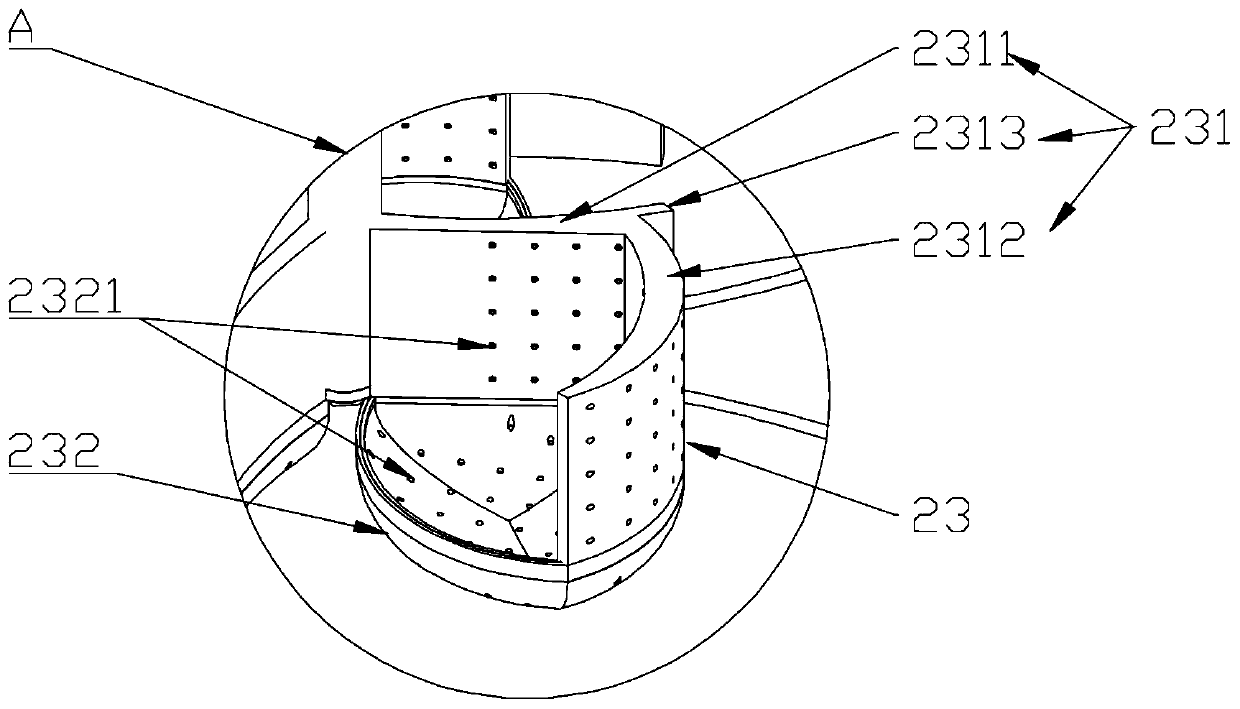
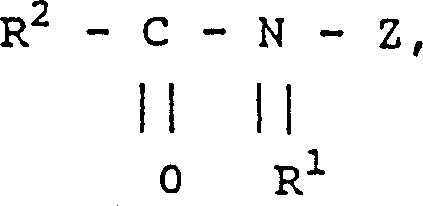
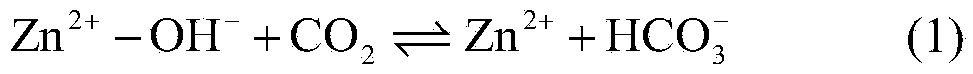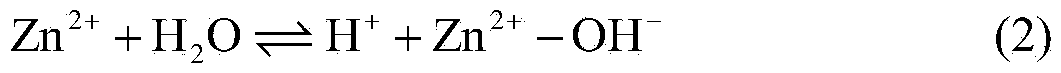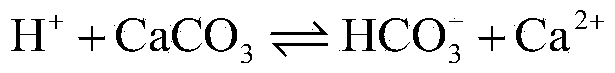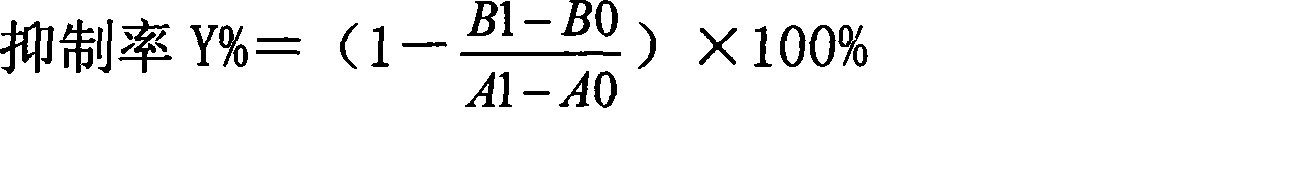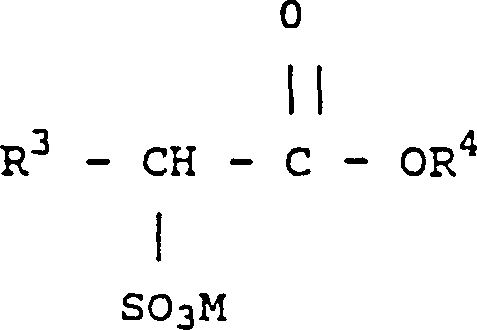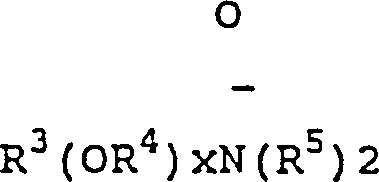Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Bacillidium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
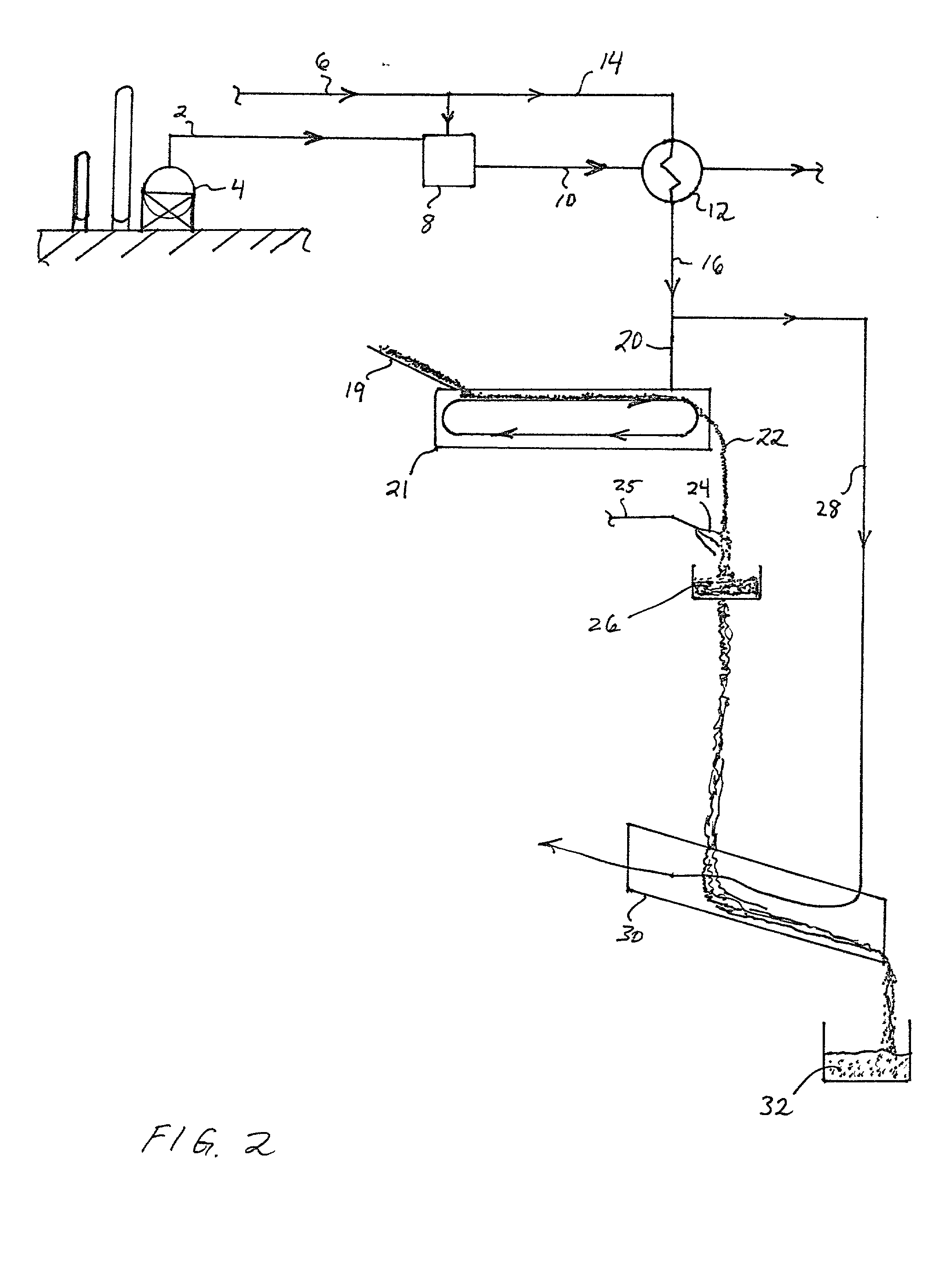
Fertilizer compositions and methods of making and using same
Fertilizer compositions for plant production are described, comprised of decontaminated manure and Bacillus spores, preferably a humic acid derived from lignite and, optionally, one or more of N compounds, P compounds, K compounds, and combinations of two or more of these compounds. Preferred compositions are those wherein the ingredients are blended into an admixture resulting in a granular product. Other preferred compositions are those blended into an admixture resulting in a powdered product. Preferably, the ingredients are formed into hardened prills or pellets. Processes for production and use are also presented.
Owner:MICROBES
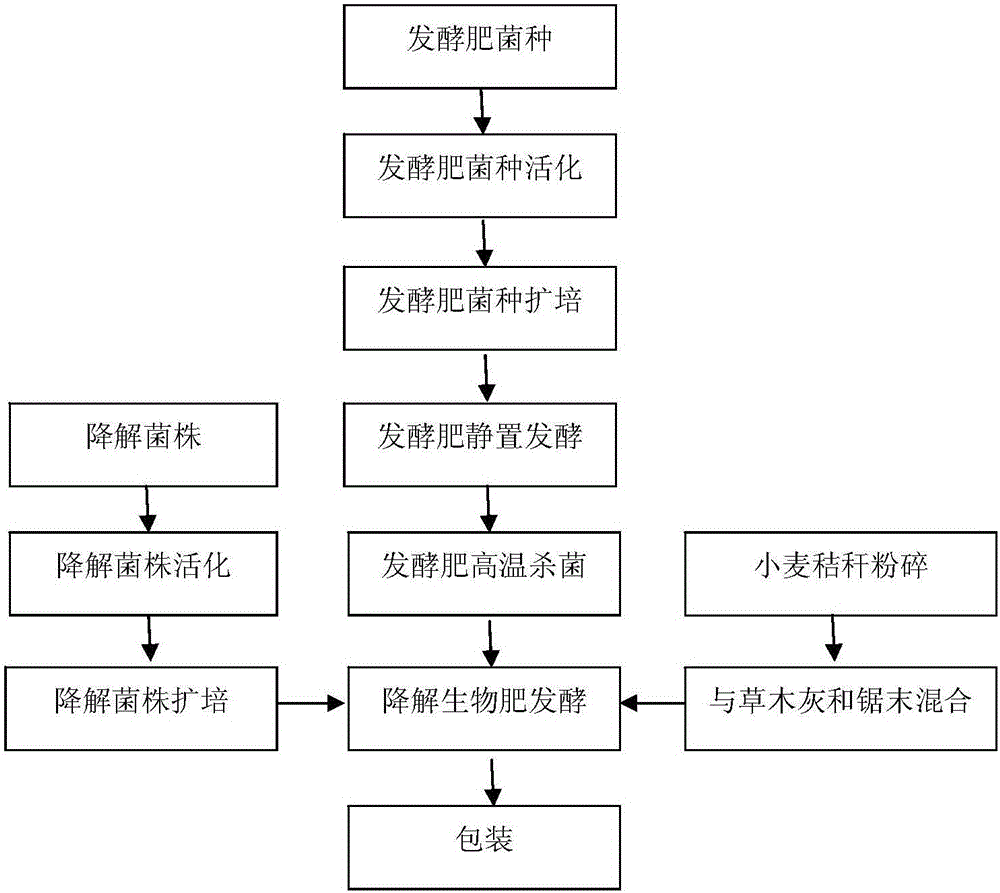
Biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of biogas residue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103848698AWon't burnDecompose thoroughlyBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelMicrobial agentPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of a biogas residue and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing the biogas residue and a swelling agent to form a fermentation raw material, inoculating a compound microbial agent in the fermentation raw material, uniformly mixing for fermenting, and adding urea, diammonium phosphate, a potassium chloride inorganic salt, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhiza fungi, silicate bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria acetic bacteria, bifidobacterium, and saccharomycetes after the fermentation is completed to prepare the biological organic fertilizer, wherein the compound microbial agent comprises strains of bacillus, pseudomonas, staphylococcus, streptomyces, penicillium, aspergillus and trichoderma. The compound microbial agent prepared by using the biological organic fertilizer has a pertinence to aerobic fermentation of the biogas residue, and is capable of effectively increasing the fermentation rate of the biogas residue, shortening the fermentation time and realizing high-additional value production, innocent treatment and recycling of the biogas residue; and the problem of resources and environment of villages and small towns is solved, and the rapid development of construction of new countryside and towns and cities can be promoted.
Owner:青岛福瑞斯生物能源科技开发有限公司
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improvedresistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including speciessuch as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
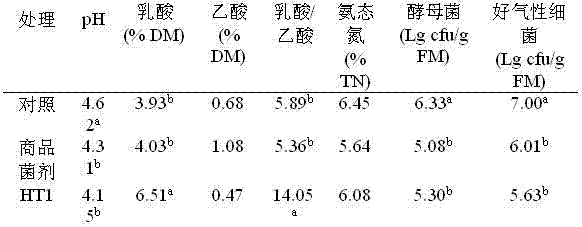
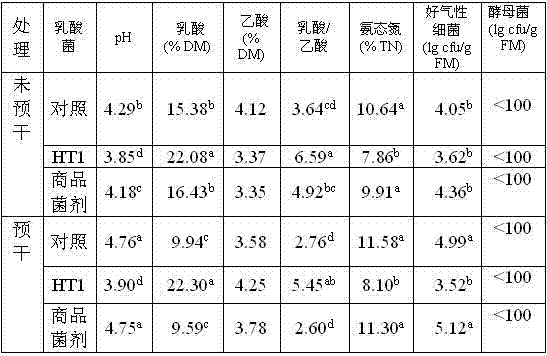
High temperature resistant lactic acid strain ht1 and its application in preparing silage
ActiveCN102286394AOvercoming Poor Fermentation ProblemsUnique effectBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resisting lactic acid strain HT1 and a method for modulating silage, belonging to the technical field of microorganism application and silage modulation and process. The strain is HT1, which is identified to be lactobacillusrhamosussp, the collection number of the strain is CGMCC4483, the Genbank accession number of 16SrDNA of the strain is JF414107, and the strain has the main biological characteristics of Gram positive bacilli, homofermentative glucose, acidproof property, quick growth speed, wide breeding temperature range and special high temperature resistance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Clostridium Daqing clostridium and application thereof
The present invention relates to clostridium 'daqing' clostridium and its uses. The present invention solves the problem it is difficult to remove or degrade polypropylene of oil field sewage. The clostridium 'daqing' clostridium -WL is preserved at CGMCC on January 10, 2007, preserving number being CGMCC No. 1911. The 'daqing' clostridium is Gram-positive bacilli, with endo-spore, facultative anaerobic, grows under pH 5.0-11.0,10-65 degree. The strain is variable in length, breadth being 0.4um-0.8um, length being 1.4um-4um, free of flagellum. The inventive 'daqing' clostridium -WL is a new strain, and can use polypropylene as unique carbon source which can be used in polypropylene biodegradation. 10ml 'daqing' clostridium -WL of concentration 6x10<6> per ml is added in oil field sewage with polypropylene concentration being 500mg / L and the polypropylene degradation rate is 35%-76% after 20 days.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for removing calcium carbonate scales by using microbial extracellular carbonic anhydrase
ActiveCN104071890AAchieve emission reductionDoes not cause dischargeTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsBiological water/sewage treatmentIndustrial water treatmentChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial water treatment, and particularly relates to a method for removing calcium carbonate scales by using microbial extracellular carbonic anhydrase. The invention aims to provide a method for relieving the phenomenon of carbonate scales in an industrial circulating water system. The method can reduce the phosphorus-containing wastewater which enters the ambient water body. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a bacillus microbial inoculant for secreting extracellular carbonic anhydrase; 2) carrying out refrigerated centrifugation, and salting out to extract a crude enzyme solution containing the carbonic anhydrase; and 3) adding the crude enzyme solution into industrial circulating water with carbonate scales. The method can be used for removing the calcium carbonate scales in the industrial circulating water system, and has the advantages of low cost and no environment pollution.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Screening of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus and application of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus to improvement on greenhouse vegetable soil hardening
The invention relates to screening of phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus JJMSH1 and application of the phosphorus and potassium decomposing bacillus to improvement on greenhouse vegetable soil hardening. The strain has a good phosphorus and potassium decomposing function. The strain is screened from rhizosphere soil of a plant in a vegetable greenhouse; the soil is enriched through an organic phosphorus culture medium and then subjected to screening through an inorganic phosphorus culture medium and a silicate culture medium successively, and a molybdenum and antimony resistant colorimetric method and a flame photometry are used for detecting the contents of effective phosphorus and rapidly available potassium in sequence, thus finally selecting the JJMSH1 as an ideal strain. The JJMSH1 is authenticated by gram staining and spore staining to be gram-positive bacillus. When the strain disclosed by the invention is used for treating hardened soil in the greenhouse, the contents of the effective phosphorus and the rapidly available potassium in the soil are relatively obviously increased, and the OD600 reaches 1.5; after being diluted 100 times, a microbial inoculum is applied to the soil, so that the content of the effective phosphorus is increased by 35.7 percent, and the content of the rapidly available potassium is increased by 26.1 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
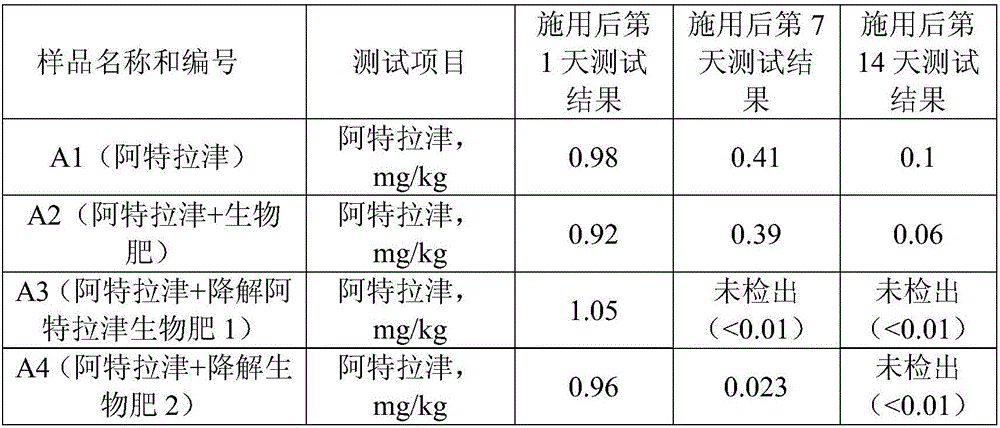
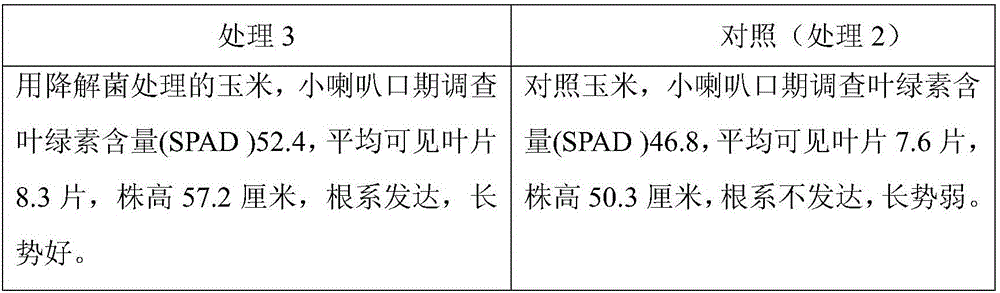
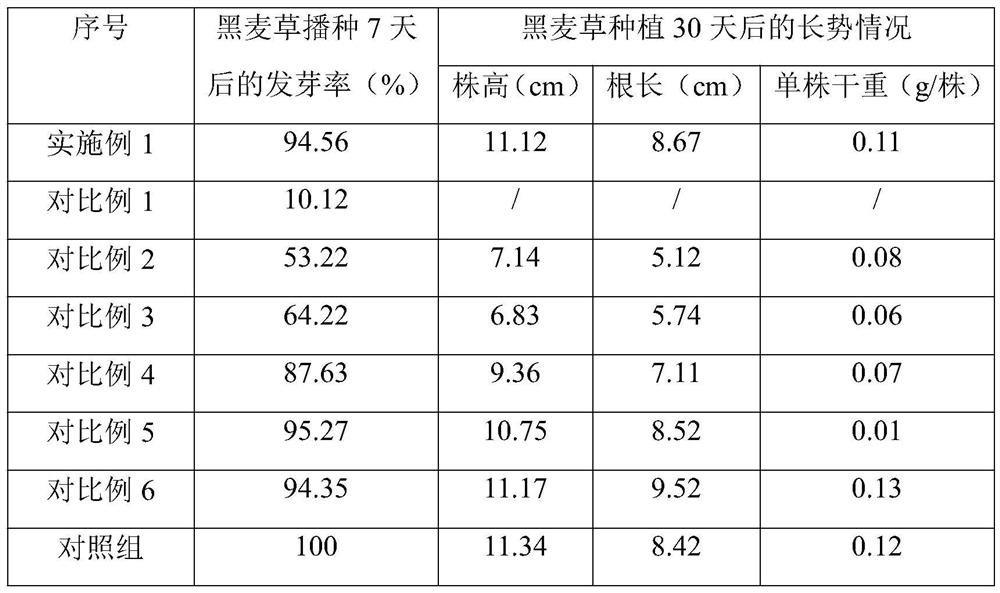
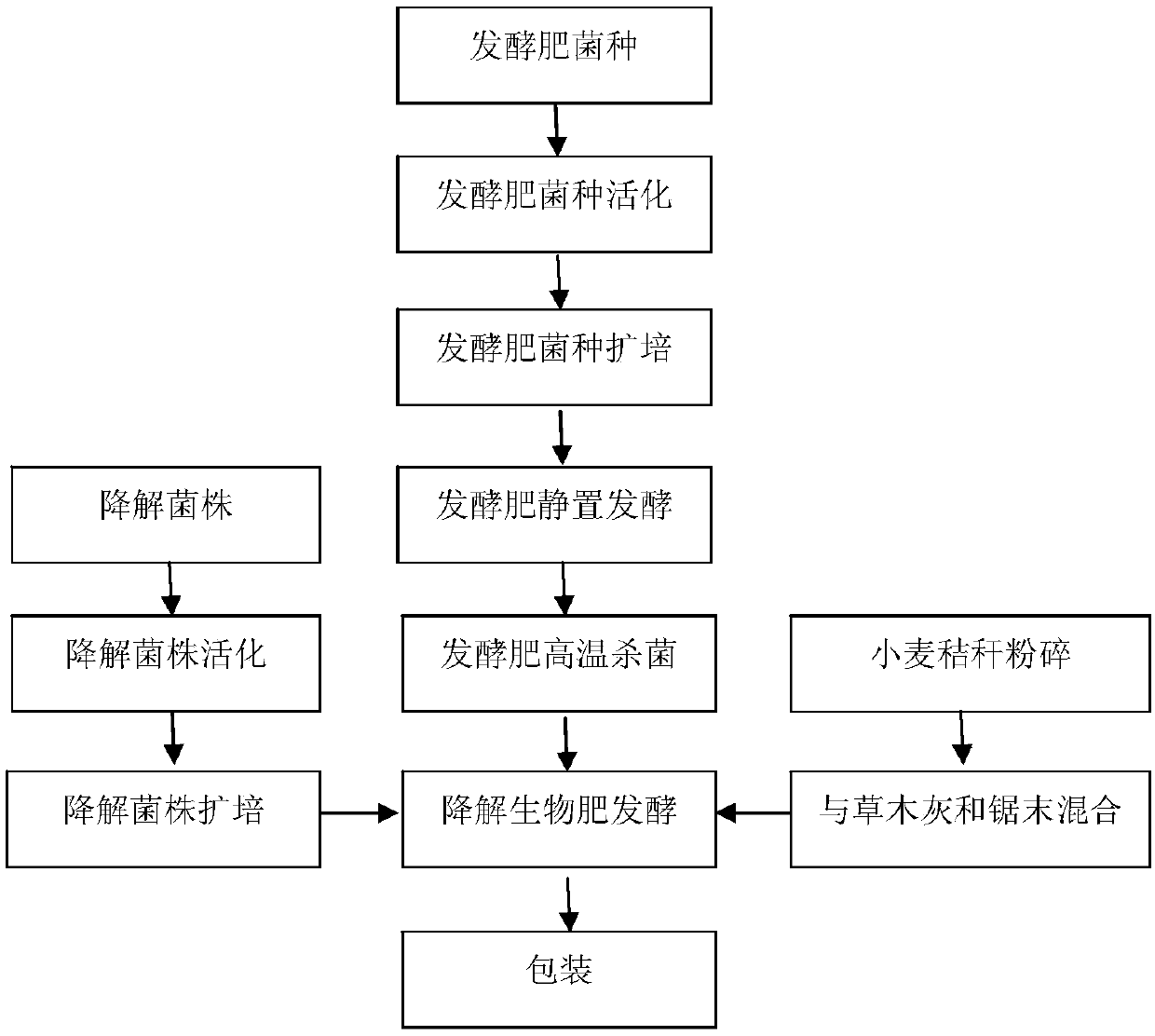
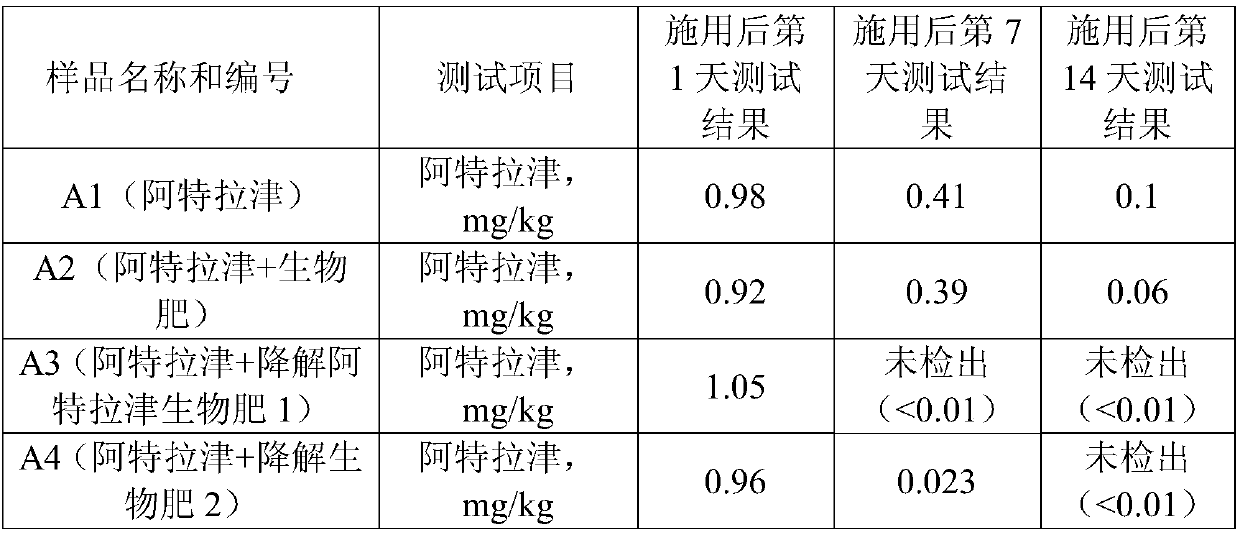
Bio-fertilizer for efficient degradation of atrazine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105967943AImprove adaptabilityImprove stabilityBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersBacillus licheniformisBioremediation
The invention discloses bio-fertilizer for efficient degradation of atrazine and a preparation method thereof. Wheat straws, plant ash, saw dust and self-made zymophyte fertilizer beneficial for strain survival and growth are compounded and the compound, Exiguobacterium strain BTAH1 and Shinella granuli HBZA0511 are mixed and are fermented to form the bio-fertilizer. The self-made zymophyte fertilizer is prepared from nutrition bases such as cake, wheat bran, corn straws and fish bone powder, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus rhamnosus through fermentation. The bio-fertilizer is sowed in the field so that soil atrazine herbicide residual quantity is fast reduced by 95% or more, is conducive to soil bioremediation, is suitable for green agricultural product production and improves soil organic content.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Improvement agent for red mud in-situ soil and application method thereof
PendingCN114015455AAchieve improvementLower pHCalcareous fertilisersAgriculture tools and machinesMicroorganismMicrobial agent
The invention provides an improvement agent for red mud in-situ soil and an application method thereof, the improvement agent comprises a main agent and an auxiliary agent, the main agent comprises inorganic acid waste and organic acid waste; the auxiliary agent comprises an organic fertilizer, an inorganic fertilizer and a microbial agent; the microbial agent comprises halomonas, Nesterensis and bacillus. The application method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a premix; step S2, preparing a neutralized substance; s3, forming a red mud improvement layer; and S4, activating and diluting the microbial agent, and spraying the microbial agent on the red mud improvement layer. The red mud environment in which plants can normally grow and develop is established, positive evolution of the red mud towards the soil direction is promoted, and thus ecological restoration and ecological reconstruction of the red mud storage yard are achieved, and the problem that the red mud storage yard returns alkali and salt to hinder vegetation growth is solved.
Owner:CHINA NONFERROUS METAL CHANGSHA SURVEY & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Alkaline xyloglucanase
A xyloglucanase having a relative xyloglucanase activity of atleast 50% at pH7 and either no or an insignificant cellulolytic activity is obtainable e.g. from a strain of Bacillus. A xyloglucanase comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in positions 30-261 of SEQ ID NO:2 or homologues may be derived from e.g. Bacillus licheniformis, ATCC 14580, and may be encoded by polynucleotide molecules comprising a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 from nucleotide 88 to nucleotide 783; and a xyloglucanase comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in positions 1-537 of SEQ ID NO:4 or homologues may be derived from e.g. B. agaradhaerens, NCIMB 40482, and may be encoded by polynucleotide molecules comprising a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:3 from nucleotide 1 to nucleotide 1611. The xyloglucanases are useful e.g. in cleaning compositions and for treatment of cellulosic fibres.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Production of fucosylated oligosaccharides in bacillus
Disclosed are non-sporulating Bacillus cells for the production of a fucosylated oligosaccharide as well as a method for producing a fucosylated oligosaccharide, wherein said Bacillus cell has been genetically engineered to possess a lactose permease, a GDP-fucose biosynthesis pathway and a fucosyltransferase.
Owner:CHR HANSEN HMO GMBH
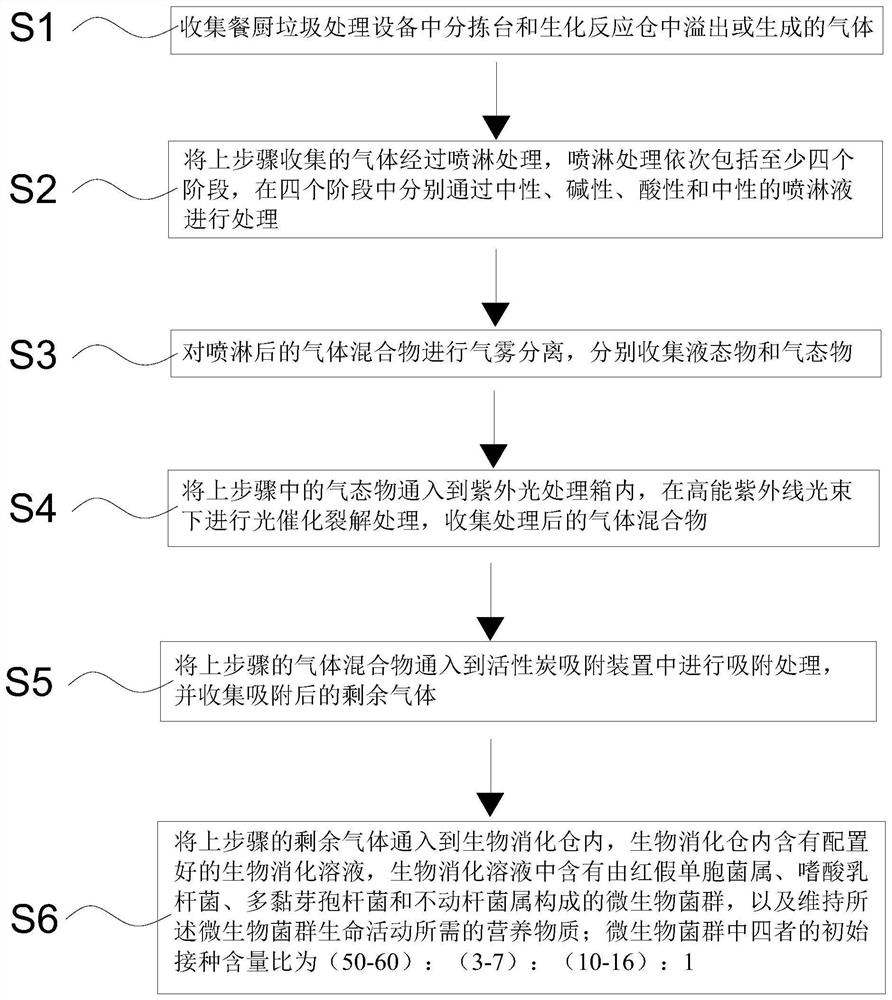
Biological digestion treatment process for odor generated by kitchen waste treatment equipment
PendingCN113648823AOdorlessTo achieve the effect of harmless dischargeGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentDigestion TreatmentUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection, in particular to a biological digestion treatment process for odor generated by kitchen waste treatment equipment. According to a treatment time sequence, the process sequentially comprises the following treatment steps: S1, gas in kitchen waste treatment equipment is collected; S2, the collected gas is subjected to spraying treatment; S3, gas-mist separation is carried out on the sprayed gas mixture; S4, the gas is subjected to photocatalytic cracking treatment under irradiation of high-energy ultraviolet light beams, and a treated gas mixture is collected; S5, the gas mixture is adsorbed, and residual gas after adsorption is collected; and S6, the residual gas in the previous step is introduced into a biological digestion bin, wherein the biological digestion bin contains a prepared biological digestion solution, and the biological digestion solution contains microbial flora composed of rhodopseudomonas, lactobacillus acidophilus, bacillus polymyxa and acinetobacter. The problems that in the kitchen waste treatment process, the odor treatment difficulty is large, the digestion efficiency is low, and the treatment cost is high are solved.
Owner:安徽坤健生物科技有限公司
Composite strain biological fluidized bed membrane reactor
ActiveCN111170470AImprove efficiencyConducive to survivalWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesBiotechnologyGenus Nitrosomonas
The invention provides a composite strain biological fluidized bed membrane reactor, which comprises a plurality of reaction tanks, a biological membrane carrier and an aeration mechanism, and is characterized in that the biological membrane carrier is provided with composite strains, and the composite strains comprise composite oil removing bacteria, composite phosphorus accumulating bacteria, composite denitrifying bacteria and composite desulfurizing bacteria. Preferably, the composite oil removing bacteria comprise bacillus, saccharomycetes and micrococcus, the composite phosphorusaccumulating bacteria comprise aeromonas, pseudomonas and acinetobacter, the composite denitrifying bacteria comprise nitrosomonas and nitrobacter, and the composite desulfurizing bacteria comprise thiobacillus, pseudomonas and acinetobacter. By the adoption of the above scheme, petroleum, gasoline hydrocarbons, phosphorus-containing substances, ammonia nitrogen, nitrites and sulfides in water can be wellremoved, rapid establishment of nitrifying bacteria, phosphorusaccumulating bacteria and desulfurization bacteria in a sewage system is promoted, and the effluent quality is improved.
Owner:杭州卡锘新材料科技有限公司
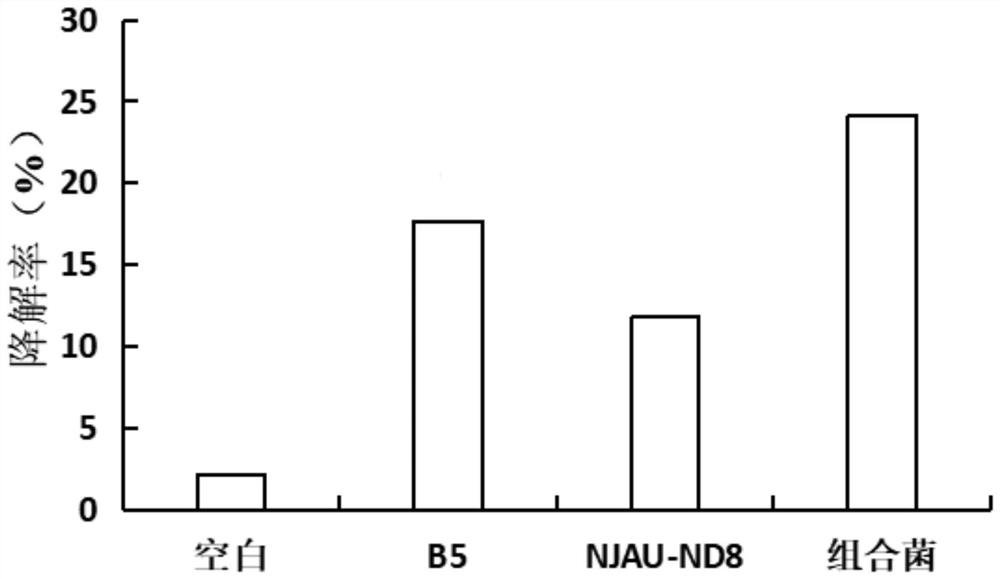
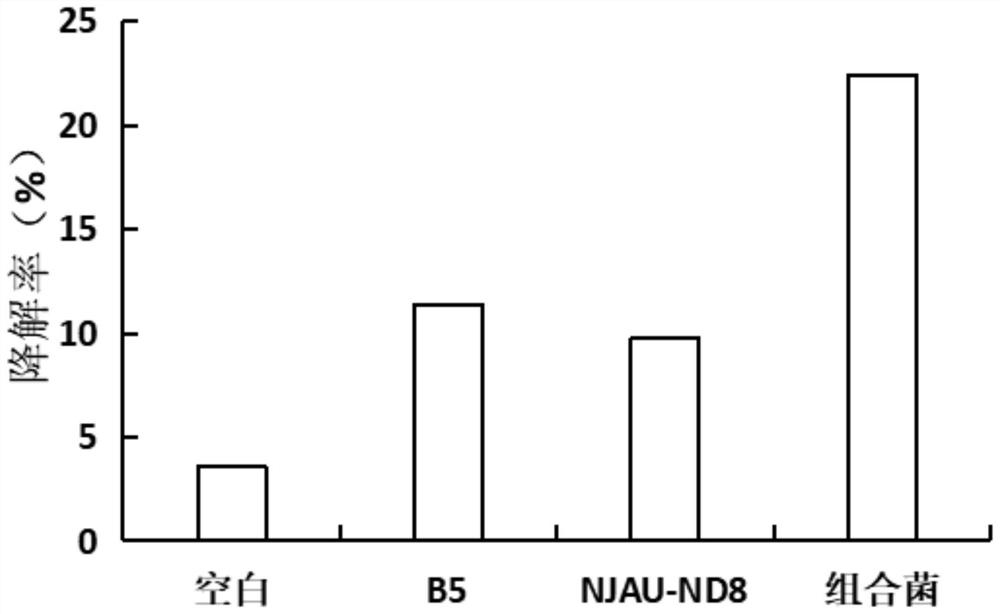
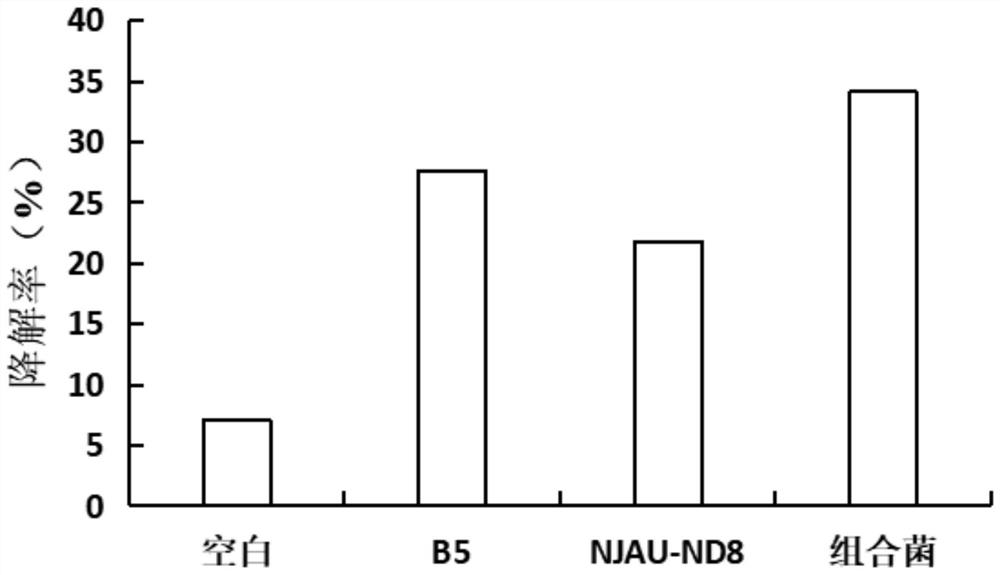
High-temperature-resistant livestock and poultry manure degradation complex microbial inoculant and application thereof
InactiveCN111849804AImprove efficiencyFully degradedBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyPoultry manure
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant livestock and poultry manure degradation complex microbial inoculant and application thereof. The invention aims to further improve the compostingeffect of livestock and poultry breeding manure, the complex microbial inoculant containing Bacillus sp. Bacteria NJAU-ND8 and Bacillus stearothermophilus is developed, and the complex microbial inoculant provides the complex microbial resource and the technical support for the livestock and poultry breeding manure. The application of the complex microbial inoculant is to accelerate degradation oflivestock and poultry breeding excrement. When the complex microbial inoculant is used for degrading the chicken manure, the degradation rate of the chicken manure reaches 24.12% after half a month,and the degradation effect is better than that of single bacteria and blank treatment; after the pig manure is degraded for half a month, the degradation rate of the pig manure reaches 22.41 percent and is better than that of single bacteria and blank treatment; after the sheep manure is degraded for half a month, the degradation rate of the sheep manure reaches 34.12 percent and is better than that of single bacteria and blank treatment.
Owner:TAICANG LVFENG BIOLOGICAL ORGANIC FERTILIZER CO LTD
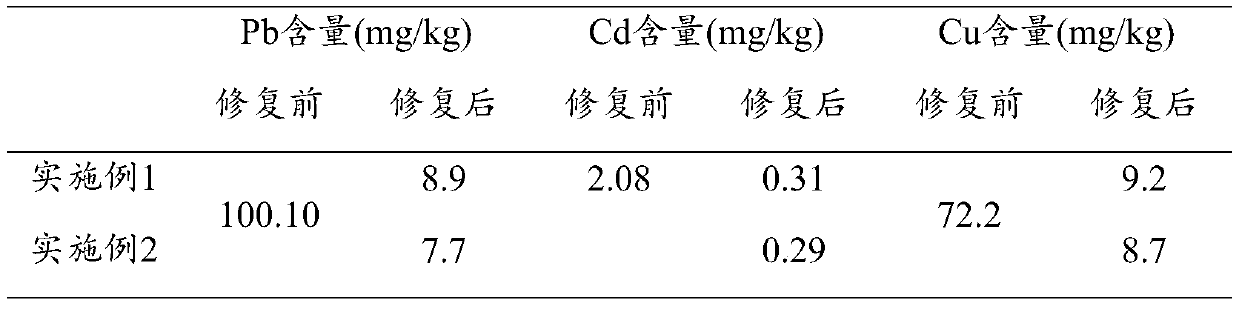
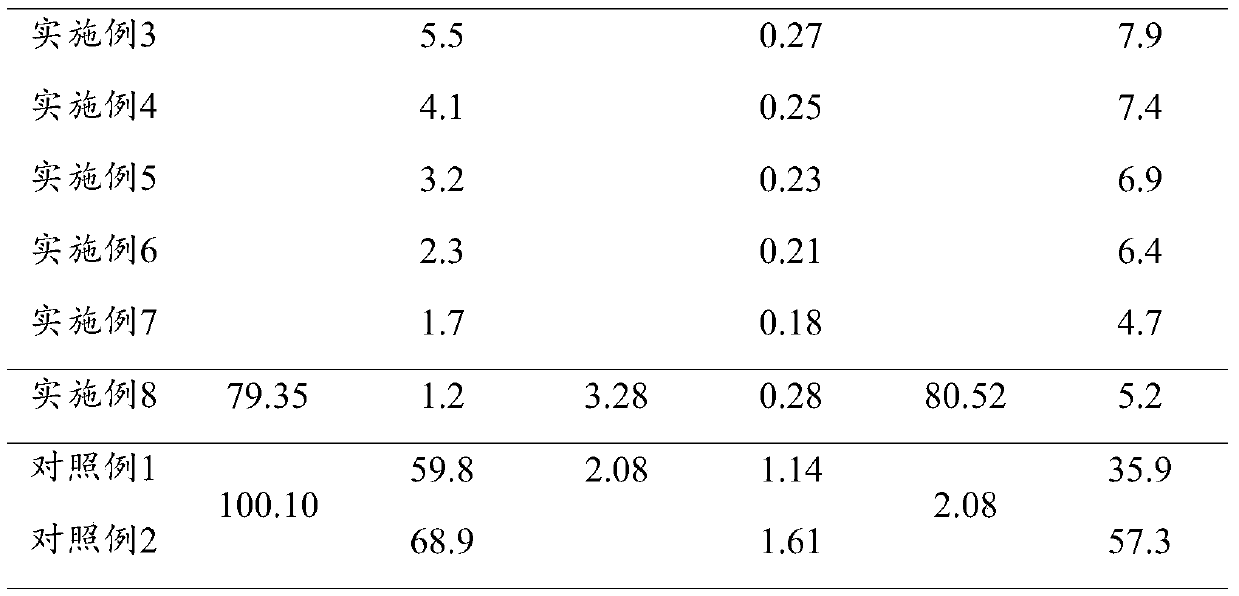
Method for repairing heavy metal polluted soil
ActiveCN110721995AImprove fertilityImprove passivation rateContaminated soil reclamationGenus LactococcusEngineering
The invention relates to a method for repairing heavy metal polluted soil. The repairing method comprises the following steps: mixing biochar into soil, performing culturing for 30-40 days, adding bacterial liquid and calcium phosphate into the soil, and continuing culturing for 60-90 days, wherein the adding amount of the biochar is 1.5-2.5g in each cubic meter of the soil, the adding amount of the bacterial liquid is 20-50L in each cubic meter of the soil, the concentration of the bacterial liquid is (2-3)*10<8> CFU / mL, the adding amount of the calcium phosphate is 5-8g in each cubic meter of the soil, and the bacterial liquid comprises at least one selected from enterobacter, bacillus and lactococcus. The method is environmentally friendly and ecological, the removal rate is artificially controllable, cost is far lower than cost of the prior art, operability is greatly higher than operability of the prior art, and a good heavy metal passivation effect can be achieved. In addition, fertility of original soil can be kept, and even fertility can be improved.
Owner:云南中钛科技有限公司
Environment-friendly deodorization device and method for kitchen wastewater
ActiveCN112499770AReduce generationEffective temperature controlGas treatmentWater contaminantsCelluloseCitrobacter
The invention discloses an environment-friendly deodorization device and method for kitchen wastewater. The environment-friendly deodorization device comprises a deodorization tank, a microbial agentmixing unit and a tank body heating unit, a feeding channel communicating with the interior of the deodorization tank is obliquely arranged on the side face of the top of the deodorization tank upwards, the microbial agent mixing unit is installed on the feeding channel, and a mixed microbial agent used for degrading starch, protein, grease and cellulose is contained in a microbial agent containing box of the microbial agent mixing unit. The mixed microbial agent is prepared from dried bacillus, citrobacter and lactobacillus. Main components including starch, protein, grease and cellulose in the kitchen wastewater are degraded by using the mixed microbial agent of bacillus, citrobacter and lactobacillus. A mechanical temperature control module can effectively control a proper temperature,so that the mixed microbial agent is promoted to degrade two odors including ammonia gas and hydrogen sulfide at the same time at the proper temperature, and odor generation can be reduced, and odor can also be degraded.
Owner:诸暨市男宇针织厂
A kind of biological emulsifier and its application
ActiveCN106701835BGood degreasing effectReduce oil contentWaste water treatment from quariesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Anode photosynthetic solar fuel cell system additionally provided with degrading strain and application thereof
InactiveCN111430766AAchieve absorptionDual useContaminated soil reclamationBiochemical fuel cellsComamonasCell system
The invention discloses an anode photosynthetic solar fuel cell system additionally provided with degradation strains and application thereof. According to the anode photosynthetic solar fuel cell system, at least one of additionally added degrading bacteria, namely comamonas or bacillus, is added, and the abundance of electrochemical active microorganisms in soil is improved in a manner of externally connecting the degrading strain so that the capability of degrading surrounding environmental pollutants is improved, and the system has a good application prospect in treating Cr and NO3-N pollution in the soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
High-concentration organic wastewater treatment system and method
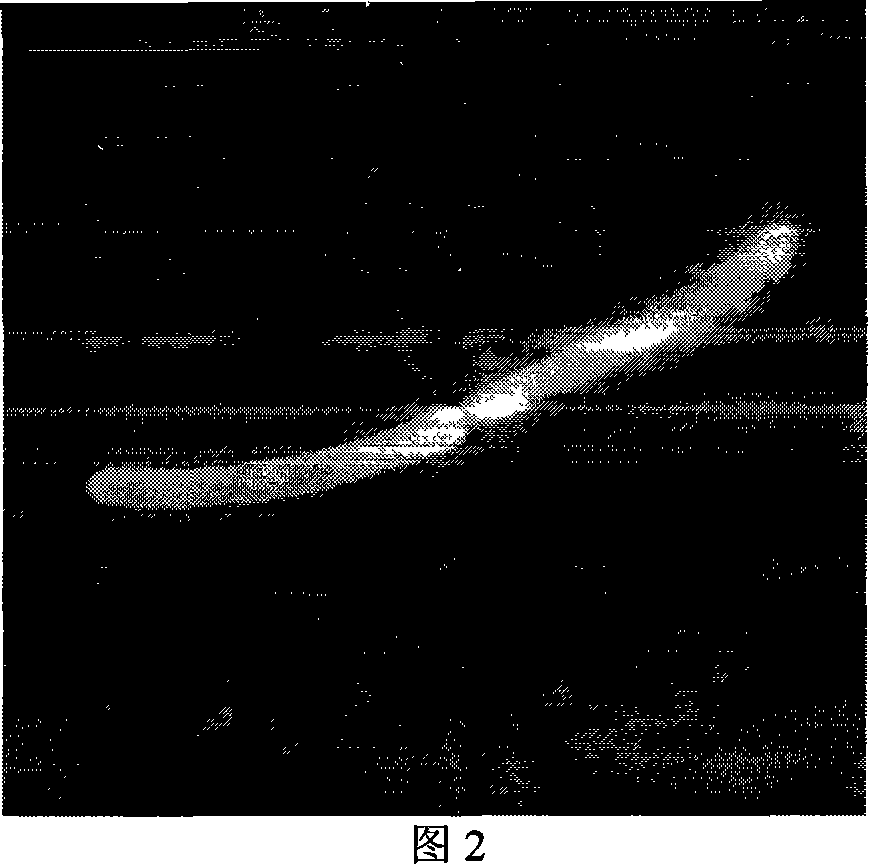
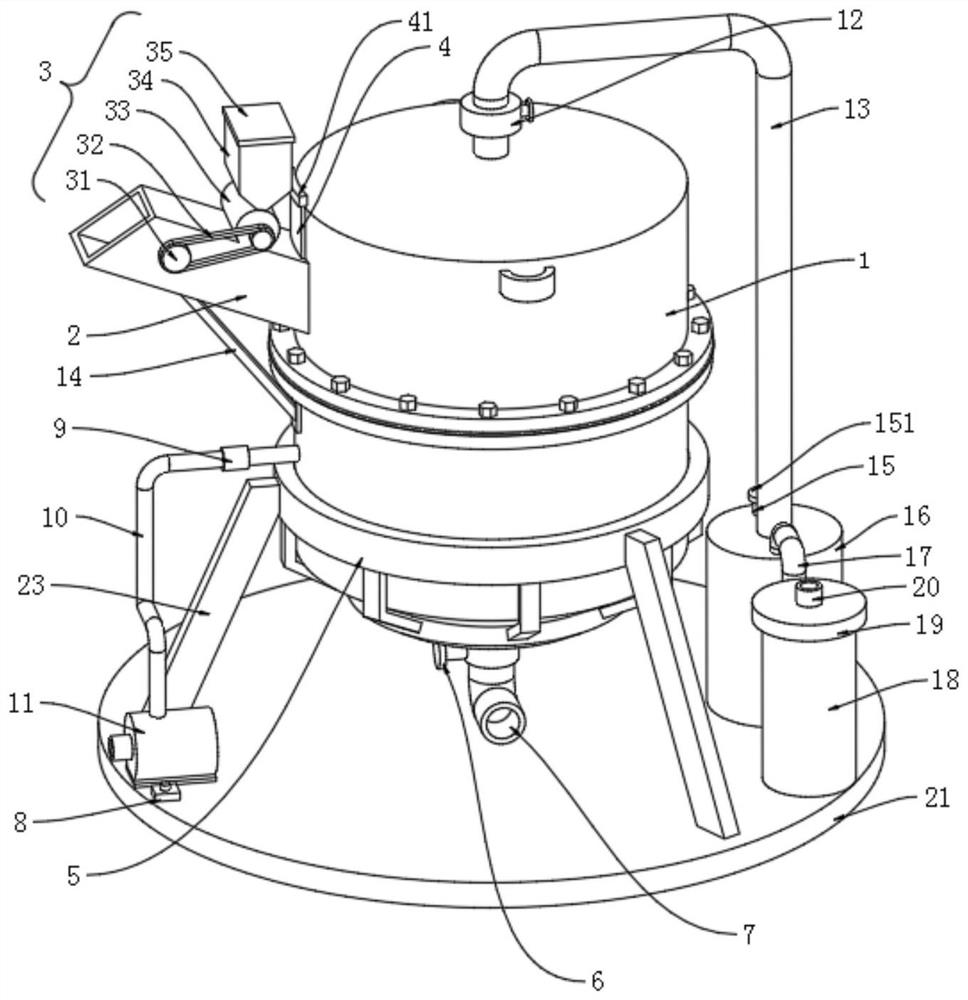
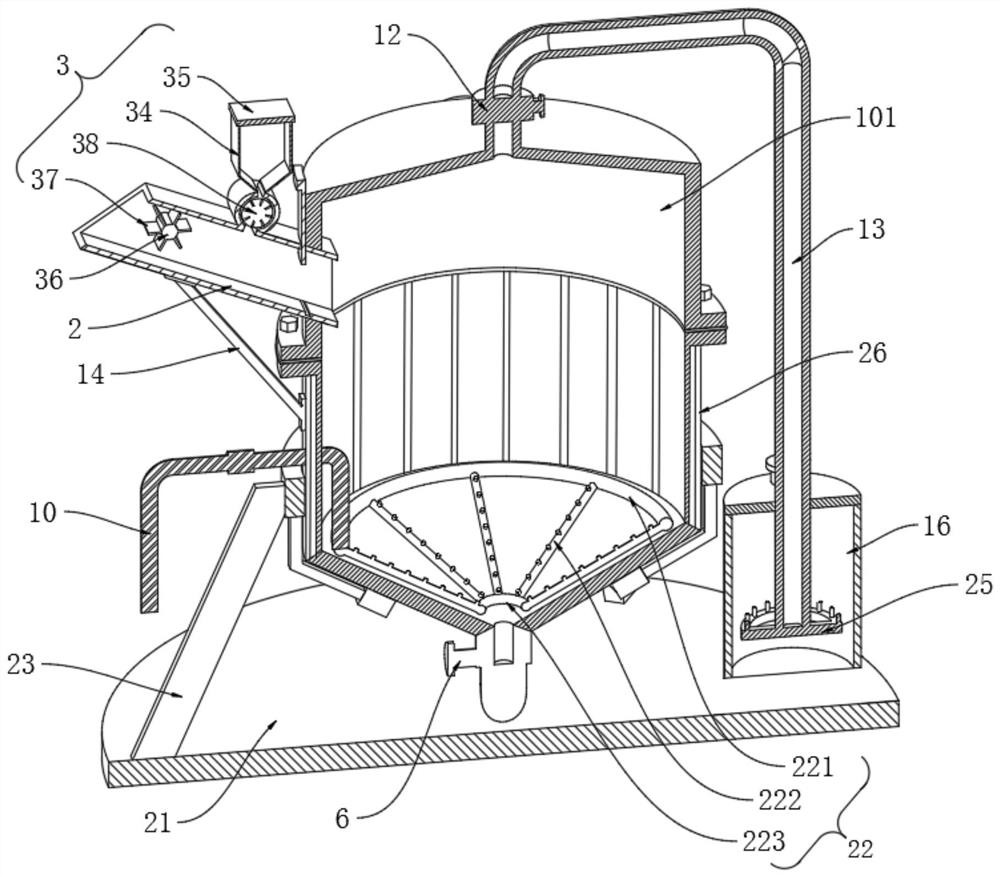
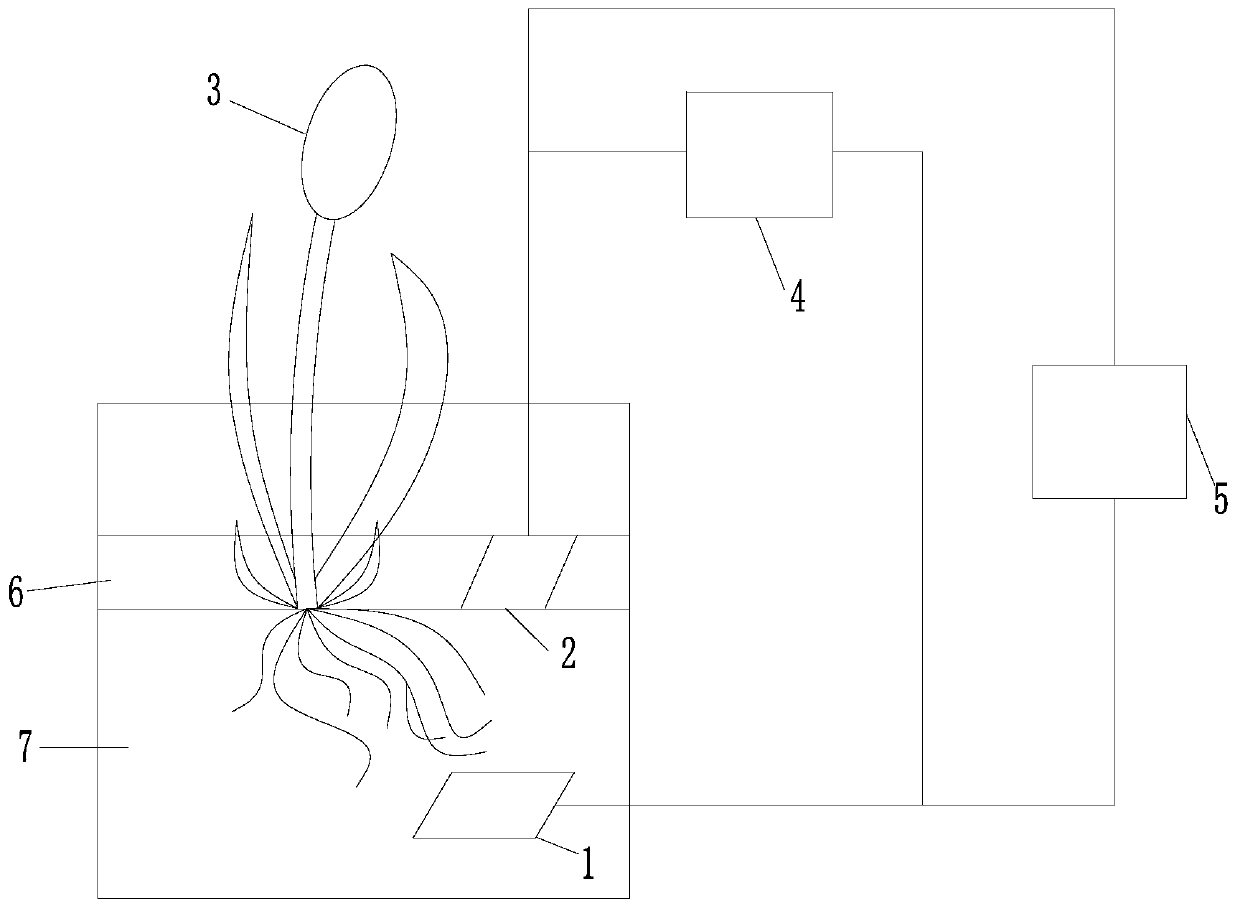
PendingCN111470711AImprove application stabilityReduce the attachment loadWaste water treatment from animal husbandryTreatment involving filtrationBiofilmBacillidium
The invention discloses a high-concentration organic wastewater treatment system and a method. The system comprises a mixing tank, wherein a nutrient solution and a carbon source are added into the mixing tank, and the mixing tank is used for mixing upstream sewage to be treated, the nutrient solution and the carbon source; a biological reaction device which is arranged at the downstream of the mixing tank, wherein a bacillus microbial film is attached to a carrier of the biological reaction device, and the biological reaction device is used for preliminarily removing COD, NH4<+>-N and TN in the to-be-treated sewage; an aeration tank which is arranged at the downstream of the biological reaction device, wherein a nutrient solution and a carbon source are added into the aeration tank, florataking bacillus microorganisms as dominant strains is added into the aeration tank, and the flora is used for removing residual COD, NH4<+>-N and TN in the to-be-treated sewage; and an aeration mechanism which is used for providing required dissolved oxygen for the aeration tank and purging a carrier of the biological reaction device. The method is implemented based on the system. The construction cost and the to-be-treated sewage treatment cost are reduced, and it can be guaranteed that effluent obtained after high-concentration organic wastewater is treated reaches the standard required bysubsequent treatment.
Owner:HKY TECH
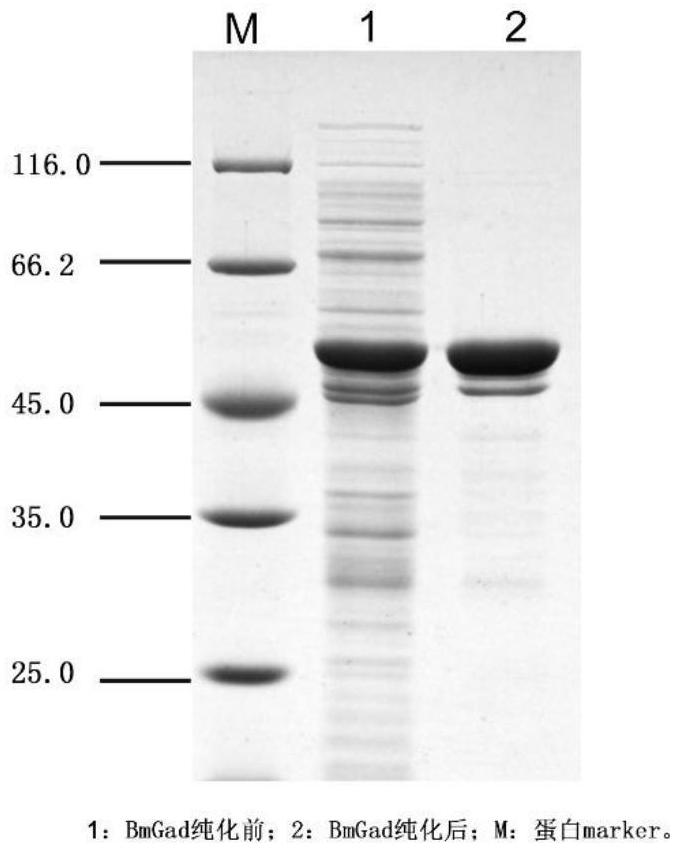
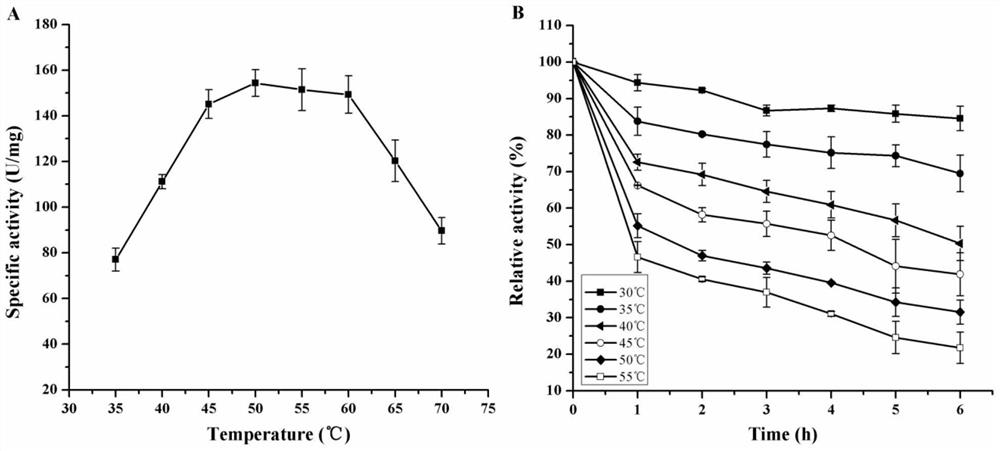
Cloning and Application of a Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Gene
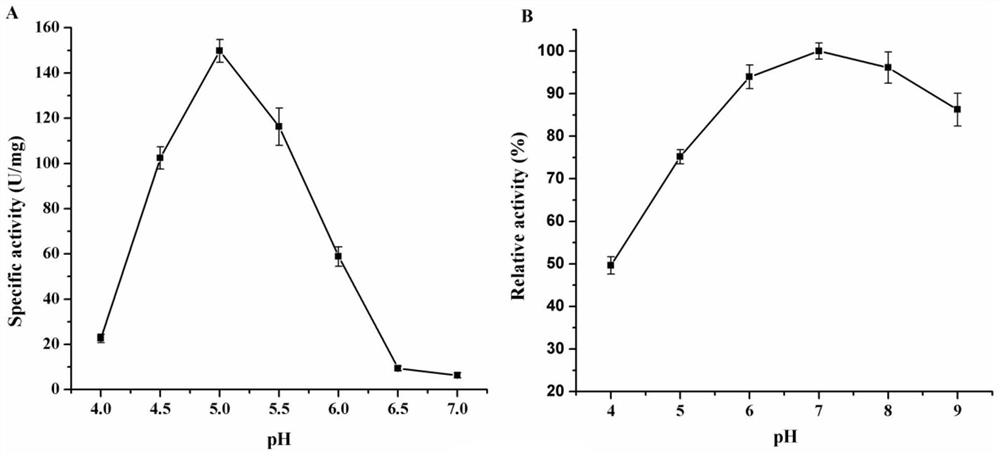
The present invention relates to the cloning and application of a novel glutamic acid decarboxylase gene. The glutamic acid decarboxylase obtained from Bacillus is induced and expressed in Escherichia coli and its properties are studied. It is found that the enzyme has a pH of 4.0 It has higher activity at ~pH6.0, the optimum temperature is between 45℃~60℃, Vmax is 150~200 U / mg, and Km is 7~9 mmol / L. The recombinant Escherichia coli containing the enzyme was transformed into whole cells, and 500 g / L L-glutamic acid was added by fed-batch feeding, at 37°C, in disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 After 12 h of conversion, 347.8 g / L of γ-aminobutyric acid was finally produced, and the molar conversion rate was 99.4%. Compared with the existing glutamic acid decarboxylase, the novel glutamic acid decarboxylase has higher catalytic efficiency and wider pH range, and is more suitable for industrial application.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Lipase inhibitor from natto, preparation method and use thereof
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis microorganism, in particular relates to a lipase inhibitor of Bacillus subtilis natto, a preparation method and the function thereof. The lipase inhibitor is prepared by the following steps of: activating and culturing the Bacillus subtilis natto, preparing a component for inhibiting the activity of the lipase by solid fermentation or liquid fermentation, i.e., the culture of natto lipase inhibin, extracting and separating, and eventually preparing the lipase inhibitor. The invention achieves the purpose of reducing weight and fat by inhibiting the activity of the lipase, which has the novelty that: (1) the lipase inhibitor derived from edible natto has no side effects to human body; and (2) the lipase inhibitor selectively acts on gastrointestinal tract lipase, especially on pancreatic lipase without inhibiting prolease, amylase and the like.
Owner:BEIJING WBL PEKING UNIV BIOTECH
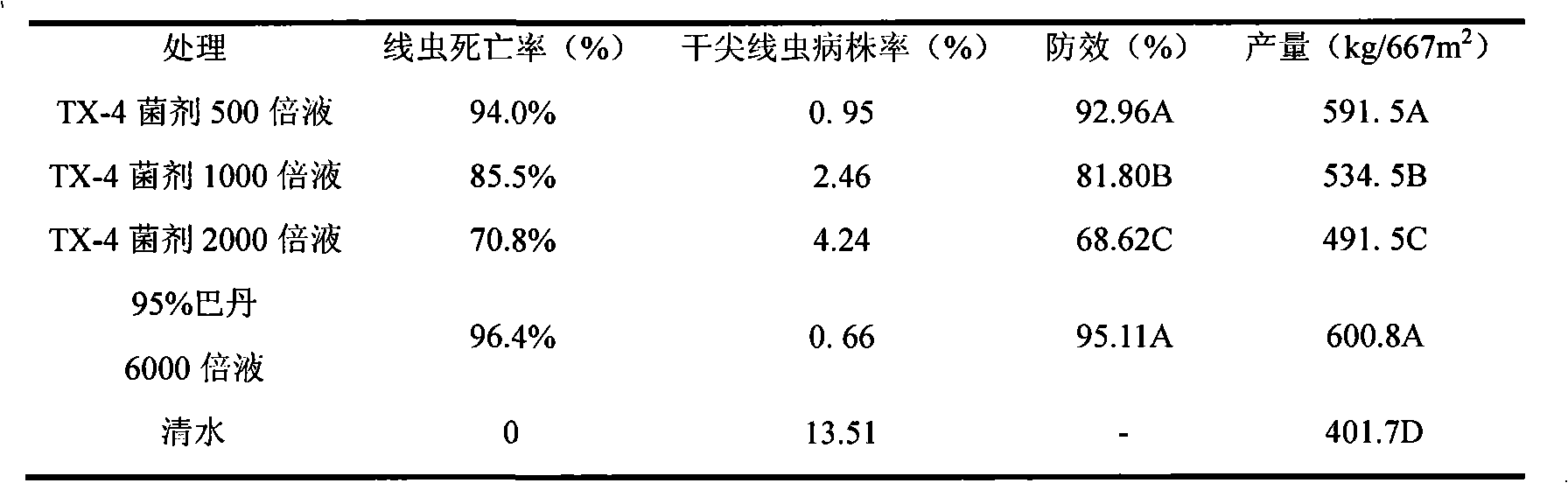
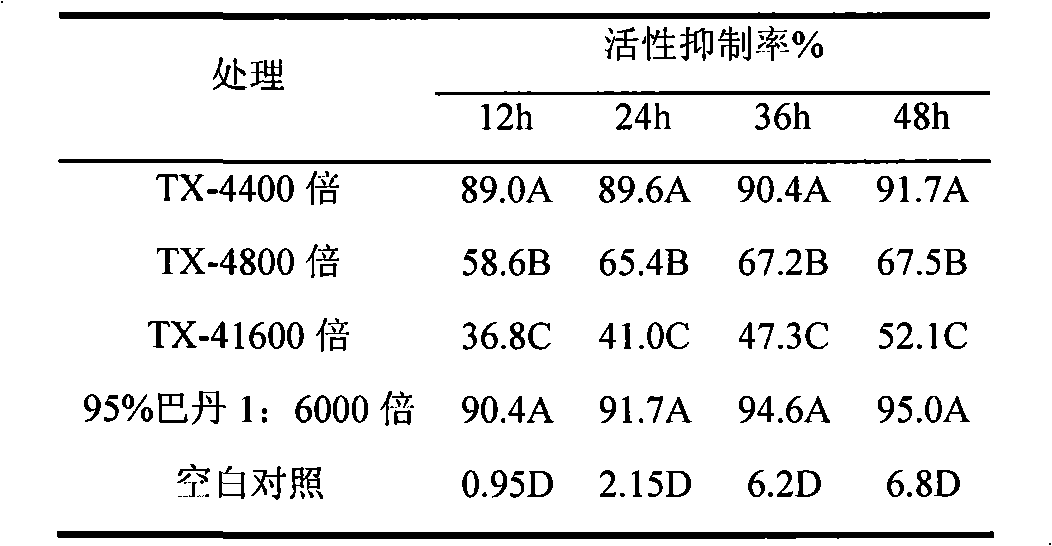
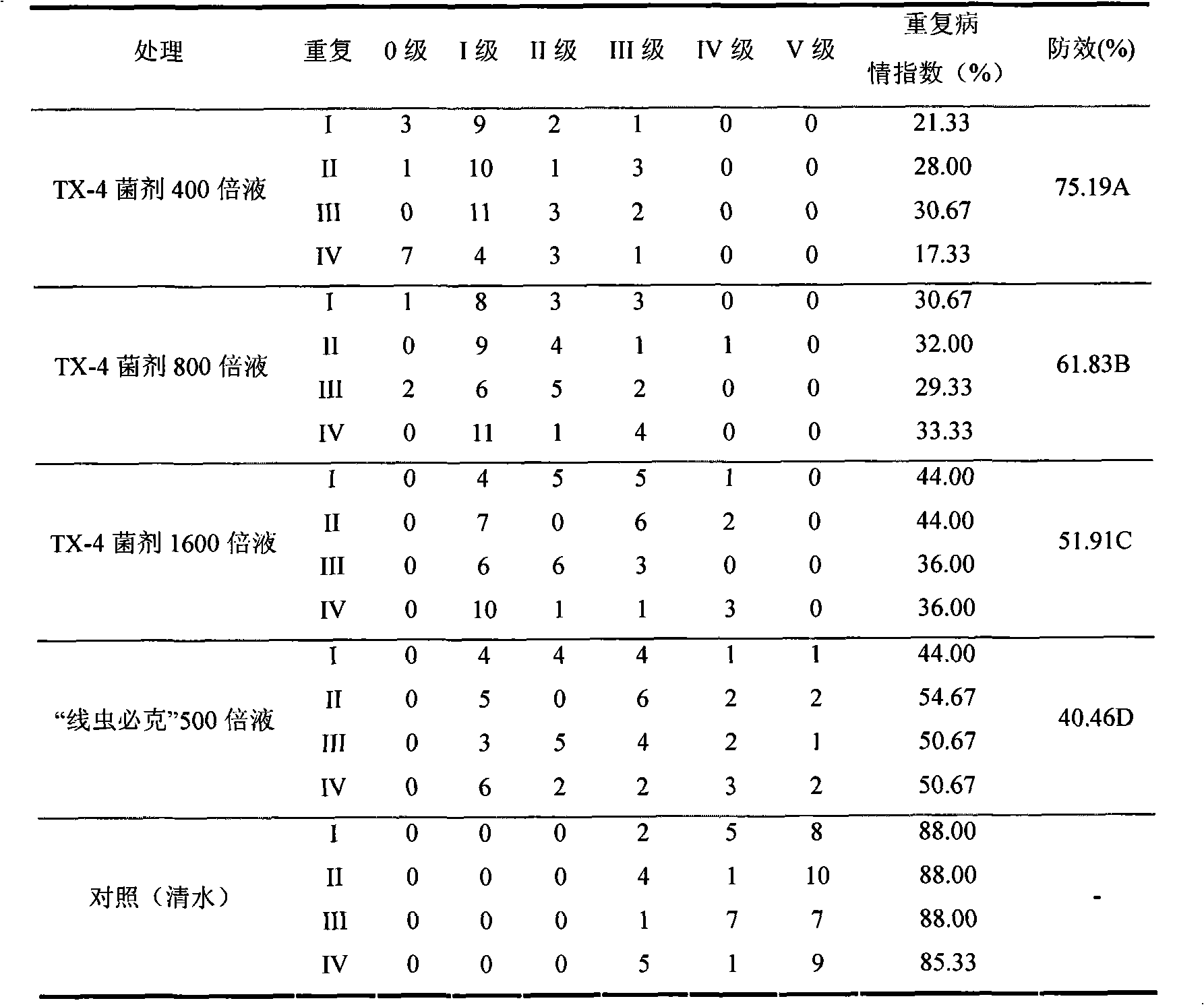
Strain TX-4 used for preventing aphelenchoides besseyi or vegetable root knot nematode and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a strain TX-4 used for preventing diseases of aphelenchoides besseyi or vegetable root knot nematode and a preparation thereof, belonging to the technical field of preventing and treating diseases of crops and being specially used for biological prevention of the crops. The prevention result of field demonstration shows that the strain has the preventing effect of more than90 percent to the aphelenchoides besseyi disease and has preventing effect of more than 70 percent to the vegetable root knot nematode disease. The strain TX-4 for preventing diseases of aphelenchoides besseyi or vegetable root knot nematode is bacillus with the Latin systematic name of Paenibacillus spp., the strain has been preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 19, 2009and the preserving number is CCTCC No: M209038.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
A kind of biological fertilizer for efficiently degrading atrazine and its preparation method
ActiveCN105967943BImprove adaptabilityImprove stabilityBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersBacillus licheniformisNutrition
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of aquaculture pond sediment heavy metal stabilizer, its preparation method and application
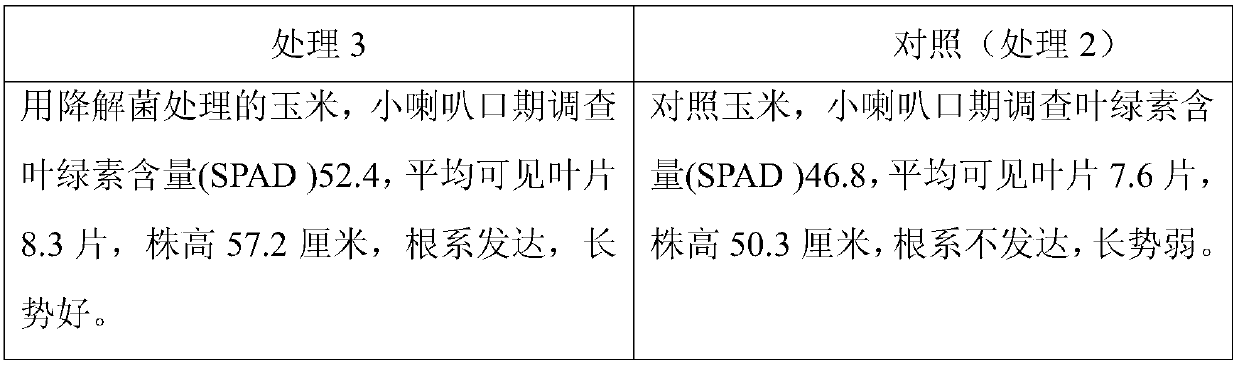
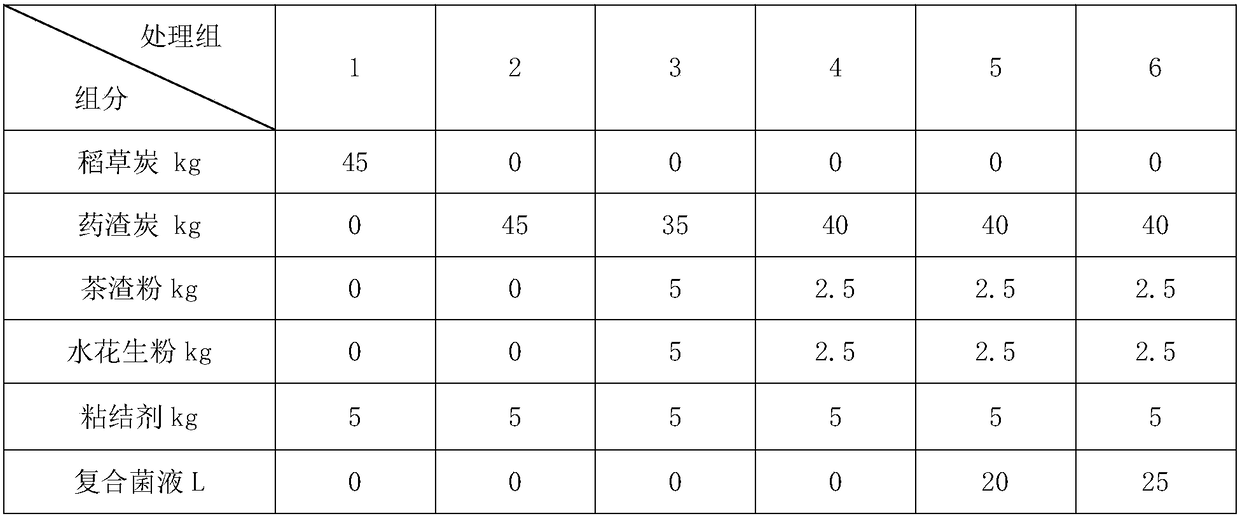
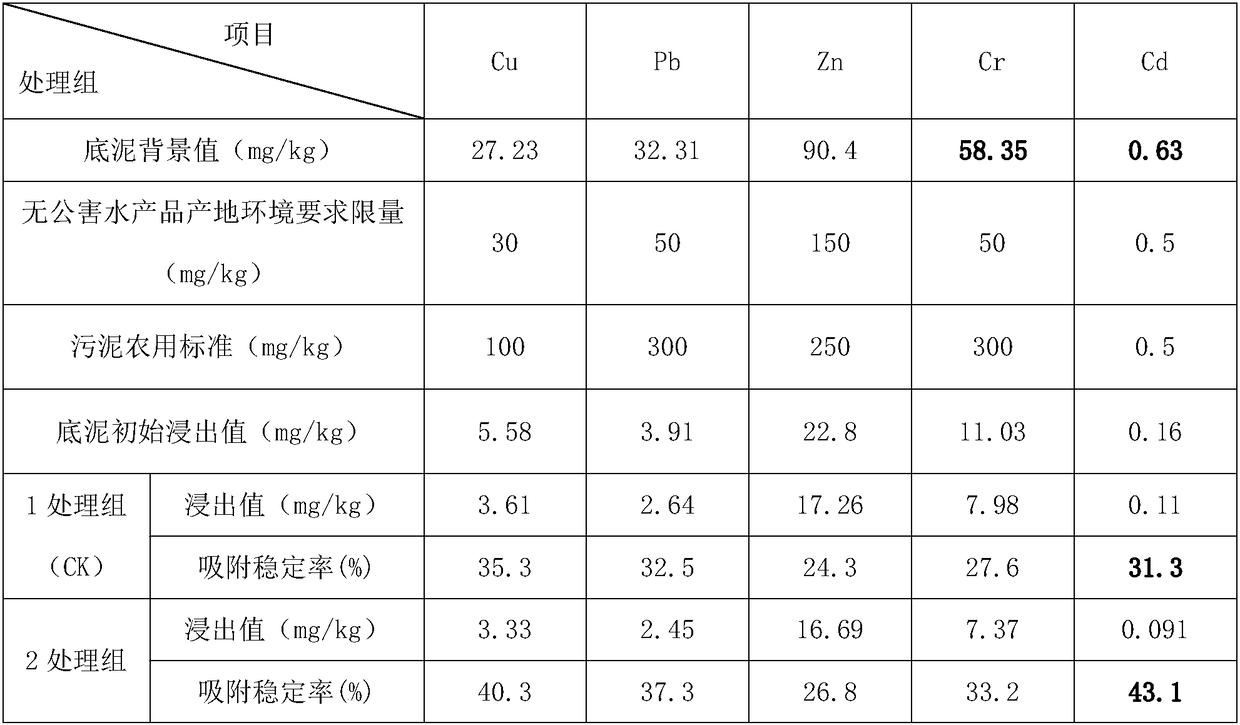
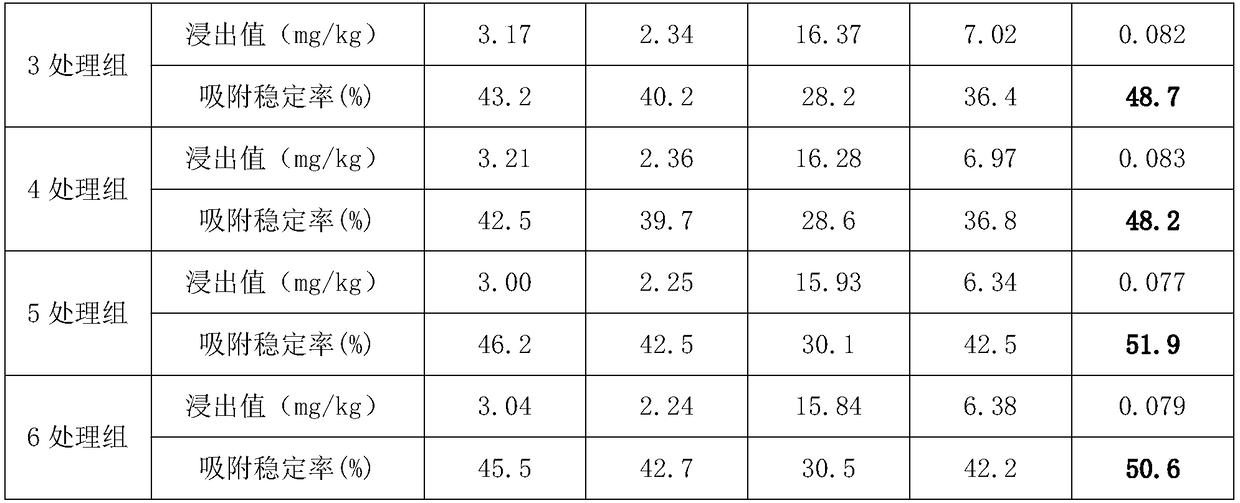
ActiveCN107935339BImprove adsorption capacityFull of nutritionFungiBacteriaMicrobial agentSoil heavy metals
A stabilizer for heavy metals in the sediment in an aquaculture pond. The stabilizer comprises a microbial carrier and a composite microbial agent loaded on the microbial carrier, the microbial carrier being a mixture of Mailuoning herb residue biomass carbon powder, tea residue powder, Alternanthera philoxeroides powder, and a binder; a composite active bacterial liquid is obtained by mixing a sediment sample and deionized water so as to obtain a supernatant diluent, carrying out culturing so as to obtain a seed solution of Bacillus and yeast, adding an EM active bacterial liquid, and carrying out culturing under the condition of aerobic fermentation. The preparation method comprises: (1) converting Mailuoning herb residues into biomass carbon at a high temperature, and then mixing the biomass carbon with raw materials so as to obtain a microbial carrier; and (2) loading a composite microbial agent onto the microbial carrier. The sediment stacked with the heavy metal stabilizer and then fermented can be used as a base fertilizer and applied to soil, so that the fertility of the soil is improved; the effectiveness of heavy metals in the soil is reduced; the amount of an inorganic fertilizer used is decreased; the yield and quality of crops are improved. Also disclosed are a method for preparing a stabilizer for heavy metals in the sediment in an aquaculture pond, and an application of the stabilizer.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
A method for spraying Robinia pseudoacacia on exposed rock walls of shale with high efficiency and rapid regreening and improving soil pH
ActiveCN110521323BPH improvementRaise the pHOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersEdaphicFabaceae
The invention discloses a method for spraying black locust on exposed rock walls of shale for efficient and rapid regreening and improving soil pH, and belongs to the technical fields of ecological restoration and soil improvement. The guest soil spraying method is used to spray mixed microorganisms, organic fertilizers, and soil on the exposed shale rock wall, and the greening plant is black locust, so as to achieve efficient and rapid regreening and improve soil pH. The mixed microorganisms are composed of Koukia X-22, Microbacterium X-26, Bacillus X-28, and Microbacterium X-18, and the mixed microorganisms are added to organic fertilizer and soil as fermentation broth. The weight ratio of the mixed microorganisms, organic fertilizer and soil is 1:1:8. This method realizes the synergy between microbial flora and leguminous nitrogen-fixing bacteria, promotes the rapid growth of Robinia pseudoacacia on the exposed shale rock wall, can significantly increase the organic matter content, available phosphorus content, and pH value of Robinia pseudoacacia soil, improve soil fertility, and reduce the application of chemical fertilizers. It can provide a low-cost, high-efficiency new method for efficient and rapid regreening of shale exposed rock walls.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
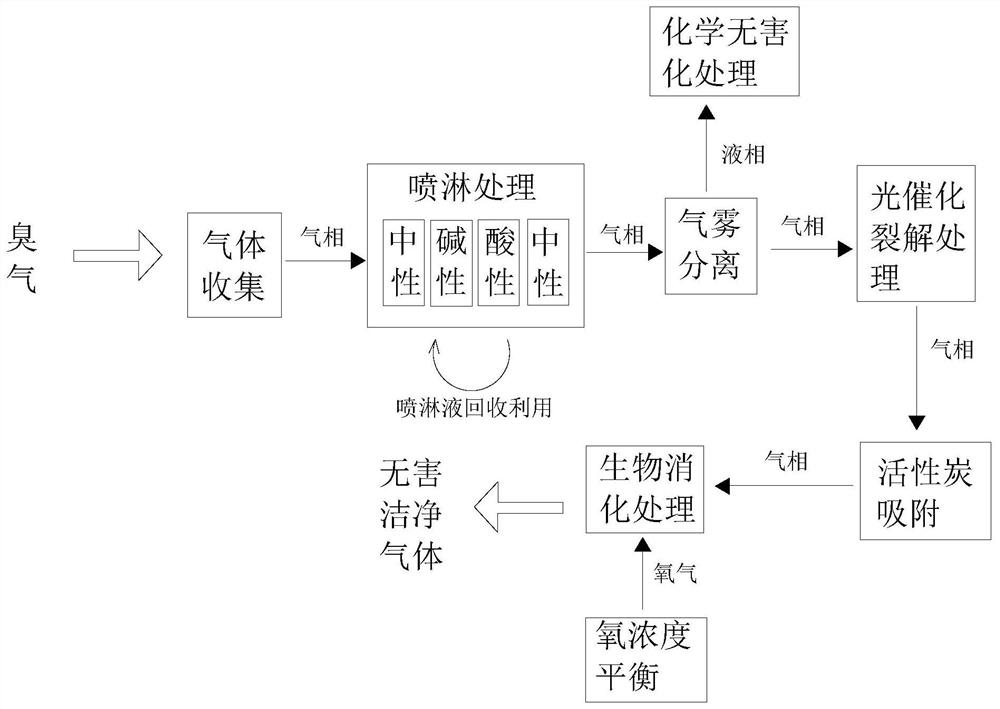
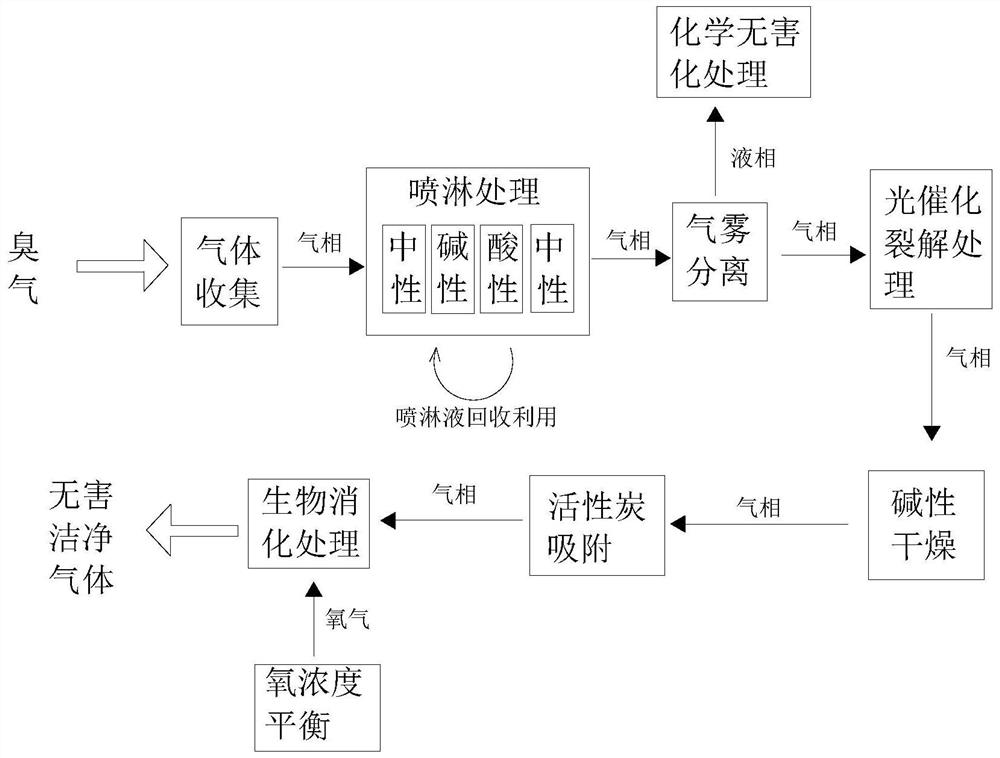
Odor treatment system for recycling organic wastes
PendingCN113634103AEasy to handleEasy to deodorizeGas treatmentDispersed particle separationEnterobacter agglomeransMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of nondestructive testing, in particular to an odor treatment system for recycling organic wastes. The odor treatment system comprises a gas collection mechanism, at least two ultraviolet photolysis purifiers, a washing tank, an adsorption bin, a biological digestion bin, a sterilization device and a controller. The two ultraviolet photolysis purifiers are installed at the rear section of an air collecting opening side by side. The washing tank comprises an alkaline tank and an acid tank. The adsorption bin is installed at the rear section of the washing tank and comprises a shell and an adsorption filler therein. The biological digestion bin is mounted at the rear section of the adsorption bin, and a biological digestion solution is contained in the biological digestion bin. The biological digestion solution comprises a microbial flora consisting of enterobacter agglomerans, lactobacillus acidophilus, bacillus polymyxa and acinetobacter. The sterilization device is used for sterilizing tail gas discharged from a discharge opening. The problem that an existing deodorization process for a composting site is not thorough in deodorization, can hardly deal with a scene with large-flow odor gas and is low in odor treatment efficiency is solved.
Owner:安徽坤健生物科技有限公司
Method for recovering and utilizing metal resources by using Bacillus extracellular polymer
ActiveCN110759454BEasy to trainSimple extraction methodFungiWater contaminantsBiotechnologyCentrifugation
The invention discloses a method for recovering and utilizing metal resources by utilizing the extracellular polymer of bacillus, and relates to the technical field of resource utilization and recovery. The present invention includes the extraction of microorganisms belonging to the genus Bacillus, which is extracted through the following steps: S1: After the bacillus is activated and cultivated by using a solid medium, it is inoculated into a liquid fermentation medium with a pH value of 7-8, and placed in an environment of 23-25°C fermentation and culture to obtain microbial fermentation broth; S2: place the microbial fermentation broth in an environment of 5-7°C for centrifugation, take the supernatant and filter, and freeze-dry the filtrate to obtain EPS powder; the EPS powder includes s- EPS powder, LB-EPS powder, TB-EPS powder; the present invention utilizes the aforementioned Bacillus microbial extracellular polymer to recycle and / or degrade and / or transform heavy metal ions and rare precious metals in wastewater and / or soil; In order to realize the purpose of developing an eco-friendly method for resource processing and recycling of heavy metals and rare and precious metals.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Polypeptides and nucleic acids encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides and isolated nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptides, as well as methods for producing and using the polypeptides in animal feed. An example of a polypeptide of the invention is the so-called L12 protein from Bacillus lichen form is ATCC 14580 which improves the Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) and / or acts as a gut microflora modulator. The invention furthermore relates to the probiotic use of strains of Bacillus which produce proteins related to L12.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Oilfield produced water treatment process for removing oil by using oil-degrading flora
InactiveCN112374701AWaste water treatment from quariesSpecific water treatment objectivesBacillus licheniformisUltrafiltration
The invention discloses an oilfield produced water treatment process for removing oil by using oil-degrading flora. The process comprises the following steps: S1, extracting three-phase separator produced water of an oilfield, inputting the produced water into a settling tank, and standing for 8-12 hours to settle large-particle impurities in sewage; S2, adding a biological agent into a microbialpool, wherein the biological agent comprises bacillus licheniformis, brevibacillus and pseudoxanthomonas, and the compounding ratio is 2:1:1; S3, introducing the effluent of the microbial pool into aninclined plate sedimentation pool; and S4, enabling the effluent to enter a membrane filter, so that the effluent reaches the oilfield flooding water quality standard. According to the invention, sulfide is removed by utilizing a high-ventilation-rate rotary mixing aerator at the front end of a microbial pool, emulsified oil and floating oil in sewage are decomposed by utilizing oil-degrading bacteria, then the sewage enters an inclined plate sedimentation pool to separate suspended dirt in the water, finally the sewage enters a hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane, and effluent after passing through a membrane filter can meet the requirements of Water quality standard and practice for analysis of oilfield injecting waters in clastic reservoirs (SYT 5329-2012) II.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Alkaline xyloglucanase
InactiveCN1177928CInhibit bindingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisNucleotide
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com