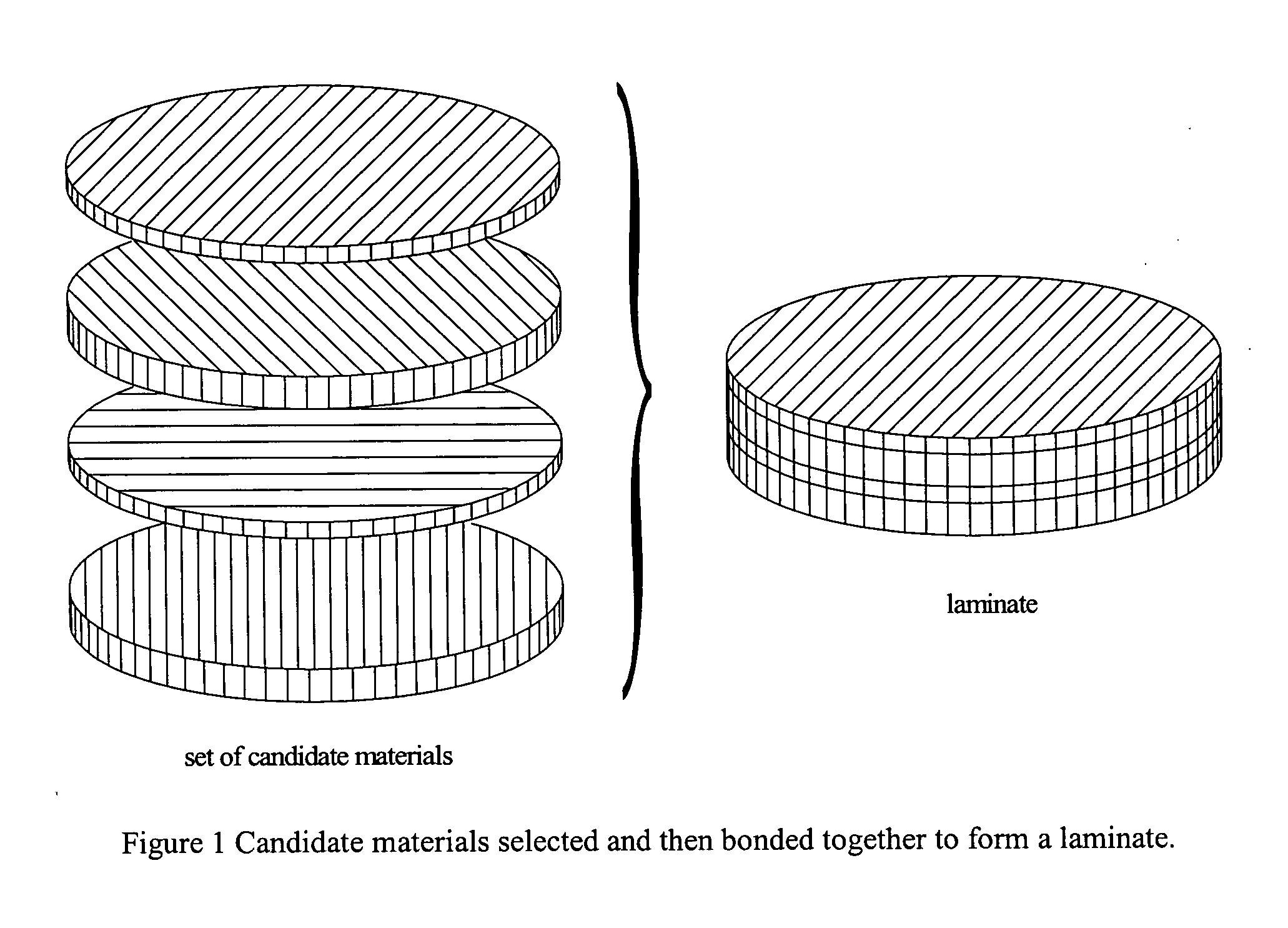
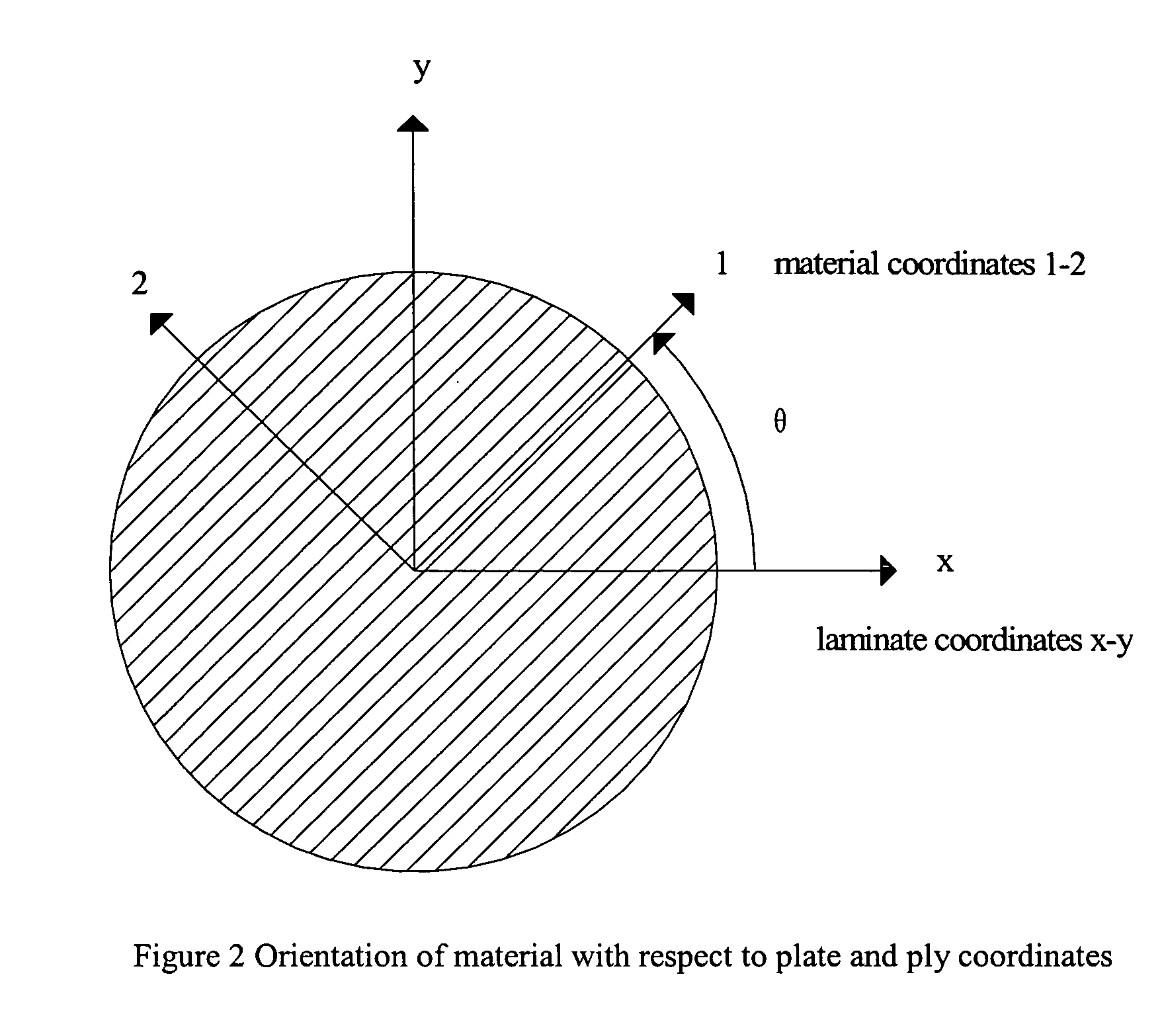
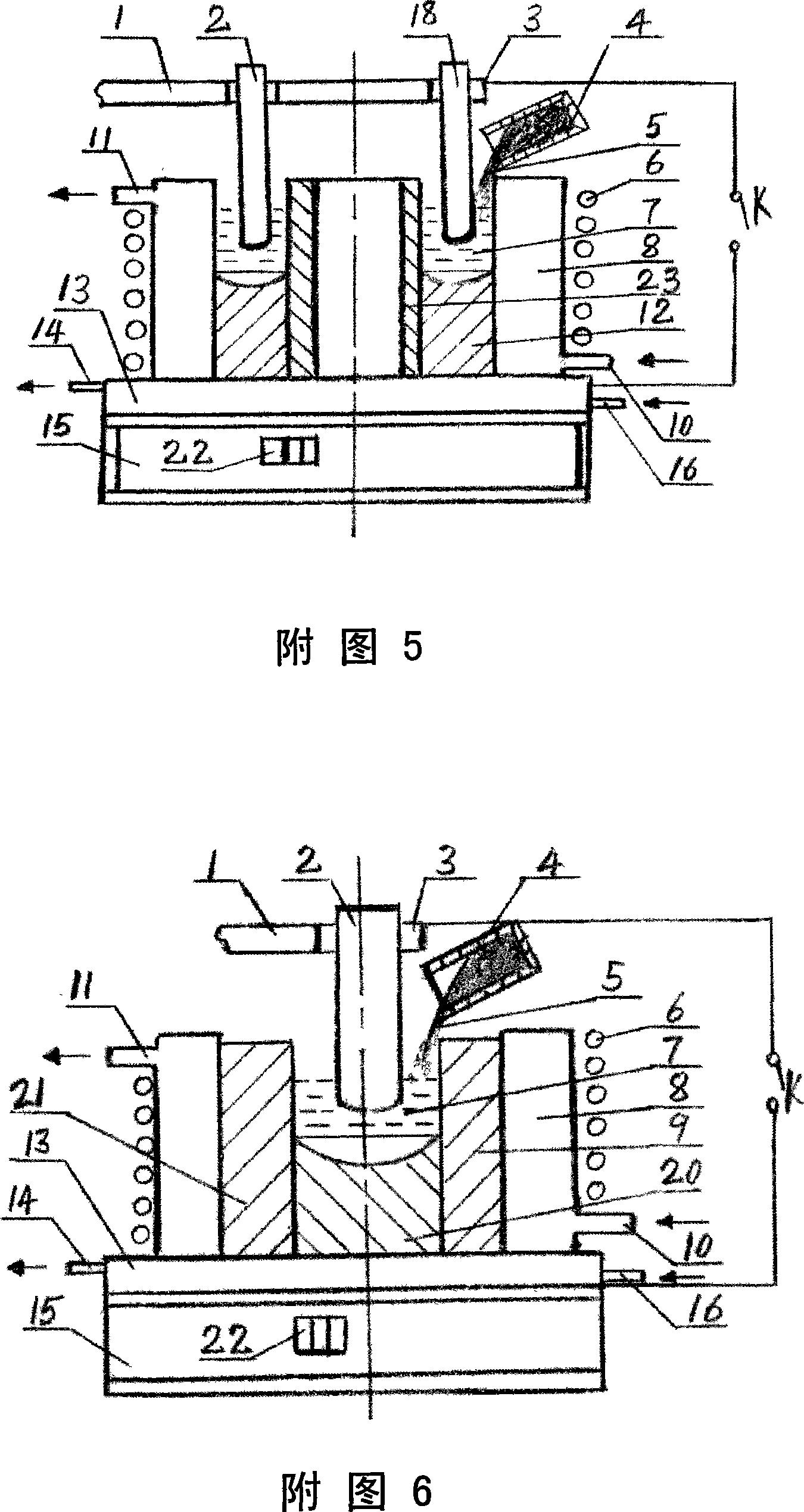
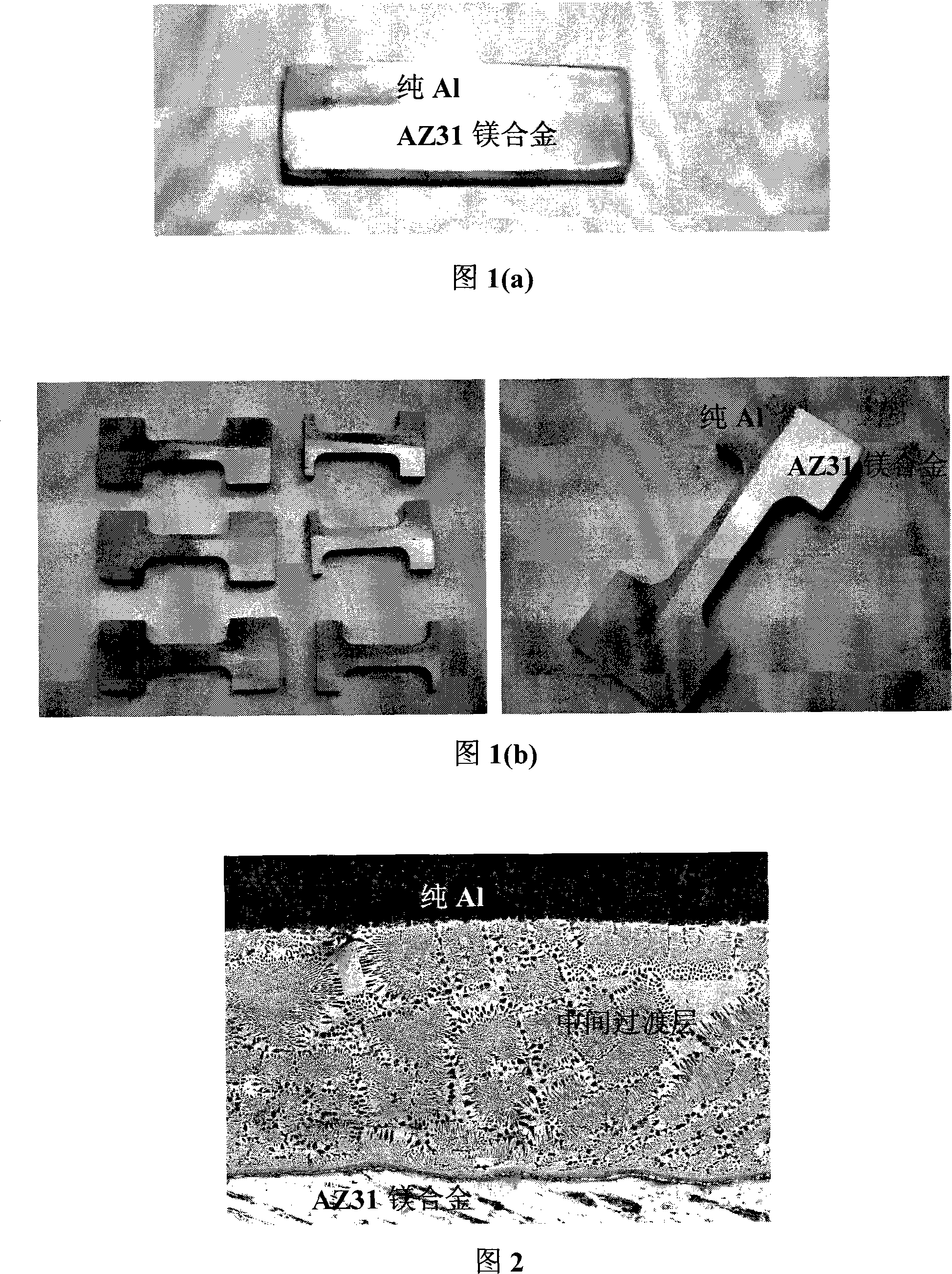
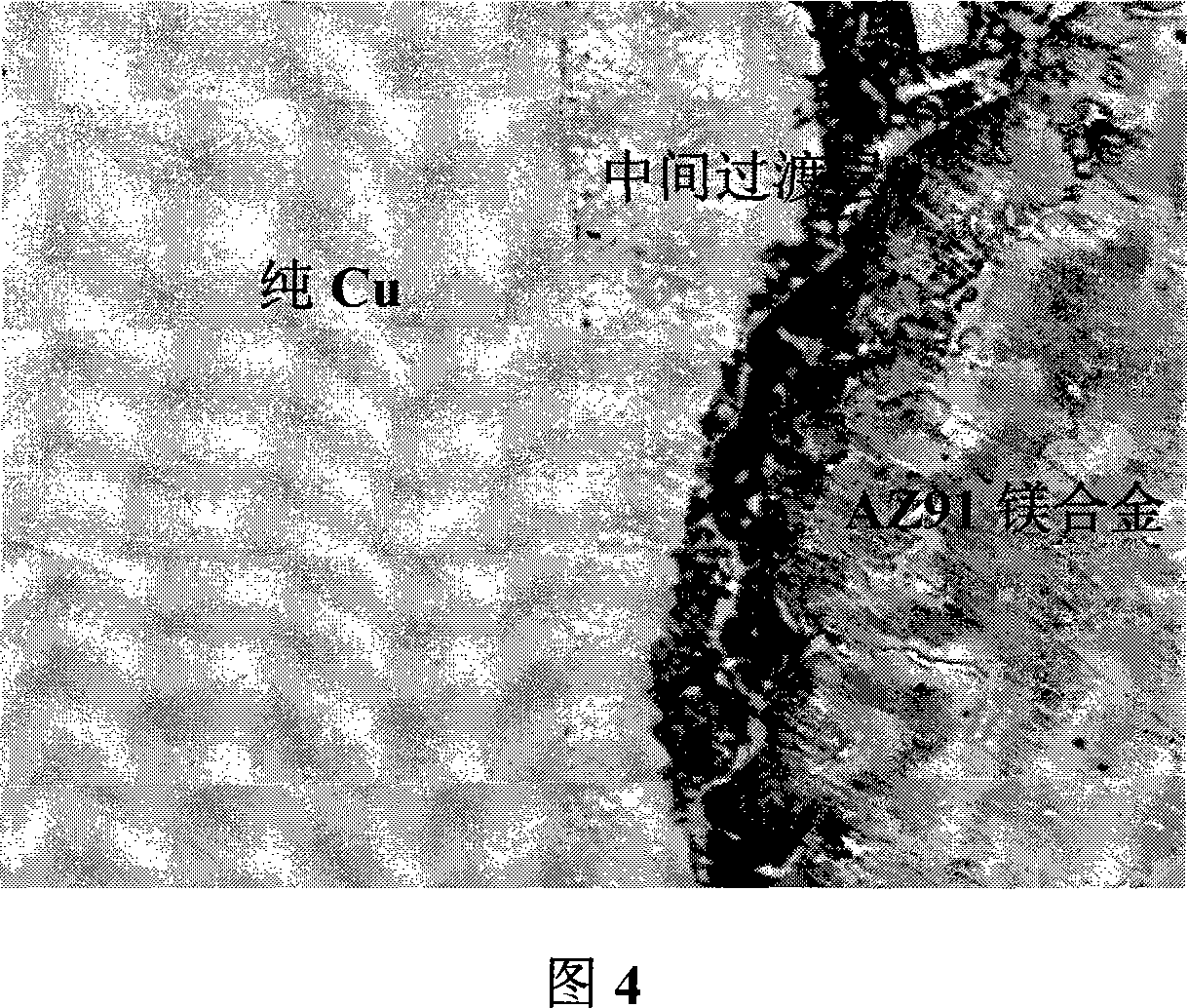
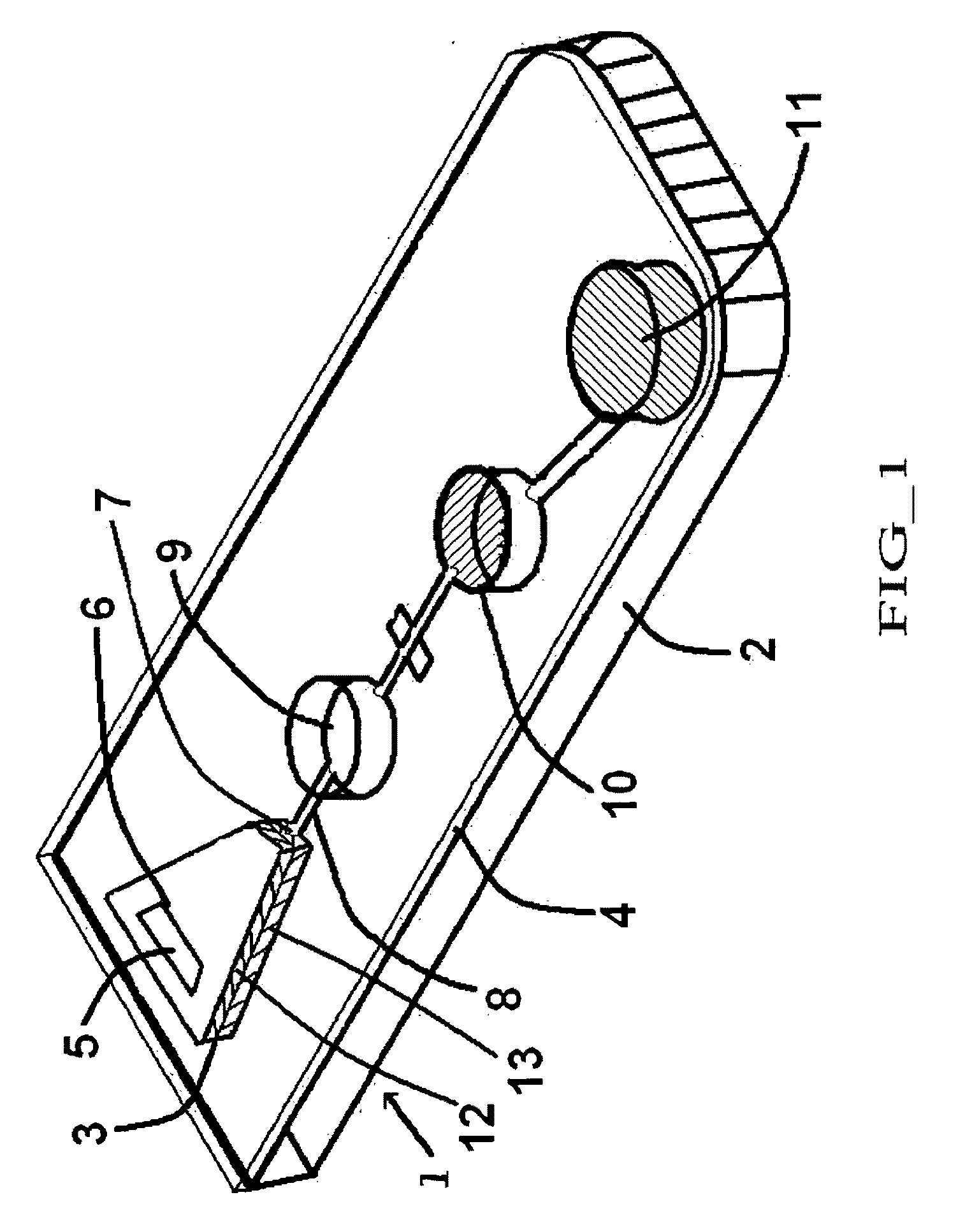
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
910 results about "Laminated composites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
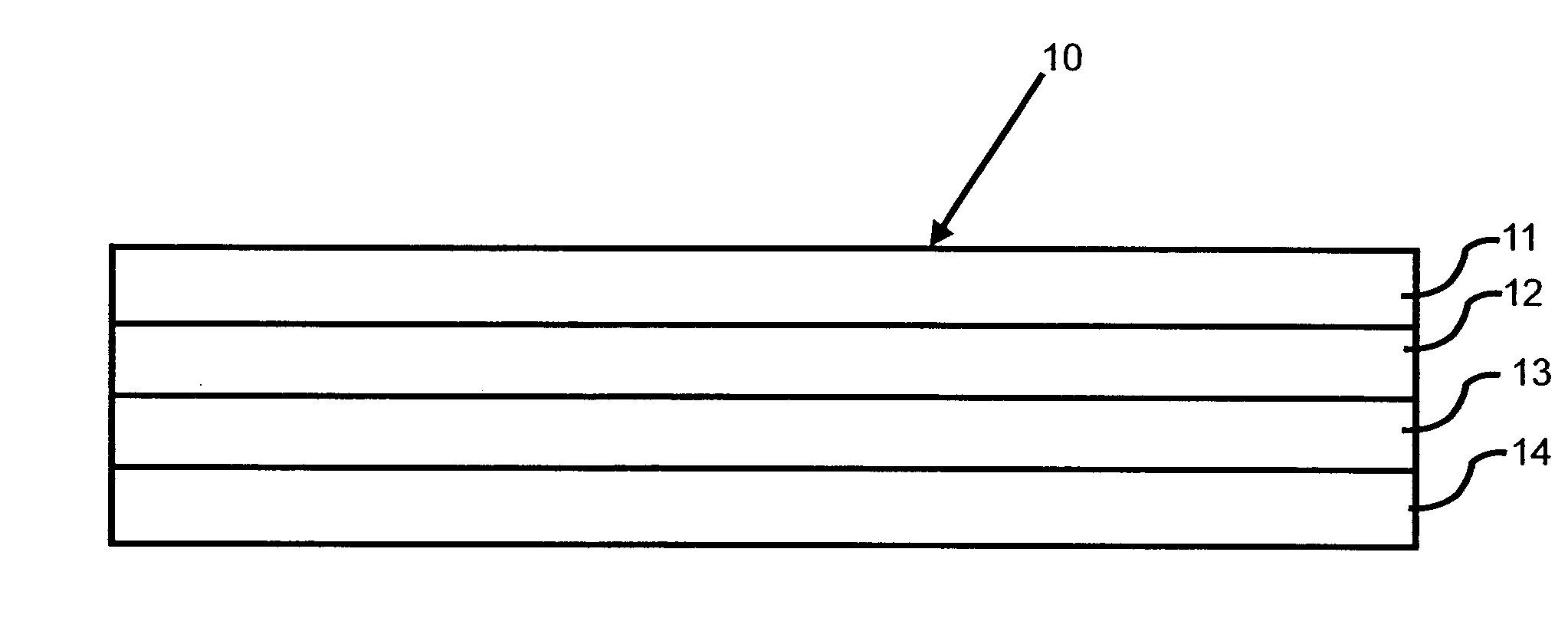
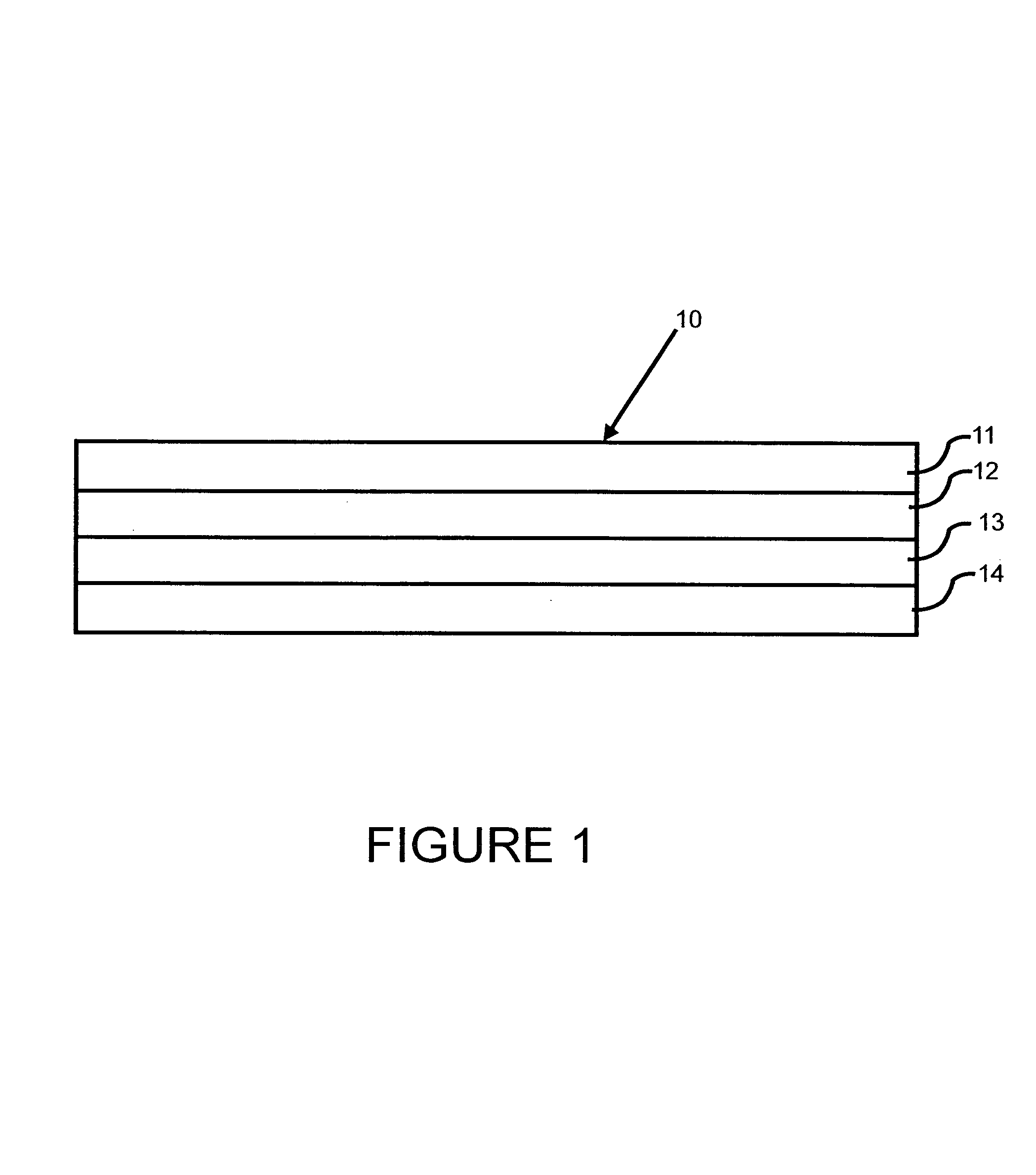
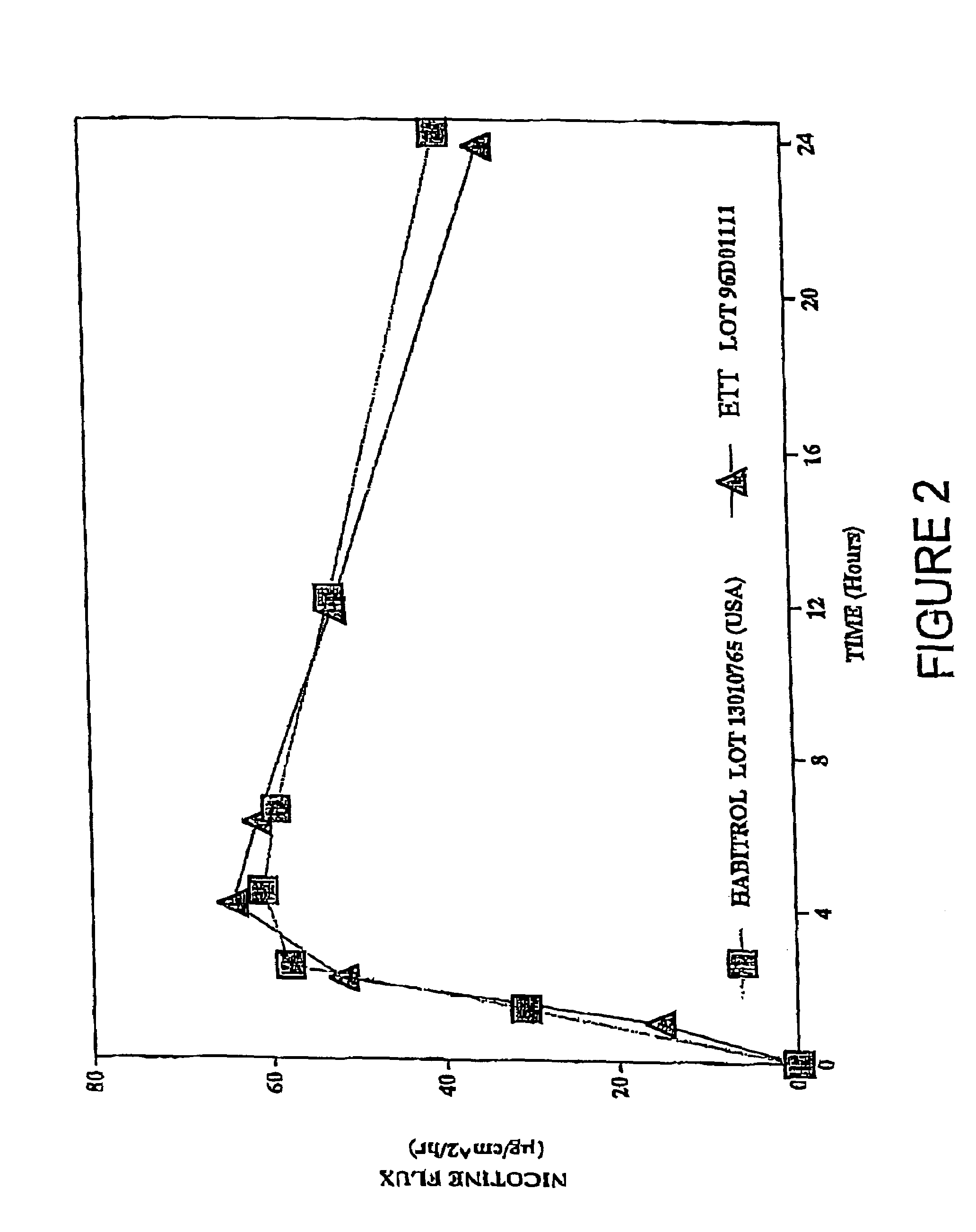
Transdermal patch for delivering volatile liquid drugs
A transdermal patch for administering a volatile liquid drug, such as nicotine, transdermally to a patient comprising a four-layer laminated composite of: a top drug impermeable backing layer; a pressure sensitive silicone adhesive layer containing the drug; a pressure sensitive acrylic adhesive layer also containing the drug; and a removable siliconized release liner layer. Also disclosed is a method for treating a person for nicotine dependence and particularly for treating a woman for nicotine dependence.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD +1
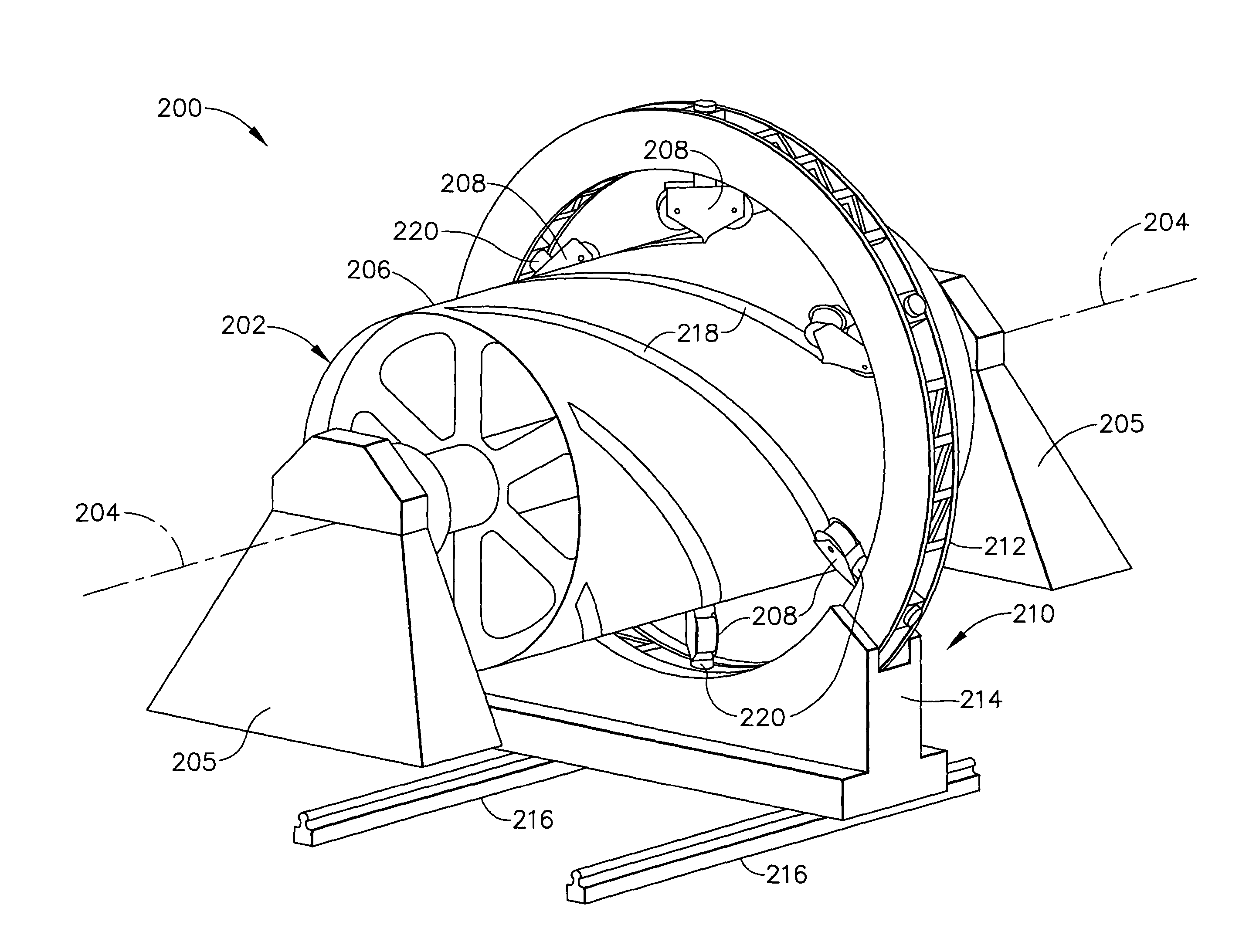
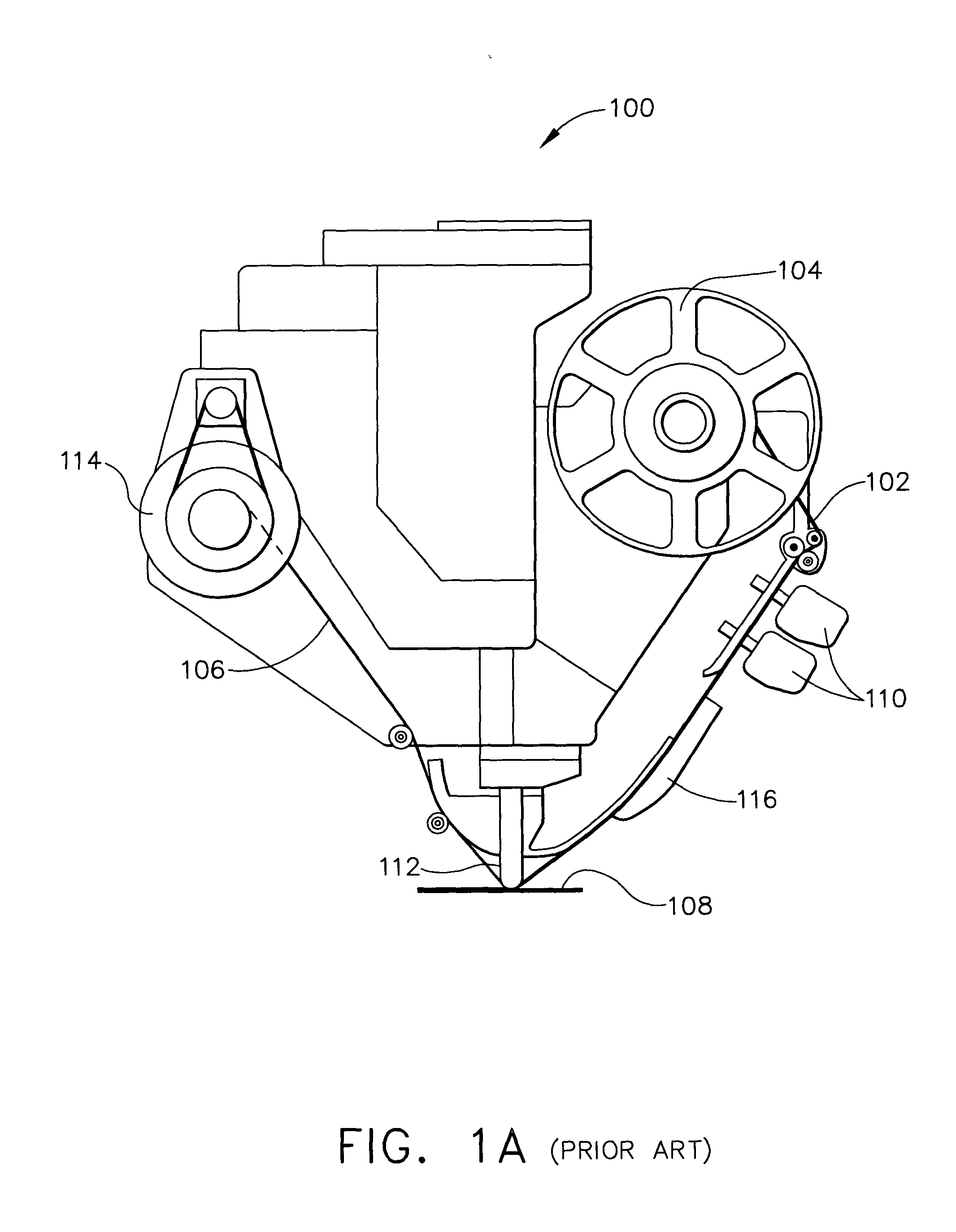
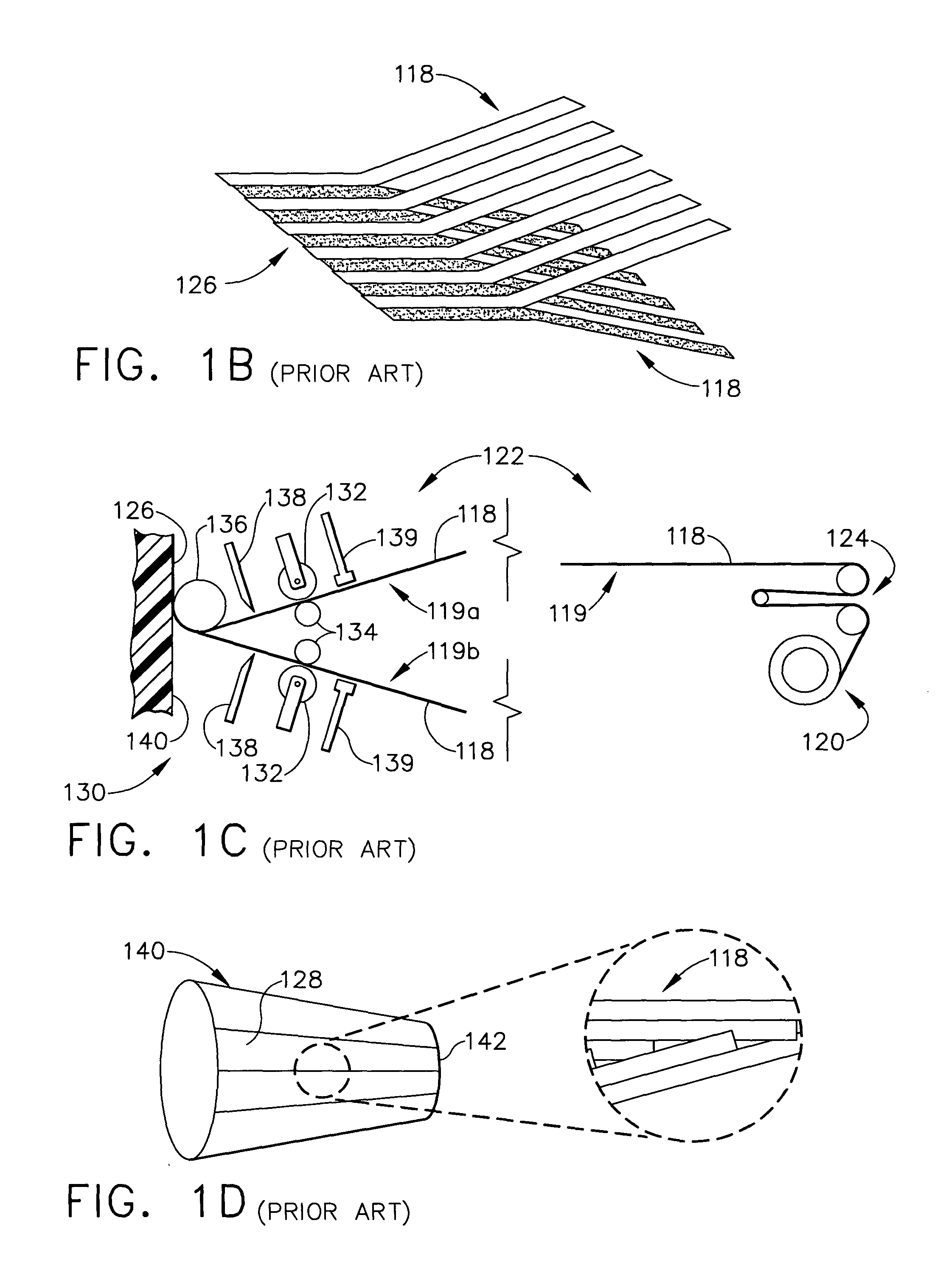
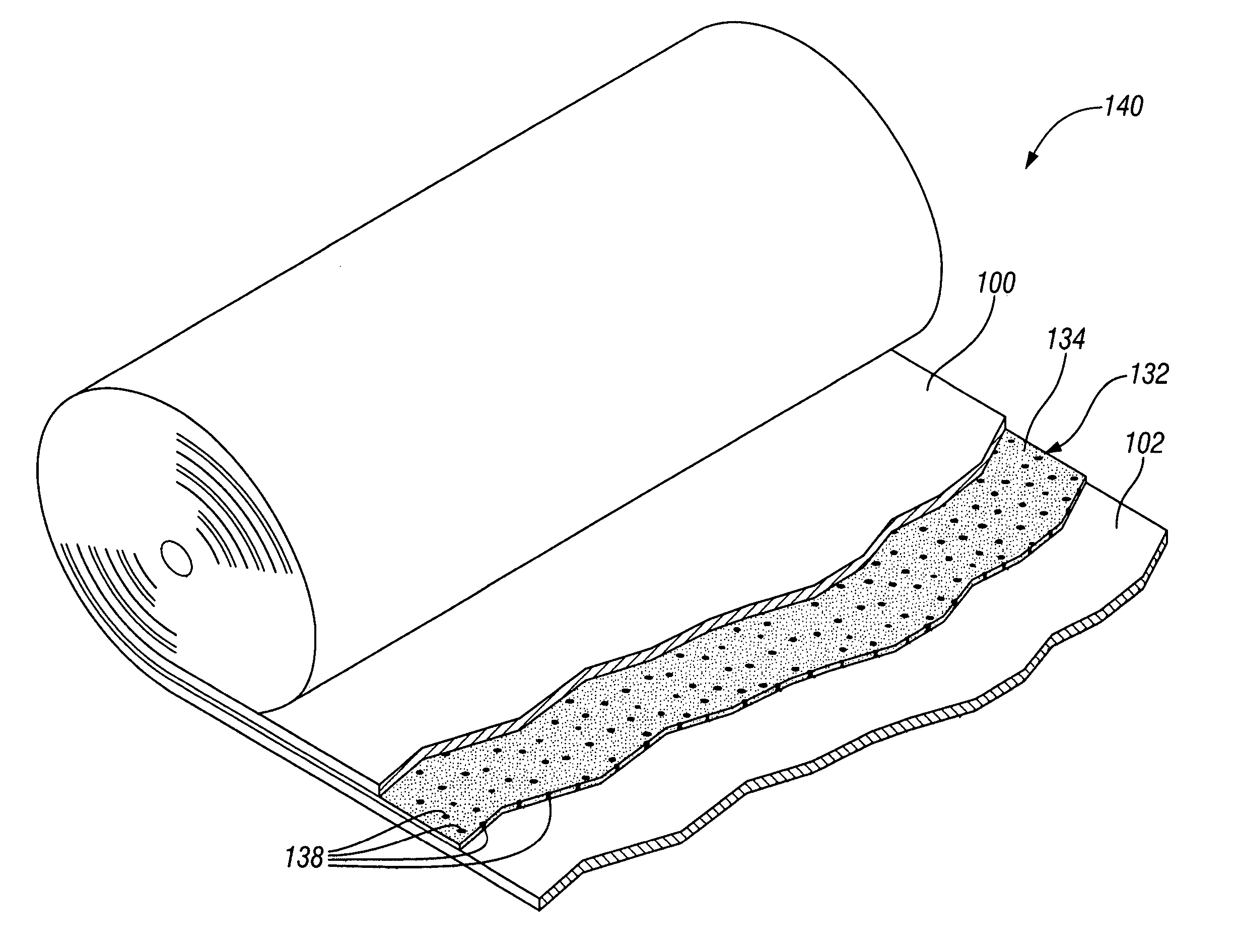
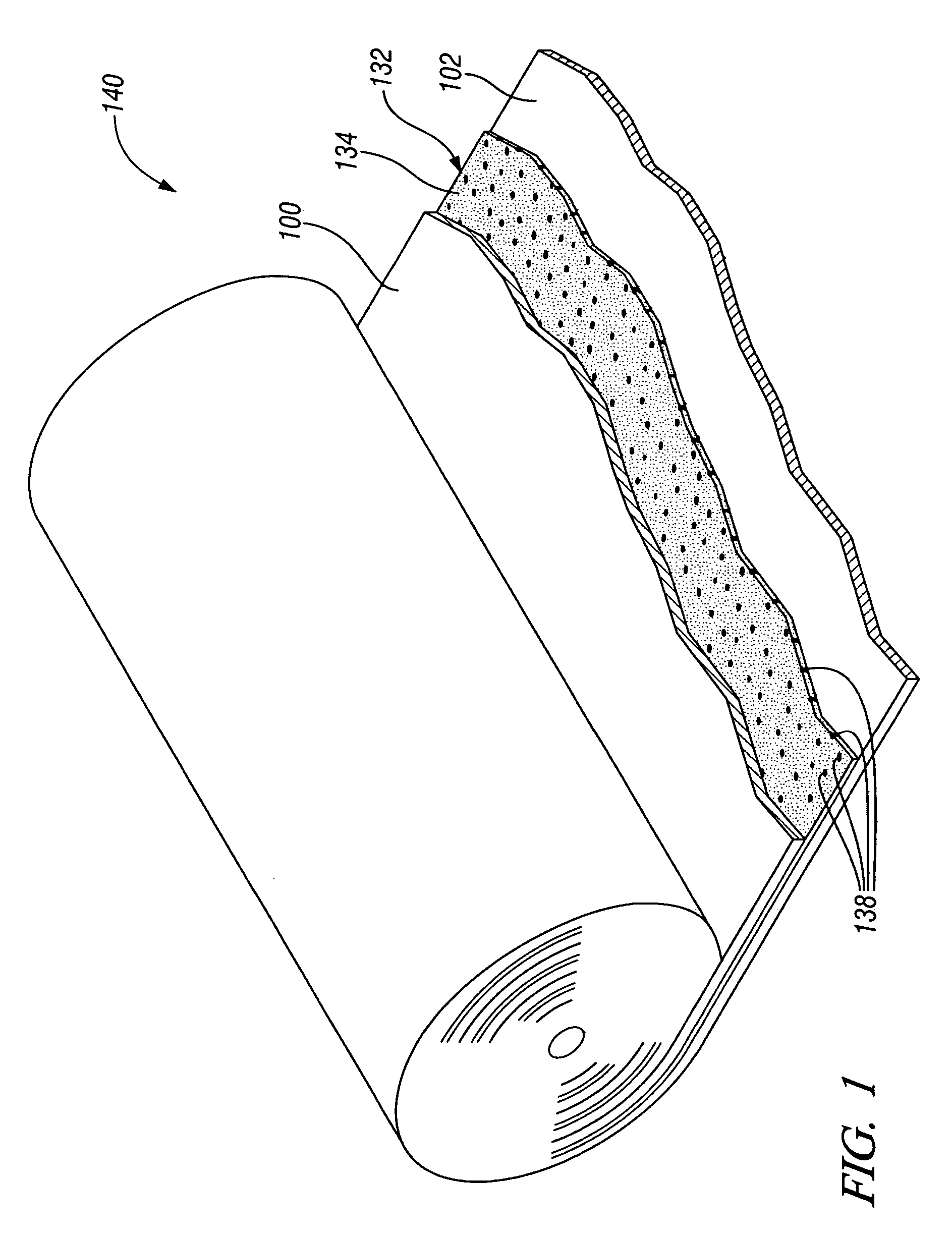
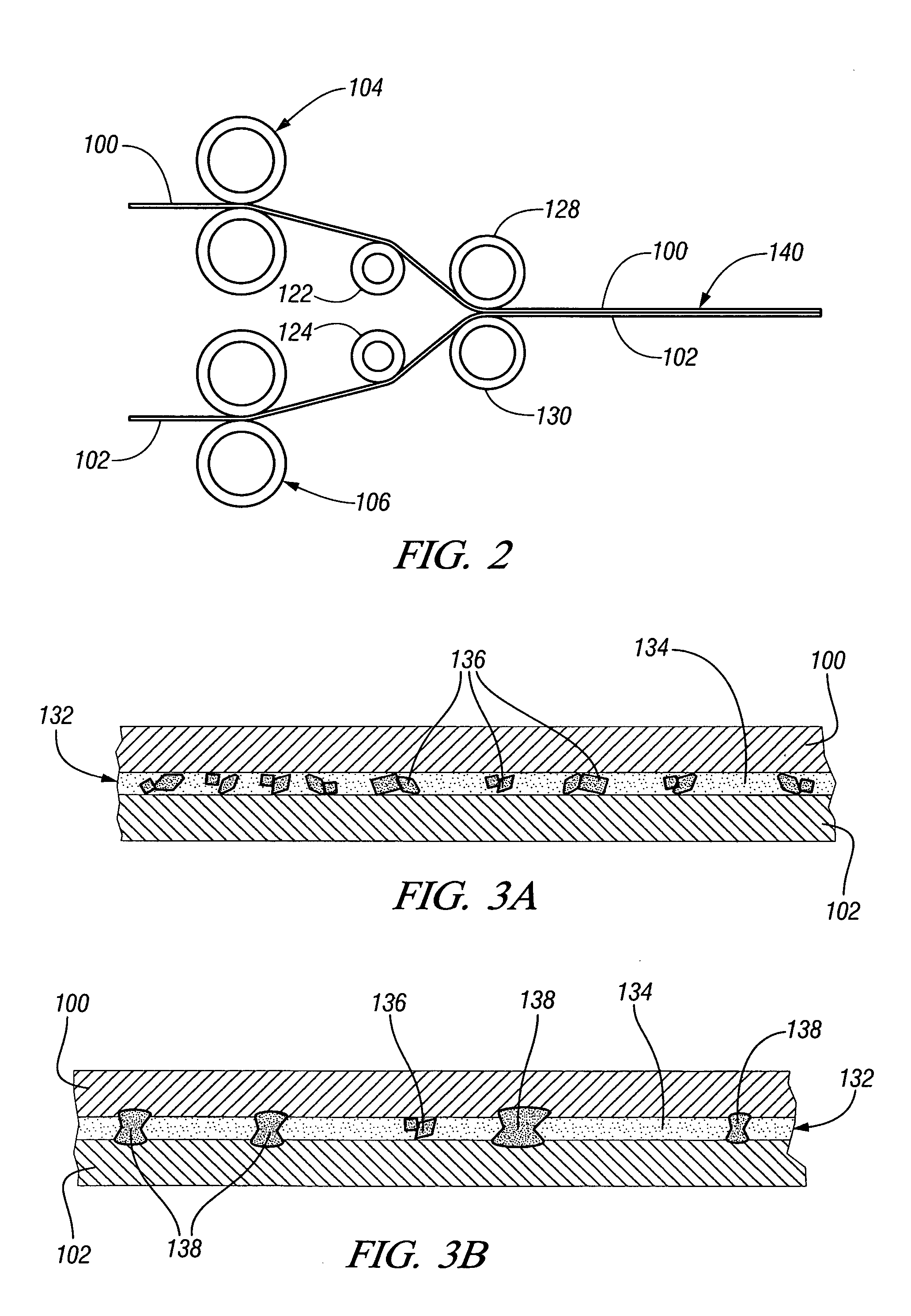
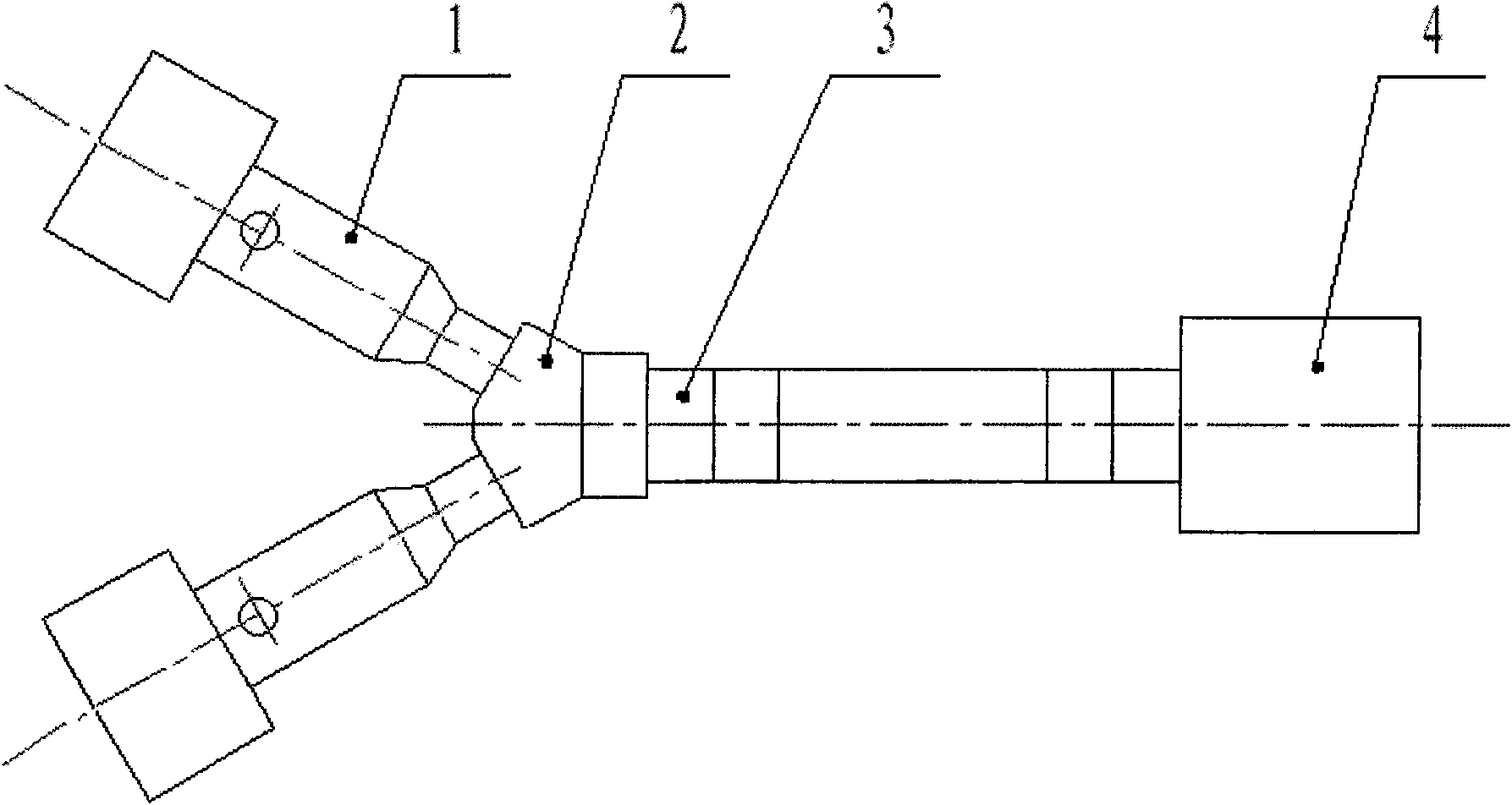
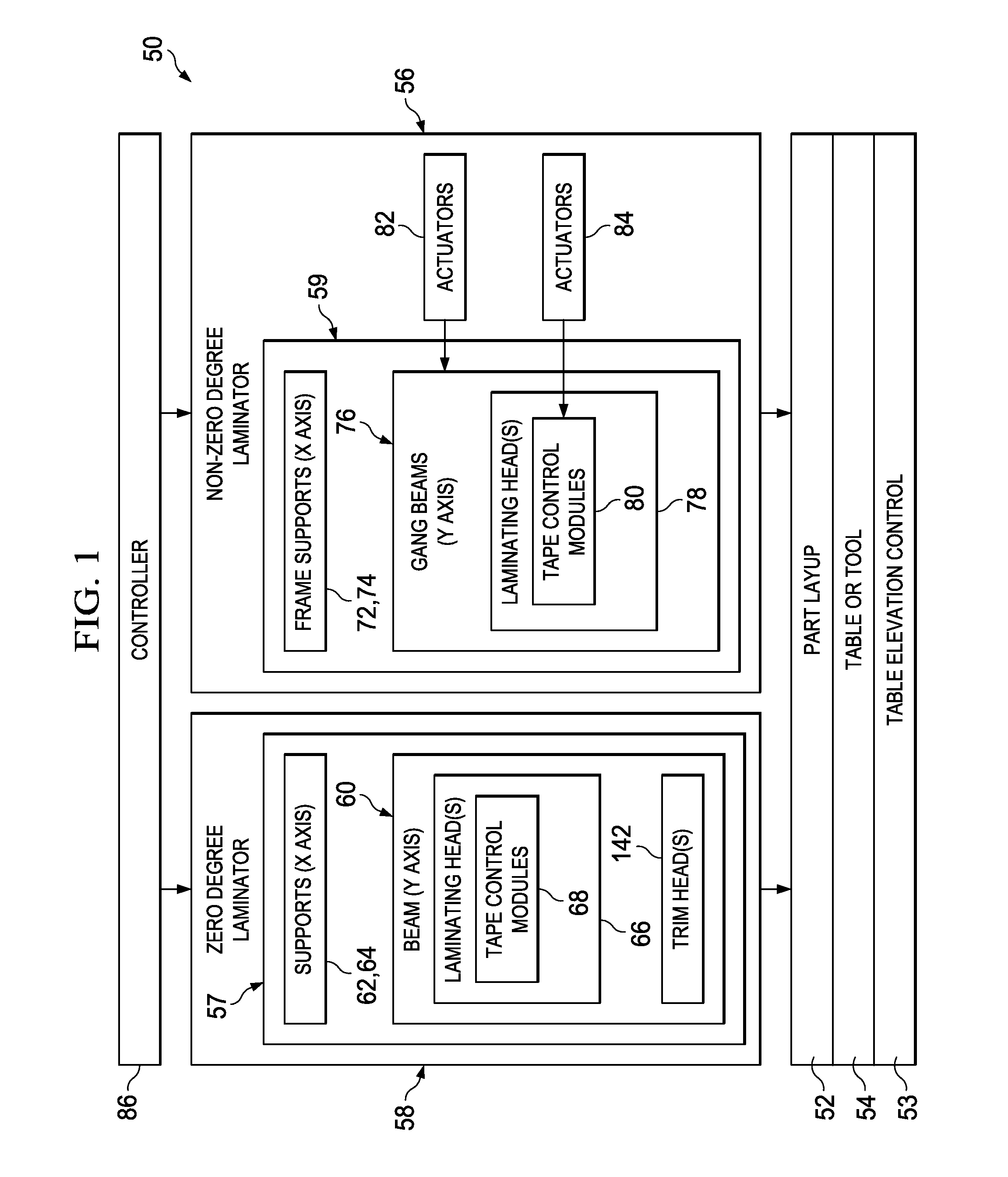
Multiple head automated composite laminating machine for the fabrication of large barrel section components
An aircraft part manufacturing device for automated composite lamination on a mandrel surface of a tool having a rotational axis includes a mechanical supporting structure that supports multiple material delivery heads. The tool is moveable and rotatable relative to the mechanical supporting structure. The mechanical supporting structure provides for axial translation of the material delivery heads relative to the mandrel surface while the mandrel surface is rotated for laying down courses of composite material over the entire mandrel surface of the tool. The position and movement of each of the plurality of material delivery heads is individually adjustable. Arm mechanisms provide motion of each material delivery head in a direction normal to the mandrel surface; rotation about an axis normal to the mandrel surface; circumferential position adjustment in a hoop direction relative to the mandrel surface; and axial position adjustment relative to the other material delivery heads.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
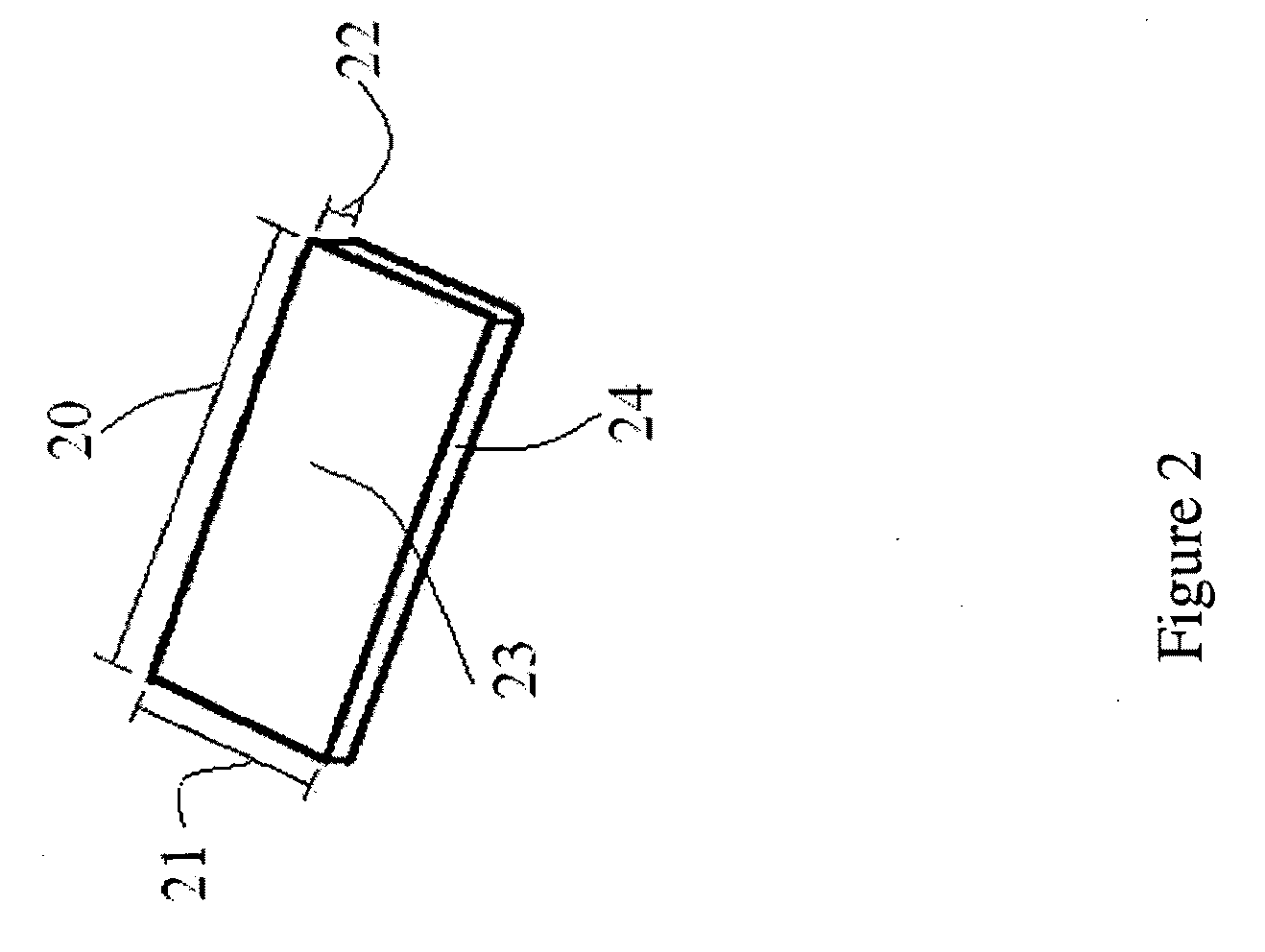
Laminated composite building component
InactiveUS6205728B1Maximized encapsulationHigh strengthBuilding roofsConstruction materialAdhesiveEngineering
A laminated composite building component, capable of sustained axial stress as a primary support structure and enclosure of a building structure, comprising a lamination of rigid and resilient material, said rigid material formed of sheets with continuous corrugations parallel to the supporting axis and which have opposite faces being bonded to and encapsulated by said resilient material, said resilient material being a cellular foam matrix, an adhesive or fusion that bonds the rigid and resilient material together in either a static or continuous laminating process, said resilient material forming two outer surfaces spaced from the rigid material, said rigid material having opposite lateral edges being exposed from said resilient material, said lateral edges of the rigid material having return flanges for interlocking said laminated composite building component with adjacent building component, and said building components capable of being supplied and distributed in generic lengths and custom field-cut like lumber.
Owner:RYN SUTELAN
Pressure lamination method for forming composite ePTFE/textile and ePTFE/stent/textile prostheses
A method of forming a composite textile and ePTFE implantable device includes the steps of (a) providing an ePTFE layer having opposed surfaces comprising a microporous structure of nodes interconnected by fibrils; (b) providing a textile layer having opposed surfaces; (c) applying a coating of an elastomeric bonding agent to one of the opposed surfaces of the ePTFE layer or the textile layer; (d) providing a hollow member having an open end and an opposed closed end defining a fluid passageway therebetween and having a wall portion with at least one hole extending therethrough, the hole being in fluid communication with the fluid passageway; (e) concentrically placing the ePTFE layer and the textile layer onto the hollow member and over the at least one hole of the hollow member to provide an interior composite layer and an exterior composite layer, thereby defining a composite assembly, wherein the interior composite layer is one of the ePTFE layer or the textile layer and the exterior composite layer is the other of the ePTFE layer or the textile layer; (f) placing the hollow member with the composite assembly within a pressure chamber; (g) applying a pressure differential so that the pressure within the chamber is greater than a pressure within the fluid passageway of the hollow member; and (h) applying heat to the bonding agent to adhesively bond the textile layer and the ePTFE layer to provide a laminated composite assembly.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
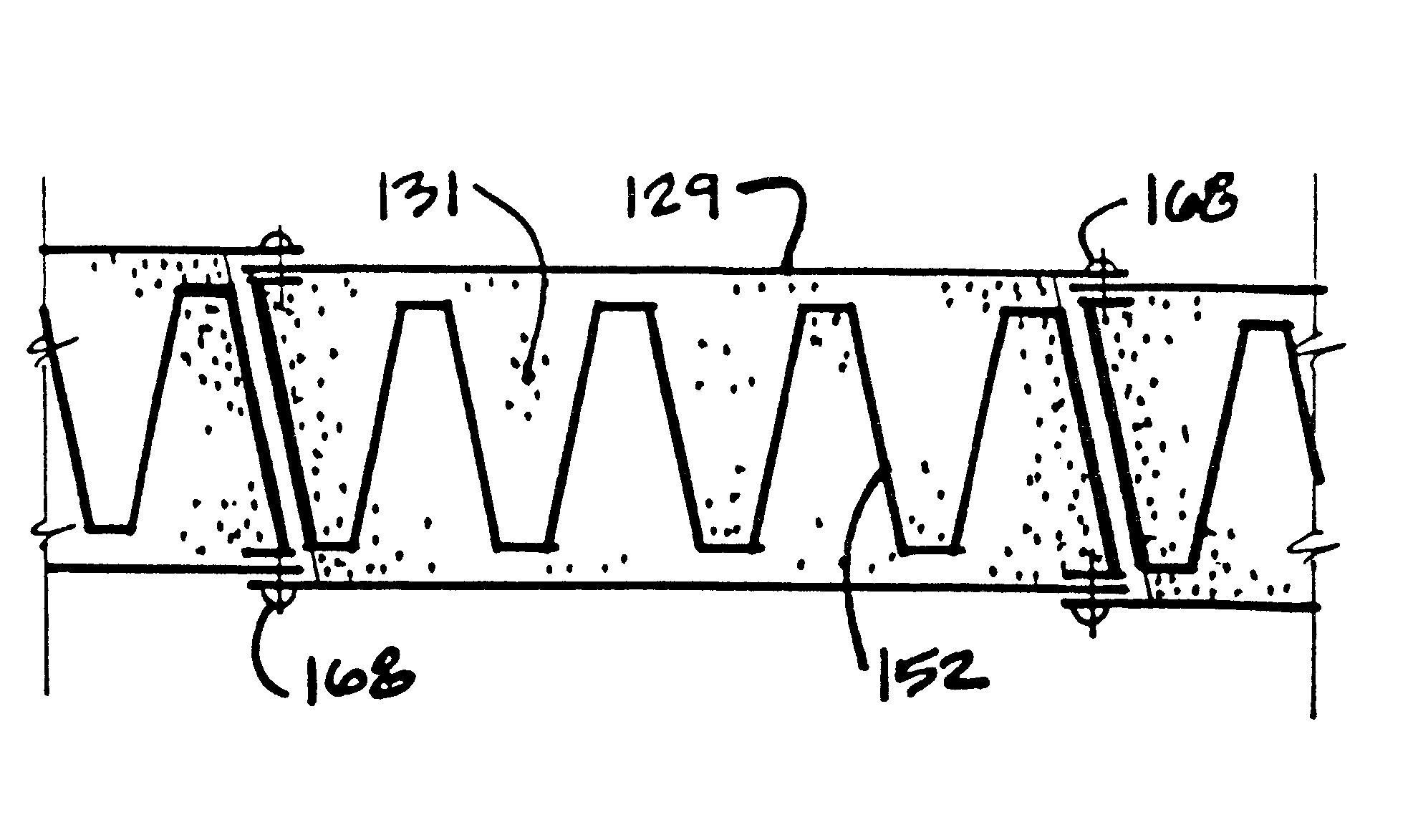
Multi-layered shingle and method of making same
InactiveUS6920730B2Good lookingSimple and efficient and economicalRoof covering using tiles/slatesLamination ancillary operationsEngineeringLaminated composites
A multi-layered shingle adapted to be positioned with other similar shingles in an overlapping arrangement on a roof to yield a simulated wooden shake roof covering comprising a headlap portion and a butt portion. The butt portion comprises a series of multi-layered tabs. All the tabs have the same number of layers and each multi-layered tab (a) is separated from the next adjacent multi-layered tab or tabs by a space or spaces, respectively, and (b) comprises an uppermost layer and at least two layers underlying the uppermost layer. Each underlying layer is laminated to the layer above it to form a multi-layered laminated composite. The laminated composite is integral with the headlap portion and the top surface of the uppermost layer of each tab is coplanar with the top surface of the headlap portion. The invention also includes an apparatus and a process for the continuous manufacture of the shingles of the invention.
Owner:CERTAINTEED CORP
Fabrication of interleaved metallic and intermetallic composite laminate materials
InactiveUS7188559B1Well formedLimit cracking and fracturingWeapon componentsDomestic articlesGramComposite laminates
Typically 20–40 films of a tough first metal, normally 0.1–1.0 mm thick films of titanium, nickel, vanadium, and / or steel (iron) and alloys thereof, interleaved with a like number of films of a second metal, normally 0.1–1.0 mm thick films of aluminum or alloys thereof, are pressed together in a stack at less than 6 MPa and normally at various pressures 2–4 MPa while being gradually heated in the presence of atmospheric gases to 600–800° C. over a period of, typically, 10+ hours until the second metal is completely compounded; forming thus a metallic-intermetallic laminate composite material having (i) tough first-metal layers separated by (ii) hard, Vickers microhardness of 400 kg / mm2+, intermetallic regions consisting of an intermetallic compound of the first and the second metals. The resulting composite material is inexpensive, lightweight with a density of typically 3 to 4.5 grams / cubic centimeter, and very hard and very tough to serve as, among other applications, lightweight armor. Upon projectile impact (i) the hard intermetallic, ceramic-like, layers are confined by the tough metal layers while (ii) cracking and fracturing is blunted and channeled in directions orthogonal to the axis of impact.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Composite product
InactiveUS6893751B2Sufficient quantityImprove dehydration propertiesLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsOptoelectronicsSlurry
A composite product comprising a substrate layer and one or more functional layers applied thereto. The slurry is applied to the substrate layer to form a functional layer and the functional layer dewatered through the substrate layer. The functional layers can be repeated to build up a laminated composite product. Functional additives may be included in each layer to provide desired properties to that layer and indeed to the subsequent composite product.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
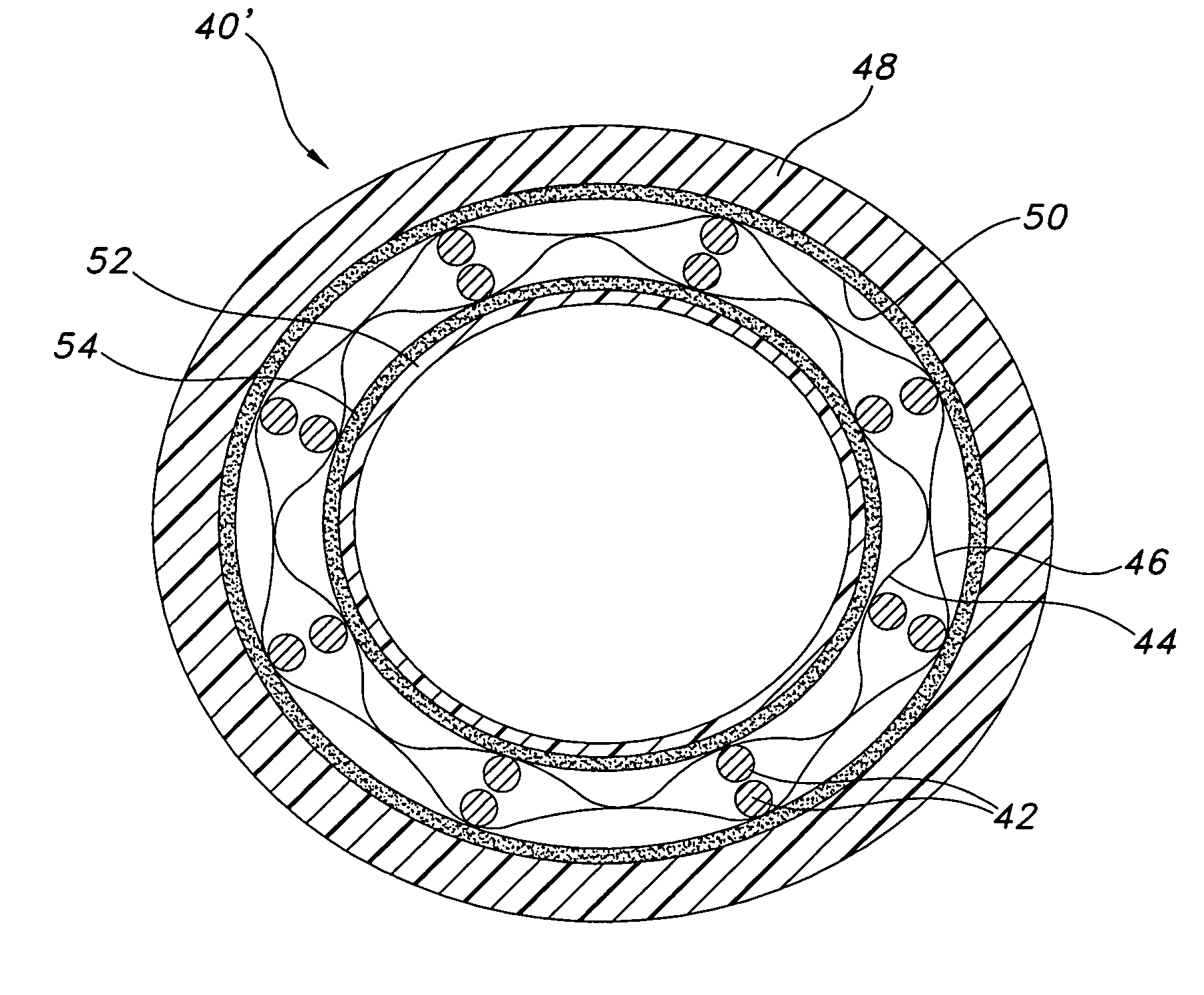
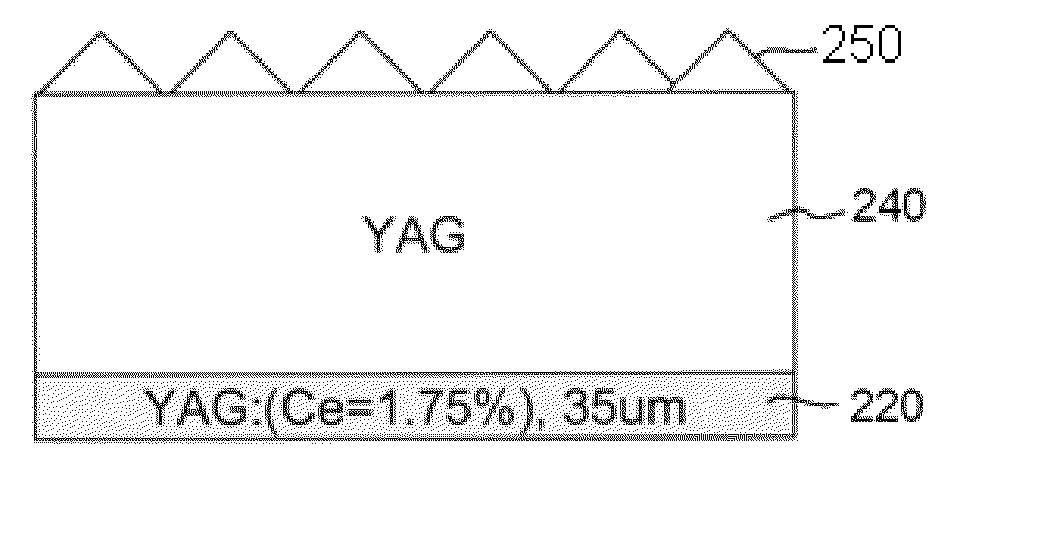
Light emissive ceramic laminate and method of making same
ActiveUS20110210658A1Incadescent screens/filtersElectric discharge tubesCeramic compositeComposite laminates
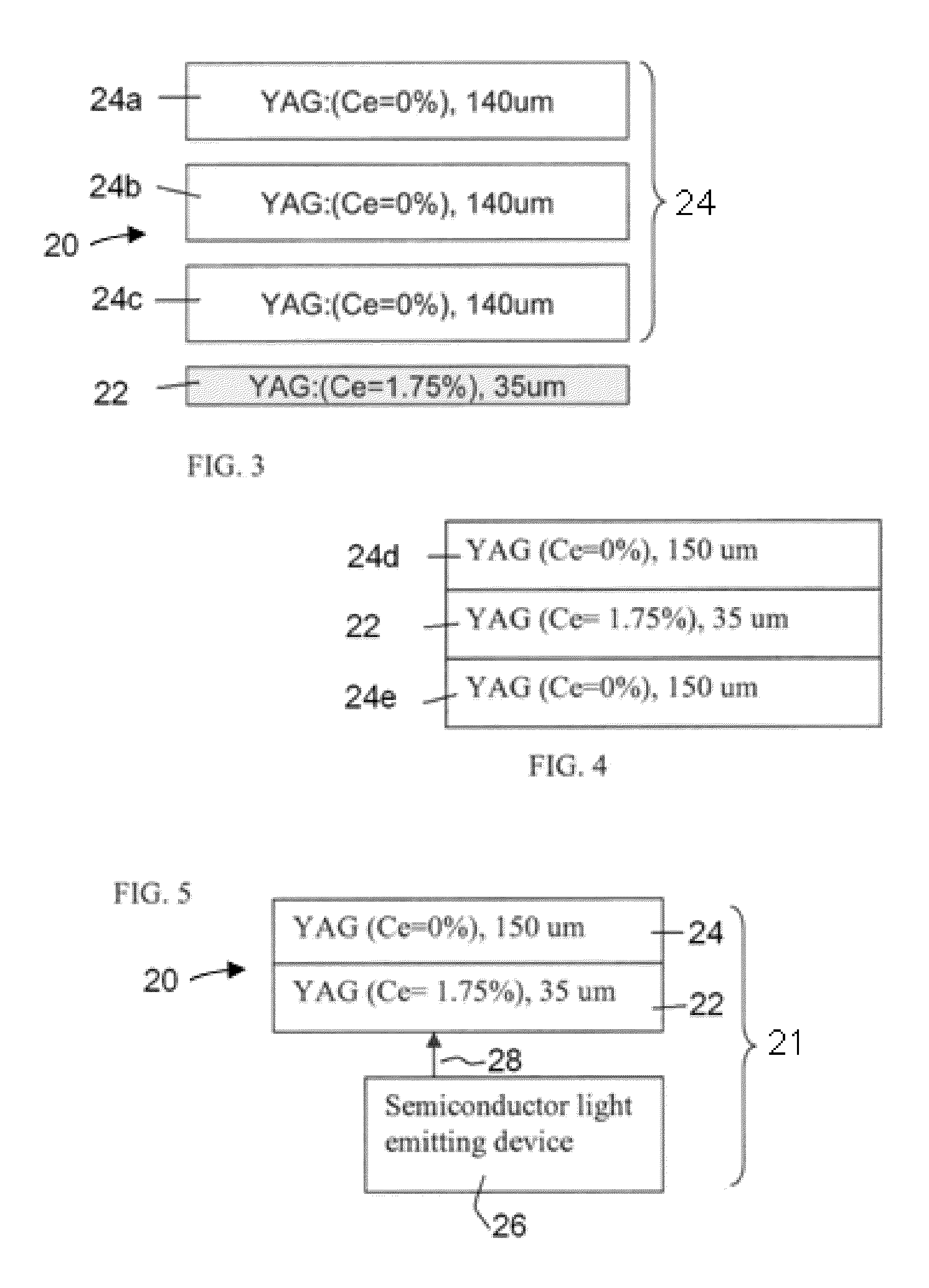
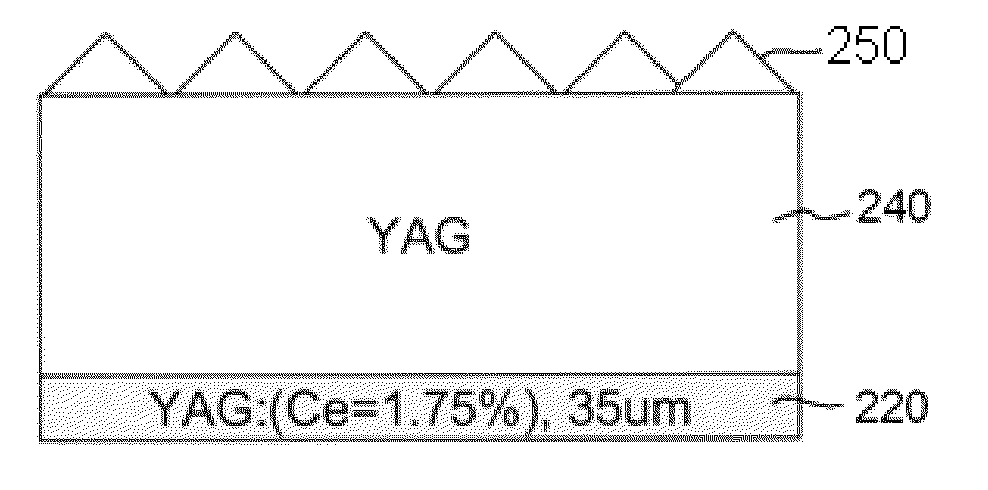
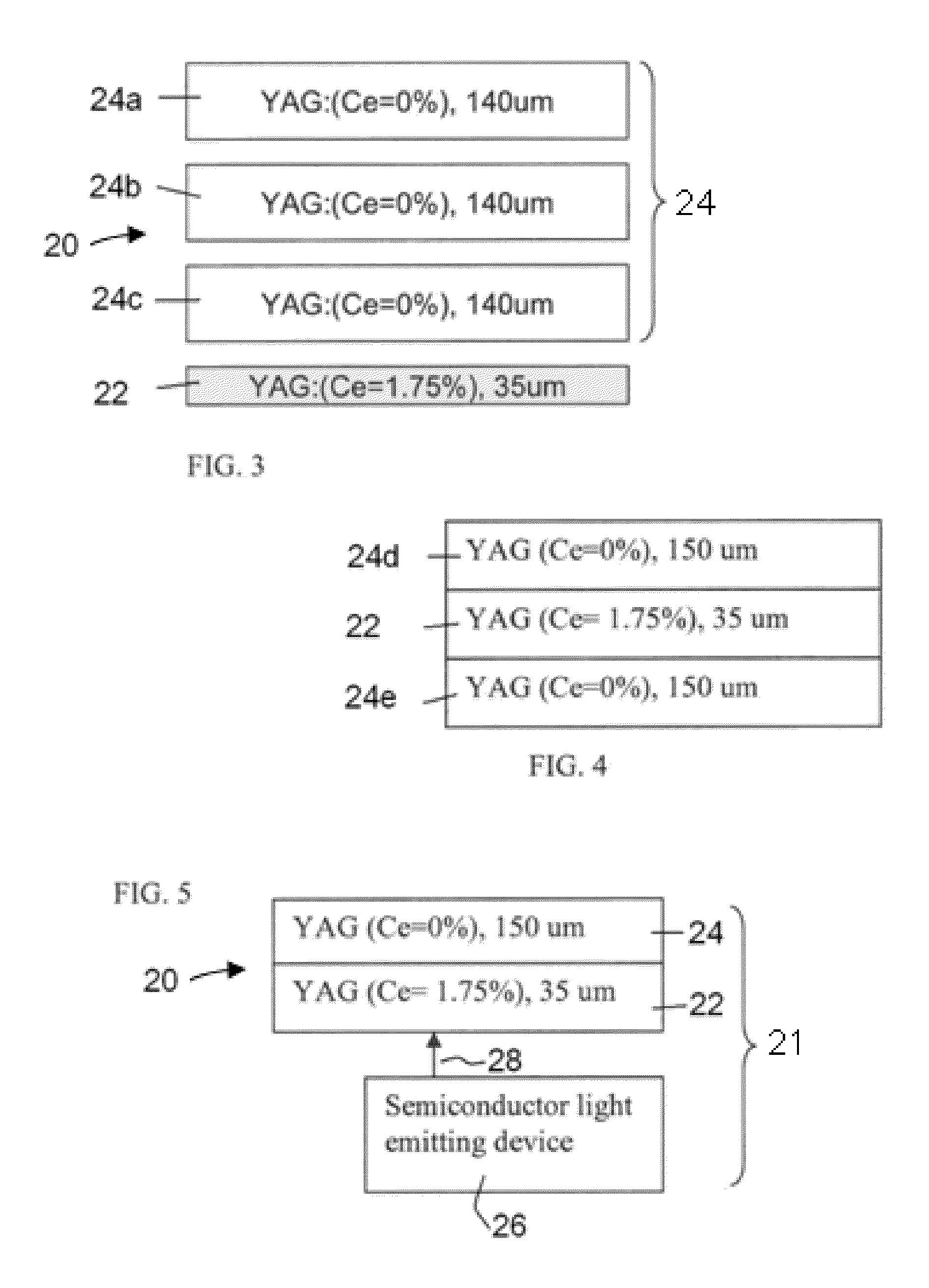
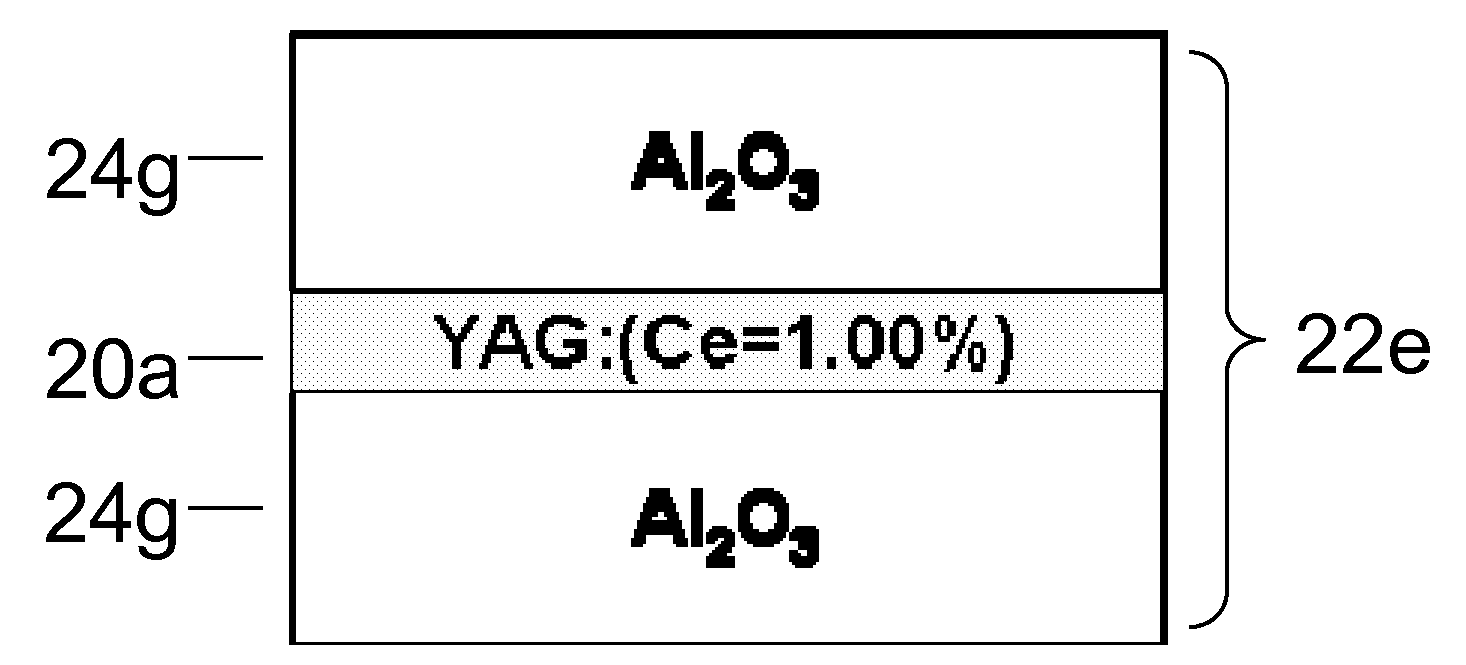
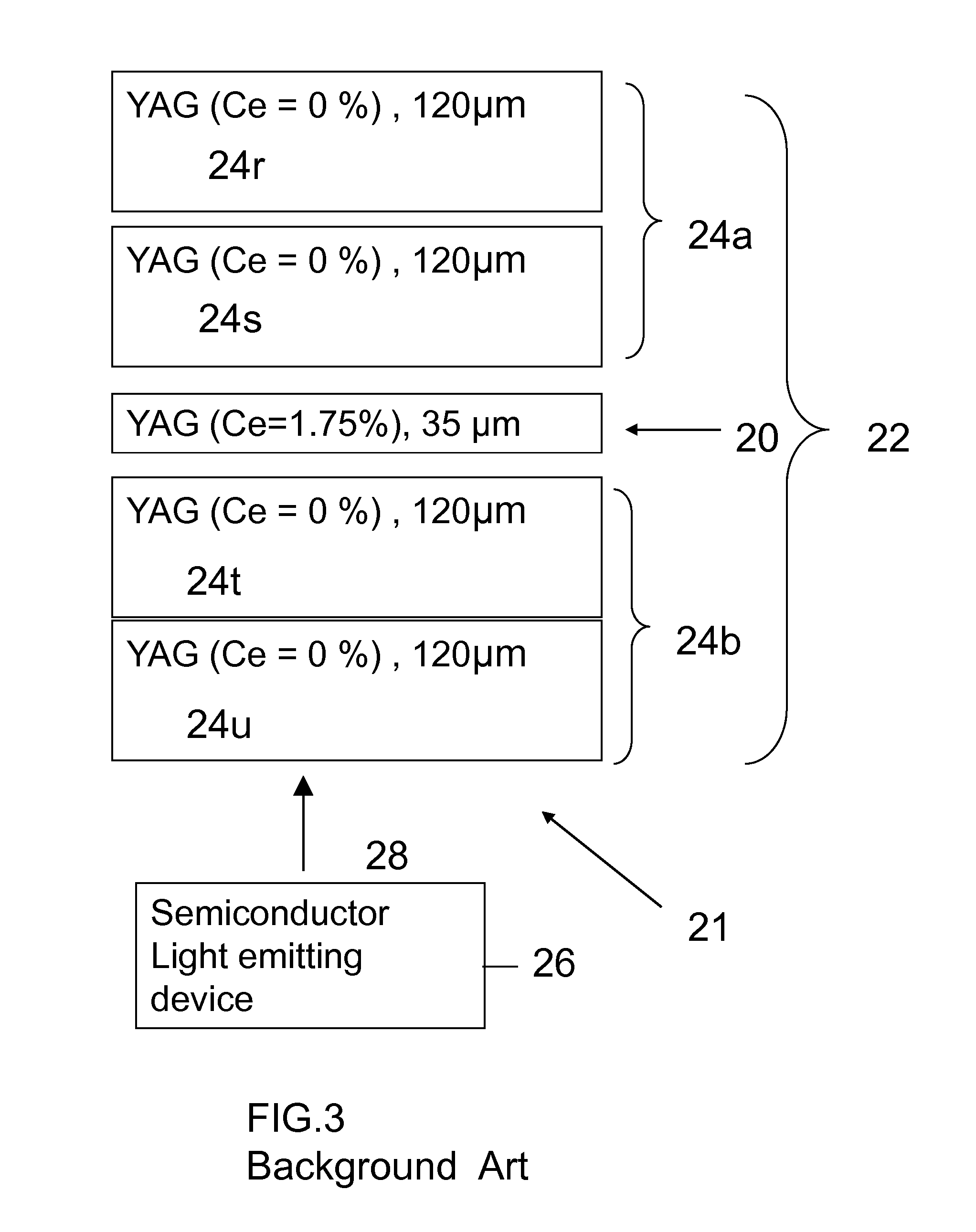
A ceramic composite laminate includes a wavelength-converting layer and a non-emissive layer, wherein the ceramic composite laminate has a wavelength conversion efficiency (WCE) of at least 0.650. The ceramic composite laminate can also include a wavelength-converting ceramic layer comprising an emissive material and a scattering material, wherein the laminated composite has a total transmittance of between about 40% to about 85%. The wavelength-converting layer may be formed from plasma YAG:Ce powder.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Bonded lightweight structural sheet
InactiveUS20060062977A1Reduce resistanceAdhesive processes with adhesive heatingLaminationAdhesiveElectrical connection
Laminated composites such as noise damping sheet metal sandwiches with viscoelastic adhesive cores are strengthened against delamination during forming and made more conductive for welding. Electrically conductive, metal-element containing particles, wires, wire meshes, or the like conductive bonding elements are included in the core material and fused to facing surfaces of the metal sheets to provide many mechanical bonding connections and electrical connections over the bonded area of the composites.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Light emissive ceramic laminate and method of making same
A ceramic composite laminate includes a wavelength-converting layer and a non-emissive layer, wherein the ceramic composite laminate has a wavelength conversion efficiency (WCE) of at least 0.650. The ceramic composite laminate can also include a wavelength-converting ceramic layer comprising an emissive material and a scattering material, wherein the laminated composite has a total transmittance of between about 40% to about 85%. The wavelength-converting layer may be formed from plasma YAG:Ce powder.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
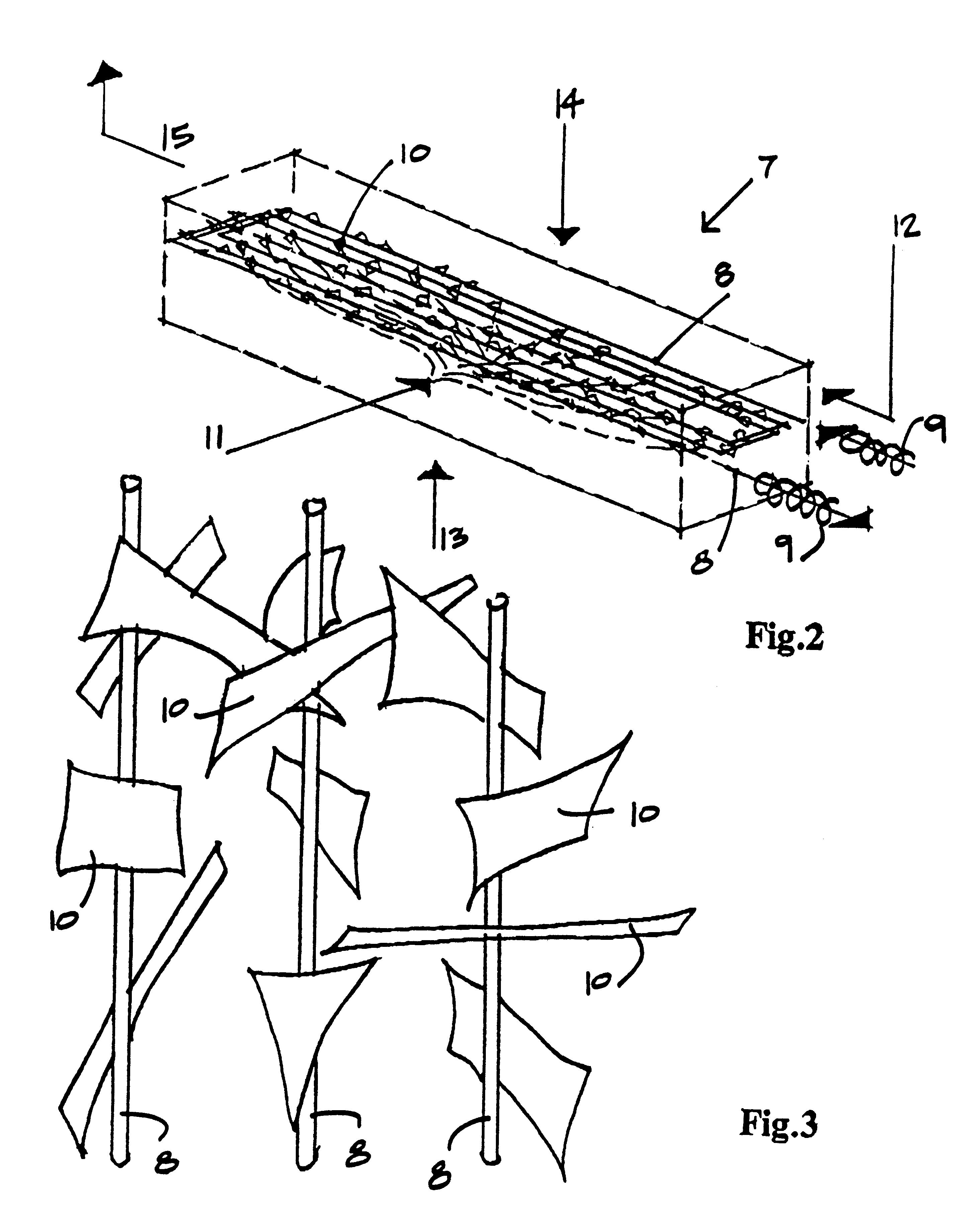
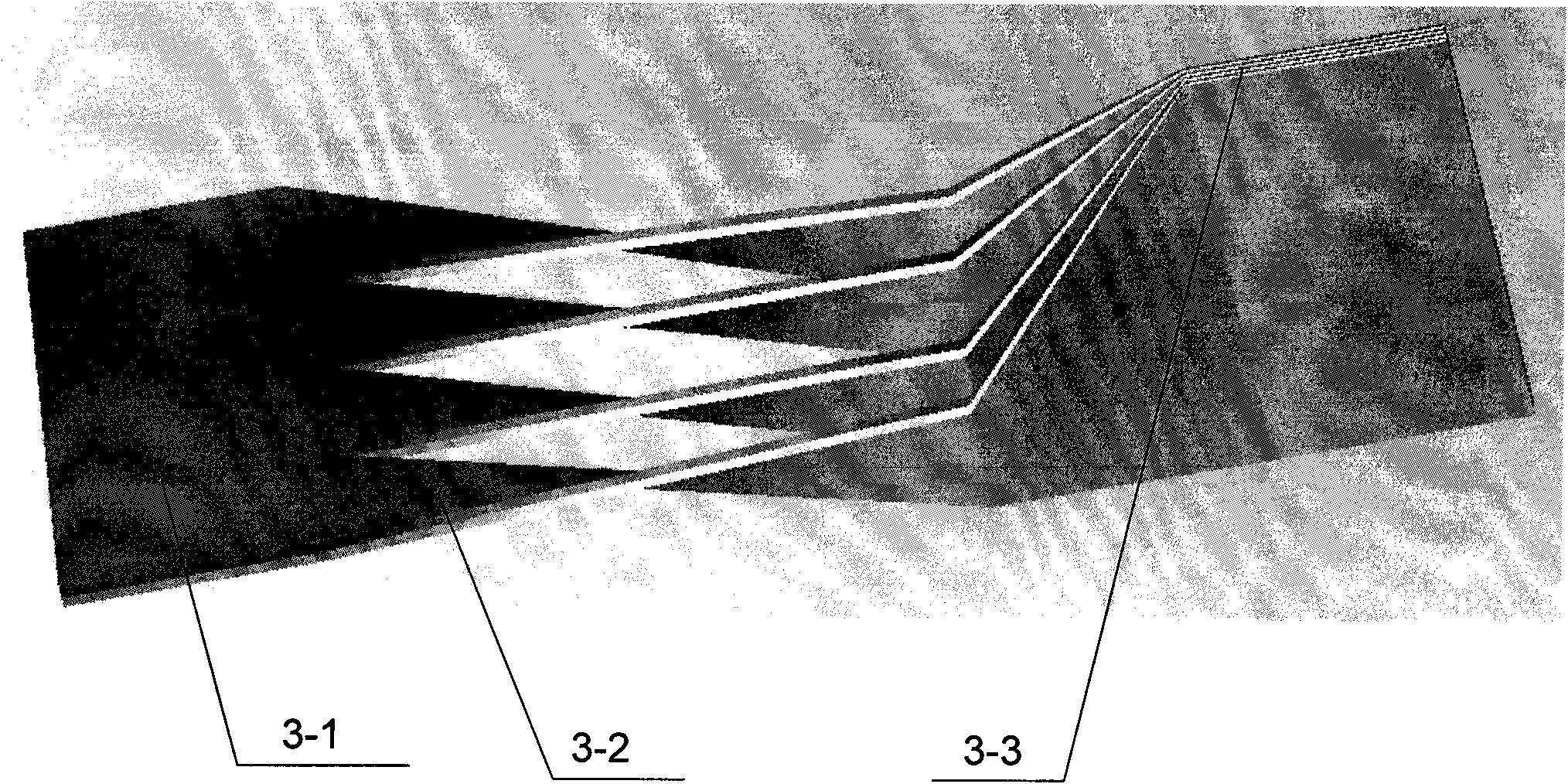
Stringer
InactiveUS20120100343A1Reduce stack thicknessIncreases geometric possibilityLamination ancillary operationsLaminationEngineeringLaminated composites
A laminated composite stringer having a termination at one end in its longitudinal direction, and including a laminated stack of composite structural plies, wherein internal plies in the stack are terminated consecutively towards the stringer termination to provide a taper of reducing stack thickness. Also, a composite structure comprising a panel and the stringer; and a method of manufacturing the stringer. The composite structure may be used in aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Light emissive ceramic laminate and method of making same
A laminated composite includes a wavelength-converting layer and a non-emissive blocking layer, wherein the emissive layer includes a garnet host material and an emissive guest material, and the non-emissive blocking layer includes a non-emissive blocking material. The metallic element constituting the non-emissive blocking material has an ionic radius which is less than about 80% of an ionic radius of an A cation element when the garnet or garnet-like host material is expressed as A3B5O12 and / or an element constituting the emissive guest material, and the non-emissive blocking layer is substantially free of the emissive guest material migrated through an interface between the emissive layer and the non-emissive blocking layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
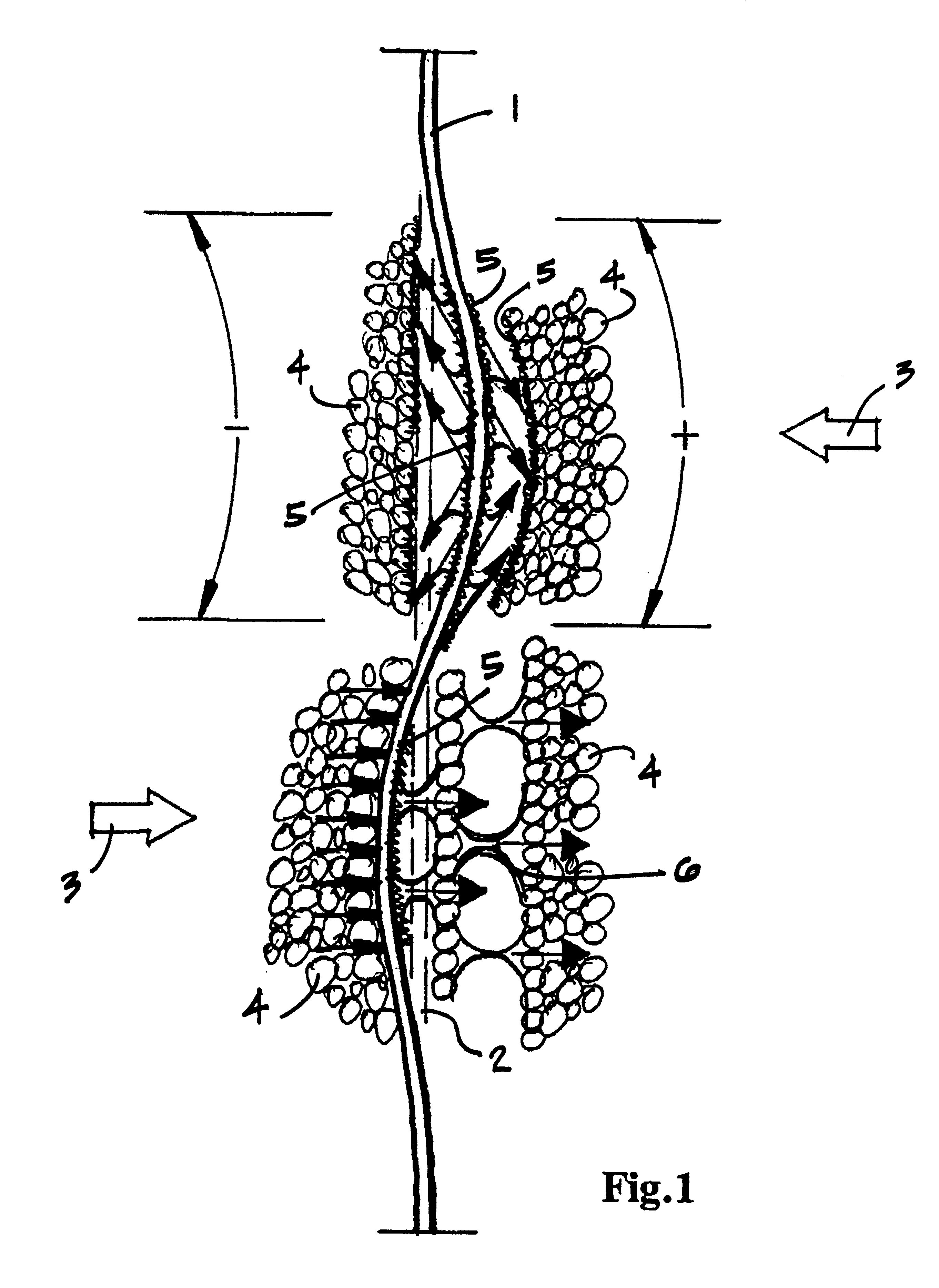
pH-responsive film for intravaginal delivery of a beneficial agent
InactiveUS20060018951A1Reduce transmissionFacilitates the incorporation of biological agentsPowder deliveryTamponsIntravaginal administrationAntioxidant
The present invention provides a delivery system for the intravaginal administration of prophylactic and therapeutic agents. In one embodiment, the invention provides a pH-responsive, biocompatible film for intravaginal administration of a beneficial agent, comprising a biocompatible, hydrophilic polymer that is positively charged at a first pH and in electronically neutral form at a higher pH; an effective amount of a beneficial agent; and, optionally, at least one film-forming binder. The pH responsive film may also include other additives such as plasticizers, sustained release polymers, antioxidants, and antimicrobial agents. In another embodiment, the pH-responsive film of the present invention comprises a laminated composite of (a) a bioadhesive layer that serves to affix the film to a mucosal surface within the vagina and, laminated thereto, (b) at least one reservoir layer comprising at least one beneficial agent and a biocompatible hydrophilic polymer. The pH responsive films of the present invention can be used for contraception, treatment and / or prevention of viral infections, treatment of vaginal infections, relief of vaginal itch, vaginal cleansing, and enhancement of vaginal lubrication.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
A gradient laminated composite supporting frame material based on bionic structures and its preparation method
The invention relates to a kind of laminated gradient composite scaffold material based on the bionic structure and its preparation method. The said material has three or more layers of porous structure, comprising of hyaluronic acid, PLGA, PLA, collagen II and nano-hydroxyapatite (nano-HA) , beta- tricalcium phosphate ( beta-TCP). The upper layer is made by collagen II / hyaluronic acid or PLGA and PLA imitating the cartilage layer. With the counterfeit the calcified cartilage layer in the middle, it is one layer or multi- sublayer, made by nano-HA or beta-TCP with collagen II / hyaluronic acid or PLGA and PLA; the bottom is made of nano-HA or beta-TCP with collagen II or PLGA and PLA. From top to bottom, the content of inorganic material increases in its layers, about 0 to 60 mass percent of layers. The aperture of the scaffold material is 50 to 450 micron, with 70 to 93 percent porosity. The scaffold material made by this invention has an adjustable degradation rate, good mechanical and biocompatible properties, can adapt to culture with cartilage bone cells and compound with growth factor and small molecular or peptides, it can be used to repair cartilage simultaneously.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
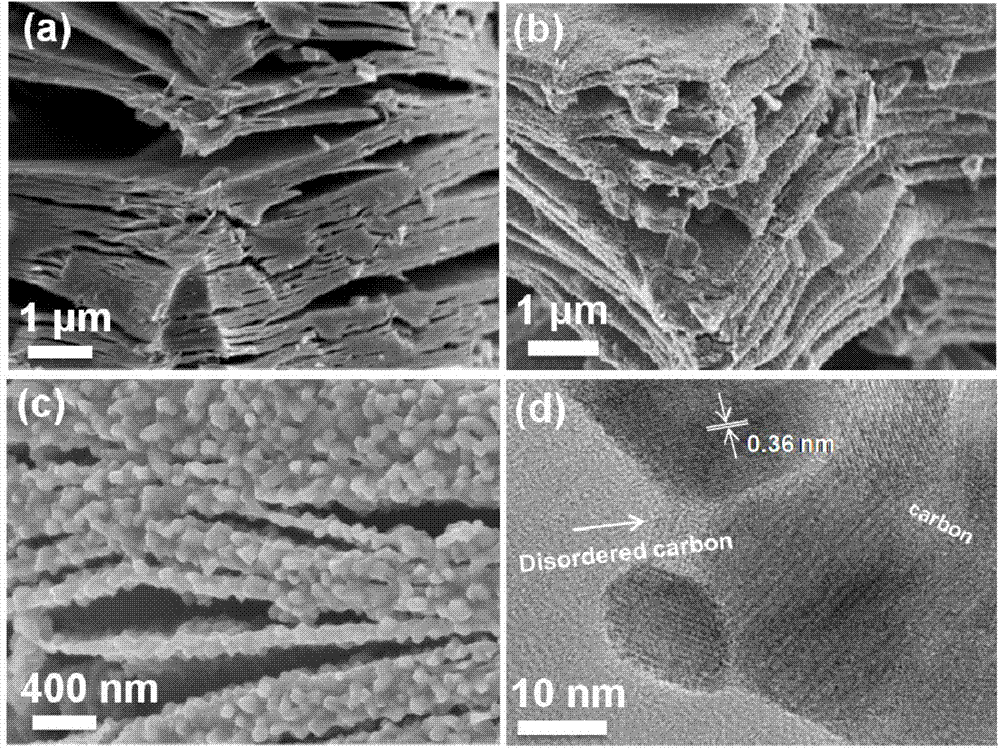
Carbon nano-pipe array/laminated composite and its production
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Laminated-structure polymer-based dielectric energy-storage composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104044318ALow breakdown field strengthImprove electrical polarization characteristicsInorganic material artificial filamentsSynthetic resin layered productsFiberComposite film
The invention discloses a laminated-structure polymer-based dielectric energy-storage composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is a laminated thin film having at least three thin film layer structures. The laminated thin film is formed by a composite membrane, composed of nanometer fibers and a polymer, and a composite membrane, composed of nanometer particles and a polymer, in an alternately laminated manner. According to the invention, a tape casting method is employed for manufacturing a single-layer composite thin film and then a laminated hot-pressing method is employed for manufacturing the laminated composite material, or a multistage tape casting method is employed for flowing out multiple thin film layers successively to obtain a laminated structure. An experimental result proves that the laminated composite material has a relative high dielectric constant, a relative low dielectric loss, relative high breakdown field intensity and a relative high energy-storage density. The laminated composite material is expected for being applied in an embedded capacitor, a static accumulator, a large-power capacitor and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
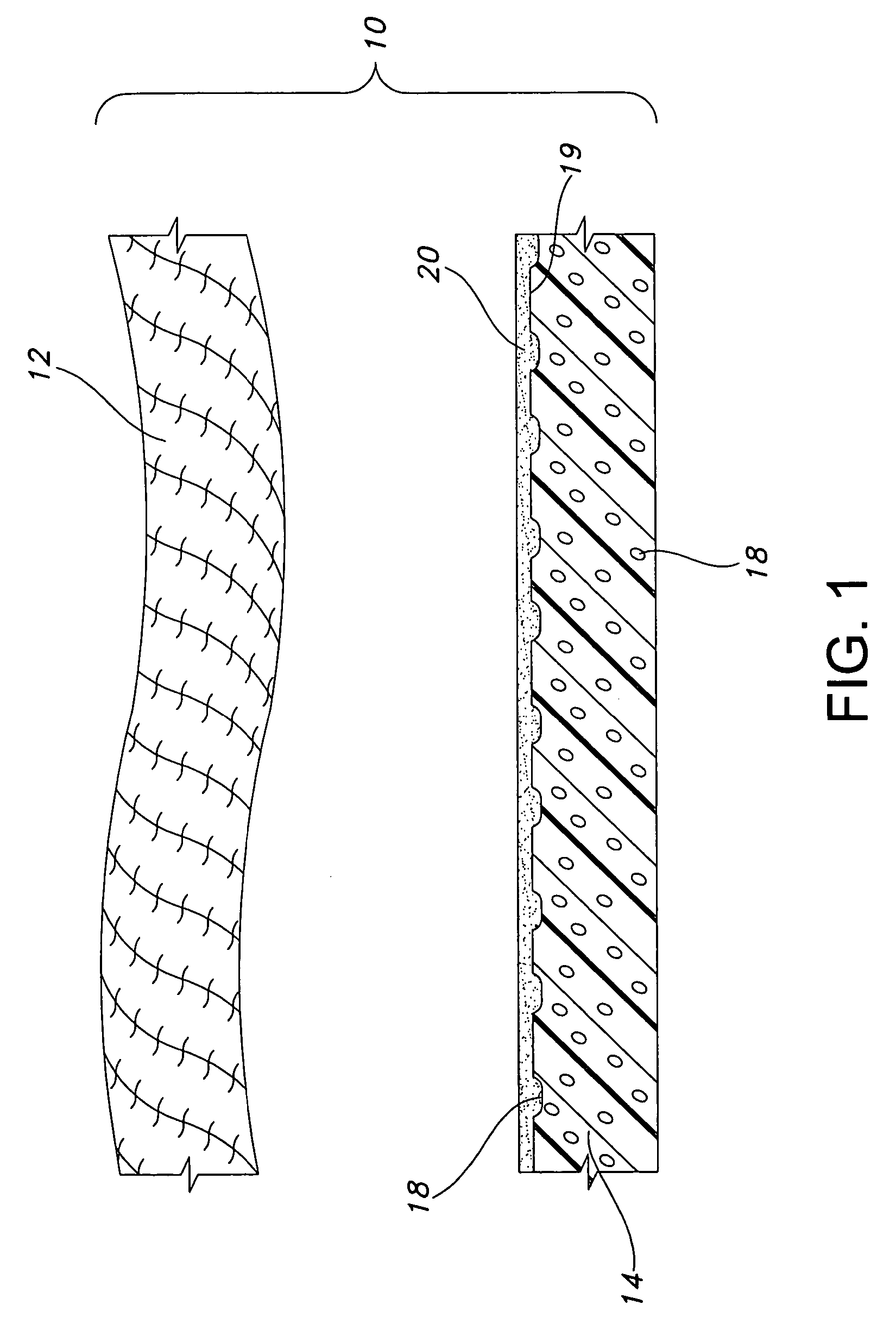
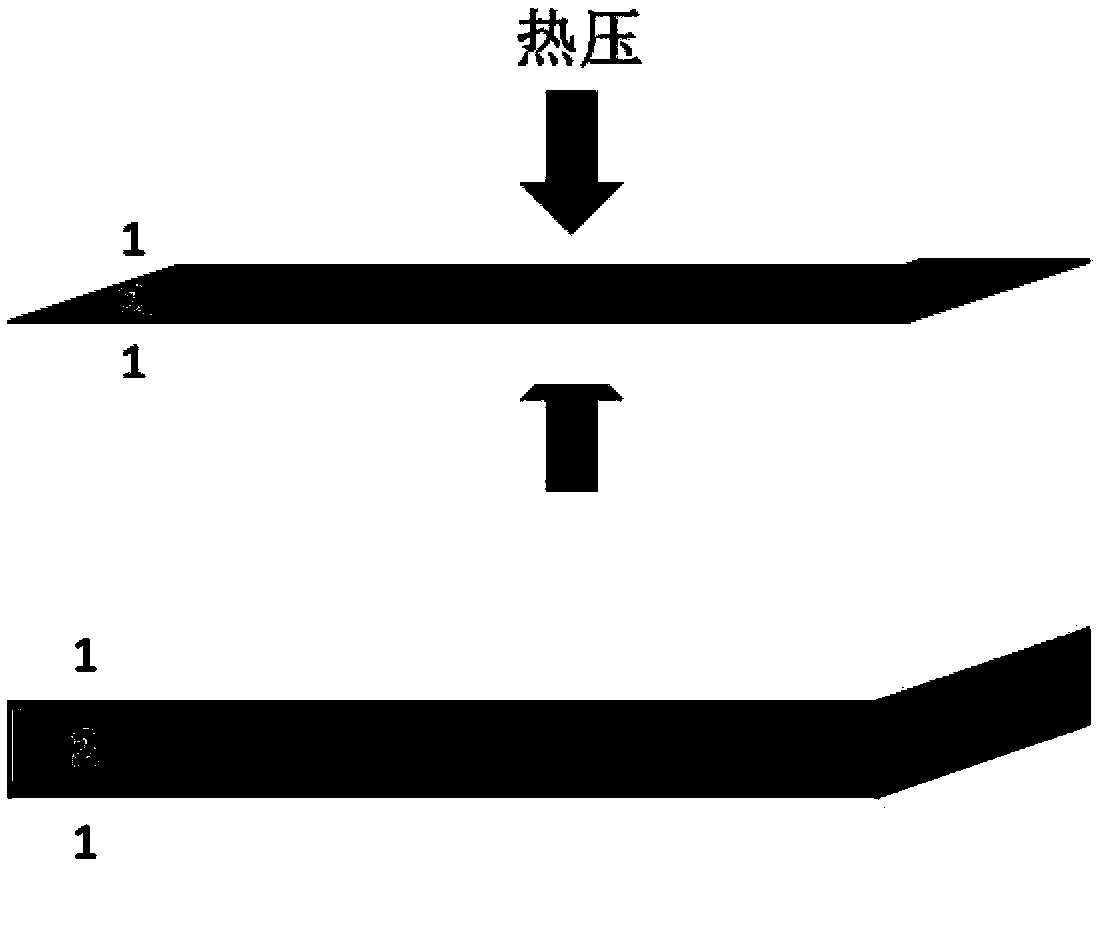
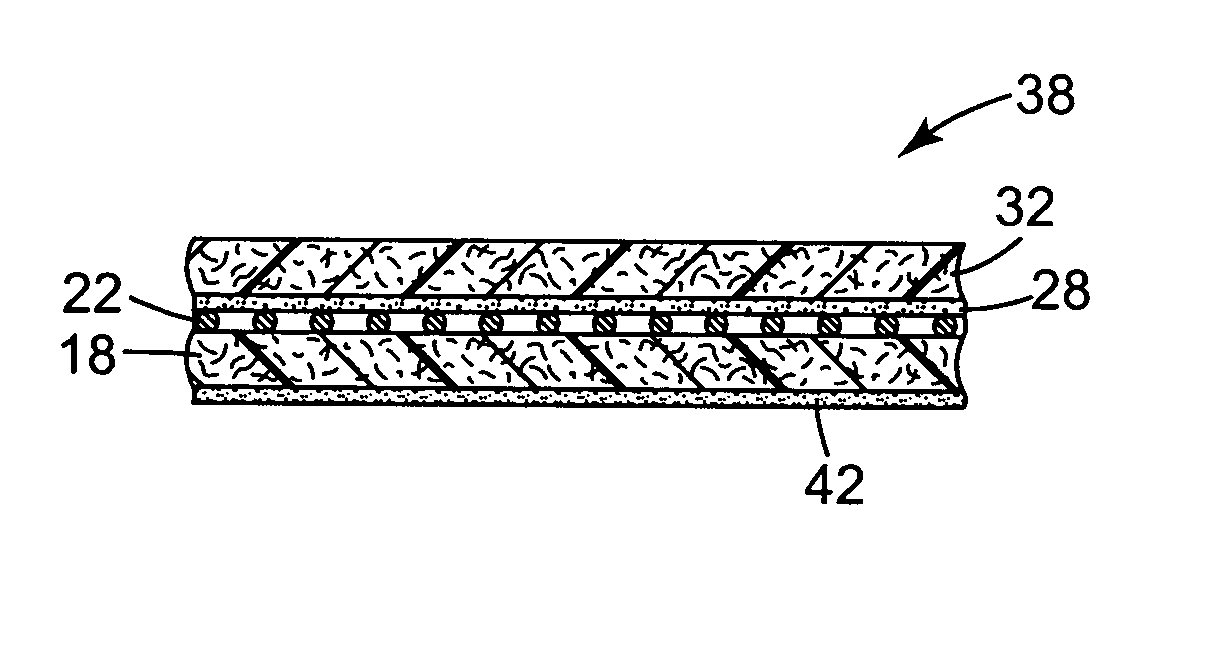
Laminated composites
InactiveUS20050084647A1High tensile strengthEasy to tearSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationMedical productLaminated composites
A laminated composite suitable for use in medical products such as tapes and wraps. The composite includes, for example, a first nonwoven fiber layer, an elastic layer, a melt blown adhesive fiber layer, and a second nonwoven fiber layer. A scrim layer serves as a deadstop, or stretch limit, to prevent over stretching. The non-woven fiber layer(s) and / or the scrim layer form suitable loops for a hook and loop fastening system. The scrim layer in some embodiments is employed to make the composite finger tearable. The melt blown adhesive layer, nonwoven web layer and elastic layer form a breathable, porous elastic composite. Methods of manufacturing the composite are also disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Preparation method of transition metal oxide/carbon-based laminated composite material
InactiveCN104733712ALengthy process routeLong process routeHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesNew energyConductive materials
The invention relates to a preparation method of a transition metal oxide / carbon-based laminated composite material. According to the preparation method, a conducting material such as metal carbide, metal nitride or metal carbonitride with a two-dimensional laminated structure is taken as a precursor, a gas containing oxygen elements is taken as an oxidant, and the two-dimensional conducting material is converted into the transition metal oxide / carbon-based laminated composite material by in-situ oxidation under the condition of controlling the oxidation temperature at 300-1000 DEG C and controlling the oxidation time at 1-300 min. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity and easiness in operation, controllable structure and morphology, controllable crystal form and electrochemical properties of metal oxides, and the like; the preparation method is environment-friendly, and nuisanceless, has no by-product, can be used for reducing the economic costs of traditional preparation methods, and can be popularized; and the transition metal oxide / carbon-based laminated composite material not only can be used as a key electrode material of a new energy storage device, but also can be used as a denitration catalyst, so that the material can be applied to the fields of environmental remediation, and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Laminate composite material
InactiveUS6602809B1Avoid Sealing ProblemsHigh permeance (WVTR)Synthetic resin layered productsGauze-woven fabricsParticulatesWater vapor
A laminate composite material comprises a layer of an open weave supporting fabric having a layer of breathable resin adhered thereto by an extruded layer of a thermoplastic resin blended with a high temperature volatile particulate. The resultant composite material is substantially impervious to air and water and permeable to water vapor and having a water vapor transmission rate exceeding one (1) perm of water vapor.
Owner:BERRY PLASTICS CORP
Composite thermally-conductive thin layer and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102909905AImprove toughnessHigh impact damage toleranceSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to design and a preparation technique of continuous laminated carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite high in thermal conductivity and toughness, and intermediate composite thermally-conductive thin layers and finished composite products of the continuous laminated carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite. The preparation technique is mainly characterized in that meshed low-surface-density nonwoven, a porous membrane or fabric are used as functional carriers to carry one or mixture of some of high-thermal-conductivity, nano-micron and small-scale carbon nanotubes, graphene, boron nitride micropowder, expanded graphene micropowder, diamond micropowder and the like so as to prepare the composite thermally-conductive thin layer with high thermal conductivity and toughening potential, the composite thermally-conductive thin layer is placed between layers of conventional carbon fiber laminated composite by intercalation technology, and forming and curing are performed to prepare the structural composite high in overall thermal conductivity and toughness. The preparation technique is simple to operate. The toughness of the obtained composite is improved greatly, inter-layer and intra-layer thermal conductivities are both improved, and the obtained composite is high in overall thermal conductivity and toughness.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Insulating and thermal conductive ablation resistant adhesive and application thereof in lightning protection
ActiveCN104789175AAvoid failureImprove lightning protectionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSynthetic resin layered productsFiberCarbon fibers
Belonging to the technical field of lightning protection, the invention relates to an insulating and thermal conductive ablation resistant adhesive and application thereof in lightning protection. The adhesive is mainly prepared from the following raw materials: 20-100% and not up to 100% of a mixture of high temperature resistant resin and a curing agent, and 0-80% and greater than 0% of an insulating and thermal conductive ablation resistant inorganic filler. After curing, the electrical conductivity of the adhesive is in the range of 10<-8>-10<-20>S / m, the DC breakdown voltage in the air is in the range of 30-300kV / mm, the thermal conductivity is in the range of 0.2-3.0W / (m.K), and the ablation resistant temperature is up to 300DEG C. A certain thickness (30-250micrometer) of the insulating and thermal conductive ablation resistant adhesive is employed to stick a conductive film to the surface of a continuous carbon fiber laminated composite material part, thus preventing conduction of current to the continuous carbon fiber laminated composite material part and improving the lightning protection effect of the conductive film.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Flexible lithium ion battery black phosphorus nanosheet-graphene composite film anode, and preparation thereof
ActiveCN106711408AHigh puritySmall sizeSecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesComposite filmFiltration
The invention belongs to the field of electrochemistry battery, and more specifically relates to a black phosphorus nanosheet-graphene composite film anode used for flexible lithium ion batteries, and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, high purity and large scale black phosphorus blocks are synthesized via mineral substance assistant vapor transporting method with high efficiency; a large amount of clean and high quality black phosphorus sheets are prepared in water via ultrasound treatment; the clean and high quality black phosphorus sheets and high conductive graphene nanosheets prepared via intercalation stripping method are subjected to mixing ultrasonic dispersion; and flexible high-strength laminated composite film is prepared via vacuum filtration. The preparation process of the flexible high-strength laminated composite film is simple and controllable; large scale low cost preparation can be realized; black phosphorus nanosheets are high in capacity, graphene is high in electrical conductivity, and the black phosphorus nanosheets and graphene both possess two-dimensional structures high in flexibility and strength, so that problems the black phosphorus is poor in electrical conductivity and stability are solved, lithium ion battery capacity, cycling stability, and entire energy density are increased, and lithium ion battery electrode integrated flexible design is realized.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for the design of laminated composite materials
InactiveUS20060029807A1Easy to solveEasy to identifyLaminationLamination apparatusDesign toolLaminated composites
The fundamental premise of designing structures with laminated composite materials is that the materials can be tailored to meet requirements by choosing the materials, thicknesses or thickness fractions, and orientation angles of constituent materials. Minimum weight, dimensional stability, natural frequency, and thermal conductivity are typical goals. This invention is NOT about the analysis of laminated materials and composites, of which there is no short supply. This invention is about the design of laminated materials, which has traditionally been an iterative event between the designer and the analysis tool. These iterations, if they occur at all, are often the most time consuming aspect of design. The fundamental premise of this invention is that tensor invariants of constituent material properties coupled with a tensor description of the specified material requirements can be used together to design laminated materials. The results of this invention can be used as a stand-alone design tool or as a value-added module in finite element codes. Specifically, by specifying material requirements, designers will use the method to select from a catalog of available materials a set that will satisfy their requirements. The designer is aided in the choice of materials, how much of each material to use, the layup angle orientation of the materials, and the sequencing of those materials in the composite laminate.
Owner:PECK SCOTT OWEN
Casting method for manufacturing layered metal composite material technology and equipment
The present invention discloses a technique and relative equipment for casting laminated and composite metal material. Target material is heated to 300 DEG C to 1200 DEG C by an electromagnetic induction heater installed on exterior of a casting die or a water cooling crystallizer. Molten electroslag liquid is poured in the casting die or the water cooling crystallizer, and an electrode is inserted in for heating. The metal liquid is poured in the casting die or the water cooling crystallizer by top casting mode or bottom casting mode. After casting, the induction heater and the electrode conduct continuous heating for 3 to 20 minutes, then heating is stopped, and layered composite material with plane gradient, laminated composite material and coated composite material of all geometric shapes can be produced. The present invention can simplify production procedures of composite material and can realize the dynamic regulation of all technical parameters during composition. The interface of the composite layer is under eay control so as to achieve excelllent metallurgical combination. The present invention has wide optional range about materal of the composite layer, high productivity, simple production technique and low cost.
Owner:丁家伟 +1
Magnesium-base layer-shaped composite material and its composite casting preparation method
InactiveCN101104325AImprove performanceImprove machinabilityMetallic material coating processesMetal layered productsTitaniumZinc
The invention relates to mg-based materials and a making method thereof, in particular to novel multifunctional mg-based laminated composite materials and the making method thereof, solving the problem that magnesium alloy is easy to rust in humid air or in the environment with chloridion, which results in poor comprehensive mechanical property. The technique proposal of the invention is that: based on the arrangement of gradient materials mixing, composite materials with different composition and different property are compounded to one or two sides of a magnesium piece or a magnesium alloy piece and the layers are metallurgically combined. The mg-based laminated composite materials made with the method have good comprehensive property and can meet the demands of different situations. Based on the compounding and casting technique of the invention, with different making methods, different metallurgically bonded mg-based laminated composite materials with compact interface can be made. The invention provides a novel method to produce new mg-based materials, suitable for the compounding of magnesium, magnesium alloy and other metal materials, such as aluminium, titanium, cuprum, zinc, nickel and steel, expanding the variety of mg-based materials and boosting the application of magnesium alloy.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid and efficient filtering whole blood in capillary flow device
ActiveUS20100089815A1Preventing filtrateAvoid particlesLaboratory glasswaresLoose filtering material filtersFiltrationCapillary channel
This invention provides lateral flow filters with pore size gradients and with features to prevent peripheral flows around the filter. The filters can be laminated composites of two or more planar filter layers. Cartridges employing the filters can include a filtration chamber configured to retain the lateral flow filters including a port for sample application and a capillary channel for filtrate egress. The fluid egress port can be positioned to receive filtrate from one filter layer but not another.
Owner:MICROPOINT BIOSCI
Device for manufacturing nano laminated composite material
The invention relates to a device for manufacturing a nano laminated composite material, which comprises a plastifying device, a converging device, a laminated composite generator and a molding device which are sequentially connected in series front and back, wherein the laminated composite generator is used for averagely dividing n layers of polymer melts extruded by the converging device into m equal parts along the width direction; when each equal part of melt continues to forwards flow in the laminated composite generator, the melt is rotated for 90 degrees and broadened by m times so as to mutually converge with an adjacent melt layer into a laminated structure at an outlet end; then an identical laminated composite generator is connected in series to obtain an n*m*m structure; and if k identical laminated composite generators are connected in series, a multi-layer structure composite material with n*mk layers can be obtained. In the invention, the laminated composite generators rotating for 90 degrees after melt segmentation are adopted, thus the segmentation quantity is large, the quantity of serial units can be reduced, and the melt is easy to maintain a symmetrical structure in a flow broadening and thinning process, so that the layer thickness precision is easy to guarantee, and a nano laminated composite multi-layer product can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
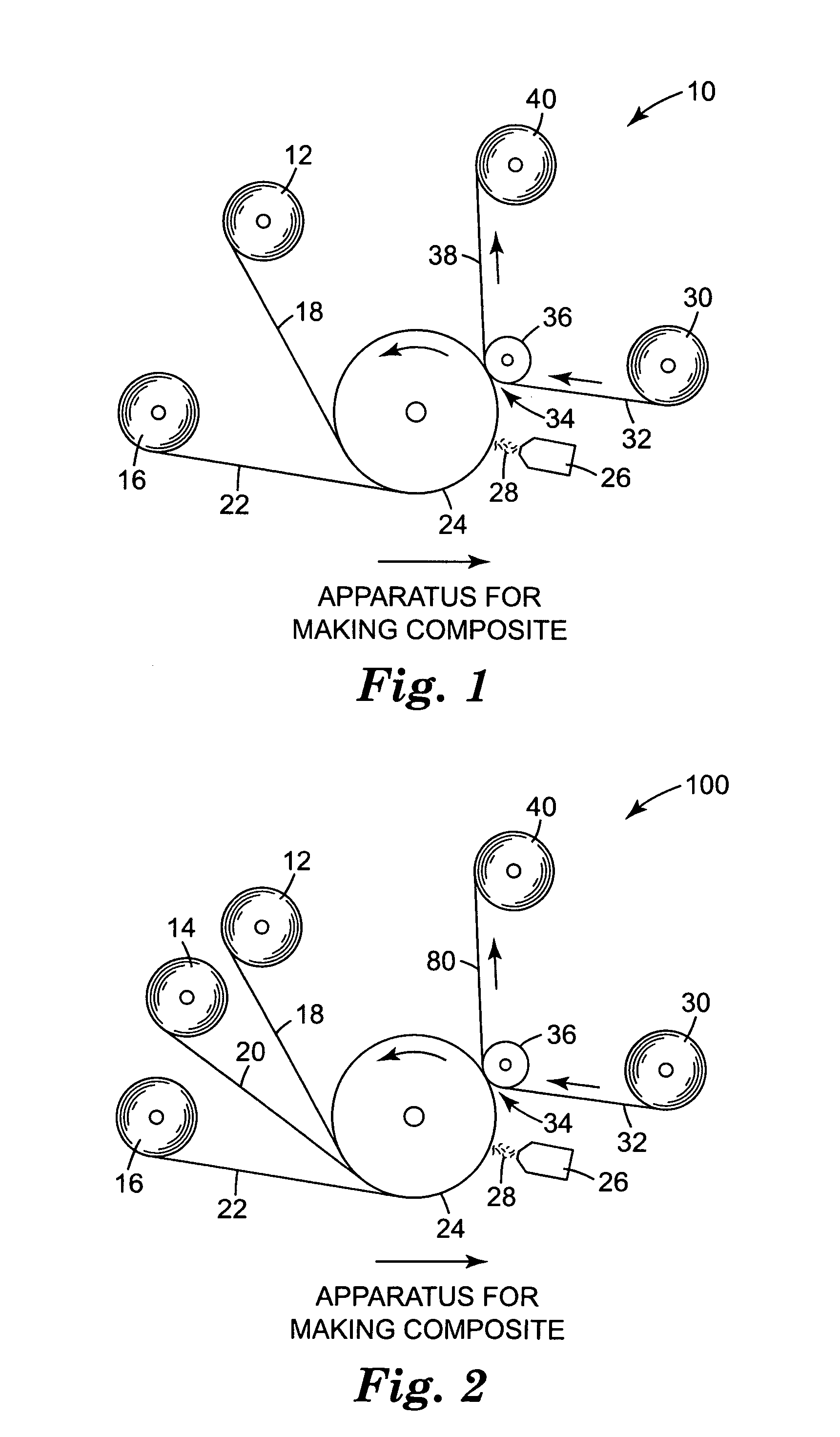
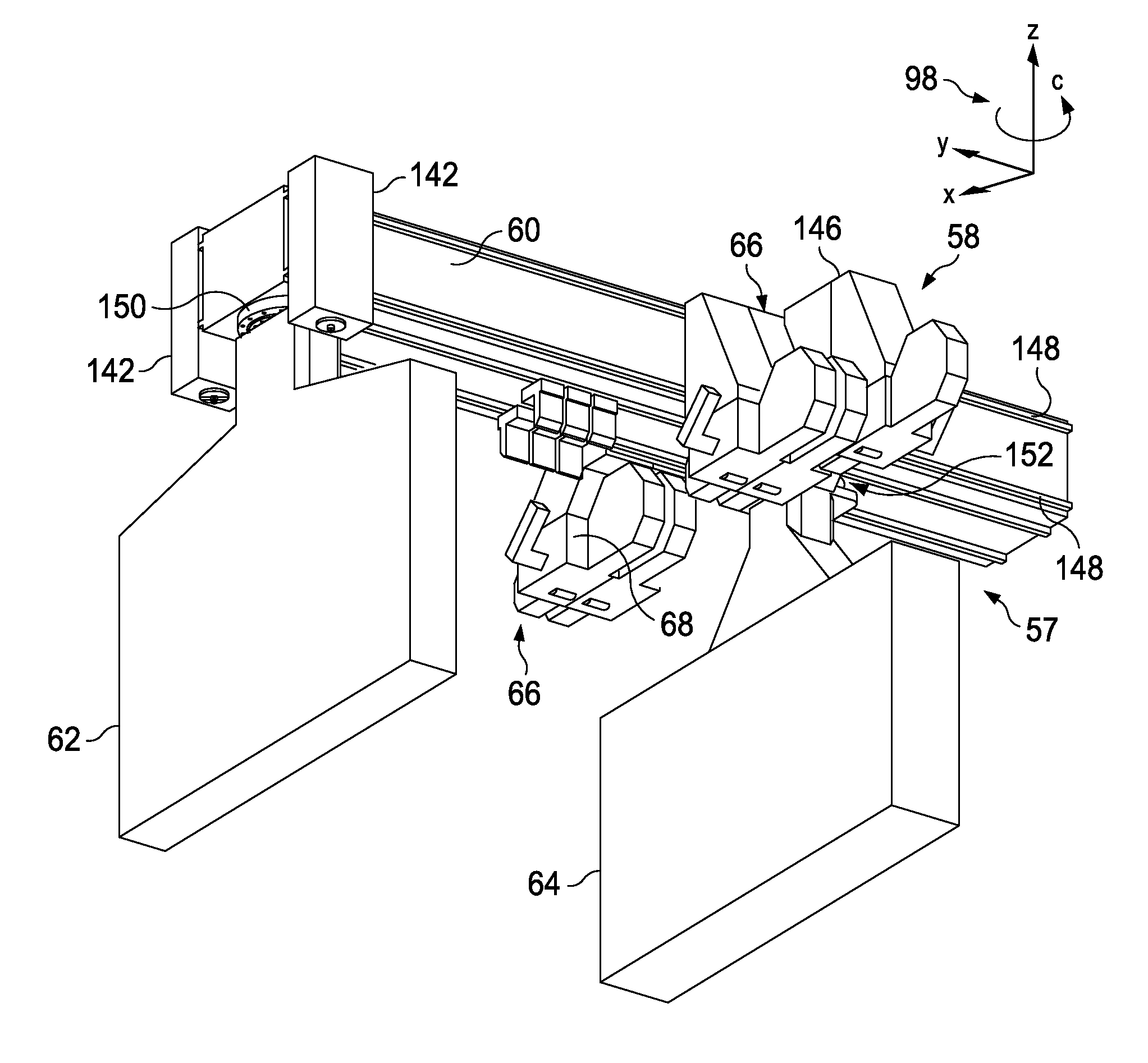
Method and Apparatus for Laminating Composites
ActiveUS20130032287A1Reduce wasteImproved wrinkle abatement measureAdhesive processesLamination ancillary operationsEngineeringAngular orientation
Composite tape is laminated onto a substrate using a gantry to move a tape laminating head along the length of the substrate. The laminating head is mounted for movement along a beam on the gantry that extends across the width of the substrate. The direction of lamination may be altered by changing the angular orientation of the beam.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
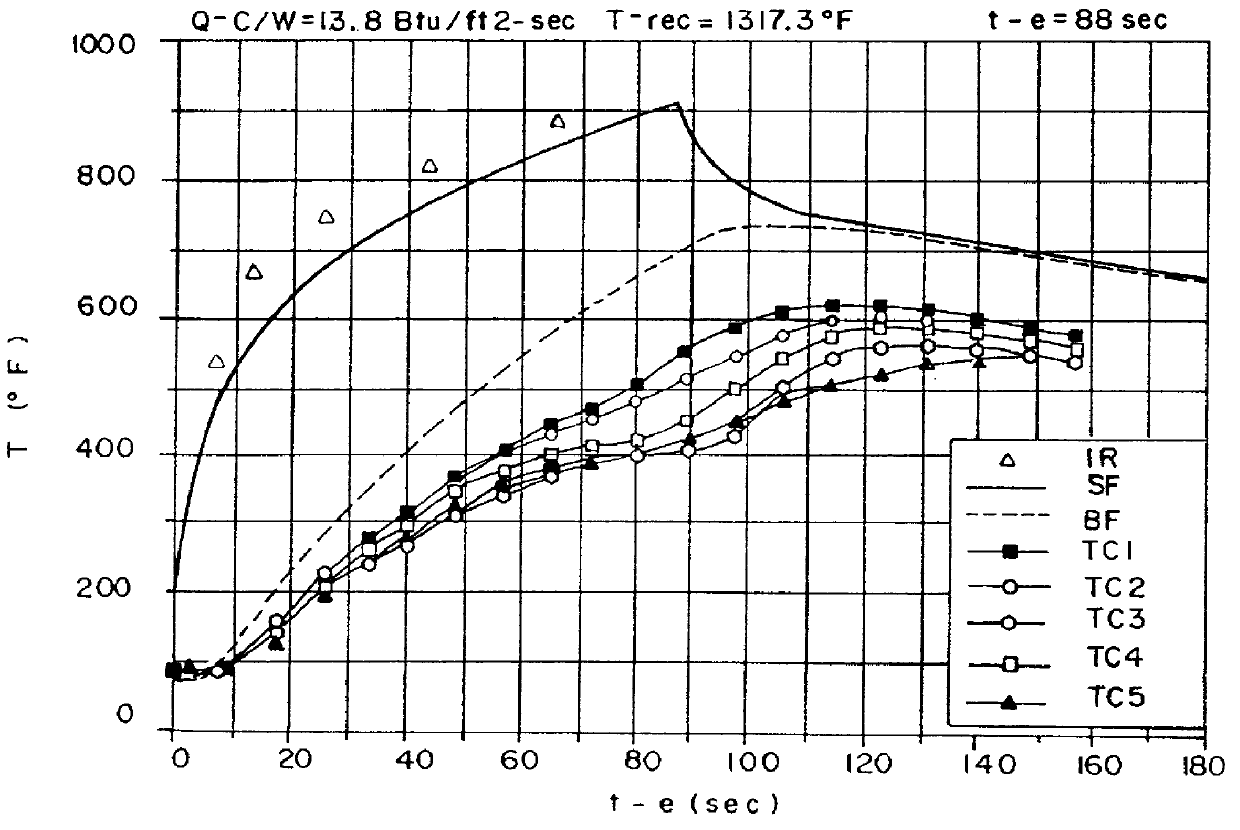
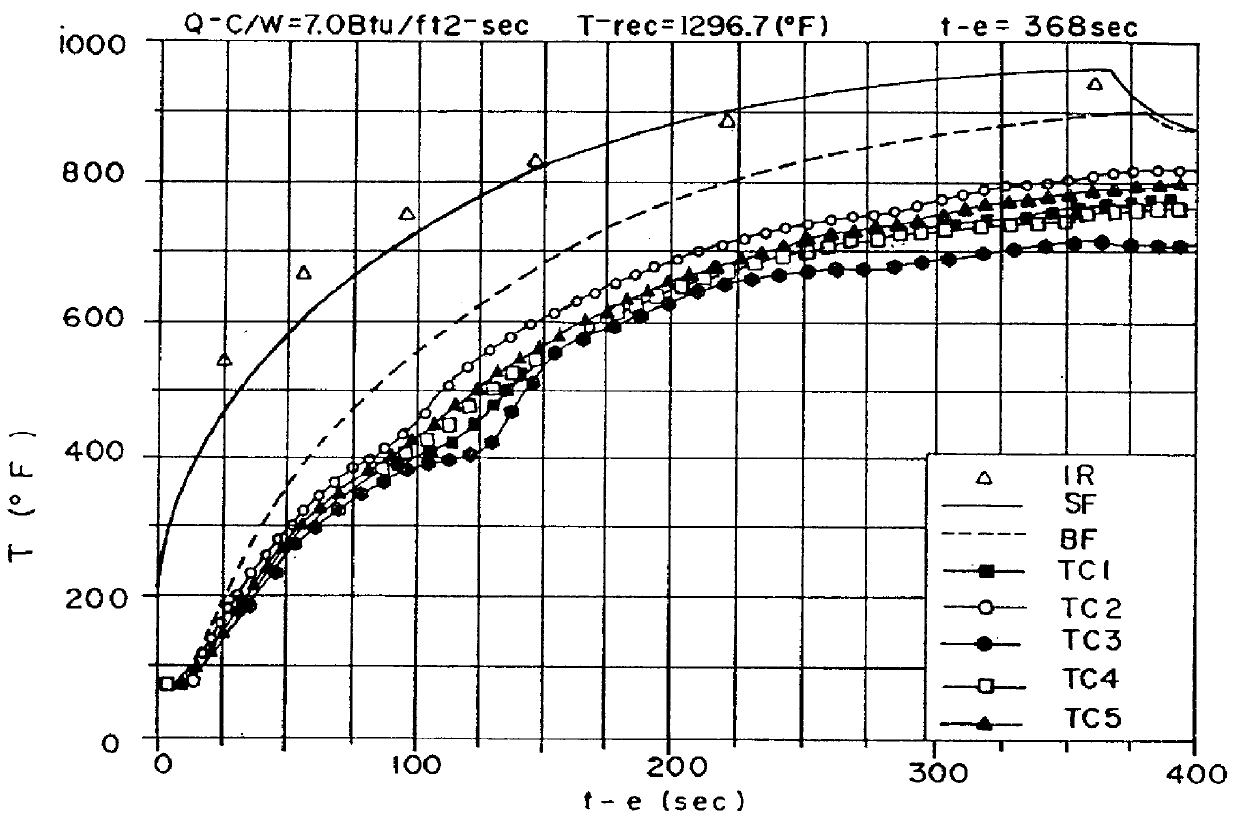
High performance structural laminate composite material for use to 1000 DEG F and above, apparatus for and method of manufacturing same, and articles made with same
InactiveUS6013361ASufficient permeabilityReduce weightCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsDamage toleranceRefractory
A novel materials technology has been developed and demonstrated for providing a high modulus composite material for use to 1000 DEG F. and above. This material can be produced at 5-20% of the cost of refractory materials, and has higher structural properties. This technology successfully resolves the problem of "thermal shock" or "ply lift," which limits traditional high temperature laminates (such as graphite / polyimide and graphite / phenolic) to temperatures of 550-650 DEG F. in thicker (0.25'' and above) laminates. The technology disclosed herein is an enabling technology for the nose for the External Tank (ET) of the Space Shuttle, and has been shown to be capable of withstanding the severe environments encountered by the nose cone through wind tunnel testing, high temperature subcomponent testing, and full scale structural, dynamic, acoustic, and damage tolerance testing.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Composite racquet with double tube head frame
A sports racquet frame is built of a composite of laminations of fibrous material as impregnated by a thermosetting resin. The head section of the frame has an upper tube preferably disposed above the string bed plane and a lower tube preferably disposed below the string bed plane. A solid bridge of material integrally joins the upper tube to the lower tube. In a preferred embodiment the bridge is disposed radially exteriorly of the center line of the tubes, to maximize the length of string segments, which are strung to the bridge.
Owner:EF COMPOSITE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com