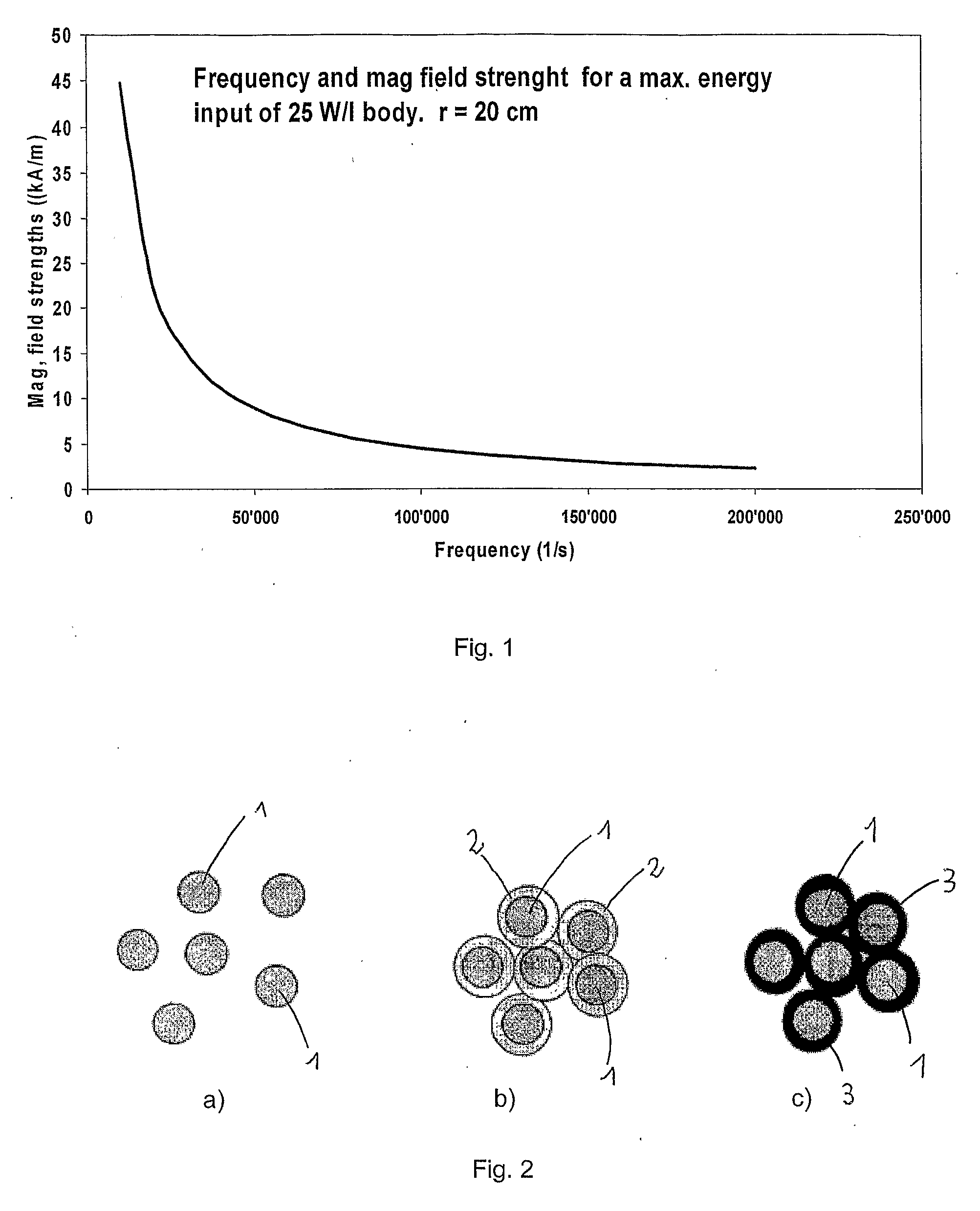
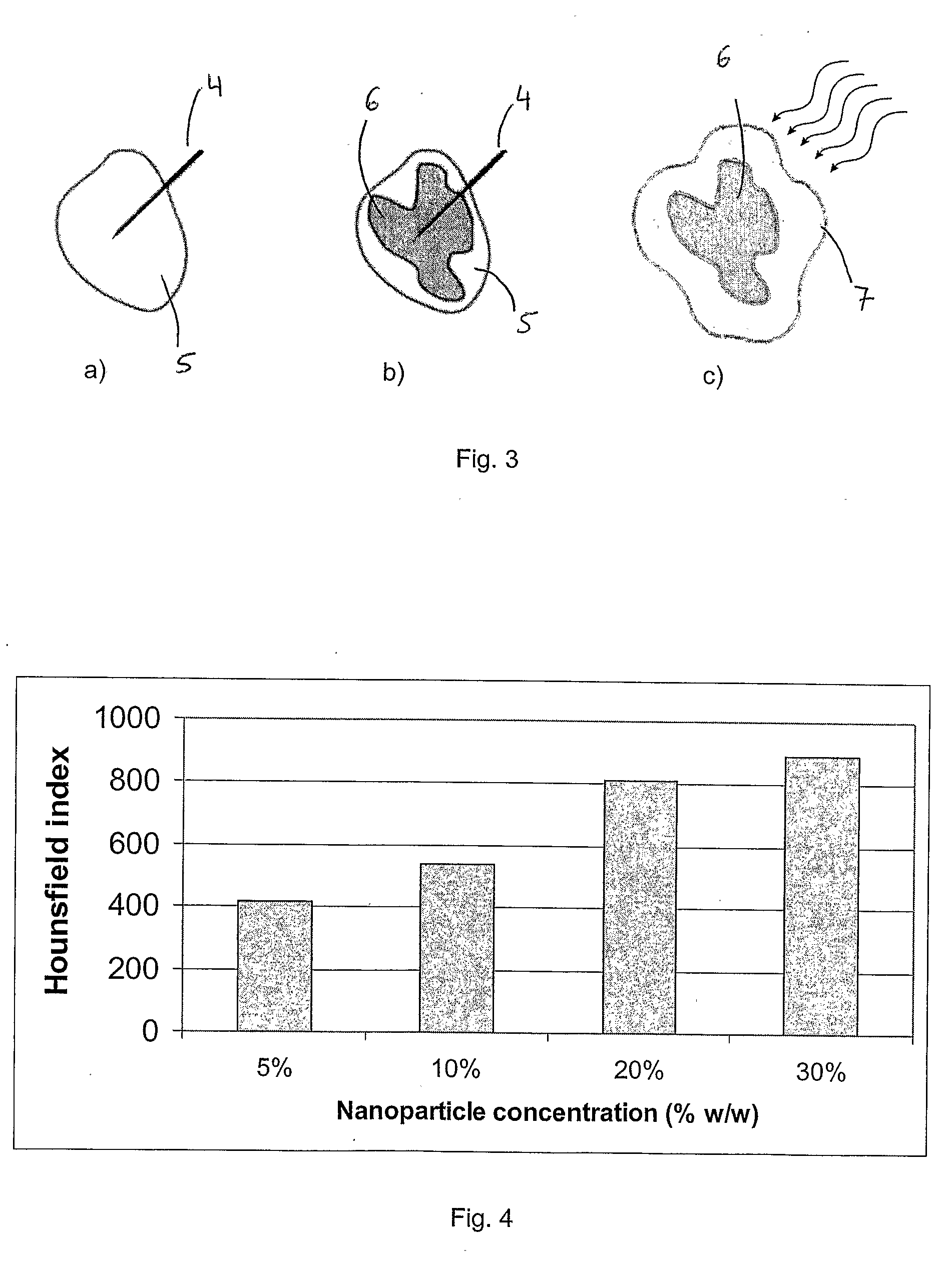
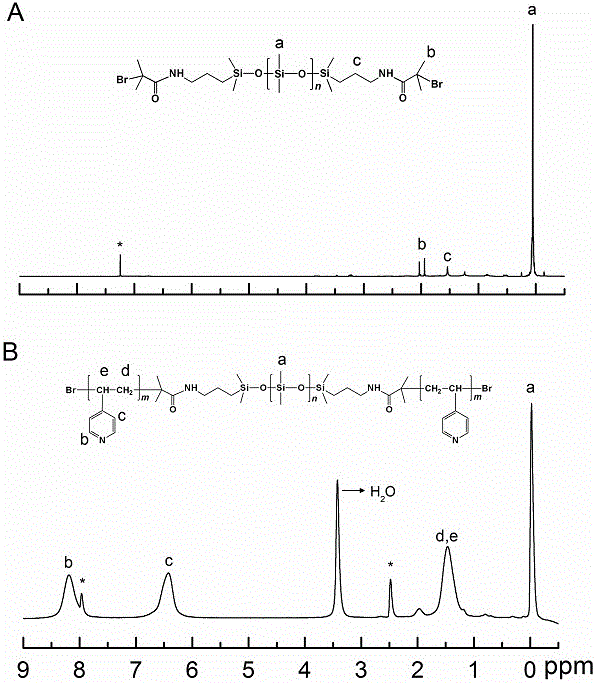
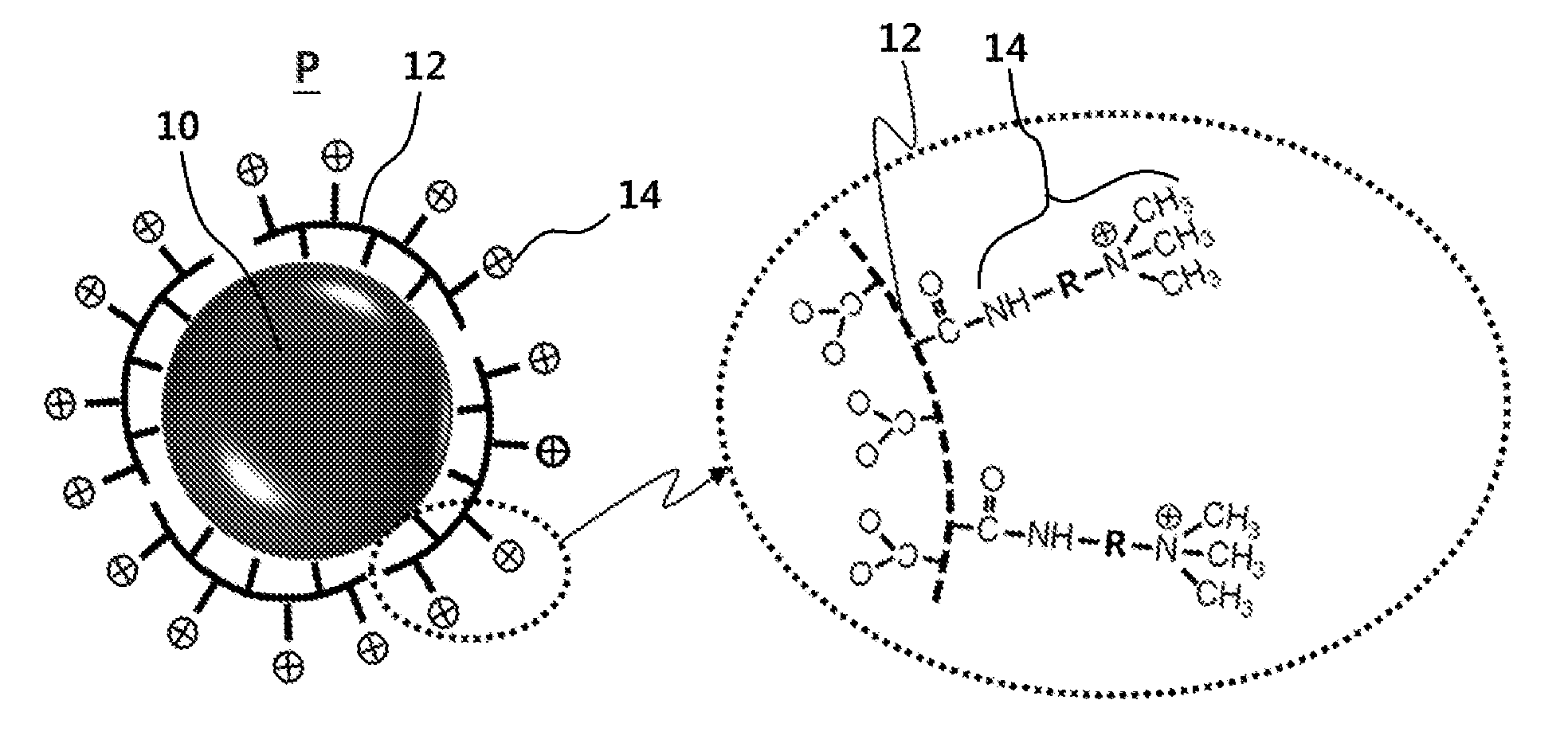
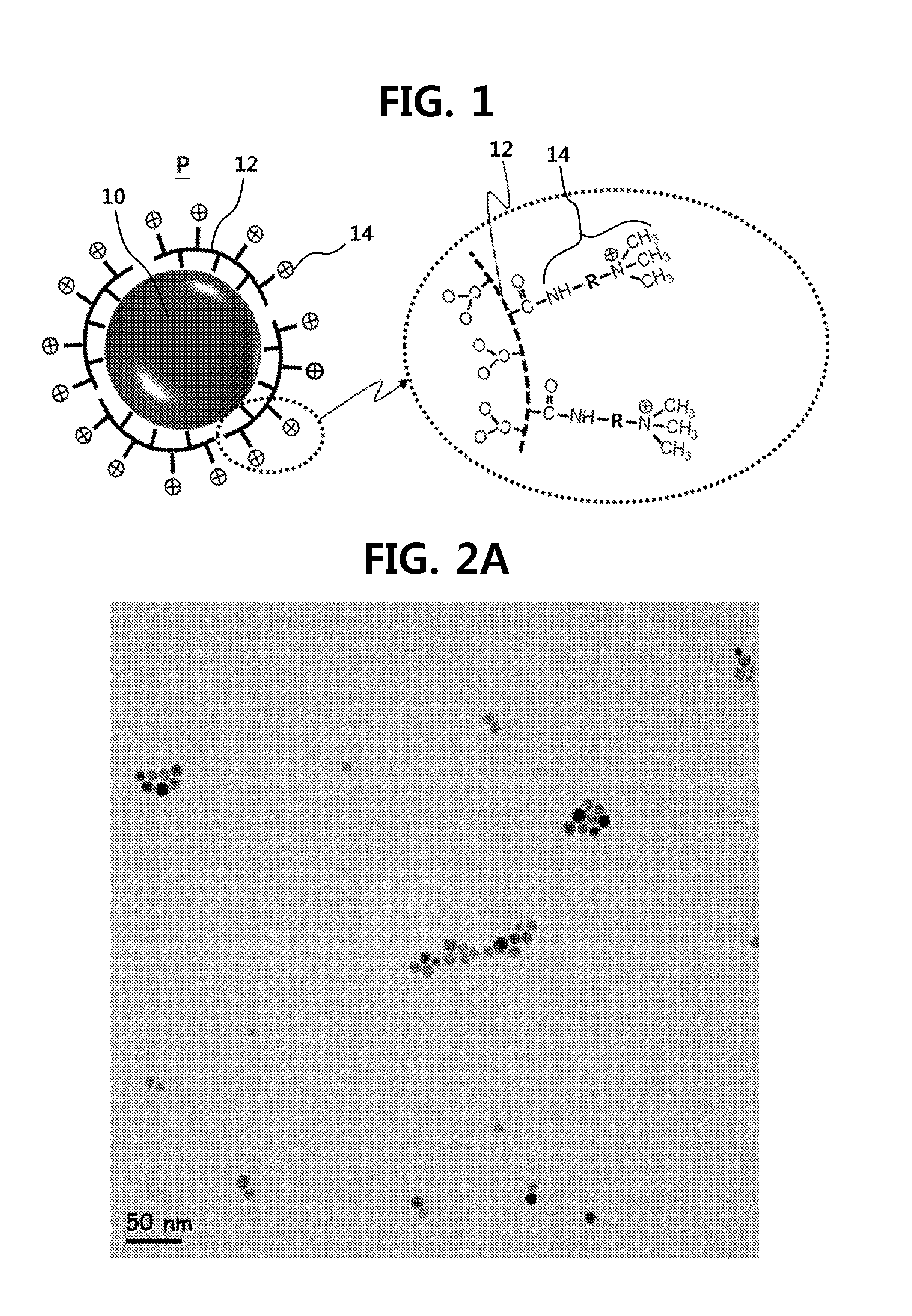
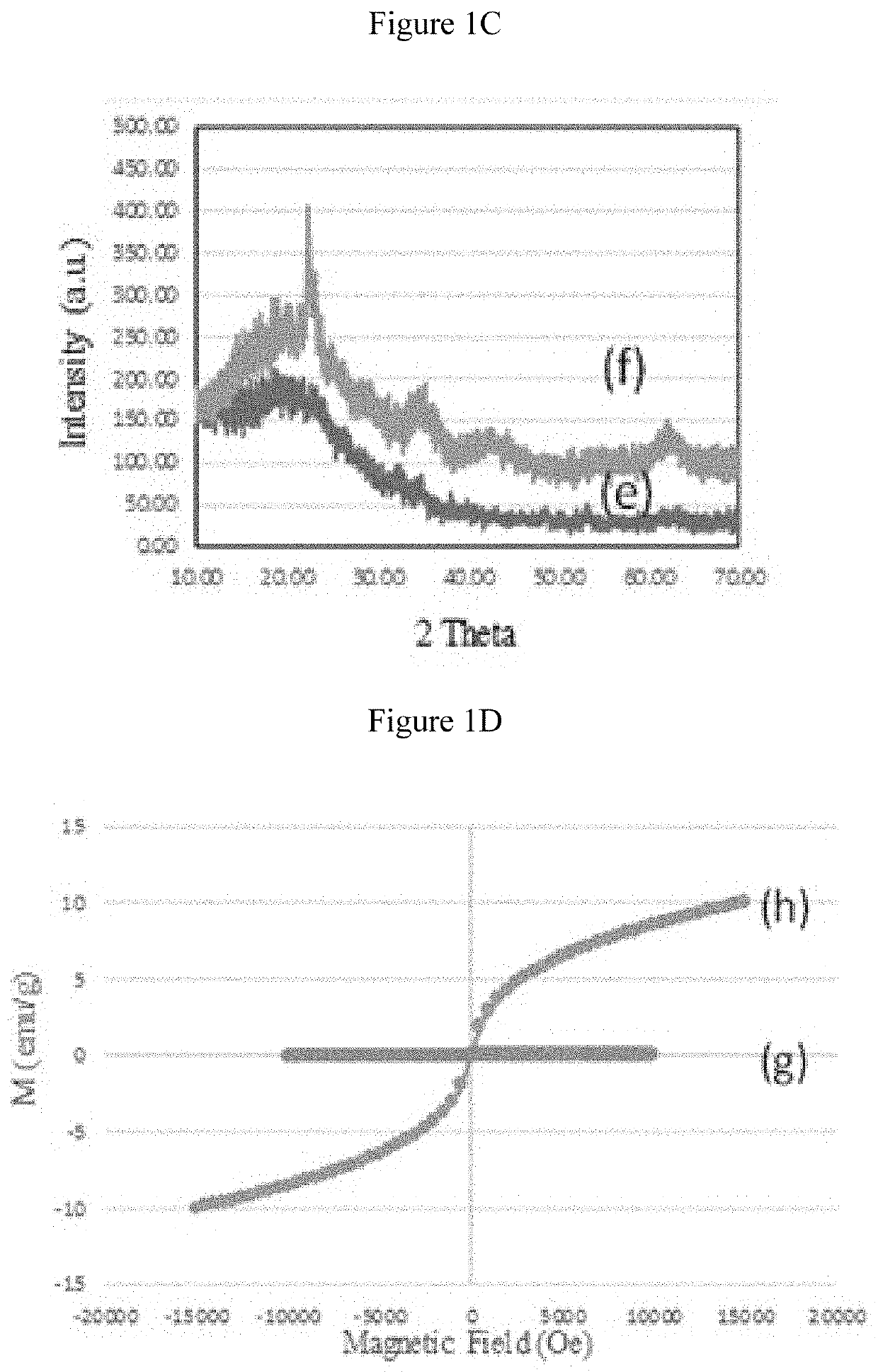
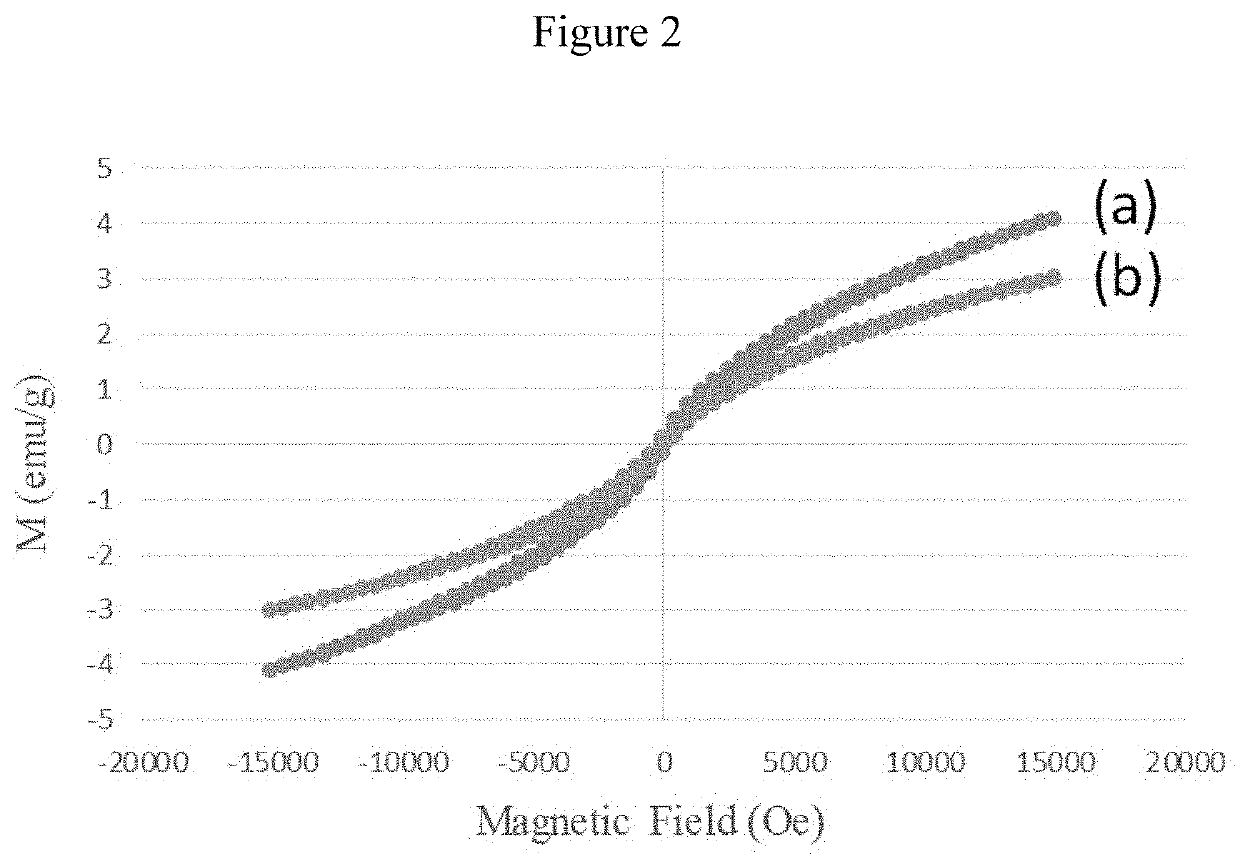
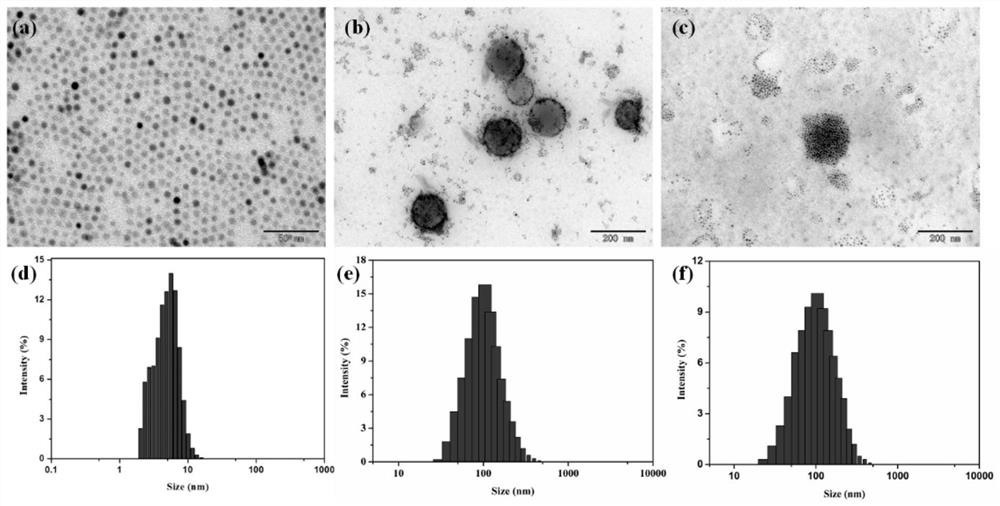
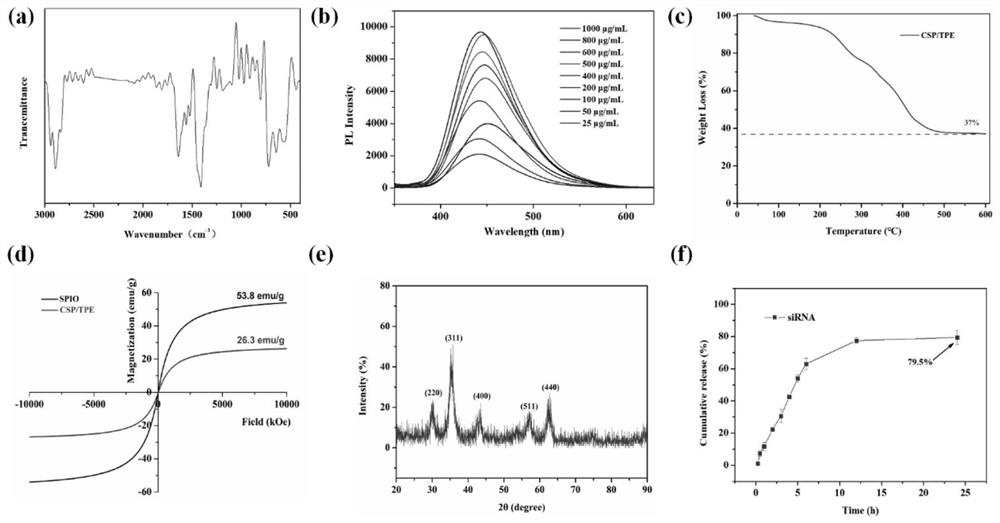
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Injectable superparamagnetic nanoparticles for treatment by hyperthermia and use for forming an hyperthermic implant
The injectable formulation for treatment by hyperthermia comprises a liquid carrier and heat-generating superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles having a mean diameter not greater than 20 nm. Said injectable formulation is able to form in-situ a hyperthermic solid or semi-solid implant upon contact with a body fluid or tissue. Said hyperthermic solid or semi-solid implant may be useful for treating a tumor or a degenerative disc disease by hyperthermia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA +2
Hybrid nanoparticle with pH and magnetic responsiveness and preparation method thereof and application of hybride nanoparticle in nano oil-water separation emulsion
InactiveCN106832159AEasy to separateImprove oil absorption efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticlesEmulsion
The invention discloses a Fe3O4@SiO2@P4VP-PDMS-P4VP hybrid nanoparticle with pH and magnetic responsiveness and a preparation method thereof and an application of the hybrid nanoparticle in a nano oil-water separation emulsion. The Fe3O4@SiO2@P4VP-PDMS-P4VP hybrid nanoparticle is obtained by coupling reaction of a pyridine group on a P4VP block in a P4VP-PDMS-P4VP triblock copolymer with pH responsiveness with a C-I active group on the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles Fe3O4@SiO2 surface and bonding the P4VP-PDMS-P4VP triblock copolymer into the Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle surface. The invention further specifically discloses the preparation method of the Fe3O4@SiO2@P4VP-PDMS-P4VP hybrid nanoparticle and the application of the Fe3O4@SiO2@P4VP-PDMS-P4VP hybrid nanoparticle in the nano oil-water separation emulsion. Due to the action of the central Fe3O4magnetic nanoparticle, the hybrid nanoparticle absorbing oil content can be easily separated from an aqueous system, and the oil absorbed hybrid nanoparticle can be recycled in an acid aqueous solution after absorption.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of RGD-modified subminiature superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
InactiveCN104399092ALow costLow signalEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of RGD-modified subminiature superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing PEI-coated subminiature superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by a mild reduction method, modifying surfaces of USPIO / PEI.NH2 nanoparticles by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FI) and a RGD compound (COOH-PEG-RGD) subjected to pegylation, and carrying out acetylation treatment on the surfaces of the nanoparticles. The preparation method has simple processes and mild reaction conditions and can be operated easily. The RGD-modified subminiature superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have small sizes, a high relaxation rate, good colloid stability and biocompatibility, and high alpha<v>beta<3> integrin high-expression tumor cell targeting, and have a latent application value in the field of in-vivo tumor targeting MR imaging diagnosis.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
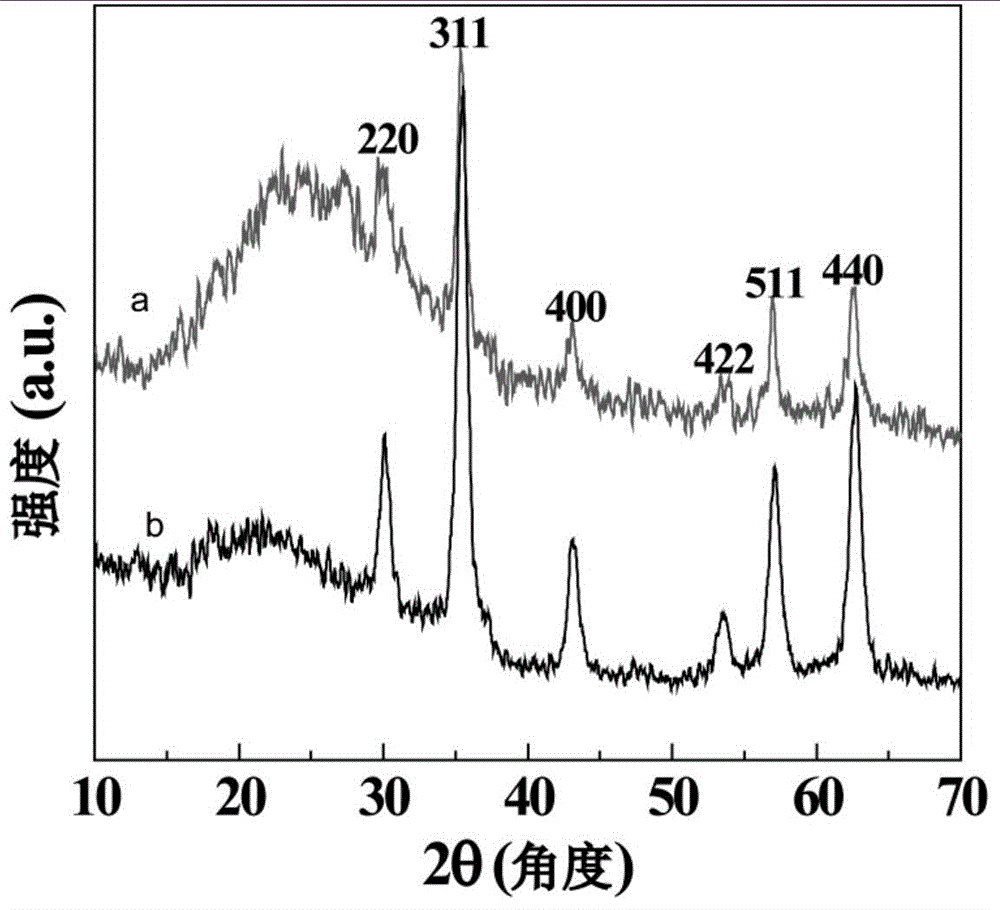
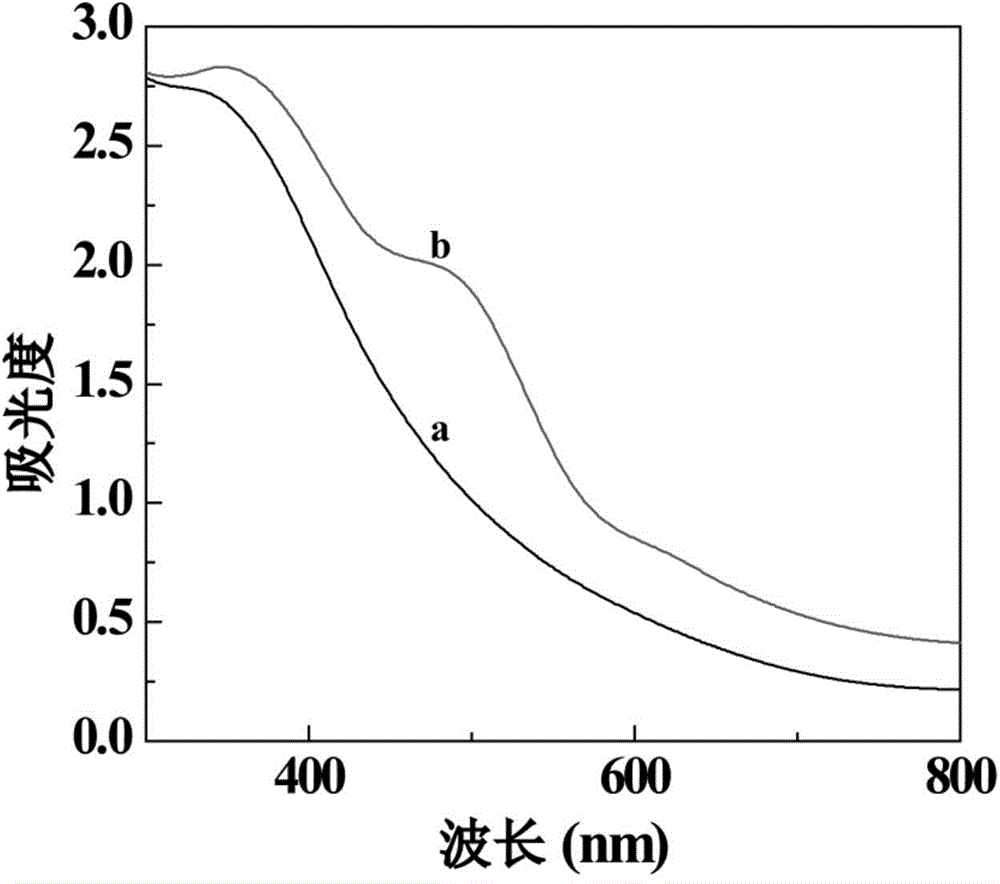
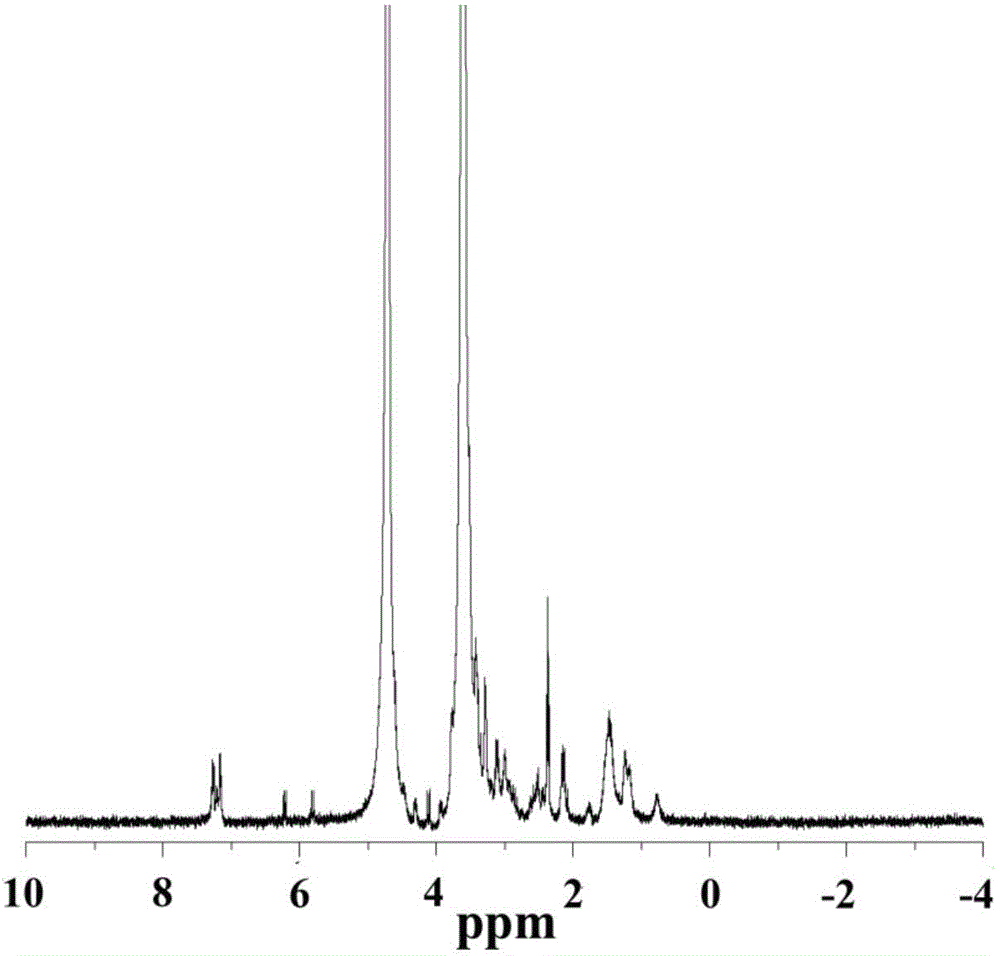
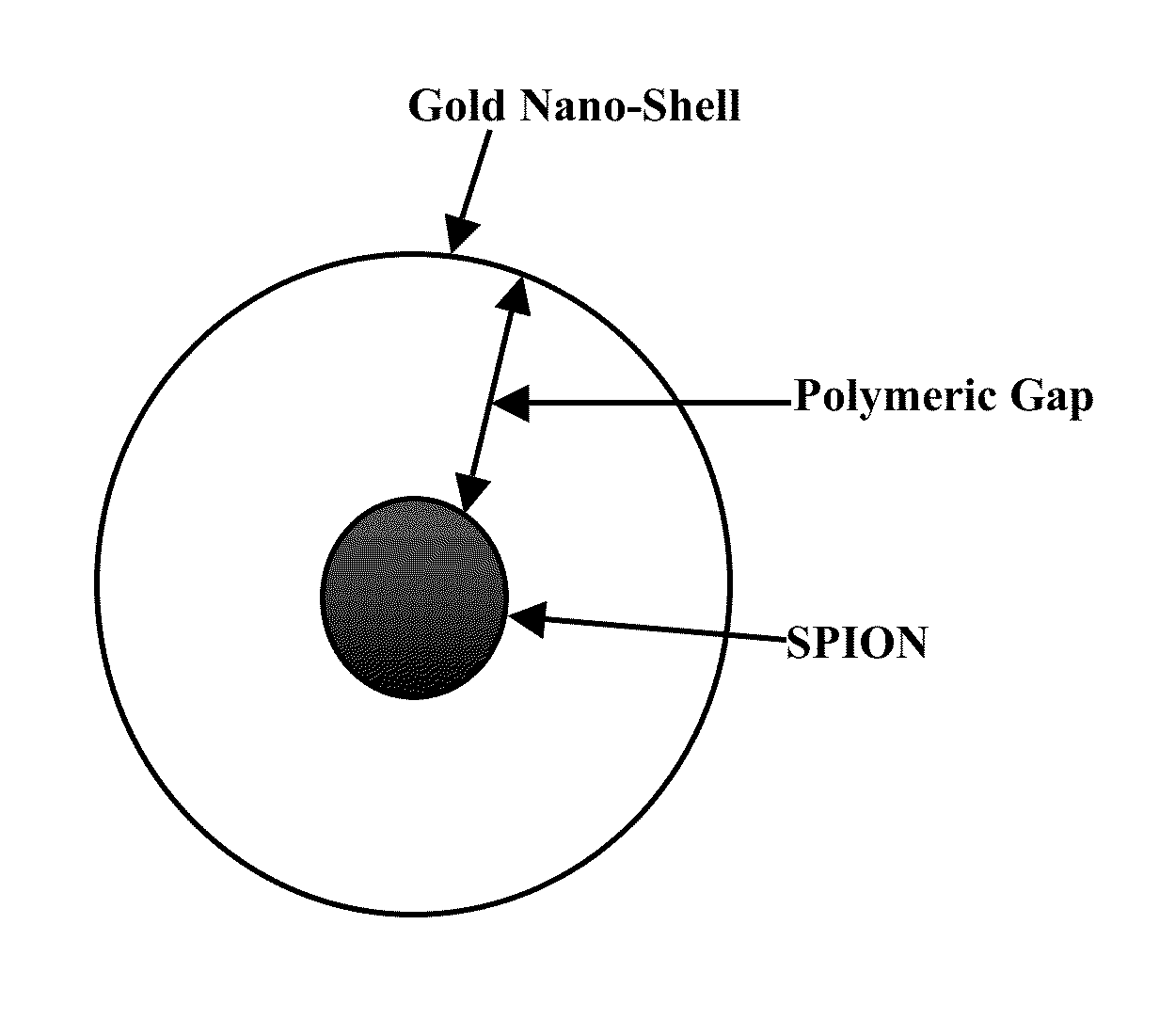
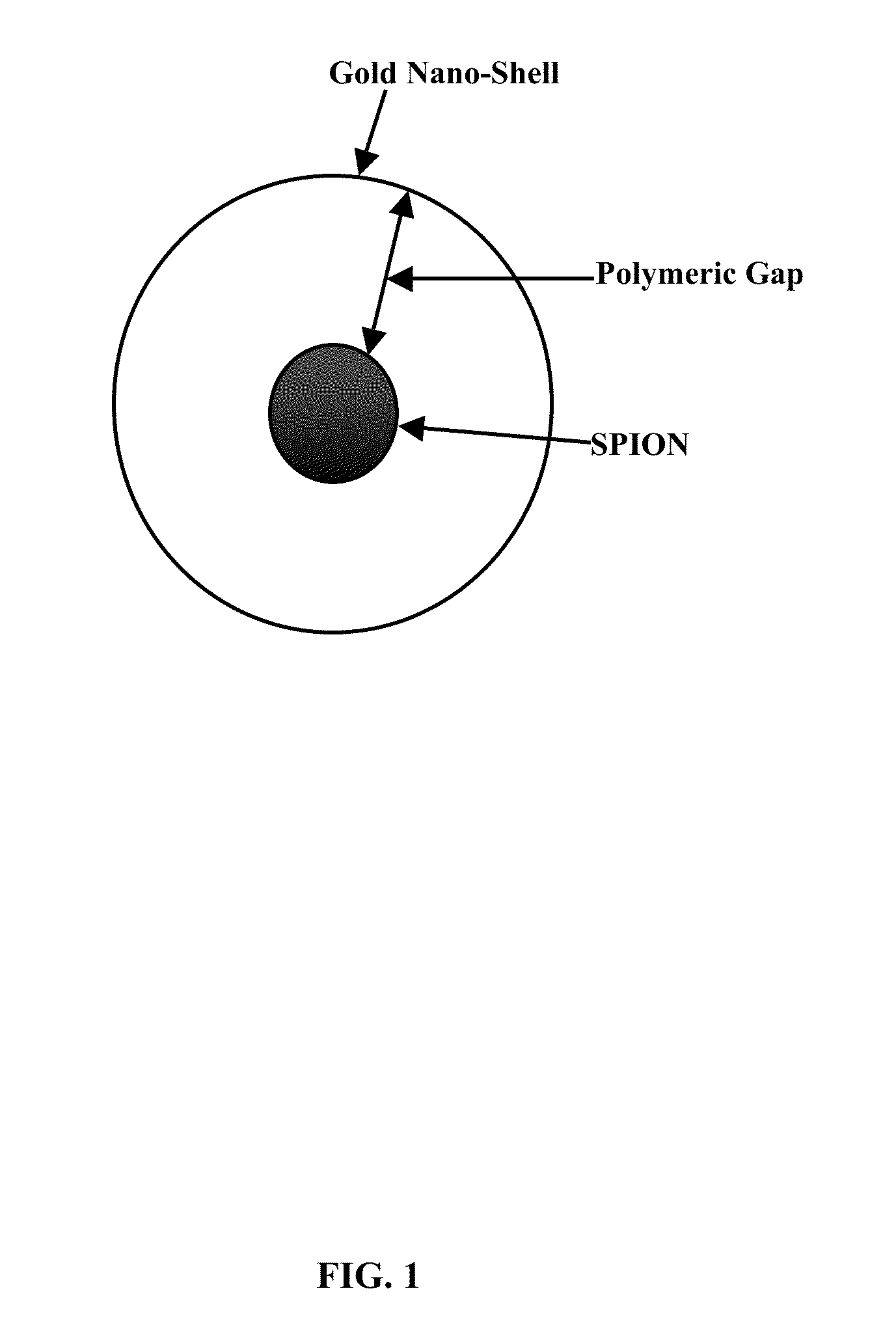
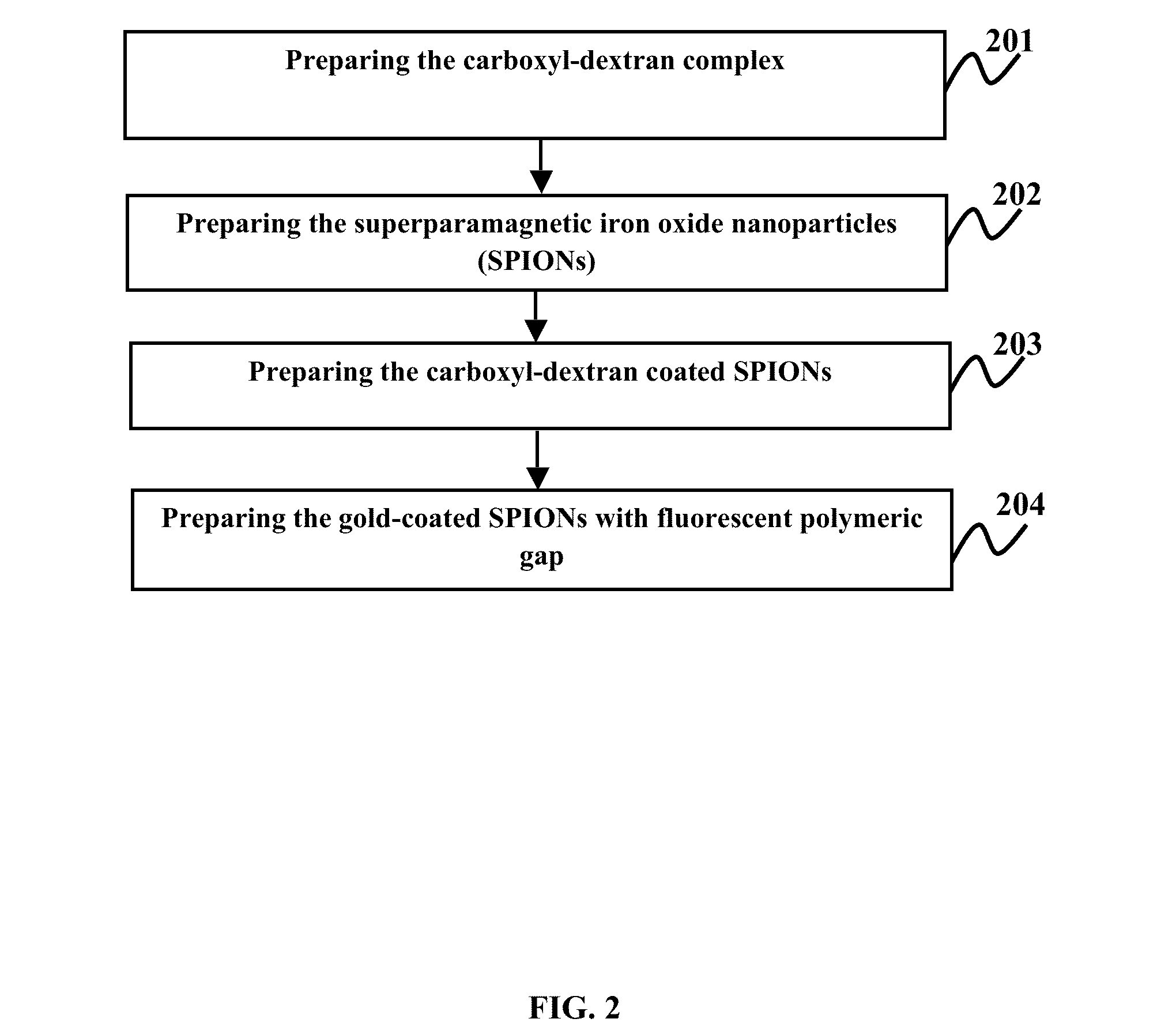
Plasmonic stable fluorescence superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a method of synthesizing the same
The various embodiments herein provide for the engineered multimodal super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) with a fluorescent dye. The SPIONs comprise fluorescent polymer dye arranged in a gap between a SPION core and a gold shell. The SPIONS are provided with a gold coating. The gap is made up of a polymeric molecule such as 6-arm anthracene terminated. The core of the nanoparticle is made up of a magnetic metal oxide. The method for synthesizing SPIONs involves preparing carboxyl-dextran complex and the SPIONS. The SPIONs are coated with carboxyl-dextran complex. The coated SPIONs coated are subjected to fluorescent polymer and gold nano shell coating. The prepared SPIONs are characterized by light scattering measurement and magnetization measurements.
Owner:MAHMOUDI MORTEZA +1
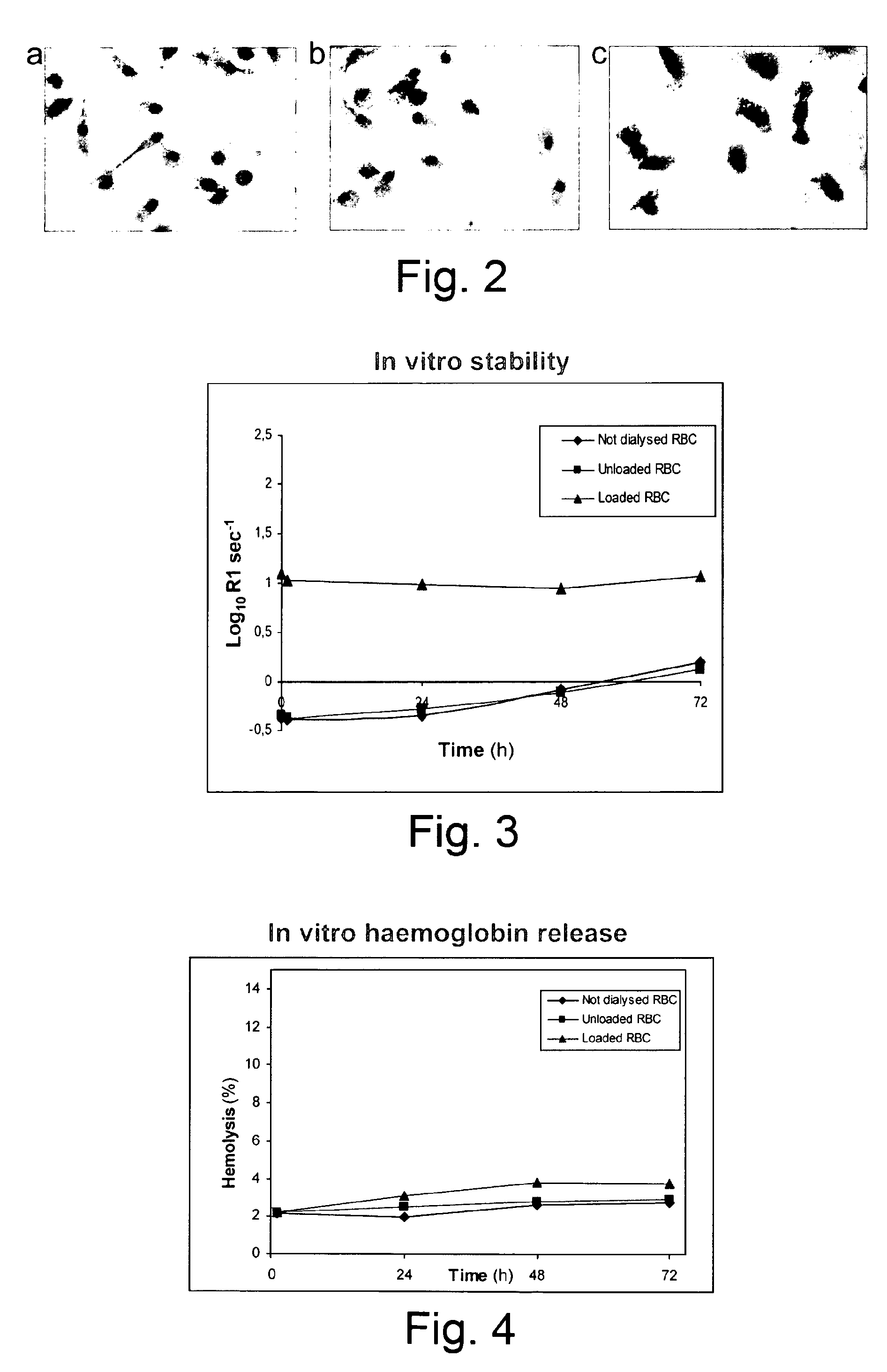
Delivery of contrasting agents for magnetic resonance imaging
Erythrocytes exposed to dialysis with an hypotonic buffer stably take up superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and may be used MRI contrast agents. Such erythrocytes may also be used as drug delivery vehicles.
Owner:ERYDEL
Curcumin-based magnetic nanostructured system for dual response of imaging and therapeutics
ActiveUS20200038525A1Reduced viabilityImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryNanomedicineNanocarriersDual response
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
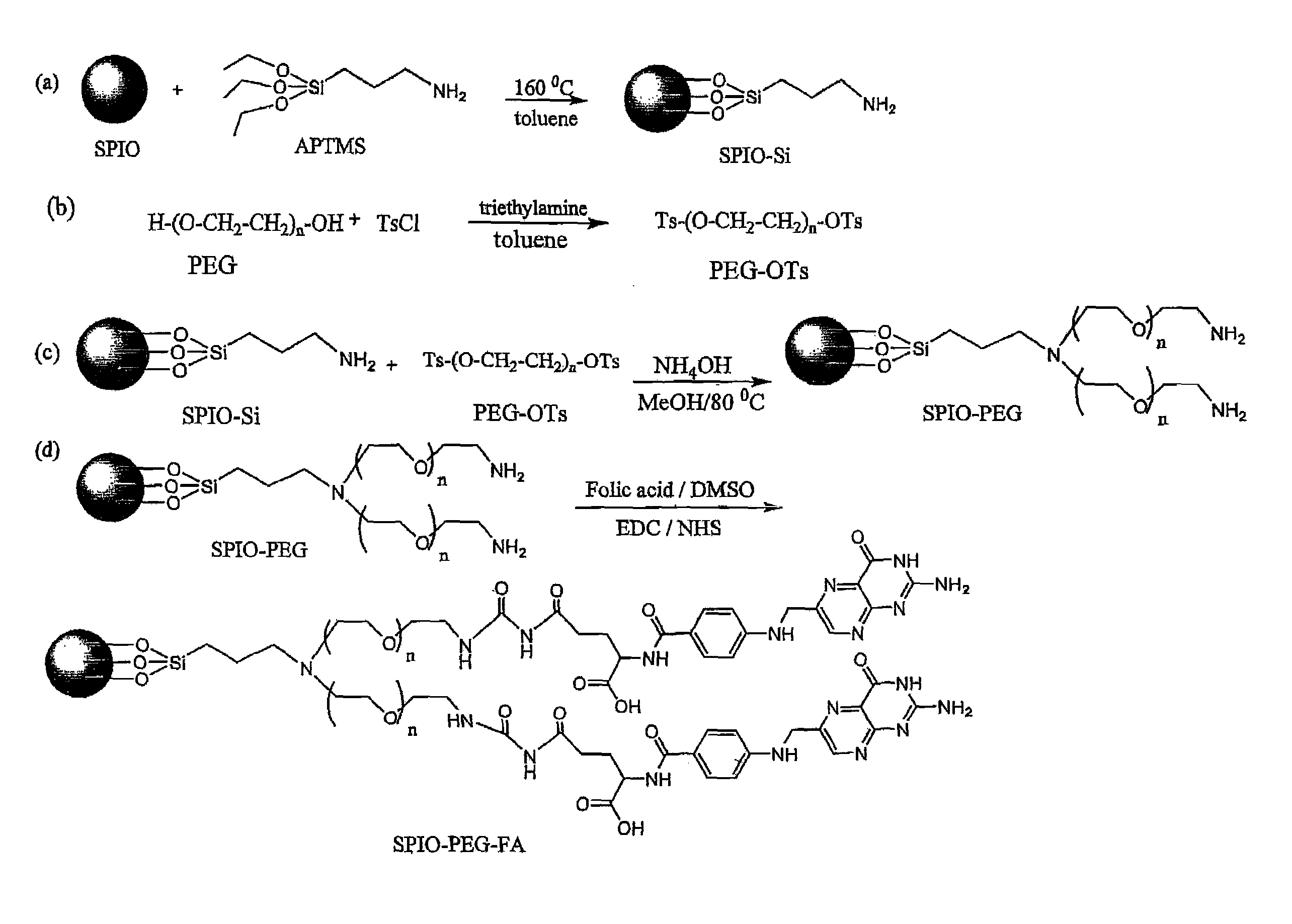
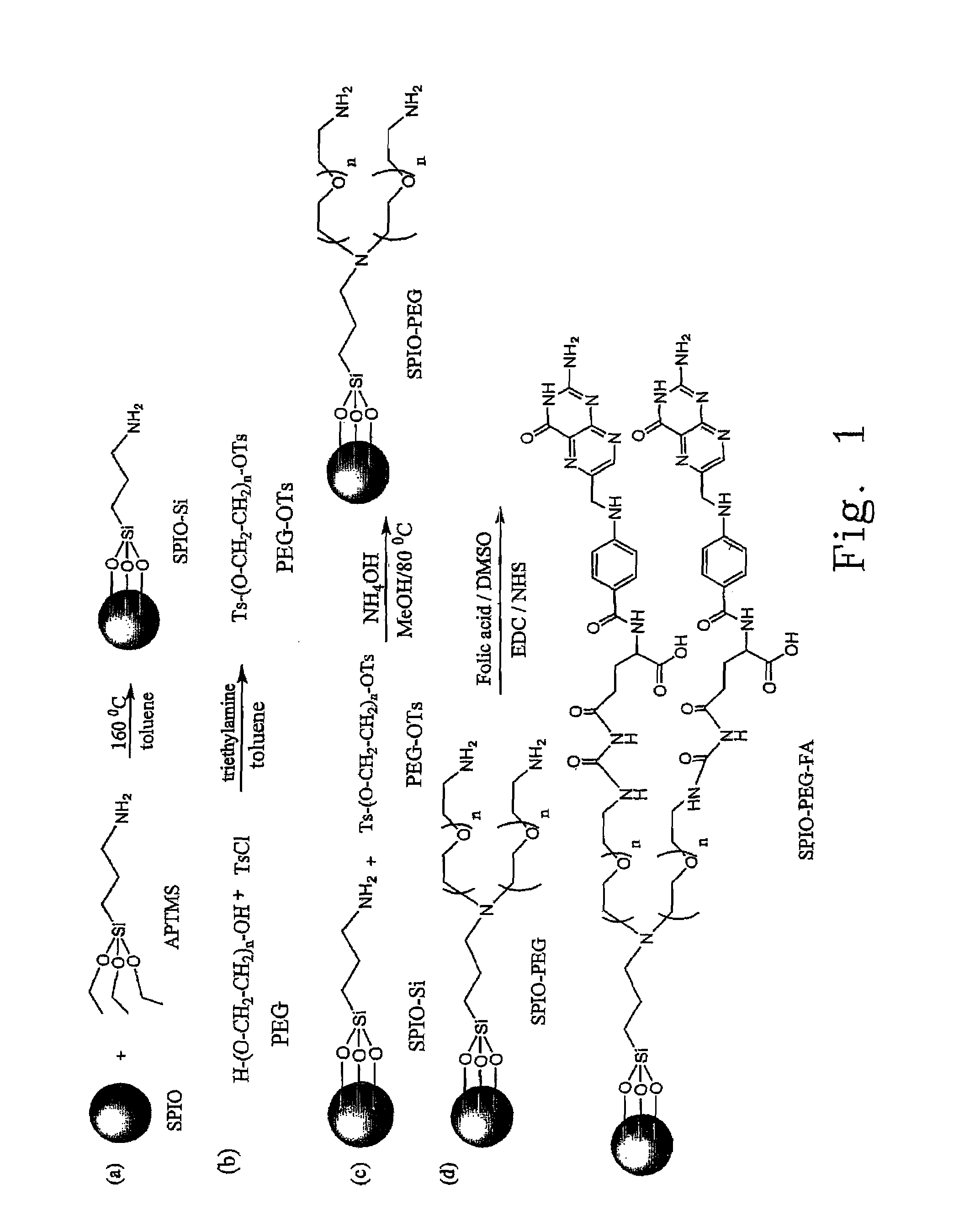
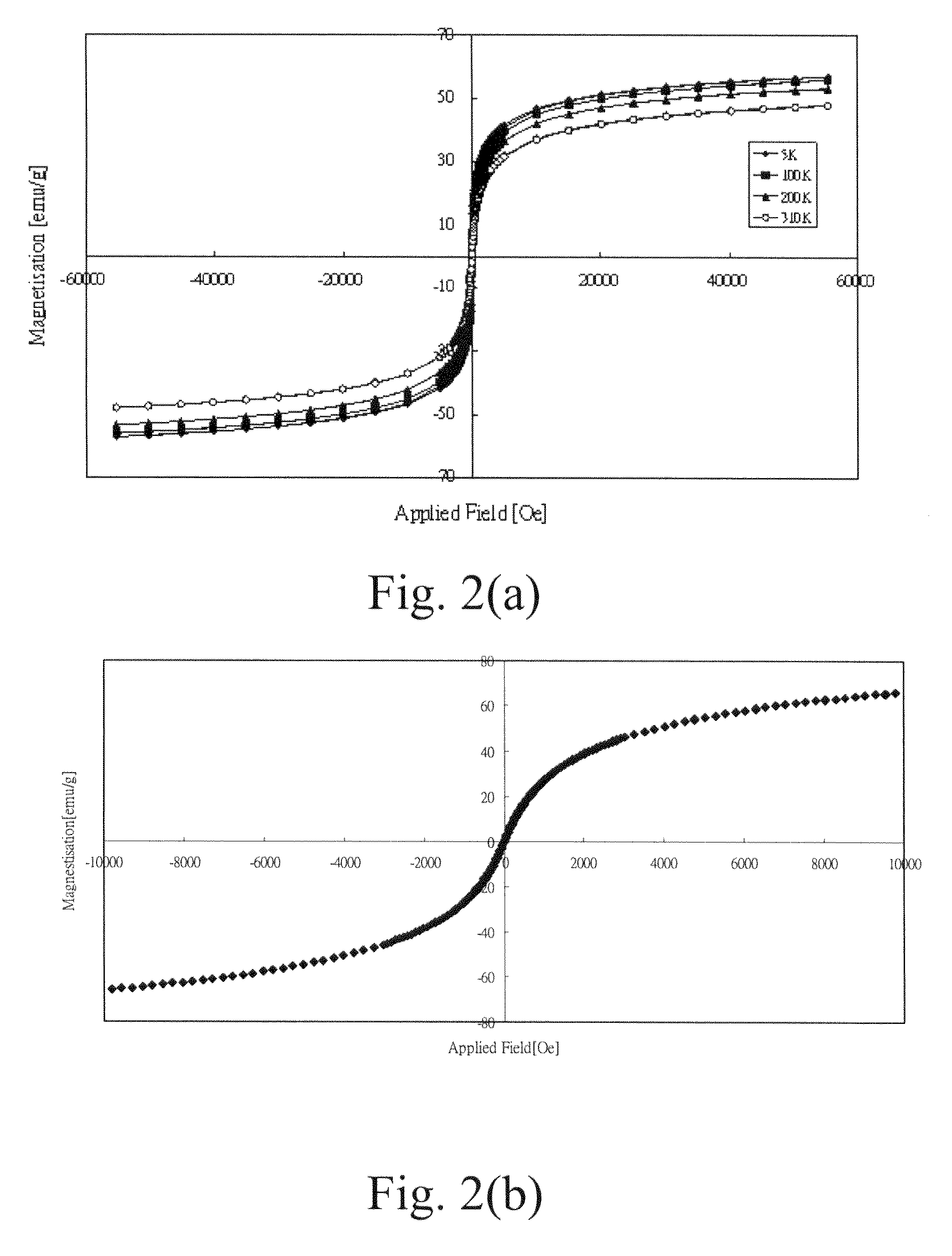
Folate-receptor-targeting iron oxide nanoparticles coated with poly(ethylene glycol)
InactiveUS7598335B2Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSynthesis methodsSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle
The present invention provides the synthetic method and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles capable of targeting to the folic acid receptors existing on the cell membranes and with high relaxivity. The iron oxide nanoparticles of the present invention can further be used as the contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Catalyst composition comprising magnetic material adapted for inductive heating
PendingUS20190070596A1Improve efficiencyReadily dispersibleGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesIron oxideSuperparamagnetic iron oxide
The invention provides a catalyst composition, including a mixture of catalytically active particles and a magnetic material, such as superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, capable of inductive heating in response to an applied alternating electromagnetic field. The catalytically active particles will typically include a base metal, platinum group metal, oxide of base metal or platinum group metal, or combination thereof, and will be adapted for use in various catalytic systems, such as diesel oxidation catalysts, catalyzed soot filters, lean NOx traps, selective catalytic reduction catalysts, ammonia oxidation catalysts, or three-way catalysts. The invention also includes a system and method for heating a catalyst material, which includes a catalyst article that includes the catalyst composition and a conductor for receiving current and generating an alternating electromagnetic field in response thereto, the conductor positioned such that the generated alternating electromagnetic field is applied to at least a portion of the magnetic material.
Owner:BASF CORP
High-sensitivity bimodal magnetic resonance contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108030933AAccurate diagnosisEnhancing the Effects of Dual-Modal Magnetic Resonance ImagingGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsNanomedicineChemical synthesisSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
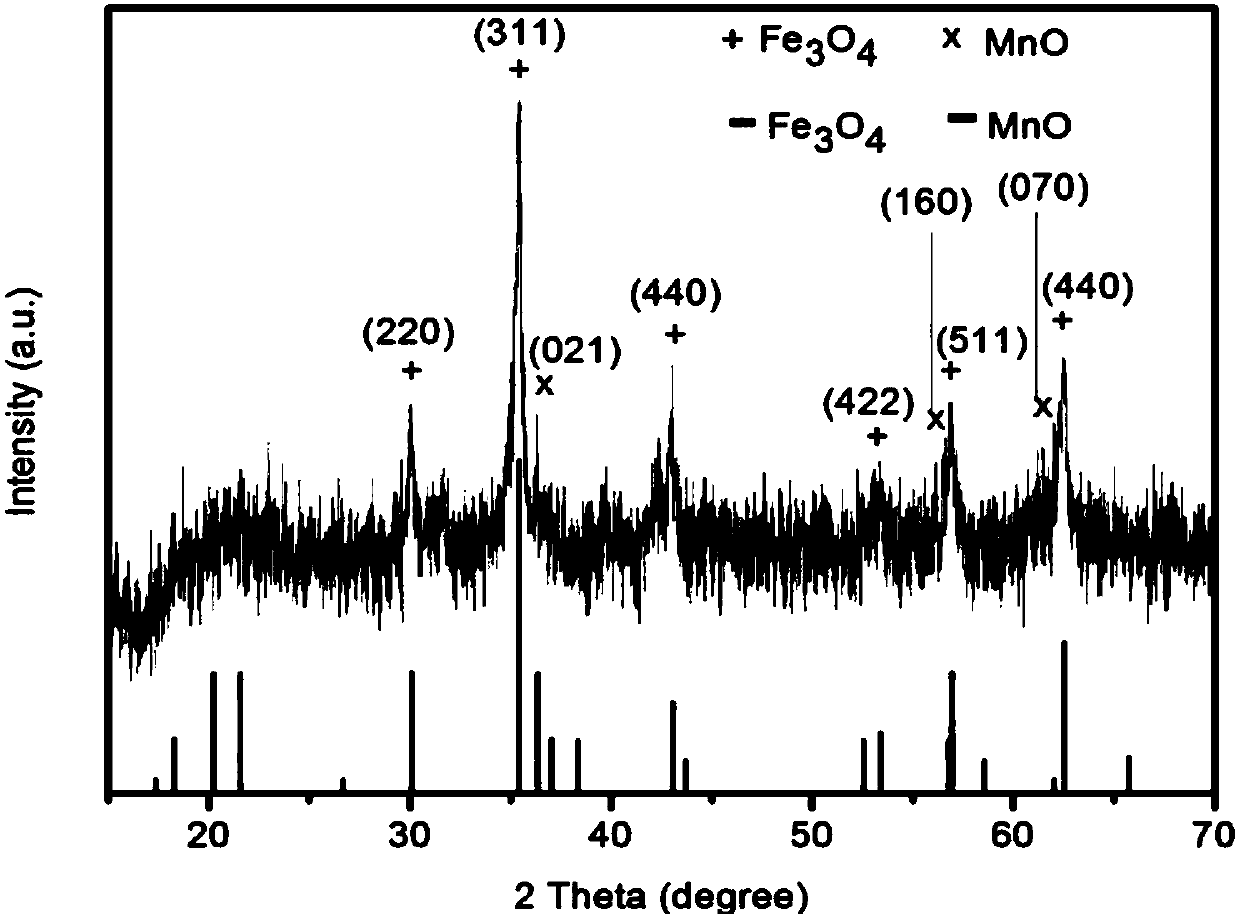
The invention discloses a preparation method for a high-sensitivity bimodal magnetic resonance contrast agent. According to the preparation method, by means of a method for preparing ferric oleate andmanganese chloride through thermal decomposition, a high-boiling-point solvent is adopted as a reaction medium, oleic acid and oleylamine are used as stabilizers, and therefore manganese oxide embedded iron oxide nanoparticles with narrow particle size distribution and high degree of crystallinity are obtained. The invention particularly relates to a preparation method for modifying the manganeseoxide embedded iron oxide nanoparticles by utilizing the oleic acid / the oleamine, or a preparation method for the biocompatible and water-soluble manganese oxide embedded iron oxide nanoparticles. The preparation method for the high-sensitivity dual-mode magnetic resonance contrast agent has the advantages that the requirements of magnetic resonance imaging for the contrast agent and the characteristics of the Nanotechnology are combined, by means of regulation and control over chemical synthesis, manganese oxide with the T1 contrast capability and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with the T2 contrast capability are combined so as to form the manganese oxide embedded iron oxide nanoparticles, and therefore the cooperatively-enhancing dual-mode magnetic resonance contrast effectcan be achieved between the two imaging modes, namely, the T1 imaging mode and the T2 imaging mode.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
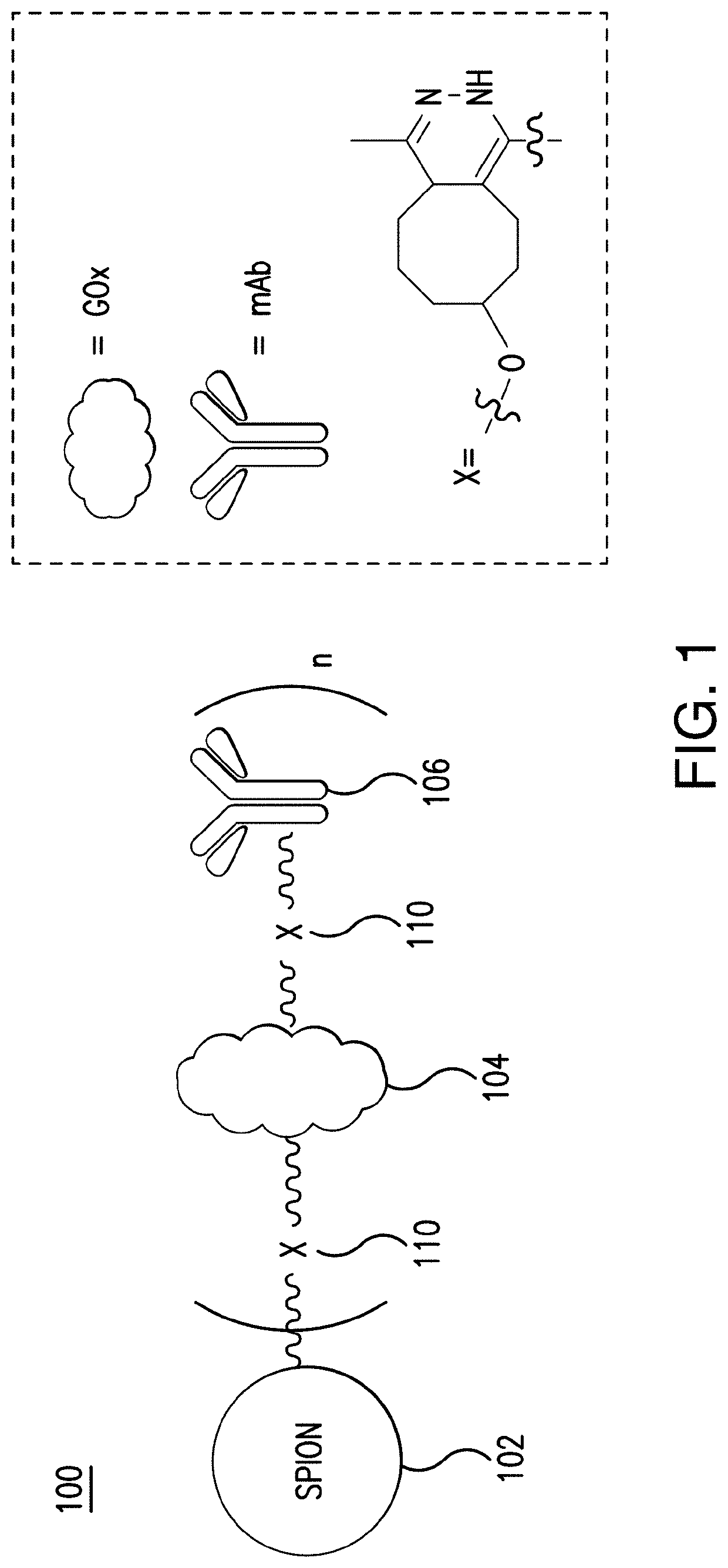
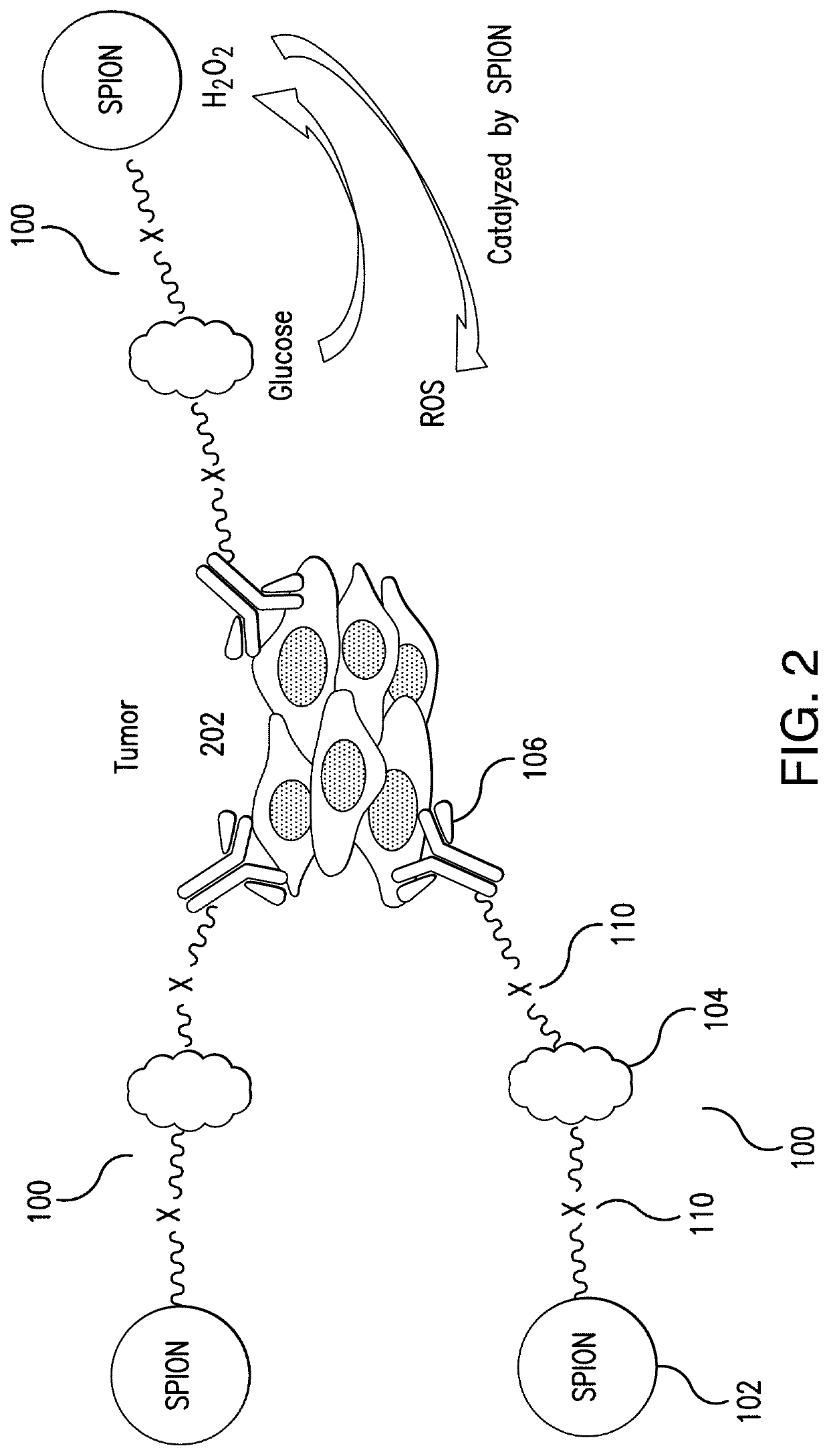
Glucose oxidase-nanoparticle bioconjugates for cancer treatment and uses thereof
PendingUS20200085966A1Facilitate specific bindingFacilitate drug deliveryPowder deliveryImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBioconjugationTumor cells
Bioconjugates and methods of making bioconjugates are provided, wherein the bioconjugates comprise glucose oxidase and nanoparticles that can kill tumor cells. For example, glucose oxidase-iron oxide bioconjugates can produce reactive oxygen species from blood glucose, causing cell death. The use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles can provide magnetic resonance imaging guidance to facilitate imaging-guided drug delivery and combine diagnostics with therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Curcumin coated magnetite nanoparticles for biomedical applications
ActiveUS20140369938A1Hydrodynamic size can be minimizedReducing possibility decompositionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsMagnetite NanoparticlesSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle
The present invention discloses biocompatible, stable curcumin or its derivatives coated ultra-small super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPION) for biomedical applications. Disclosed herein is also a simple one-pot process for the synthesis of biocompatible, stable curcumin or its derivatives coated ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in absence of a linker or binder. The curcumin or its derivatives coated ultra-small super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles of the present invention retains the medicinal, radical scavenging and fluorescence properties of curcumin.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Positively-charged superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle, contrast agent using the same and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20120045399A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial nanotechnologySuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticlesIron oxide nanoparticles
Provided are a positively-charged superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION), a contrast agent using the same, and a method of preparing the same. The positively-charged SPION includes a SPION, a polymer layer including a polymer containing many carboxyl groups coated on a surface of the SPION, and a cationic material coupled via an amide bond to a surface of the polymer layer. Therefore, the SPION may be prepared in a simple and reproducible process to have hydrophilicity and a strong positive charge. The prepared positively-charged SPION may have high uptake into a cell and stability, and be used in various applications as an effective contrast agent through non-invasive in vivo imaging.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT
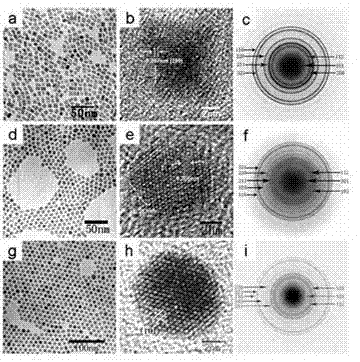
Method for preparing monodispersed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by pyrolysis of ferrocene
ActiveCN105271428ASmall sizeImprove magnetic propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyIron oxides/hydroxidesMagnetizationMagnetite Nanoparticles
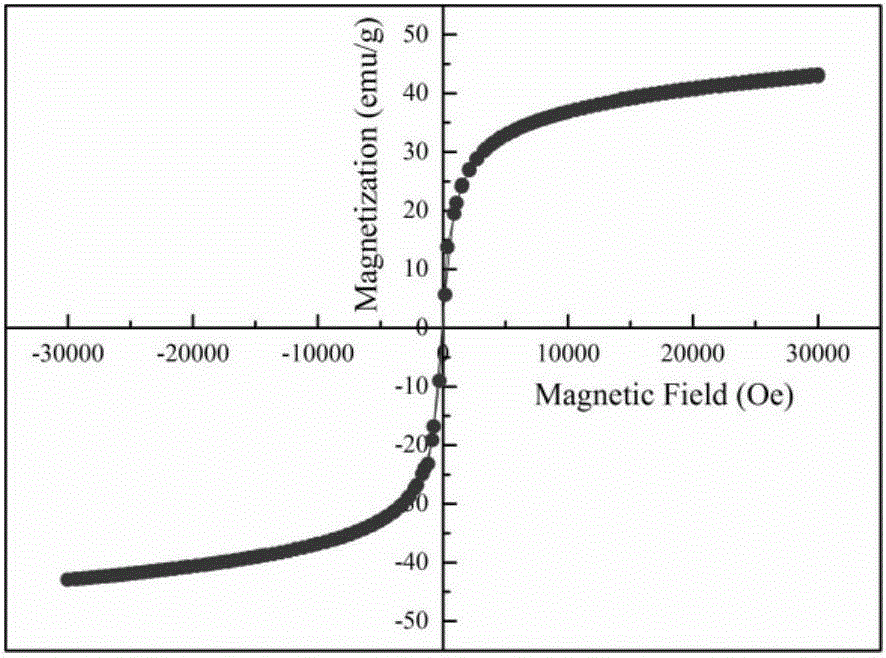
The invention relates to a method for preparing monodispersed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by pyrolysis of ferrocene. The method comprises the following steps: using ferrocene as an iron source and dispersing ferrocene in a high boiling point solvent, adding a surfactant, reacting at high temperature without inert gas shielding, naturally cooling the system after the reaction, fully washing a product with a solvent and removing unreacted raw materials, the high boiling point solvent and the surfactant so as to obtain monodispersed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The invention has advantages as follows: there is no need to prepare an iron source in advance; inert gas shielding is not required during the pyrolysis reaction process; the prepared magnetic nanoparticles are monodispersed and superparamagnetic and have good magnetic performance; specific saturation magnetization reaches 43 emu / g; dimension of the nanoparticles is small, and particle size is 6-10 nm; and the monodispersed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles can be widely applied in biomedical fields such as magnetic bioseparation, magnetic targeted drug release, magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic biolabeling and the like.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Core shell superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with functional metal silicate core shell interface and a magnetic core containing the nanoparticles
ActiveUS20150357102A1High total magnetic momentLittle and no core lossInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSuperparamagnetismParamagnetism
Core shell nanoparticles of an iron oxide core, a silicon dioxide shell and an iron silicate interface between the core and the shell are provided. The magnetic properties of the nanoparticles are tunable by control of the iron silicate interface thickness. A magnetic core of high magnetic moment obtained by compression sintering the thermally annealed superparamagnetic core shell nanoparticles is also provided. The magnetic core has little core loss due to hysteresis or eddy current flow.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
T1-T2 double-activated magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112494666AHigh quality imagingDouble QuenchingNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliverySilicon oxideSuperparamagnetic iron oxide
The invention provides a T1-T2 double-activated magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The T1-T2 double-activated magnetic resonance imagingcontrast agent has a core-shell structure and sequentially comprises T2 contrast agent nanoparticles, a silicon dioxide layer, a T1 contrast agent layer and a modification layer from inside to outside, and the T2 contrast agent nanoparticles are superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The T1-T2 double-activated magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent is in a T1 and T2 contrast agent signaldouble-quenching state in normal tissues around an in-vivo tumor, and T1 and T2 contrast agent signals can be activated at the same time at a tumor part, so that the tumor part and the surrounding normal tissues have a remarkable MRI signal difference, and the T1-T2 double-activated magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent has targeting property on tumor cells, so as to realize high-quality imaging for the tumor part.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
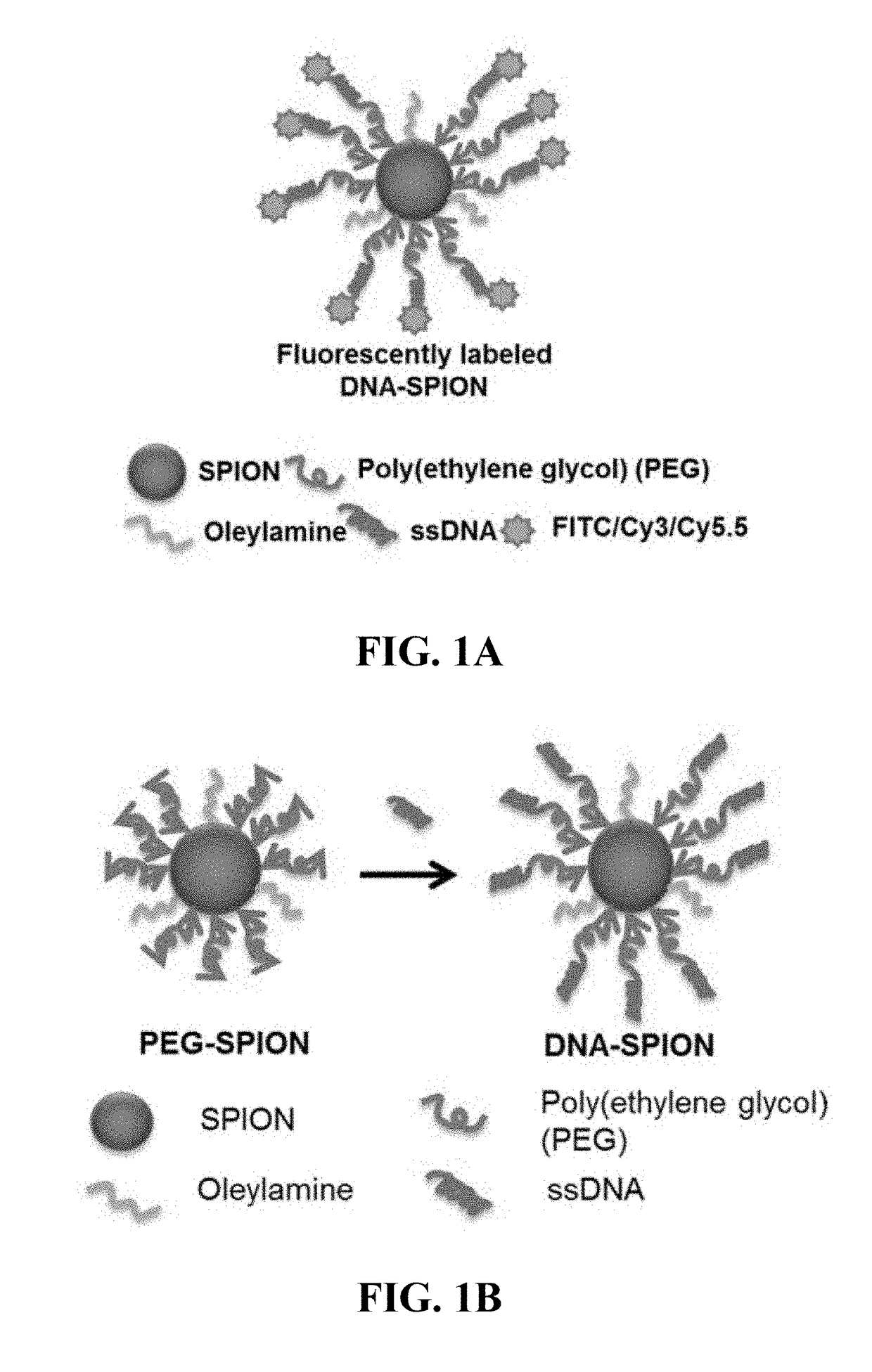
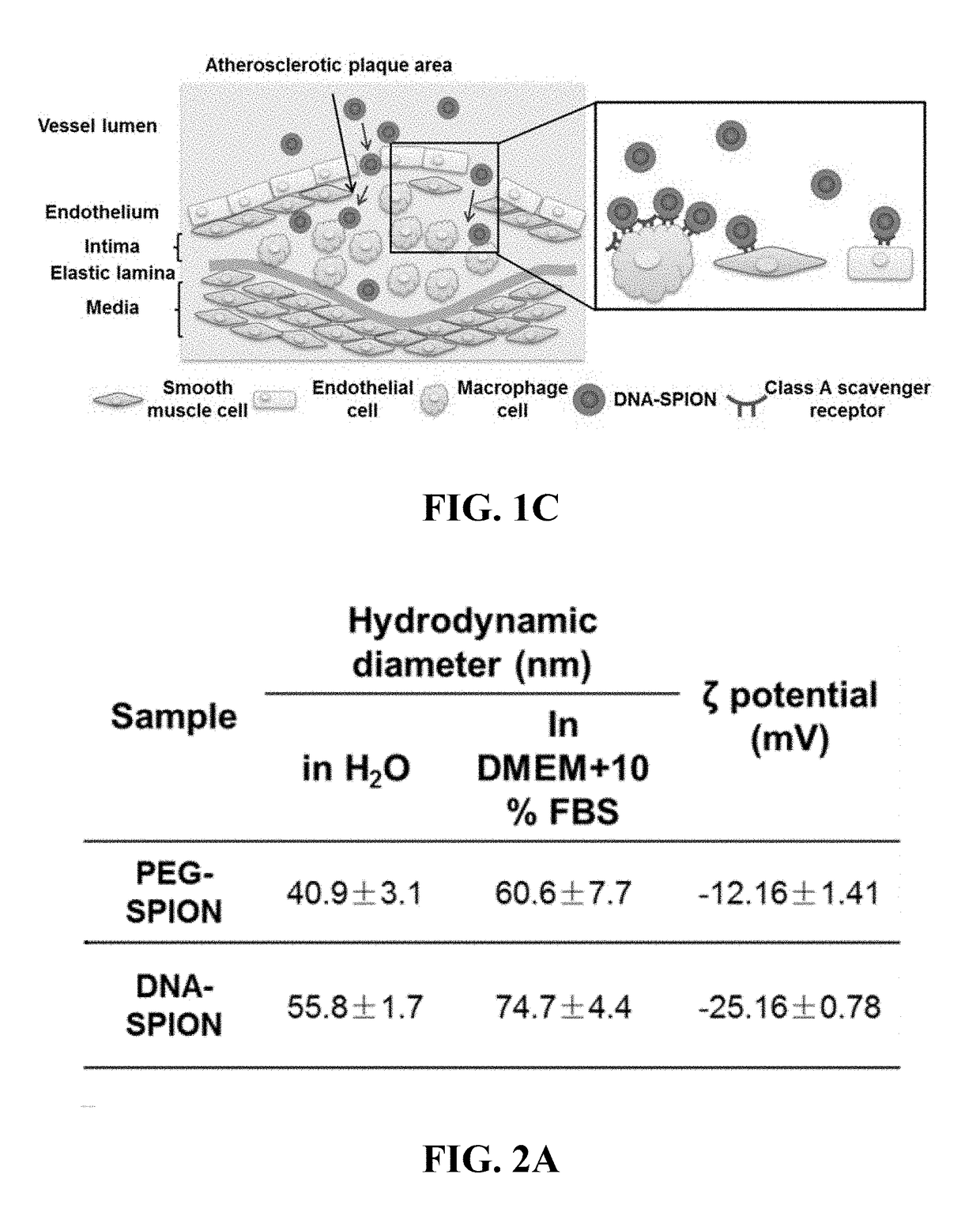
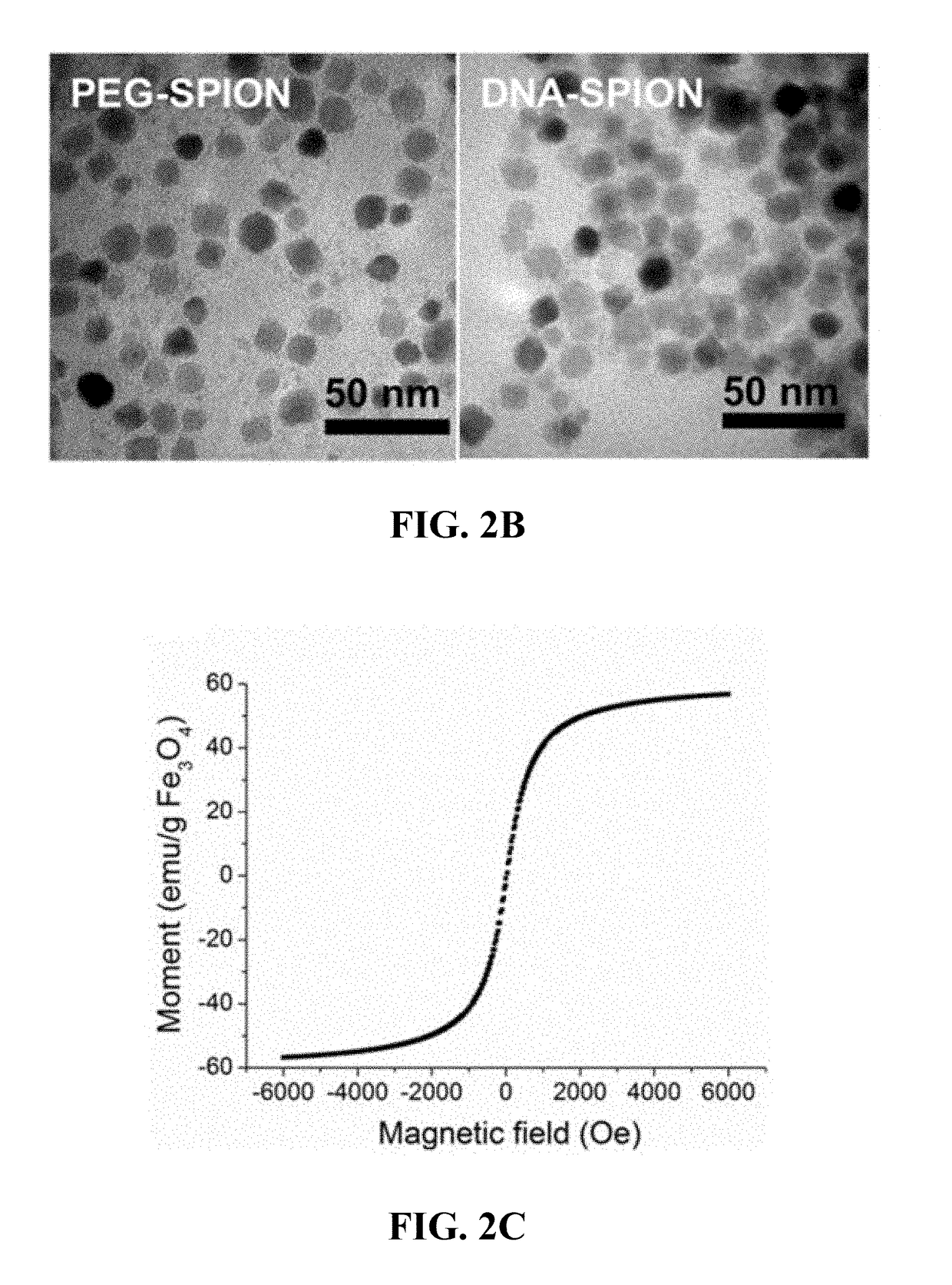
Materials and methods for effective in vivo delivery of DNA nanostructures to atherosclerotic plaques
ActiveUS20190060485A1Promote rapid accumulationPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticlesImaging agent
Provided are DNA-coated nanoparticles (DNA-NPS), superparamagnetic nanoparticles (DNA-SPNs), and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (DNA-SPIONs) as efficient imaging agents for targeting and imaging atherosclerotic lesions and treating atherosclerotic disease. The DNA-NS, DNA-SPNs, and DNA-SPIONs can enter macrophage cells via the Class A scavenger receptor (SR-A)-mediated pathways and can be used to specifically target atheroscleortic plaques.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
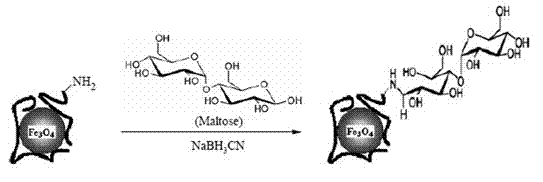
Application of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle applied in transdermal drug delivery system
ActiveCN103182086AAchieve transdermal absorptionWay to overcomePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticlesMedicine
The invention provides application of a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle applied in a transdermal drug delivery system. The superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle is taken as a drug carrier of epirubicin; an epirubicin-superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle transdermal drug delivery system is prepared; and a primary amine group (-NH2) exists on the surface of the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle. The superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle can achieve transdermal absorption and has no poison, stimulation or anaphylactic reaction to skins, and the defects that a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle is single in drug-delivery manner and the magnetic field implementation is limited are overcome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
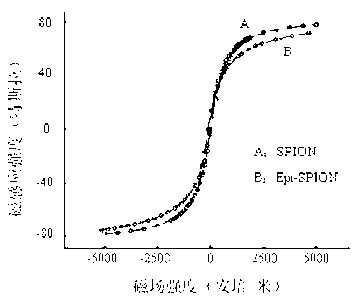
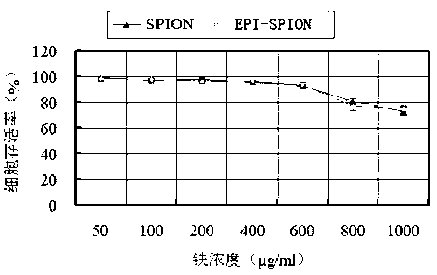
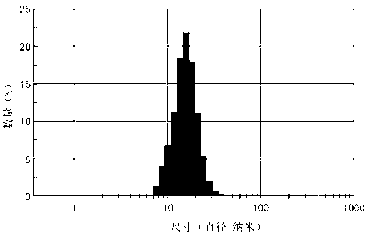
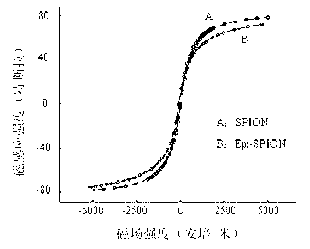
EPI (epirubicin) SPION (superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103181900AEasy accessImprove conductivityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySodium metasilicateCoupling reagent
The invention provides an EPI SPION, which comprises ferrous chloride, ferric trichloride, sodium metasilicate, carbodiimide, EDC.HCI, N-hydroxyl succinimide and EPI. Fe<3+>, Fe<2+>, SiO3<2-> are taken as main raw materials, and the SPION is prepared through a chemical coprecipitation method; hydroxide radicals which exist on the surface of the SPION have a silane reaction with a silane coupling agent, and an active group carbonyl group is introduced; and by the aid of a nucleophilic reaction between amido and the carbonyl group, the EPI is grafted to the nanoparticle, so that a target product EPI SPION is obtained. The EPI-SPION has good conductivity and magnetic permeability, and under the action of an applied magnetic field, the nanoparticle can reach a tumor diseased region, normal tissue cells are not damaged, and an application value of targeted treatment for tumors is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Superparamagnetic composite material of carbon nanotube coated coupling agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104183345AImprove adsorption capacityEasy to separateInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsIron sulfateMagnetite Nanoparticles
Provided are a superparamagnetic composite material of a carbon nanotube coated coupling agent and a preparation method thereof. The surfaces of CNTs (carbon nanotubes) are covered with a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle layer respectively, and the surface of the magnetic nanoparticle layer is modified with a silane coupling agent film. The preparation method includes the steps of (1) dispersing the CNTs in a mixed acid solution of concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid at the ratio of 3:1 for pretreatment reaction at the temperature of 60 DEG C to 80 DEG C; (2) adding the pre-treated multi-walled CNTs in an ammonium iron sulfate solution, dropwise adding aqueous ammonia and stirring at the temperature of 40 DEG C to 60 DEG C; (3) separating the generated magnetic multi-walled CNTs with a magnet after the reaction and drying in vacuum at the temperature of 60 DEG C to 100 DEG C; (4) dispersing the magnetic carbon nanotube material in anhydrous ethanol, adding acetic acid and 3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane, stirring at the temperature of 30 DEG C to 60 DEG C, adding acetone for reacting for 3 hours, performing centrifugal separation and drying in vacuum at the temperature of 40 DEG C to 80 DEG C to obtain the material.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
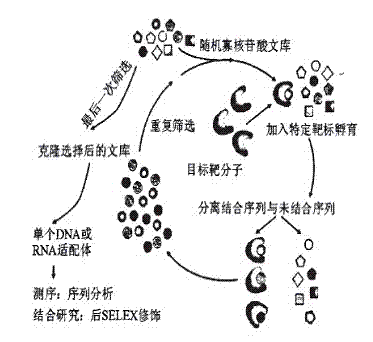
Aptamer target-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite magnatic resonance imaging contrast agent
InactiveCN102526770AEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsPolyethylene glycolBiocompatibility
The invention provides an aptamer target-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite magnatic resonance imaging contrast agent. The aptamer target-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite magnatic resonance imaging contrast agent comprises the following components: (a) oligonucleotides or peptide aptamers for molecular recognition; (b) superparamagneticiron oxide nanoparticles; and (c) a biocompatible amphiphilic dextran block copolymer carrier, which is used for connecting the superparamagneticiron oxide nanoparticles and the oligonucleotides or peptide aptamers for molecular recognition. The aptamers, the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a block copolymer of polyethylene glycol, polycaprolactone and polysaccharide are assembled into a nanomicelles complex; through the targeting effect of specifically bounding the aptamers and a target molecule and magnetic resonance imaging features of SPIO nanoparticles, the complex nanomicelles is established by the biocompatible block copolymer; and after the aptamer target-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite magnatic resonance imaging contrast agent enters a body, small foci are positioned in a targeting way so as to realize early targeting positioning and diagnosis of the small foci in vitro and in vivo through the conventional magnetic resonance imaging diagnostic equipment. By selecting a proper target molecule aptamer, the aptamer target-based superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocomposite magnatic resonance imaging contrast agent can be applied to cell signaling, metabolic process, gene detection, virus detection, tumor detection and other biological researches.
Owner:戴永强 +1
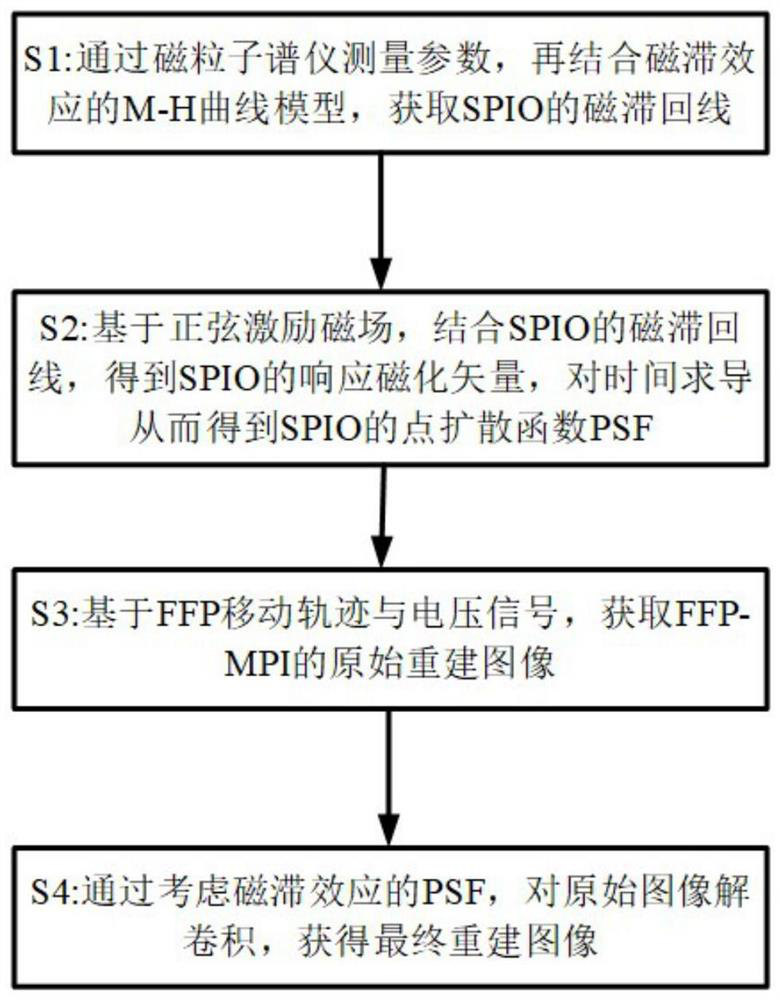
Magnetic-field-point-free magnetic nanoparticle imaging method based on hysteresis effect
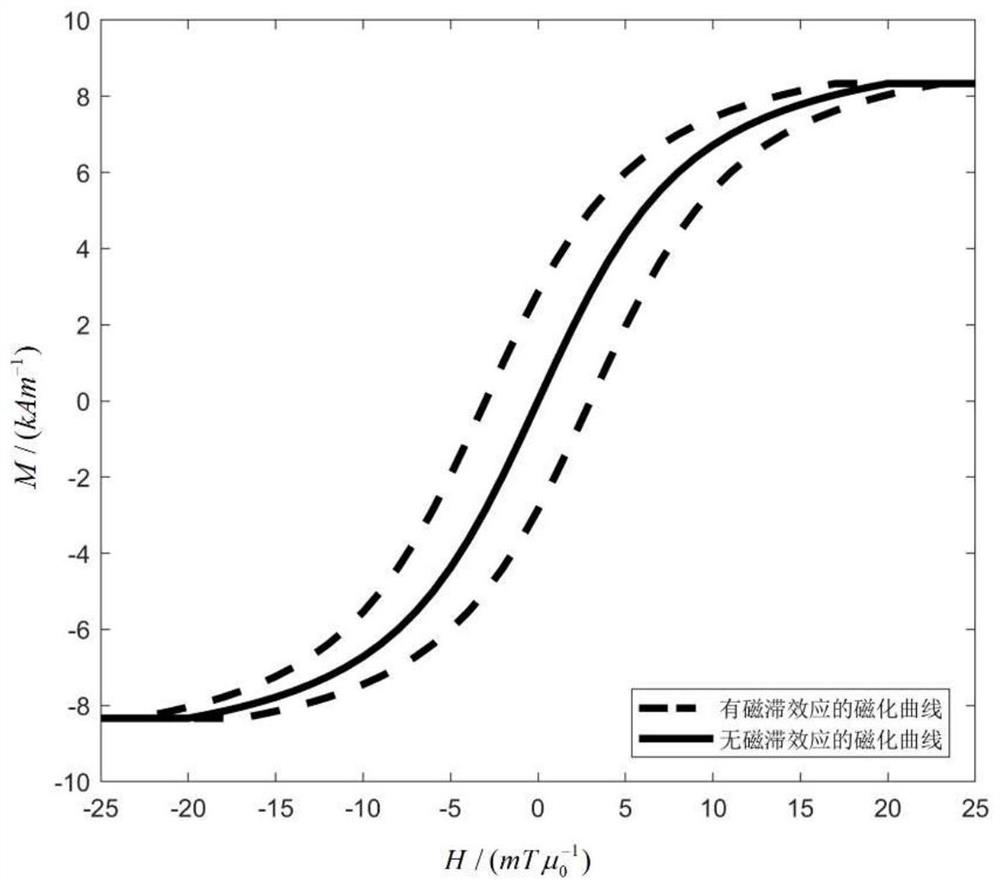
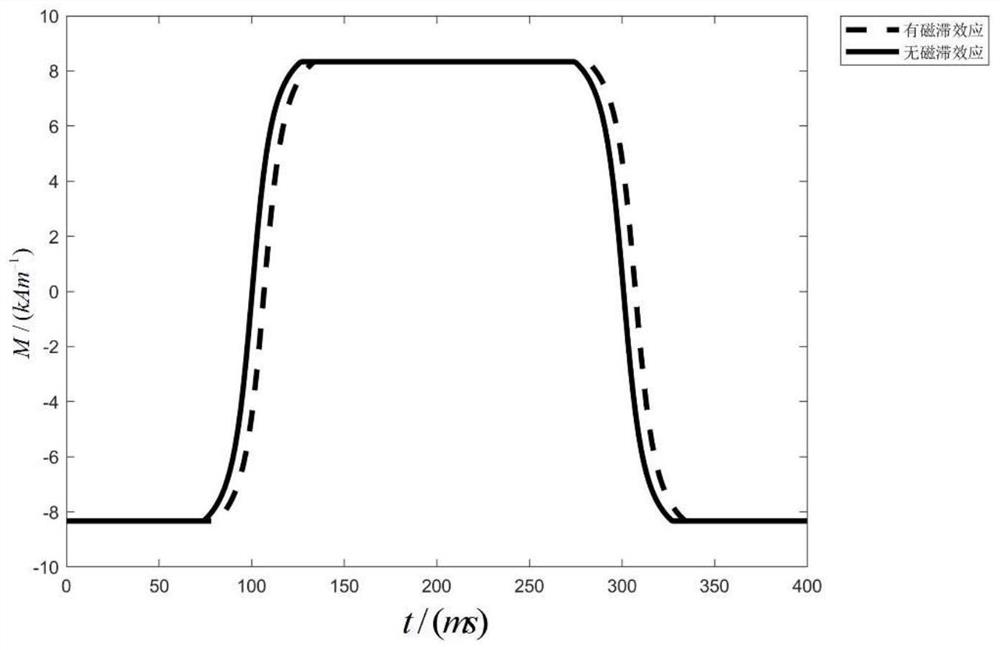
ActiveCN113558597AReduce artifactsReduce phase errorDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHysteresisReconstruction method
The invention discloses a magnetic-field-point-free magnetic nanoparticle imaging method based on a hysteresis effect. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a hysteresis loop model of a superparamagnetic nanoparticle (Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles, SPIO); carrying out calculating based on a sine excitation magnetic field and the hysteresis loop model of the SPIO, so as to obtain a point spread function (PSF) of the SPIO; acquiring an original reconstructed image of field free point-magnet particle imaging (FFP-MPI) based on a field free point (FFP) moving track and a voltage signal; and carrying out deconvolution on the PSF considering the hysteresis effect of the original image, thereby obtaining a final reconstructed image. According to the method, artifacts and phase errors generated by the hysteresis effect of the large-particle-size SPIO on image reconstruction are reduced, the defect of the traditional reconstruction method that reconstruction is carried out by ignoring the hysteresis effect is overcome, the reconstruction speed and resolution are greatly improved, and the application range of the SPIO is widened.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
T1-T2 double quenching-activated MRI contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114272396AEnsure consistencyHigh precisionMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsMRI contrast agentMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a T1-T2 double quenching-activation MRI contrast agent and a preparation method thereof, the MRI contrast agent has a core-shell structure, the core-shell structure sequentially comprises a T2 layer composed of a T2 contrast agent, an MOF structure layer composed of metal organic framework particles and a T1 layer composed of a T1 contrast agent from inside to outside, and one metal organic framework particle coats one T2 contrast agent; the T2 contrast agent is superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, the T1 contrast agent is a gadolinium-containing ionic compound or a manganese-containing ionic compound, and the dosage ratio of Fe in the T2 contrast agent to Gd or Mn in the T1 contrast agent is 1: (10-40). The MRI contrast agent provided by the invention can realize significant difference imaging signals between normal tissues and acidic lesion tissues, so that the purpose of imaging detection is achieved, and the MRI contrast agent has higher sensitivity, higher response speed and higher release efficiency.
Owner:广州远想医学生物技术有限公司
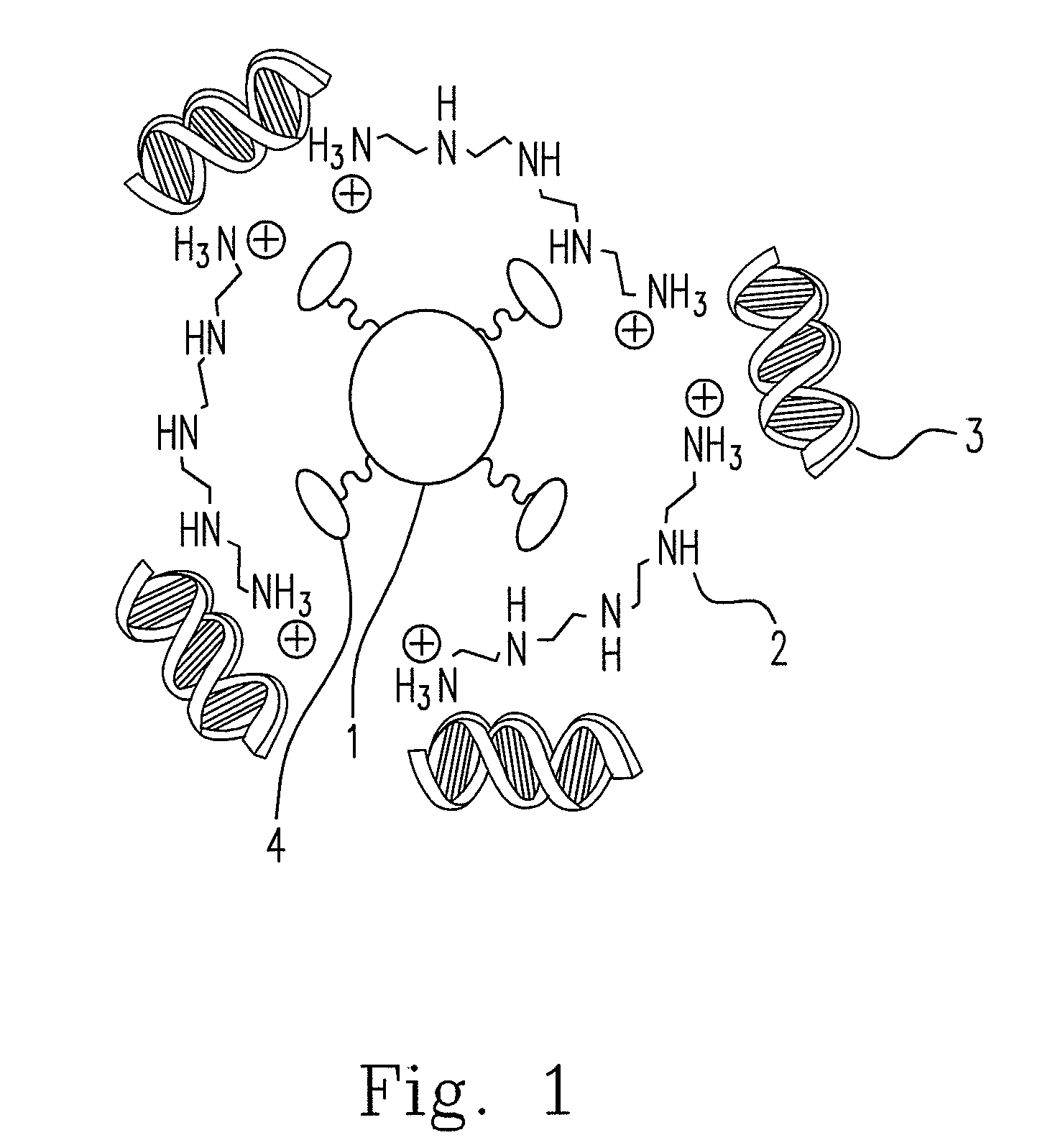
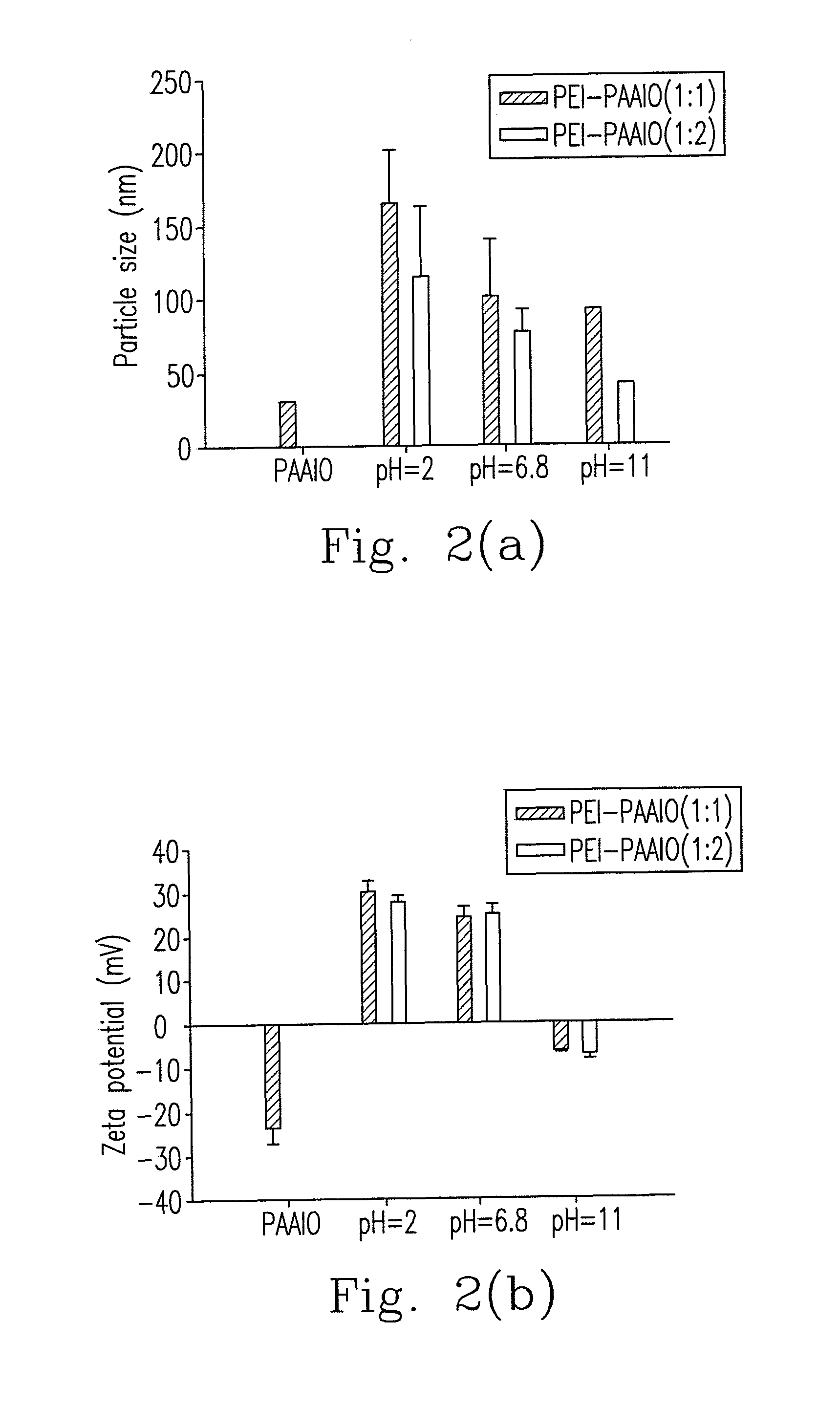
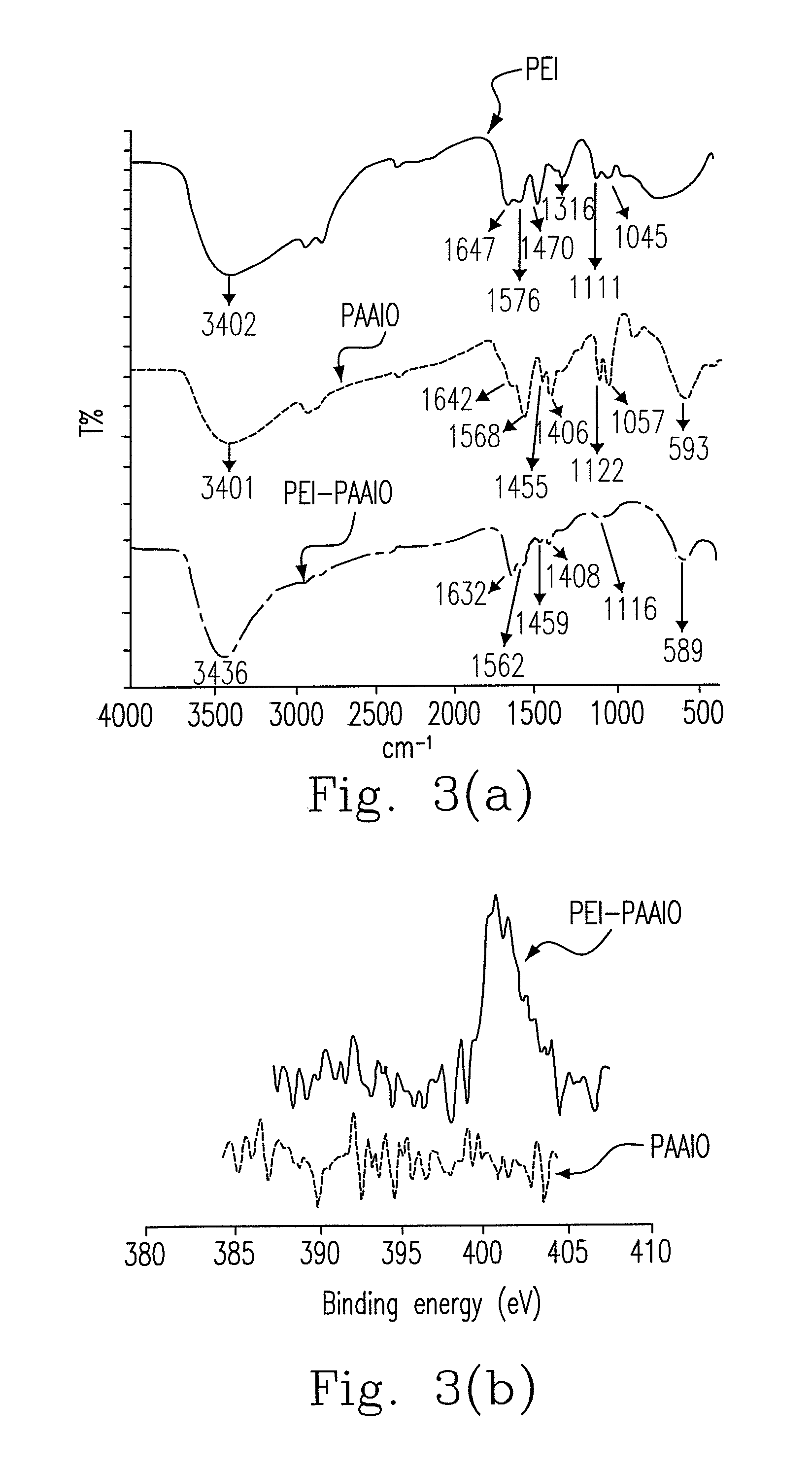
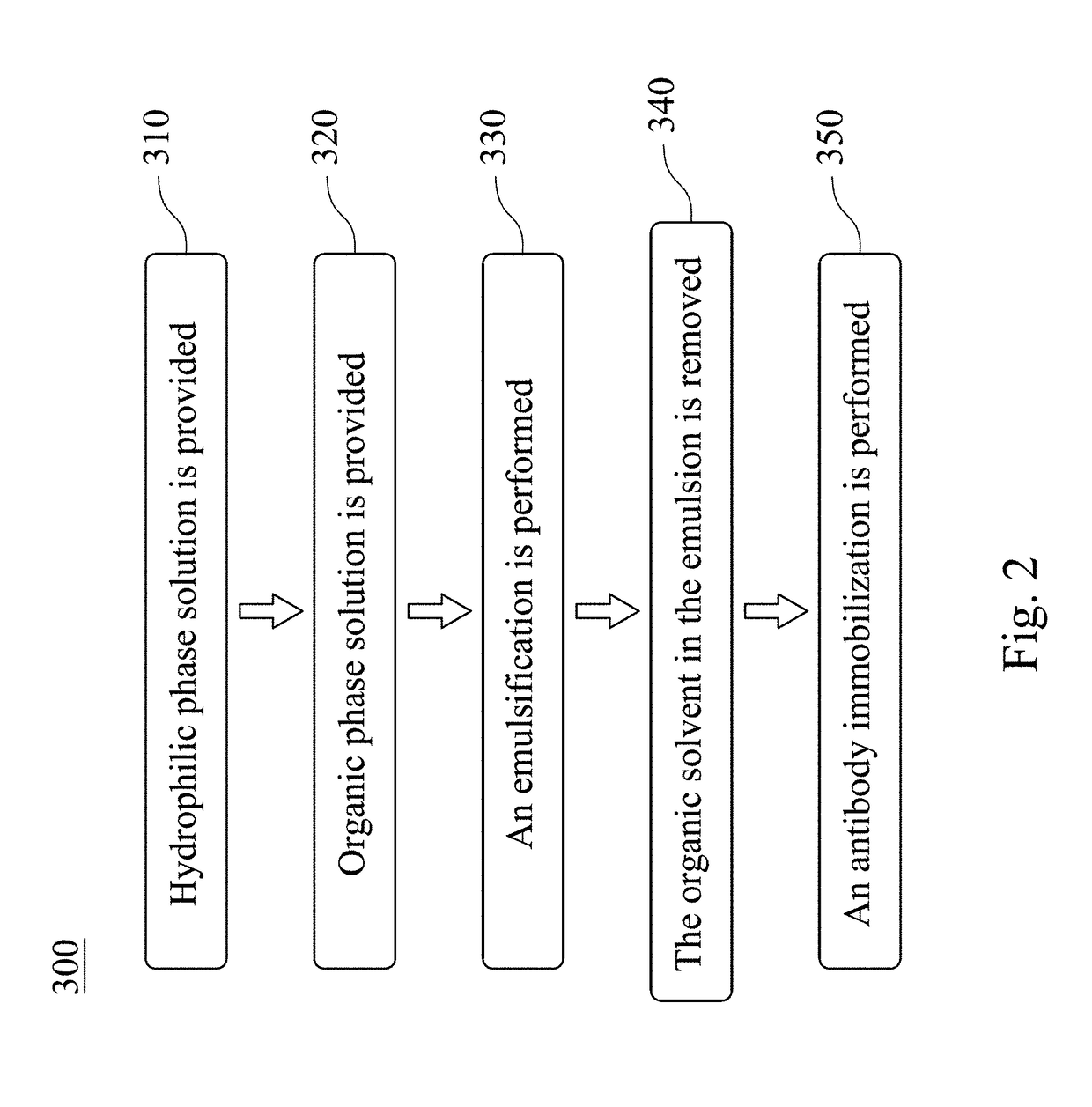
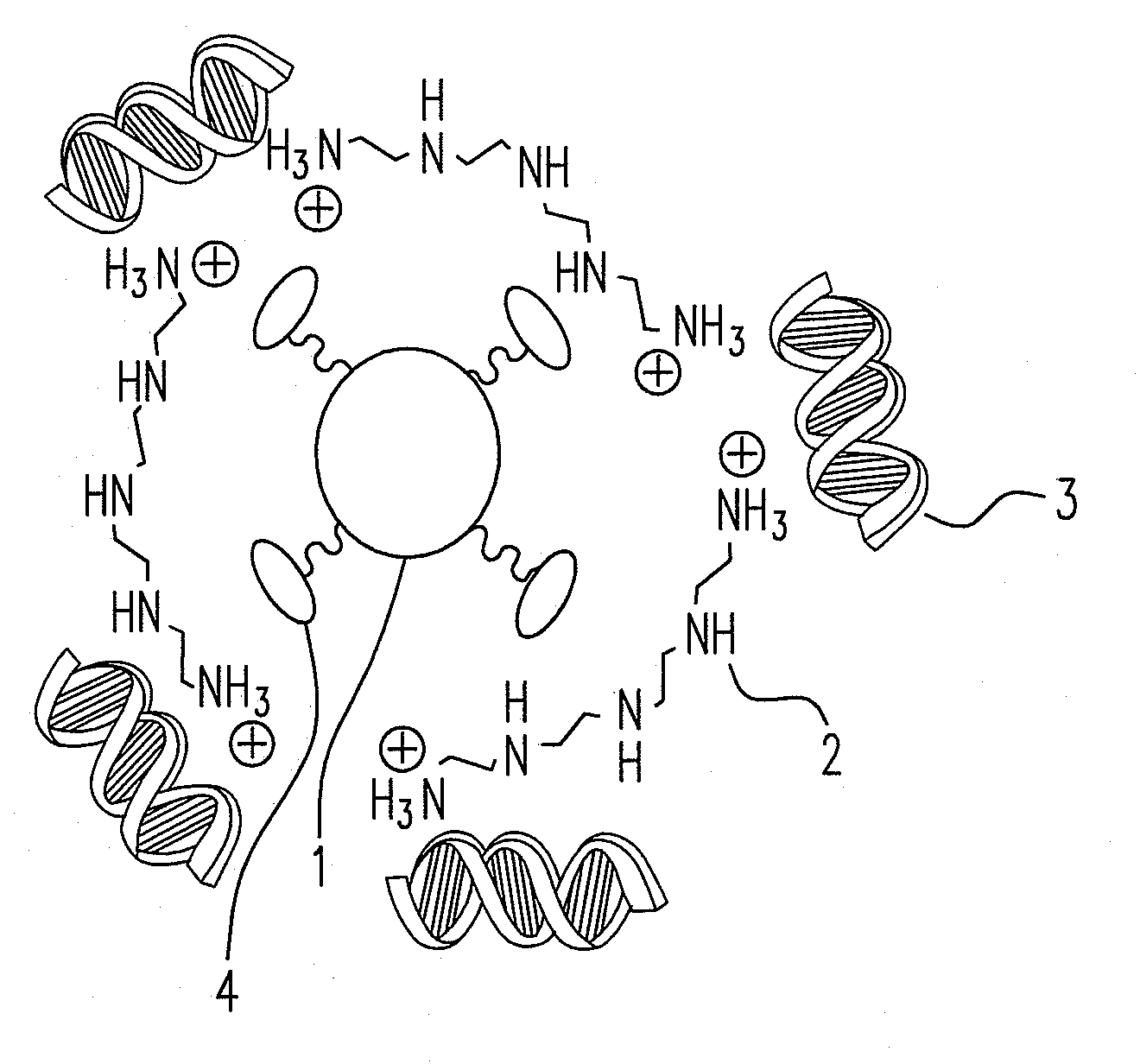
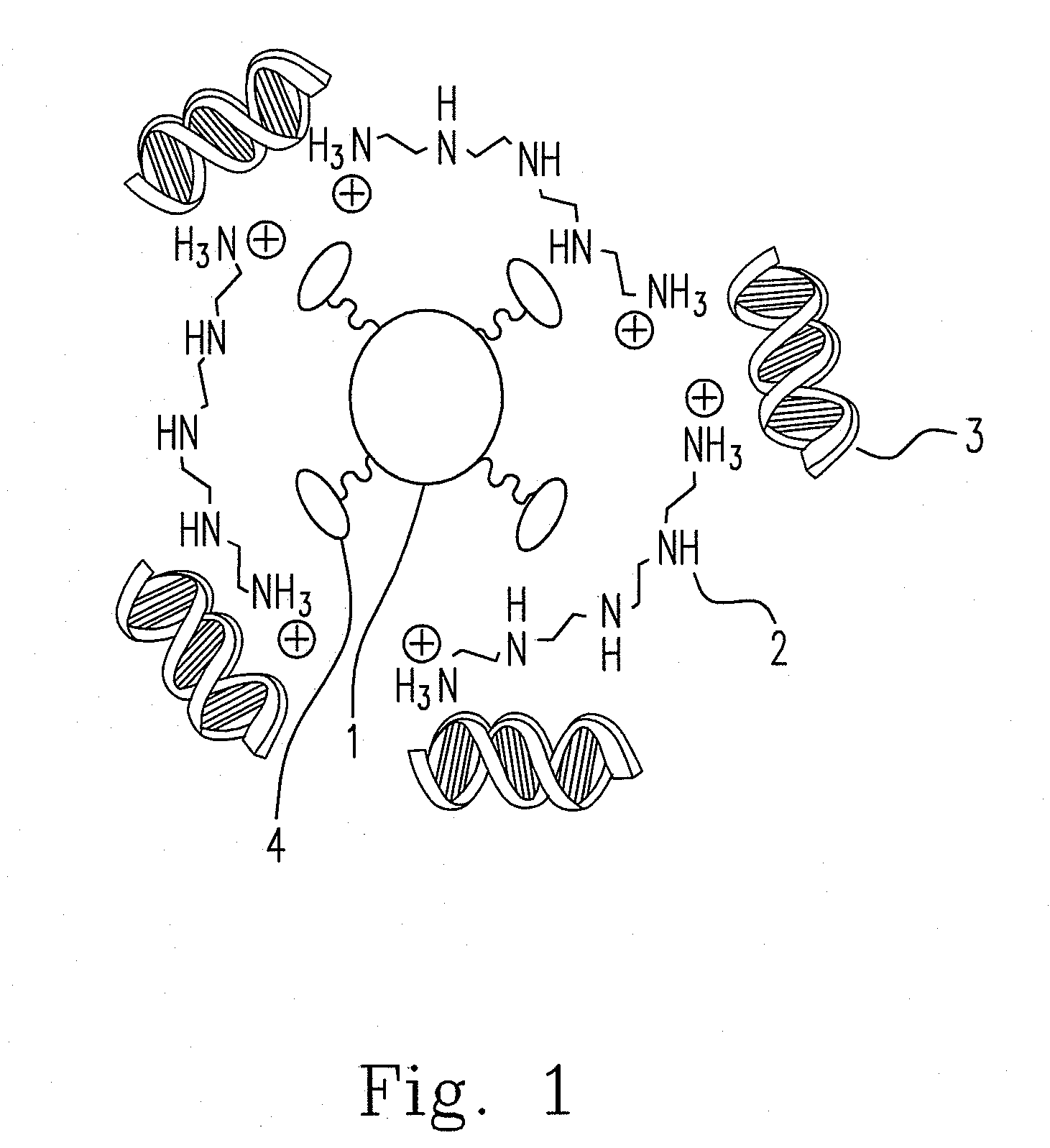
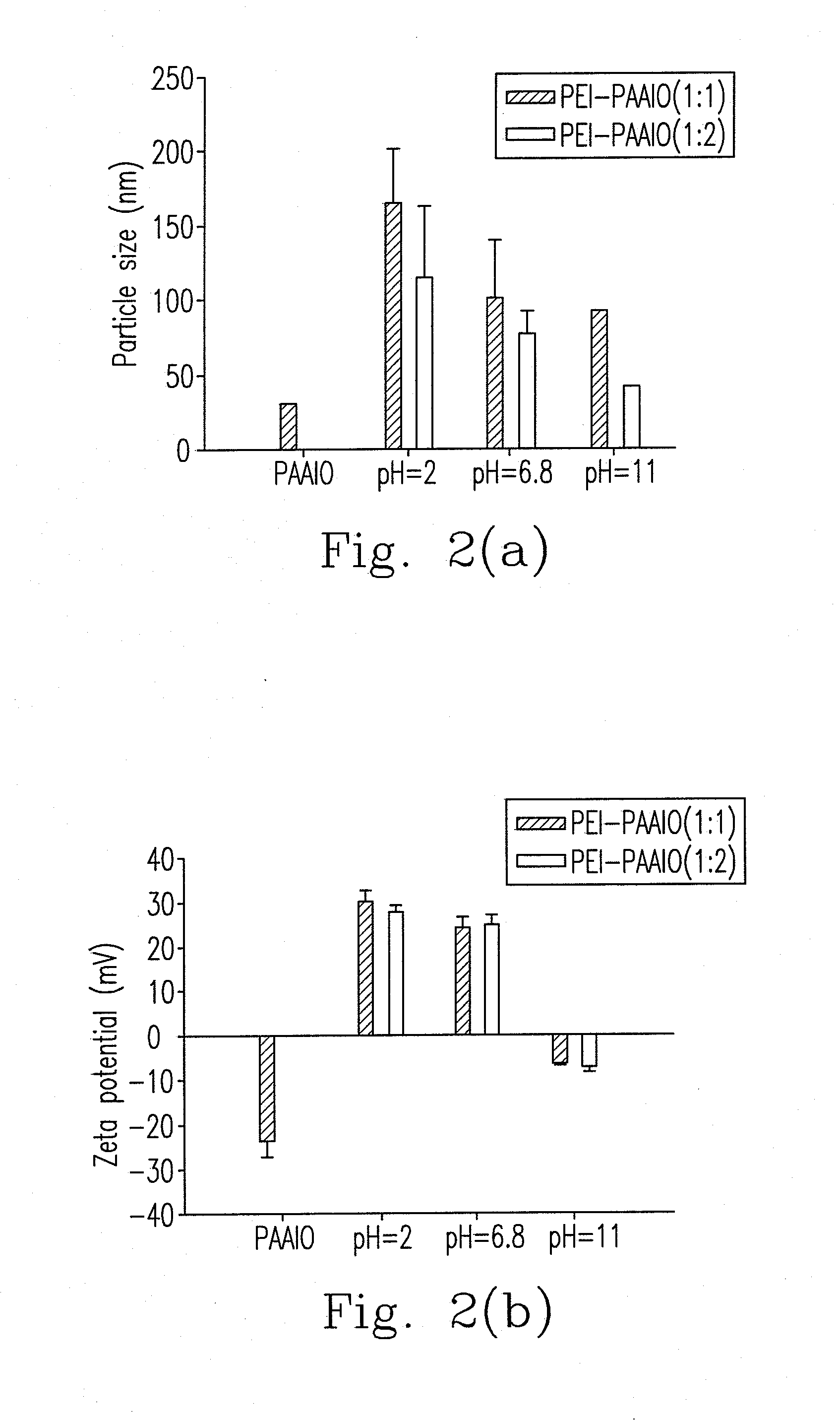
Hybrid superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and polyethylenimine as a magnetoplex for gene transfection
ActiveUS8445025B2Highly water dispensableLow cytotoxicityPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsWater dispersibleMagnetite Nanoparticles
Disclosed are the nanoparticle and the method for the same, and the preparing method includes steps of mixing polyethylenimine (PEI) with the poly(acrylic acid)-bound iron oxide (PAAIO) to form a PEI-PAAIO polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) and mixing the PEI-PAAIO PEC with genetic material such as plasmid DNA to form the PEI-PAAIO / pDNA magnetic nanoparticle. The PEI-PAAIO / pDNA magnetoplex is highly water dispersible and suitable for long term storage, shows superparamagnetism, low cytotoxicity, high stability and nice transfection efficiency, and thus the PEI-PAAIO PEC can replace PEI as a non-viral gene vector.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Multifunctional ph responsive drug delivery system and method of use
ActiveUS20200281864A1Heavy metal active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsMedicineSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle
A multi-functional drug composition capable of pH responsive drug release comprising siliceous nanoparticles having three dimensional cage structures type silica with thick pore walls and mesosilicalite, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) and pharmaceutical composition thereof is disclosed. The drug delivery system is useful for targeting a drug to particular diseased tissues such as cancerous tissues.
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
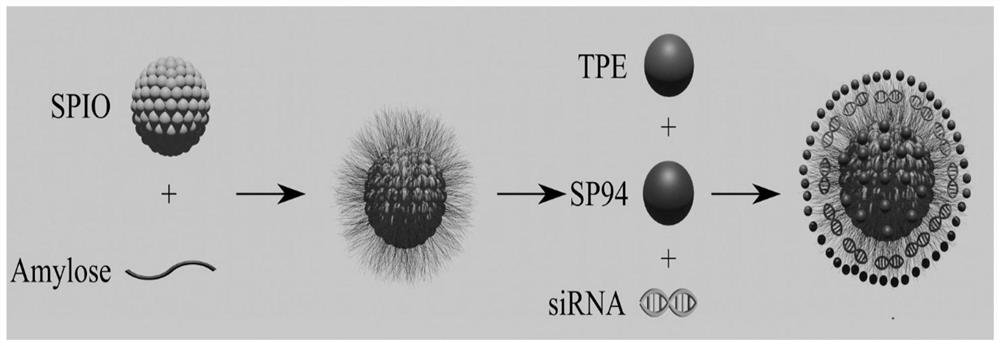
Magnetic nano-drug carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112870387AGood biocompatibilityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsQuaternary ammonium cationTarget peptide
The invention relates to the technical field of drug carriers, in particular to a magnetic nano-drug carrier as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The magnetic nano-drug carrier comprises an SP94 targeting peptide and a coupling product of an siRNA delivery carrier, and the coupling product of the siRNA delivery carrier comprises superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and quaternary ammonium cationized amylose-tetraphenylethylene-superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles formed by coupling quaternary ammonium cationized amylose and tetraphenylethylene, and the siRNA is adsorbed in the magnetic nano-drug carrier. The cytotoxicity experiments prove that the nano-drug carrier has good biocompatibility, good stability, targeting property and drug release property, and the magnetic nano-drug carrier can be applied to preparation of cancer gene therapy drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Folic acid molecule-containing reduction response type vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate micelle as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112121010AGood biocompatibilityQuick releaseOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryDisulfide bondingTumor target
The invention relates to a folic acid molecule-containing reduction response type vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate micelle. The micelle is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by weight: 10 parts of folic acid molecule-containing reduction response type vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate, 1-2 parts of adriamycin and 1-2 parts of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. According to the micelle disclosed by the invention, disulfide bonds with corresponding reduction characteristics are respectively connected with a hydrophilic polyethylene glycol chain segment and a hydrophobic vitamin E chain segment thereof, and folic acid molecules are introduced, so that the micelle has a tumor targeting characteristic, micelle nanoparticles obtained by self-assembly have excellent biocompatibility, and the micelle can respond to glutathione in a tumor reducing microenvironment, realizes rapid release of drugs, and has the advantages of tumor targeting and intelligent controlled release of the drugs.
Owner:广州市第一人民医院
Dual-modality nanoprobe targeting glioblastoma and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20210338842A1Imaging results are clearImprove in vivo stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismAnatomical structuresGlioblastoma
A dual-modality nanoprobe targeting glioblastoma and preparation method thereof are described. The dual-modality nanoprobe of the present disclosure comprises DSPE-PEG(2000)-Amine, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs), Cy7-NHS molecule, targeting polypeptide and / or trans-mirror structure (i.e., enantiomer) thereof. The dual-modality nanoprobe can integrate the advantages of magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging and thus provide clearer anatomical structure information of brain tumors; in the imaging process, the dual-modality nanoprobe can not only provide clearer image results, but also can specifically identify target sites. Also, the dual-modality nanoprobe of the present disclosure also has good in vivo stability.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Medical nano composite
InactiveCN103893783AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPolyethylene glycolMicroparticle
The invention provides a medical nano composite including (a) an oligonucleotides or peptide aptamer for molecular identification; (b) a superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle; and (c) a biocompatible amphiphilic glucan block copolymer carrier used for the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle and connecting the oligonucleotides or peptide aptamer for molecular identification. The medical nano composite is assembled by use of the aptamer, the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle, and a polyethylene glycol, polycaprolactone and polysaccharide block copolymer, by use of the targeting effect of specific binding of the aptamer and a target molecule and magnetic resonance imaging (mri) features of the superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticle, composite nano micelle is constructed by a biocompatible block copolymer, enters the body for target positioning of small disease focus, and is used for early target positioning diagnosis of minimal lesion in vitro and vivo by use of conventional nuclear magnetic resonance imaging diagnostic equipment. By choosing of an appropriate target molecule aptamer, the medical nano composite also can be used in cell signaling, metabolic process, gene detection, virus detection, tumor detection and other bioresearches.
Owner:SHANGHAI TREEFUL PHARMA
Immunomagnetic nanocapsule, pharmaceutical composition thereof for treating cancer and kit for treating cancer
An immunomagnetic nanocapsule includes a core, a shell and an outer layer. The shell is formed by a complex, and the complex is fabricated by a combination of fucoidan, oxidized dextran, and a plurality of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via a hydrophobic interaction. The core is encapsulated in the shell. The outer layer includes at least one antibody immobilized to outside of the shell to form the outer layer, wherein the antibody is an immune checkpoint inhibitor and / or a T cell expansion antibody.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Hybrid Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles And Polyethylenimine As A Magnetoplex For Gene Transfection
ActiveUS20120157626A1Low cytotoxicityImprove stabilityPowder deliveryBiocideWater dispersibleCytotoxicity
Disclosed are the nanoparticle and the method for the same, and the preparing method includes steps of mixing polyethylenimine (PEI) with the poly(acrylic acid)-bound iron oxide (PAAIO) to form a PEI-PAAIO polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) and mixing the PEI-PAAIO PEC with genetic material such as plasmid DNA to form the PEI-PAAIO / pDNA magnetic nanoparticle. The PEI-PAAIO / pDNA magnetoplex is highly water dispersible and suitable for long term storage, shows superparamagnetism, low cytotoxicity, high stability and nice transfection efficiency, and thus the PEI-PAAIO PEC can replace PEI as a non-viral gene vector.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com