Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49results about How to "Avoid feature degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
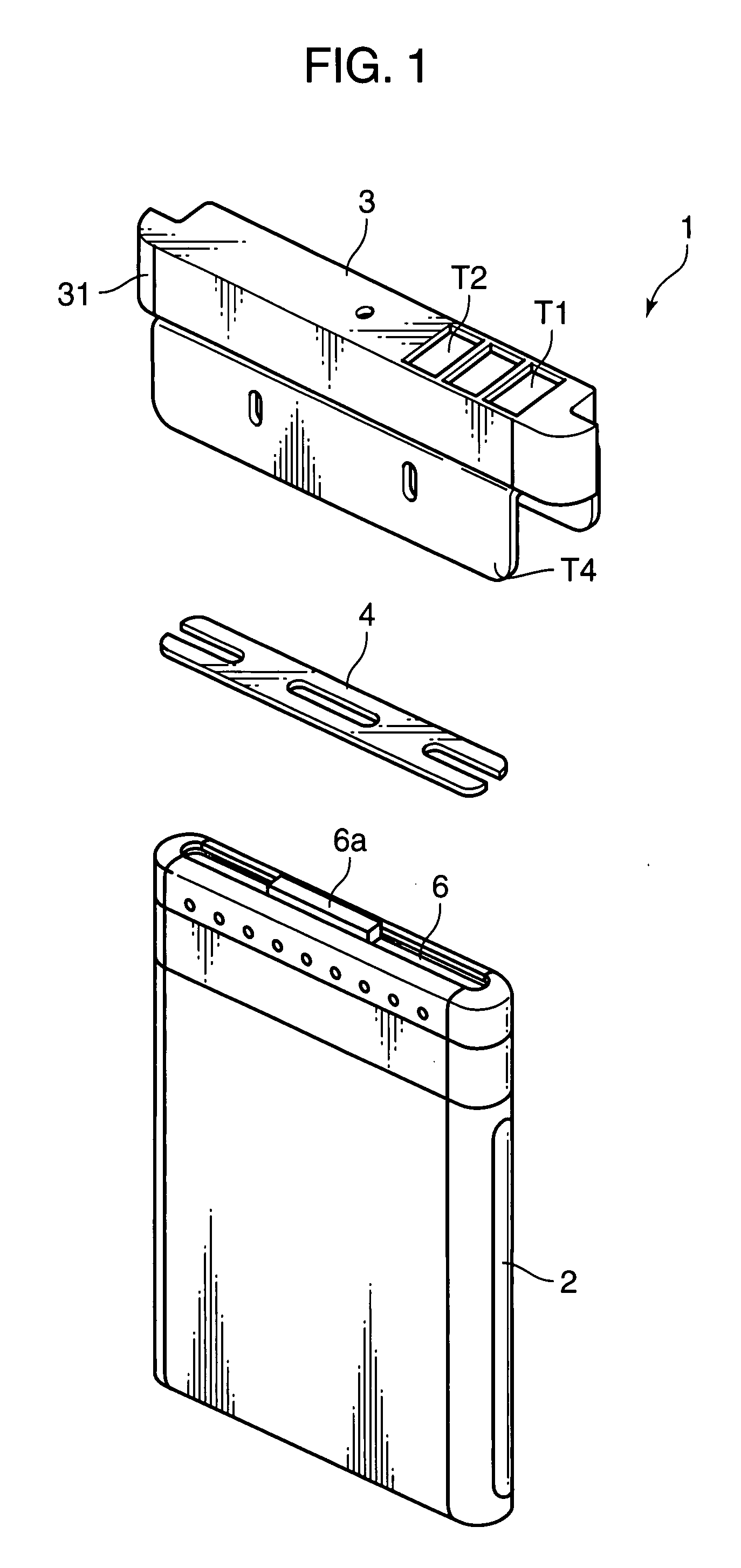
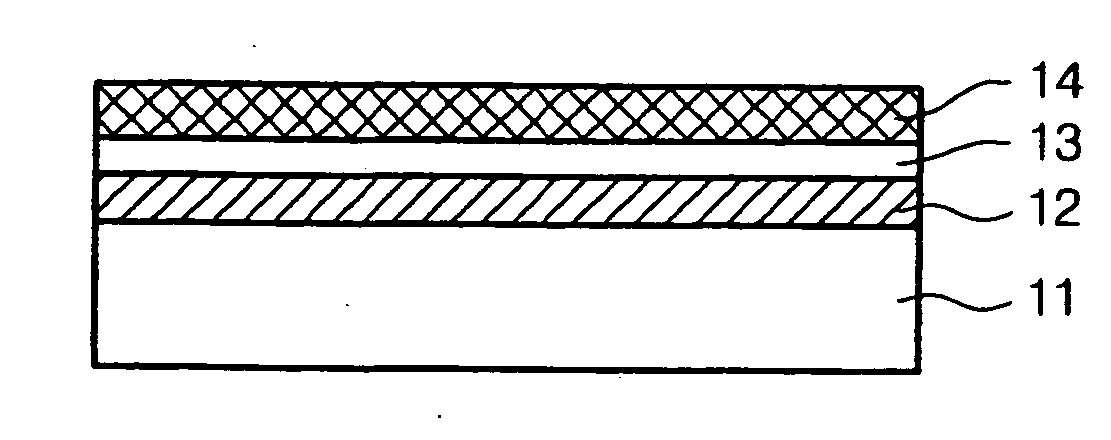
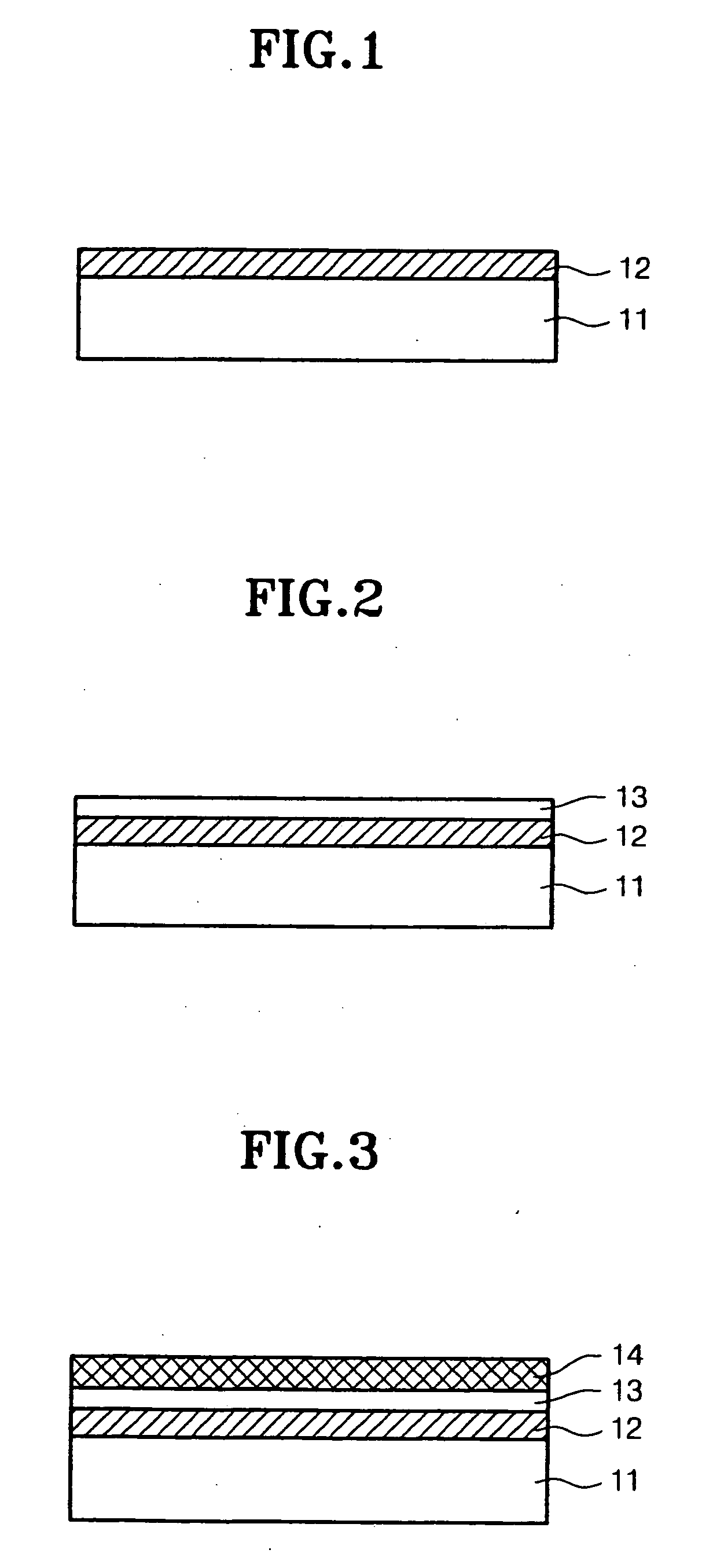
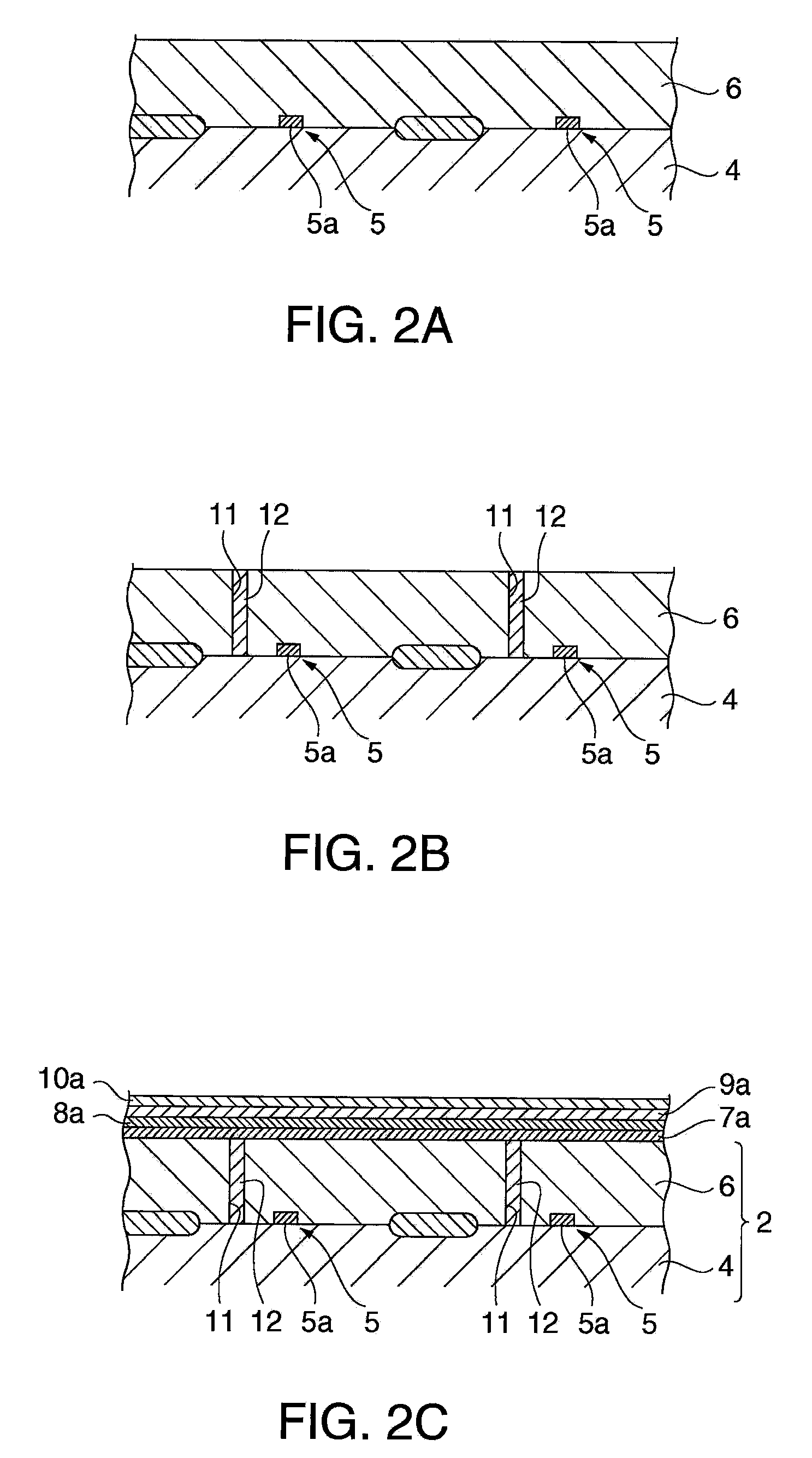
Secondary Battery Protection Circuit, Battery Pack and Thermosensitive Protection Switch Device
InactiveUS20080116851A1Reduced characteristicsReduce degradationElectrothermal relaysEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringDischarge current
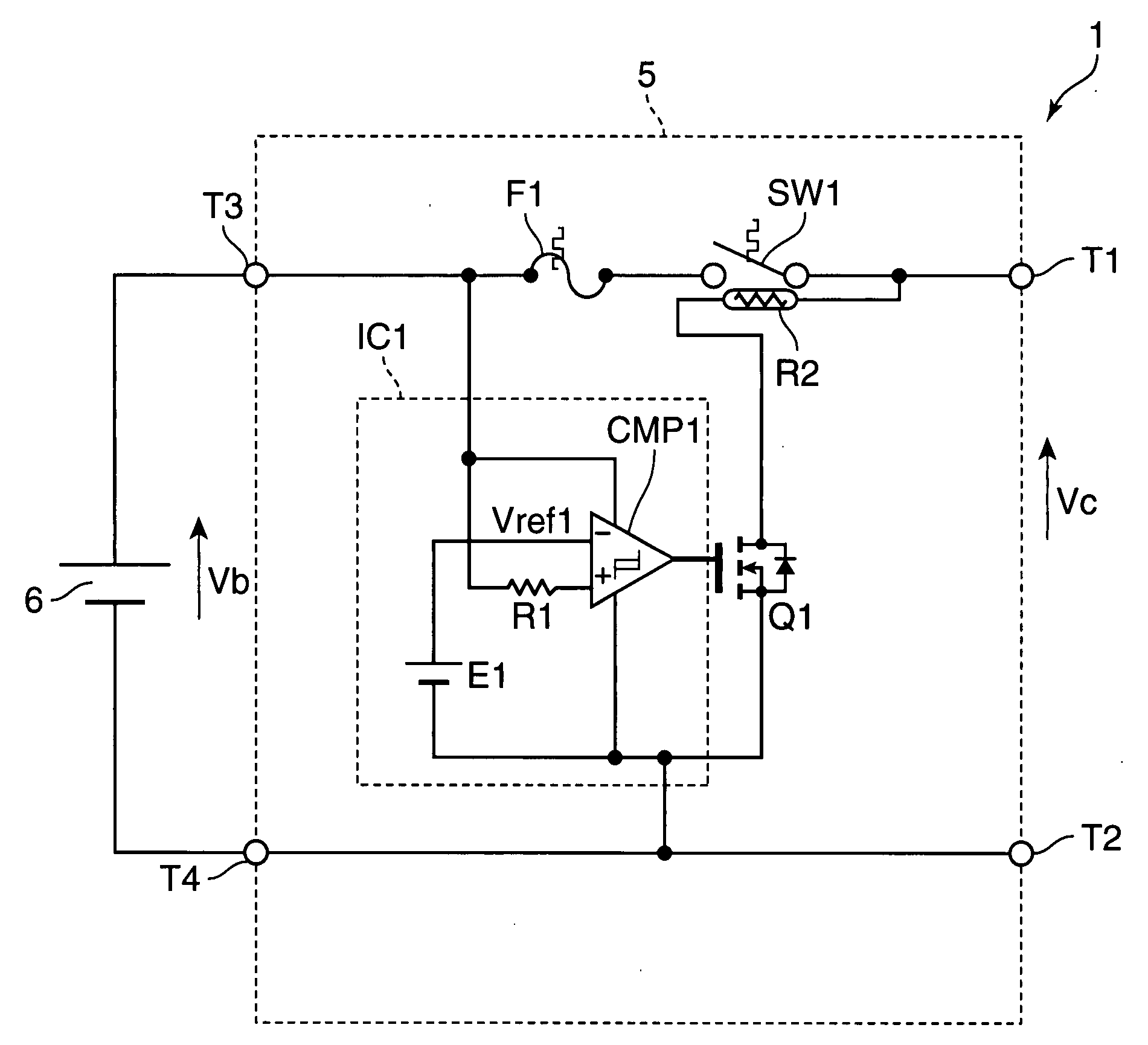
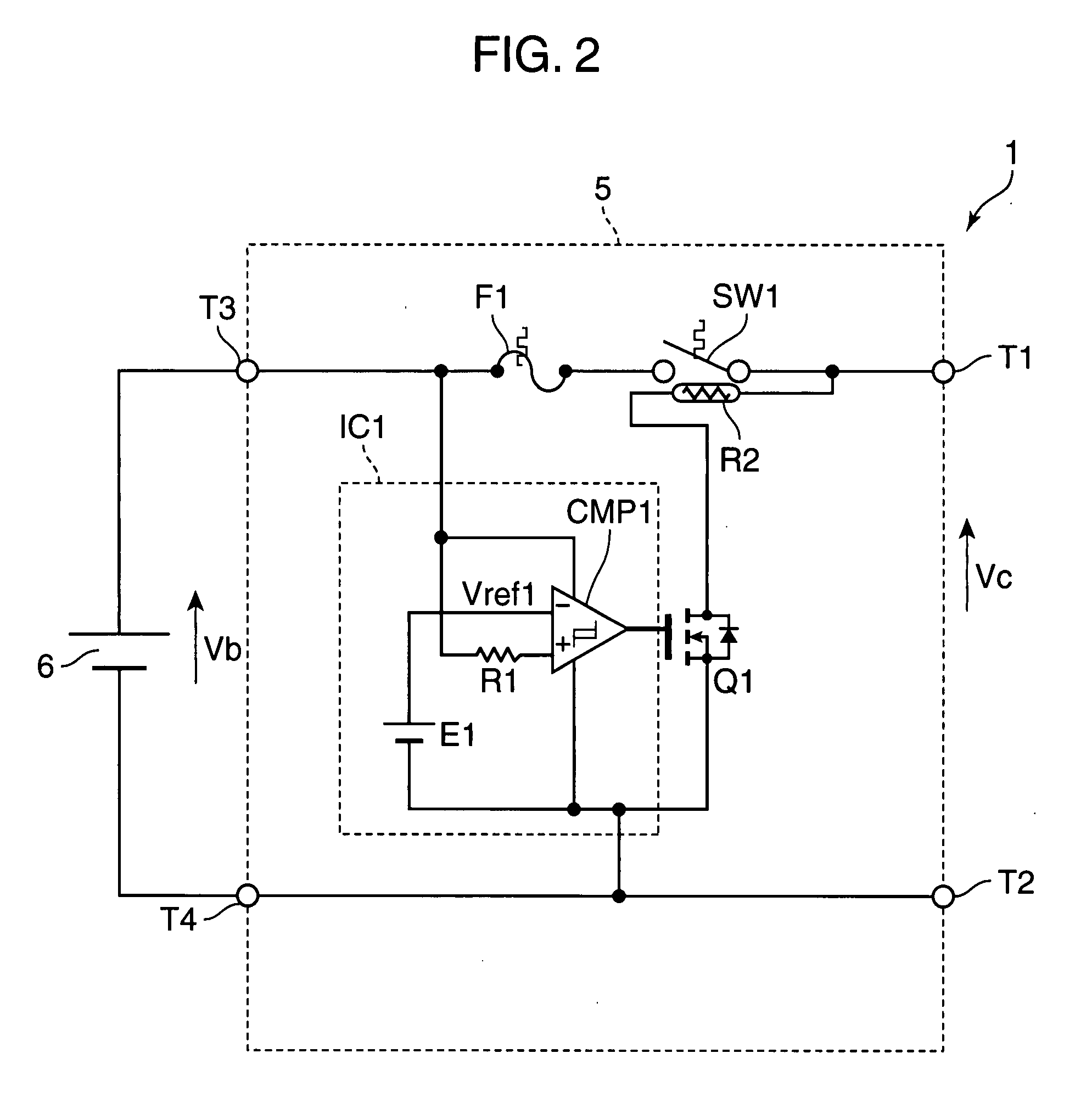
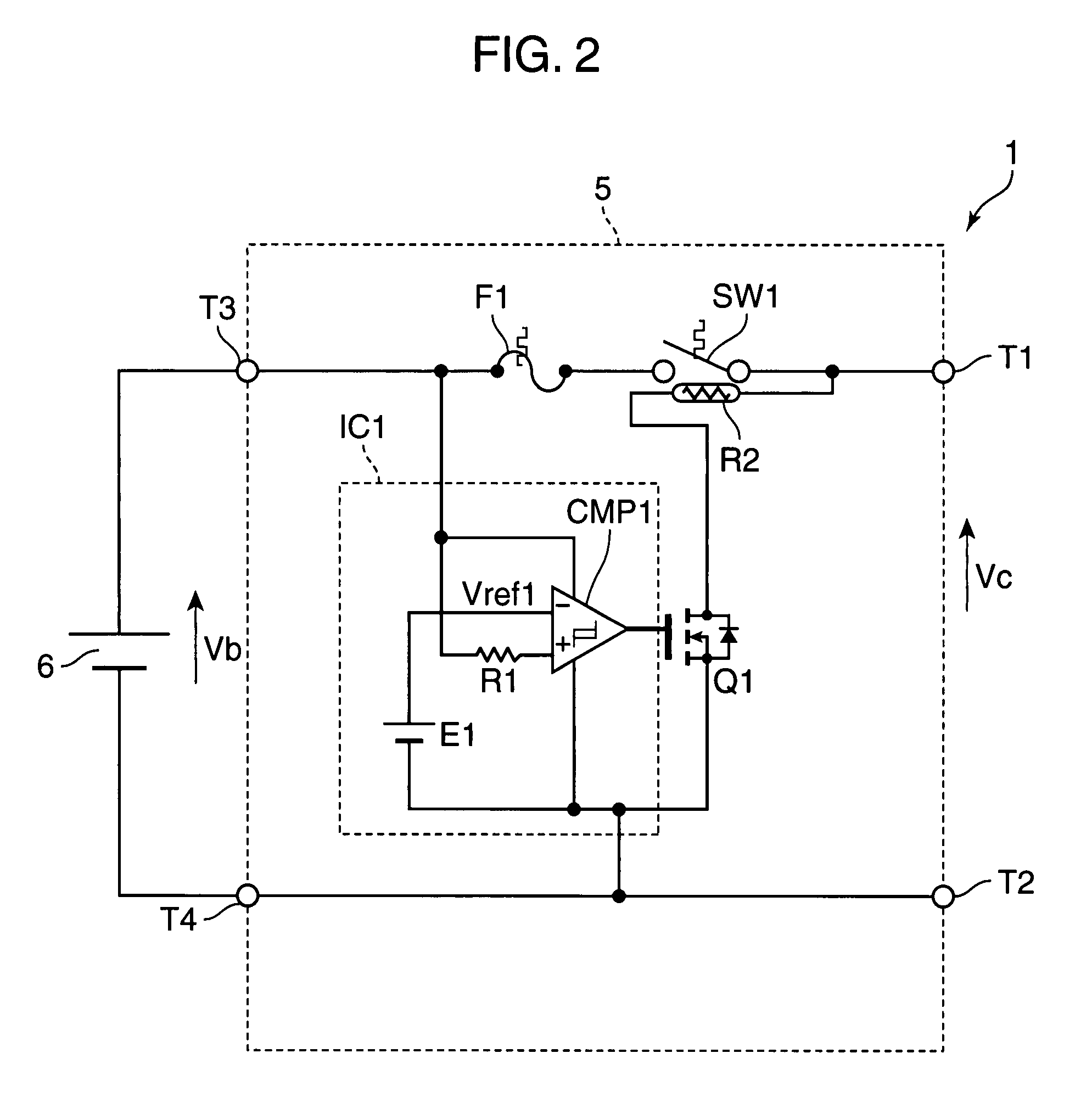
A protection circuit is provided for protecting a secondary battery from overcharging and excessive discharge current by a simple circuit. The protection circuit is provided with a connection terminal (T3) for connecting the secondary battery (6); a connection terminal (T1) for connecting a charging device for charging the secondary battery (6) and / or a load device driven by a discharge current from the secondary battery (6); a bimetal switch (SW1) that is provided between the connection terminals (T1, T3) and turned off in the case of exceeding a specified temperature set beforehand; a heater (R2) for heating the bimetal switch (SW1); and an integrated circuit (IC1) for turning the bimetal switch (SW1) off by causing the heater (R2) to generate heat if a voltage applied to the connection terminal (T3) by the secondary battery (6) exceeds a preset reference voltage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Secondary battery protection circuit, battery pack and thermosensitive protection switch device
InactiveUS7952330B2Avoid feature degradationReduced characteristicsSecondary cellsElectric powerSimple circuitBattery pack
A protection circuit is provided for protecting a secondary battery from overcharging and excessive discharge current by a simple circuit. The protection circuit is provided with a connection terminal (T3) for connecting the secondary battery (6); a connection terminal (T1) for connecting a charging device for charging the secondary battery (6) and / or a load device driven by a discharge current from the secondary battery (6); a bimetal switch (SW1) that is provided between the connection terminals (T1, T3) and turned off in the case of exceeding a specified temperature set beforehand; a heater (R2) for heating the bimetal switch (SW1); and an integrated circuit (IC1) for turning the bimetal switch (SW1) off by causing the heater (R2) to generate heat if a voltage applied to the connection terminal (T3) by the secondary battery (6) exceeds a preset reference voltage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electronic component and method for manufacturing electronic component
InactiveUS20130208401A1Small sizePrevent penetrationFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricThin film electrodeAlloy
An electronic component has an element body and an external electrode arranged on the element body. The element body has a pair of end faces opposed to each other, a pair of principal faces opposed to each other, and a pair of side faces opposed to each other. The external electrode is formed so as to cover the end face and a partial region of the principal face and / or a partial region of the side face. The external electrode has a thick film electrode, a thin film electrode, and a plated layer. The thick film electrode is formed on the end face. The thin film electrode is formed so as to cover the thick film electrode and the partial region of the principal face and / or the partial region of the side face. The plated layer is formed outside the thin film electrode and contains Sn or an Sn alloy.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
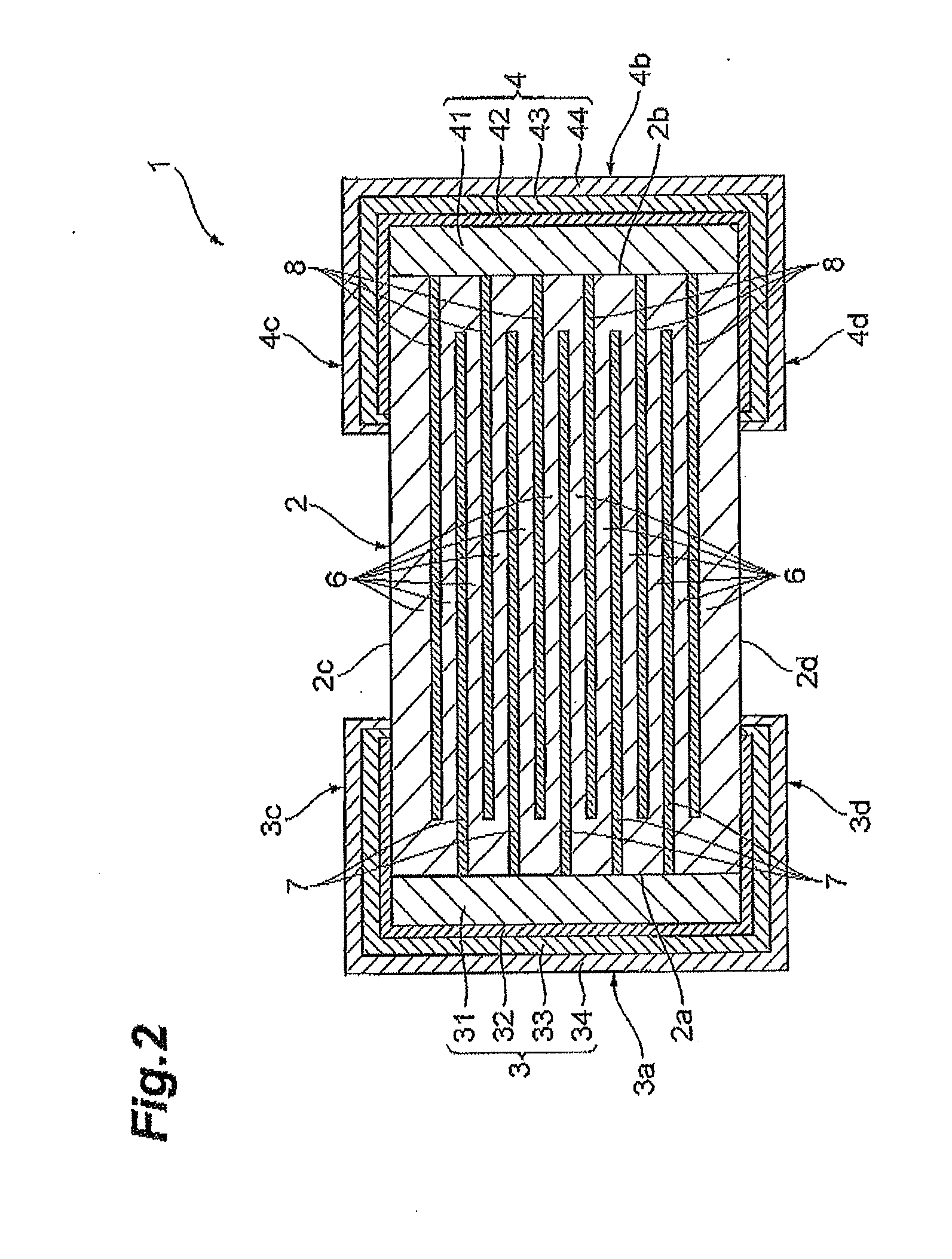
Communication module
ActiveUS20150119102A1Improve installation densityImprove cooling efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionComputer moduleElectronic component
A communication module includes a circuit substrate having a first high-frequency processing section related to mobile phone communication, a second high-frequency processing section that processes reception signals related to satellite positioning systems, a system section having a baseband processing section and application processing section, and a power circuit section, a sealing member covering the electronic components mounted on the circuit substrate, a conductive shield layer formed on a surface of the sealing member, and a shield wall formed in the sealing member so as to demarcate a mounting area of the first high-frequency processing section and a mounting area of the second high-frequency processing section.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
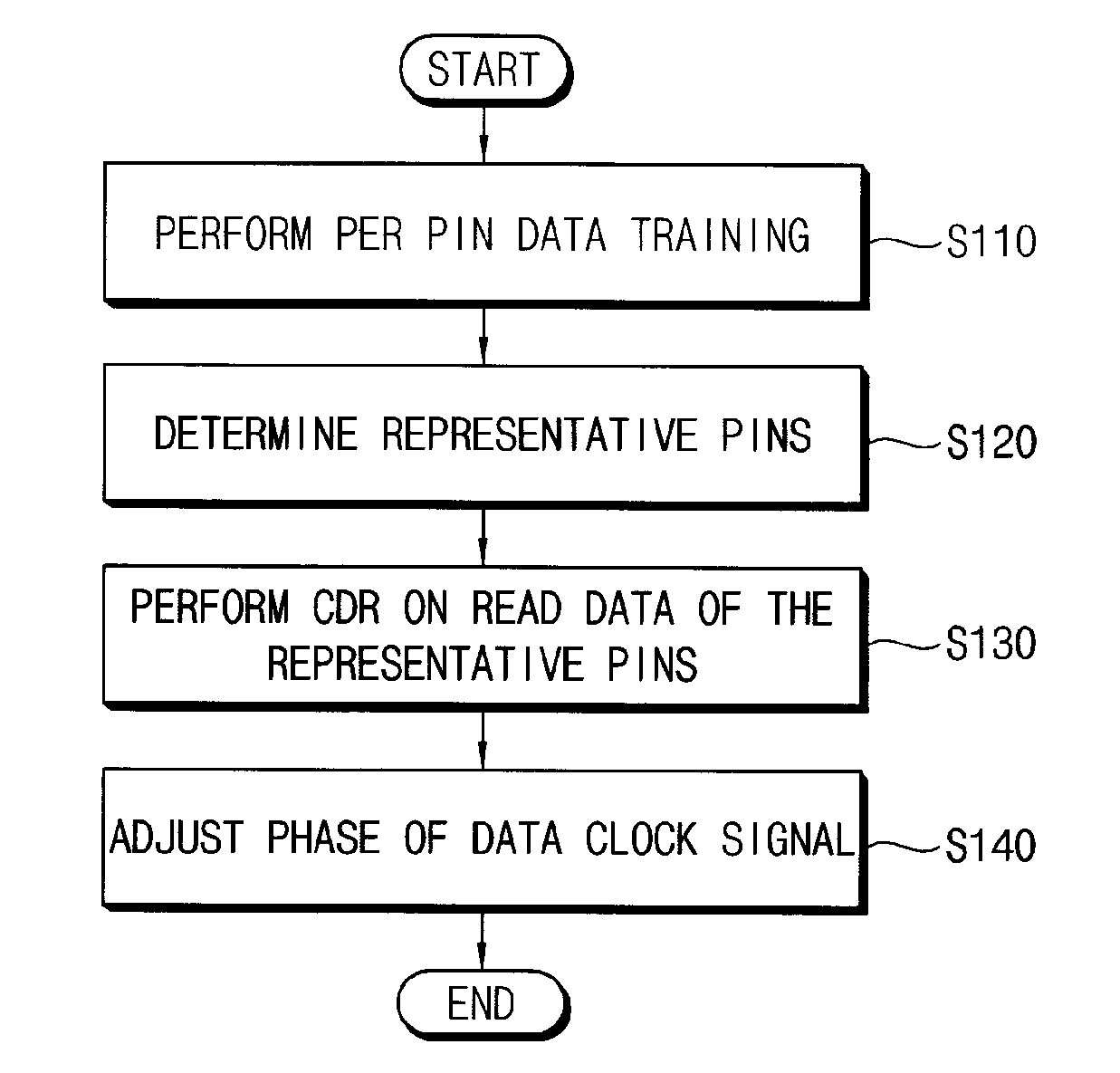
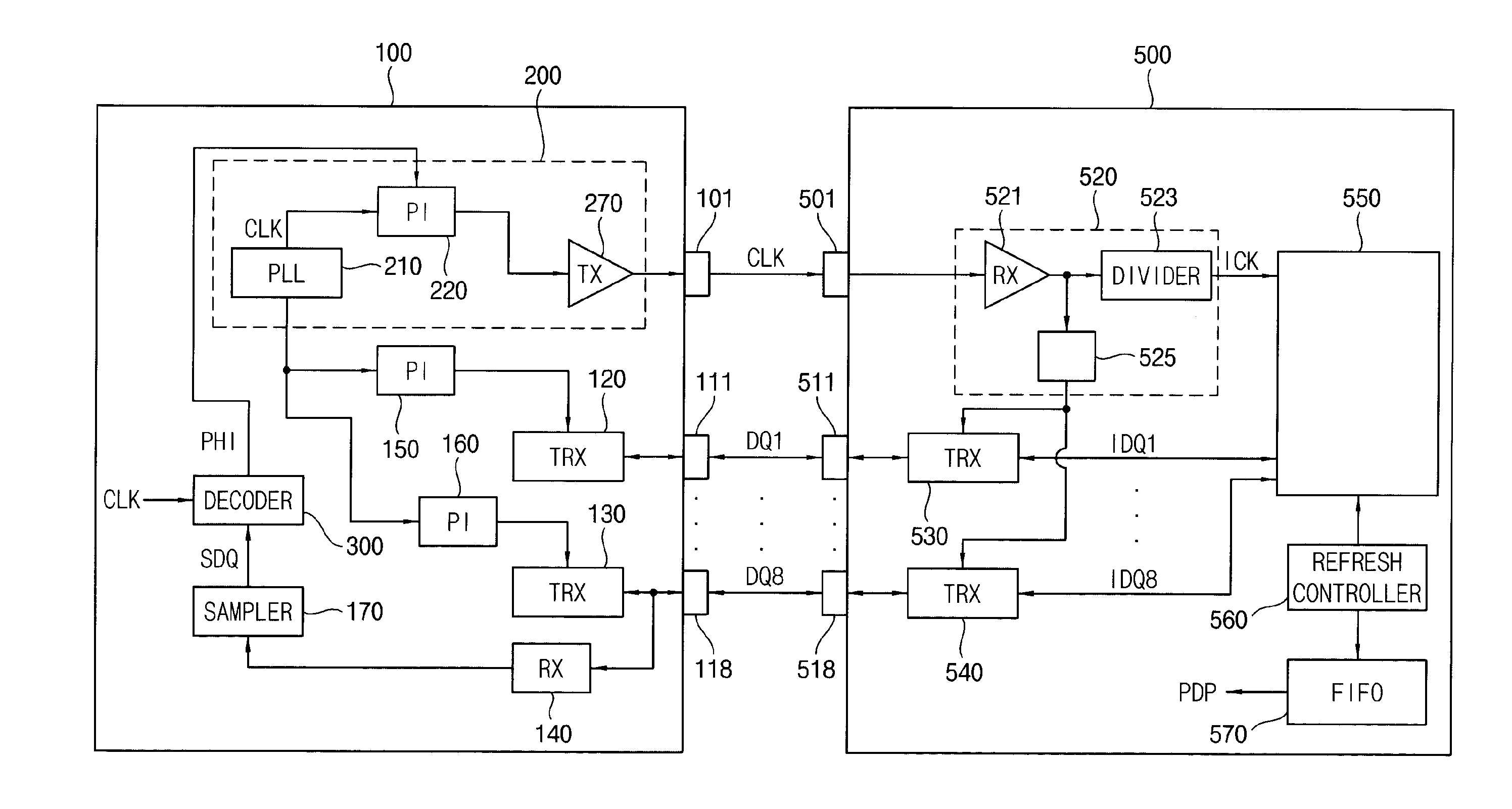
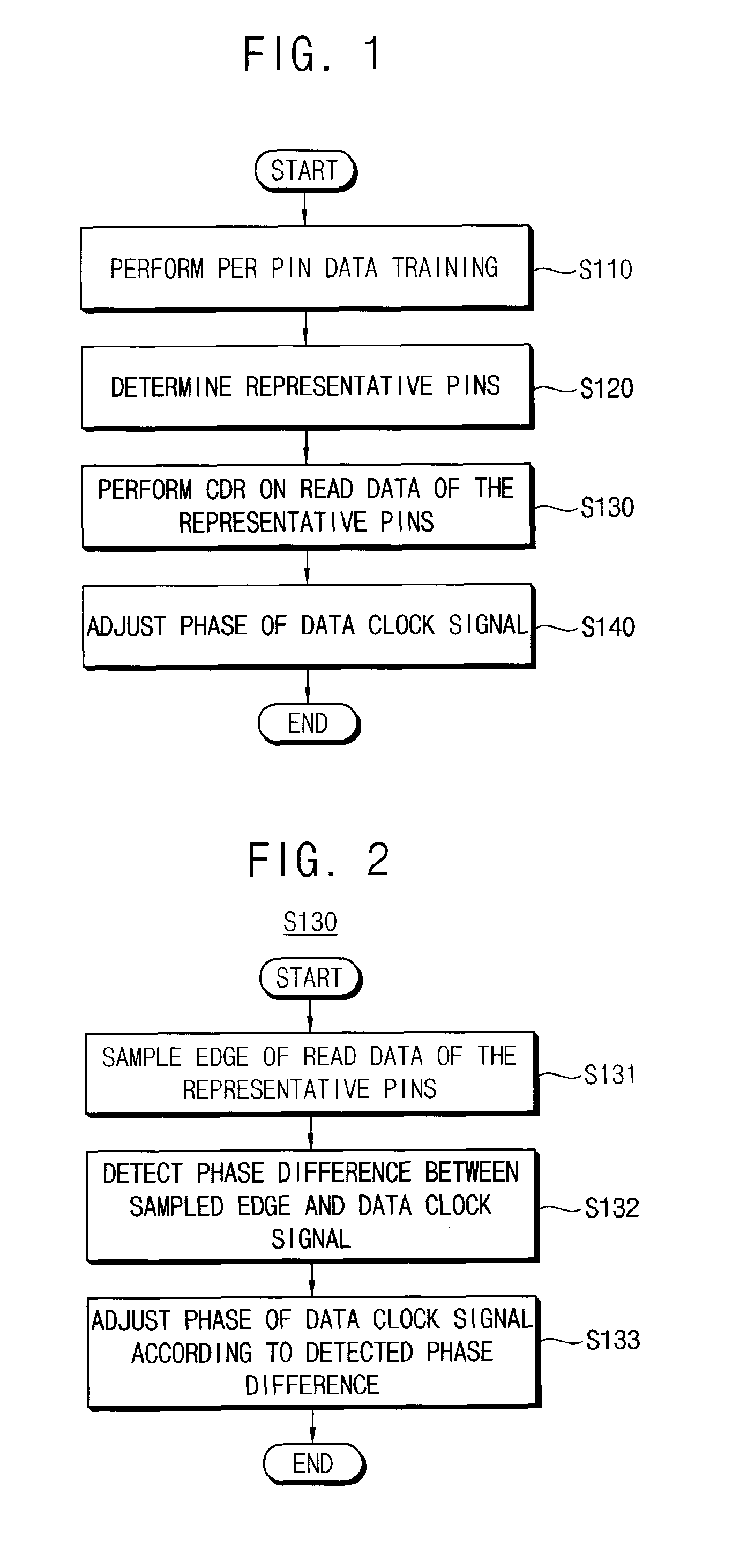
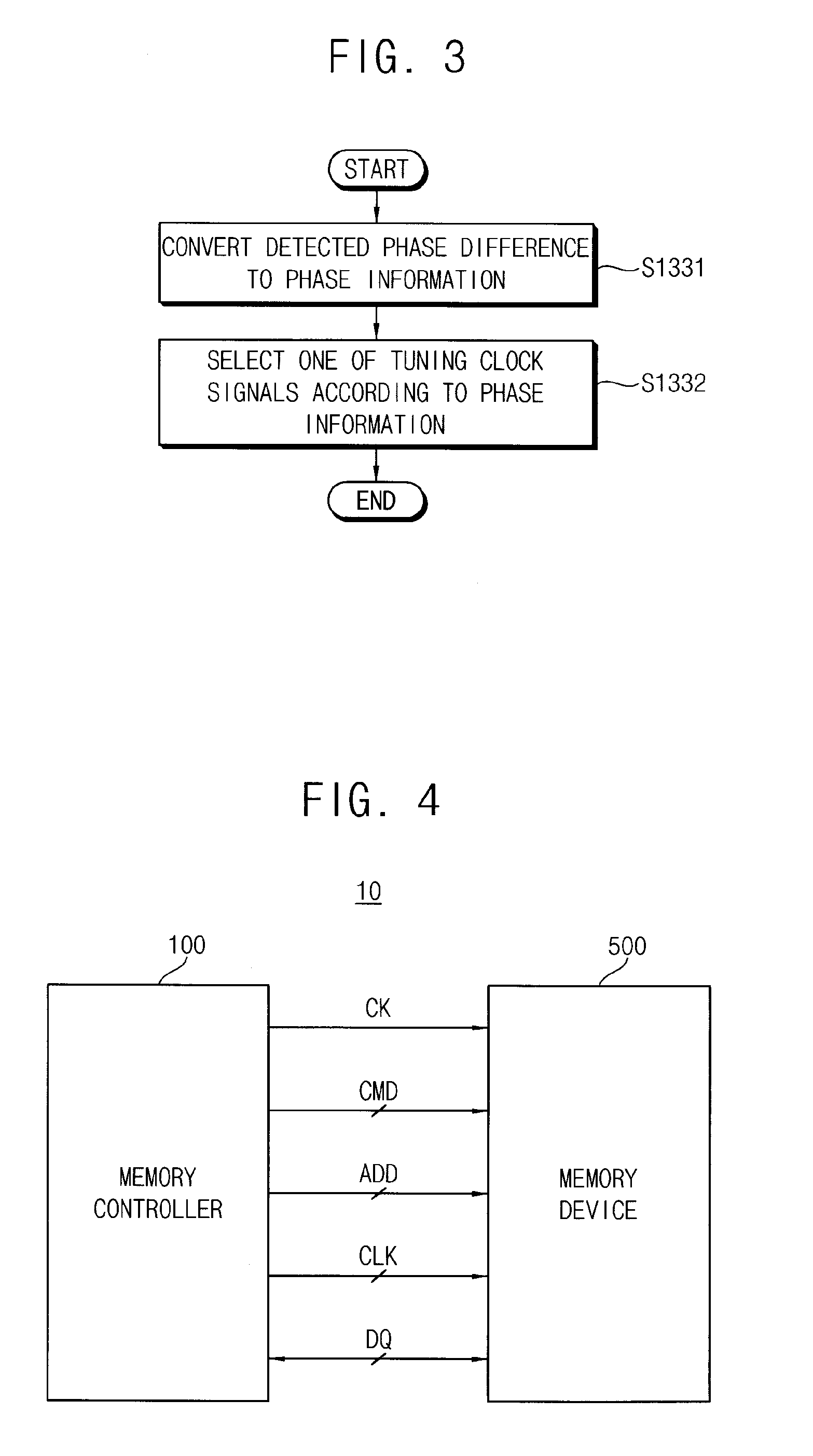
Semiconductor memory device and method of controlling the same
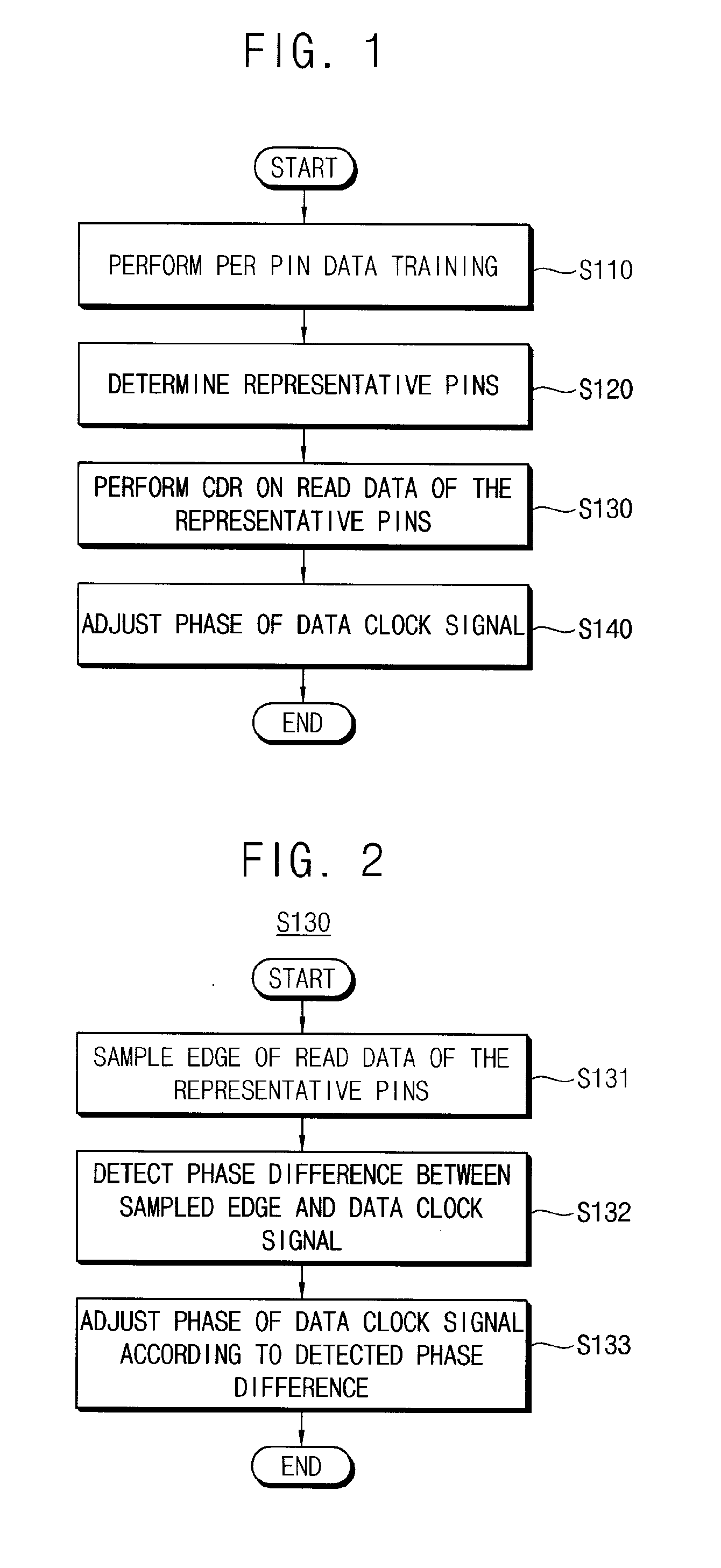
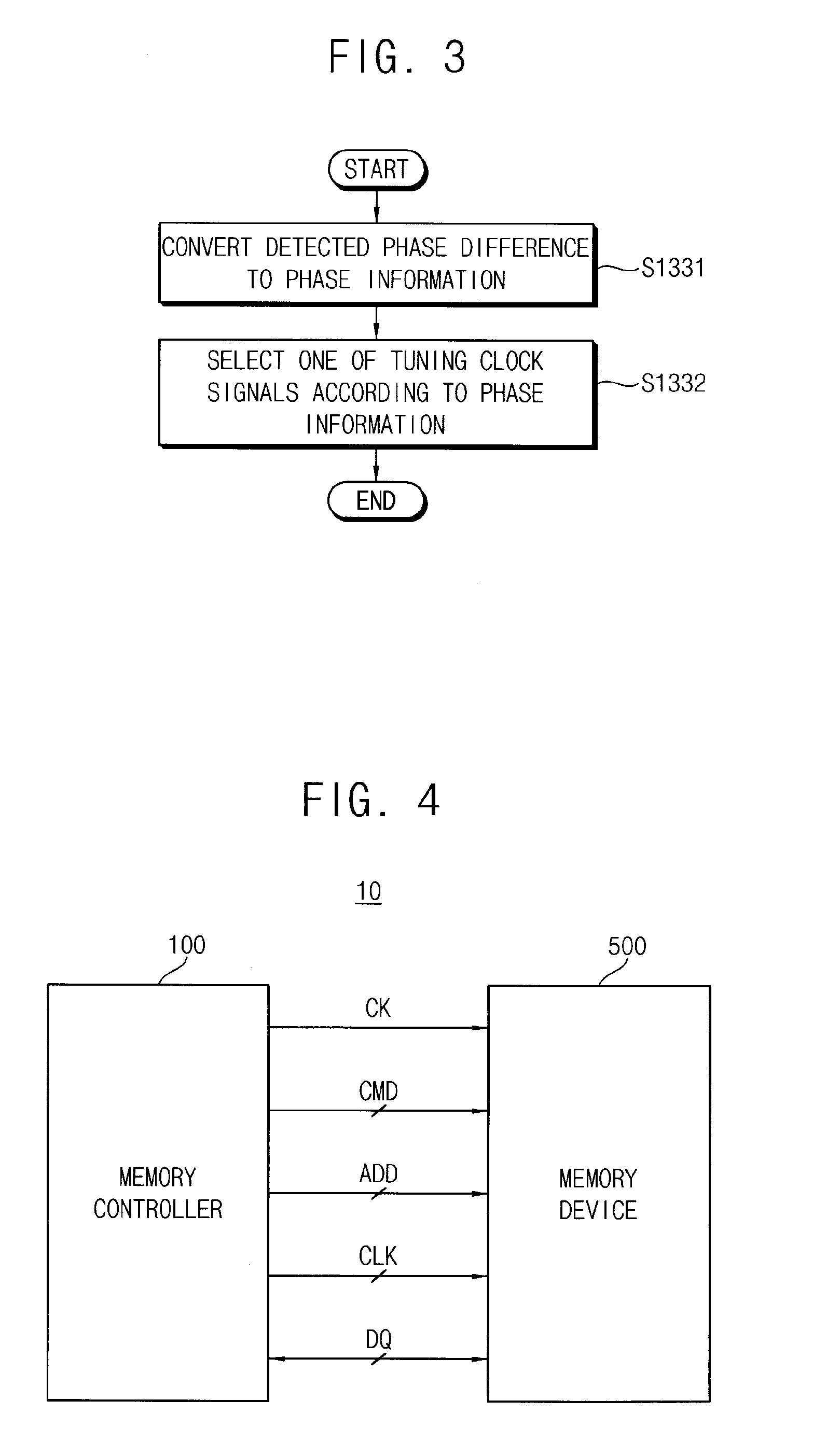
ActiveUS20110243289A1Avoid feature degradationDigital storageSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlComputer scienceData recovery
A method of tuning a phase of a clock signal includes performing data training on a plurality of data pins through which data are input and output, in synchronization with a data clock signal; determining one of the data pins to be a representative pin; performing clock and data recovery (CDR) on read data of the representative pin; and adjusting a phase of the data clock signal based on the CDR.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
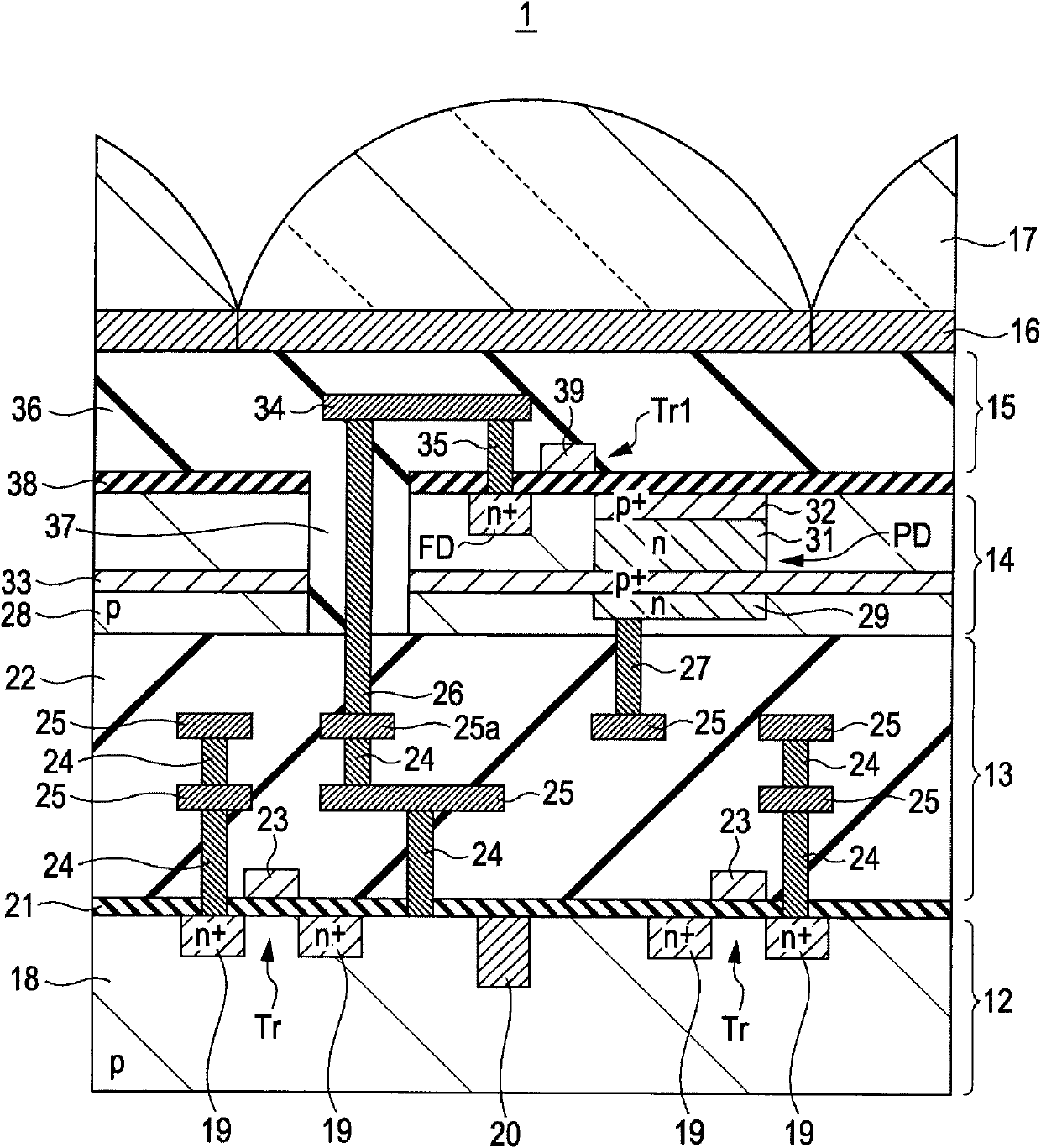
Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method therefor, and electronic device
ActiveCN102005460AAvoid feature degradationReduce light receiving areaTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerLight sensing
The invention relayes to a solid-state imaging device, a manufacturing method therefor, and an electronic device using the solid-state imaging device. The solid-state imaging device includes: a plurality of substrates stacked via a wiring layer or an insulation layer; a light sensing section that is formed in a substrate, of the plurality of substrates, disposed on a light incident side and that generates a signal charge in accordance with an amount of received light; and a contact portion that is connected to a non-light incident-surface side of the substrate in which the light sensing section is formed and that supplies a desired voltage to the substrate from a wire in a wiring layer disposed on a non-light incident side of the substrate. The solid-state imaging device could reduce the size of the solid-state imaging device without reducing the light receiving area.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of fabricating semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110300697A1Preventing reduction in dopant concentrationAvoid feature degradationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor device modeling
Disclosed is a method of fabricating a semiconductor device, including the steps of forming a diffusion preventing mask on a surface of a semiconductor substrate, applying a dopant diffusing agent containing a dopant of a first conductivity type or a second conductivity type onto the surface of the semiconductor substrate at a spacing from the diffusion preventing mask, and forming a dopant diffusion layer by diffusing the dopant from the dopant diffusing agent into the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
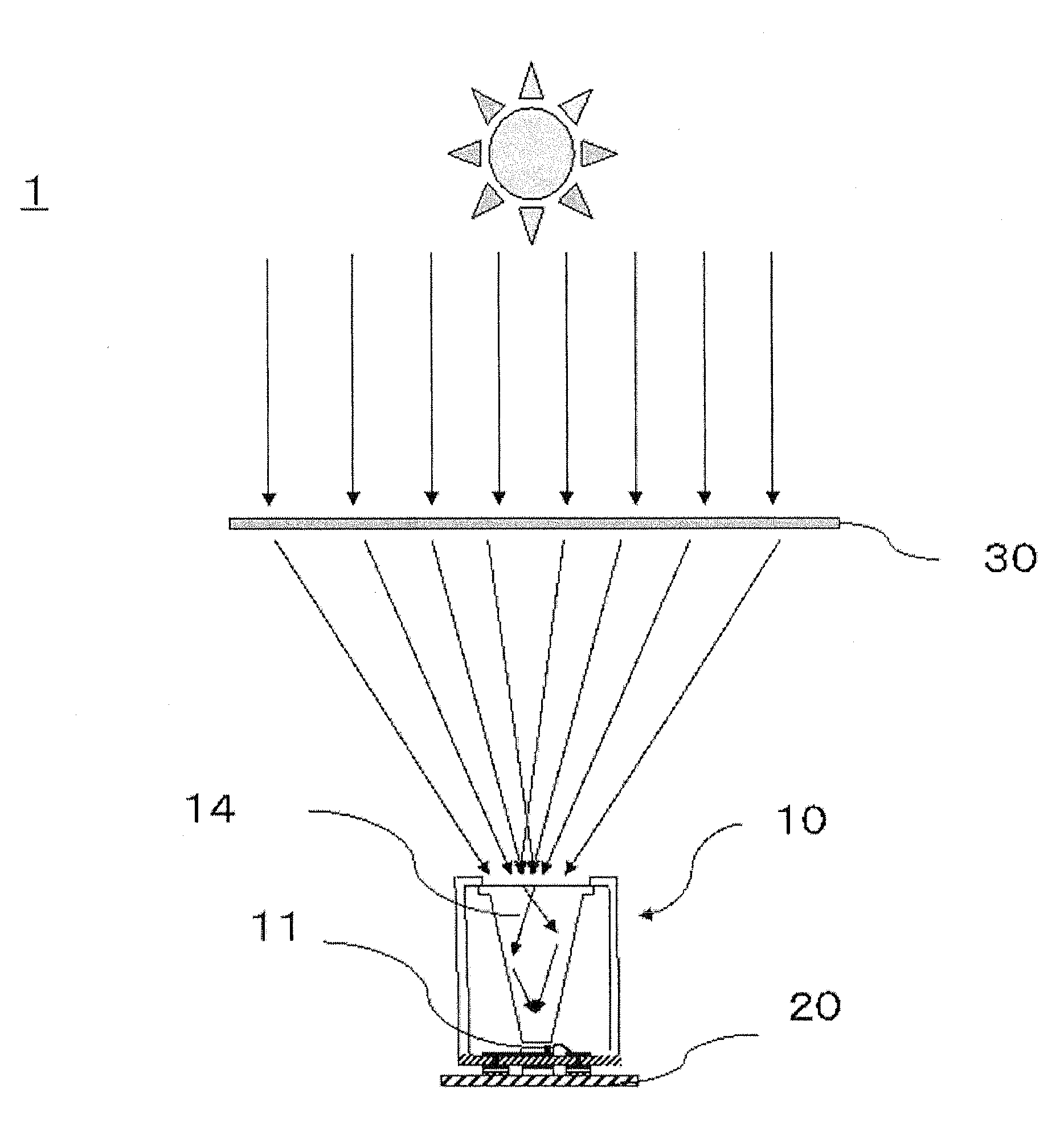
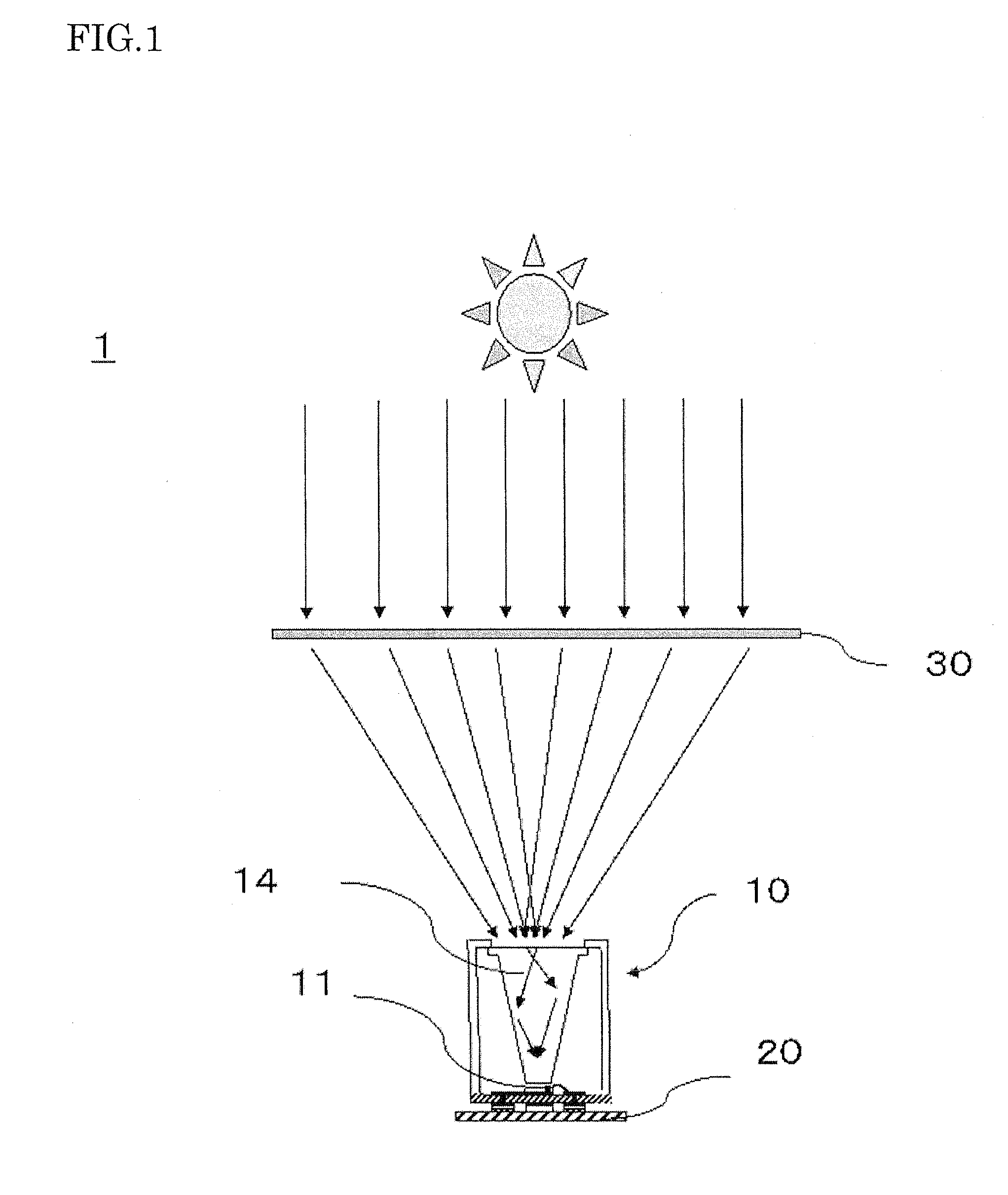
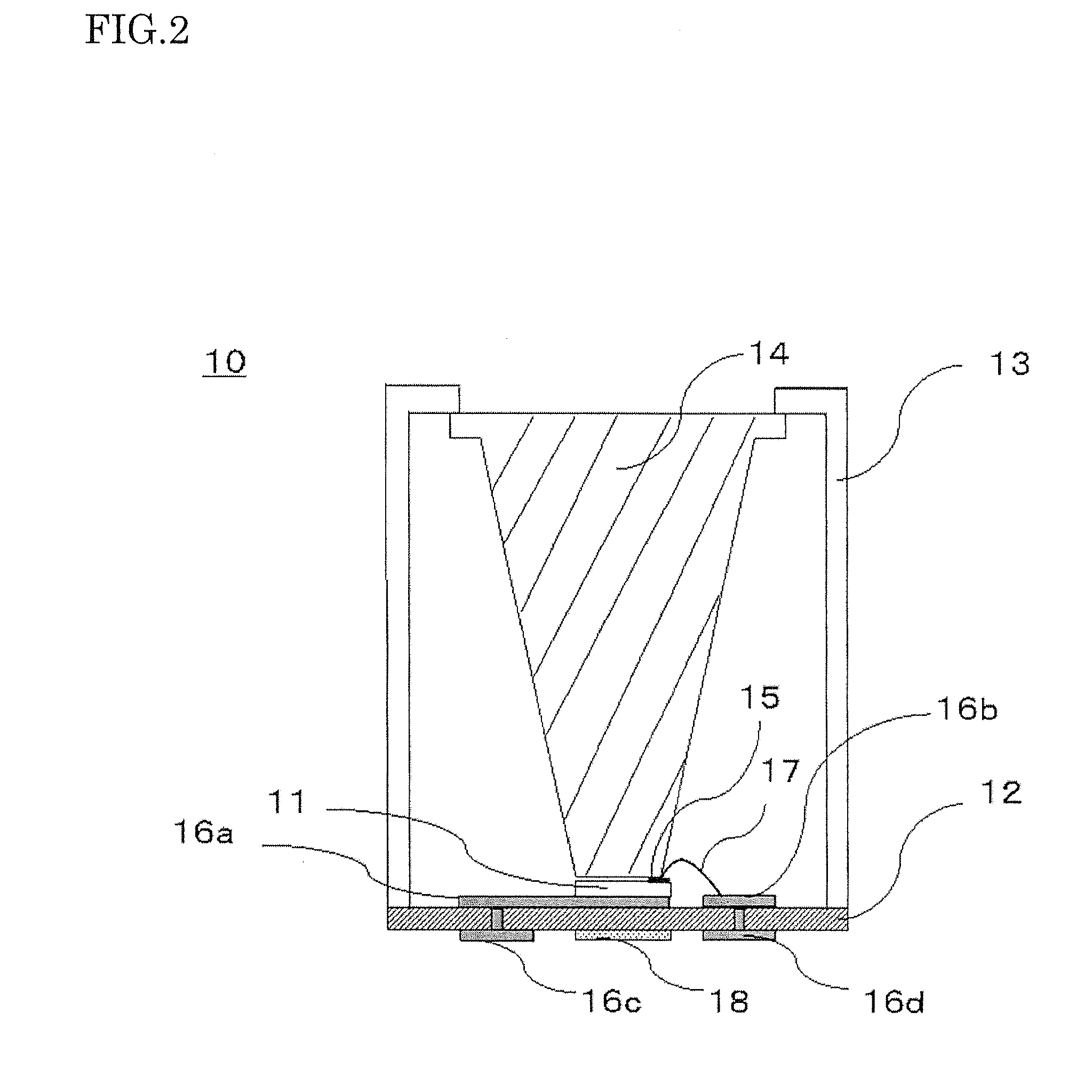
Concentrating solar battery, concentrating solar battery module, concentrating solar battery system, method for manufacturing concentrating solar battery, and method for manufacturing concentrating solar battery module
InactiveUS20120291850A1Avoid feature degradationAffecting light concentration efficiencyPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight guideEngineering
A concentrating solar battery in which concentrated sunlight is guided to a solar battery cell, the concentrating solar battery including: a substrate on which the solar battery cell is mounted; a light guide member disposed above the solar battery cell such that a lower surface thereof opposes the solar battery cell; and a support member that holds an upper portion of the light guide member in a hanging manner and is provided upright on the substrate, wherein the concentrating solar battery has a structure hermetically sealed by the substrate, the light guide member and the support member.
Owner:SHARP KK
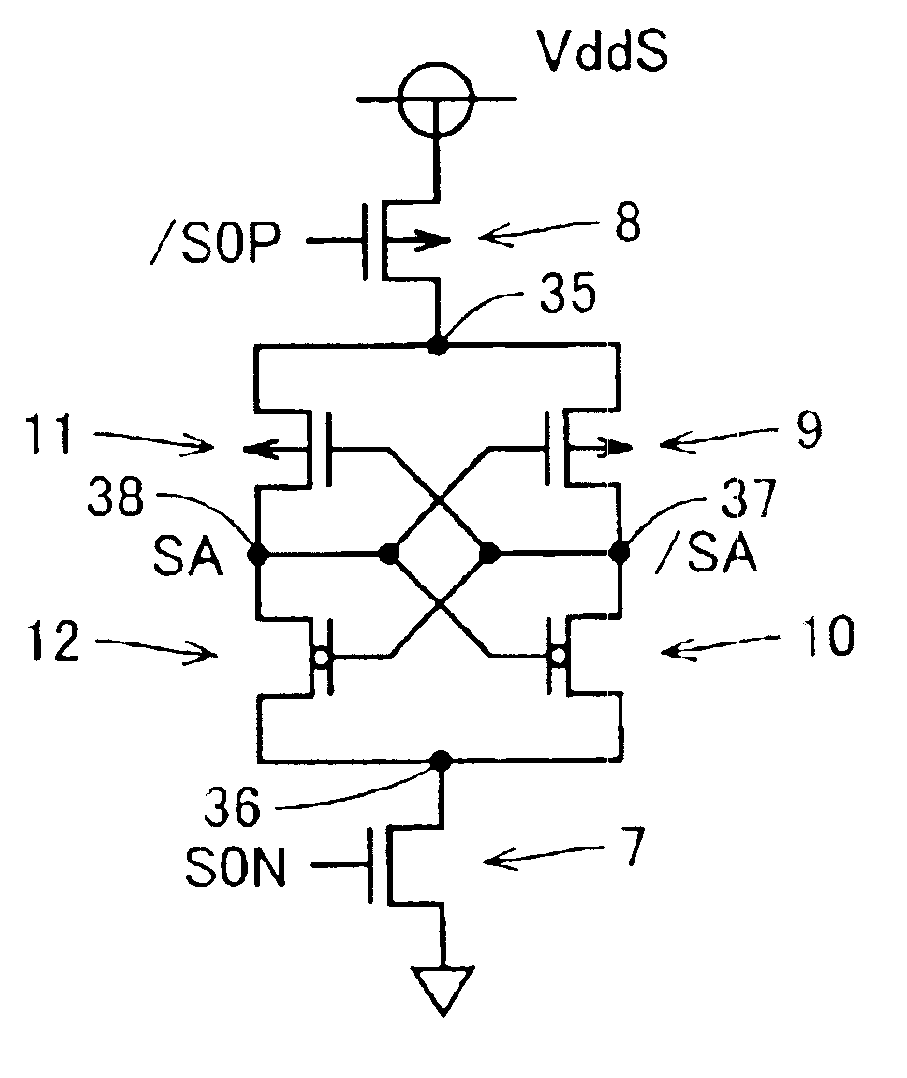
Semiconductor memory device with sense amplifier
InactiveUS6879539B2Reduce chip areaPrevent degradationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSense amplifierEngineering
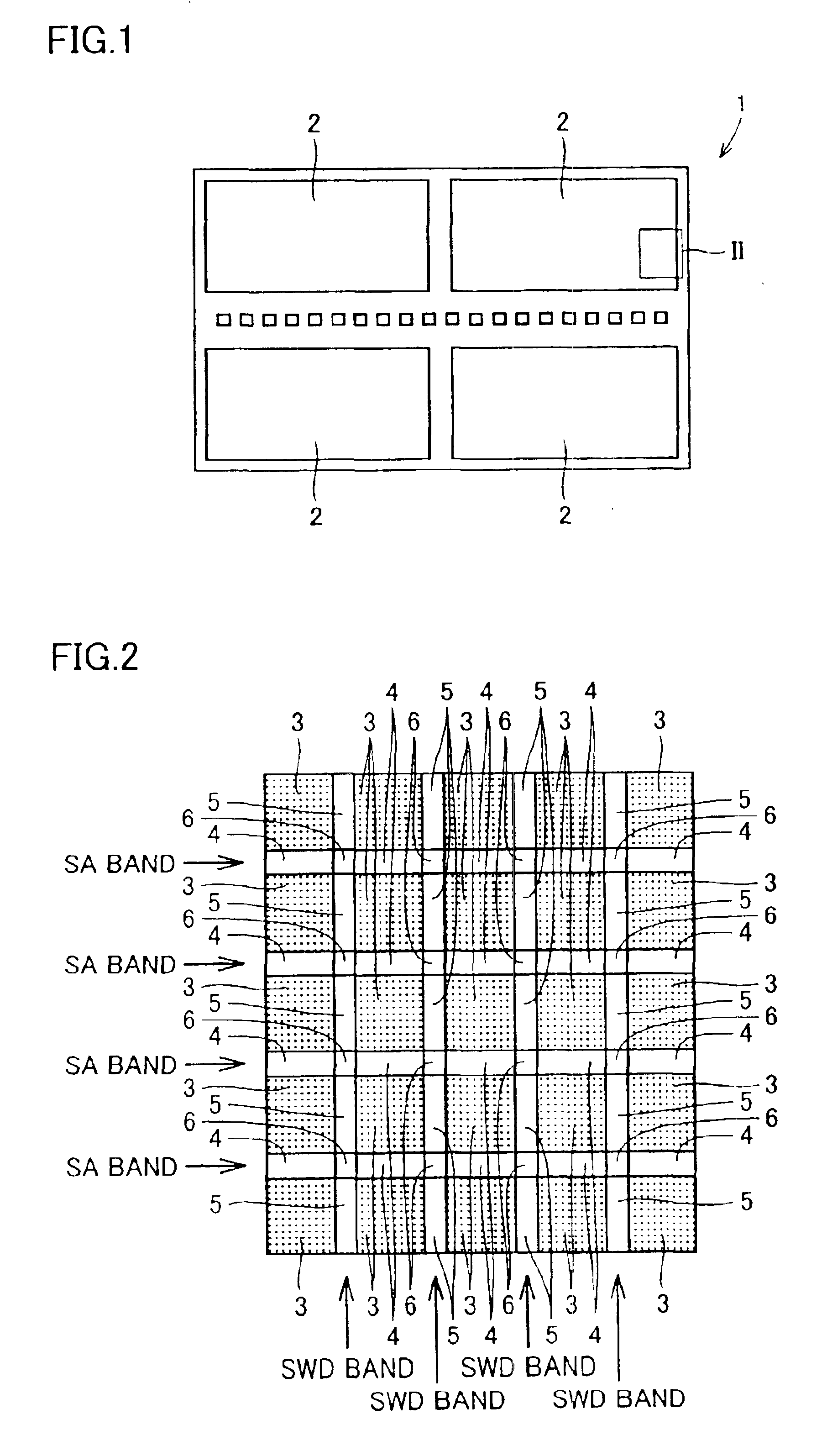
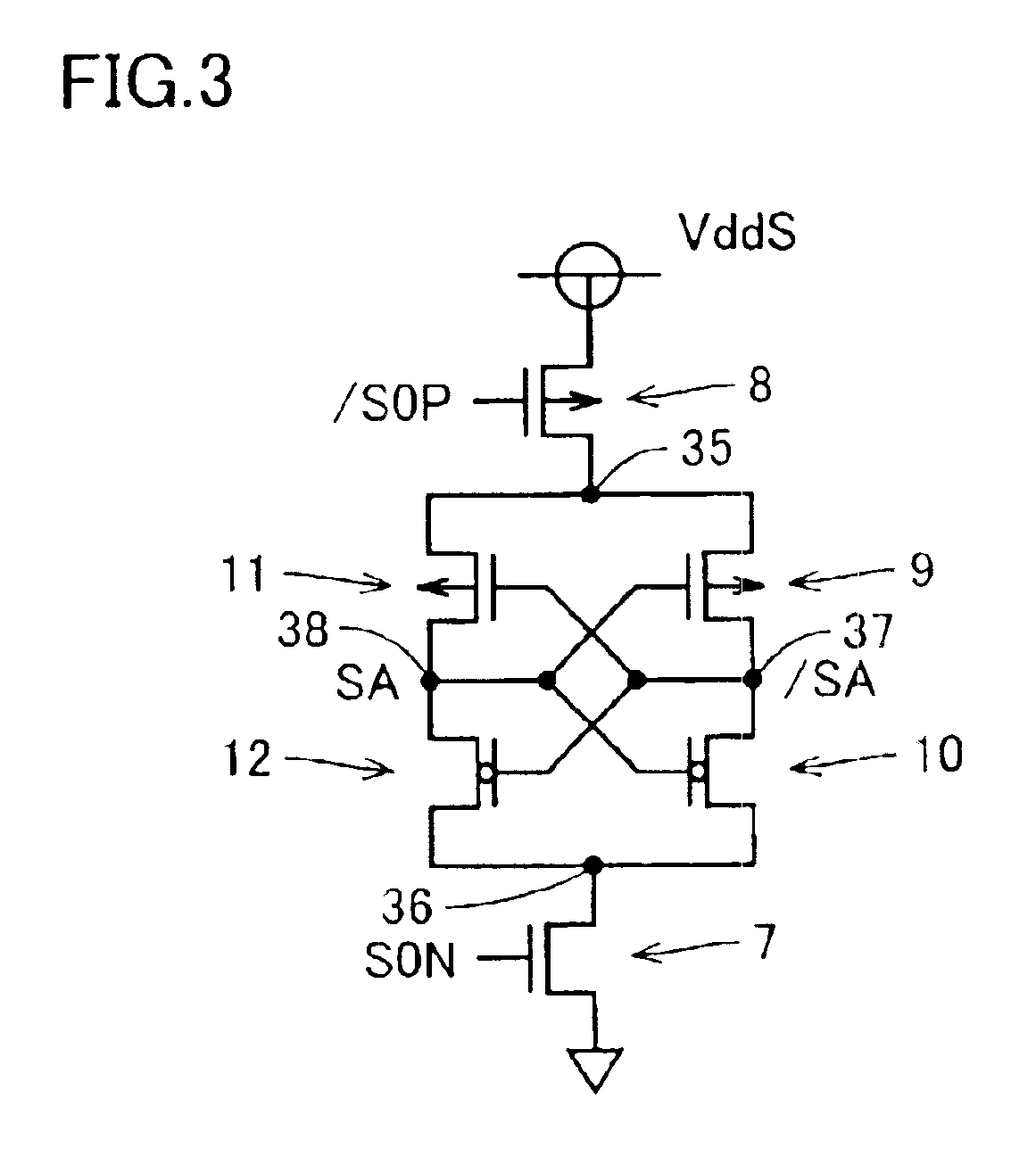
A semiconductor memory device that can be reduced in chip area while preventing degradation in characteristic is obtained. In DRAM, a plurality of memory cell array regions are arranged in matrix, spaced apart from each other in a row direction and in a column direction, on a semiconductor substrate. A sense amplifier region is arranged in a gap between the memory cell array regions in the column direction. An element forming a sense amplifier is arranged in the sense amplifier region. A subdecoder region is arranged in a gap between the memory cell array regions in the row direction. A cross region is arranged at an intersection of the sense amplifier regions in line and the subdecoder regions in line. A sense amplifier driver element is arranged in the subdecoder region and used in a sense amplifier operation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20180261594A1Simple structurePrevent degradationTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
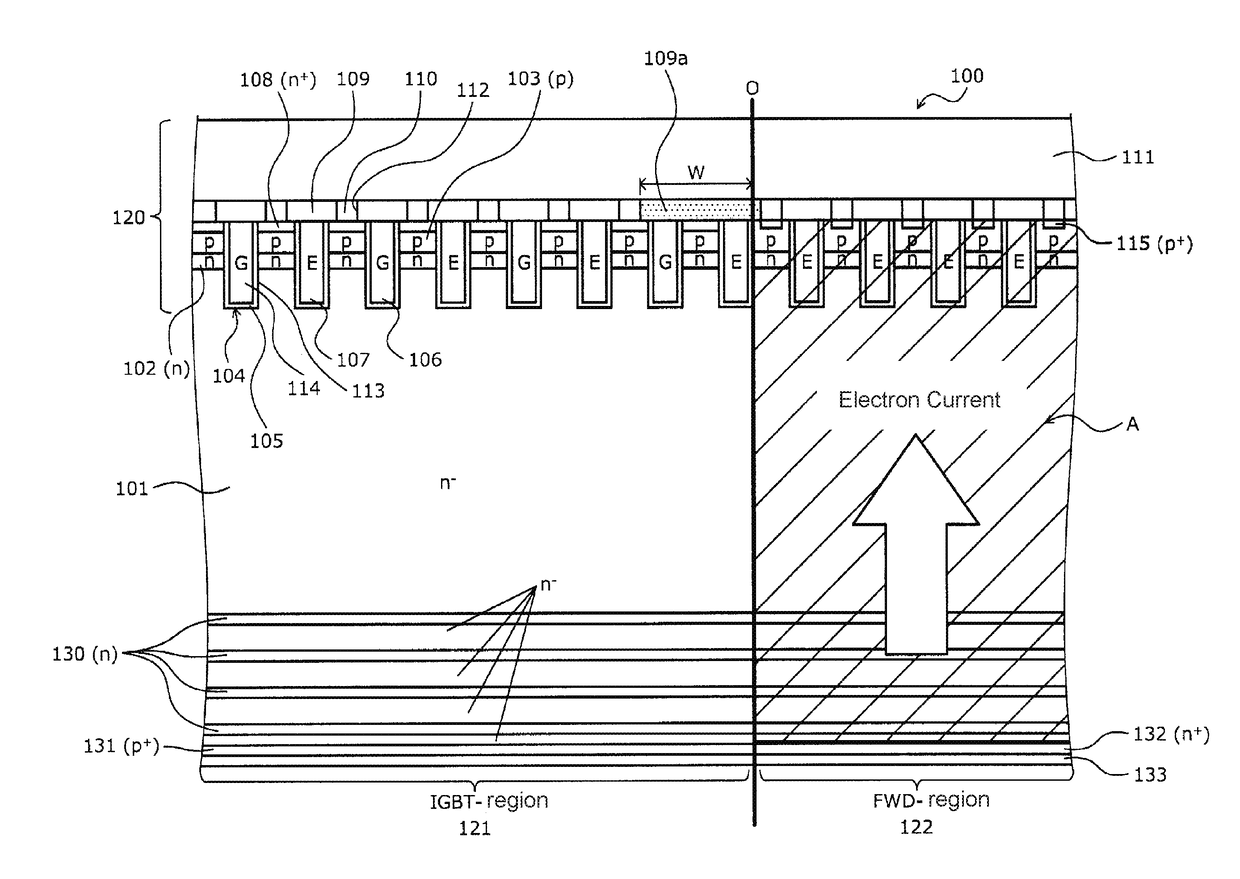
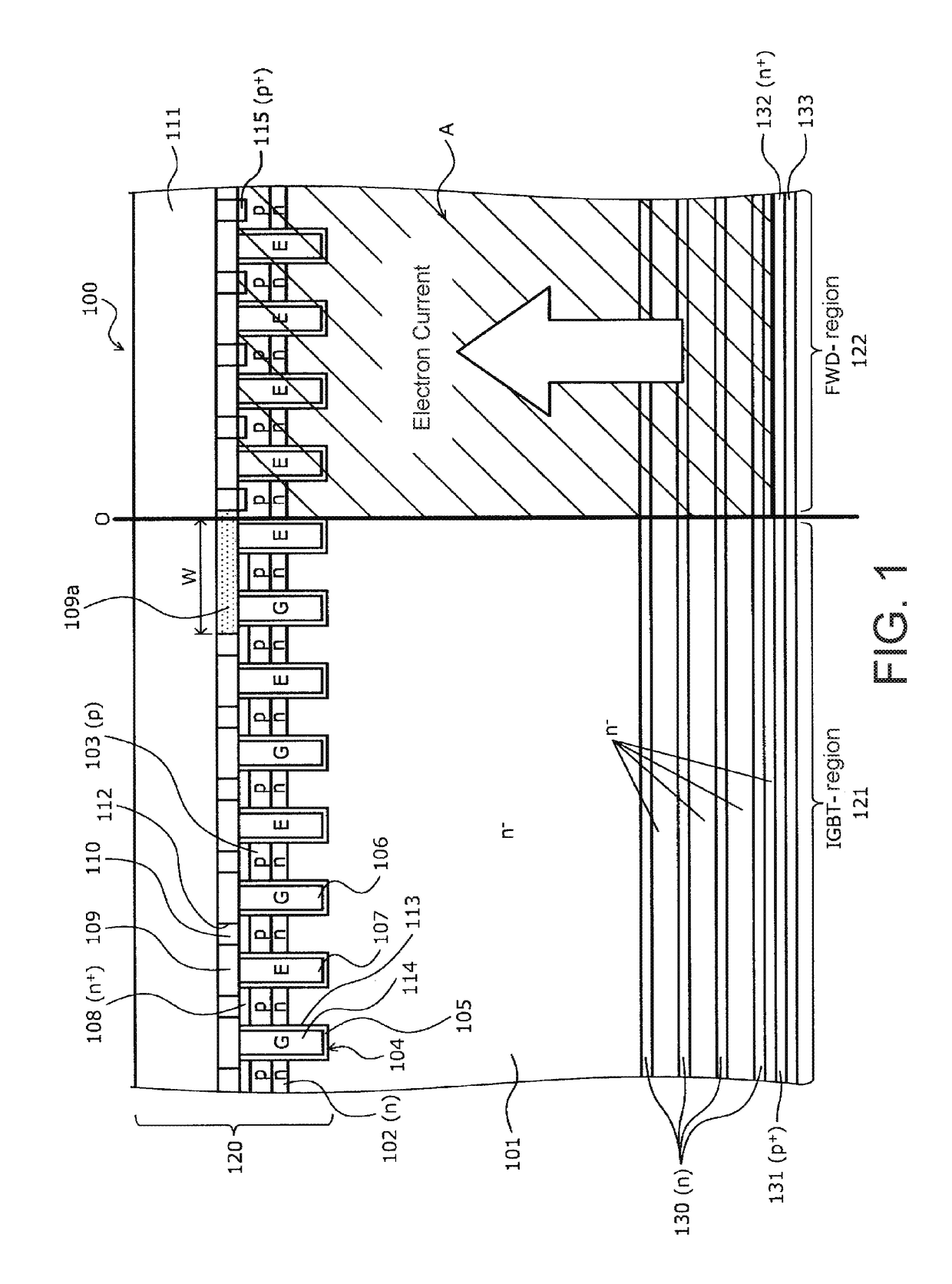
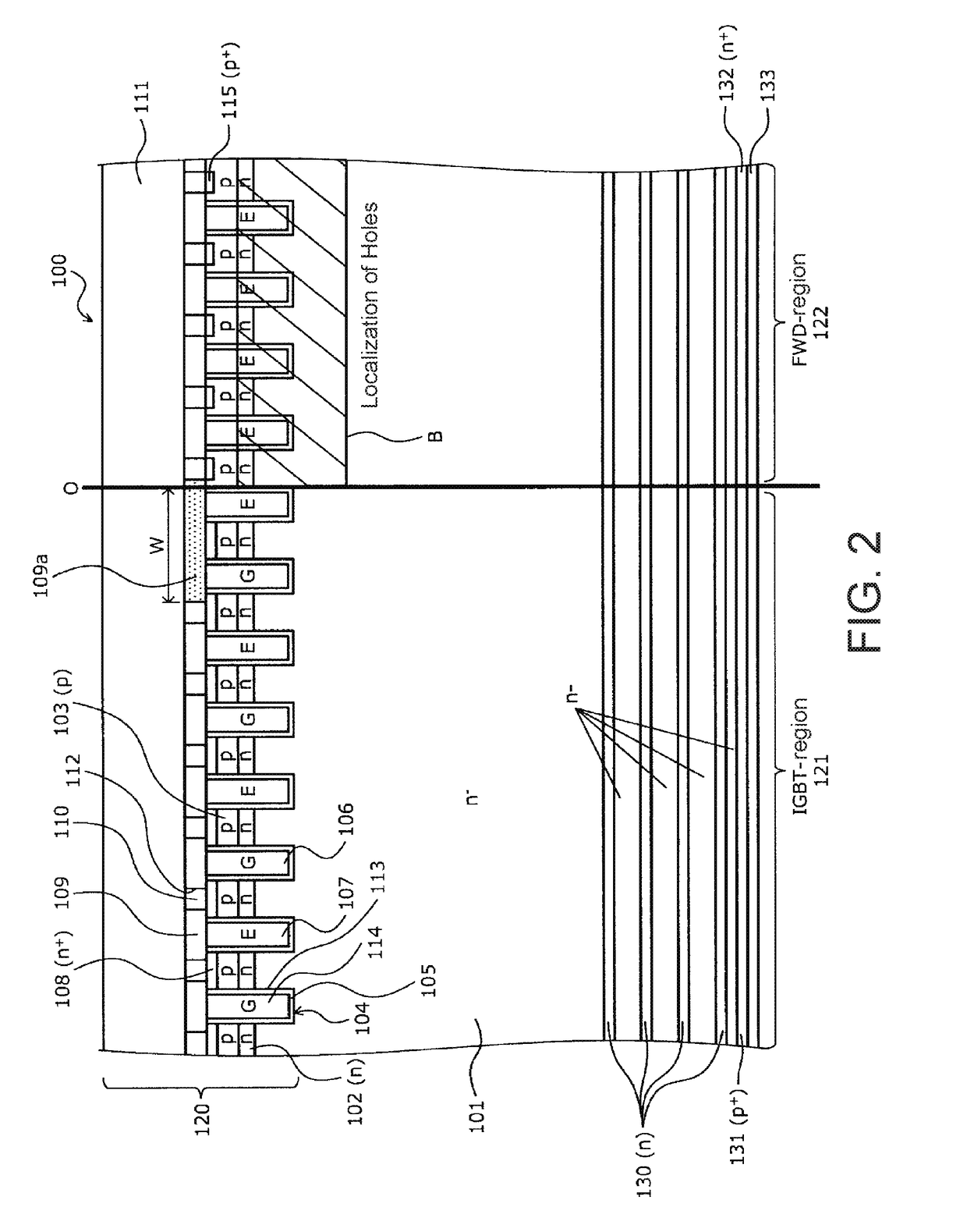
A semiconductor device includes an IGBT region and a FWD region. The IGBT region includes a plurality of trench structures, p-type base regions provided between the trench structures, n+ emitter regions provided on the p-type base regions, an interlayer insulating film provided on the n+ emitter regions and containing contact holes therein, and an emitter electrode connected to the n+ emitter regions through the contact holes. In a portion of the IGBT region that abuts the FWD region, the interlayer insulating film covers and insulates the trench structures without having the contact holes.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Manufacturing method for semiconductor device
InactiveUS20040171242A1Good choiceFavorable uniform characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesBoron trichlorideEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to enhance a selection ratio in an etching process, and provide a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device that has favorable uniform characteristics with high yield. In a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device according to the present invention, a semiconductor layer is formed, a gate insulating film is formed on the semiconductor film, a first conductive layer is formed on the gate insulating film, a second conductive layer is formed on the first conductive layer, the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer are etched to form a first conductive-layer pattern, the second conductive layer in the first conductive-layer pattern is selectively etched with plasma of boron trichloride, chlorine, and oxygen to form a second conductive-layer pattern, and a first impurity region and a second impurity region are formed in the semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Battery, electrolyte, battery pack, electronic device, electric motor vehicle, electrical storage device, and power system
ActiveCN105594054AAvoid feature degradationImprove cooling effectCell electrodesFinal product manufactureElectricity systemElectrical battery
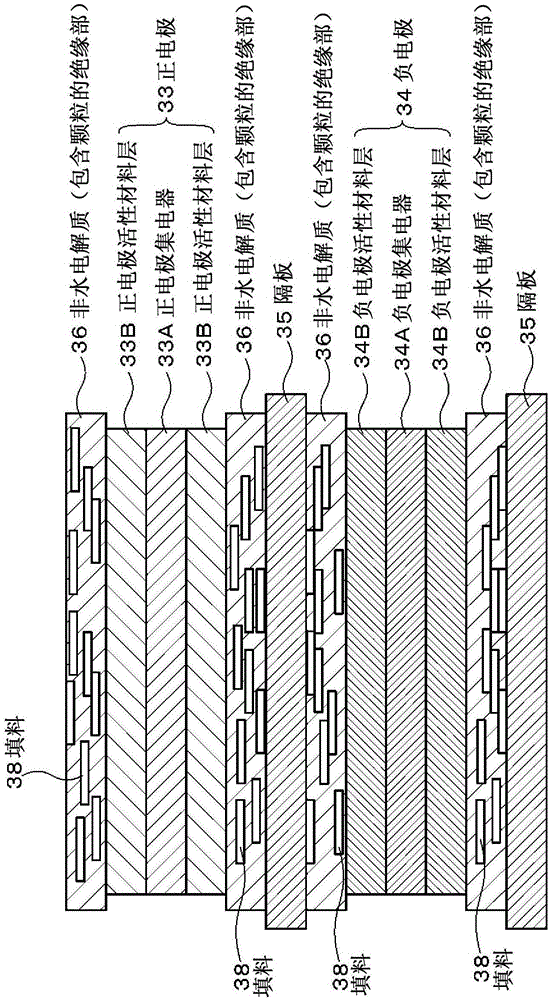
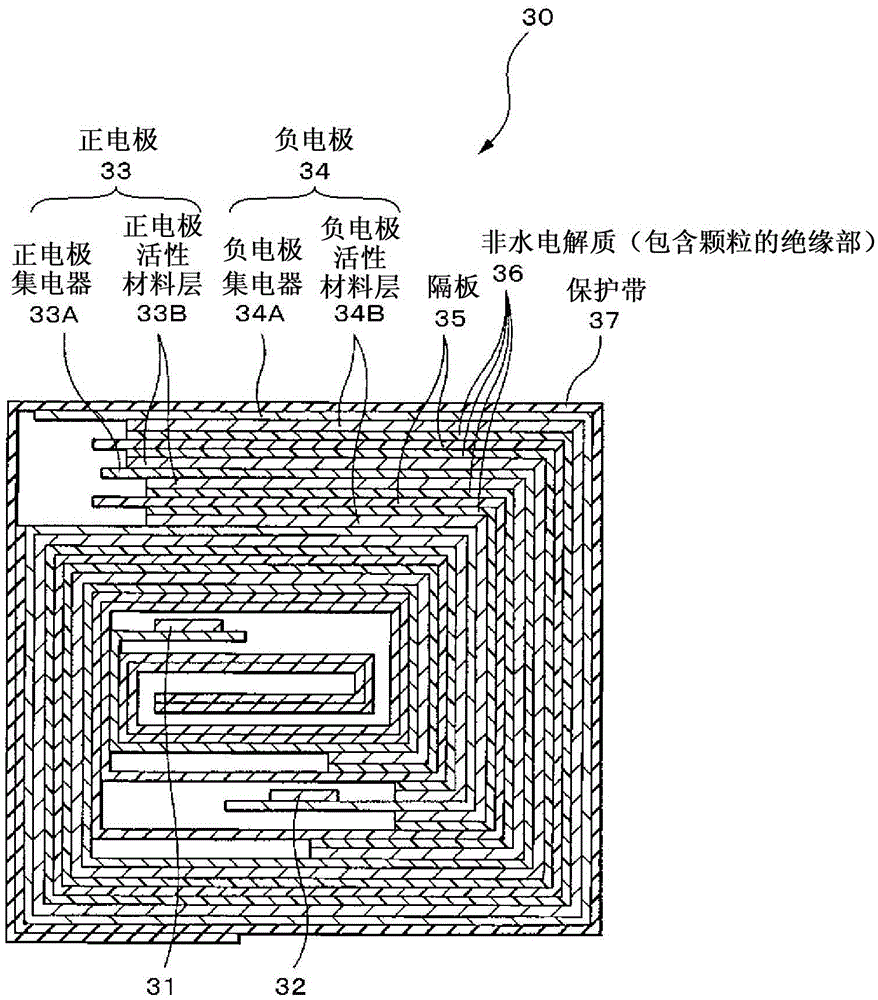
This battery is provided with: electrodes including a positive electrode and a negative electrode; and a particle-containing insulating portion provided between the positive electrode and negative electrode and including particles and a resin, the particles being made of a substance that undergoes a dehydration endothermic reaction, and having a flat shape with an aspect ratio of 2 / 1 or greater.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
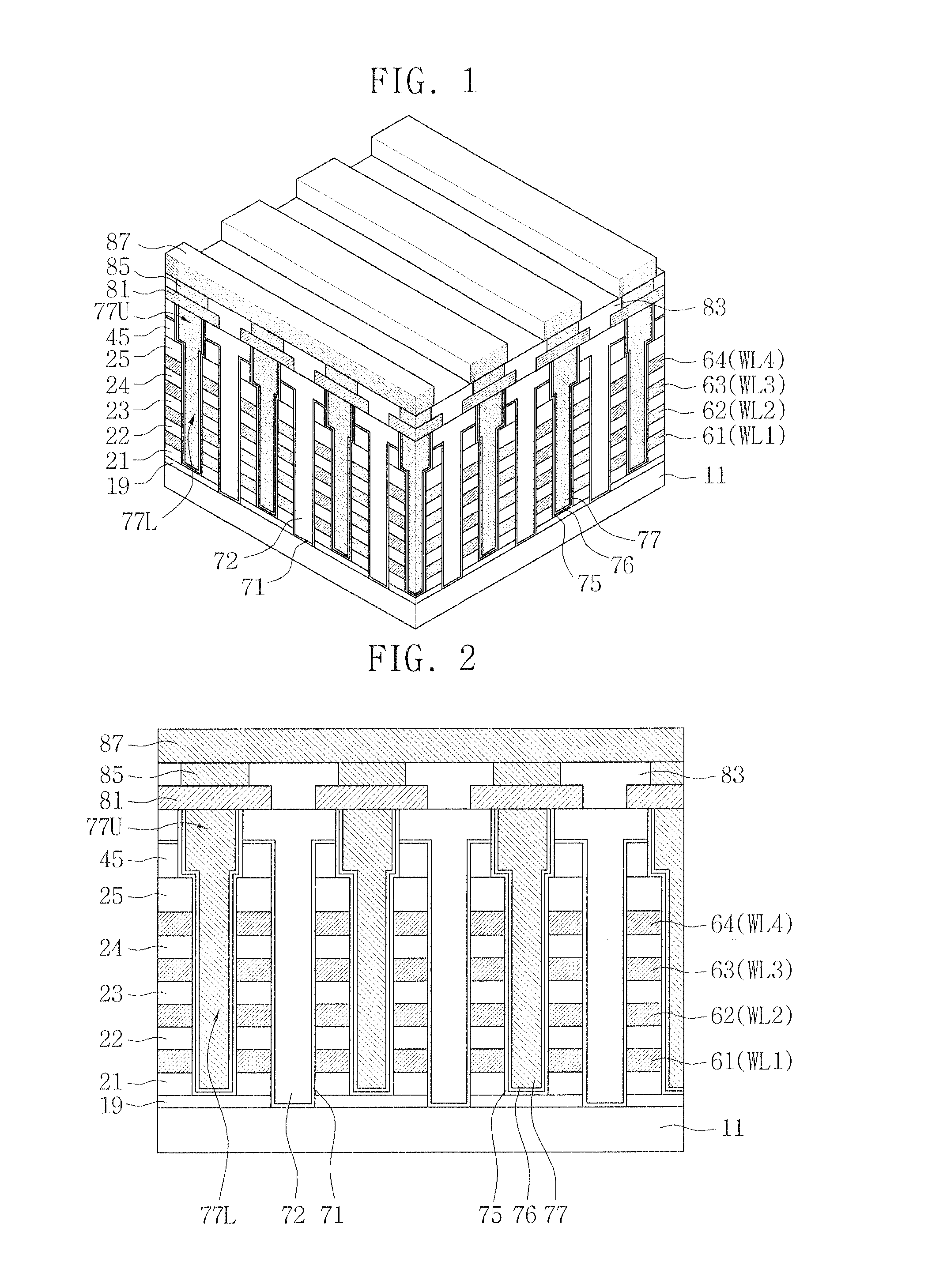
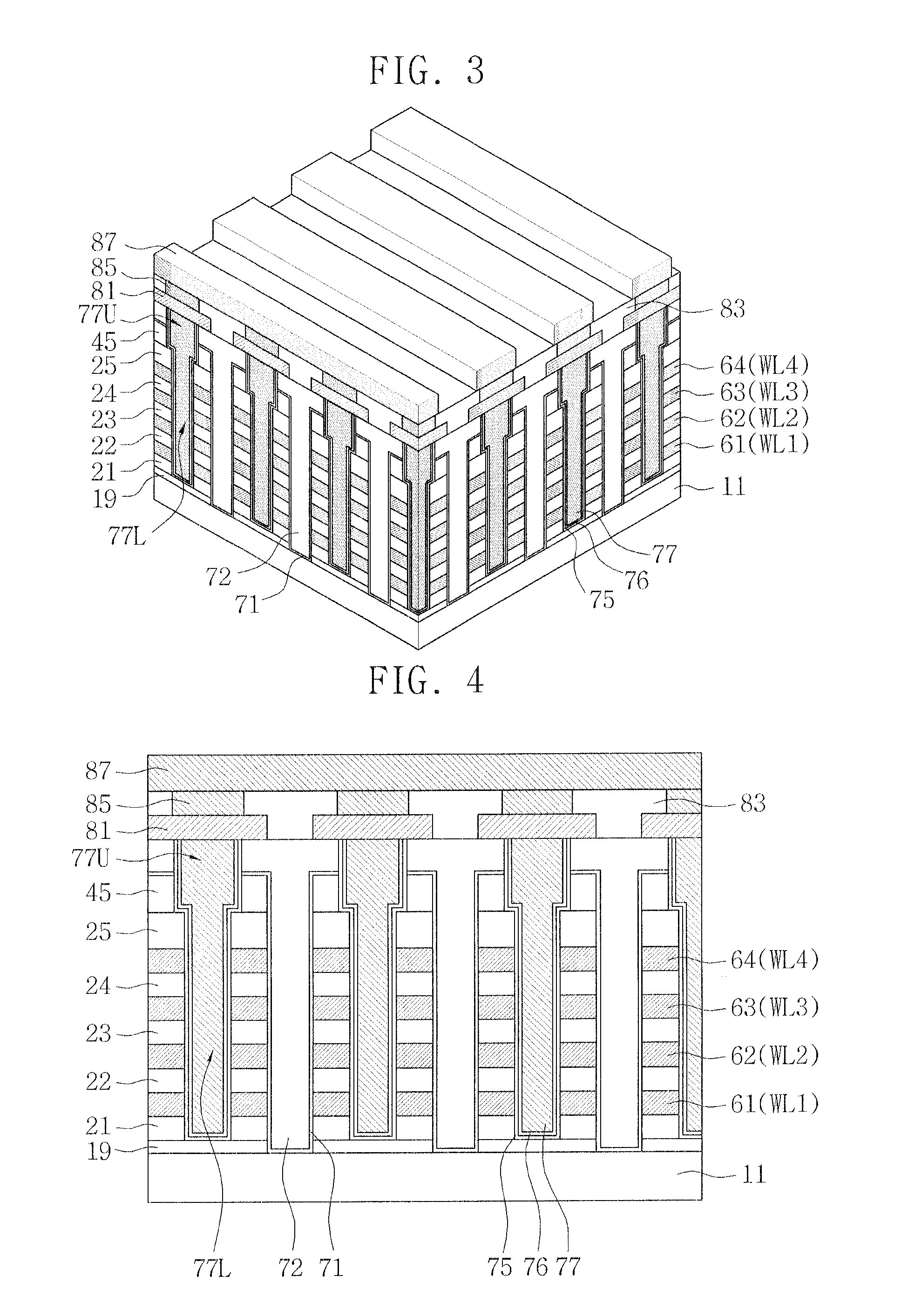
Non-volatile memory device having a resistance-changeable element and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20120305877A1Prevent degradationAvoid feature degradationSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesVolatile memoryLower upper
A non-volatile memory device is provided wherein a lower molding layer is formed on a substrate; a first horizontal interconnection is formed on the lower molding layer; an upper molding layer is formed on the first horizontal interconnection; a pillar is formed connected to the substrate by vertically passing through the upper molding layer, the first horizontal interconnection and the lower molding layer. The pillar has a lower part and an upper part, wherein the lower part is disposed on the same level as the first horizontal interconnection and has a first width and the upper part is disposed on a higher level than the first horizontal interconnection and has a second width different from the first width.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
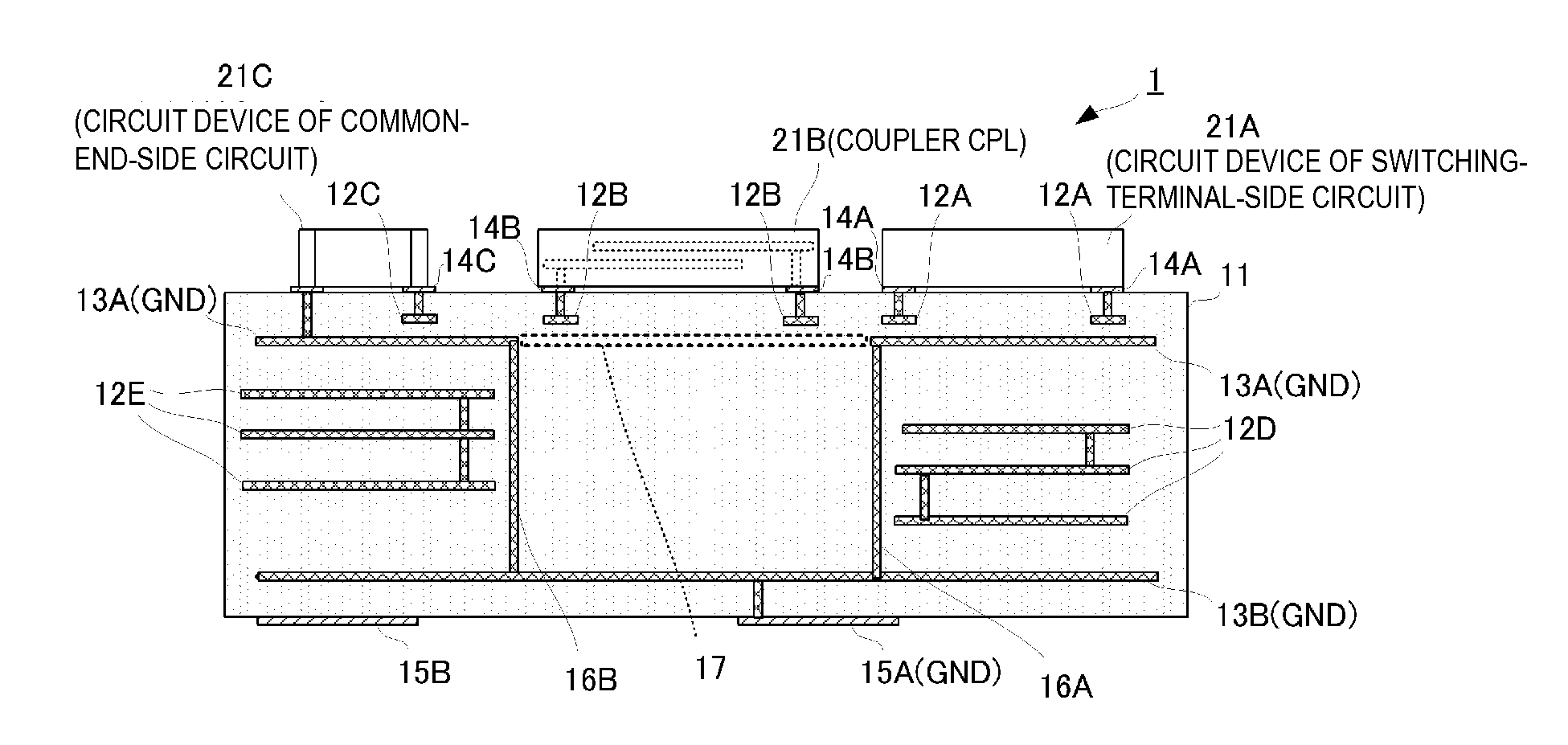
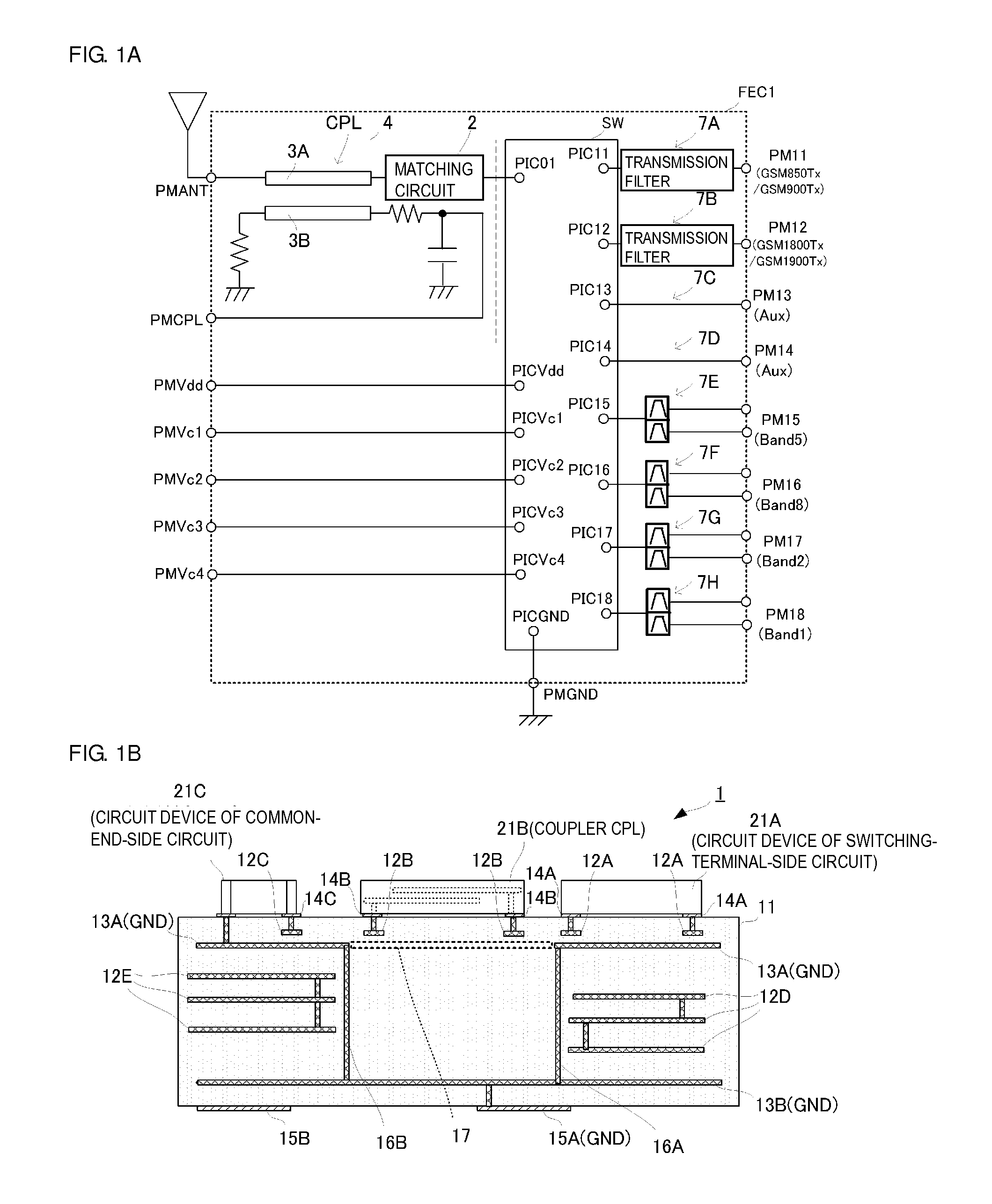
Switch module
ActiveUS20150061406A1Avoid feature degradationReduces and prevents generationBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsPrinted circuit groundingEngineeringGrounding electrodes
A switch module includes a switch circuit, a chip device which is a coupler, a chip device that defines together with the coupler a common-terminal-side circuit, chip devices defining switching-terminal-side circuits, and a multilayer substrate. The multilayer substrate includes inner-layer ground electrodes. A first inner-layer ground electrode is closer to the chip device than a second inner-layer ground electrode and includes an opening arranged so as not to be superposed with the chip device when viewed in plan in the stacking direction of the multilayer substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Magnetic disk drive with air bearing surface design for data area expansion
InactiveUS20070091506A1Suppresses degradation of flying characteristicAvoid feature degradationFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageMagnetic transducersPositive pressure
Embodiment of the invention provides a magnetic disk drive that may suppress the decrease of a recording region by preventing a magnetic head slider from abutting a magnetic disk at the time of loading, and suppress the degradation of the flying characteristics. In one embodiment a magnetic disk drive of the present invention is provided with a magnetic head slider including a magnetic transducer, a ramp that unloads the magnetic head slider, and an actuator that moves the magnetic head slider. The magnetic head slider includes a rail surface that generates a positive pressure on an air-bearing surface, a step bearing surface, and a taper section that is formed to a slider corner section that is brought closest to the surface of a recording disk at the time of loading with a space from the rail surface and the step bearing surface.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method for fabricating MOS transistors
InactiveUS6852599B2Degradation of characteristicLower junction capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceGate oxide
A method for fabricating a metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor, which can reduce the junction capacitance without degradation of transistor characteristics including forming a buffer oxide layer on a semiconductor substrate; successively conducting ion implantations for well formation and field stop formation in the substrate through the buffer oxide layer; removing the buffer oxide layer; forming and patterning a sacrificial layer to form a trench successively conducting ion implantations for threshold voltage adjustment and punch stop formation on the semiconductor substrate area exposed by the trench; forming a gate oxide layer on the exposed surface of the substrate; forming a polysilicon layer so as to completely fill the trench; polishing the polysilicon layer to form a gate electrode; removing the sacrificial layer; forming an LDD region in the substrate; forming spacers on side walls of the gate electrode; and forming source / drain regions.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Driver and display device using the same
InactiveCN102194398AAvoid feature degradationSmall sizeStatic indicating devicesNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
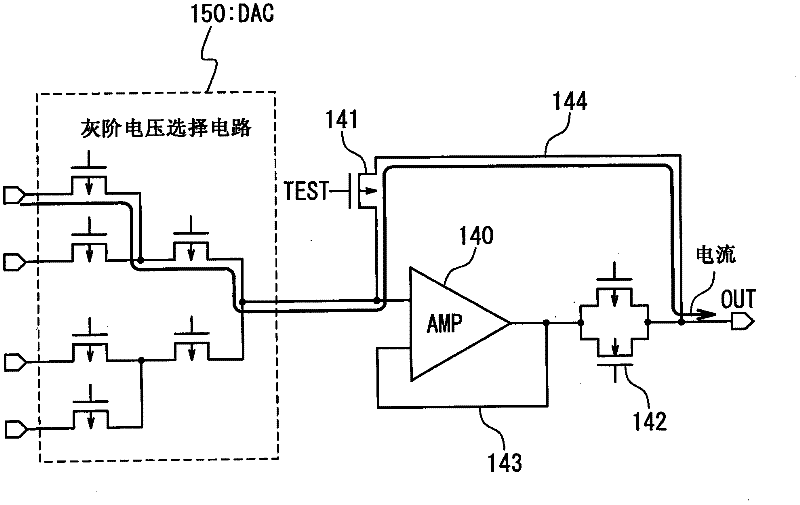
The invention relates to a driver and a display device using the same. The driver includes a digital-to-analog converter configured to perform digital-to-analog conversion on digital gray scale data to output an analog output gray scale voltage; an output amplifier section having a first input connected with an output of the digital-to-analog converter, and an output connected with an output node, and a second input connected with the output of the output amplifier section through a negative feedback wiring, and configured to output the output gray scale voltage to the output node in response to a control signal in an operation mode. A test switch is connected between the first input and the second input in the output amplifier section and is configured to output the output gray scale voltage to the output node in response to a test signal in a test mode for a test of an output of the digital-to-analog converter.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Transistor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108447907AReduce electric field strengthAvoid feature degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectric field modulationGallium nitride
The invention provides a transistor and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the technical field of transistors (especially gallium nitride transistors) and is capable of at least partially solving the problems of characteristic degradation and poor reliability of an existing transistor provided with a P-type cap layer along with use. The transistor provided by the invention comprises superimposed channel layer and barrier layer, a source, a drain and a gate, wherein the source, the drain and the gate are arranged at one side, far away from the channel layer, of the barrier layer at intervals; the gate is located between the source and the drain; the P-type cap layer is arranged between the gate and the barrier layer; schottky contact is formed between the P-type cap layer and the gate; two side edge areas, close to the source and the drain, of the P-type cap layer are two interspaced electric field modulation areas; and the electric field modulation areas can induce positive charges under positive gate-source voltage.
Owner:INNOSCIENCE (ZHUHAI) TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20110024837A1Avoid feature degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDepletion regionSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes a gate formed over a substrate, a junction region formed in the substrate at both sides of the gate, and a depletion region expansion prevention layer surrounding sidewalls of the junction region in the substrate.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Methods of manufacturing a vertical memory device
PendingCN111223869AAvoid feature degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerEngineering
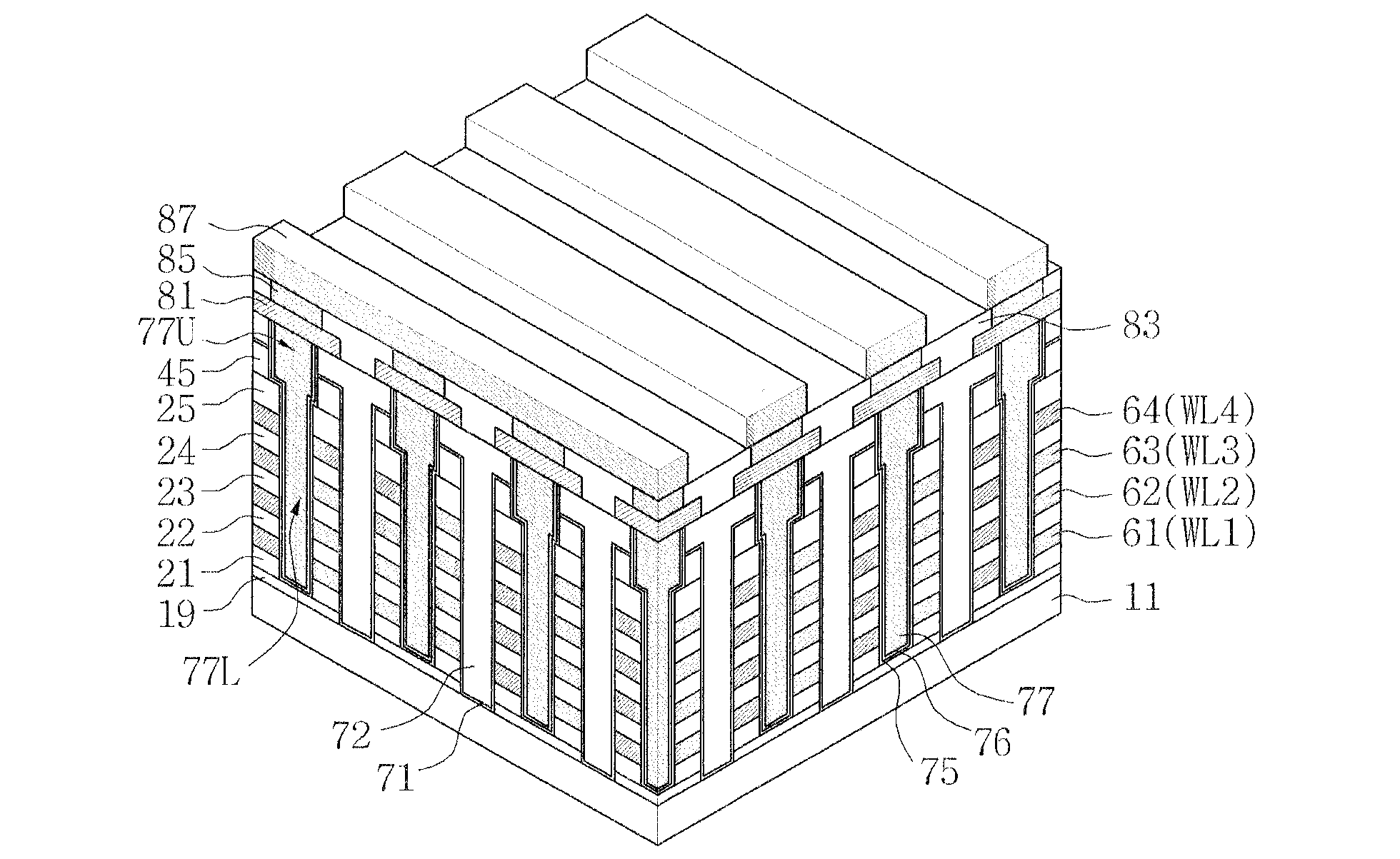
In a method of manufacturing a vertical memory device, a first sacrificial layer including a nitride is formed on a substrate. A mold including an insulation layer and a second sacrificial layer alternately and repeatedly stacked is formed on the first sacrificial layer. The insulation layer and the second sacrificial layer include a first oxide and a second oxide, respectively. A channel is formed by passing through the mold and the first sacrificial layer. An opening is formed by passing through the mold and the first sacrificial layer to expose an upper surface of the substrate. The first sacrificial layer is removed through the opening to form a first gap. A channel connecting pattern is formed to fill the first gap. The second sacrificial layer is replaced with a gate electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
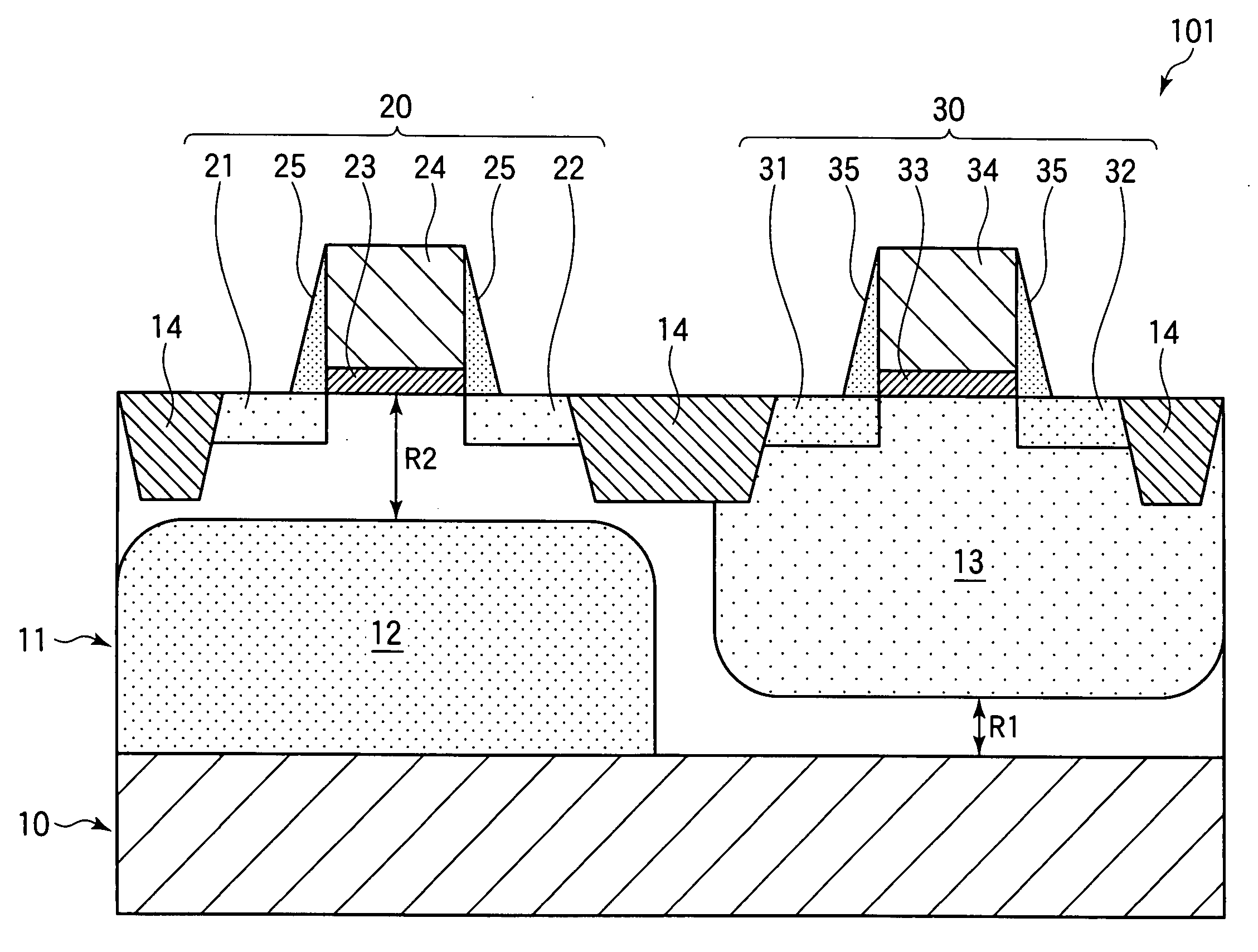
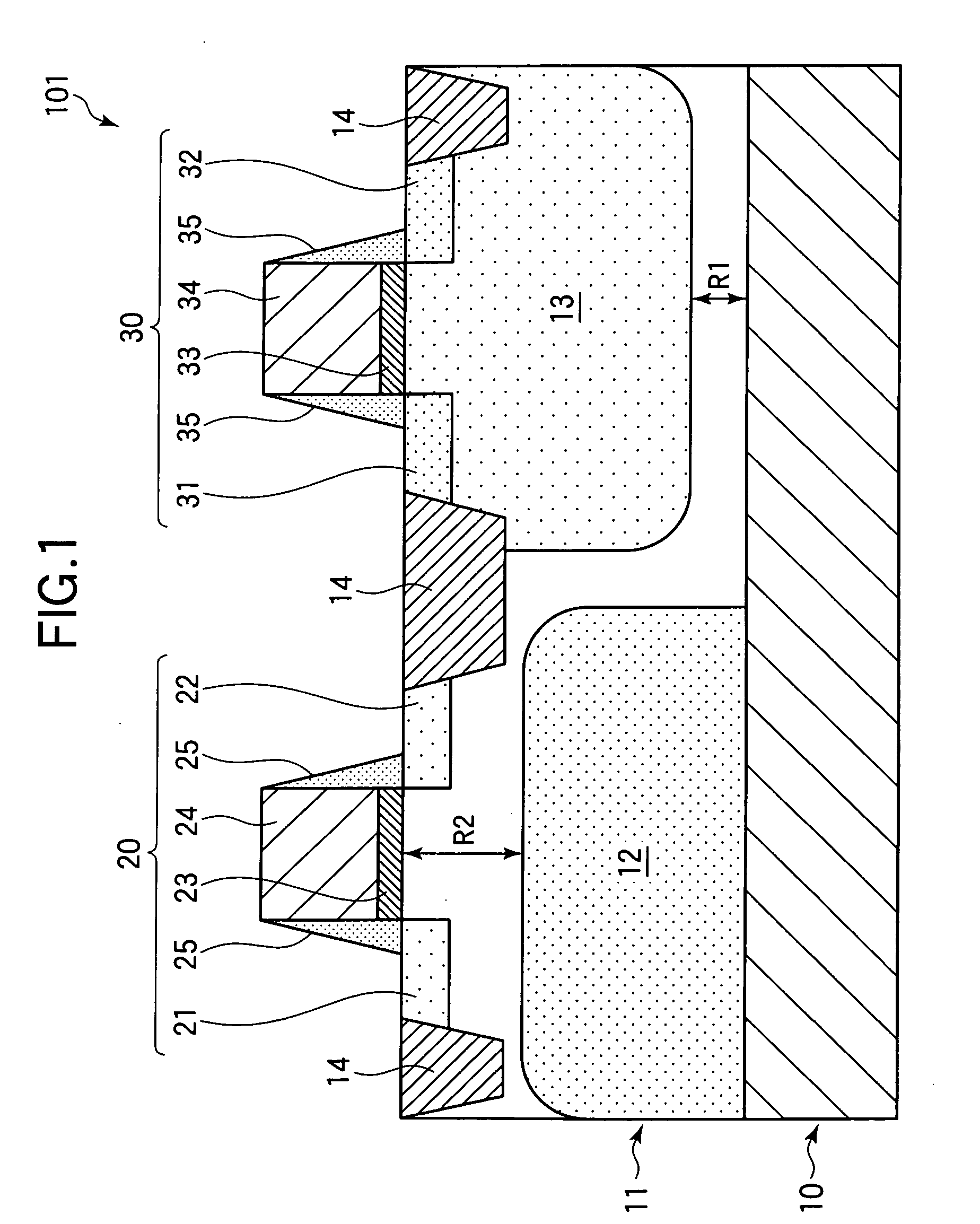
ActiveUS20130082349A1Prevent degradationAvoid feature degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMoisture
Provided is a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device capable of preventing, in a SOG etch back planarization process in a multi-layered wiring process, degradation in long-term reliability with respect to the entering of moisture caused by a fuse opening portion. A fuse is shaped so that polycrystalline silicon extends to a lower part of a guard ring provided in a first layer of metal for preventing the entering of moisture from the fuse opening portion. Thus, a metal wiring used for connection to an electrode of the fuse and a metal wiring of the guard ring become equal in height, and hence an SOG layer can be prevented from reaching the inside of an IC.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Irradiation resistant multi-interdigital CMOS device
The invention discloses an irradiation resistant multi-interdigital CMOS device, belonging to the technical field of electron and comprising an active area, an STI area and a grid electrode, wherein the grid electrode is connected with the active area and the STI area and is in a multi-interdigital shape. The irradiation resistant multi-interdigital CMOS device is characterized in that the width of the active area along the transverse direction of the active area is longer than the width of the grid electrode along the transverse direction of the active area within the range of the active area; preferably, inner contour lines of root parts of two adjacent fingers are not in a fold line shape with each break angle of 90 degrees, and outer contour lines of root parts of two fingers positioned on the end part of the irradiation resistant multi-interdigital CMOS device are not in a right-angle shape. The irradiation resistant multi-interdigital CMOS device can effectively reduce the grid series resistance, thereby enhancing the performance of a circuit; and in addition, the invention also reduces the domain occupying area, thereby enhancing the integration level of a chip.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
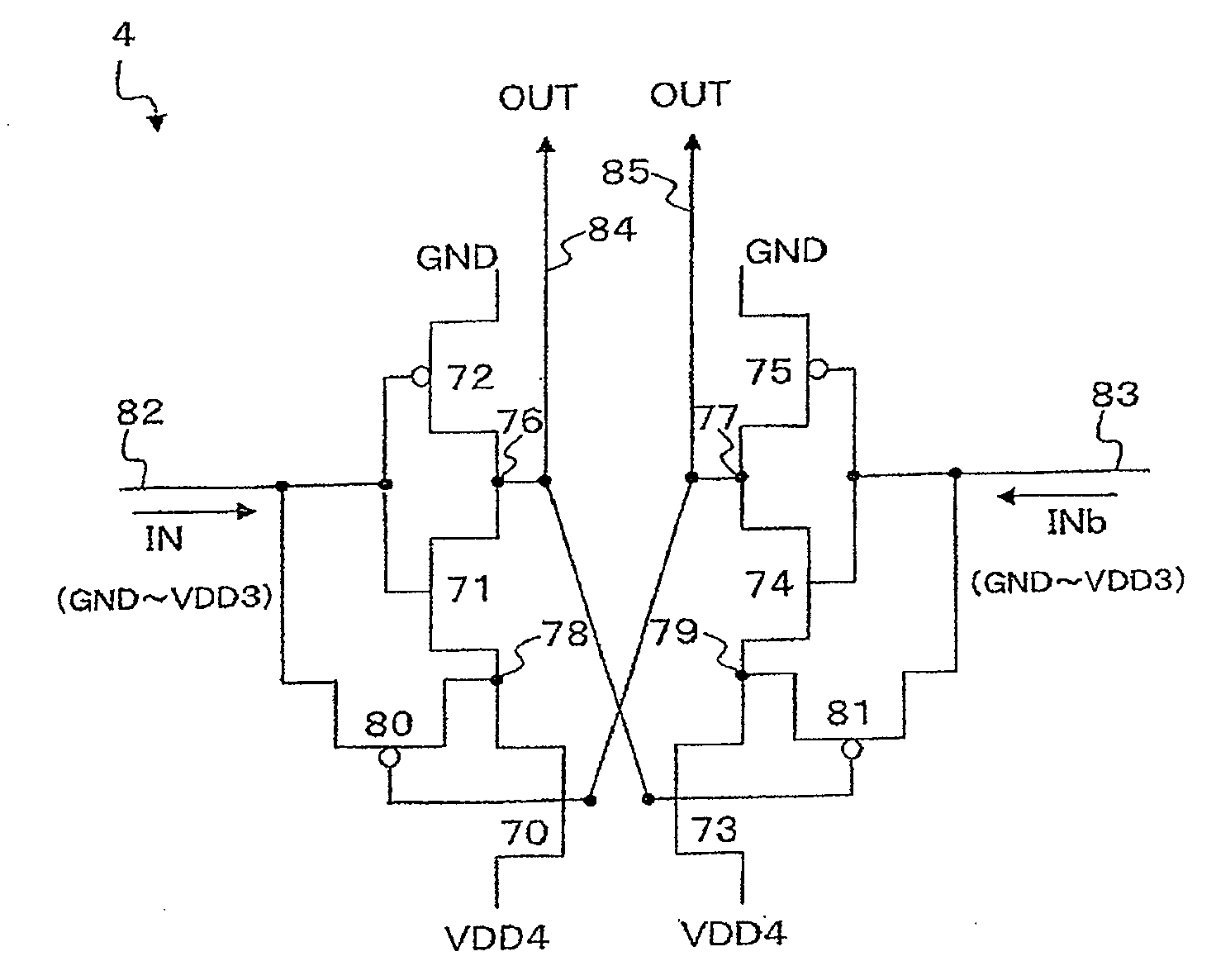
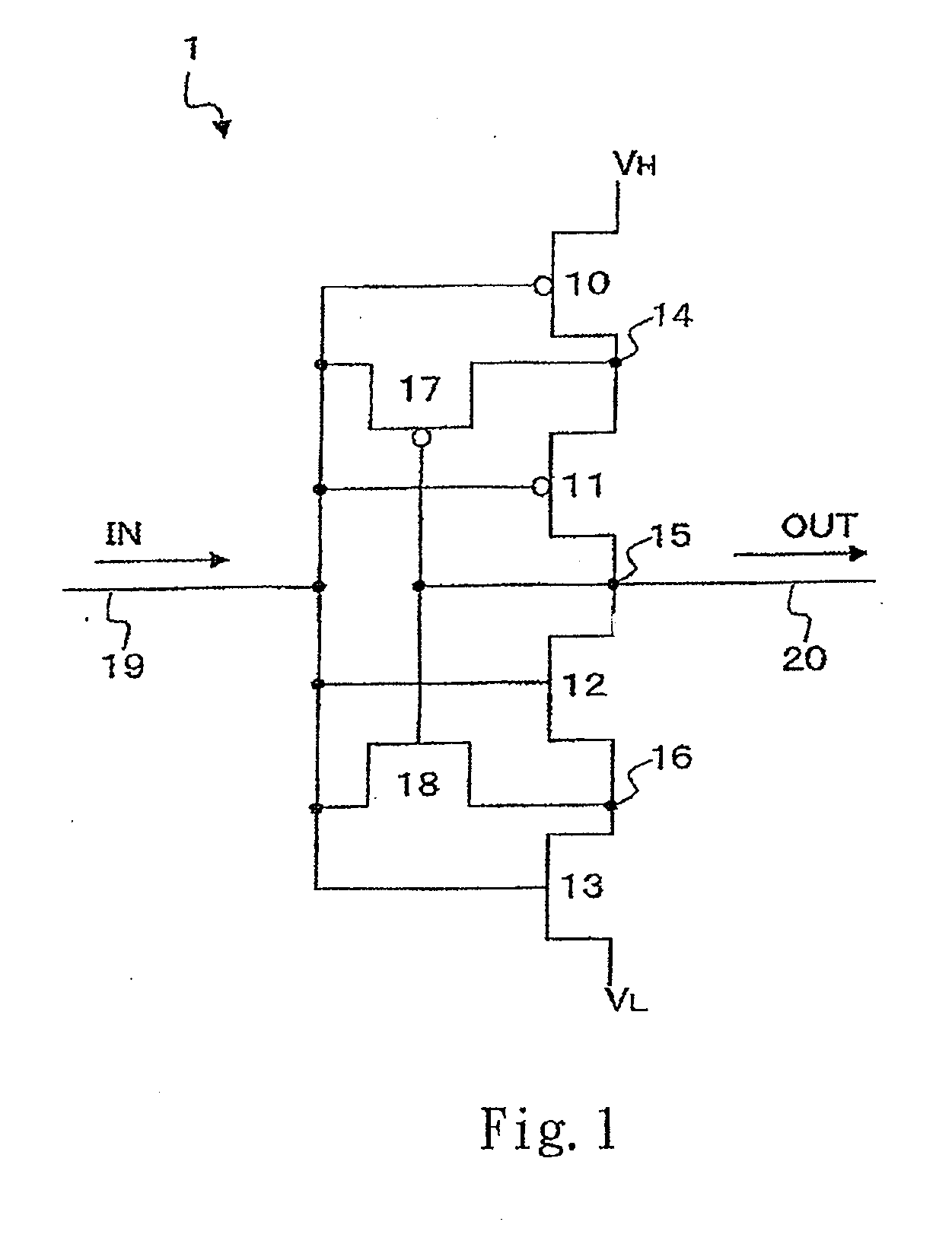
Semiconductor integrated circuit
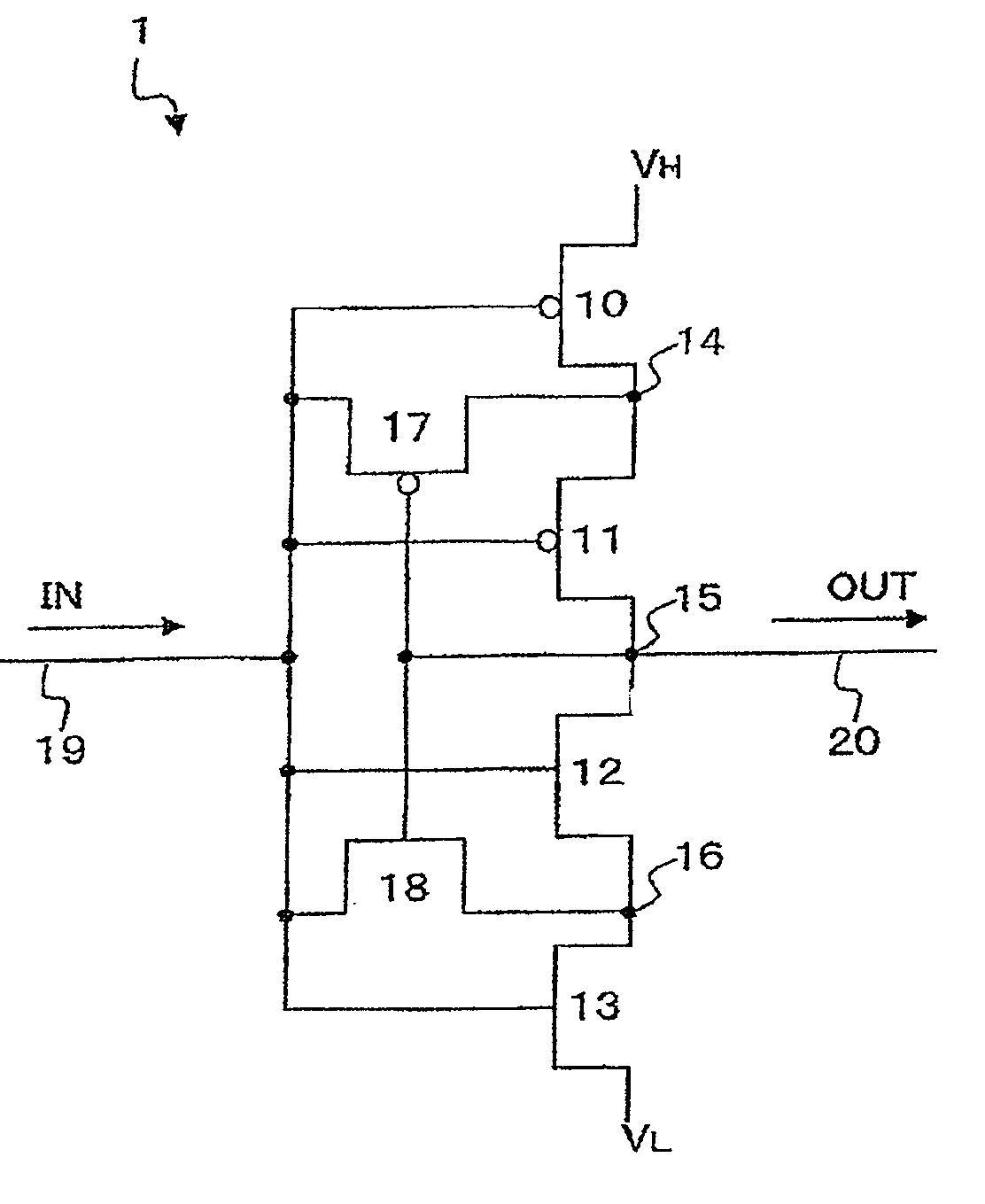
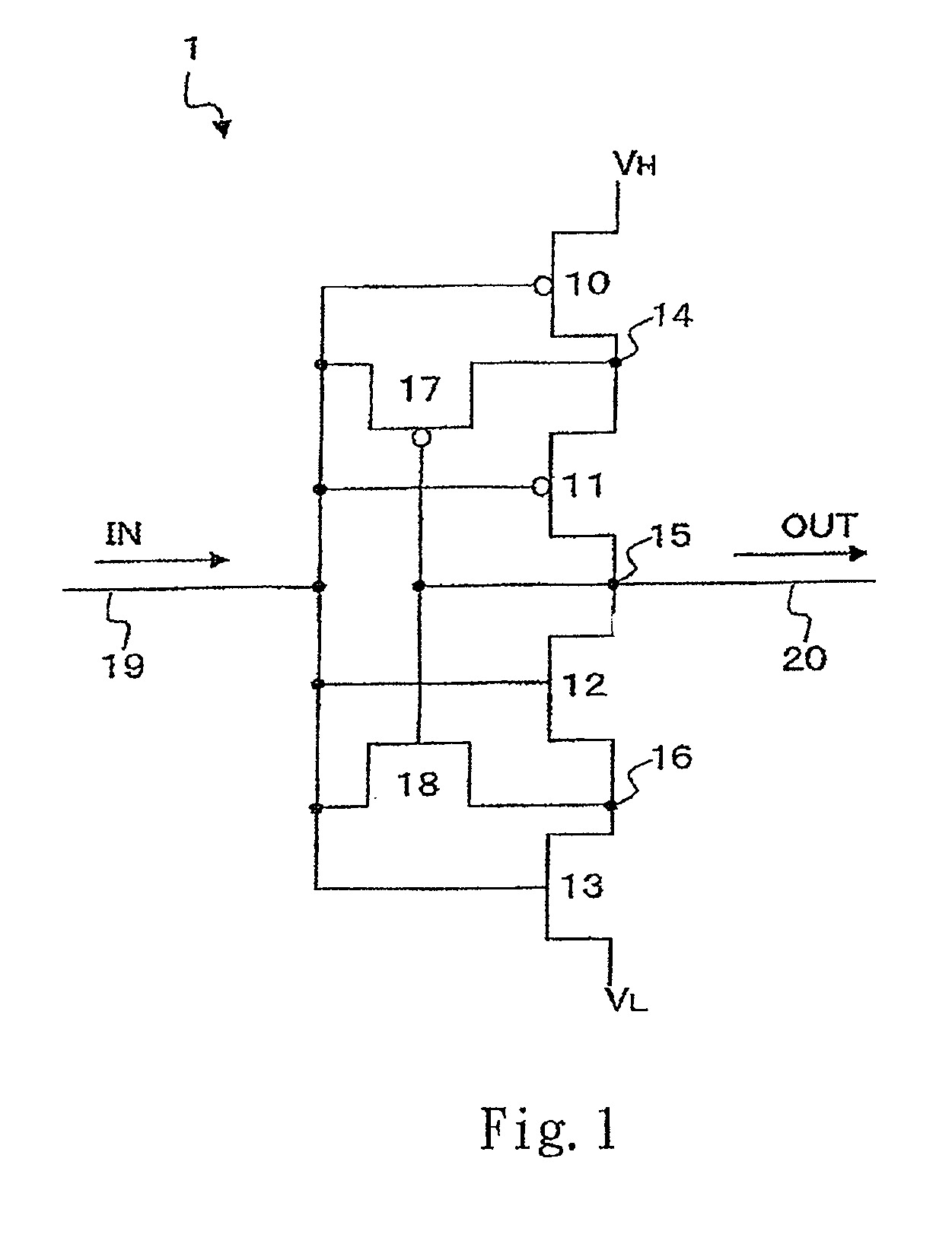
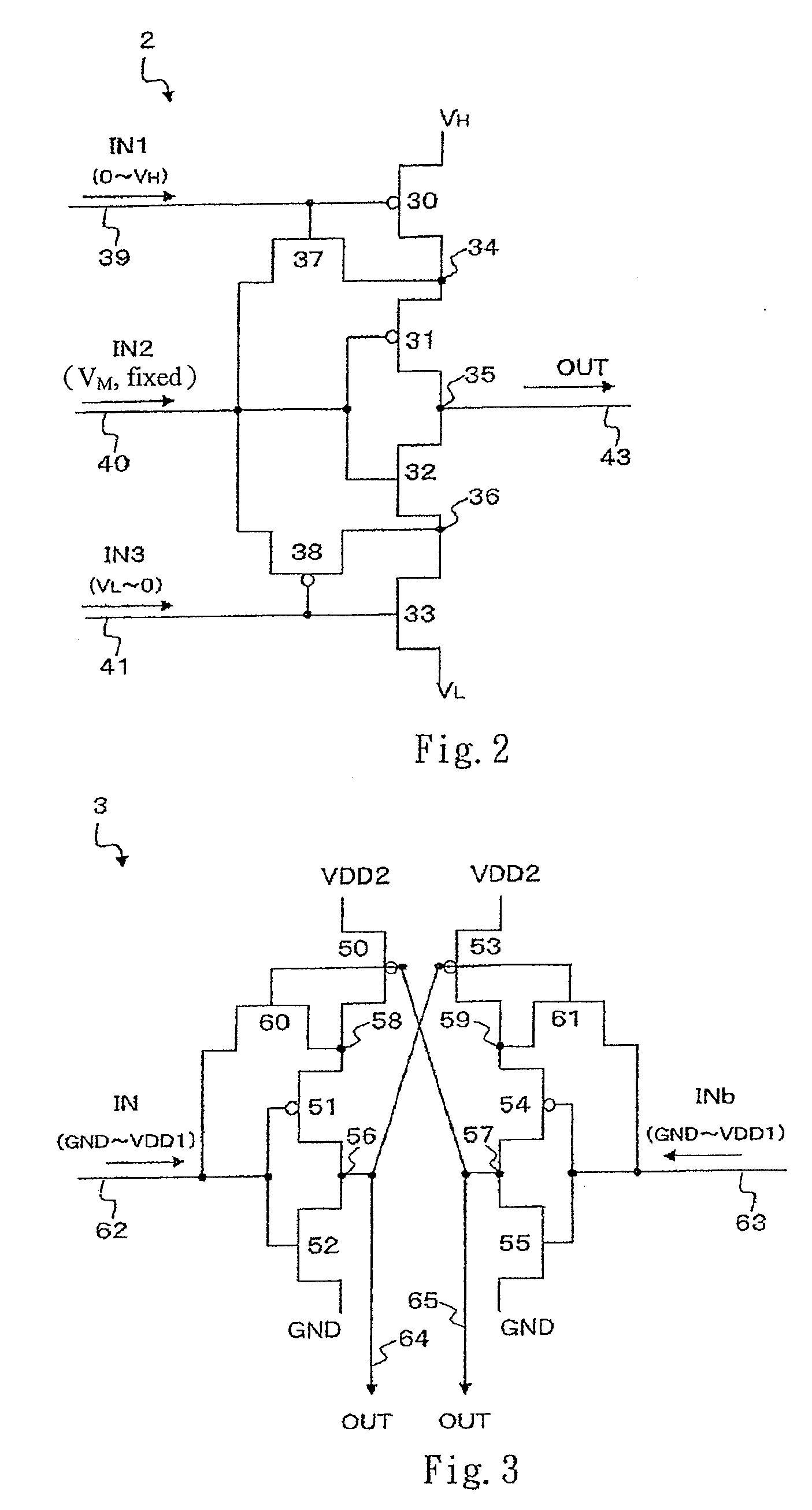
ActiveUS7940083B2Avoid feature degradationPulse automatic controlLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor integrated circuit capable of maintaining characteristics of transistors in a circuit including a plurality of cascade connected transistors. The circuit includes an inverter which has a series connection of P-MOS transistors and a pair of N-MOS transistors. The P-MOS transistor is connected to a high potential source VH and the N-MOS transistor is connected to a low potential source VL. The gate of each MOS transistor is connected to an input signal line. The inverter circuit further includes a P-MOS transistor connected between a node and input signal line, and an N-MOS transistor connected between a node of the N-MOS transistors and the input signal line. The gates of the P-MOS transistor and the N-MOS transistor are connected to an output signal line of the inverter circuit.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Method of forming capacitor of semiconductor device by successively forming a dielectric layer and a plate electrode in a single processing chamber
InactiveUS20060234500A1Simple processAvoid feature degradationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle chamberDielectric layer
A capacitor in a semiconductor device is formed by successively forming a dielectric layer and a plate electrode in a single chamber according to an ALD process. The method includes the steps of forming a storage electrode on a semiconductor substrate; loading the semiconductor substrate into an ALD chamber with the storage electrode formed thereon; forming a metal oxide dielectric layer on the storage electrode in the chamber according to an ALD process; and successively forming a metal plate electrode on the metal oxide dielectric layer in the same chamber according to the ALD process.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20090027103A1Prevent degradationAvoid feature degradationPulse automatic controlLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsSemiconductorHigh potential
A semiconductor integrated circuit capable of maintaining characteristics of transistors in a circuit including a plurality of cascade connected transistors. The circuit includes an inverter which has a series connection of P-MOS transistors and a pair of N-MOS transistors. The P-MOS transistor is connected to a high potential source VH and the N-MOS transistor is connected to a low potential source VL. The gate of each MOS transistor is connected to an input signal line. The inverter circuit further includes a P-MOS transistor connected between a node and input signal line, and an N-MOS transistor connected between a node of the N-MOS transistors and the input signal line. The gates of the P-MOS transistor and the N-MOS transistor are connected to an output signal line of the inverter circuit.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Semiconductor memory device using hot electron injection
InactiveUS20100244145A1Avoid feature degradationLess voltage dropTransistorSolid-state devicesVoltage dropSemiconductor package
A semiconductor memory device has a low-resistivity semiconductor substrate on which a higher-resistivity semiconductor layer of the same conductivity type is formed. Memory cell transistors are formed in the semiconductor layer. A diffusion region, also of the same conductivity type, is formed below the memory cell transistors. The resistivity of the diffusion region is lower than the resistivity of the semiconductor layer. In the programming of data into the memory cell transistors by hot electron injection, the diffusion region reduces the voltage drop due to current flow from the part of the semiconductor layer near the memory cell transistors into the semiconductor substrate, thereby reducing unwanted elevation of the potential of the semiconductor layer.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS8631266B2Avoid feature degradationError detection/correctionData resettingComputer scienceData recovery
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060141776A1Prevents deterioration of electrical characteristicsAvoid feature degradationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
Electrical characteristics of a semiconductor device may be enhanced by completely removing a residue such as a polymer formed in a trench when the semiconductor device is manufactured by a method including: forming a via hole and a trench on a semiconductor substrate by an etching process; coating a photoresist on an entire surface of the semiconductor substrate such that the via hole and the trench may be filled thereby; removing a polymer defect in the trench while removing the coated photoresist by a plasma treatment under predetermined process conditions; and performing a wet cleaning process so as to remove a residue of the photoresist.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing ferroelectric memory device and ferroelectric memory device
InactiveUS20070212796A1Avoid feature degradationPromote formationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium oxideFerroelectric capacitor
A method for manufacturing a ferroelectric capacitor includes the steps of: forming a ferroelectric capacitor having at least a lower electrode, a ferroelectric film and an upper electrode on a base substrate; and applying an anneal treatment to the ferroelectric capacitor in an oxygen atmosphere, wherein the step of forming the ferroelectric capacitor includes forming the ferroelectric capacitor to have a structure in which an electrode protection film composed of titanium oxide is provided on the upper electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
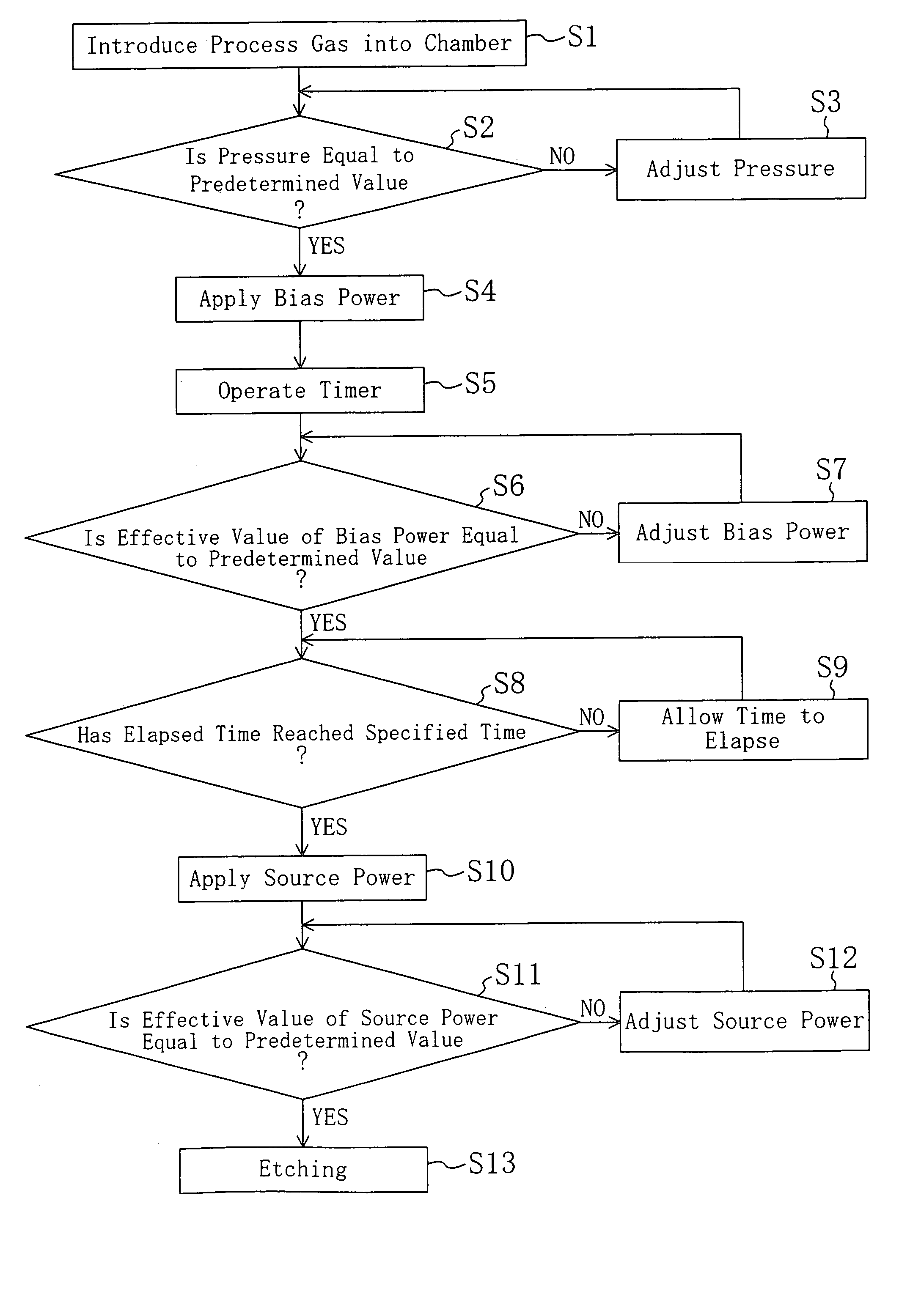
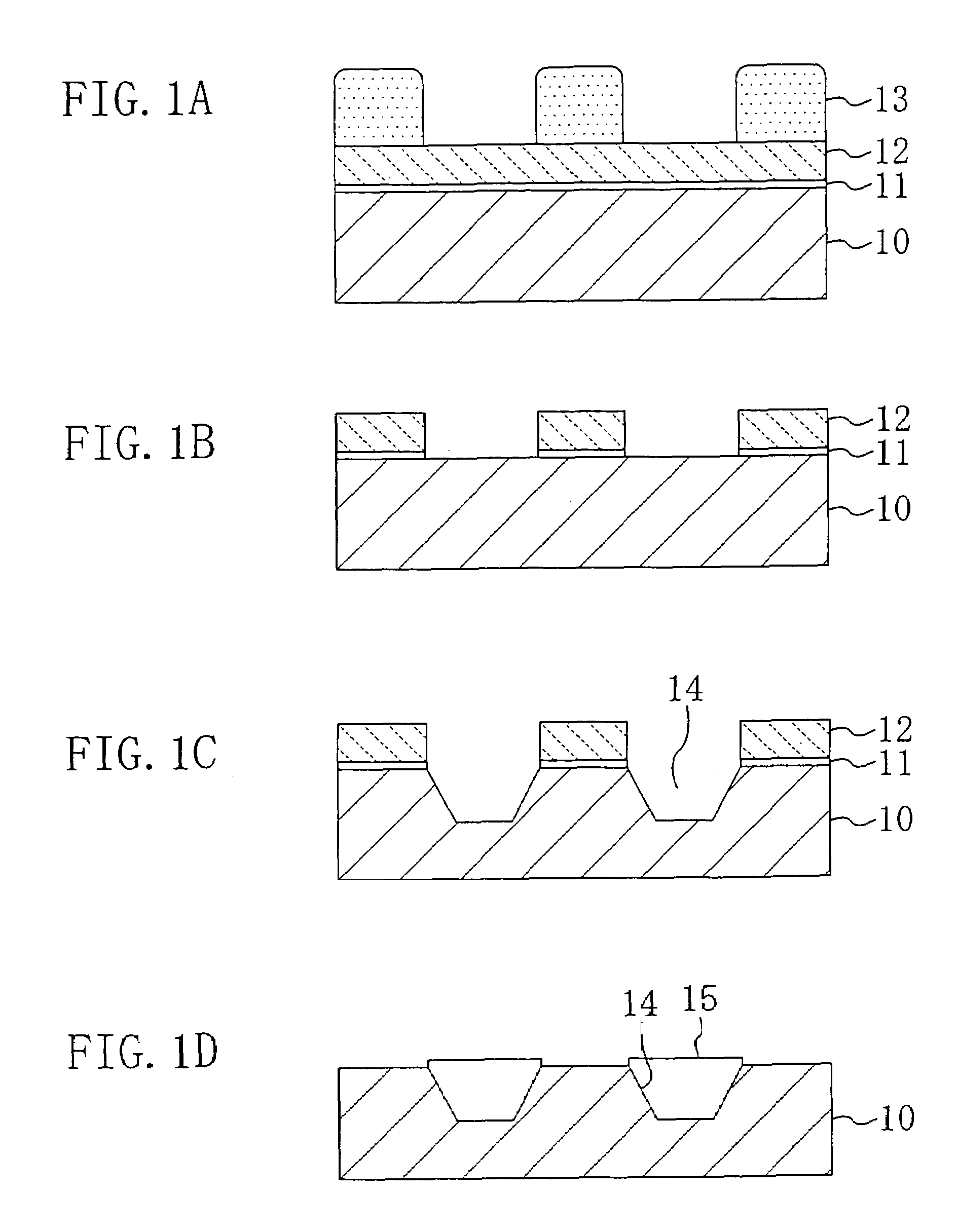
Dry etching method, fabrication method for semiconductor device, and dry etching apparatus
InactiveUS7148151B2Avoid feature degradationReduce surface stateElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringSilicon
When etching is performed with respect to a silicon-containing material by using a dry etching apparatus having a dual power source, the application of bias power is initiated before oxidization proceeds at a surface of the silicon-containing material. Specifically, the application of the bias power is initiated before the application of source power is initiated. Alternatively, the source power and the bias power are applied such that the effective value of the source power reaches a second predetermined value after the effective value of the bias power reaches a first predetermined value.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com