Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Log reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
"Log reduction" is a mathematical term (as is "log increase") used to show the relative number of live microbes eliminated from a surface by disinfecting or cleaning. For example, a "5-log reduction" means lowering the number of microorganisms by 100,000-fold, that is, if a surface has 100,000 pathogenic microbes on it,...
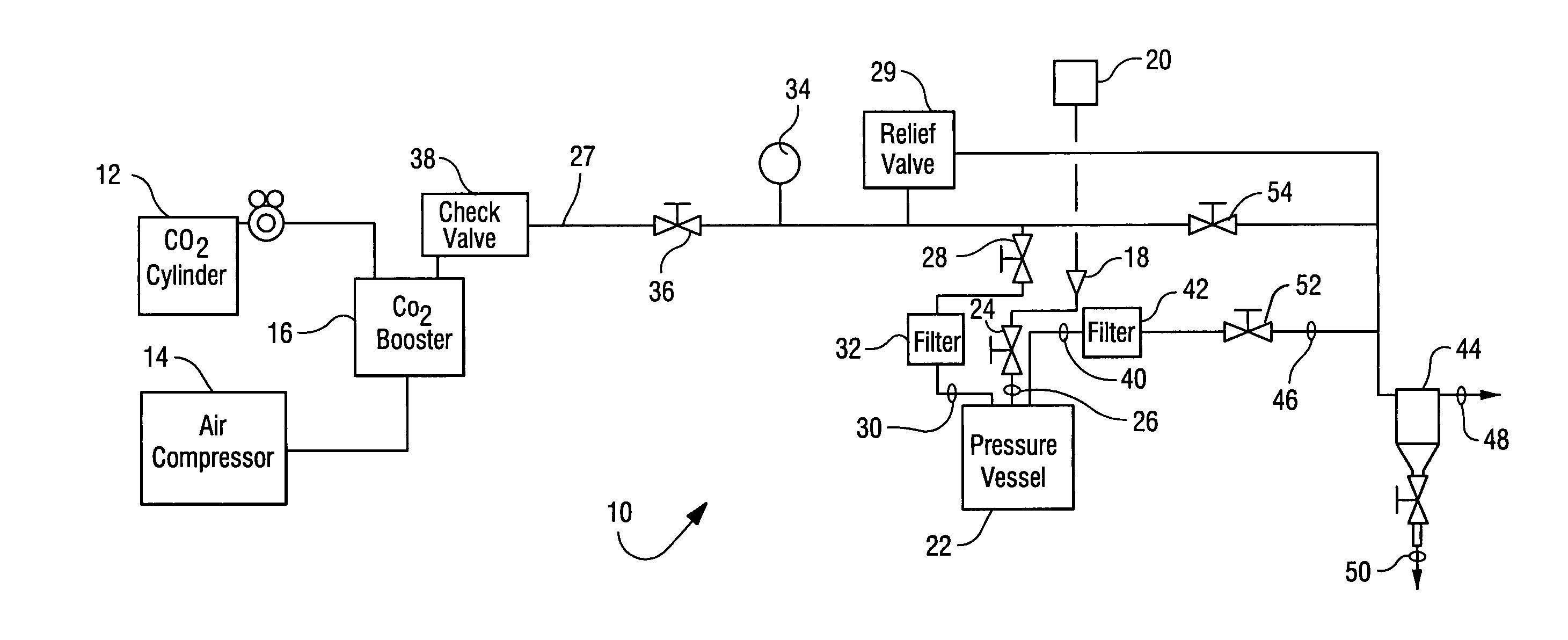
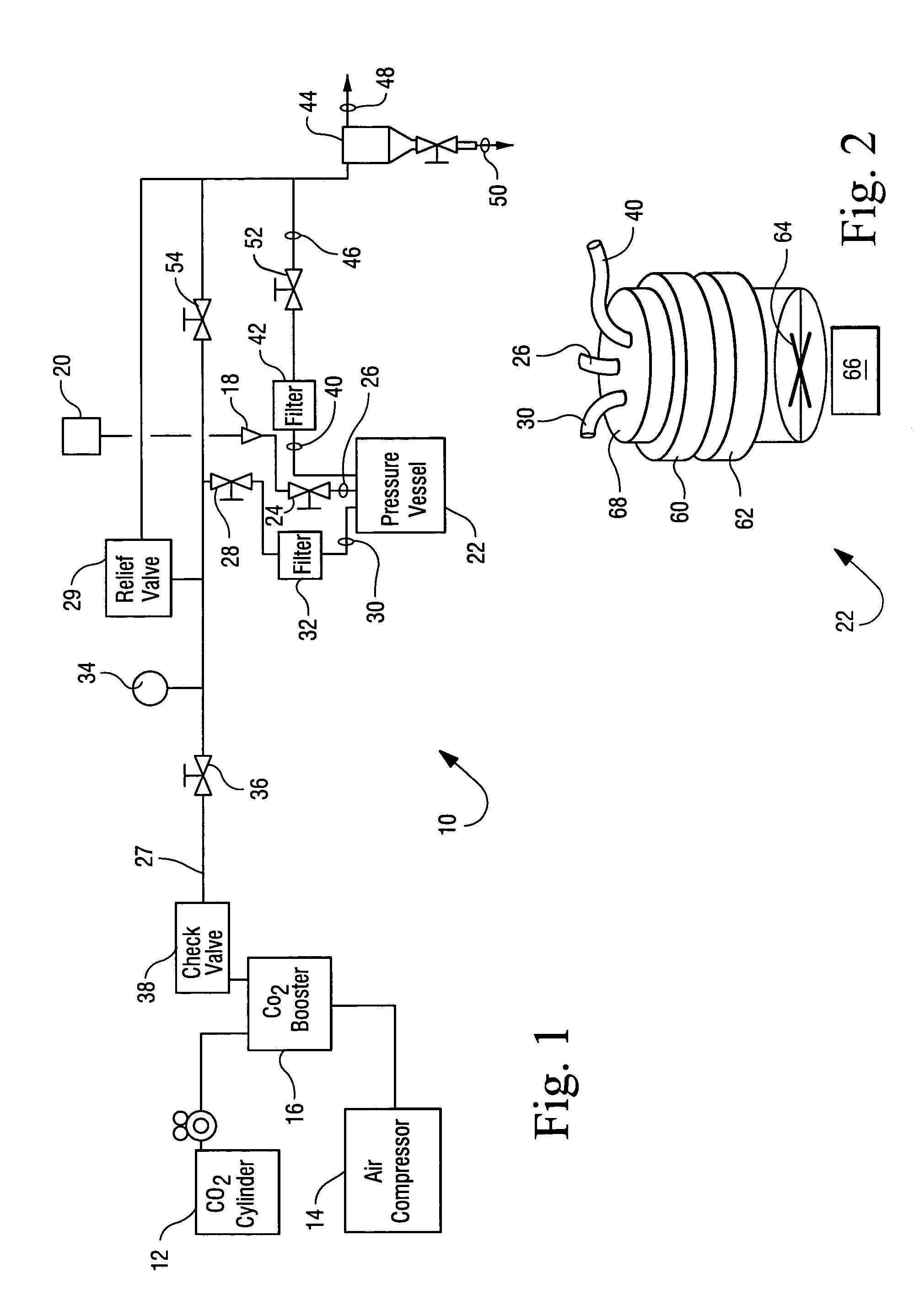
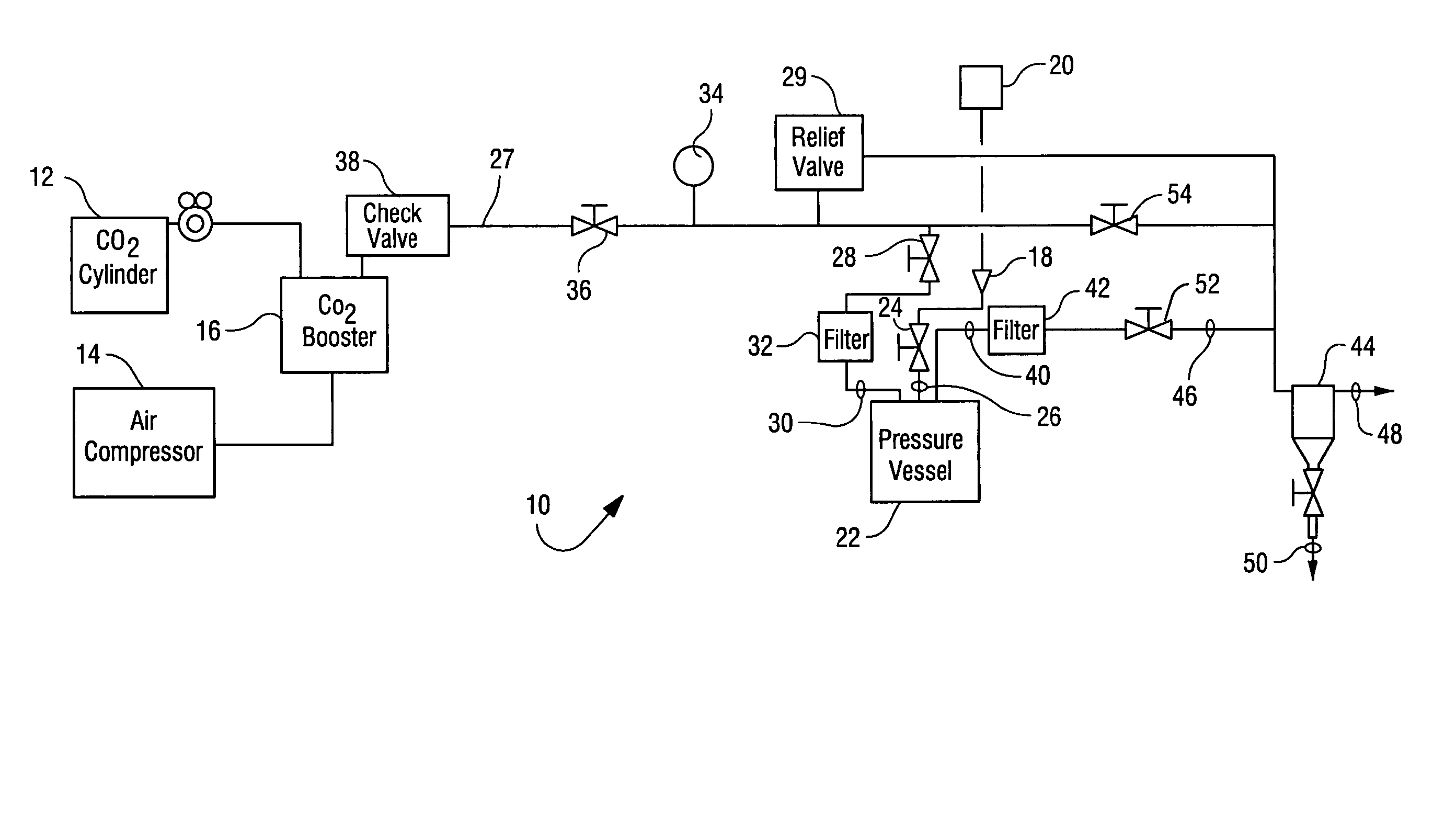
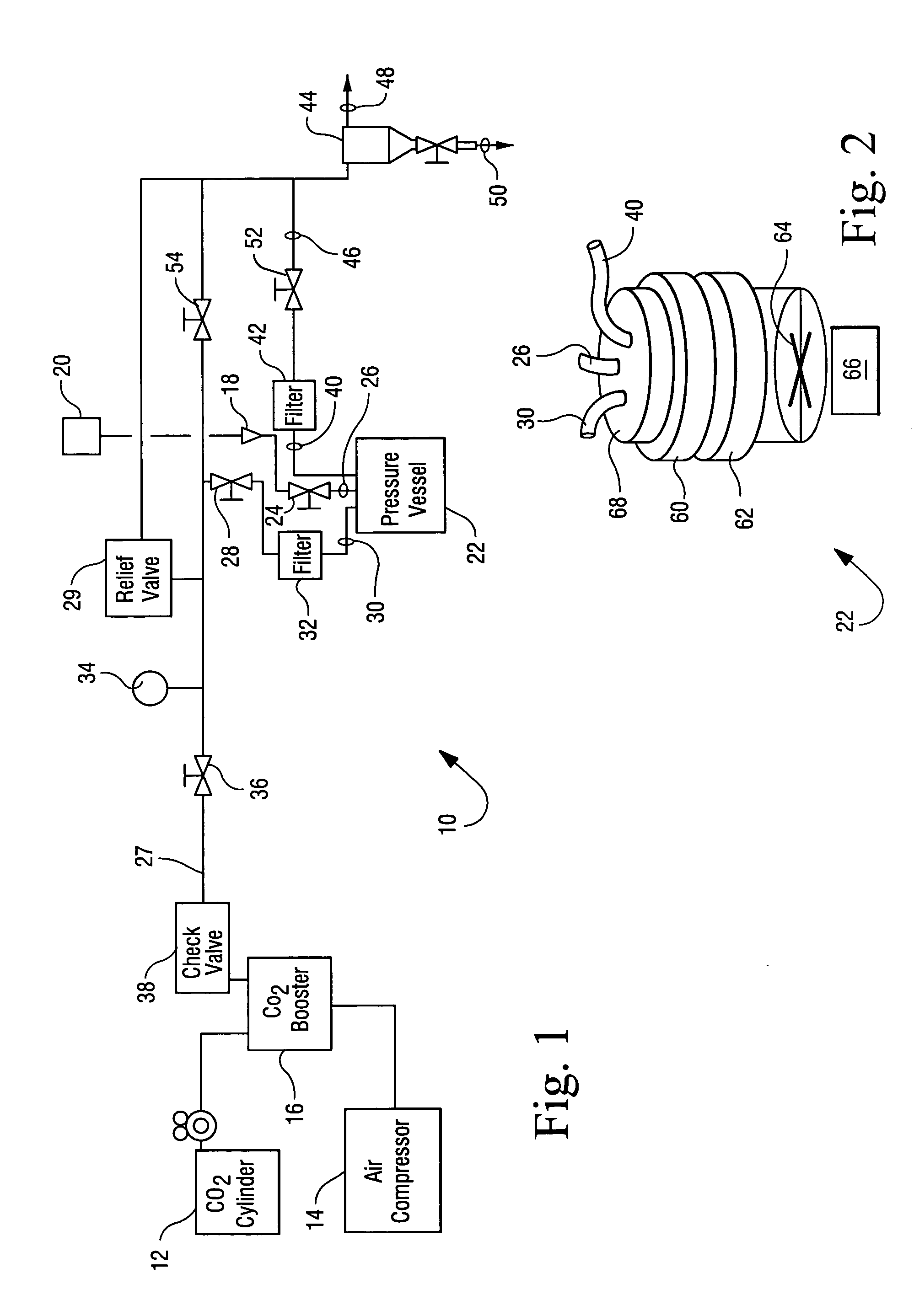
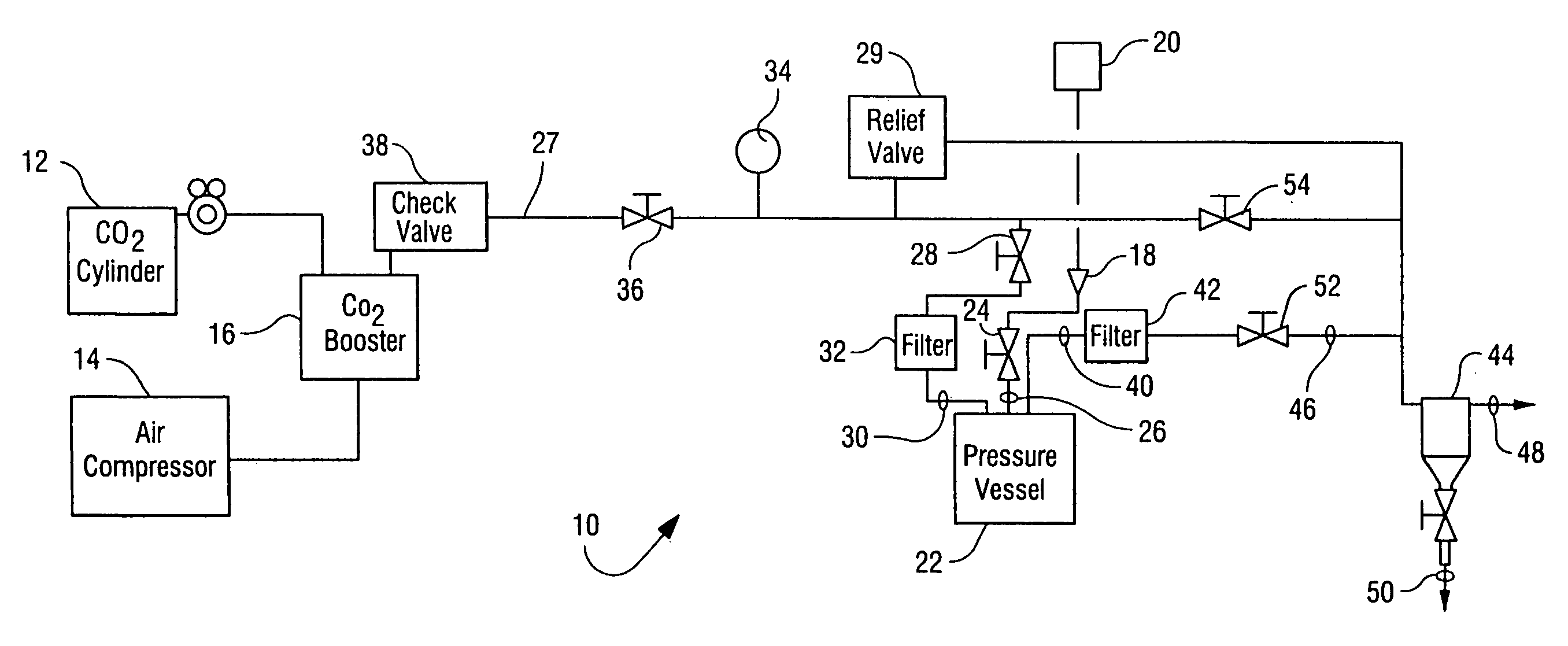
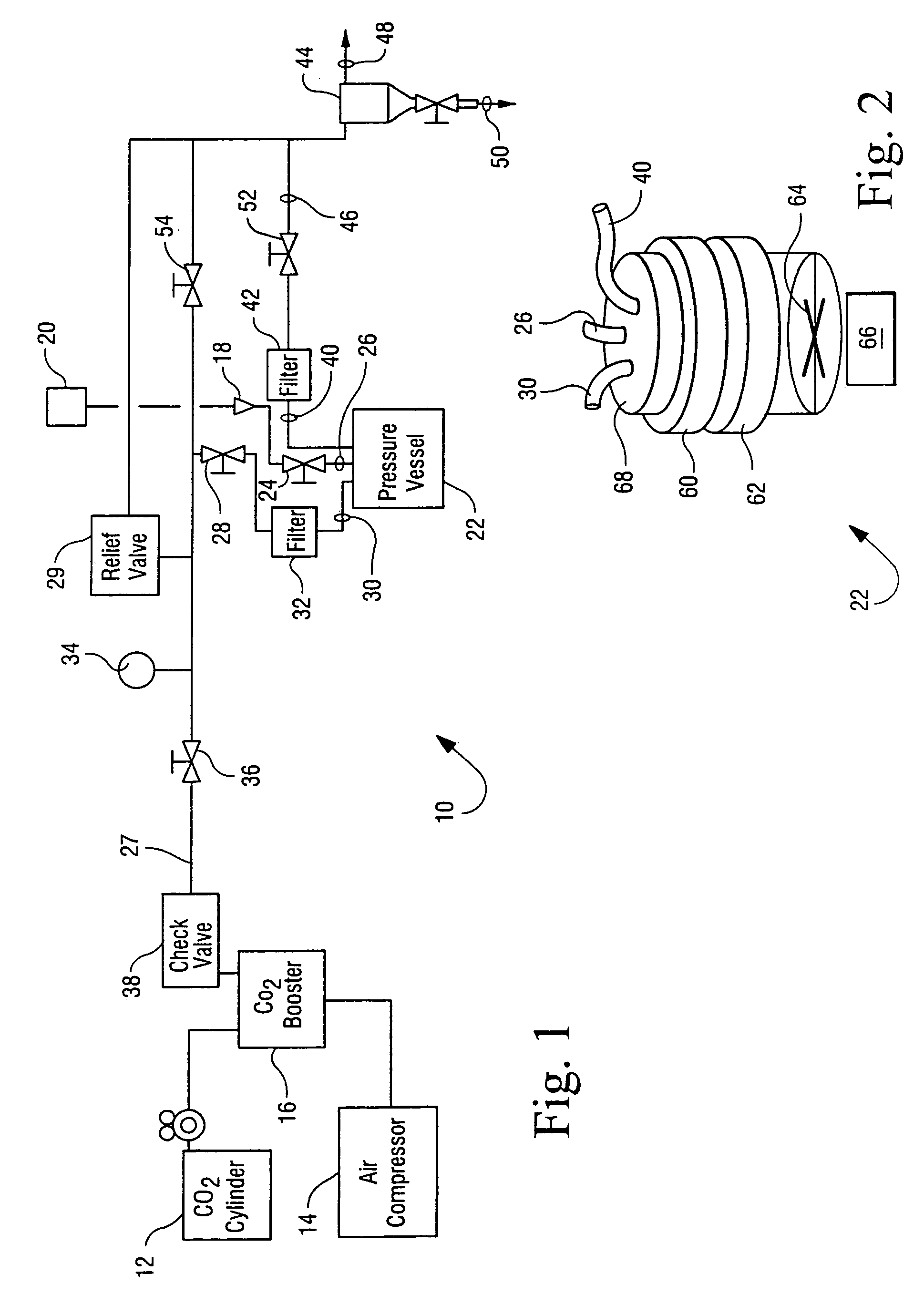
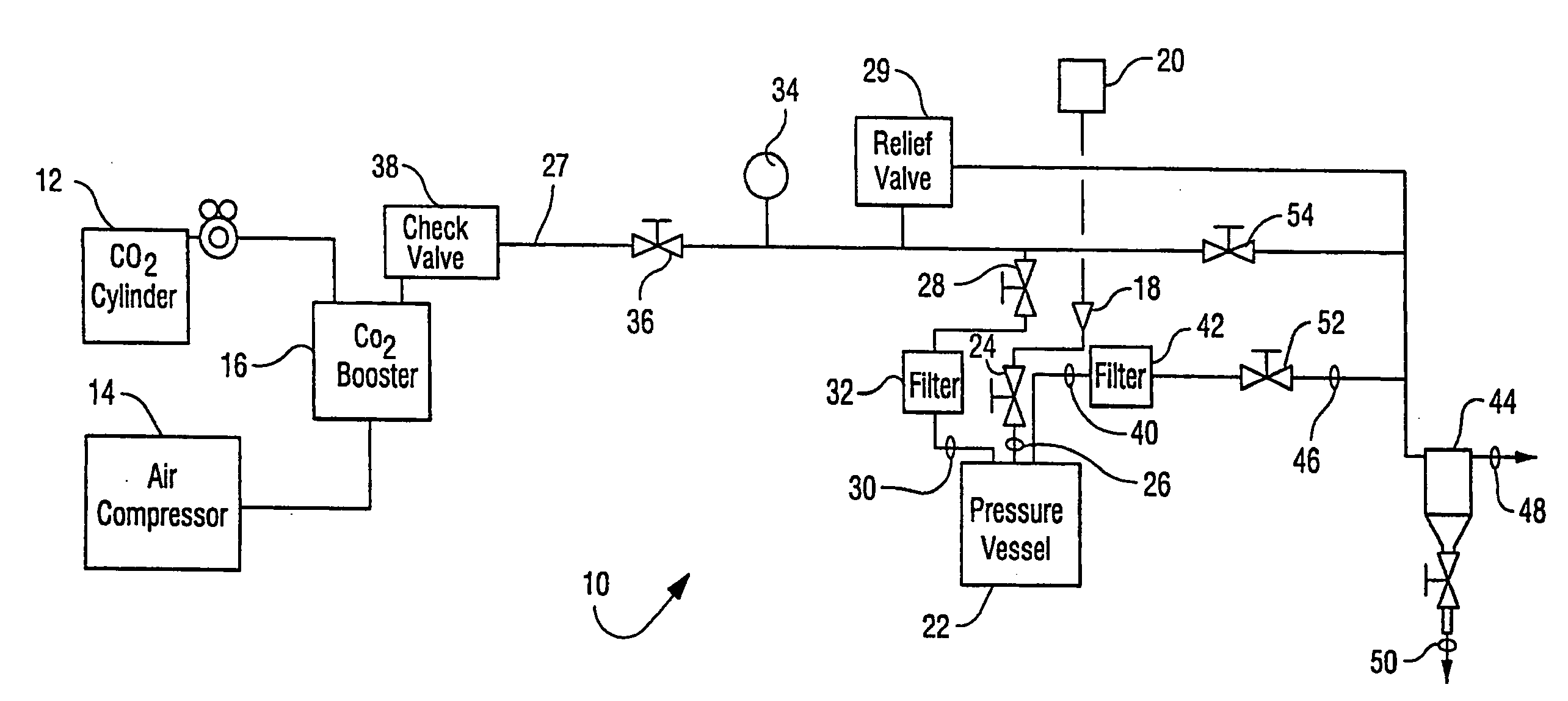
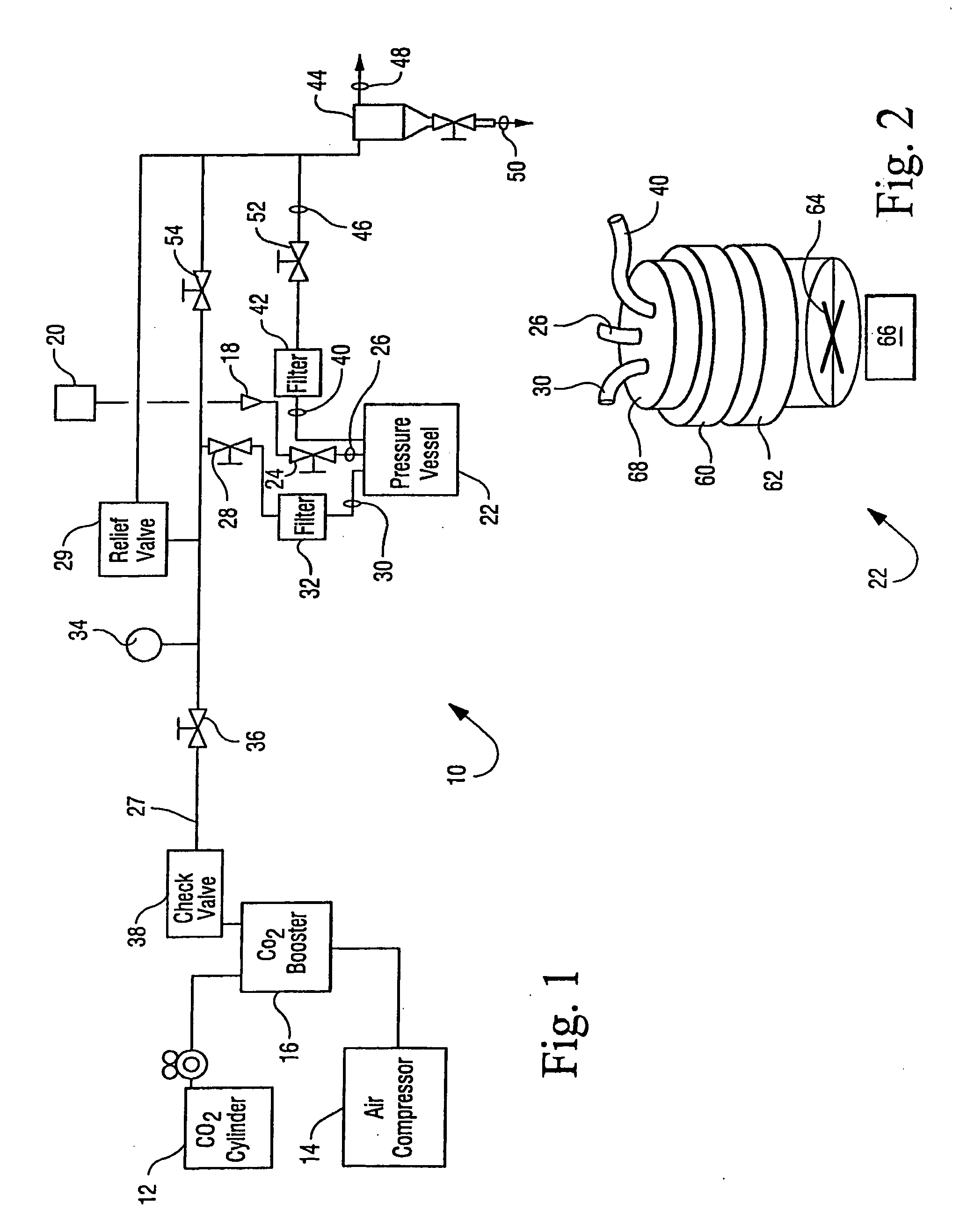
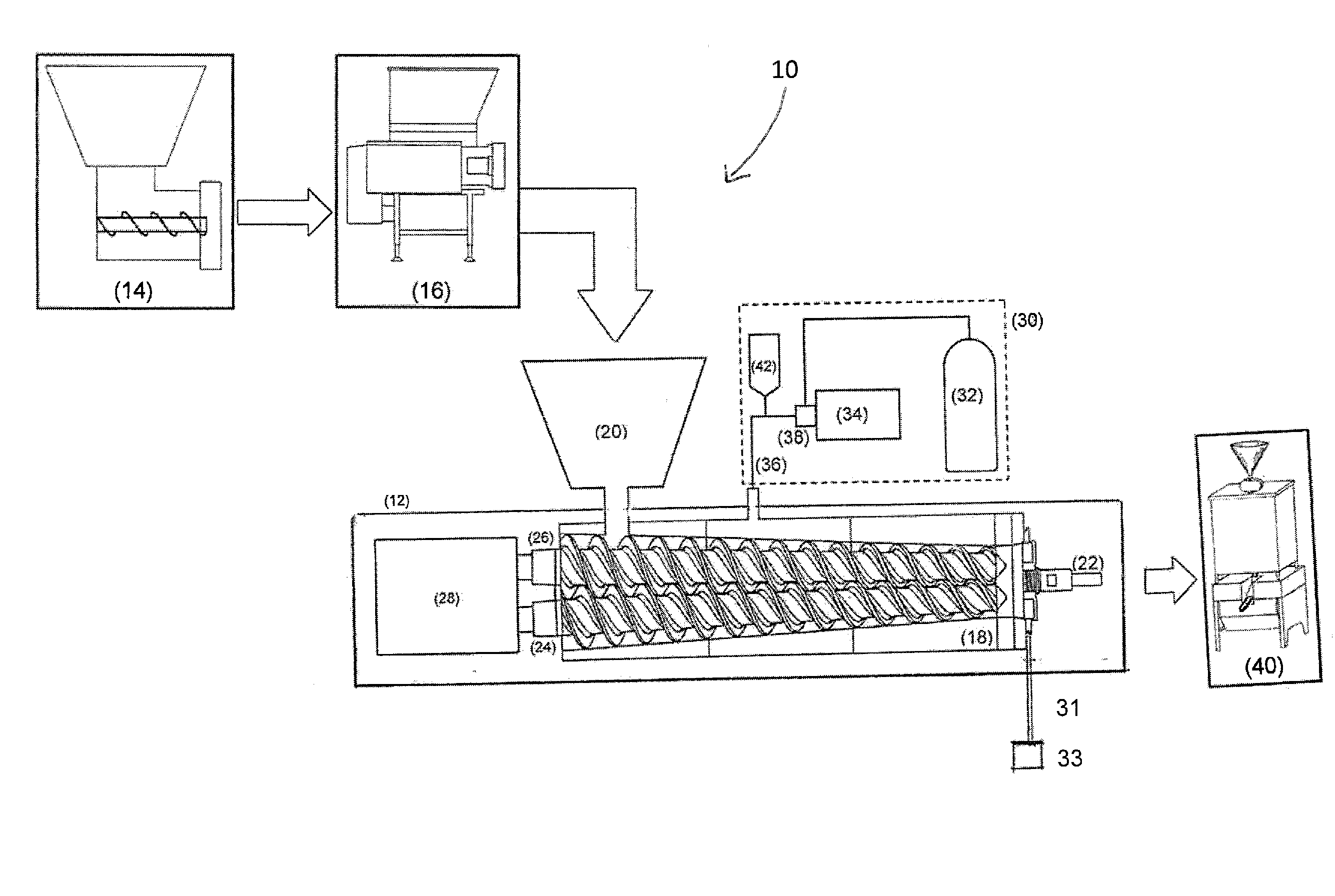
Sterialization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
ActiveUS7108832B2Enhances mass transfer and sterilizationImprove sterilizationSamplingOther chemical processesSporePressure cycling
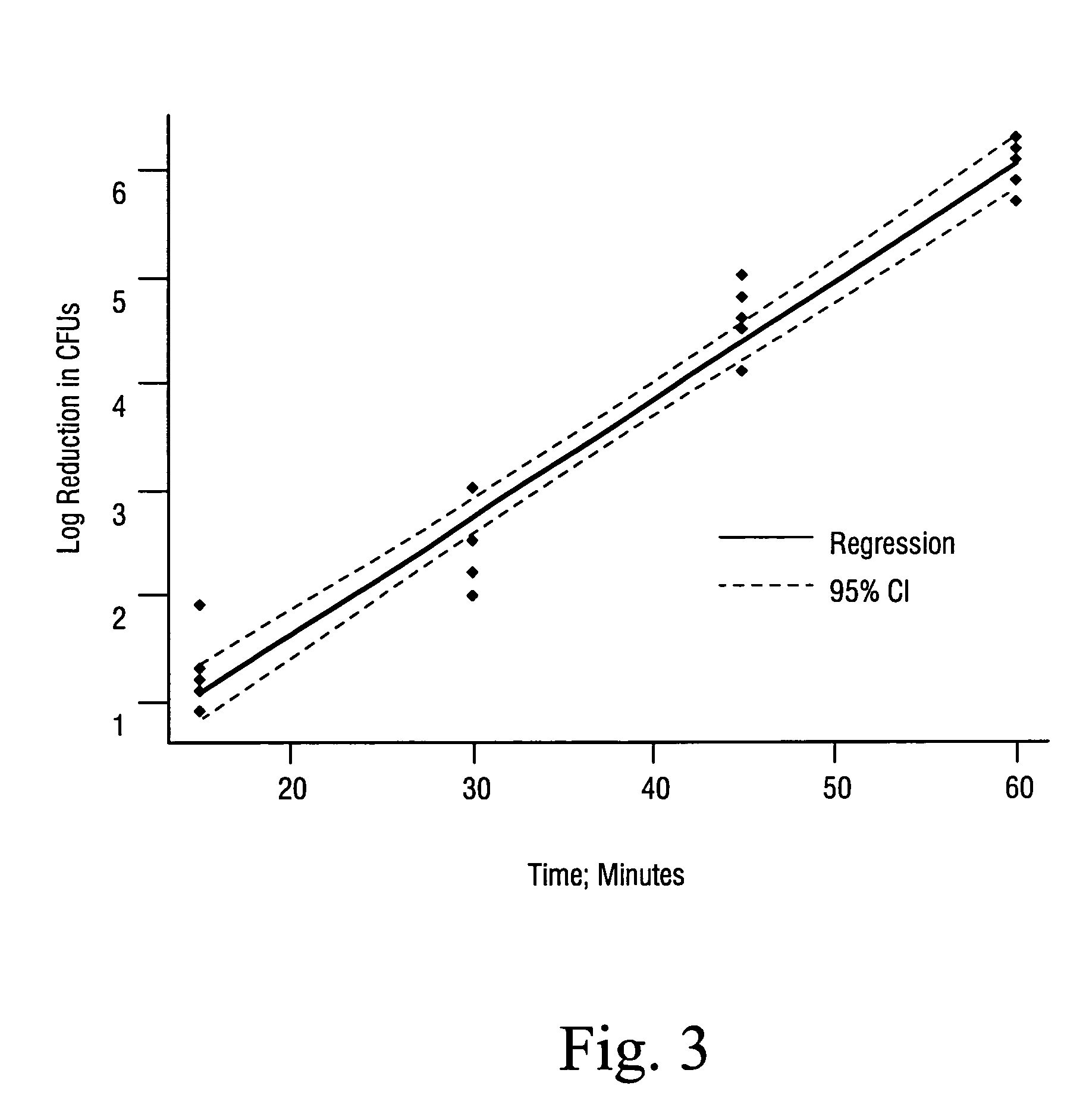
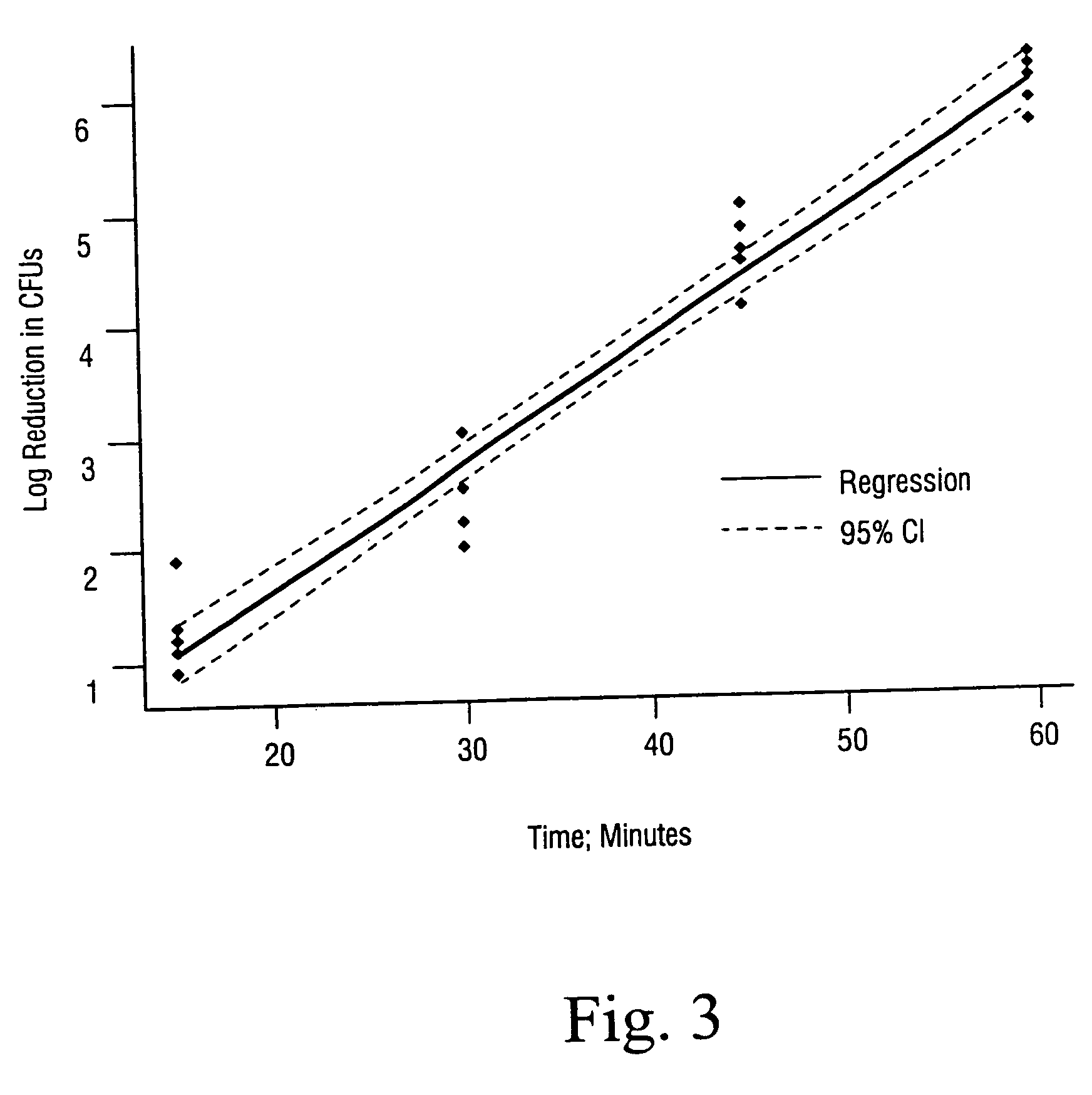
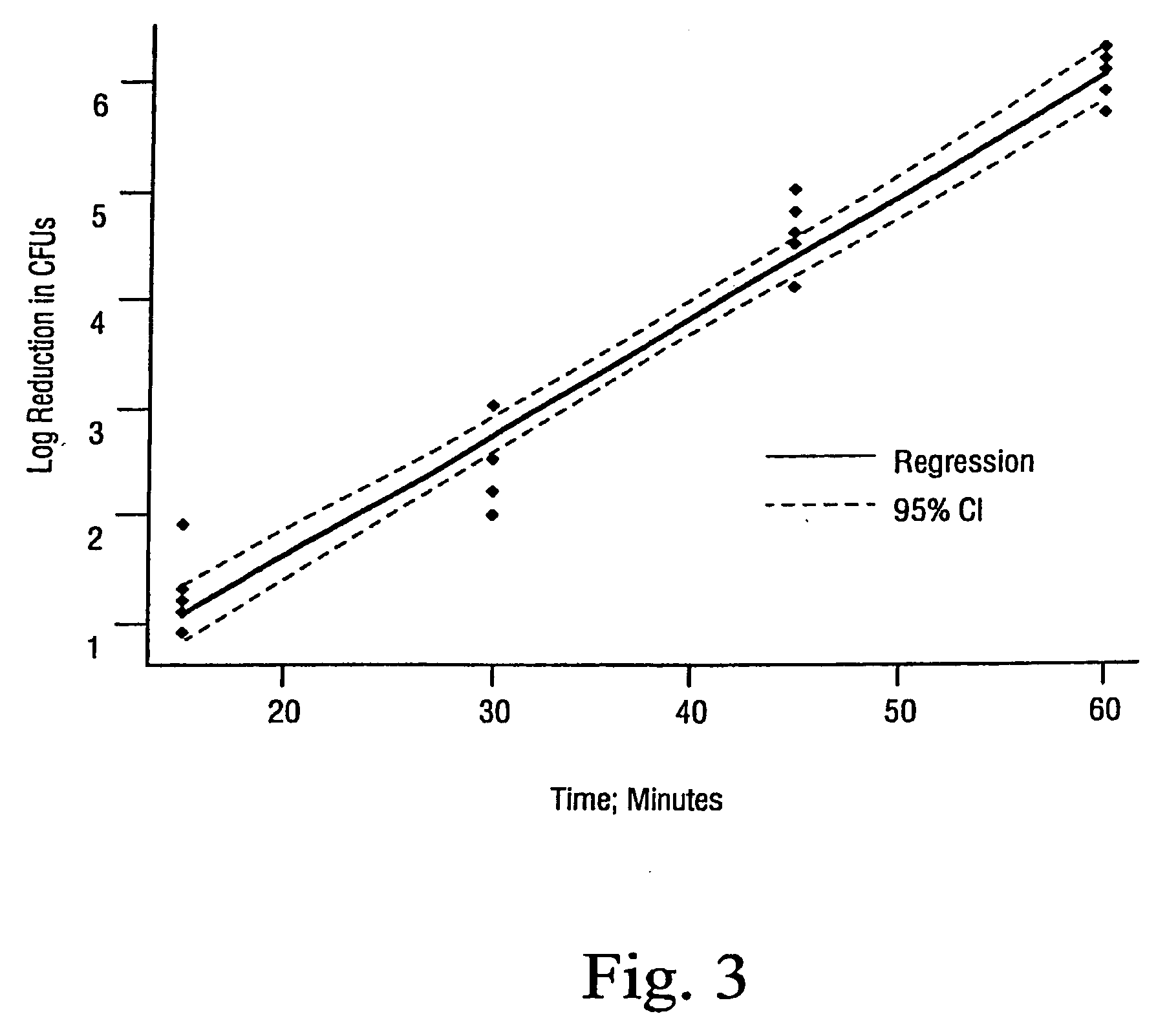
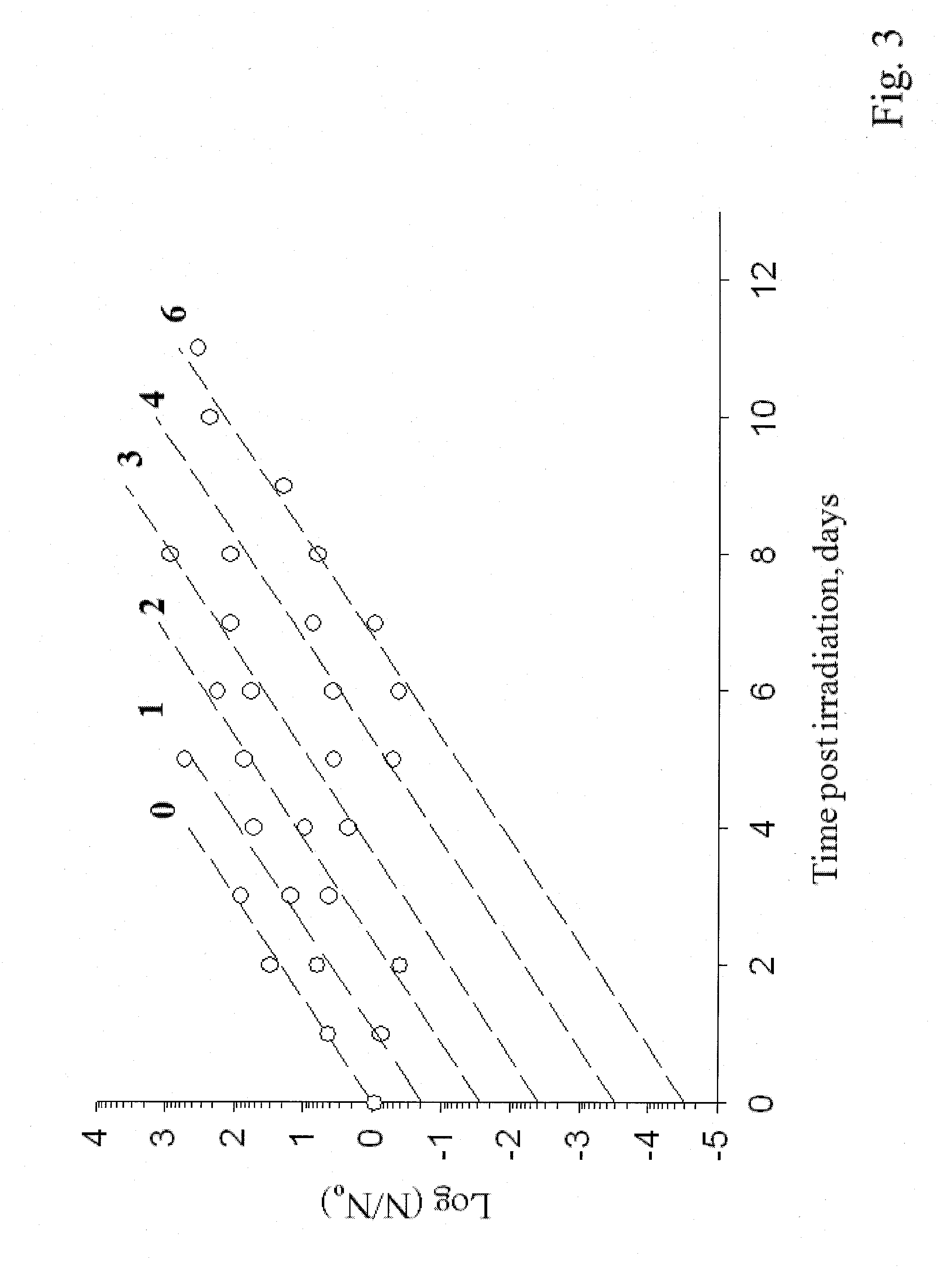
Sterilization methods and apparatus are effective to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores, i.e., B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis spores, by subjecting sterilizable materials to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions. Most preferably, the chemical additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant fluid is agitated during sterilization, e.g., via mechanical agitation or via pressure cycling.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
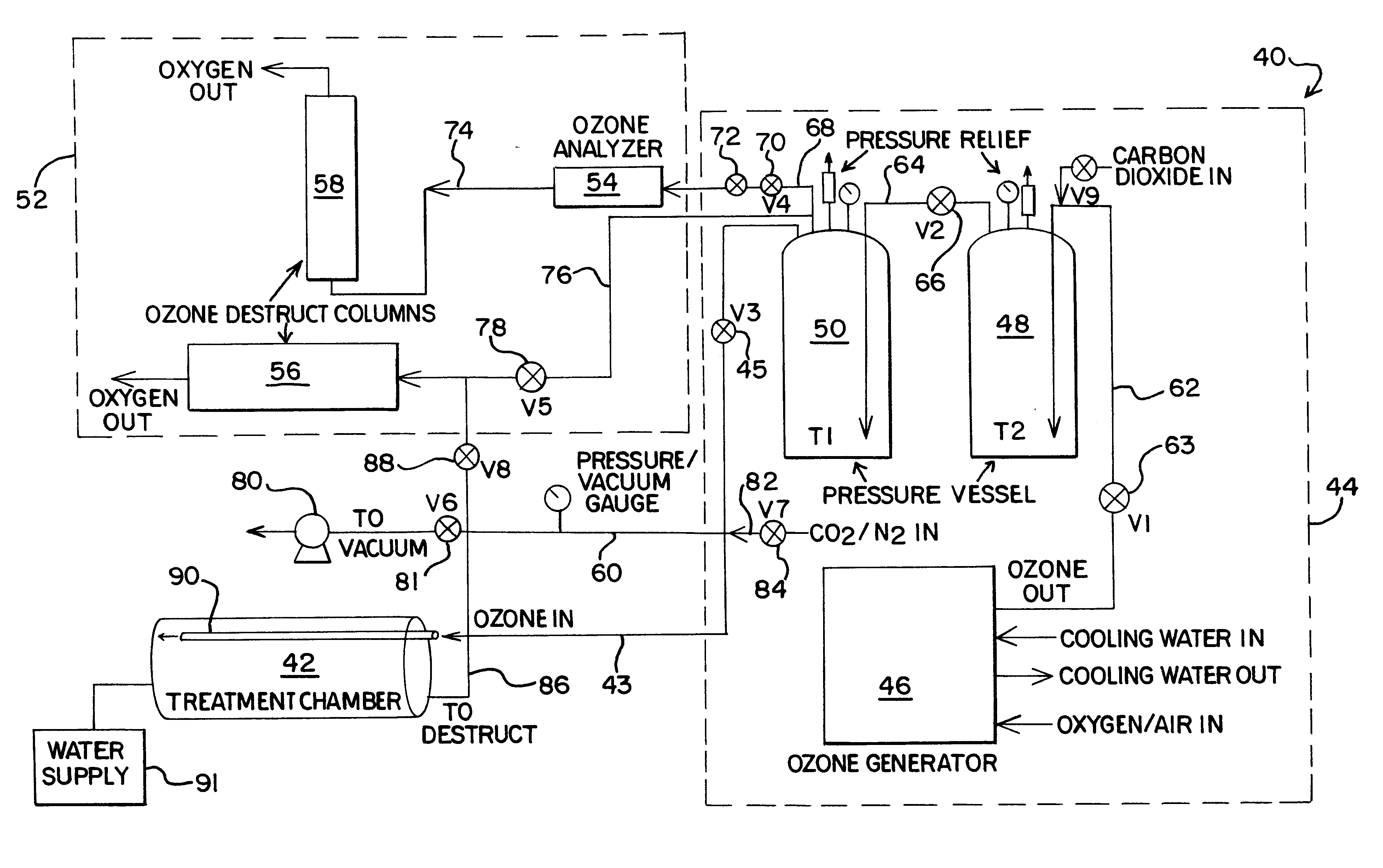
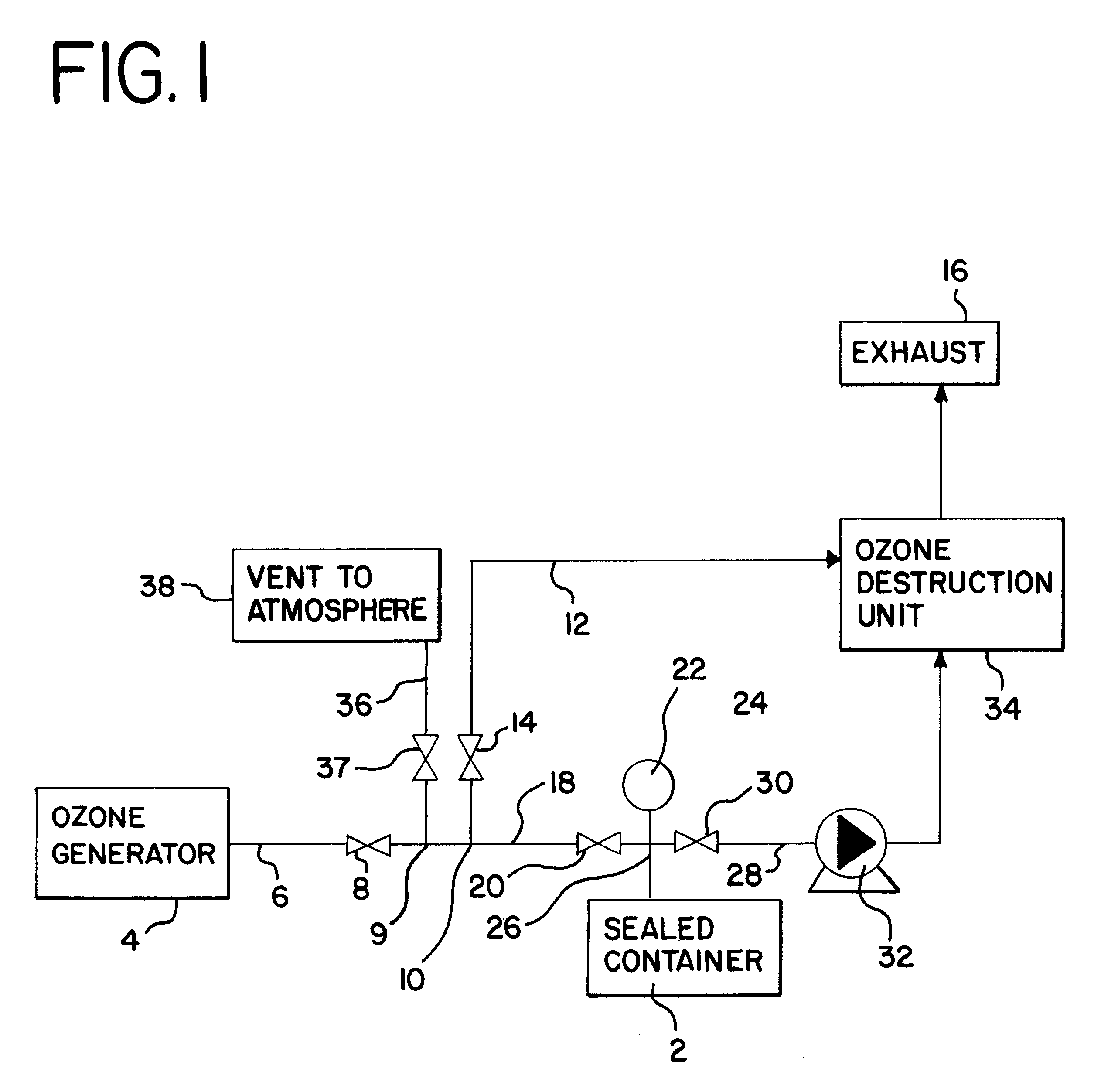
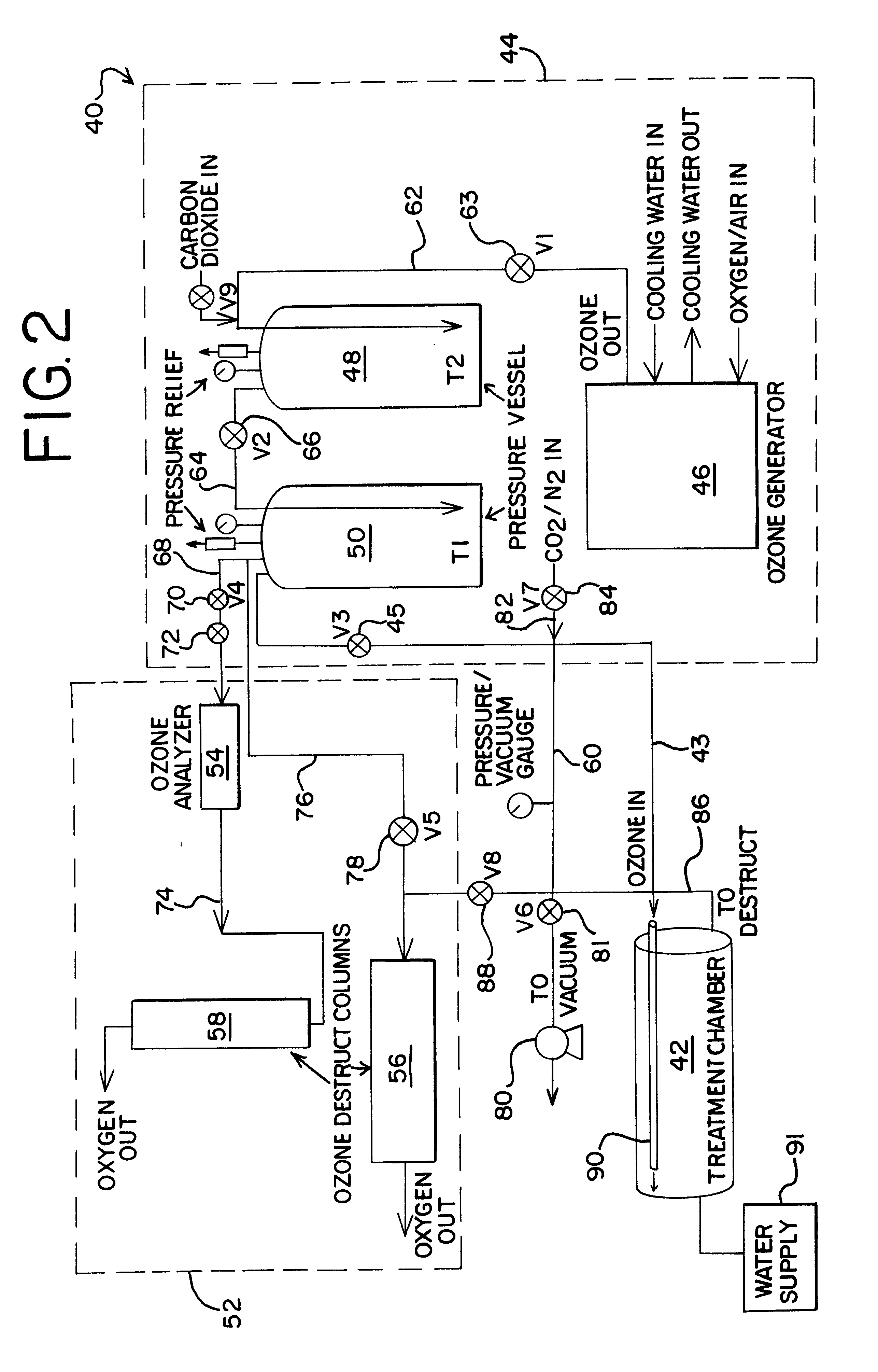
Food disinfection using ozone
Methods and apparatus are provided for decreasing the bacteria count of a food commodity without affecting its overall organoleptic quality (taste, odor, and color). This is accomplished using a treatment fluid comprising ozone, which is injected into a treatment chamber containing the food commodity. Some water is preferably added to obtain better contact of the ozone with the food by forming a thin film of ozonated water on the food surface. Spices and / or other ingredients may preferably be added with the water. The food is placed in a tumbler and the tumbler is set in motion. During treatment good contact between the treatment fluid and the food commodity is obtained by reversibly oscillating the tumbler. A log reduction of 40% or more in bacteria count may be obtained as compared without the ozone.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +2
High pressure pasteurization of liquid food product
InactiveUS20080311259A1Reduce moistureProvide securityDough treatmentMilk preservationLiquid productMicroorganism
The present invention is a method for pasteurization or sterilization of liquid food products using high pressure in a continuous or semi-continuous flow. The invention involves pressurizing and depressurizing the liquid product for a sufficient duration of time to achieve a 2.5 log cycle reduction in microorganisms. The uniform application of high pressure to the liquid food product coupled with a controlled pH and temperature of the liquid food product, the setting and maintaining the pressurizing media temperature, and the rapid depressurization resulting in cellular disruption of the microorganisms within the liquid product inactivating or destroying the microorganisms, such as vegetative microorganisms, while preserving the functionality of the liquid product.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Sterilization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
ActiveUS20050025667A1Enhances mass transfer and sterilizationImprove sterilizationSamplingOther chemical processesSporePressure cycling
Sterilization methods and apparatus are effective to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores, i.e., B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis spores, by subjecting sterilizable materials to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions. Most preferably, the chemical additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant fluid is agitated during sterilization, e.g., via mechanical agitation or via pressure cycling.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
Method for removing viruses from high concentration monoclonal antibody solution
ActiveUS20120077963A1High yieldHigh removal ratePeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsHigh concentrationMonoclonal antibody
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for removing even small viruses from a high concentration monoclonal antibody solution using a membrane, and thus for recovering the antibody within a short time at high yield in the form of a filtrate. The present invention provides a method for producing a preparation containing a monoclonal antibody, which comprises a step of removing viruses by filtering viruses in a monoclonal antibody solution using a virus-removing membrane, wherein(1) the monomer content of the monoclonal antibody accounts for 90% or more;(2) the monoclonal antibody concentration in the monoclonal antibody solution ranges from 20 mg / ml to 100 mg / ml;(3) the monoclonal antibody solution contains at least a basic amino acid; and(4) the parvovirus removal rate of the virus-removing membrane satisfies the following conditions:LRV (Log Reduction Value: logarithmic reduction value) ≧4.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
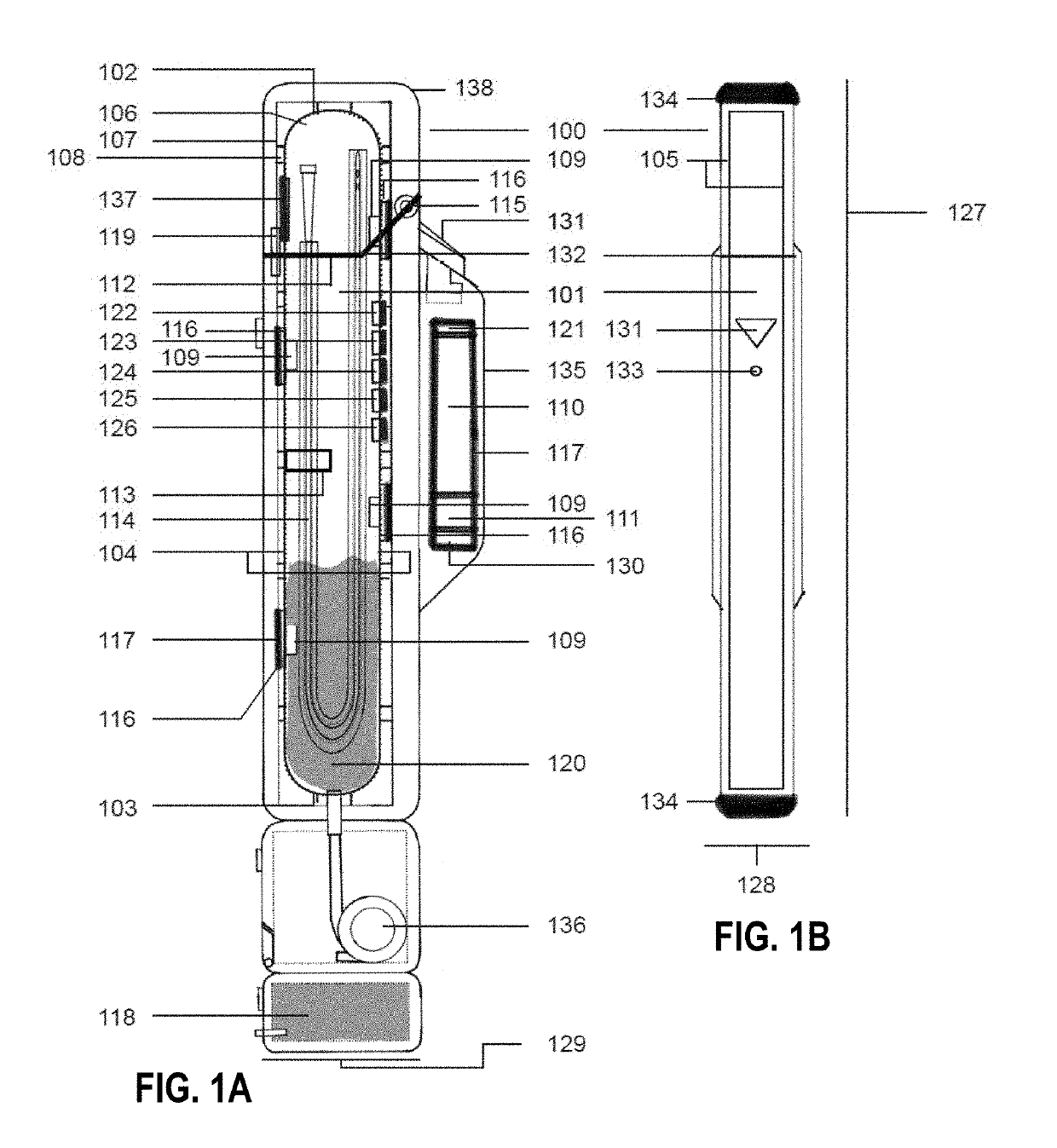
Methods and devices for portable sterilization and containment of medical devices
ActiveUS20190328915A1Prevent sterilizationAvoid environmentCatheterRadiationData acquisitionLog reduction
An at-home sterilization and data acquisition and deposition device including a housing having an opening or series of openings for receiving up to six medical devices, a sterilization chamber formed within the housing that is lined with sterilizing radiation reflecting material, and several sources of sterilizing radiation disposed within the sterilization chamber for sufficient emission of radiation to achieve a significant log reduction of any pathogens present on the medical devices, and an RFID scanner and sensor suite configured into the housing that prevents sterilization of non-system components, radiation emission into the environment, and that can pair with a user's mobile device. An individual catheterization system includes an at-home sterilization and data acquisition device, a software-enabled analysis of data acquired through the system, a set of accessories to enable proper lubrication, cleaning, and radiation-based sterilization of medical devices, and a set of RFID-enabled medical devices designed to facilitate sterile emptying of the bladder by providing a tactile interface that prevents direct contact between the individual and the parts of the medical devices that enter the individual's body.
Owner:CATHBUDDY INC
Sterilization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
InactiveUS20070003432A1Enhances mass transfer and sterilizationImprove sterilizationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsSporePressure cycling
Sterilization methods and apparatus are effective to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores, i.e., B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis spores, by subjecting sterilizable materials to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions. Most preferably, the chemical additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant fluid is agitated during sterilization, e.g., via mechanical agitation or via pressure cycling.
Owner:LIFECELL
Oral care method and kit
InactiveUS20100285148A1Increase flexibilityImprove efficacyAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsOral tissueMammalian tissue
A method of moisturizing while decolonizing mammalian tissue, the method comprising applying a multi-valent cationic antiseptic composition to the tissue, and applying a moisturizer composition to at least a portion of the same tissue; wherein the mammalian tissue is oral tissue of a subject; wherein the multi-valent cationic antiseptic is other than a metal ion; and wherein the applied compositions essentially exclude any component which causes a precipitate when combined with a multi-valent cationic antiseptic contained in the multi-valent cationic antiseptic composition when tested according to Test Method F, and / or wherein the moisturizer composition is such that a log reduction in the number of viable bacterial cells of at least 2 is provided when 106 cfu of Pseudomonas auerginosa are combined with a mixture 1.1 g of the moisturizer composition and 1.5 g of the multi-valent cationic antiseptic composition containing 0.12 weight percent of the multi-valent cationic antiseptic according to Test Method B; an oral care kit comprising a composition comprising the multi-valent cationic antiseptic and the moisturizer composition; and a method of moisturizing oral tissue of a patient requiring intubation using the moisturizer composition and an endotracheal tube coated or impregnated with a cationic antiseptic are provided.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High pressure processing of foods
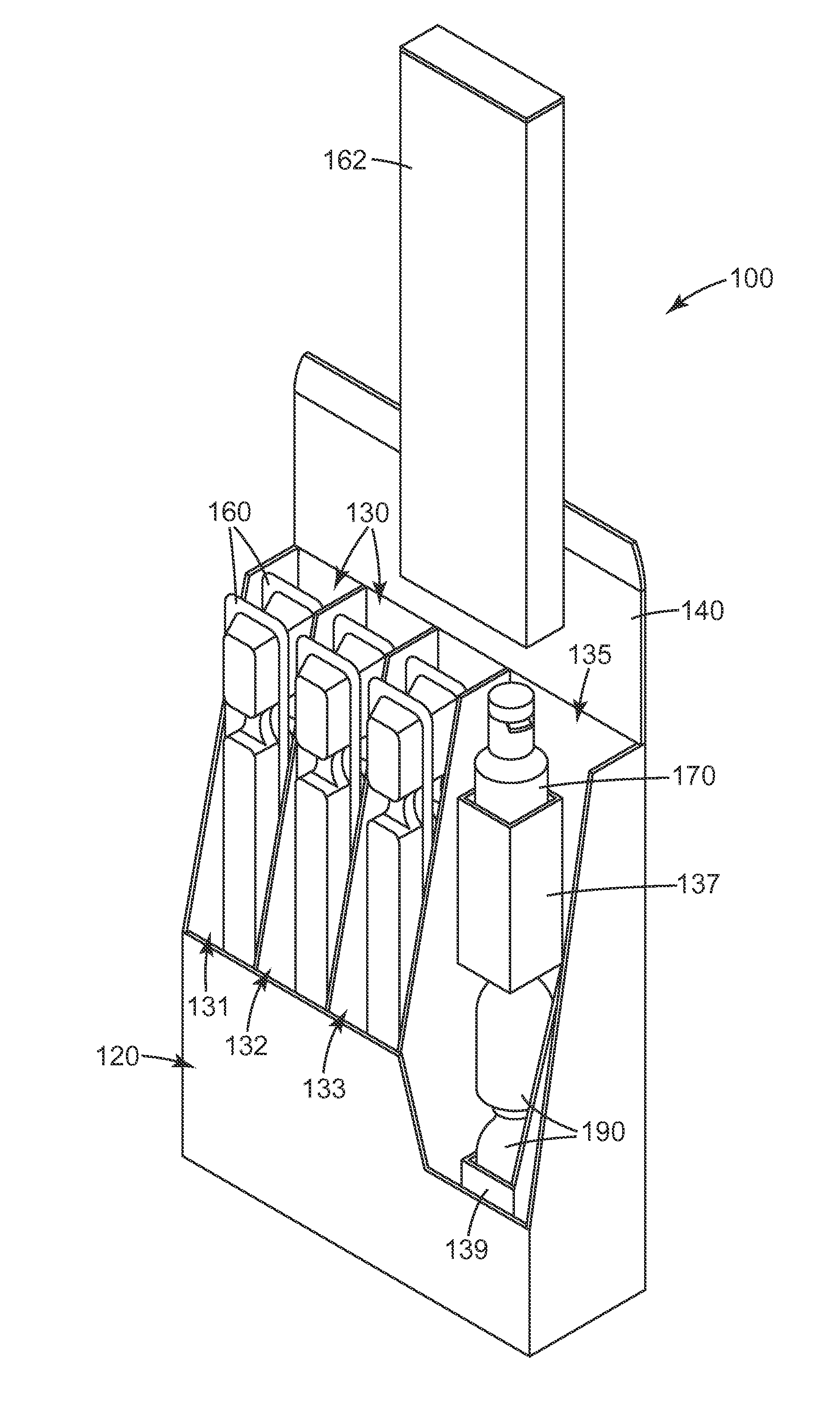
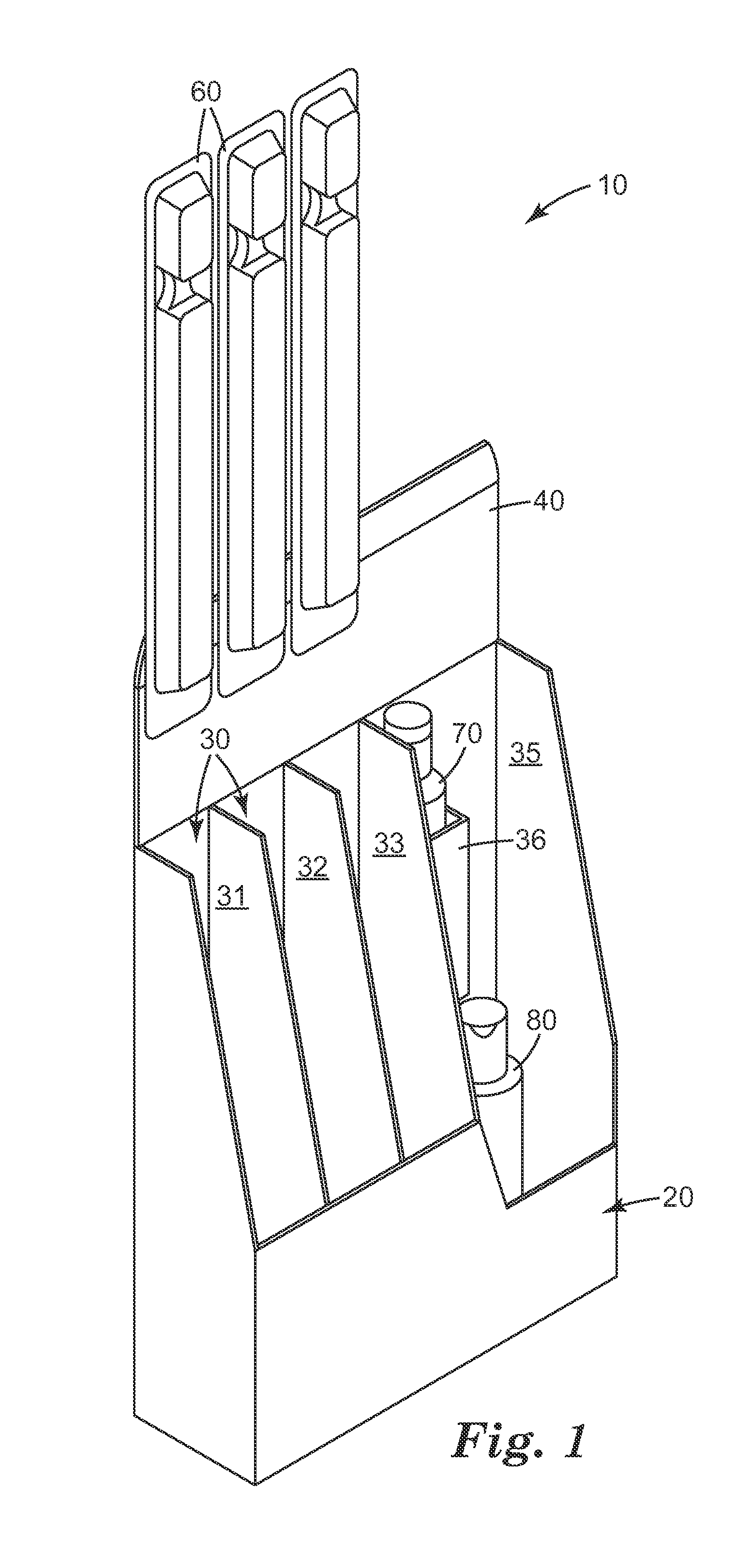
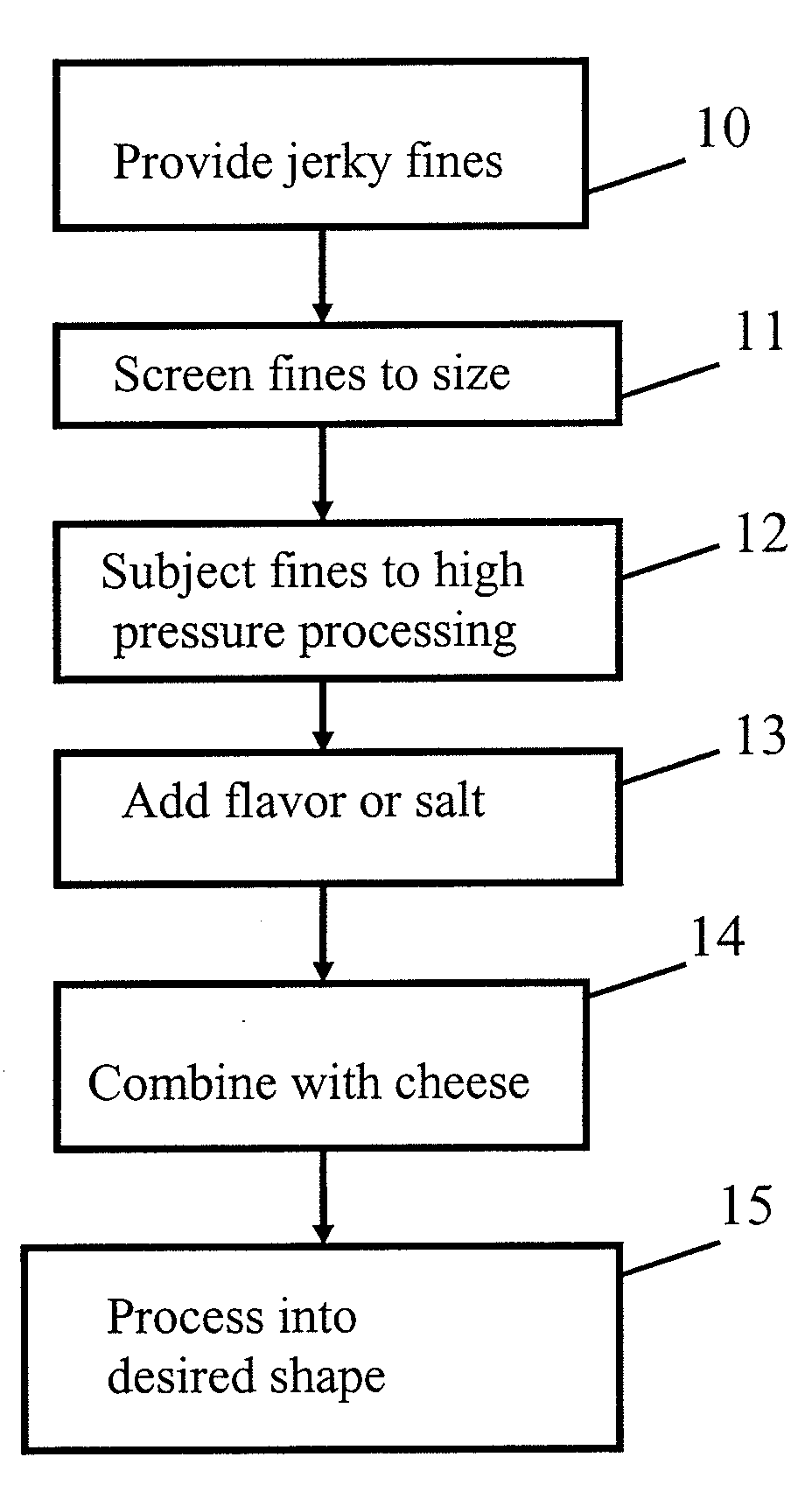
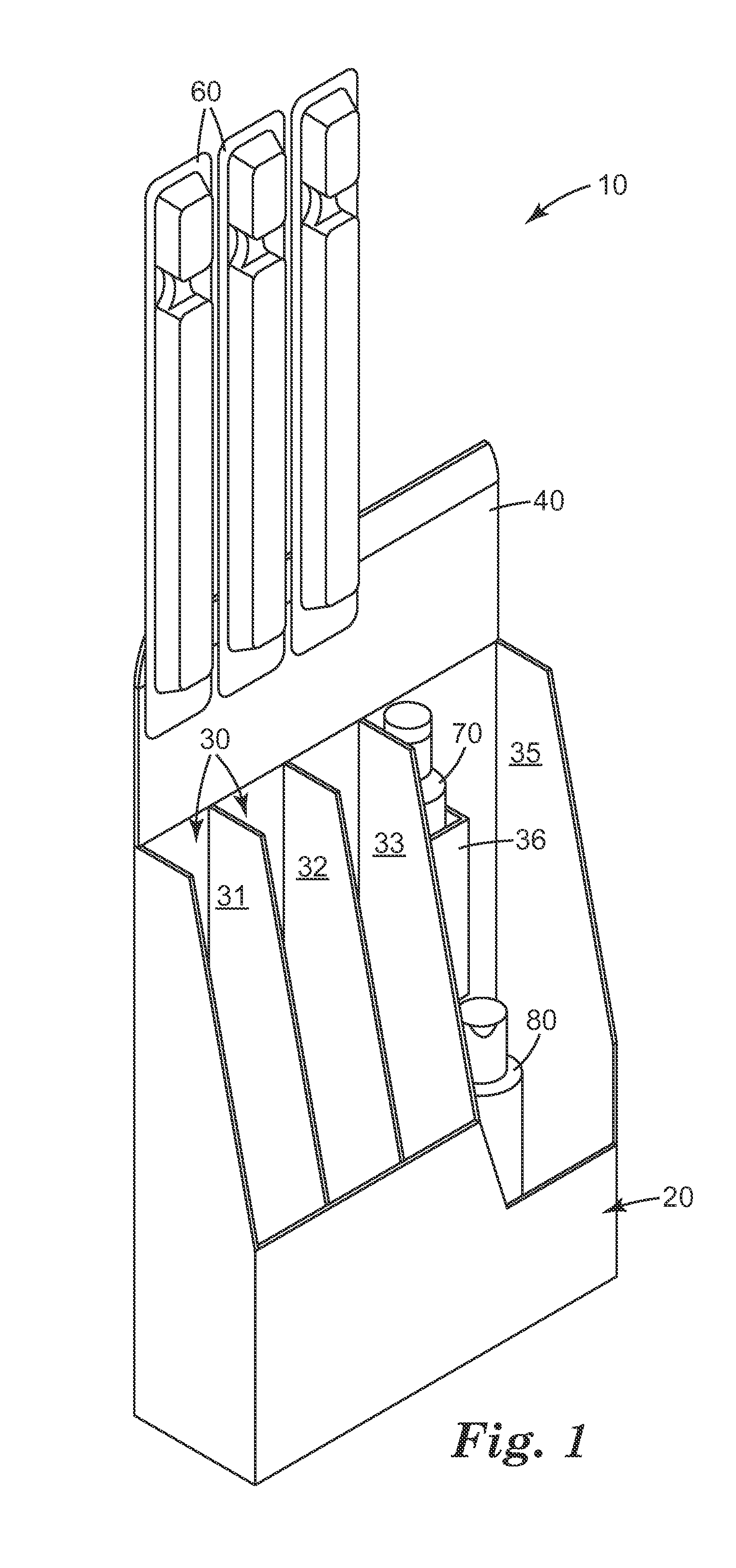
High pressure processing (HPP) uses isostatic pressure to evenly apply great pressures to foods on all sides of the foods. Because the pressure is isostatic, the food is not deformed, so long as there is no internal cavity in the food. The pressures used are preferably from about 100 MPa (about 14.5 ksi) to about 1000 MPa (about 145 ksi), and the temperature rise is preferably limited to about 3° C. (about 5° F.) per 100 MPa (about 14.5 ksi). The high pressure dramatically reduces pathogens in the food so processed, as much as a four or five-log reduction in counts of colony forming units (CFU). The process has been shown to be effective in achieving these reductions in E. Coli, listeria, and salmonella. Pieces or sticks of beef jerky or sausage may be processed via HPP and combined with cheese to form a food product with a long shelf life.
Owner:SNACK PATROL
Oral care method and kit
InactiveUS8460689B2Reduced activityReduced effectivenessAntibacterial agentsBiocideOral tissueMedicine
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
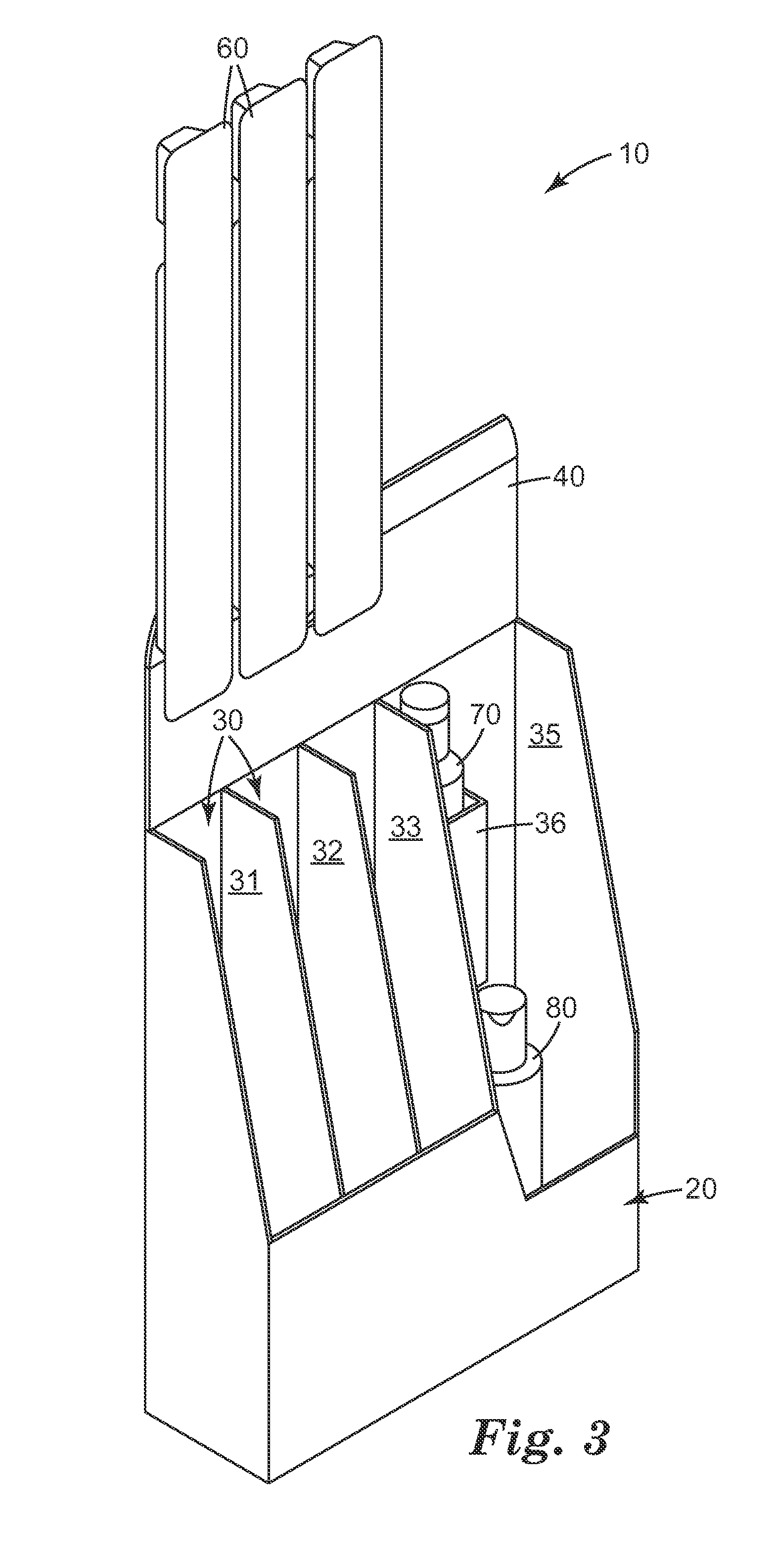
System for automatic/continuous sterilization of packaging machine components
An automatic, continuous sterilization system is for use in a form, fill and seal packaging machine for forming, filling and sealing packages. The machine has a turret carrying a plurality of mandrels on which the packages are carried. A bottom panel heating station has a reciprocating bottom panel heater. The sterilization system includes a sterilant source for supplying a sterilant and a sterilant inlet at the bottom panel heater. Packages are positioned on one of the plurality of mandrels and are indexed to the bottom panel heater. The sterilant is introduced to the mandrel when the carton is positioned thereon. Introduction of the sterilant provides a log reduction of microbial colony forming units of at least about 5.9 after ten minutes of machine operation. A method for continuous mandrel sterilization is also disclosed.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
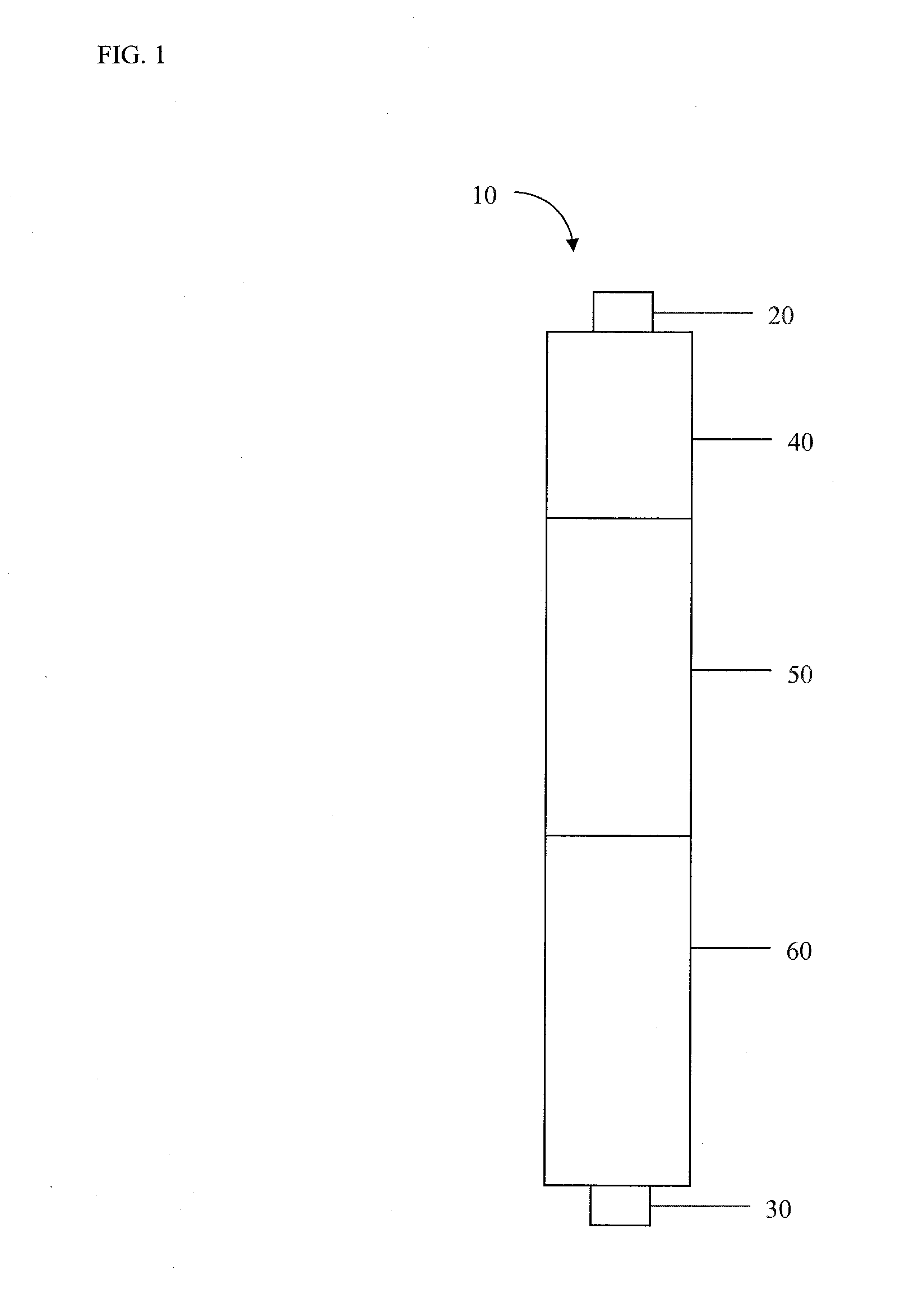
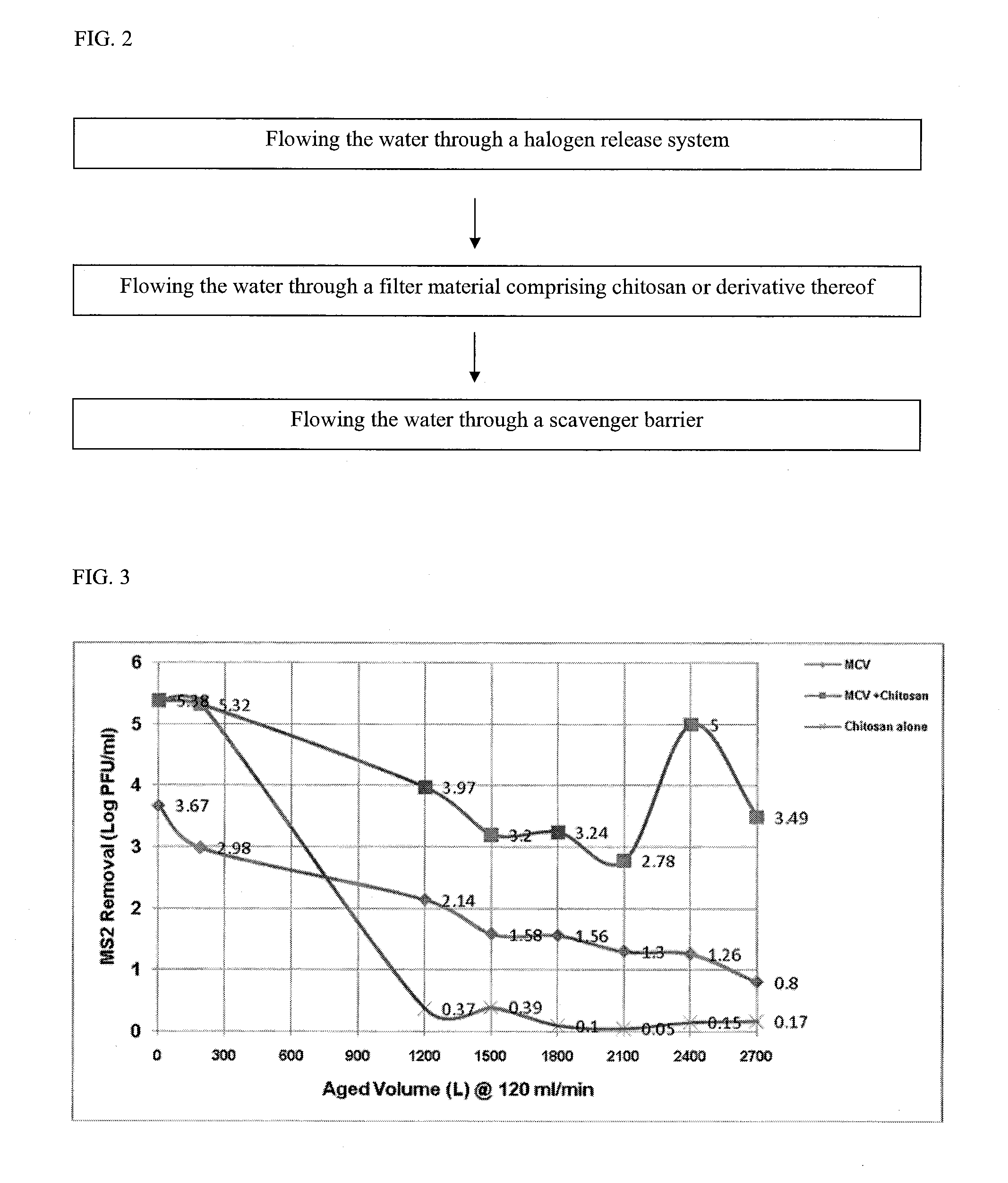
Filter comprising a halogen release system and chitosan
ActiveUS20110226706A1Efficient water treatment systemEfficient processTreatment involving filtrationLoose filtering material filtersScavengerHalogen
A filter to provide potable water may generally comprise an inlet in fluid communication with an outlet, a halogen release system intermediate the inlet and the outlet, a filter material comprising chitosan or a derivative thereof intermediate the halogen release system and the outlet, and a scavenger barrier intermediate the filter material and the outlet. The filter material may comprise a chitosan-halogen complex. The filter material is capable of regeneration during periods of stagnation. The filter may have a Log reduction value for viruses of at least 4 and a Log reduction value for bacteria of at least 6.
Owner:WATER SECURITY CORP
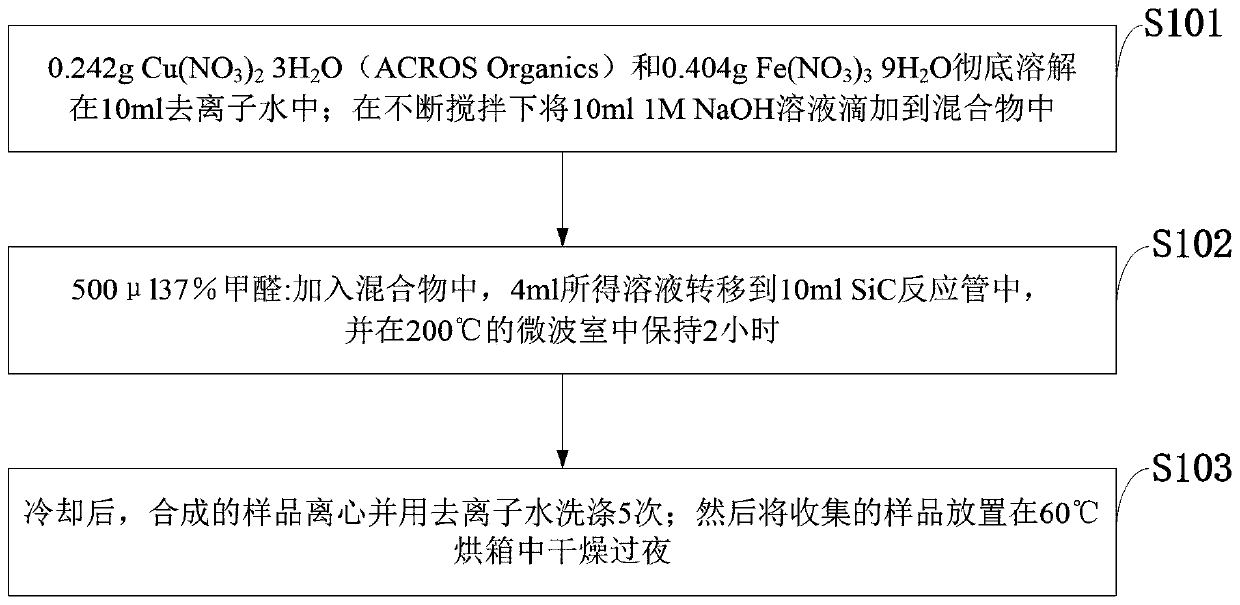
Preparation method of copper-iron oxide and mixed nanoparticles and antibacterial application
ActiveCN110074136AImprove the bactericidal effectEasy to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsBiocideLog reductionKlebsiella pneumoniae
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of nanoparticles, and discloses a preparation method of copper-iron oxide and mixed nanoparticles and an antibacterial application. Cu(NO3)2.3H2O and Fe(NO3)3.9H2O in a certain ratio are dissolved in deionized water; a NaOH solution is dropwise added to the mixture under continuous stirring condition; formaldehyde is added to the mixture,the obtained solution is transferred into a SiC reaction tube and subjected to a reaction in a microwave chamber, and copper-iron oxide and mixed nanoparticles are produced; after cooling, a synthesized sample is centrifuged and washed with deionized water; the collected sample is placed in a drying oven and dried overnight. An experiment indicates that the nanoparticles have efficient antibacterial performance on at least nine important human pathogenic bacteria, for example, the nanoparticles can kill escherichia coli at a 10<9>-log reduction speed within 15 min; after incubation is performed for 4 h, about 10<8>-log reduction of klebsiella pneumoniae strains with multidrug resistance is realized .
Owner:赵奕平 +1
Sterilization of drugs using supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
A sterilization method for drugs to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores is effective by subjecting the drugs to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions and controlling the pressurization and depressurization rates.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
Antimicrobial-antireflective articles and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20180251399A1Improved antimicrobial efficacyImproved antireflective propertyBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsCopper testLog reduction
Described herein are antimicrobial articles having improved antimicrobial efficacy and antireflective properties. Further described are methods of making and using the improved articles. The antimicrobial articles generally include an antimicrobial element and an antireflective element. The antireflective element, in some cases, can be disposed directly on a glass, glass-ceramic or ceramic substrate and the antimicrobial element is disposed on the antireflective element. The article can exhibit a reflectance of about 4% or less (and less than 1% in some cases) in the range of about 425 nm to about 725 nm. Further, the article can be characterized with an antimicrobial efficacy by exhibiting at least a 2 log reduction in a concentration of at least Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria under a Modified EPA Copper Test Protocol.
Owner:CORNING INC
Sterilization methods and apparatus which employ additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
InactiveUS20090110596A1Enhances mass transfer and sterilizationImprove sterilizationBiocideChemosterilantsSporePressure cycling
Sterilization methods and apparatus are effective to achieve a 6-log reduction in CFUs of industry standard bacteria and bacterial spores, i.e., B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis spores, by subjecting sterilizable materials to a chemical additive-containing carbon dioxide sterilant fluid at or near its supercritical pressure and temperature conditions. Most preferably, the chemical additive-containing supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant fluid is agitated during sterilization, e.g., via mechanical agitation or via pressure cycling.
Owner:CHRISTENSEN TIMOTHY WAYNE +4
Anti-microbial foams containing polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles
An absorbent wound dressing comprises a hydrophilic porous substrate and polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles distributed throughout the porous substrate. The silver nanoparticles have a particle size d50 in the range of about 45 nm to about 85 nm and the silver nanoparticles are present in the substrate in an amount of about 0.16% to about 1.5% by weight of the total weight of the substrate. The wound dressing produces a 7-day log reduction of 4 or more for bacteria in accordance with the Modified AATCC Test Method 100. The wound dressing is also non-cytotoxic in accordance with ISO 10993-5 standard procedure for medical device cytotoxicity assessment.
Owner:POREX TECHNOLOGIES CORP
Preservative system and composition based on glycinate and dihydroxypropyl quaternary ammonium salt combination
A preservative system and a personal care composition containing that system is provided which includes the preservative combination of a C10C24 acyl glycinate salt and a dihydroxypropyl quaternary ammonium salt, and wherein the system exhibits a Log Reduction against Pseudomonas aeruginosa of at least 2 within 48 hours of application to an aqueous system. This preservative system is effective against gram negative bacteria, particularly Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Preparation process of low-oxygen copper rods
ActiveCN108950237ALow costIncrease productivityReverberatory furnaceProcess efficiency improvementMetallurgyLog reduction
The invention provides a preparation process of low-oxygen copper rods, and belongs to the technical field of copper rod production. The preparation process of the low-oxygen copper rods comprises thesteps of feeding, melting, oxidation and decontamination, reduction, continuous casting and continuous rolling; in the reduction step, natural gas is used for reduction; the pressure of the natural gas is controlled within 0.35-0.45 MPa, and the flow is controlled within 90-120 m3 / h; the reduction time is 1-2 h; and when the natural gas is introduced, an exhaust fan is used for controlling the air pressure in a furnace within 0.01-0.03 MPa. The preparation process of the low-oxygen copper rods has the following beneficial effects: the method of cooperating the natural gas reduction with the furnace internal air pressure control is adopted to replace the log reduction, so that the production efficiency is greatly improved, the environment is protected, the process is simple and easy to control, meanwhile, the product quality is high, and the large-scale popularization and application are facilitated; and such recovered materials as waste copper are used as raw materials, so that the energy is saved.
Owner:朱军良
Wood pulp paper with high antimicrobial barrier level
Wood pulp papers are provided that are useful in end uses requiring microbial barrier properties such as medical packaging, air filters, liquid filters, and other uses and the papers have significantly improved bacterial barrier properties in contrast to wood pulp papers known in the art as measured by Log Reduction Values determined by ASTM F-1608.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Sliding window scanning method based on margin cutting method
InactiveCN110310278AWill not be damagedGuaranteed no distortionImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsSlide window
The invention provides a sliding window scanning method based on a margin cutting method, and belongs to the technical field of graphic processing. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps that step 1, inputting an original large image; step 2, cutting allowance of the large image; step 3, performing conventional detection on subgraphs; and step 4, performing unified annotation and log reduction; step 5, completing the whole scanning process. The method has the advantages that the large image is divided into the sub-images of the same size to ensure that thesubimages are not damaged, and meanwhile a small target is not distorted. The small target is amplified in a phase-varying manner in the subgraph. The detection precision of the detection difficulty target is greatly reduced. An intermediate result of the subgraph detection is stored. Unified marking according to logs in the statute stage is performed, so that although cutting detection is performed, no extra internal storage is consumed, and the subgraphs are detected according to the sliding sequence of the time window, so that the graph taking mode can ensure that the target detection is not heavy and is not leaked.
Owner:国网山东省电力公司建设公司 +2
Use of centrifugation-aided infection to increase virus titer
InactiveUS10066213B2Easy to detectEasy to calculateGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCentrifugationLog reduction
The invention relates to a process for increasing the observed titer of a virus stock for the purpose of increasing the calculated log reduction (LRV) in virus clearance studies. A tissue culture or assay plate is seeded with an indicator cell line and titrated with a virus stock followed, by a centrifugation step for about 5 minutes to about 24 hours at a g-force ranging from about 50×g to about 2400×g, and at a temperature from about 4° C. to about 39° C. The resulting calculated virus titer after undergoing the centrifugation step is 10-fold higher than the virus titer would be if determined in the absence of the centrifuging step.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Anti-microbial foams containing polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles
An absorbent wound dressing comprises a hydrophilic porous substrate and polymer-stabilized silver nanoparticles distributed throughout the porous substrate. The silver nanoparticles have a particle size d50 in the range of about 45 nm to about 85 nm and the silver nanoparticles are present in the substrate in an amount of about 0.16% to about 1.5% by weight of the total weight of the substrate. The wound dressing produces a 7-day log reduction of 4 or more for bacteria in accordance with the Modified AATCC Test Method 100. The wound dressing is also non-cytotoxic in accordance with ISO 10993-5 standard procedure for medical device cytotoxicity assessment.
Owner:POREX TECHNOLOGIES CORP
Laser-based treatment for malaria
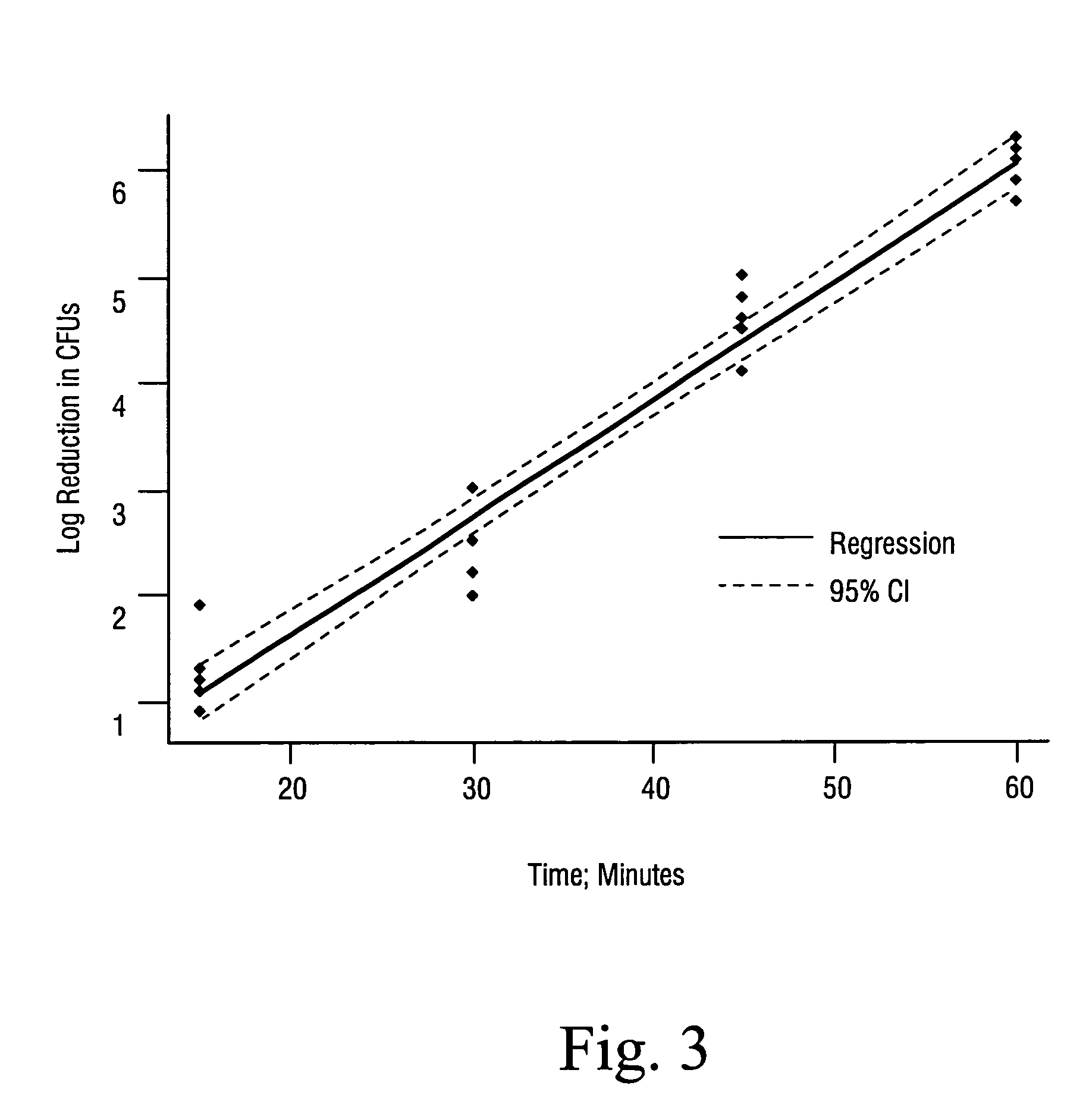
InactiveUS20150025600A1Effective germicidal treatmentSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesNon pharmacologicalUltraviolet
Malaria, caused by the parasite Plasmodium, is a devastating disease killing more than 800,000 people a year worldwide. Plasmodium replicates within erythrocytes by digesting hemoglobin, producing haemozoin as a byproduct which accumulates within the parasite. The development of vaccines is hampered by lack of memory immune response, while the long-term effectiveness of current anti-malaria drugs is limited due to the emergence of drug-resistant strains. Furthermore, people who are deficient of the enzyme glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase exhibit fatally-adverse drug effects. To overcome these hurdles, I propose a novel laserbased, non-pharmacological treatment for malaria. The treatment is based on the ability of haemozoin to convert light in the near infra-red into ultra-violet (UV) radiation via Third Harmonic Generation. The UV light produced by haemozoin can in turn kill the parasite. In experiments with infected erythrocytes we obtained a 4-log reduction in parasetemia following six passes of the blood through the laser beam.
Owner:GROSS EITAN ZVI
Sterilization of drugs using supercritical carbon dioxide sterilant
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
Computer quick recovery system
InactiveCN107678881ARun fastShorten the timeRedundant operation error correctionOperational systemRecovery period
The invention discloses a computer fast restoration system, which includes a main control module, a backup module, a main program storage module and a restoration module, the main control module includes a control panel, a manual input, a power supply circuit and a cache module, a control panel, a manual input, The backup module includes data backup and running log backup, the main program storage module includes data management and control, running memory, database and cascade control, and the restoration module includes log reading, system restoration, automatic startup and periodic restoration. The computer rapid restoration system of the present invention can The operating system of the computer system is restored within a cycle, which is equivalent to a self-starting backup system, and the computer is restored periodically, which greatly shortens the restoration time, simplifies the system structure of the restoration system, and reduces the system load. Speed up your computer.
Owner:苏州千阙传媒有限公司
Wood Pulp Paper with High Antimicrobial Barrier Level
Wood pulp papers are provided that are useful in end uses requiring microbial barrier properties such as medical packaging, air filters, liquid filters, and other uses and the papers have significantly improved bacterial barrier properties in contrast to wood pulp papers known in the art as measured by Log Reduction Values determined by ASTM F-1608.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method and apparatus for the sterilization of ground meat using supercritical co2
A method for sterilizing a ground meat product through the application supercritical CO2 during the processing of the meat by introducing supercritical CO2 into an extruder as the meat passes through the extruder while controlling the pressure and speed at which the meat passes through the extruder to maintain the meat in contact with the supercritical CO2 for a time sufficient achieve a log reduction in colony forming units of microbial contaminants.
Owner:NOVASTERILIS
Method for removing viruses from high concentration monoclonal antibody solution
ActiveUS9056896B2High yieldHigh removal rateSerum immunoglobulinsPeptide preparation methodsHigh concentrationMonoclonal antibody
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for removing even small viruses from a high concentration monoclonal antibody solution using a membrane, and thus for recovering the antibody within a short time at high yield in the form of a filtrate. The present invention provides a method for producing a preparation containing a monoclonal antibody, which comprises a step of removing viruses by filtering viruses in a monoclonal antibody solution using a virus-removing membrane, wherein(1) the monomer content of the monoclonal antibody accounts for 90% or more;(2) the monoclonal antibody concentration in the monoclonal antibody solution ranges from 20 mg / ml to 100 mg / ml;(3) the monoclonal antibody solution contains at least a basic amino acid; and(4) the parvovirus removal rate of the virus-removing membrane satisfies the following conditions:LRV (Log Reduction Value: logarithmic reduction value)≧4.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
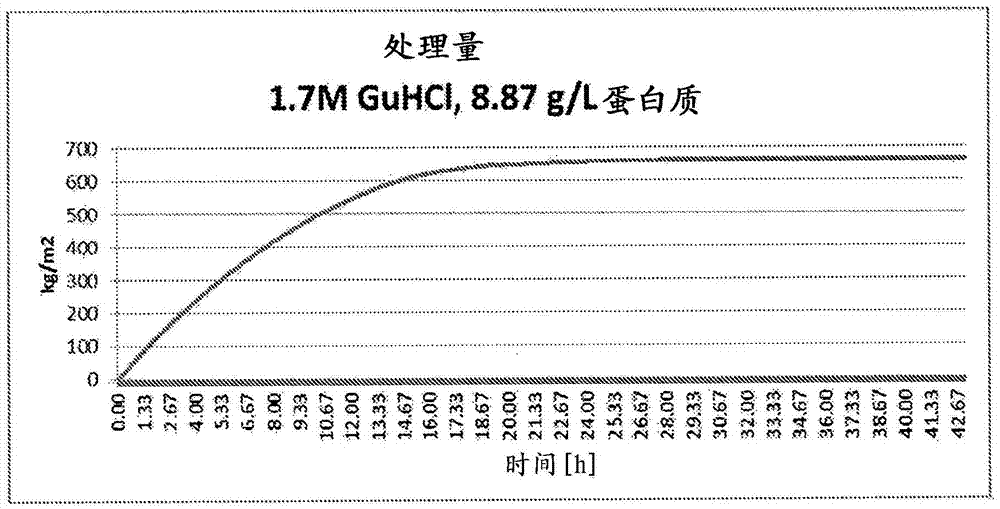
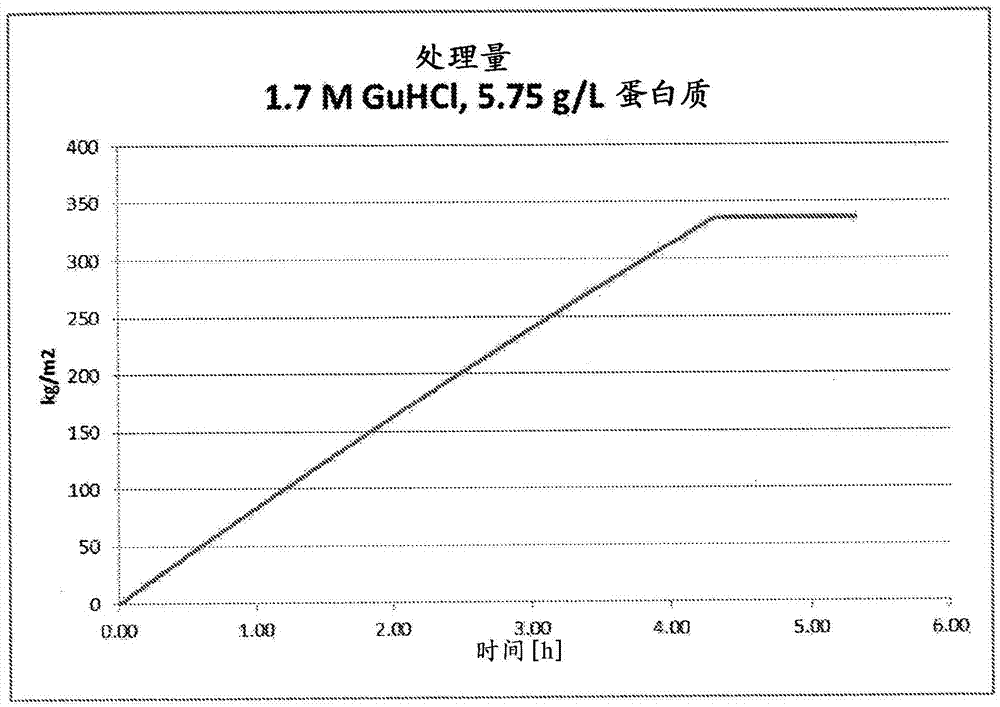
Contaminant removal method
ActiveCN105452291AReduce volumeReduce filter areaApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsLog reductionDrug
A method for purifying Apo A-l is provided including the steps of providing a solution comprising Apo A-l and guanidine hydrochloride and filtering the solution through a filter having a pore size in a range from 15 nrn to 35 nm to thereby reduce viral contamination of the Apo A-l. An Apo A-f preparation is provided having at least a 12 log LRV (log reduction value) for a parvovirus; and / or at least 9 log LRV for a non-enveloped virus; and / or at least 8.5 log LRV for a lipid enveloped virus. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and reconstituted high density lipoprotein formulation comprising Apo A-l and methods of treating diseases disorders or conditions.
Owner:JET
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com