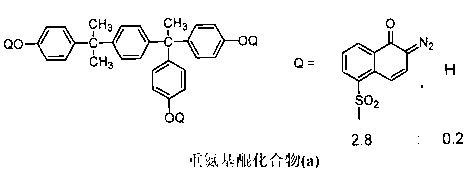
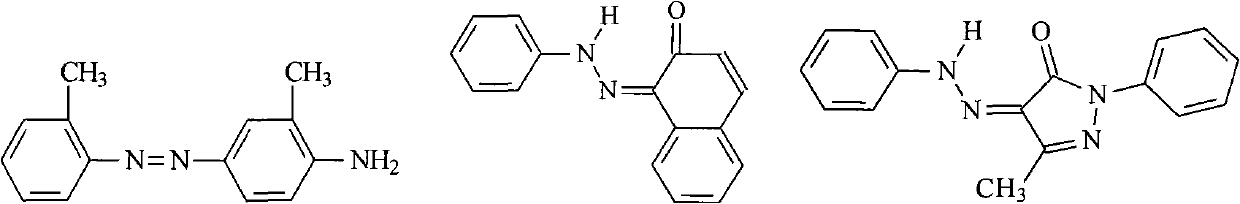
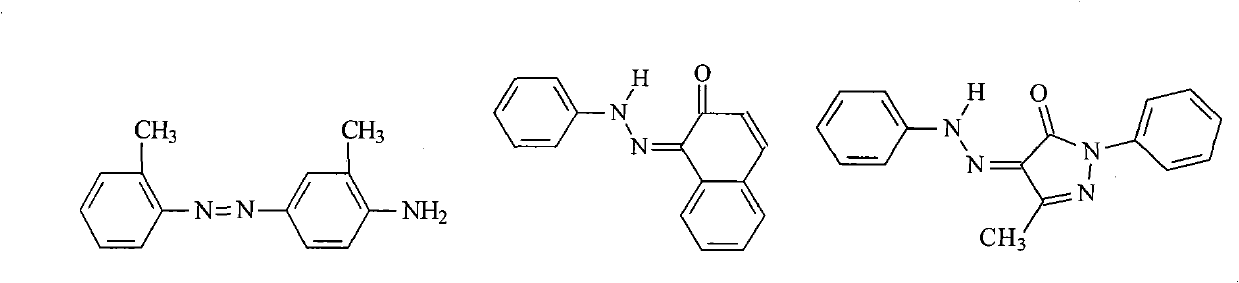
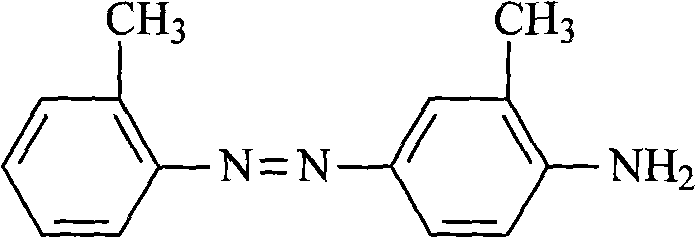
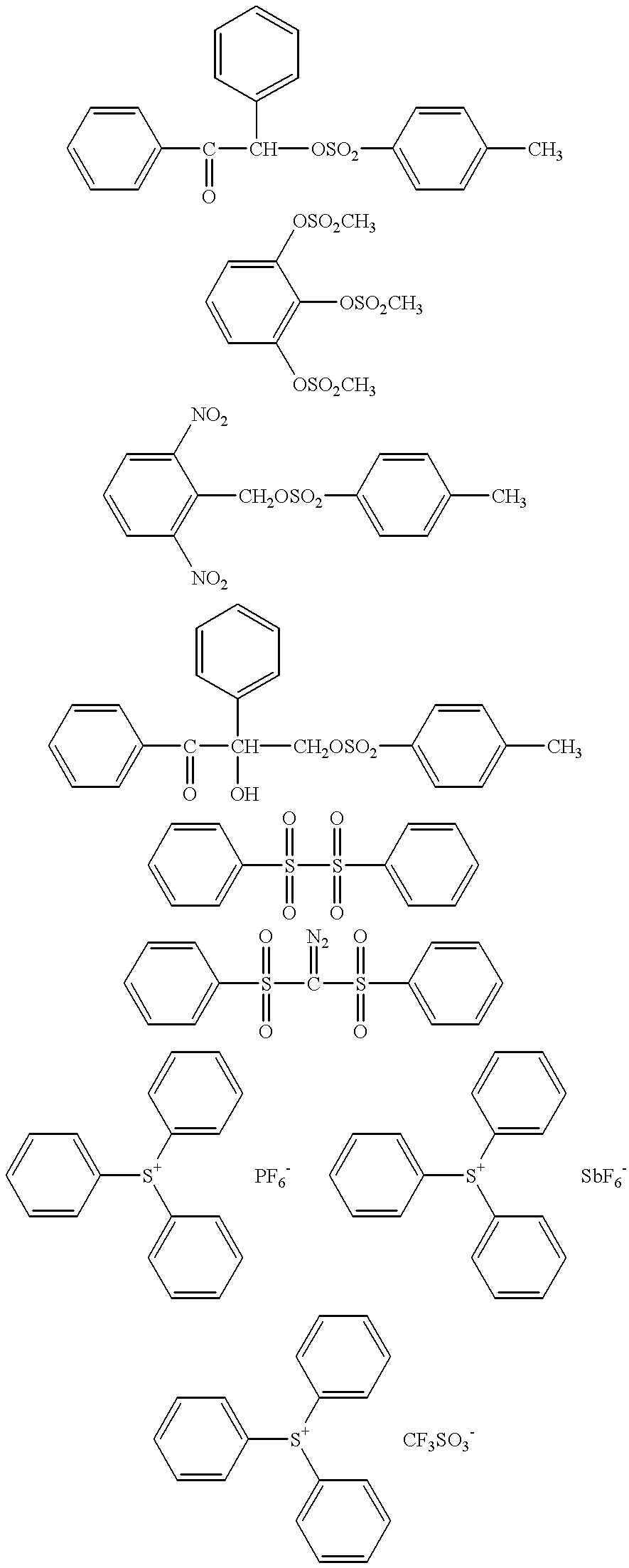
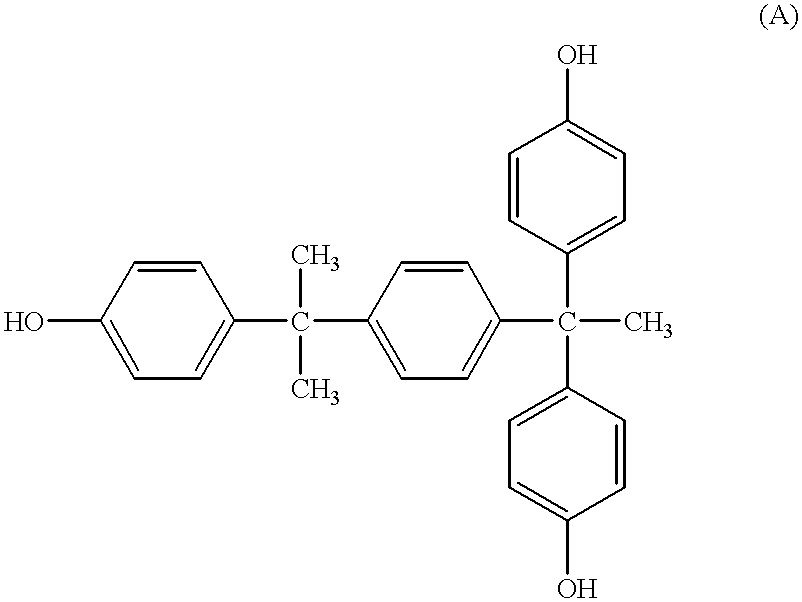
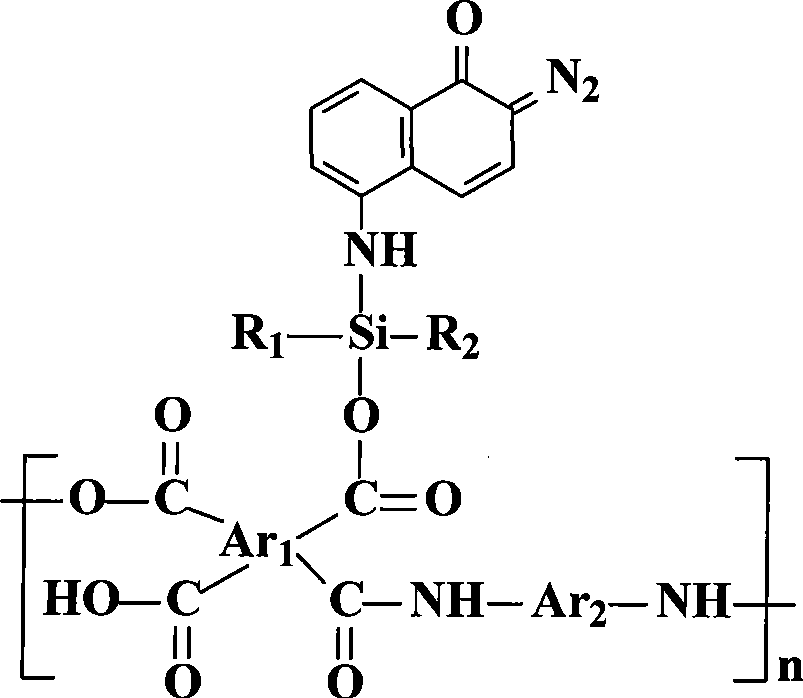
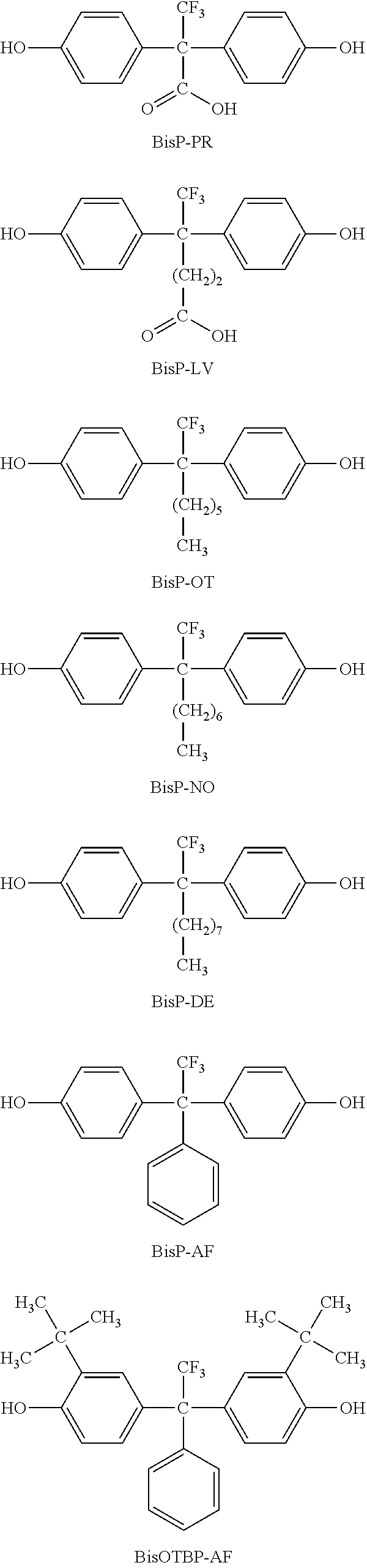
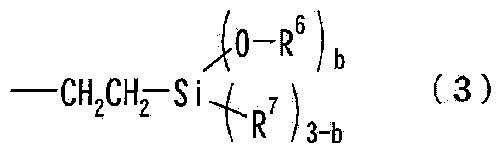Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Diazonaphthoquinone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diazonaphthoquinone (DNQ) is a diazo derivative of naphthoquinone. Upon exposure to light, DNQ converts to a derivative that is susceptible to etching. In this way, DNQ has become an important reagent in photoresist technology in the semiconductor industry.
Positive photosensitive siloxane composition
ActiveUS20130216952A1High sensitivityImprove heat resistancePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesSolvent
A positive photosensitive siloxane composition containing: a polysiloxane (Ia), which is obtained by hydrolyzing and condensing the silane compound represented by RSi(OR1)3 in general formula (1) and the silane compound represented by Si(OR1)4 in general formula (2) in the presence of a basic catalyst, and a pre-baked film of which has a dissolution rate of 1,000 Å / second or less in a 5 wt % TMAH aqueous solution; a polysiloxane (Ib), which is obtained by hydrolyzing and condensing at least the silane compound represented by general formula (1) in the presence of an acid or basic catalyst, and a pre-baked film of which has a dissolution rate of 100 Å / second or more in a 2.38 wt % TMAH aqueous solution; and a diazonaphthoquinone derivative and solvent. (In the formula: R represents a linear, branched or cyclic alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, in which any methylene may be replaced by oxygen, or represents an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, in which any hydrogen may be replaced by fluorine; and R1 is an alkyl group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms.)
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
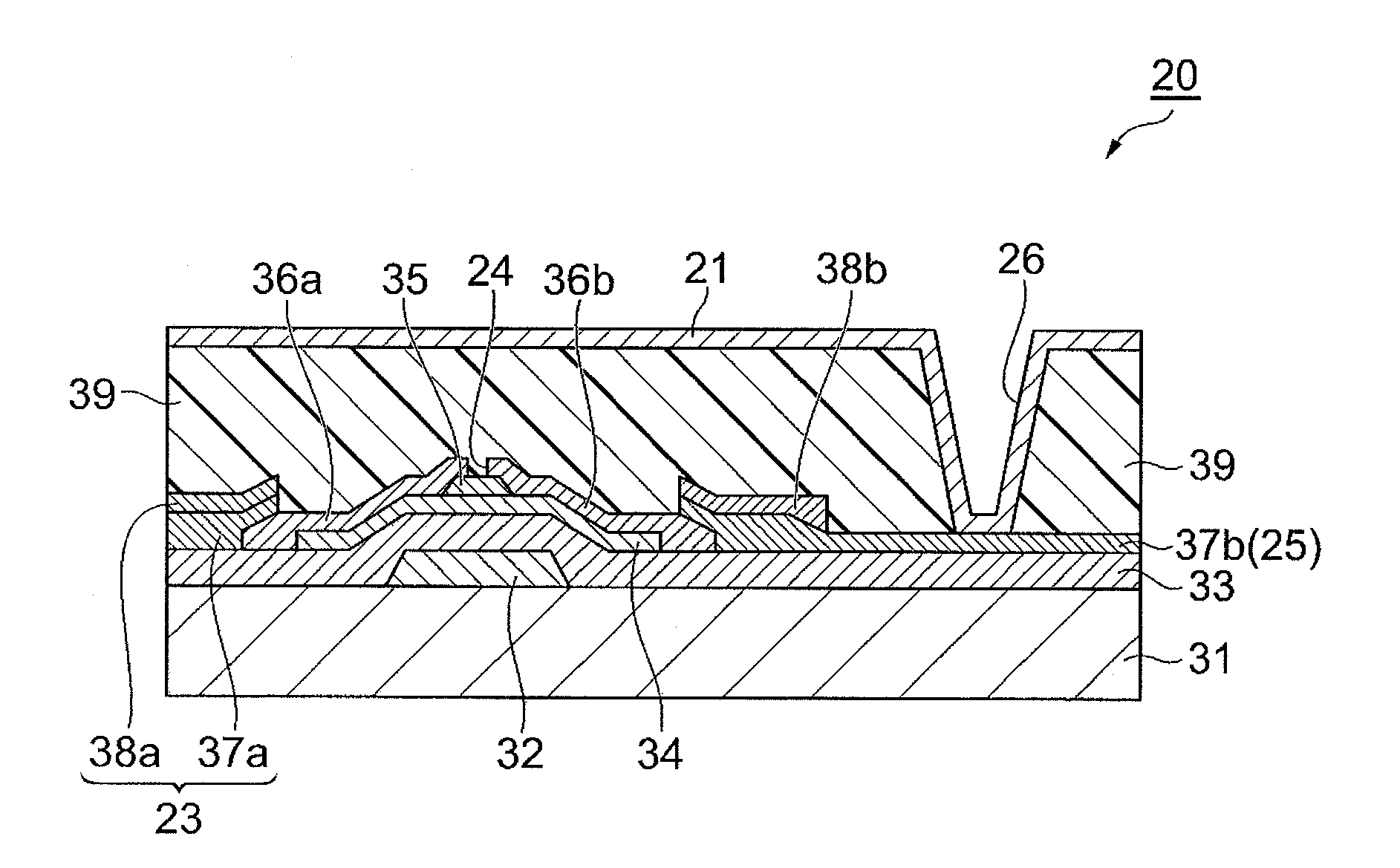
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20030027382A1Reduce exposure energyLow overall dimensionTransistorSolid-state devicesResistPositive type
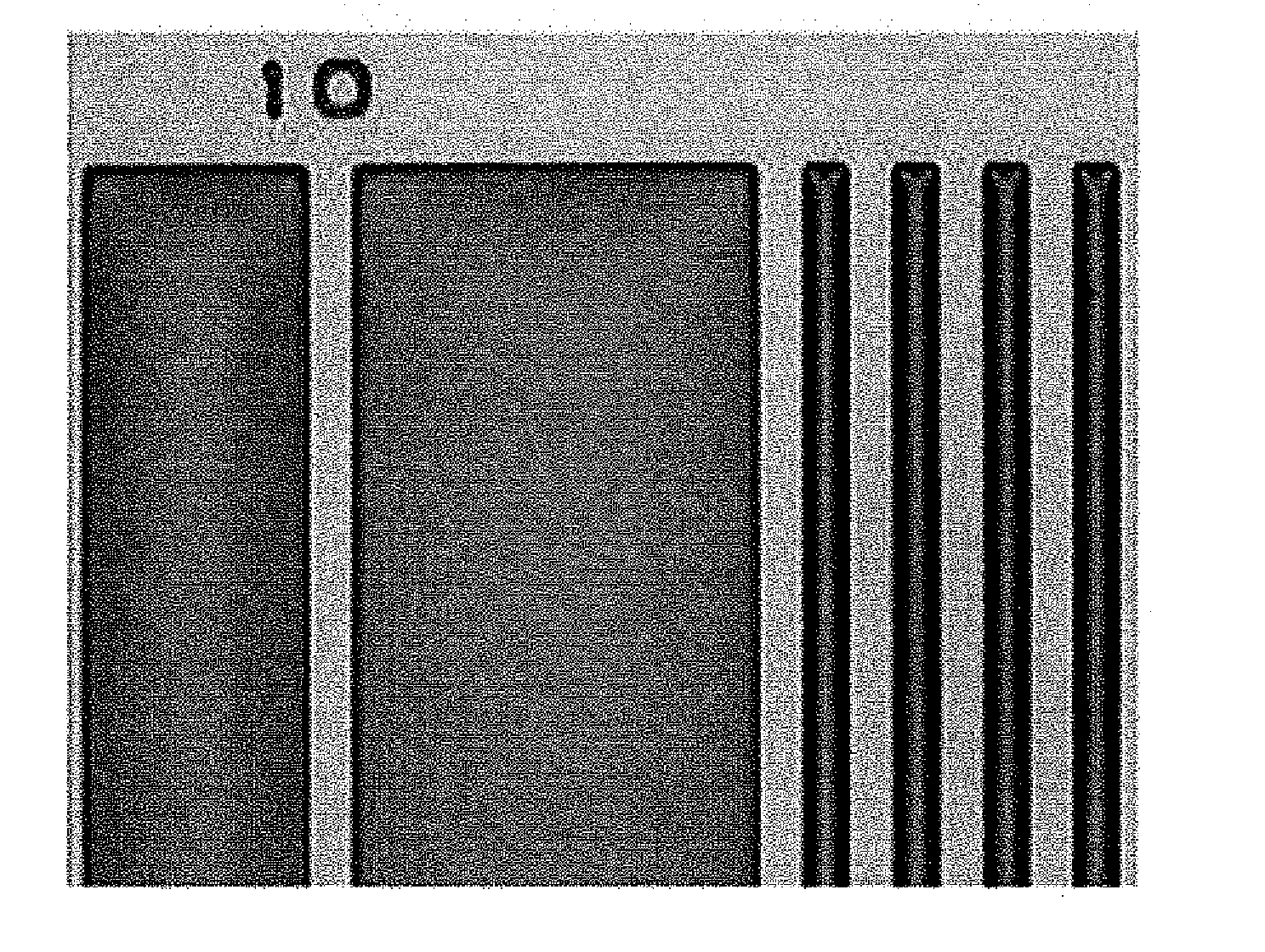
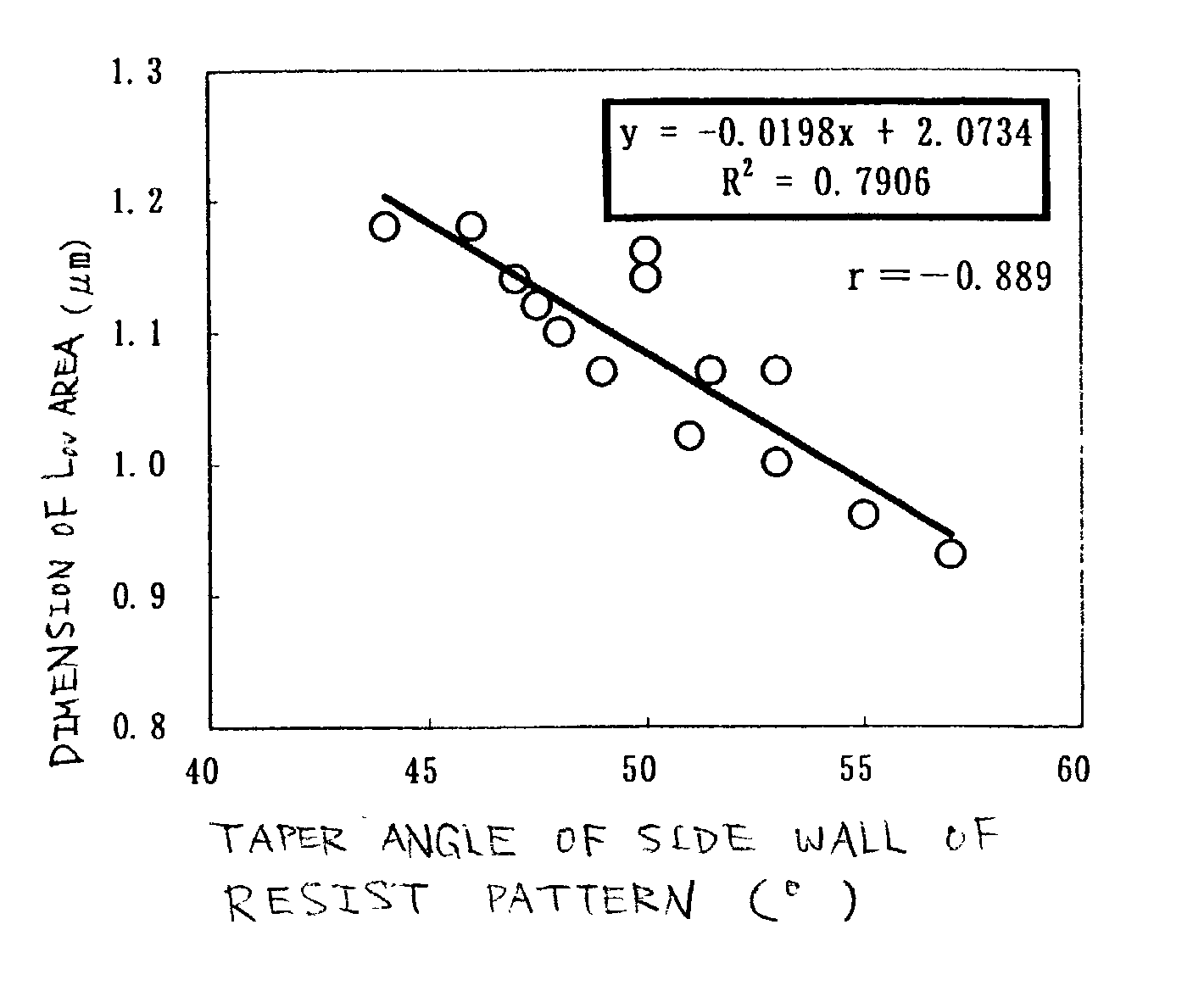
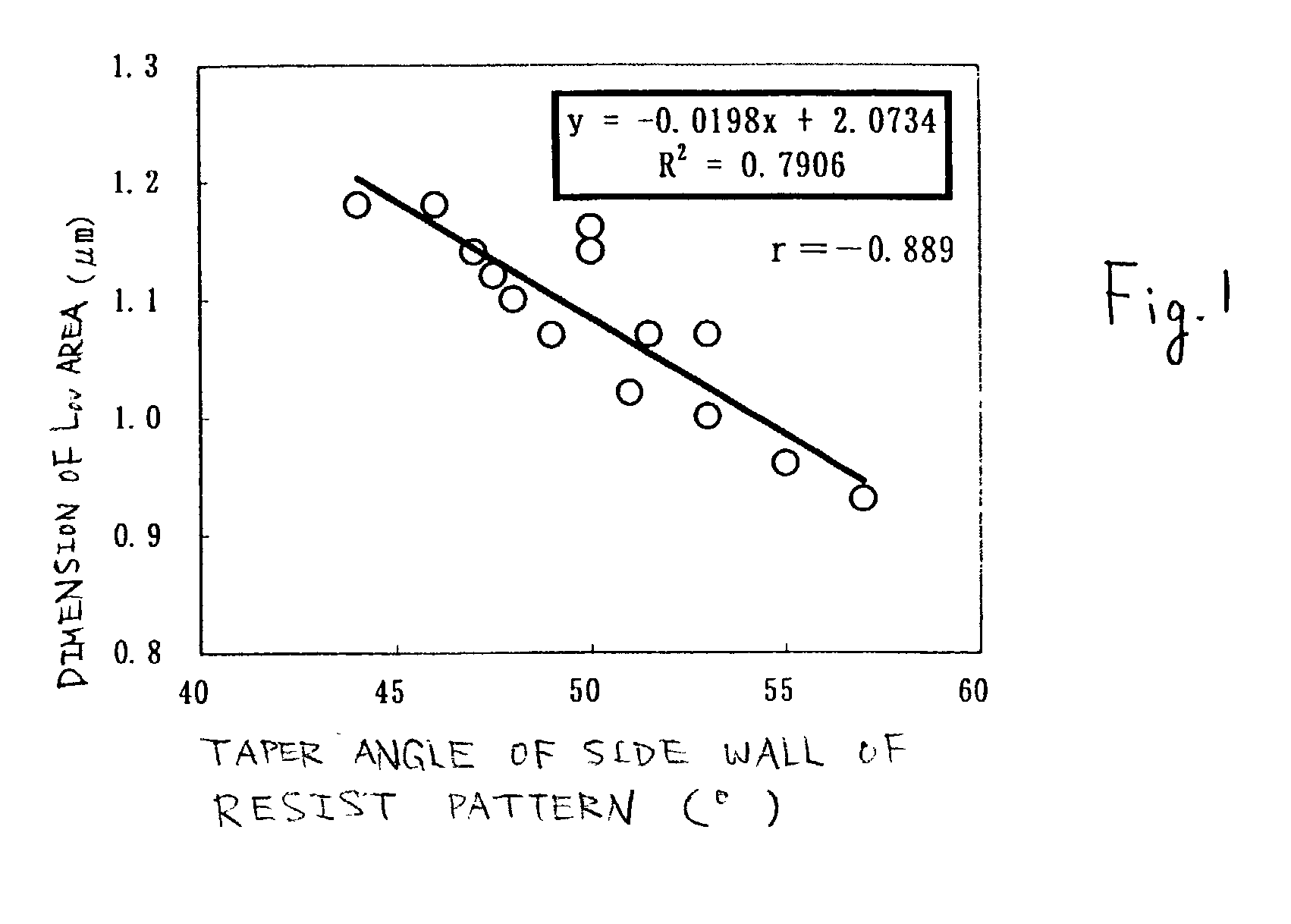
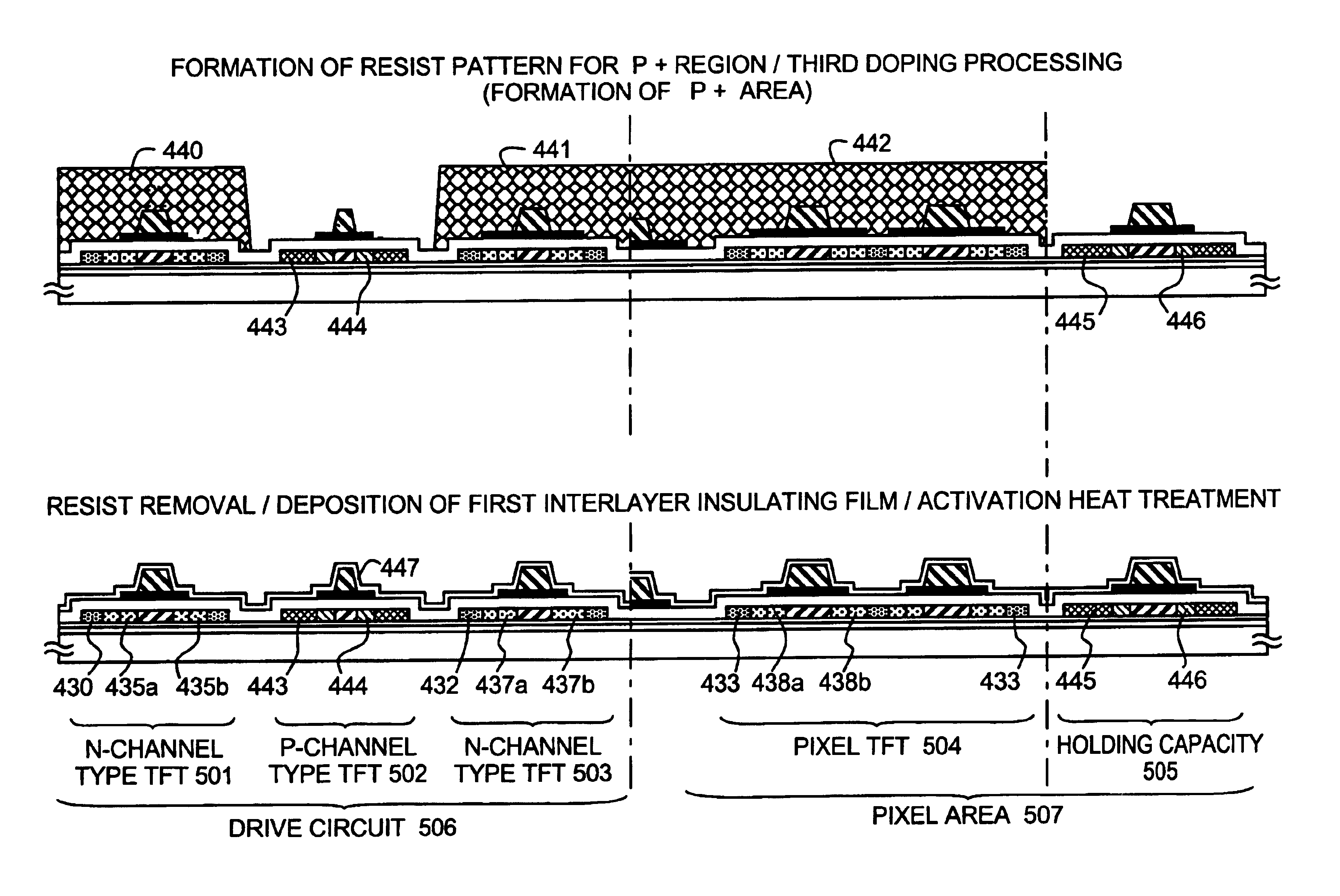
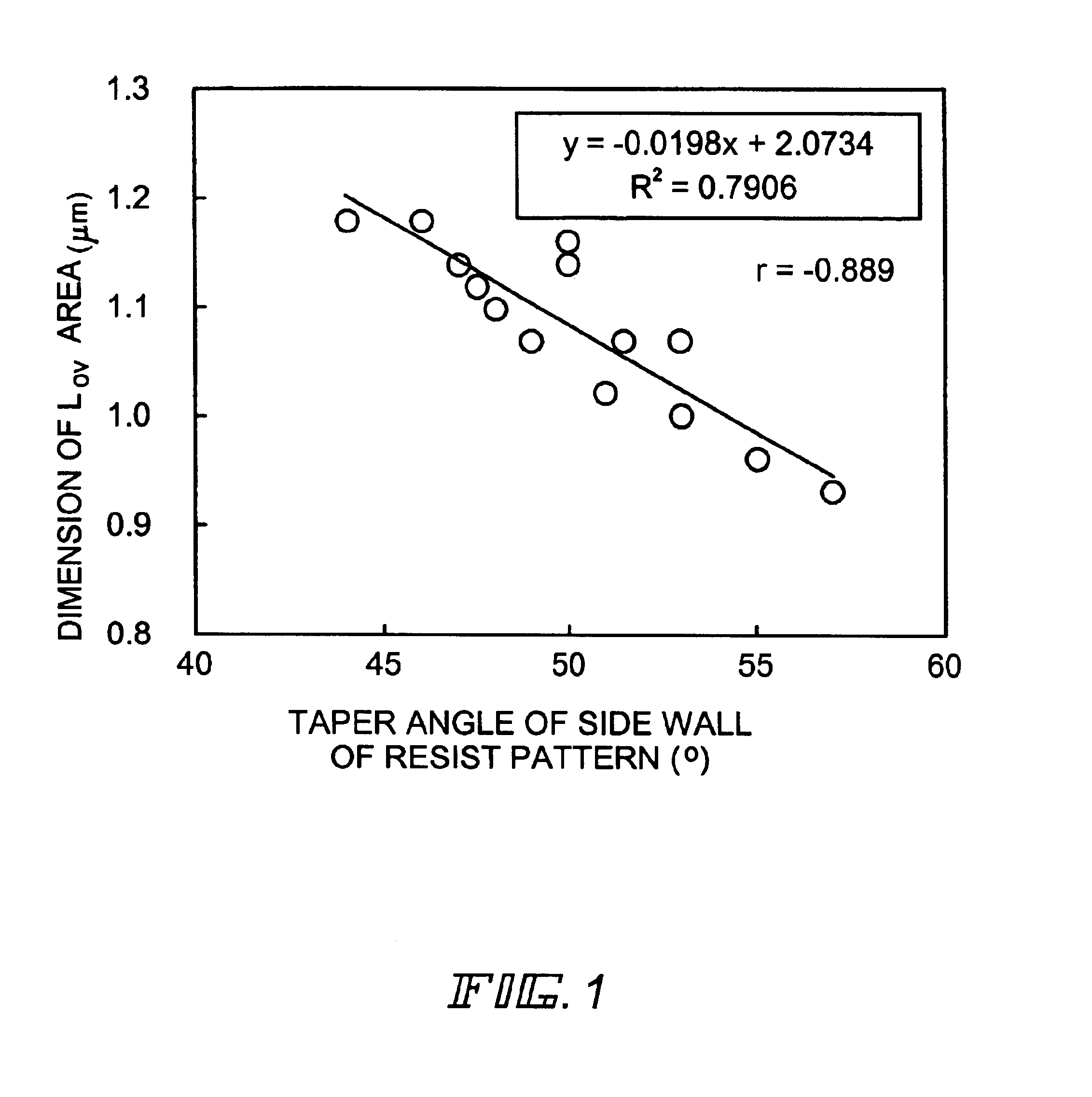
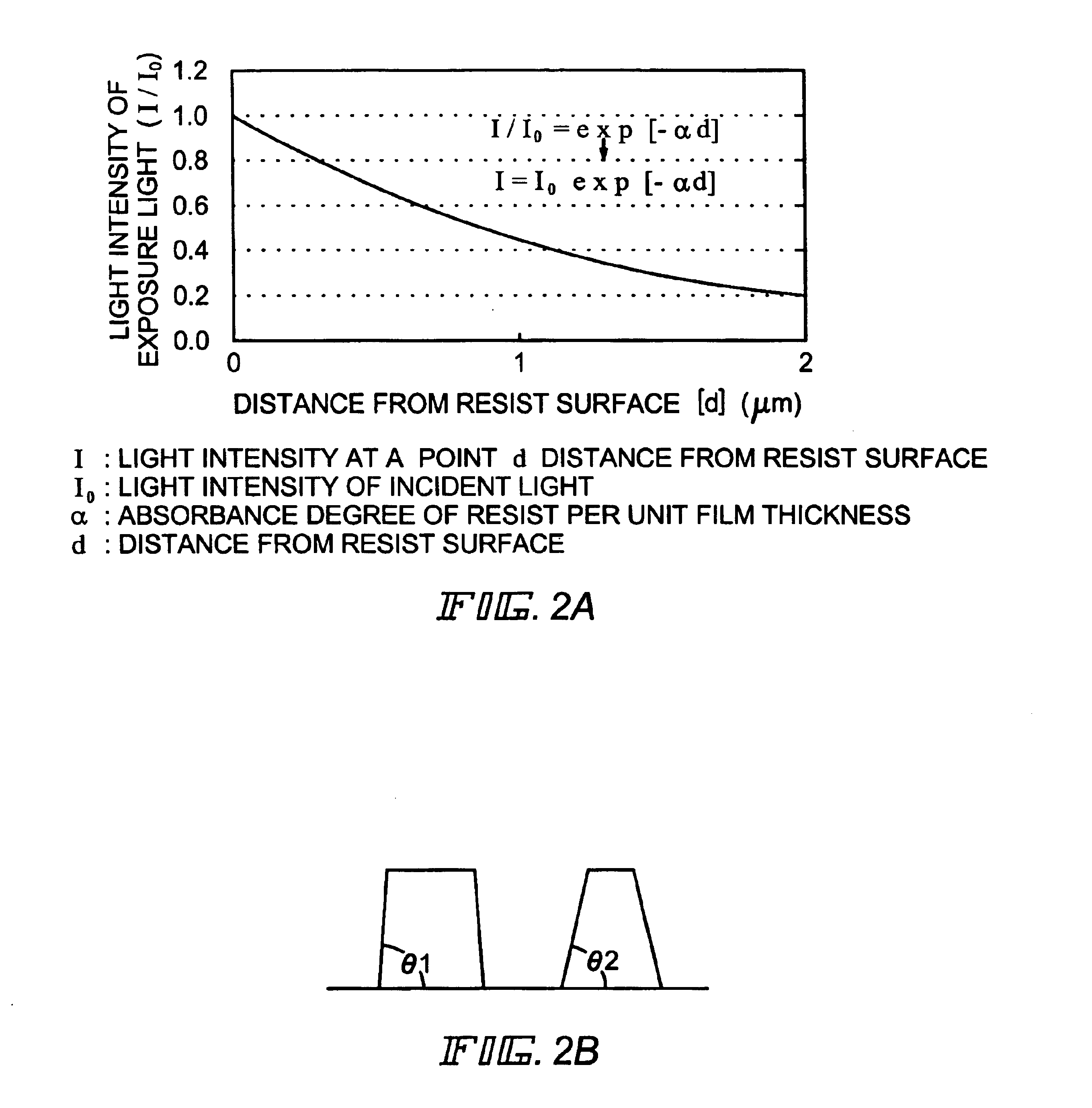
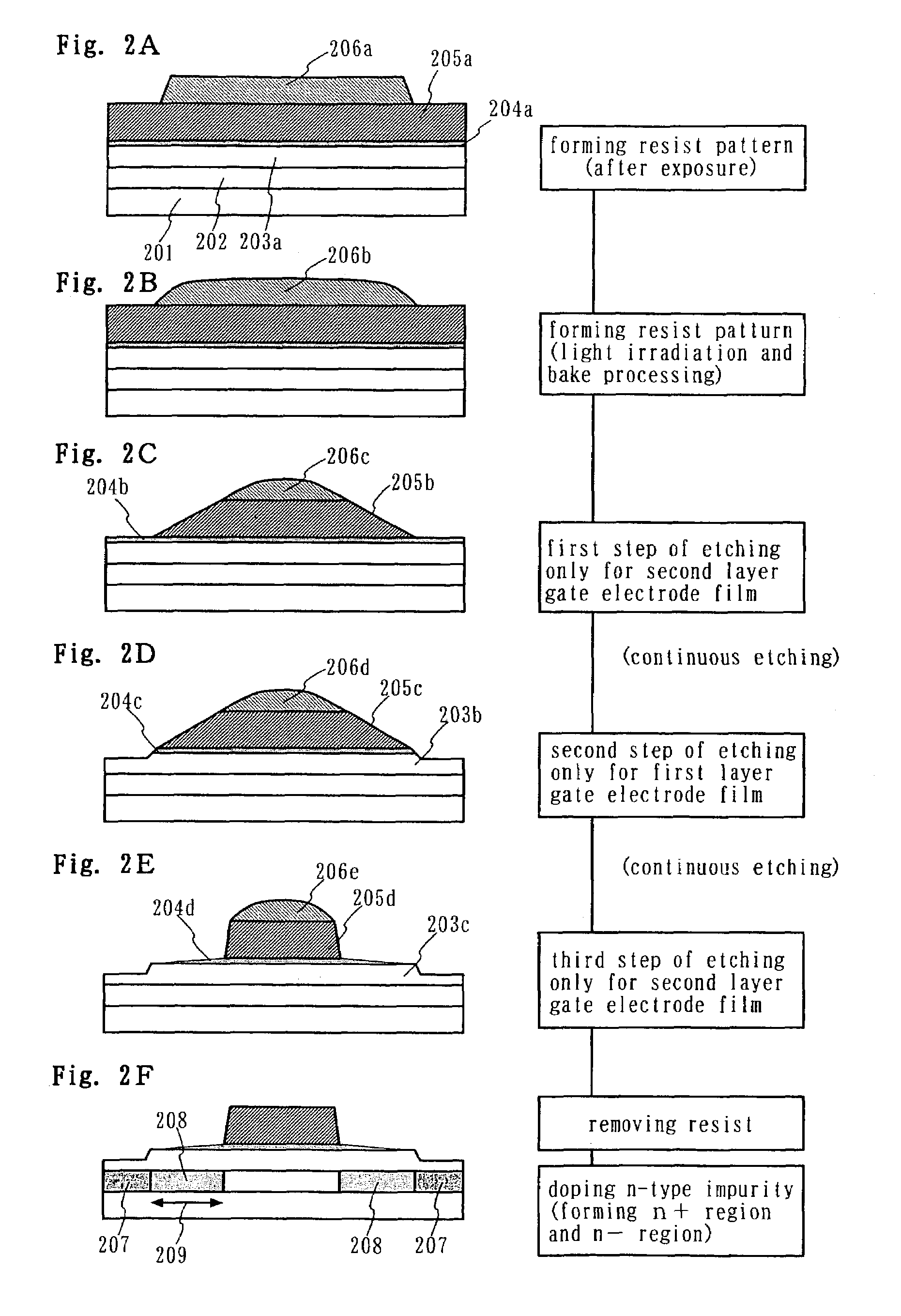
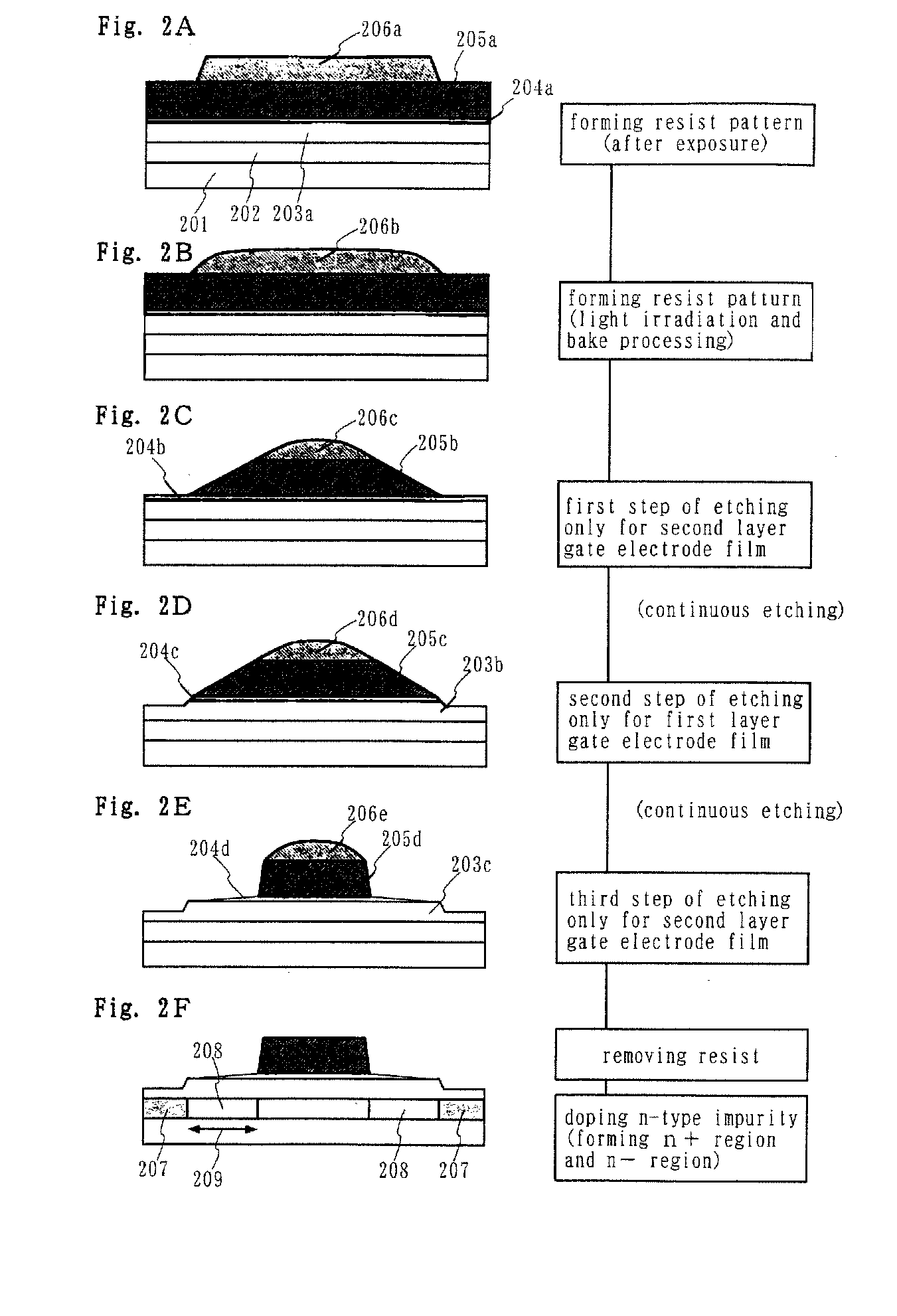
In the manufacturing method of a GOLD structured TFT having a gate electrode of double-layered structure, in which, compared to a second layer gate electrode, the first layer gate electrode is thinner in film thickness and longer in dimension of the channel direction, by controlling the density of the photo-absorbent contained in a positive type resist, which contains a photo-absorbent of diazonaphthoquinone (DNQ)-novolac resin series, the taper angle of the side wall is controlled to a desired angle range so that the angle thereof becomes smaller. Owing to this, it is possible to control the retreat amount of the resist when carrying out dry etching and the dimension of Lov area to a desired dimensional range so that the dimension thereof becomes larger.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS6746965B2Reduce exposure energyLow overall dimensionTransistorSolid-state devicesResistPositive type
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Positive photosensitive siloxane composition
ActiveUS20140335452A1High sensitivityImprove heat resistancePhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusPolymer scienceSilanes
A positive photosensitive siloxane composition comprising at least three types of following polysiloxanes (A), (B) and (C) obtained by hydrolyzing and condensing a silane compound represented by general formula (1) R1nSi (OR2)4-n, a diazonaphthoquinone derivative, and a solvent: a polysiloxane (A) such that if pre-baked the film thereof will be soluble in a 5 weight % TMAH aqueous solution and the solution rate of said film will be 1,000 Å / sec or less; a polysiloxane (B) such that if pre-baked the solution rate of the film thereof will be 4,000 Å / sec or more relative to a 2.38 weight % TMAH aqueous solution; and a polysiloxane (C) such that if pre-baked the solution rate of the film thereof will be between 200 and 3,000 Å / sec relative to a 2.38 weight % TMAH aqueous solution. (In the formula, R1 represents a C1-20 linear or branched cyclic alkyl group, in which any methylene may be substituted by oxygen, or a C6-20 aryl group, in which any hydrogen may be substituted by fluorine; n represents a 0 or a 1; and R2 represents a C1-5 alkyl group.)
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
An ultraviolet positive photoresist
ActiveCN109062008AHigh resolutionIncrease photosensitivityPhotomechanical apparatusSulfonyl chlorideSolvent
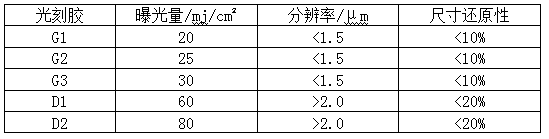
The invention provides an ultraviolet positive photoresist suitable for exposure under a UV light source. The photoresist is composed of, by mass percent, 1 to 10% of diazonaphthoquinone sulfonate photosensitizer with special structure, 10 to 50% of linear phenolic resin, 0.2 to 1% of sensitizer, 0.1 to 1% of toughening agent, 0.4 to 1% of adhesion promoter, 0.2 to 1% of leveling agent and the balance of solvent; wherein the diazonaphthoquinone sulfonate photosensitizer with special structure is obtained by subjecting 1, 1- P-hydroxyphenyl-[1-Biphenyl group-4-Isopropyl group-(1-o-methyl-4-phenol)] propane and 2-Diazo-1-Naphthoquinone-5-sulfonyl chloride to substitution reaction or esterification reaction according to the ratio of 1: 2; The linear phenol-formaldehyde resin is a mixture oflinear phenol-formaldehyde resin 1 and linear phenol-formaldehyde resin 2, and the weight ratio of linear phenol-formaldehyde resin 1 and linear phenol-formaldehyde resin 2 is 2-8: 8-2. The ultraviolet positive photoresist of the present invention has higher resolution, photosensitivity and size reducibility than the conventional diazonaphthoquinone sulfonate Phenolic resin system photoresist.
Owner:XILONG SCI CO LTD
Process for preparing water base developing photosensitive polyimide material
InactiveCN1648154AHigh photosensitivityGood film formingPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusWater basedBenzoic acid
The present invention belongs to the preparation process of water base developing photosensitive polyimide material. Aromatic dialphanyl diacyl chloride, 3,5-diamino benzoic acid, 4, 4'-diamino-3, 3'-dihydroxy diphenyl methane and 4, 4'-diamino-3, 3'-dihydroxy diphenyl sulfone are polymerized to produce polyamate as one kind of imide prepolymer. The prepolymer has characteristic viscosity of 0.35-0.50, and when 2-diazo naphthoquinone derivative as photosensitizer is added, the prepolymer becomes excellent photosensitive material with high photosensitive performance, good filming performance and high heat resistance.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photosensitive resin composition and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6440632B2Promote absorptionHard surfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsImage resolutionLength wave
A photosensitive resin composition comprises a base resin (e.g., novolak resins, polyvinylphenol-series polymers), a first photoactive ingredient (e.g., diazobenzoquinone derivatives, diazonaphthoquinone derivatives) and a second photoactive ingredient (e.g., mixtures with azide compounds) each having an absorption range at wavelength lambd1 or lambd2, the wavelengths thereof being different from each other. Between the first and second photoactive ingredients, at least one photoactive ingredient is substantially inert at the absorption wavelength of the other. After exposing the photosensitive resin composition to a light to form a pattern, the whole surface of the photosensitive layer is exposed to a light of the other wavelength to make the surface hardly soluble (in the case a positive pattern is formed) or readily soluble (in the case a negative pattern is formed) in a developer, and developed, thereby forming a pattern of high resolution. Utilizing an existing exposure system, there can be obtained photosensitive resin compositions (especially, resists for semiconductor production) having improved sensitivity and resolution.
Owner:KRI INC
Polyimide and light-sensitive resin composition comprising the same
InactiveCN102388086AHigh resolutionIncrease photosensitivityPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusTransmittancePolyamic acid
Provided are a polyimide and a light-sensitive resin composition comprising the same, which are employed in the buffer coatings of semiconductors. The polyimide is a polyimide polymer represented by Formula 1. Further, provided is a light-sensitive resin composition which comprises: 1) a soluble BDA series polyimide having an i-ray transmittance of at least 70%; 2) poly(amic acid) having a percentage elongation of at least 40%; 3) a novolac resin; and 4) a diazonaphthoquinone-based light-sensitive substance, and which has a high degree of resolution, high sensitivity, outstanding film characteristics and mechanical properties which are characteristics required of the buffer coatings of semiconductors.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Method for manufacturing display device and composition of sealant therefor
InactiveUS20090053965A1High glass transition temperatureLamination ancillary operationsPhotomechanical apparatusEpoxyDisplay device
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Positive photosensitive resin composition
ActiveCN101278234AWon't swellIncreased sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingOrtho positionDiazonaphthoquinone
A photosensitive resin composition comprising 100 parts by mass of polycondensate (A) having a structure resulting from dehydration condensation between one or two or more tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride and one or two or more aromatic diamines having mutually ortho-positioned amino and phenolic hydroxyl groups and 1 to 100 parts by mass of photosensitive diazonaphthoquinone compound (B), wherein the polycondensate (A) has a weight average molecular weight of 3000 to 70,000.
Owner:HEFEI HANZHIHE MATERIAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Photosensitive composition, cured film formed from same, and element having cured film
ActiveCN103180784AImprove heat resistanceHigh transparencyPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusNon-linear opticsHeat resistanceMetal chelate
Provided is a positive photosensitive composition containing (A) an alkali-soluble resin, (B) a naphthoquinonediazide compound, (C) a solvent and (D) a metal chelate compound, which is characterized in that the (D) metal chelate compound has a structure represented by general formula (1) and the content of the (D) metal chelate compound is 0.1-5 parts by weight relative to 100 parts by weight of the (A) alkali-soluble resin. The positive photosensitive composition has characteristics such as high heat resistance and high transparency, while exhibiting excellent adhesion during development and excellent wet heat resistance.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method of fabricating semiconductor device, and developing apparatus using the method
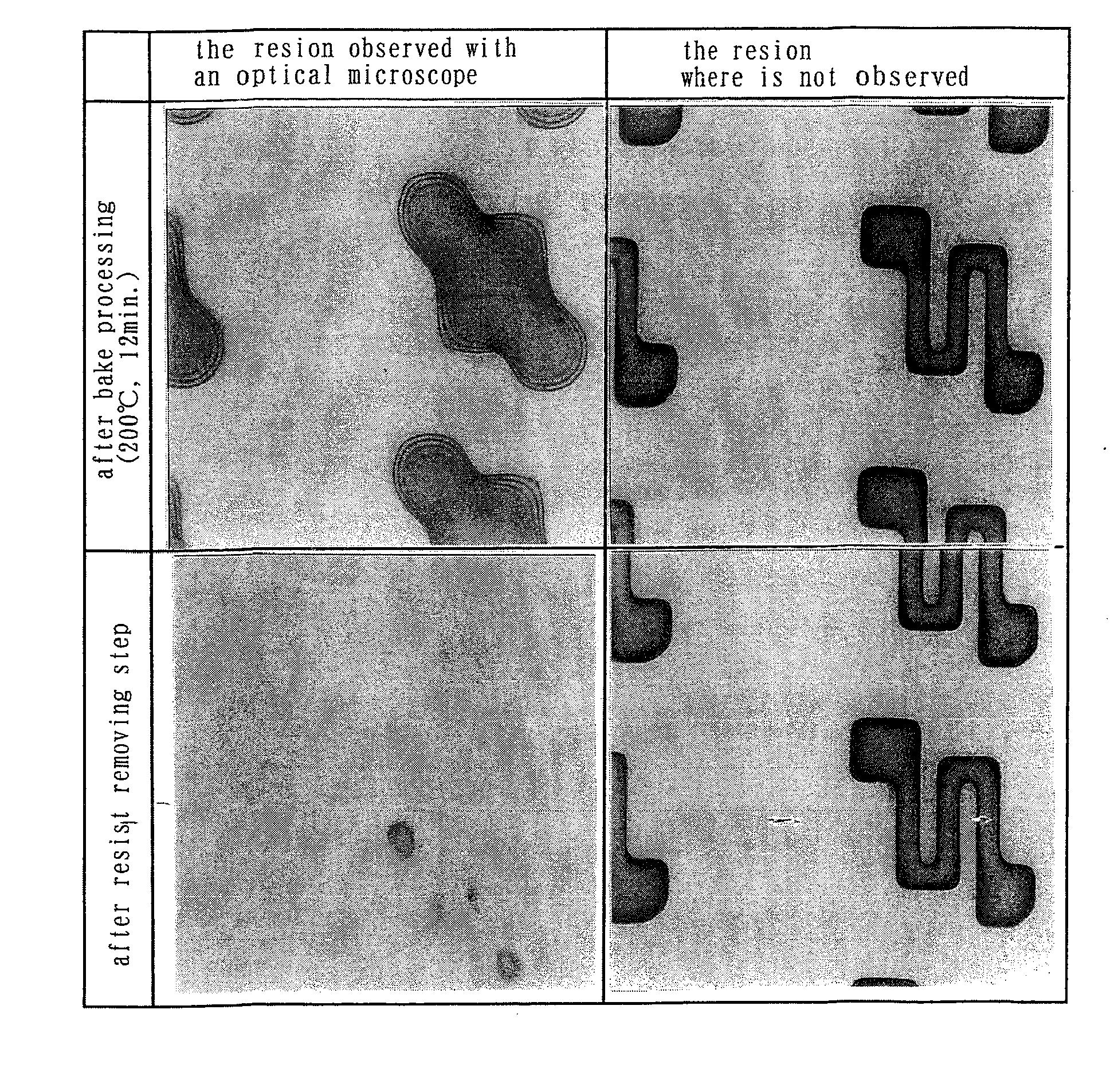
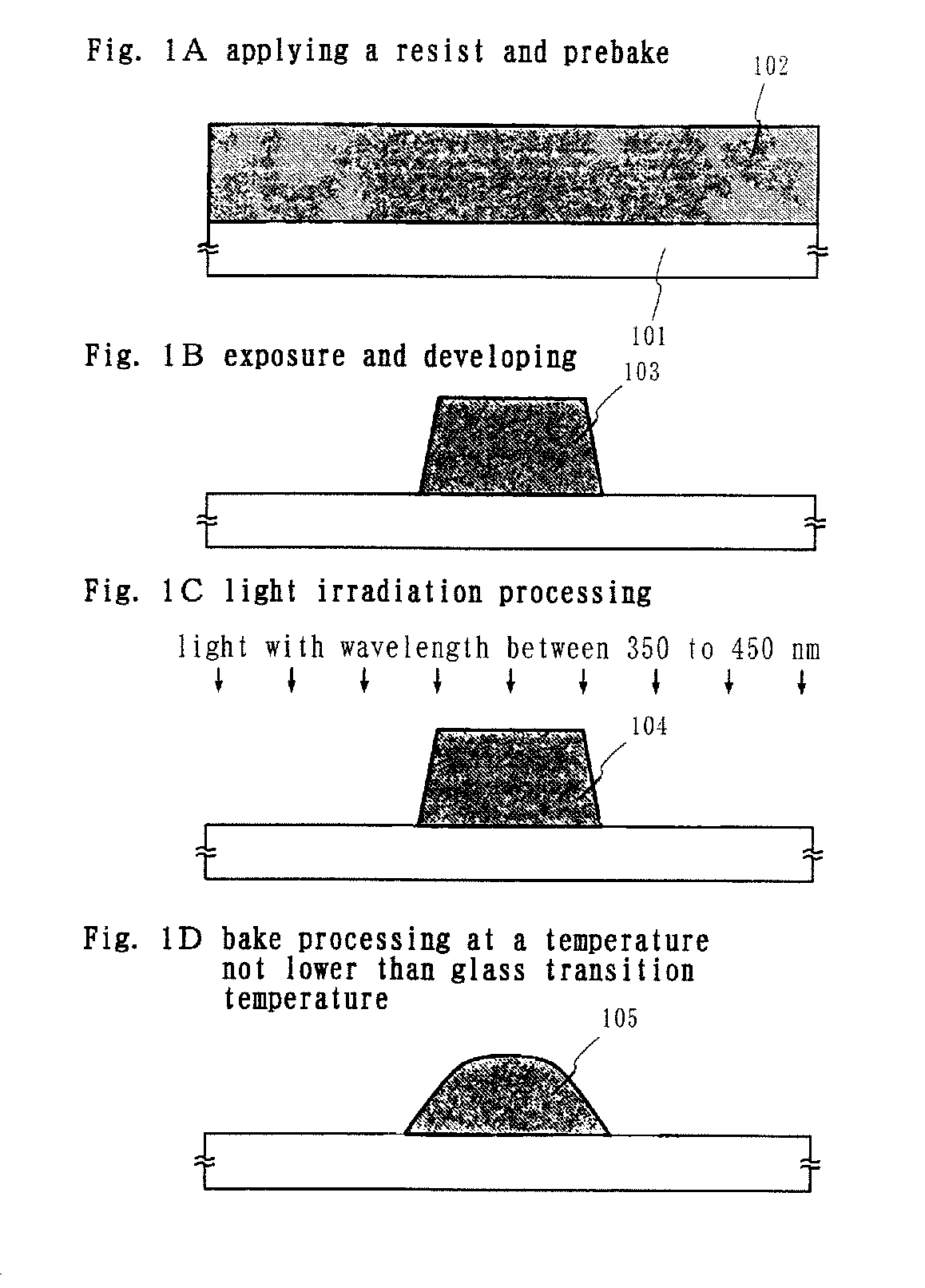
InactiveUS7344825B2High-throughput processingImprove solubilityTransistorSolid-state devicesVitrificationResist
In a resist pattern forming method in which bake processing is performed at a temperature not lower than a glass transition temperature in order to obtain the desired sidewall angle, resist removable is difficult. Accordingly, in the resist pattern forming method of performing bake processing at a temperature not lower than a glass transition temperature, a process margin for resist removability cannot be ensured, so that there is the problem that it is impossible to compatibly realize both the formation of a resist pattern having the desired sidewall angle and the resist removability of the resist pattern. The invention aims to solve the problem. A resist pattern including a diazonaphthoquinone (DNQ)-novolac resin type of positive resist is formed, and the resist pattern is irradiated with light within the range of photosensitive wavelengths of a DNQ photosensitizer to perform bake processing on the resist pattern at a temperature not lower than the glass transition temperature of the resist pattern.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Positive lithograph plate photosensitive composition with high resolution and high sensitivity
ActiveCN101770169APhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusImage resolutionExposure latitude
Owner:LUCKY HUAGUANG GRAPHICS +1
Photosensitive resin composition and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20020012867A1Improve cross-linking efficiencyGenerate efficientlySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsNaphthoquinonePerylene derivatives
A photosensitive resin composition comprises a base resin (e.g., novolak resins, polyvinylphenol-series polymers), a first photoactive ingredient (e.g., diazobenzoquinone derivatives, diazonaphthoquinone derivatives) and a second photoactive ingredient (e.g., mixtures with azide compounds) each having an absorption range at wavelength lambd1 or lambd2, the wavelengths thereof being different from each other. Between the first and second photoactive ingredients, at least one photoactive ingredient is substantially inert at the absorption wavelength of the other. After exposing the photosensitive resin composition to a light to form a pattern, the whole surface of the photosensitive layer is exposed to a light of the other wavelength to make the surface hardly soluble (in the case a positive pattern is formed) or readily soluble (in the case a negative pattern is formed) in a developer, and developed, thereby forming a pattern of high resolution. Utilizing an existing exposure system, there can be obtained photosensitive resin compositions (especially, resists for semiconductor production) having improved sensitivity and resolution.
Owner:KRI INC
Positive photosensitive siloxane composition
ActiveUS8883397B2High sensitivityImprove heat resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsSilanesOxygen
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Patterning of ionic polymers
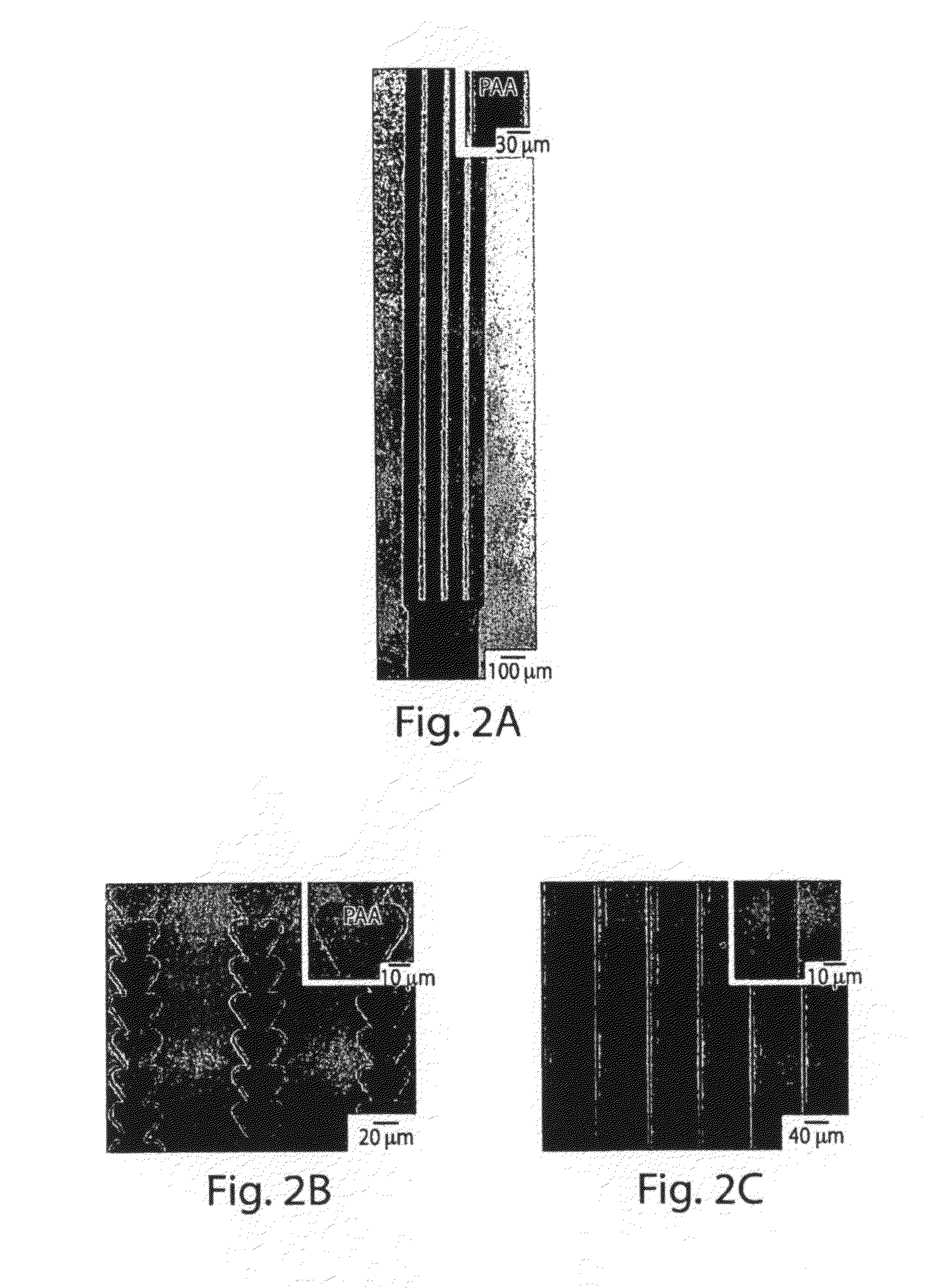
In one aspect, methods of patterning of thin films of an ionotropic polymer (e.g., poly(acrylic acid)) are provided. These processes can create micron or sub-micron-scale patterns of ionotropic polymers such as cation crosslinked poly(acrylic acid) (CCL-PAA). In one embodiment, patterning may be performed within microfluidic channels by flowing a solution of crosslinking agent (e.g., metal cations such as Ag+, Ca2+, Pd2+, Al3+, La3+, and Ti4+) that can crosslink a portion of an ionotropic polymer in contact with the solution. In another embodiment, methods of patterning ionotropic polymers involve photolithography. Upon patterning a positive photoresist (e.g., diazonaphthoquinone-novolac resin) on a film of CCL-PAA, the exposed regions of CCL-PAA can be etched by an aqueous solution. Advantageously, the patterned, crosslinked polymer may also serve as both a reactant and a matrix for subsequent chemistry. For example, in some embodiments, the initial crosslinking cation can be exchanged for a second cation that could not be patterned photolithographically. Patterned films of CCL-PAA can also be used to host and template the reduction of metallic cations to metallic nanoparticles, and to fabricate porous, low-k dielectric substrates.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Positive-type photosensitive siloxane composition
ActiveUS20150291749A1High sensitivityImprove heat resistancePhotomechanical apparatusOrganic dyesTetramethylammonium hydroxidePositive type
A positive-type photosensitive siloxane composition which comprises (I) two or more polysiloxanes that differ in the rate of dissolution in aqueous tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) solutions, (II) a polysiloxane that gives a film which after prebaking has a rate of dissolution in 2.38 wt-% aqueous TMAH solution of 50-1,000 Å / sec and that has a group soluble in aqueous TMAH solution, other than silanol, (III) a diazonaphthoquinone derivative, and (IV) a solvent.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Positive photosensitive resin composition
InactiveUS20090267239A1High sensitivityGood relief patternElectric discharge tubesPhotosensitive materialsOrtho positionDiazonaphthoquinone
A photosensitive resin composition comprising parts by mass of polycondensate (A) having a structure resulting from dehydration condensation between one or two or more tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride and one or two or more armatic diamines having mutually ortho-positioned amino and phenolic hydroxyl groups and 1 to 100 parts by mass of photosensitive diazonaphthoquinone compound (B), wherein the polycondensate (A) has a weight average molecular weight of 3000 to 70,000.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI E-MATERIALS CORPORATION +1
Method of Fabricating Semiconductor Device, and Developing Apparatus Using the Method
InactiveUS20080182209A1Improve solubilityLow baking temperatureTransistorSolid-state devicesVitrificationResist
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Photosensitive resin composition, method for forming silica coating film, and apparatus and member each comprising silica coating film
InactiveUS20120021190A1Improve heat resistanceHigh resolutionPhotosensitive materialsDecorative surface effectsSilane compoundsAlcohol
The photosensitive resin composition of the invention comprises component (a): a first siloxane resin obtained by hydrolytic condensation of a first silane compound comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1), component (b): a solvent in which component (a) dissolves, and component (c): an ester of a phenol or alcohol and naphthoquinone diazide sulfonic acid.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Polyimide and photoresist resin composition comprising thereof
ActiveUS20110111341A1High resolutionImprove featuresPhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusPolyamic acidDiazonaphthoquinone
The present invention provides polyimide applied to the buffer coating of semiconductors and a photosensitive resin composition including the same. The polyimide is a polyimide polymer represented by Chemical Formula 1 below. Further, the present invention provides a photosensitive resin composition, including 1) BDA-series soluble polyimide having an i-ray permeability of 70% or more; 2) a polyamic acid having elongation of 40% or more; 3) a novolak resin, and 4) diazonaphthoquinone-series photosensitive substance and having a high resolution, high sensitivity, an excellent film characteristic, and mechanical physical properties which are the requirements of semiconductor buffer coating.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Photosensitizer containing diazo group, photoresist composition and preparation methods of photosensitizer and photoresist composition
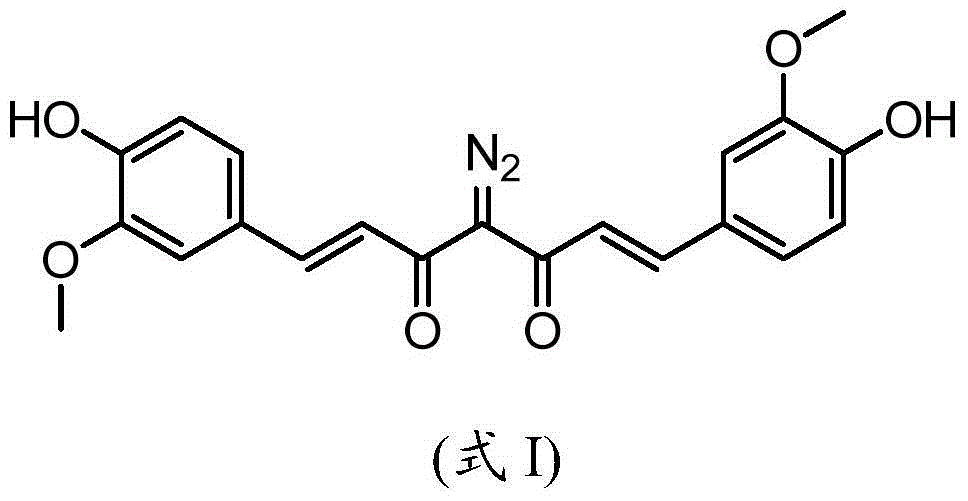
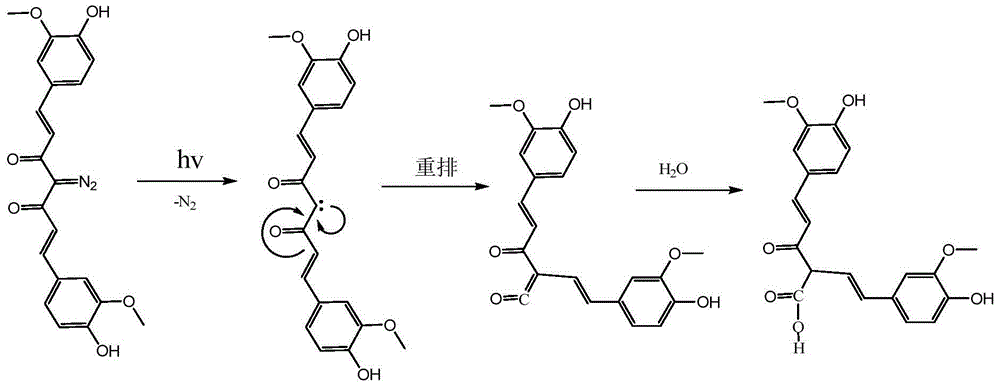
ActiveCN104391428AProduct yield is highImprove thermal stabilityOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusSulfonyl chlorideOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a photosensitizer containing a diazo group, a diazo positive photoresist composition for a liquid crystal display (LCD) and preparation methods of the photosensitizer and the photoresist composition. The curcumin photosensitizer containing the diazo group is a compound with the structure shown in formula I described in the specification; the photoresist composition comprises film-forming resin, the curcumin photosensitizer containing the diazo group, and an organic solvent. The curcumin photosensitizer containing the diazo group has the molecular weight of 394; compared with the existing diazo naphthoquinone photosensitizer formed by carrying out esterification on esterification parent and diazo naphthoquinone sulfonyl chloride, the curcumin photosensitizer containing the diazo group is higher in resolution ratio and small in molecular weight, enables the photoresist removing process to be easy, and is less in residue. Furthermore, the curcumin photosensitizer is high in preparation yield and good in heat stability. The positive photoresist which is used for an LCD thin film transistor (TFT) and is good in storage stability and high in resolution ratio can be formed by combining the curcumin photosensitizer and the traditional film-forming resin, so that the problems that the existing diazo naphthoquinone system LCD photoresist is difficult to refine, poor in storage stability and lower in resolution ratio can be solved. The following is the formula I (in the specification).
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
FPD/TP positive photoresist used for flexible substrate
The invention provides a FPD / TP positive photoresist applicable to a flexible substrate. The photoresist is composed of the following components by mass: 5 to 30% of diazonaphthoquinone sulphonate, 30 to 90% of phenolic novolac resin, 2 to 30% of long-chain alkylphenol, 0.01 to 10% of a silicone coupling agent, 0.01 to 10% of epoxy soybean butyl oleate, 5 to 50% of a nanometer reinforcing agent (nanometer carbon black), 5 to 30% of melamine resin and 50 to 90% of propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate. The positive phenolic photoresist has good adhesion and all technical performances (like coating property, resolution and sensitivity) of a traditional positive phenolic photoresist, can be well applied in production of FPD / TP with high requirement for resolution (about 5 [mu]m), and has good application prospects.
Owner:SUZHOU RUIHONG ELECTRONIC CHEM CO LTD
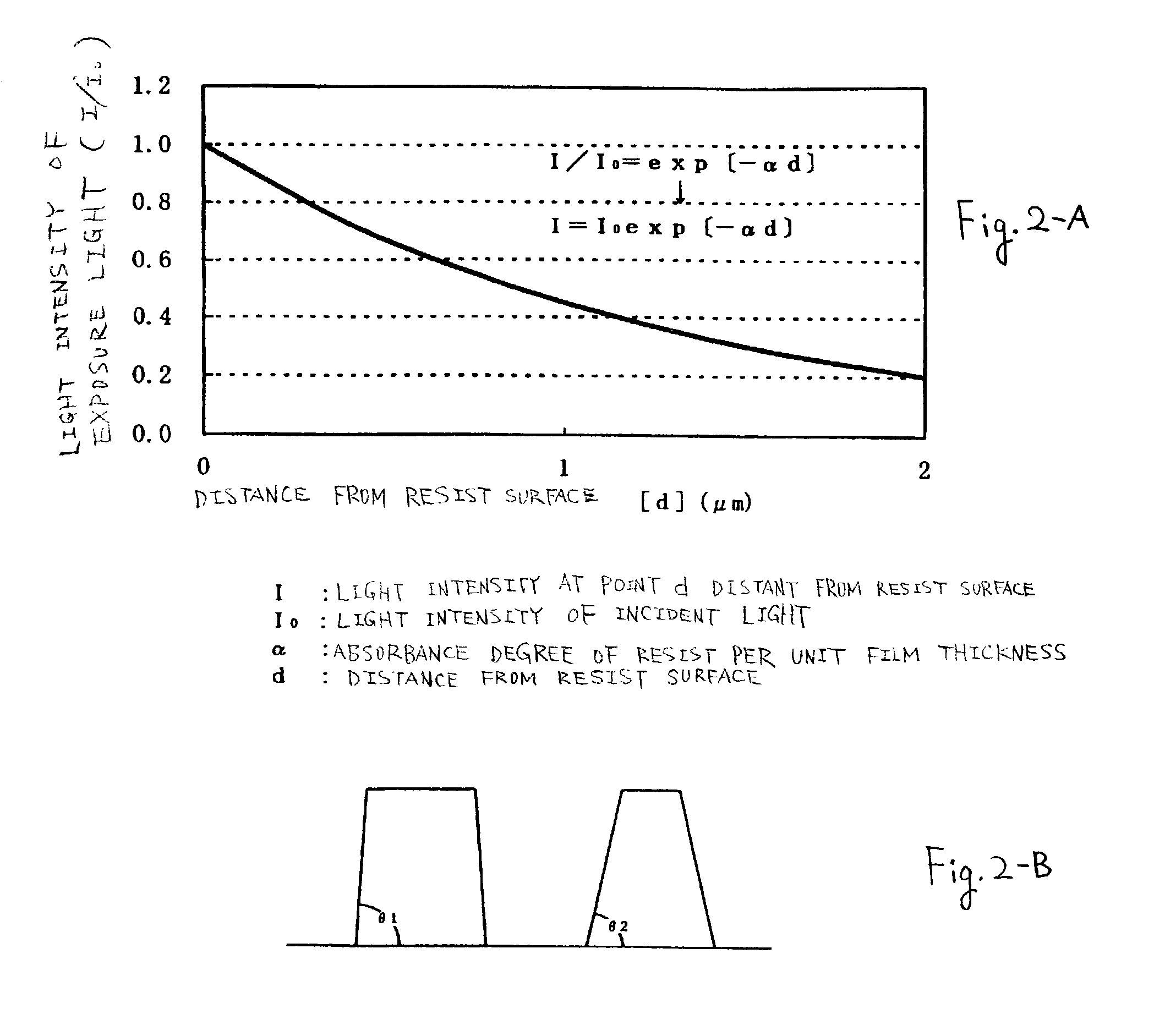
Method for simulating three-dimensional light intensity distribution in thick resist ultraviolet (UV) shifting mask lithography
InactiveCN103472686ASolve the problem of three-dimensional light intensity distributionSimplified Diffraction Integral EquationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusUltravioletParaxial approximation
The invention provides a method for simulating three-dimensional light intensity distribution in thick resist ultraviolet (UV) shifting mask lithography. The method comprises the following steps of pushing forward a three-dimensional light intensity calculation model suitable for a diazonaphthoquinone (DNQ) resist UV shifting mask lithography process by utilizing the paraxial approximation technology of incident UV to treat a Fresnel-Kirchhoff diffraction integral equation based on the optical scalar diffraction theory and shifting the upper and lower limits of the Fresnel integral horizontally; comprehensively considering the reflection and refraction effects on an air / DNQ resist interface and the reflection effect on an DNQ resist / substrate interface in the UV propagation process as well as the UV absorption factors of DNQ resist to highly accurately simulate three-dimensional light intensity distribution in the DNQ resist UV shifting mask lithography process; in the three-dimensional light intensity calculation model of UV in photoresist, embedding the position function of shifting of a mask plate with time into the light intensity distribution function to obtain light intensity distribution changing with time and exposure doses in different positions of photoresist in the whole exposure process. The problem that three-dimensional light intensity distribution in the DNQ resist UV shifting mask lithography process can not be simulated by the traditional light intensity distribution simulation methods based on the scalar diffraction theory is solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Positive photosensitive polyimide containing silazane chain structure and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a positive photosensitive polyimide containing a silicon-amine chain structure and a preparation method thereof, which pertains to the technical field of material and relates to a high polymer material with high heat resistance and a sensitization function. The positive photosensitive polyimide containing the silicon-amine chain structure is an organic fiber-shaped polymer material of which the main material is composed of polyamic acid with lateral chains of different polymerization degrees containing photosensitive groups. tetracarboxylic dianhydride and diamine are taken as raw materials, dissolved with an organic solvent, and reacts at room temperature with stirring; reagent is filtered, washed and dried to obtain the polyamic acid; the polyamic acid and chlorosilane amido diazonaphthoquinone are dissolved in an organic solvent and reacts at room temperature with stirring, reagent is filtered, washed and dried to obtain the positive photosensitive polyimide containing the silicon-amine chain structure. The positive photosensitive polyimide containing a silicon-amine chain structure has strong adhesion, good film forming ability, and high resolution ratio and heat resistance. The positive photosensitive polyimide can be used in photolithographic processes of optical devices, optoelectronic devices, microelectronic devices and other devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Photosensitive siloxane composition
ActiveUS20190077961A1Low dielectric constantGood chemical resistancePhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhotosensitive material processingPolymer scienceImage resolution
[Object] To provide a composition capable of forming a cured film having low permittivity and excellence in chemical resistance, in heat resistance and in resolution; and further to provide a production process employing the composition. [Means] The present invention provides a composition comprising: an alkali-soluble resin, namely, a polymer comprising a carboxyl-containing polymerization unit and an alkoxysilyl-containing polymerization unit; a polysiloxane; a diazonaphthoquinone derivative; a compound generating acid or base when exposed to heat or light; and a solvent.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Polyimide and photoresist resin composition comprising thereof
ActiveUS9012595B2High resolutionImprove featuresDiazo compound compositionsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusPolyamic acidDiazonaphthoquinone
The present invention provides polyimide applied to the buffer coating of semiconductors and a photosensitive resin composition including the same. The polyimide is a polyimide polymer represented by Chemical Formula 1 below. Further, the present invention provides a photosensitive resin composition, including 1) BDA-series soluble polyimide having an i-ray permeability of 70% or more; 2) a polyamic acid having elongation of 40% or more; 3) a novolak resin, and 4) diazonaphthoquinone-series photosensitive substance and having a high resolution, high sensitivity, an excellent film characteristic, and mechanical physical properties which are the requirements of semiconductor buffer coating.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Nanometer silicon-containing ultraviolet thick film positive photoresist and film forming resin thereof
ActiveCN101979435AImprove adhesionGood flexibilityPhotomechanical apparatusSolventPhotosensitizing compounds
The invention relates to ultraviolet thick film photoresist, which is mainly prepared from 10 to 35 parts of phenolic resin, 1 to 10 parts of nanometer silicon-containing copolymer film forming resin, 5 to 20 parts of diazo naphthoquinone light-sensitive compound, 30 to 85 parts of solvent and a small number of other additives such as n-butylamine and surfactants which serve as raw materials by blending the raw materials and filtering through 5 micrometers, 1 micrometer and 0.2 micrometer filters. The nanometer silicon-containing alkaline soluble copolymer film forming resin is added into the film forming resin to increase the adhesivity, flexibility, side-wall verticality and mechanical properties of a film-forming agent and fulfill the aims of preventing adhesive films from cracking and patterns from deforming and even dropping in a salient point process, three-dimensional (3D) combined encapsulation and the manufacturing of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS).
Owner:昆山西迪光电材料有限公司
Corrosion-resistant stable soldering flux
InactiveCN108296672AAccelerated corrosionImprove stabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaPolyethylene glycolPhytic acid
The invention discloses corrosion-resistant stable soldering flux. Raw materials of the corrosion-resistant stable soldering flux comprise, by weight, 25-35 parts of modified rosin, 10-15 parts of phytic acid, 3-8 parts of lactic acid, 2-5 parts of citric acid, 2-4 parts of itaconic acid, 1-2 parts of triethylamine, 10-15 parts of polyethylene glycol, 1-2 parts of rosin amine, 0.5-1 part of O-diazonaphthoquinone-5-sulfonyl rosin amine, 0.8-1.2 parts of aniline hydrochloride, 0.5-1.5 parts of octaphenyl polyoxyethyiene, 0.8-1.5 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfonate, 0.2-0.5 part of aluminum chloride, 0.5-1 part of catechol and 200-300 parts of a solvent. The corrosion-resistant stable soldering flux has good welding aiding activity, and effectively prevents oxygen and the like from entering themetal surface, and therefore the corrosion resistant performance and the stability of the soldering flux are improved.
Owner:TIANCHANG FEILONG BRAND STEEL GRID
Positive-acting photosensitive composition and hardened material thereof
InactiveCN103380400AReduce thicknessLess thickness reductionSilicon organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic solventOrganic group
A positive-acting photosensitive composition containing: (A) a silanol-group-containing polysiloxane compound having a structure obtained by subjecting a compound represented by formula (1) and a compound represented by formula (2) to hydrolysis and a condensation reaction; (B) a compound having at least two epoxy-containing organic groups; (C) a diazonaphthoquinone; and (D) an organic solvent. R1 represents a C1-4 alkyl group or the like, R2 represents a C2-10 divalent hydrocarbon group, R3 represents a C2-10 divalent saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon group, and X represents a group (see description for details) represented by general formulas (3-5). Furthermore, m, n and p represent numbers in a manner such that the following are satisfied: m:n:p=1:2.1-12:1-6, and m+n+p=3-6. R4 represents a C1-4 alkyl group or the like, R5 represents a C1-4 alkyl group, and a represents 1-2.
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com