, rotationally symmetric substrate which comprises a material with high thermal conductivity of more than 50 W / mK and in which channels for cooling and temperature management are incorporated in the substrate so that a heat transport medium can flow through directly and for rapidly stabilizing the temperature of the optically active mirror surface. Heat of transient temperature spikes which occur in pulsed operation for plasma generation at the mirror surface and which temporarily exceed the temperature average by a multiple is quickly dissipated.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Process and system for operating magnetron discharges
InactiveUS6340416B1Improve efficiencyReduce output lossCellsElectric discharge tubesLoad carryingSupply energy
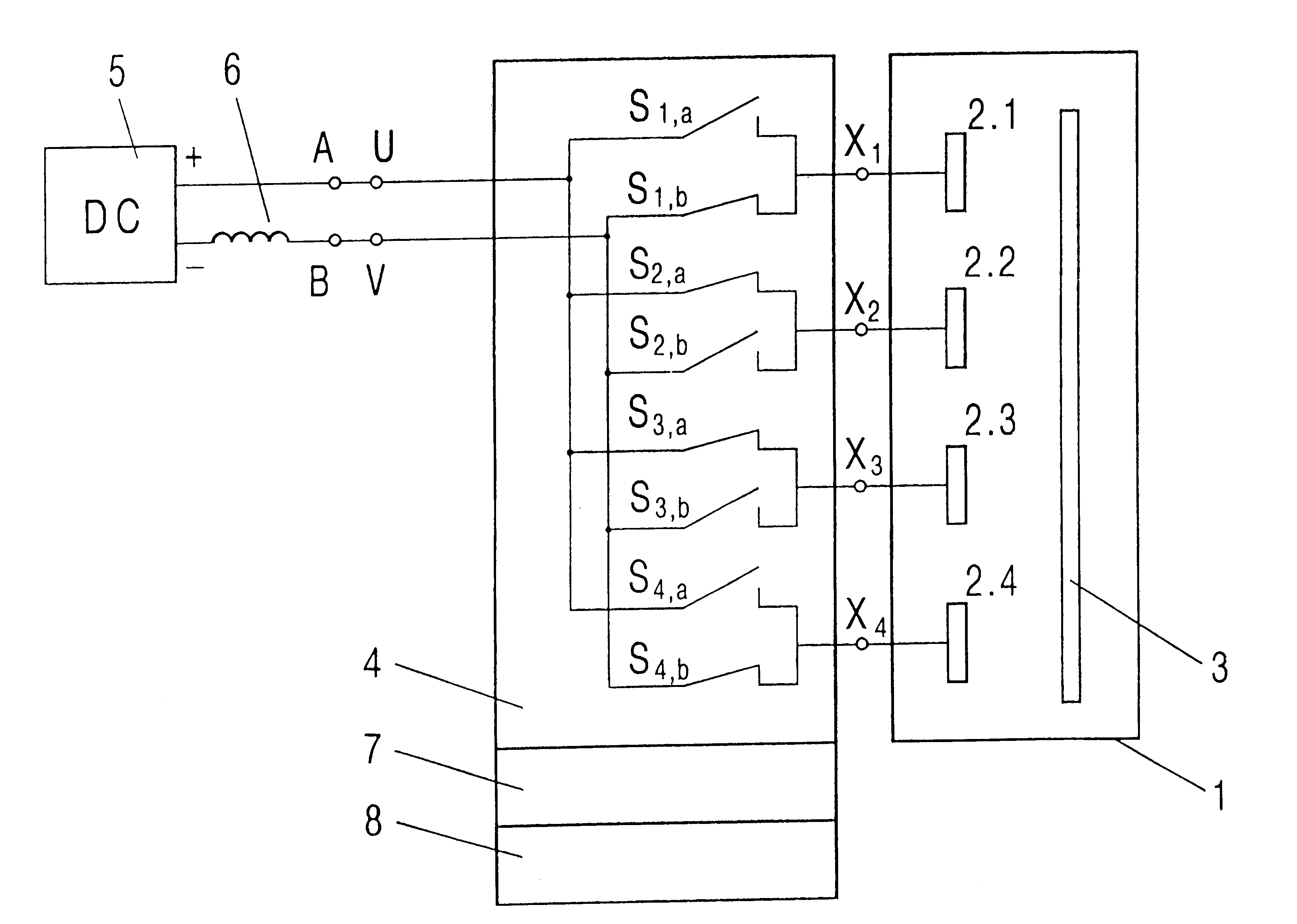
Magnetron discharges are pulse-operated to avoid the so-called "arcing". In the case of magnetron discharges from alternating current-fed magnetrons, the process is limited to the minor power of the energy supply because of the load-carrying capacity of the required electric components. When the magnetron discharges are fed by direct current, their effectiveness deteriorates because of the deposition of layers on the anode surfaces. The new process should enable a high supply power and prevent arcing. In magnetron discharges with at least two magnetron electrodes, the energy is supplied in such a way that at least one magnetron electrode is a cathode or anode and a number n1 of direct current pulses of said polarity is supplied. The poles of at least one magnetron electrode are then reversed and a number n2 of direct currents of this polarity are supplied. The process is carried on in this manner, the frequency of the direct current pulses being higher than that of the polarity reversals. The energy supply effectiveness is thus improved. This process and system enable the production of layers having the most different properties, for example for the glass, packaging, electronic, and machine construction industries.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
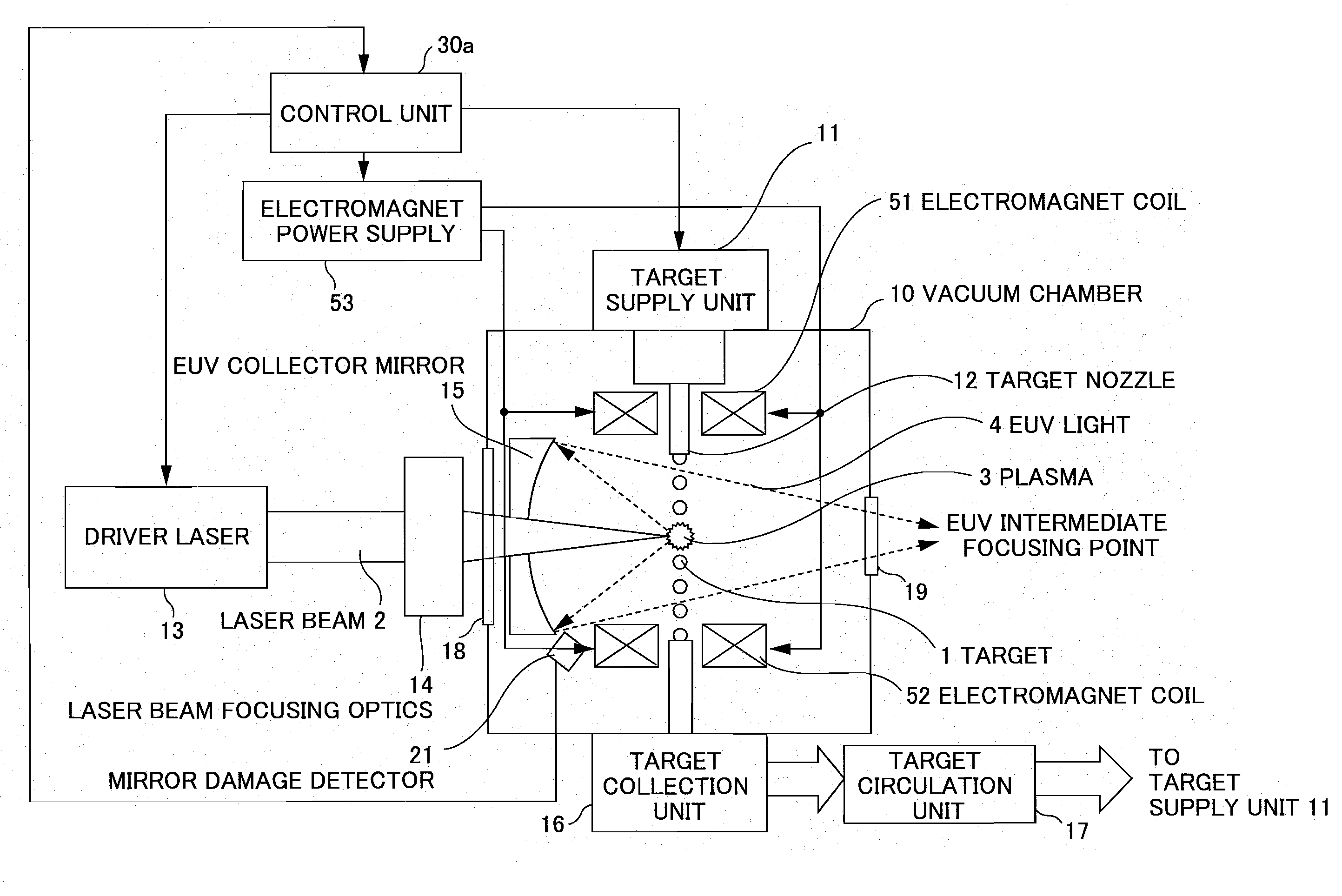
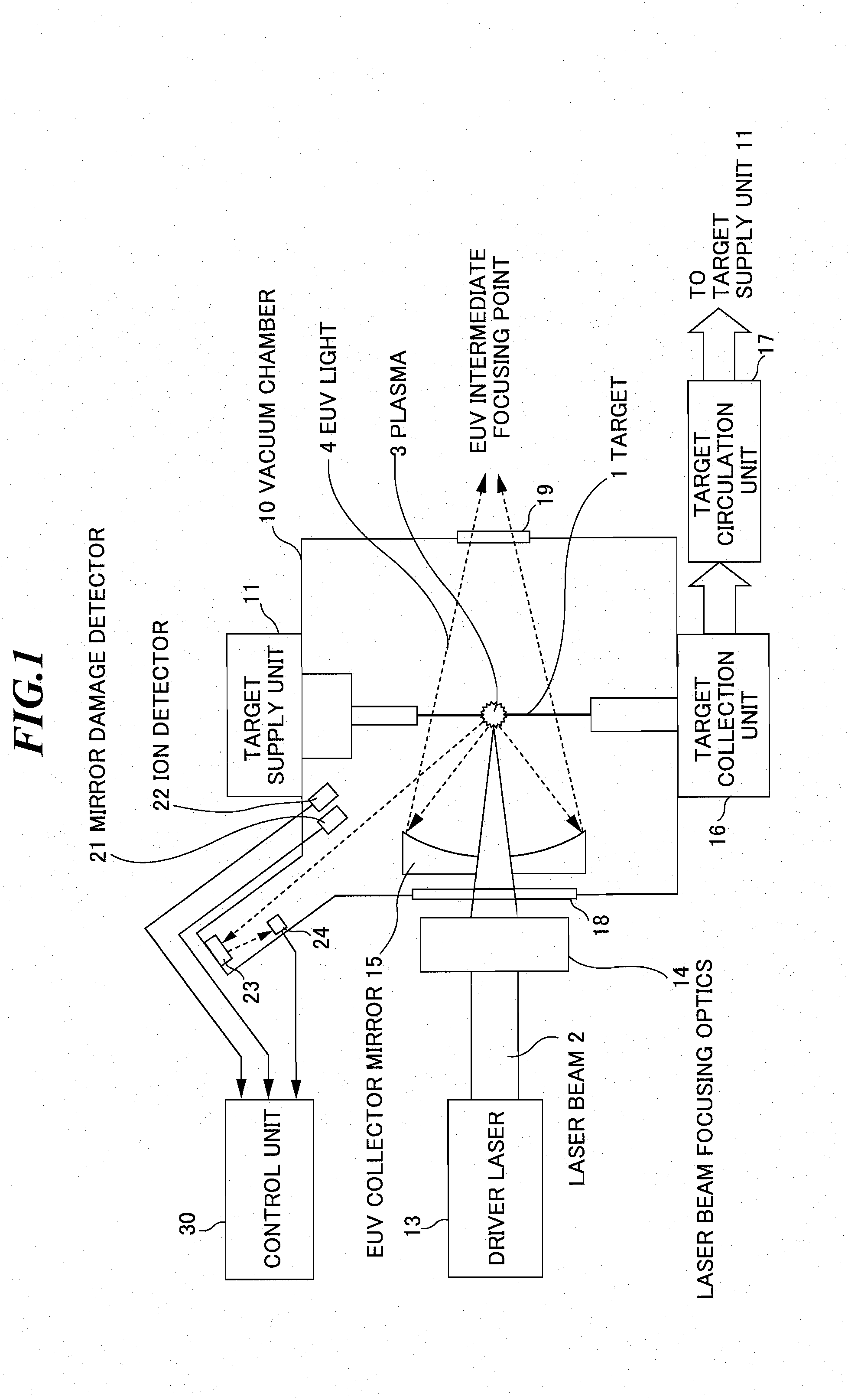
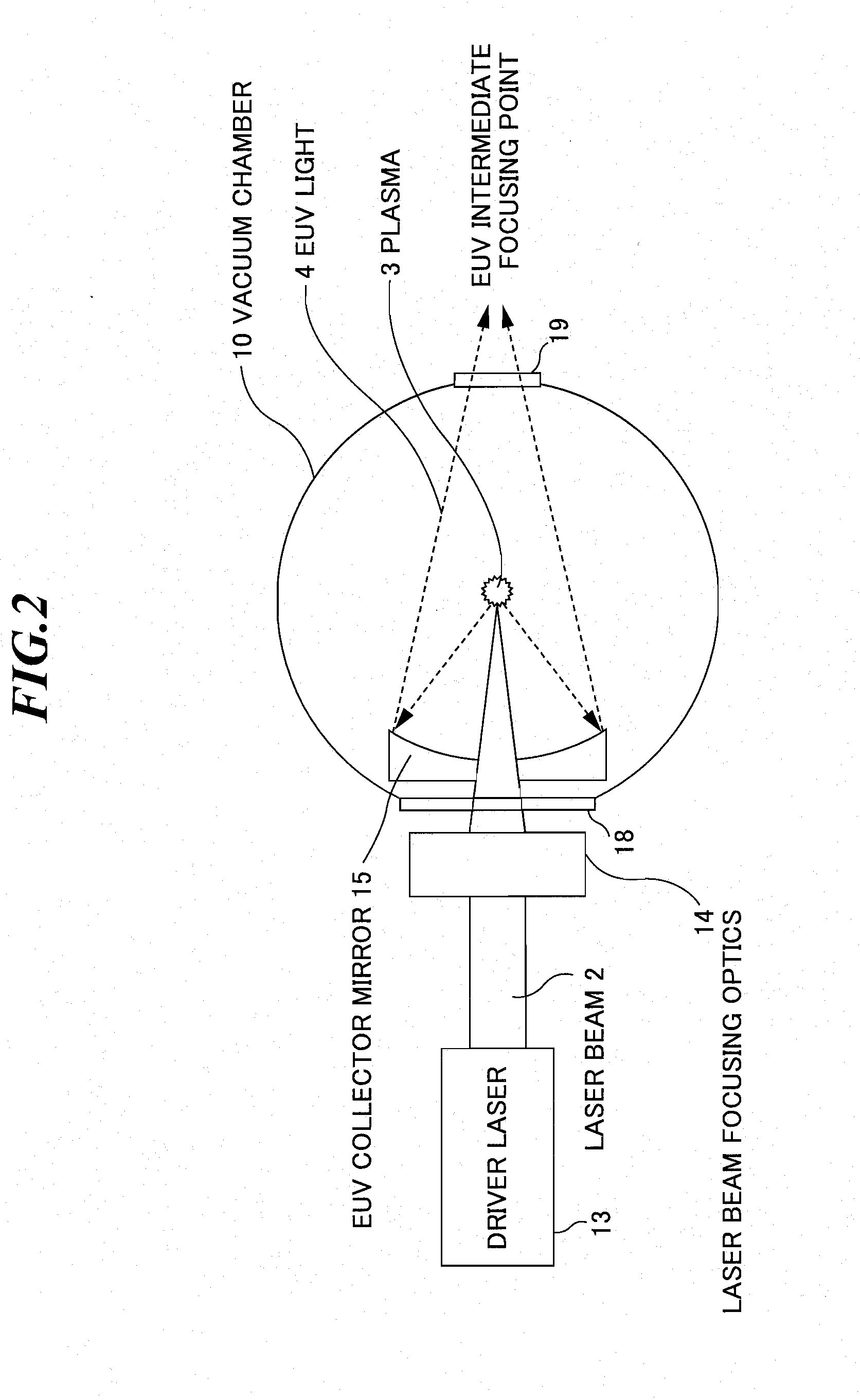
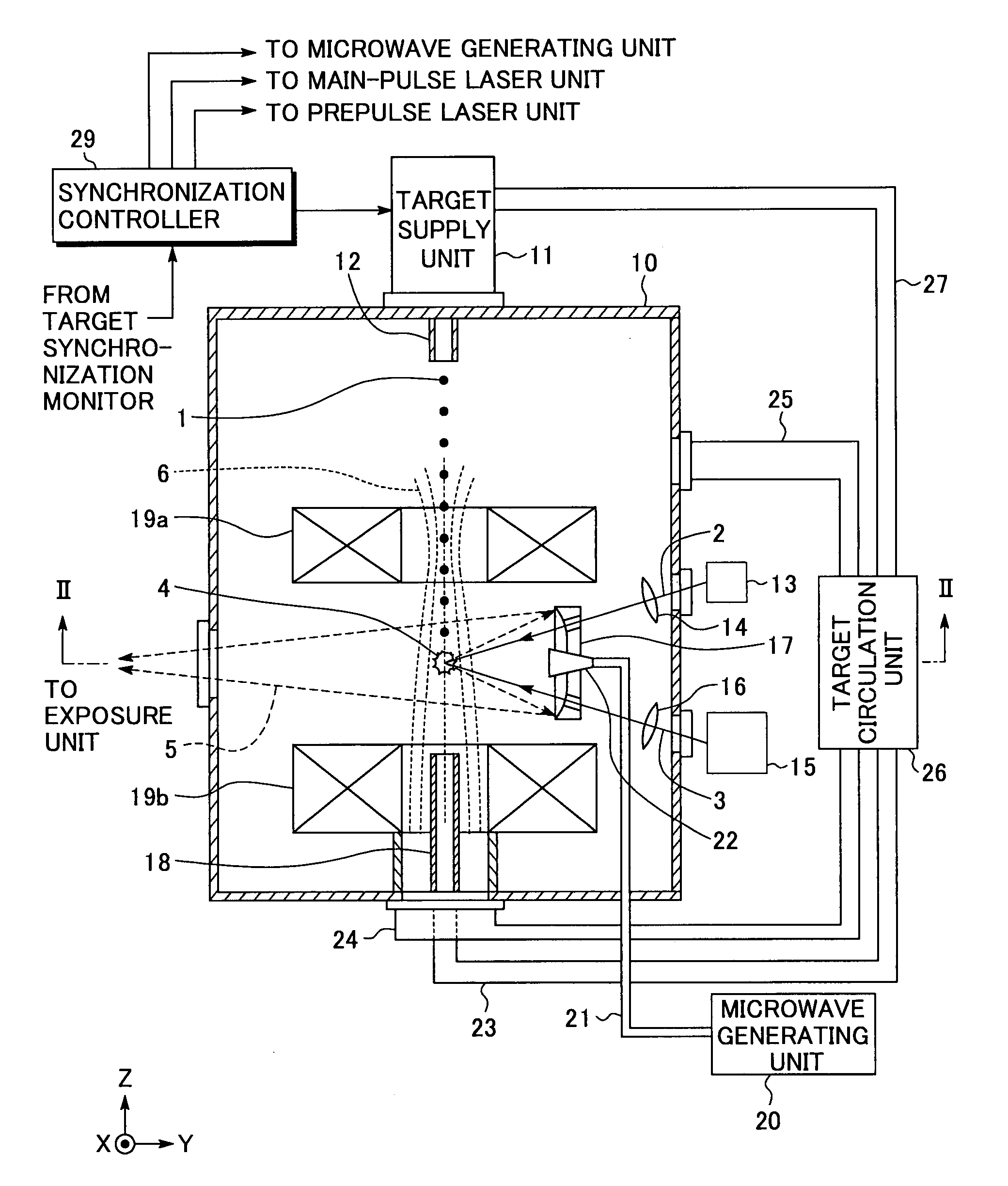
Extreme ultra violet light source apparatus
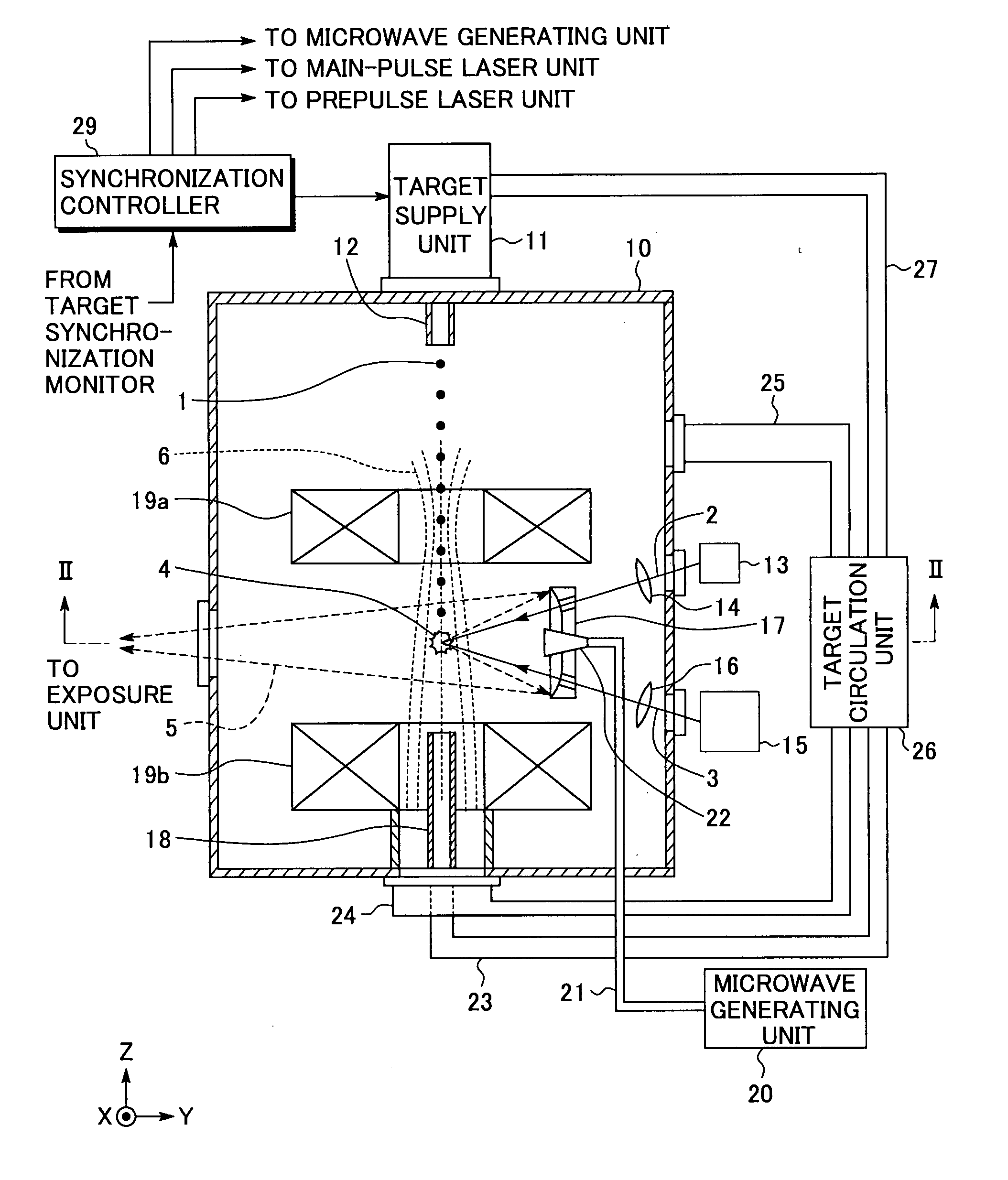
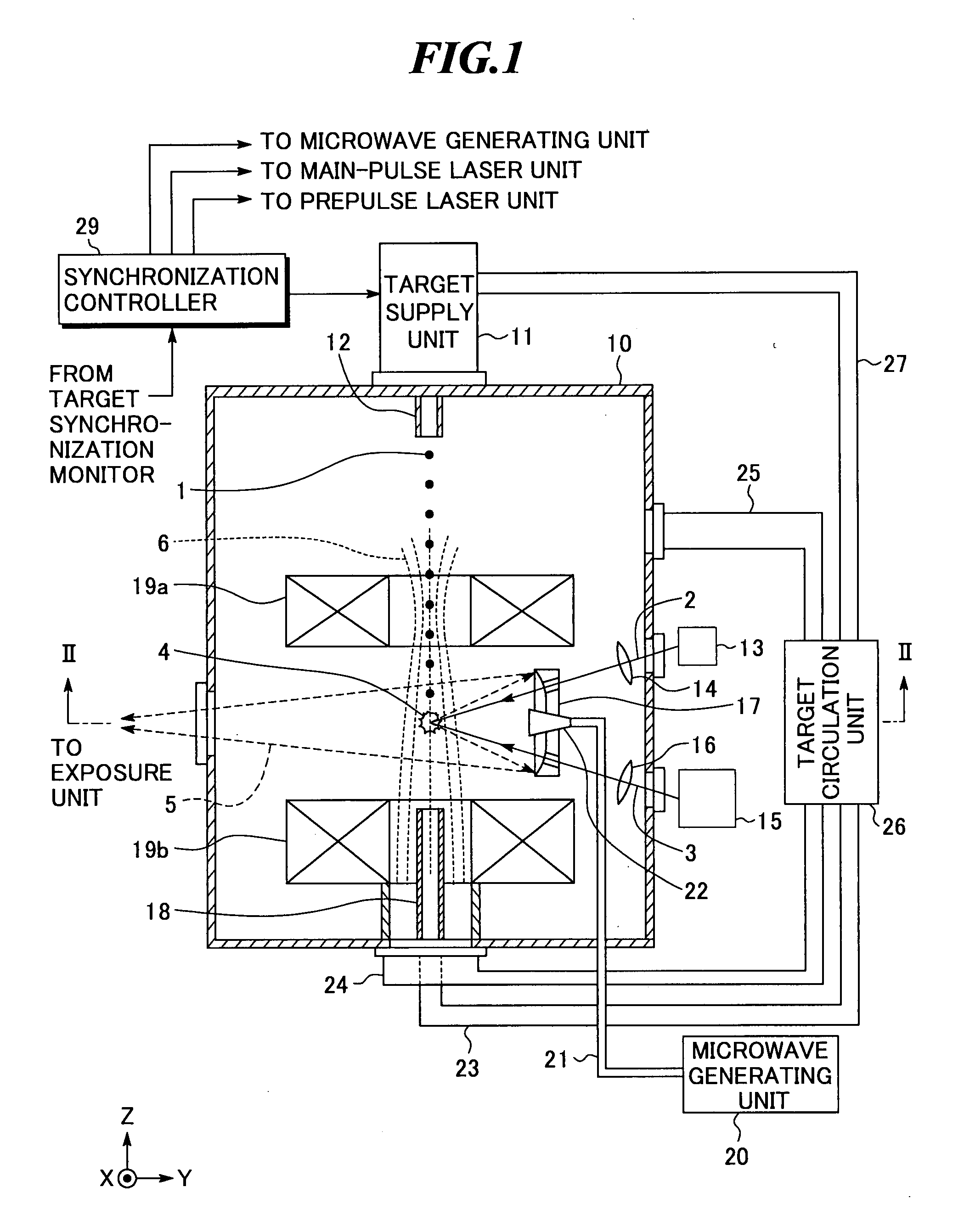
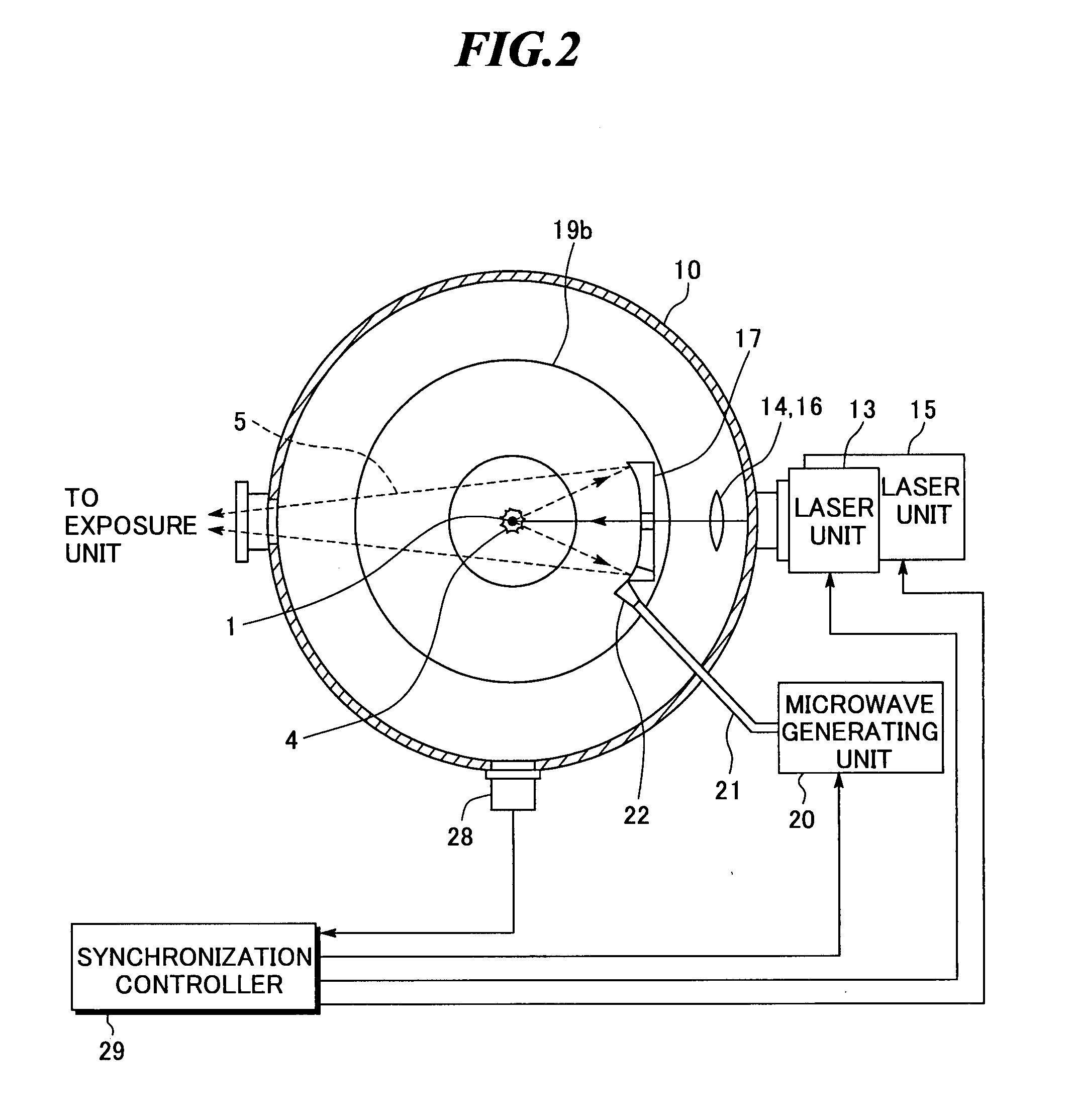
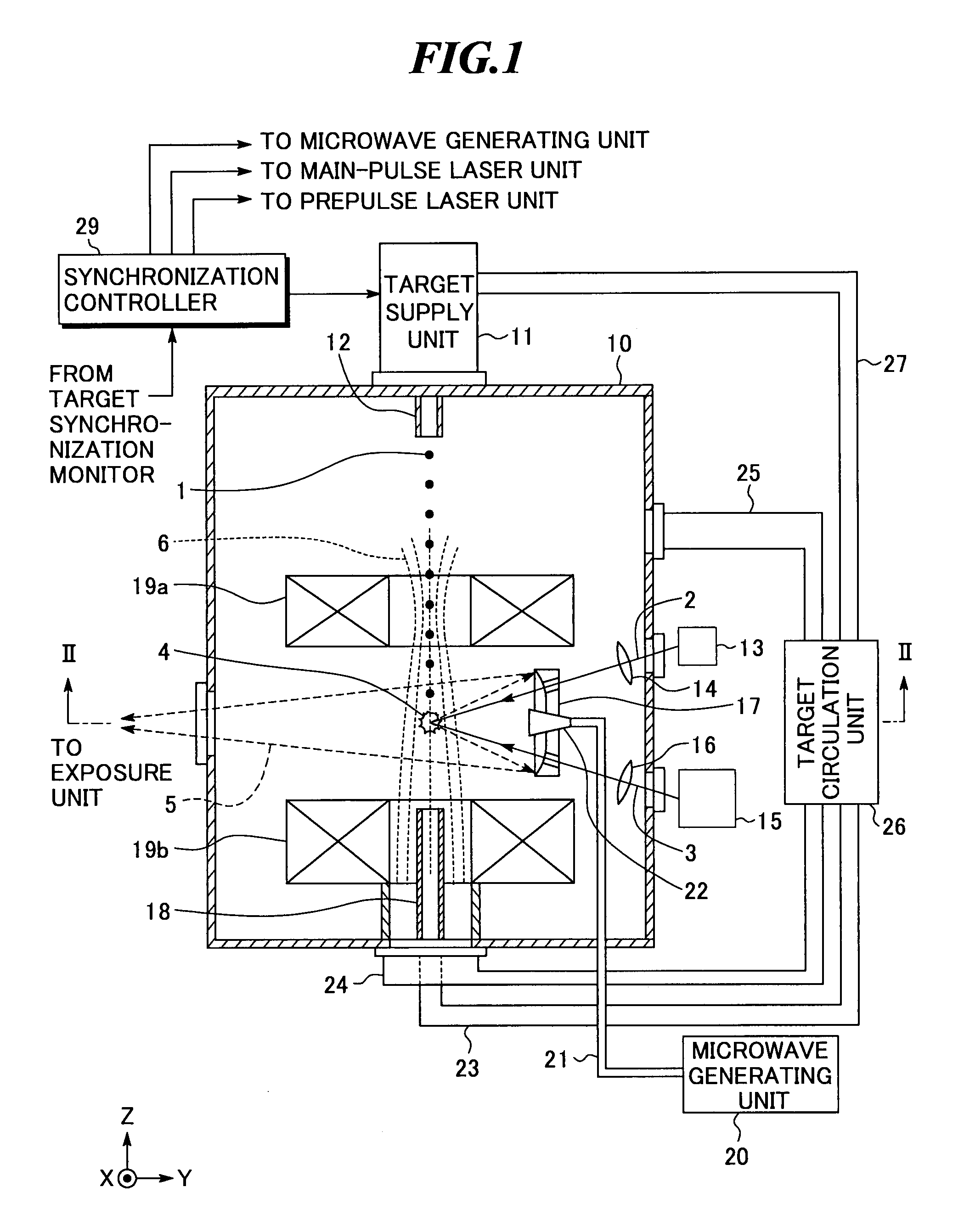
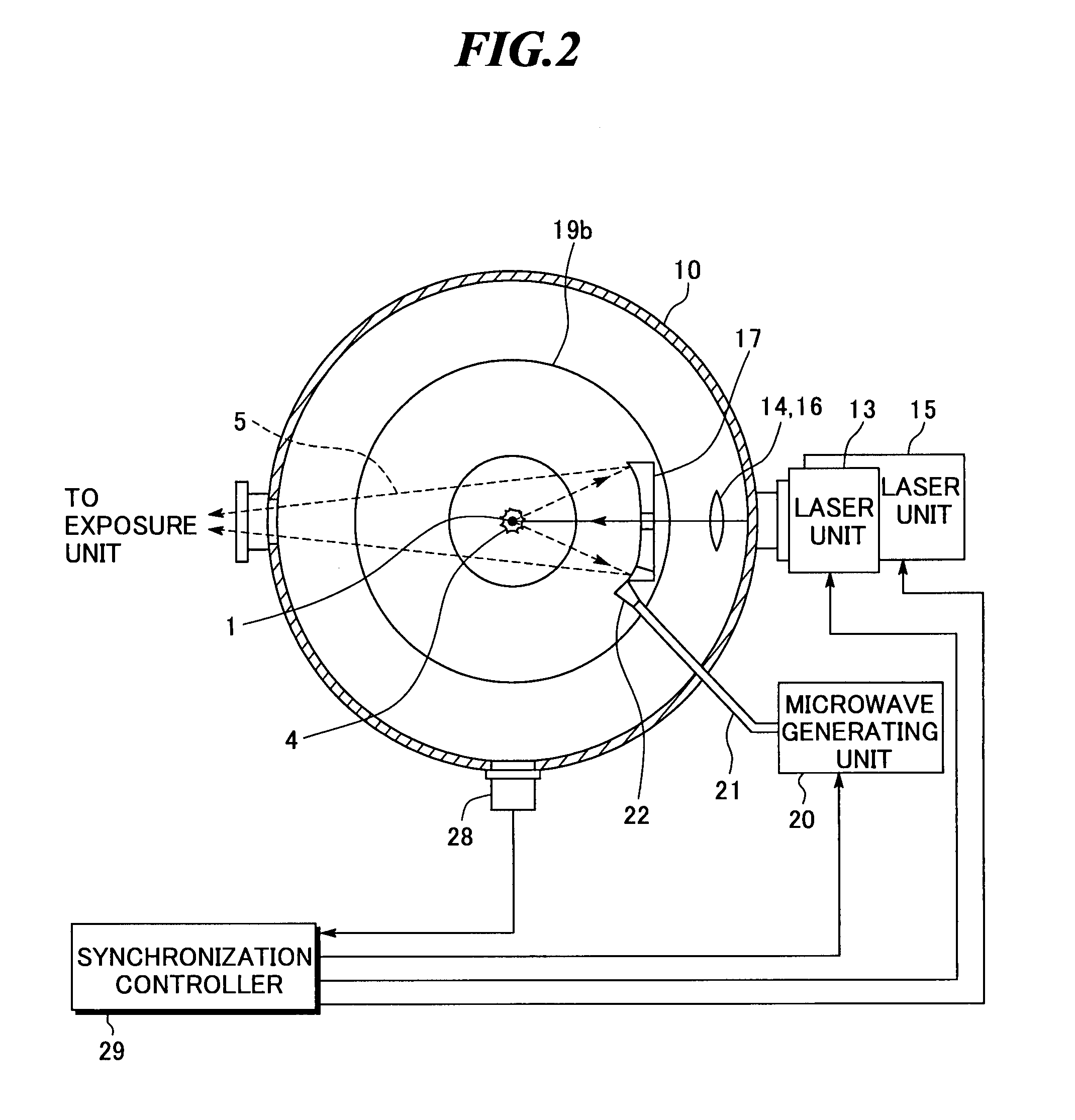
ActiveUS20080087840A1Production can be suppressedRadiation pyrometryNanoinformaticsLithiumExtreme ultraviolet
An extreme ultra violet light source apparatus having relatively high output for exposure, in which debris are suppressed to be produced as much as possible in stead of disposing debris that has been once produced. The extreme ultra violet light source apparatus includes: a chamber in which extreme ultra violet light is generated; a target supply unit for supplying solid tin or lithium as a target to a predetermined position within the chamber; a CO2 laser for applying a laser beam based on pulse operation to the target supplied by the target supply unit so as to generate plasma; and a collector mirror having a multilayer film on a reflecting surface thereof, for collecting the extreme ultra violet light radiated from the plasma to output the extreme ultra violet light.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
High-power laser using thulium-doped fiber amplifier and frequency quadrupling for blue output
ActiveUS8953647B1Low costSmall footprintWave based measurement systemsLaser using scattering effectsGratingHigh power lasers
An apparatus, method and associated fiber-laser architectures for high-power pulsed operation and pumping wavelength-conversion devices. Some embodiments generate blue laser light by frequency quadrupling infrared (IR) light from Tm-doped gain fiber using non-linear wavelength conversion. Some embodiments use a fiber MOPA configuration to amplify a seed signal from a semiconductor laser or ring fiber laser. Some embodiments use the frequency-quadrupled blue light for underwater communications, imaging, and / or object and anomaly detection. Some embodiments amplitude modulate the IR seed signal to encode communication data sent to or from a submarine once the modulated light has its wavelength quartered. Other embodiments transmit blue-light pulses in a scanned pattern and detect scattered light to measure distances to objects in a raster-scanned underwater volume, which in turn are used to generate a data structure representing a three-dimensional rendition of the underwater scene being imaged for viewing by a person or for other software analysis.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Handheld reflectometer for measuring macular pigment
ActiveUS20120092619A1Short time intervalReduce relative motionOthalmoscopesDocking stationMedical record
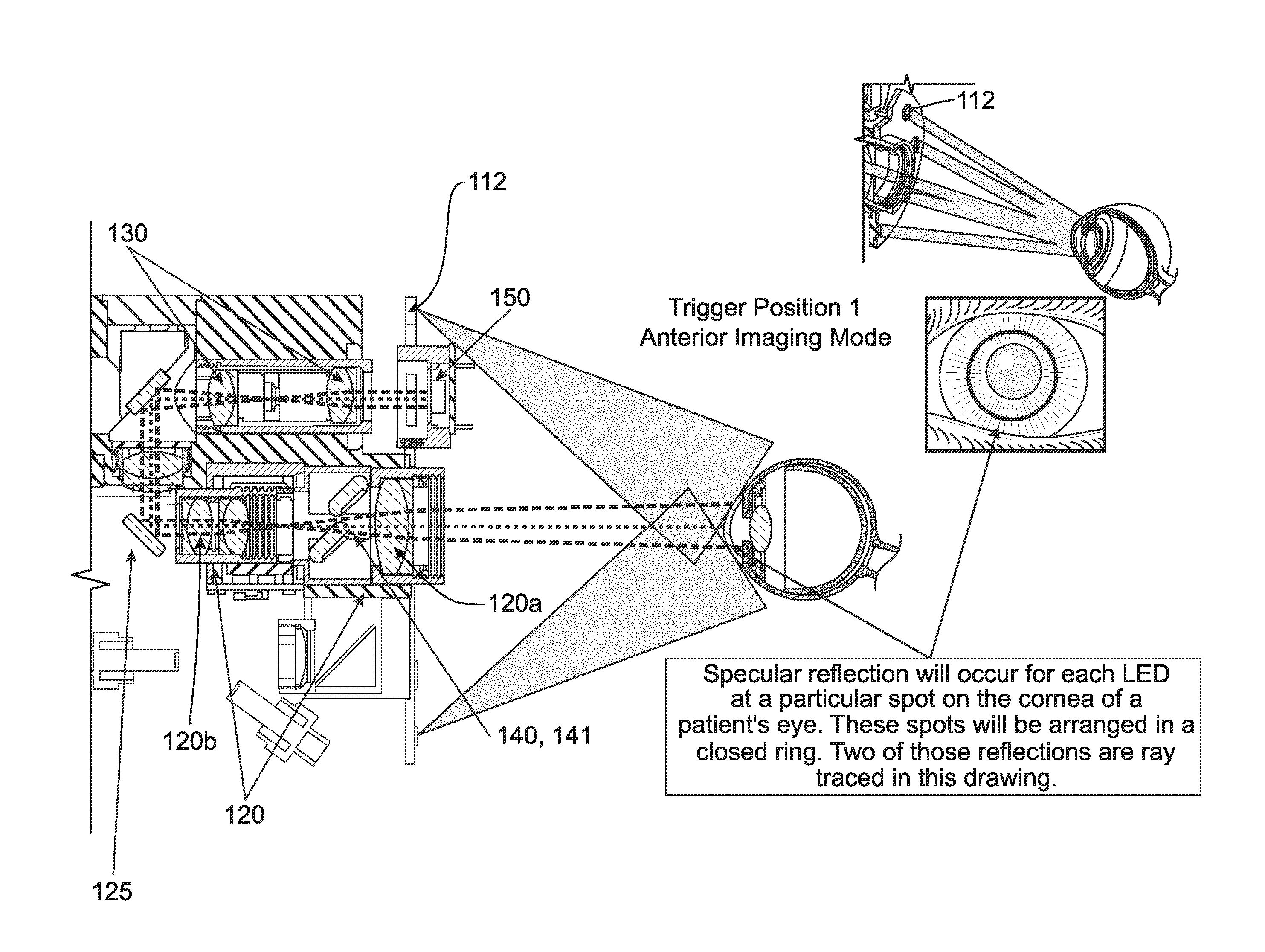
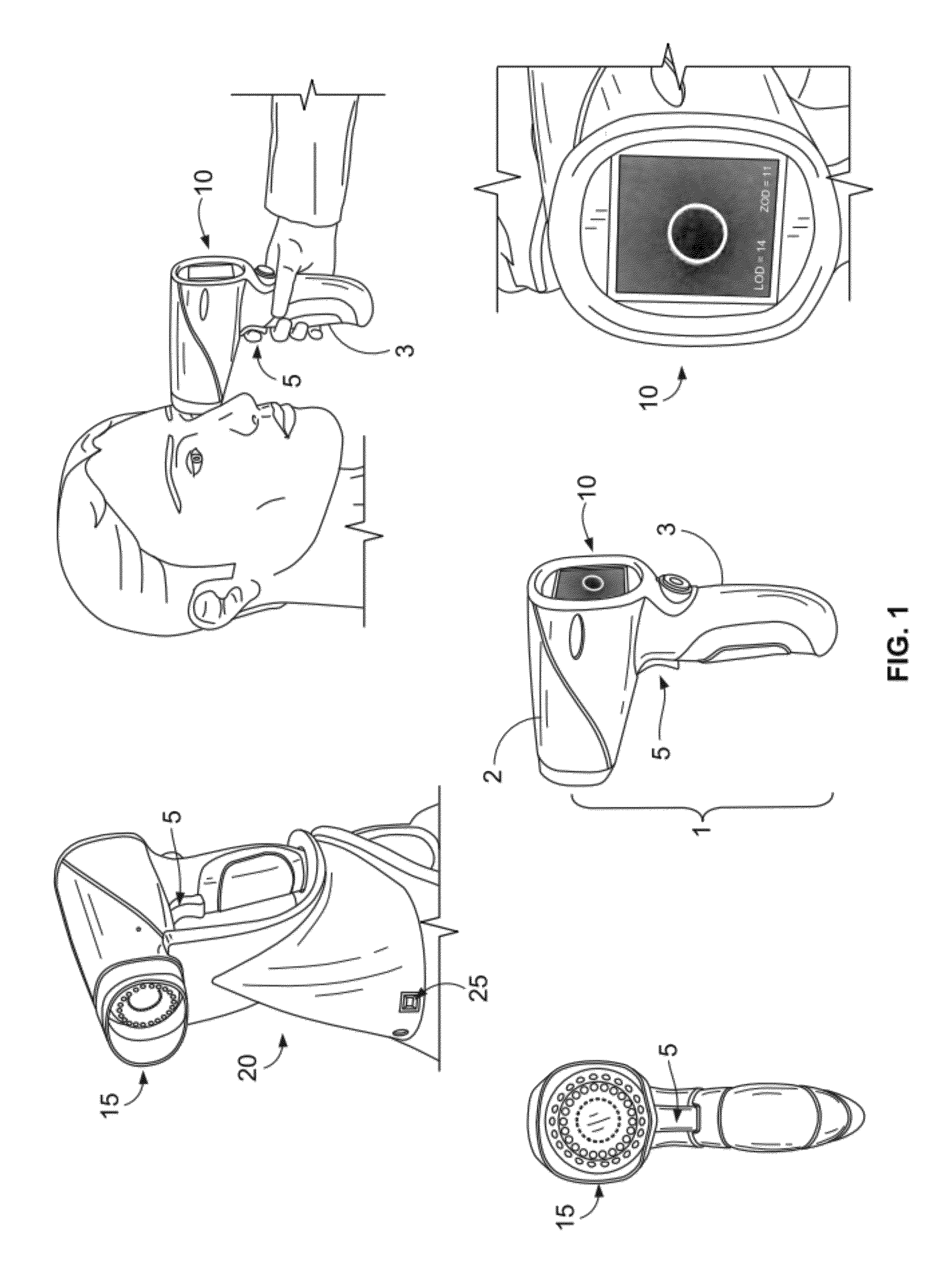
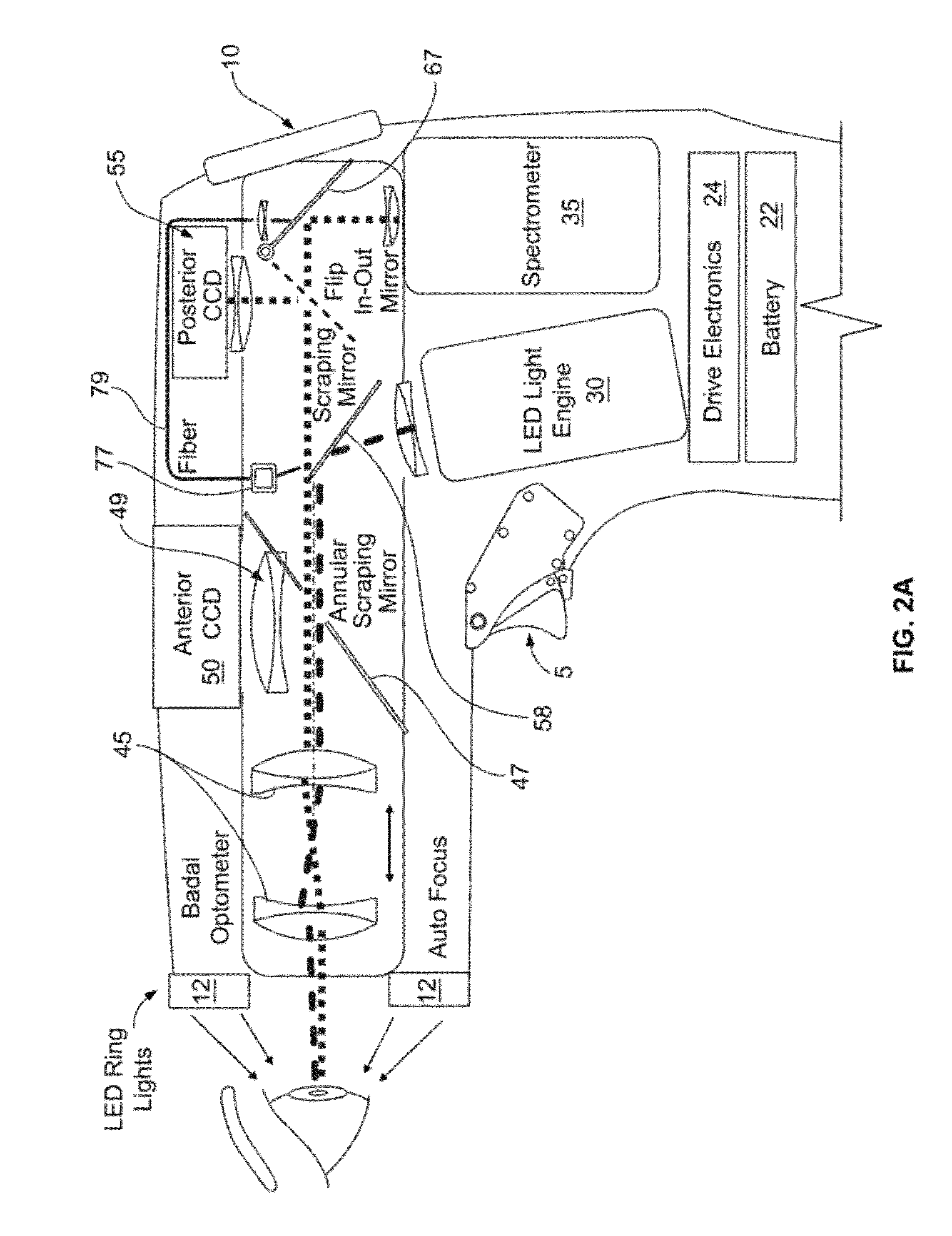
A macular pigment reflectometer is handheld, light, and portable. It can be provided as a part of a self-contained system. The self-contained system includes a docking station in which the macular pigment reflectometer is placed between uses. The docking station is used to recharge the battery of the handheld macular pigment reflectometer. The docking station also has one or more types of communication ports, such as one for a wired or wireless internet connection, through which the handheld macular pigment reflectometer can communicate with a computer or an electronic medical records system. The instrument operates in a pulsed operating mode wherein relative instrument-to-eye motion is reduced and, preferably, nearly eliminated. The handheld macular pigment reflectometer contains an on-board spectrometer which is designed to capture spectra in very short intervals of time. A trigger on the instrument allows for a rapid, intuitive, and sequential alignment followed by rapid data gathering.
Owner:OCULAR PROGNOSTICS
Optical Pump for High Power Laser
ActiveUS20130208753A1More powerReduce complexityLaser detailsSolid-state devicesHigh power lasersEngineering
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
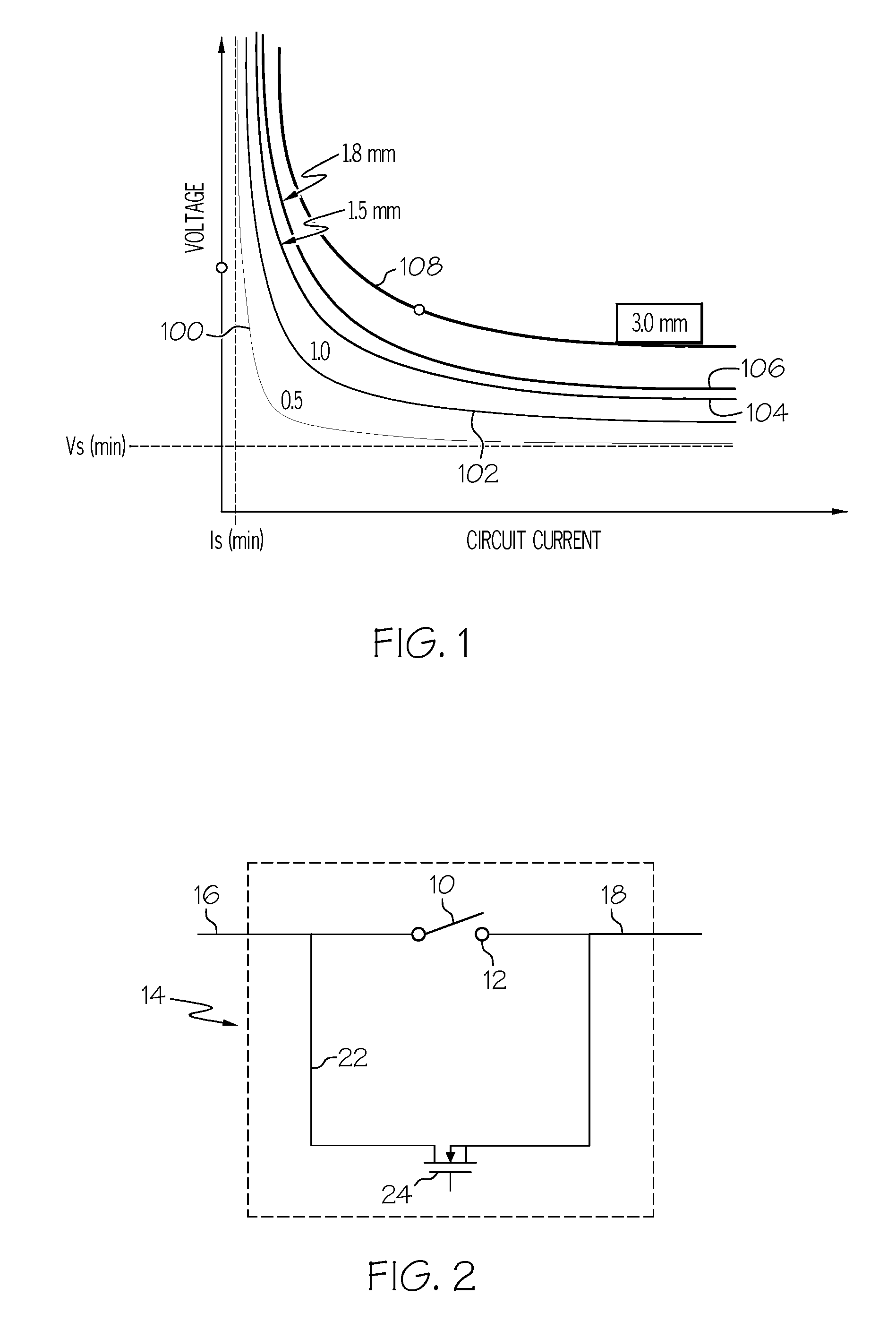
Hybrid high voltage DC contactor with arc energy diversion
InactiveUS20090168273A1Electric switchesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionShunt DevicePulse control
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Extreme ultra violet light source apparatus
ActiveUS20080083887A1Improve efficiencyEfficient ionizationLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowaveElectron cyclotron resonance
In an extreme ultra violet light source apparatus that exhausts debris including fast ions and neutral particles by the effect of a magnetic field, neutral particles emitted from plasma are efficiently ionized. The extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus includes: a plasma generating unit that generates plasma, that radiates at least extreme ultra violet light, through pulse operation; collective optics that collects the extreme ultra violet light radiated from the plasma; a microwave generating unit that radiates microwave through pulse operation into a space in which a magnetic field is formed to cause electron cyclotron resonance, and thereby ionizes neutral particles emitted from the plasma; a magnetic field forming unit that forms the magnetic field and a magnetic field for trapping at least ionized particles; and a control unit that synchronously controls at least the plasma generating unit and the microwave generating unit.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
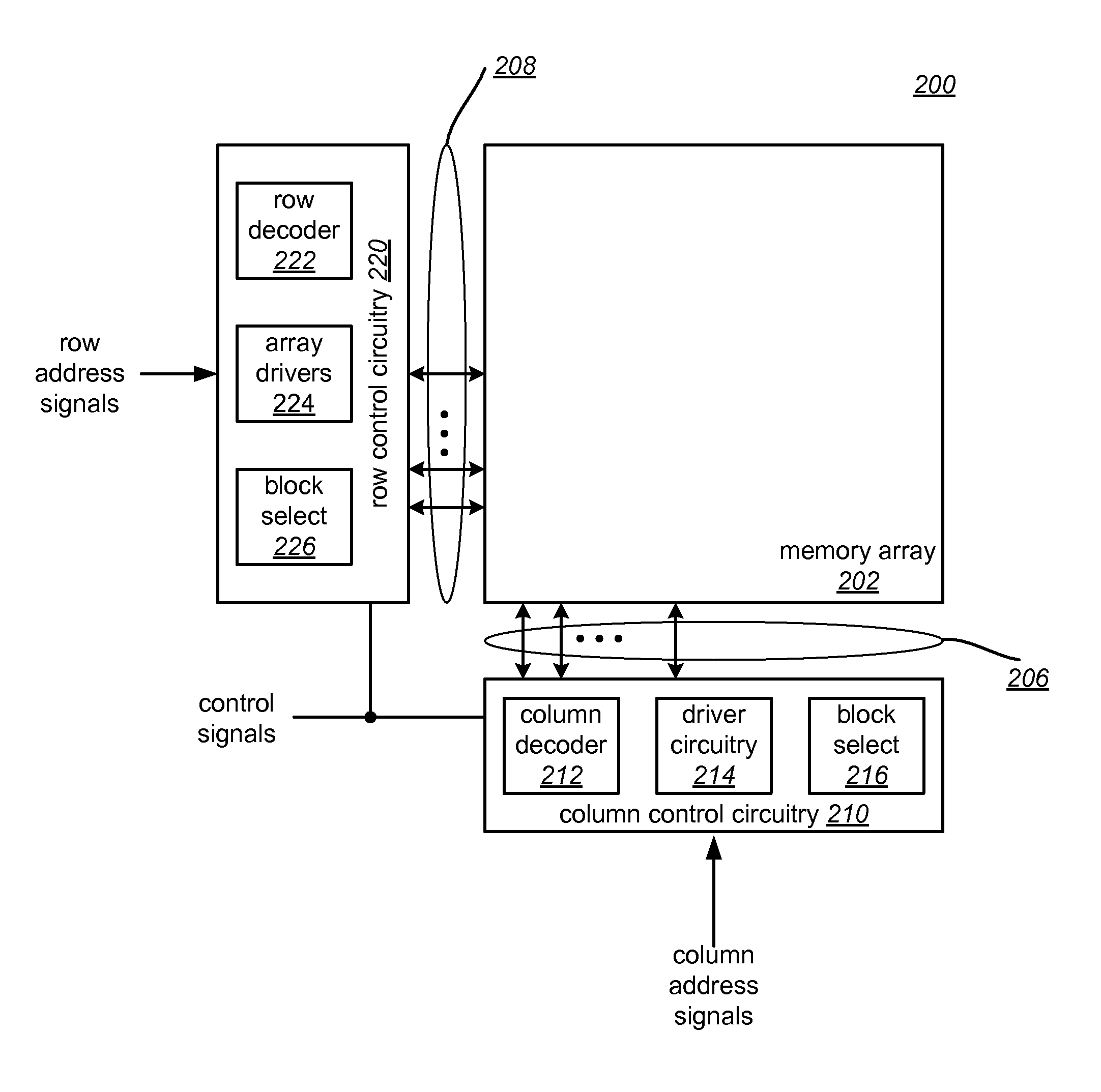
Systems for controlled pulse operations in non-volatile memory
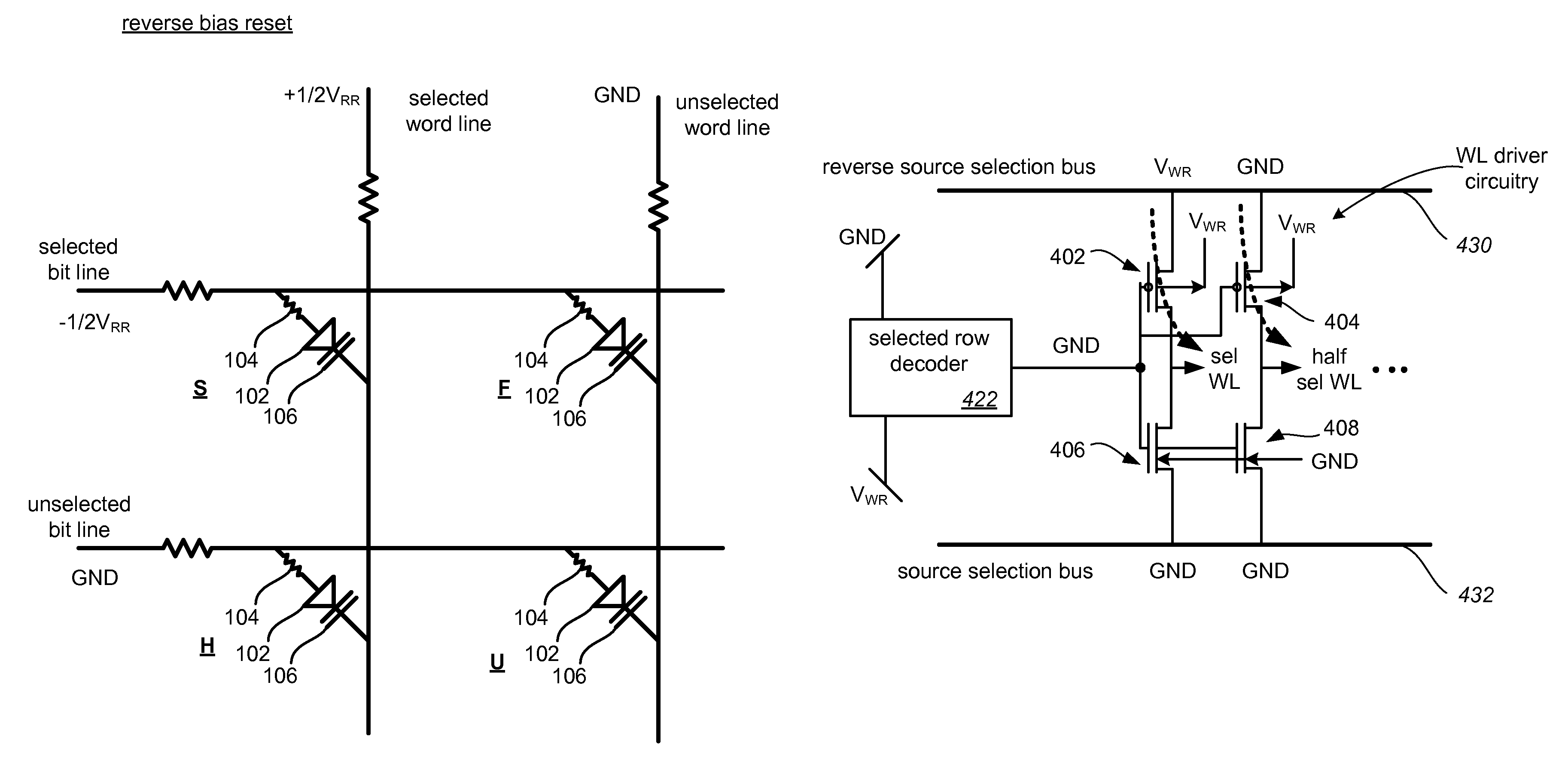
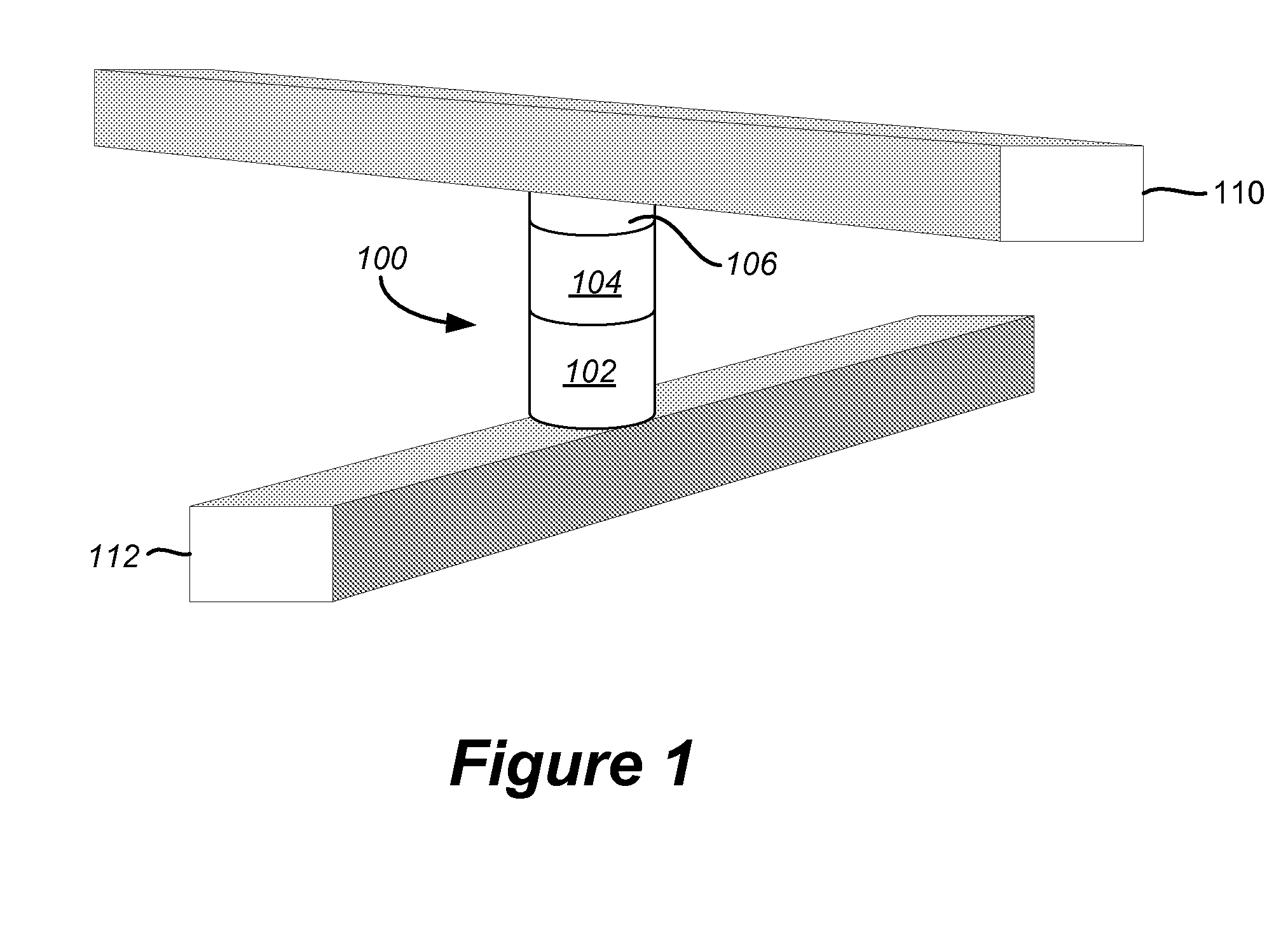
InactiveUS20080025077A1EfficientlySafely switch resistanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageHigh resistanceVoltage pulse
A passive element memory device is provided that includes memory cells comprised of a state change element in series with a steering element. Controlled pulse operations are used to perform resistance changes associated with set and reset operations in an array of memory cells. Selected memory cells in an array are switched to a target resistance state in one embodiment by applying a positive voltage pulse to selected first array lines while applying a negative voltage pulse to selected second array lines. An amplitude of voltage pulses can be increased while being applied to efficiently and safely switch the resistance of cells having different operating characteristics. The cells are subjected to reverse biases in embodiments to lower leakage currents and increase bandwidth. The amplitude and duration of voltage pulses are controlled, along with the current applied to selected memory cells in some embodiments. These controlled pulse-based operations can be used to set memory cells to a lower resistance state or reset memory cells to a higher resistance state in various embodiments.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for driving laser diodes
InactiveUS7792166B2Fast rise timeImprove efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCapacitanceMode control
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
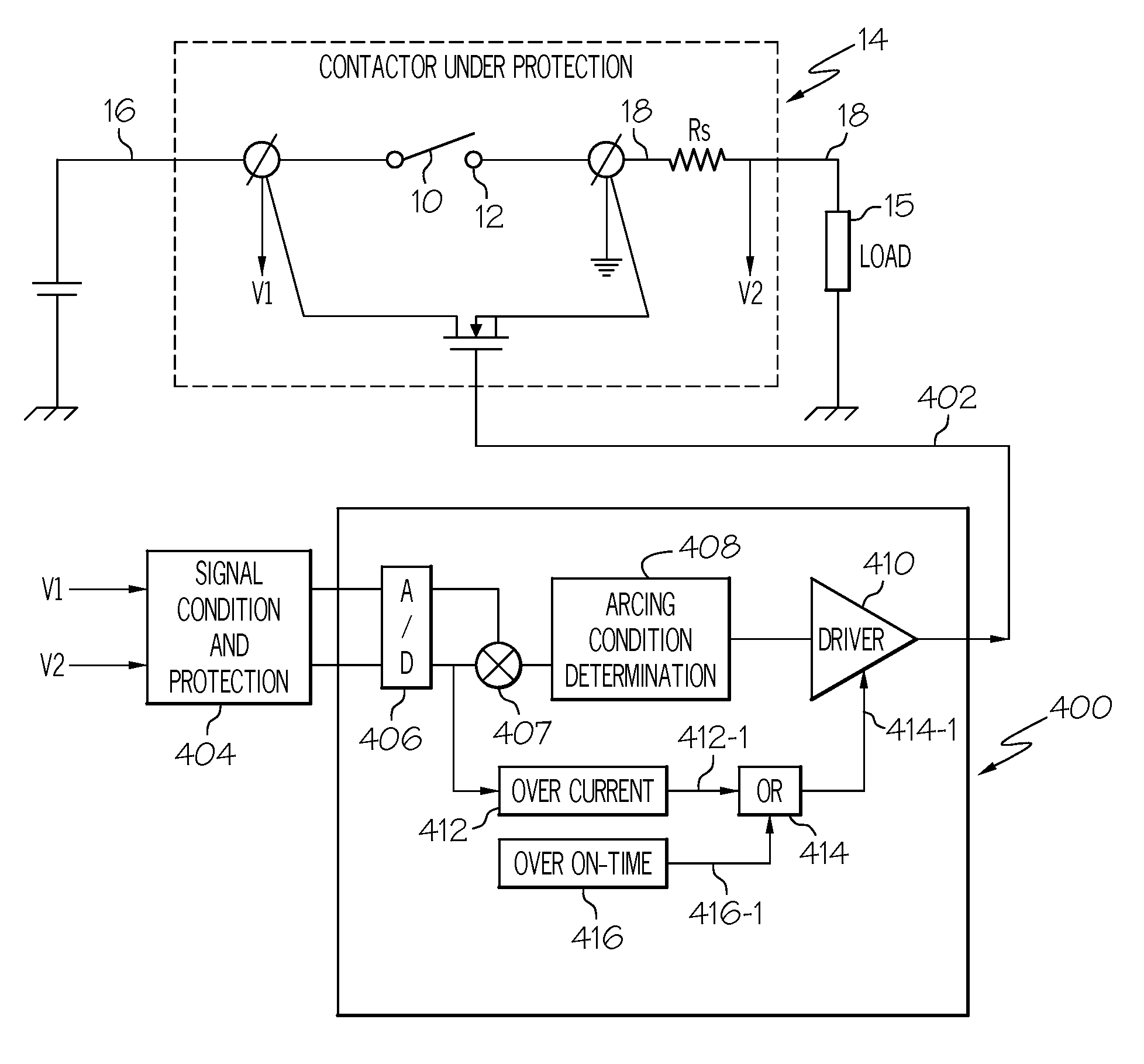
Electronic fuse
ActiveUS20050135037A1Avoid OverloadingEasy resetTransistorElectronic switchingDriver circuitCurrent limiting
An electronic fuse comprising an integrated circuit having a control output terminal coupled to a control electrode of a power semiconductor switching device, the power semiconductor switching device being coupled in series with a load between first and second potentials, the integrated circuit further comprising a current sense input for sensing the current through the power semiconductor switching device, the integrated circuit further comprising a driver circuit for driving the power semi-conductor switching device, the driver circuit being coupled to a current limiting circuit responsive to the sensed current in the power semiconductor switching device, the current limiting circuit controlling the driver circuit whereby if the current through the power semiconductor switching device exceeds a predetermined threshold, the current limiting circuit generates a command to pulse the power semiconductor switching device on and off in a period of pulsed operation to maintain the current in the power semiconductor switching device below a predetermined level, further comprising a first timer circuit for limiting the period of pulsed operation to a preprogrammed first duration and further for controlling the power semiconductor switching device whereby if two commands to pulse the power semiconductor switching device are generated by the current limiting circuit within a duration less than a predetermined second duration, the power semiconductor switching device is turned off.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
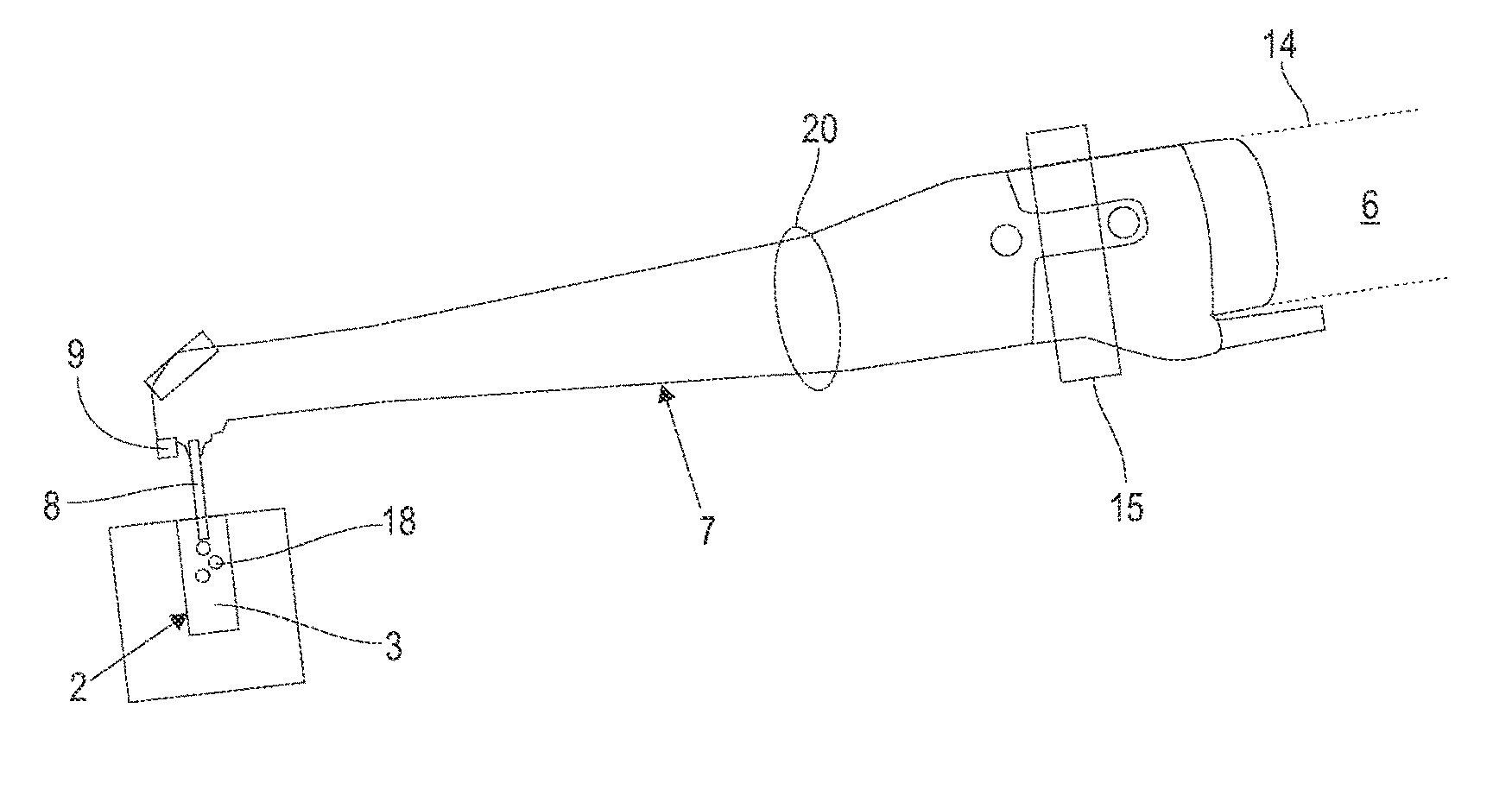
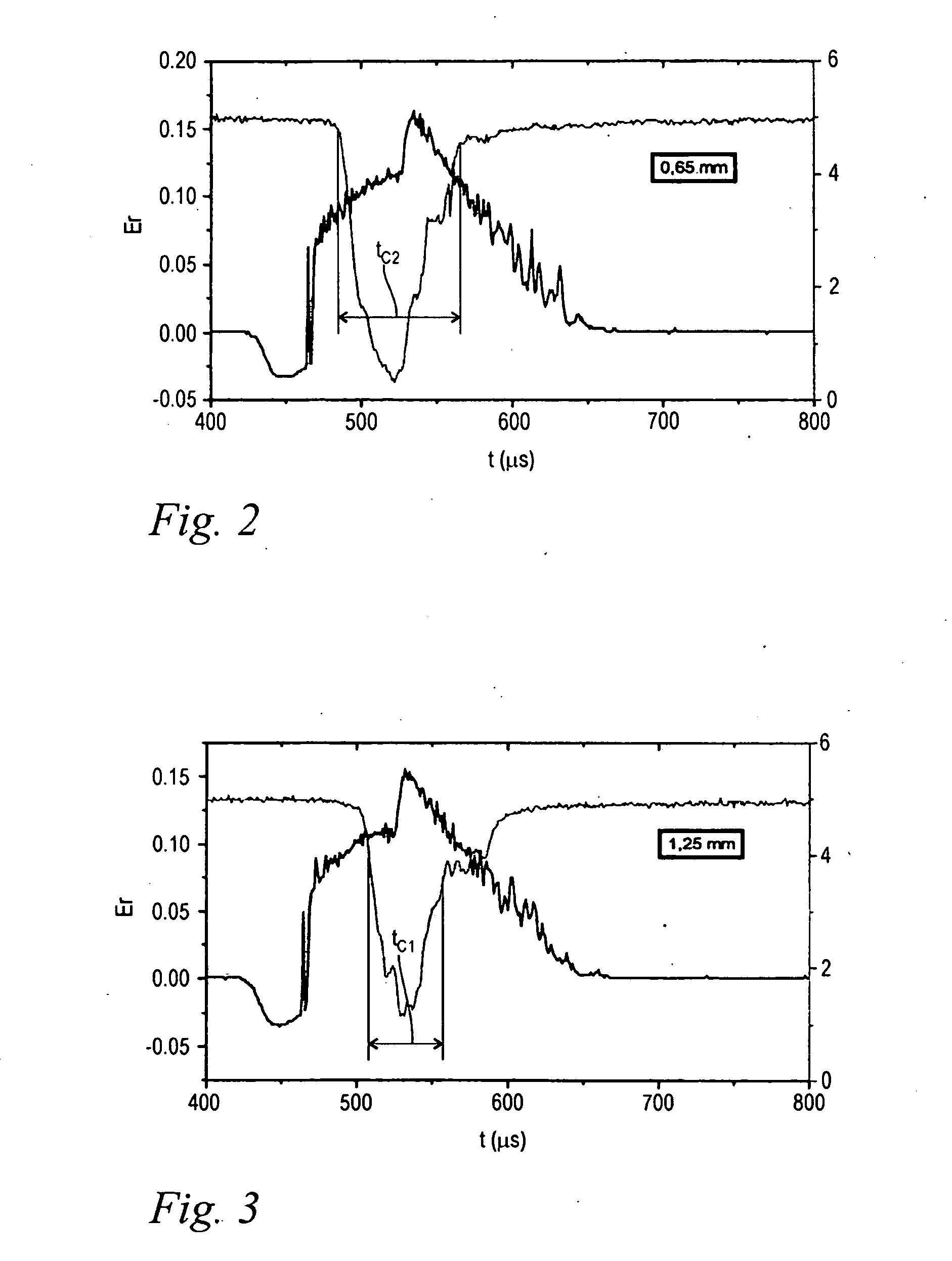
Laser system and method for controlling the laser pulse shape
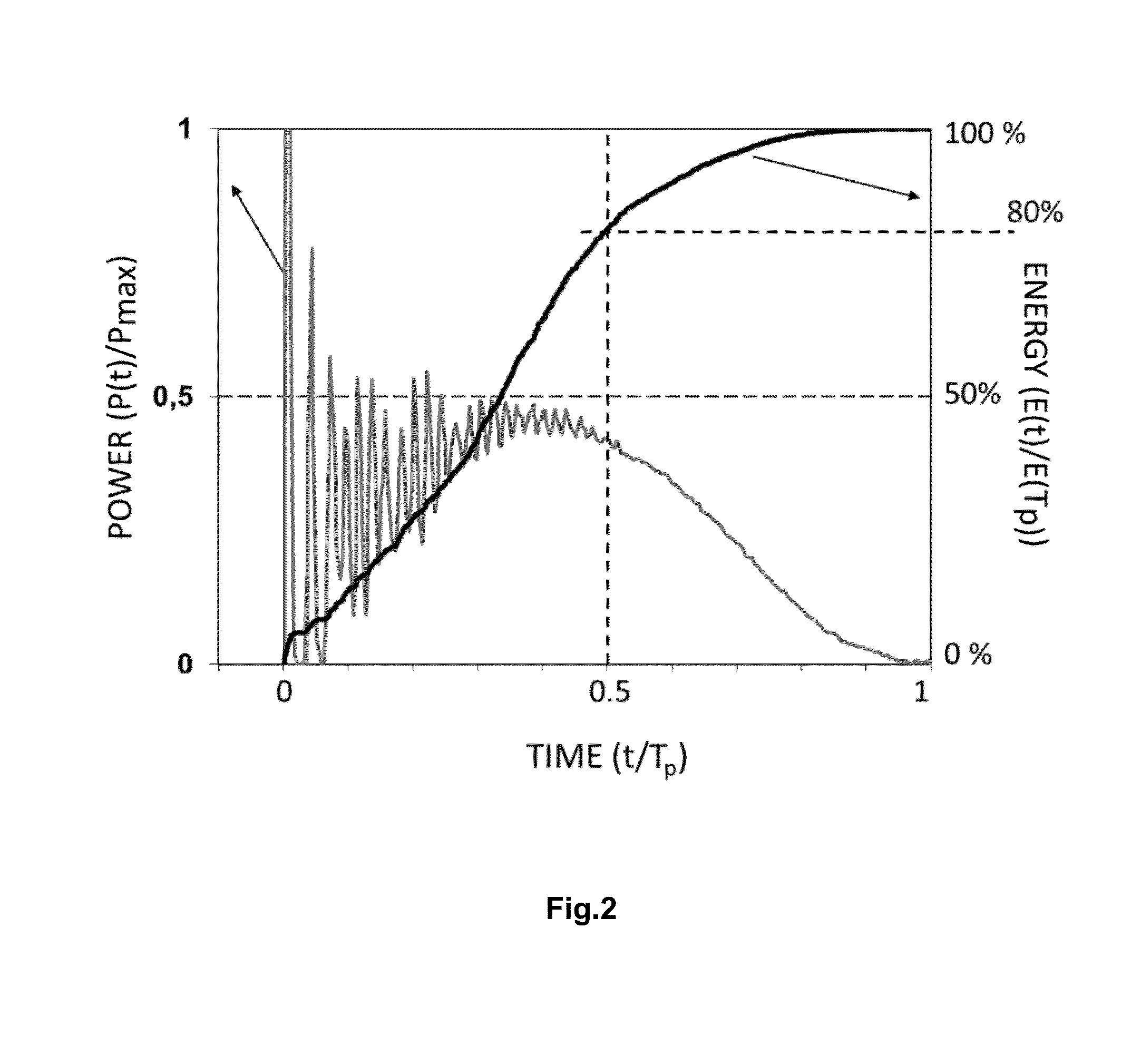
ActiveUS20160149370A1Reduce initial high laser intensity spikingHigh intensity/powerLaser detailsDiagnosticsLaser pulse shapingOptoelectronics
A laser system for medical treatment is disclosed which comprises a pump, wherein the laser system is adapted to be operated in pulsed operation so that at least one laser pulse of a temporally limited pulse duration (Tp) is generated. The generated laser pulse irradiates some part of the human or animal body so that a two-dimensional laser spot S is located on the top layer of the irradiated part of the human or animal body. The pump power of the pump of the laser system is modulated in such a way that the cumulative energy ES(Tp / 2) which is delivered by said laser pulse to said laser spot S during the first half of the pulse duration is less than 45% of the energy ES(Tp) which is delivered by said laser pulse to said laser spot S during the entire pulse duration Tp.
Owner:FOTONA D O O
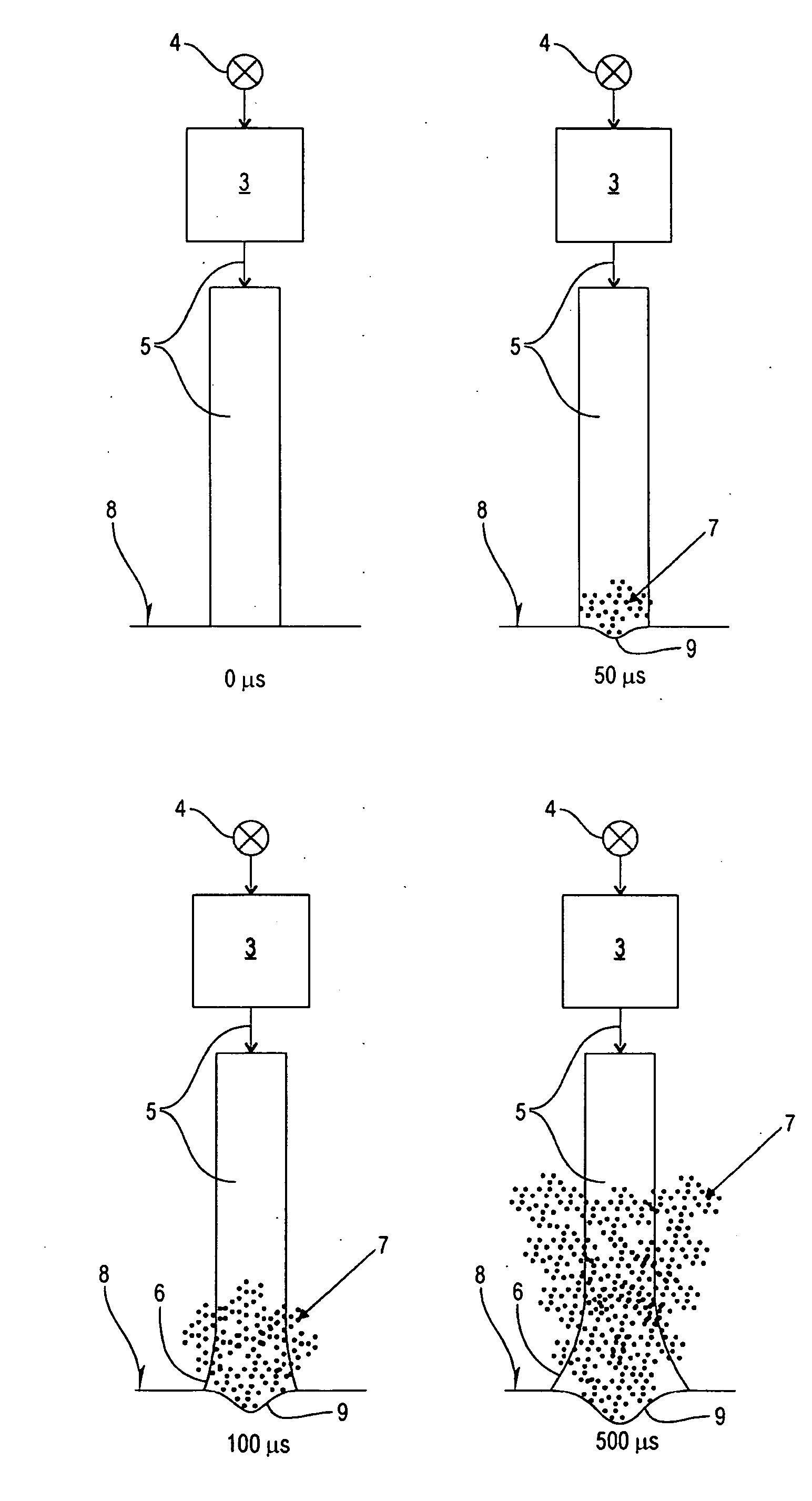
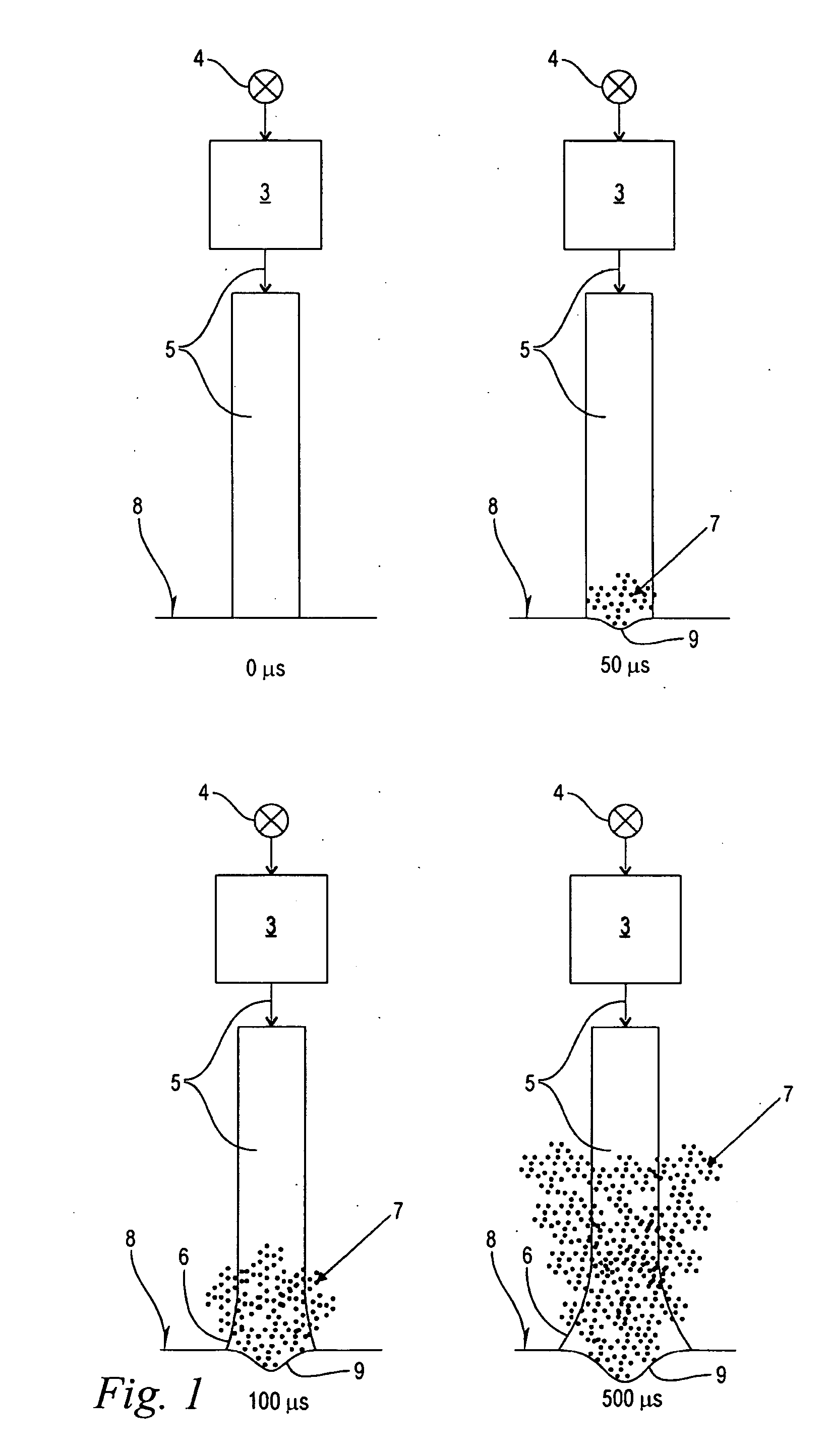
Laser system for tissue ablation
ActiveUS20160149372A1Avoid overall overheatingMinimize heat depositionLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsPulse operationTissue ablation
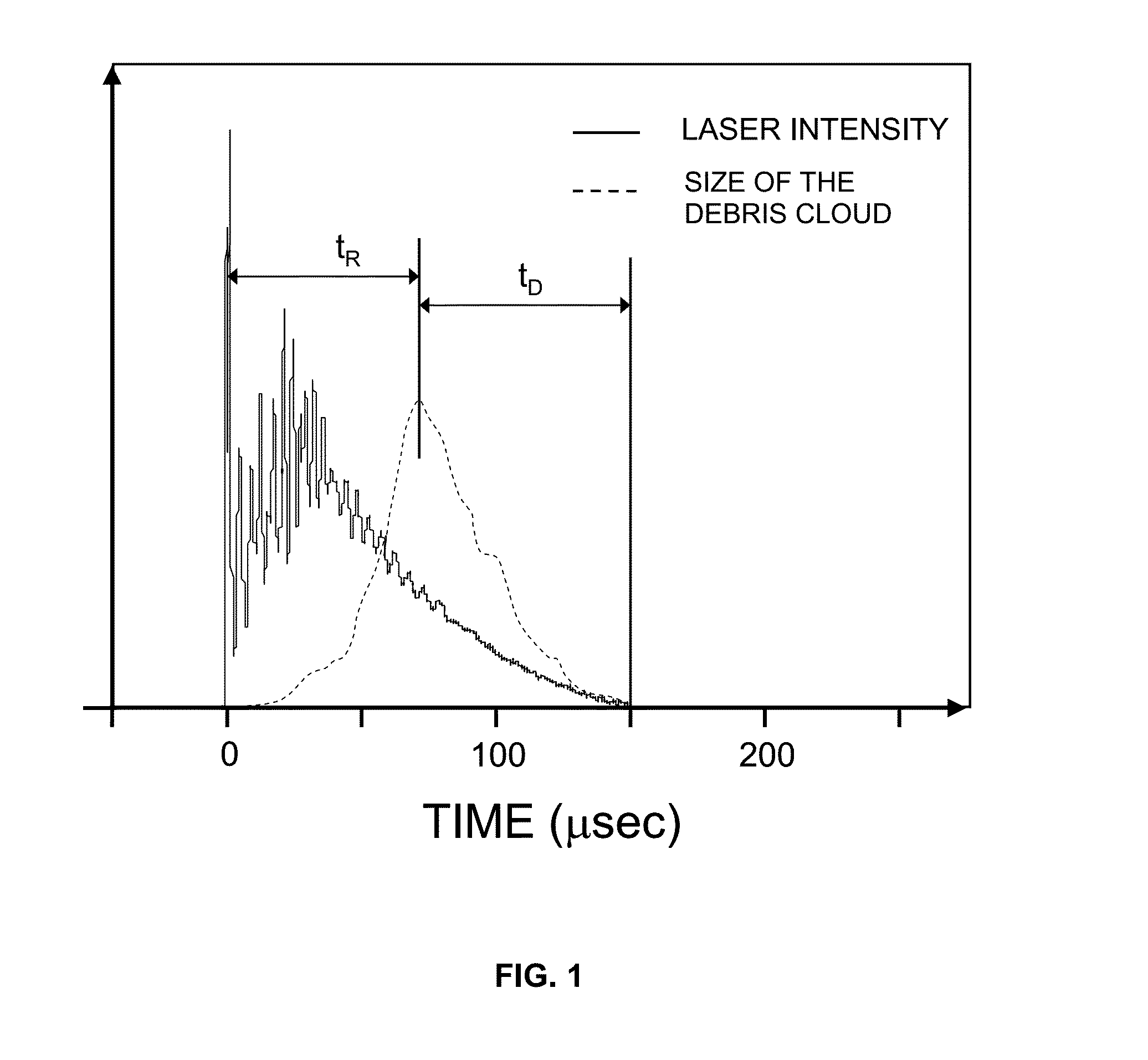
A Laser system is disclosed which comprises a pump, wherein the laser system is adapted to be operated in pulsed operation so that at least one individual pulse of a temporally limited pulse duration (T0) is generated, wherein the pulse ablates a material such that a debris cloud forms above the ablated material. Further, the pump power of the pump is modulated in such a way that the following three conditions are fulfilled: (1) the intensity of the pulse oscillates between maximum values and minimum values during the pulse duration, wherein the laser pulse comprises a plurality of intensity maxima Imax which occur at times {Ti, i=1, . . . N}; and a plurality of intensity minima Imin which occur at times {tk, k=1, . . . (N−1)}, wherein the intensity does not vanish at the intensity minima; (2) the intensity oscillations of the laser pulse induce oscillations of the size of the debris cloud so that, during the pulse duration (T0), there are at least two maxima of the size of the debris cloud which occur at times {tj, J=1, . . . M} and which are located in between two intensity maxima of the laser pulse; and (3) at least 70 percent of the maxima of the size of the debris cloud occur near an intensity minimum of the pulse such that, for at least 70 percent of the maxima of the size of the debris cloud, the intensity of the pulse I(tj) at the time of the maximum of the size of the debris cloud is smaller than Imin(tk)+0.5× [Imax(Ti)−Imin(tk)], wherein Imin(tk) is the intensity minimum of the pulse which is closest to the maximum of the size of the debris cloud at time tj and Imax(Ti) is the intensity maximum of the pulse which is closest to the maximum of the size of the debris cloud at time tj.
Owner:FOTONA D O O
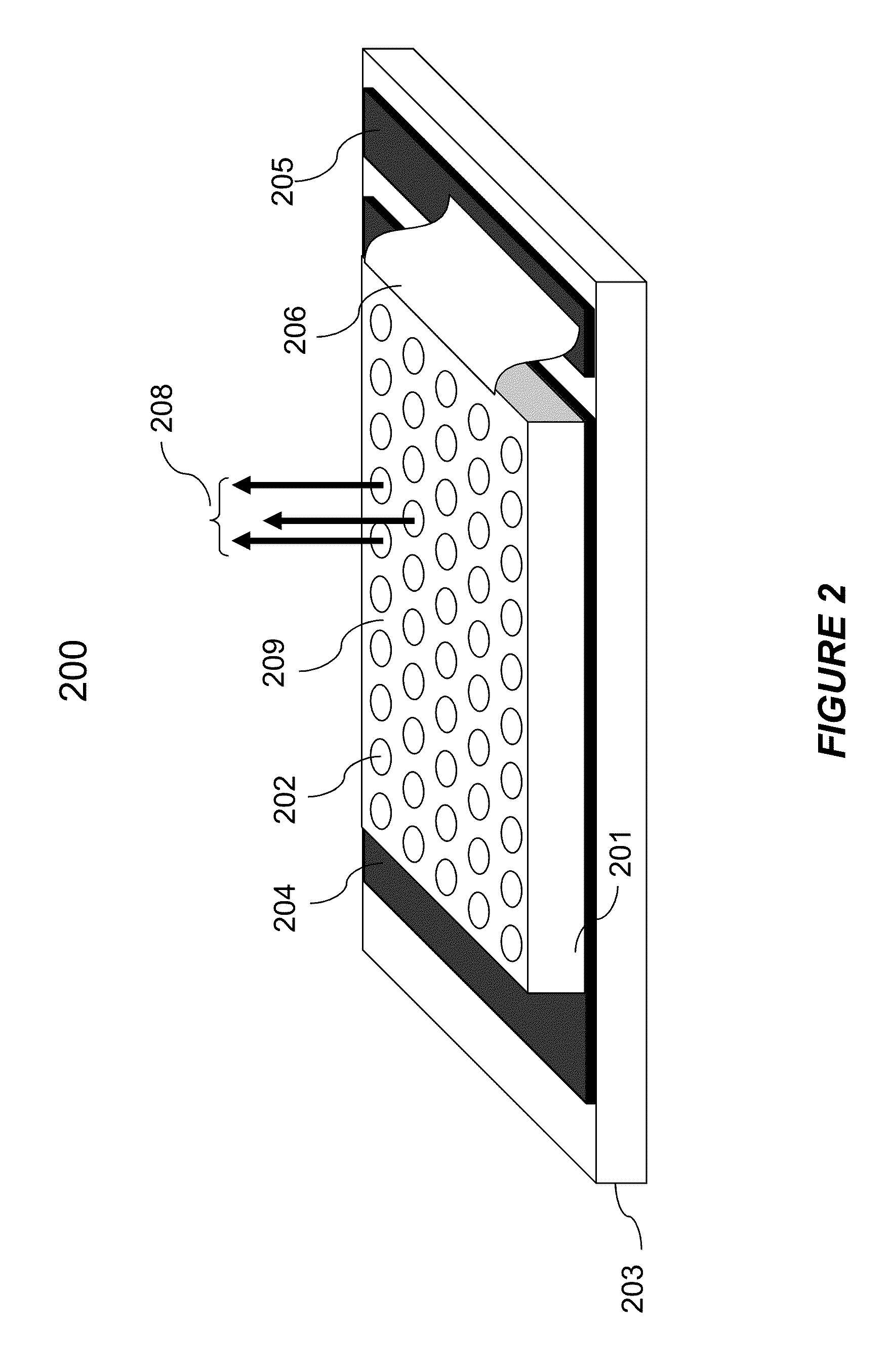
VCSEL pumped fiber optic gain systems
ActiveUS8824519B1Increase laser output powerEnhance input optical pump powerLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionDouble-clad fiberEngineering
Optical pump modules comprising VCSEL and VCSEL array devices provide high optical power for configuring fiber optic gain systems such as fiber laser and fiber amplifier particularly suited for high power operation. Pump modules may be constructed using two reflector or three reflector VCSEL devices optionally integrated with microlens arrays and other optical components, to couple high power pump beams to a fiber output port. The pump module having a fiber output port is particularly suited to couple light to an inner cladding of a double-clad fiber, often used to configure high power fiber laser and fiber amplifier. The pump modules may be operated in CW, QCW and pulse modes to configure fiber lasers and amplifiers using single end, dual end, and regenerative optical pumping modes. Multiple-pumps may be combined to increase pump power in a modular fashion without significant distortion to signal, particularly for short pulse operation.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
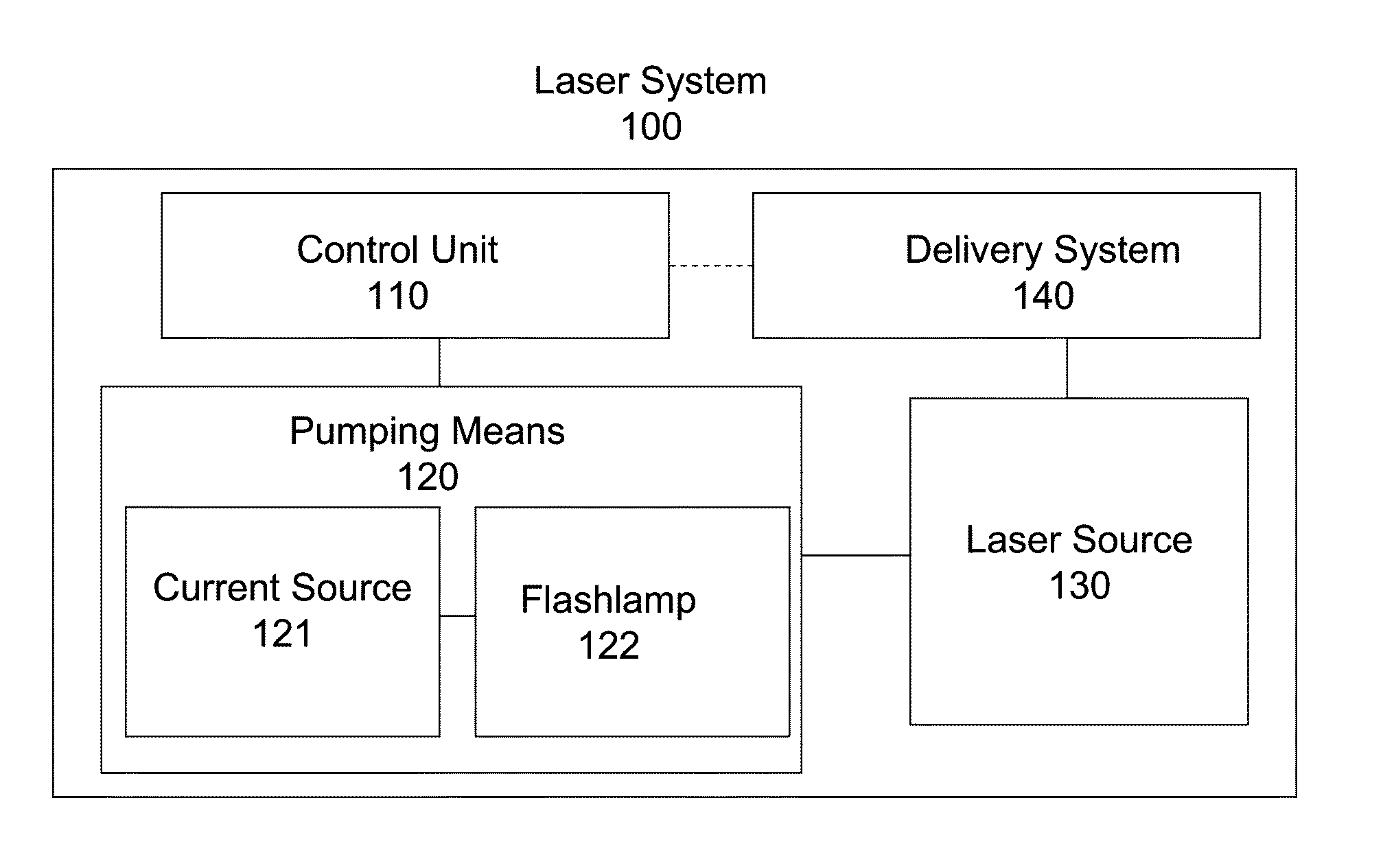
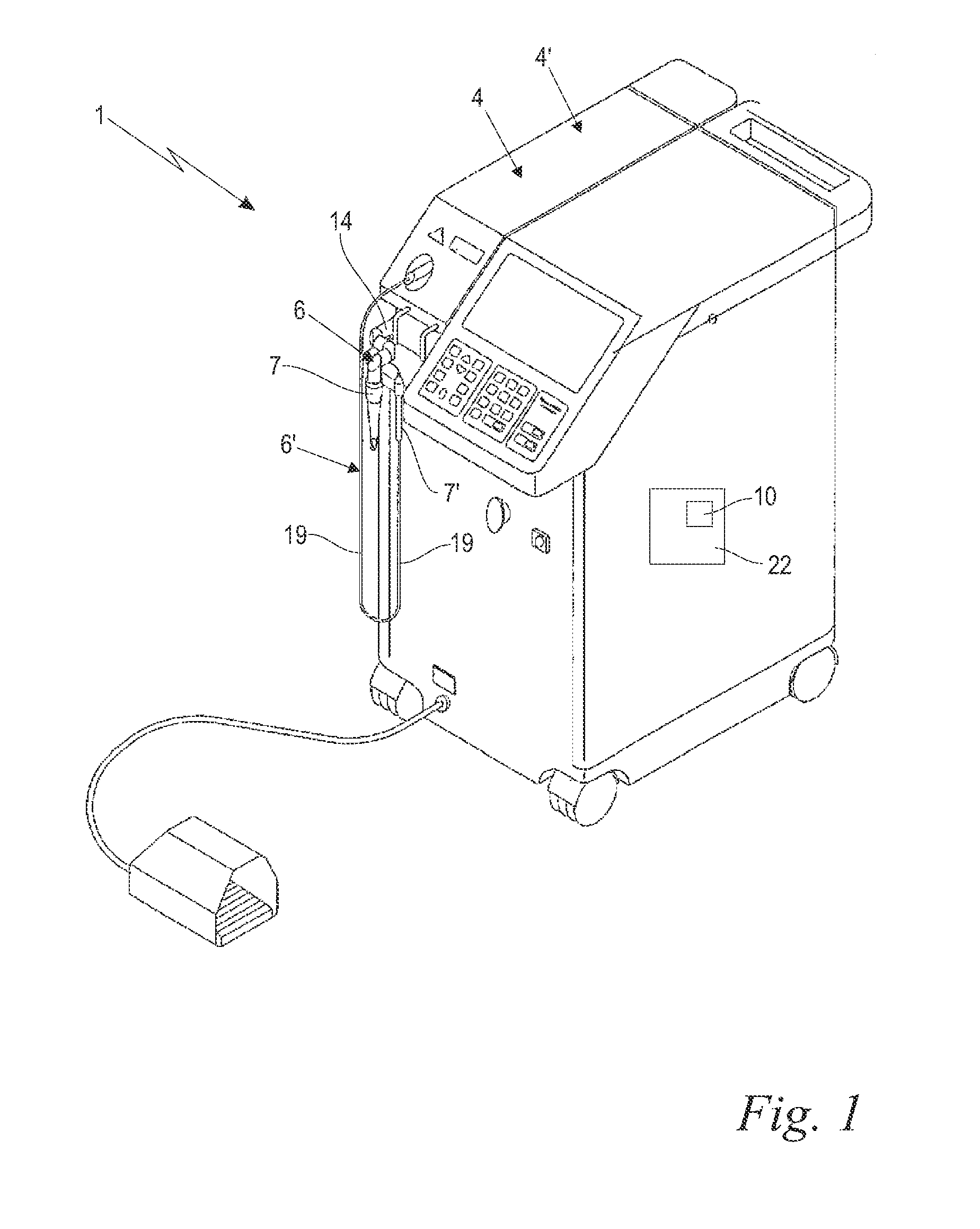
Laser system and method for operating the laser system
ActiveUS9572632B2Improve scienceExtended durationGum massageSurgical instrument detailsVapor bubbleLength wave
A dental irrigation system is provided with a laser source for generating a laser beam and an optical delivery system for the laser beam. The laser beam wavelength ranges from 0.4 μm to 11.0 μm. The laser system operates in pulsed operation with pulse sets of 2 to 20 individual pulses of temporally limited pulse length. The pulse sets follow one another with temporal separation. The individual pulses follow one another with pulse repetition rate. The laser system generates at least one vapor bubble within the liquid irradiated with the laser beam. A single pulse causes the vapor bubble to oscillate between a maximal and a minimal volume with a bubble oscillation frequency. The pulse repetition rate within one pulse set is adjusted relative to the bubble oscillation frequency such that synchronization between delivery of the pulses and bubble oscillation is achieved.
Owner:FOTONA D O O
Laser System for Hard Body Tissue Ablation
InactiveUS20080285600A1Improve efficiencyLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsOptoelectronicsPulse operation
A laser system for hard body tissue ablation has a pumped laser, wherein the laser system is operated in pulsed operation with several individual pulses of a temporally limited pulse length and wherein the individual pulses follow one another with temporal pulse spacing. The pumped laser has an inversion population remaining time, the inversion population remaining time being the time within which, in the absence of pumping, the remaining inversion population of the laser energy status is reduced by 90%. The pulse spacing is in the range of ≧50 μs and ≦ to the inversion population remaining time.
Owner:FOTONA D D
Laser System for Hard Body Tissue Ablation
InactiveUS20130131656A1Improve efficiencySurgical instrument detailsBoring toolsLeg lengthOptoelectronics
A laser system for hard body tissue ablation has a pumped laser, wherein the laser system is operated in pulsed operation with several individual pulses of a temporally limited pulse length and wherein the individual pulses follow one another with temporal pulse spacing. The pumped laser has an inversion population remaining time, the inversion population remaining time being the time within which, in the absence of pumping, the remaining inversion population of the laser energy status is reduced by 90%. The pulse spacing is in the range from 50 μs, inclusive, to the inversion population remaining time of ≧50 μs. The pulse length is selected to be in a pulse length range of ≧10 μs to ≦120 μs.
Owner:FOTONA D O O
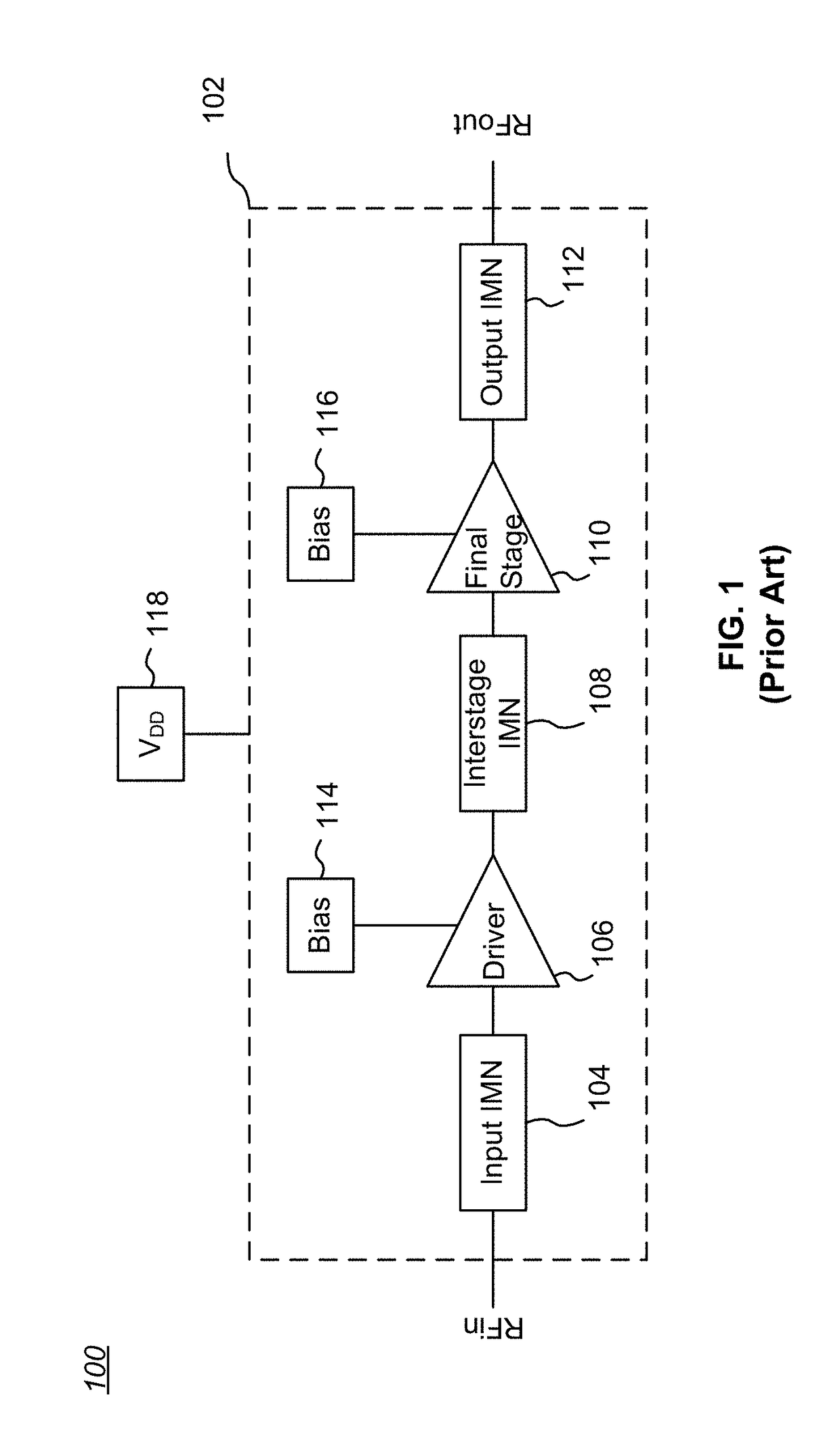
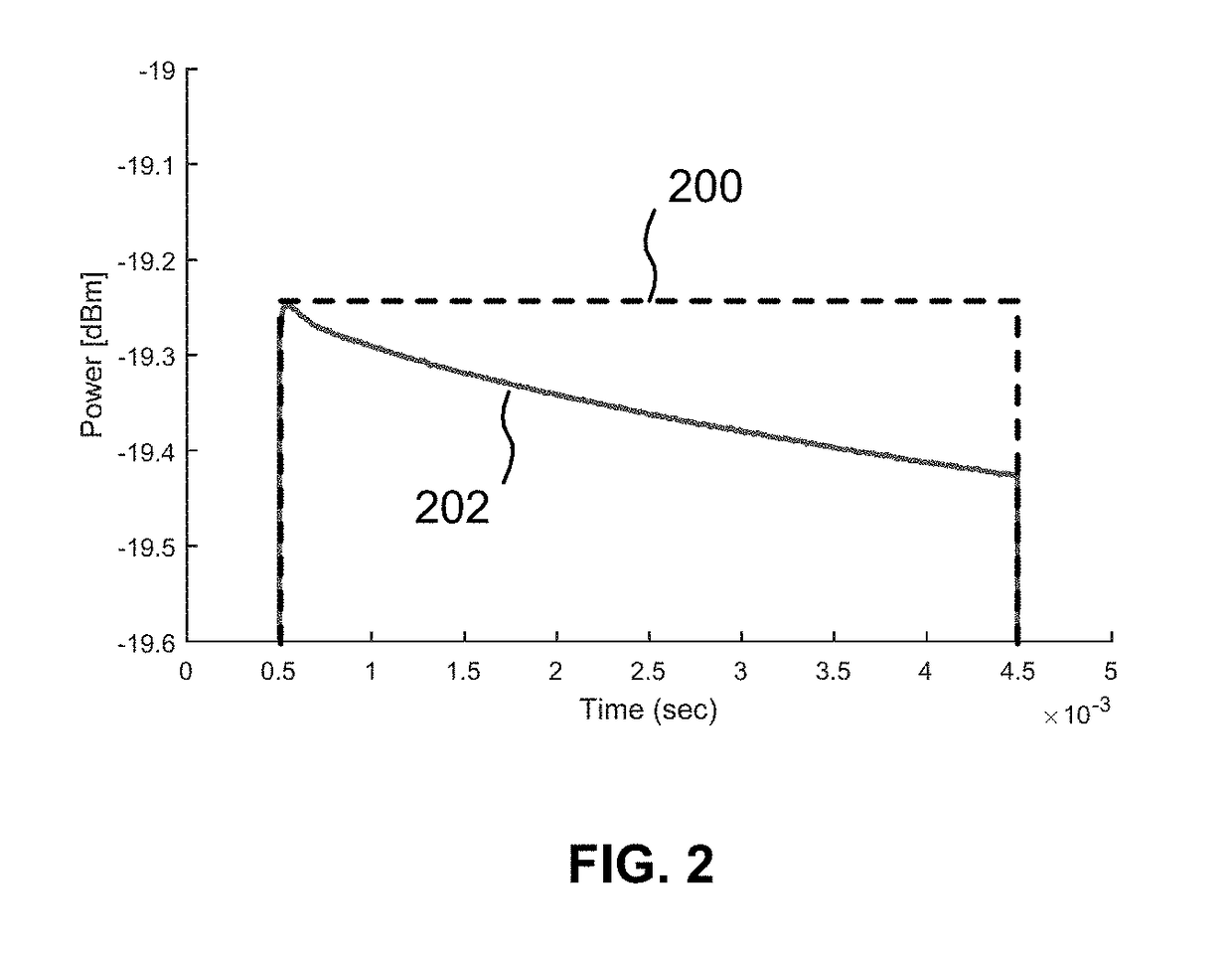
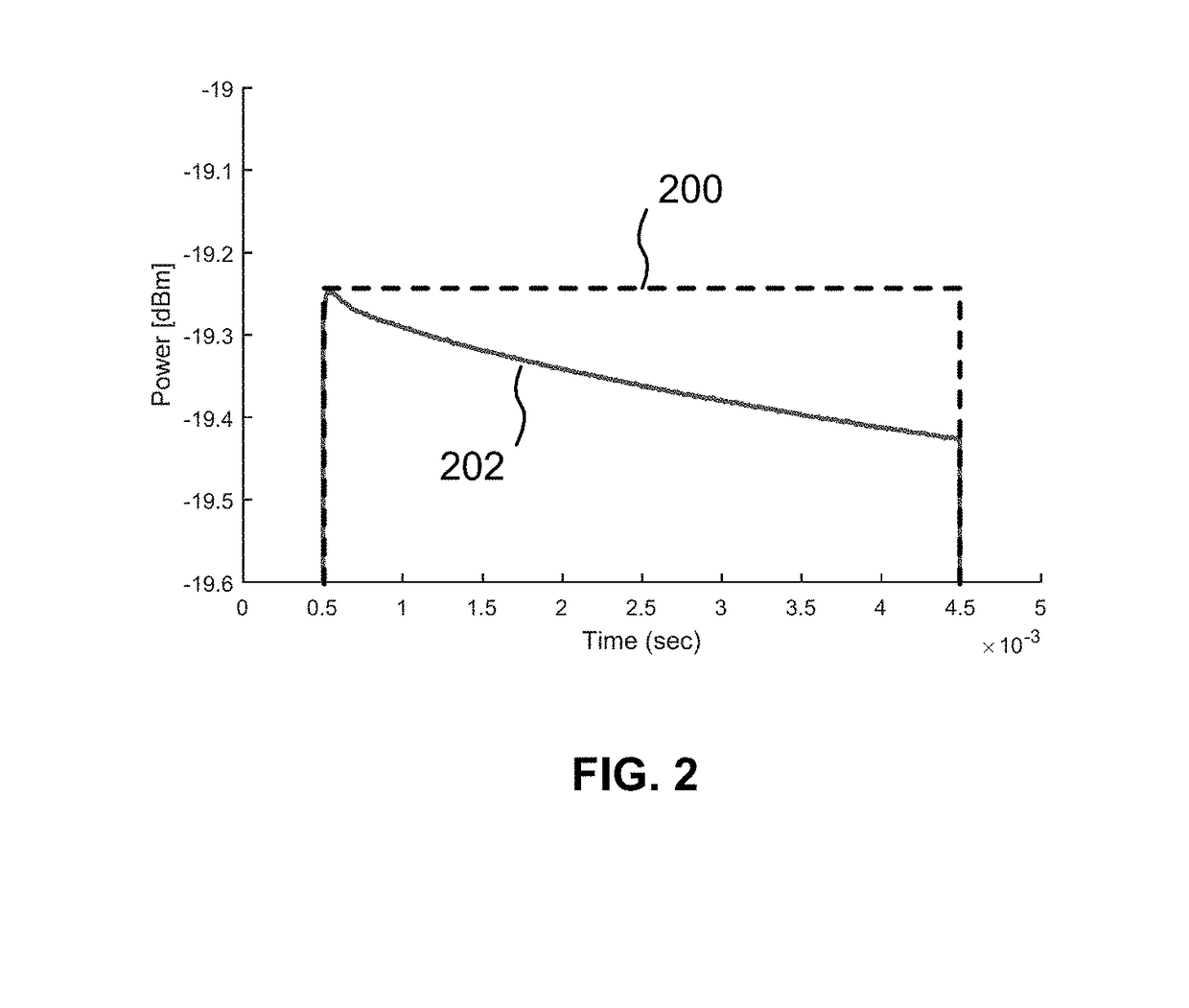
Power Amplifier Self-Heating Compensation Circuit
ActiveUS20180262164A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationRF amplifierContinuous measurementAudio power amplifier
Temperature compensation circuits and methods for adjusting one or more circuit parameters of a power amplifier (PA) to maintain approximately constant Gain versus time during pulsed operation sufficient to substantially offset self-heating of the PA. Some embodiments compensate for PA Gain “droop” due to self-heating using a Sample and Hold (S&H) circuit. The S&H circuit samples and holds an initial temperature of the PA at commencement of a pulse. Thereafter, the S&H circuit generates a continuous measurement that corresponds to the temperature of the PA during the remainder of the pulse. A Gain Control signal is generated that is a function of the difference between the initial temperature and the operating temperature of the PA as the PA self-heats for the duration of the pulse. The Gain Control signal is applied to one or more adjustable or tunable circuits within a PA to offset the Gain droop of the PA.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Device for generating a pulsed magnetic field
InactiveUS20070001521A1Minimizes problemImprove cooling effectWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsRefrigerant distributionEngineering
A pulsed magnetic field is generated by a device having a magnet to be operated in pulse operation which contains at least one superconductive refrigerant-free winding that is disk-shaped or saddle-shaped. Also included is a refrigerating unit which has at least one cold head. A line system, having a refrigerant circulating in it according to a thermosiphon effect, thermally couples the winding to the cold head. The line system has a plurality of separate pipes lying next to one another. The pipes, open onto a common refrigerant distributor and closed at the other end, are thermally coupled to the surface of the disk-shaped or saddle-shaped winding.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
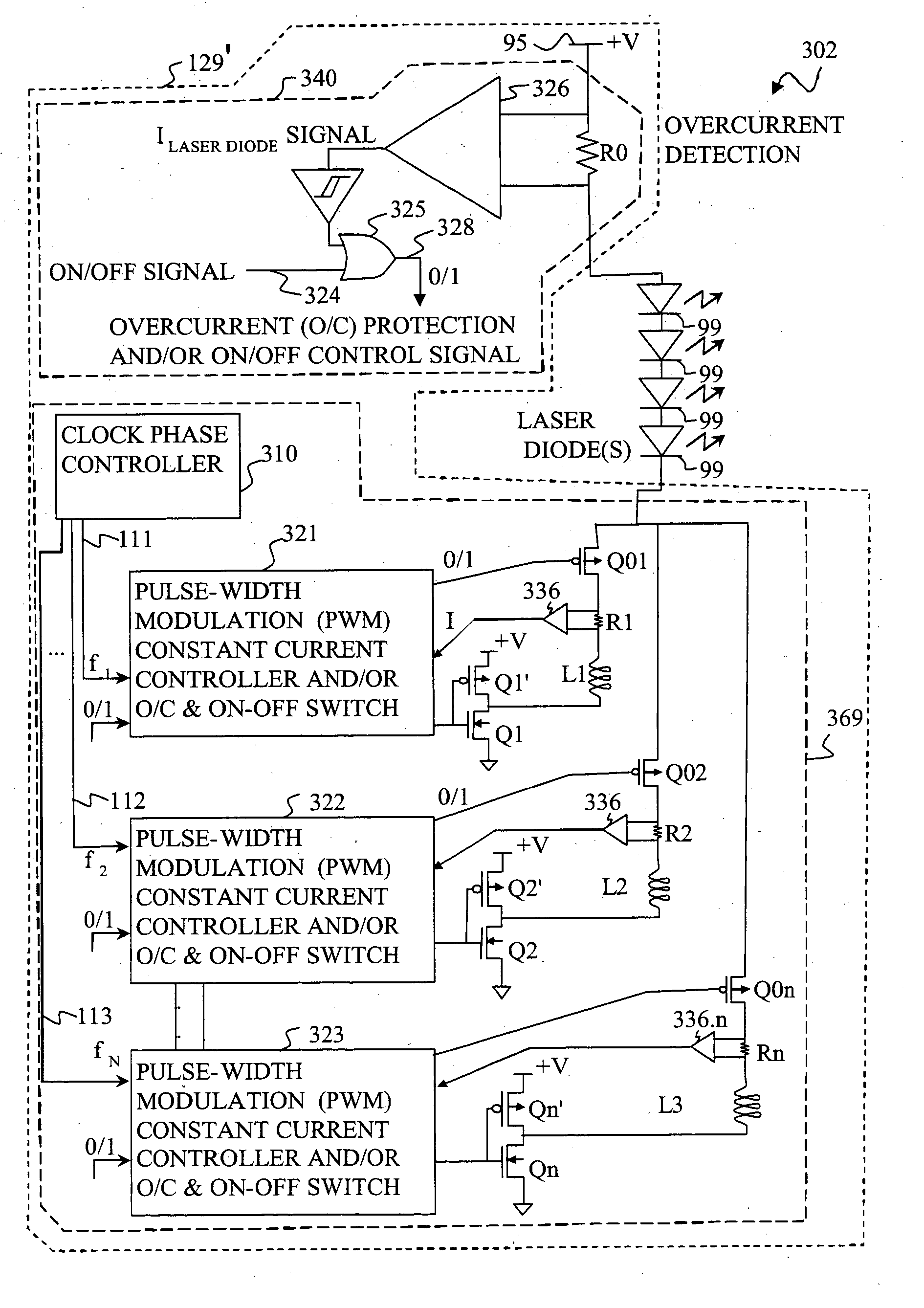
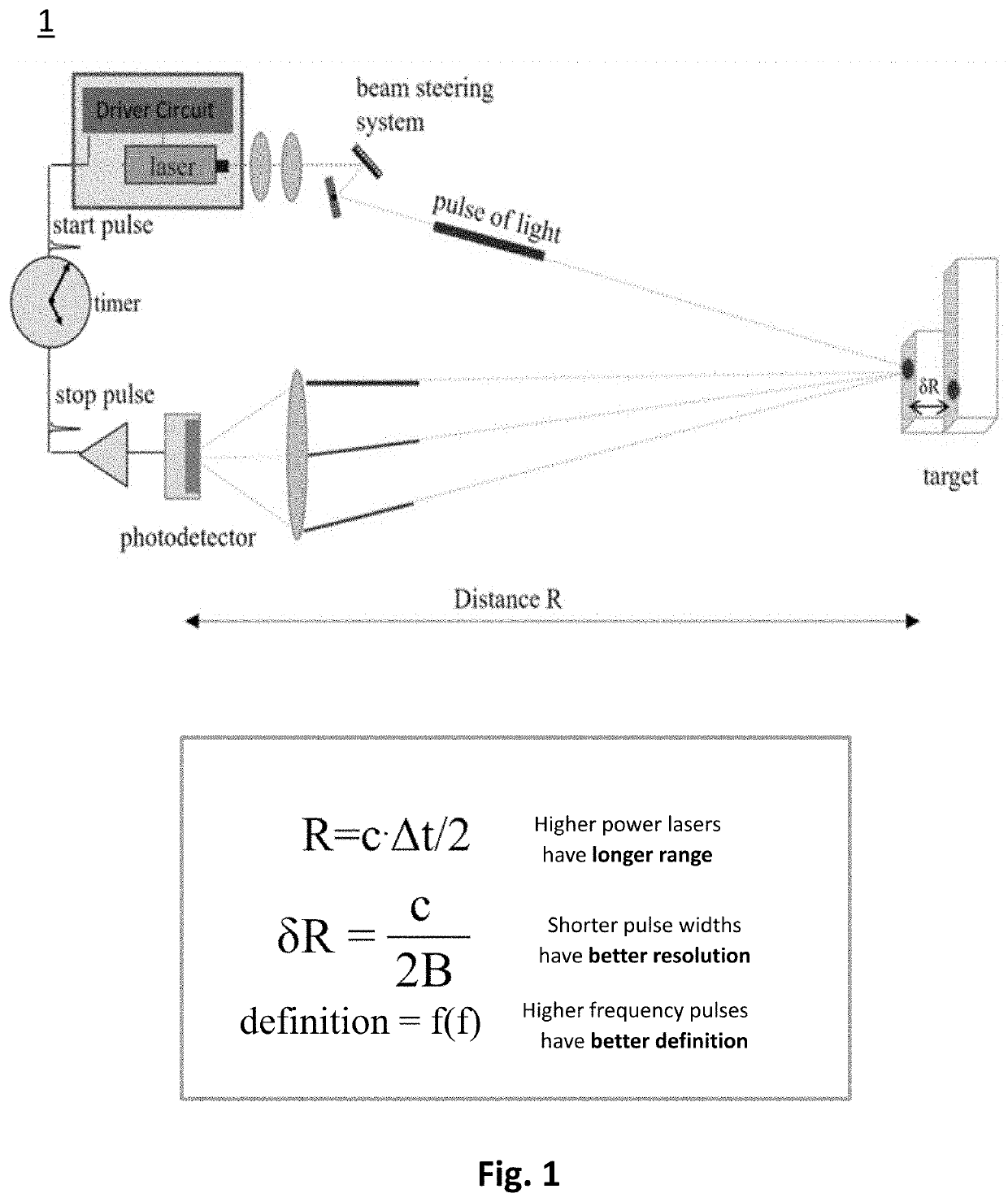
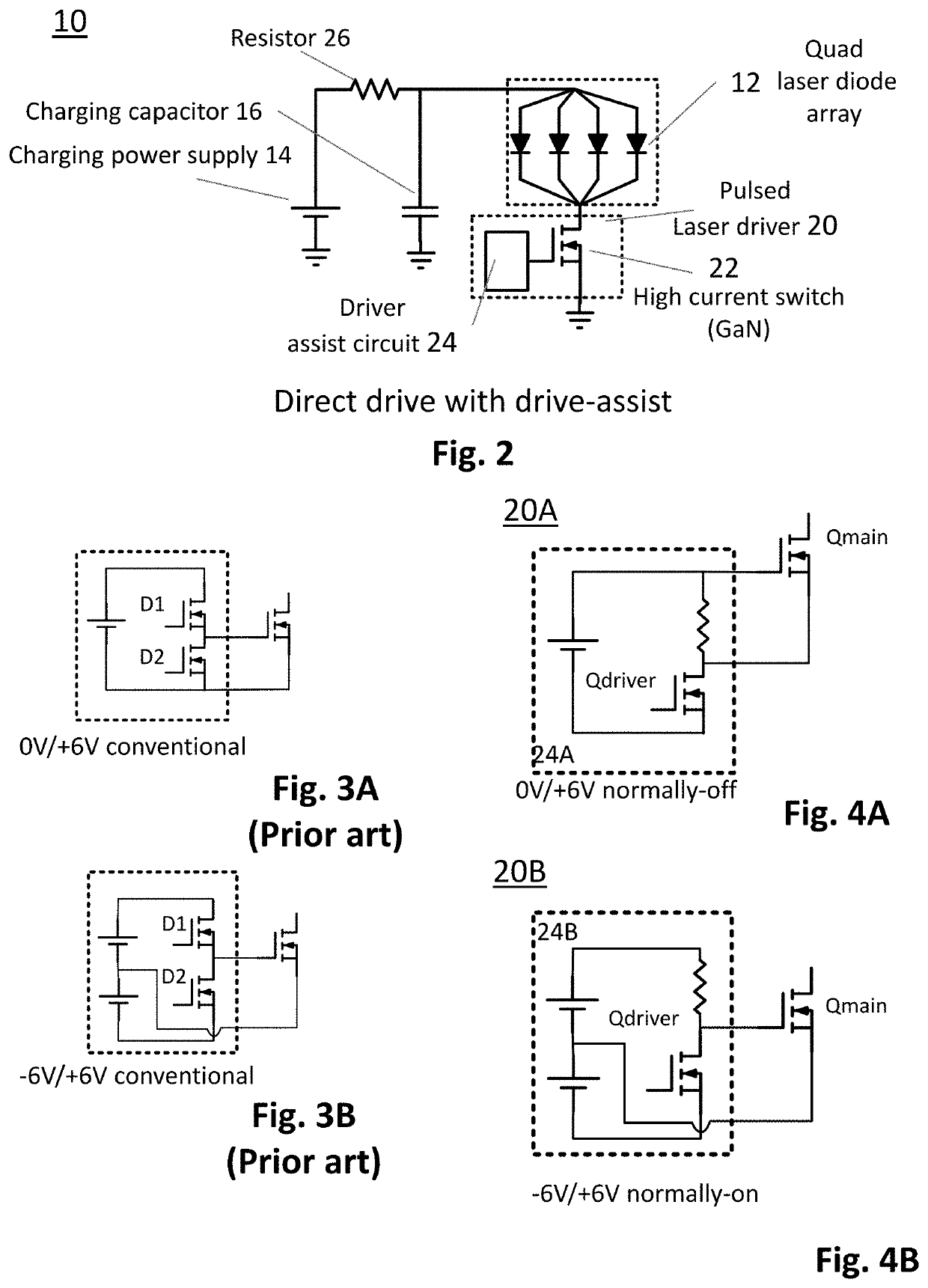
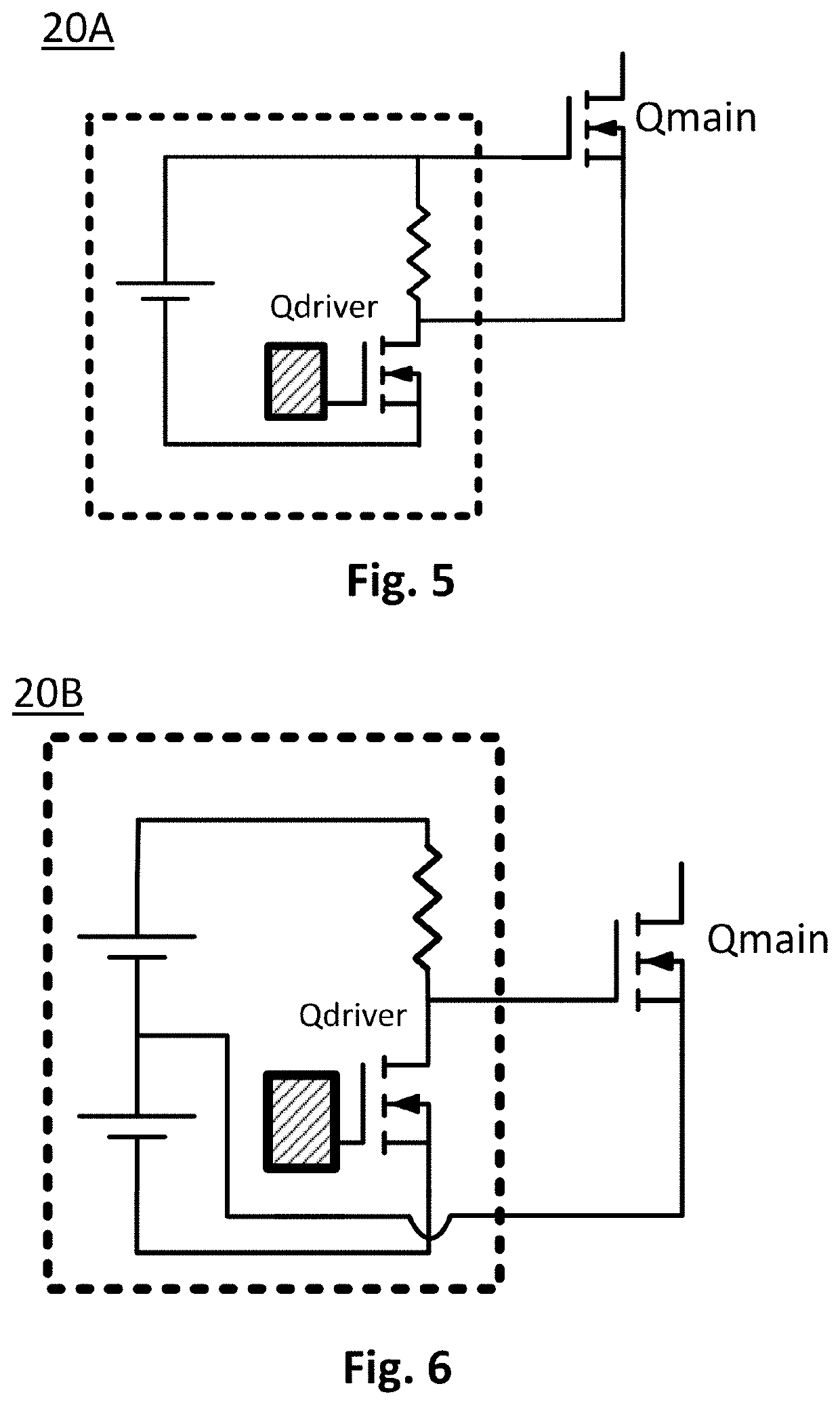
Fast pulse, high current laser drivers
PendingUS20210111533A1Quick switchHigh peak powerSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsHemt circuitsFast charging
Pulsed laser drivers are disclosed comprising Gallium Nitride (GaN) power transistors for driving diode laser systems requiring high current and fast pulses, such as laser drivers for LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems. Drivers are capable of delivering pulses with peak current ≥100 A, e.g. 170 A to provide high peak power, fast pulses with nanosecond rise times and nanosecond pulse duration, for driving multi-channel laser diode arrays with 40 A per channel for 120 W output per channel for a combined peak output of 480 W. For lower duty cycle, example driver circuits are disclosed comprising a high current power transistor for direct drive with drive assist. For higher duty cycle, example resonant driver circuits are disclosed comprising two high current power transistors. Implementation of resonant driver circuits with GaN technology provides fast charging for short pulse operation at higher repetition rates or for pulse code modulation.
Owner:GAN SYST
Current Mirror Bias Compensation Circuit
ActiveUS20180262163A1High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPulse operationPositive temperature
Temperature compensation circuits and methods for adjusting one or more circuit parameters of a power amplifier (PA) to maintain approximately constant Gain versus time during pulsed operation sufficient to substantially offset self-heating of the PA. Some embodiments compensate for PA Gain “droop” due to self-heating using a Sample and Hold (S&H) circuit. Other embodiments include bias compensation circuits that directly regulate a bias signal to an amplifier stage as a function of localized heating of one or more of amplifier stages. Such bias compensation circuits include physical placement of at least one bias compensation circuit element in closer proximity to at least one amplifier stage than other bias compensation circuit elements. One bias compensation circuit embodiment includes a temperature-sensitive current mirror circuit for regulating the bias signal. Another bias compensation circuit embodiment includes a temperature-sensitive element having a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) for regulating the bias signal.
Owner:PSEMI CORPOPRATION +1
Extreme ultra violet light source apparatus
ActiveUS7705333B2Efficient ionizationEnergy efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowaveElectron cyclotron resonance
In an extreme ultra violet light source apparatus that exhausts debris including fast ions and neutral particles by the effect of a magnetic field, neutral particles emitted from plasma are efficiently ionized. The extreme ultra violet light source apparatus includes a plasma generating unit that generates plasma, that radiates at least extreme ultra violet light, through pulse operation; collective optics that collects the extreme ultra violet light radiated from the plasma; a microwave generating unit that radiates microwave through pulse operation into a space in which a magnetic field is formed to cause electron cyclotron resonance, and thereby ionizes neutral particles emitted from the plasma; a magnetic field forming unit that forms the magnetic field and a magnetic field for trapping at least ionized particles; and a control unit that synchronously controls at least the plasma generating unit and the microwave generating unit.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Systems for controlled pulse operations in non-volatile memory
InactiveUS7719874B2EfficientlySafely switch resistanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageHigh resistanceVoltage pulse
A passive element memory device is provided that includes memory cells comprised of a state change element in series with a steering element. Controlled pulse operations are used to perform resistance changes associated with set and reset operations in an array of memory cells. Selected memory cells in an array are switched to a target resistance state in one embodiment by applying a positive voltage pulse to selected first array lines while applying a negative voltage pulse to selected second array lines. An amplitude of voltage pulses can be increased while being applied to efficiently and safely switch the resistance of cells having different operating characteristics. The cells are subjected to reverse biases in embodiments to lower leakage currents and increase bandwidth. The amplitude and duration of voltage pulses are controlled, along with the current applied to selected memory cells in some embodiments. These controlled pulse-based operations can be used to set memory cells to a lower resistance state or reset memory cells to a higher resistance state in various embodiments.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Collector mirror for plasma-based, short-wavelength radiation sources
ActiveUS7329014B2Great expenditureImprove reflectivityMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingTransport mediumThermostat
The invention is directed to a collector mirror for short-wavelength radiation based on a plasma. It is the object of the invention to find a novel possibility for managing the temperature of a collector mirror for focusing short-wavelength radiation generated from a plasma which allows an efficient thermal connection to be produced between the optically active mirror surface and a thermostat system without the disadvantages relating to space requirements or high-precision manufacture of the collector mirror. This object is met, according to the invention, in that the collector mirror has a solid, rotationally symmetric substrate which comprises a material with high thermal conductivity of more than 50 W / mK and in which channels for cooling and temperature management are incorporated in the substrate so that a heat transport medium can flow through directly and for rapidly stabilizing the temperature of the optically active mirror surface. Heat of transient temperature spikes which occur in pulsed operation for plasma generation at the mirror surface and which temporarily exceed the temperature average by a multiple is quickly dissipated.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Variable valve timing system
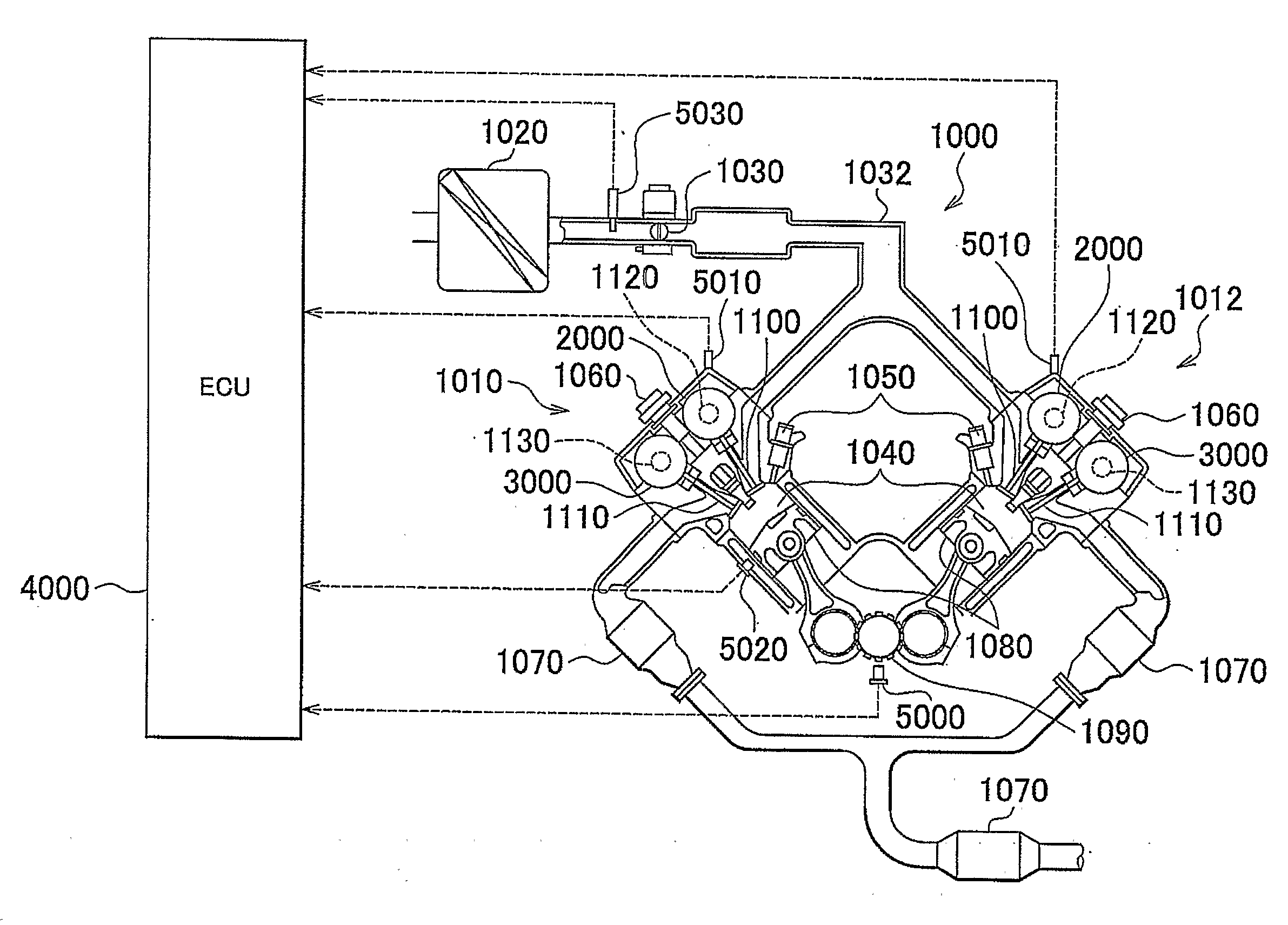
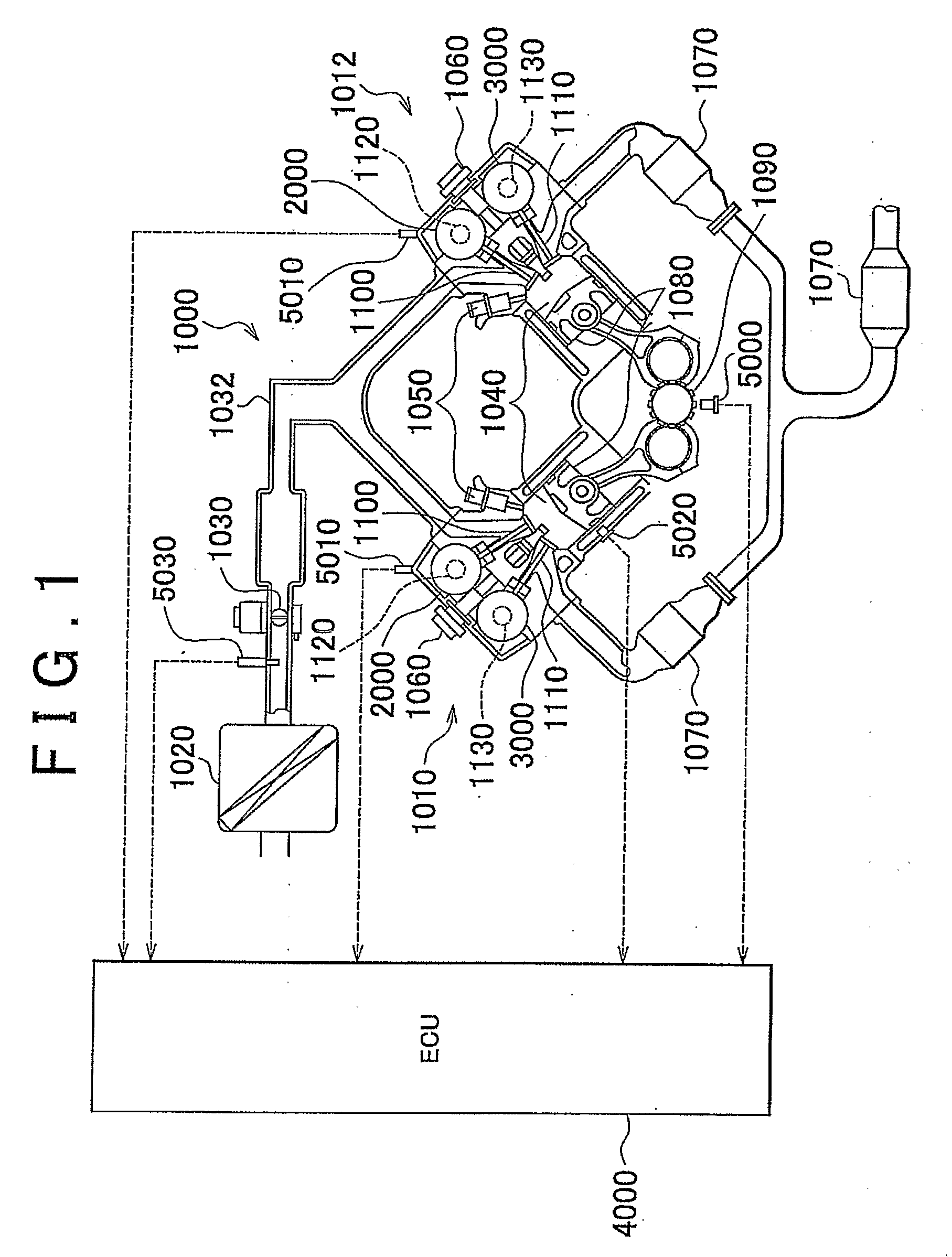
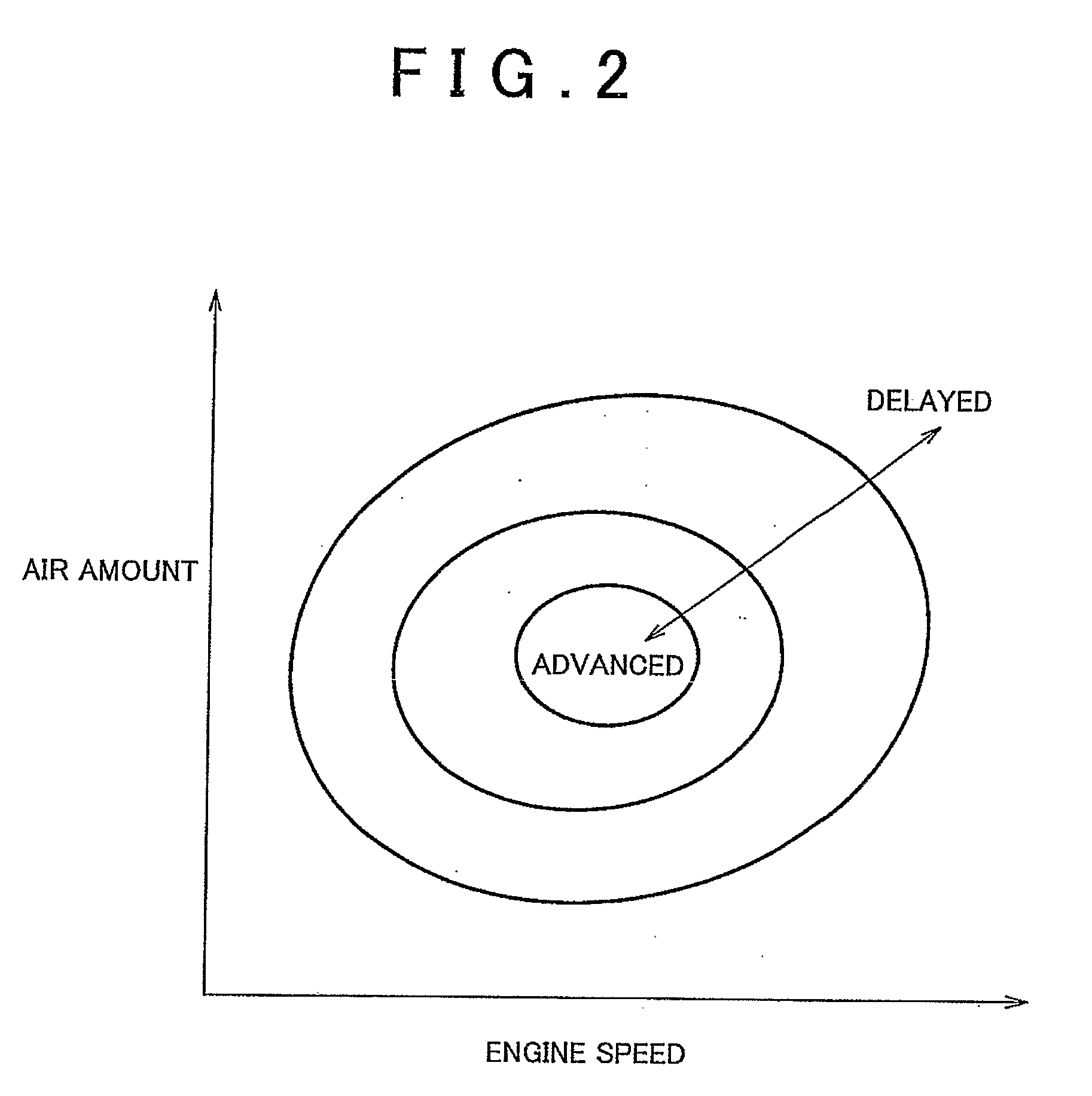
InactiveUS20090101094A1Stable executionMinimization is negatively influencedElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesVariable valve timingActuator
An ECU transmits a pulsed operation command signal, indicating operation commands for an electric motor used as a VVT actuator, to an electric-motor EDU. The electric-motor EDU recognizes the combination of the direction in which the actuator should be operated (actuator operation direction) and the control mode based on the duty ratio of the operation command signal, and the rotational speed command value based on the frequency of the operation command signal. The electric-motor EDU controls the electric motor according to the control commands. The duty ratio indicating the combination is set such that even if the duty ratio is falsely recognized, a false recognition concerning the actuator operation direction is prevented, such false recognition causing the valve phase to change in an undesirable direction, and even if the actuator operation direction is falsely recognized, the rate of change in the phase is restricted.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com