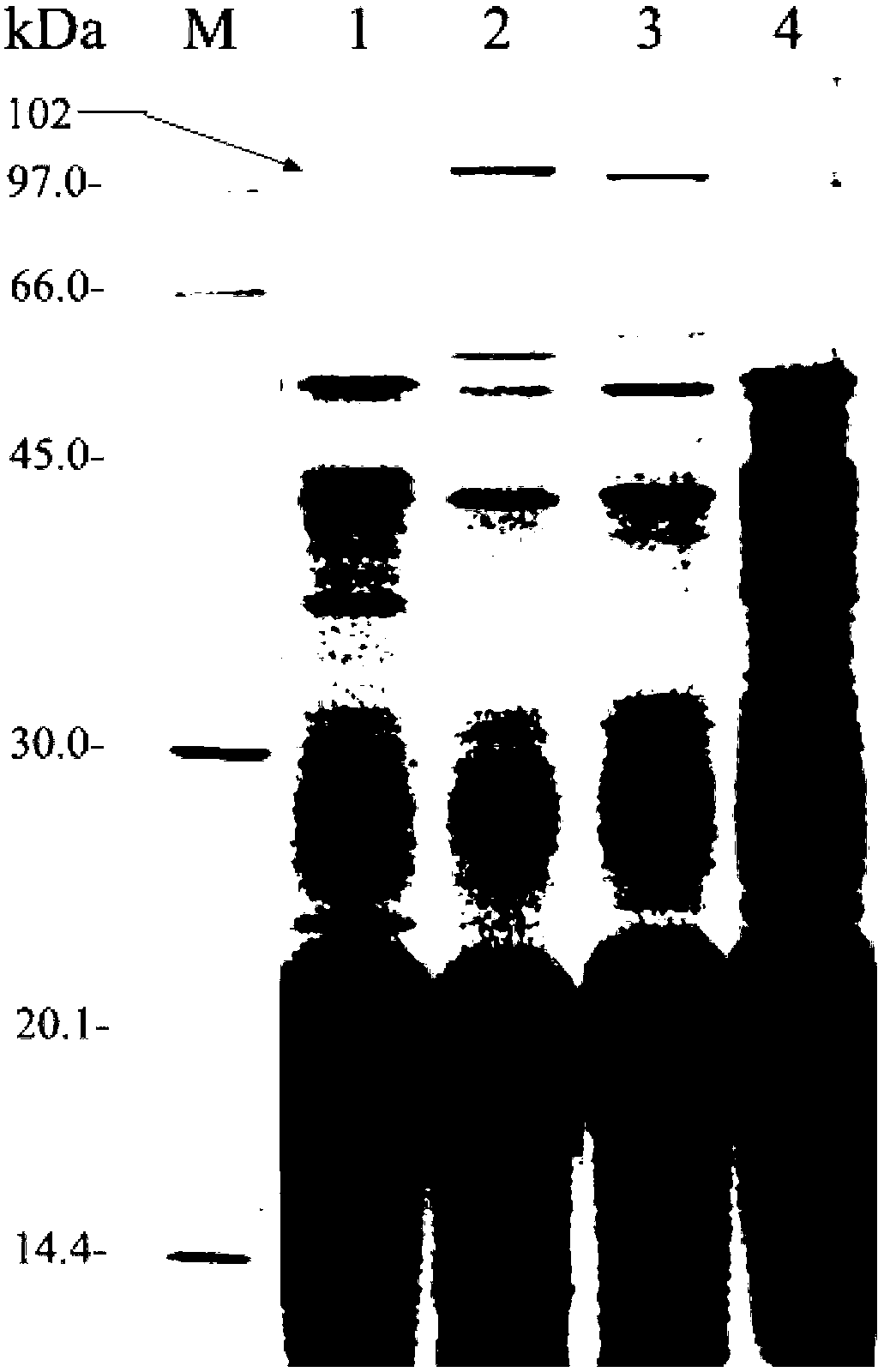Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Protein band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
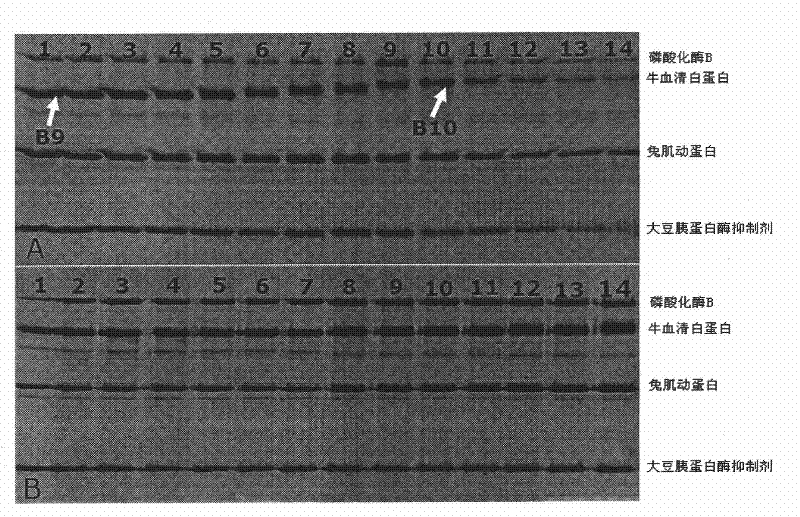
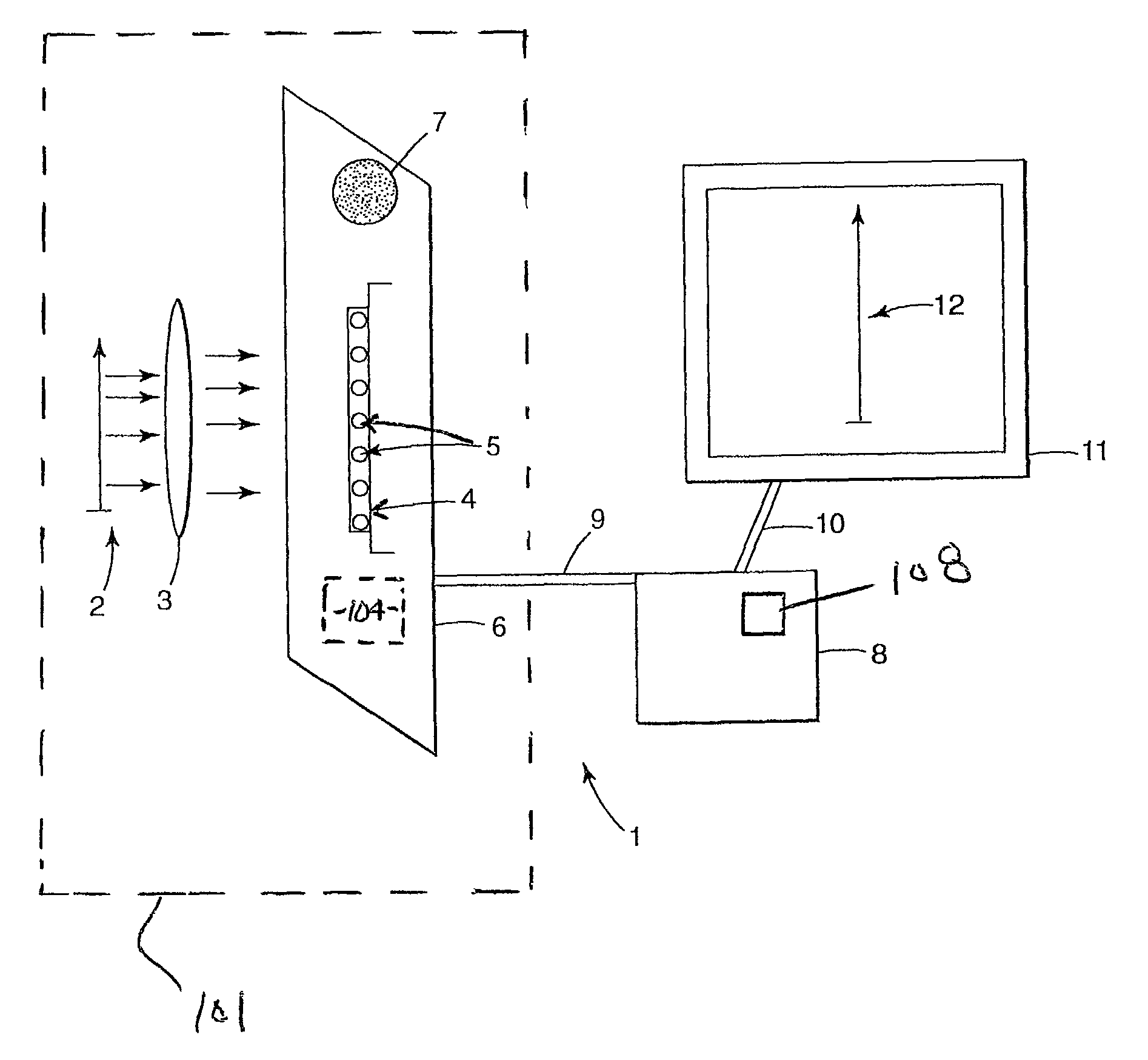
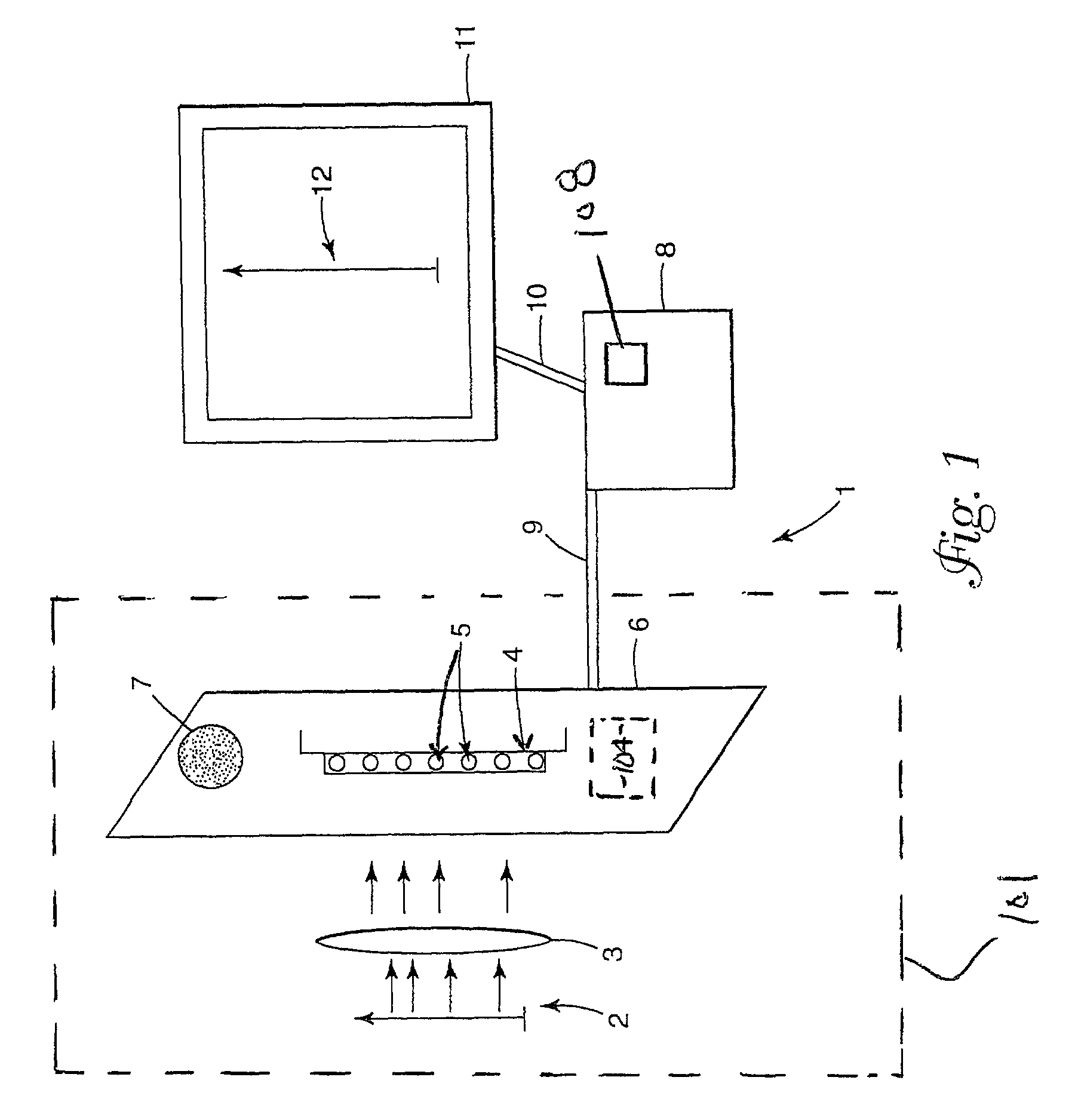
Imaging of biological samples using electronic light detector
A system and method using an electronic light detector array, e.g., a CCD or a CMOS-based detector array, is used to acquire a visual image of a biological sample that includes biological material associated with a biological material holding structure (e.g., a DNA spot array on a DNA chip, protein bands in a 2-D gel, etc.). For example, fluorescence from a biological sample may be detected.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
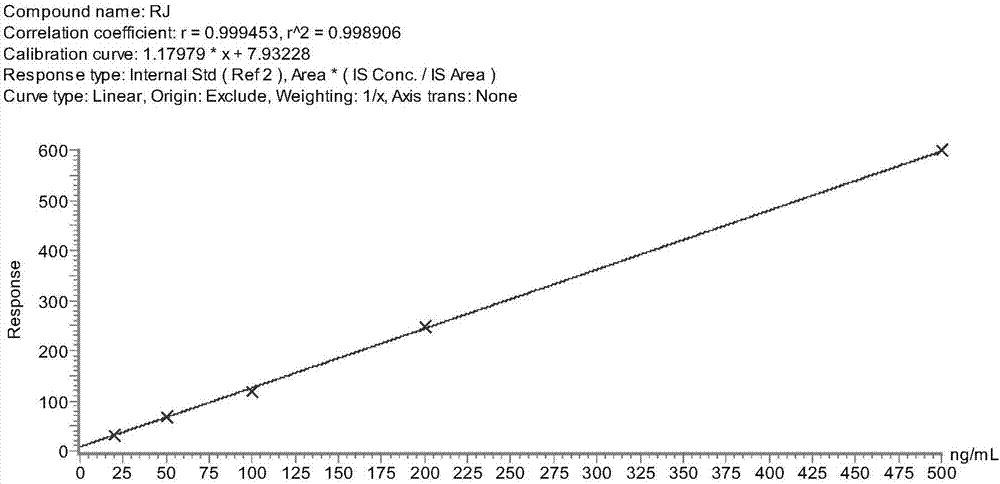
Method of establishing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis of royal jelly sensitized protein
ActiveCN107290461AAccurate quantitative analysisStrong specificityComponent separationElectrophoresisMass spectrometry imaging
The invention discloses a method of establishing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis of a royal jelly sensitized protein. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out electrophoresis analysis on royal jelly proteins, preprocessing the sensitized protein bands, analyzing sensitized protein bands by LC-MS, screening the specific peptide fragments of sensitized proteins; extracting proteins from a royal jelly sample, digesting the proteins by enzymes, and quantitatively measuring the sensitized proteins by LC-MS / MS. The provided sensitized protein quantitative method has the advantages of high specificity and sensitivity, good repeatability, high accuracy, and wide linear range, and is capable of precisely and quantitatively analyzing a sensitized protein in a sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
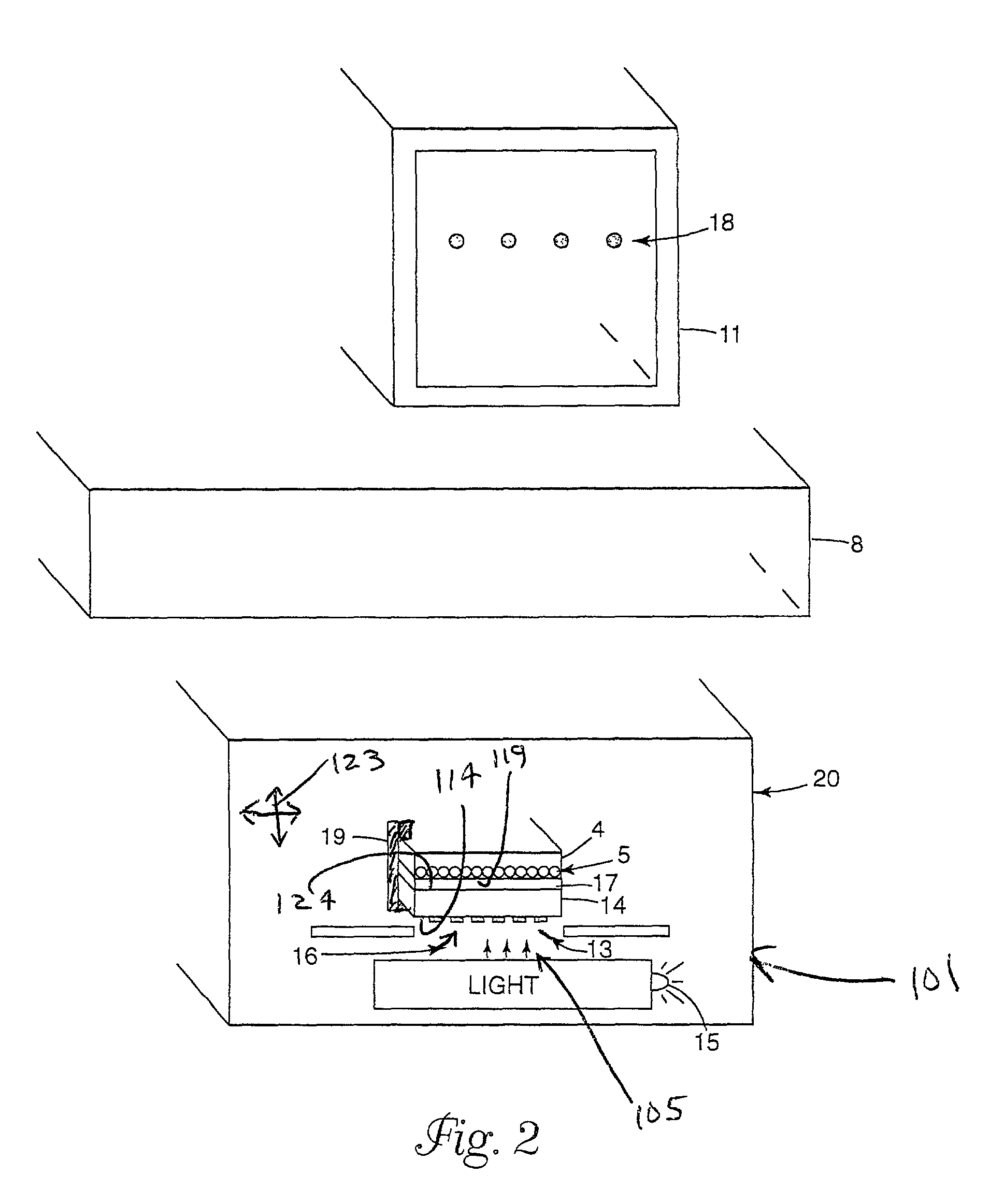
Targeted delivery of reagents to spots on a planar support through patterned transfer sheets
ActiveUS20140027284A1Readily apparentAvoid large quantitiesSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementProtein bandAmount of substance
Molecular species that are immobilized in discrete locations on a planar support such as protein bands on a gel or a blotting membrane or species applied in dots or spots on a membrane are reacted with binding reagents that are applied through a porous hydrophilic transfer sheet placed over the planar support, the sheet having at least one region that is laterally bordered by a barrier with the binding reagent retained within the bordered region. The bordered region is placed directly over an area on the planar support where the molecular species are expected to reside if they are present on the support. The binding reagent is then delivered into the support to contact the species. Targeted delivery of the binding reagent is thus achieved with improved efficiency.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for distinguishing Chinese honeybee honey from Apis mellifera honey based on major royal jelly protein ingredients
InactiveCN106153705AResolve indistinguishableCurb the chaos of counterfeiting high-priced Chinese bee honeyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAdditive ingredientElectrophoresis
The invention provides a method for distinguishing Chinese honeybee honey from apis mellifera honey based on major royal jelly protein ingredients. By means of a biological method and the difference between Chinese honeybee honey and apis mellifera honey in protein, different protein bands appear by conducting protein electrophoresis on a honey sample after the honey sample processed, protein categories are determined by conducting mass spectrometry on the different protein bands, and then the two kinds of honey from different bee species are identified. The problems that Chinese honeybee honey and apis mellifera honey available in market are hard to distinguish, and apis mellifera honey pretends to be Chinese honeybee honey or is mixed in Chinese honeybee honey are solved, and the situation that low-price apis mellifera honey pretends to be high-price Chinese honeybee honey can be inhibited. The method is used for distinguishing Chinese honeybee honey from apis mellifera honey.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting ancient argillic silk fabric on basis of immunoblotting
ActiveCN107389641AReduce lossesGuaranteed accuracyFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to the field of cultural relic detection and discloses a method for detecting ancient argillic silk fabric on the basis of immunoblotting. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, a silk secondary antibody marked with fluorescent carbon points is prepared, a modern silk sample and an ancient argillic silk fabric sample are hydrolyzed with an ionic liquid and PM13-alkaline protease step by step, a protein extraction solution is obtained and subjected to dialysis, purification and SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis, an obtained protein band is transferred to a PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) film and subjected to incubation with a silk first antibody and the silk secondary antibody marked with the fluorescent carbon points, an immunofluorescence band can be observed in a gel imaging system, and the type of ancient silk is identified. The consumption of chemical reagents is low, the reaction is mild, and the method is environment-friendly and harmless; during detection for the ancient silk fabric, the method has the characteristics of being low in sample consumption, direct, rapid and high in sensitivity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Imaging of Biological Samples
A system and method using an electronic light detector array, e.g., a CCD or a CMOS-based detector array, is used to acquire a visual image of a biological sample that includes biological material associated with a biological material holding structure (e.g., a DNA spot array on a DNA chip, protein bands in a 2-D gel, etc.). For example, fluorescence from a biological sample may be detected.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Device for establishing single-cell level connection between neurons and growth connecting method
InactiveCN101748061AConvenience platformConvenient ArrangementTissue cultureTissue/virus culture apparatusBasementEngineering
The invention discloses a device and a method for establishing single-cell level connection between neurons; the device comprises a basement whose upper surface is provided with protein band, and the region outside the protein band at the basement is covered by a polyether F127 layer; a PDMS stamp which is covered to the upper surface of the basement and whose lower surface is provided with a micro-groove unit; the micro-groove unit comprises: a linear type intermediate groove and at least one linear type side groove which is arranged at the left side or / and the right side of the intermediate groove, the middle section of the side groove does not intersect with the intermediate groove, and two end sections outside the middle section of the side groove incline to the direction away from the intermediate groove; the groove end is provided with a vertical hole channel; the protein band intersects with the groove without superposition; neurons are sent into the channel and only adhere to the protein band, the neurite directionally grows along the protein band without branching, thereby obtaining single-line connection of neuron single-cell level; the structure is simple, the operation is easy, and the orderly growth of the neurite can be controlled, and the electrical signal transduction between the neurocytes can be precisely studied, furthermore, the invention provides foundation support for manufacturing of bio-sensors.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method for identifying apis cerana honey and apis mellifera honey
InactiveCN105548321AAccurate identificationSimple designMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansApis ceranaProtein target
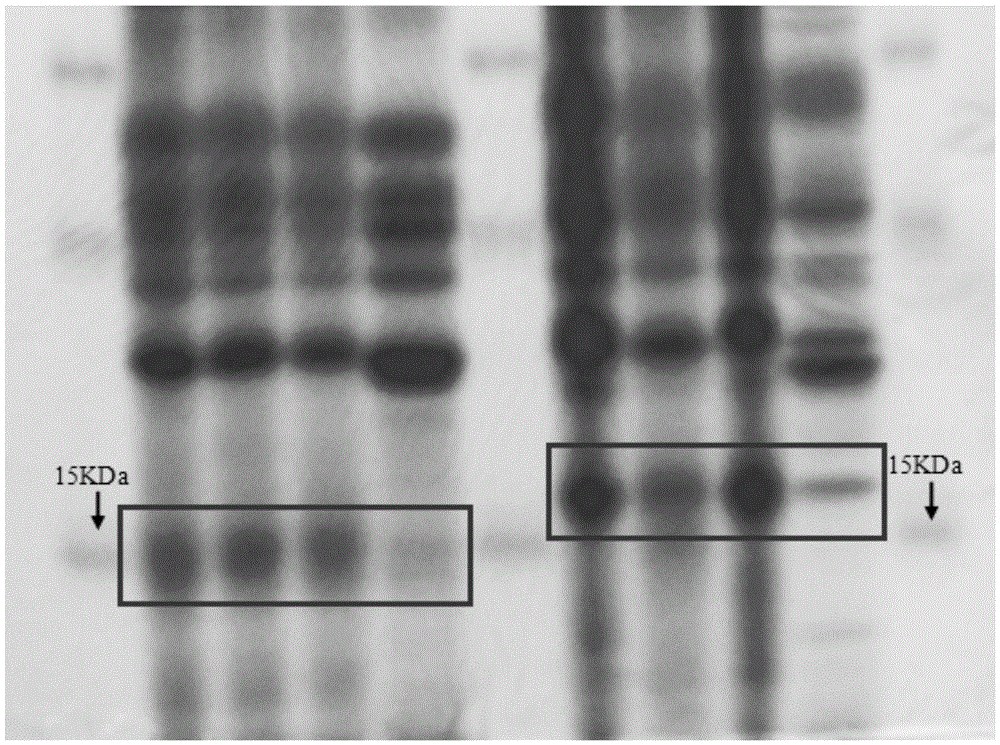
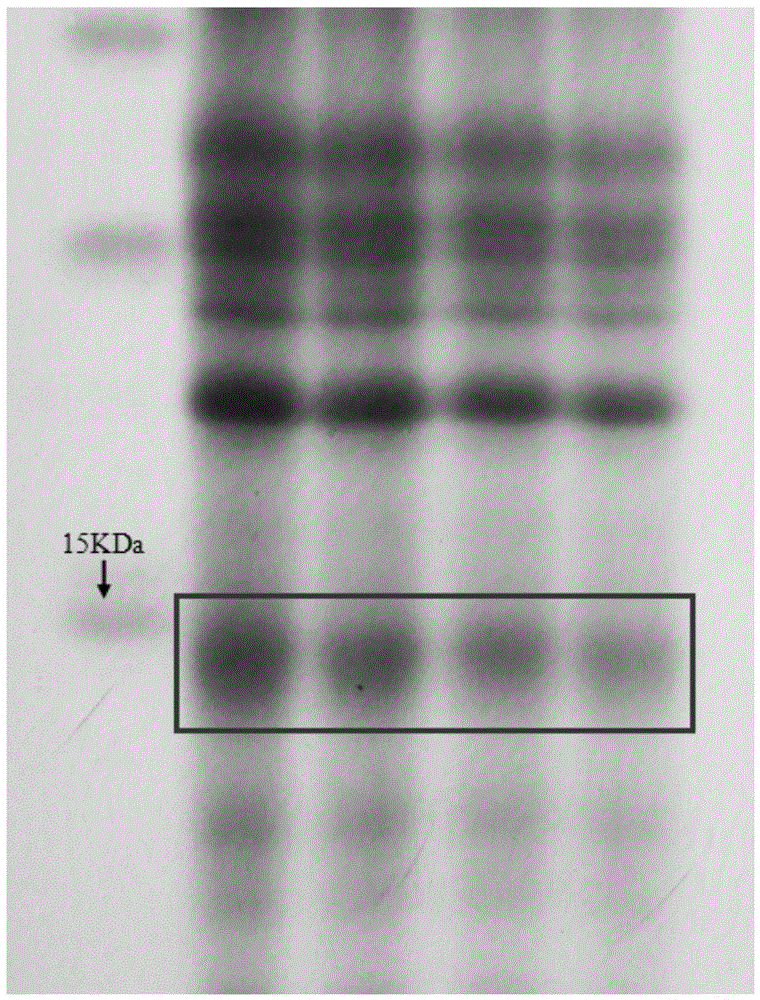
The invention provides a method for identifying apis cerana honey and apis mellifera honey, which achieves the purpose of identifying the apis cerana honey and the apis mellifera honey according to the specific band difference between the proteins of the apis cerana honey and the apis mellifera honey. After an apis cerana honey sample is treated, protein electrophoresis is conducted, the apis cerana honey has a 15.0KDa protein band, the apis mellifera honey has a 16.5KDa protein band, and a mixed honey sample of the both has both the 15.0KDa protein band and the 16.5KDa protein band. By differentiating the specific protein bands of the different honeys to achieve the purpose of identification, the method can accurately identify the apis cerana honey and the apis mellifera honey. In the method disclosed by the invention, the target proteins stably exist in the apis cerana honey and the apis mellifera honey, not affected by honey resources, concentration processing and shelf life. The design of the method disclosed by the invention is reasonable and simple, instruments are common, cost is low, identification is accurate, and the method is also suitable for identifying a certain proportion of apis mellifera honey mixed in the apis cerana honey.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for identifying varieties of residual silk of antique silk fabric based on immune trace method
ActiveCN107462728ATake advantage ofGood fluorescence stabilityBiological testingEnvironmental resistanceFluorescence
The invention relates to the field of detection of cultural relics and discloses a method for identifying the varieties of residual silk of antique silk fabric based on an immune trace method. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a fluorescent carbon point by taking a sweet potato as a carbon source, marking secondary antibodies of mulberry silk and tussah silk by using the fluorescent carbon point, hydrolyzing promiscuous antique silk fabric cultural relic samples by using ionic liquid and PM13-alkaline protease step by step, performing dialysis and purification after protein extracting liquid is obtained, performing SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis, transferring the obtained protein band to a PVDF membrane, incubating silk primary antibodies and the secondary antibodies marked by the fluorescent carbon point, observing the immunofluorescence band in a gel imaging system, and identifying the varieties of the antique silk fabric. According to the method, the use amount of a chemical reagent is small, and the reaction is mild, environment-friendly and harmless; and when the antique silk fabric is detected, the method has the characteristics of small use amount of samples, intuitive performance, rapidness and high sensitivity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Sex determination method for apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN106680352AReduce harmSimple equipment requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein bandCoelomocyte
The invention discloses a sex determination method for apostichopus japonicas. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking apostichopus japonicas coelomic fluid, and respectively preparing coelomic fluid supernatant and coelomocyte breaking fluid supernatant; (2) taking the coelomic fluid supernatant to carry out SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis), and taking the coelomocyte breaking fluid supernatant to carry out native-PAGE; (3) judging whether SDS-PAGE gel contains a 50kDa protein band or not to determine whether the apostichopus japonicas is male or not, and judging whether a phenoloxidase zymogram after the native-PAGE is carried out contains three bands or not to determine whether the apostichopus japonicas is female or not. The sex determination method has the following advantages: 1) the apostichopus japonicas is slightly harmed; 2) reagent, equipment and technical requirements are simple, and a result is visual; 3) determination speed is high, and handling capacity is high; 4) two technologies are used for respectively determining male and female apostichopus japonicas, and accuracy is 90% or above.
Owner:LIAONING OCEAN & FISHERIES SCI RES INST
Qualitative detection method capable of distinguishing cow milk doped in human milk
ActiveCN102200526ASimple and fast operationImprove analytical accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGel electrophoresis of proteinsGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to a qualitative detection method capable of distinguishing cow milk doped in human milk. The qualitative detection method is a protein gel electrophoresis method. The electrophoresis method comprises the following steps of: putting a prepared gel plate into an electrophoresis slot, adding an electrode buffer solution, performing pre-electrophoresis under 30 to 120 volts for 15 to 60 minutes, injecting the treated test sample solution into a gel sample application hole, performing electrophoresis under 50 to 200 volts until a bromophenol blue indicator is electrophoresized to the bottom of the gel, and finally taking out the gel and fixing in a fixing solution, dyeing in a dyeing solution and decoloring in a decoloring solution so as to obtain a protein electrophoresis pattern; and comparing the sample electrophoresis pattern with a characteristic protein band in the electrophoresis pattern of pure human milk and pure cow milk prepared under the same condition so as to determine whether liquid cow milk or milk powder reconstituted milk is doped into the sample milk. In the method, only one gel electrophoresis apparatus and a conventional chemical reagent are needed, the operation is simple and the result is reliable; and the cow milk or a product of the cow milk doped into the human milk can be detected.
Owner:山东天源人乳库科技发展有限公司
Preparation method of standard protein sample and protein lysate
InactiveCN101865796ANo smearing effectReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSulphate IonElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a preparation method of a standard protein sample and protein lysate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a standard protein sample into protein lysate with urea, and keeping the solution at the room temperature, thereby obtaining the standard protein sample which can be directly used for sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis SDS-PAGE without heating during loading for electrophoresis. The invention also discloses protein lysate applied in the preparation of the standard protein sample, which contains 7-9M of urea. The standard protein sample prepared in the method can be kept for a long time, no heating is needed, the operation is simple, and protein bands on the electrophoresis pattern are clear without obvious tailing.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
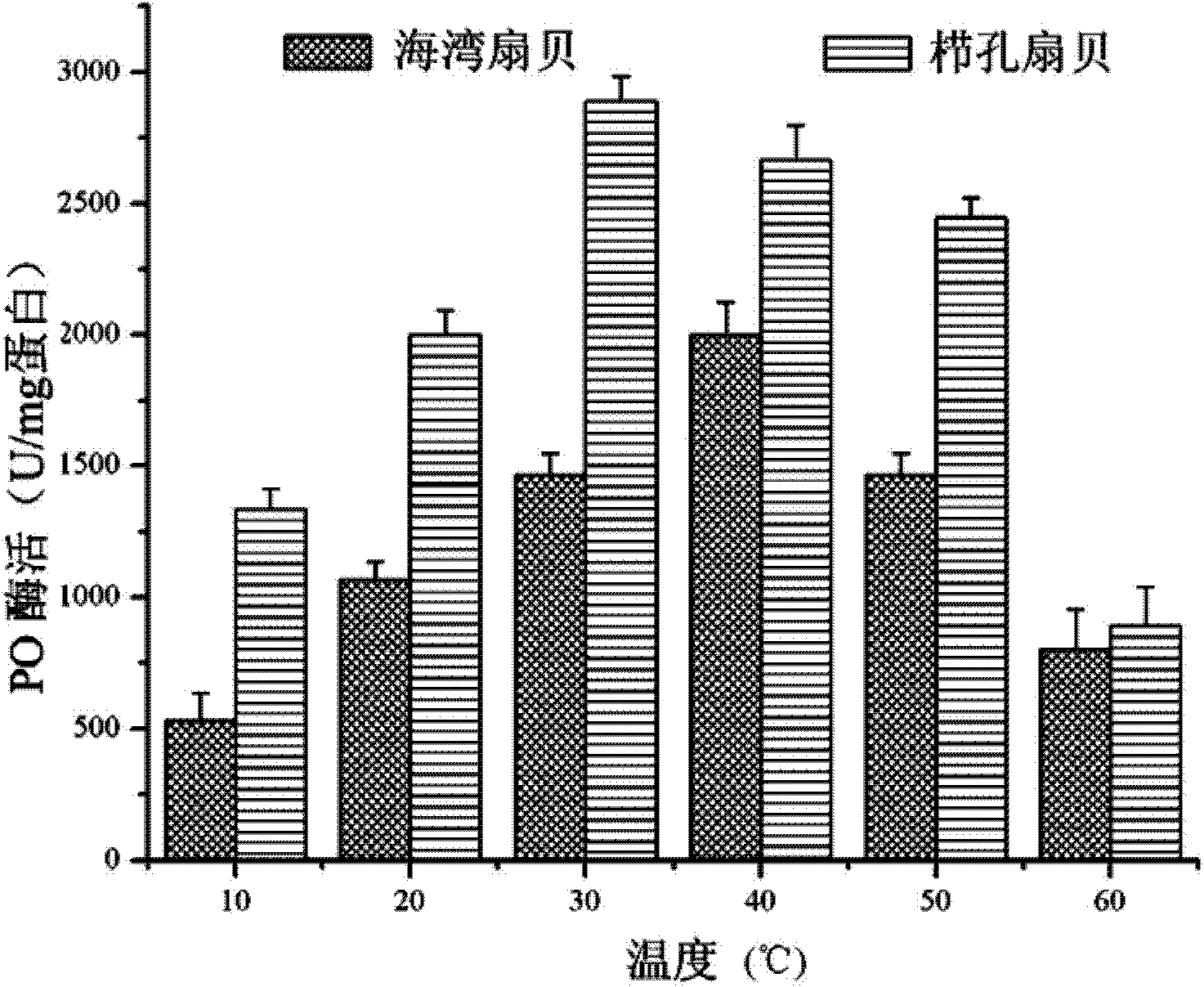
Method for separating and purifying scallop phenol oxidase
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying scallop phenol oxidase. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) obtaining haemolymph from adductor muscles of scallops, centrifuging, suspending and crushing the haemolymph, then centrifuging the crushed haemolymph, and taking the supernate, namely obtaining blood cell crushed supernate; (2) performing continuous gradient non-denaturing electrophoresis on the blood cell crushed supernate serving as a sample; (3) positioning a phenol oxidase protein band of non-denaturing electrophoresis by using a specific substrate coloring method; and (4) performing glue cutting on a destination band, reclaiming the phenol oxidase protein band by an electro-elution method, and obtaining purified scallop phenol oxidase protein after dialysis and freeze-drying. The method has the advantages that: (1) the method has short purification time; (2) the method has simple and convenient operation, simple equipment requirement and low cost, and greatly reduces the treatment steps of the sample; and (3) the purified sample has high purity, only presents one band by non-denaturing and denaturing electrophoresis detection, keeps the bioactivity of enzyme well and improves the purifying efficiency.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for expressing and purifying low temperature chitinase gene chiA in kluyveromyceslactis
PendingCN109825490AReduce the cost of separation and purificationImprove expression efficiencyMicroorganism based processesEnzymesYeastChitinase
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, microbiology, enzyme engineering and fermentation engineering, and provides a method for expressing and purifying a low temperature chitinasegene chiA (chitinase A) in kluyveromyceslactis.The method for expressing and purifying the low temperature chitinase gene chiA (chitinase A) in the kluyveromyceslactissuccessfully constructs a recombinant kluyveromyceslactis producing the low temperature chitinasechiA and purifiesthe recombinant kluyveromyceslactisto obtain a high purity recombinant chitinasechiA, and a pure recombinant chitinasechiA is obtained by using a nickel column affinity chromatography. After SDS-PAGE analysis, protein bands of the desired size appear near 110 kDa.According to the method for expressing and purifying the low temperature chitinase gene chiA (chitinase A) in the kluyveromyceslactis, the chitinasechiAexpressed is mostly secreted outside cell, thereby reducing the separation and purification cost and improving the expression efficiency.The protein concentration of purified protein chiAis 1.26 mg / mL and the enzyme activity is 51.45 U / mg.The purified chitinaseChiA has been studied in enzymatic properties such as temperature and temperature stability, pH and pH stability and synergistic degradation, and a foundation for industrial application of such enzyme is laid.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
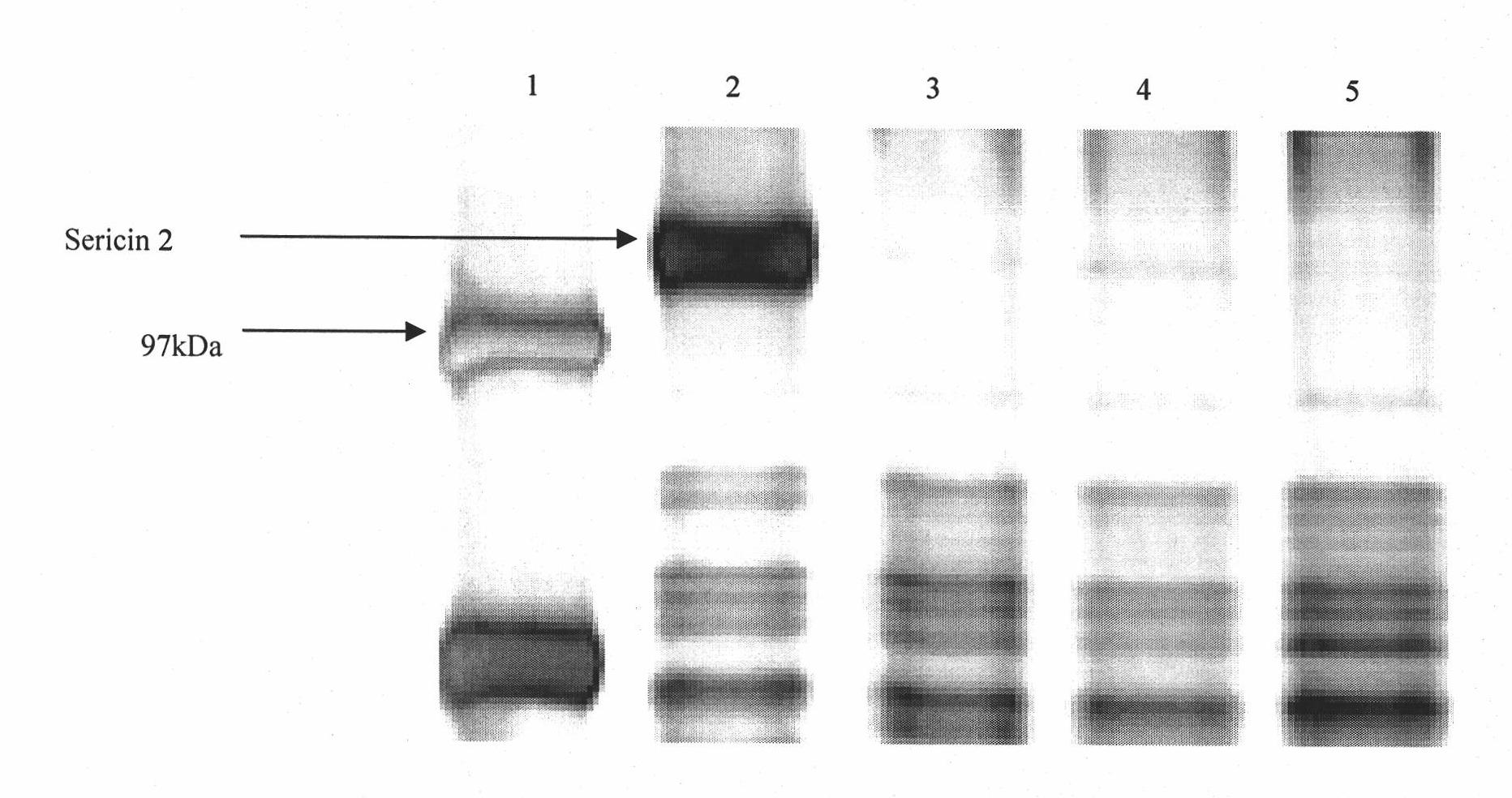
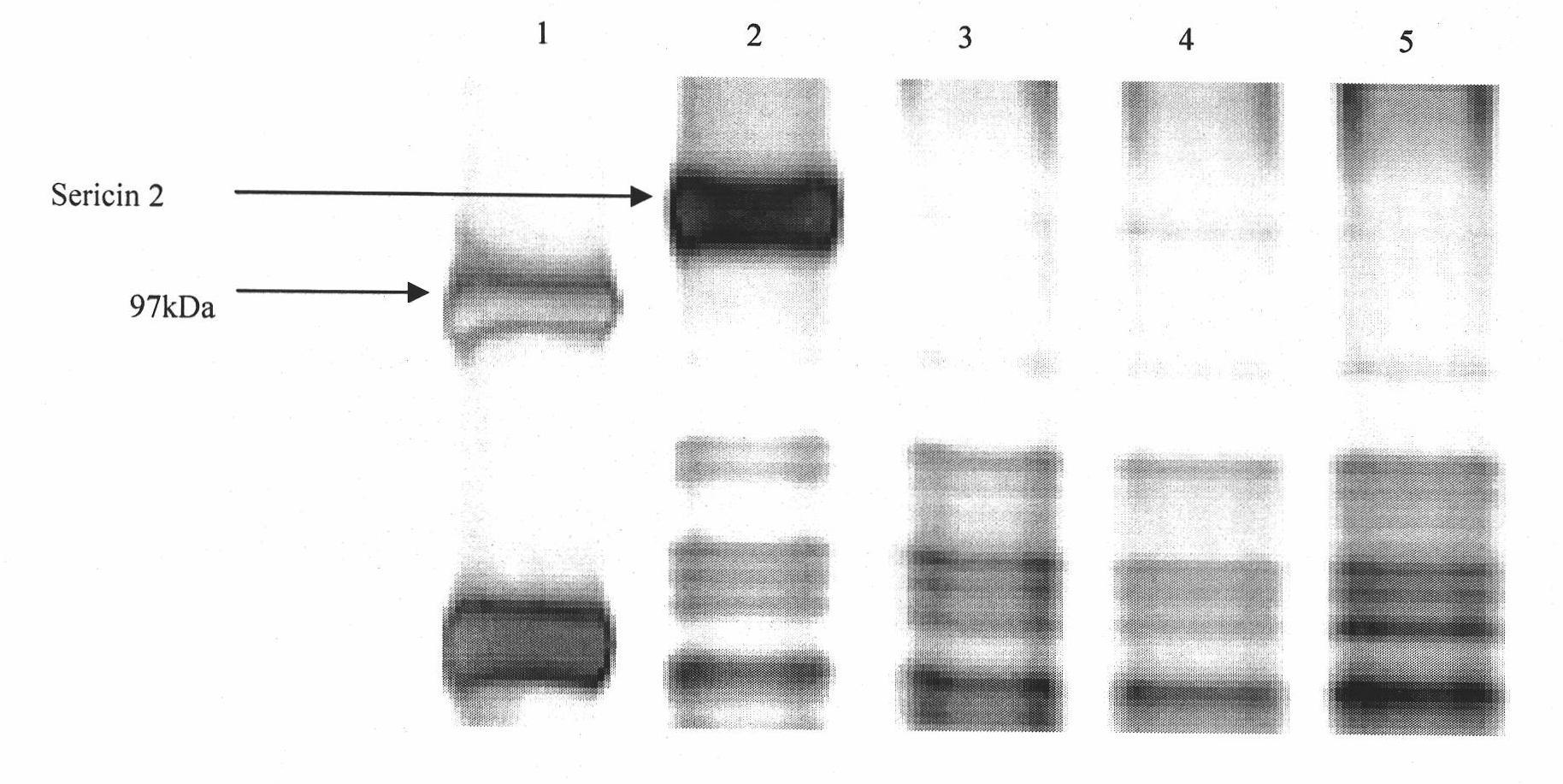
Method for selecting high-reelability bombyx mori cocoons by utilizing protein molecular marker
InactiveCN102121920AImprove relaxation propertiesFeed size reductionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater bathsStaining
The invention relates to an assisted bombyx mori breeding technology, and aims at providing a method for selecting high-reelability bombyx mori cocoons by utilizing a protein molecular marker. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing SDSPAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) gel, and drilling sample holes on the gel; (2) shearing cocoon shells from breeding cocoons, adding the cocoon shells to an aqueous solution containing urea, mercaptoethanol (BME) and sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS), performing water bath treatment at the temperature of 80 DEG C, and absorbing samples for electrophoresis; (3) putting the electrophoresis gel and staining solution in a closed container, incubating at the temperature of 60 DEG C, washing the gel with water, adding a destaining solution, oscillating, changing the destaining solution and oscillating again; and (4) for the cocoon shells which show 110kDa protein bands in electrophoresis results, taking the corresponding breeding cocoons as sample individuals with the Sericin2 protein molecular marker. The method has the advantages that sericin protein Sericin2 is taken as the molecular marker so as to accurately and effectively select the high-reelability individuals, thus greatly improving the reelability of the bombyx mori cocoons and enhancing the breeding efficiency. For the individuals with the labeled protein Sericin2, the reelability percentage of the bombyx mori cocoons is more than 90% and the raising scale of the individuals for seed selection can be reduced by 30-50%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of laccase in protein gel decoloration
InactiveCN104634850AReduce pollutionSave energyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiotechnologyLacquer
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, more particularly relates to an application of laccase in protein gel decoloration, and specifically relates to an application of laccase in decoloration of protein gel electrophoresis after conventional dyeing. The application aims at decoloring dyed protein gels by using laccase; and the application is environment-friendly, rapid, simple and convenient, does not need organic solvents, and can be used for saving energy and reducing the pollution caused by dye wastewater. According to the application of decoloring the protein gels by using laccase, disclosed by the invention, rapid decoloration can be achieved (a low-background clear protein band can be obtained within 2 hours), simplicity and convenience in operations can be achieved (boiling or decoloring liquid replacement is not needed), and environmental protection can be achieved (organic solvents such as methanol and acetic acid required by conventional decoloring liquid are not used, dye degradation can be achieved while decoloring, and no waste liquid treatment problems and cost can be produced). According to the application, by optimizing factors such as laccase concentration, medium types and concentration and decoloring time, good decoloring effects can be achieved in a relatively short time, and simplicity and convenience in operations and environmental protection can be achieved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Amino acid sequence and polynucleotide sequence for chicken intestinal canal beta alexin and extraction method thereof
InactiveCN101210243ANo pollution in the processNo side effectsPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesSodium acetateAntibacterial activity
A chicken intestinal tract Beta-defensin cDNA is characterized in that the cDNA has the following sequence: tcagacagcc agctgtgcag gaacaaccat ggccactgcc ggaggctctg cttccacatg gagagctggg ctgggagctg catgaacggc cgcctgcgct gctgcaggtt ctccaccaag cagccctttt ccaaccctaa acattcagtg ctgcacacag cagagcagga cccttcccca agccttggag ggacgtga. The amino acid sequence of the Beta-defensin is Ser-Asp-Ser-Gln-Leu Cys-Arg-Asn-Asn-His Gly-His-Cys-Arg- Arg Leu-Cys-Phe-His-Met Glu- Ser-Trp-Ala-Gly Ser-Cys-Met-Asn-Gly Arg-Leu-Arg-Cys-Cys Arg-Phe-Ser-Thr-Lys-Gln Pro-Phe-Ser-Asn-Pro Lys-His-Ser-Val-Leu His-Thr-Ala-Glu-Gln Asp-Pro-Ser-Pro-Ser Leu-Gly-Gly-Thr. The extraction method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting broken mucosa cells of chicken intestinal tract; (2) breaking vesicles; (3) leaching with 5% acetic acid under stirring, centrifuging, collecting supernatant, removing sediment, subpackaging the supernatant and freeze-storing to obtain crude chicken intestinal tract Beta-defensin; (4) separating the supernatant with Sephadex G-100 gel column at low temperature, eluting with 0.2mol / L sodium acetate (constant flow pump speed 3*1), detecting with nucleic acid-protein detector, collecting the eluate with an automatic collector (1.5mL each tube), and recording with a recorder (speed 6cm / h, and range 20mV); (5) detecting the antibacterial activity of the liquid in each tube to Pasteurella with agarose diffusion method, collecting the eluate with bacteriostatic activity, and storing under vacuum freeze drying; (6) purifying the the eluate with bacteriostatic activity with Tricine-PAGE, PVDF membrane blotting the protein bands, and performing amino acid sequence analysis with Sanger partial hydrolysis method; and (7) deriving chicken intestinal tract Beta-defensin cDNA with BLAST software.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for distinguishing degree of production traits of spirulina strain
InactiveCN103149211ALow costSuitable for high throughput screeningMaterial analysis by optical meansBiotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a spirulina development and application technology and aims to provide a method for distinguishing the degrees of production traits of a spirulina strain. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: extracting water-soluble protein of spirulina cells with an tris-HCl extracting solution, separating a protein sample by carrying out sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, then detecting the light intensity value of a protein band at a 102kD site of a protein electrophoretogram, and constructing a hierarchical diagram among algae plants according to the light intensity value; if the light intensity value of the protein band of a candidate strain at the 102kD site is more than 140 and the candidate strain and a known strain with good production traits get together, indicating that the candidate strain has good production traits and applicable to large-scale cultivation production; and if the light intensity value of the protein band of the candidate strain at the 102kD site is less than 40 and the candidate strain and a known strain with poor production traits get together, indicating that the candidate strain has bad production traits and is not applicable to large-scale cultivation production. The method provided by the invention is simple, efficient, reliable and low in cost, and no complex test and analysis such as nucleic acid sequencing and bioinformatics comparison is carried out, so that the method provided by the invention is applicable to large-scale high throughput screening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of Coomassie brilliant blue dyeing solution and dyeing method
ActiveCN104004382BReduce stainingHigh sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationOrganic dyesChemistryShort cycle
The invention discloses a coomassie brilliant blue staining solution and a staining method. The coomassie brilliant blue staining solution comprises 0.1-10 percent by volume of acid, 1-15 percent by volume of ethyl alcohol, 10-50g / L of soluble starch and 20-1000mg / L of coomassie brilliant blue aqueous solution. The staining solution does not contain reagents harmful to human bodies and is environmental friendly. The staining method using the staining solution has the beneficial effects that due to addition of the soluble starch, the staining background of gel can be reduced, a protein band can be specifically stained, the sensitivity of staining is effectively improved, and therefore, the whole staining process of the protein band can be completed within 20 minutes by using the staining method, the steps such as gel fixation, sensitization and destaining in a conventional dyeing process are omitted, operating steps are greatly simplified, and the dyeing time is saved; the staining method has the advantages of short cycle, high sensitivity and small background interference.
Owner:BEIJING VICNOVO SCI TECH
Method for extracting and purifying lycoris radiata lectin from lycoris radiata bulbs and lycoris radiata lectin produced by method
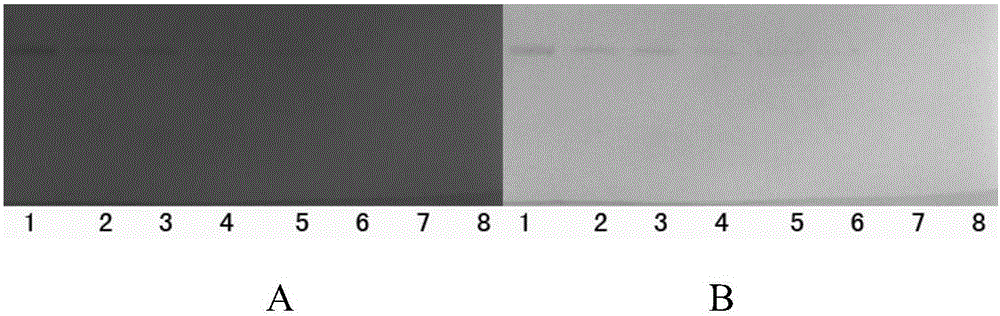
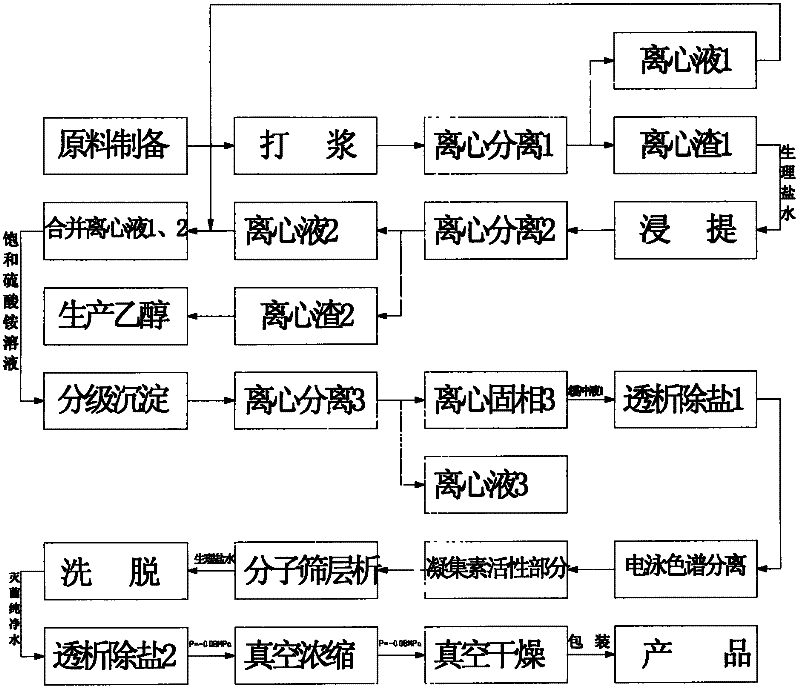
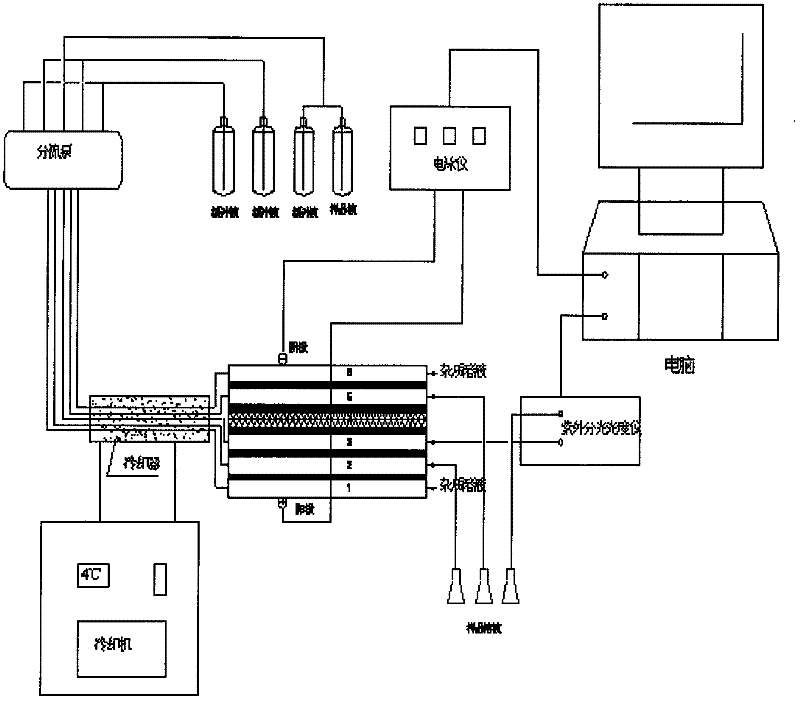
ActiveCN102304177AShorten pure timeEasy to separatePeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesLycoris radiataAlkaloid
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying lycoris radiata lectin from lycoris radiata bulbs and the lycoris radiata lectin produced by the method. The lycoris radiata bulbs are taken as raw materials and are extracted and purified by a specific process to form pure lycoris radiata lectin with a single protein band, and the pure lycoris radiata lectin has the apparent molecular weight of 48KD, is protein consisting of four subunits with the same molecular weight, is amorphous powder and has the lycoris radiata lectin content of 90 percent. The method comprises the following process steps of: (1) preparing raw materials; (2) pulping; (3) performing centrifugal separation for the first time; (4) leaching; (5) performing centrifugal separation for the second time; (6) mixing centrifugal separation solutions 1 and 2; (7) performing fractional precipitation; (8) performing centrifugal separation for the third time; (9) performing dialysis demineralizing for the first time; (10) performing electrochromatophoresis separation; (11) performing molecular sieve chromatography; (12) eluting; (13) performing dialysis demineralizing for the second time; (14) performing vacuum concentration; and (15) performing vacuum drying. The invention provides a method capable of extracting the lycoris radiata lectin, lycoris radiata polypeptides and lycoris radiata gelatin and also capable of extracting and separating total alkaloids of lycoris radiata; the process is simple; and the energy is saved and the consumption is reduced.
Owner:贵州芊芊园艺新技术发展公司
Extraction method of soil protein
InactiveCN106632582AEliminate distractionsAvoid degradationPeptide preparation methodsIce waterFreeze-drying
The invention provides an extraction method of soil protein. The extraction method comprises the following steps of adding soil protein extraction buffer liquid into a soil sample, oscillating, and standing; putting into boiling water for heating, cooling in 0 DEG C ice water, oscillating, and centrifuging; filtering supernatant, adding Tris saturated phenol into the filtered supernatant, oscillating, centrifuging, removing the supernatant, and collecting lower phenol solution; adding an ammonium acetate methanol solution into the lower phenol solution, and storing for 6 to 8h at the temperature of -20 DEG C; centrifuging, removing out the supernatant, collecting protein precipitate, cleaning the protein precipitate by acetone, and freeze-drying, so as to obtain protein dry powder. After detecting by SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gelelectrophoresis) electrophoresis, compared with the protein band obtained by other two representative extraction methods of the soil protein, the band of the soil protein extracted by the method is clearer.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
SDS-polyacrylamide electrophoresis gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106124597AEasy to separateGood Colloidal PropertiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTaurinePolyacrylamide
The invention discloses an SDS‑polyacrylamide electrophoresis gel, which is characterized in that: acrylamide monomers are mixed with a crosslinking agent methylenebisacrylamide in proportion, and triisopropanolamine, taurine, glycolic acid, A buffer system composed of glycine and tris-hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, and anionic surfactant sodium lauryl sulfate, initiator ammonium persulfate and catalyst tetramethylethylenediamine are added. The SDS-polyacrylamide electrophoresis gel prepared by the method of the present invention not only has good separation efficiency and colloidal performance, but also has high resolution and definition of protein bands, and the separation speed and gelation speed of the colloid are faster than Laemmli gel. Although the traditional Laemmli colloid has excellent performance, it does not possess long-term preservation ability. Compared with the Laemmli colloid, the electrophoretic gel of the present invention can maintain a longer shelf life, and it can still maintain normal separation efficiency when stored at a constant temperature of 37 ° C for more than 12 days. Equivalent to more than one year at 4 °C.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
Method for detecting production trait goodness and badness of spirulina strain
InactiveCN103018311ALow costSuitable for high throughput screeningMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGel electrophoresis of proteinsOrganism
The invention relates to the technique of development and application of spirulina and aims at providing a method for detecting production trait goodness and badness of spirulina strains. According to the method, a Tris-HC1 extracting solution is utilized for extraction so as to obtain water-soluble protein of spirulina cells; protein samples are separated by using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, subsequently the optical density value of a protein zone at 102kD of a protein electrophoresis diagram is detected, and a dendrogram of the spirulina plants is established according to the value; if the optical density value of a candidate strain at the protein zone at the 102kD is larger than 140 and the candidate strain is gathered together with a known stain with good production nature, the stain is good in production nature and is applicable to large-scale cultivation and production; and if the optical intensity value of the protein zone at 102kD is less than 40 and the candidate strain is gathered together with known strains with poor production nature, the stain is poor in production nature and is not applicable to large-scale cultivation and production. The method is simple, efficient, reliable and low in cost, and complex tests and analysis on nucleic acid sequencing and bioinformatics comparison do not need to be carried out, therefore, the method is applicable to large-scale and high flux separation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for identifying doping or not of foreign starch in potato food
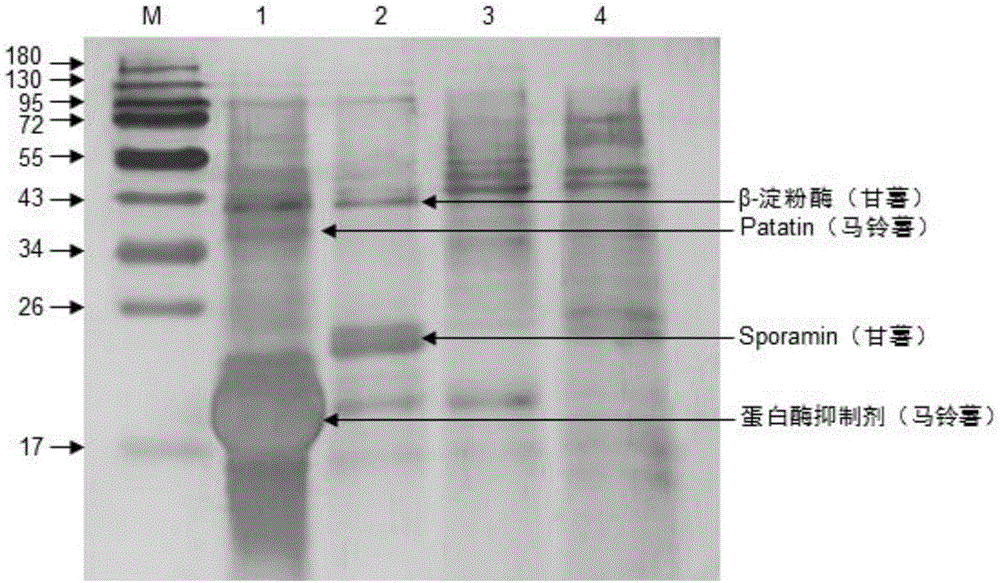
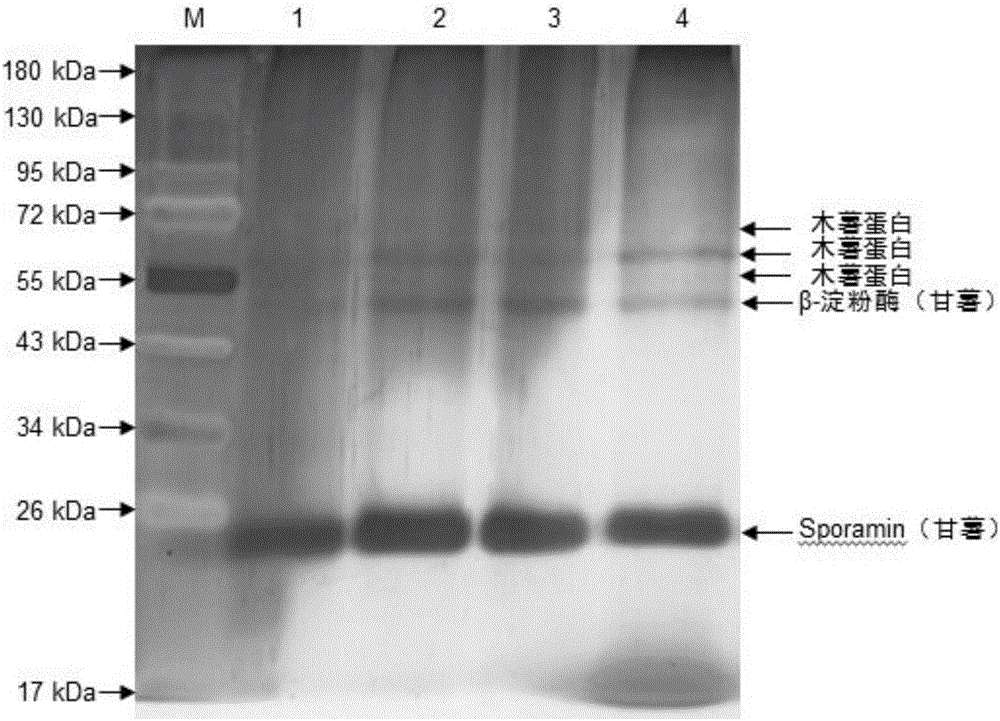
ActiveCN106841361AFast and accurate quality monitoringSolubility can be adjustedMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansForeign proteinProtein band
The invention relates to the technical field of food, in particular to a method for identifying doping or not of foreign starch in potato food. The method specifically comprises the following steps: extracting proteins in a sample to be measured and a potato noodle standard, then performing measurement by adopting polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and judging whether the sample to be measured contains foreign proteins or not and specific foreign starch through protein bands in the sample to be measured and the potato noodle standard. According to the method, the foreign starch to be identified is directly adopted as the standard, so that all information about the proteins in raw noodles can be accurately reflected, detection omission can be prevented, and the accuracy of an identification result can be improved.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
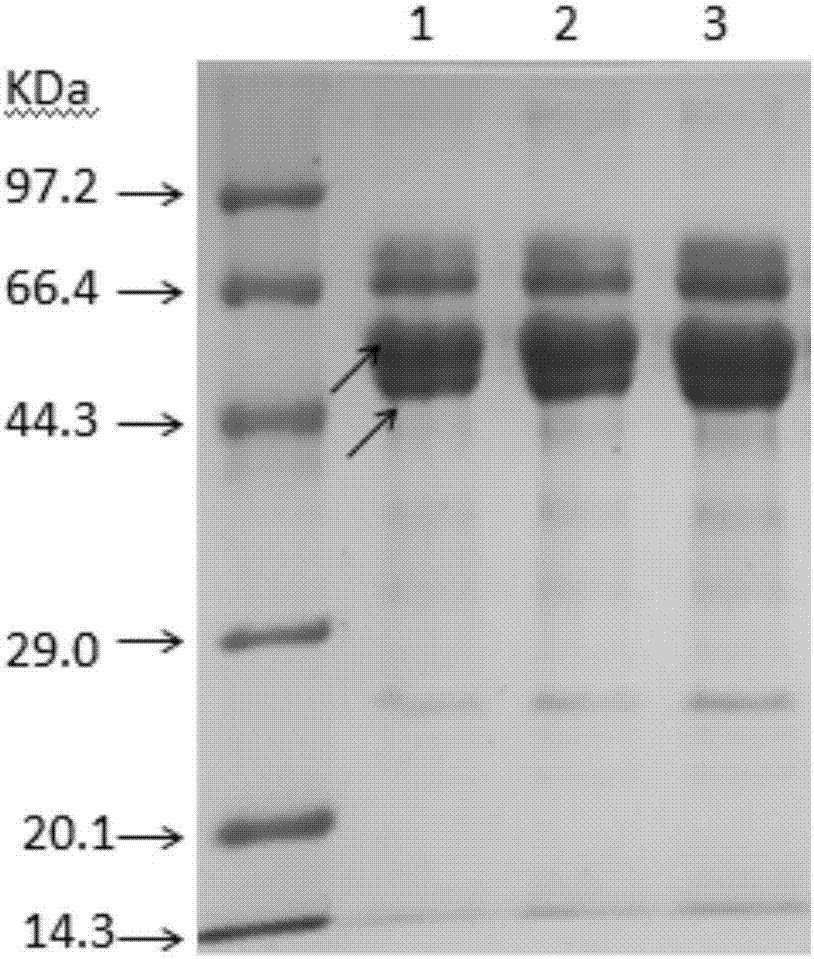
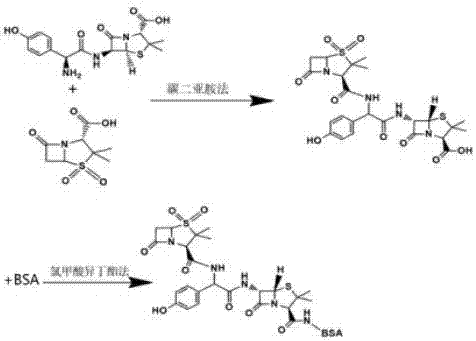
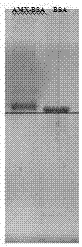
Synthesis method of amoxicillin artificial antigen
InactiveCN107474130AHigh molecular weightImproving immunogenicitySerum albuminPeptide preparation methodsSynthesis methodsBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an amoxicillin artificial antigen, and belongs to the technical field of biochemical industry. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: coupling an amoxicillin parent nuclear structural analogue sulbactam and an amoxicillin hapten to obtain a novel amoxicillin hapten, then coupling the hapten and bovine serum albumin (BSA) by an isobutyl chloroformate method, and dialyzing to obtain an amoxicillin complete antigen. Through gel electrophoresis analysis on the complete antigen and a BSA protein band, a result shows that the amoxicillin is successfully coupled to the BSA, and an antibody obtained through animal immunization confirms the successful synthesis of the artificial antigen. By the synthesis method, the molecular weight of the amoxicillin is increased, the immunogenicity of the amoxicillin is further enhanced, the immunizing effect is enhanced, and an important basis is provided for preparation of a high-sensitivity amoxicillin antibody.
Owner:樊之雄
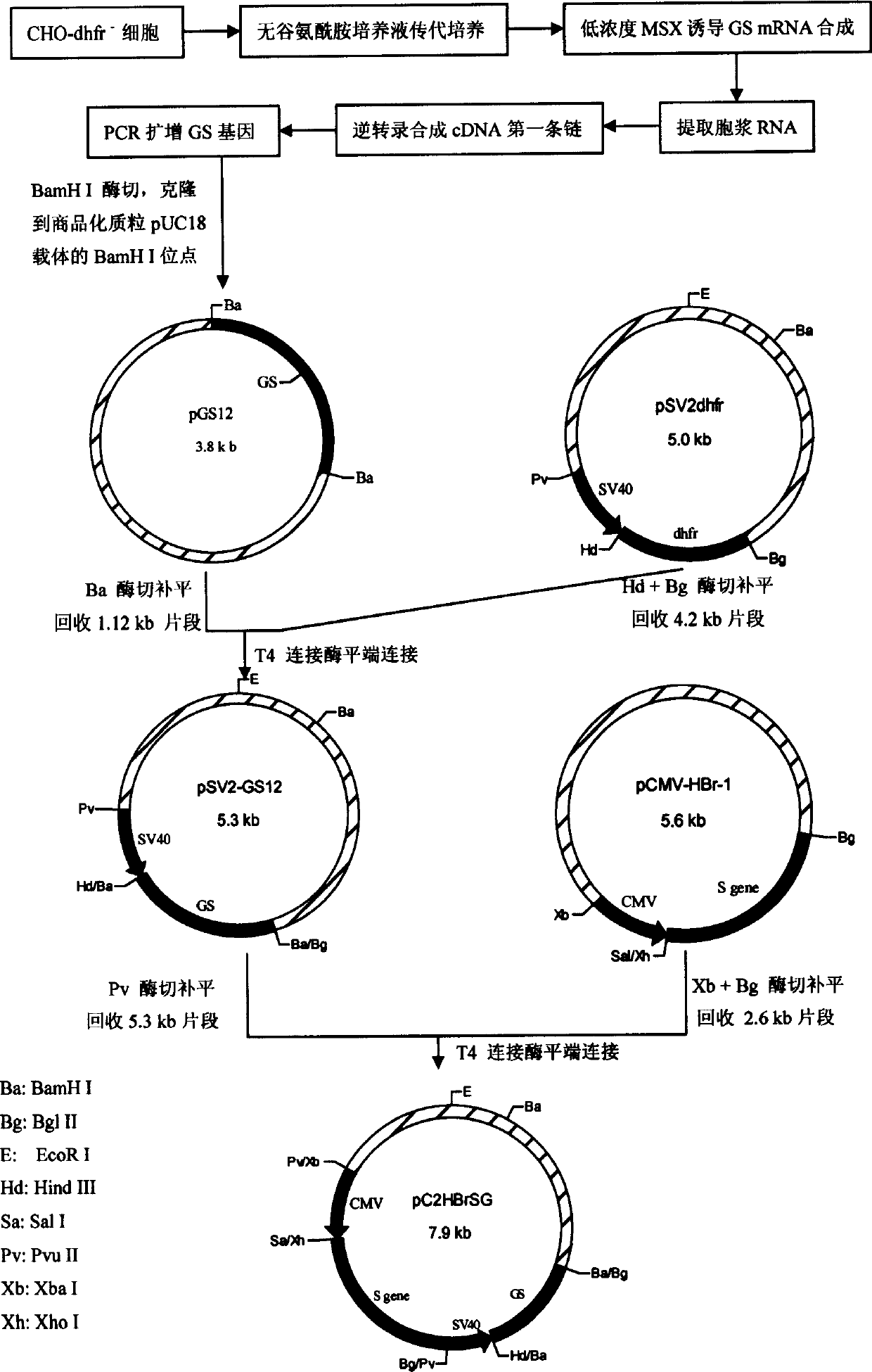
Cell line of transgene mammal with fusion antigen of S (main protein) and previous SI (large protein) of hepatitis B surface expressed in high efficiency
InactiveCN1796563AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMammalHepatitis B Surface Antigens
Based on the connection of gene fragment of hepatitis B surface antigen PreS1 (21-47) to Site 223 of S gene, RNA addition polymerization signal AATAA, hepatitis B virus enhancement vector 1 (En1), enhancement vector 2 (En2) and mutational x gene (mX) are introduced in its down stream to form plasmid pCHBSS1G. Plasmid pCHBSS1G and plasmid pSV2dhfr are transferred to CHO-dhfr-cell, cloned, selected and amplified with the addition of MSX and MTX to obtain a series of genetic engineering cell lines that can efficiently express the fusion protein for hepatitis B surface antigen S and of the former S1. SS1 fusion protein displays 27KD protein band in SDS-PAGE analysis as well as 30KD protein band. Specific antibody against S and S1 can be produced by mice immunization.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Method for obtaining endophytic bacteria for degrading verticillium dahlia toxin protein and application in preventing and treating plant verticillium wilt
The invention relates to a method for obtaining endophytic bacteria for degrading verticillium dahlia toxin protein and an application in preventing and treating plant verticillium wilt, and belongs to the biotechnological field. The method for obtaining endophytic bacteria for degrading verticillium dahlia toxin protein comprises the steps of culturing endophytic bacteria separated from the plant and verticillium dahlia toxin; using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to detect protein band after culture, comparing with protein band of the original toxin; and taking mixed culture system without 26KD protein band as a target strain. The method has clear target and mechanism. The method overcomes the shortcomings that the bio-control microorganism in biological control soil borne disease is easily influenced by soil environment and has unstable effect. The method uses pathogenic character of the verticillium dahlia and conduction characteristic of the endophytic bacteria in the plant to directly screen endophytic bacteria for grading verticillium wilt toxin result in plant disease so as to achieve the aim of effectively preventing and treating plant verticillium wilt.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Targeted delivery of reagents to spots on a planar support through patterned transfer sheets
ActiveUS9594054B2Avoid large quantitiesReadily apparentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein bandReagent
Molecular species that are immobilized in discrete locations on a planar support such as protein bands on a gel or a blotting membrane or species applied in dots or spots on a membrane are reacted with binding reagents that are applied through a porous hydrophilic transfer sheet placed over the planar support, the sheet having at least one region that is laterally bordered by a barrier with the binding reagent retained within the bordered region. The bordered region is placed directly over an area on the planar support where the molecular species are expected to reside if they are present on the support. The binding reagent is then delivered into the support to contact the species. Targeted delivery of the binding reagent is thus achieved with improved efficiency.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method of determining anti-thrombin activity of hirudin
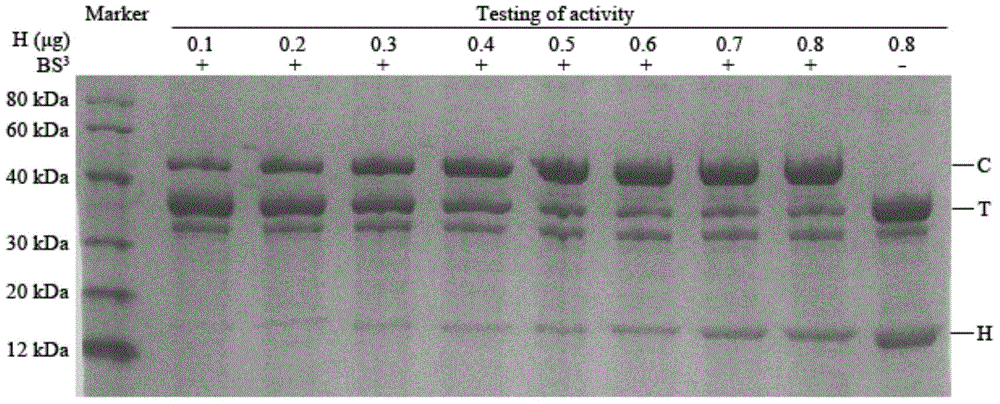
InactiveCN104965017ASmall sample sizeEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCross-linkElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a method of determining anti-thrombin activity of hirudin. The method includes: allowing hirudin having certain mass and containing unknown activity to react with sufficient thrombin, allowing cross-linking reaction under the action of cross-linking agent BS3 to obtain a first mixture system containing the hirudin, the thrombin and a hirudin-thrombin compound after completion of cross-linking, performing optical density scanning after electrophoresis, acquiring mass of the hirudin-thrombin compound according to protein band density of the hirudin-thrombin compound on the basis of a control having known protein band density, combining the hirudin and the thrombin according to a mass ratio: 1:5 so as to obtain the hirudin-thrombin compound so as to acquire mass of effective thrombin participating in reaction, and performing calculating according to the mass fraction of the effective thrombin in the thrombin and the mass of the hirudin so as to obtain an activity value of the hirudin, having the certain mass, in inhibiting the thrombin, namely an anti-thrombin activity value of the hirudin. The method is simple to operate, good in accuracy and low in investment and has low equipment requirements.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Preparation method of standard protein sample and protein lysate
InactiveCN101865796BNo smearing effectReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSulphate IonElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a preparation method of a standard protein sample and protein lysate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a standard protein sample into protein lysate with urea, and keeping the solution at the room temperature, thereby obtaining the standard protein sample which can be directly used for sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis SDS-PAGE without heating during loading for electrophoresis. The invention also discloses protein lysate applied in the preparation of the standard protein sample, which contains 7-9M of urea. The standard protein sample prepared in the method can be kept for a long time, no heating is needed, the operation is simple, and protein bands on the electrophoresis pattern are clear without obvious tailing.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com