Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
577results about How to "Increase available space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
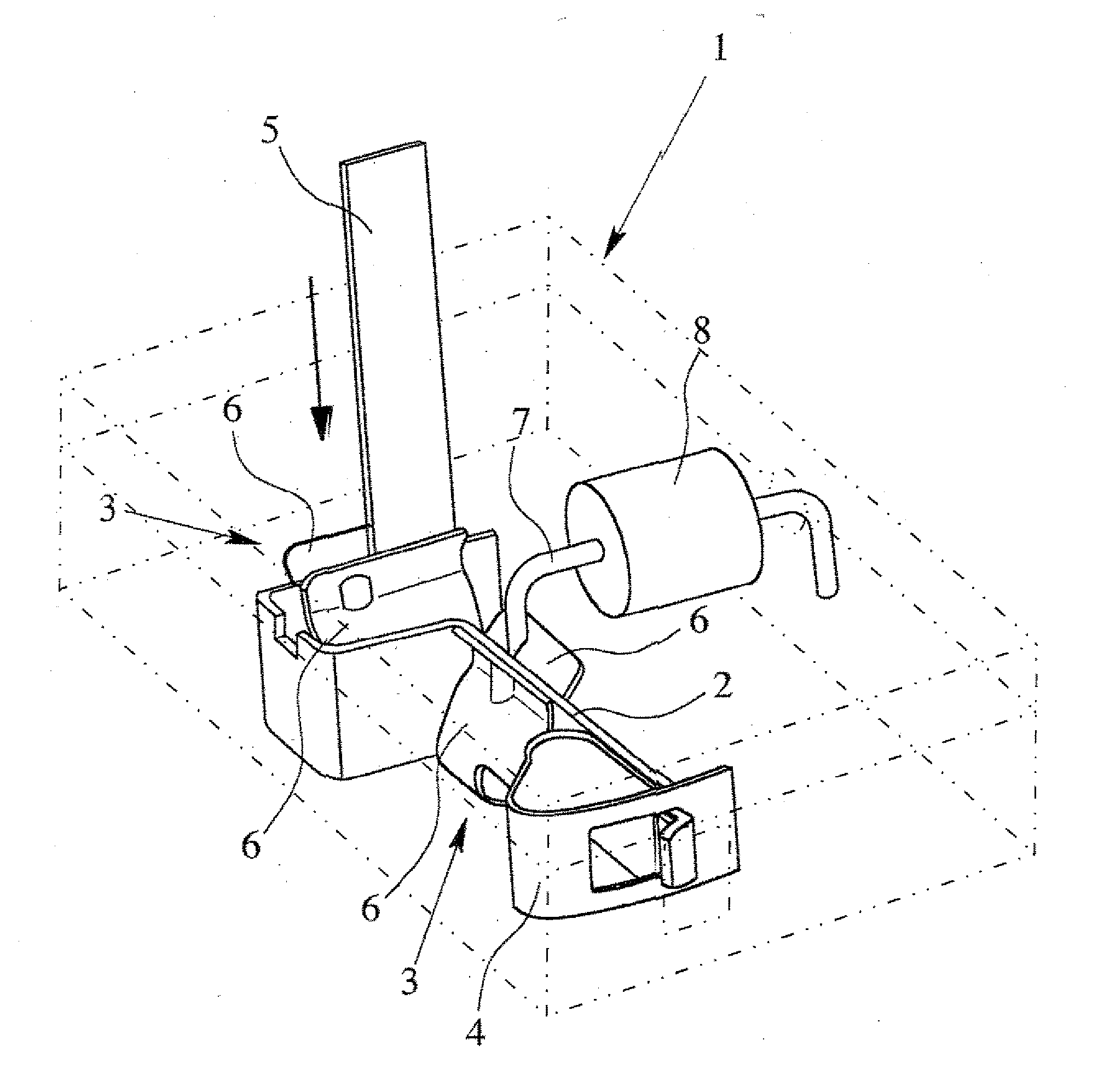
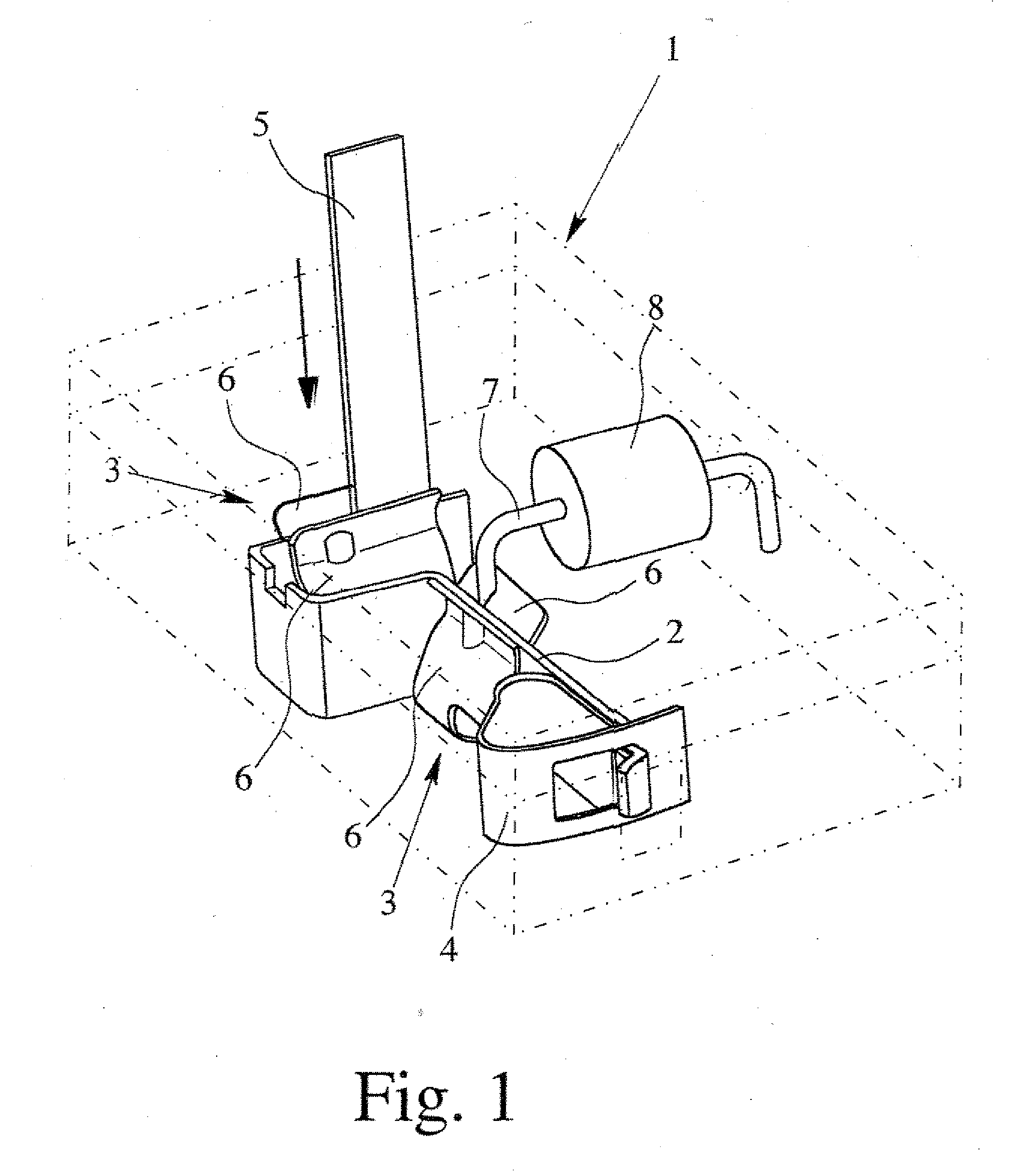
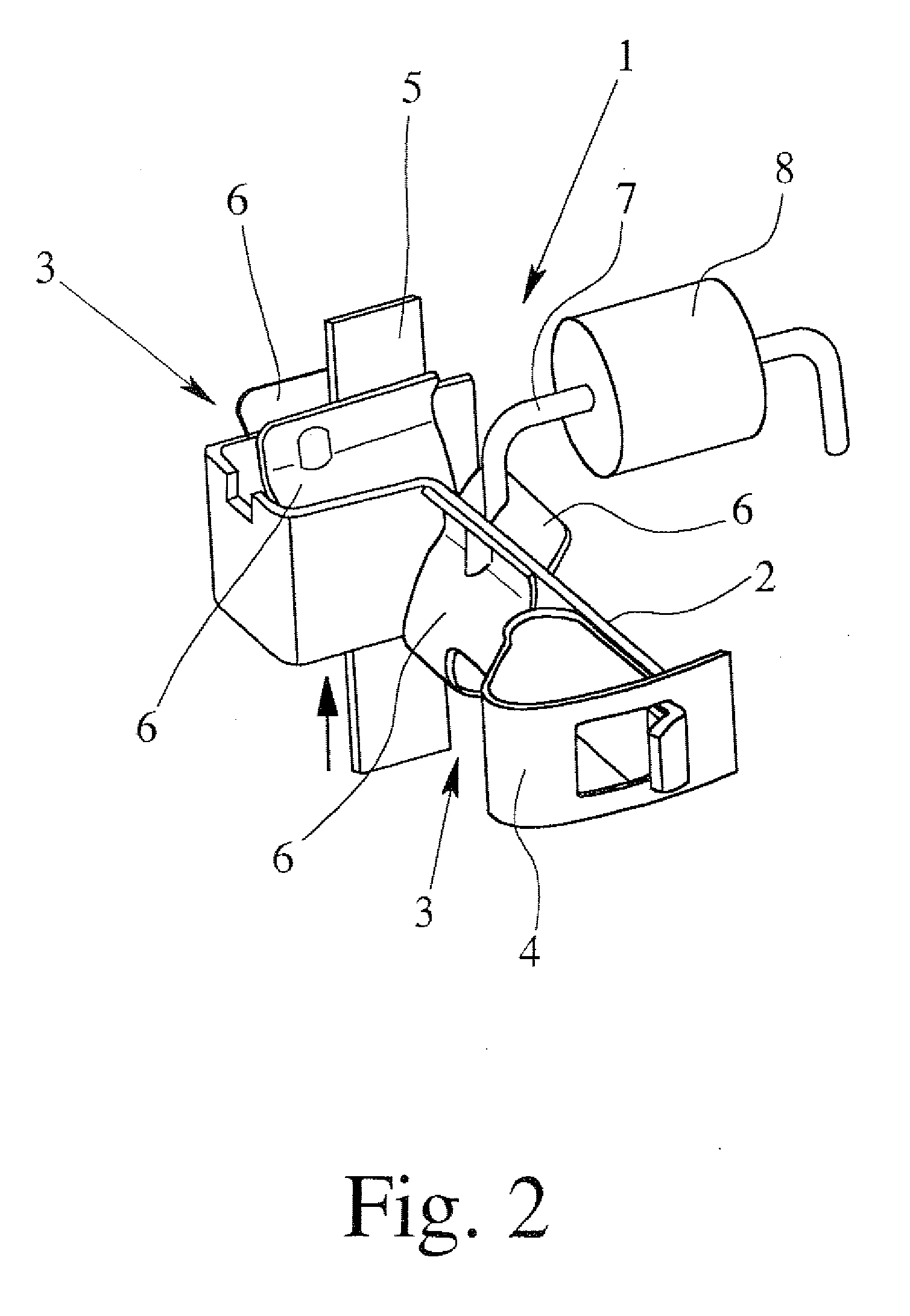
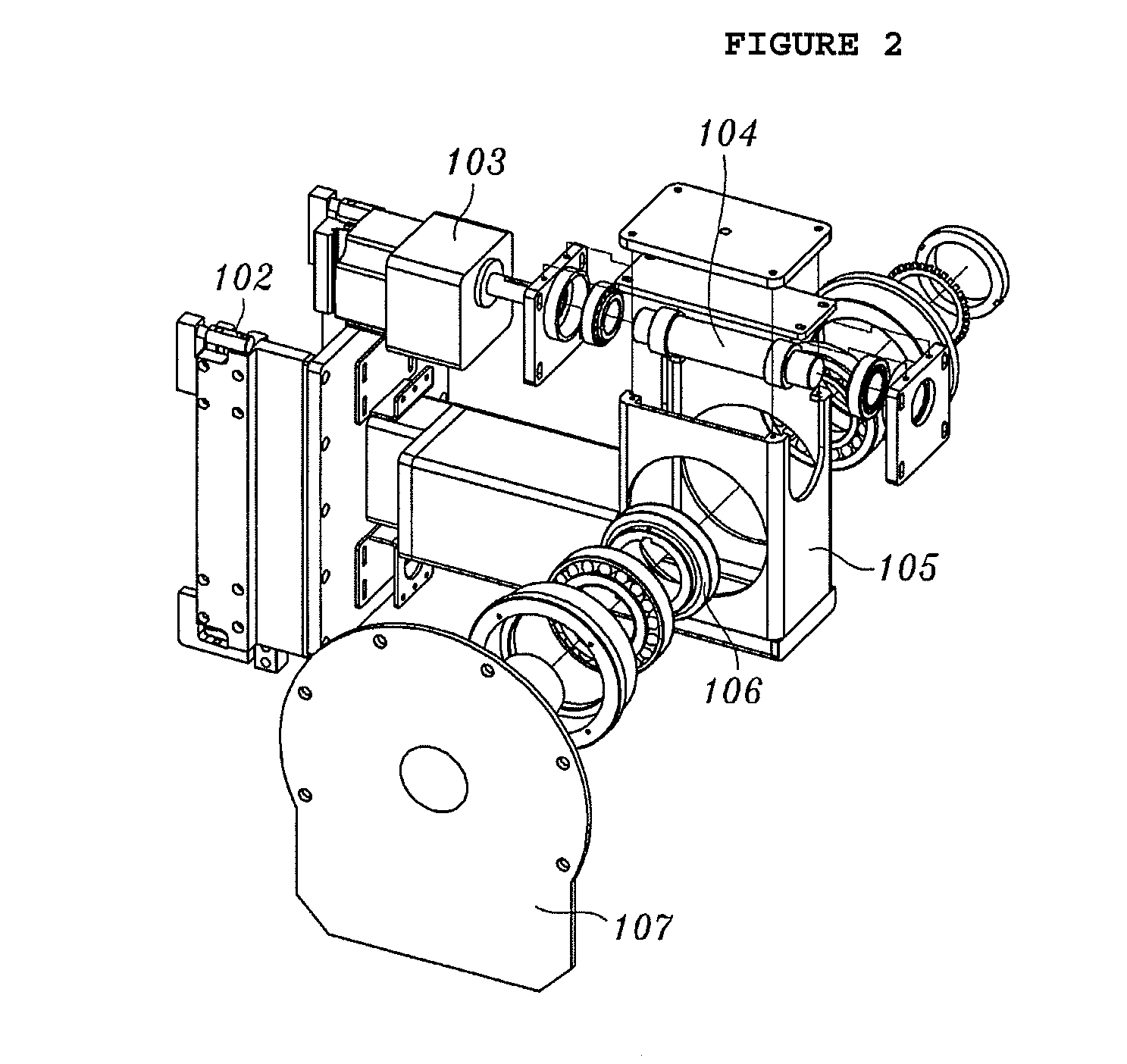
Burnishing head
InactiveUS7314404B2Less time for to recoverIncrease heightRevolution surface grinding machinesFluid-dynamic spacing of headsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A burnishing head comprises at least two rails, each rail having an inner wall and an outer wall. The outer walls are at an angle relative to one another and relative to a central axis of the burnishing head. This angle permits the burnishing head to exhibit improved recovery time if it contacts a disk being burnished. The rail walls are vertical, and the corner between the rail walls and the top surface of the rails is sharp.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
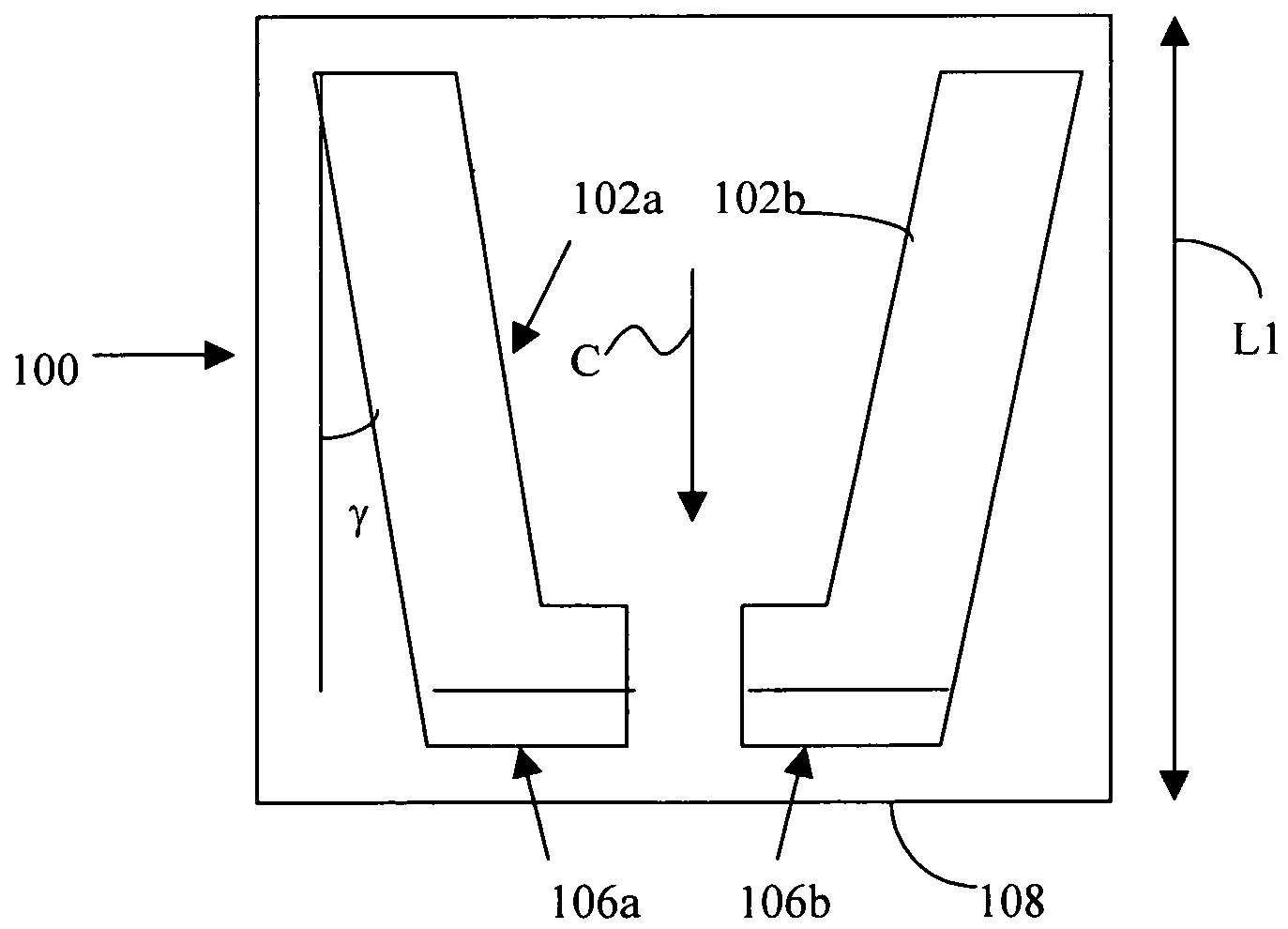
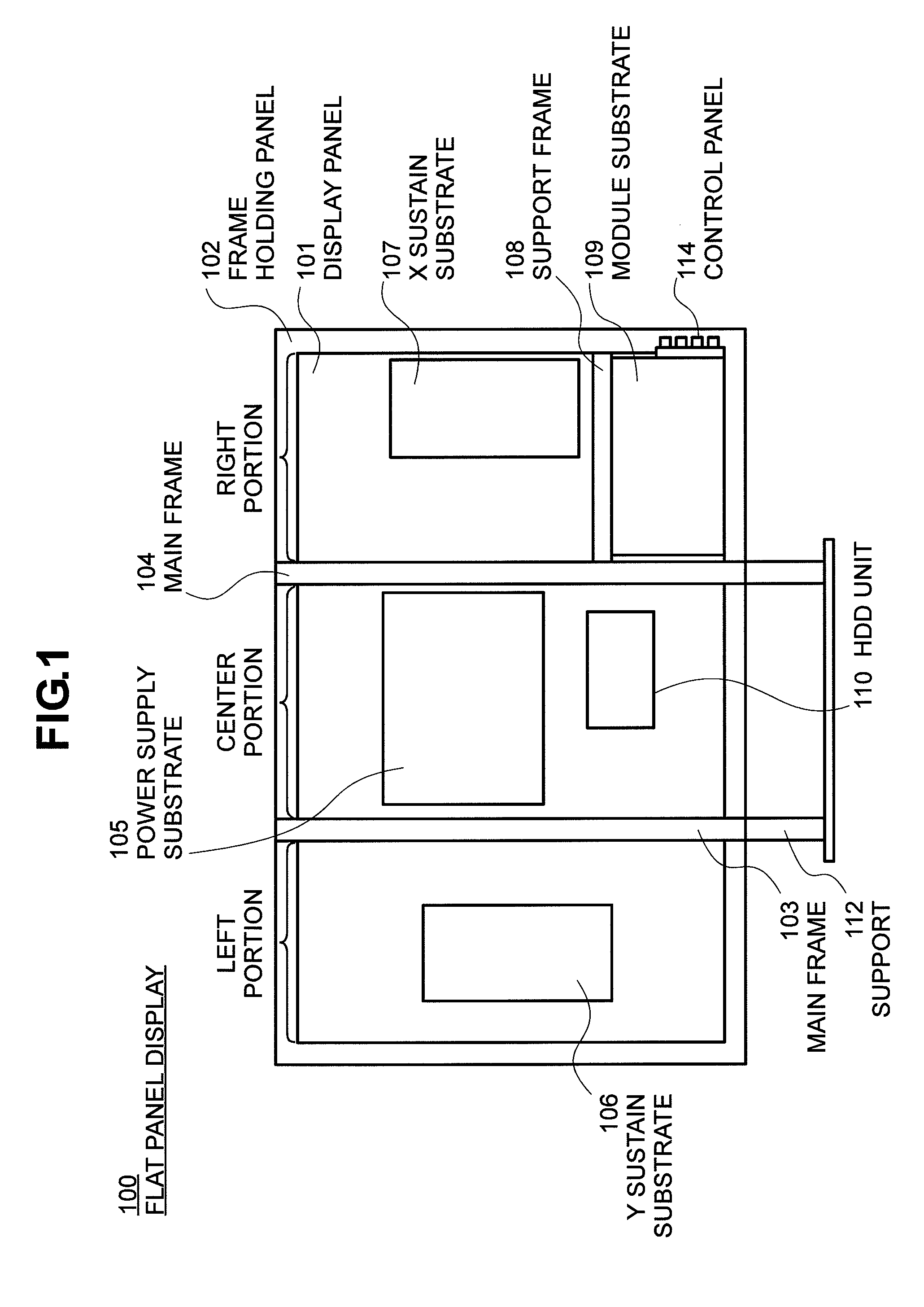
Flat Panel Display
InactiveUS20090115919A1Reduce the numberShorten the lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDisplay deviceThermal radiation
Space is decreased in the direction of thickness on a side of a substrates mounted on a back of a flat panel display to adapt requirement for increasing and thinning its size, and most flat panel displays forcibly radiate heat with a fan provided thereon. The present invention provides a flat panel display having fewer heat radiating fans to secure a channel for causing a heat radiating air to flow. Portions where electronic circuit device on a back of a display panel are mounted are divided into three: left; center; and right portions; with a main frame as a border, the electronic circuit device are constructed of four module substrates, the substrate which is the greatest in heating value in the four module substrates (hereinafter referred to as a substrate) is arranged in the center portion and the substrates which are the smallest and the second smallest in heating value therein are arranged in the same portion.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Structure with semiconductor chips embeded therein
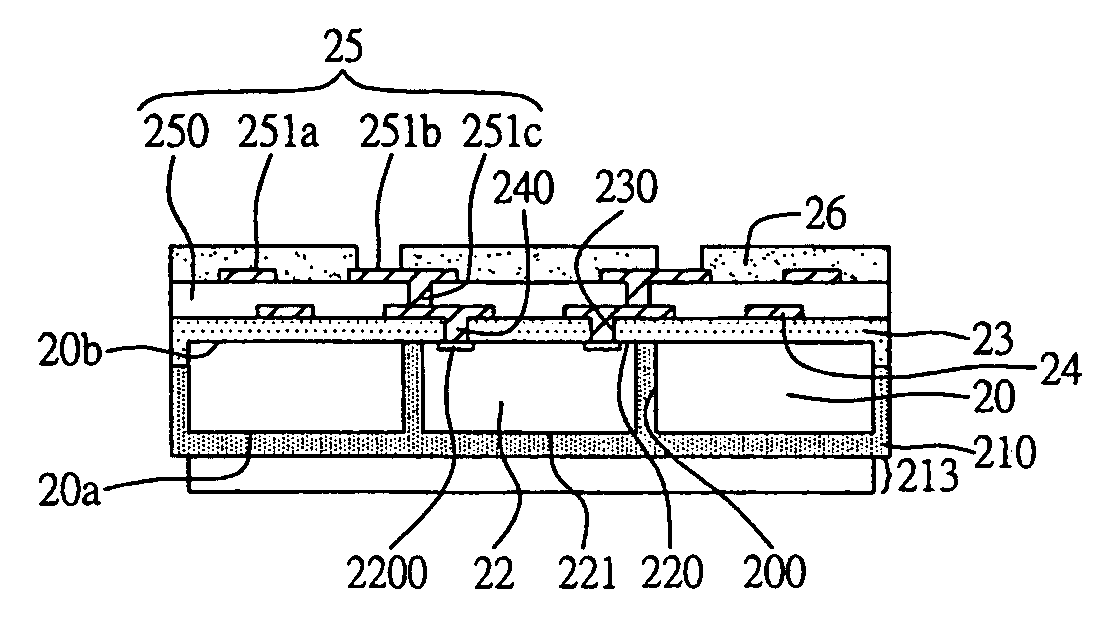
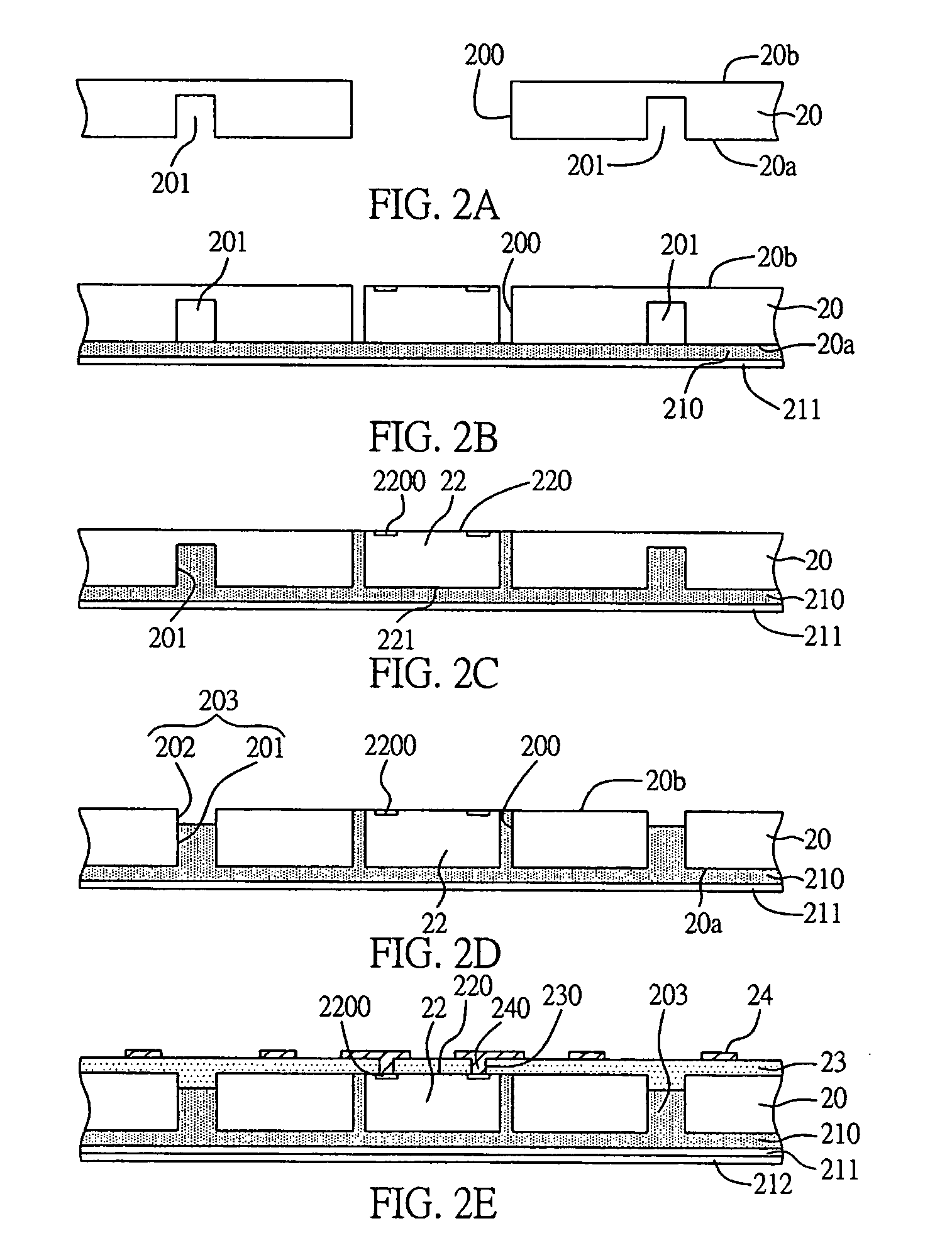
ActiveUS7763969B2Efficient layoutIncrease available spaceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
An embedded semiconductor chip structure and a method for fabricating the same are proposed. The structure comprises: a carrier board, therewith a plurality of through openings formed in the carrier board, and through trenches surrounding the through openings in the same; a plurality of semiconductor chips received in the through openings of the carrier board. Subsequently, cutting is processed via the through trenches. Thus, the space usage of the circuit board and the layout design are more efficient. Moreover, shaping time is also shortened.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Pipe having replaceable wear resistant lined coupler
InactiveUS6467812B1Rapid and cost-effective formationQuick inexpensive replacementFlanged jointsThermal insulationWear resistantEngineering
A pipe section for concrete includes an end coupler interconnecting to another pipe section in a flow line. The coupler has an outer clamp secured extended from the pipe end with a coupling groove. An encircling clamp has sides located in the grooves of adjacent pipe sections to lock the pipe section together. The body and pipe end form an inner recess extending from the pipe end. An insert liner has a tubular portion matching the recess, with the outer surface of the tubular portion tapered to form a gap within the recess. The insert liner has an outer flange matching the outer diameter of the body and abuts the body. The inner wall of the liner has a central transition point from which the wall tapers inwardly in opposite directions to the outer end. The body member is formed of a high strength ductile steel. The insert liner is formed of a wear resistant material having a Rockwell hardness of 80 to 90. A carbide alloy consisting essentially of carbides, martensite, bainite and austenite, and 12-15% chromium, 2-3% carbon and traces nickel, molybdenum and austenite. A toughened ceramic is disclosed. The liner is adhesively bonded to the body using an epoxy adhesive which is responsive to heat for release of the liner. The liner is inserted by applying adhesive on the tubular portion and then pushing the liner into the recess.
Owner:CONSTR FORMS
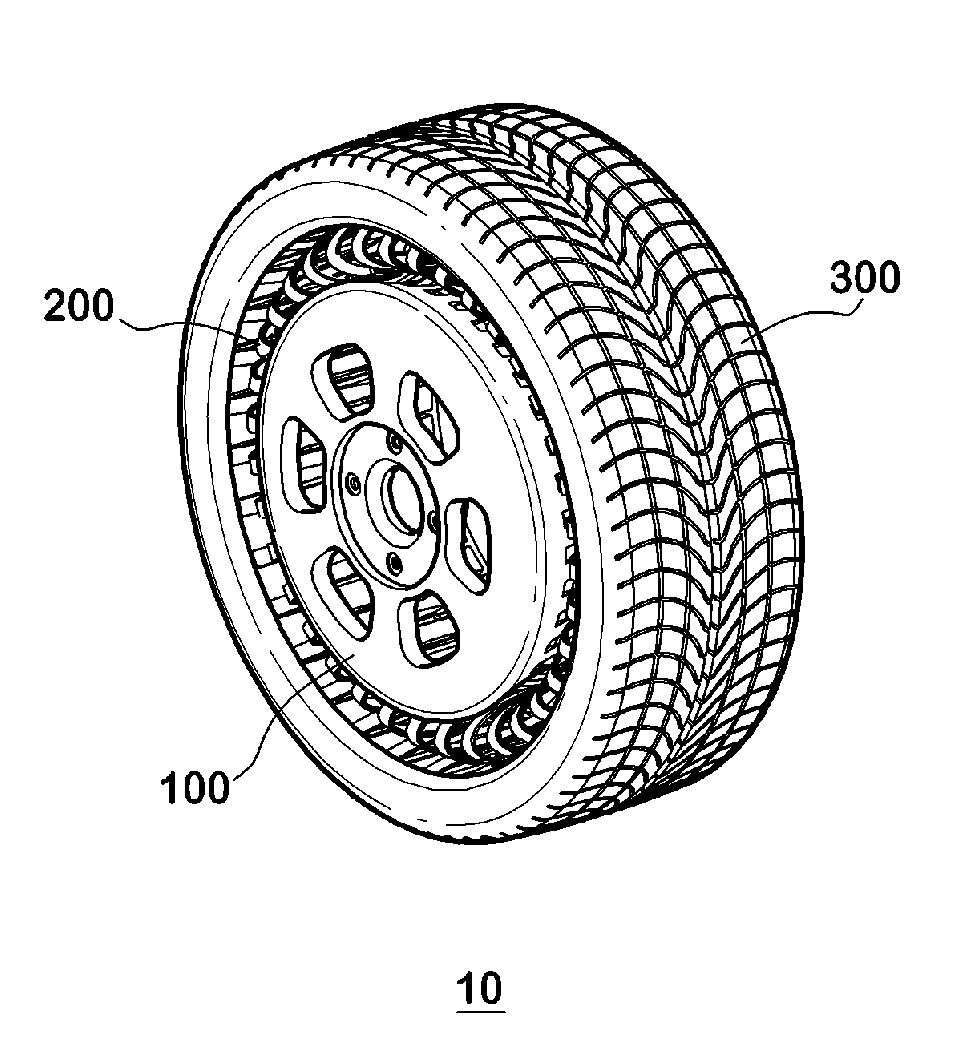
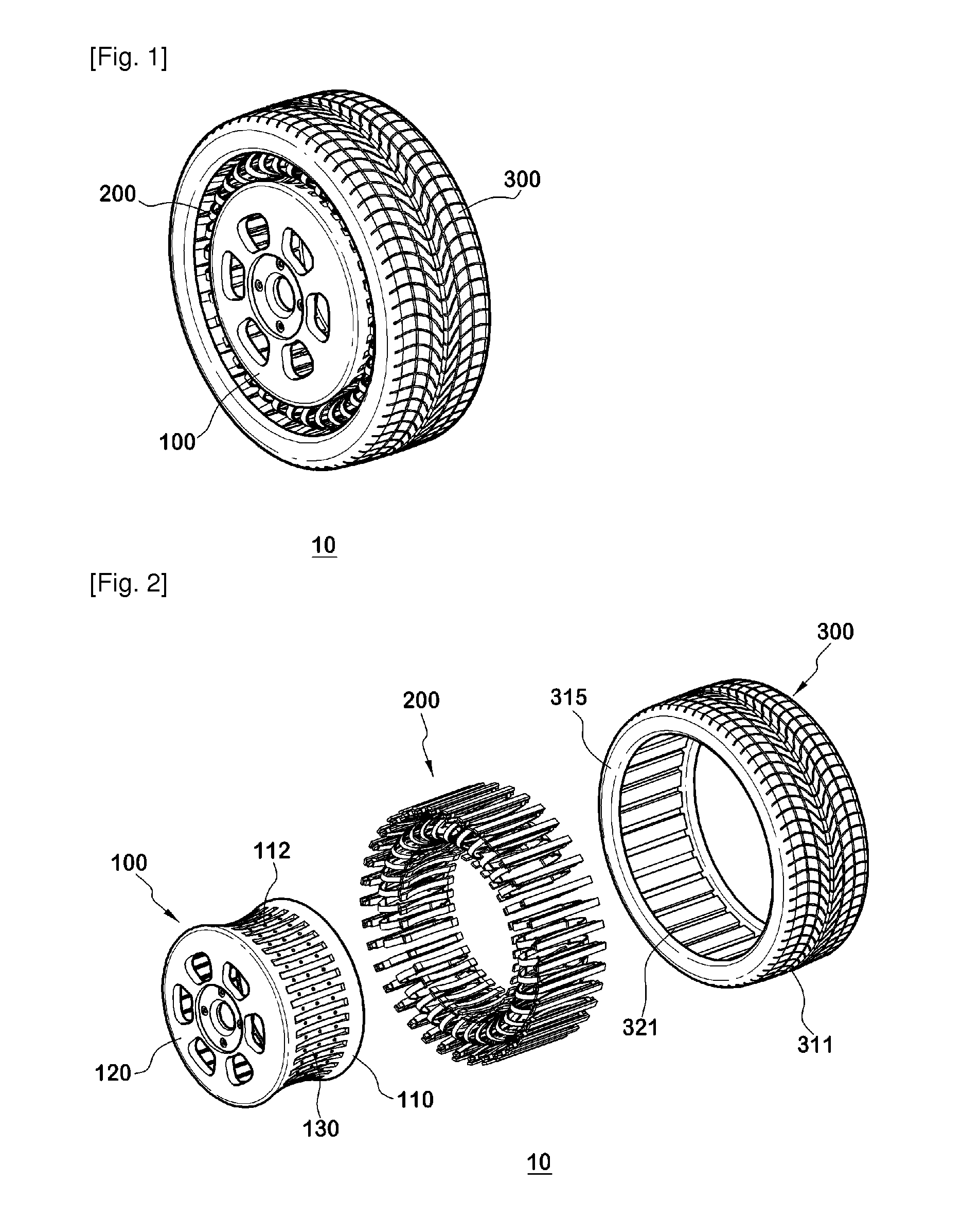
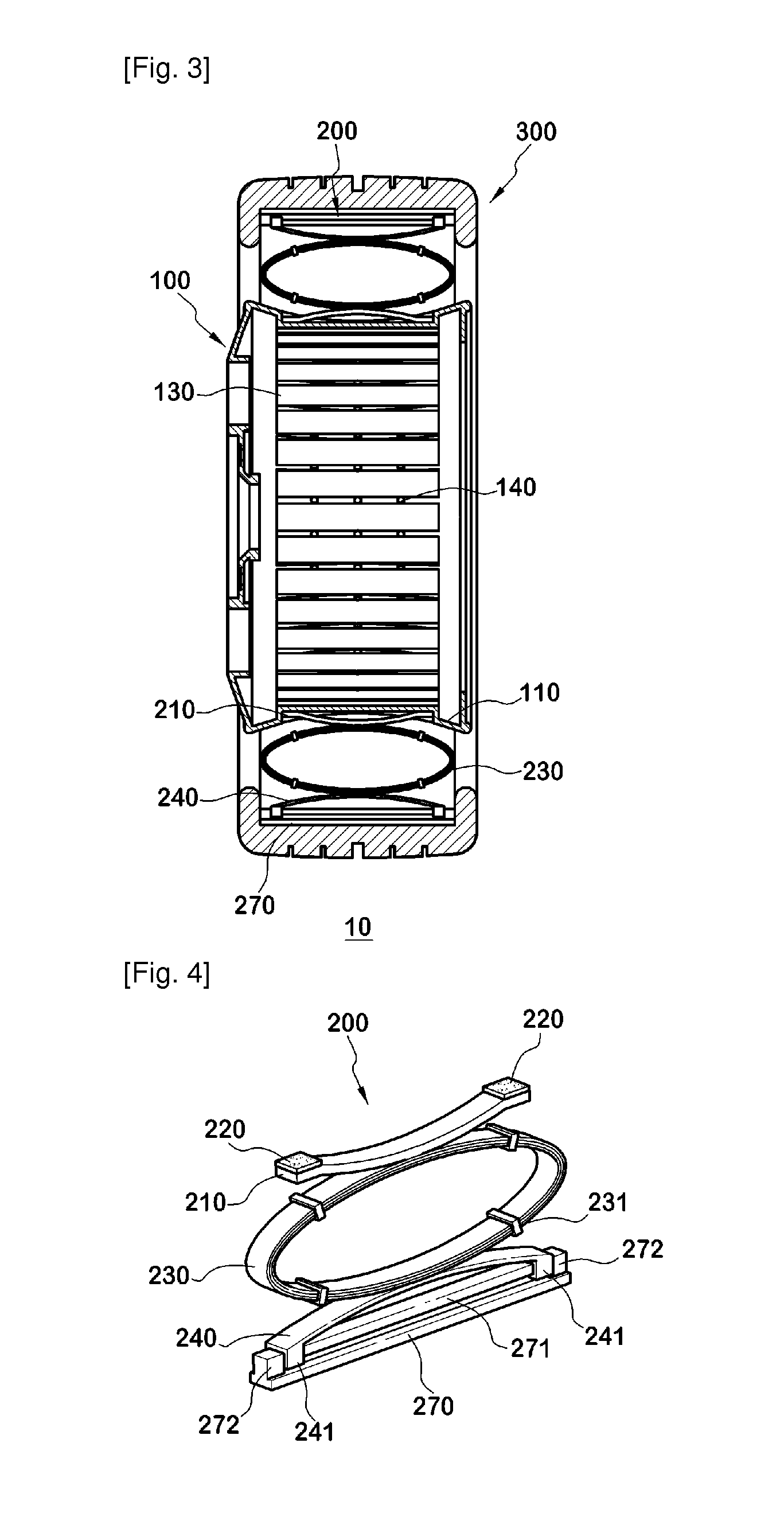
Non-pneumatic wheel and wheel, suspension and tire used therein
InactiveUS20110248554A1Prevent tire blowoutReduce vehicle accidentRimsLeaf springsCornering forceBrake fade
Provided is a non-pneumatic wheel (100) for a vehicle, and a wheel (100), suspension (200; 200-1), and tire (300) used therein that are capable of ensuring driving stability because there is no air chamber between a wheel (100) and a tire (300) to blowout. They are also capable of ensuring good road holding, preventing standing waves, reducing brake fade and cornering force, providing good handling and ride comfort, staying quiet when rolling, and are economical and environmentally friendly. The non-pneumatic wheel (100) includes a wheel (100), a shock absorbing member (220; 220-1) coupled to an outer periphery of the wheel (100) and absorbing or attenuating noise and vibration due to external shock, a plurality of resilient members (230; 230-1; 230-2) arranged around and coupled to an outer periphery of the shock absorbing member (220; 220-1) in a radial direction and having a plurality of resilient rings (230-1a) that are resiliently deformed in response to an external force, resilient links (240) respectively coupled to the resilient rings (230-1a) to evenly transmit external shock to the resilient rings (230-1a), rail plates (270) to which sliders (261) formed at both ends of the resilient links (240) are slidably coupled, and a tire (300) having a plurality of coupling grooves (321) formed along an inner periphery such that the rail plates (270) are inserted into the coupling grooves (321).
Owner:CHON YOUNG ILL +4
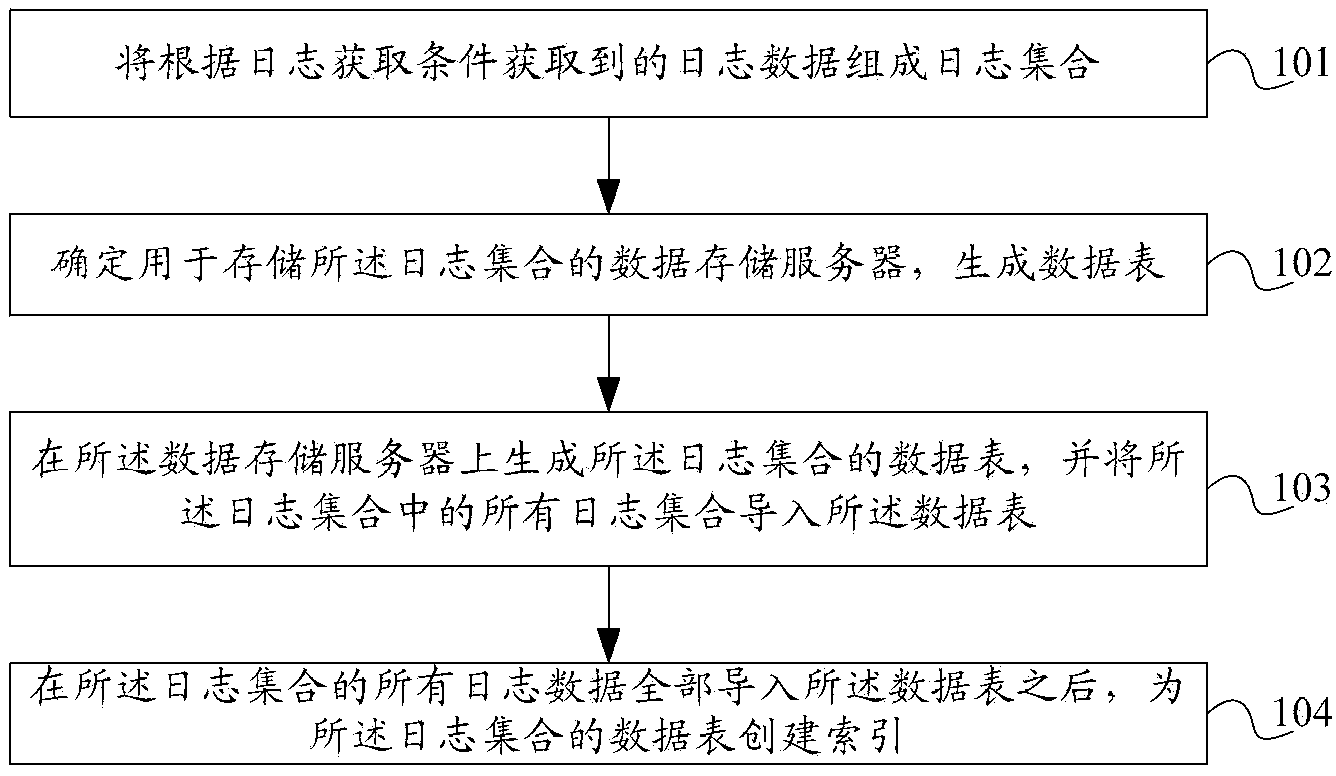
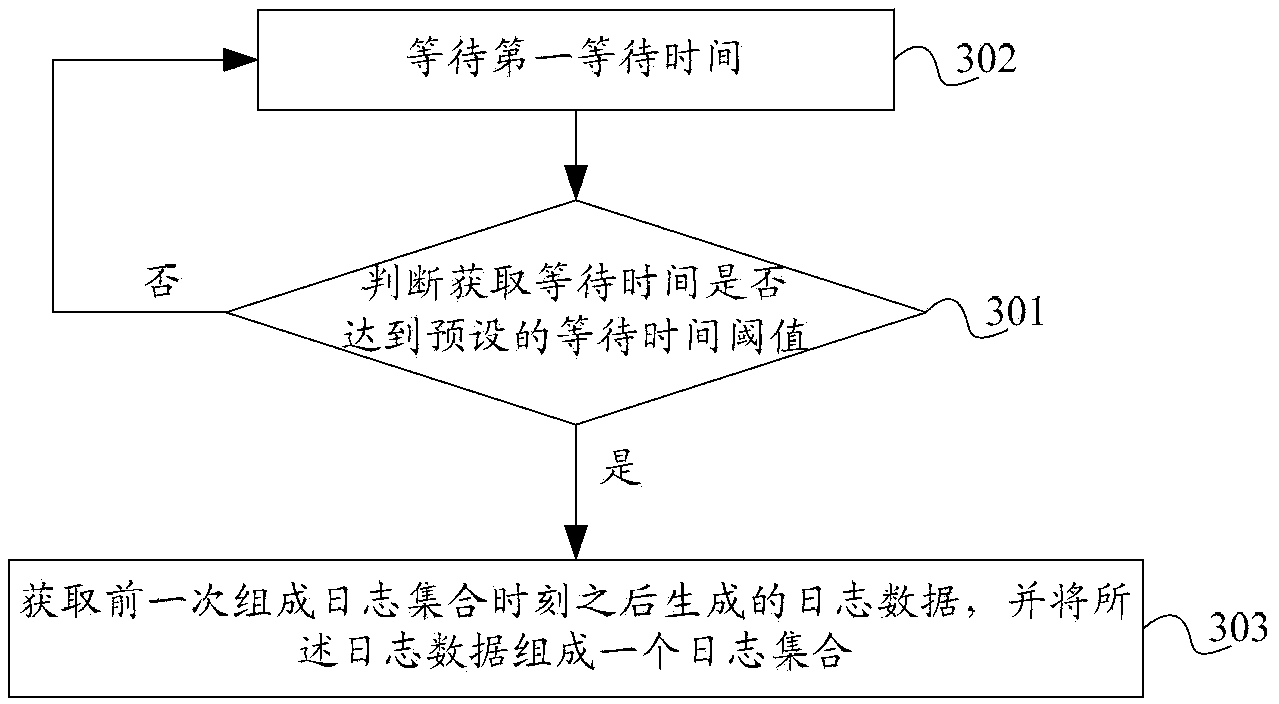
Method, log server and system for recording log data
The invention discloses a method, log server and system for recording log data. The method comprises that log data obtained according to the log obtaining condition forms a log set; a data storage server for storing the log set is determined; the log set is stored in the data storage server, and a data sheet of the log set is generated in the data storage server; and after all log data of the log set is introduced into the data sheet, an index is created for the data sheet of the log set. According to the method, log server and system, the storage speed of log data can be improved, a network platform can timely record a lot of log data that is generated in a short time, data loss is prevented, and delayed query time can be shortened.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
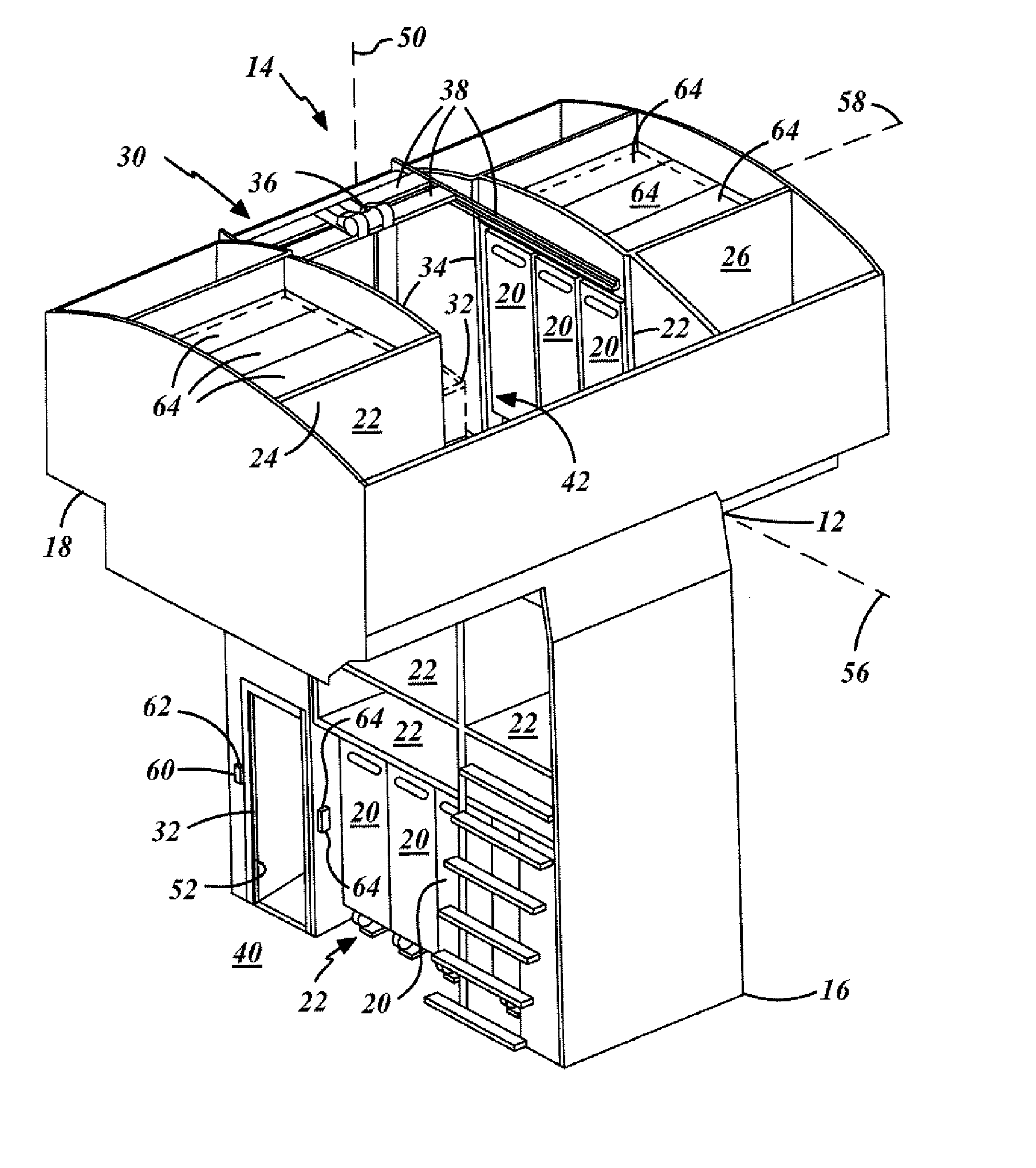
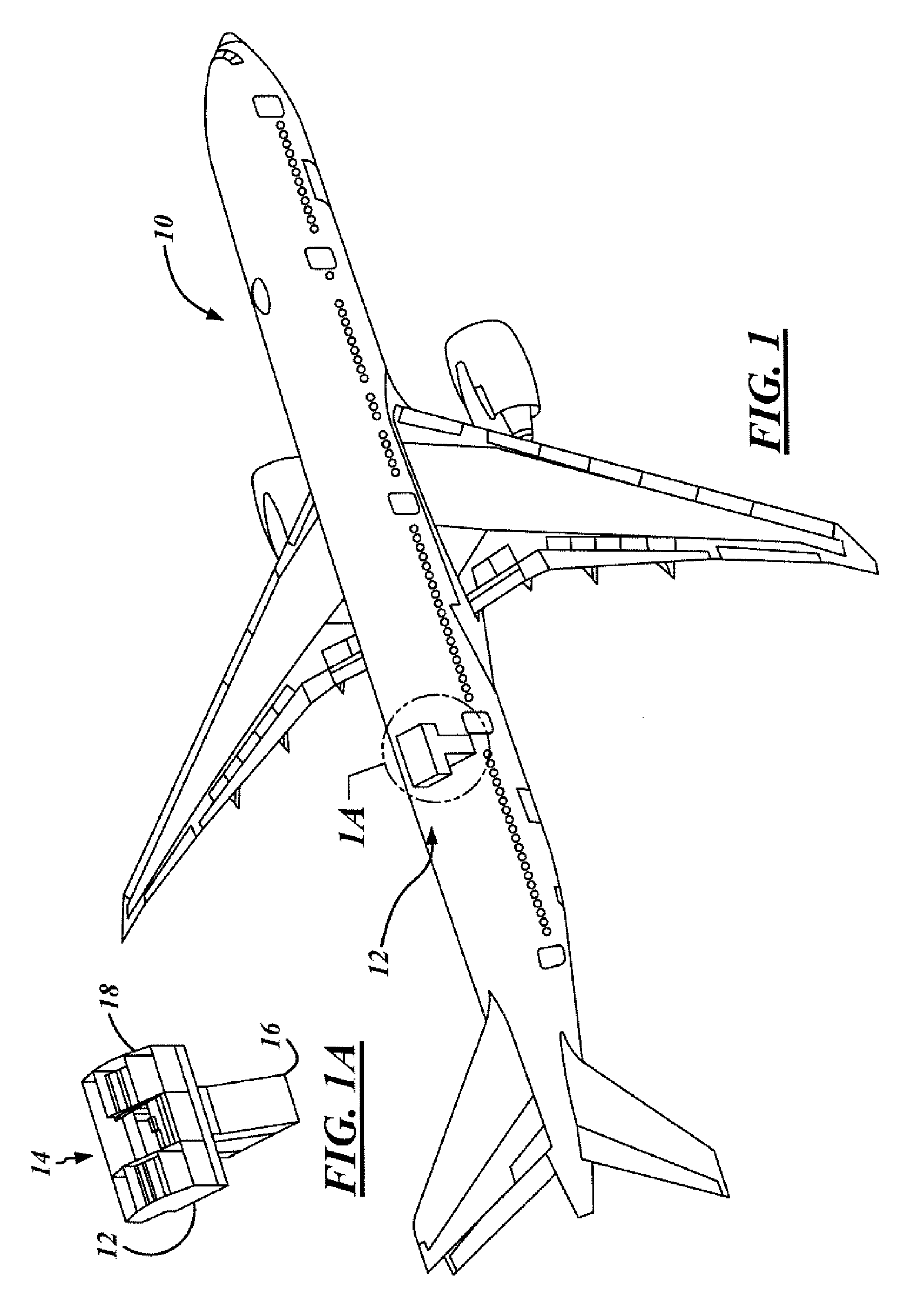
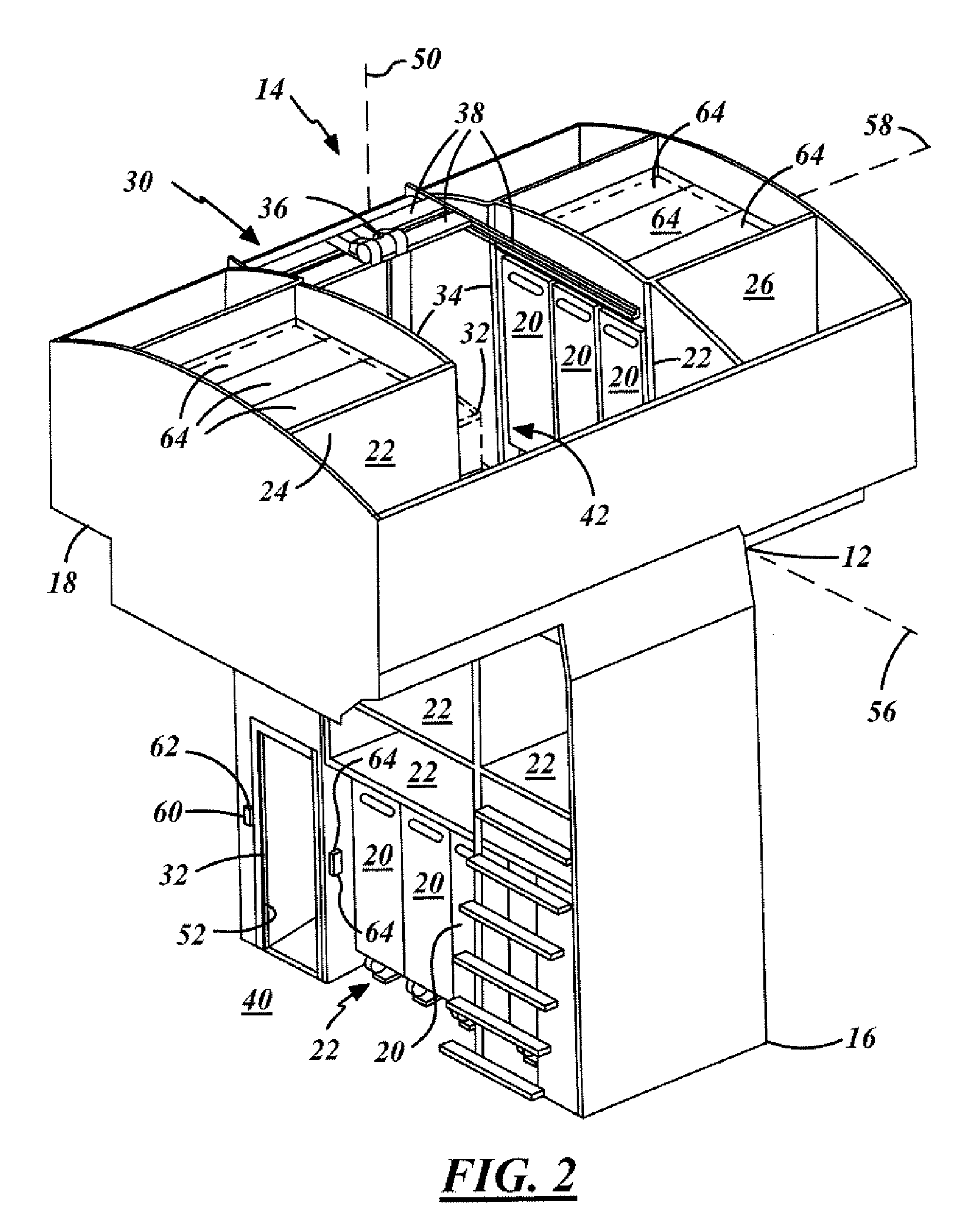
Aircraft cart transport and stowage system
ActiveUS20060186268A1Eliminate disadvantagesAvoid Operator InjuryGalleysAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsControl theoryStowage
An object transport and stowage system for an aircraft (10) includes a transport unit (32) for the transport of an object (20) within the aircraft (10). A first transfer drive system (62) is attached to the transport unit (32) and includes object engagement devices (92) that are engagable with the object (20). A motor (120) is mechanically coupled to and rotates one or more of the object engagement devices (92). A controller (66) is electrically coupled to the motor (120) and translates the object (20) relative to the transport unit (32). Another object transport and stowage system for an aircraft (10) includes a housing (150) for the stowage of an object (20) on the aircraft (10). A transfer drive system (64) is attached to the housing (150) and includes object engagement devices (168, 176), which are engagable with the object (20). A motor (162) is mechanically coupled to and rotates one or more of the object engagement devices (168, 176). A controller (68) is electrically coupled to the motor (162) and translates the object (20) relative to the housing (150).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Electrical junction box for a solar cell module
InactiveUS20060289053A1Simple and reliable connectionReduce effortElectrically conductive connectionsPV power plantsElectrical junctionElectricity
An electrical junction box for a solar cell module of solar cells which are connected with thin conductor strips, with a housing and electrical and / or electronic devices provided in the housing, and at least one electrical connection device (1) which has at least one terminal (3) and which is provided in the housing. The clamping mechanism (3) for producing clamping contact is made and arranged such that at least one thin conductor strip (5) routed out of the solar cell module can be inserted into the clamping mechanism in two different opposing entry directions. Thus, simple and reliable connection of thin conductor strips (5) routed out of the solar cell module can be guaranteed.
Owner:GUNTHER SPELSBERG GMBH CO
Shower bar assembly
A shower bar assembly that includes a pair of mounting brackets configured and arranged to be mounted to a wall of a shower stall is disclosed. Each of the mounting brackets has a base portion with a first shelf and a second shelf projecting from the base portion. The first and second shelves each have a retaining peg projecting from each shelf, respectively. A tubular shower bar is included and has two opposing ends. Each of the ends of the tubular shower bar has a pair of surfaces in which each defines an aperture through the tubular shower bar. Each end of the tubular shower bar is configured and arranged to slide onto the first and second shelves of the mounting brackets, with the apertures interlocking with each of the retaining pegs, respectively, to suspend the shower bar between the mounting brackets and to prevent the shower bar from rotating between the brackets.
Owner:KENNEY MFG
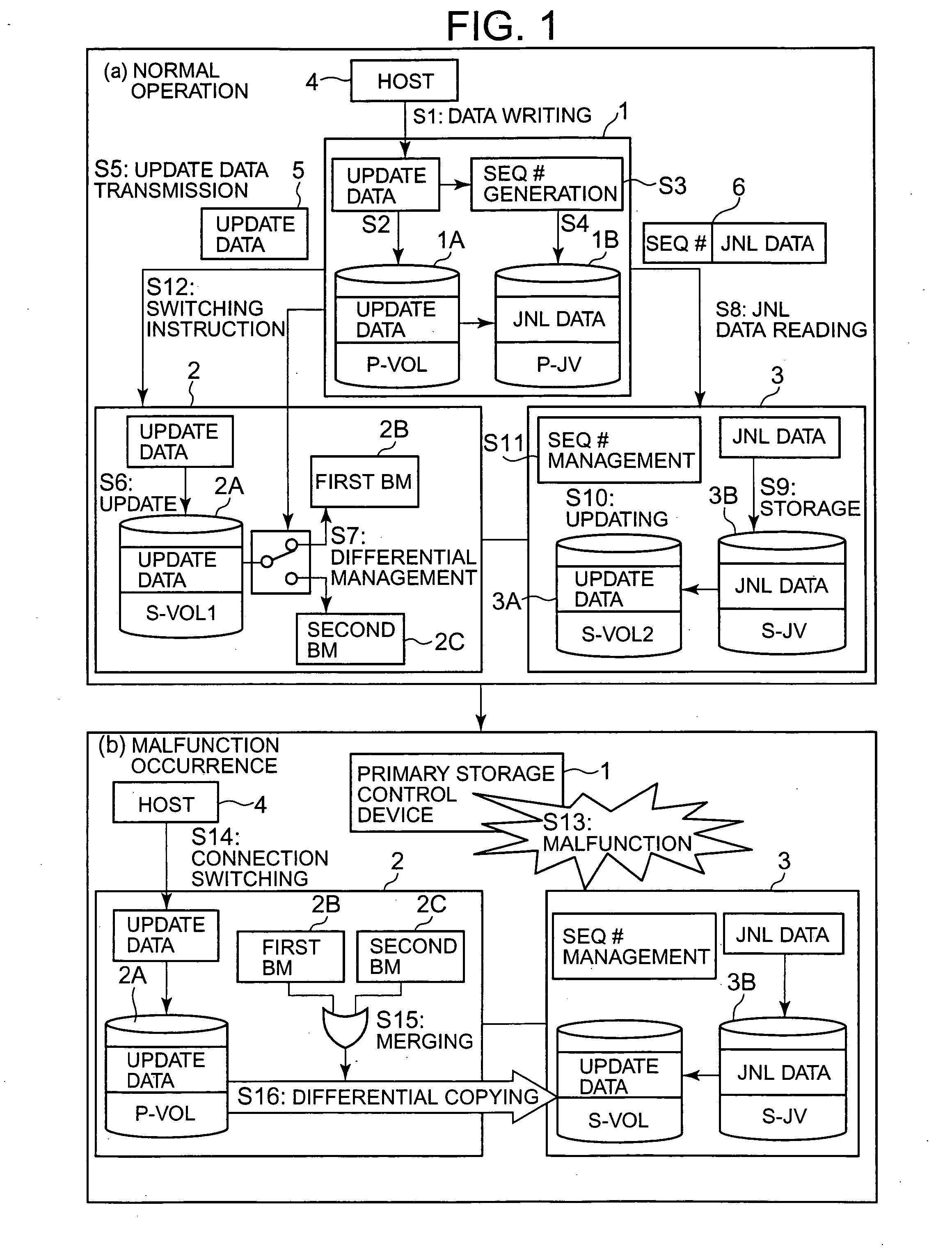
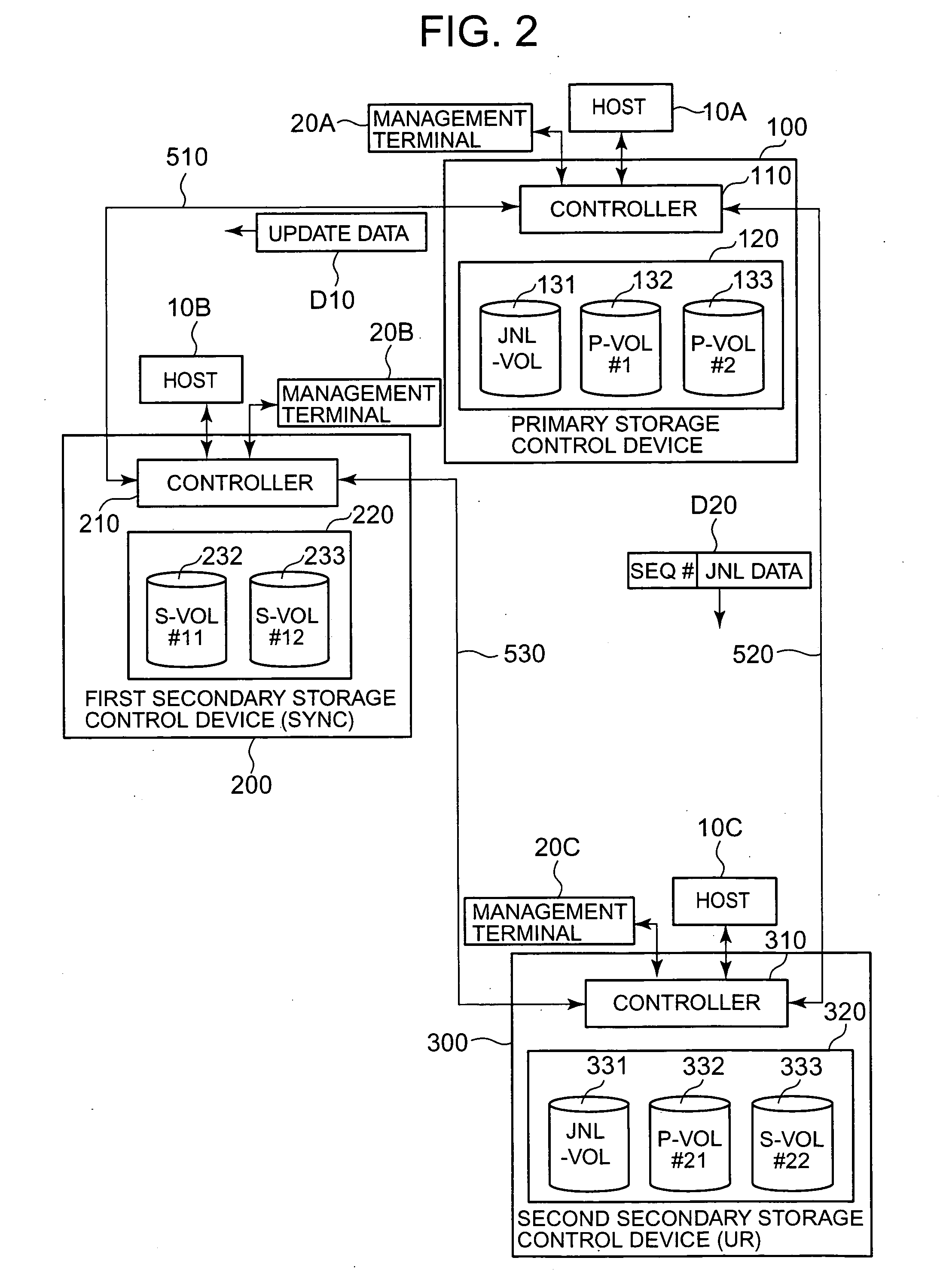
Storage system and storage system management method
ActiveUS20070050574A1Shorten the switching timeImprove ease of useMemory loss protectionRedundant hardware error correctionSystems managementBitmap
A storage system secures system redundancy through a simple configuration. A primary storage control device and first secondary storage control device are connected by a synchronous method, and the primary storage control device and a second secondary storage control device are connected by an asynchronous method. The primary storage control device sets control numbers for update data, and saves journal data. The primary storage control device transmits the update data to the first secondary storage control device. The first secondary storage control device writes update data to a first secondary volume, and uses a plurality of bitmap tables to manage differences. If the primary storage control device stops operation, the first secondary storage control device becomes the new primary storage control device. Differential copying is performed from the first secondary storage control device to the second secondary storage control device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electrical junction box for a solar cell module
InactiveUS7530837B2Simple and reliable connectionReduce effortCoupling device detailsPhotovoltaicsElectrical junctionElectrical conductor
An electrical junction box for a solar cell module of solar cells which are connected with thin conductor strips, with a housing and electrical and / or electronic devices provided in the housing, and at least one electrical connection device (1) which has at least one terminal (3) and which is provided in the housing. The clamping mechanism (3) for producing clamping contact is made and arranged such that at least one thin conductor strip (5) routed out of the solar cell module can be inserted into the clamping mechanism in two different opposing entry directions. Thus, simple and reliable connection of thin conductor strips (5) routed out of the solar cell module can be guaranteed.
Owner:GUNTHER SPELSBERG GMBH CO
Apparatus for pre-treatment and subsequent plastification or agglomeration of synthetic plastic materials
InactiveUS6883953B1Quality improvementIncrease productionDischarging apparatusMixing operation control apparatusPlastic materialsPre treatment
An apparatus for pre-processing and subsequent plastification or agglomeration of synthetic plastic materials, in particular thermoplastic waste plastics for recycling purposes, has a receptacle (1) in which at least one comminuting tool (6) circulates. The housing (7) of a screw (8) is connected to the receptacle (1). The diameter (D) of the receptacle (1) has the following relationship to the screw diameter (d):D=10.{square root over (K.d2)}, wherein D is the inner diameter of the receptacle in mm,d is the screw diameter in mm andK is a dimension-less constant which amounts to at least 190.Thereby the dwell times of the synthetic plastic material within the receptacle (1) are kept at optimal values.
Owner:BACHER HELMUT +2
Retractable shower expander assembly
A retractable shower expander assembly for a shower stall or tub enclosure having an access opening includes a shower expander rod, two expander ports and a tension rod. The shower expander rod is formed with right angles on each end and is selectively adjustable in the middle to fit various access opening widths. The retractable shower expander assembly, being portable, is held in place by means of an adjustable tension rod, that, when enjoined inside the cavities of the two expander ports, holds the retractable shower expander assembly horizontally and fixedly in use against the two end walls of a shower stall or tub enclosure at the top of the access opening. A shower curtain is attached to the shower expander rod by hooks or rings that can slide along the shower expander rod to selectively close or open the access opening of a shower stall or tub enclosure. When outwardly force is applied to the shower expander rod the two right-angle ends extend or telescope through the apertures in the center of the expander ports and move the shower expander rod with the attached shower curtain outwardly away from the access opening to provide the maximum amount of increased area inside the shower stall or tub enclosure. When inwardly force is applied to the shower expander rod the opposite retracting or telescoping effect moves the shower curtain toward the access opening and returns it to a straight hanging position within the shower stall or tub enclosure access opening to be more aesthetically pleasing and conserve space in the bathroom.
Owner:BATHURST DAVID B +1
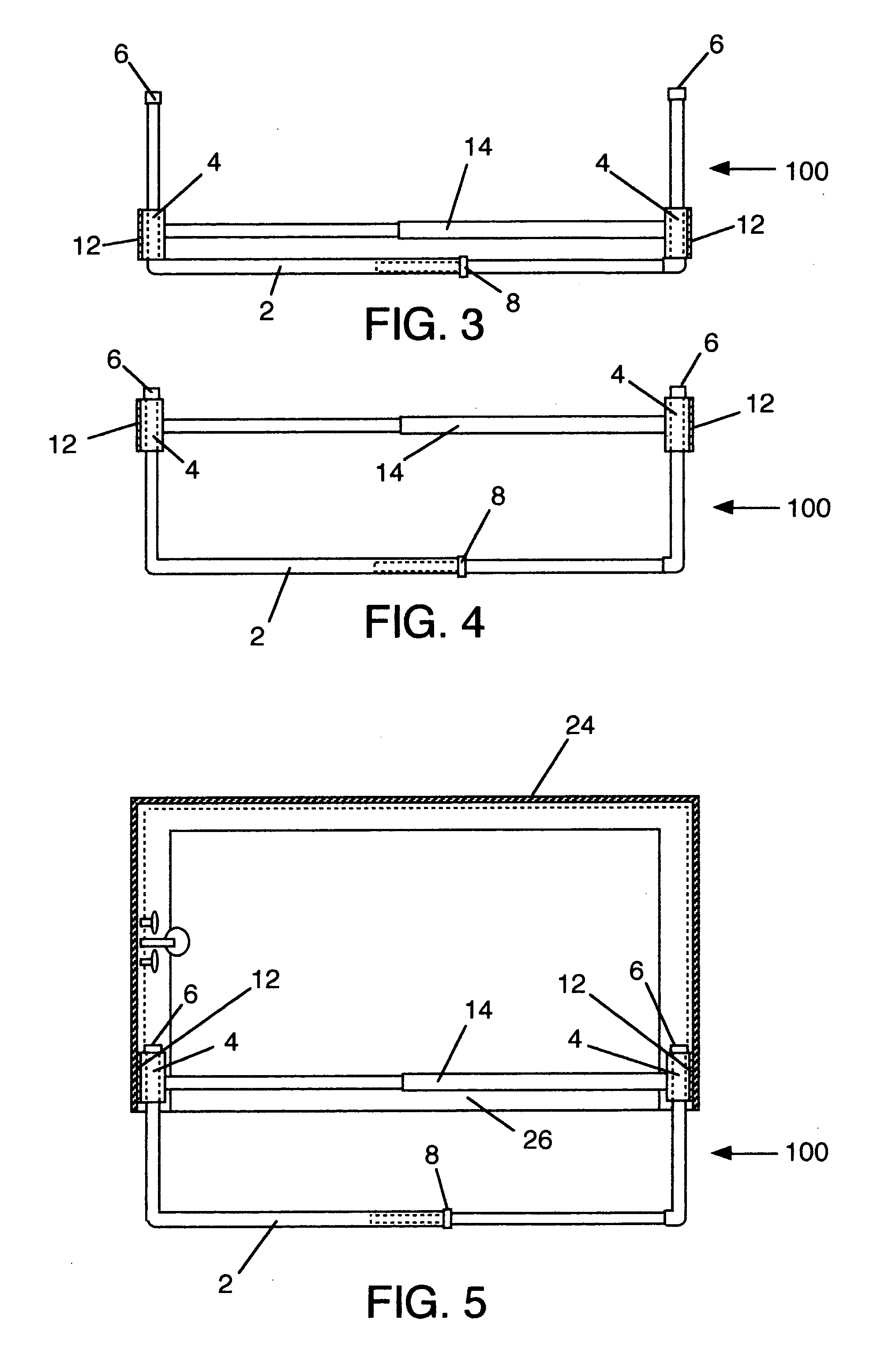
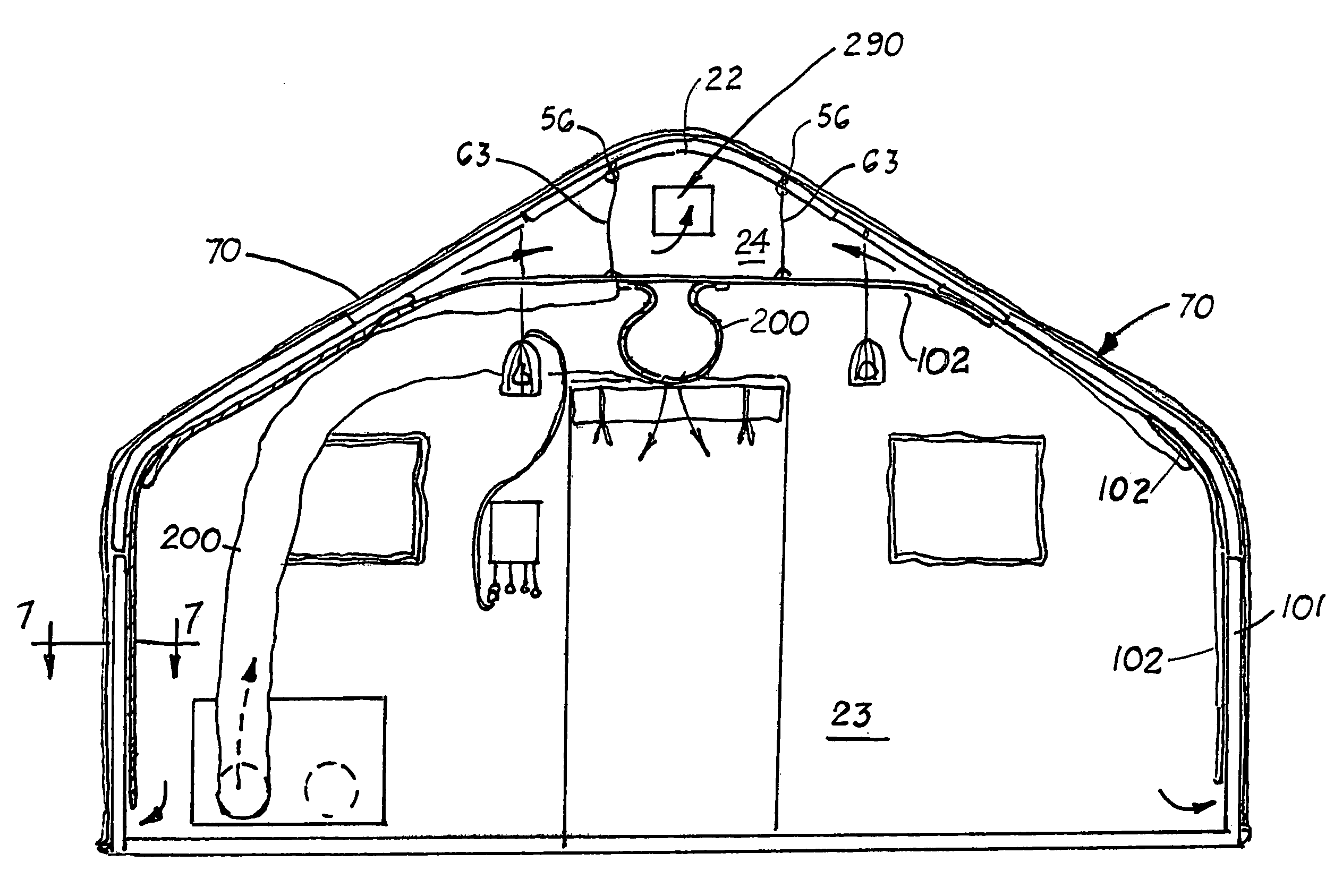
Compact, all-weather temporary shelter
ActiveUS7735502B1Easy and fast assembly and disassemblyEliminate needArched structuresTents/canopiesPurlinEaves
A compact, temporary shelter that includes at least two vertical frame members aligned transversely over a base frame. Each frame member includes two opposite straight lower sections, two curved eave sections, two optional straight roof sections and a curved, central peak section. Adjacent frame members are interconnected by a plurality of purlins. The shelter includes an inner liner disposed over the inside surfaces of the frame members. The inner liner creates wall air spaces between two adjacent frame members and an upper attic and a lower living space that are partially isolated. When attached to an HVAC unit, air from the living space and flows and circulates into the wall air spaces between the frame members and into the attic. From the attic, air travels through a vent opening formed on an end cover to the outside environment. Located inside the shelter is a flexible air sock that connects at one end to the output port on the HVAC unit to evenly distribute the air into the living space. Because the frame member includes straight sidewalls and the inner lining forms a relatively high ceiling, greater storage and living space is created.
Owner:CALIFORNIA IND FACILITIES RESOURCES INC DBA CAMSS SHELTERS
Closet system
InactiveUS20080289264A1Increase storage spaceNo room for improvementChestsDressing tablesEngineeringLower upper
The present invention is directed to a closet system with a housing that includes four adjacent sidewalls having a lower portion and an upper portion, a cap coupled to the upper portion, and an opening; a motor assembly including a motor connected to a power supply, at least two pulleys, a shaft rotatably connected to the motor, and at least one cable having a first end and a second end, wherein the first end is guided by the one pulley and the second end is guided by the other pulley, and wherein the cable is retractably connected to the shaft; and a platform wherein the cable first end is connected proximate the middle of an edge of the platform and wherein the cable second end is connected proximate the middle of an opposing edge of the platform.
Owner:BOWMAN MARK E
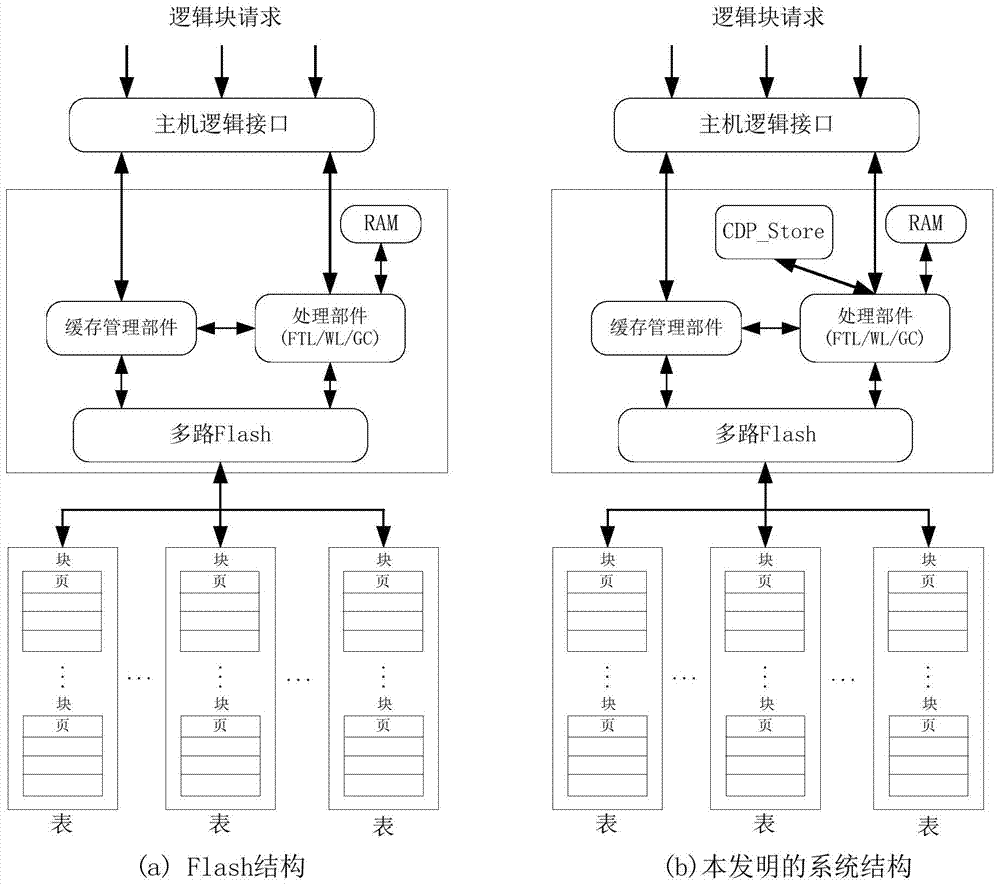
Solid state disk (SSD) and space management method thereof
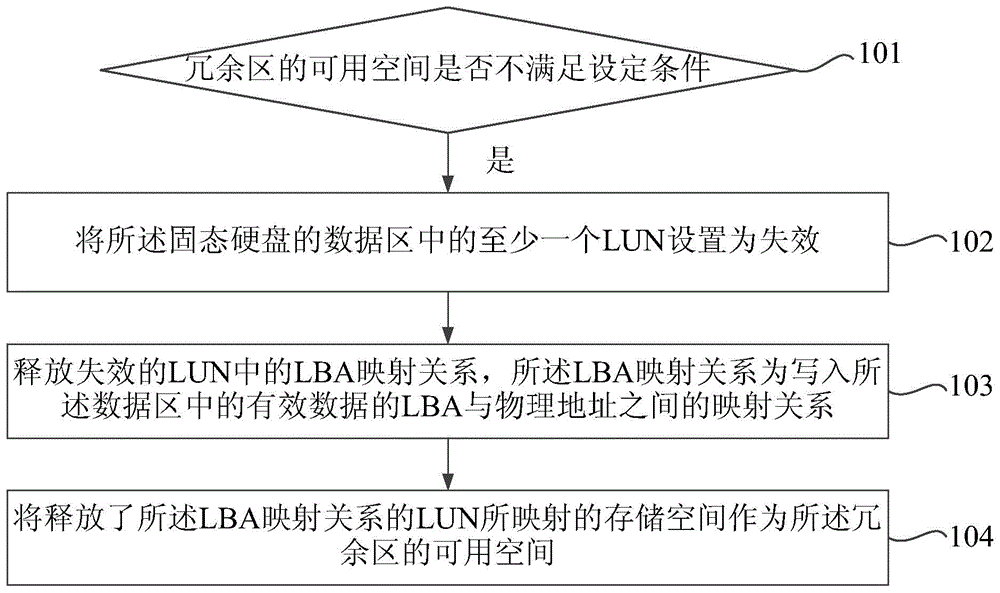
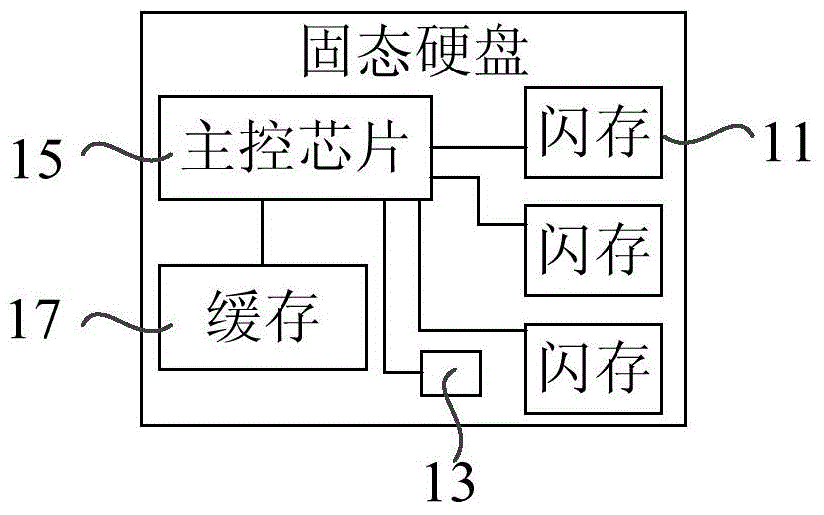
ActiveCN103559138AIncrease available spaceExtended service lifeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPhysical addressSolid-state drive
The invention relates to a solid state disk (SSD) and a space management method thereof. The method includes: when available space in a redundancy are cannot satisfy the set condition, failing at least one logic unit number (LUN) in the data area of the solid state disk; releasing the logic block address (LBA) mapping relations in the failed LUNs; using the storage space mapped to the LUNs with the released LBA mapping relations as the available space of the redundant area; wherein the LBA mapping relations are the mapping relations between the LBA of the effective data written into the data area and the physical addresses. By the method, when the available space of the redundancy area cannot satisfy the preset condition, at least one LUN of the SSD can be failed, the LBA mapping relations of the failed LUNs can be released to increase the available space of the redundancy area, and the service life of the SSD is prolonged by failing part of the data area of the SSD.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
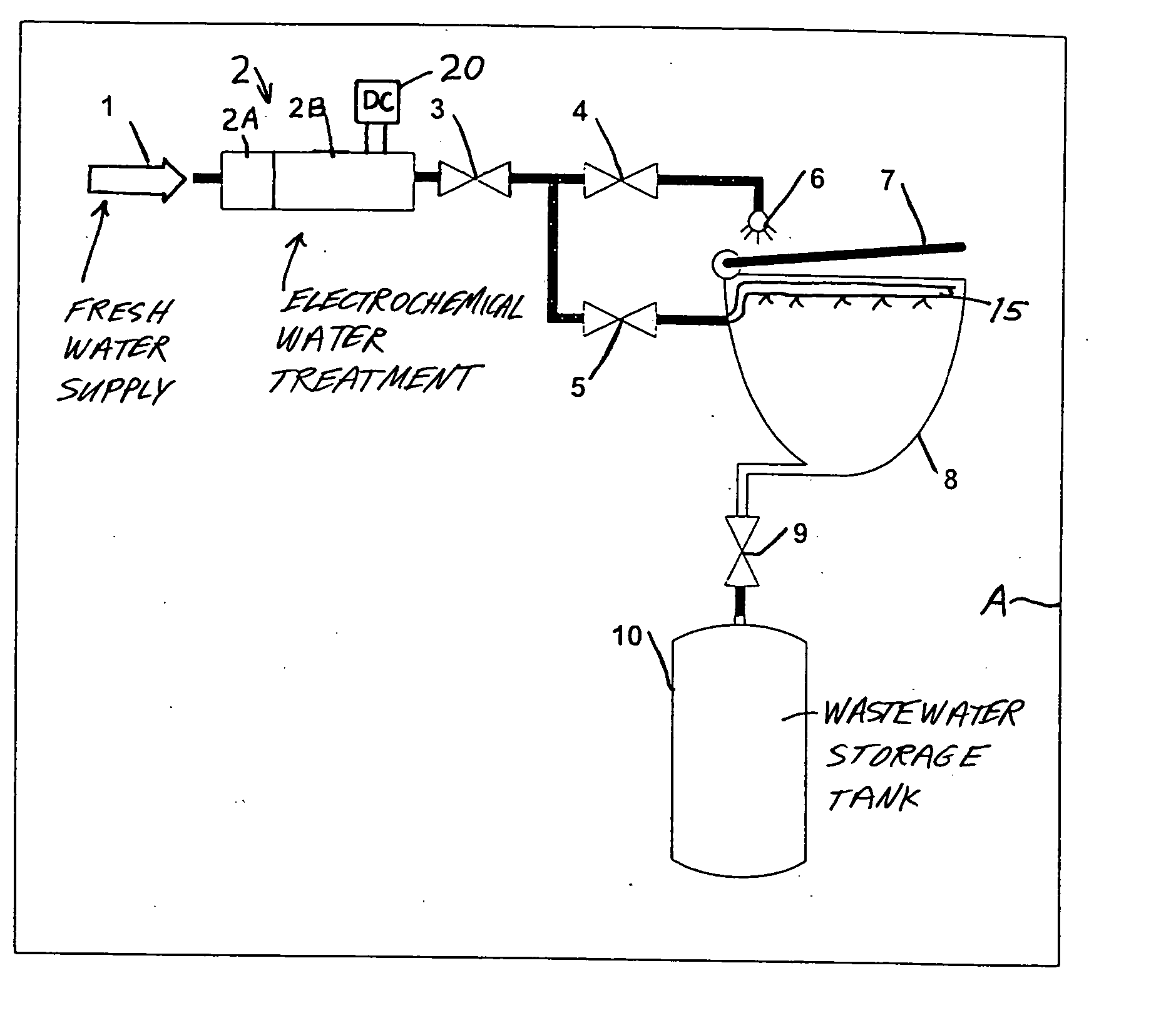
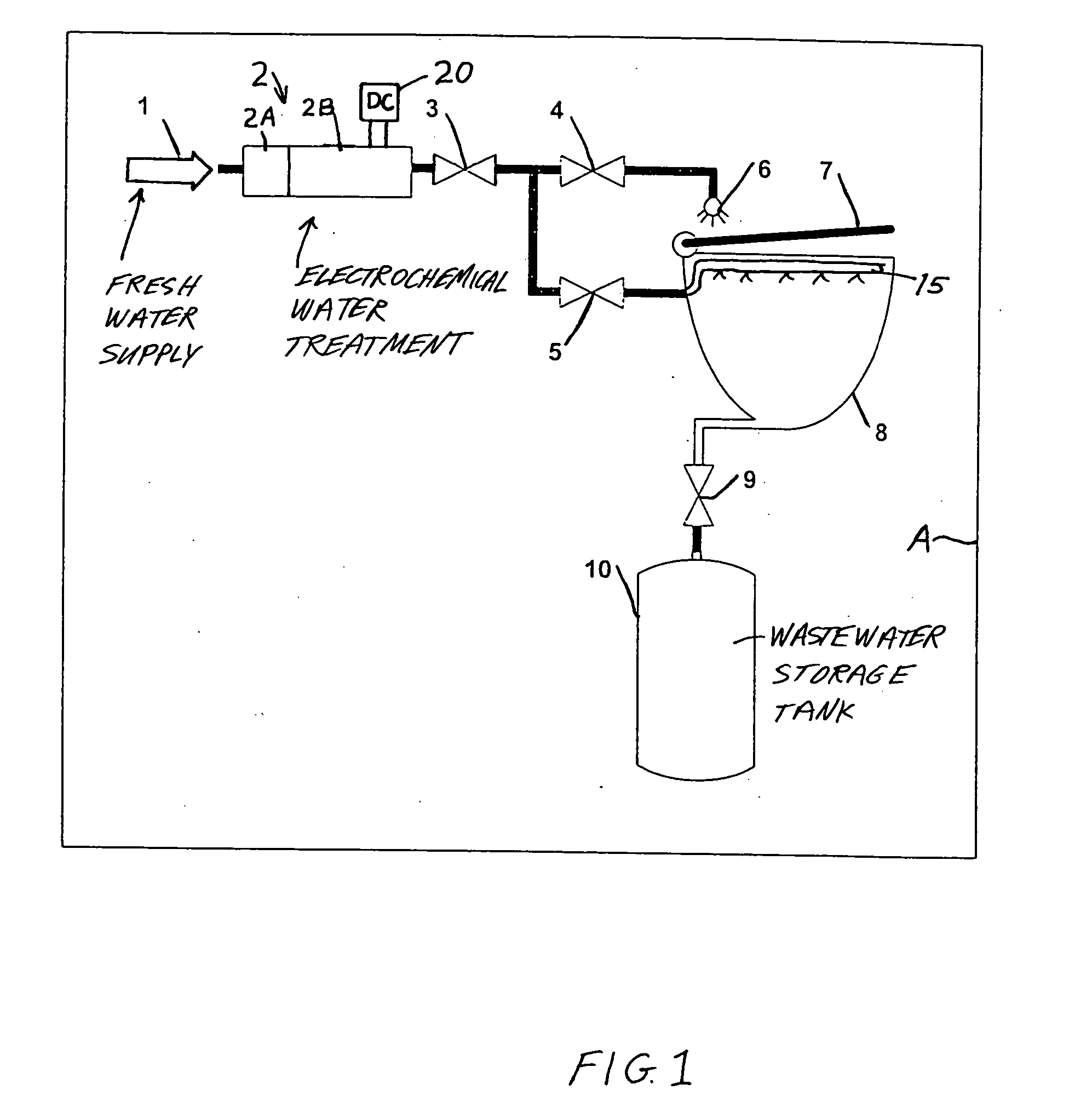
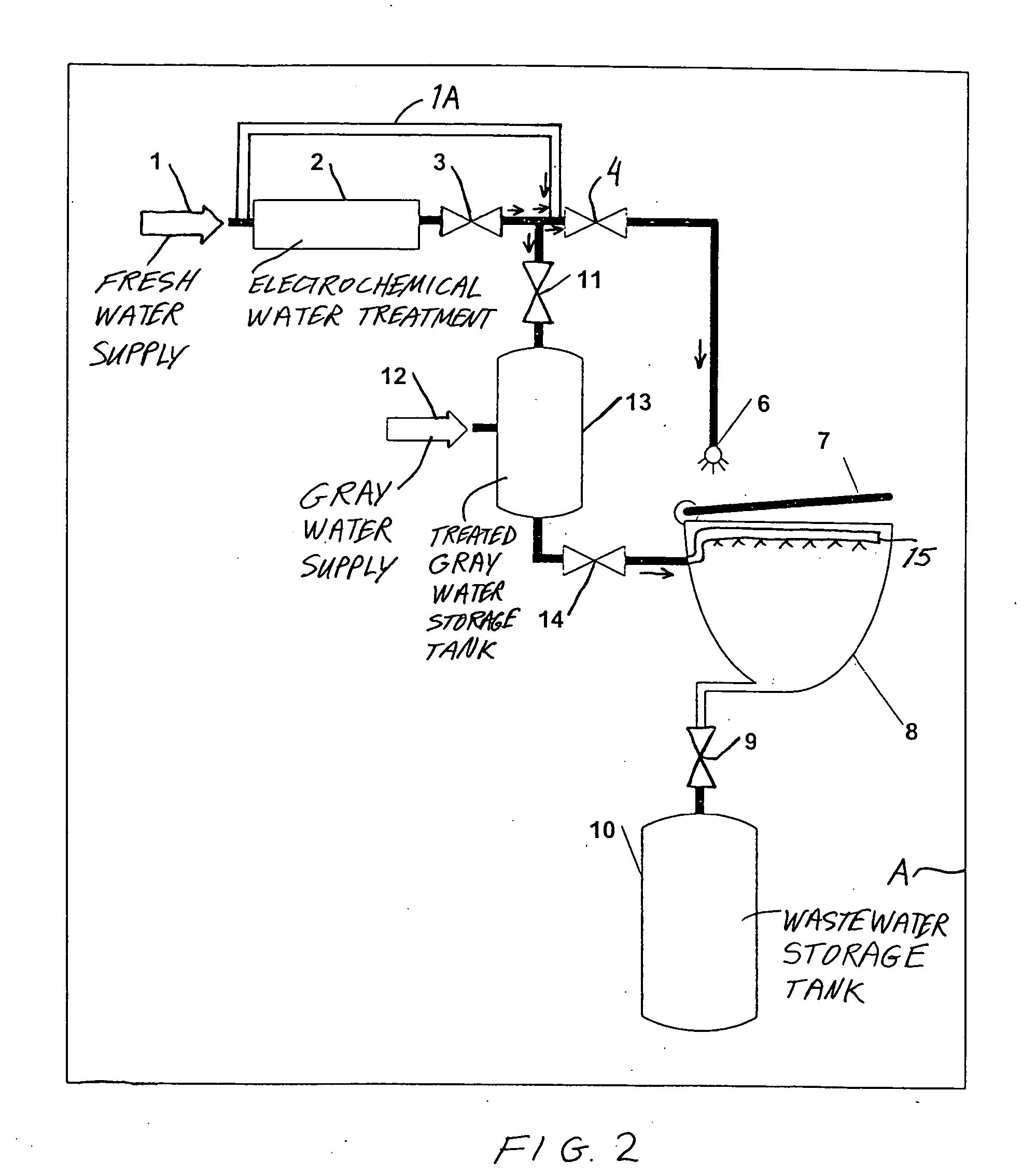
Method and apparatus for cleaning and disinfecting a toilet system in a transport vehicle such as a passenger aircraft
InactiveUS20040133968A1Inhibition formationKeep it goingFlushing devicesBathroom coversElectricityPotable water
Water, preferably fresh potable water, is electrochemically, e.g. electrolytically, treated to achieve disinfectant properties. The electrochemically treated water is sprayed onto the toilet seat and directed into the toilet bowl for each flush cycle of an aircraft toilet system, so as to clean and disinfect the toilet seat and the toilet bowl. The electrochemically treated water has a direct germ-killing effect on the seat and bowl, and also disinfects the arising wastewater that is conveyed to and stored in a storage tank. For flushing the toilet bowl, the electrochemically treated water may further be mixed with reused graywater, which is thereby disinfected.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
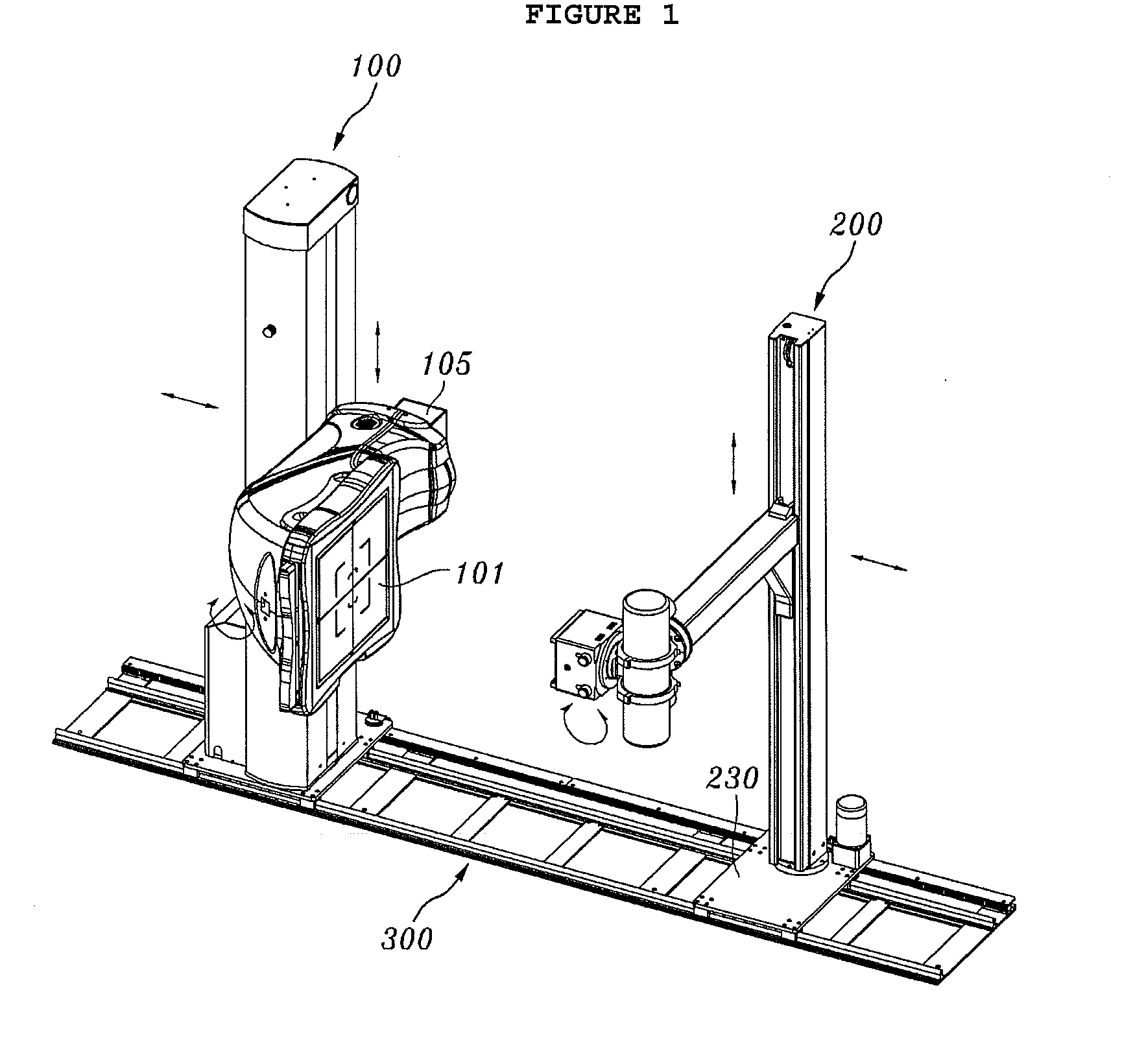
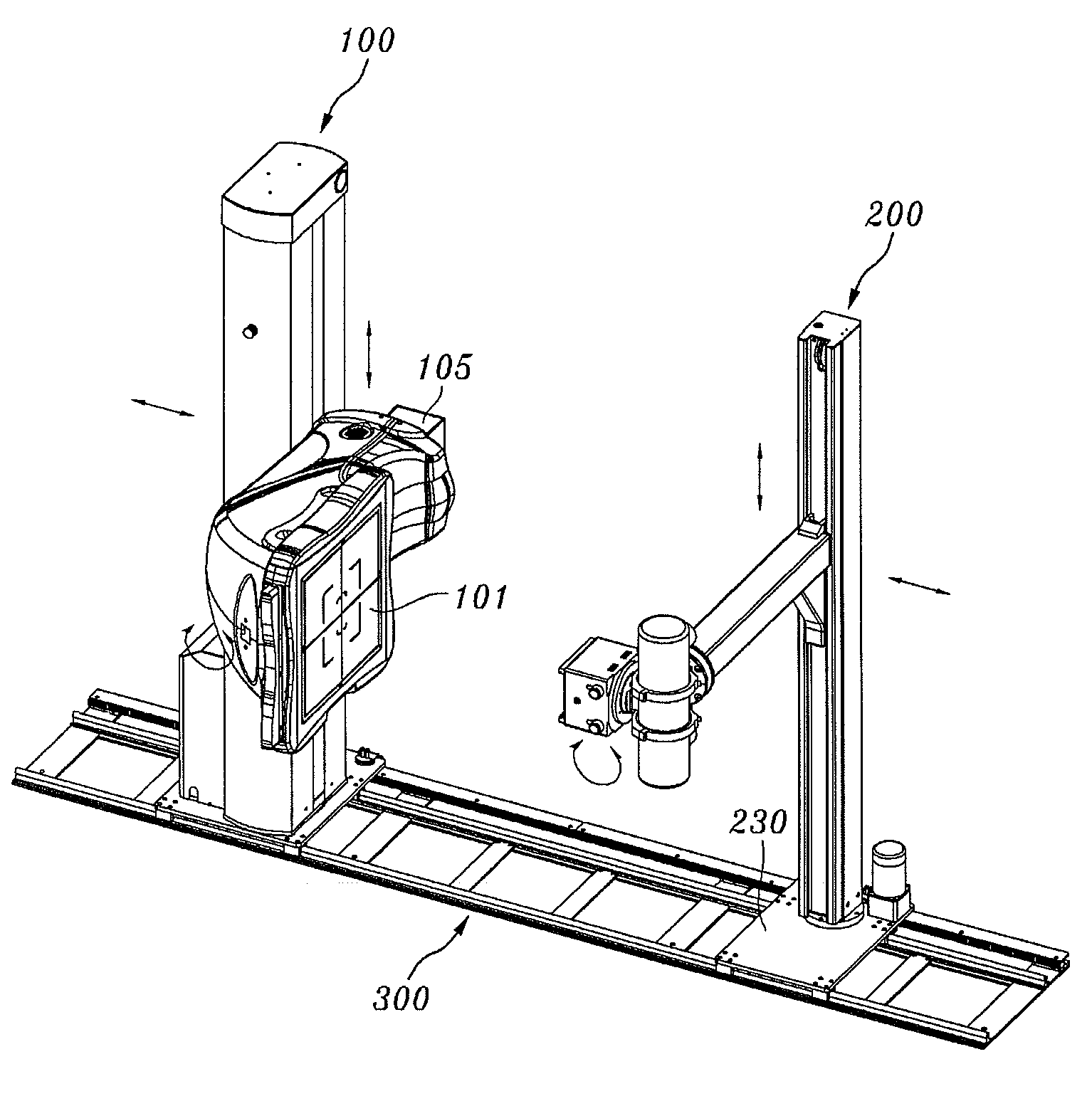
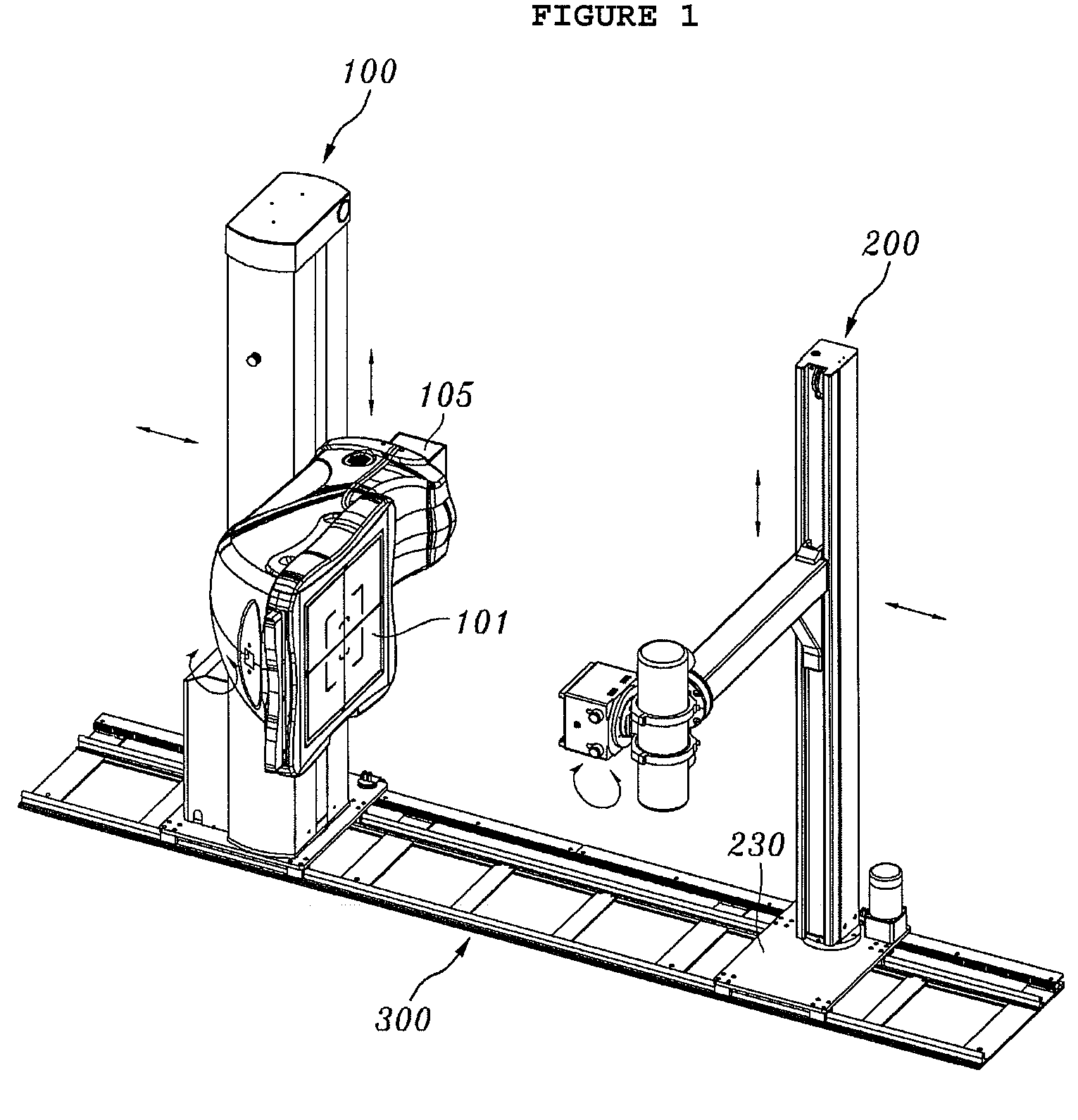
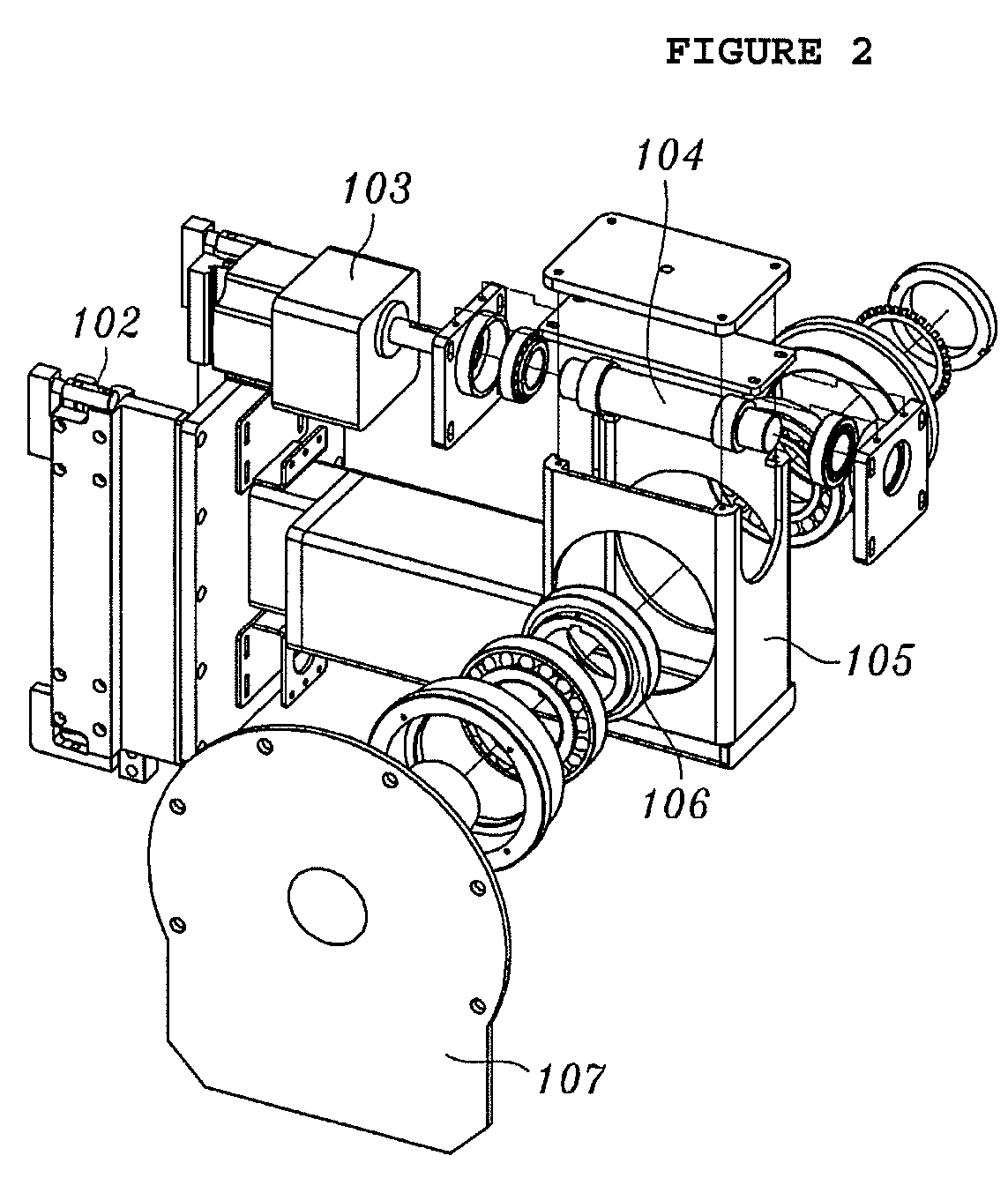
Rail system and x-ray imaging apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20100232574A1Reduce spacingIncrease available spaceX-ray/infra-red processesImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesX-rayEngineering
Disclosed herein are a rail system and an X-ray imaging apparatus using the same. The rail system includes a rail unit, a detecting unit and an X-ray generating unit. The rail unit is provided on a support surface and extends for a predetermined length. The detecting unit is provided on the rail unit and includes a detector stand which is provided on the rail unit so as to be movable in the longitudinal direction of the rail unit, a detector arm which has a bent structure and is provided on a side surface of the detector stand so as to be movable upwards and downwards, and a detector which is rotatably coupled to the detector arm. The X-ray generating unit is provided on the rail unit at a position facing the detector and includes a tube stand which is provided on the rail unit so as to be movable in the longitudinal direction of the rail unit, a tube arm which is provided on the tube stand so as to be movable upwards and downwards, an X-ray tube which is coupled to the tube arm so as to be rotatable with respect to the tube arm, and a collimator which is fastened to the X-ray tube.
Owner:MEDIEN INT
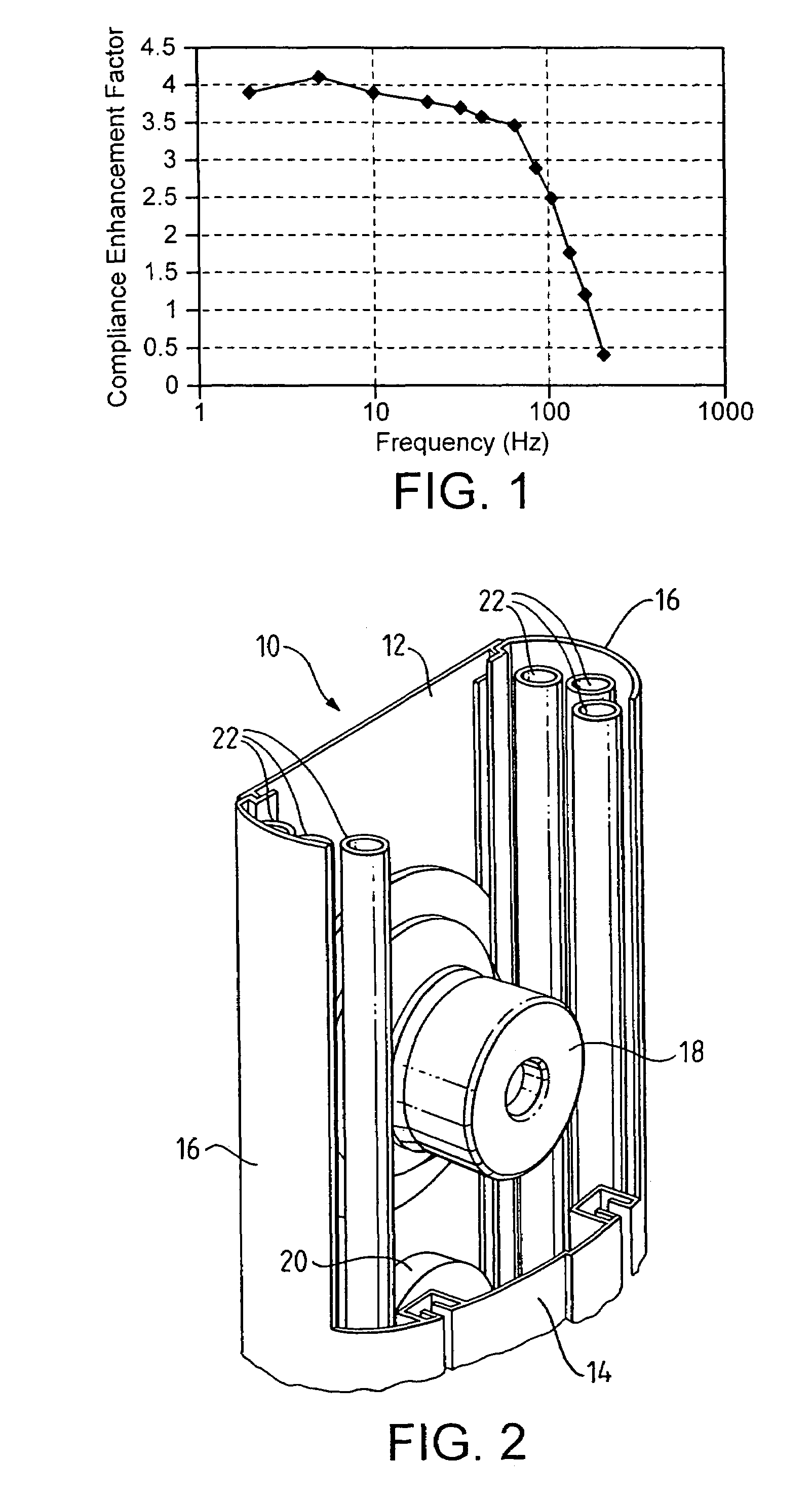
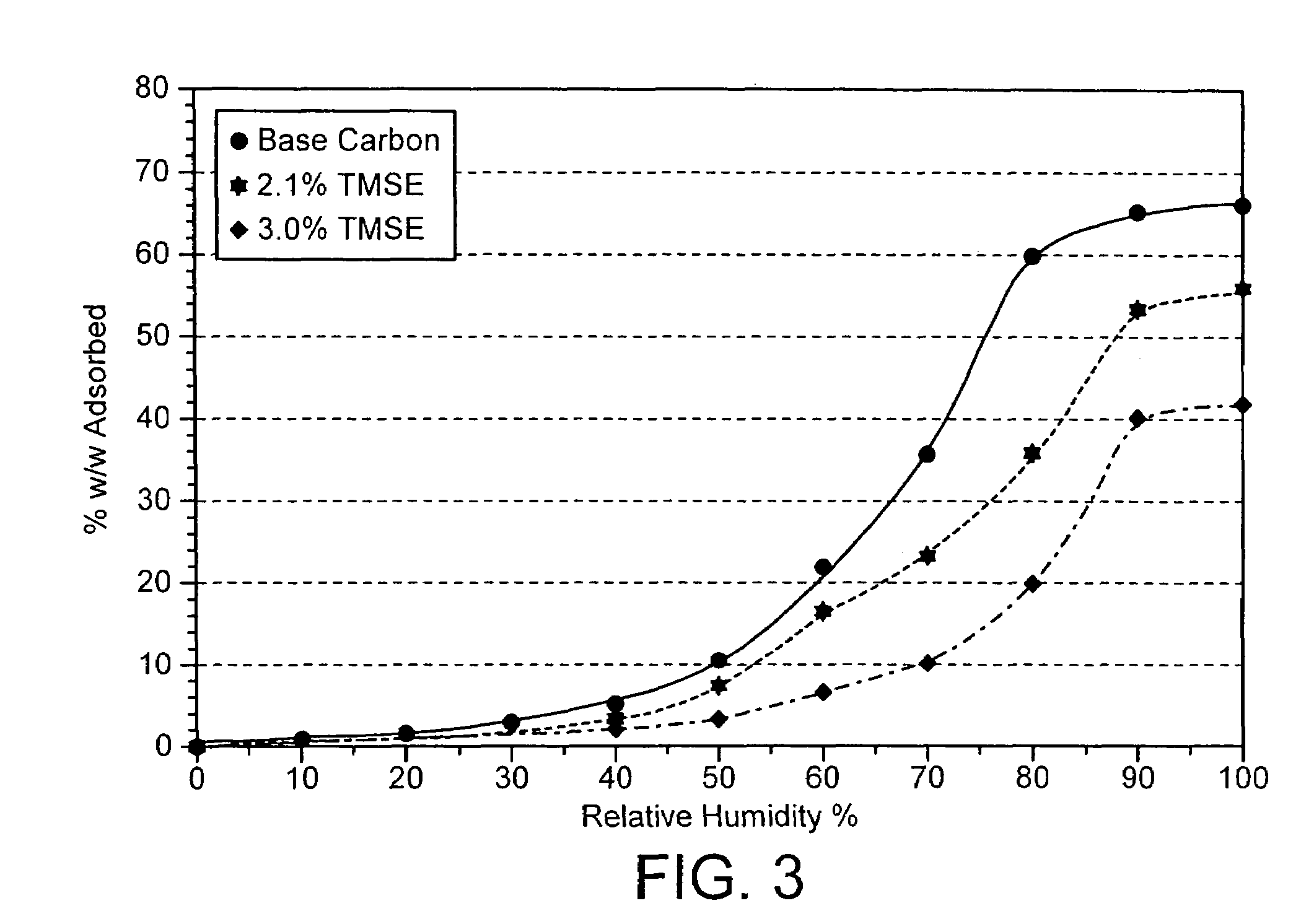
Acoustic enclosures
InactiveUS7448467B2Improve complianceSame acoustic outputCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsCabinetsActivated carbonChemical compound
An acoustic enclosure such as a loudspeaker (10) uses within the cabinet adsorbent material, and / or containment means (22) for the adsorbent material, which is at least partially hydrophobic. Preferably, the material is activated carbon treated to provide it with hydrophobic properties. Preferably, the adsorbent material is treated with a silicon-containing compound. This improves the acoustic compliance of the acoustic enclosure.
Owner:KH TECH +1
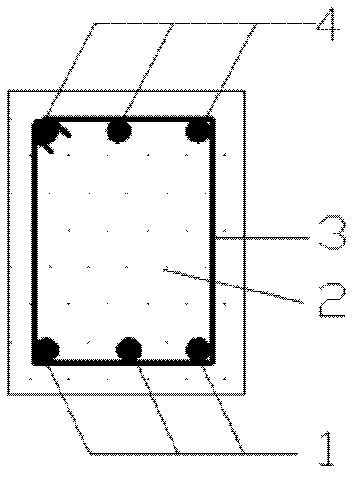
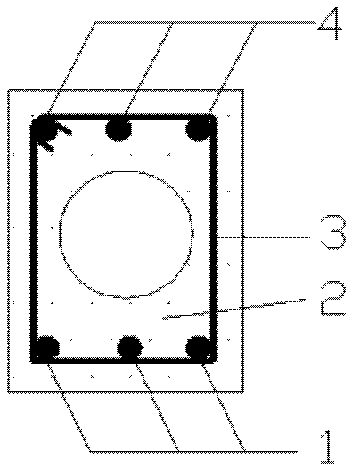
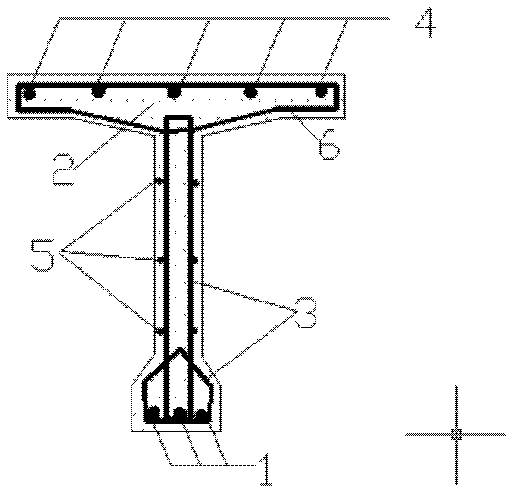
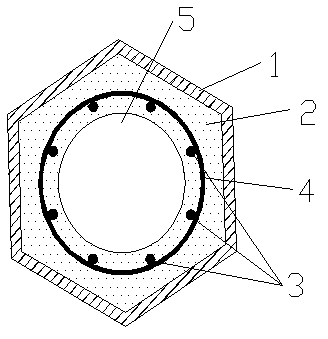
High-strength reinforcement built-in ultra high performance concrete (UHPC) beam member
The invention provides a high-strength reinforcement built-in ultra high performance concrete (UHPC) beam member, which is particularly suitable for the field of beam members with high-rise, heavy load and long span structures. The member comprises UHPC and a reinforcement cage which is poured inside and is formed by high-strength reinforcement and common reinforcement. The beam member has the following advantages: the advantages of the UHPC and the high-strength reinforcement are fully utilized, thus effectively reducing the section of the member, improving the ductility of the member and enlarging the available space while saving materials and energy; and the beam member dispenses with application of prestress, has simple construction process, is suitable for prefabrication production, improves the construction speed and is beneficial to popularization and application of the two materials in the engineering and research and development of novel materials.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
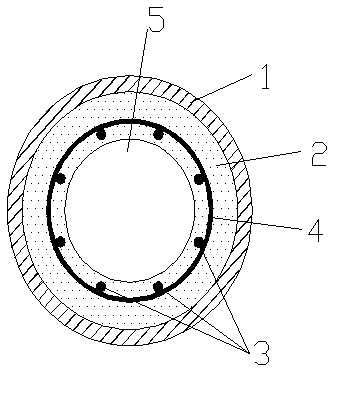
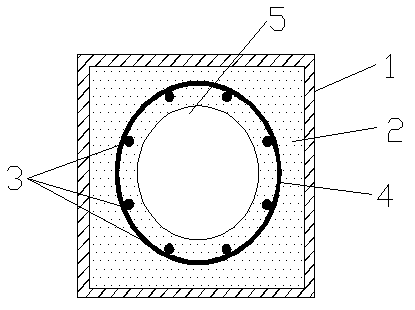
Hollow column member with built-in high tensile steel bars and pipes for confinement of ultra high performance concrete
InactiveCN102296753AReduce section sizeImprove bearing capacityStrutsBuilding reinforcementsRebarHigh rise
The invention provides a hollow column member with built-in high tensile steel bars and pipes for a confinement of ultra high performance concrete, especially being suitable for the field of pier column member of high rise, heavy load and longspan structures. The member comprises a reinforcement cage consisting of outer steel pipes, longitudinal high tensile steel bars and stirrups, and hollow ultra high performance concrete poured on the internal surface of the outer steel pipes wrapping the reinforcement cage. The invention fully utilizes the advantages of the ultra high performance concrete, the high tensile steel bars, and the hoop confinement of the outer steel pipes, effectively reduces the cross section of the member, improves the bearing capacity and stretch ability of the member, so that the member has good earthquake resistant behavior, the materials are saved and the available space is increased at the same time. According to the invention, prestress is not needed, the construction technology is simple, and the construction speed is improved. The member is suitable for the precasting production, is good for application of the two high tensile materials in projects, and meets the design concepts of energy saving, environmental protection and new style.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Rail system and X-ray imaging apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7949094B2Reduce spacingIncrease available spaceX-ray/infra-red processesImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesX-rayEngineering
Owner:MEDIEN INT
Block-level continuous data protection method based on solid-state disc
InactiveCN103544110ANo lasting effectIncrease available spaceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationBlock levelSolid-state
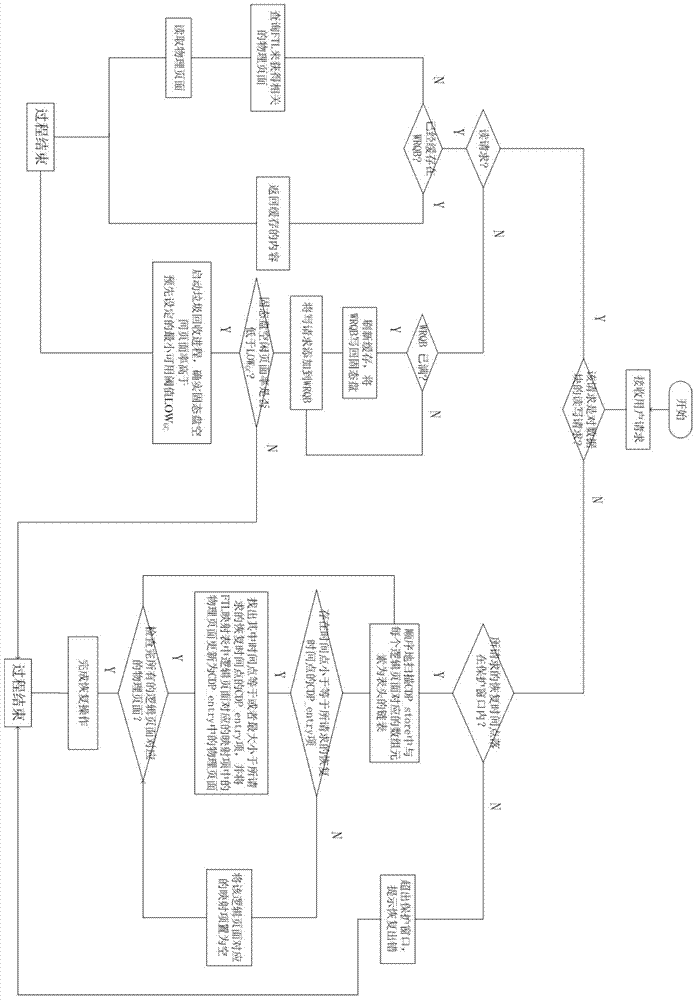
The invention discloses a block-level continuous data protection method based on a solid-state disc. The block-level continuous data protection method based on the solid-state disc comprises the steps that an empty write request queue cache is built in the inner memory and used for storing write requests from a user in a buffering mode, and an inner memory space CDP_store is initialized in an FTL layer of solid-state disc and used for recording historical records CDP_entry of an FTL mapping chart, receiving the requests from the user and judging that the requests are read-write requests or recovery requests on data blocks. If the requests are the read-write requests on the data blocks, the inner memory space CDP_store judges that the requests are read requests or write requests, if the requests are write requests, whether the write request queue cache has residual cache space or not is judged, and if not, the content in the write request queue cache is written back onto the solid-state disc. The block-level continuous data protection method based on the solid-state disc combines the characteristics of the solid-state disc and utilizes the characteristics left by 'covered' historical data, generated in an internal 'non-local updating' process of the solid-state disc, in the solid-state disc, thereby achieving the function of continuous data protection based on SSD.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
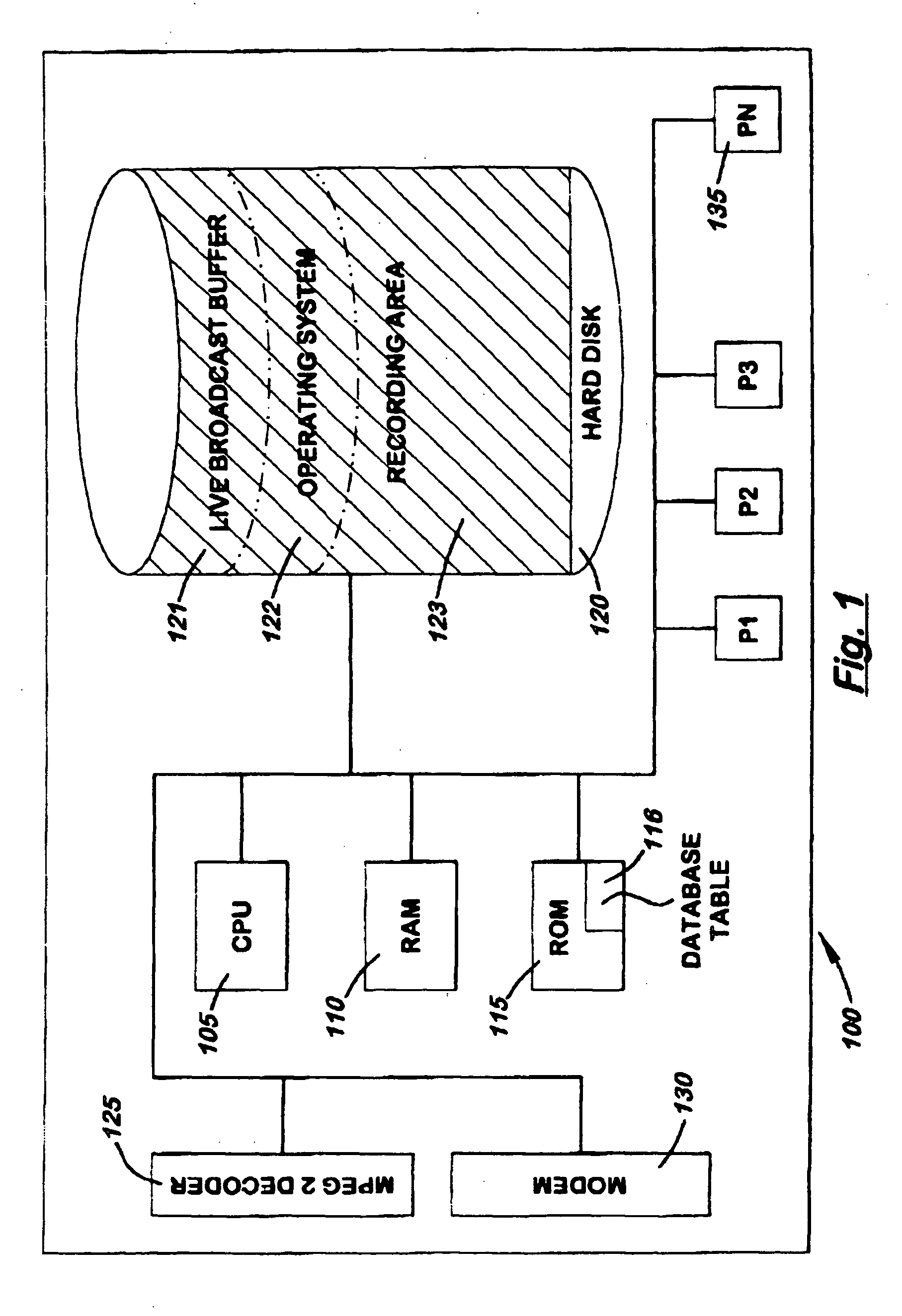
User automated content deletion
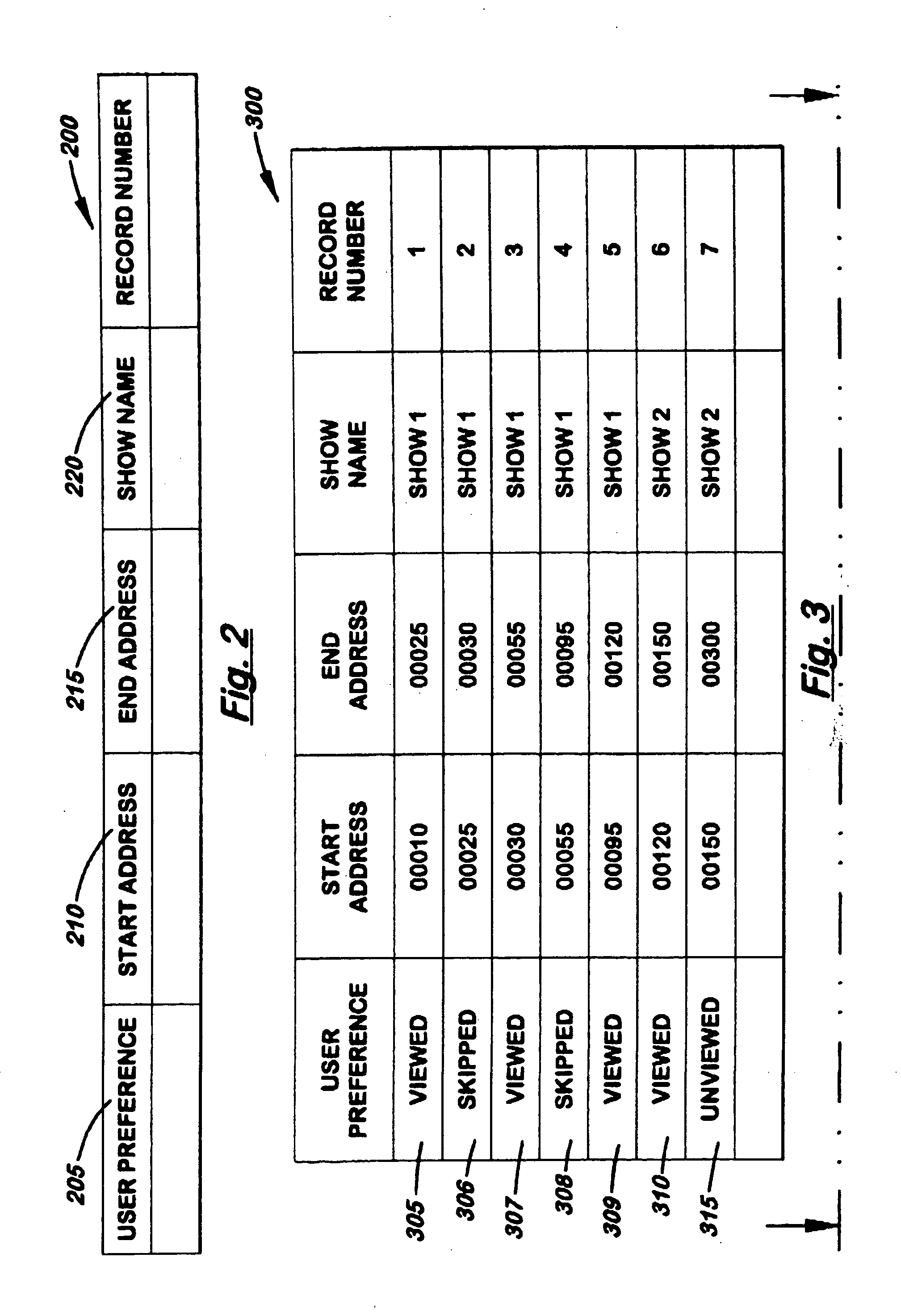
InactiveUS20050232610A1Increase available spaceEffective maintenanceTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsResource allocationOperating system
The present invention provides a method of efficient resource-allocation of space on the hard disk of a PVR by furnishing a viewer with an automated content deletion capacity. The system may maintain individual scene segments on the hard disk along with the associated database table. The database table may contain viewer preference information (viewed, skipped, or unviewed) and starting / ending address information for each scene segment. By consulting the database table, the system may know what scene segments would be played or skipped. Further, upon reception of the user's request, the system may update the database table, which results to have more available space on the hard disk. Thus, the system may utilize the hard disk space efficiently.
Owner:XLAB D O O
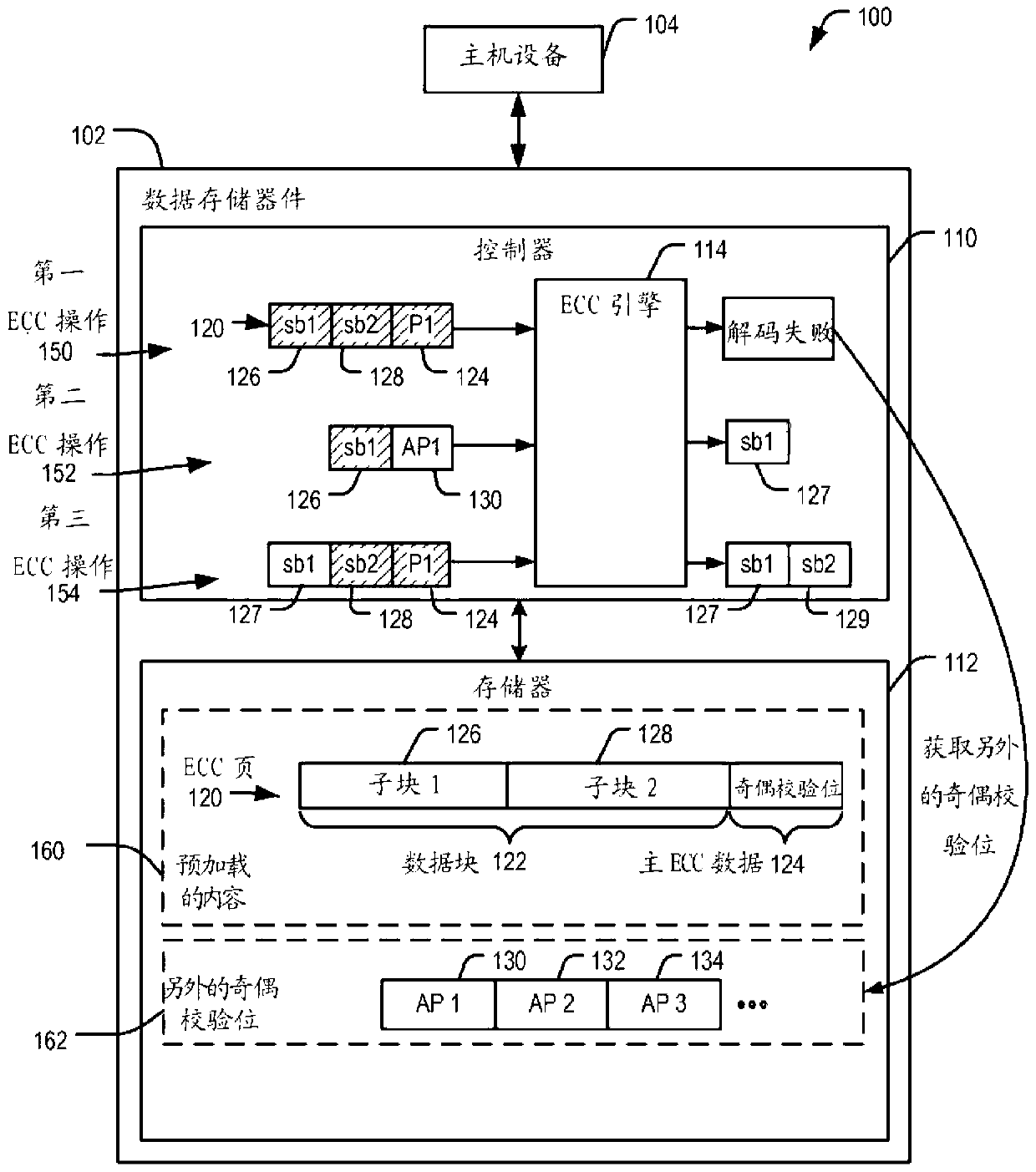
Data recovery using additional error correction coding data
A method in a data storage device receiving data including a data block and main error correction coding (ECC) data for the data block. The data block includes a first sub-block of data and a second sub-block of data. The method also includes initiating an ECC operation to process the data block using the main ECC data. In response to the ECC operation indicating uncorrectable errors in the data block, first additional ECC data that is external to the data block is retrieved and a second ECC operation is initiated to process the first sub-block of data using the first additional ECC data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
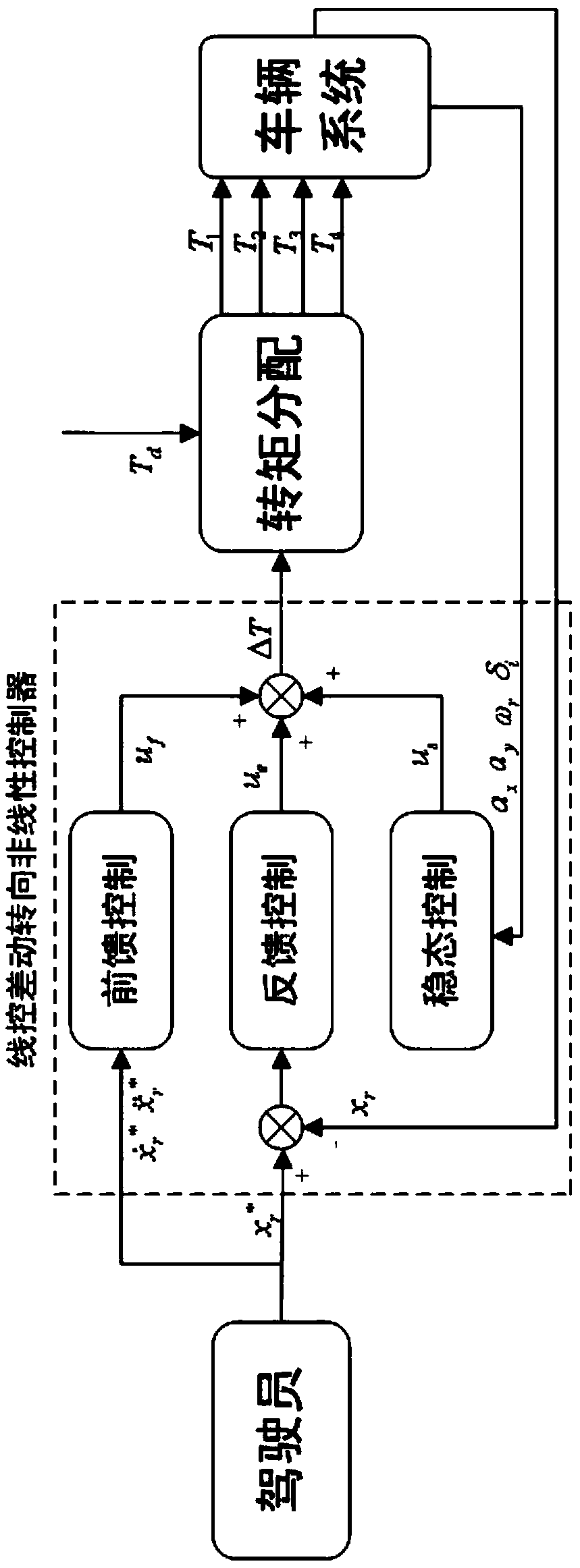
Drive-by-wire differential steering system for wheel type independent drive vehicle and control method thereof
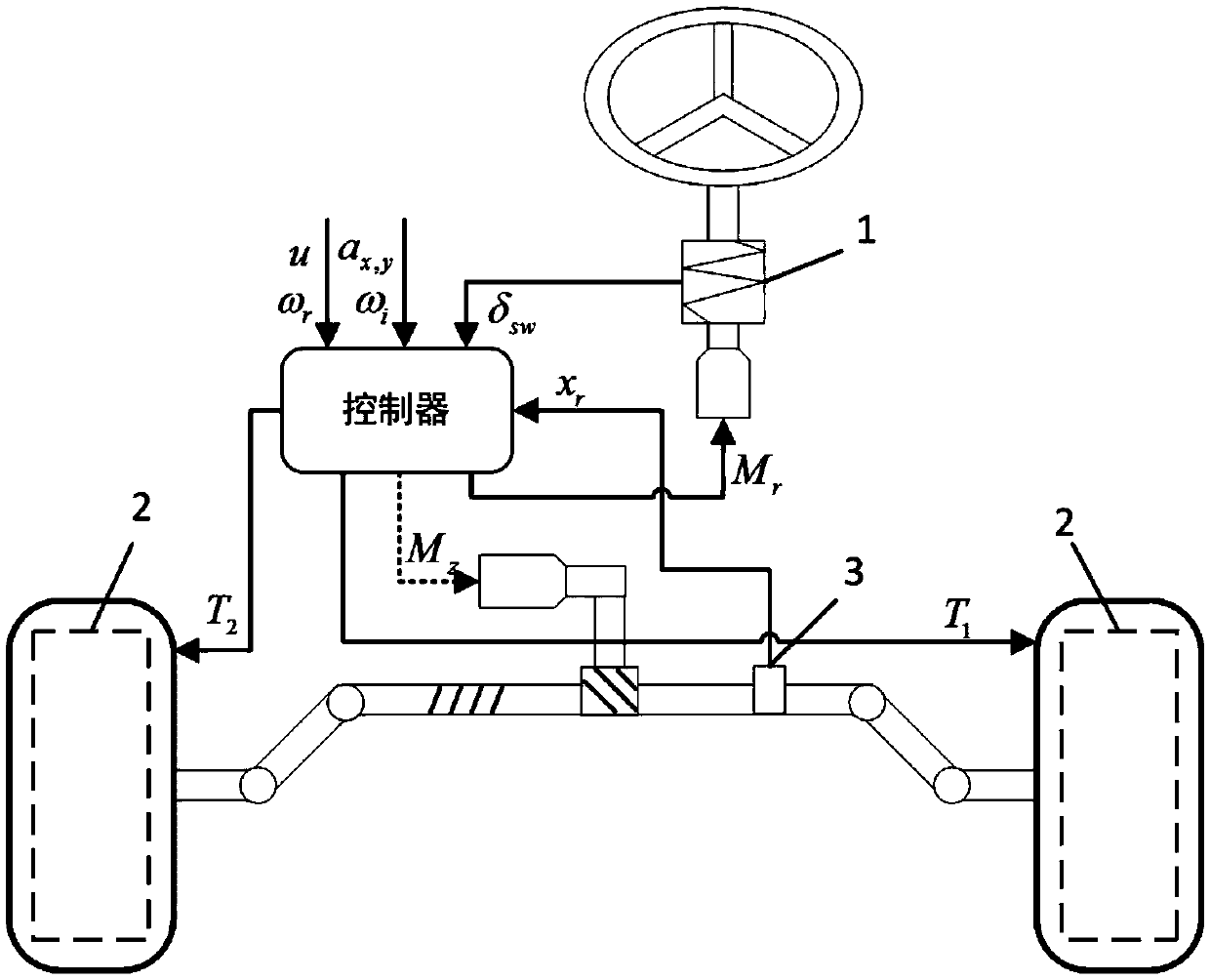
ActiveCN109515512ASimple structureIncrease available spaceSpeed controllerMechanical steeringSteering systemSystem integration
The invention relates to a drive-by-wire differential steering system for a wheel type independent drive vehicle, the system comprising: an information detection module for detecting various state information of the vehicle; a controller used for judging steering modes according to the various kinds of detected state information of the vehicle, including a steer-by-wire mode and a drive-by-wire differential steering mode, deciding target torque required by each motor, and sending corresponding motor control signals; and a steering execution module used for making a corresponding torque response according to the motor control signal so as to drive the steering mechanism to move and realize differential steering of the electric automobile. The invention further discloses a control method ofthe drive-by-wire differential steering system for the wheel type independent drive vehicle. The invention also provides a control method of the drive-by-wire differential steering system for a wheeltype independent drive vehicle. Front axle left and right wheel hub motors serve as steering power sources, so that steering mechanical connection, a steering power assisting device and the like are omitted, the structure of a steering system is simplified, the available space in a vehicle is increased, system integration is easier, and cost is reduced.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
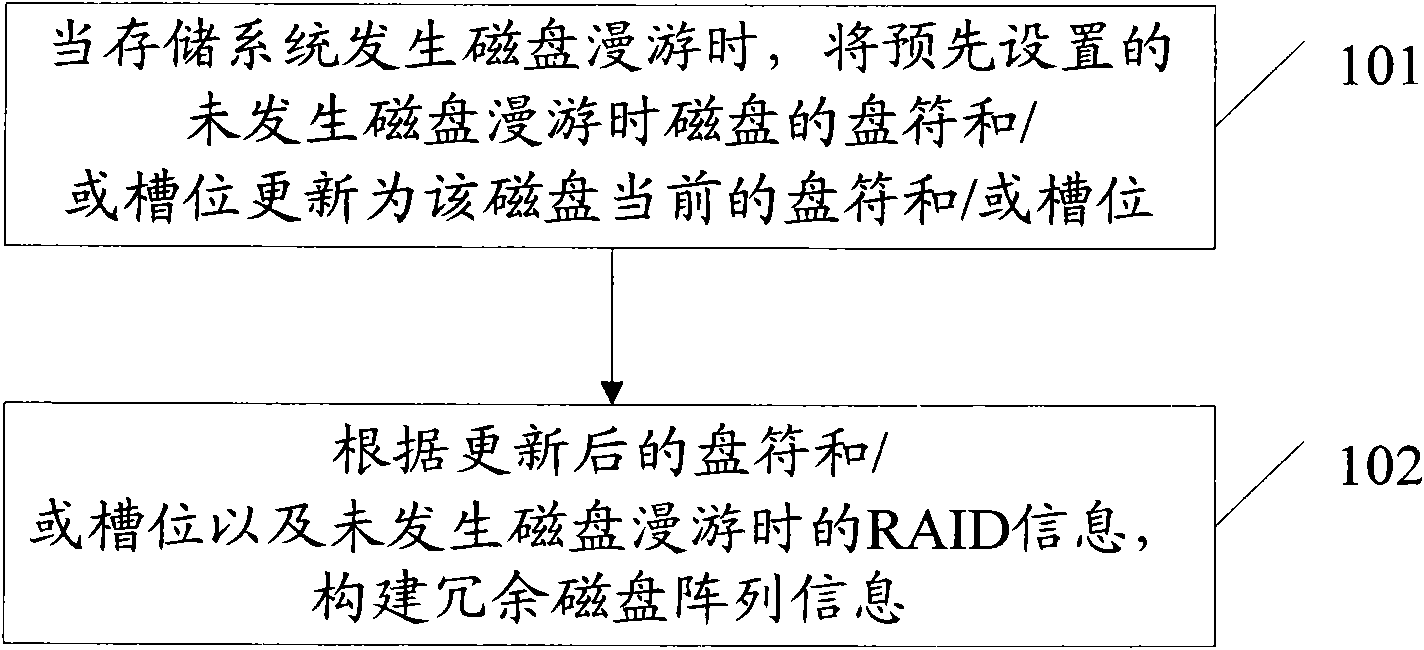
Method and device for processing disk roam in storage system
ActiveCN101776984AIncrease available spaceGuaranteed to be availableInput/output to record carriersRAIDEngineering
The invention provides a method and a device for processing disk roam in a storage system, which relates to the field of storage. The method comprises the following steps of: when a storage system generates disk roam, updating the drive and / or the slot position of a preset disk which does not generate the disk roam into the current drive and / or the slot position of the disk; and according to the updated drive and / or slot position and PAD information when the disk roam is not generated, constructing the information of Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID).
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Pedal board
ActiveUS20170206879A1Increase available spaceElectrophonic musical instrumentsSurface structureElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:DIGITAL MUSIC CORP DBA VOODOO LAB
Extension type hanging basket
The invention relates to a device in the technical field of cleaning equipment, in particular to an expansion type hanging basket for a window-cleaning machine. The extension type hanging basket comprises a main body basket, a hoister and a rope guide pulley, wherein the guide rails of the rope guide pulley are mounted on both sides of the main body basket; a lower guide pulley is mounted on the lower side of the main body basket; a movable platform comprises an upper guide pulley and connected with the guide rails through the upper guide pulley; the lower end of the movable platform is supported and guided by the lower guide pulley; and the movable platform can move along the guide rails. The extension type hanging basket overcomes the defects in the prior art, can finish cleaning work on the concave-convex wall surface, and is simple in the whole structure and convenient to operate.
Owner:PINGHU POINT HIGH RISE EQUIP
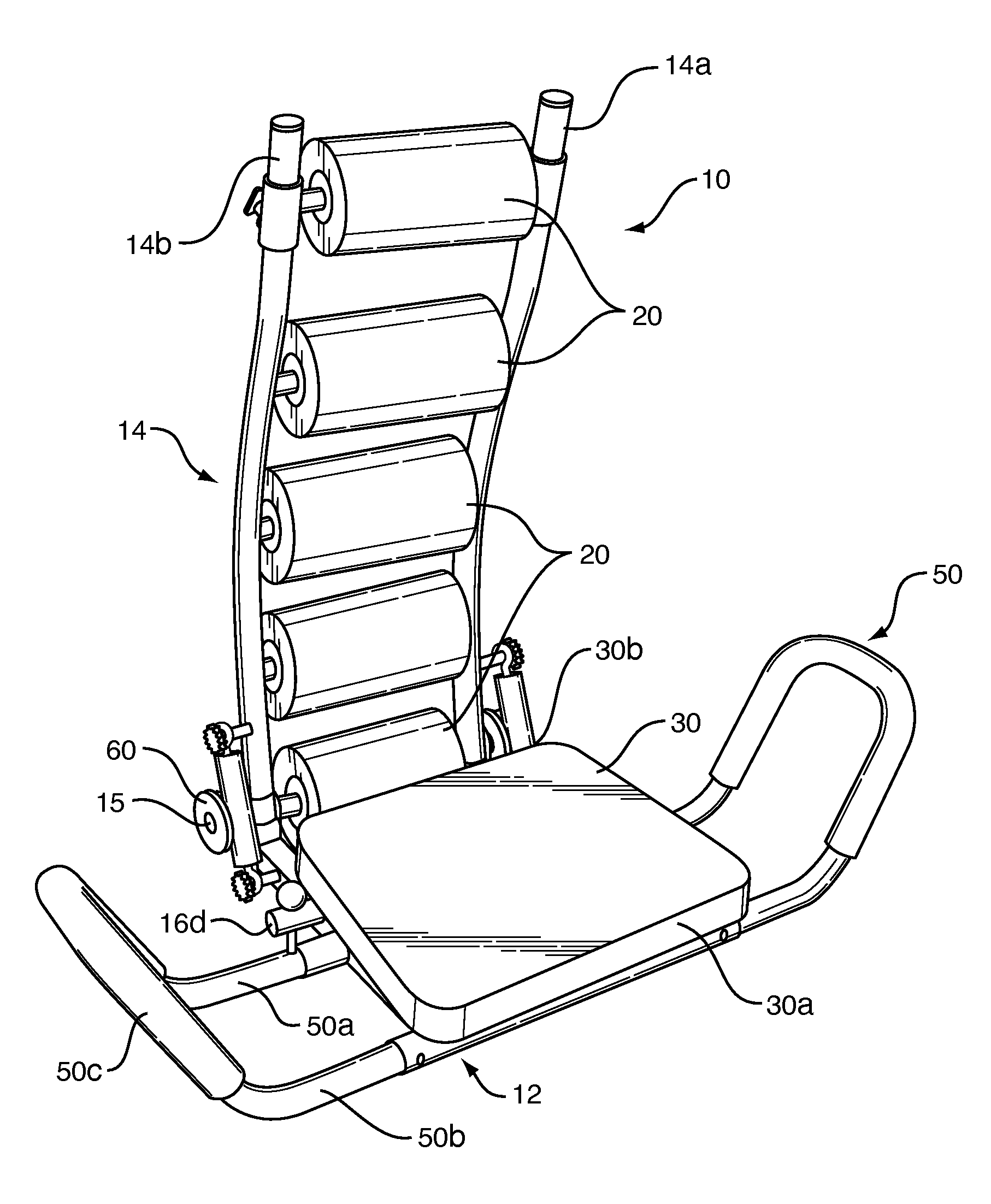
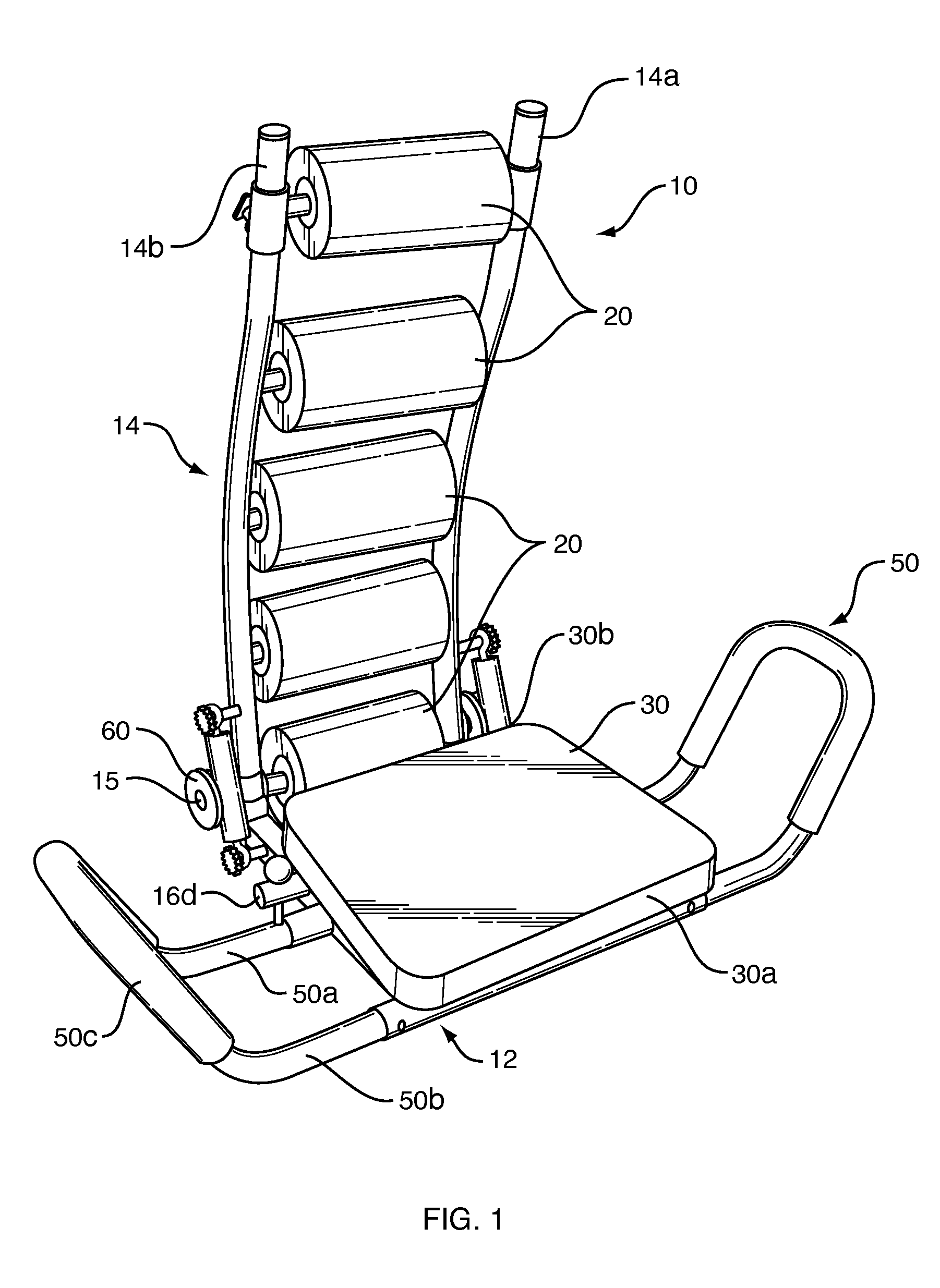
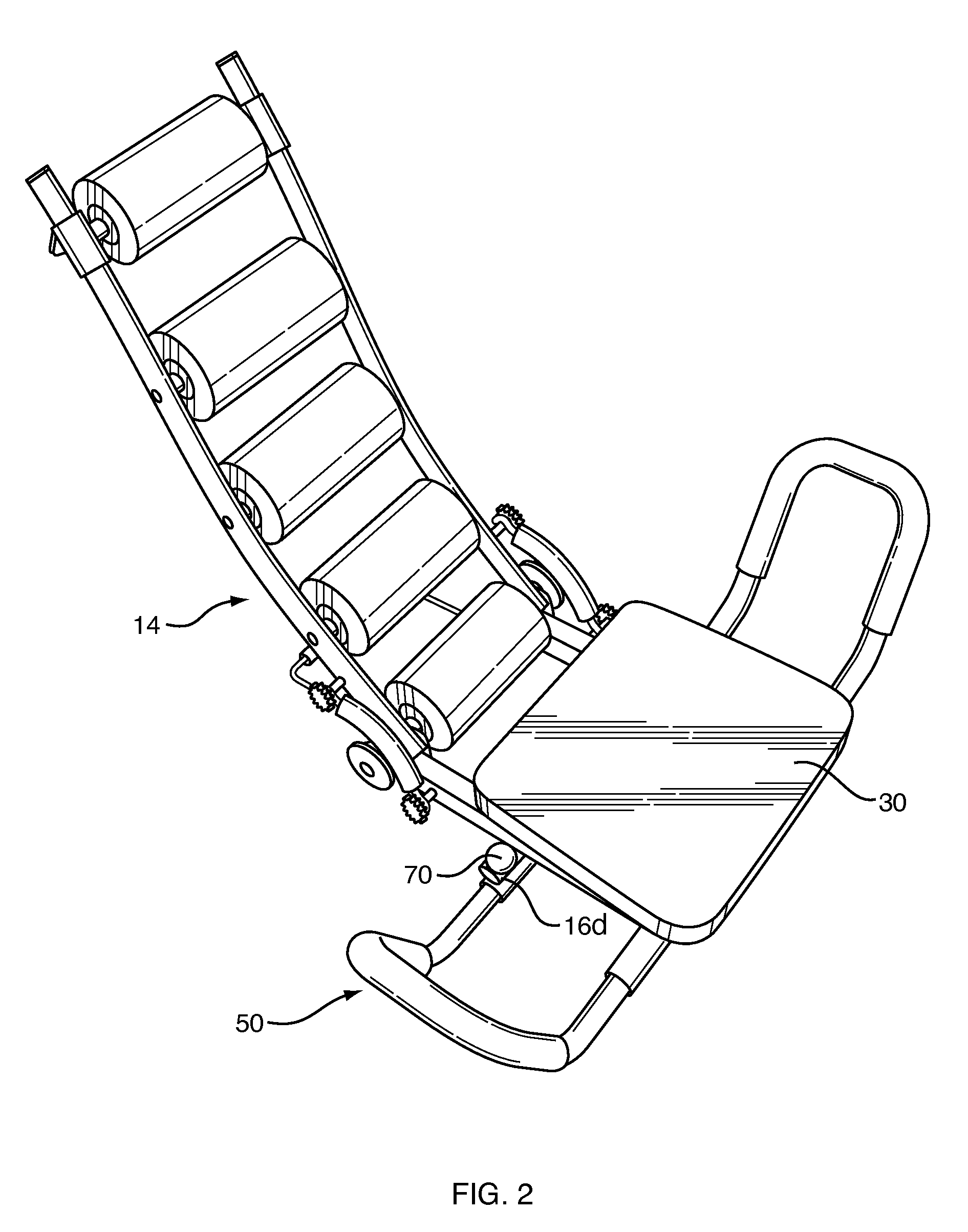
Abdominal exerciser with rotatable seat and tandem pulley features
An abdominal exerciser has base and back frames pivotally mounted for movement between upright and recumbent positions, and a seat frame with cushion rotatable on the base frame. A low friction journal between the base and seat frames supports a user's weight. The journal is about 30 to 42% the distance from a rear end of the cushion to its front end so the user's coccyx is vertically aligned with the journal. Arms at each side of the base frame have a pair of extensions connected to either the base or seat frame, each with a U-shaped handhold lying in a plane at an acute angle of about 30 to 80 degrees to the horizontal. A pair of single pulleys or a pair of tandem pulleys are mounted near the rear of the base frame and are engaged by sleeve-covered springs for biasing the back frame toward the upright position.
Owner:E MISHAN & SONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com