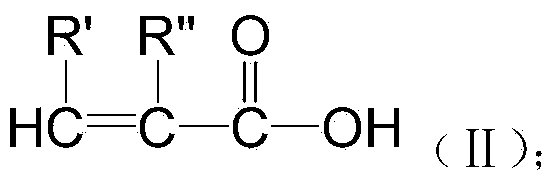
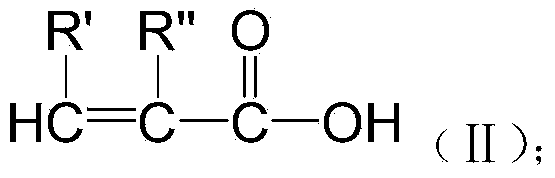
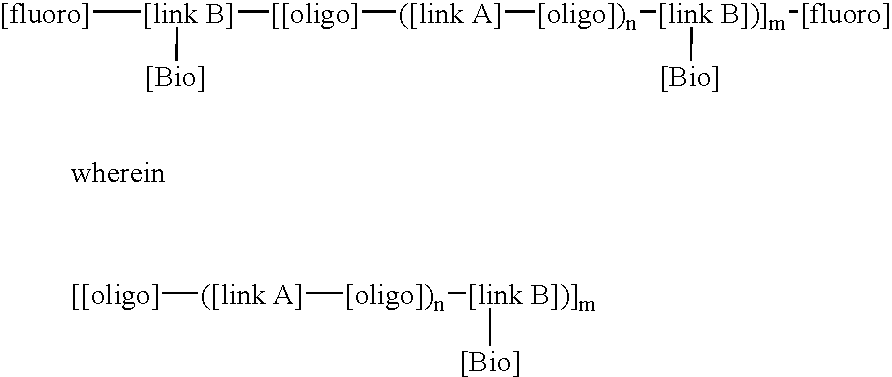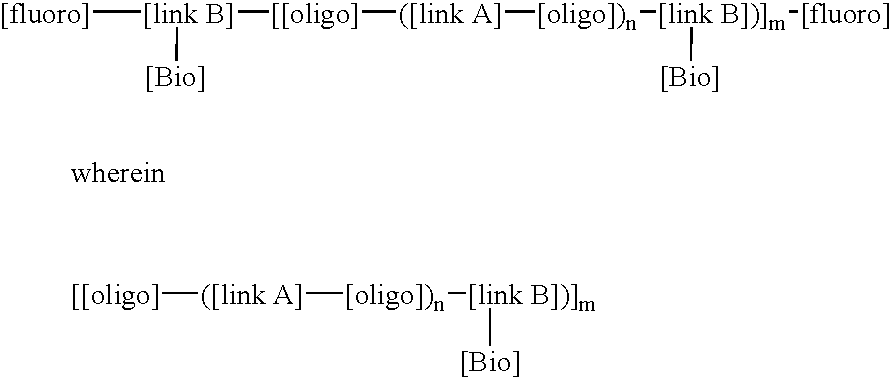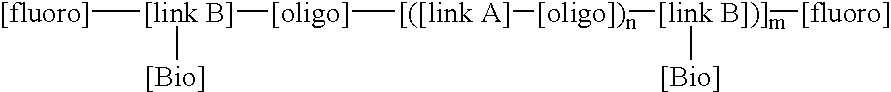Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170 results about "Biomedical polymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymer composites for biomedical applications and methods of making
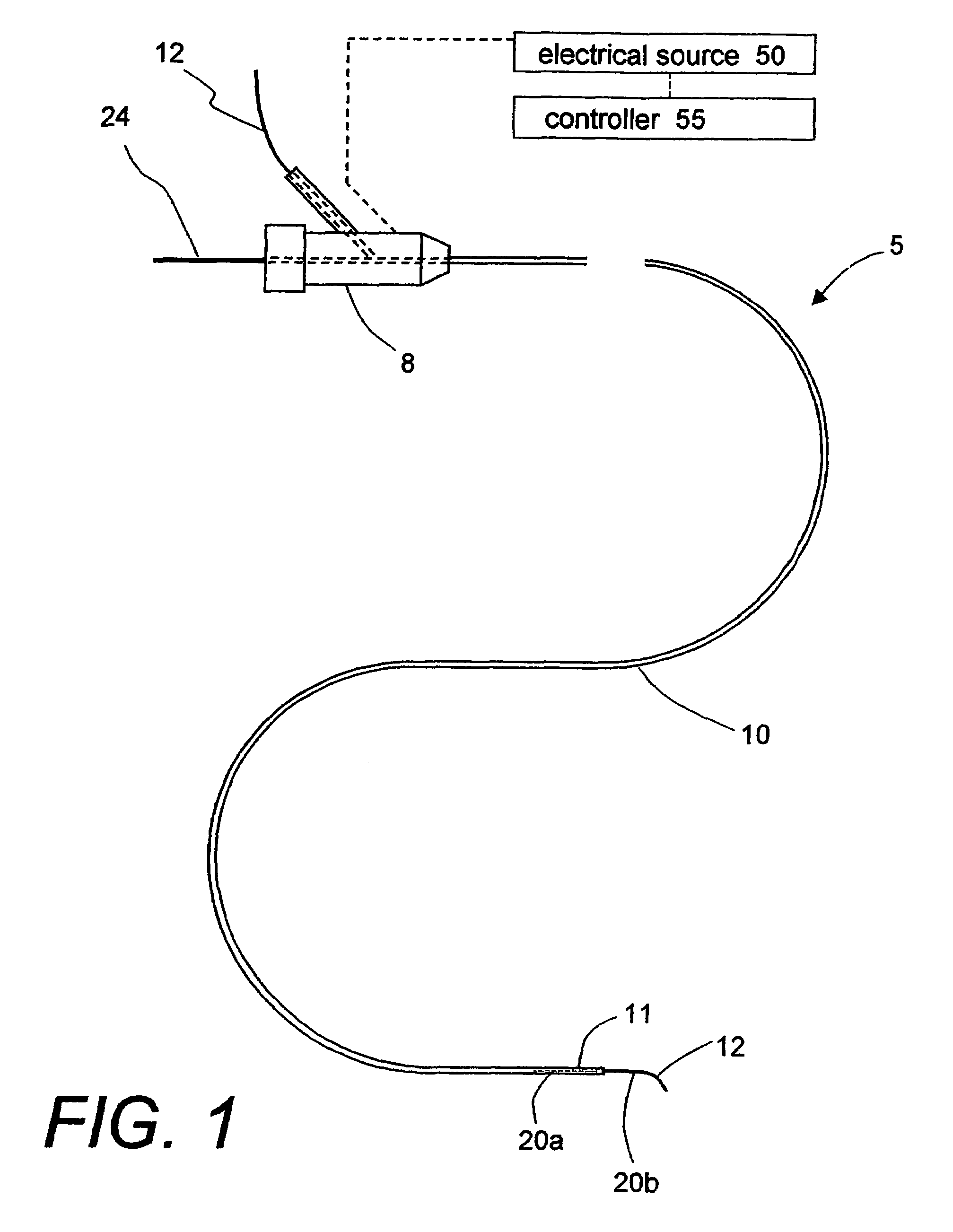
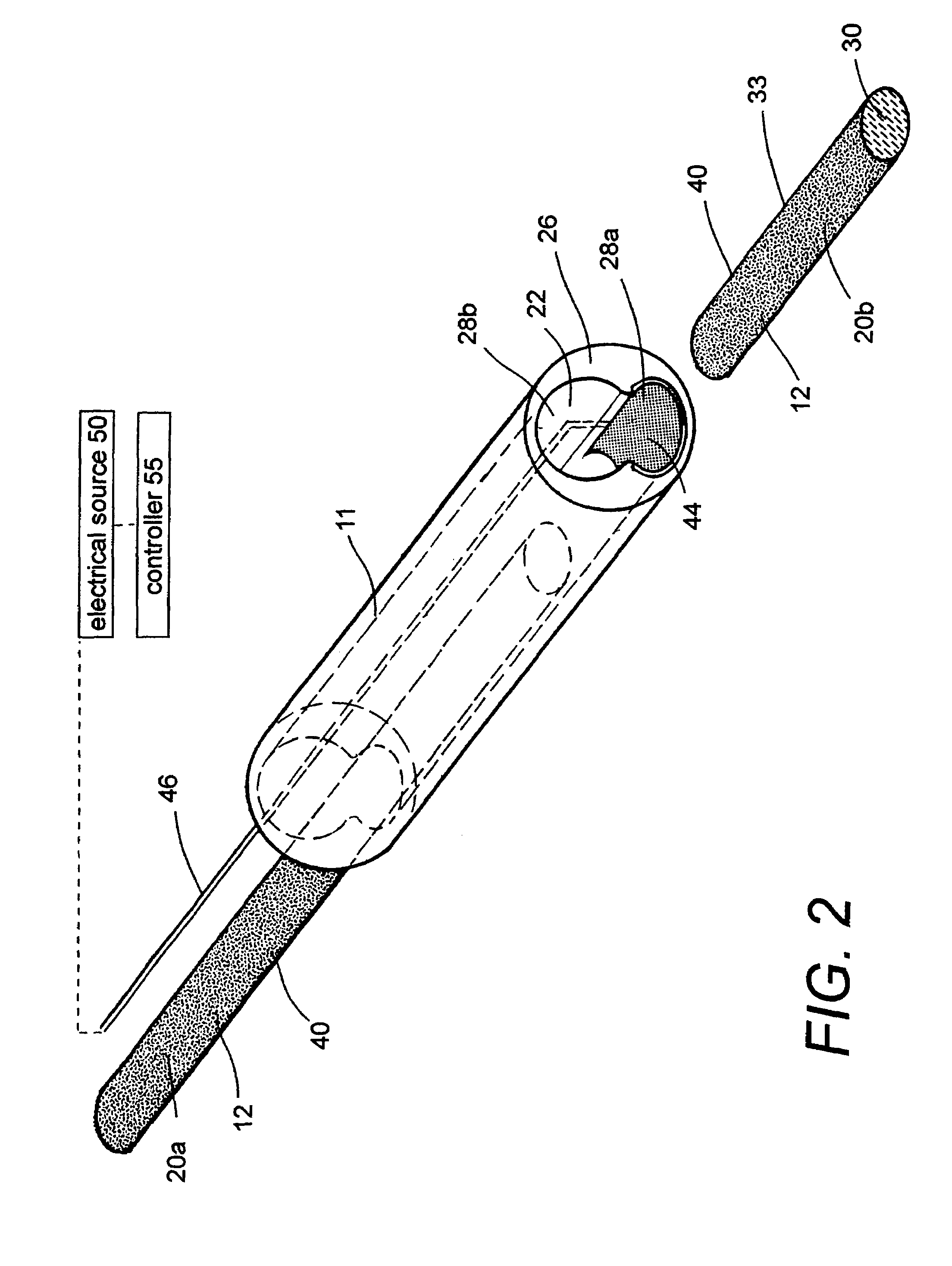
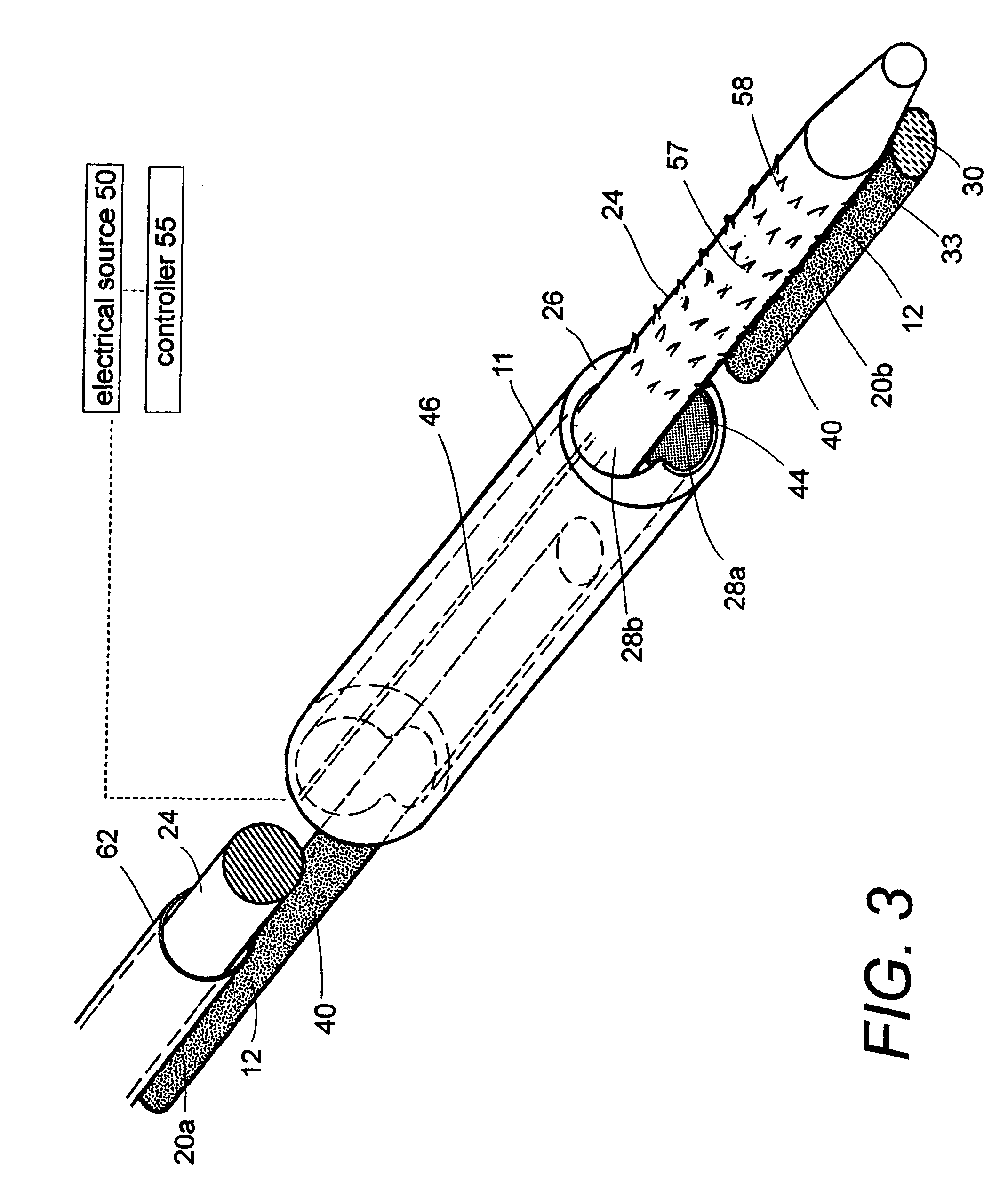
ActiveUS7569626B2Desired lengthInhibit transferSurgical instruments for heatingOcculdersMicrosphereEnergy coupling
A biomedical polymer composite that exhibits ultra-low thermal conductivity properties. In a preferred embodiment, the biomedical polymer composite comprises a base polymer component with a dispersed thermally non-conductive filler component consisting of glass or ceramic nanospheres or microspheres that have a thermal conductivity of less than 5 W / m-K, and preferably less than 2 W / m-K. In one embodiment, the polymer composite is has an electrically conductive filler and can be used in a filament for treating arteriovascular malformations. In another embodiment, the polymeric composite can be used as an energy-coupling means to apply energy to tissue.
Owner:DFINE INC
Modular Bioresorbable or Biomedical, Biologically Active Supramolecular Materials
The present invention relates to a modular supramolecular bioresorbable or biomedical material comprising (i) a polymer comprising at least two 4H-units and (ii) a biologically active compound. Optionally, the supramolecular bioresorbable or bio medical material comprises a bioresorbable or biomedical polymer as third component to tune its properties (mechanical and bioresorption properties). The supramolecular bioresorbable or biomedical material is especially suitable for biomedical applications such as controlled release of drugs, materials for tissue-engineering, materials for the manufacture of a prosthesis or an implant, medical imaging technologies.
Owner:SUPRAPOLIX
Bioactive surface modifiers for polymers and articles made therefrom
InactiveUS6770725B2Improve surface propertiesGood biocompatibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesCouplingBiomedical polymers
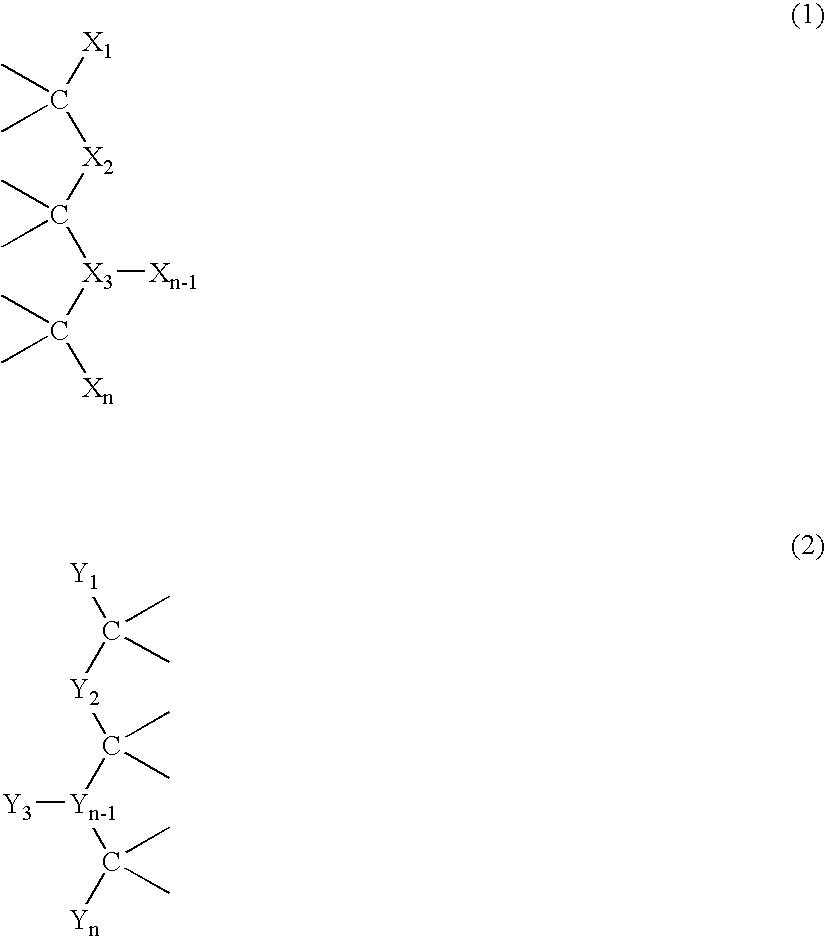
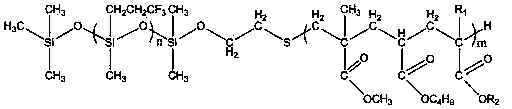
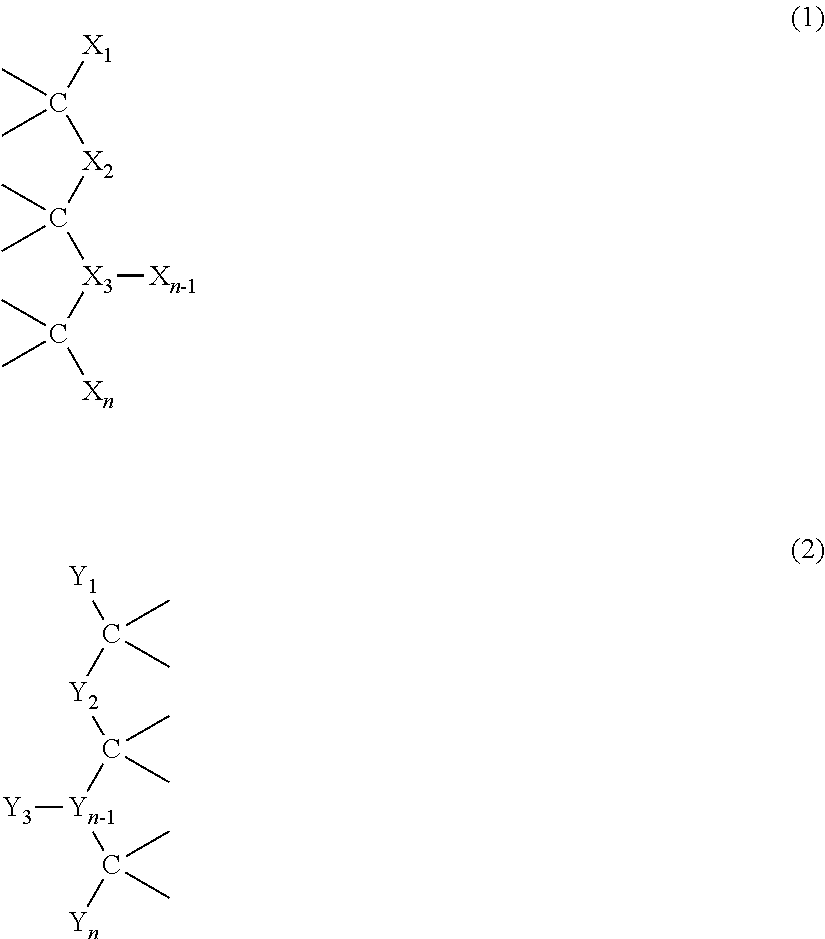
This invention relates to macromolecule modifiers containing biologically active drugs / biomolecules, or precursors thereof, and fluoroligomers; compositions comprising the macromolecules containing the drugs and fluoroligomers in admixture with polymers, particularly biomedical polymers; articles made from the admixtures, particularly medical devices. Specifically, the modifier has the general formulais a central portion comprising an oligomeric polymeric segment having a theoretical molecular weight of less than 15,000, and being compatible with said base polymer; wherein[oligo] is a first oligomeric segment;[link A] is a second coupling segment linking one [oligo] to another [oligo] within said central portion;n is 0 to 20;[fluoro] is a polyfluoro oligomeric group; and[link B] is a first coupling segment linking said central portion to said [fluoro] through said first coupling segment; and coupled to a bioactive moiety [Bio] or precursor thereof; andm is 1 to 20.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOLOGICS INC
Beta-cyclodextrin based pH responsive star polymer, micelle and composite material
ActiveCN105017445ARealize the combinationImprove treatment efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsX-ray constrast preparationsWater insolubleTumor chemotherapy
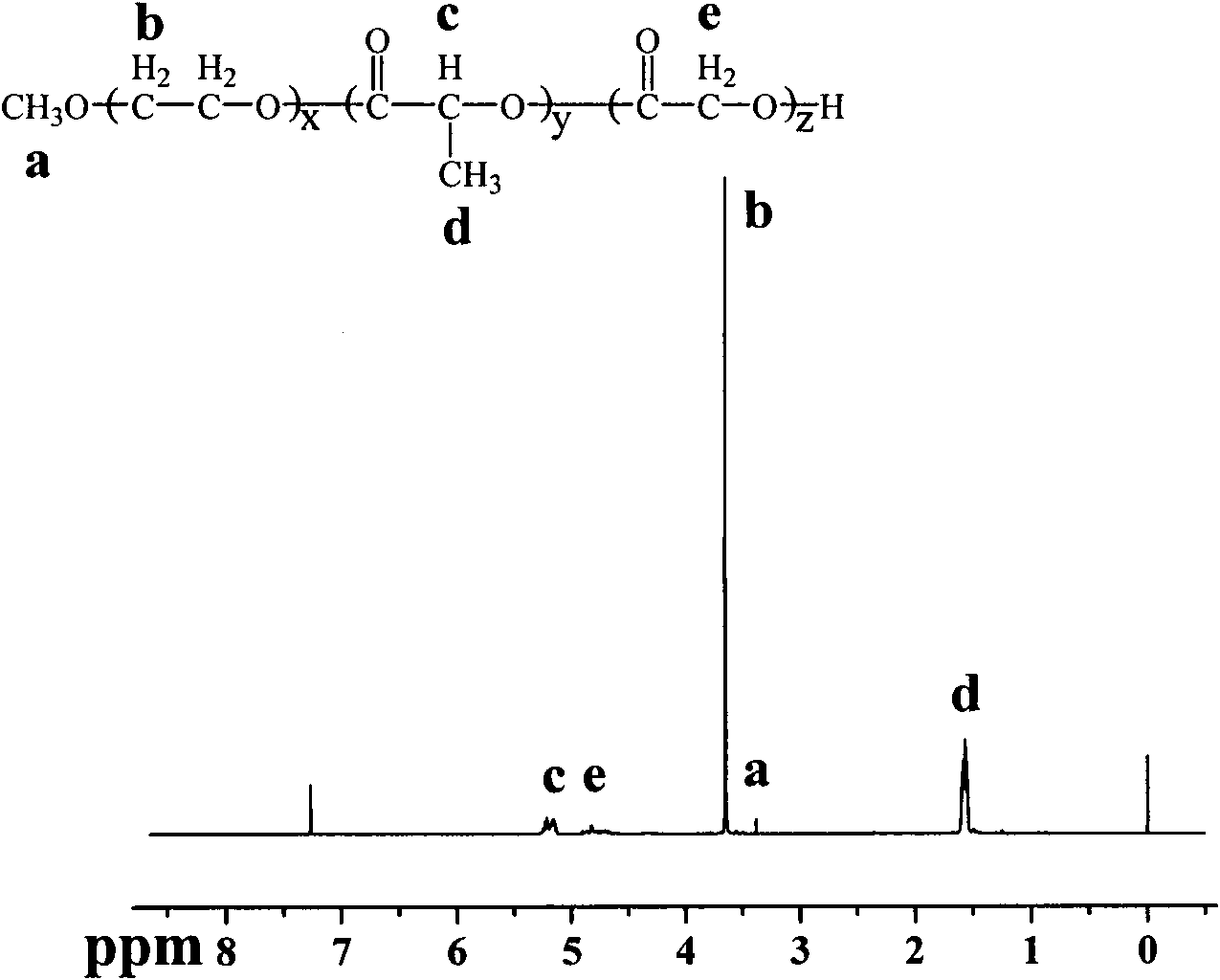
Belonging to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials, the invention discloses a beta-cyclodextrin based amphiphilic pH responsive star polymer and a preparation method thereof, a micelle system based thereon, a composite material and application thereof. The polymer has a structure shown as the formula (1) in the specification, wherein x=3-20, y=2-30, z=5-35, and n=2-10. The polymer can be reduced in situ to obtain nanogold with small particle size and good stability. The invention also provides a micelle system based on the polymer, the micelle system has strengthened entrapment ability to water-insoluble drugs, can efficiently load hydrophobic drugs, gold nanoparticles and other substances, realizes the combination of tumor imaging diagnosis and tumor chemotherapy, and improves the therapeutic efficiency of cancer. And the polymer is easy to control the proportion of each block, and can be applied to preparation of the water-insoluble drug loaded micelle system to satisfy the release requirements of different drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Hydrophobically modified succinylated chitosan derivative and its prepn process
Hydrophobically modified succinylated chitosan derivative and its preparation process belongs to the field of biomedical polymer material. The hydrophobically modified succinylated chitosan derivative is prepared through reaction between chitosan and succinic anhydride in acid condition to obtain water soluble succinylated chitosan, and the subsequent reaction of the succinylated chitosan with alkyl glycidol ether or alkyl halide as long chain alkane derivative to obtain the hydrophobically modified succinylated chitosan derivative. The present invention is amphipatic chitosan derivative with excellent surface activity and emulsifying property, and provides cosmetics, medicine, food, etc. with multifunctional, high quality and cheap material.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Hydrogel microspheres based on glucan and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105348548AHigh biosecurityImprove stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFreeze-dryingBiomedical polymers
The invention relates to hydrogel microspheres based on glucan and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving glucan in water at room temperature, adding sodium periodate to obtain a mixed liquor, stirring and dialyzing the mixed liquor, performing freeze drying on the mixed liquor to obtain a partial aldehyde glucan solid; dissolving the partial aldehyde glucan solid in deionized water, adding a cyclohexane solution with a dissolved emulsifier, adding an amine crosslinker and stirring the solution, finally collecting precipitate through centrifugation, cleaning the precipitate to obtain the chemical cross-linking type glucan hydrogel microspheres; adding sodium borohydride in the chemical cross-linking type glucan hydrogel microspheres dispersed in deionized water, stirring the material for 24 hours under room temperature, finally collecting the precipitate through centrifugation, and cleaning the precipitate by the deionized water to obtain the reduced glucan hydrogel microspheres. According to the invention, a water-in-oil anti-phase microemulsion system is taken as a reaction medium, and the glucan hydrogel microspheres with a controllable particle size and good stability can be prepared.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Beta-cyclodextrin based 21-arm star-shaped polymers as well as preparation method thereof and prepared monomolecular micelle/gold nanoparticle hybrid material
InactiveCN107652410AEasy to control the degree of polymerizationMild reaction conditionsX-ray constrast preparationsNanoparticleHybrid material
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials, and discloses beta-cyclodextrin based 21-arm star-shaped polymers as well as a preparation method thereof and a monomolecular micelle / gold nanoparticle hybrid material system based on the beta-cyclodextrin based 21-arm star-shaped polymers and an imaging application. The polymers have a structure represented by a following formula (1) in the description, wherein x is one selected from 4 to 20, y is one selected from 4 to 15, and z is one selected from 5 to 25. According to the invention, the ratio of each block of the polymers is easily regulated and controlled, so that monomolecular micelles with stable structures and small particle sizes can be prepared. The invention also provides gold nanoparticles with the small particle sizes and good stability prepared by an in-situ method based on the above polymer monomolecular micelle system, and the in-vitro CT imaging is realized, and the valuable preparation technology is provided for the future integrated treatment system.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of ivermectin sustained-release microspheres
ActiveCN102302457AMicrosphere surface roundingImprove uniformityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMass ratioMicrosphere
The invention relates to ivermectin sustained-release microspheres used as an animal medicine for animal injection, and a preparation method thereof. The invention belongs to an interdisciplinary field of biomedical polymer materials and controlled release preparations. The invention discloses ivermectin sustained-release microspheres, which are characterized in that: the ivermectin sustained-release microspheres have particle sizes of 0.1 to 10mum, a medicine loading capacity of 20% to 35%, and an entrapment rate of above 80%. The preparation method of the ivermectin sustained-release microspheres comprises steps that: a carrier material and the medicine ivermectin with a mass ratio of 1:1-10 are dissolved in an organic solvent; the solution is processed through supersonic wave or mechanical stirring, such that the solution is emulsified into an oil phase, wherein a volume ratio of oil phase to water phase is 1:5-10; under a temperature of -10 DEG C to 30 DEG C, the oil phase is injected into a water phase disperse medium solution step-by-step; constant-temperature magnetic stirring is carried out with a rotation speed of 400 to 10000rpm, the mixture is sufficiently emulsified, such that an S / O / W type emulsion is obtained; the emulsion is stirred under room temperature for 3 to 4 hours, such that the organic solvent is sufficiently volatilized; the obtained product is centrifuged, washed, collected, and is vacuum-dried with a pressure of 0.01 to 0.04MPa under room temperature for 10 to 12 hours or is lyophilized under a temperature of -0 DEG C to -20 DEG C. With the processes, ivermectin sustained-release microspheres with particle sizes of 0.1 to 10mum are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
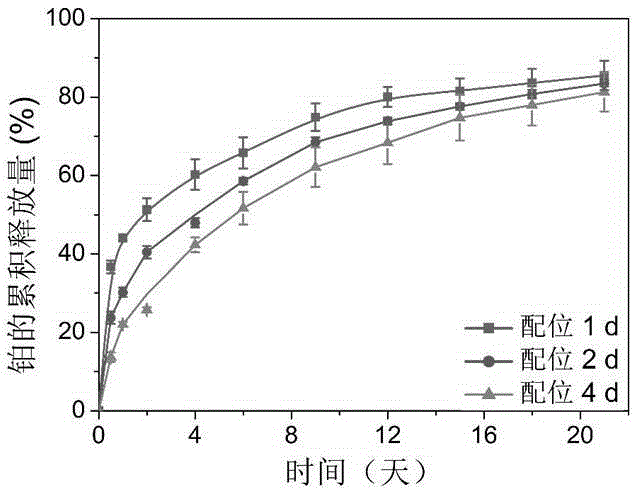
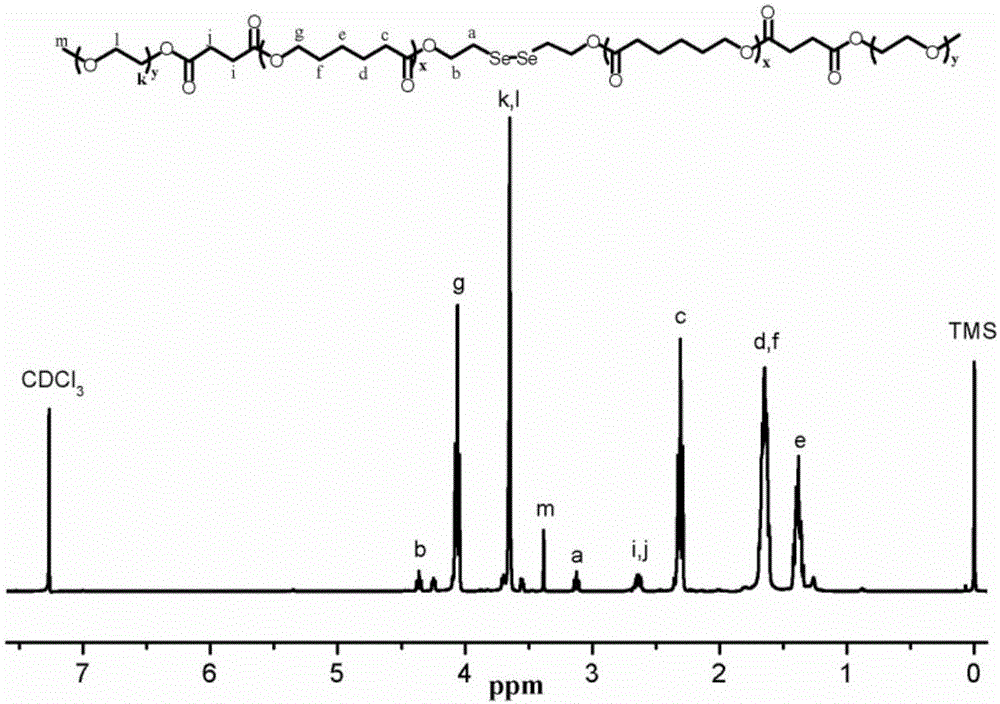
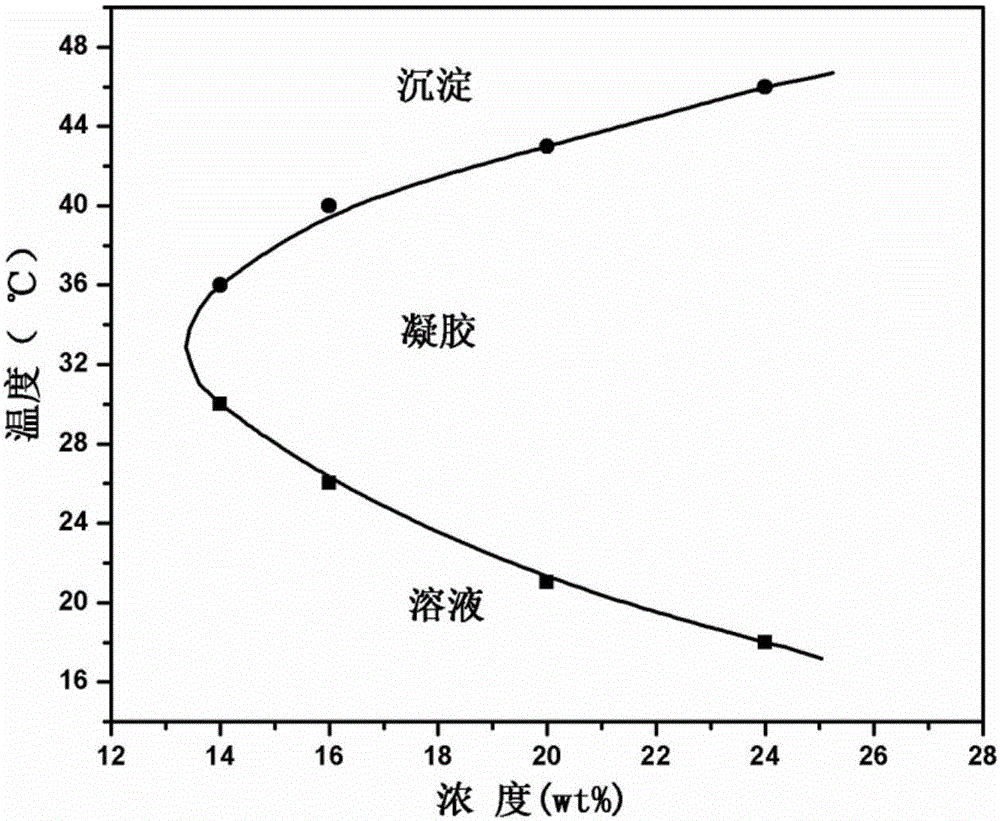
Thermally induced hydrogel containing selenium or tellurium, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN105287362APossesses thermally induced gelation propertiesGood injectabilityHeavy metal active ingredientsAerosol deliveryWhole bodyTe element
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical polymer materials, and specifically relates to a thermally induced hydrogel containing selenium or tellurium, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The thermally induced hydrogel is composed of an amphiphilic block copolymer containing selenium or tellurium and a solvent; thermally induced gelatinization phase transformation of a water system of the amphiphilic block copolymer and the solvent can be realized with temperature increasing so as to realize spontaneous formation of a physical hydrogel, wherein the amphiphilic block copolymer containing selenium or tellurium is obtained via covalent bonding of small molecules containing selenium or tellurium with an amphiphilic block copolymer. Long-acting platinum drug gel sustained-release preparations can be obtained via coordination of the thermally induced hydrogel with platinum drugs. The long-acting platinum drug gel sustained-release preparations are capable of prolonging and adjusting release behavior of the loaded platinum antitumor drugs. Drug administration of the long-acting platinum drug gel sustained-release preparations in tumor, around tumor, or in tumor cavity can be realized via injection; in situ formation of gel is realized at body temperature, and the platinum drugs loaded via coordination bonds can be released from the gel slowly, so that administration frequency is reduced, and drug whole body toxicity is reduced. The long-acting platinum drug gel sustained-release preparations can be applied to tumor treatment at different periods.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Degradable conductive biological medical polymer material
The invention discloses a degradable electricity-conducting biomedical polymer material, which has a molecular constitution as shown in formula I: the polymer material takes the polymer in the formula, which comprises polyphosphazene, chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol, poly-beta-malic acid or modified polyester, as the main chain, a conductive group and a degradable group are grafted, and the modified polyester is lactic acid, polyglycolide, polycarbonate, polyanhydride, polycaprolactone or copolymers between each two thereof; the conductive group comprises oligo-pyrrole, oligo-thiophene, oligo-aniline or copolymers between each two thereof; the degradable group mainly comprises: (1) amino: glycine ethyl ester, phenylalanine ethyl ester, imidazole and the like; and (2) alkoxy: glycerol, glucose, lactic acid, p-methyl phenol, glycolic acid and polyester. The polymer material has degradability and conductivity and can be prepared into guide pipes, suture threads, membranes, sheet bodies, block bodies and materials for frames of tissue engineering.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic nano-carrier with targeted hydrophobic drug delivery to tumor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101632834ASolve solubilityReduce usageInorganic non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsNanocarriersSide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical polymer material and nanobiomaterial, particularly relates to a magnetic nano-carrier with targeted hydrophobic drug delivery to tumor and a preparation method thereof. The magnetic nano-carrier is formed by encapsulating superparamagnetic nano-particles with amphiphilic segmented copolymer methoxy polye thylene glycol-poly(lactide- glycolide) (MePEG-PLGA) micelles. First, a large amount of MePEG-PLGA with good dispersion is synthesized by the improved solution polymerization process, and then the MePEG-PLGA is used as raw materials to encapsulate Fe3O4 nano-particles by the solvent evaporation process to obtain a magnetic nano drug carrier. The carrier is expected to solve the solubility problem of insoluble drugs, achieves slow release of drugs, and achieves the passive-targeting of the drugs by the EPR effect of tumor; Fe3O4 nano-particles are used in the active-targeting of the drugs to reduce the dosage and the side effect and improve the treatment efficiency; besides, the carrier can be used in the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of tumor.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
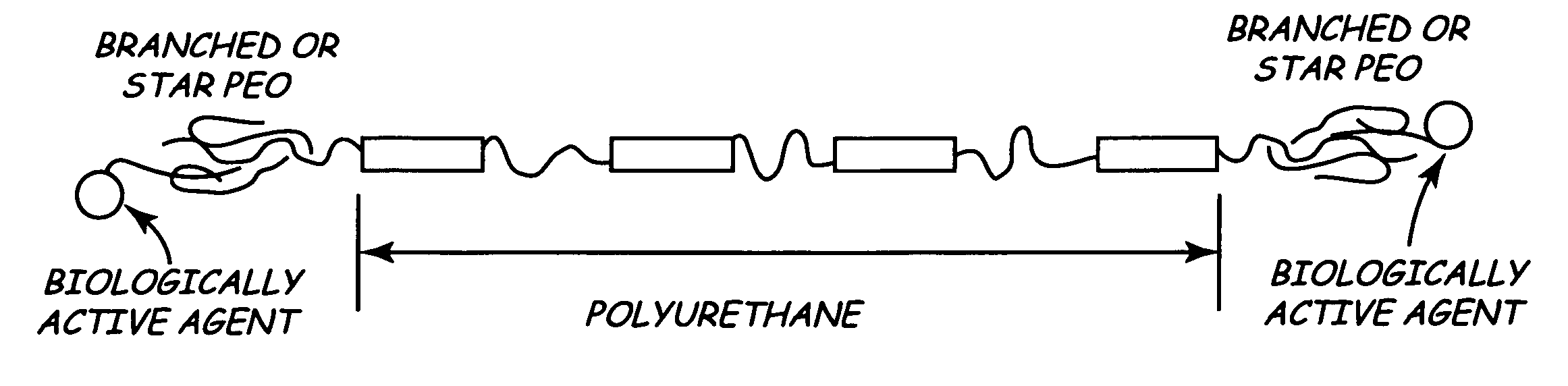
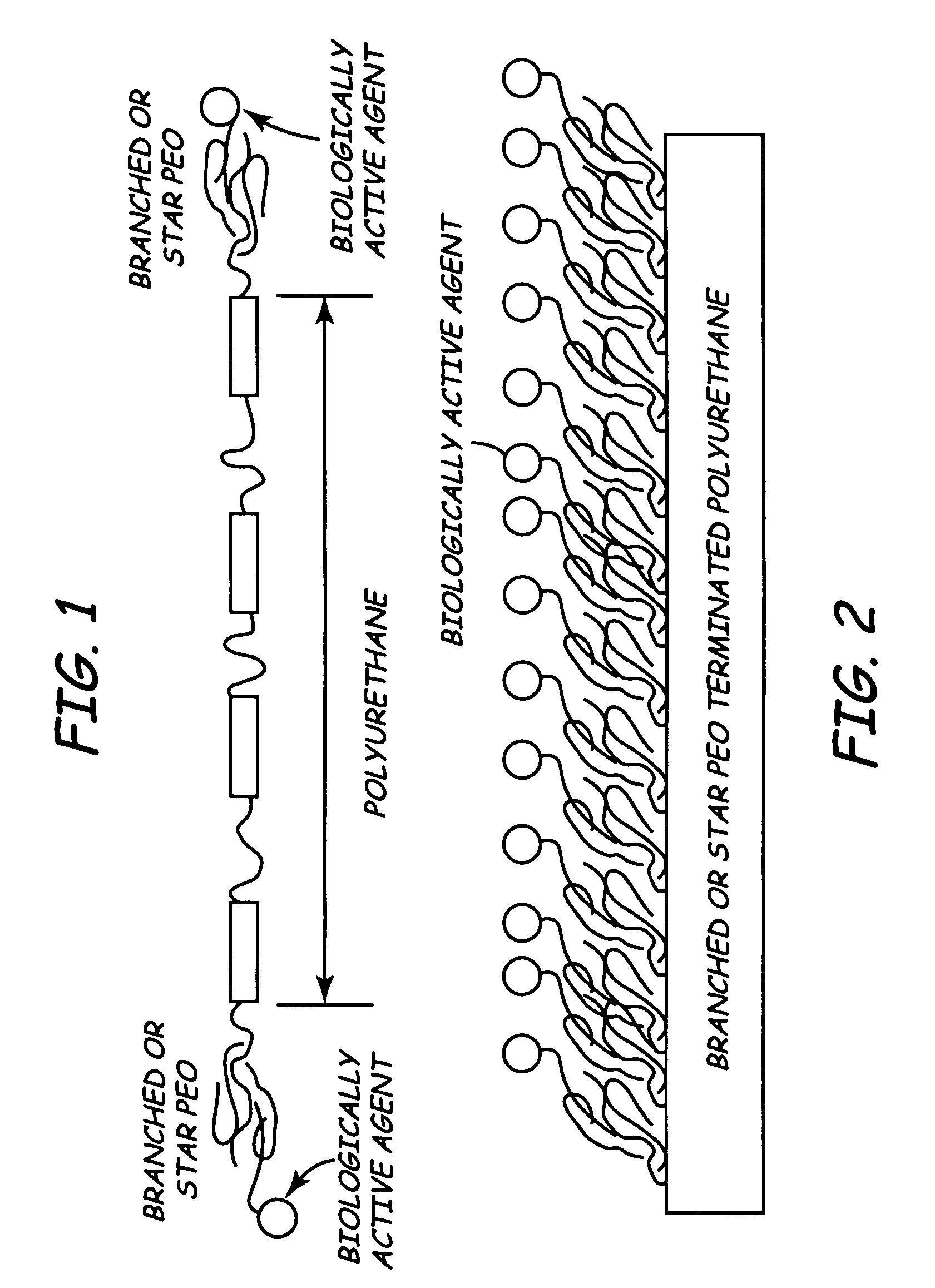
Branched polyethylene oxide terminated biomedical polymers and their use in biomedical devices
A biomedical polymer has a substantially linear base polymer; and branched polyethylene oxide covalently bonded to the base polymer as surface active end groups. The branched polyethylene oxide has at least two, more particularly at least four, and still more particularly at least six branches. Suitable base polymers include epoxies, polyurethanes, polyurethane copolymers, fluoropolymers, polyolefins and silicone rubbers. Biologically active agents may be attached to the branched polyethylene oxide. Suitable biologically active agents include microbial peptide agents, detergents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, cations, amine-containing organosilicones, diphosphonates, fatty acids, fatty acid salts, heparin and glucocorticosteroids. The biological polymer may be used as a casing for a medical unit of an implantable medical device, such as a pacemaker. In this case, the casing at least partially encloses the medical unit.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
High molecular material surface modification method and its product and application
ActiveCN107189096AAchieve covalently grafted loadingAchieve biomimetic surface modificationAfter treatmentCompound (substance)
The invention discloses a high molecular material surface modification method and its product and application. The surface modification method particularly relates to a biomedical polymer material surface treated on the basis of plasma immersion ion injection and a surface covalent grafting bioactive molecule after treatment so as to realize its bionic modification; the method particularly includes steps of 1), treating the high molecular material through gas plasma immersed ion injection; 2), incubating the treated high molecular material in the solution containing biological molecules. The high molecular material with modified gas plasma immersion ion injection surface has good stability; the grafting ability still cannot be significantly declined even though the high molecular material is stored in the air for a long time, and the high molecular material does not use chemical crosslinking agent; the whole surface modification technique is simple in process, low in cost, and suitable for batch and industrial production. The method and its product have wide application prospects in medical implant materials, functional materials, bioactive materials and other domain.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Selenium or tellurium containing polymer as well as preparation method and application of selenium or tellurium containing polymer
ActiveCN105384920ASmall toxicityHas a restore responsePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTreatment effectSide effect
The invention belongs to the fields of biomedical polymer materials and particularly relates to a selenium or tellurium containing polymer as well as a preparation method and application of the selenium or tellurium containing polymer. The polymer is a selenium or tellurium containing amphiphilic block copolymer obtained by chemically bonding selenium or tellurium containing micromolecules and an amphiphilic block copolymer. The polymer can form micelles, microparticles, vesicles and microspheres under a proper condition and has the functions such as reductive response and coordination response. The particles can coat a drug to form a controlled-release drug conveying system, injection administration can be realized through various ways, and the coated drug can be released from the conveying system in a controlled-release way according to demands, so that the administration frequency is reduced, the treating effect is improved, and the toxic and side effects of the drug are reduced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Synthesizing process and use of unsaturation cyclic aliphatic carbonate monomer and its polymer
This invention involves unsaturated cyclic aliphatic carbonate monomer and polymer synthesis and uses, and is biomedical polymer materials. From 2,2 - dimethylolpropionic acid departing, to synthesize 2-methyl-2-allyl-oxygen carbonyl trimethylene carbonate and 2-methyl-2-propargyl oxygen carbonyl trimethylene carbonate, and then through ring-opening polymerization or aliphatic monomers cycloate monomer opening loop and copolymerization, gain copolymer of aliphatic polycarbonate or aliphatic polyester-carbonate that side group contains double and Triple bond. Such polymer has advantage of both aliphatic polyester and carbonate, is biodegradable, degradation products is non-toxic. Use the functional side group of Double and Triple bond can connect drugs, active peptides or other bioactive elements with the polymer, improving the biocompatibility and biological activity of polymer, which may has real application in controlled-release drug, polymer pro-drug and tissue engineering fields.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
pH/temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer, and preparation method and applications thereof
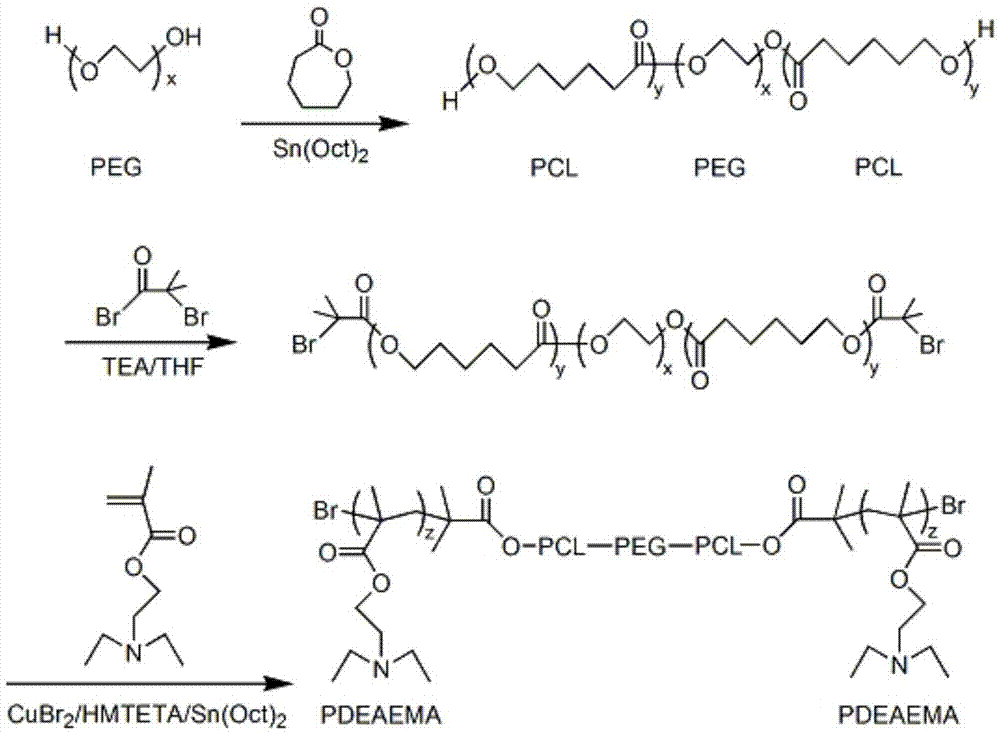
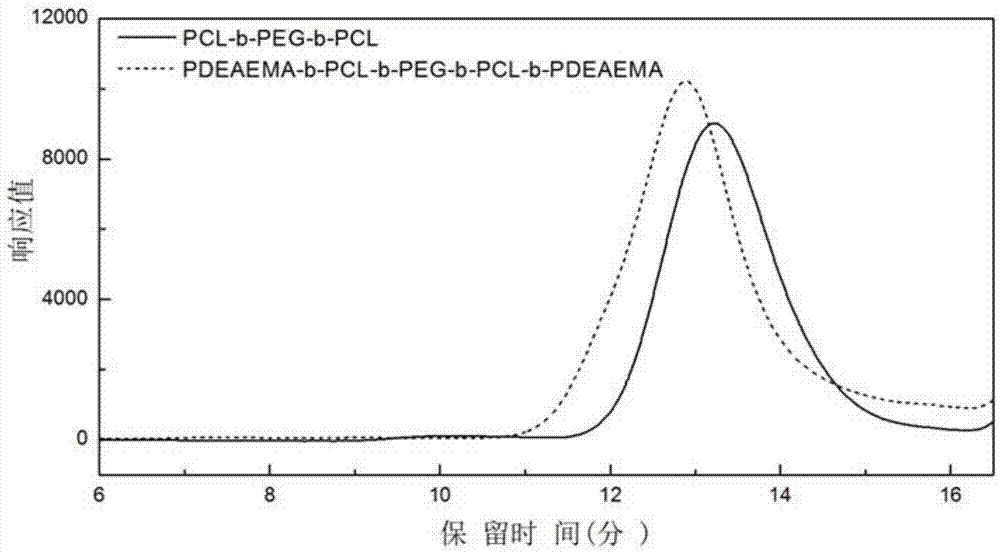
ActiveCN105440229APromote degradationNon-cytotoxicOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryTreatment effectWater insoluble
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical polymer material preparation, and discloses a pH / temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer, a preparation method thereof, and applications of the pH / temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer in preparing degradable in-situ gel materials and in coating water-insoluble anti-cancer drugs. The structural formula of the pH / temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer is PDEAEMA-b-PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL-b-PDEAEMA, and the number-average molecular weight ranges from 5300 to 14300g / mol. The pH / temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer is prepared via ring opening polymerization and electron transfer activation regeneration atom transfer radical polymerization. The pH / temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer can be converted into in-suit gel in aqueous solution, is capable of coating water-insoluble anti-cancer drugs effectively, and can be injected into diseased regions or parts close to the diseased regions directly via subcutaneous injection, and curative effect on solid tumor is improved. The pH / temperature sensitive amphiphilic polymer possesses excellent biodegradability, and no cytotoxicity; no residue is left in human body; and side effect on health tissues is small.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process to create 3D tissue scaffold using electrospun nanofiber matrix and photosensitive hydrogel
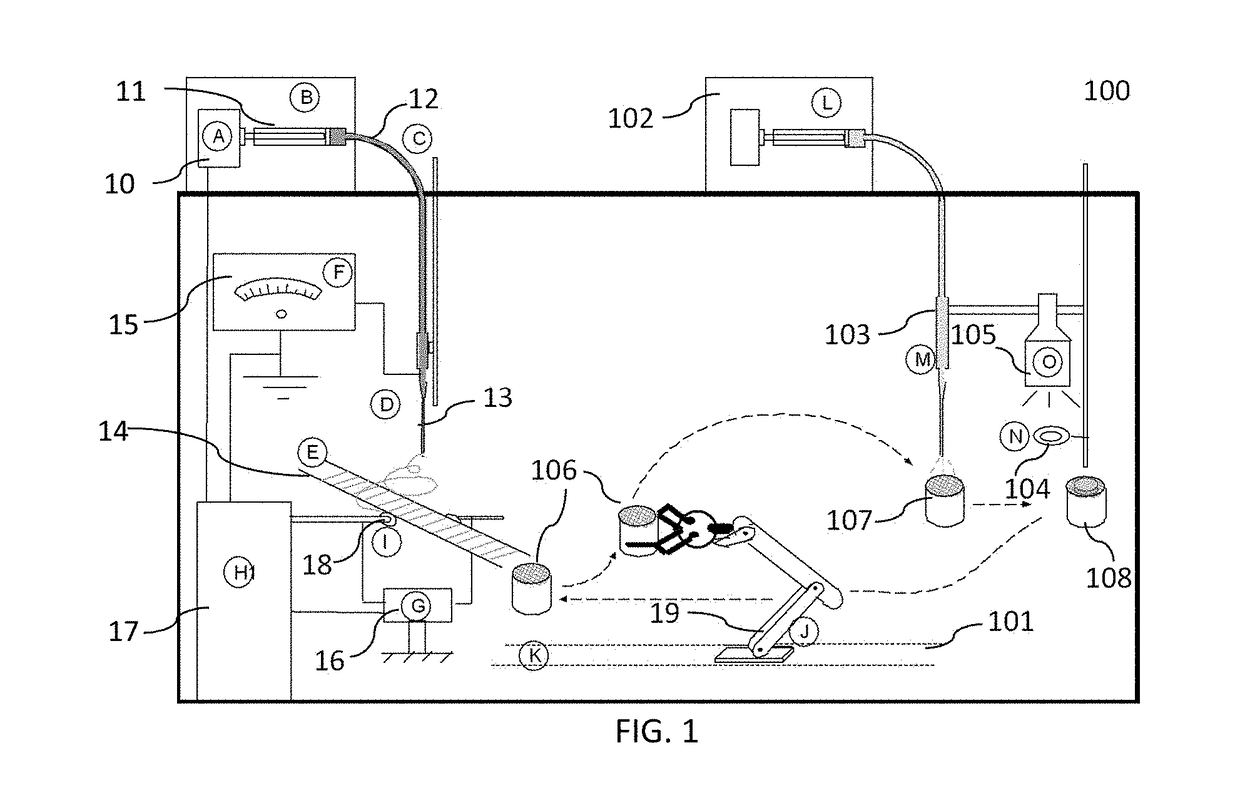
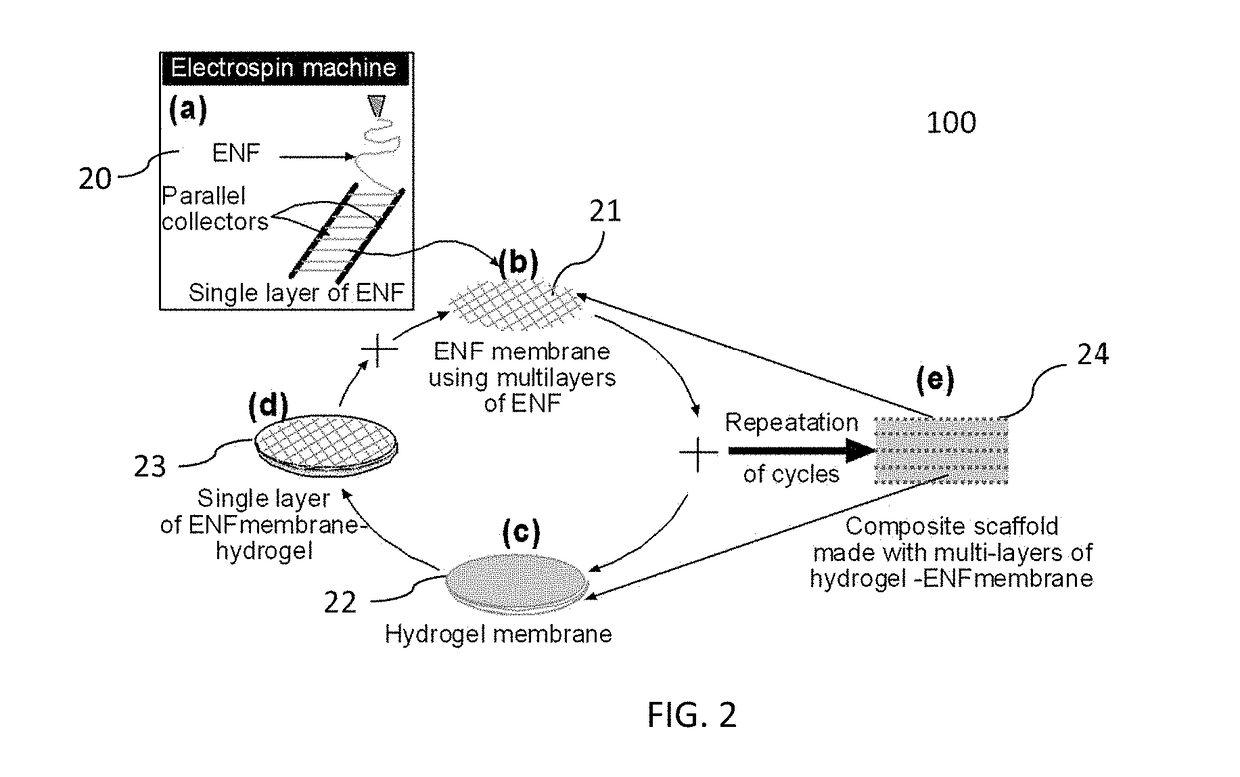
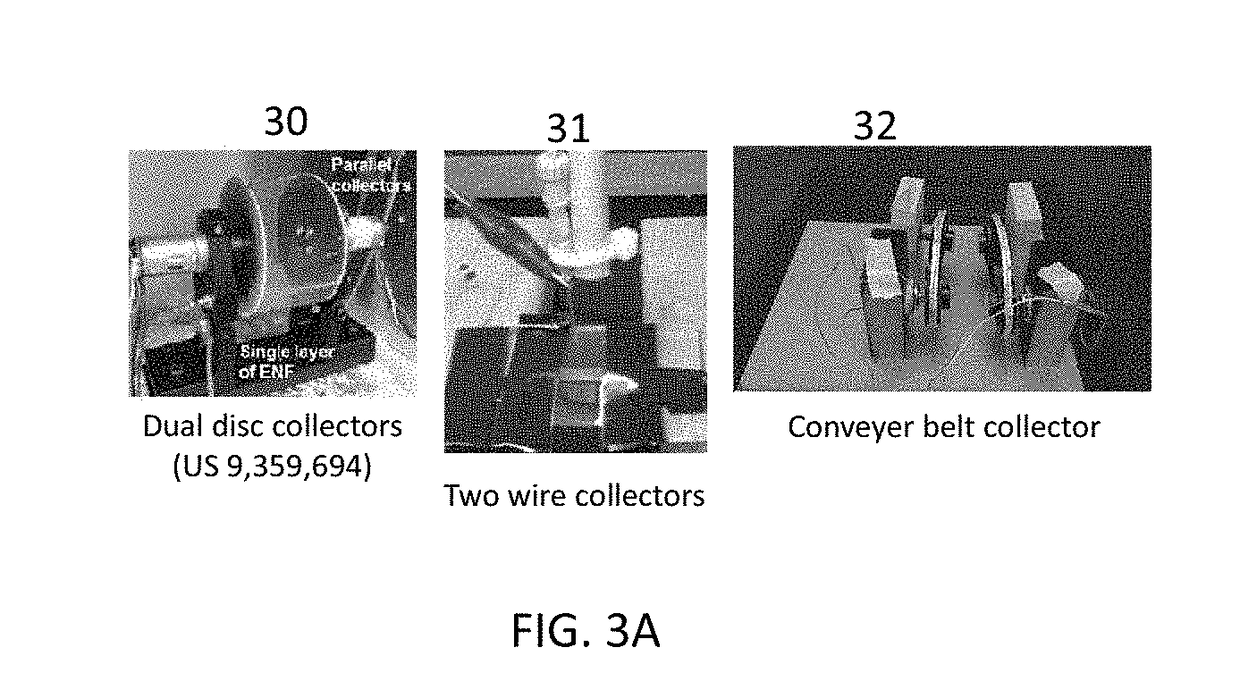
ActiveUS20170239388A1High mechanical strengthProfitable/superior microstructureFibre typesEpidermal cells/skin cellsElectrospun nanofiberPolymer science
A process providing a method to create 3D scaffolds using nano-scale fibers, comprising: deposition and alignment of a plurality of electrospun fiber layers on a substrate; application of a photosensitive biomedical polymer liquid to each fiber layer deposited on said substrate; deposition and cross-alignment of a plurality of electrospun fiber layers on said substrate; retaining said polymer liquid in place using said cross-aligned fiber layers; curing said polymer liquid on top of each fiber layer using UV light.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL OKLAHOMA
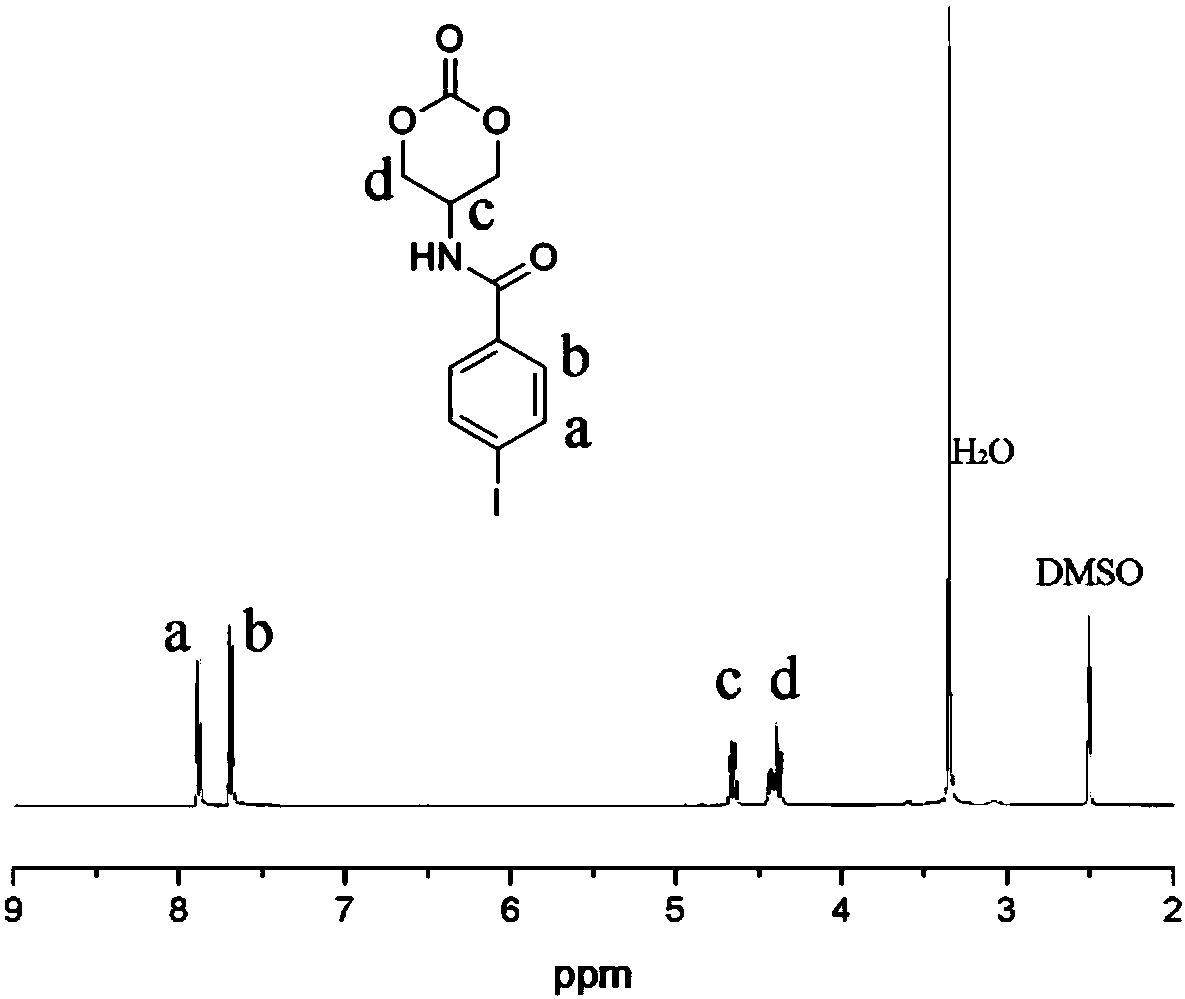
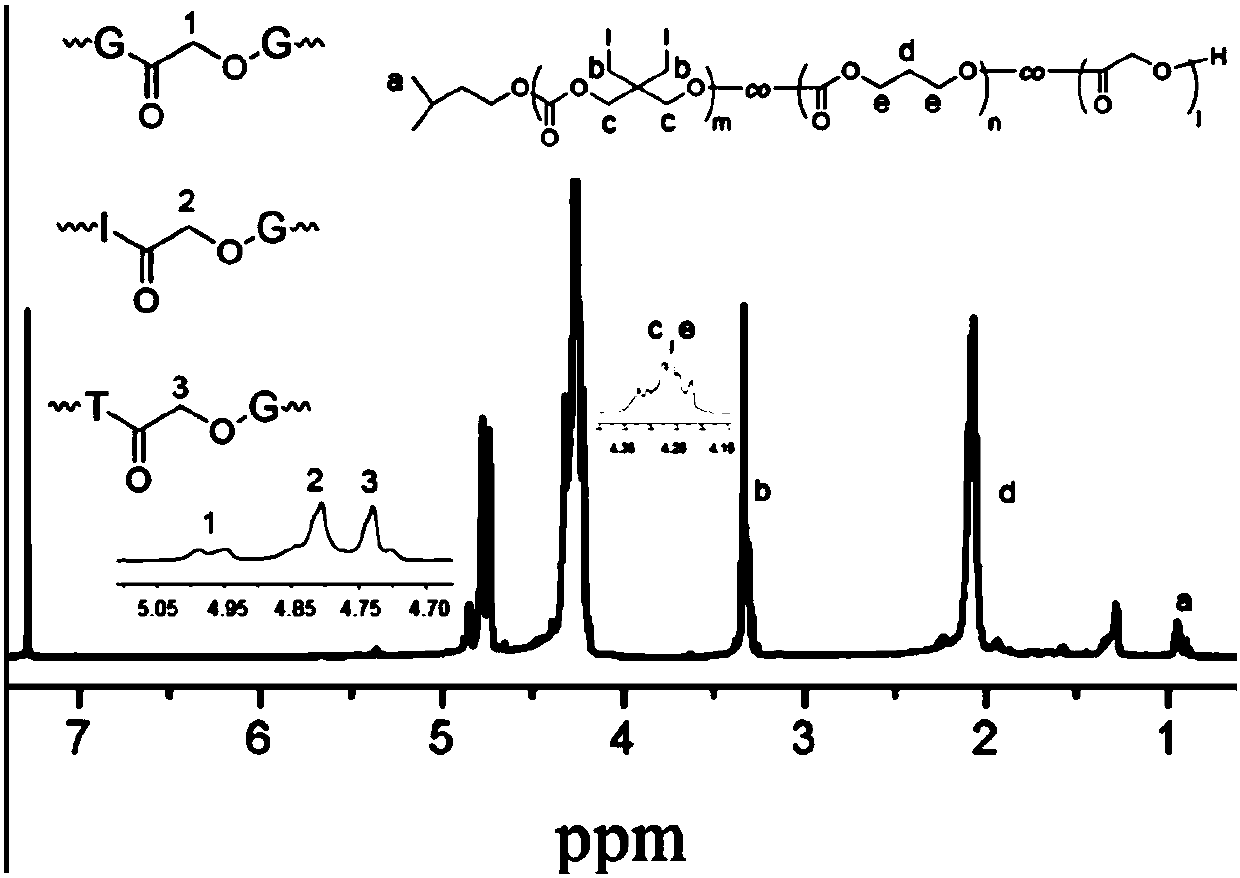
Iodine-containing polycarbonate/polyester material for X-ray development and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107915832ASuperior impermeabilityX-ray superiorSurgical adhesivesMetabolism disorderIodine deficiencyPolyester
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical polymer materials, and particularly relates to an iodine-containing polycarbonate / polyester polymer for X-ray development and a preparation method andapplication thereof. The iodine-containing polycarbonate / polyester polymer disclosed by the invention has excellent X-ray radiopacity or property of weakening X-rays. Under the existence of a catalyst, with a small-molecule hydroxyl compound as an initiator, through the ring-opening homopolymerization of an iodine-containing carbonate monomer or the ring-opening copolymerization of the iodine-containing carbonate monomer and other lactone, lactide and / or carbonate monomers, the iodine-containing polycarbonate / polyester material is obtained. The iodine-containing polycarbonate / polyester polymercan be applied in fields such as visualized embolization materials, anti-counterfeit labels, contrast media, antibacterial materials, prevention or treatment of iodine deficiency disorders, flame-retardant materials, tissue engineering and drug delivery systems.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Fluorosiloxane-POSS acrylate block copolymers, blood-compatible coating thereof and preparation method of the fluorosiloxane-POSS acrylate block copolymers
ActiveCN103524752AImprove hydrophobicityNo deformationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPolymer sciencePolyvinyl chloride
The invention relates to fluorosiloxane-POSS acrylate block copolymers, a blood-compatible coating thereof and a preparation method of the fluorosiloxane-POSS acrylate block copolymers, and belongs to the fields of fluorosilicone copolymer preparation and biomedical polymers. The blood-compatible coating prepared from the fluorosiloxane-POSS acrylate block copolymers has good hydrophobicity, a static contact angle with water of more than 107 degrees, and an improved anticoagulation time compared with polyvinyl chloride surfaces. Adhesive platelet adhesion and aggregation states are observed under a scanning electron microscope. Compared to a bank PVC surface, surface adhesive platelets of the surface after being coated are obviously reduced above 85%, the surface adhesive platelets are distortionless largely, and blood compatibility is good. The preparation process of the blood-compatible coating is simple with easily available raw materials, is prone to industrialization and large-scale production, and has high practical value. The fluorosiloxane-POSS acrylate block copolymers are shown as the formula 1 and the formula 2. The formula 1 and the formula 2 are shown in the description.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Injectable hydrogel material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110404083AGood exercise toleranceMulti-modal imagingAerosol deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsBiocompatibility TestingBiomedical polymers
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical polymer material, and provides an injectable hydrogel material for solving the problems that existing injectable hydrogel is slow in condensation, low in strength, and poor in biocompatibility and biodegradability, and consequently fixed point forming and long-term exercise tolerance of the hydrogel after injection are not facilitated. Theinjectable hydrogel material is generated from a component A and a component B in-situ through isovolumetric injection by adopting dual-linking injection technology; and the component A is carboxymethyl chitosan, and the component B is prepared from reaction of double hydroformylation polysaccharide and an auxiliary cross-linking agent and a formylation contrast agent. According to the injectablehydrogel material, the exercise tolerance is good, the requirements of the biocompatibility and the biodegradability are met, the functions of multimoding development and controlled degradation are further achieved, the effect that the multiple functions of protection, tracing, customized treatment and the like are integrated is achieved, and the wide application prospects in the field of integration of diagnosis and treatment are achieved.
Owner:杭州碧泰生物医疗科技有限责任公司
Preparation method of biomedical polymer material of polyunsaturated acid gallic acid epoxy ester
InactiveCN103694430ACause permanent pollutionHigh epoxy valueNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesGraft polymer adhesivesEpoxyPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a biomedical polymer material of a polyunsaturated acid gallic acid epoxy ester. The method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing the following components in parts by weight to carry out polymerization reaction: 60-90 parts of polyunsaturated acid gallic acid epoxy ester, 0-45 parts of unsaturated acid polyol ester, 2-4.5 parts of initiator, 0-5 parts of anti-ageing agent, 0-10 parts of micron grade silicon dioxide, 0-20 parts of polymethyl methacrylate powder, 0-0.5 parts of antioxidant and 0-5 parts of benzoic sulfimide. The method can be used for preparing the biomedical polymer material; preferably used as a dental or surgical high polymer material, the biomedical polymer material can be also applied to a sclerotin adhesive and the like. The biomedical polymer material is safe and nontoxic, and the decomposition product of the biomedical polymer material has an anti-cancer effect.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Synthetic method of non-linear structure polycaprolactone-block-polyethyleneglycol
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing polycaprolactone-block-polyethylene glycol with a non-linear structure in the chemical technical field, which is finished through a one-step click chemical reaction, namely the method is finished by polycaprolactone with an acetylene terminated sector structure and polyethylene glycol with an azido-terminated linear structure through a click chemical reaction, and the reaction takes cuprous bromide and pentamethyldiethylenetriamine as a co-catalyst and is performed in a N, N-dimethylformamide solution. The method provides a simple and effective approach for the preparation of degradable amphiphilic biomedical polymers with non-linear structures, and provides a theoretical evidence for obtaining a novel polymer drug carrier with controllable degradation rate and drug release rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cationic polyhydroxylated polymer embolization microspheres and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107899066AIncrease elasticityReduce procurement costsSurgical adhesivesTissue regenerationCross-linkMicrosphere
The invention relates to cationic polyhydroxylated polymer embolization microspheres and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials. The cationicpolyhydroxylated polymer embolization microspheres are formed by cross-linking and polymerizing functional macromolecules with biocompatibility through an amino compound, an alkyl acid derivative andan amino alkyl acid derivative or an ammonium salt thereof serving as a cross-linking agent; a main chain of each cationic polyhydroxylated polymer embolization microsphere is provided with a 1,2-glycol or 1,3-glycol structural functional group, and is also provided with an amino acetal or ester structure; a side chain is an amino alkyl olefine acid derivative. Compared with the existing polyvinylalcohol cationic microspheres, the microspheres greatly simplify the types of raw materials, reduce raw material purchase cost, and simplify a production process, and meanwhile, avoid environmental pollution caused by discharging a large number of dispersing agents and organic solvents.
Owner:SUZHOU HENGRUI CALLISYN BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of long-acting sustained-release microspheres containing bevacizumab
InactiveCN102988301AGood volatilization effectReduce evaporation rateSenses disorderAntibody ingredientsMicrosphereWater soluble drug
The invention discloses a preparation method of long-acting sustained-release microspheres containing bevacizumab, which is a preparation method of the sustained-release microspheres formed by encapsulating water-soluble drug protein bevacizumab in a degradable biomedical polymer material. The microspheres are prepared by a W / O / W (water-in-oil-in-water) solvent evaporation method, which comprises the steps of: dispersing bevacizumab and a solution thereof and alginate as inner water phases into a solution which uses the degradable biomedical polymer material as an oil phase to form colostrum; dispersing the colostrum into an outer water phase which is water liquid containing emulsifier to form multiple emulsion; and stirring, distilling in reduced pressure, centrifuging, washing and drying to obtain the bevacizumab sustained-release microspheres. According to the long-acting sustained-release microspheres containing bevacizumab prepared by the method, the encapsulation efficiency of the water-soluble protein drug can be effectively improved, the drug protein activity is not influenced, the releasing time of water-soluble protein can be effectively prolonged, and the sustained release period can be 2-3 months, even longer, so that the number of injection times can be reduced. The preparation method is convenient for clinical application.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Injectable thermosensitive physical hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105396137AAdjust modulusRegulation of degradation rateAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryTissue repairPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials, in particular to injectable thermosensitive physical hydrogel with functional side groups and a preparation method thereof. Polyethylene glycol serves as a hydrophilic block (B), polycaprolactone serves as a hydrophobic block (A), a polymer composition with the functional side groups is connected, an aqueous solution, with a certain mass percentage, of the composition is in a free flowing sol state when the temperature of the aqueous solution is lower than that of a human body and is in a non-flowing gel state when the temperature of the aqueous solution is equal to that of the human body, and conversion from sol to gel is achieved when the low temperature is raised to the high temperature. The hydrogel is injectable and biodegradable, has good biocompatibility and can be widely applied to medicine conveying, cell encapsulation and tissue repair.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing selenium-containing degradable polymer through ring-opening polymerization and application thereof to hydrogel
InactiveCN105732990APrecise structureAggregation is controllableOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryPolymer scienceHydrophobic polymer
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical polymer materials, in particular to a method for preparing a selenium-containing degradable amphiphilic polymer through ring-opening polymerization and application thereof to hydrogel.The polymer is a BAB type tri-block polymer synthesized with selenium-containing micromolecules as an initiating agent, the hydrophobic polymer block A is formed by biodegradable polycaprolactone, and the hydrophilic polymer block B is formed by polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether; a polymer water solution of a certain concentration is liquid at the room temperature or below room temperature, is in a stable gel state at the human body temperature and has syringeability.The method has the advantages that ring-opening polymerization is adopted, polymerization is controllable, the obtained product is accurate in molecular structure, and molecular weight distribution is controllable.The prepared polymer has multiple stimulative responsibility to temperature and redox, and therefore the physical hydrogel is high in applicability to the field of drug carriers.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modular bioresorbable or biomedical, biologically active supramolecular materials
The present invention relates to a modular supramolecular bioresorbable or biomedical material comprising (i) a polymer comprising at least two 4H-units and (ii) a biologically active compound. Optionally, the supramolecular bioresorbable or bio medical material comprises a bioresorbable or biomedical polymer as third component to tune its properties (mechanical and bioresorption properties). The supramolecular bioresorbable or biomedical material is especially suitable for biomedical applications such as controlled release of drugs, materials for tissue-engineering, materials for the manufacture of a prosthesis or an implant, medical imaging technologies.
Owner:SUPRAPOLIX
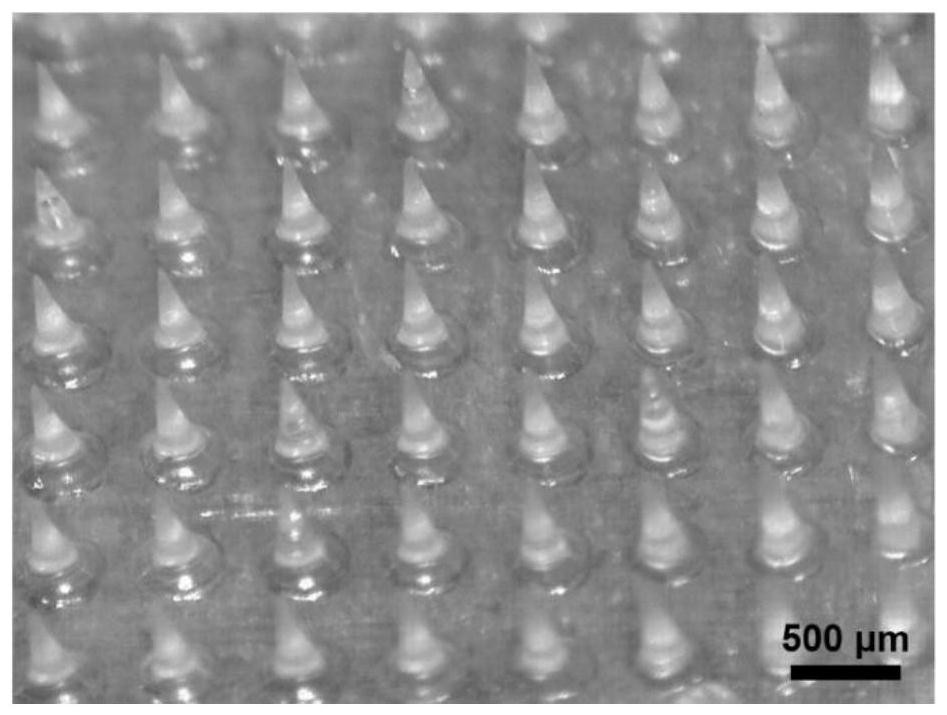
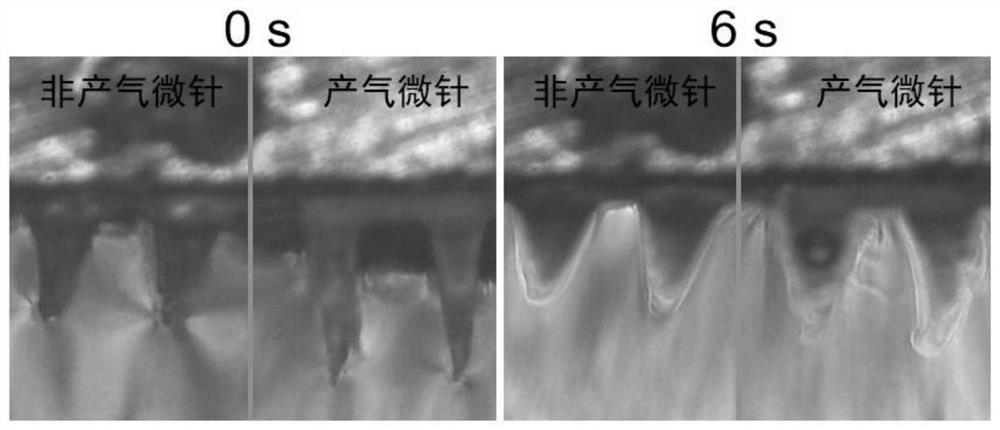
Micro-needle array patch capable of generating gas to take effect quickly and preparation and application thereof
PendingCN113679692AImprove solubilityIncrease the speed of diffusionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue fluidBiocompatibility
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical polymer materials, and discloses a micro-needle array patch capable of generating gas to take effect quickly and preparation and application thereof. The micro-needle array patch comprises a substrate and a needle tip located on the substrate, the substrate is composed of a biocompatible matrix, the needle tip is mainly composed of the biocompatible matrix and inorganic particles capable of generating gas, and the inorganic particles capable of generating gas are formed on the surface and / or in the biocompatible matrix of the needle tip; the needle tip part of the micro-needle array patch can interact with skin tissue fluid to generate gas during application, rapid dissolution of micro-needles and diffusion of drugs to a corium layer are promoted, and the drugs can be efficiently and rapidly delivered to subcutaneous parts and take effect without the help of external equipment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hemostasis needle and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109330654AEffectively blockedEffective synchronous hemostasisSurgical needlesOcculdersCross-linkDrug administration
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical polymer materials, and particularly relates to a hemostasis needle and a preparing method and application thereof. The hemostasis needle comprises a syringe needle and a hemostasis coating for coating the surface of the periphery of the syringe needle, wherein the hemostasis coating is a non-toxic cross-linked polymer which can swell and shed off from the surface of the periphery of the syringe needle when meeting a solvent. The hemostasis needle prepared by means of the method is utilized for puncturing the blood vessels and the visceral organs, after the hemostasis needle is pulled out, the coating is left at the puncturing position to block a puncturing hole, and thus synchronous hemostasis is achieved. The preparing method of the hemostasis needle is easy to operate and low in cost, takes effect quickly, and can be widely applied to the fields such as drug administration, blood sampling, sampling and interventional therapy on patients with normal or abnormal clinical blood coagulation functions. The hemostasis needle is adjustable in size, easy to produce on a large scale, capable of effectively solving the problem that unnecessary hemorrhage is caused when the patients with normal or abnormal clinical blood coagulation functions are subjected to blood vessel and visceral organ puncturing, and free of obvious untoward effects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
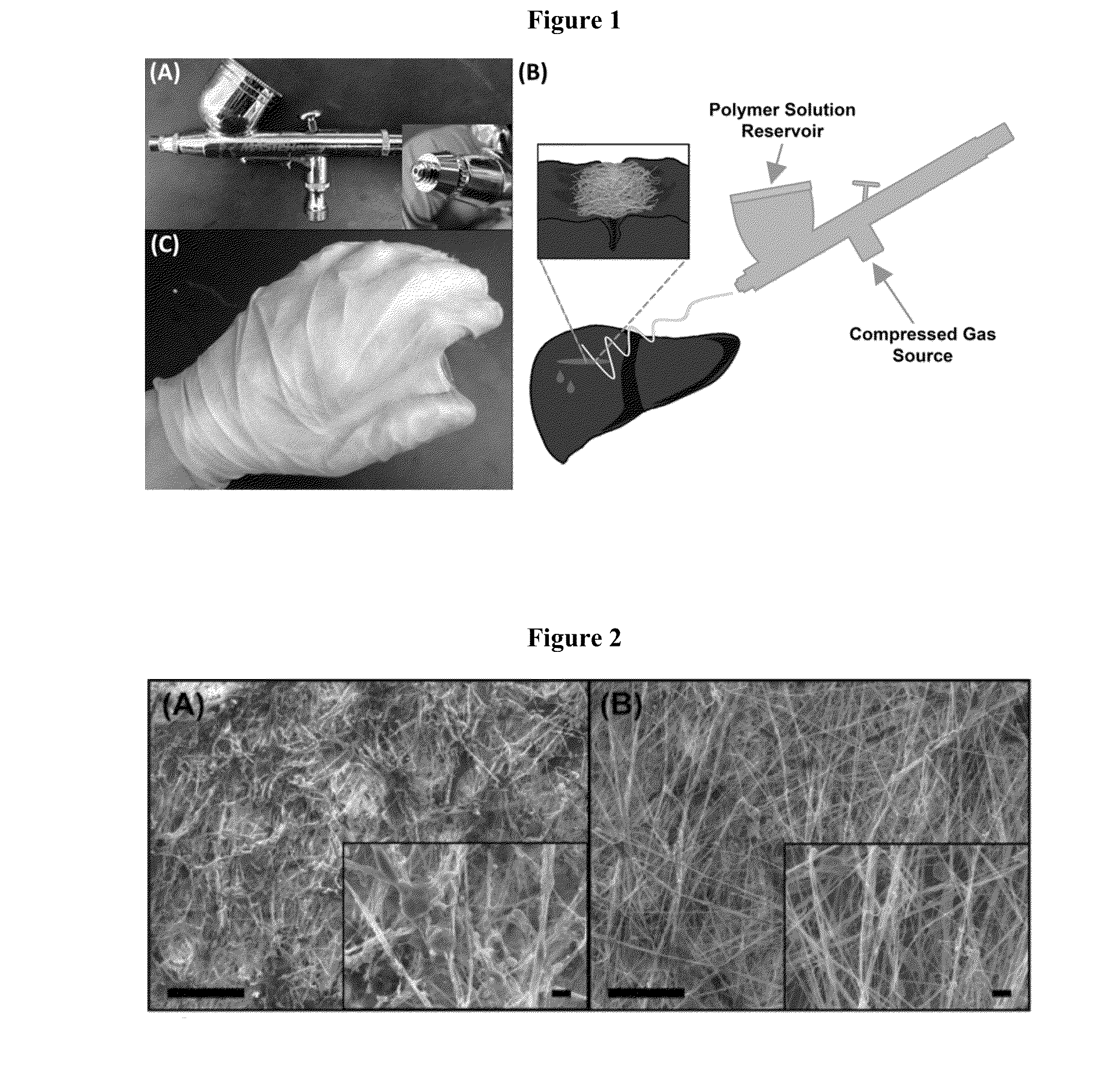
Solution Blow Spun Polymer Fibers, Polymer Blends Therefor and Methods of Use Thereof
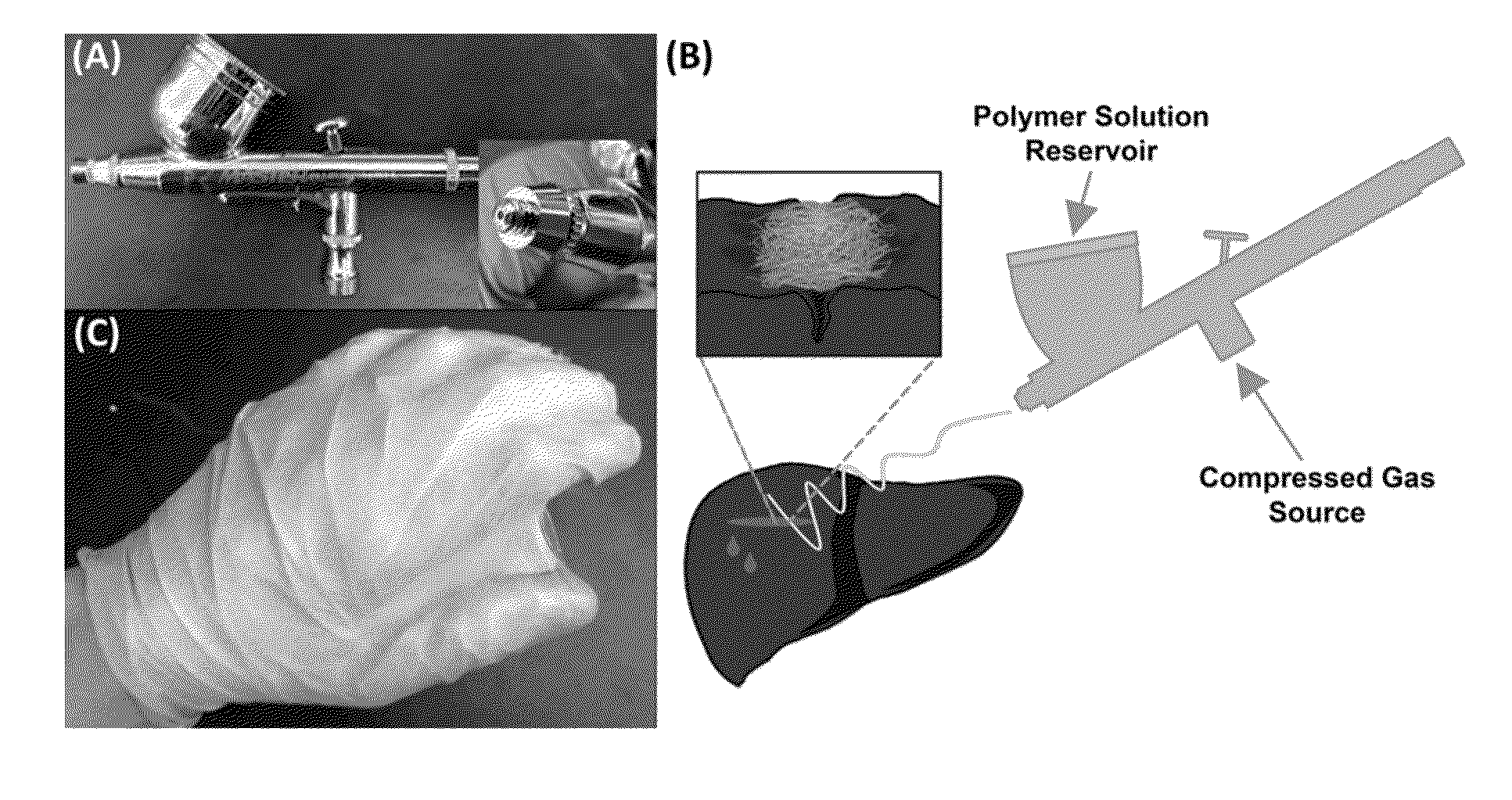
Compositions comprising biomedical polymers, and in particular unique blends of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) are provided. Methods of forming polymer fibers using such compositions and solution blow spinning techniques are also provided, as well as methods of delivering the blow spun polymer fibers onto a surface (e.g., such as tissue for use as a surgical scaffold, sealant or tissue adhesive).
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com