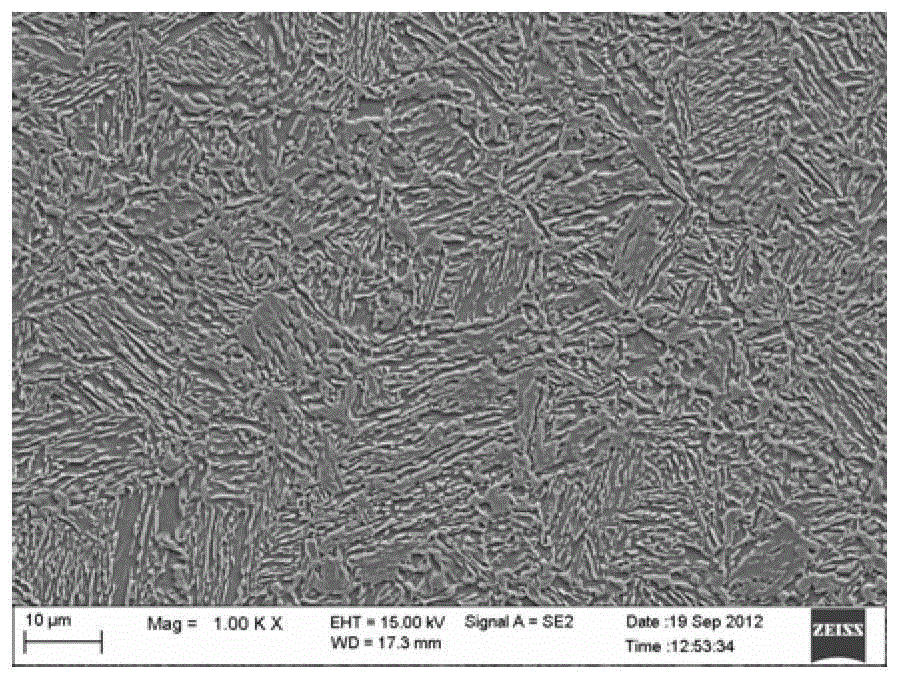
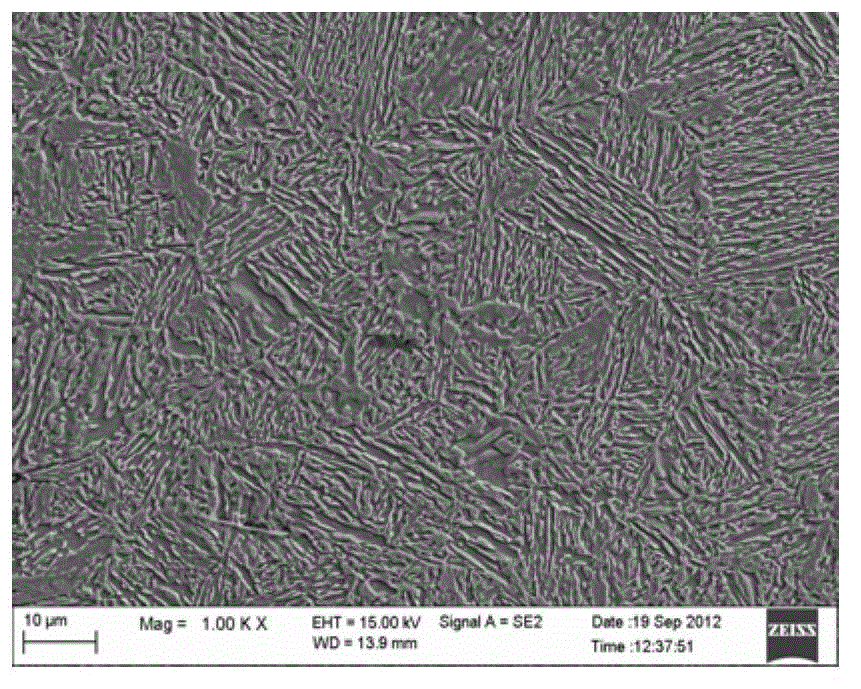
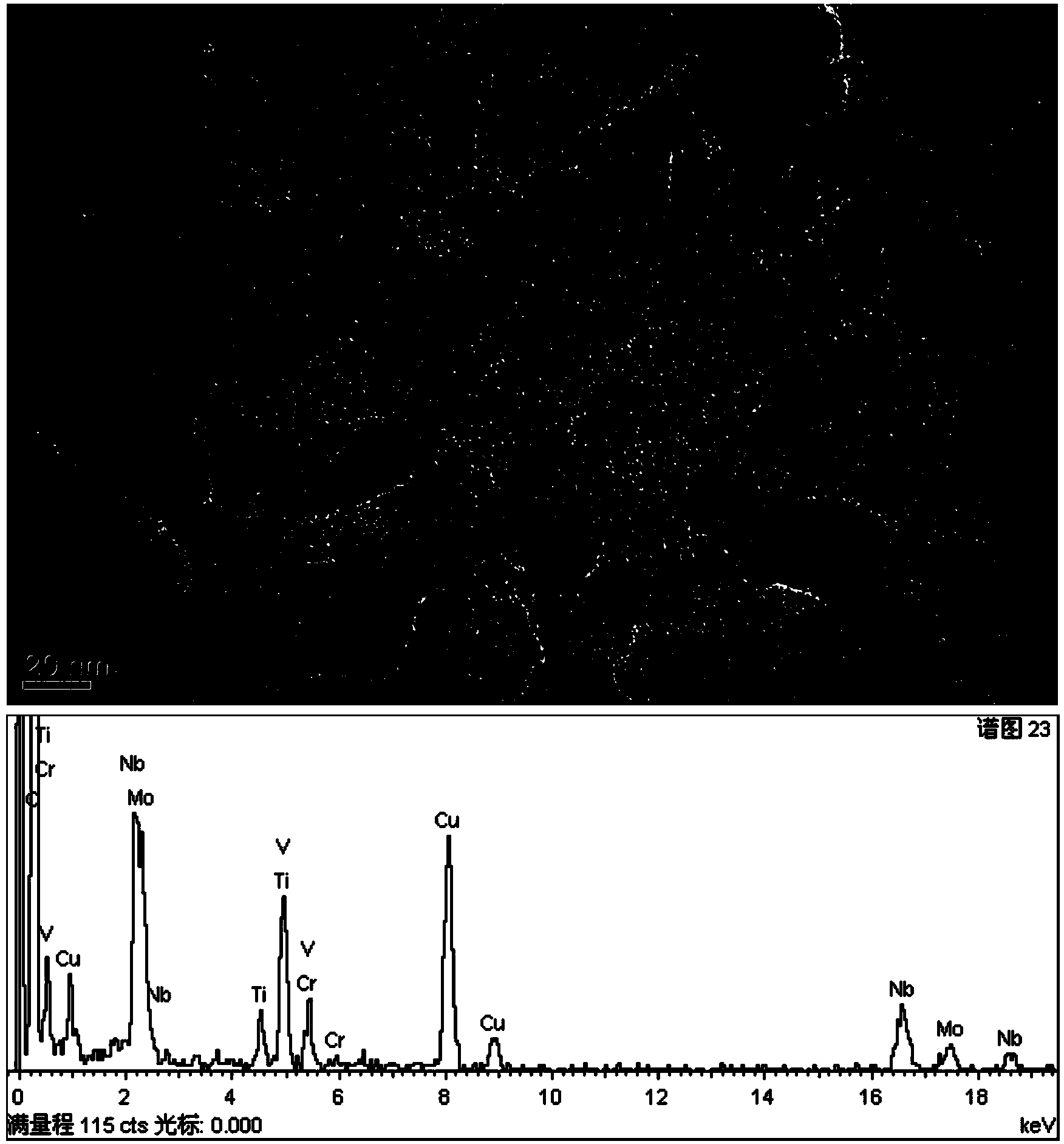
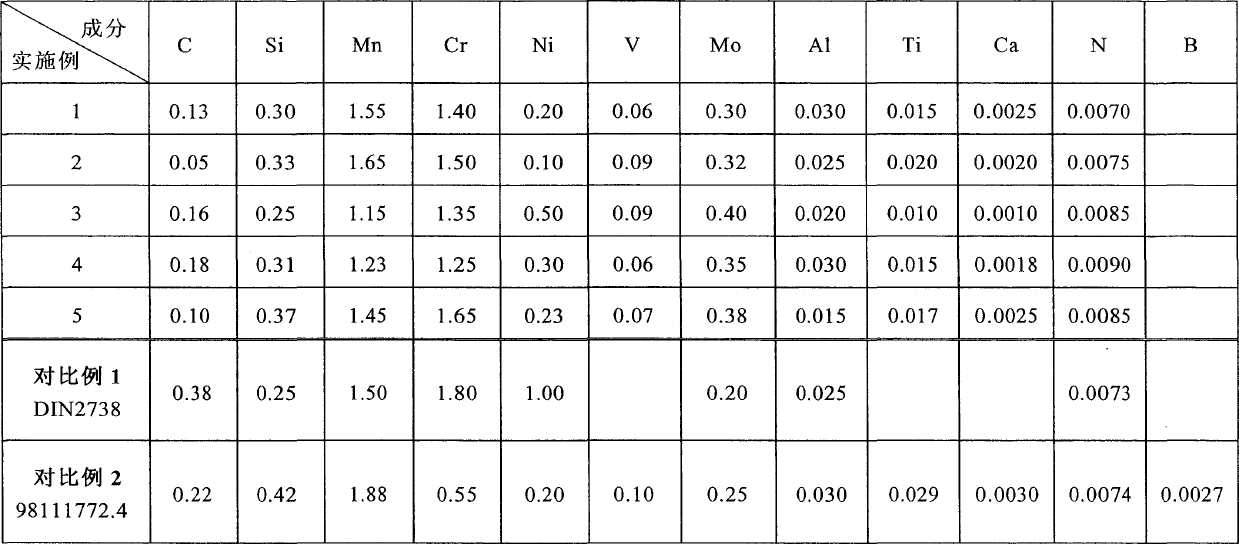
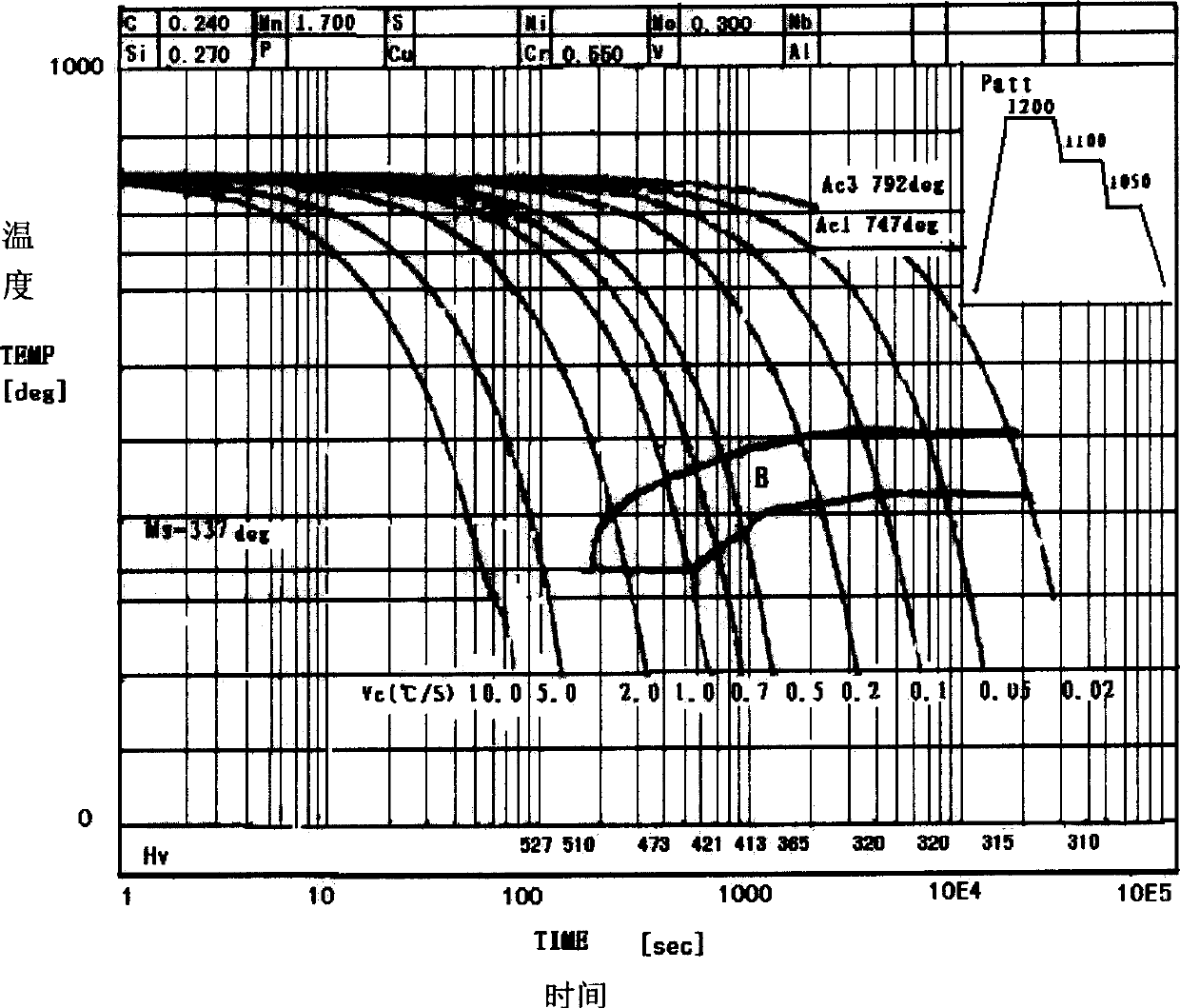
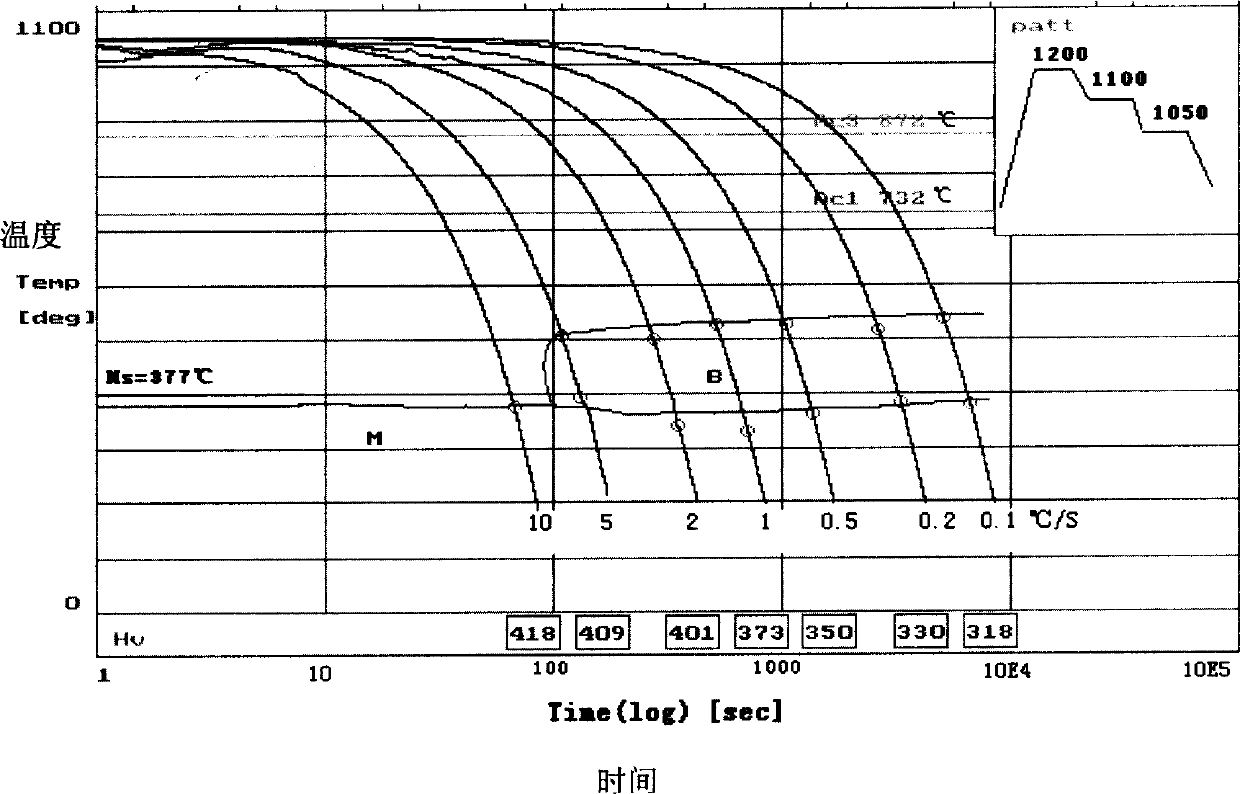
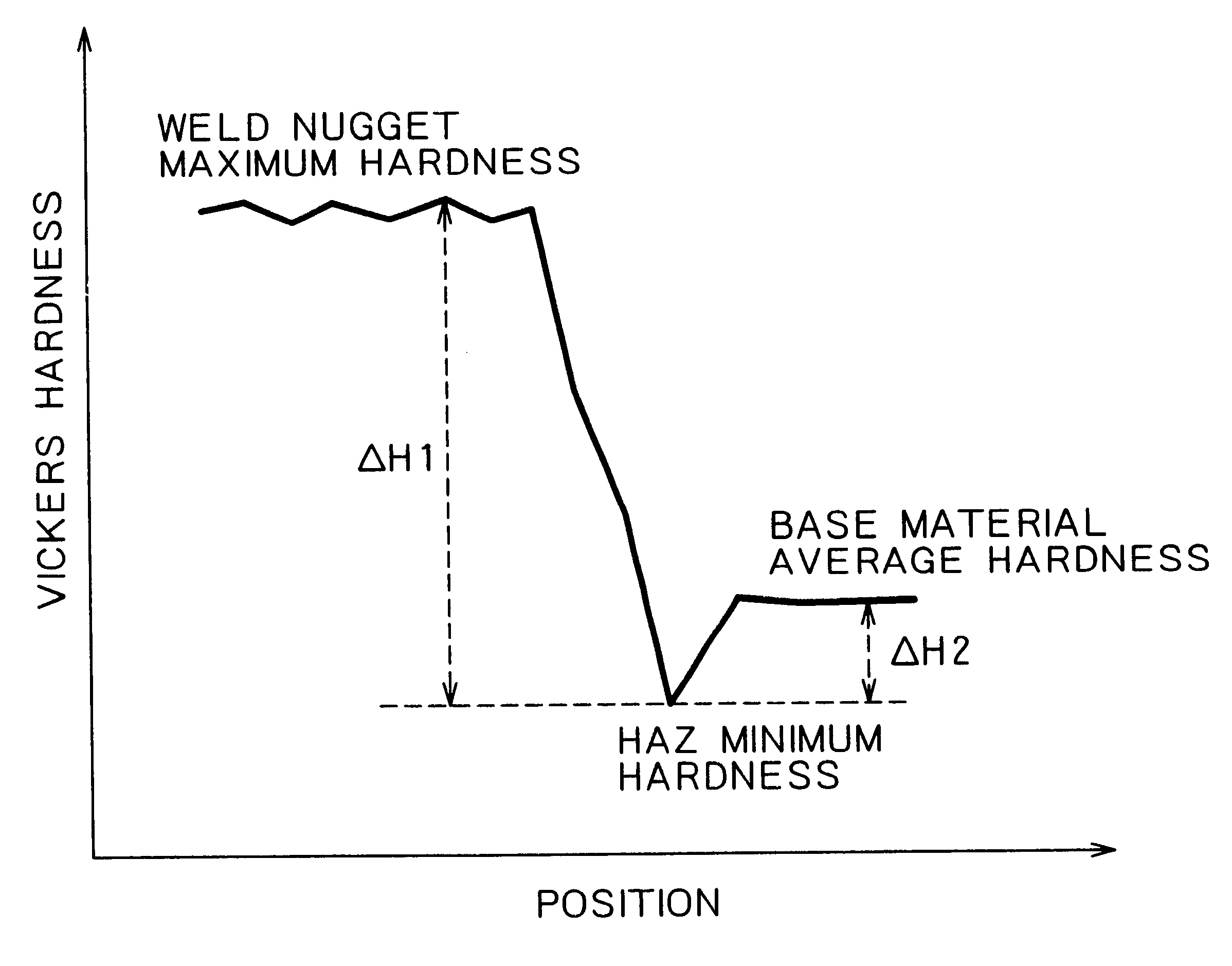
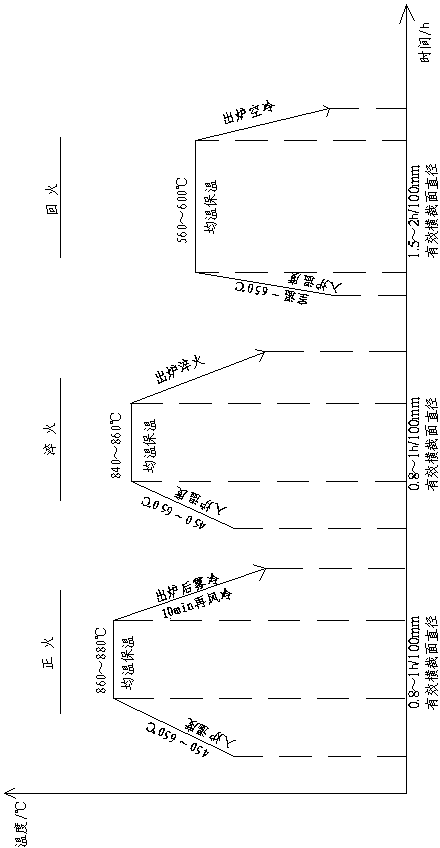
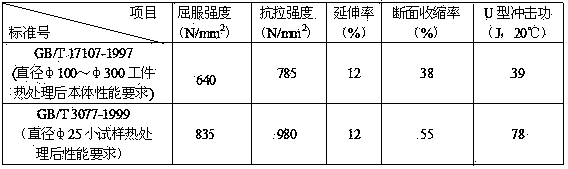
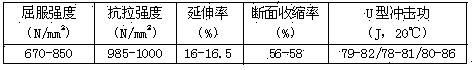
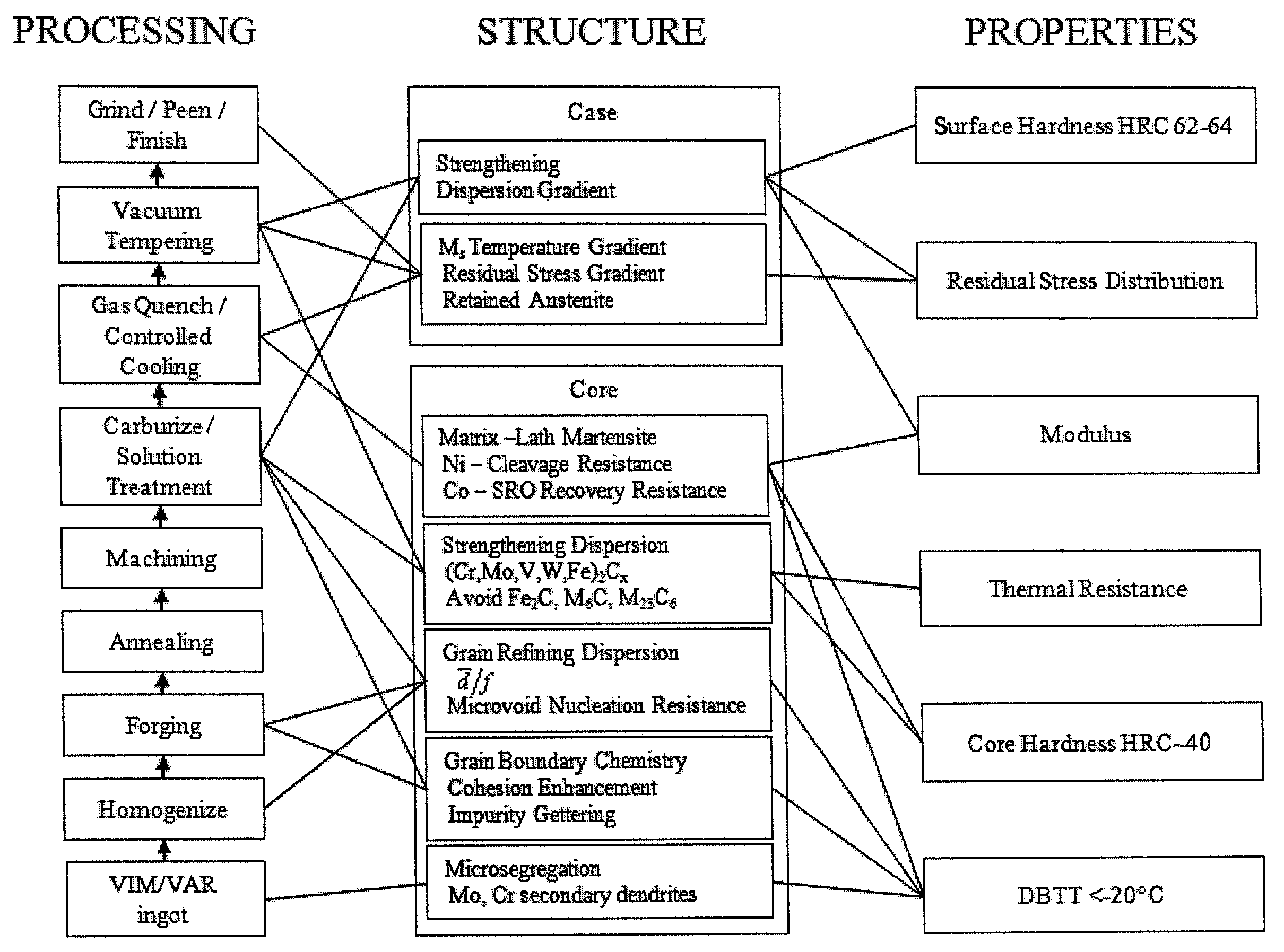
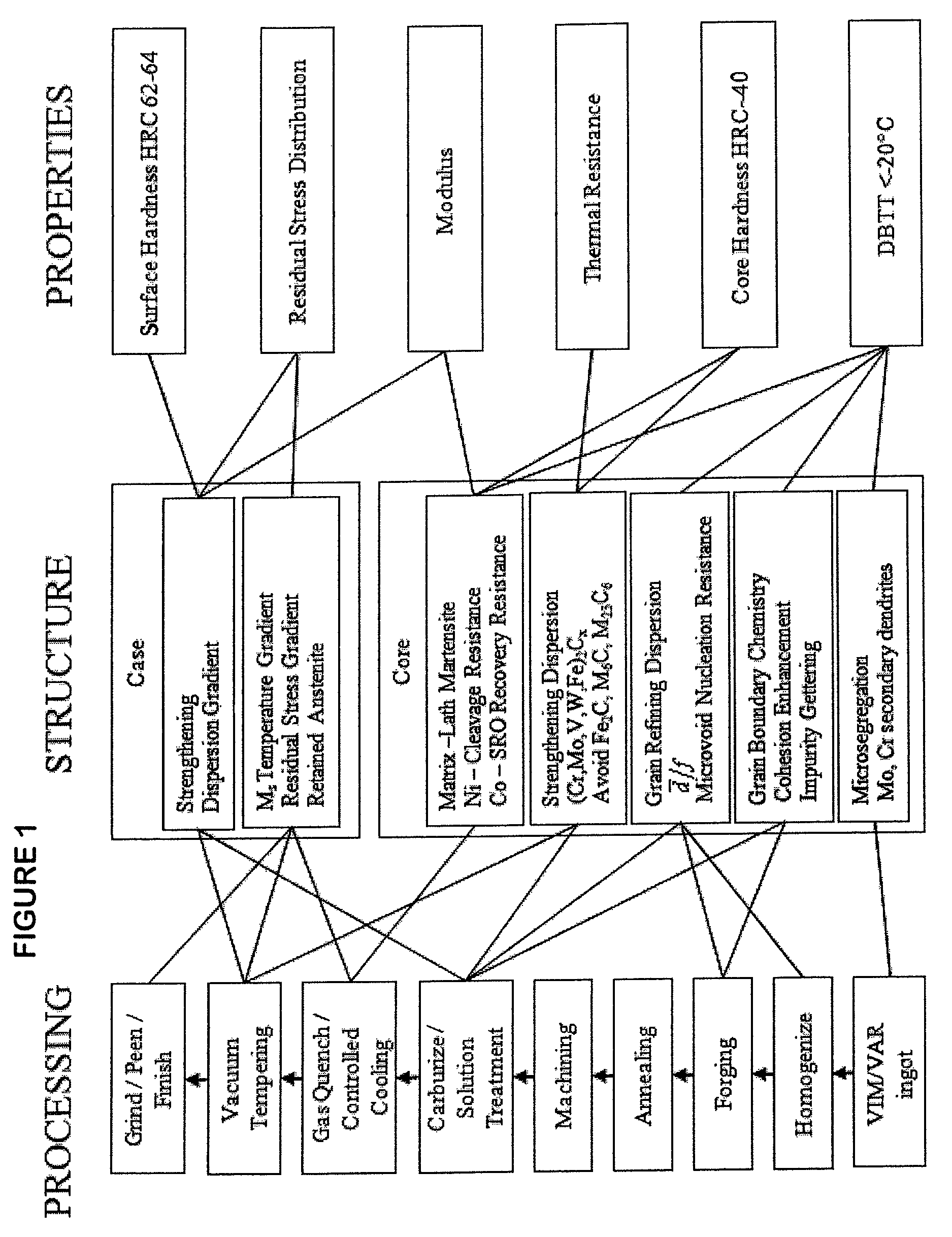
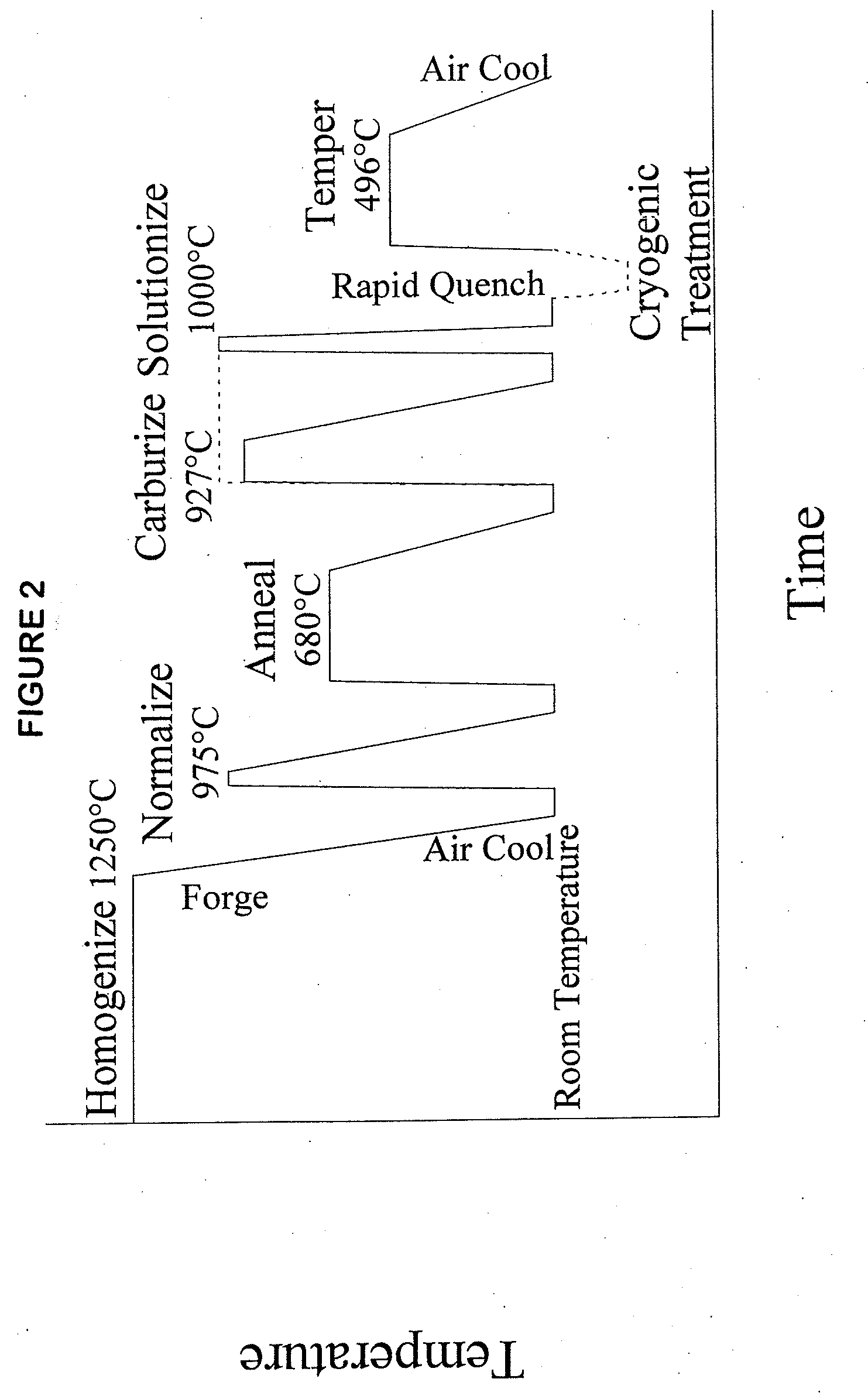
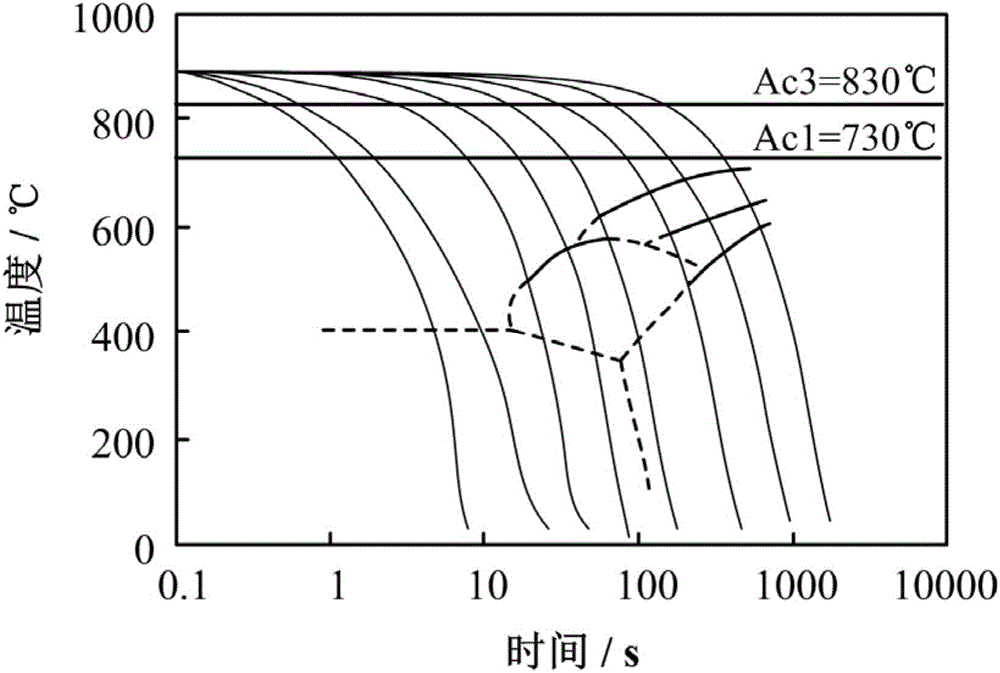
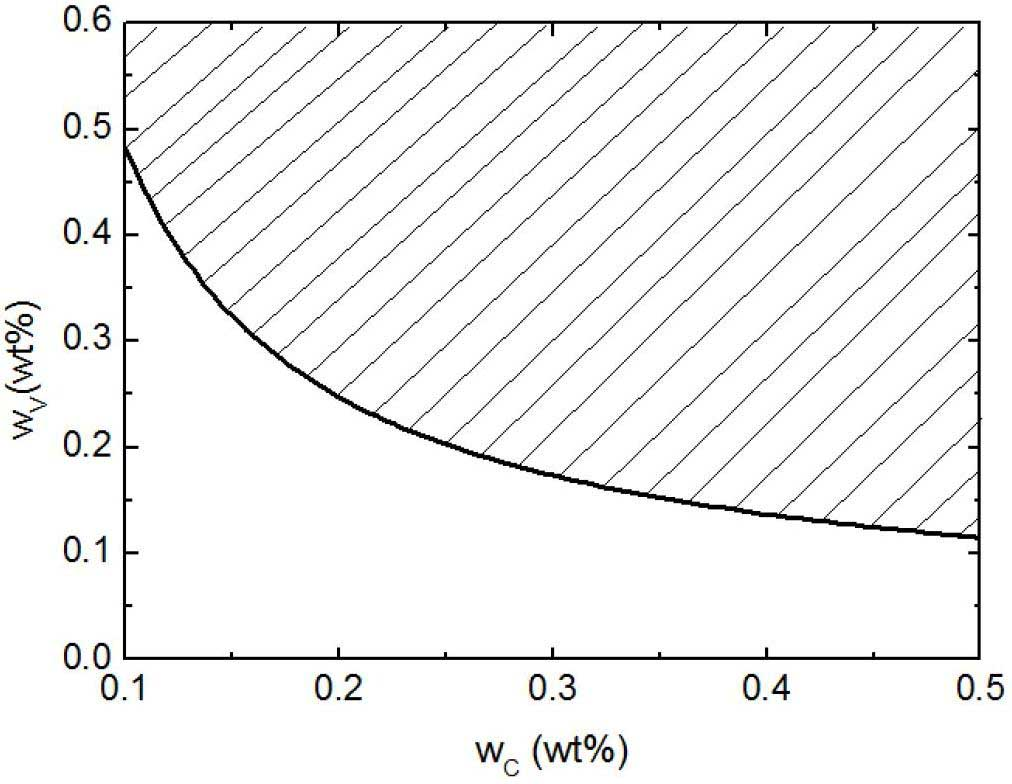
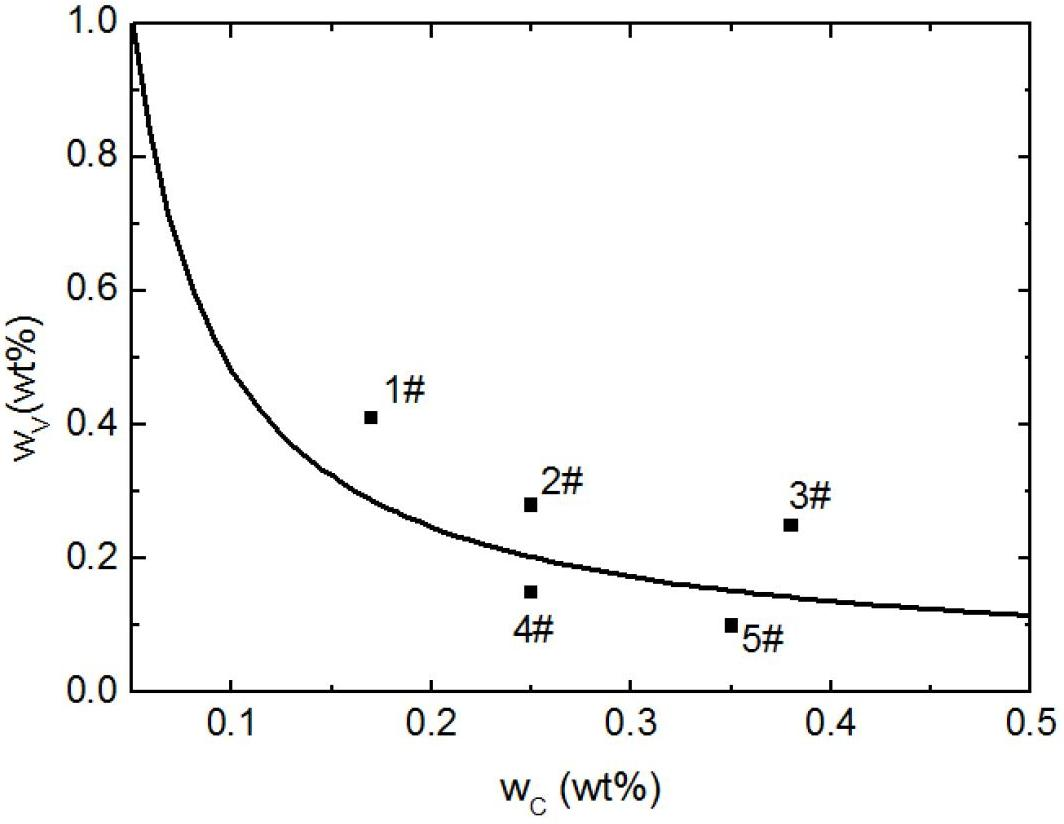
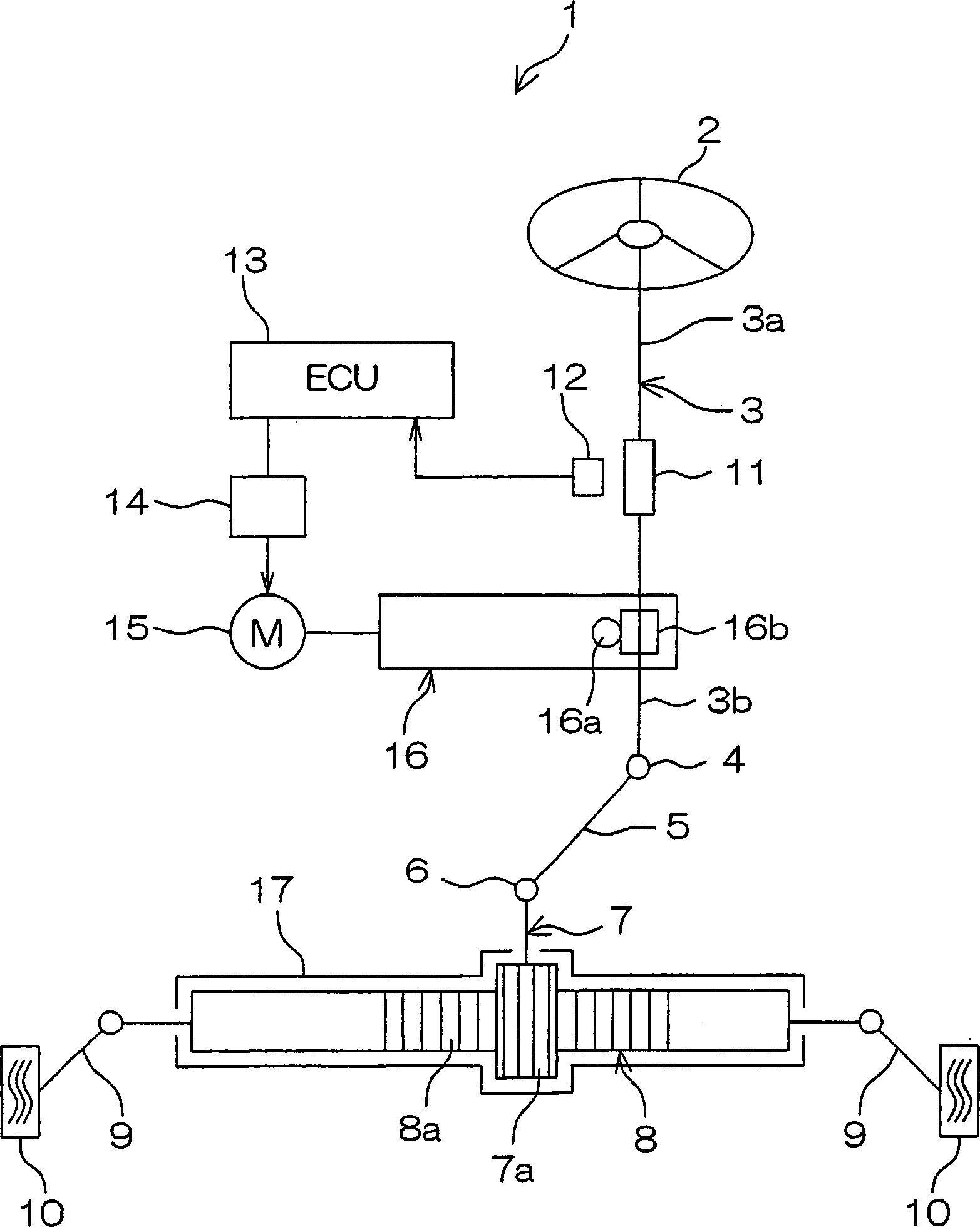
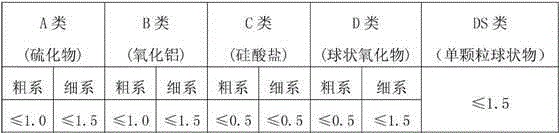
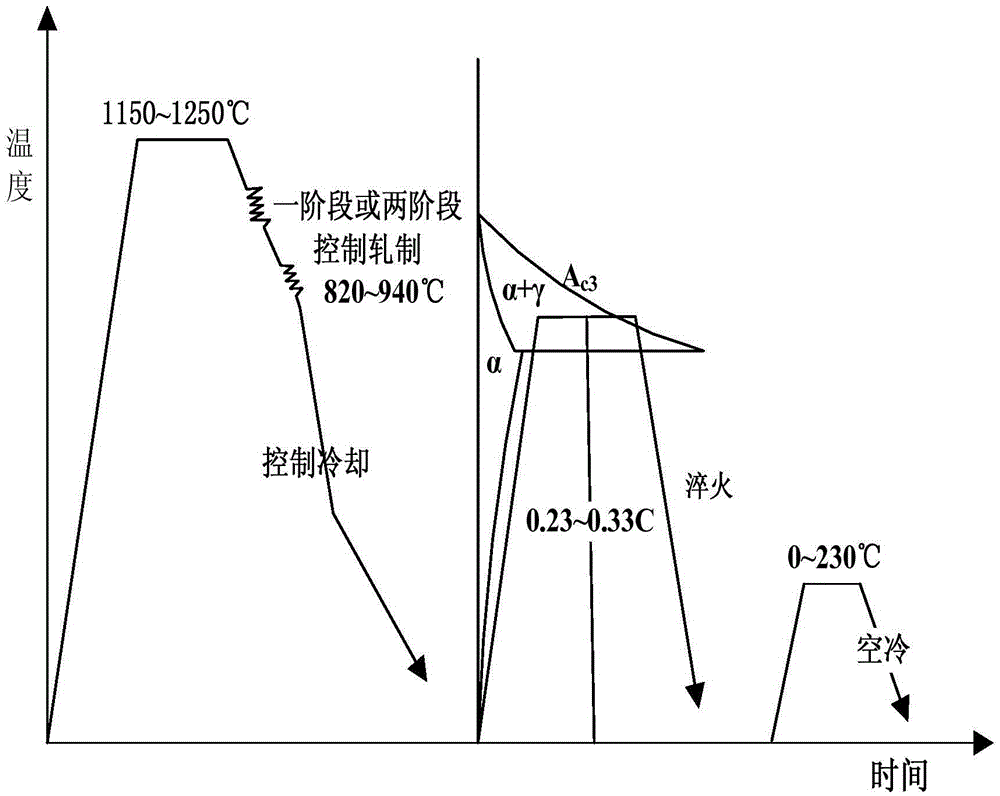
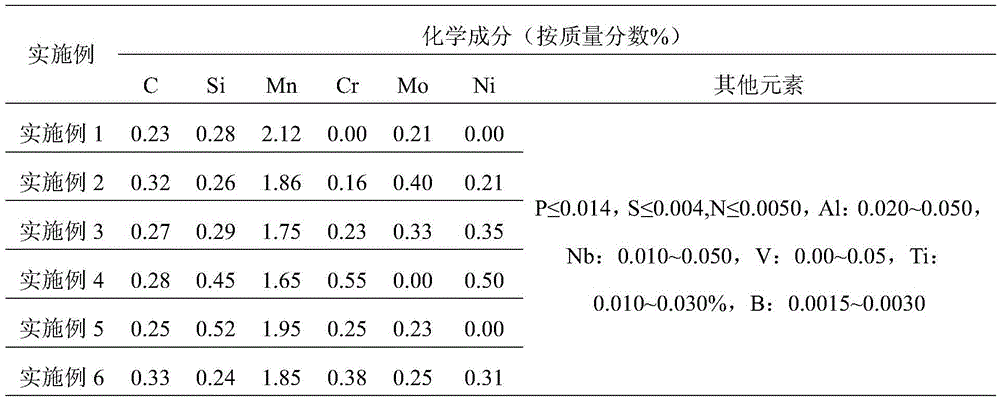
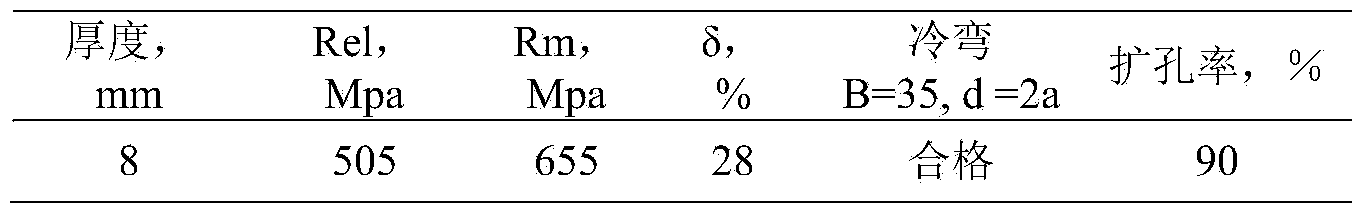Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
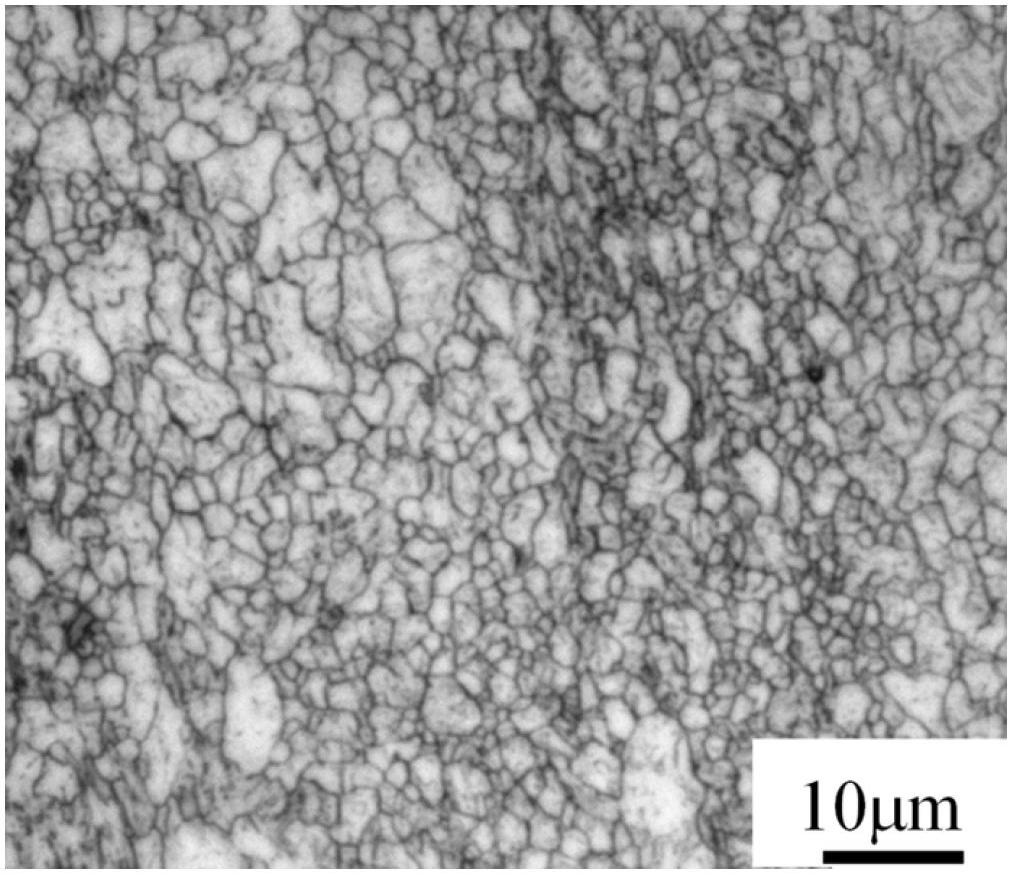
615 results about "Martensitic microstructure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Automobile steel with low cost and high strength ductility balance and preparation method thereof
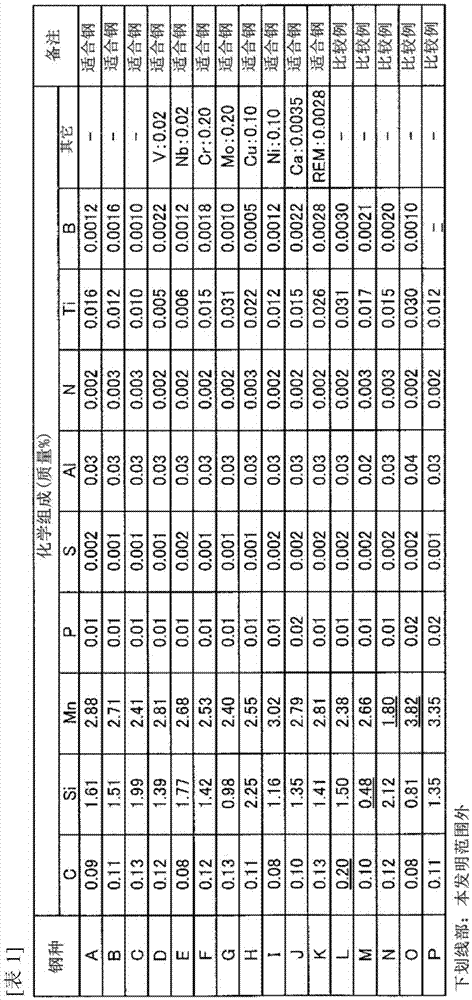
The invention provides automobile steel with low cost and high strength ductility balance and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of automobile steel. A multiphase, metastable and multiscale M<3> type organization structure is obtained based on reasonable design of chemical composition and partition of alloy elements and crucially based on the control of martensite phasetransformation, the repartition of solute such as C / Mn and the like and the austenite inverse phase transformation. The invention is characterized in that the martensite structure is obtained by using 0.02-0.50 wt%C and 3.50-9.00 wt%Mn in the cooling process of the inductrial production of steel plates and steel coils and the like; and superfine adverse transformation austenite and alpha phase substrate can be obtained through the partition of Mn and C in the heat preserving process between 100 DEG C below Acl and Acl, thus realizing the industrial production of hot rolled sheets and cold rolled sheets with high strength ductility balance used in automobiles. The invention has the advantages that the intensity is 0.7-1.3 GPa, the extension rate is 55-30% and the strength ductility balanceis 35-55 GPa%.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Superhigh-strength dual-phase steel sheet of excellent fatigue characteristic in a spot welded joint
InactiveUS20030221752A1Good effectIncrease volume fractionHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingHardnessUltimate tensile strength
A superhigh-strength dual-phase steel sheet containing ferritic microstructure and a martensitic microstructure-containing composite-phase steel sheet containing: C: 0.08-0.20% (mass % here and hereinafter), Si: 0.5% or less (inclusive of 0%) Mn: 3.0% or less (exclusive of 0%) P: 0.02% or less (inclusive of 0%) S: 0.02% or less (inclusive of 0%), and Al: 0.001-0.15%, and further containing Mo: 0.05-1.5%, and Cr: 0.05-1.5%, and which satisfying that: the average Vickers hardness of the ferritic microstructure is 150 Hv or more and the average Vickers hardness of the martensitic microstructure is 500 Hv or more, the superhigh-strength dual-phase steel sheets being of excellent fatigue characteristic in a spot welded joint.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Quenching and annealing preparation method of ultrahigh-strength thin steel plate for automobiles
ActiveCN102943169AImprove mechanical propertiesHeat treatment process control is simple and feasibleFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMetallic materialsQuenching
A quenching and annealing preparation method of an ultrahigh-strength thin steel plate for automobiles belongs to the field of metal material heat treatment. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, heating a low-carbon steel cold-rolled sheet containing microalloy elements such as Si, Mn and Nb to a fully austenitic area and performing quenching heat treatment after austenization; secondly, heating the low-carbon steel cold-rolled sheet to a two-phase area so that the lath martensite quenched previously is decomposed and partially inverted to form the austenite, and then quickly cooling the steel sheet above Ms point and preserving heat for secondary partition; and finally, rapidly cooling to the room temperature. The steel sheet has a complex-phase structure composed of a quasi-recrystallized ferrite, a carbide, residual austenite and tiny bainite or martensite structure; and the quasi-recrystallized ferrite structure formed after annealing inherits the lath morphology feature of the martensite, which is advantageous for improving the ductility. The ultrahigh-strength thin steel prepared through the process is high in product of strength and elongation, and has the tensile strength of more than 1100 MPa, the ductility of 20% and the product of strength and elongation of 22000 MPa.%.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Postweld heat treatment method of welded joint of bainite steel rail
ActiveCN103898310AImprove impact toughnessEvenly distributedFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSafe operationHeat treated
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
690MPa-yield-strength low-yield-tensile-ratio antiseismic steel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103710622AMeet the mechanical performance requirementsChemical compositionMechanical property
The invention relates to a 690MPa-yield-strength low-yield-tensile-ratio antiseismic steel and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of architectural structural steel. The antiseismic steel comprises the following chemical components: 0.05-0.13wt.% of C, 0.00-0.50wt.% of Si, 1.50-2.50wt.% of Mn, less than 0.012wt.% of P, less than 0.006wt.% of S, 0.15-0.50wt.% of Mo, 0.02-0.12wt.% of Nb, 0.00-0.15wt% of V, 0.01-0.025wt.% of Ti, 0.0010-0.0030wt.% of B, 0.01-0.06wt.% of Al and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. On such basis, one or more of the following alloy elements are added: 0.00-0.80wt% of Cu, 0.00-0.50wt% of Cr and 0.00-1.00wt% of Ni. The total addition amount of the alloy elements in the steel is not greater than 5%. A heavy and medium plate mill is utilized to perform controlled rolling and controlled cooling to obtain the fine-grain bainite-martensite structure; and two-phase region secondary isothermal heat treatment is combined to obtain a certain amount of metastable austenite / microalloy precipitate enhanced substrate; the antiseismic steel satisfies the requirements for mechanical properties of 690MPa-yield-strength architectural antiseismic design code, can be used in an antiseismic structure, and can also be used in the field of engineering machinery.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Bainite die steel in large section for plastic and preparation method
A bainite steel used for large-cross section plastic mould contains C (0.05-0.19 Wt%), Si (0.1-0.6), Mn (1-1.65), V (0.04-0.2), Cr (1.0-1.70), Mo (0.15-0.50), P (0-0.02), S (0-0.01), Ni (0-0.5), N (0-0.01), Ti (0.005-0.025), Ca (0-0.005), Al (0.01-0.04) and Fe (rest). Its preparing process includes smelting in converter, refining, casting, heating, rolling, cooling, and tempering.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Superhigh-strength dual-phase steel sheet of excellent fatigue characteristic in a spot welded joint
InactiveUS6709535B2Hot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingHardnessUltimate tensile strength
A superhigh-strength dual-phase steel sheet containing ferritic microstructure and a martensitic microstructure-containing composite-phase steel sheet containing:C: 0.08-0.20% (mass% here and hereinafter),Si: 0.5% or less (inclusive of 0%)Mn: 3.0% or less (exclusive of 0%)P: 0.02% or less (inclusive of 0%)S: 0.02% or less (inclusive of 0%), andAl: 0.001-0.15%, and further containingMo: 0.05-1.5%, andCr: 0.05-1.5%, and which satisfying that:the average Vickers hardness of the ferritic microstructure is 150 Hv or more and the average Vickers hardness of the martensitic microstructure is 500 Hv or more, the superhigh-strength dual-phase steel sheets being of excellent fatigue characteristic in a spot welded joint.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
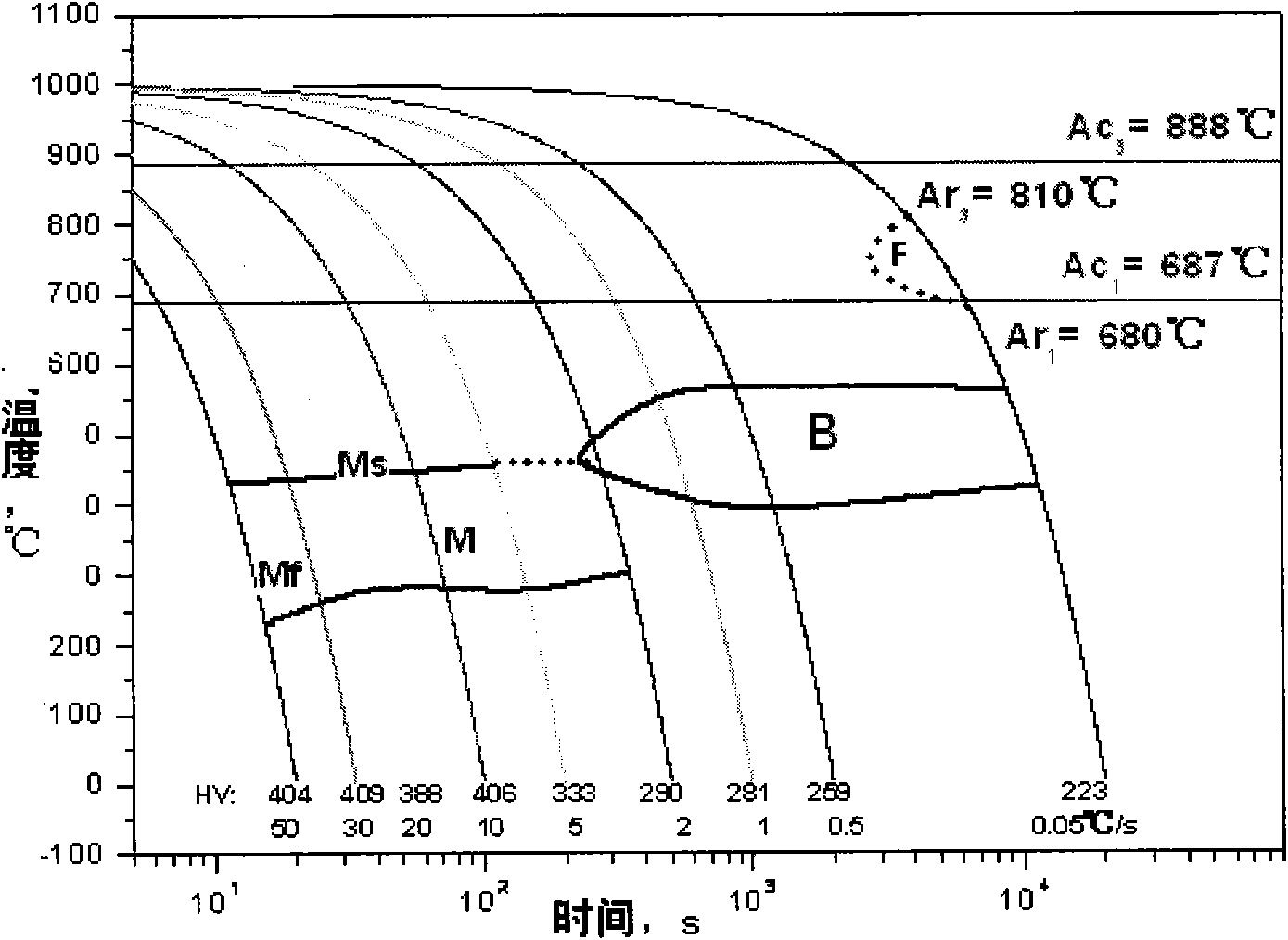
Method for manufacturing steel plate with high strength and high toughness by using hot-rolling coiled plate
The invention relates to a manufacture method for manufacturing a steel plate with high strength and high toughness by using a hot-rolling coiled plate. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, after a hot-rolling coiled plate is leveled on a leveling machine set, refining heat treatment is carried out on the hot-rolling coiled plate, i.e. the hot-rolling coiled plate is heated in induction heating equipment, the heating time is within 60-140s, and the hot-rolling coiled plate is heated to 910DEG C to 960DEG C and austenized; then, the hot-rolling coiled plate enters a water-cooling or steam-cooling quenching machine set to carry out quenching, the quenching and cooling speed of the hot-rolling coiled plate is greater than or equal to 5DEG C / s, and a quenched martensite organization is obtained after quenching; tempering is carried out after quenching, induction heating is carried out by adopting the induction heating equipment in the tempering, the heating temperature of the quenched martensite organization is 220DEG C to 440DEG C, the tempering time is 80 to 180s, and a tempered martensite organization is obtained; and finally, straightening, flaw detection, surface inspection and sampling inspection are carried out to finally obtain the steel plate with excellent performance, high strength and high toughness. The invention has the advantages that as refining treatment adopts an induction heating method, the heating time is short, austenite crystal grains are fine, the mechanical property is superior to that of a similar product produced by the traditional technology, the plate type of the steel plate is good, and the invention has high production efficiency, low equipment investment, little maintenance cost of the equipment, small occupation area and little environmental pollution.
Owner:武汉武钢实业机电材料工程有限公司
High-strength cold rolled steel sheet having high yield ratio and method for producing said sheet
ActiveCN105452513AHigh yield ratioHigh elongationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelHigh intensity
Provided is a high-strength cold rolled steel sheet exhibiting exceptional elongation and stretch-flangeability as well as a high yield ratio. A high-strength cold rolled steel sheet having a high yield ratio, which: contains 0.05-0.15% of C, 0.6-2.5% of Si, 2.2-3.5% of Mn, 0.08% or less of P, 0.010% or less of S, 0.01-0.08% of Al, 0.010% or less of N, 0.002-0.05% of Ti, and 0.0002-0.0050% of B, the remainder comprising Fe and unavoidable impurities (percentages given with respect to mass); includes 20-55% by volume of ferrite with an average crystal particle diameter of 7 [mu]m or less, 5-15% by volume of residual austenite, and 0.5-7% by volume of martensite with an average crystal particle diameter of 4 [mu]m or less; includes a structure of bainite and / or tempered martensite having an average crystal particle diameter of 6 [mu]m or less; and has a microstructure in which the difference in nanohardness between the ferrite and the bainite and / or tempered martensite structure is 3.5 GPa or less, and the difference in nanohardness between the bainite and / or tempered martensite structure and the martensite is 2.5 GPa or less.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
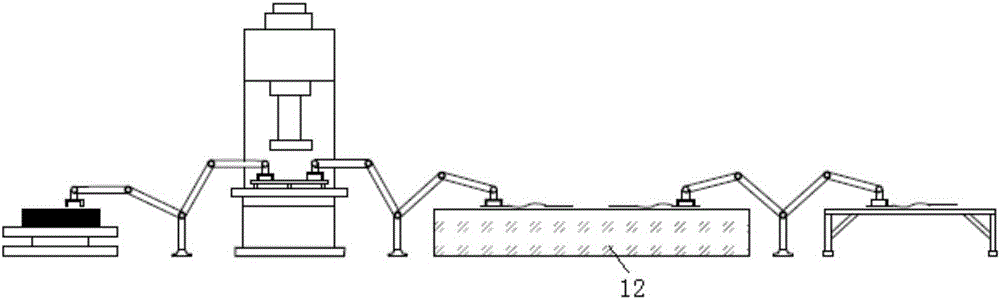
Multi-station continuous hot stamping production line and method
ActiveCN105215160AGuaranteed surface qualityReduce lossesShaping toolsMetal-working feeding devicesHot stampingProduction line
The invention discloses a multi-station continuous hot stamping production line and method. The production line comprises a material loading table, a feeding robot, a press unit, a material conveying robot, a quenching device, a material unloading robot and a conveyor belt which are arranged in sequence. The press unit comprises a heating device, a mould device and at least one press used for installation of the mould device; the heating device is used for wholly or locally heating a prefabricated blank to obtain a hot blank, and the mould device is used for conducting stamping forming, pressure maintaining setting and trimming and punching on the hot blank to obtain a hot stamped part. The rapid heating, stamping forming, pressure maintaining setting, trimming and punching and quenching can be continuously completed, so that the heating efficiency is improved, and the transportation process before punching of the hot blank is also avoided. For steel plates, stamped parts are blanked at a high temperature, increasing of cutting difficulty caused by generation of a martensitic structure at normal temperature is avoided, the blanking force is reduced, and the optimal blanked edge can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
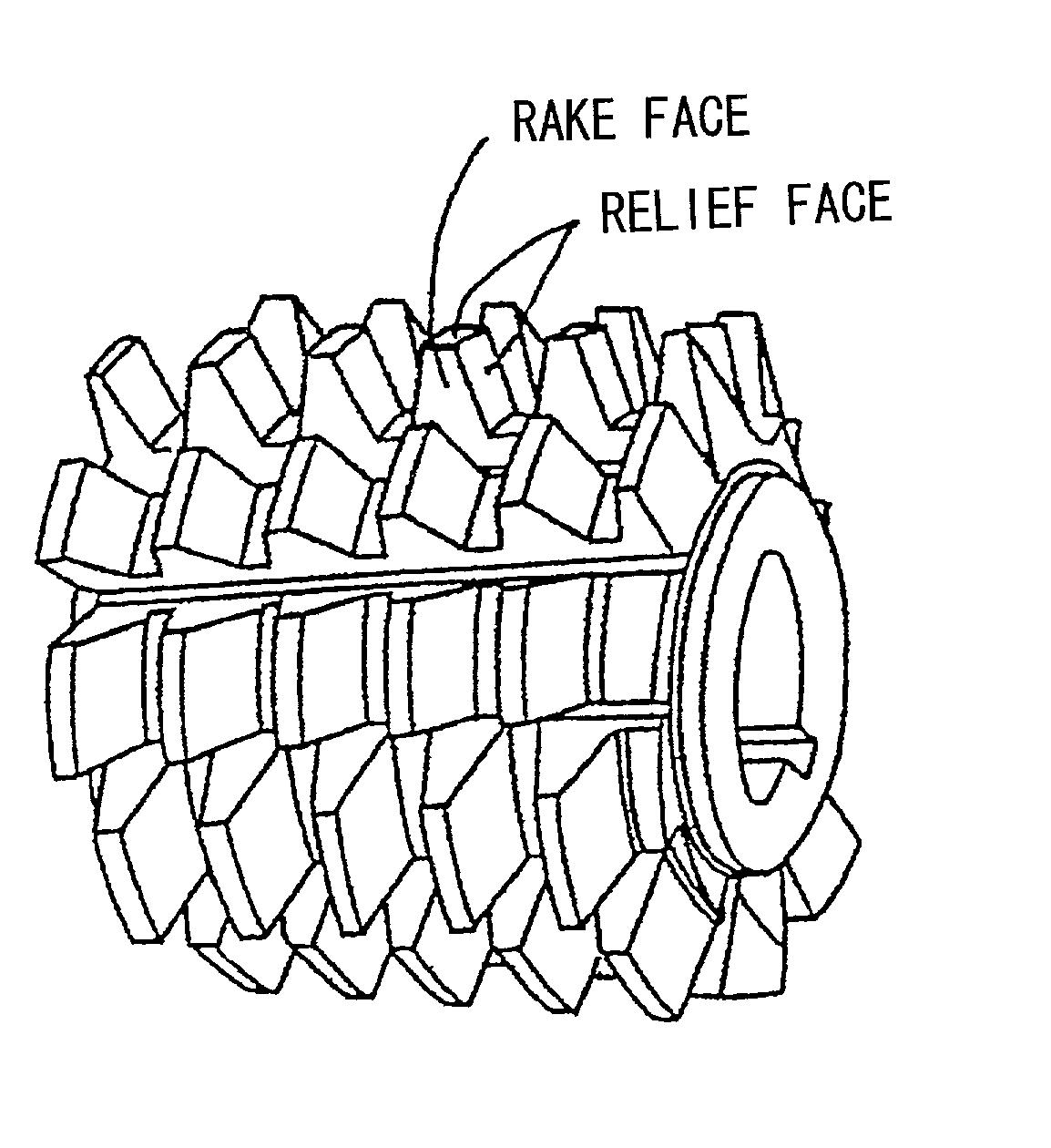
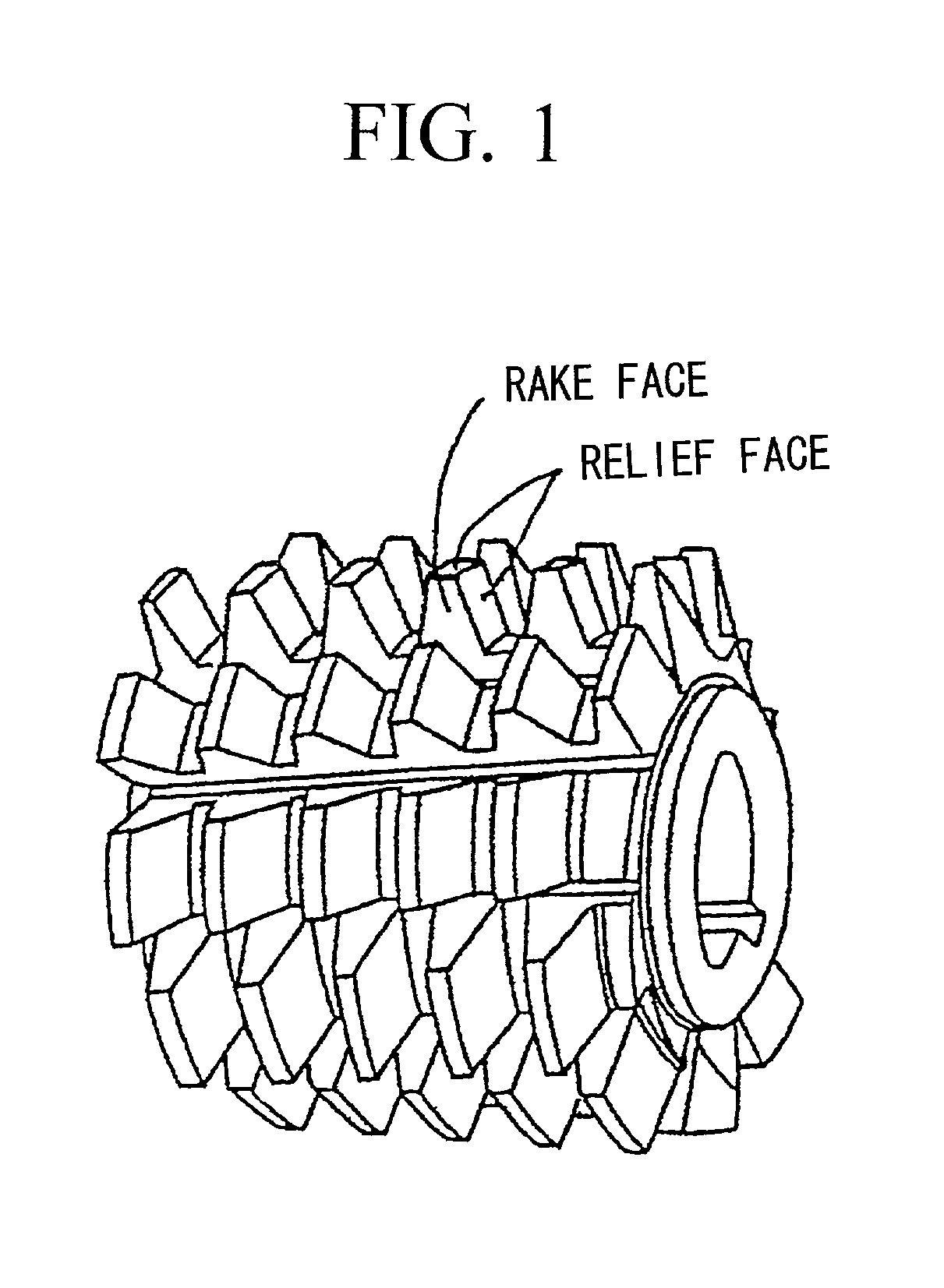
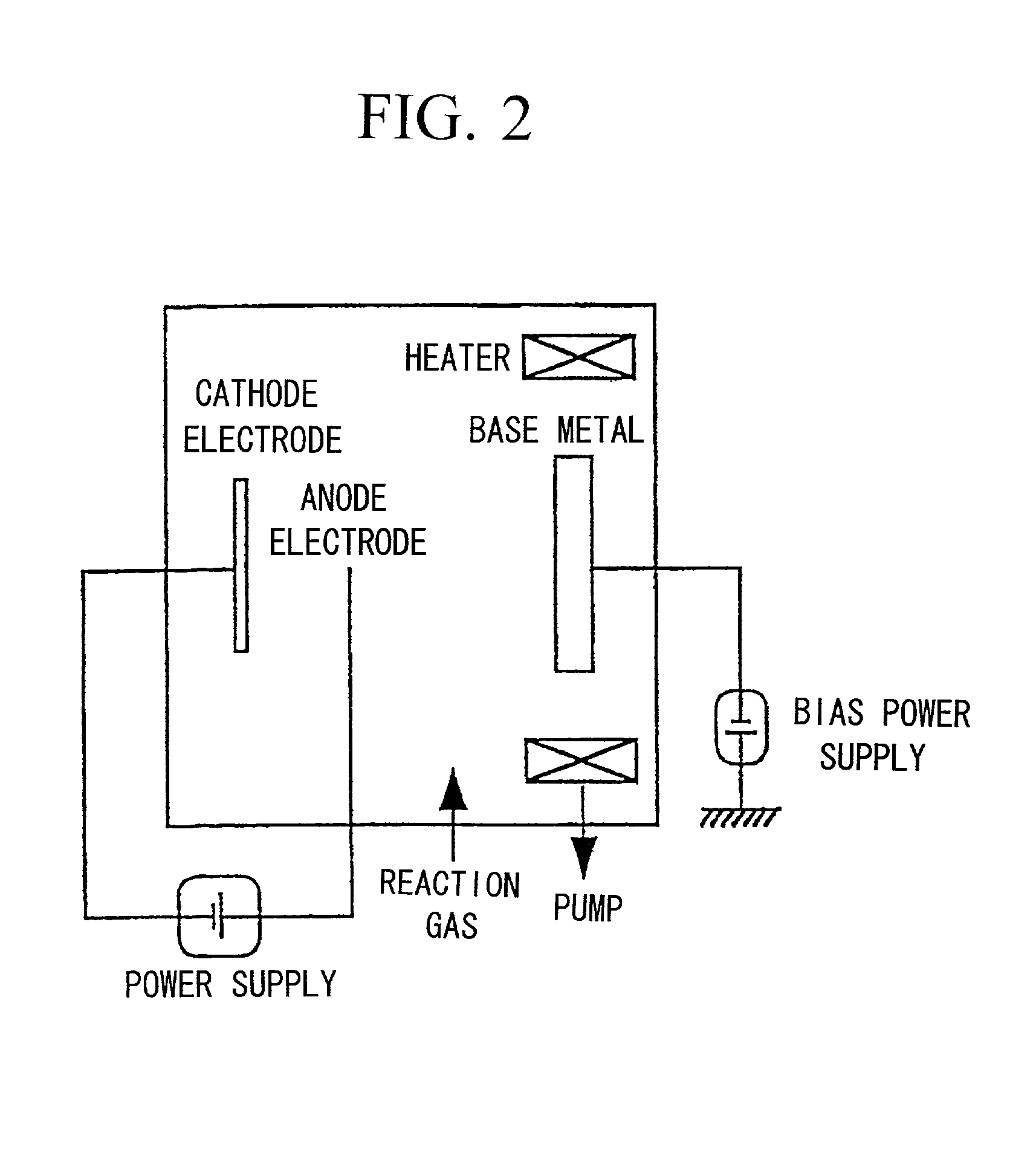
High-speed tool steel gear cutting tool and manufacturing method therefor
The invention provides a high-speed tool steel gear cutting tool in which fracture or chipping does not occur at the cutting edge, and which realizes excellent cutting performance over long periods. Moreover, a method of manufacturing a gear cutting tool including: a step for quenching a tool material comprising high-speed tool steel and which has been rough processed to a shape corresponding to a final shape of a gear cutting tool, to transform a structure of the tool material into martensite, a step for temperling the tool material after quenching to transform any residual austenite dispersingly distributed throughout a matrix of the martensite structure formed by the quenching, into martensite, and a step for finishing the tool material after tempering to a final shape, is characterized in that the tool material after quenching is subjected to sub-zero treatment involving cooling and holding at a temperature of less than -150° C.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Bainite steel plate with high elongation, high strength and low carbon and production method thereof
InactiveCN101942616AReduce the total amount addedControl carbon contentTemperature control deviceFurnace typesImpurityMaterials science
The invention discloses a bainite steel plate with high elongation, high strength and low carbon and a production method thereof. The production method can produce the steel plates with high elongation, high strength and good low-temperature toughness and welding performance, wherein the elongation is more than or equal to 20% and the yield strength is more than or equal to 1100 MPa. The steel plate comprises the following chemical compositions in percentage by mass: 0.06-0.18% of C, 0.55-1.7% of Si, 1.1-1.7% of Mn, more than or equal to 0.007% of P, more than or equal to 0.006% of S, more than or equal to 0.0040% of N, 0.02-0.06% of Nb, 0.25-0.4% of Mo, 0.01-0.02% of Ti, 0.3-0.5% of Cr, 0.3-0.8% of Ni, 0.3-0.8% of Cu, 0.025-0.05% of V, and 0.0005-0.0015% of B, optionally 0.015-0.02% of ALs, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The microstructure of the steel plate is a multiphase structure and contains bainite structure, martensite structure, a small amount of residual austenite structure and carbide with dispersedly distributed Nb, V, Ti and others elements at the same time. The method for producing the bainite steel plate with high elongation, high strength and low carbon comprises the following steps of preparation of materials, converter or smelting in electric furnace, external refining, continuous casting, reheating of slabs, controlled rolling, controlled cooling, and heat treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Thermal treatment process for 40CrNiMoA core rod and 40CrNiMoA core rod obtained through process
ActiveCN103849746ASufficient quenching and cooling intensityAvoid crackingMandrelsFurnace typesPearliteRejection rate
The invention belongs to the field of forging technology, and particularly relates to a thermal treatment process for a 40CrNiMoA core rod and the 40CrNiMoA core rod obtained through treatment. The thermal treatment process comprises three processes, namely normalizing treatment, quenching treatment and tempering treatment, and the 40CrNiMoA core rod is obtained through the three processes. The thermal treatment process adopts the method of normalizing and quenching; through normalizing and accelerating cooling after normalizing, the as-forged particle size can be improved and thick lamellar pearlite can be eliminated, so that quenching is ready; the water-air-water gap cooling method is adopted when quenching cooling is performed, initial water temperature and temperature rise in the process of cooling are strictly controlled; enough quenching severity of a wokpiece is guaranteed to obtain so that a martensitic structure is obtained, while the quenching stress is reduced to the maximum to avoid cracking of the workpiece due to too large stress; a fine and even tempered sorbite is obtained by virtue of high-temperature quenching; relatively high impact toughness is obtained while the high strength is guaranteed; the thermal treatment process has the advantages of being high in production efficiency and low in rejection rate, and improving the impact toughness while ensuring the high strength.
Owner:HENAN ZHONGYUAN SPECIAL STEEL EQUIP MFG CO LTD
Secondary-hardening gear steel
ActiveUS8801872B2Increase in surface hardness and core fracture toughnessHigh operating temperatureSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesCase hardeningToughness
A case hardened gear steel having enhanced core fracture toughness includes by weight percent about 16.3Co, 7.5Ni, 3.5Cr, 1.75Mo, 0.2W, 0.11C, 0.03Ti, and 0.02V and the balance Fe, characterized as a predominantly lath martensitic microstructure essentially free of topologically close-packed (TCP) phases and carburized to include fine M2C carbides to provide a case hardness of at least about 62 HRC and a core toughness of at least about 50 ksi√in.
Owner:QUESTEK INNOVATIONS LLC
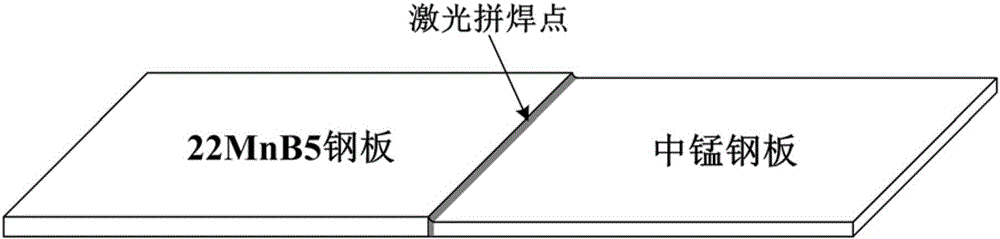
Laser tailor-welded high-strength steel warm forming preparation method
InactiveCN106350741AReduce manufacturing costLow quenching rateLaser beam welding apparatusThree-phaseQuenching
The invention discloses a laser tailor-welded high-strength steel warm forming preparation method. The laser tailor-welded high-strength steel warm forming preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: manufacturing a 22MnB5 steel plate and a medium manganese steel plate into a steel part for later use; carrying out laser tailor-welded connection treatment; carrying out heating treatment on the steel part for later use, which is subjected to laser tailor-welding; transferring the steel part onto a stamping mold to carry out stamping forming and quenching; finally obtaining a two-phase or three-phase microstructure formed by lots of ferrite, martensite or bainite in the 22MnB5 steel area of the tailor-welded steel part; and obtaining a martensite organization structure in the medium manganese steel area, thereby forming a warm forming technology of the laser tailor-welded high-strength steel, which has no need for coating treatment in advance and has gradient distributed mechanical property. The laser tailor-welded high-strength steel warm forming preparation method has the beneficial effects that the process combination of laser tailor-welding and the warm forming technology is realized; the warming forming technology is used for enabling 22MnB5 steel to form the two-phase or three-phase microstructure; the two-phase or three-phase microstructure is matched with medium manganese steel having martensitic structure in the end to obtain a custom-made warm forming part with gradient distributed performances; the technological process is simplified; and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Rolling parts and producing process thereof
Various inexpensive rolling elements for use under high interface pressure such as induction hardened gears are provided, which have improved seizure resistance at tooth flanks and a temper hardness of HRC 50 or more at 300 DEG C. To this end, a rolling element is made from a steel material which contains at least 0.5 to 1.5 wt % carbon and 0.2 to 2.0 wt % one or more alloy elements selected from V, Ti, Zr, Nb, Ta and Hf; and in which 0.4 to 4.0% by volume one or more compounds selected from the carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides of the above alloy elements and having an average particle diameter of 0.2 to 5 mum are dispersed. In such a rolling element, the soluble carbon concentration of a martensite parent phase of a rolling contact surface layer is adjusted to 0.3 to 0.8 wt %, the martensite parent phase having been subjected to induction hardening and low temperature tempering, and one or more of the above carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides are dispersed in an amount of 0.4 to 4.0% by volume within the martensite parent phase.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Carburized induction-hardened component
InactiveCN101184860AIncrease power outputImprove fatigue strengthFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencySurface layerHardness
A component is subjected to carburizing treatment and then induction-hardening treatment, and is formed from steel consisting essentially of, by mass, C: minimum 0.08% and under 0.3%; Si: maximum 2.0%; Mn: from 0.2% to 3.0%; P: maximum 0.03%; S: from 0.005% to 0.05%; Ni: maximum 1.5%; Cr: maximum 3.0%; Mo: maximum 1.0%; O: maximum 0.0025%; and N: from 0.005% to 0.03%; and further including either or both of, by mass, Al: from 0.005% to 0.05%, and Ti: from 0.005% to 0.05%; and still further including either or both of, by mass, V: maximum 0.3%, and Nb: maximum 0.3%; and a residual portion includes Fe and unavoidable impurities. The hardness of a surface layer is at least 55 HRC and the hardness of a core part is from 20 to 50 HRC. A metal structure of the core part does not include a martensite structure.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD +1
Ultra-fine grained martensite steel plate and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ultra-fine grained martensite steel plate and belongs to the technical field of alloy steel. By adopting a V / C reasonable ratio and controlled rolling, an ultra-fine grained structure is obtained under the traditional heat treatment process conditions, and the ultra-fine grained structure comprises the following chemical compositions in percentage by weight: 0.10 to 0.50 percent of C, 0.1 to 0.50 percent of Si, 0.30 to 1.50 percent of Mn, V which meet the formula shown in the specifications, less than 0.02 percent of P, less than 0.01 percent of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. On the basis, one or more alloy elements, such as 0 to 0.50 percent of Cr, 0 to 0.50 percent of Ni, 0 to 0.50 percent of Mo, 0 to 0.40 percent of Cu, 0 to 0.05 percent of Nb, 0.005 to 0.04 percent of Ti, 0.0005 to 0.003 percent of B and 0.01 to 0.06 percent of Al are added. The steel plate is subjected to controlled rolling and quenched by keeping the temperature of between 880 and 900DEG C, and the ultra-fine grained martensite structure of which the austenite grain size is less than 5 micrometers can be obtained; and moreover, the process is simple and can adapt to the current industrial production equipment and flows.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Method and die for obtaining variable-intensity hot stamping part
ActiveCN104889218AReduce cooling rateImprove mechanical propertiesShaping toolsFurnace typesHot stampingEngineering
The invention relates to the field of hot stamping forming and discloses a method and a die for obtaining a variable-intensity hot stamping part. The method for obtaining the variable-intensity hot stamping part is characterized by including steps that 1) preparing the die; 2) preparing; 3) stamping, to be specific, quickly moving a completely austenitized part blank to the die from a heating furnace; enabling a fixed insert of an upper die and a movable insert of the upper die to synchronously move downward till the die is closed, and finishing the hot stamping forming; 4) maintaining pressure and quenching, to be specific, quenching the constant-intensity region of the part by means of a die cooling system, and enabling the austenite to completely convert into a martensitic structure; enabling the movable insert of the upper die and a movable insert of a lower die corresponding to the variable-intensity region of the part to separate from the surface of the variable-intensity region of the part after maintaining a closed pressure maintaining state for 1 to 3 seconds, and forming a clearance; 5) returning and taking the part, to be specific, enabling the fixed insert of the upper die and the movable insert of the upper die to synchronously move towards the upside, opening the die, and taking out the part. The method for obtaining the variable-intensity hot stamping part can make different regions of the hot stamping part have different structures and intensities, and the multi-performance requirement of a single part is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Heat treatment method of high-chromium martensitic stainless steel
ActiveCN102719627ASufficient quenching and cooling intensityAvoid crackingMartensitic stainless steelQuenching
The invention relates to a stainless-steel heat treatment technology, in particular to a heat treatment method of high-chromium martensitic stainless steel. The heat treatment method comprises the following steps of: 1) annealing; 2) preheating; 3) quenching; and 4) tempering. The heat treatment method has the following advantages that 4Cr16Mo stainless steel heat treatment process comprises the following procedures of: (1) complete annealing, controlling the furnace entering temperature after forging, the heating speed, the heating temperature, the insulating time and the furnace cooling speed; (2) quenching heating, controlling the preheating temperature, the heating speed, the heating temperature and the insulating time; (3) quenching cooling, adopting a gap-cooling mode of air-liquid-air-liquid-air-liquid, the quenching stress is furthest reduced while ensuring that a workpiece obtains enough quenching cooling severity and obtains a martensitic structure, and the cracking of the workpiece caused by excessive stress is avoided; and (4) tempering, strictly controlling the tempering furnace-entering time, tempering heating temperature and the insulating time, the structure transformation is complete, the quenching stress is eliminated, and fine and uniform tempering sorbite is obtained.
Owner:HENAN ZHONGYUAN SPECIAL STEEL EQUIP MFG CO LTD
High-strength steel product excelling in fatigue strength and process for producing the same
A high-strength and high-fatigue-strength steel having a base metal strength of 1000 MPa or more and a rotating bending fatigue strength of 550 MPa or more is provided. The steel contains 0.3-0.8 percent by mass of C, 0.01-0.9 percent by mass of Si, 0.01-2.0 percent by mass of Mn, and Fe and unavoidable impurities as the remainder. The steel has a ferrite-cementite structure having a grain size of 7 mum or less or a ferrite-cementite-pearlite structure having a grain size of 7 mum or less. A surface metal of the steel after high-frequency induction quenching has a martensite structure having a prior austenite grain size of 12 mum or less. Alternatively, a surface metal of the steel after nitriding has a fine structure having a ferrite grain size of 10 mum or less.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Method of designing a low cost, high strength, high toughness, martensitic steel and an article made thereof
InactiveUS20090291013A1Low costImprove toughnessHeat treatment process controlMathematical modelLaboratory scale
A method for designing a low cost, high strength, high toughness martensitic steel in which a mathematical model is used to establish an optimum low cost alloying concentration that provides specified levels of strength toughness. The model also predicts critical temperatures and the amount of retained austenite. Laboratory scale ingots of the optimum alloying composition were produced comprising by % wt. of about: 0.37 of C; 1.22 of Ni; 0.68 of Mn; 0.86 of Si; 0.51 of Cu; 1.77 of Cr; and 0.24 of V; and the balance Fe and incidental impurities were melted in an open induction furnace. After homogenized annealing, hot rolling, recrystallization annealing, and further oil quenching, refrigerating, and low tempering, a tempered martensite microstructure was produced consisting of small packets of martensitic laths, fine vanadium carbide, as centers of growth of the martensitic lathes, and retained austenite. Mechanical tests showed the following results: HRC of 52; UTS of 282 ksi; YS of 226 ksi; Charpy V-notch impact toughness energy of 31 ft-lbs. Energy consumption vacuum arc remelting (VAR) and electroslag remelting (ESR) were not required for improving strength and toughness.
Owner:FEDCHUN VLADIMIR A +1
Multiphase steel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103667948ATo achieve phase transformation strengtheningEasy to achieve phase transformation strengtheningToughnessImpurity
The invention discloses a kind of high-strength multiphase steel and a preparation method thereof. The multiphase steel comprises the following elements in percentage by weight: 0.06 to 0.10% of C, 0.61 to 1.1% of Si, 0.80 to 1.80% of Mn, 0.03 to 0.049% of P, not more than 0.05% of S, 0.02 to 0.05% of Al, 0.02 to 0.04% of Ti, 0.2 to 1.2% of Cr, not more than 0.003% of O, not more than 0.005% of N, and the balance being iron and inevitable impurities. The multiphase steel comprises an ultrafine polygonal ferrite structure, a bainite structure, and a martensitic structure, wherein the polygonal ferrite structure is the main component, and a certain amount of bainite structure and martensitic structure is dispersedly distributed in the polygonal ferrite structure. The preparation method achieves the phase-transition enhancement and fine crystal enhancement of the multiphase steel, improves the welding performance of the multiphase steel, and makes the multiphase steel have a good plasticity and toughness.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Hot galvanizing high-strength steel with tension strength grade of 800MPa and reduction production method thereof
ActiveCN108823507ASave the cold rolling processGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesSteelmakingEnergy consumption
The invention relates to hot galvanizing high-strength steel with the tension strength grade of 800MPa and a reduction production method thereof. The hot galvanizing high-strength steel is prepared from the following components: 0.03 to 0.10 percent of C, 1.50 to 2.50 percent of Mn, 0.005 to 0.10 percent of Si, 0.005 to 0.05 percent of Als, 0.10 to 0.25 percent of V, smaller than or equal to 0.015percent of P, smaller than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, smaller than or equal to 0.008 percent of N and 0.0005 to 0.0050 percent of B, and a product microstructure is mainly prepared from 88 to 94percent of ferrite, 3 to 10 percent of bainite and 0 to 9 percent of martensite structure. The production method of the hot galvanizing high-strength steel comprises the following steps: steelmaking,refining, continuous casting and hot rolling, acid pickling, annealing and galvanizing, and finishing. A cold rolling procedure of a traditional production technological process is omitted, the production process is remarkably shortened, the energy consumption and the CO2 emission during the production process are greatly reduced, and the production efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
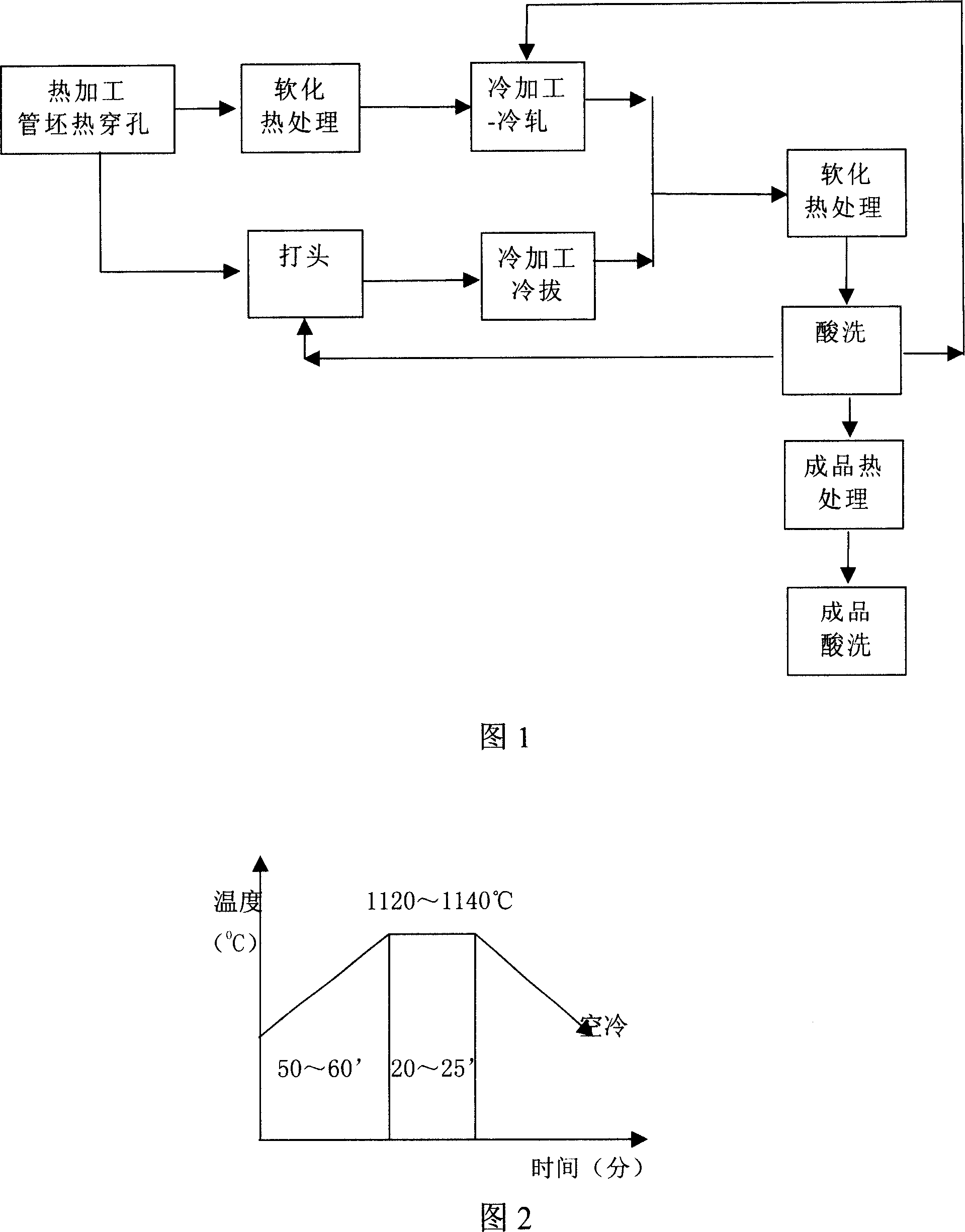
Manufacturing method of 17-4PH steel pipe
InactiveCN101007384ASolve the unclear picklingSolve the problem of overacidFurnace typesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsAcid washingHeating temperature
17-4PH steel pipe manufacturing method includes the following steps: a. thermal processing and pipe blank heat perforating: heating temperature is 1090 ~ 1150 degree C and insulation time is 15 ~ 35 minutes; b. softening heat treatment: temperature is 650 ~ 700 degree C, insulation time is 4~5.5 hours; c. cold-working: cold rolling; d. softening heat treatment: temperature is 650 ~ 700 degree C, insulation time is 4 ~ 5.5 hours; e. acid-washing; f. repeating steps c ~ e cycles rolling until finished product size; g . finished product heat treatment: solid solution treatment 1020 ~ 1050 degree C +15 ~30 minutes, precipitation hardening treatment 450-630DEG C+3.5-4.5 hours, the finished product forms precipitation hardening martensitic structure with high strength and excellent corrosion resistance; h. finished product acid-washing. The invention replaces the original pipe elements art through boring and turning the pipe elements to reaching the required diameter and wall thickness with the technology of cold-working to getting the required diameter and wall thickness after heat perforating, it shortens production cycles, reduces production costs, improves product metal yield rate and increases economic efficiency.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Steel bar for steering rack, method for producing the same, and steering rack using the same
InactiveCN1791696AImprove wear resistanceImprove impact resistanceMechanical steering gearsFurnace typesMetallurgySteel bar
The present invention provides a steel bar for steering rack, which contains C: 0.50-0.60% by mass, Si: 0.05-0.5% by mass, Mn: 0.2-1.5% by mass, B: 0.0005-0.003% by mass, Ti: 0.005-0.05% by mass % by mass, Al: 0.0005 to 0.1% by mass, and N: 0.002 to 0.02% by mass. Assuming that the diameter of the steel bar is D, the quenched and tempered structure of the portion of the steel bar at a depth of D / 4 from the surface satisfies the conditions of I), II) and III) below. I) The total area percentage of the tempered bainite structure and the tempered martensite structure is 30 to 100%. II) The area percentage of the regenerated pearlite structure is 0-50%. III) The total area percentage of tempered bainite structure, tempered martensite structure and regenerated pearlite structure is 50-100%.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
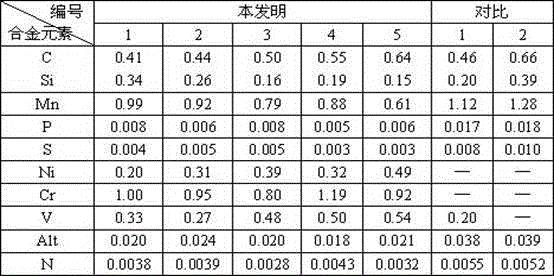
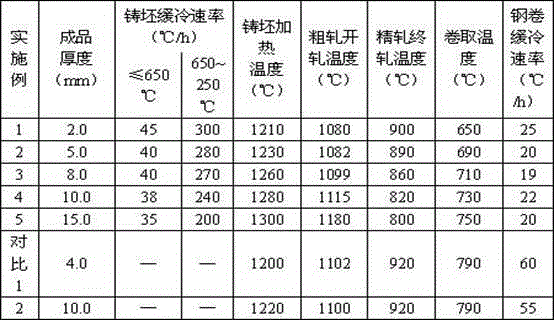
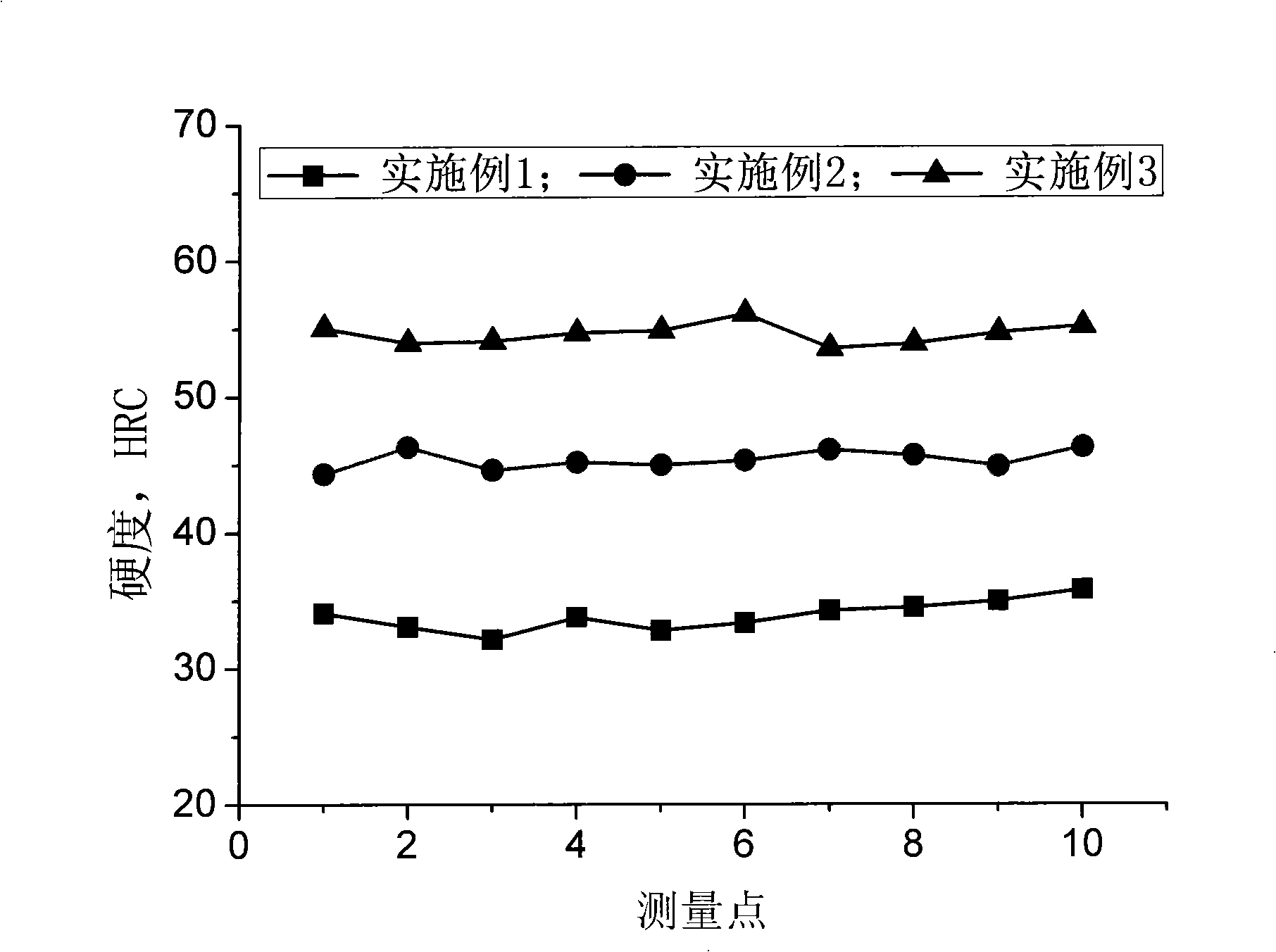
Automotive cold-rolled diaphragm spring steel and production method thereof
The invention relates to automotive cold-rolled diaphragm spring steel and a production method thereof. The automotive cold-rolled diaphragm spring steel comprises the following components by weight percentage: C of 0.40-0.65, Si of 0.15-0.35, Mn of 0.60-1.00, P of less than or equal to 0.010. S of less than or equal to 0.007, Alt of less than or equal to 0.040, Ni of 0.20-0.50, Cr of 0.80-1.20, V of 0.27-0.55 and N of less than or equal to 0.005, and a tempered sorbite body is adopted as a control metallographic structure. The process comprises the steps of: desulphurization, smelting, refining, vacuum processing, continuous casting into a billet, thermal insulation in segments according to the temperature, heating of the cast billet, rolling, coiling, slow cooling, cutting, first annealing, first cold rolling, second annealing, second cold rolling, formation, quenching, tempering and preparation for use. The automotive cold-rolled diaphragm spring steel has excellent comprehensive mechanical properties. Difficulties in cutting and cold rolling can be reduced due to annealing, a tempered martensite structure is obtained due to heat treatment of quenching and tempering, and sufficient strength and wear resistance of the steel can be ensured due to composite reinforcing effects of micro-alloys such as Cr, Ni and V in the steel.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Cast iron series mould material thermal treatment method capable of acquiring controllable and uniform rigidity
The invention relates to a heat treatment method which can obtain the cast iron die material, the hardness of which is controllable and uniform. The heat treatment method has the steps as follows: in the first step, the cast iron die material is put in a vacuum firing furnace for prewarming until the temperature reach 900 to 950 DEG C, and is air-cooled after being taken out of the vacuum firing furnace after austenization; in the second step, a workpiece is put in the vacuum firing furnace, is heated until the temperature reaches 600 to 650 DEG C, is processed through heat preservation, is again heated until the temperature reaches 890 to 900 DEG C, then is taken out of the vacuum firing furnace after being processed through heat preservation, and is quenched in an oil cooling manner, so as to obtain a martensite structure; in the third step, the workpiece is put in the martensite structure for three temperature variations and tempers; wherein, in the first temper, the temperature ranges from 230 to 600 DEG C, and the heat preservation and the oil cooling are executed; in the second temper, the temperature ranges from 230 to 600 DEG C, and the heat preservation and the oil cooling are executed; in the third second temper, the temperature ranges from 250 to 600 DEG C, and the heat preservation and the oil cooling are executed. By the heat treatment method, the hardness of the obtained cast iron die can be controlled between 33HRC and 55HRC in a deterministic manner, the hardness fluctuation can be controlled within 10 percent, and the effect that the whole die is hardened is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Air cooling hardened spring steel with high obdurability, low-medium-carbon and microalloy and forming and heat treatment process thereof
ActiveCN105112774AAvoid the many disadvantages of quenchingSave energyChemical compositionSpring steel
The invention discloses an air cooling hardened spring steel with high obdurability, low-medium-carbon and microalloy and a forming and heat treatment process thereof. Existing spring steel is high in cost due to components. The air cooling hardened spring steel with the high obdurability, low-medium-carbon and the microalloy comprises, by weight, 0.15%-0.50% of C, 0.30%-2.00% of Si, 0.60%-2.50% of Mn, 0-0.020% of S, 0-0.025% of P, 0.0005% ~ 0.0035% of B, and the balance Fe. After the steel is heated to 900-1500 DEG C and the temperature is kept, metallographic structure containing the major bainite and martensite, a small amount of retained austenite, and no other non-martensitic structures (free ferrite, pearlite and upper bainite) can be obtained by adopting controlled cooling. Then properties can be further improved through low temperature tempering treatment; material mechanical property Rm>=1350 MPa; yield strength Rp0.2>=1050MPa; percentage elongation after fracture A>=10%; section shrinkage Z>=35%. The air cooling hardened spring steel with the high obdurability, the low-medium-carbon and the microalloy is adopted, so that the manufacturing process of springs is simplified, energy is saved, and cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEILI HIGH TECH
Martensite-ferrite double-phase wear-resisting steel plate and preparing method thereof
The invention provides a martensite-ferrite double-phase wear-resisting steel plate and a preparing method thereof. The martensite-ferrite double-phase wear-resisting steel plate comprises a martensite and ferrite double-phase structure, the volume fraction of the martensite structure is larger than 90%, the hardness of the martensite structure ranges from 480HB to 560HB, and the martensite structure is obtained by preparing C, Si, Mn, P, S, Nb, V, Ti, Mo, Ni, Cr, Al, B, N, Fe and other elements of the specific amount. The martensite-ferrite double-phase wear-resisting steel plate has the higher hardness and meanwhile has the good low-temperature toughness and wear-resisting performance; and manufacturing of mechanical parts under the atrocious environment particularly the condition with the extremely low temperature is facilitated. The preparing method of the martensite-ferrite double-phase wear-resisting steel plate is simple in process, the martensite and ferrite double-phase structure can be obtained, the hardness, the low-temperature toughness and the wear-resisting performance of the martensite and ferrite double-phase structure can be comprehensively improved, and large-scale production is facilitated.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com