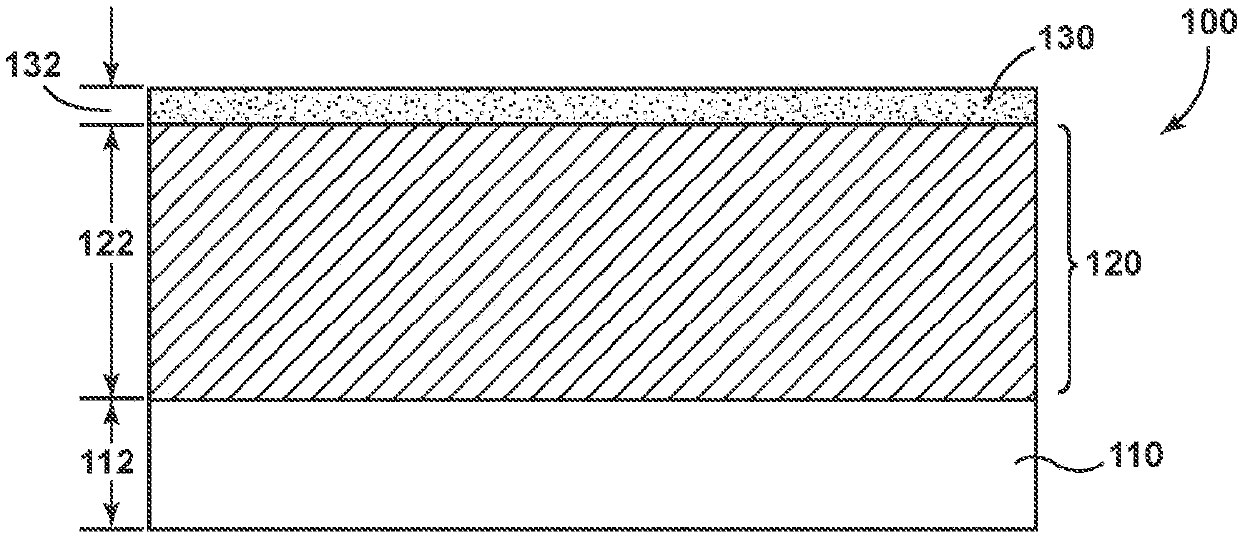
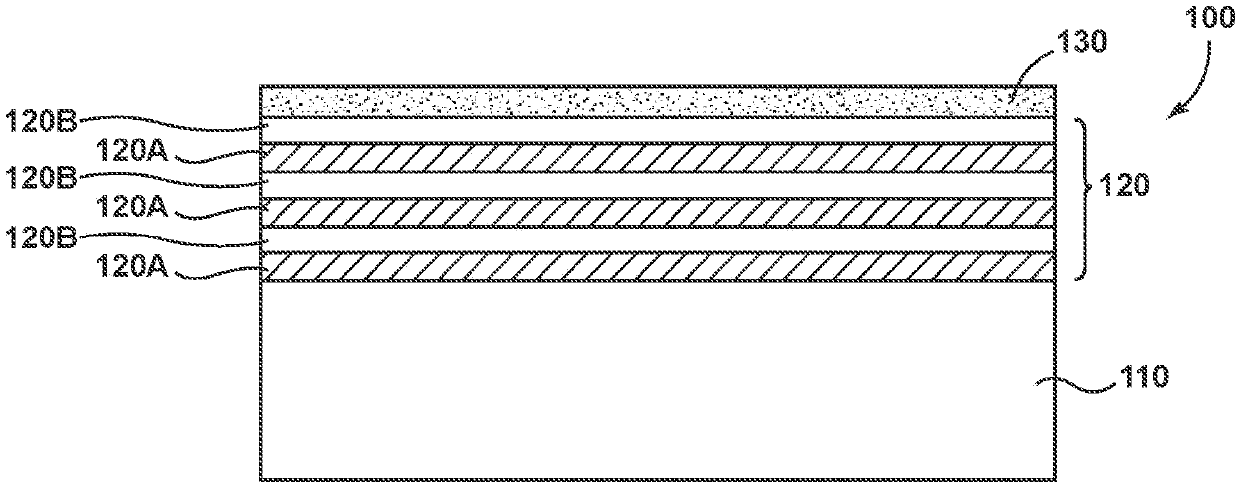
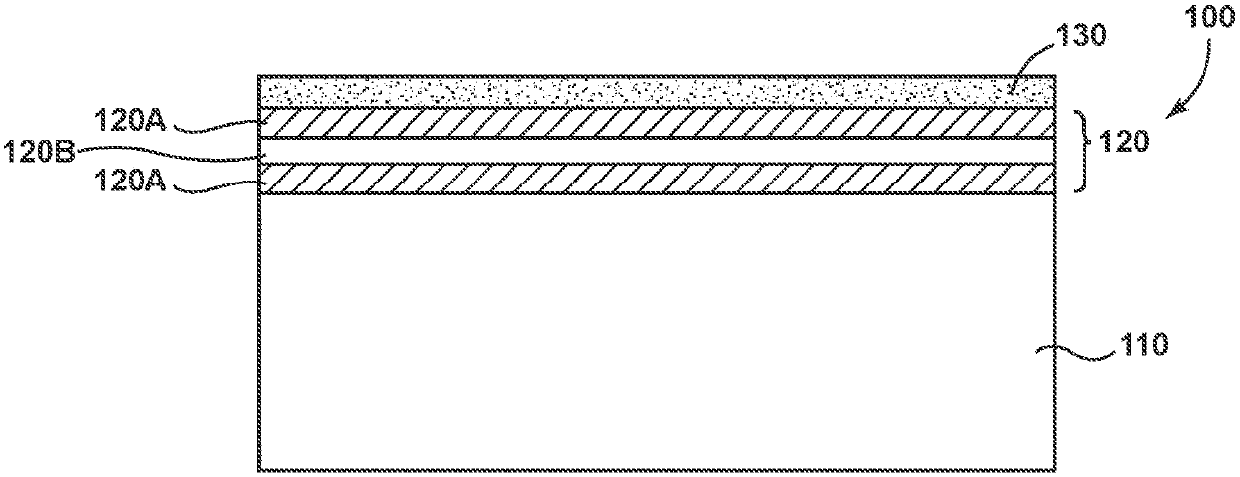
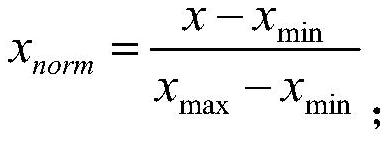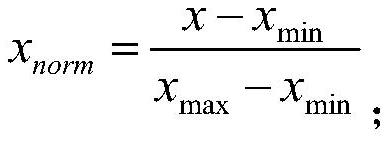Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Copper test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
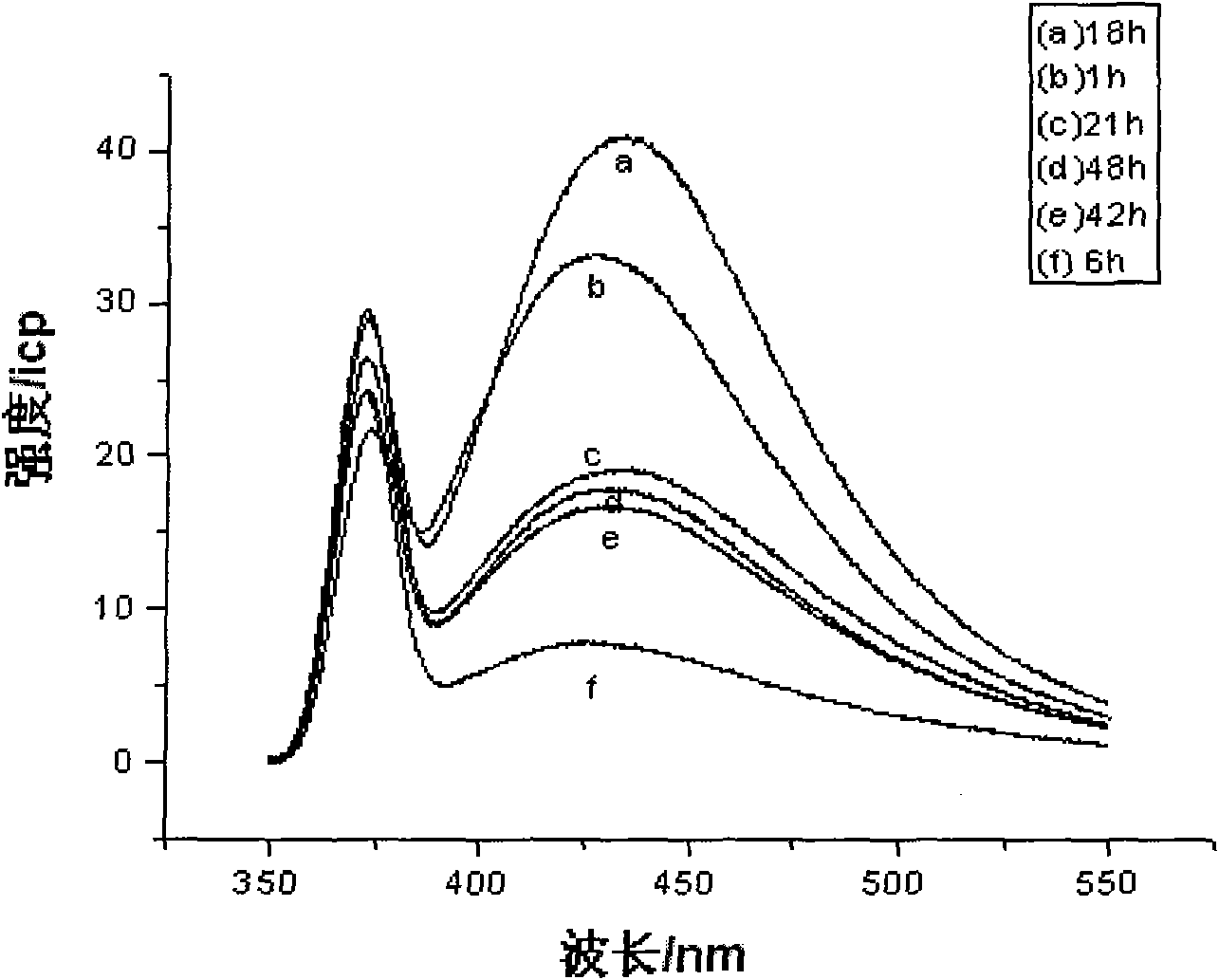
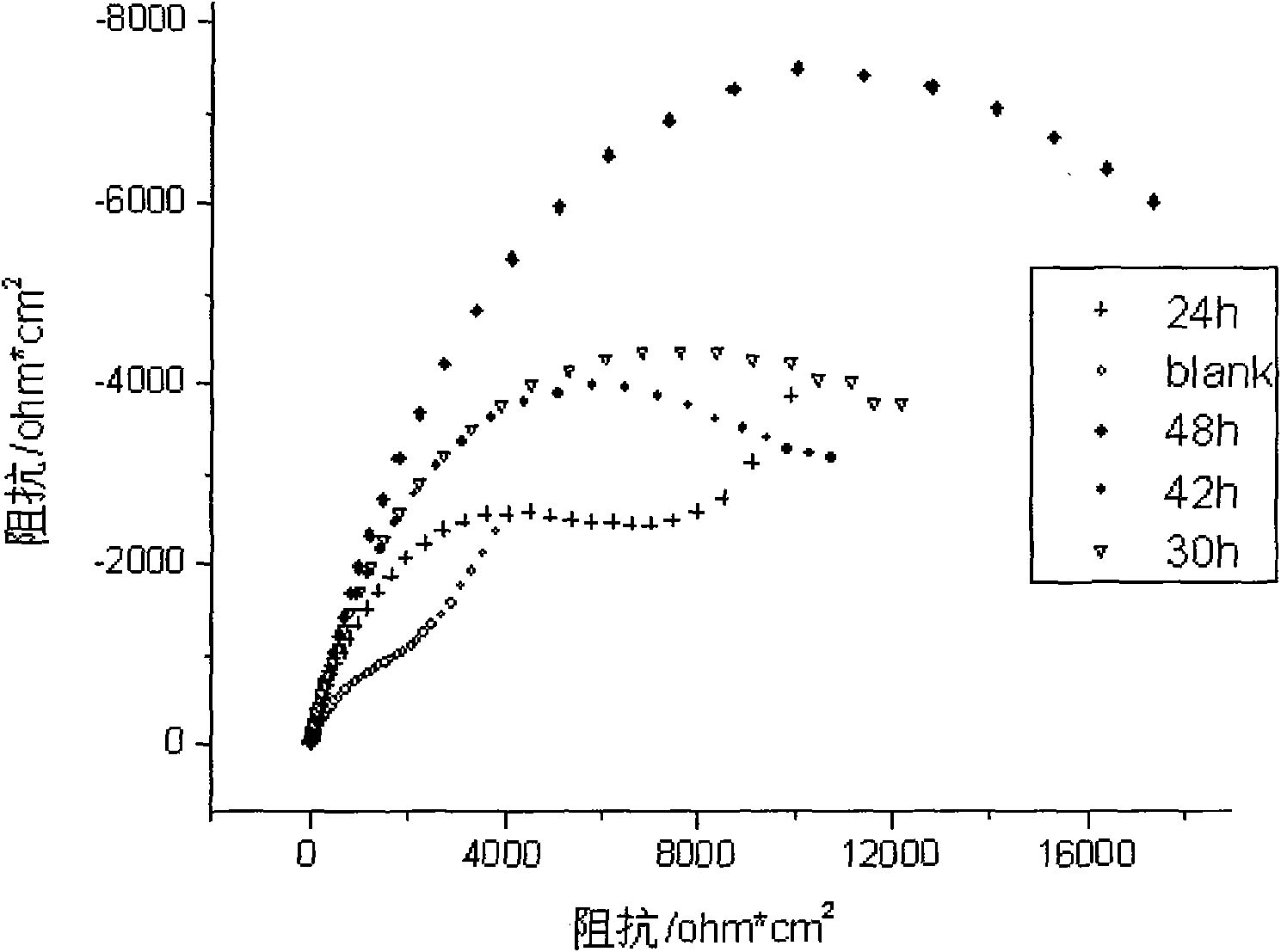
Method for forming amino acid self-assembly corrosion inhibition membrane with fluorescent characteristics on copper surface
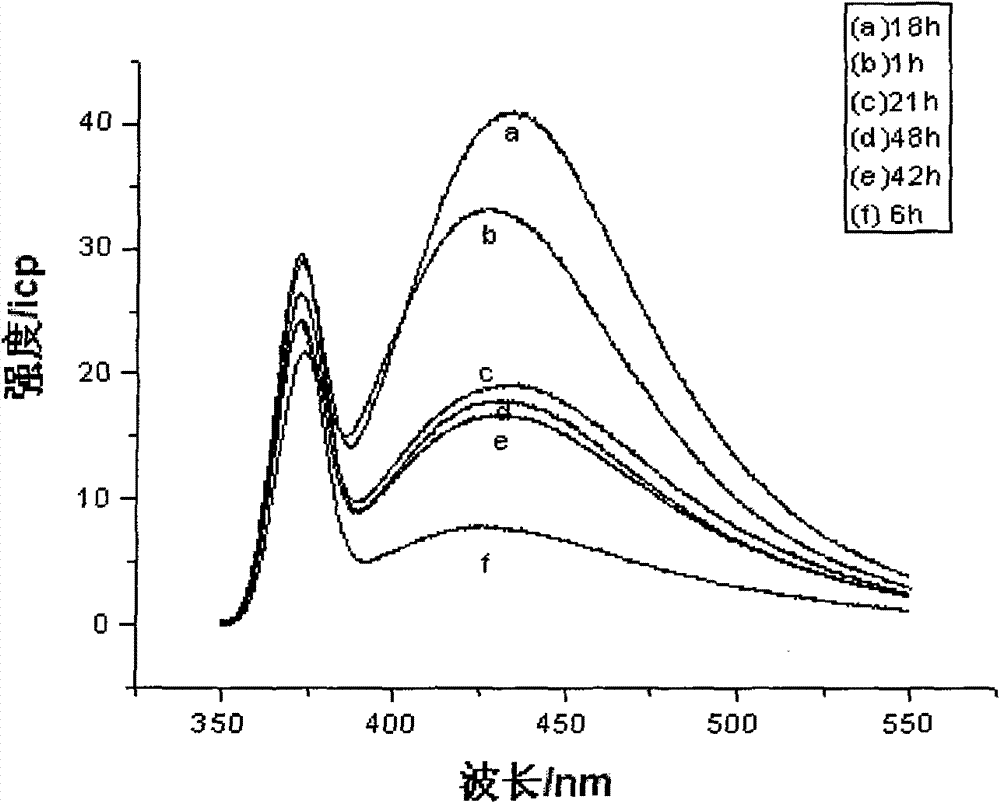
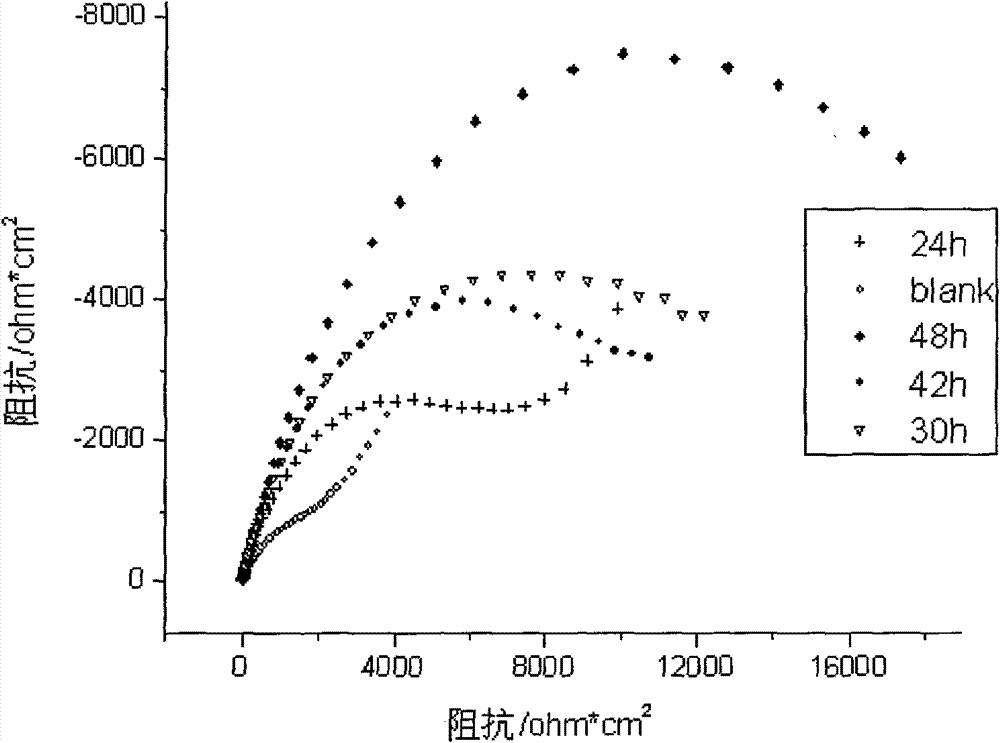
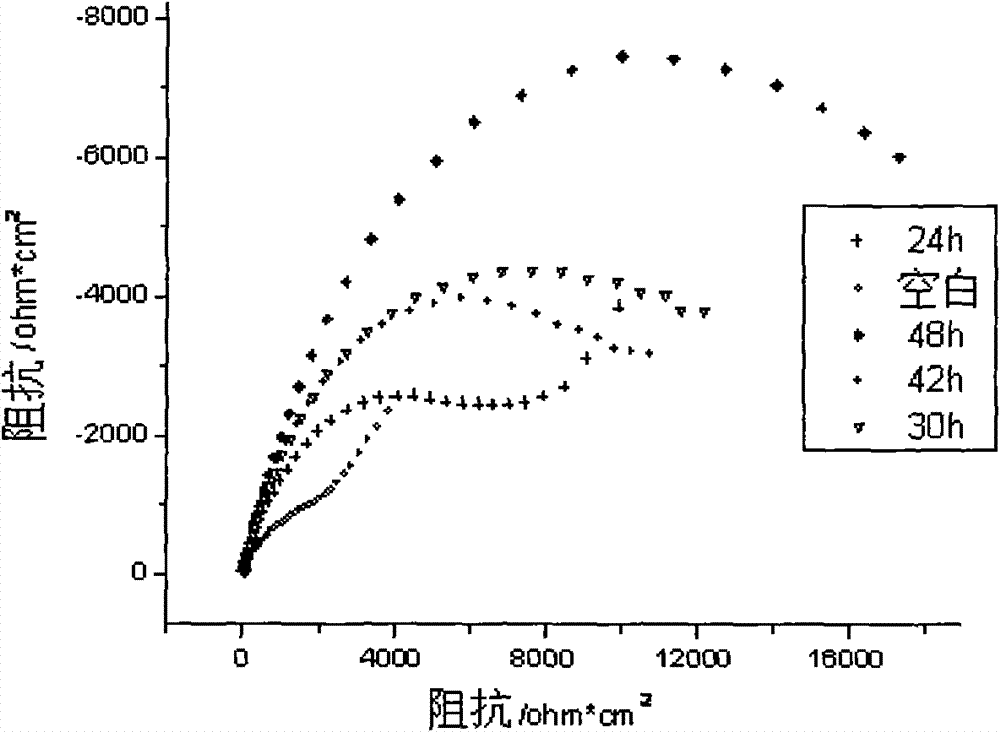
The invention discloses a method for forming an amino acid self-assembly corrosion inhibition membrane with fluorescent characteristics on a copper surface, which comprises the following steps of: polishing pure copper step by step by metallographical sand paper from No.1 to No.6, degreasing with absolute ethyl alcohol and cleaning with deionized water for later use; processing a copper test specimen by using aqueous solution of amino acid to obtain the copper test specimen modified by the amino acid; and assembling fluorescent reagent onto the surface of the copper test specimen indirectly under the electrostatic attraction action between 1-naphthylamine sodium diacetate (NADA) serving as the fluorescent reagent and the amino acid to prepare a dual-layer photosensitive corrosion inhibition self-assembly corrosion inhibition functional membrane, and characterizing the fluorescent characteristics and corrosion inhibition effect of the membrane respectively by adopting fluorescence spectra and an electrochemic impedance method. Researches show that in the corrosion inhibition functional membrane with the fluorescent characteristics, the relevance exists between fluorescence intensity and corrosion inhibition performance, and the corrosion inhibition characteristics of the assembly membrane are subjected to on-line detection and real-time monitoring through a fluorescence signal,so the method has great significance for promoting the application of the amino acid self-assembly membrane.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Antimicrobial-antireflective articles and methods for making the same
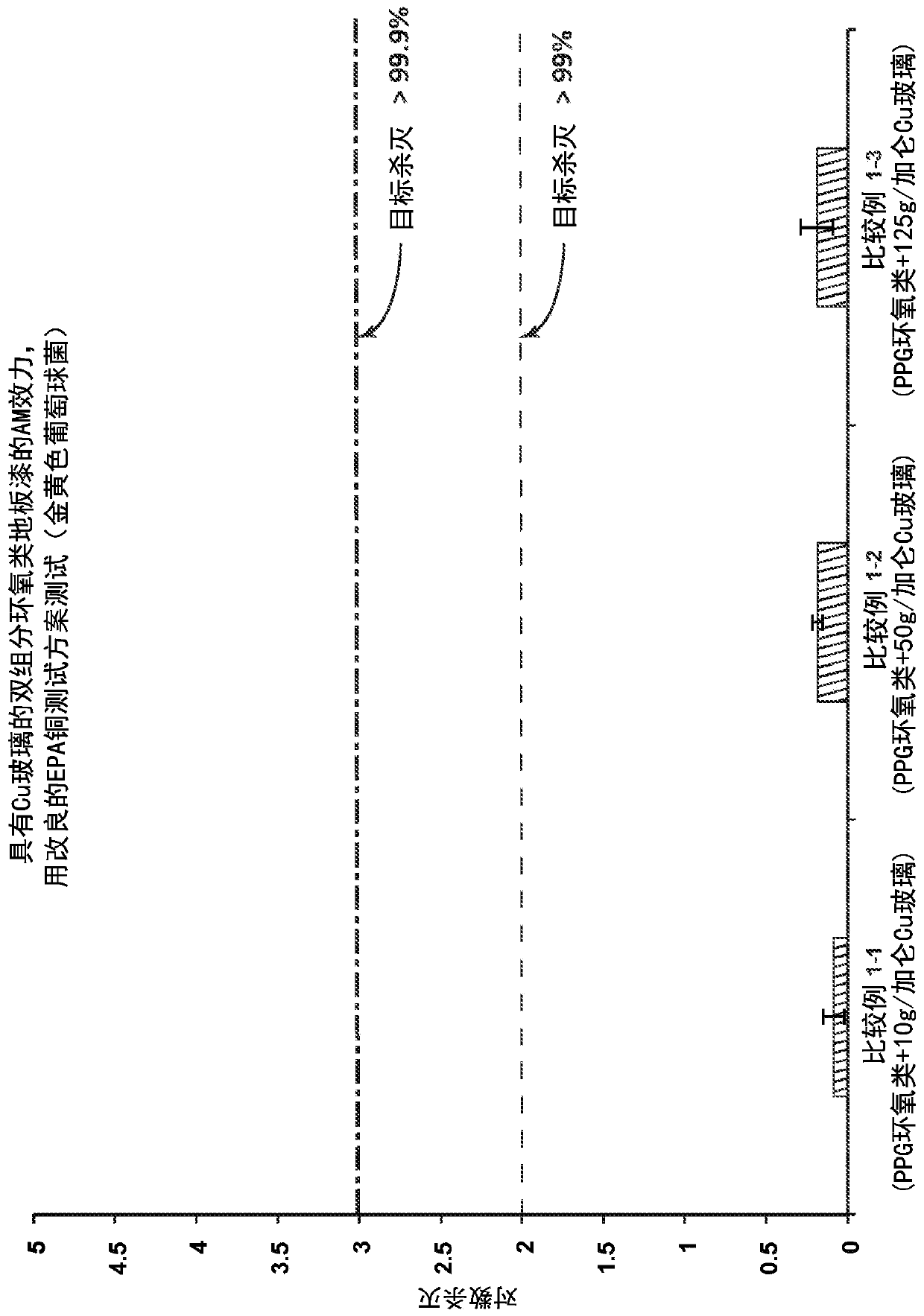
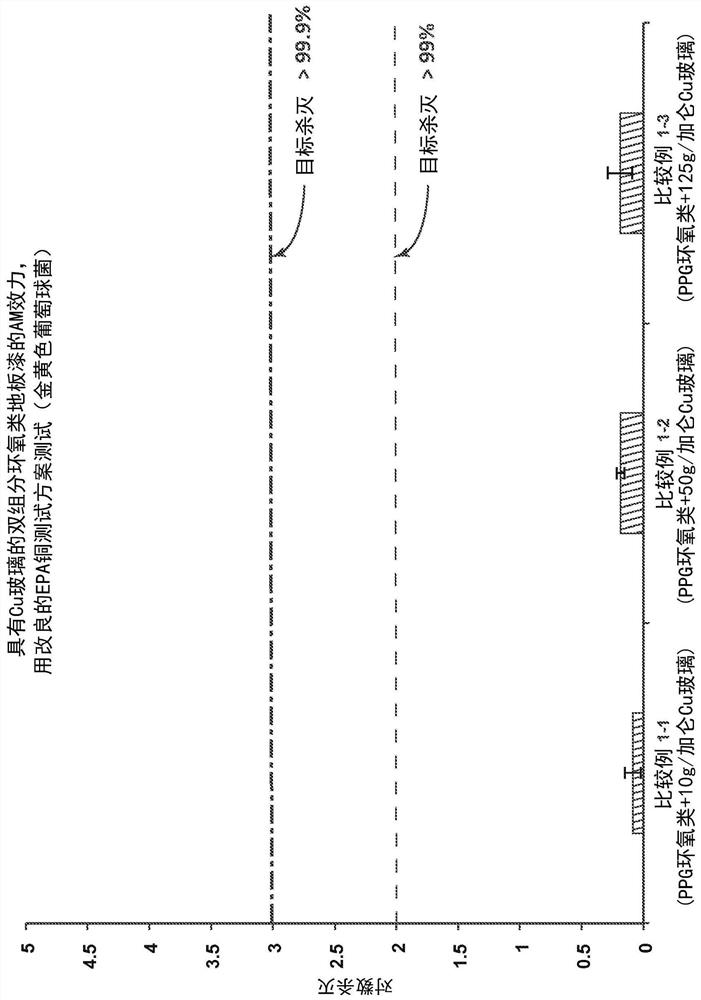
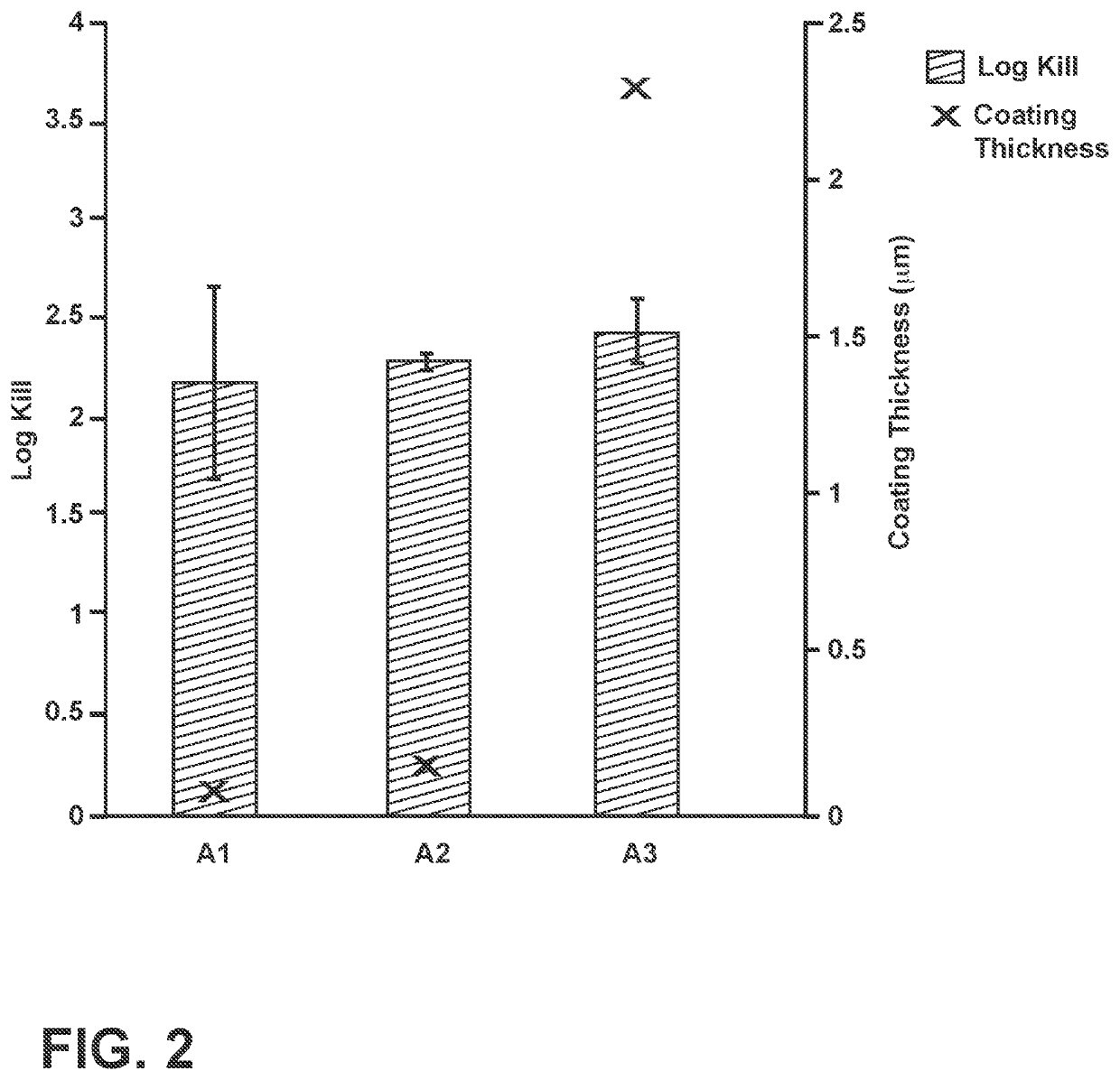
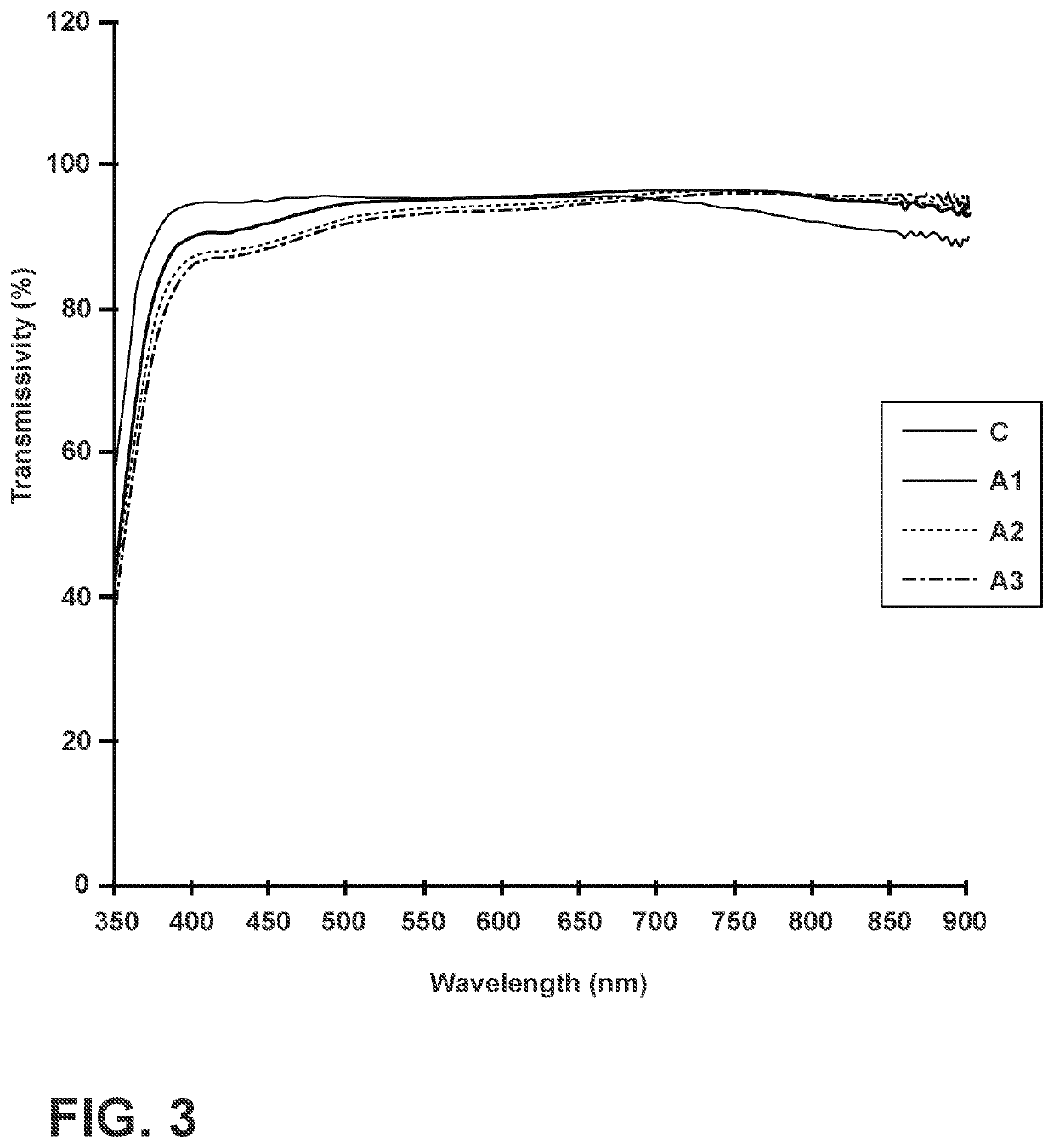
ActiveUS20180251399A1Improved antimicrobial efficacyImproved antireflective propertyBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsCopper testLog reduction
Described herein are antimicrobial articles having improved antimicrobial efficacy and antireflective properties. Further described are methods of making and using the improved articles. The antimicrobial articles generally include an antimicrobial element and an antireflective element. The antireflective element, in some cases, can be disposed directly on a glass, glass-ceramic or ceramic substrate and the antimicrobial element is disposed on the antireflective element. The article can exhibit a reflectance of about 4% or less (and less than 1% in some cases) in the range of about 425 nm to about 725 nm. Further, the article can be characterized with an antimicrobial efficacy by exhibiting at least a 2 log reduction in a concentration of at least Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria under a Modified EPA Copper Test Protocol.
Owner:CORNING INC
Device for testing electrical performances of diode
InactiveCN108459258AImprove affordabilityReasonable designIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityCopper test
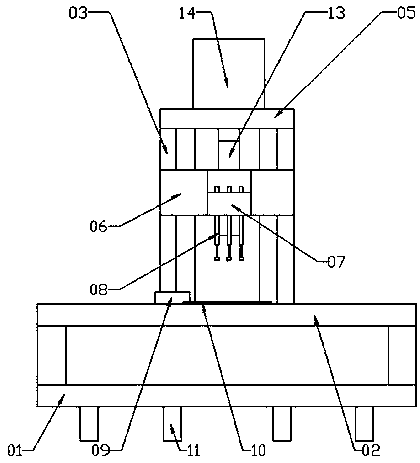
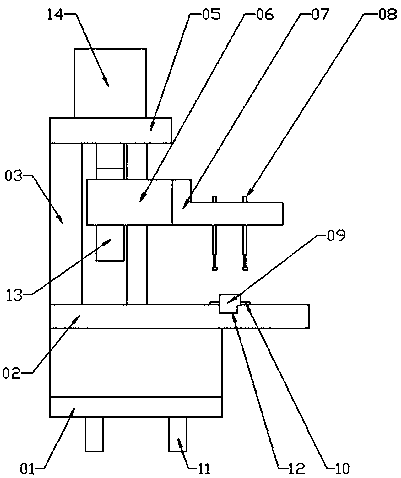
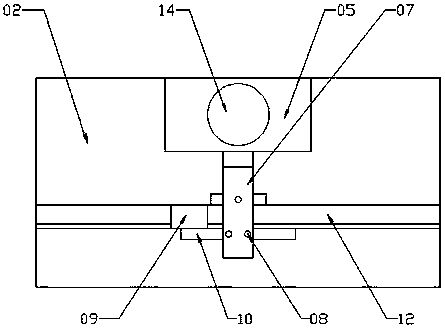
The invention relates to a device for testing electrical performances of a diode. The device comprises a bracket, a substrate and a pedestal. A base plate is arranged on the pedestal; the bracket is arranged at one side of the base plate; two sliding rods are arranged at one side of the bracket at an interval; and the tops of the sliding rods are fixed at the bracket by a horizontal plate. A sliding block is installed on the sliding rods; a measuring block is arranged at one side of the sliding block; three testing pins are arranged below the measuring block; a trough is formed at the other side of the base plate horizontally and penetrates the base plate; and three copper testing pieces are arranged at the two sides of the trough, wherein the copper testing pieces correspond to the testing pins one by one. A plurality of plugs are arranged at the bottom of the pedestal and are connected with the testing pins and the copper testing pieces; and the plugs are connected with a diode electrical performance testing instrument in a pluggable manner. The testing device has advantages of reasonable design and simple structure; the testing points are optimized; with a ceramic-based copper-clad plate, the testing area is increased and the current bearing capacity is enhanced substantially; and when testing is carried out by using 60-A currents, no risk is caused.
Owner:NANTONG HORNBY ELECTRONICS
Dynamic simulation experiment device for circulating cooling water system and running method thereof
InactiveCN108982340AHigh degree of automationEasy to controlWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCopper testAir blower
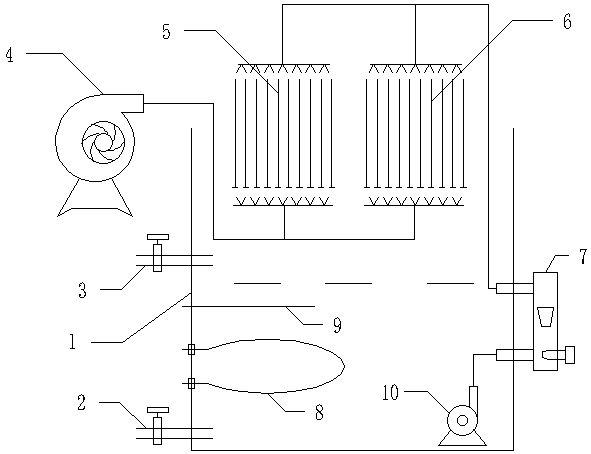
The invention discloses a dynamic simulation experiment device for a circulating cooling water system and a running method thereof. A cooling water draining valve and a supplemental water feeding valve are arranged on one side of a tank body of a circulating water tank; a fixing hole is formed on the circulating water tank between the cooling water draining valve and the supplemental water feedingvalve; a heating rod and a thermocouple are arranged in the fixing hole; the heating rod and the thermocouple are respectively connected with an external temperature controller through wires; a carbon steel test block and a red copper test block are respectively fixed on the two sides of the middle part on the upper part of the circulating water tank; air distributors are respectively arranged onthe lower parts of the carbon steel test block and the red copper test block; the air distributors are connected with an external air blower; a circulating water pump is arranged on the bottom of thecirculating water tank; the circulating water pump is connected with a circulating water meter fixed on the circulating water tank; water distributors on the upper ends of the carbon steel test blockand the red copper test block are respectively connected with the circulating water meter through water pipes. The dynamic simulation experiment device disclosed by the invention is high in degree ofautomation of equipment, can be conveniently controlled and operated and can be used for researching the problems related to equipment corrosion and scaling of the circulating cooling water system.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for calibrating Rockwell hardness tester
InactiveCN107389483AAvoid measurement errorsAccurate CalibrationInvestigating material hardnessObservational errorCopper test
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a Rockwell hardness tester. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking a cylindrical pure copper test block, and grinding the upper and lower surfaces of pure copper to smoothness and flatness; (2) cleaning the top surface of a screw rod and the upper and lower end surfaces of a workbench; (3) putting the workbench on a screw rod table; (4) putting the pure copper test block horizontally on the workbench, rotating a hand wheel, so that the workbench slowly rises and extrudes a pressure head, and stopping applying force to the hand wheel when a small pointer in an indicator panel points at a red point. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the pure copper test block is prepared, the hardness values of multiple measurement points on the pure copper test block are measured by the Rockwell hardness tester, and the average value of the hardness values is calculated; the average value is compared with a standard hardness value of the pure copper to obtain an indication error; during calculating the average value, the measurement error is effectively avoided by removing the maximum value and the minimum value, thus the calibration is more accurate; the method disclosed by the invention is easy to operate and has high precision.
Owner:安吉元融仪器仪表检测有限公司
Printed circuit board hole copper abnormity monitoring method
InactiveCN111077435AObserve intuitivelyGood precisionElectronic circuit testingPrinted element electric connection formationCopper testElectrical resistance and conductance
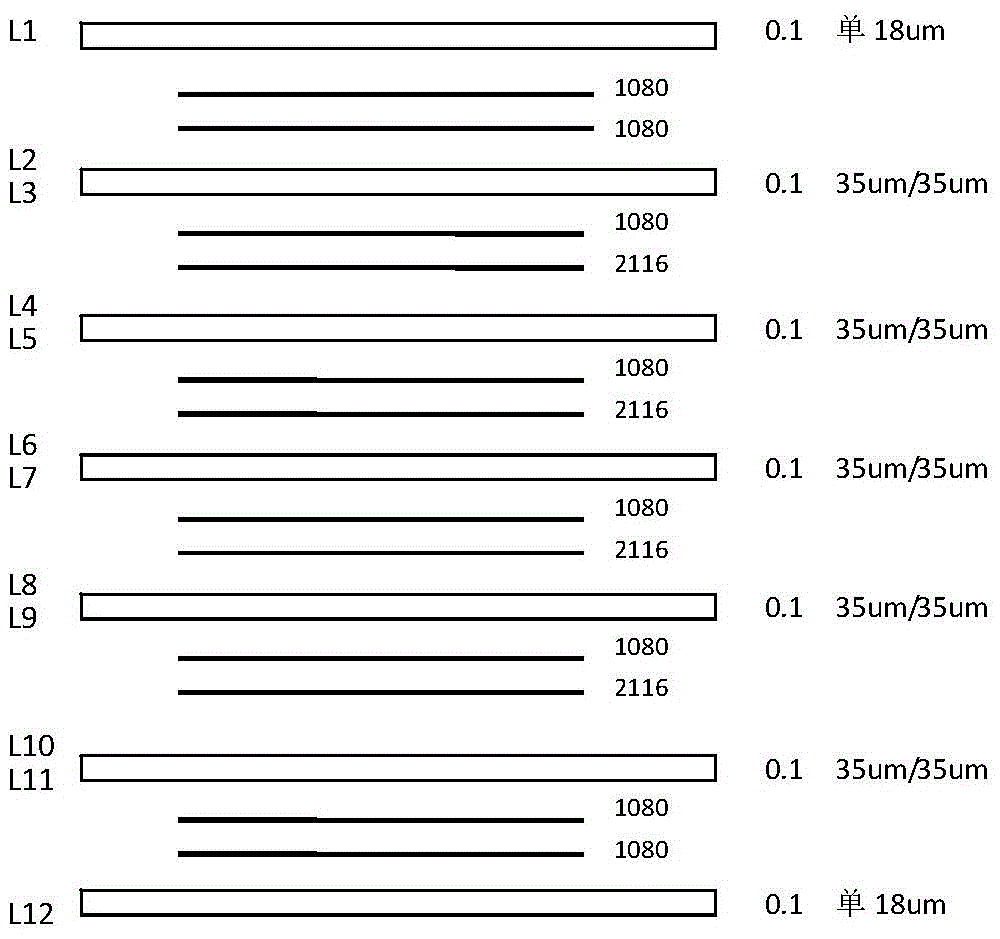
The invention relates to a printed circuit board hole copper abnormity monitoring method, which comprises the following steps: S1, manufacturing a test board, including S1.1, selecting raw materials;S1.2, manufacturing copper testing PADs, namely, manufacturing a plurality of copper testing PADs on a circuit board as surface copper testing points, and enabling the plurality of surface copper testing points to be distributed in a square array shape; and S1.3, manufacturing through holes, namely, drilling a plurality of through holes with different sizes in the circuit board, and enabling the through holes with the same size to be arranged in the same row or the same column; and S2, carrying out a testing method, including S2.1, placing the test board and a normal board together, and conducting copper deposition, electroplating and board baking according to normal steps; S2.2, testing through hole resistance and surface copper data, namely, measuring the through hole resistance by usinga universal meter, and measuring the surface copper data by using the copper measuring PADs; and S2.3, performing screening and analysis, namely, screening out normal holes and abnormal holes according to test results in the step S3, observing the deep plating capacity in the normal holes by slicing the normal holes, and judging the cause of abnormality by slicing the abnormal holes and combiningsurface copper data. According to the invention, the problem of electroplating hole copper can be periodically and diversely monitored.
Owner:惠州市大亚湾科翔科技电路板有限公司
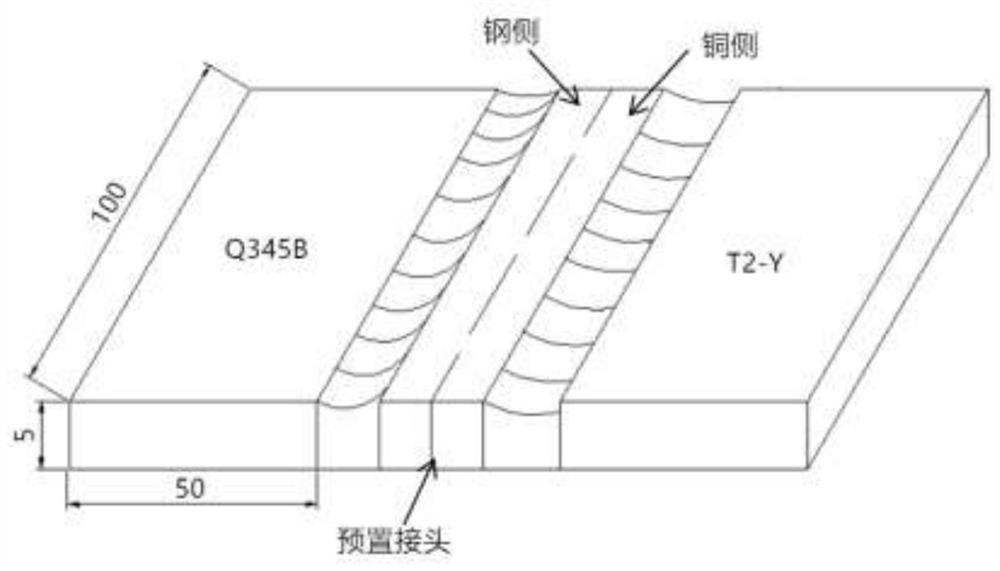
Copper/ steel composite material connecting method for preset joint
ActiveCN111673239AReduce welding difficultyImprove mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusCopper testMechanical property
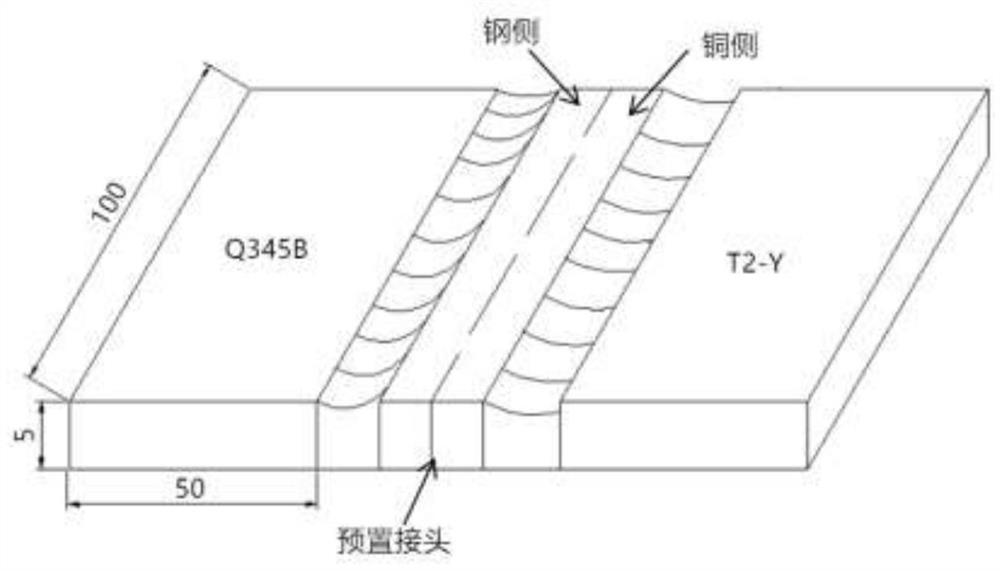
The invention discloses a copper / steel composite material connecting method for a preset joint. The method comprises the specific operation steps that 1, the copper-steel preset joint is prepared, specifically, a copper-steel composite weld joint with the reasonable specification is prepared through an electric arc additive technology to serve as the preset joint; and 2, according to the components of base metal, solid welding wires with the same components are selected, and welding of a copper test plate, a steel test plate and the copper-steel preset joint is completed through gas metal arcwelding. According to the method, the welding quality and the comprehensive mechanical property of the copper-steel dissimilar metal welding joint can be improved, and a brand-new thought is providedfor connection of copper / steel dissimilar metal.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
A method for measuring the corrosivity of the service environment of electronic appliances
ActiveCN106442303BAccurate measurementAvoid low measurement accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCopper testTotal thickness
The invention discloses a measurement method of the corrosiveness of an electronic and electrical appliance service environment. The measurement method comprises the following steps: placing a copper test piece into the measured electronic and electrical appliance service environment, reducing a corrosive product film on the surface of the copper test piece through a cathode reducing method, then calculating the average thickness TCuO2 of a Cu2O corrosion product, the average thickness TCuO of a CuO corrosion product and the average thickness TCu2S of a Cu2S corrosion product, and finally calculating the total thickness average value Te, serving as a measurement result, of a surface corrosion product to acquire the corrosiveness of the measured electronic and electrical appliance service environment. Therefore, the measurement method can accurately measure the weak corrosiveness of the electronic and electrical appliance service environment under a condition of not affecting the electronic and electrical appliance service environment, so that the problem of low measurement precision caused by the adoption of a copper hanging piece weight loss method for calculating the corrosion rate in the prior art is solved.
Owner:CHINA NAT ELECTRIC APP RES INST
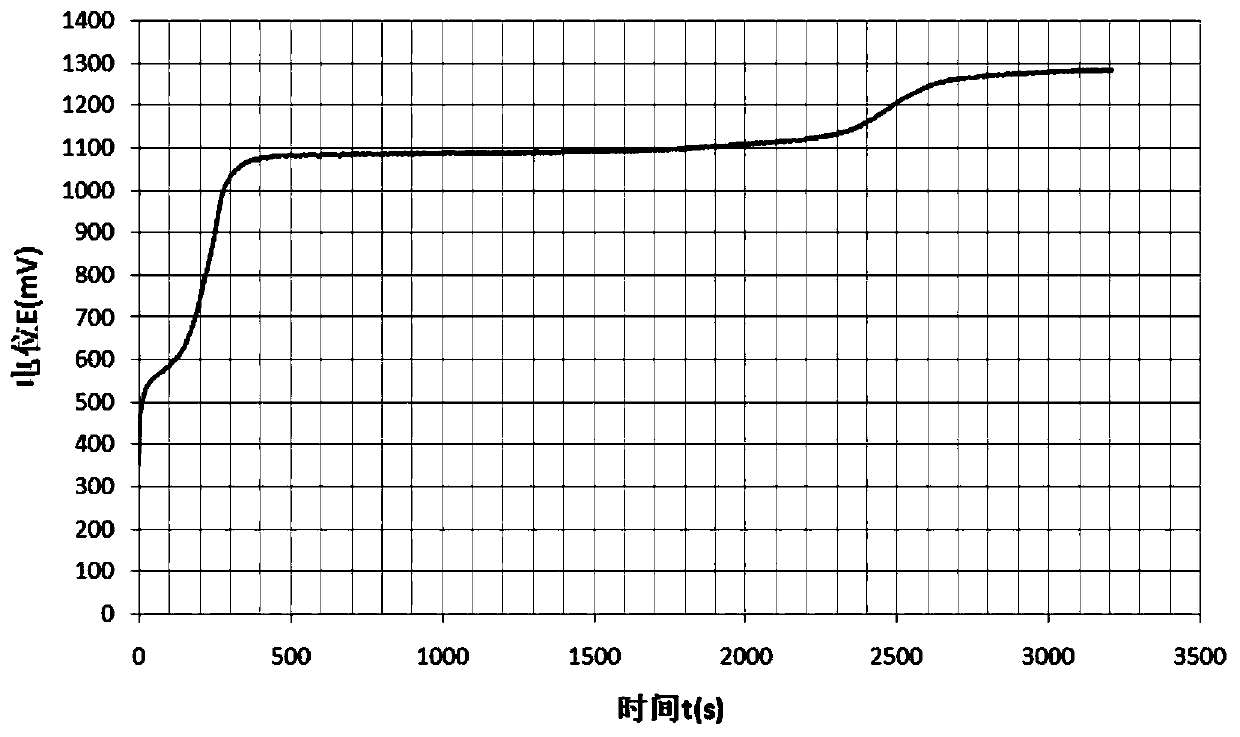
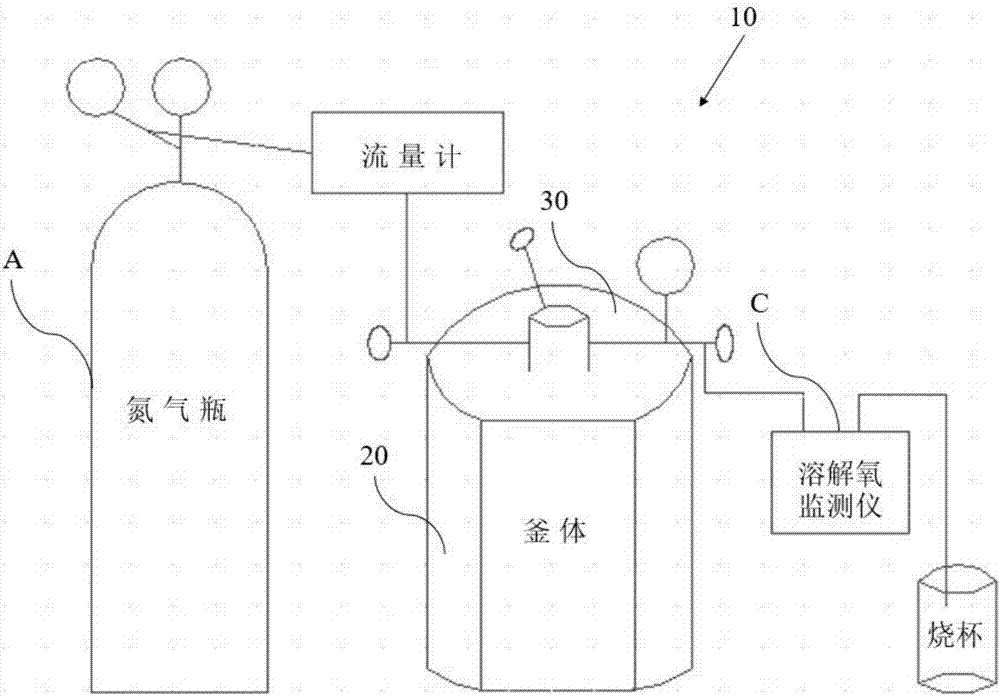
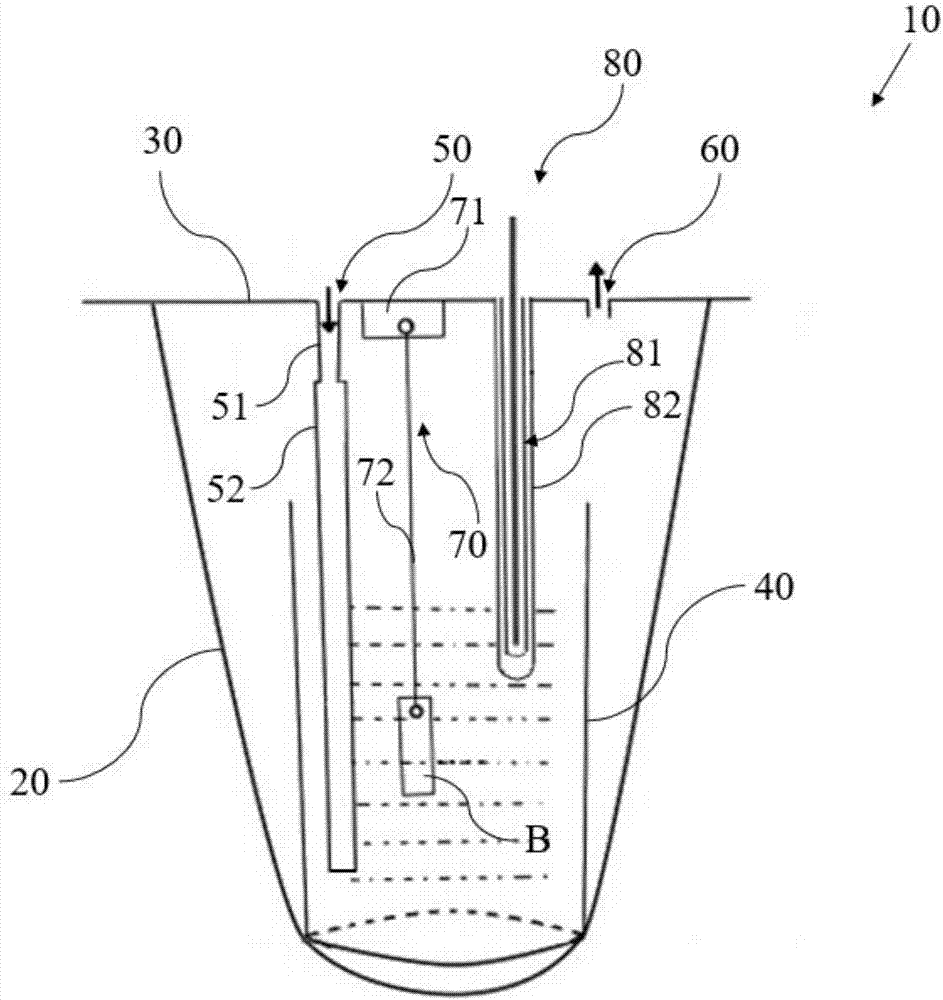
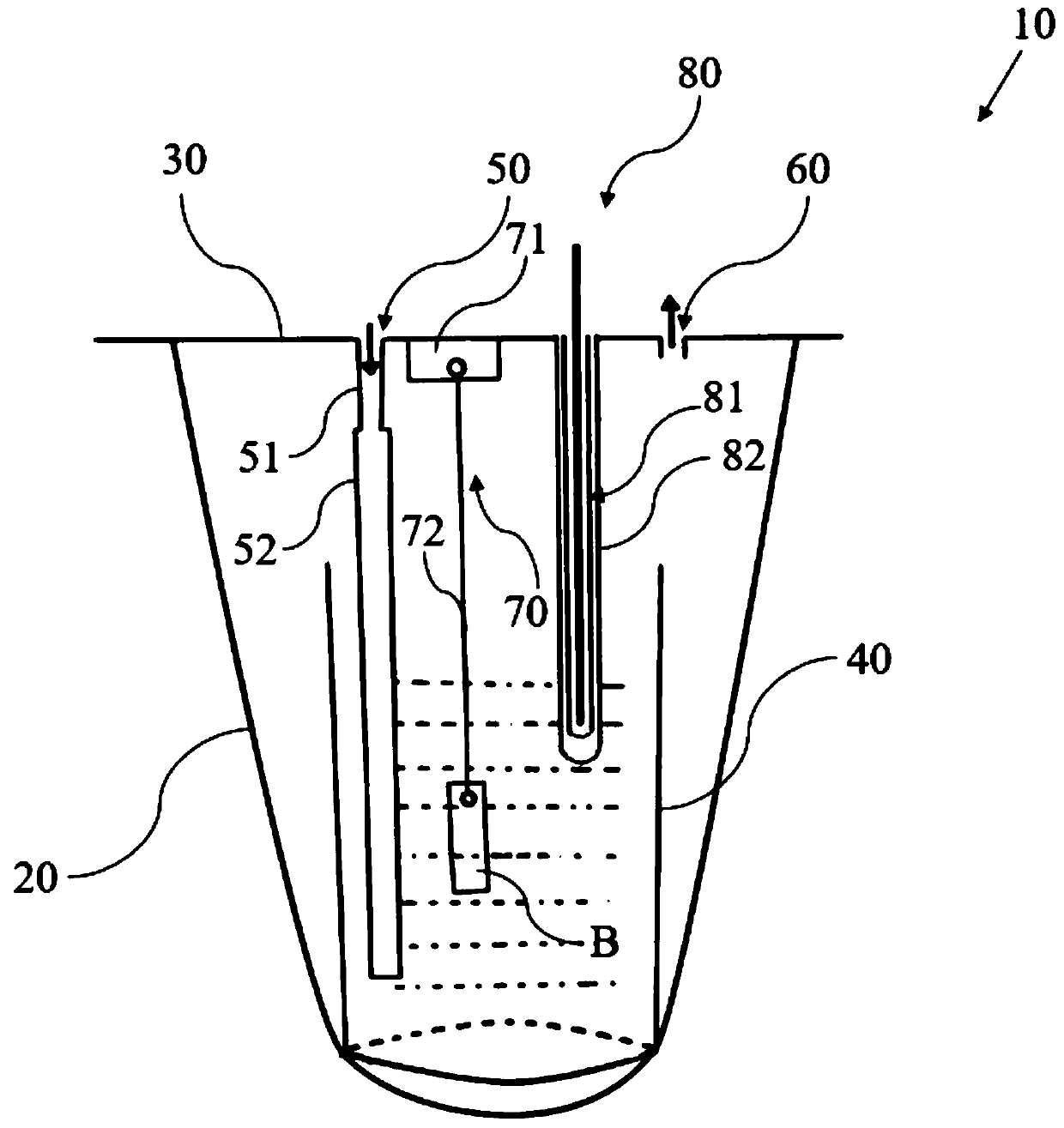
Test device and method for simulating corrosion of hollow copper conductor of generator in inner cooling water
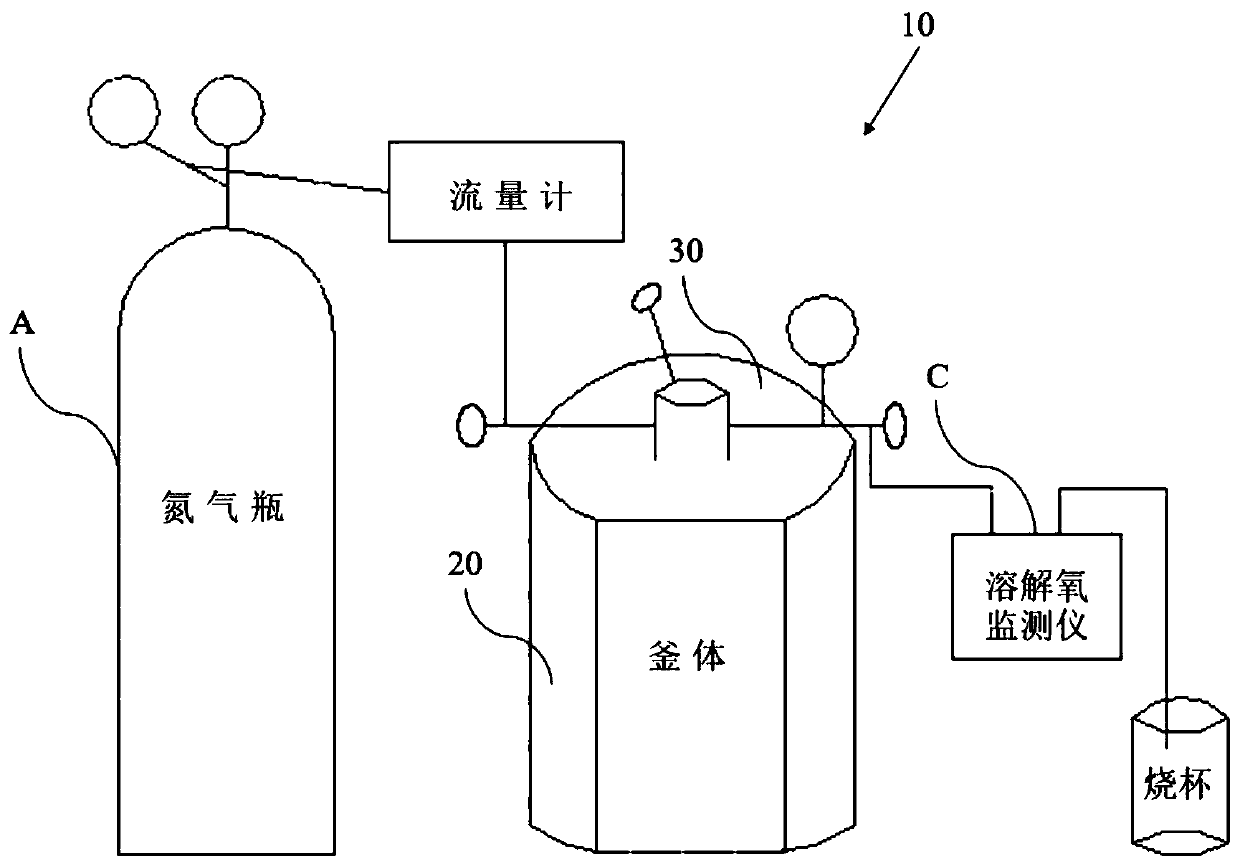
InactiveCN107478567AAvoid pollutionConvenient researchWeather/light/corrosion resistanceTemperature controlCopper test
The invention provides a test device and a corresponding test method for simulating corrosion of a hollow copper conductor of a generator in inner cooling water. The provided test device is characterized by comprising a kettle body, a kettle lid closely covering the kettle body, a wide-mouth glass bottle arranged in the kettle body and used for accommodating demineralized water, a gas inlet part, a gas outlet part, a test piece suspending part and a temperature control part, wherein the gas inlet part comprises a short gas inlet pipe arranged on the kettle lid and a soft polyethylene extending pipe, the upper end of the soft polyethylene extending pipe is connected with a bottom outlet of the short gas inlet pipe, and the lower end of the soft polyethylene extending pipe extends into the wide-mouth glass bottle; the gas outlet part is arranged on the kettle lid and used for exhausting gas; the test piece suspending part comprises a mounting part mounted on the inner surface of the kettle lid and a suspending line for suspending a copper test piece in a proper position in the wide-mouth glass bottle; the temperature control part comprises a thermocouple component which is inserted into the kettle lid and extends into the kettle body, a polyethylene outer sleeve sleeving upper and lower end sealing ports of the thermocouple component as well as a temperature adjuster connected with the thermocouple component.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for calibrating Rockwell hardometer
InactiveCN107462487ATo achieve the purpose of calibrating the Rockwell hardness testerSimple methodStrength propertiesCopper testMeasurement point
Owner:安吉元融仪器仪表检测有限公司
Antimicrobial-antireflective articles and methods for making the same
Described herein are antimicrobial articles having improved antimicrobial efficacy and antireflective properties. Further described are methods of making and using the improved articles. The antimicrobial articles generally include an antimicrobial element and an antireflective element. The antireflective element, in some cases, can be disposed directly on a glass, glass-ceramic or ceramic substrate and the antimicrobial element is disposed on the antireflective element. The article can exhibit a reflectance of about 4% or less (and less than 1% in some cases) in the range of about 425 nm to about 725 nm. Further, the article can be characterized with an antimicrobial efficacy by exhibiting at least a 2 log reduction in a concentration of at least staphylococcus aureus, enterobacter aerogenes, and pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria under a modified EPA copper test protocol.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for calibrating Rockwell hardometer
InactiveCN107247005AAvoid measurement errorsAccurate CalibrationInvestigating material hardnessObservational errorCopper test
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a Rockwell hardometer. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a cylindrical fine copper test block is selected, the two ends of the fine copper test block are subjected to coarse grinding by using a grinding wheel, the two ends of the fine copper test block obtained after coarse grinding are sequentially polished with 200 # dry abrasive paper, 400 # dry abrasive paper, 600 # dry abrasive paper and800 # dry abrasive paper, and the fine copper test block after polishing is subjected to buffing; secondly, the top face of a lead screw and the upper and lower end faces of a working table are wiped up; thirdly, the working table is placed on a lead screw table; fourthly, the fine copper test block is horizontally placed on the working table, a hand wheel is rotated so that the working table slowly rise, a pressure head is extruded, and force application is stopped until a small pointer in an indicating dial points to a red dot. In the method, by preparing the fine copper test block, the hardness numbers on a plurality of measurement points on the fine copper test block are measured by using the Rockwell hardometer, the average value of the hardness numbers is calculated, the average value is compared with the standard hardness number of finer copper, and the indication error can be obtained; while the average value is calculated, the maximum value and the minimum value are removed, so that the measuring errors are effectively avoided, and calibration is more accurate.
Owner:安吉元融仪器仪表检测有限公司
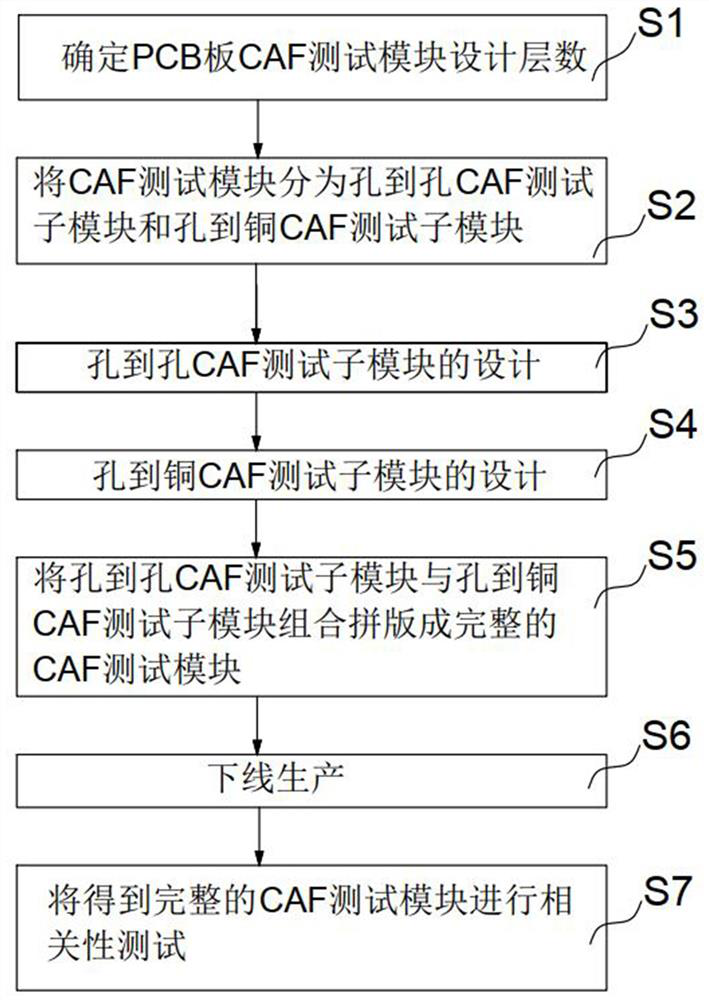
PCB CAF test module design method
PendingCN112858875AFacilitate root cause analysisEasy to identifyPrinted circuit testingCopper testSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a PCB CAF test module design method. The method comprises the steps that the number of designed layers of a PCB CAF test module is determined; the CAF test module is divided into a hole-to-hole CAF test sub-module and a hole-to-copper CAF test sub-module; the hole-to-hole CAF test sub-module is designed; the hole-to-copper CAF test sub-module is designed; and the hole-to-hole CAF test sub-module and the hole-to-copper CAF test sub-module are combined and spliced into a complete CAF test module, and testing is performed. The CAF test module is divided into the hole-to-hole CAF test sub-module and the hole-to-copper CAF test sub-module, the hole-to-hole CAF test sub-module can analyze CAF probabilities under different hole center-to-hole center distances and measure the influence proportion of drilling on CAF, and the hole-to-copper CAF test sub-module can analyze CAF probabilities under different hole center-to-hole center distances, and measures the influence proportion of the distances from different holes to the copper sheet, and the refined test module design is convenient for the true cause analysis of the CAF influence factors and is beneficial to the discrimination of primary and secondary factors.
Owner:广州广合科技股份有限公司
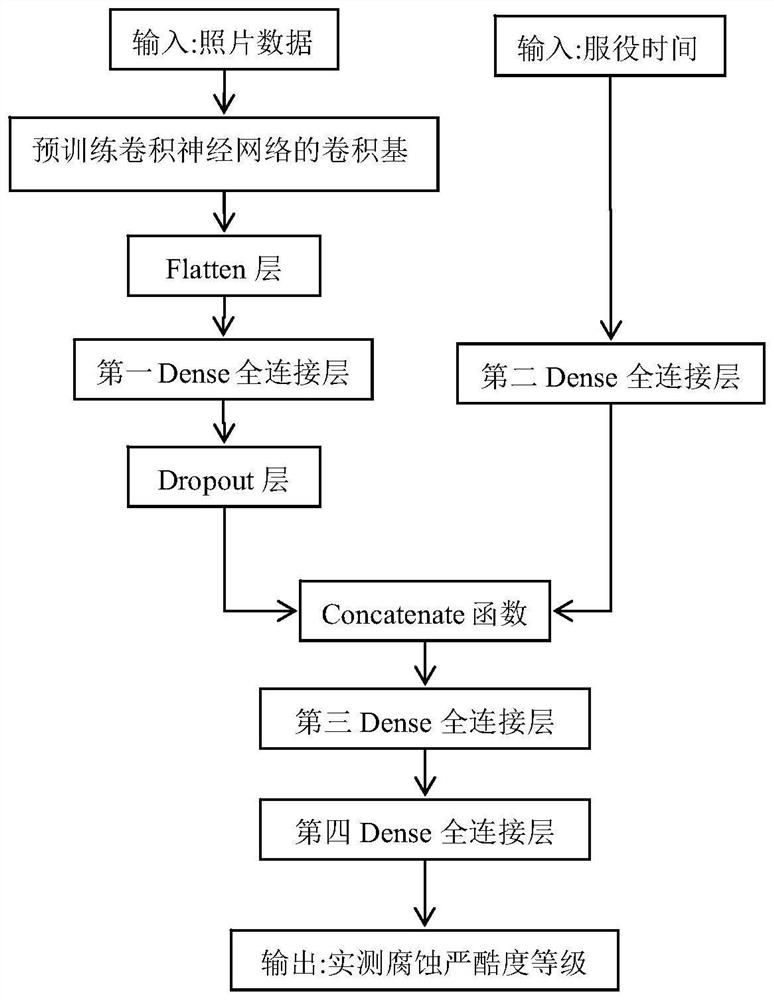
Convolutional neural network deep learning-based environmental corrosion severity recognition method
ActiveCN114066819AReduce transportationLow costImage enhancementImage analysisCopper testTest sample
The invention discloses an environmental corrosion severity recognition method based on convolutional neural network deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out the training through a neural network deep learning model, and building the incidence relation between the photo data and service time of a copper test piece and the actually measured corrosion severity level of an electric appliance service environment; an environment corrosion severity grade recognition model is obtained; and collecting photo data after the copper test piece is placed in the service environment of the target electric appliance for a preset service time, so that the predicted corrosion severity grade of the service environment of the target electric appliance can be quickly recognized through an environment corrosion severity grade recognition model. The application stage shown in the step S3 can be completed on site in the service environment of the target electric appliance, and the test sample does not need to be transported to a laboratory for testing, so that the time for recognizing the predicted corrosion severity grade of the service environment of the target electric appliance can be greatly shortened, and the cost for transporting the test sample and manually analyzing and judging is reduced.
Owner:CHINA NAT ELECTRIC APP RES INST
Rapid detection method for nickel corrosion of immersion gold lines
InactiveCN110320154AAvoid damageQuick checkWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCopper testUltimate tensile strength
Owner:重庆科迈电子科技有限公司
Water-cooling mechanical moving device for test piece in high-vacuum single-crystal growth furnace
InactiveCN106337203AAchieve transformationPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateCopper testSingle crystal
A water-cooling mechanical moving device for a test piece in a high-vacuum single-crystal growth furnace relates to a mechanical device. The water-cooling mechanical moving device mainly comprises a speed reducer, a transmission lead screw, a square nut, a connecting base, a water-cooling machine frame, a moveable lifting and pulling rod, a connecting flange and the like. The water-cooling mechanical moving device is arranged on the high-vacuum single-crystal growth furnace through the connecting flange. The mechanical moving device is subjected to heat-sink cooling by a circulating water-cooling method. The lower end of an output piece of the set of water-cooling mechanical moving device penetrates into the high-vacuum single-crystal growth furnace, and a copper test piece which needs heat treatment is clamped at the lower end head of the moveable lifting and pulling rod. The moving speed of the moveable lifting and pulling rod in the water-cooling mechanical moving device is controlled according to requirements of a heat treatment process, and the copper test piece can be slowly and uniformly changed from a high-temperature solid-state phase to a low-temperature solid-state phase, so that metal single-crystal copper with low-temperature solid-state phase is obtained. The water-cooling mechanical moving device can effectively solve the problem about control on moving and heat treatment states of the test piece in the high-vacuum single-crystal growth furnace.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
The preparation method of dl-p-thymphenyl phenylserine ester
ActiveCN111302982BSimple production processSolve the complex recycling processOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCopper testDrugs synthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine synthesis. The invention discloses a preparation method of DL-p-thiamphenicyl phenylserine ester. DL-p-thiamphenicol phenylserine ester is prepared by reacting L-p-thiamphenicol phenylserine ester or its salt, specifically comprising two Method, one, L-p-thiamphenyl phenylserine ester or its salt is directly produced after racemization DL-p-thiamphenicol phenylserine ester, the second, L-p-thiamphenicyl phenylserine ester or its salt After lye racemization and saponification, DL-p-thiamphenyl phenylserine or salt is obtained, and then copper reagent is used to obtain D-p-thiamphenyl phenylserine copper, and finally esterified to obtain DL-p-thiamphenyl phenylserine Serine ester. The invention simplifies the existing production process of DL-p-thymphenylphenylserine ester, greatly improves the recovery efficiency; solves the complex recovery process of racemic copper salt in the existing process, reduces pollution, and is more conducive to industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG KANGMU PHARMA
A research and development method for weathering steel based on rapid collection of corrosion data
ActiveCN110346273BCorrosion resistanceReliable test resultsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCopper testCurrent meter
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Antimicrobial floor coatings and formulations
An antimicrobial floor coating is provided that includes a matrix comprising a polymeric material; and a plurality of second phase particles comprising a controlled release agent, the controlled release agent comprising a plurality of antimicrobial copper ions. The polymeric material comprises an epoxy and an acrylic, and the plurality of second phase particles is distributed within the matrix. Further, an exterior surface of the coating exhibits at least a 2 log reduction in a concentration of Staphylococcus aureus under a Modified EPA Copper Test Protocol. Further, the controlled release agent can comprise a phase-separable glass.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for forming amino acid self-assembly corrosion inhibition membrane with fluorescent characteristics on copper surface
The invention discloses a method for forming an amino acid self-assembly corrosion inhibition membrane with fluorescent characteristics on a copper surface, which comprises the following steps of: polishing pure copper step by step by metallographical sand paper from No.1 to No.6, degreasing with absolute ethyl alcohol and cleaning with deionized water for later use; processing a copper test specimen by using aqueous solution of amino acid to obtain the copper test specimen modified by the amino acid; and assembling fluorescent reagent onto the surface of the copper test specimen indirectly under the electrostatic attraction action between 1-naphthylamine sodium diacetate (NADA) serving as the fluorescent reagent and the amino acid to prepare a dual-layer photosensitive corrosion inhibition self-assembly corrosion inhibition functional membrane, and characterizing the fluorescent characteristics and corrosion inhibition effect of the membrane respectively by adopting fluorescence spectra and an electrochemic impedance method. Researches show that in the corrosion inhibition functional membrane with the fluorescent characteristics, the relevance exists between fluorescence intensity and corrosion inhibition performance, and the corrosion inhibition characteristics of the assembly membrane are subjected to on-line detection and real-time monitoring through a fluorescence signal, so the method has great significance for promoting the application of the amino acid self-assembly membrane.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
A kind of electroless copper backlight test method
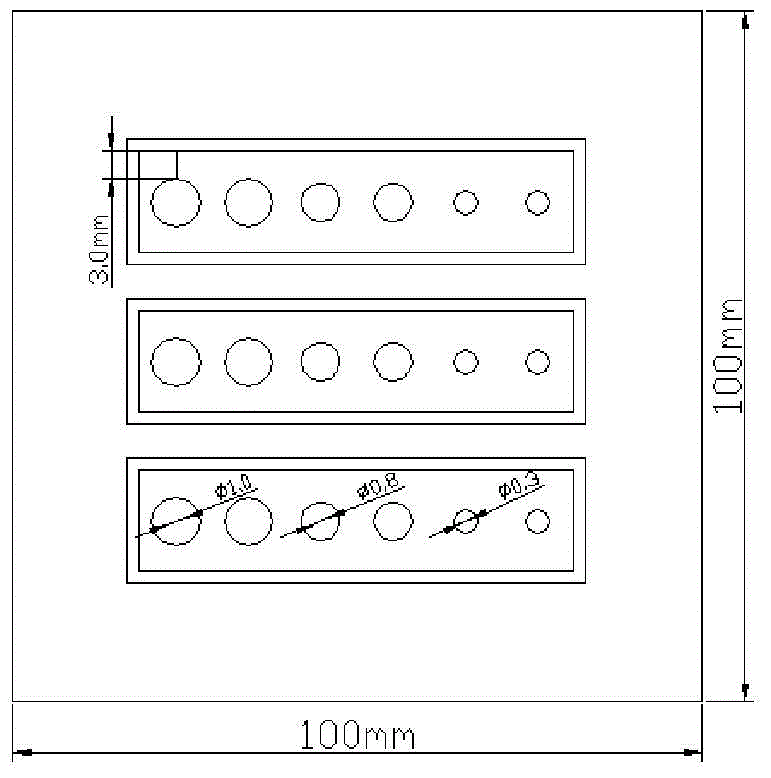
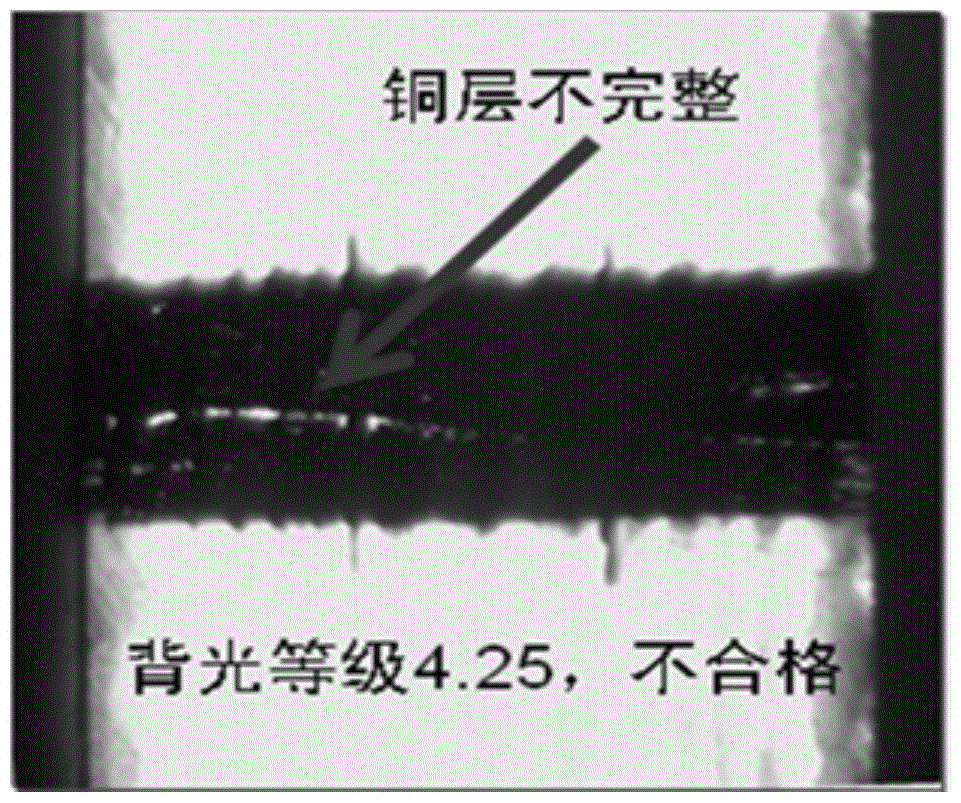
ActiveCN104034659BAchieve standardizationReduce the phenomenon of unqualified backlight detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansCopper testEpoxy
The invention relates to a hole metallization of a printed circuit board, in particular to a test method for electroless copper backlighting, which uses a copper-clad epoxy resin glass cloth laminate to etch into a light board and then presses it into a 12-layer board with a thickness of 2.0mm. board; drill two backlight test holes with diameters of 0.3mm, 0.8mm, and 1.0mm respectively; process the backlight standard sheet into a standard backlight test sheet with a size of 100mm×100mm; after electroless copper deposition on the standard backlight test board , and then perform cold buried resin potting, cut and grind after 5 minutes, and finally judge the backlight level under a microscope. The damage caused by the sandpaper rotating at medium and high speeds to the hole wall greatly reduces the influencing factors in the backlight level determination process, reducing the unqualified backlight level from 8.9% to 0.40%, which improves the pass rate of backlight detection.
Owner:NO 771 INST OF NO 9 RES INST CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
Quantitative evaluation method for measuring corrosive sulfur by X-fluorescence
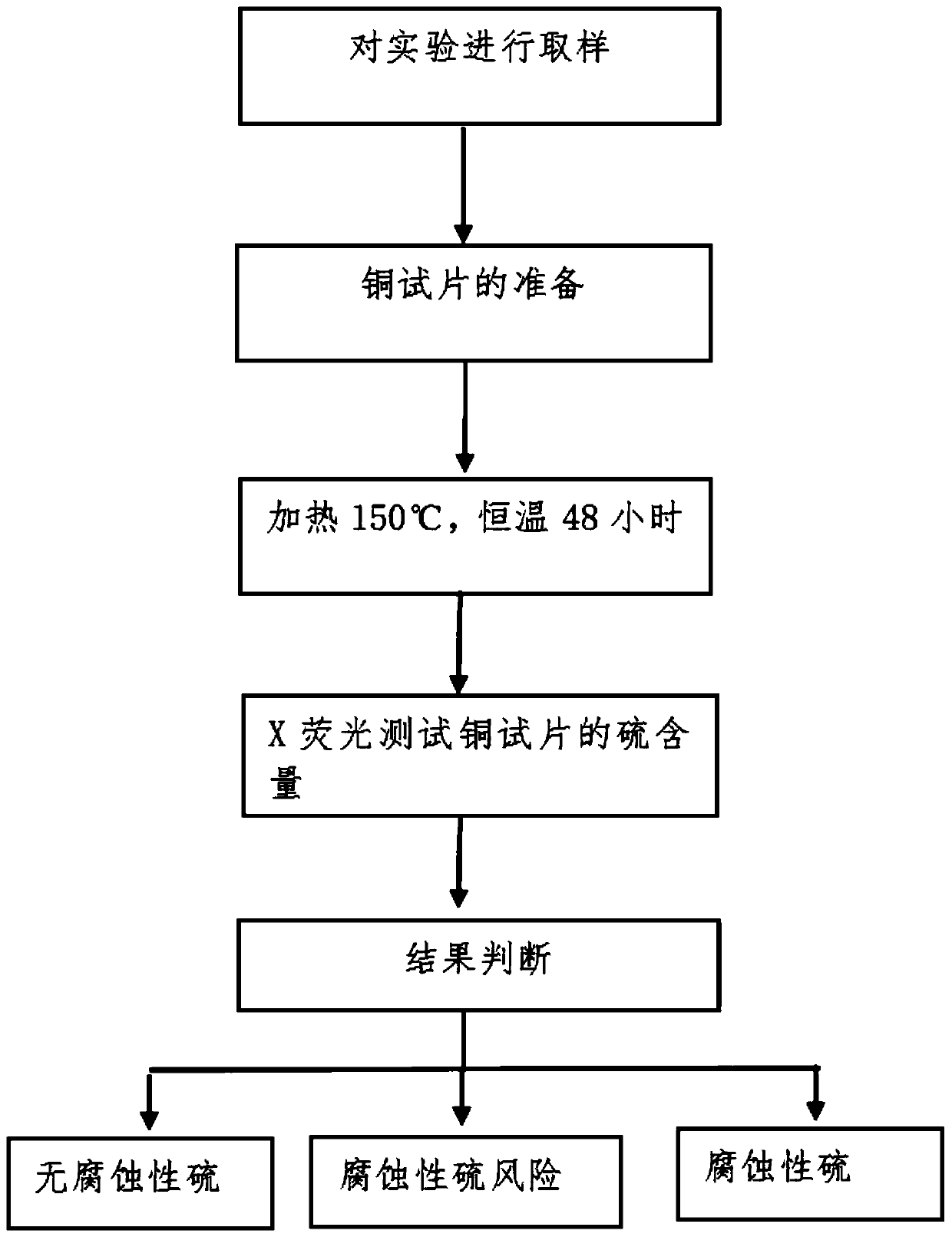
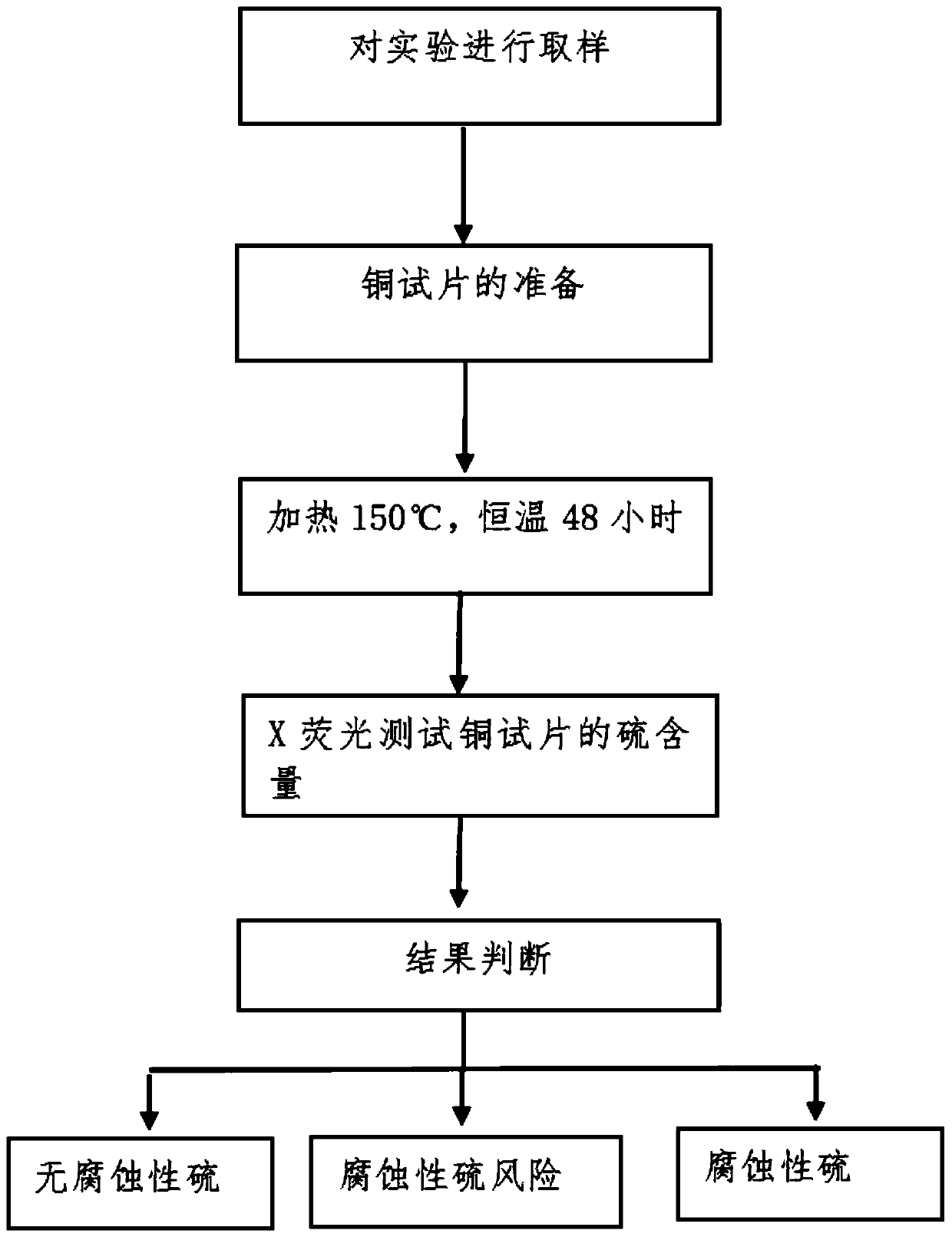
InactiveCN110018190AAccurate judgmentQuick judgmentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCopper testChemical reaction
The invention discloses a quantitative evaluation method for measuring corrosive sulfur by X-fluorescence. The quantitative evaluation method for measuring corrosive sulfur by the X-fluorescence comprises the following steps that (1) a sample is placed into a container; (2) a sulfur-free copper test piece is placed into the container with the sample taken out, it is ensured that the copper test piece is completely immersed into oil, and the container is sealed; (3) the container containing the cooper test piece in the step (2) is placed into an oven with the temperature of 150 DEG C+ / -3 DEG C,constant temperature is carried out for 24-72h, and the container is taken out after an experiment is completed; (4) the sample is poured out after heating is completed, the cooper test piece is taken out and immersed into a cleaning solvent, and the attached sample on the cooper test piece is cleaned; (5) sulfur content test is carried out on the cooper test piece by using the X-fluorescence; and (6) a result is judged. According to the quantitative evaluation method for measuring corrosive sulfur by the X-fluorescence, after cooper, sulfur and a compound generate chemical reaction through the experiment, the condition of cooper test piece sulfur-containing compound is tested through X-fluorescence to judge whether an active sulfur compound exists in the oil or not, the quantitative evaluation method for measuring corrosive sulfur by the X-fluorescence can accurately judge the condition of corrosive sulfur and non-corrosive sulfur, and the operation practicability is high.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MECHANICAL ENG RES INST
A copper/steel composite material connection method with a preset joint
ActiveCN111673239BReduce welding difficultyImprove mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusCopper testMechanical property
The invention discloses a method for connecting copper / steel composite materials with preset joints. The specific operation steps are as follows: Step 1: preparation of copper-steel preset joints: using arc additive technology to prepare copper-steel composite welds of reasonable specifications, as Preset joint; Step 2: According to the composition of the base metal, select the solid welding wire of the same composition, and use MIG welding to complete the welding of the copper test plate, the steel test plate and the copper-steel preset joint. The method of the invention can improve the welding quality and comprehensive mechanical properties of the copper-steel dissimilar metal welded joint, and provides a new idea for the connection of copper / steel dissimilar metals.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Experimental device and method for simulating the corrosion of hollow copper conductors of generators in inner cooling water
InactiveCN107478567BAvoid pollutionConvenient researchWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCopper testCopper conductor
The invention provides a test device and a corresponding test method for simulating corrosion of a hollow copper conductor of a generator in inner cooling water. The provided test device is characterized by comprising a kettle body, a kettle lid closely covering the kettle body, a wide-mouth glass bottle arranged in the kettle body and used for accommodating demineralized water, a gas inlet part, a gas outlet part, a test piece suspending part and a temperature control part, wherein the gas inlet part comprises a short gas inlet pipe arranged on the kettle lid and a soft polyethylene extending pipe, the upper end of the soft polyethylene extending pipe is connected with a bottom outlet of the short gas inlet pipe, and the lower end of the soft polyethylene extending pipe extends into the wide-mouth glass bottle; the gas outlet part is arranged on the kettle lid and used for exhausting gas; the test piece suspending part comprises a mounting part mounted on the inner surface of the kettle lid and a suspending line for suspending a copper test piece in a proper position in the wide-mouth glass bottle; the temperature control part comprises a thermocouple component which is inserted into the kettle lid and extends into the kettle body, a polyethylene outer sleeve sleeving upper and lower end sealing ports of the thermocouple component as well as a temperature adjuster connected with the thermocouple component.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Antimicrobial floor coatings and formulations
An antimicrobial floor coating is provided comprising: a matrix comprising a polymeric material; and a plurality of second phase particles comprising a controlled release agent comprising a plurality of antimicrobial copper ions. Polymeric materials include epoxies and acrylics, and the plurality of second phase particles are distributed within the matrix. Further, the outer surface of the coating exhibits at least a 2 log reduction in the concentration of Staphylococcus aureus according to the modified EPA copper test protocol. Further, the controlled release agent may comprise phase separable glass.
Owner:CORNING INC
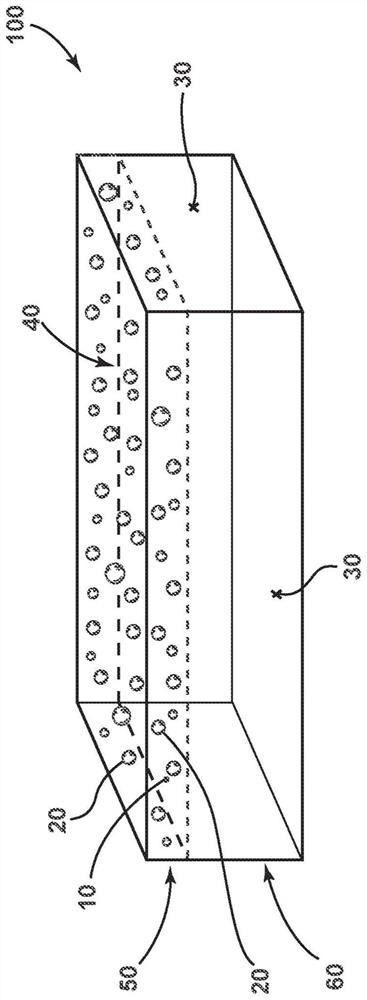
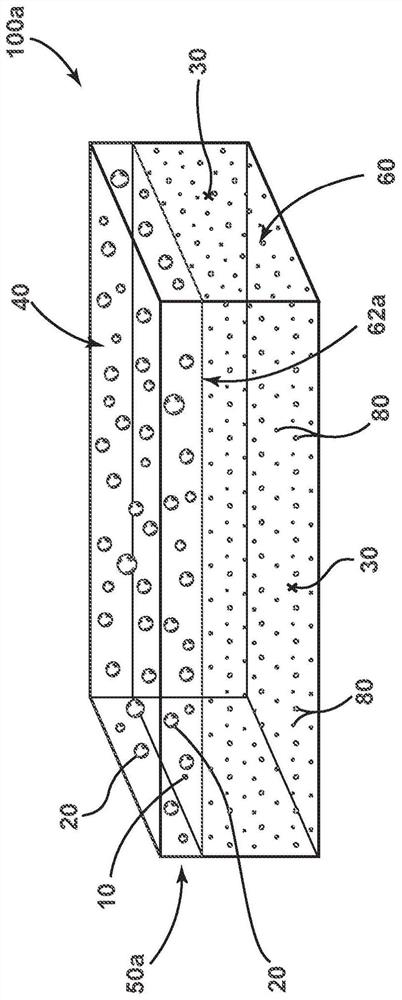
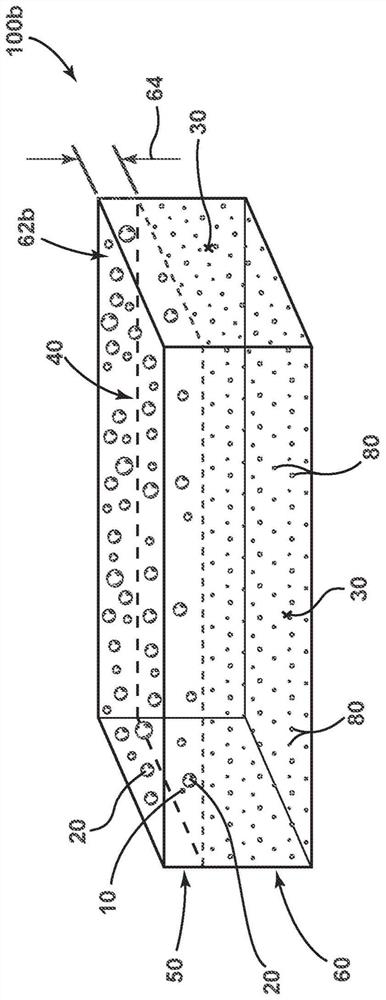
Antimicrobial phase-separable glass/polymer articles and methods of making the same
An antimicrobial article comprising: an antimicrobial composite region comprising a matrix comprising a polymeric material and a first plurality of particles within the matrix. The particles comprise phase-separable glass with a copper-containing antimicrobial agent. The antimicrobial composite region may be a film containing said first plurality of particles, which is subsequently laminated to the block element. The first plurality of particles may also be pressed into a membrane or block element to define an antimicrobial composite region. The exposed surface portion of the antimicrobial composite area may exhibit at least a 2-log reduction in concentrations of at least one of Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa according to the modified EPA copper test protocol.
Owner:CORNING INC
Antimicrobial phase-separable glass/polymer articles and methods for making the same
An antimicrobial article that includes: an antimicrobial composite region that includes a matrix comprising a polymeric material, and a first plurality of particles within the matrix. The particles include a phase-separable glass with a copper-containing antimicrobial agent. The antimicrobial composite region can be a film containing the first plurality of particles that is subsequently laminatedto a bulk element. The first plurality of particles can also be pressed into the film or a bulk element to define an antimicrobial composite region. An exposed surface portion of the antimicrobial composite region can exhibit at least a log 2 reduction in a concentration of at least one of Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria under a Modified EPA Copper Test Protocol.
Owner:CORNING INC
Antimicrobial-antireflective articles and methods for making the same
Described herein are antimicrobial articles having improved antimicrobial efficacy and antireflective properties. Further described are methods of making and using the improved articles. The antimicrobial articles generally include an antimicrobial element and an antireflective element. The antireflective element, in some cases, can be disposed directly on a glass, glass-ceramic or ceramic substrate and the antimicrobial element is disposed on the antireflective element. The article can exhibit a reflectance of about 4% or less (and less than 1% in some cases) in the range of about 425 nm to about 725 nm. Further, the article can be characterized with an antimicrobial efficacy by exhibiting at least a 2 log reduction in a concentration of at least Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria under a Modified EPA Copper Test Protocol.
Owner:CORNING INC
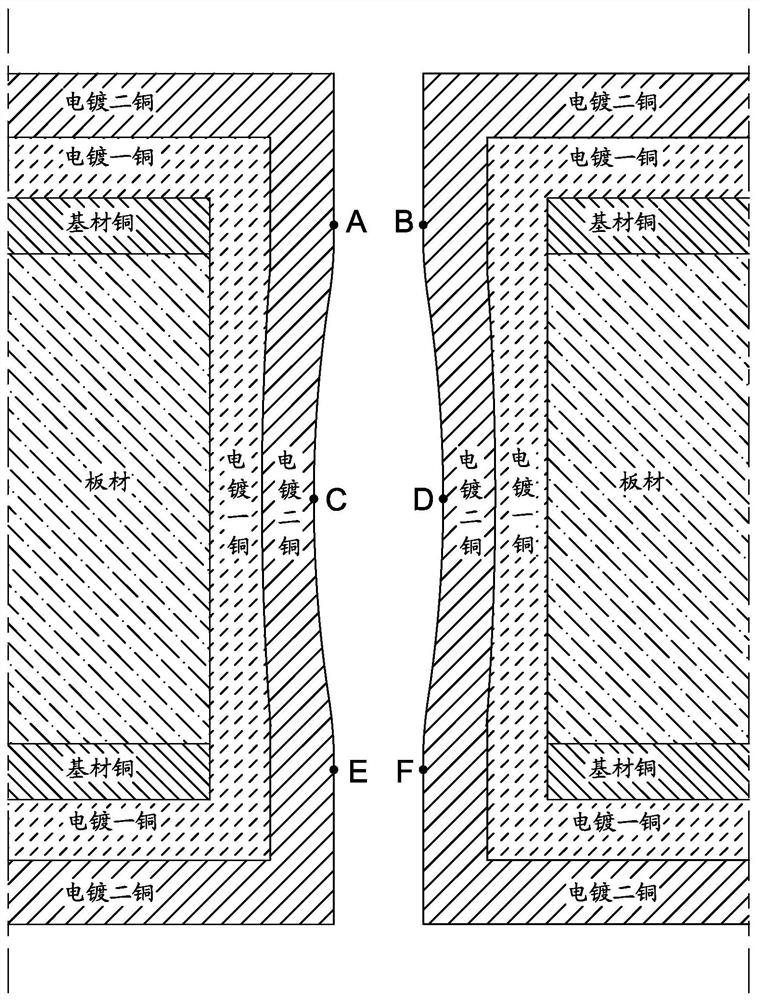
A method for quickly estimating the copper thickness of pcb via holes
ActiveCN110519925BQuick calculationFast and accurate calculationMeasurement devicesPrinted circuit manufactureCopper testTester device
The invention provides a method for quickly calculating the copper thickness of a PCB via hole, comprising: measuring the copper thickness of the surface copper through a surface copper tester, measuring the copper thickness of the via hole through a slicing technique and calculating the deep plating capacity, and the statistics are not less than the designed A certain number of PCB boards are measured, and the average value of surface copper thickness and deep plating ability are obtained respectively, and then the surface copper thickness of the PCB board to be tested is measured by the surface copper tester, and the correction error is also introduced. The measurement results are corrected, and finally the calculation formula can be used to quickly calculate the copper thickness of the via hole center of the PCB board to be tested by measuring the surface copper thickness of the target PCB board. In the case that the PCB board has only via holes, the invention quickly calculates the hole copper thickness in the center of the via hole without destroying the PCB board to be tested.
Owner:福州瑞华印制线路板有限公司
Copper detecting paper and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1189737CEasy to makeEasy to carryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingCopper testAlcohol
A copper test paper comprises base plate and colour display paper which is filter paper. The method to prepare the copper test paper includes the following steps: The said filter paper is placed into the solution of 15-20 g / L dithioazyl-sodium formate alcohol to be sufficiently soaked, and then to take it out for drying; furthermore the filter paper is placed in solution of 450-510 mg / L zinc soluble salt water to be sufficiently soaked and then to take out for drying and the copper test paper can be obtained by sticking the prepared filter paper on the base plate.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com